CN109907732B - A method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture - Google Patents
A method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm ruptureDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN109907732B CN109907732BCN201910280012.7ACN201910280012ACN109907732BCN 109907732 BCN109907732 BCN 109907732BCN 201910280012 ACN201910280012 ACN 201910280012ACN 109907732 BCN109907732 BCN 109907732B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- aneurysm
- target
- virtual
- parameters
- parent artery
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 201000008450Intracranial aneurysmDiseases0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription69
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription39
- 210000001367arteryAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription230
- 230000000877morphologic effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription132
- 206010002329AneurysmDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription118
- 230000000004hemodynamic effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription101
- 238000007917intracranial administrationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription92
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription57
- 238000010801machine learningMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription47
- 238000012502risk assessmentMethods0.000claimsdescription118
- 238000004422calculation algorithmMethods0.000claimsdescription89
- 230000011218segmentationEffects0.000claimsdescription43
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription37
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsdescription23
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000claimsdescription21
- 208000004717Ruptured AneurysmDiseases0.000claimsdescription15
- 230000017531blood circulationEffects0.000claimsdescription15
- 238000012549trainingMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000claimsdescription11
- 238000012911target assessmentMethods0.000claimsdescription8
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- 206010028980NeoplasmDiseases0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 210000000709aortaAnatomy0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000003628erosive effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000claims2
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description6
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description6
- 238000004590computer programMethods0.000description6
- 239000012530fluidSubstances0.000description4
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000004069differentiationEffects0.000description3
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description3
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description3
- 230000036772blood pressureEffects0.000description2
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000description2
- 238000003384imaging methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000description2
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description2
- 238000007619statistical methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000012795verificationMethods0.000description2
- 208000032929Cerebral haemangiomaDiseases0.000description1
- 208000032851Subarachnoid HemorrhageDiseases0.000description1
- 230000002159abnormal effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003044adaptive effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000004204blood vesselAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000969carrierSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003086colorantSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003066decision treeMethods0.000description1
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000002513implantationMethods0.000description1
- 150000002632lipidsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000007477logistic regressionMethods0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 238000003062neural network modelMethods0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000010355oscillationEffects0.000description1
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description1
- 238000007637random forest analysisMethods0.000description1
- 238000012706support-vector machineMethods0.000description1
- 230000001960triggered effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000009966trimmingMethods0.000description1
- 208000019553vascular diseaseDiseases0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Apparatus (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及颅内动脉瘤医学技术领域,尤其涉及一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法及系统。The invention relates to the medical technical field of intracranial aneurysm, in particular to a method and system for assessing the rupture risk of intracranial aneurysm.
背景技术Background technique
颅内动脉瘤,又称脑血管瘤,是由颅内动脉内腔异常扩张,形成动脉壁的一种瘤状突起,是一种常见的血管性疾病。据统计,我国每100个成年人中,就有7个是动脉瘤携带者。颅内动脉瘤可分为非破裂动脉瘤和破裂动脉瘤,绝大部分的颅内动脉瘤为非破裂动脉瘤,一般终生不会破裂,其年破裂率仅为0.05%。然而非破裂动脉瘤一旦破裂,会引发自发性蛛网膜下隙出血,变成破裂动脉瘤,其致死致残率超过50%,严重威胁患者的生命。Intracranial aneurysm, also known as cerebral hemangioma, is a tumor-like protrusion on the arterial wall formed by abnormal expansion of the lumen of the intracranial artery. It is a common vascular disease. According to statistics, out of every 100 adults in my country, 7 are carriers of aneurysms. Intracranial aneurysms can be divided into non-ruptured aneurysms and ruptured aneurysms. The vast majority of intracranial aneurysms are non-ruptured aneurysms, which generally will not rupture for life, and the annual rupture rate is only 0.05%. However, once a non-ruptured aneurysm ruptures, it will cause spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage and become a ruptured aneurysm. The mortality and disability rate exceeds 50%, which seriously threatens the lives of patients.
目前颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估手段主要为基于PHASES得分的评估手段,该评价手段基于统计学从动脉瘤位置、动脉瘤大小、患病人群、患者过往病史以及患者年龄分析动脉瘤,从而推测出动脉瘤的五年破裂风险。然而,实践发现,该评估手段仅是对动脉瘤患病人群进行统计学分析,忽略了动脉瘤患者个体实际情况的分析,因此对动脉瘤的风险评估的准确率较低。At present, the evaluation method for the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture is mainly based on the evaluation method of PHASES score. This evaluation method is based on statistical analysis of aneurysm location, aneurysm size, patient population, patient past medical history and patient age, so as to speculate five-year risk of aneurysm rupture. However, it has been found in practice that this assessment method is only a statistical analysis of the population with aneurysms, ignoring the analysis of the actual situation of the individual aneurysm patients, so the accuracy of the risk assessment of aneurysms is low.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明所要解决的技术问题在于,提供一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法及系统,能够通过颅内动脉瘤的形态学参数、血流动力学参数以及临床参数对患者的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险进行全面自动分析,从而提高动脉瘤破裂风险评估的准确率。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a method and system for assessing the rupture risk of intracranial aneurysms, which can assess the risk of intracranial aneurysms in patients through the morphological parameters, hemodynamic parameters and clinical parameters of intracranial aneurysms. Comprehensive and automatic analysis of rupture risk, thereby improving the accuracy of aneurysm rupture risk assessment.
为了解决上述技术问题,本发明实施例第一方面公开了一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法,所述方法应用于颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统中,所述方法包括:In order to solve the above technical problems, the first aspect of the embodiment of the present invention discloses a method for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture. The method is applied to an assessment system for the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture. The method includes:
根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和所述载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,所述三维模型包括与所述载瘤动脉相匹配的虚拟载瘤动脉以及与所述动脉瘤相匹配的虚拟动脉瘤;Establish a three-dimensional model including the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery according to the intracranial image data, the three-dimensional model includes a virtual parent artery matching the parent artery and a virtual parent artery matching the aneurysm virtual aneurysm;
基于所述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,所述目标形态学参数包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的形态学参数以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的形态学参数;determining target morphological parameters based on the three-dimensional model, where the target morphological parameters include morphological parameters of the virtual parent artery and morphological parameters of the virtual aneurysm;
基于所述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数,所述目标血流动力学参数包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的血流动力学参数以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的血流动力学参数;determining target hemodynamic parameters based on the three-dimensional model, where the target hemodynamic parameters include hemodynamic parameters of the virtual parent artery and hemodynamic parameters of the virtual aneurysm;
基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到所述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果,所述评估结果用于评估所述动脉瘤的破裂风险,所述目标临床参数包括预先确定出的所述颅内影像数据对应的用户的临床参数。Based on the pre-trained machine learning model, the target morphological parameters, the target hemodynamic parameters and the target clinical parameters are calculated to obtain the evaluation result of the virtual aneurysm, and the evaluation result is used to evaluate the The rupture risk of the aneurysm, the target clinical parameter includes a predetermined clinical parameter of the user corresponding to the intracranial image data.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第一方面中,所述基于所述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,包括:As an optional implementation manner, in the first aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, the determining target morphological parameters based on the three-dimensional model includes:
基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割所述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型,并基于所述分割后的三维模型确定目标形态学参数;segmenting the three-dimensional model based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm to obtain a segmented three-dimensional model, and determining target morphological parameters based on the segmented three-dimensional model;
其中,所述基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割所述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型,包括:Wherein, the 3D model is segmented based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm to obtain a segmented 3D model, including:
基于预先确定的模型分割算法确定所述虚拟载瘤动脉上的某一像素点所在位置作为第一模拟波的第一波源点,以及确定所述虚拟动脉瘤上的某一像素点所在位置作为第二模拟波的第二波源点,所述第一模拟波和所述第二模拟波为同一类型的模拟波;Based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm, determine the position of a certain pixel point on the virtual parent artery as the first wave source point of the first simulation wave, and determine the position of a certain pixel point on the virtual aneurysm as the second wave source point. The second wave source point of the two analog waves, the first analog wave and the second analog wave are analog waves of the same type;
同时发射所述第一模拟波以及所述第二模拟波,并记录所述第一模拟波和所述第二模拟波的传播时长,所述传播时长的起始传播时刻为发射所述第一模拟波和所述第二模拟波的时刻,所述传播时长的终止传播时刻为所述第一模拟波的波峰和所述第二模拟波的波峰第一次重叠的时刻;Simultaneously transmit the first analog wave and the second analog wave, and record the propagation duration of the first analog wave and the second analog wave, the initial propagation moment of the propagation duration is when the first analog wave is emitted The moment of the analog wave and the second analog wave, the end propagation moment of the propagation duration is the moment when the peak of the first analog wave and the peak of the second analog wave overlap for the first time;
确定在所述传播时长内所述第一模拟波传播所覆盖的区域和所述第二模拟波传播所覆盖的区域之和,作为与所述虚拟载瘤动脉以及所述虚拟动脉瘤相对应的分割区域,并根据所述分割区域分割所述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型。Determining the sum of the area covered by the first simulated wave propagation and the area covered by the second simulated wave propagation within the propagation time as the corresponding to the virtual parent artery and the virtual aneurysm segmenting the region, and segmenting the 3D model according to the segmented region to obtain a segmented 3D model.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第一方面中,所述基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到所述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之后,所述方法还包括:As an optional implementation, in the first aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, the pre-trained machine learning model is used to perform the target morphological parameter, the target hemodynamic parameter and the target clinical parameter. After obtaining the evaluation result of the virtual aneurysm, the method further includes:
根据所述评估结果生成所述颅内影像数据的评估报告,所述评估报告包括所述目标形态学参数的形态学风险分析结果、所述目标血流动力学参数的血流动力学风险分析结果、所述目标临床参数的临床风险分析结果以及综合风险分析结果,所述综合风险分析结果为基于所述形态学风险分析结果、所述血流动力学风险分析结果以及所述临床风险分析结果生成的结果;Generate an evaluation report of the intracranial image data according to the evaluation result, the evaluation report includes the morphological risk analysis result of the target morphological parameter, the hemodynamic risk analysis result of the target hemodynamic parameter , the clinical risk analysis results of the target clinical parameters and the comprehensive risk analysis results, the comprehensive risk analysis results are generated based on the morphological risk analysis results, the hemodynamic risk analysis results and the clinical risk analysis results the result of;
