CN110045994B - Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium - Google Patents
Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110045994B CN110045994BCN201810032323.7ACN201810032323ACN110045994BCN 110045994 BCN110045994 BCN 110045994BCN 201810032323 ACN201810032323 ACN 201810032323ACN 110045994 BCN110045994 BCN 110045994B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- heart rate
- type
- application
- target
- target application
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/024—Measuring pulse rate or heart rate
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/103—Measuring devices for testing the shape, pattern, colour, size or movement of the body or parts thereof, for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/11—Measuring movement of the entire body or parts thereof, e.g. head or hand tremor or mobility of a limb
- A61B5/1118—Determining activity level
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/44—Arrangements for executing specific programs
- G06F9/445—Program loading or initiating
- G06F9/44594—Unloading
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Telephone Function (AREA)
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及计算机技术领域,特别是涉及一种应用程序处理方法和装置、电子设备、计算机可读存储介质。The present application relates to the field of computer technology, and in particular, to a method and apparatus for processing an application program, an electronic device, and a computer-readable storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
智能设备可以通过应用程序实现不同的应用操作,比如可以通过购物类应用程序购买商品、通过视频类应用程序查看视频等。应用程序可以被冻结,冻结后的应用程序无法再继续运行,不会占用智能设备中处理器资源。但是由于应用程序还是存在与智能设备中的,因此还会占用智能设备中的内存、硬件等资源。Smart devices can implement different application operations through applications, such as purchasing goods through shopping applications, viewing videos through video applications, and so on. The application can be frozen, and the frozen application cannot continue to run, and will not occupy the processor resources in the smart device. However, since the application still exists in the smart device, it will also occupy resources such as memory and hardware in the smart device.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本申请实施例提供一种应用程序处理方法和装置、电子设备、计算机可读存储介质,可以降低电子设备的功耗。Embodiments of the present application provide an application processing method and apparatus, an electronic device, and a computer-readable storage medium, which can reduce the power consumption of the electronic device.
一种应用程序处理方法,包括:An application processing method comprising:
获取目标用户的心率数据,并根据所述心率数据判断所述目标用户是否处于运动状态;Acquire the heart rate data of the target user, and determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data;
若所述目标用户处于运动状态,则从所述目标用户使用的电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序;If the target user is in a motion state, obtain the first type of target application program from the application program installed on the electronic device used by the target user;
根据所述心率数据对所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。Freeze or unfreeze the first type of target application according to the heart rate data.
一种应用程序处理装置,包括:An application processing device, comprising:
数据获取模块,用于获取目标用户的心率数据,并根据所述心率数据判断所述目标用户是否处于运动状态;a data acquisition module, used for acquiring the heart rate data of the target user, and judging whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data;
应用获取模块,用于若所述目标用户处于运动状态,则从所述目标用户使用的电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序;an application acquisition module, configured to acquire a first type of target application program from an application program installed on an electronic device used by the target user if the target user is in a motion state;
应用处理模块,用于根据所述心率数据对所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。An application processing module, configured to freeze or unfreeze the first type of target application according to the heart rate data.
一种电子设备,包括存储器及处理器,所述存储器中储存有计算机程序,所述计算机程序被所述处理器执行时,使得所述处理器执行如下步骤:An electronic device includes a memory and a processor, wherein a computer program is stored in the memory, and when the computer program is executed by the processor, the processor executes the following steps:
获取目标用户的心率数据,并根据所述心率数据判断所述目标用户是否处于运动状态;Acquire the heart rate data of the target user, and determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data;
若所述目标用户处于运动状态,则从所述目标用户使用的电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序;If the target user is in a motion state, obtain the first type of target application program from the application program installed on the electronic device used by the target user;
根据所述心率数据对所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。Freeze or unfreeze the first type of target application according to the heart rate data.
一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序被处理器执行时实现如下步骤:A computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the following steps are implemented:
获取目标用户的心率数据,并根据所述心率数据判断所述目标用户是否处于运动状态;Acquire the heart rate data of the target user, and determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data;
若所述目标用户处于运动状态,则从所述目标用户使用的电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序;If the target user is in a motion state, obtain the first type of target application program from the application program installed on the electronic device used by the target user;
根据所述心率数据对所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。Freeze or unfreeze the first type of target application according to the heart rate data.
上述实施例提供的应用程序处理方法和装置、电子设备、计算机可读存储介质,电子设备可以获取目标用户的心率数据,从而根据心率数据判断目标用户是否处于运动状态。若目标用户处于运动状态,则获取第一类目标应用程序,并根据心率数据控制第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。这样可以规律性地将应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理,既能够保证应用程序能够及时地接收消息,又能够通过减少应用程序的运行,从而降低电子设备的功耗。With the application processing method and device, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium provided by the above embodiments, the electronic device can obtain the heart rate data of the target user, so as to determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data. If the target user is in an exercising state, the first type of target application is acquired, and the first type of target application is controlled to freeze or thaw according to the heart rate data. In this way, the application program can be frozen or thawed regularly, which can not only ensure that the application program can receive messages in time, but also reduce the power consumption of the electronic device by reducing the running of the application program.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本申请实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本申请的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiments of the present application or the technical solutions in the prior art, the following briefly introduces the accompanying drawings required for the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only These are some embodiments of the present application. For those of ordinary skill in the art, other drawings can also be obtained based on these drawings without any creative effort.
图1为一个实施例中应用程序处理方法的应用环境示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of an application environment of an application processing method in one embodiment;
图2为一个实施例中电子设备的内部结构示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of the internal structure of an electronic device in one embodiment;
图3为一个实施例中应用程序处理方法的流程图;3 is a flowchart of an application processing method in one embodiment;
图4为另一个实施例中应用程序处理方法的流程图;4 is a flowchart of an application processing method in another embodiment;
图5为一个实施例中心率曲线的示意图;Fig. 5 is the schematic diagram of one embodiment center rate curve;
图6为一个实施例中应用程序的资源限制状态的示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of a resource limitation state of an application in one embodiment;
图7为一个实施例中电子设备的部分架构图;7 is a partial architecture diagram of an electronic device in one embodiment;
图8为一个实施例中应用程序处理装置的结构示意图;8 is a schematic structural diagram of an application processing apparatus in an embodiment;
图9为与本申请实施例提供的电子设备相关的手机的部分结构的框图。FIG. 9 is a block diagram of a partial structure of a mobile phone related to an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本申请的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本申请进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅仅用以解释本申请,并不用于限定本申请。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the present application more clearly understood, the present application will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present application, but not to limit the present application.
可以理解,本申请所使用的术语“第一”、“第二”等可在本文中用于描述各种元件,但这些元件不受这些术语限制。这些术语仅用于将第一个元件与另一个元件区分。举例来说,在不脱离本申请的范围的情况下,可以将第一客户端称为第二客户端,且类似地,可将第二客户端称为第一客户端。第一客户端和第二客户端两者都是客户端,但其不是同一客户端。It will be understood that the terms "first", "second", etc. used in this application may be used herein to describe various elements, but these elements are not limited by these terms. These terms are only used to distinguish a first element from another element. For example, a first client may be referred to as a second client, and similarly, a second client may be referred to as a first client, without departing from the scope of this application. Both the first client and the second client are clients, but they are not the same client.
图1为一个实施例中应用程序处理方法的应用环境示意图。如图1所示,该应用环境包括客户端102和服务器104。客户端102上可以安装应用程序,客户端102可以获取用户的心率数据,并根据心率数据判断客户端102是否处于运动状态;若客户端102处于运动状态,则从安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序;根据心率数据对第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。服务器104可以用于向客户端102推送应用程序处理算法,客户端102根据该应用程序处理算法对应用程序进行处理。其中,客户端102为处于计算机网络最外围,主要用于输入用户信息以及输出处理结果的电子设备,例如可以是个人电脑、移动终端、个人数字助理、可穿戴电子设备等。服务器104是用于响应服务请求,同时提供计算服务的设备,例如可以是一台或者多台计算机。可以理解的是,本申请提供的其他实施例中,应用程序处理方法的应用环境可以只包含客户端102。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an application environment of an application processing method in an embodiment. As shown in FIG. 1 , the application environment includes a
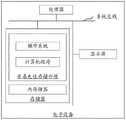
如图2所示,提供了一种电子设备的内部结构示意图。该电子设备包括通过系统总线连接的处理器、存储器和显示屏。其中,该处理器用于提供计算和控制能力,支撑整个电子设备的运行。存储器用于存储数据、程序、和/或指令代码等,存储器上存储至少一个计算机程序,该计算机程序可被处理器执行,以实现本申请实施例中提供的适用于电子设备的应用程序处理方法。存储器可包括磁碟、光盘、只读存储记忆体(Read-Only Memory,ROM)等非易失性存储介质,或随机存储记忆体(Random-Access-Memory,RAM)等。例如,在一个实施例中,存储器包括非易失性存储介质及内存储器。非易失性存储介质存储有操作系统和计算机程序。该计算机程序可被处理器所执行,以用于实现本申请各个实施例所提供的一种应用程序处理方法。内存储器为非易失性存储介质中的操作系统和计算机程序提供高速缓存的运行环境。显示屏可以是触摸屏,比如为电容屏或电子屏,用于显示前台进程对应的应用的界面信息,还可以被用于检测作用于该显示屏的触摸操作,生成相应的指令,比如进行前后台应用的切换指令等。As shown in FIG. 2 , a schematic diagram of the internal structure of an electronic device is provided. The electronic device includes a processor, memory, and a display screen connected by a system bus. Among them, the processor is used to provide computing and control capabilities to support the operation of the entire electronic device. The memory is used to store data, programs, and/or instruction codes, etc., and at least one computer program is stored in the memory, and the computer program can be executed by the processor to implement the application program processing method applicable to the electronic device provided in the embodiments of the present application . The memory may include a non-volatile storage medium such as a magnetic disk, an optical disk, and a read-only memory (Read-Only Memory, ROM), or a random-access-memory (Random-Access-Memory, RAM) and the like. For example, in one embodiment, the memory includes a non-volatile storage medium and internal memory. The nonvolatile storage medium stores an operating system and a computer program. The computer program can be executed by the processor to implement an application program processing method provided by various embodiments of the present application. The internal memory provides a cached execution environment for the operating system and computer programs in the non-volatile storage medium. The display screen can be a touch screen, such as a capacitive screen or an electronic screen, which is used to display the interface information of the application corresponding to the foreground process, and can also be used to detect the touch operation acting on the display screen and generate corresponding instructions, such as performing front-end and back-end processes. Application switching instructions, etc.
本领域技术人员可以理解,图2中示出的结构,仅仅是与本申请方案相关的部分结构的框图,并不构成对本申请方案所应用于其上的电子设备的限定,具体的电子设备可以包括比图中所示更多或更少的部件,或者组合某些部件,或者具有不同的部件布置。如该电子设备还包括通过系统总线连接的网络接口,网络接口可以是以太网卡或无线网卡等,用于与外部的电子设备进行通信,比如可用于同服务器进行通信。Those skilled in the art can understand that the structure shown in FIG. 2 is only a block diagram of a part of the structure related to the solution of the present application, and does not constitute a limitation on the electronic device to which the solution of the present application is applied. The specific electronic device may be Include more or fewer components than shown in the figures, or combine certain components, or have a different arrangement of components. For example, the electronic device further includes a network interface connected through a system bus, and the network interface may be an Ethernet card or a wireless network card, etc., for communicating with external electronic devices, for example, for communicating with a server.
图3为一个实施例中应用程序处理方法的流程图。本实施例中的应用程序处理方法,以运行于图1中的终端或服务器上为例进行描述。如图3所示,该应用程序处理方法包括步骤302至步骤306。其中:FIG. 3 is a flowchart of an application processing method in one embodiment. The application processing method in this embodiment is described by taking the terminal or the server as shown in FIG. 1 as an example for description. As shown in FIG. 3 , the application processing method includes steps 302 to 306 . in:
步骤302,获取目标用户的心率数据,并根据心率数据判断目标用户是否处于运动状态。Step 302: Acquire the heart rate data of the target user, and determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data.
在一个实施例中,心率数据是指表示用户的心脏跳动规律的数据,具体可以是指用户每分钟内心跳的次数。一般用户在安静状态下和运动状态下的心率数据是不同的,在安静状态下时,用户的心率数据会在一个静态心率范围内变化,而不同给用户在安静状态下的静态心率范围也是不同的。在运动状态下时,用户的心率数据会超过静态心率范围,一般运动越剧烈,心率数据越大。因此,可以根据用户的心率数据来判断用户是否处于运动状态。In one embodiment, the heart rate data refers to data representing the beating regularity of the user's heart, and may specifically refer to the number of heartbeats per minute of the user. Generally, the heart rate data of users in the resting state and the exercise state are different. In the resting state, the user's heart rate data will change within a static heart rate range, and the static heart rate range for different users in the resting state is also different. of. During exercise, the user's heart rate data will exceed the static heart rate range. Generally, the more intense the exercise, the larger the heart rate data. Therefore, whether the user is in an exercise state can be determined according to the user's heart rate data.
电子设备可以采集目标用户的心率数据。具体地,电子设备上可以安装摄像头,然后通过电子设备上安装的摄像头采集目标用户的用户图像,根据采集用户图像获取目标用户的心率数据。可以理解的是,用户的心脏在收缩和舒张的时候,会使血液的流动速度产生变化,从而使皮肤表层的血管产生变化。摄像头采集的用户图像可以反映用户皮肤表层反射的光强度的变化,从而反映血管的血流速度的变化规律。因此根据用户图像可以获取用户皮肤表层的血流速度的变化规律,从而计算用户的心率数据。例如,用户在跑步机上跑步的时候,可以通过摄像头采集用户的面部图像或手部图像,并根据采集的面部图像或手部图像获取用户的心率数据。The electronic device may collect heart rate data of the target user. Specifically, a camera may be installed on the electronic device, and then a user image of the target user is collected through the camera installed on the electronic device, and heart rate data of the target user is obtained according to the collected user image. It can be understood that when the user's heart contracts and relaxes, the flow speed of the blood changes, thereby causing changes in the blood vessels on the surface of the skin. The user image collected by the camera can reflect the change of the light intensity reflected by the user's skin surface, thereby reflecting the change rule of the blood flow velocity of the blood vessel. Therefore, the change rule of the blood flow velocity of the user's skin surface layer can be obtained according to the user image, so as to calculate the user's heart rate data. For example, when the user is running on the treadmill, the user's face image or hand image can be collected through the camera, and the user's heart rate data can be obtained according to the collected face image or hand image.
在本申请提供的其他实施例中,还可以通过可穿戴设备来目标用户的采集心率数据。可穿戴设备是指可直接穿戴在用户身上的设备,例如可穿戴设备可以是智能手环、智能眼镜、智能手表等设备。可穿戴设备一般可直接与用户的皮肤表层接触,可穿戴设备上安装采集用户心率数据的传感器,然后通过传感器检测皮肤表层的脉搏跳动,并根据脉搏的跳动计算心率数据。可穿戴设备可将采集的心率数据进行存储,并将心率数据发送到电子设备。In other embodiments provided in this application, the wearable device may also be used to collect heart rate data of the target user. A wearable device refers to a device that can be directly worn on a user, for example, a wearable device can be a smart bracelet, smart glasses, smart watches and other devices. Wearable devices can generally be in direct contact with the user's skin surface. The wearable device is installed with a sensor that collects the user's heart rate data, and then detects the pulse beat of the skin surface through the sensor, and calculates the heart rate data according to the pulse beat. The wearable device can store the collected heart rate data and send the heart rate data to the electronic device.
步骤304,若目标用户处于运动状态,则从目标用户使用的电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序。
应用程序(Application,APP)是指电子设备中针对某种应用目的所撰写的软体,电子设备可以通过应用程序实现对用户的需求服务。例如,用户可以通过游戏类应用程序玩游戏,也可以通过视频类应用程序看视频,还可以通过音乐类应用程序播放音乐等。应用程序可以根据运行的状态分为前台应用程序和后台应用程序。前台应用程序是指在电子设备的前台运行的应用程序,前台应用程序可以在与在前台显示并与用户实现交互。后台应用程序是指在电子设备的后台运行的应用程序,后台应用程序一般不能在前台显示并与用户实现交互过程。An application program (Application, APP) refers to a software written in an electronic device for a certain application purpose, and the electronic device can realize the demand service for the user through the application program. For example, users can play games through game applications, watch videos through video applications, and play music through music applications. Applications can be divided into foreground applications and background applications according to the running state. A foreground application refers to an application running in the foreground of an electronic device, and the foreground application can be displayed in the foreground and interact with the user. Background applications refer to applications running in the background of electronic devices. Background applications generally cannot be displayed in the foreground and interact with users.