基于预设风险等级规则确定所述评估报告包括的所述综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级,并显示所述评估报告以及所述综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级;determining the risk level corresponding to the comprehensive risk analysis result included in the assessment report based on preset risk level rules, and displaying the risk level corresponding to the assessment report and the comprehensive risk analysis result;
以及,所述方法还包括:And, the method also includes:
基于所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及所述目标临床参数从预先建立的动脉瘤数据库中确定与所述评估报告最相似的目标评估报告,并显示所述目标评估报告,所述预先建立的动脉瘤数据库用于存储所有动脉瘤患者中每个所述动脉瘤患者的评估报告。determining a target assessment report most similar to the assessment report from a pre-established aneurysm database based on the target morphological parameter, the target hemodynamic parameter, and the target clinical parameter, and displaying the target assessment report , the pre-established aneurysm database is used to store an assessment report for each aneurysm patient among all aneurysm patients.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第一方面中,所述基于所述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,包括:As an optional implementation manner, in the first aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, the determining target morphological parameters based on the three-dimensional model includes:
基于预先确定的中心线提取算法以及所述三维模型提取所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线;extracting the artery centerline of the virtual parent artery based on a predetermined centerline extraction algorithm and the three-dimensional model;
基于预先确定的区域区分算法对所述三维模型进行区域区分,得到目标区域,所述目标区域包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域、所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域、所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域;The three-dimensional model is divided into regions based on a predetermined region discrimination algorithm to obtain a target region, the target region includes the arterial inlet region of the virtual parent artery, the artery outlet region of the virtual parent artery, the virtual the arterial wall area of the parent artery and the aneurysm wall area of the virtual aneurysm;
基于预先确定的形态学参数算法对所述目标区域包括的内容进行计算几何分析,得到目标形态学参数。Based on a predetermined morphological parameter algorithm, computational geometric analysis is performed on the content included in the target area to obtain the target morphological parameters.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第一方面中,所述基于预先确定的区域区分算法对所述三维模型进行区域区分,得到目标区域,包括:As an optional implementation manner, in the first aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, the region differentiation of the 3D model based on the predetermined region differentiation algorithm to obtain the target area includes:
基于预先确定的区域区分算法确定所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口横截面、动脉出口横截面以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的瘤颈平面;determining the arterial inlet cross-section, the arterial outlet cross-section, and the virtual aneurysm neck plane of the virtual parent artery based on a predetermined area discrimination algorithm;
根据所述动脉入口横截面切割所述三维模型,得到所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域,以及根据所述出口横截面切割所述三维模型,得到所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域,以及根据所述瘤颈平面切割所述三维模型,得到所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域。cutting the three-dimensional model according to the arterial inlet cross-section to obtain an artery inlet region of the virtual parent artery, and cutting the three-dimensional model according to the outlet cross-section to obtain an artery outlet region of the virtual parent artery, and cutting the three-dimensional model according to the aneurysm neck plane to obtain the arterial wall area of the virtual parent artery and the aneurysm wall area of the virtual aneurysm.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第一方面中,所述基于所述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数,包括:As an optional implementation manner, in the first aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, the determining the target hemodynamic parameters based on the three-dimensional model includes:
基于预先确定的网格划分算法划分所述三维模型,得到多个目标体网格模型,所有所述目标体网格模型均为多面体网格模型;Dividing the three-dimensional model based on a predetermined mesh division algorithm to obtain a plurality of object mesh models, all of the object mesh models are polyhedral mesh models;
确定所述三维模型的目标边界条件,所述目标边界条件至少包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口边界的边界条件、所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口边界的边界条件;determining a target boundary condition of the three-dimensional model, the target boundary condition at least including a boundary condition of an artery inlet boundary of the virtual parent artery, and a boundary condition of an artery outlet boundary of the virtual parent artery;
基于所有所述目标体网格模型以及所述目标边界条件模拟所述虚拟载瘤动脉的血液流动以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的血液流动,得到目标血流动力学参数。The blood flow of the virtual parent artery and the blood flow of the virtual aneurysm are simulated based on all the target volume mesh models and the target boundary conditions to obtain target hemodynamic parameters.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第一方面中,所述基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到所述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之前,所述方法还包括:As an optional implementation, in the first aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, the pre-trained machine learning model is used to perform the target morphological parameter, the target hemodynamic parameter and the target clinical parameter. Before obtaining the evaluation result of the virtual aneurysm, the method further includes:
构建机器学习模型,所述机器学习模型用于确定所述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果;Constructing a machine learning model, the machine learning model is used to determine the assessment result of the virtual aneurysm;
其中,所述构建机器学习模型,包括:Wherein, said building machine learning model includes:
获取多个样本颅内影像数据,每个所述样本颅内影像数据对应一个动脉瘤患者;Acquiring multiple samples of intracranial image data, each of the sample intracranial image data corresponds to a patient with an aneurysm;
确定每个所述样本颅内影像数据的样本特征参数,每个所述样本特征参数包括样本形态学参数、与所述样本形态学参数对应的样本血流动力参数以及与该样本形态学参数对应的样本临床参数;Determine the sample characteristic parameters of each sample intracranial image data, each of the sample characteristic parameters includes a sample morphological parameter, a sample hemodynamic parameter corresponding to the sample morphological parameter, and a sample hemodynamic parameter corresponding to the sample morphological parameter The clinical parameters of the sample;
标记每个所述样本特征参数,得到标记后的样本特征参数以及所述标记后的样本特征参数对应的标记值;Marking each of the sample characteristic parameters to obtain the marked sample characteristic parameters and the marked value corresponding to the marked sample characteristic parameters;
基于预先确定的训练算法训练每个所述标记后的样本特征参数,得到机器学习模型;training each of the marked sample feature parameters based on a predetermined training algorithm to obtain a machine learning model;
其中,所述标记每个所述样本特征参数,得到标记后的样本特征参数对应的标记值,包括:Wherein, the marking of each of the sample characteristic parameters obtains a marked value corresponding to the marked sample characteristic parameters, including:
当所述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为破裂动脉瘤,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第一预设值;When the aneurysm included in the sample intracranial image data is a ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is a first preset value;
当所述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为非破裂动脉瘤,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第二预设值;When the aneurysm included in the sample intracranial image data is a non-ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is a second preset value;
其中,所述第一预设值与所述第二预设值不相同。Wherein, the first preset value is different from the second preset value.
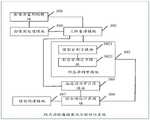
本发明实施例第二方面公开了一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统,所述评估系统包括三维重建模块、形态学测量模块、血流动力学计算模块以及综合风险计算模块,其中:The second aspect of the embodiment of the present invention discloses an assessment system for the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm. The assessment system includes a three-dimensional reconstruction module, a morphological measurement module, a hemodynamic calculation module, and a comprehensive risk calculation module, wherein:
所述三维重建模块,用于根据颅内影像数据建立包括目标载瘤动脉和所述目标载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,所述三维模型包括与所述目标载瘤动脉相匹配的虚拟载瘤动脉以及与所述动脉瘤相匹配的虚拟动脉瘤;The three-dimensional reconstruction module is configured to establish a three-dimensional model including a target parent artery and an aneurysm on the target parent artery according to intracranial image data, and the three-dimensional model includes a virtual model that matches the target parent artery. The parent artery and a virtual aneurysm matching the aneurysm;
所述形态学测量模块,用于基于所述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,所述目标形态学参数包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的形态学参数以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的形态学参数;The morphological measurement module is configured to determine target morphological parameters based on the three-dimensional model, where the target morphological parameters include morphological parameters of the virtual parent artery and morphological parameters of the virtual aneurysm;
所述血流动力学计算模块,用于基于所述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数,所述目标血流动力学参数包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的血流动力学参数以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的血流动力学参数;The hemodynamic calculation module is configured to determine target hemodynamic parameters based on the three-dimensional model, and the target hemodynamic parameters include the hemodynamic parameters of the virtual parent artery and the virtual artery Tumor hemodynamic parameters;
所述综合风险计算模块,用于基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到所述动脉瘤的评估结果,所述评估结果用于评估所述动脉瘤的破裂风险,所述目标临床参数为预先确定的所述颅内影像数据对应的用户的临床参数。The comprehensive risk calculation module is used to calculate the target morphological parameters, the target hemodynamic parameters and the target clinical parameters based on the pre-trained machine learning model to obtain the evaluation result of the aneurysm, so The assessment result is used to assess the rupture risk of the aneurysm, and the target clinical parameter is a predetermined clinical parameter of the user corresponding to the intracranial image data.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第二方面中,所述形态学测量模块包括模型分割子模块以及形态学确定子模块,其中:As an optional implementation, in the second aspect of the embodiment of the present invention, the morphological measurement module includes a model segmentation submodule and a morphological determination submodule, wherein:
所述模型分割子模块,用于基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割所述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型;The model segmentation submodule is used to segment the 3D model based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm to obtain a segmented 3D model;
所述形态学确定子模块,用于基于所述分割后的三维模型确定目标形态学参数;The morphological determination submodule is used to determine target morphological parameters based on the segmented three-dimensional model;
其中,所述模型分割子模块基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割所述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型的方式具体为:Wherein, the model segmentation sub-module segments the 3D model based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm, and obtains the segmented 3D model specifically as follows:
基于预先确定的模型分割算法确定所述虚拟载瘤动脉上的某一像素点所在位置作为第一模拟波的第一波源点,以及确定所述虚拟动脉瘤上的某一像素点所在位置作为第二模拟波的第二波源点,所述第一模拟波和所述第二模拟波为同一类型的模拟波;Based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm, determine the position of a certain pixel point on the virtual parent artery as the first wave source point of the first simulation wave, and determine the position of a certain pixel point on the virtual aneurysm as the second wave source point. The second wave source point of the two analog waves, the first analog wave and the second analog wave are analog waves of the same type;
同时发射所述第一模拟波以及所述第二模拟波,并记录所述第一模拟波和所述第二模拟波的传播时长,所述传播时长的起始传播时刻为发射所述第一模拟波和所述第二模拟波的时刻,所述传播时长的终止传播时刻为所述第一模拟波的波峰和所述第二模拟波的波峰第一次重叠的时刻;Simultaneously transmit the first analog wave and the second analog wave, and record the propagation duration of the first analog wave and the second analog wave, the initial propagation moment of the propagation duration is when the first analog wave is emitted The moment of the analog wave and the second analog wave, the end propagation moment of the propagation duration is the moment when the peak of the first analog wave and the peak of the second analog wave overlap for the first time;