一般地,应用程序的应用操作是由一个或多个进程(process)来共同完成,进程是是计算机中的程序关于某数据集合上的一次运行活动,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位。同时,一个进程可以对应一个或多个线程,线程是程序中一个单一的顺序控制流程,是进程内一个相对独立的、可调度的执行单元。进程可包括前台进程和后台进程,前台进程即为在电子设备前台运行的进程,后台进程即为在电子设备后台运行的进程。电子设备可以控制前台进程和后台进程的切换,前台进程可切换到后台运行,后台进程也可以切换到前台运行。具体地,可以通过进程池来实现对进程的管理,进程池中可以存放一个或多个进程对应的进程标识。进程标识用于唯一标示一个进程。进程池可以包括前台进程池和后台进程池,前台进程池中包括前台进程对应的进程标识,后台进程池中包括后台进程对应的进程标识。当检测到前台进程和后台进程的运行状态发生改变时,进程池会相应地添加或删除产生变化的进程标识。例如,进程A的进程标识为“0123”,当检测到进程A由后台进程变成前台进程时,可将该进程A的进程标识“0123”从后台进程池中移除,并添加到前台进程池中。Generally, the application operation of an application program is jointly completed by one or more processes. A process is a running activity of a program in a computer on a certain data set, and is the basic unit of resource allocation and scheduling in the system. At the same time, a process can correspond to one or more threads. A thread is a single sequential control flow in a program and a relatively independent and schedulable execution unit within a process. The process may include a foreground process and a background process. The foreground process is the process running in the foreground of the electronic device, and the background process is the process running in the background of the electronic device. The electronic device can control the switching between the foreground process and the background process, the foreground process can be switched to run in the background, and the background process can also be switched to run in the foreground. Specifically, process management can be implemented through a process pool, and process identifiers corresponding to one or more processes can be stored in the process pool. Process ID is used to uniquely identify a process. The process pool may include a foreground process pool and a background process pool. The foreground process pool includes a process identifier corresponding to the foreground process, and the background process pool includes a process identifier corresponding to the background process. When it is detected that the running state of the foreground process and the background process changes, the process pool will add or delete the changed process ID accordingly. For example, the process ID of process A is "0123". When it is detected that process A has changed from a background process to a foreground process, the process ID "0123" of process A can be removed from the background process pool and added to the foreground process. in the pool.
目标用户在处于运动状态时,对电子设备的使用也会受到限制。例如,在跑步的时候,没有办法玩游戏,也不能看小说,但是可以听音乐。因此,当用户处于运动状态时,电子设备可以将部分无法使用的应用程序进行冻结,可能用到的应用程序进行周期性地冻结,在运动过程中可以使用的应用程序不进行冻结处理,以减少电子设备的功耗。具体地,电子设备可以预先将安装的应用程序进行分类,并通过分类标签对应用程序的分类进行标记。并在用户处于运动状态时,对不同类型的应用程序进行不同的处理。When the target user is in a state of exercise, the use of electronic devices will also be limited. For example, while running, there is no way to play games or read novels, but you can listen to music. Therefore, when the user is exercising, the electronic device can freeze some applications that cannot be used, the applications that may be used are periodically frozen, and the applications that can be used during exercise are not frozen to reduce Power consumption of electronic equipment. Specifically, the electronic device may classify the installed application programs in advance, and mark the classification of the application programs through the classification label. And when the user is in motion, different types of applications are handled differently.
步骤306,根据心率数据对第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。Step 306: Freeze or unfreeze the first type of target application according to the heart rate data.
第一类目标应用程序表示用户在运动状态下可能使用的应用程序。例如,当用户在运动状态下,可能接收到语音通话的消息,则可以对即时通讯类应用程序进行周期性的冻结或解冻处理,从而既能够及时地接收通讯消息,又能降低电子设备的功耗。具体地,心率数据一般是周期性地进行变化,则可以根据心率数据对第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。例如,每检测到用户的心脏跳动一次,就改变一次第一类目标应用程序的状态,从而交替性地控制第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻。The first category of target applications represents the applications that the user may use in the state of motion. For example, when a user may receive a voice call message while exercising, the instant messaging application can be frozen or unfrozen periodically, so that the communication message can be received in a timely manner and the function of the electronic device can be reduced. consumption. Specifically, the heart rate data generally changes periodically, and the first type of target application program may be frozen or unfrozen according to the heart rate data. For example, every time the user's heart beat is detected, the state of the first type of target application is changed, so as to alternately control the first type of target application to freeze or unfreeze.
电子设备可以通过第一目标应用列表将第一类目标应用程序进行管理,该第一目标应用列表中存储着多个第一目标应用标识,每一个第一目标应用标识用于唯一标示一个第一类目标应用程序。当检测到用户处于运动状态时,电子设备可从第一目标应用列表中获取第一目标应用标识,并根据第一目标应用标识获取第一类目标应用程序,并将第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。The electronic device can manage the first type of target applications through the first target application list, and the first target application list stores a plurality of first target application identifiers, and each first target application identifier is used to uniquely identify a first target application. class target application. When detecting that the user is in a motion state, the electronic device may obtain the first target application identifier from the first target application list, obtain the first type of target application according to the first target application identifier, and perform the first type of target application Freeze or thaw processing.
上述实施例提供的应用程序处理方法,电子设备可以获取目标用户的心率数据,从而根据心率数据判断目标用户是否处于运动状态。若目标用户处于运动状态,则获取第一类目标应用程序,并根据心率数据控制第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。这样可以规律性地将应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理,既能够保证应用程序能够及时地接收消息,又能够通过减少应用程序的运行,从而降低电子设备的功耗。In the application processing method provided by the above embodiment, the electronic device can obtain the heart rate data of the target user, so as to determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data. If the target user is in an exercising state, the first type of target application is acquired, and the first type of target application is controlled to freeze or thaw according to the heart rate data. In this way, the application program can be frozen or thawed regularly, which can not only ensure that the application program can receive messages in time, but also reduce the power consumption of the electronic device by reducing the running of the application program.
图4为另一个实施例中应用程序处理方法的流程图。本实施例中的应用程序处理方法,以运行于图1中的终端或服务器上为例进行描述。如图4所示,该应用程序处理方法包括步骤402至步骤414。其中:FIG. 4 is a flowchart of an application processing method in another embodiment. The application processing method in this embodiment is described by taking the terminal or the server as shown in FIG. 1 as an example for description. As shown in FIG. 4 , the application processing method includes
步骤402,连接可穿戴设备,接收可穿戴设备发送的目标用户的心率数据。
在一个实施例中,电子设备可以与可穿戴设备建立连接,建立连接之后,电子设备和可穿戴设备之间可以进行数据传输。电子设备与可穿戴设备之间可以进行有线连接,也可以进行无线连接。例如,可穿戴设备可以与电子设备通过WiFi(Wireless Fidelity,无线保真)、蓝牙(Bluetooth)等进行连接。电子设备和可穿戴设备打开蓝牙开关后,电子设备可以搜索可穿戴设备的蓝牙接口,并向可穿戴设备发起蓝牙连接请求。当电子设备接收到可穿戴设备返回的允许连接的信息之后,电子设备与可穿戴设备连接成功。In one embodiment, the electronic device can establish a connection with the wearable device, and after the connection is established, data transmission can be performed between the electronic device and the wearable device. The electronic device and the wearable device can be wired or wirelessly connected. For example, the wearable device can be connected with the electronic device through WiFi (Wireless Fidelity, wireless fidelity), Bluetooth (Bluetooth), and the like. After the electronic device and the wearable device turn on the Bluetooth switch, the electronic device can search for the Bluetooth interface of the wearable device and initiate a Bluetooth connection request to the wearable device. After the electronic device receives the connection permission information returned by the wearable device, the electronic device is successfully connected with the wearable device.
具体地,可穿戴设备在获取用户的心率数据之后,可将用户的心率数据进行存储。当电子设备和可穿戴设备建立连接之后,可穿戴设备将获取的心率数据发送到电子设备。可穿戴设备在获取心率数据的时候,常用的方法包括光电法、心电信号、压力振荡法等。由于血液是红色的,因此绿光在透过血液地的时候就会被吸收,绿光吸收得越多,说明血液越多。光电法就是通过可穿戴设备发射绿光,根据绿光被吸收的多少来判断血液的流动规律,从而测量得到心率数据。当心脏周期性地跳动的时候,心肌细胞也会随之产生规律性变化,心电信号法就是通过可穿戴设备来获取心肌收缩和舒张过程中的电信号,并通过获取的电信号变化来计算心率数据。压力振荡法则是通过压力传感器探测动脉血管的搏动振幅,根据搏动规律来计算心率数据。Specifically, after acquiring the user's heart rate data, the wearable device may store the user's heart rate data. After the electronic device and the wearable device are connected, the wearable device sends the acquired heart rate data to the electronic device. When the wearable device acquires heart rate data, the commonly used methods include photoelectric method, electrocardiographic signal, pressure oscillation method, etc. Since blood is red, green light is absorbed when it passes through the blood. The more green light is absorbed, the more blood there is. The photoelectric method emits green light through a wearable device, and judges the blood flow law according to how much green light is absorbed, thereby measuring the heart rate data. When the heart beats periodically, the cardiomyocytes will also change regularly. The ECG signal method is to obtain electrical signals during myocardial contraction and relaxation through wearable devices, and to calculate the changes in the obtained electrical signals. Heart rate data. The pressure oscillation law is to detect the pulse amplitude of the arterial blood vessel through the pressure sensor, and calculate the heart rate data according to the pulse law.
步骤404,判断心率数据是否大于动态心率阈值。
用户在处于安静状态时,心率数据是在一个静态心率范围内变化的。每个人的静态心率范围不同,因此电子设备可以预先存储目标用户的静态心率范围。该静态心率范围可以通过用户进行设置,也可以通过电子设备根据目标用户的历史心率数据进行获取。例如,电子设备可以获取凌晨00:00到6:00的历史心率数据,并获取历史心率数据的平均值,并通过平均值确定静态心率范围。电子设备还可以根据历史心率数据进行机器学习,并根据学习的结果得到静态心率范围。具体地,根据静态心率范围可以获取动态心率阈值,并根据动态心率阈值判断用户是否处于运动状态。一般动态心率阈值可以取静态心率范围的较大边界值,也可以取大于该较大边界值的值。When the user is at rest, the heart rate data changes within a static heart rate range. The resting heart rate range of each person is different, so the electronic device can pre-store the resting heart rate range of the target user. The static heart rate range may be set by the user, or may be acquired by the electronic device according to the historical heart rate data of the target user. For example, the electronic device may acquire historical heart rate data from 00:00 am to 6:00 am, acquire an average value of the historical heart rate data, and use the average value to determine a static heart rate range. The electronic device can also perform machine learning based on historical heart rate data, and obtain a static heart rate range based on the learning result. Specifically, a dynamic heart rate threshold can be obtained according to the static heart rate range, and whether the user is in an exercise state can be determined according to the dynamic heart rate threshold. Generally, the dynamic heart rate threshold may take a larger boundary value of the static heart rate range, or may take a value larger than the larger boundary value.
步骤406,若心率数据大于动态心率阈值,则判定目标用户处于运动状态。
在一个实施例中,可穿戴设备可以将采集的心率数据实时发送到电子设备中,电子设备在获取到心率数据之后,将心率数据与动态心率阈值进行比较。若心率数据超过该动态心率阈值,则认为目标用户处于运动状态。例如,用户的静态心率范围为80~90次/分钟,根据静态心率范围获取动态心率阈值,得到动态心率阈值为95次/分钟。则当检测到目标用户的心率数据为85次/分钟时,认为该目标用户处于安静状态;当检测到目标用户的心率数据为100次/分钟时,则认为该目标用户处于运动状态。In one embodiment, the wearable device can send the collected heart rate data to the electronic device in real time, and after acquiring the heart rate data, the electronic device compares the heart rate data with the dynamic heart rate threshold. If the heart rate data exceeds the dynamic heart rate threshold, the target user is considered to be in a state of exercise. For example, the static heart rate range of the user is 80-90 beats/min, the dynamic heart rate threshold is obtained according to the static heart rate range, and the obtained dynamic heart rate threshold is 95 beats/min. Then, when the heart rate data of the target user is detected to be 85 beats/min, the target user is considered to be in a quiet state; when the heart rate data of the target user is detected to be 100 beats/min, the target user is considered to be in a state of exercise.
可以理解的是,为了防止用户心率数据的偶然性变化,可以根据心率数据大于动态心率阈值的持续时长来判断用户是否处于运动状态。例如,当心率数据大于动态心率阈值的持续时长只有1秒钟时,则可以认为目标用户仍然是处于安静状态的;若持续时长达到10秒钟,则可以认为目标用户是处于运动状态的。具体地,获取心率数据大于动态心率阈值的持续时长,若该持续时长超过时长阈值,则判定目标用户处于运动状态。It can be understood that, in order to prevent accidental changes in the user's heart rate data, whether the user is in an exercise state may be determined according to the duration of the heart rate data greater than the dynamic heart rate threshold. For example, when the heart rate data is greater than the dynamic heart rate threshold for only 1 second, it can be considered that the target user is still in a quiet state; if the duration reaches 10 seconds, it can be considered that the target user is in a state of exercise. Specifically, the duration of the heart rate data greater than the dynamic heart rate threshold is obtained, and if the duration exceeds the duration threshold, it is determined that the target user is in an exercise state.
步骤408,若目标用户处于运动状态,则从目标用户使用的电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序。Step 408 , if the target user is in a motion state, obtain the first type of target application program from the application programs installed on the electronic device used by the target user.
在本申请提供的实施例中,可将电子设备中安装的应用程序分为三类,即第一类目标应用程序、第二类目标应用程序和第三类目标应用程序。第一类目标应用程序表示用户在运动状态下需要进行周期性冻结或解冻的应用程序,第二类目标应用程序用于表示用户在运动状态下需要冻结的应用程序,第三类目标应用程序表示用户在运动状态下无需冻结的应用程序。用户或系统可以根据需要对第一类目标应用程序、第二类目标应用程序和第三类目标应用程序进行设置,在本申请中不进行限定。电子设备可以建立第一目标应用列表、第二目标应用列表和第三目标应用列表,第一目标应用列表用于存储第一类目标应用程序对应的第一目标应用标识,第二目标应用列表用于存储第二类目标应用程序对应的第二目标应用标识,第三目标应用列表用于存储第三类目标应用程序对应的第三目标应用标识。In the embodiments provided in this application, the applications installed in the electronic device can be divided into three types, namely, the first type of target application, the second type of target application and the third type of target application. The first type of target application represents the application that the user needs to freeze or thaw periodically in the state of motion, the second type of target application is used to represent the application that the user needs to freeze in the state of exercise, and the third type of target application represents the application that the user needs to freeze or unfreeze periodically. Apps that users don't need to freeze while in motion. The user or the system can set the first type of target application, the second type of target application and the third type of target application as required, which are not limited in this application. The electronic device may establish a first target application list, a second target application list, and a third target application list, where the first target application list is used to store the first target application identifier corresponding to the first type of target application program, and the second target application list is used for storing the first target application identifier corresponding to the first type of target application program. The second target application identifier corresponding to the second type of target application is stored, and the third target application list is used for storing the third target application identifier corresponding to the third type of target application.
例如,第一类目标应用程序可以但不限于是指即时通讯类应用程序,在用户处于运动状态时,根据用户的心率周期将第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理,以保证用户在运动过程中能够及时地接收消息,同时能够减少电子设备的功耗。第二类目标应用程序是指用户在运动过程中无法使用的应用程序,例如可以是视频类应用程序、游戏类应用程序等。用户在处于运动状态时,可以将第二类目标应用程序进行冻结。第三类目标应用程序可以但不限于是指音乐类应用程序,用户处于运动状态时,还可以对第三类目标应用程序进行使用,因此不需要对第三类目标应用程序进行冻结处理。For example, the first type of target application may be, but is not limited to, instant messaging applications. When the user is exercising, the first type of target application is frozen or thawed according to the user's heart rate cycle to ensure that the user is exercising. During the process, the message can be received in time, and the power consumption of the electronic device can be reduced at the same time. The second type of target application refers to an application that a user cannot use during exercise, for example, a video application, a game application, and the like. When the user is in a motion state, the second type of target application can be frozen. The third type of target application may, but is not limited to, refer to music applications. When the user is in motion, the third type of target application can also be used, so the third type of target application does not need to be frozen.
步骤410,根据心率数据绘制心率曲线,根据心率曲线对第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。Step 410: Draw a heart rate curve according to the heart rate data, and freeze or unfreeze the first type of target application according to the heart rate curve.
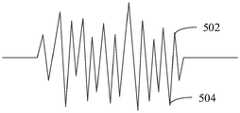
心率曲线是指心率数据的变化曲线,电子设备可以根据心率数据绘制心率曲线,心率曲线可以反映历史心率数据的变化过程。根据心率曲线对第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理具体包括:当检测到心率曲线的波峰时,对第一类目标应用程序进行冻结处理;当检测到心率曲线的波谷时,对第一类目标应用程序进行解冻处理。波峰是指心率曲线变化的极大值,波谷是指心率曲线变化的极小值。当检测到心率曲线的波峰时,将第一类目标应用程序进行冻结处理。冻结之后的第一类目标应用程序无法在继续运行,也不占用CPU资源,能够深层地限制应用程序对资源的占用,减少了电子设备的功耗。当检测心率曲线的波谷时,将第一类目标应用程序进行解冻处理,解冻后的第一类目标应用程序可以正常运行。The heart rate curve refers to the change curve of the heart rate data. The electronic device can draw the heart rate curve according to the heart rate data, and the heart rate curve can reflect the change process of the historical heart rate data. Freezing or thawing the first type of target application according to the heart rate curve specifically includes: when the peak of the heart rate curve is detected, freezing the first type of target application; when the trough of the heart rate curve is detected, the first type of target application is frozen. The class target application is thawed. The peak refers to the maximum value of the heart rate curve change, and the trough refers to the minimum value of the heart rate curve change. When the peak of the heart rate curve is detected, the first type of target application is frozen. The first type of target application program after freezing cannot continue to run and does not occupy CPU resources, which can deeply limit the resource occupation of the application program and reduce the power consumption of the electronic device. When the trough of the heart rate curve is detected, the first type of target application is thawed, and the thawed first type of target application can run normally.