确定在所述传播时长内所述第一模拟波传播所覆盖的区域和所述第二模拟波传播所覆盖的区域之和,作为与所述虚拟载瘤动脉以及所述虚拟动脉瘤相对应的分割区域,并根据所述分割区域分割所述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型。Determining the sum of the area covered by the first simulated wave propagation and the area covered by the second simulated wave propagation within the propagation time as the corresponding to the virtual parent artery and the virtual aneurysm segmenting the region, and segmenting the 3D model according to the segmented region to obtain a segmented 3D model.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第二方面中,所述综合风险计算模块,还用于在基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到所述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之后,根据所述评估结果生成所述颅内影像数据的评估报告,所述评估报告包括所述目标形态学参数的形态学风险分析结果、所述目标血流动力学参数的血流动力学风险分析结果、所述目标临床参数的临床风险分析结果以及综合风险分析结果,所述综合风险分析结果为基于所述形态学风险分析结果、所述血流动力学风险分析结果以及所述临床风险分析结果生成的结果;As an optional implementation, in the second aspect of the embodiment of the present invention, the comprehensive risk calculation module is also used to calculate the target morphological parameters, the target blood After calculating the flow dynamic parameters and the target clinical parameters, after obtaining the evaluation results of the virtual aneurysm, an evaluation report of the intracranial image data is generated according to the evaluation results, and the evaluation report includes the target morphological parameters. Morphological risk analysis results, hemodynamic risk analysis results of the target hemodynamic parameters, clinical risk analysis results of the target clinical parameters, and comprehensive risk analysis results, the comprehensive risk analysis results are based on the morphology medical risk analysis results, said hemodynamic risk analysis results, and results generated from said clinical risk analysis results;
所述综合风险计算模块,还用于基于预设等级规则确定所述评估报告包括的所述综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级,并显示所述评估报告以及所述综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级;The comprehensive risk calculation module is further configured to determine the risk level corresponding to the comprehensive risk analysis result included in the assessment report based on preset level rules, and display the risk level corresponding to the assessment report and the comprehensive risk analysis result ;
以及,所述综合风险计算模块,还用于基于所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及所述目标临床参数从预先建立的动脉瘤数据库中确定与所述评估报告最相似的目标评估报告,并显示所述目标评估报告,所述预先建立的动脉瘤数据库用于存储所有动脉瘤患者中每个所述动脉瘤患者的评估报告。And, the comprehensive risk calculation module is also used to determine from the pre-established aneurysm database based on the target morphological parameters, the target hemodynamic parameters and the target clinical parameters, which is most similar to the assessment report and display the target assessment report, and the pre-established aneurysm database is used to store the assessment report of each aneurysm patient among all the aneurysm patients.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第二方面中,所述形态学测量模块包括中心线提取子模块、区域区分子模块以及形态学计算子模块,其中:As an optional implementation, in the second aspect of the embodiment of the present invention, the morphological measurement module includes a centerline extraction submodule, an area division submodule, and a morphological calculation submodule, wherein:
所述中心线提取子模块,用于基于预先确定的中心线提取算法以及所述三维模型提取所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线;The centerline extraction submodule is configured to extract the artery centerline of the virtual parent artery based on a predetermined centerline extraction algorithm and the three-dimensional model;
所述区域区分子模块,用于基于预先确定的区域区分算法对所述三维模型进行区域区分,得到目标区域,所述目标区域包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域、所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域、所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域;The region distinguishing submodule is configured to perform region distinction on the three-dimensional model based on a predetermined region distinguishing algorithm to obtain a target region, and the target region includes the arterial entrance region of the virtual parent artery, the virtual parent tumor an arterial outlet area of an artery, an arterial wall area of the virtual parent artery, and an aneurysm wall area of the virtual aneurysm;
所述形态学计算子模块,用于基于预先确定的形态学参数算法对所述目标区域包括的内容进行计算几何分析,得到目标形态学参数。The morphological calculation sub-module is configured to perform computational geometric analysis on the content included in the target area based on a predetermined morphological parameter algorithm to obtain target morphological parameters.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第二方面中,所述区域区分子模块基于预先确定的区域区分算法对所述三维模型进行区域区分,得到目标区域的方式具体为:As an optional implementation manner, in the second aspect of the embodiment of the present invention, the region distinguishing submodule performs region distinction on the 3D model based on a predetermined region distinguishing algorithm, and the method of obtaining the target region is specifically as follows:
基于预先确定的区域区分算法确定所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口横截面、动脉出口横截面以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的瘤颈平面;determining the arterial inlet cross-section, the arterial outlet cross-section, and the virtual aneurysm neck plane of the virtual parent artery based on a predetermined area discrimination algorithm;
根据所述动脉入口横截面切割所述三维模型,得到所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域,以及根据所述出口横截面切割所述三维模型,得到所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域,以及根据所述瘤颈平面切割所述三维模型,得到所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域。cutting the three-dimensional model according to the arterial inlet cross-section to obtain an artery inlet region of the virtual parent artery, and cutting the three-dimensional model according to the outlet cross-section to obtain an artery outlet region of the virtual parent artery, and cutting the three-dimensional model according to the aneurysm neck plane to obtain the arterial wall area of the virtual parent artery and the aneurysm wall area of the virtual aneurysm.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第二方面中,所述血流动力学计算模块基于所述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数的方式具体为:As an optional implementation manner, in the second aspect of the embodiment of the present invention, the manner in which the hemodynamic calculation module determines the target hemodynamic parameters based on the three-dimensional model is specifically:
基于预先确定的网格划分算法划分所述三维模型,得到多个目标体网格模型,所有所述目标体网格模型均为多面体网格模型;Dividing the three-dimensional model based on a predetermined mesh division algorithm to obtain a plurality of object mesh models, all of the object mesh models are polyhedral mesh models;
确定所述三维模型的目标边界条件,所述目标边界条件至少包括所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口边界的边界条件、所述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口边界的边界条件;determining a target boundary condition of the three-dimensional model, the target boundary condition at least including a boundary condition of an artery inlet boundary of the virtual parent artery, and a boundary condition of an artery outlet boundary of the virtual parent artery;
基于所有所述目标体网格模型以及所述目标边界条件模拟所述虚拟载瘤动脉的血液流动以及所述虚拟动脉瘤的血液流动,得到目标血流动力学参数。The blood flow of the virtual parent artery and the blood flow of the virtual aneurysm are simulated based on all the target volume mesh models and the target boundary conditions to obtain target hemodynamic parameters.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在本发明实施例第二方面中,所述评估系统还包括模型构建模块,其中:As an optional implementation manner, in the second aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, the evaluation system further includes a model building module, wherein:
所述模型构建模块,用于在所述综合风险计算模块基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对所述目标形态学参数、所述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到所述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之前,构建机器学习模型,所述机器学习模型用于确定所述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果;The model construction module is used to calculate the target morphological parameters, the target hemodynamic parameters and the target clinical parameters based on the pre-trained machine learning model in the comprehensive risk calculation module to obtain the virtual Before the evaluation result of the aneurysm, construct a machine learning model, and the machine learning model is used to determine the evaluation result of the virtual aneurysm;
其中,所述模型构建模块构建机器学习模型的方式具体为:Wherein, the mode of constructing the machine learning model by the model building module is specifically as follows:
获取多个样本颅内影像数据,每个所述样本颅内影像数据对应一个动脉瘤患者;Acquiring multiple samples of intracranial image data, each of the sample intracranial image data corresponds to a patient with an aneurysm;
确定每个所述样本颅内影像数据的样本特征参数,每个所述样本特征参数包括样本形态学参数、与所述样本形态学参数对应的样本血流动力参数以及与该样本形态学参数对应的样本临床参数;Determine the sample characteristic parameters of each sample intracranial image data, each of the sample characteristic parameters includes a sample morphological parameter, a sample hemodynamic parameter corresponding to the sample morphological parameter, and a sample hemodynamic parameter corresponding to the sample morphological parameter The clinical parameters of the sample;
标记每个所述样本特征参数,得到每个所述样本特征参数的标记值;marking each of the sample characteristic parameters to obtain a marked value of each of the sample characteristic parameters;
基于预先确定的训练算法训练每个所述样本特征参数以及每个所述样本特征参数的标记值,得到机器学习模型;training each of the sample feature parameters and the label value of each of the sample feature parameters based on a predetermined training algorithm to obtain a machine learning model;
其中,所述模型构建模块标记每个所述样本特征参数,得到每个所述样本特征参数的标志值的方式具体为:Wherein, the model construction module marks each of the sample characteristic parameters, and obtains the flag value of each of the sample characteristic parameters as follows:
当所述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为破裂动脉瘤,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第一预设值;When the aneurysm included in the sample intracranial image data is a ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is a first preset value;
当所述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为非破裂动脉瘤,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第二预设值;When the aneurysm included in the sample intracranial image data is a non-ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is a second preset value;
其中,所述第一预设值与所述第二预设值不相同。Wherein, the first preset value is different from the second preset value.
本发明第三方面公开了另一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统,所述装置包括:The third aspect of the present invention discloses another assessment system for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk, the device includes:
存储有可执行程序代码的存储器;a memory storing executable program code;
与所述存储器耦合的处理器;a processor coupled to the memory;
所述处理器调用所述存储器中存储的所述可执行程序代码,执行本发明第一方面公开的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法。The processor invokes the executable program code stored in the memory to execute the method for assessing the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in the first aspect of the present invention.
本发明第四方面公开了一种计算机可存储介质,所述计算机存储介质存储有计算机指令,所述计算机指令被调用时,用于执行本发明第一方面公开的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法。The fourth aspect of the present invention discloses a computer-storable medium, the computer storage medium stores computer instructions, and when the computer instructions are called, it is used to perform the assessment of the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in the first aspect of the present invention method.
与现有技术相比,本发明实施例具有以下有益效果:Compared with the prior art, the embodiments of the present invention have the following beneficial effects:
本发明实施例中,根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,该三维模型包括与载瘤动脉相匹配的虚拟载瘤动脉以及与动脉瘤相匹配的虚拟动脉瘤;基于三维模型确定目标形态学参数,该目标形态学参数包括虚拟载瘤动脉的形态学参数以及虚拟动脉瘤的形态学参数;基于三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数,该目标血流动力学参数包括虚拟载瘤动脉的血流动力学参数以及虚拟动脉瘤的血流动力学参数;基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对目标形态学参数、目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果,该评估结果用于评估动脉瘤的破裂风险,目标临床参数包括预先确定出的颅内影像数据对应的用户的临床参数。可见,实施本发明能够通过对患者颅内动脉瘤的形态学参数、血流动力学参数以及临床参数对颅内动脉瘤破裂风险进行全面自动分析,能够提高动脉瘤破裂风险评估的准确率,从而为医生在作治疗决策时提供科学性的参考,进而使得医生快速给患者提供有效的治疗方案。In the embodiment of the present invention, a three-dimensional model including the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery is established according to the intracranial image data, and the three-dimensional model includes a virtual parent artery matching the parent artery and an aneurysm matching Virtual aneurysm; determine the target morphological parameters based on the three-dimensional model, the target morphological parameters include the morphological parameters of the virtual parent artery and the virtual aneurysm; determine the target hemodynamic parameters based on the three-dimensional model, the target blood The flow dynamic parameters include the hemodynamic parameters of the virtual parent artery and the hemodynamic parameters of the virtual aneurysm; based on the pre-trained machine learning model, the target morphological parameters, target hemodynamic parameters and target clinical parameters The calculation is performed to obtain an assessment result of the virtual aneurysm, and the assessment result is used to assess the rupture risk of the aneurysm. The target clinical parameters include the predetermined clinical parameters of the user corresponding to the intracranial image data. It can be seen that the implementation of the present invention can comprehensively and automatically analyze the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture through the morphological parameters, hemodynamic parameters and clinical parameters of the patient's intracranial aneurysm, and can improve the accuracy of aneurysm rupture risk assessment, thereby Provide scientific reference for doctors when making treatment decisions, and then enable doctors to quickly provide patients with effective treatment plans.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例中的技术方案,下面将对实施例描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention, the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments will be briefly introduced below. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention. For those skilled in the art, other drawings can also be obtained based on these drawings without creative effort.