在本申请提供的其他实施例中,可以将心率曲线的两个波峰或波谷之间间隔的时长作为一个周期,然后根据心率曲线周期性地控制第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。具体地,根据心率曲线对第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理可以包括:检测心率曲线的波峰或波谷;在每间隔预设个数的波峰或波谷时,检测第一类目标应用程序的工作状态;若第一类目标应用程序处于冻结状态,则将第一类目标应用程序进行解冻处理;若第一类目标应用程序处于运行状态,则将第一类目标应用程序进行冻结处理。例如,首先获取心率曲线的所有波峰,获取的波峰会组成一个波峰序列。将每间隔3个波峰的时长作为一个周期,每到一个周期时,控制第一类目标应用程序交替地进行冻结和解冻处理。In other embodiments provided in this application, the interval between two peaks or troughs of the heart rate curve may be used as a period, and then the first type of target application is periodically controlled to freeze or unfreeze according to the heart rate curve. Specifically, freezing or thawing the first type of target application according to the heart rate curve may include: detecting the peaks or troughs of the heart rate curve; at every preset number of peaks or troughs, detecting the first type of target application Working state; if the first type of target application is in a frozen state, the first type of target application is thawed; if the first type of target application is in a running state, the first type of target application is frozen. For example, first acquire all the peaks of the heart rate curve, and the acquired peaks form a peak sequence. The duration of every 3 peaks is regarded as a cycle, and the first type of target application is controlled to freeze and thaw alternately when a cycle is reached.
图5为一个实施例中心率曲线的示意图。如图5所示,该心率曲线可以反映心率数据的历史变化规律,心率曲线中包含若干个波峰502,和若干个波谷504。在波峰502时,心率数据从递增变为递减的变化趋势;在波谷504时,心率数据从递减变为递增的变化趋势。FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of a center rate curve of one embodiment. As shown in FIG. 5 , the heart rate curve can reflect the historical variation law of heart rate data, and the heart rate curve includes
步骤412,从电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第二类目标应用程序。Step 412: Obtain the second type of target application program from the application program installed on the electronic device.
步骤414,将第二类目标应用程序进行冻结处理。
在一个实施例中,电子设备可以获取第二目标应用列表,并根据第二目标应用列表获取第二类目标应用程序。第二类目标应用程序表示在运动过程中用户无法使用的应用程序,则电子设备可以获取第二类目标应用程序,并将第二类目标应用程序进行冻结处理,这样可以减少电子设备的功耗。In one embodiment, the electronic device may acquire the second target application list, and acquire the second type of target application program according to the second target application list. The second type of target application represents an application that cannot be used by the user during exercise, the electronic device can obtain the second type of target application and freeze the second type of target application, which can reduce the power consumption of the electronic device .
在一个实施例中,步骤414之后还可以包括:若检测到目标用户处于安静状态,则控制第一类目标应用程序和第二类目标应用程序恢复正常运行状态。具体地,电子设备将电子设备的心率数据与静态心率范围进行比较,若心率数据在静态心率范围内,则判定目标用户处于安静状态。当目标用户为安静状态时,则将第一类目标应用程序和第二类目标应用程序恢复正常运行状态。恢复到正常运行状态后,应用程序对电子设备资源的使用不再受到限制。In one embodiment, after
以Android系统中,实现应用程序的冻结和及解冻的方法有多种。以其中一种为例,可以通过pm(package manager,包管理)命令来实现,在pm命令中,可以通过冻结命令pmdisable[–user USER_ID]PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT将应用程序设置为冻结状态,然后还可以通过解冻命令pm enable[–user USER_ID]PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT将处于冻结状态的应用程序进行解冻,通过冻结列表查询命令pm list packages–d获取处于冻结状态的应用程序列表,以查看处于冻结状态的应用程序。可以理解的是,本申请中以Android操作系统为例对应用程序处理方法进行说明,但是本申请的应用程序处理方法并不仅限于在Android系统中实现,还可以应用在IOS、塞班、Windows、MAC OS(Macintosh Operating System)等操作系统中。In the Android system, there are many ways to realize freezing and thawing of applications. Taking one of them as an example, it can be implemented by the pm (package manager, package management) command. In the pm command, the application can be set to a frozen state by the freeze command pmdisable[–user USER_ID]PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT, and then the application can be unfrozen by The command pm enable[–user USER_ID]PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT will unfreeze the application in the frozen state, and use the frozen list query command pm list packages –d to obtain the list of the application in the frozen state to view the application in the frozen state. It can be understood that the application processing method is described by taking the Android operating system as an example in this application, but the application processing method of this application is not limited to being implemented in the Android system, and can also be applied to IOS, Saipan, Windows, MAC OS (Macintosh Operating System) and other operating systems.
在用户的运行过程中,第三类目标应用程序可以不进行冻结处理,但为了降低电子设备的功耗,可以将第三类目标应用程序进行资源限制处理。其中,处于资源限制状态的应用程序在运行时对电子设备的资源占用率小于占用率阈值。当第三类目标应用程序处于资源限制状态时,第三类目标应用程序对电子设备的资源占用率就不能超过占用率阈值,这样可以控制第三类目标应用程序对电子设备的资源占用,从而降低电子设备的功耗。例如,控制第三类目标应用程序在运行时的CPU占用率不能超过5%,这样可以保证第三类目标应用程序的运行,又可以防止第三类目标应用程序对CPU的过度消耗。在手机系统中可以通过cgroups(control groups,控制组)来控制第三类目标应用程序的CPU、内存、IO等资源占用率,即控制所获取的第三类目标应用程序进入资源限制状态。During the running process of the user, the third type of target application may not be frozen, but in order to reduce the power consumption of the electronic device, the third type of target application may be subject to resource limitation processing. Wherein, the resource occupancy rate of the electronic device when the application program in the resource-limited state is running is less than the occupancy rate threshold. When the third type of target application is in a resource-limited state, the resource occupancy rate of the third type of target application on the electronic device cannot exceed the occupancy rate threshold, so that the resource occupation of the third type of target application on the electronic device can be controlled, thereby Reduce power consumption of electronic equipment. For example, controlling the CPU usage rate of the third type of target application during running can not exceed 5%, which can ensure the operation of the third type of target application and prevent the third type of target application from excessive CPU consumption. In the mobile phone system, cgroups (control groups, control groups) can be used to control the CPU, memory, IO and other resource occupancy rates of the third type of target application, that is, to control the obtained third type of target application to enter the resource limit state.
在对第三类目标应用程序进行资源限制处理的时候,可以根据电子设备的资源占用率来控制对第三类目标应用程序的资源限制程度。其中,资源总占用率是指电子设备中被占用的资源和总资源的比例。具体地,可以获取电子设备的资源总占用率,并根据资源总占用率来控制第三类目标应用程序进入资源限制状态。例如,当电子设备的资源占用率较高时,对第三类目标应用程序进行程度较深的资源限制处理;当电子设备的资源占用率较低时,对第三类目标应用程序进行程度较轻的资源限制处理。When the resource limitation processing is performed on the third type of target application, the degree of resource limitation on the third type of target application can be controlled according to the resource occupancy rate of the electronic device. The total resource occupancy rate refers to the ratio of occupied resources and total resources in the electronic device. Specifically, the total resource occupancy rate of the electronic device can be acquired, and the third type of target application program can be controlled to enter the resource limitation state according to the total resource occupancy rate. For example, when the resource occupancy rate of the electronic device is high, the third type of target application is subject to a relatively deep resource restriction process; when the resource occupancy rate of the electronic device is low, the third type of target application is processed to a greater extent. Light resource limit handling.
电子设备可以预先建立资源总占用率和资源限制级别的对应关系,处于不同的资源限制级别时,第三类目标应用程序对应的占用率阈值不同。获取电子设备的资源总占用率,并根据资源总占用率获取资源限制级别;控制第三类目标应用程序进入资源限制级别对应的资源限制状态。例如,将电子设备的资源总占用率划分为50%~60%、60%~80%、80%~100%等三个占用级别,然后分别对应轻度资源限制级别、普通资源限制级别和深度资源限制级别等三个等级,根据资源总占用率可以获取对应的资源限制级别,不同的资源限制级别对应的占用率阈值不同。可以理解的是,不同资源对应的占用率阈值还可以不同。比如,CPU占用率阈值可以为5%,内存占用率阈值可以为10%。The electronic device may pre-establish a corresponding relationship between the total resource occupancy rate and the resource restriction level. When the electronic device is at different resource restriction levels, the occupancy rate thresholds corresponding to the third type of target applications are different. The total resource occupancy rate of the electronic device is acquired, and the resource restriction level is acquired according to the total resource occupation rate; the third type of target application is controlled to enter the resource restriction state corresponding to the resource restriction level. For example, divide the total resource occupancy rate of electronic equipment into three occupancy levels, 50% to 60%, 60% to 80%, and 80% to 100%, and then correspond to the light resource restriction level, the normal resource restriction level and the depth respectively. There are three levels such as resource restriction level. The corresponding resource restriction level can be obtained according to the total resource occupancy rate. Different resource restriction levels correspond to different occupancy rate thresholds. It can be understood that the occupancy thresholds corresponding to different resources may also be different. For example, the CPU usage threshold may be 5%, and the memory usage threshold may be 10%.
在其他实施例中,还可以根据第三类目标应用程序的应用优先级来控制对资源的占用情况,预先建立应用优先级与资源限制级别的对应关系,然后根据第三类目标应用程序的应用优先级来控制进入资源限制状态的资源限制级别。具体可以包括:获取第三类目标应用程序对应的第三应用优先级;根据该第三应用优先级获取对应的资源限制级别;控制第三类目标应用程序进入资源限制级别对应的资源限制状态。In other embodiments, the occupancy of resources may also be controlled according to the application priority of the third type of target application, the corresponding relationship between the application priority and the resource restriction level may be established in advance, and then according to the application priority of the third type of target application Priority to control the resource limit level that enters the resource limit state. Specifically, it may include: acquiring a third application priority corresponding to the third type of target application; acquiring a corresponding resource restriction level according to the third application priority; and controlling the third type of target application to enter a resource restriction state corresponding to the resource restriction level.
图6为一个实施例中应用程序的资源限制状态的示意图。如图6所示,电子设备的资源包括CPU、内存、IO、网络资源等,应用程序的状态可以分为正常运行状态、资源限制状态和冻结状态。其中,资源限制状态又可以分为轻度资源限制状态、普通资源限制状态和深度资源限制状态。在不同资源限制状态下,对应的可用资源602和不可用资源604不相同。从轻度资源限制状态、普通资源限制状态到深度资源限制状态,可用资源602递减。在正常运行状态下,应用程序的可用资源602为100%。FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of the resource limit state of an application in one embodiment. As shown in FIG. 6 , the resources of the electronic device include CPU, memory, IO, network resources, etc., and the state of the application program can be divided into a normal running state, a resource-limited state, and a frozen state. Among them, the resource limitation state can be further divided into a light resource limitation state, a normal resource limitation state, and a deep resource limitation state. In different resource restriction states, the corresponding
上述实施例提供的应用程序处理方法,电子设备可以获取目标用户的心率数据,从而根据心率数据判断目标用户是否处于运动状态。若目标用户处于运动状态,则获取第一类目标应用程序,并根据心率数据控制第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。这样可以规律性地将应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理,既能够保证应用程序能够及时地接收消息,又能够通过减少应用程序的运行,从而降低电子设备的功耗。同时获取第二类目标应用程序,并将第二类目标应用程序进行冻结。冻结后的第二类目标应用程序无法继续运行,减少了电子设备的功耗。In the application processing method provided by the above embodiment, the electronic device can obtain the heart rate data of the target user, so as to determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data. If the target user is in an exercising state, the first type of target application is acquired, and the first type of target application is controlled to freeze or thaw according to the heart rate data. In this way, the application program can be frozen or thawed regularly, which can not only ensure that the application program can receive messages in time, but also reduce the power consumption of the electronic device by reducing the running of the application program. At the same time, the second type of target application is acquired, and the second type of target application is frozen. The frozen second type of target application cannot continue to run, reducing the power consumption of the electronic device.
应该理解的是,虽然图3和图4的流程图中的各个步骤按照箭头的指示依次显示,但是这些步骤并不是必然按照箭头指示的顺序依次执行。除非本文中有明确的说明,这些步骤的执行并没有严格的顺序限制,这些步骤可以以其它的顺序执行。而且,图3和图4中的至少一部分步骤可以包括多个子步骤或者多个阶段,这些子步骤或者阶段并不必然是在同一时刻执行完成,而是可以在不同的时刻执行,这些子步骤或者阶段的执行顺序也不必然是依次进行,而是可以与其它步骤或者其它步骤的子步骤或者阶段的至少一部分轮流或者交替地执行。It should be understood that, although the steps in the flowcharts of FIG. 3 and FIG. 4 are shown in sequence according to the arrows, these steps are not necessarily executed in the sequence shown by the arrows. Unless explicitly stated herein, the execution of these steps is not strictly limited to the order, and these steps may be performed in other orders. Moreover, at least a part of the steps in FIG. 3 and FIG. 4 may include multiple sub-steps or multiple stages. These sub-steps or stages are not necessarily executed and completed at the same time, but may be executed at different times. These sub-steps or stages may be executed at different times. The order of execution of the stages is also not necessarily sequential, but may be performed alternately or alternately with other steps or sub-steps of other steps or at least a portion of a stage.
在一个实施例中,如图7所示,提供了一种电子设备的部分架构图。其中,该电子设备的架构系统中包括JAVA空间层71、本地框架层72以及内核(Kernel)空间层73。JAVA空间层71上可包含策略应用程序710,电子设备可通过该策略应用程序710来发起对各个应用程序的冻结和解冻策略,从而实现对电子设备中的各个应用程序实现冻结和解冻的操作。例如,通过策略应用程序710来判断后台耗电的应用程序,并发起对该后台耗电的应用程序做冻结操作。本地框架层72中包含资源优先级和限制管理模块720及平台冻结管理模块722。电子设备可通过资源优先级和限制管理模块720来实时维护应用程序的优先级和对应的资源组,根据上层的需求来调整应用程序的优先级和资源组,从而达到优化性能,节省功耗的作用。电子设备可通过平台冻结管理模块722将后台可以冻结的任务按照进入冻结时间的长短,分配到对应预设的不同层次的冻结层,可选地,该冻结层可包括:CPU限制睡眠模式、CPU冻结睡眠模式、进程深度冻结模式。内核空间层73中包括UID管理模块730、Cgroup模块732、超时冻结退出模块734、Binder管控模块737、进程内存回收模块738。其中,UID管理模块730可以基于应用程序的用户身份标识(User Identifier,UID)来管理第三方应用程序的资源或进行冻结。相比较于基于进程身份标识(Process Identifier,PID)来进行进程管控,通过UID更便于统一管理一个用户的应用的资源。Cgroup模块732用于提供一套完善的中央处理器(Central Processing Unit,CPU)、CPUSET、内存(memory)、输入/输出(input/output,I/O)和Net相关的资源限制机制。超时冻结退出模块734用于解决出现冻结超时场景产生的异常。Binder管控模块736用于实现后台binder通信的优先级的控制。进程内存回收模块738用于实现进程的深度冻结模式,当第三方应用程序长期处于冻结状态的时候,可以释放进程的文件区,从而达到节省内存的模块,也加快该应用程序在下次启动时的速度。通过上述的架构,可实现本申请各个实施例中的应用程序处理方法。In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 7 , a partial architecture diagram of an electronic device is provided. The architecture system of the electronic device includes a JAVA space layer 71 , a local framework layer 72 and a kernel (Kernel) space layer 73 . The JAVA space layer 71 may include a
图8为一个实施例中应用程序处理装置的结构示意图。如图8所示,该应用程序处理装置800包括数据获取模块802、应用获取模块804和应用处理模块806。其中:FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of an application processing apparatus in an embodiment. As shown in FIG. 8 , the application processing apparatus 800 includes a
数据获取模块802,用于获取目标用户的心率数据,并根据所述心率数据判断所述目标用户是否处于运动状态。The
应用获取模块804,用于若所述目标用户处于运动状态,则从所述目标用户使用的电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第一类目标应用程序。The
应用处理模块806,用于根据所述心率数据对所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。An
上述实施例提供的应用程序处理装置,电子设备可以获取目标用户的心率数据,从而根据心率数据判断目标用户是否处于运动状态。若目标用户处于运动状态,则获取第一类目标应用程序,并根据心率数据控制第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。这样可以规律性地将应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理,既能够保证应用程序能够及时地接收消息,又能够通过减少应用程序的运行,从而降低电子设备的功耗。In the application processing apparatus provided by the above embodiments, the electronic device can acquire the heart rate data of the target user, so as to determine whether the target user is in an exercise state according to the heart rate data. If the target user is in an exercising state, the first type of target application is acquired, and the first type of target application is controlled to freeze or thaw according to the heart rate data. In this way, the application program can be frozen or thawed regularly, which can not only ensure that the application program can receive messages in time, but also reduce the power consumption of the electronic device by reducing the running of the application program.