图1是本发明实施例公开的一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法的流程示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic flowchart of a method for assessing the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention;
图2是本发明实施例公开的一种分割后的虚拟载瘤动脉的三维模型的结构示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a three-dimensional model of a segmented virtual parent artery disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明实施例公开的一种裁剪后的虚拟载瘤动脉的三维模型的结构示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic structural view of a three-dimensional model of a virtual parent artery after trimming disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention;
图4是本发明实施例公开的一种以瘤颈平面作为分界线的虚拟载瘤动脉的三维模型的结构示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic structural view of a three-dimensional model of a virtual parent artery with the neck plane as the dividing line disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention;
图5是本发明实施例公开的一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention;
图6是本发明实施例公开的另一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图;Fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of another assessment system for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention;
图7是本发明实施例公开的又一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图;Fig. 7 is a structural schematic diagram of another system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention;
图8是本发明实施例公开的又一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图。Fig. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of another system for assessing the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本技术领域的人员更好地理解本发明方案,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the solutions of the present invention, the following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only It is a part of embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
本发明的说明书和权利要求书及上述附图中的术语“第一”、“第二”等是用于区别不同对象,而不是用于描述特定顺序。此外,术语“包括”和“具有”以及它们任何变形,意图在于覆盖不排他的包含。例如包含了一系列步骤或单元的过程、方法、装置、产品或设备没有限定于已列出的步骤或单元,而是可选地还包括没有列出的步骤或单元,或可选地还包括对于这些过程、方法、产品或设备固有的其他步骤或单元。The terms "first", "second" and the like in the description and claims of the present invention and the above drawings are used to distinguish different objects, rather than to describe a specific order. Furthermore, the terms "include" and "have", as well as any variations thereof, are intended to cover a non-exclusive inclusion. For example, a process, method, device, product or equipment comprising a series of steps or units is not limited to the listed steps or units, but optionally also includes steps or units not listed, or optionally further includes For other steps or units inherent in these processes, methods, products or devices.
在本文中提及“实施例”意味着,结合实施例描述的特定特征、结构或特性可以包含在本发明的至少一个实施例中。在说明书中的各个位置出现该短语并不一定均是指相同的实施例,也不是与其它实施例互斥的独立的或备选的实施例。本领域技术人员显式地和隐式地理解的是,本文所描述的实施例可以与其它实施例相结合。Reference herein to an "embodiment" means that a particular feature, structure, or characteristic described in connection with the embodiment can be included in at least one embodiment of the present invention. The occurrences of this phrase in various places in the specification are not necessarily all referring to the same embodiment, nor are separate or alternative embodiments mutually exclusive of other embodiments. It is understood explicitly and implicitly by those skilled in the art that the embodiments described herein can be combined with other embodiments.
本发明公开了一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法及系统,该方法应用于颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统中,能够通过对患者颅内动脉瘤的形态学参数、血流动力学参数以及临床参数对颅内动脉瘤破裂风险进行全面自动分析,能够提高动脉瘤破裂风险评估的准确率,从而为医生在作治疗决策时提供科学性的参考,进而使得医生快速给患者提供有效的治疗方案。以下分别进行详细说明。The invention discloses a method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture. The method is applied to the assessment system for the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture. Comprehensive and automatic analysis of intracranial aneurysm rupture risk by parameters and clinical parameters can improve the accuracy of aneurysm rupture risk assessment, thereby providing scientific reference for doctors when making treatment decisions, and enabling doctors to quickly provide patients with effective treatment treatment plan. Each will be described in detail below.
实施例一Embodiment one
请参阅图1,图1是本发明实施例公开的一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法的流程示意图。其中,图1所描述的方法可以应用在风险评估终端中,并且该风险评估终端包括所有能评估患者动脉瘤的破裂风险的终端。进一步的,该风险评估终端还可以与用户终端无线连接,其中,该用户终端可以包括智能手机(Android手机、iOS手机等)、智能电话手表、平板电脑、掌上电脑、车载电脑、台式电脑、上网本、个人数字助理(Personal DigitalAssistant,PDA)、智能导航仪以及移动互联网设备(Mobile Internet Devices,MID)等终端,本发明实施例不做限定,如图1所示,该颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法可以包括以下操作:Please refer to FIG. 1 . FIG. 1 is a schematic flowchart of a method for assessing the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention. Wherein, the method described in FIG. 1 can be applied in a risk assessment terminal, and the risk assessment terminal includes all terminals capable of assessing the rupture risk of a patient's aneurysm. Further, the risk assessment terminal can also be wirelessly connected to a user terminal, wherein the user terminal can include a smart phone (Android phone, iOS phone, etc.), a smart phone watch, a tablet computer, a handheld computer, a vehicle computer, a desktop computer, a netbook, etc. , personal digital assistant (Personal Digital Assistant, PDA), intelligent navigator, and mobile Internet device (Mobile Internet Devices, MID) and other terminals, the embodiment of the present invention is not limited, as shown in Figure 1, the intracranial aneurysm rupture risk Evaluation methods can include the following actions:
101、风险评估终端根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,该三维模型包括与载瘤动脉相匹配的虚拟载瘤动脉以及与动脉瘤相匹配的虚拟动脉瘤。101. The risk assessment terminal establishes a three-dimensional model including the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery based on the intracranial image data. The three-dimensional model includes a virtual parent artery that matches the parent artery and a virtual parent artery that matches the aneurysm. Aneurysm.
本发明实施例中,颅内影像数据包括但不限于CTA颅内影像数据、MRA颅内影像数据以及DSA颅内影像数据中的任意一种。In the embodiment of the present invention, the intracranial image data includes but not limited to any one of CTA intracranial image data, MRA intracranial image data and DSA intracranial image data.
本发明实施例中,作为一种可选的实施方式,风险评估终端根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,可以包括:In the embodiment of the present invention, as an optional implementation, the risk assessment terminal establishes a three-dimensional model including the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery according to the intracranial image data, which may include:
风险评估终端采集患者的颅内影像数据,并基于预先确定的阈值分割算法对颅内影像数据进行阈值分割处理,得到分割后的颅内影像数据,以及根据分割后的颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型。The risk assessment terminal collects the patient's intracranial image data, performs threshold segmentation processing on the intracranial image data based on a predetermined threshold segmentation algorithm, obtains the segmented intracranial image data, and establishes the 3D model of the aneurysm on the aneurysmal artery and parent artery.
其中,风险评估终端基于预先确定的阈值分割算法对颅内影像数据进行阈值分割处理,可以包括:Wherein, the risk assessment terminal performs threshold segmentation processing on the intracranial image data based on a predetermined threshold segmentation algorithm, which may include:
风险评估终端基于预先确定的阈值分割算法对颅内影像数据进行灰度处理,得到灰度处理后的颅内影像数据,并将颅内影像数据中灰度值大于等于预设灰度阈值的像素值标记为第一预设值,将颅内影像数据中灰度值小于预设灰度阈值的像素值标记为第二预设值。The risk assessment terminal performs grayscale processing on the intracranial image data based on the predetermined threshold segmentation algorithm to obtain the grayscale processed intracranial image data, and divides the pixels whose grayscale value is greater than or equal to the preset grayscale threshold in the intracranial image data The value is marked as the first preset value, and the pixel value in the intracranial image data whose grayscale value is less than the preset grayscale threshold is marked as the second preset value.
该可选的实施方式中,第一预设值和第二预设值不相同。具体的,当第一预设值为1时,第二预设值为0;当第一预设值为0时,第二预设值为1,本发明实施例不做限定。In this optional implementation manner, the first preset value is different from the second preset value. Specifically, when the first preset value is 1, the second preset value is 0; when the first preset value is 0, the second preset value is 1, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention.
该可选的实施方式中,预先确定的阈值分割算法可以包括Otsu阈值分割算法、自适应阈值分割算法、最大熵阈值分割算法、Roberts阈值分割算法、Prewitt阈值分割算法、Sobel阈值分割算法、Marr-Hilderth阈值分割算法、Canny阈值分割算法中的任意一种算法或者多种算法组合,本发明实施例不做限定。In this optional embodiment, the predetermined threshold segmentation algorithm may include Otsu threshold segmentation algorithm, adaptive threshold segmentation algorithm, maximum entropy threshold segmentation algorithm, Roberts threshold segmentation algorithm, Prewitt threshold segmentation algorithm, Sobel threshold segmentation algorithm, Marr- Any one algorithm or a combination of multiple algorithms among the Hilderth threshold segmentation algorithm and the Canny threshold segmentation algorithm are not limited in this embodiment of the present invention.
作为一种可选的实施例,风险评估终端基于颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和该载瘤动脉上动脉瘤的三维模型之前,还可以:As an optional embodiment, before the risk assessment terminal establishes the three-dimensional model including the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery based on the intracranial image data, it may also:
判断颅内影像数据的影像质量指标是否达到预设影像质量指标;judging whether the image quality index of the intracranial image data reaches a preset image quality index;
当判断的结果为是时,触发执行上述的根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和该载瘤动脉上动脉瘤的三维模型的操作;When the judgment result is yes, trigger the above-mentioned operation of establishing a three-dimensional model including the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery according to the intracranial image data;
当判断的结果为否时,基于预设影像算法对上述颅内影像数据进行预处理,直至该颅内影像数据的影像质量指标达到预设影像质量指标,并触发执行上述的根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和该载瘤动脉上动脉瘤的三维模型的操作。When the result of the judgment is no, the above-mentioned intracranial image data is preprocessed based on the preset image algorithm until the image quality index of the intracranial image data reaches the preset image quality index, and the execution of the above-mentioned intracranial image data is triggered. An operation of establishing a three-dimensional model including the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery.