在一个实施例中,数据获取模块802还用于连接可穿戴设备,接收所述可穿戴设备发送的目标用户的心率数据。In one embodiment, the
在一个实施例中,数据获取模块802还用于判断所述心率数据是否大于动态心率阈值;若所述心率数据大于所述动态心率阈值,则判定所述目标用户处于运动状态。In one embodiment, the
在一个实施例中,应用处理模块806还用于根据所述心率数据绘制心率曲线,根据所述心率曲线对所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结或解冻处理。In one embodiment, the
在一个实施例中,应用处理模块806还用于当检测到所述心率曲线的波峰时,对所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结处理;当检测到所述心率曲线的波谷时,对所述第一类目标应用程序进行解冻处理。In one embodiment, the
在一个实施例中,应用处理模块806还用于检测所述心率曲线的波峰或波谷;在每间隔预设个数的波峰或波谷时,检测所述第一类目标应用程序的工作状态;若所述第一类目标应用程序处于冻结状态,则将所述第一类目标应用程序进行解冻处理;若所述第一类目标应用程序处于运行状态,则将所述第一类目标应用程序进行冻结处理。In one embodiment, the
在一个实施例中,应用处理模块806还用于若所述目标用户处于运动状态,则从所述电子设备安装的应用程序中获取第二类目标应用程序;将所述第二类目标应用程序进行冻结处理。In one embodiment, the
上述应用程序处理装置中各个模块的划分仅用于举例说明,在其他实施例中,可将应用程序处理装置按照需要划分为不同的模块,以完成上述应用程序处理装置的全部或部分功能。The division of each module in the above application processing apparatus is only for illustration. In other embodiments, the application processing apparatus may be divided into different modules as required to complete all or part of the functions of the above application processing apparatus.
本申请实施例中提供的应用程序处理装置中的各个模块的实现可为计算机程序的形式。该计算机程序可在终端或服务器上运行。该计算机程序构成的程序模块可存储在终端或服务器的存储器上。该计算机程序被处理器执行时,实现本申请实施例中所描述方法的步骤。The implementation of each module in the application processing apparatus provided in the embodiments of the present application may be in the form of a computer program. The computer program can be run on a terminal or server. The program modules constituted by the computer program can be stored in the memory of the terminal or the server. When the computer program is executed by the processor, the steps of the methods described in the embodiments of the present application are implemented.
本申请实施例还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质。一个或多个包含计算机可执行指令的非易失性计算机可读存储介质,当所述计算机可执行指令被一个或多个处理器执行时,使得所述处理器执行上述实施例提供的应用程序处理方法。Embodiments of the present application also provide a computer-readable storage medium. One or more non-volatile computer-readable storage media containing computer-executable instructions, when the computer-executable instructions are executed by one or more processors, causing the processors to execute the application programs provided by the above embodiments Approach.
一种包含指令的计算机程序产品,当其在计算机上运行时,使得计算机执行上述实施例提供的应用程序处理方法。A computer program product containing instructions, when running on a computer, causes the computer to execute the application program processing method provided by the above embodiments.
本申请实施例还提供了一种电子设备。如图9所示,为了便于说明,仅示出了与本申请实施例相关的部分,具体技术细节未揭示的,请参照本申请实施例方法部分。该电子设备可以为包括手机、平板电脑、PDA(Personal Digital Assistant,个人数字助理)、POS(Point of Sales,销售终端)、车载电脑、穿戴式设备等任意终端设备,以电子设备为手机为例:The embodiments of the present application also provide an electronic device. As shown in FIG. 9 , for the convenience of description, only the part related to the embodiment of the present application is shown, and the specific technical details are not disclosed, please refer to the method part of the embodiment of the present application. The electronic device may be any terminal device including a mobile phone, a tablet computer, a PDA (Personal Digital Assistant), a POS (Point of Sales, a sales terminal), a vehicle-mounted computer, a wearable device, etc. The electronic device is a mobile phone as an example :
图9为与本申请实施例提供的电子设备相关的手机的部分结构的框图。参考图9,手机包括:射频(Radio Frequency,RF)电路910、存储器920、输入单元930、显示单元940、传感器950、音频电路960、无线保真(wireless fidelity,WiFi)模块970、处理器980、以及电源990等部件。本领域技术人员可以理解,图9所示的手机结构并不构成对手机的限定,可以包括比图示更多或更少的部件,或者组合某些部件,或者不同的部件布置。FIG. 9 is a block diagram of a partial structure of a mobile phone related to an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present application. Referring to FIG. 9 , the mobile phone includes: a radio frequency (RF)
其中,RF电路910可用于收发信息或通话过程中,信号的接收和发送,可将基站的下行信息接收后,给处理器980处理;也可以将上行的数据发送给基站。通常,RF电路包括但不限于天线、至少一个放大器、收发信机、耦合器、低噪声放大器(Low Noise Amplifier,LNA)、双工器等。此外,RF电路910还可以通过无线通信与网络和其他设备通信。上述无线通信可以使用任一通信标准或协议,包括但不限于全球移动通讯系统(Global System ofMobile communication,GSM)、通用分组无线服务(General Packet Radio Service,GPRS)、码分多址(Code Division Multiple Access,CDMA)、宽带码分多址(Wideband CodeDivision Multiple Access,WCDMA)、长期演进(Long Term Evolution,LTE))、电子邮件、短消息服务(Short Messaging Service,SMS)等。The
存储器920可用于存储软件程序以及模块,处理器980通过运行存储在存储器920的软件程序以及模块,从而执行手机的各种功能应用以及数据处理。存储器920可主要包括程序存储区和数据存储区,其中,程序存储区可存储操作系统、至少一个功能所需的应用程序(比如声音播放功能的应用程序、图像播放功能的应用程序等)等;数据存储区可存储根据手机的使用所创建的数据(比如音频数据、通讯录等)等。此外,存储器920可以包括高速随机存取存储器,还可以包括非易失性存储器,例如至少一个磁盘存储器件、闪存器件、或其他易失性固态存储器件。The
输入单元930可用于接收输入的数字或字符信息,以及产生与手机900的用户设置以及功能控制有关的键信号输入。具体地,输入单元930可包括触控面板931以及其他输入设备932。触控面板931,也可称为触摸屏,可收集用户在其上或附近的触摸操作(比如用户使用手指、触笔等任何适合的物体或附件在触控面板931上或在触控面板931附近的操作),并根据预先设定的程式驱动相应的连接装置。在一个实施例中,触控面板931可包括触摸检测装置和触摸控制器两个部分。其中,触摸检测装置检测用户的触摸方位,并检测触摸操作带来的信号,将信号传送给触摸控制器;触摸控制器从触摸检测装置上接收触摸信息,并将它转换成触点坐标,再送给处理器980,并能接收处理器980发来的命令并加以执行。此外,可以采用电阻式、电容式、红外线以及表面声波等多种类型实现触控面板931。除了触控面板931,输入单元930还可以包括其他输入设备932。具体地,其他输入设备932可以包括但不限于物理键盘、功能键(比如音量控制按键、开关按键等)等中的一种或多种。The
显示单元940可用于显示由用户输入的信息或提供给用户的信息以及手机的各种菜单。显示单元940可包括显示面板941。在一个实施例中,可以采用液晶显示器(LiquidCrystal Display,LCD)、有机发光二极管(Organic Light-Emitting Diode,OLED)等形式来配置显示面板941。在一个实施例中,触控面板931可覆盖显示面板941,当触控面板931检测到在其上或附近的触摸操作后,传送给处理器980以确定触摸事件的类型,随后处理器980根据触摸事件的类型在显示面板941上提供相应的视觉输出。虽然在图9中,触控面板931与显示面板941是作为两个独立的部件来实现手机的输入和输入功能,但是在某些实施例中,可以将触控面板931与显示面板941集成而实现手机的输入和输出功能。The
手机900还可包括至少一种传感器950,比如光传感器、运动传感器以及其他传感器。具体地,光传感器可包括环境光传感器及接近传感器,其中,环境光传感器可根据环境光线的明暗来调节显示面板941的亮度,接近传感器可在手机移动到耳边时,关闭显示面板941和/或背光。运动传感器可包括加速度传感器,通过加速度传感器可检测各个方向上加速度的大小,静止时可检测出重力的大小及方向,可用于识别手机姿态的应用(比如横竖屏切换)、振动识别相关功能(比如计步器、敲击)等;此外,手机还可配置陀螺仪、气压计、湿度计、温度计、红外线传感器等其他传感器等。Cell phone 900 may also include at least one
音频电路960、扬声器961和传声器962可提供用户与手机之间的音频接口。音频电路960可将接收到的音频数据转换后的电信号,传输到扬声器961,由扬声器961转换为声音信号输出;另一方面,传声器962将收集的声音信号转换为电信号,由音频电路960接收后转换为音频数据,再将音频数据输出处理器980处理后,经RF电路910可以发送给另一手机,或者将音频数据输出至存储器920以便后续处理。
WiFi属于短距离无线传输技术,手机通过WiFi模块970可以帮助用户收发电子邮件、浏览网页和访问流式媒体等,它为用户提供了无线的宽带互联网访问。虽然图9示出了WiFi模块970,但是可以理解的是,其并不属于手机900的必须构成,可以根据需要而省略。WiFi is a short-distance wireless transmission technology. The mobile phone can help users to send and receive emails, browse web pages, and access streaming media through the
处理器980是手机的控制中心,利用各种接口和线路连接整个手机的各个部分,通过运行或执行存储在存储器920内的软件程序和/或模块,以及调用存储在存储器920内的数据,执行手机的各种功能和处理数据,从而对手机进行整体监控。在一个实施例中,处理器980可包括一个或多个处理单元。在一个实施例中,处理器980可集成应用处理器和调制解调处理器,其中,应用处理器主要处理操作系统、用户界面和应用程序等;调制解调处理器主要处理无线通信。可以理解的是,上述调制解调处理器也可以不集成到处理器980中。The
手机900还包括给各个部件供电的电源990(比如电池),优选的,电源可以通过电源管理系统与处理器980逻辑相连,从而通过电源管理系统实现管理充电、放电、以及功耗管理等功能。The mobile phone 900 also includes a power supply 990 (such as a battery) for supplying power to various components. Preferably, the power supply can be logically connected to the
在一个实施例中,手机900还可以包括摄像头、蓝牙模块等。In one embodiment, the mobile phone 900 may further include a camera, a Bluetooth module, and the like.
在本申请实施例中,该电子设备所包括的处理器980执行存储在存储器上的计算机程序时实现上述实施例提供的应用程序处理方法的步骤。In the embodiment of the present application, when the
本申请所使用的对存储器、存储、数据库或其它介质的任何引用可包括非易失性和/或易失性存储器。非易失性存储器可包括只读存储器(ROM)、可编程ROM(PROM)、电可编程ROM(EPROM)、电可擦除可编程ROM(EEPROM)或闪存。易失性存储器可包括随机存取存储器(RAM),它用作外部高速缓冲存储器。作为说明而非局限,RAM以多种形式可得,诸如静态RAM(SRAM)、动态RAM(DRAM)、同步DRAM(SDRAM)、双数据率SDRAM(DDR SDRAM)、增强型SDRAM(ESDRAM)、同步链路(Synchlink)DRAM(SLDRAM)、存储器总线(Rambus)直接RAM(RDRAM)、直接存储器总线动态RAM(DRDRAM)、以及存储器总线动态RAM(RDRAM)。Any reference to a memory, storage, database, or other medium as used herein may include non-volatile and/or volatile memory. Nonvolatile memory may include read only memory (ROM), programmable ROM (PROM), electrically programmable ROM (EPROM), electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM), or flash memory. Volatile memory may include random access memory (RAM), which acts as external cache memory. By way of illustration and not limitation, RAM is available in various forms such as static RAM (SRAM), dynamic RAM (DRAM), synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), double data rate SDRAM (DDR SDRAM), enhanced SDRAM (ESDRAM), synchronous Link (Synchlink) DRAM (SLDRAM), Memory Bus (Rambus) Direct RAM (RDRAM), Direct Memory Bus Dynamic RAM (DRDRAM), and Memory Bus Dynamic RAM (RDRAM).
以上所述实施例仅表达了本申请的几种实施方式,其描述较为具体和详细,但并不能因此而理解为对本申请专利范围的限制。应当指出的是,对于本领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本申请构思的前提下,还可以做出若干变形和改进,这些都属于本申请的保护范围。因此,本申请专利的保护范围应以所附权利要求为准。The above-mentioned embodiments only represent several embodiments of the present application, and the descriptions thereof are relatively specific and detailed, but should not be construed as a limitation on the scope of the patent of the present application. It should be pointed out that for those skilled in the art, without departing from the concept of the present application, several modifications and improvements can be made, which all belong to the protection scope of the present application. Therefore, the scope of protection of the patent of the present application shall be subject to the appended claims.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810032323.7ACN110045994B (en) | 2018-01-12 | 2018-01-12 | Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810032323.7ACN110045994B (en) | 2018-01-12 | 2018-01-12 | Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110045994A CN110045994A (en) | 2019-07-23 |
| CN110045994Btrue CN110045994B (en) | 2022-09-16 |
Family
ID=67264281
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810032323.7AExpired - Fee RelatedCN110045994B (en) | 2018-01-12 | 2018-01-12 | Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110045994B (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113545765B (en)* | 2021-07-16 | 2024-04-09 | 厦门硅田系统工程有限公司 | Continuous heart rate output method of heart rate measuring device and heart rate measuring device |
| WO2023220894A1 (en)* | 2022-05-16 | 2023-11-23 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | Statistical method and apparatus for motion physiological data, device, storage medium and chip |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4343041A (en)* | 1980-04-03 | 1982-08-03 | Codex Corporation | Modem circuitry |
| CN106250177A (en)* | 2016-07-26 | 2016-12-21 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | application program freezing method and system |
| CN106959857A (en)* | 2017-03-29 | 2017-07-18 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | The application control method and apparatus of a kind of electronic equipment |
| CN107562539A (en)* | 2017-08-25 | 2018-01-09 | 广东欧珀移动通信有限公司 | Applied program processing method and device, computer equipment, storage medium |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104317608A (en)* | 2014-09-30 | 2015-01-28 | 北京金山安全软件有限公司 | Management method and device for pre-installed application program in mobile terminal and client |
| CN106155788A (en)* | 2016-06-28 | 2016-11-23 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | A kind of application program freezing method and terminal unit |
| CN106131337A (en)* | 2016-07-19 | 2016-11-16 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | A kind of method and device out of service based on User Status control application |
| CN107291242B (en)* | 2017-06-30 | 2020-06-26 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | A control method of an intelligent terminal and an intelligent terminal |
- 2018
- 2018-01-12CNCN201810032323.7Apatent/CN110045994B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4343041A (en)* | 1980-04-03 | 1982-08-03 | Codex Corporation | Modem circuitry |
| CN106250177A (en)* | 2016-07-26 | 2016-12-21 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | application program freezing method and system |
| CN106959857A (en)* | 2017-03-29 | 2017-07-18 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | The application control method and apparatus of a kind of electronic equipment |
| CN107562539A (en)* | 2017-08-25 | 2018-01-09 | 广东欧珀移动通信有限公司 | Applied program processing method and device, computer equipment, storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110045994A (en) | 2019-07-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109992438A (en) | Information processing method, apparatus, computer device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN110008008A (en) | Applied program processing method and device, electronic equipment, computer readable storage medium | |
| CN107368400A (en) | CPU monitoring method, device, computer readable storage medium and mobile terminal | |
| CN110032321B (en) | Application processing method and device, electronic equipment, computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN107544842A (en) | Application program processing method and device, computer equipment, storage medium | |
| CN110032431A (en) | Application processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN109992376B (en) | Application freezing method, device, terminal and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN108334345B (en) | Application processing method, device, readable storage medium and mobile terminal | |
| CN109992369B (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN109992323B (en) | Process processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN109992380B (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN109992425A (en) | Information processing method, apparatus, computer device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN110045994B (en) | Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN110032397A (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN109992363B (en) | Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN110046033B (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN109992360B (en) | Process processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN109992309B (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN109992362A (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN110045811B (en) | Application program processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN109993525B (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN107491349A (en) | Application program processing method and device, computer equipment, storage medium | |
| CN109992371A (en) | Application processing method, apparatus, electronic device, computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN109992368B (en) | Application processing method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN110046030B (en) | Application processing method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| CB02 | Change of applicant information | ||
| CB02 | Change of applicant information | Address after:Changan town in Guangdong province Dongguan 523860 usha Beach Road No. 18 Applicant after:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATIONS Corp.,Ltd. Address before:Changan town in Guangdong province Dongguan 523860 usha Beach Road No. 18 Applicant before:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATIONS Corp.,Ltd. | |
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20220916 |