该可选的实施例中,颅内影像数据的影像质量指标包括但不限于颅内影像数据的色彩深度、颅内影像数据的分辨率、颅内影像数据的图像失真、颅内影像数据的数据格式、颅内影像数据的文件大小。In this optional embodiment, the image quality index of the intracranial image data includes but not limited to the color depth of the intracranial image data, the resolution of the intracranial image data, the image distortion of the intracranial image data, and the data of the intracranial image data. Format, file size of intracranial image data.
可见,该可选的实施例通过在建立载瘤动脉以及载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型之前,判断颅内影像数据的影像质量指标是否达到预设标准,当没有达到预设标准时,将颅内影像数据的影像质量指标进行预处理,直至达到预设影像质量指标才建立载瘤动脉以及载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,能够降低因影像质量指标不达标而导致建立载瘤动脉以及动脉瘤的三维模型不精准的可能性。It can be seen that in this optional embodiment, before establishing the three-dimensional model of the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery, it is judged whether the image quality index of the intracranial image data reaches the preset standard, and when the preset standard is not reached, the The image quality index of the intracranial image data is preprocessed, and the three-dimensional model of the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery is not established until the preset image quality index is reached, which can reduce the risk of establishing the parent artery due to the substandard image quality index. And the possibility of inaccurate 3D models of aneurysms.
102、风险评估终端基于上述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,该目标形态学参数包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的形态学参数以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的形态学参数。102. The risk assessment terminal determines target morphological parameters based on the above-mentioned three-dimensional model, and the target morphological parameters include the above-mentioned morphological parameters of the virtual parent artery and the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm.
本发明实施例中,目标形态学参数可以包括虚拟动脉瘤的瘤径、虚拟动脉瘤的瘤高、虚拟动脉瘤的瘤宽、虚拟动脉瘤的颈宽、虚拟载瘤动脉的流入角、虚拟载瘤动脉的流出角、虚拟动脉瘤的非球形指数、虚拟动脉瘤的椭圆指数、虚拟动脉瘤的长宽比、虚拟动脉瘤的偏斜角等形态参数中的至少一种,本发明实施例不做限定。In the embodiment of the present invention, the target morphological parameters may include the diameter of the virtual aneurysm, the height of the virtual aneurysm, the width of the virtual aneurysm, the neck width of the virtual aneurysm, the inflow angle of the virtual parent artery, the virtual At least one of the morphological parameters such as the outflow angle of the aneurysm artery, the aspheric index of the virtual aneurysm, the ellipse index of the virtual aneurysm, the aspect ratio of the virtual aneurysm, the deflection angle of the virtual aneurysm, etc., the embodiment of the present invention does not Do limited.
本发明实施例中,作为一种可选的实施方式,风险评估终端基于上述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,可以包括:In the embodiment of the present invention, as an optional implementation manner, the risk assessment terminal determines the target morphological parameters based on the above three-dimensional model, which may include:
风险评估终端基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割上述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型,并基于分割后的三维模型确定目标形态学参数;The risk assessment terminal segments the above three-dimensional model based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm to obtain a segmented three-dimensional model, and determines target morphological parameters based on the segmented three-dimensional model;
该可选的实施方式中,可选的,风险评估终端基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割上述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型,可以包括:In this optional implementation manner, optionally, the risk assessment terminal splits the above-mentioned 3D model based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm to obtain a segmented 3D model, which may include:
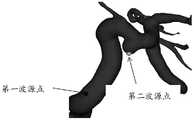
风险评估终端基于预先确定的模型分割算法确定上述虚拟载瘤动脉上的某一像素点所在位置作为第一模拟波的第一波源点(请参照图2中的第一波源点),以及确定上述虚拟动脉瘤上的某一像素点所在位置作为第二模拟波的第二波源点(请参照图2中的第二波源点),该第一模拟波和该第二模拟波为同一类型的模拟波。Based on the predetermined model segmentation algorithm, the risk assessment terminal determines the position of a certain pixel point on the above-mentioned virtual parent artery as the first wave source point of the first simulation wave (please refer to the first wave source point in Figure 2), and determines the above-mentioned The position of a certain pixel point on the virtual aneurysm is used as the second wave source point of the second simulation wave (please refer to the second wave source point in Figure 2), and the first simulation wave and the second simulation wave are the same type of simulation Wave.
风险评估终端同时发射上述第一模拟波以及上述第二模拟波,并记录第一模拟波和第二模拟波的传播时长,该传播时长的起始传播时刻为发射第一模拟波和第二模拟波的时刻,该传播时长的终止传播时刻为第一模拟波的波峰和第二模拟波的波峰第一次重叠的时刻;The risk assessment terminal transmits the above-mentioned first analog wave and the above-mentioned second analog wave at the same time, and records the propagation time of the first analog wave and the second analog wave. The moment of the wave, the end propagation moment of the propagation duration is the moment when the crest of the first analog wave and the crest of the second analog wave overlap for the first time;
风险评估终端确定在上述传播时长内第一模拟波传播所覆盖的区域和第二模拟波传播所覆盖的区域之和,作为与上述虚拟载瘤动脉以及上述虚拟动脉瘤相对应的分割区域,并根据该分割区域分割上述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型。The risk assessment terminal determines the sum of the area covered by the first simulated wave propagation and the area covered by the second simulated wave propagation within the above-mentioned propagation time as the segmented area corresponding to the above-mentioned virtual parent artery and the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm, and The above three-dimensional model is segmented according to the segmented area to obtain a segmented three-dimensional model.
该可选的实施例中,预先确定的模型分割算法可以包括碰撞前端算法(也称碰撞检测算法),本发明实施例不做限定。In this optional embodiment, the predetermined model segmentation algorithm may include a collision front-end algorithm (also called a collision detection algorithm), which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention.
本发明实施例中,基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割上述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型可以如图2所示,图2为本发明实施例公开的一种分割后的虚拟载瘤动脉的三维模型的结构示意图。In the embodiment of the present invention, the above-mentioned 3D model is segmented based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm, and the segmented 3D model can be obtained as shown in Figure 2, which is a segmented virtual parent artery disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention. Schematic diagram of the structure of the 3D model.
该可选的实施方式通过预先确定的模型分割算法分割三维模型,能够更精确地定位以及重建虚拟载瘤动脉和虚拟动脉瘤的三维模型,从而有利于获得更精确的虚拟载瘤动脉以及虚拟动脉瘤的形态学参数及血流动力学参数。In this optional implementation, the three-dimensional model is segmented by a predetermined model segmentation algorithm, which can more accurately locate and reconstruct the three-dimensional model of the virtual parent artery and virtual aneurysm, which is beneficial to obtain a more accurate virtual parent artery and virtual artery. Morphological parameters and hemodynamic parameters of the tumor.
本发明实施例中,作为又一种可选的实施方式,风险评估终端基于上述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,可以包括:In the embodiment of the present invention, as another optional implementation manner, the risk assessment terminal determines the target morphological parameters based on the above three-dimensional model, which may include:
风险评估终端基于预先确定的中心线提取算法以及上述三维模型提取上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线;The risk assessment terminal extracts the artery centerline of the virtual parent artery based on the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm and the above three-dimensional model;
风险评估终端基于预先确定的区域区分算法对上述三维模型进行区域区分,得到目标区域,该目标区域包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域、上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域、上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域;The risk assessment terminal differentiates the above-mentioned three-dimensional model based on a predetermined area-distinguishing algorithm to obtain a target area, which includes the arterial entrance area of the virtual parent artery, the arterial outlet area of the virtual parent artery, the virtual The arterial wall area of the artery and the aneurysm wall area of the aforementioned virtual aneurysm;
风险评估终端基于预先确定的形态学参数算法对上述目标区域包括的内容进行计算几何分析,得到目标形态学参数。Based on the predetermined morphological parameter algorithm, the risk assessment terminal performs computational geometric analysis on the content included in the target area to obtain the target morphological parameters.
该可选的实施方式中,预先确定的中心线提取算法包括但不限于基于拓扑细化算法、基于Hessian追踪算法、基于距离变换算法中的任意一种。In this optional implementation manner, the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm includes, but is not limited to, any one based on a topology refinement algorithm, a Hessian-based tracking algorithm, and a distance transformation algorithm.
该可选的实施方式中,进一步可选的,当预先确定的中心线提取算法为上述基于距离变换算法时,风险评估终端基于预先确定的中心线提取算法以及上述三维模型提取上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线,可以包括:In this optional embodiment, further optionally, when the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm is the above-mentioned algorithm based on distance transformation, the risk assessment terminal extracts the above-mentioned virtual parent artery based on the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm and the above-mentioned three-dimensional model The arterial centerline can include:
风险评估终端基于距离变换算法确定上述虚拟载瘤动脉的开端节点以及末端节点;The risk assessment terminal determines the start node and end node of the virtual parent artery based on the distance transformation algorithm;
风险评估终端基于上述开端节点以上述末端节点生成上述三维模型的维诺图,并记录第三模拟波从该开端节点传播到维诺图的所有目标节点所需的到达时间,其中,该所有目标节点为维诺图上除了开端节点之外的所有节点;The risk assessment terminal generates the Voronoi diagram of the above-mentioned three-dimensional model based on the above-mentioned start node and the above-mentioned end node, and records the arrival time required for the third analog wave to propagate from the start node to all target nodes in the Voronoi diagram, wherein all target The nodes are all nodes on the Voronoi diagram except the start node;
风险评估终端确定上述维诺图的目标节点集合,并将该目标节点集合中的每个节点依次连接起来得到的线段,作为上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线,其中,该目标节点集合为上述第三模拟波从末端节点沿到达时间的最大空间梯度方向传播所经过的所有节点组成的集合。The risk assessment terminal determines the target node set of the above-mentioned Voronoi diagram, and connects each node in the target node set in turn to obtain a line segment, which is used as the arterial center line of the virtual parent artery, wherein the target node set is the above-mentioned A set of all nodes that the third simulated wave propagates from the terminal node along the direction of the maximum spatial gradient of the arrival time.
该可选的实施方式中,风险评估终端将上述目标节点集合中的每个节点依次连接起来得到的线段,作为上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线,具体的,虚拟支架植入终端确定目标节点集合中离虚拟载瘤动脉的流入进口区域最近的一个节点作为起始节点,并从该起始节点依次将目标节点集合中的每个节点依次连接起来得到的线段作为上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线。In this optional implementation, the risk assessment terminal sequentially connects each node in the target node set to obtain a line segment as the arterial centerline of the virtual parent artery. Specifically, the virtual stent implantation terminal determines the target node The node closest to the inflow and inlet area of the virtual parent artery in the set is used as the starting node, and the line segment obtained by sequentially connecting each node in the target node set from the starting node is used as the artery of the virtual parent artery center line.
该可选的实施方式中,又进一步可选的,当预先确定的中心线提取算法为上述基于拓扑细化算法时,风险评估终端基于预先确定的中心线提取算法以及上述三维模型提取上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线,可以包括:In this optional implementation manner, it is further optional that when the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm is the above-mentioned algorithm based on topology refinement, the risk assessment terminal extracts the above-mentioned virtual carrier based on the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm and the above-mentioned three-dimensional model. The arterial centerline of the aneurysm can include:
风险评估终基于拓扑细化方法对上述虚拟载瘤动脉执行形态学腐蚀操作,直到该虚拟载瘤动脉的拓扑结构保持不变,并从保持不变的拓扑结构上的起始点将拓扑结构上的每个点依次连接起来得到的线段作为虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线。The risk assessment is finally based on the topology refinement method to perform a morphological erosion operation on the above-mentioned virtual parent artery until the topology of the virtual parent artery remains unchanged, and from the starting point on the topological structure that remains unchanged, the topological structure The line segment obtained by connecting each point in turn was used as the arterial centerline of the virtual parent artery.
该可选的实施方式中,拓扑结构的起始点为距离虚拟载瘤动脉的流入进口区域最近的一个点。In this optional embodiment, the starting point of the topology is a point closest to the inflow and inlet area of the virtual parent artery.
该可选的实施方式中,又进一步可选的,当预先确定的中心线提取算法为上述基于Hessian追踪算法时,风险评估终端基于预先确定的中心线提取算法以及上述三维模型提取上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线,可以包括:In this optional embodiment, it is further optional that when the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm is the above-mentioned Hessian-based tracking algorithm, the risk assessment terminal extracts the above-mentioned virtual tumor base based on the predetermined centerline extraction algorithm and the above-mentioned three-dimensional model. The arterial centerline of the artery, which can include:
风险评估终端基于Hessian矩阵的追踪方法计算上述三维模型的Hessian矩阵,得到该三维模型的特征向量,并确定该特征向量的方向作为虚拟载瘤动脉的轴线方向;The risk assessment terminal calculates the Hessian matrix of the above three-dimensional model based on the tracking method of the Hessian matrix, obtains the eigenvector of the three-dimensional model, and determines the direction of the eigenvector as the axis direction of the virtual parent artery;
风险评估终端获取上述虚拟载瘤动脉的局部特征点集合,并确定该局部特征点集合中每个局部特征点垂直于上述轴线方向的截面的中心点,得到该局部特征点集合的中心点集合,以及从起始中心点依次将中心点集合中的每个中心点连接所形成的曲线作为虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线。The risk assessment terminal acquires the local feature point set of the above-mentioned virtual tumor parent artery, and determines the center point of the section of each local feature point in the local feature point set perpendicular to the above-mentioned axial direction, and obtains the center point set of the local feature point set, And the curve formed by sequentially connecting each center point in the center point set from the starting center point is used as the artery centerline of the virtual parent artery.
该可选的实施方式中,局部特征点可以包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉上的斑点和/或角点,其中,斑点可以包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉中灰度值高于预设灰度值的像素点。角点可以包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的拐角点和/或上述虚拟载瘤动脉的主动脉与该虚拟载瘤动脉的支动脉所形成的点。起始中心点为距离上述虚拟载瘤动脉的流入进口区域最近的一个点。In this optional embodiment, the local feature points may include spots and/or corner points on the above-mentioned virtual parent artery, where the spots may include pixels with a gray value higher than a preset gray value in the above-mentioned virtual parent artery point. The corner points may include the corner points of the virtual parent artery and/or the points formed by the aorta of the virtual parent artery and the branch arteries of the virtual parent artery. The starting center point is the closest point to the inflow and inlet area of the above-mentioned virtual parent artery.
可见,通过多种动脉中心线的提取方法,不仅能够丰富虚拟载瘤动脉的提取方法,还能够根据虚拟载瘤动脉的实际情况选择合适的动脉中心线提取方法,从而有利于快速确定形态学参数以及血流动力学参数。It can be seen that through a variety of arterial centerline extraction methods, not only can the extraction methods of the virtual parent artery be enriched, but also the appropriate arterial centerline extraction method can be selected according to the actual situation of the virtual parent artery, which is conducive to the rapid determination of morphological parameters and hemodynamic parameters.
该可选的实施方式中,进一步可选的,风险评估终端基于预先确定的区域区分算法对上述三维模型进行区域区分,得到上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域、上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域,可以包括:In this optional embodiment, it is further optional that the risk assessment terminal differentiates the regions of the above-mentioned three-dimensional model based on a predetermined region-distinguishing algorithm, and obtains the arterial inlet region of the virtual parent artery and the artery outlet of the virtual parent artery. area, which can include:
风险评估终端确定虚拟载瘤动脉的流入动脉(也称流入血管)上的某一点作为第一目标点,以及确定虚拟载瘤动脉的流出动脉(也称流出血管)上的某一点作为第二目标点;The risk assessment terminal determines a certain point on the inflow artery (also called the inflow vessel) of the virtual parent artery as the first target point, and determines a certain point on the outflow artery (also called the outflow vessel) of the virtual tumor parent artery as the second target point;
风险评估终端基于第一目标点确定其对应的动脉中心线上的第一中心点,以及基于第二目标点分别确定其对应的动脉中心线上的第二中心点;The risk assessment terminal determines a first center point on its corresponding arterial center line based on the first target point, and determines a second center point on its corresponding arterial center line based on the second target point;
风险评估终端基于第一目标点与第一中心点切割虚拟载瘤动脉的流入动脉,得到虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域,以及风险评估终端基于第二目标点与第二中心点切割虚拟载瘤动脉的流出动脉,得到虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域。The risk assessment terminal cuts the inflow artery of the virtual parent artery based on the first target point and the first center point to obtain the arterial entrance area of the virtual parent artery, and the risk assessment terminal cuts the virtual parent artery based on the second target point and the second center point Arterial outflow arteries to obtain the arterial exit area of the virtual parent artery.
该可选的实施方式中,第一中心点为第一目标点与中心线上的连接线段长度最小的点,同样第二中心点为第二目标点与中心线上的连接线段长度最小的点。第一目标点以及第二目标点也可以是医护人员选择的点,本发明实施例不做限定。这样切割出来的动脉入口区域以及动脉出口区域有利于确保计算边界条件里的正确血流方向,从而有助于计算虚拟载瘤动脉的血流动力学参数。In this optional embodiment, the first center point is the point where the length of the connecting line segment between the first target point and the center line is the smallest, and the second center point is also the point where the length of the connecting line segment between the second target point and the center line is the smallest. . The first target point and the second target point may also be points selected by medical personnel, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention. The arterial inlet area and arterial outlet area cut out in this way are beneficial to ensure the correct direction of blood flow in the calculation of boundary conditions, thereby helping to calculate the hemodynamic parameters of the virtual parent artery.
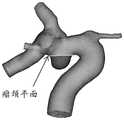
本发明实施例中,基于预先确定的区域区分算法对上述三维模型进行区域区分,得到分割后的三维模型可以如图3所示,图3为本发明实施例公开的一种裁剪后的虚拟载瘤动脉的三维模型的结构示意图。In the embodiment of the present invention, the above-mentioned 3D model is divided into regions based on a predetermined region distinguishing algorithm, and the obtained 3D model after segmentation can be shown in Figure 3, which is a cut virtual carrier disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention Schematic diagram of the structure of the 3D model of the aneurysmal artery.
该可选的实施方式中,进一步可选的,风险评估终端基于预先确定的区域区分算法对上述三维模型进行区域区分,得到上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域,可以包括:In this optional embodiment, it is further optional that the risk assessment terminal performs regional differentiation on the above-mentioned three-dimensional model based on a predetermined area distinguishing algorithm, and obtains the arterial wall area of the above-mentioned virtual parent artery and the aneurysm wall of the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm area, which can include:
风险评估终端在虚拟动脉瘤以及虚拟载瘤动脉的交界处出选择两点,连接此两点形成一线段,再把该线段沿三维模型的视平面的法向方向(正、反)扫掠所形成的面作为虚拟动脉瘤的瘤颈平面(请参照图4中的瘤颈平面),并以该瘤颈平面作为分界线区分虚拟载瘤动脉和虚拟动脉瘤,得到虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域。如图4所示,图4为本发明公开的一种以瘤颈平面作为分界线的虚拟载瘤动脉的三维模型的结构示意图。The risk assessment terminal selects two points at the junction of the virtual aneurysm and the virtual parent artery, connects these two points to form a line segment, and then sweeps the line segment along the normal direction (forward and reverse) of the viewing plane of the 3D model. The formed surface is used as the neck plane of the virtual aneurysm (please refer to the neck plane in Figure 4), and the neck plane is used as a dividing line to distinguish the virtual parent artery from the virtual aneurysm, and the arterial wall of the virtual parent artery is obtained area and the aneurysm wall area of the virtual aneurysm. As shown in FIG. 4 , FIG. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a three-dimensional model of a virtual parent artery with the neck plane as the dividing line disclosed in the present invention.
103、风险评估终端基于上述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数,该目标血流动力学参数包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的血流动力学参数以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的血流动力学参数。103. The risk assessment terminal determines target hemodynamic parameters based on the three-dimensional model, and the target hemodynamic parameters include the hemodynamic parameters of the virtual parent artery and the hemodynamic parameters of the virtual aneurysm.
本发明实施例中,步骤102和步骤103可以同时发生,本发明实施例不做限定。In this embodiment of the present invention,
本发明实施例中,血流动力学参数包括但不限于虚拟载瘤动脉的壁面切应力平均值WSS-mean、虚拟载瘤动脉的壁面切应力最大值WSS-max、虚拟载瘤动脉的壁面切应力最小值WSS-min、虚拟载瘤动脉的壁面低切应力区的面积、虚拟载瘤动脉的壁面高切应力区的面积、该壁面切应力的震荡系数OSI、能量损失系数EL、压力损失系数、剪切力空间梯度、剪切力时间梯度。其中,壁面低切应力区为壁面切应力平均值WSS-mean小于12.8μQ/d3的区域的面积与虚拟动脉瘤壁表面积之比,壁面高切应力区为壁面切应力平均值WSS-mean大于64μQ/d3的区域的面积与虚拟动脉瘤壁表面积之比。In the embodiment of the present invention, the hemodynamic parameters include but are not limited to the mean value of the wall shear stress of the virtual parent artery WSS-mean, the maximum value of the wall shear stress of the virtual parent artery WSS-max, the wall shear stress of the virtual parent artery The minimum value of stress WSS-min, the area of the low shear stress area on the wall of the virtual parent artery, the area of the high shear stress area on the wall of the virtual parent artery, the oscillation coefficient OSI of the wall shear stress, the energy loss coefficient EL, and the pressure loss coefficient , the spatial gradient of the shear force, and the time gradient of the shear force. Among them, the area of low wall shear stress is the ratio of the area of the area where the average wall shear stress WSS-mean is less than 12.8 μQ/d3 to the surface area of the virtual aneurysm wall, and the area of high wall shear stress is the area where the average wall shear stress WSS-mean is greater than 64 μQ The ratio of the area of the region of /d3 to the surface area of the virtual aneurysm wall.
本发明实施例中,风险评估终端基于上述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数,可以包括:In the embodiment of the present invention, the risk assessment terminal determines the target hemodynamic parameters based on the above three-dimensional model, which may include:
风险评估终端基于预先确定的网格划分算法划分上述三维模型,得到多个目标体网格模型,该所有目标体网格模型均为多面体网格模型;The risk assessment terminal divides the above three-dimensional model based on a predetermined grid division algorithm to obtain multiple target volume grid models, and all the target volume grid models are polyhedral grid models;
风险评估终端确定上述三维模型的目标边界条件,该目标边界条件至少包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口边界的边界条件、上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口边界的边界条件;The risk assessment terminal determines the target boundary conditions of the three-dimensional model, and the target boundary conditions include at least the boundary conditions of the artery inlet boundary of the virtual parent artery and the boundary conditions of the artery outlet boundary of the virtual parent artery;
风险评估终端基于所有上述目标体网格模型以及上述目标边界条件模拟上述虚拟载瘤动脉的血液流动以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的血液流动,得到目标血流动力学参数。The risk assessment terminal simulates the blood flow of the above-mentioned virtual parent artery and the blood flow of the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm based on all the above-mentioned target volume mesh models and the above-mentioned target boundary conditions, and obtains target hemodynamic parameters.
本发明实施例中,基于预先确定的网格划分算法划分上述三维模型,得到多个目标体网格模型可以如图4所示,图4为本发明公开的一种网格划分后的虚拟载瘤动脉的三维模型的结构示意图。In the embodiment of the present invention, the above-mentioned three-dimensional model is divided based on a predetermined grid division algorithm, and multiple target body grid models can be obtained as shown in Figure 4. Figure 4 is a virtual load after grid division disclosed in the present invention. Schematic diagram of the structure of the 3D model of the aneurysmal artery.
本发明实施例中,风险评估终端基于所有上述目标体网格模型以及上述目标边界条件模拟上述虚拟载瘤动脉的血液流动以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的血液流动,得到目标血流动力学参数。具体的,血液流动满足三维流体运动控制方程如下所示:In the embodiment of the present invention, the risk assessment terminal simulates the blood flow of the above-mentioned virtual parent artery and the blood flow of the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm based on all the above-mentioned target volume mesh models and the above-mentioned target boundary conditions to obtain target hemodynamic parameters. Specifically, the blood flow satisfies the three-dimensional fluid motion control equation as follows:
其中,方程(1)为流体质量守恒方程,方程(2)为流体动量守恒方程。以及式中:其中ρ代表血液密度,v代表血液的运动粘度,u为血液的速度,p为血压。Among them, Equation (1) is the fluid mass conservation equation, and Equation (2) is the fluid momentum conservation equation. And in the formula: where ρ represents the blood density, v represents the kinematic viscosity of the blood, u is the velocity of the blood, and p is the blood pressure.
该可选的实施方式中,流体运动控制方程是一组偏微分方程,具体的求解方法可以包括有限元、有限差分法、有限体积法中的一种或多种组合,本发明实施例不做限定。In this optional implementation, the fluid motion control equation is a set of partial differential equations, and the specific solution method may include one or more combinations of finite element, finite difference method, and finite volume method. limited.
104、风险评估终端基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果,该评估结果用于评估所述动脉瘤的破裂风险。104. The risk assessment terminal calculates the above-mentioned target morphological parameters, the above-mentioned target hemodynamic parameters, and the target clinical parameters based on the pre-trained machine learning model, and obtains the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm assessment results, which are used to assess all risk of aneurysm rupture.
本发明实施例中,目标临床参数包括预先确定出的颅内影像数据对应的用户的临床参数。其中,临床参数包括但不限于血压、血脂、年龄、性别、过往病史、家族史、是否携带易感基因、是否为多发颅内动脉瘤以及颅内动脉瘤部位。In the embodiment of the present invention, the target clinical parameters include predetermined clinical parameters of the user corresponding to the intracranial image data. Among them, the clinical parameters include but not limited to blood pressure, blood lipids, age, gender, past medical history, family history, whether to carry susceptibility genes, whether there are multiple intracranial aneurysms, and the location of intracranial aneurysms.
作为又一种可选的实施例,风险评估终端基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之前,还可以包括:As another optional embodiment, the risk assessment terminal calculates the target morphological parameters, the target hemodynamic parameters and the target clinical parameters based on the pre-trained machine learning model to obtain the assessment result of the virtual aneurysm Before, you can also include:
风险评估终端构建机器学习模型,该机器学习模型用于确定上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果。The risk assessment terminal constructs a machine learning model, and the machine learning model is used to determine the assessment result of the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm.
其中,风险评估终端构建机器学习模型,可以包括:Among them, the risk assessment terminal constructs a machine learning model, which may include:
风险评估终端获取多个样本颅内影像数据,每个样本颅内影像数据对应一个动脉瘤患者;The risk assessment terminal acquires multiple samples of intracranial image data, and each sample of intracranial image data corresponds to an aneurysm patient;
风险评估终端确定每个样本颅内影像数据的样本特征参数,每个样本特征参数可以包括样本形态学参数、与该样本形态学参数对应的样本血流动力参数以及与该样本形态学参数对应的样本临床参数;The risk assessment terminal determines the sample characteristic parameters of the intracranial image data of each sample, and each sample characteristic parameter may include sample morphological parameters, sample hemodynamic parameters corresponding to the sample morphological parameters, and sample morphological parameters corresponding to the sample morphological parameters. Sample clinical parameters;
风险评估终端标记每个样本特征参数,得到标记后的样本特征参数以及该标记后的样本特征参数对应的标记值;The risk assessment terminal marks each sample characteristic parameter, and obtains the marked sample characteristic parameter and the marked value corresponding to the marked sample characteristic parameter;
风险评估终端基于预先确定的训练模型训练每个标记后的样本特征参数,得到机器学习模型。The risk assessment terminal trains each marked sample feature parameter based on a predetermined training model to obtain a machine learning model.
该可选的实施例中,风险评估终端标记每个样本特征参数,得到标记后的样本特征参数对应的标记值,可以包括:In this optional embodiment, the risk assessment terminal marks each sample characteristic parameter, and obtains the marked value corresponding to the marked sample characteristic parameter, which may include:
当上述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为破裂动脉瘤时,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第一预设值;When the aneurysm included in the above-mentioned sample intracranial image data is a ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is marked with a first preset value;
当上述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为非破裂动脉瘤时,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第二预设值;When the aneurysm included in the above sample intracranial image data is a non-ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is a second preset value;
该可选的实施例中,上述第一预设值与上述第二预设值不相同。具体的,当上述第一预设值为1时,则第二预设值为0;当上述第一预设值为0时,则第二预设值为1,本发明实施例不做限定。In this optional embodiment, the above-mentioned first preset value is different from the above-mentioned second preset value. Specifically, when the above-mentioned first preset value is 1, then the second preset value is 0; when the above-mentioned first preset value is 0, then the second preset value is 1, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention .
该可选的实施例中,风险评估终端基于预先确定的训练模型训练每个样本特征参数,得到机器学习模型,可以包括:In this optional embodiment, the risk assessment terminal trains each sample feature parameter based on a predetermined training model to obtain a machine learning model, which may include:
风险评估终端将所有标记后的样本特征参数进行划分,得到训练集、验证集以及测试集,并基于预先确定的训练模型训练上述作为训练集的标记后的样本特征参数,得到第一子机器学习模型,以及利用作为验证集的标记后的样本特征参数验证第一子机器学习模型,得到第二子机器学习模型,最后基于作为测试集的标记后的样本特征参数测试第二子机器学习模型,得到机器学习模型。The risk assessment terminal divides all marked sample feature parameters to obtain a training set, a verification set, and a test set, and trains the above-mentioned marked sample feature parameters as the training set based on a predetermined training model to obtain the first sub-machine learning model, and verify the first sub-machine learning model by using the marked sample feature parameters as the verification set to obtain the second sub-machine learning model, and finally test the second sub-machine learning model based on the marked sample feature parameters as the test set, Get the machine learning model.
该可选的实施例中,预先确定的训练模型可以包括逻辑回归模型、决策树模型、贝叶斯模型、k-邻近算法模型、随机森林模型、支持向量机模型、神经网络模型、Adaboost模型、GradientBoost模型中的一种模型或多种模型组合,本发明实施例不做限定。In this optional embodiment, the predetermined training model may include a logistic regression model, a decision tree model, a Bayesian model, a k-neighbor algorithm model, a random forest model, a support vector machine model, a neural network model, an Adaboost model, One model or a combination of multiple models in the GradientBoost model is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention.
可见,该可选的实施例通过预先建立好用于确定虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果的机器学习模型,能够在确定患者的形态学参数、血流动力学参数以及临床参数后,直接利用该机器学习模型进行运算,从而快速确定患者的动脉瘤的破裂风险,进而进一步快速为患者提供有效的治疗方案。It can be seen that this optional embodiment can directly use the machine learning model after determining the patient's morphological parameters, hemodynamic parameters and clinical parameters by establishing a machine learning model for determining the evaluation results of the virtual aneurysm in advance. The model can be used to quickly determine the risk of rupture of the patient's aneurysm, and further quickly provide the patient with an effective treatment plan.
作为又一个可选的实施例,风险评估终端基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之后,还可以:As yet another optional embodiment, the risk assessment terminal calculates the above-mentioned target morphological parameters, the above-mentioned target hemodynamic parameters and target clinical parameters based on the pre-trained machine learning model, and obtains the assessment results of the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm ,is acceptable:
根据上述评估结果生成上述颅内影像数据的评估报告,该评估报告包括上述目标形态学参数的形态学风险分析结果、上述目标血流动力学参数的血流动力学风险分析结果、上述目标临床参数的临床风险分析结果以及综合风险分析结果,该综合风险分析结果为基于形态学风险分析结果、血流动力学风险分析结果以及临床风险分析结果生成的结果;According to the above evaluation results, an evaluation report of the above-mentioned intracranial imaging data is generated, and the evaluation report includes the results of the morphological risk analysis of the above-mentioned target morphological parameters, the results of the hemodynamic risk analysis of the above-mentioned target hemodynamic parameters, and the above-mentioned target clinical parameters. The clinical risk analysis results and the comprehensive risk analysis results, the comprehensive risk analysis results are the results generated based on the morphological risk analysis results, hemodynamic risk analysis results and clinical risk analysis results;
基于预设风险等级规则确定上述评估报告包括的综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级,并显示上述评估报告以及该综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级。Determine the risk level corresponding to the comprehensive risk analysis result included in the assessment report based on the preset risk level rules, and display the risk level corresponding to the assessment report and the comprehensive risk analysis result.
该可选的实施例中,该预设风险等级规则为根据颅内动脉瘤的综合风险分析结果的破裂概率进行设置的风险等级规则,以及预设风险等级可以包括若干等级,例如:1级-5级,或1级-10级,例如:破裂概率为0%-20%对应的风险等级为1级,破裂概率为80%100%对应的风险等级为5级,或破裂概率为0%-10%对应的风险等级为1级,破裂概率为90%-100%对应的风险等级为10级,本发明实施例不做限定。具体的,颅内动脉瘤破裂风险越高对应的风险等级越高,或颅内动脉瘤破裂风险越高对应的风险等级越低。In this optional embodiment, the preset risk level rule is a risk level rule set according to the rupture probability of the comprehensive risk analysis result of the intracranial aneurysm, and the preset risk level may include several levels, for example: level 1- Level 5, or level 1-10, for example: the probability of rupture is 0%-20%, the corresponding risk level is 1, the probability of rupture is 80%, 100% corresponds to the risk level 5, or the probability of rupture is 0%- 10% corresponds to a risk level of 1, and a rupture probability of 90%-100% corresponds to a risk level of 10, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, a higher risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture corresponds to a higher risk level, or a higher risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture corresponds to a lower risk level.
该可选的实施例中,进一步的,风险评估终端标记评估报告中的分析结果,得到标记后的分析结果,并根据不同的标记确定动脉瘤破裂的风险。具体的,将分析结果用不同的颜色进行标记,颜色越深,代表动脉瘤破裂的风险越高,本发明实施例不做限定。这样通过将评估报告的分析结果以颜色和/或图文标记出来,以及将颅内动脉瘤的破裂风险以破裂风险等级标记出来,能够直观地了解动脉瘤破裂的情况。In this optional embodiment, further, the risk assessment terminal marks the analysis results in the evaluation report, obtains the marked analysis results, and determines the risk of aneurysm rupture according to different marks. Specifically, the analysis results are marked with different colors, and the darker the color, the higher the risk of aneurysm rupture, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention. In this way, by marking the analysis results of the evaluation report with color and/or graphics and text, and marking the rupture risk of the intracranial aneurysm with a rupture risk grade, it is possible to intuitively understand the rupture situation of the aneurysm.
该可选的实施例中,又进一步的,风险评估终端基于上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及上述目标临床参数从预先建立的动脉瘤数据库中确定与上述评估报告最相似的目标评估报告,并显示该目标评估报告,该预先建立的动脉瘤数据库用于存储所有动脉瘤患者中每个动脉瘤患者的评估报告。In this optional embodiment, further, the risk assessment terminal determines the most similar to the above assessment report from the pre-established aneurysm database based on the above target morphological parameters, the above target hemodynamic parameters and the above target clinical parameters. The target assessment report is displayed, and the pre-established aneurysm database is used to store the assessment report of each aneurysm patient among all the aneurysm patients.
该可选的实施例中,风险评估终端从预先建立的动脉瘤数据库中确定与上述评估报告最相似的目标评估报告,即风险评估终端从预先建立的动脉瘤数据库中确定与当前病例最相似的以往病例,其中,该与当前病例最相似的以往病例是根据当前病例的目标形态学参数、目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数作为参考从动脉瘤数据库筛选出来的。并且与当前病例最相似的以往病例的分析可以包括该以往病例的临床信息(例如:50岁)、三维血管模型以及相似程度(例如:80%)中的至少一种,本发明实施例不做限定。进一步的,该临床信息为匿名化后的信息。这样通过将与当前病例最相似的以往病例的分析显示在评估报告中,能够为医护人员提供参考,从而快速为当前动脉瘤患者的做出诊断结果。In this optional embodiment, the risk assessment terminal determines the target assessment report most similar to the above assessment report from the pre-established aneurysm database, that is, the risk assessment terminal determines the target assessment report most similar to the current case from the pre-established aneurysm database. The previous cases, wherein the previous case most similar to the current case is selected from the aneurysm database according to the target morphological parameters, target hemodynamic parameters and target clinical parameters of the current case as reference. And the analysis of the previous case most similar to the current case may include at least one of the clinical information (for example: 50 years old), the three-dimensional blood vessel model and the degree of similarity (for example: 80%) of the previous case, the embodiment of the present invention does not limited. Further, the clinical information is anonymized information. In this way, by displaying the analysis of the previous case most similar to the current case in the evaluation report, it can provide reference for medical staff, so as to quickly make a diagnosis for the current aneurysm patient.
该可选的实施例中,风险评估终端将评估报告发送至该评估报告对应的患者的用户终端,供患者查看。这样将评估报告发送至患者,便于患者保存评估报告,并实时查看评估报告。In this optional embodiment, the risk assessment terminal sends the assessment report to the user terminal of the patient corresponding to the assessment report, for the patient to view. In this way, the evaluation report is sent to the patient, and it is convenient for the patient to save the evaluation report and view the evaluation report in real time.
可见,该可选的实施例通过生成包括形态学参数评估结果、血流动力学参数评估结果以及临床参数评估结果以及综合性评估结果的评估报告,能够获取更准确、更全面的动脉瘤的评估结果。It can be seen that in this optional embodiment, a more accurate and comprehensive evaluation of aneurysm can be obtained by generating an evaluation report including evaluation results of morphological parameters, evaluation results of hemodynamic parameters, evaluation results of clinical parameters and comprehensive evaluation results result.
可见,实施图1所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法能够通过对患者颅内动脉瘤的形态学参数、血流动力学参数以及临床参数对颅内动脉瘤破裂风险进行全面自动分析,能够提高动脉瘤破裂风险评估的准确率,从而为医生在作治疗决策时提供科学性的参考,进而使得医生快速给患者提供有效的治疗方案。It can be seen that implementing the method for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture described in Figure 1 can conduct a comprehensive and automatic analysis of the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture through the morphological parameters, hemodynamic parameters and clinical parameters of the patient's intracranial aneurysm. It can improve the accuracy of aneurysm rupture risk assessment, thereby providing scientific reference for doctors when making treatment decisions, and then enabling doctors to quickly provide patients with effective treatment plans.
实施例二Embodiment two
请参阅图5,图5是本发明实施例公开的一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图。如图5所示,该颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统可以包括三维重建模块501、形态学测量模块502、血流动力学计算模块503以及综合风险计算模块504,其中:Please refer to FIG. 5 . FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a system for assessing the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 5 , the system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture may include a three-
三维重建模块501,用于根据颅内影像数据建立包括目标载瘤动脉和该目标载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,该三维模型包括与目标载瘤动脉相匹配的虚拟载瘤动脉以及与动脉瘤相匹配的虚拟动脉瘤。The three-
形态学测量模块502,用于基于上述三维模型确定目标形态学参数,该目标形态学参数包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的形态学参数以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的形态学参数。The
血流动力学计算模块503,用于基于上述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数,该目标血流动力学参数包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的血流动力学参数以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的血流动力学参数。The
综合风险计算模块504,用于基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果,该评估结果用于评估动脉瘤的破裂风险,该目标临床参数为预先确定的颅内影像数据对应的用户的临床参数。The comprehensive
可见,实施图5所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统能够通过对患者颅内动脉瘤的形态学参数、血流动力学参数以及临床参数对颅内动脉瘤破裂风险进行全面自动分析,能够提高动脉瘤破裂风险评估的准确率,从而为医生在作治疗决策时提供科学性的参考,进而使得医生快速给患者提供有效的治疗方案。It can be seen that the implementation of the assessment system for the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture described in Figure 5 can conduct a comprehensive and automatic analysis of the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture through the morphological parameters, hemodynamic parameters and clinical parameters of the patient's intracranial aneurysm. It can improve the accuracy of aneurysm rupture risk assessment, thereby providing scientific reference for doctors when making treatment decisions, and then enabling doctors to quickly provide patients with effective treatment plans.
作为一种可选的实施例,如图5所示,综合风险计算模块504,还用于在基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之后,根据该评估结果生成上述颅内影像数据的评估报告,该评估报告包括上述目标形态学参数的形态学风险分析结果、上述目标血流动力学参数的血流动力学风险分析结果、上述目标临床参数的临床风险分析结果以及综合风险分析结果,该综合风险分析结果为基于上述形态学风险分析结果、上述血流动力学风险分析结果以及临床风险分析结果生成的结果;As an optional embodiment, as shown in Figure 5, the comprehensive
综合风险计算模块504,还用于基于预设等级规则确定上述评估报告包括的综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级,并显示该评估报告以及该综合风险分析结果对应的风险等级。The comprehensive
可见,实施图5所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统还能够将评估报告的分析结果以颜色和/或图文标记出来,以及将颅内动脉瘤的破裂风险以破裂风险等级标记出来,能够直观地了解动脉瘤破裂的情况。It can be seen that the implementation of the assessment system for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk described in Figure 5 can also mark the analysis results of the assessment report with color and/or graphics, and mark the rupture risk of intracranial aneurysm with a rupture risk level , can intuitively understand the situation of aneurysm rupture.
以及,综合风险计算模块504,还用于基于上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及上述目标临床参数从预先建立的动脉瘤数据库中确定与上述评估报告最相似的目标评估报告,并显示该目标评估报告,该预先建立的动脉瘤数据库用于存储所有动脉瘤患者中每个动脉瘤患者的评估报告。And, the comprehensive
可见,实施图5所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统还能够通过将与当前病例最相似的以往病例的分析显示在评估报告中,能够为医护人员提供参考,从而快速为当前动脉瘤患者的做出诊断结果。It can be seen that the implementation of the assessment system for the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture described in Figure 5 can also provide references for medical staff by displaying the analysis of previous cases most similar to the current case in the assessment report, so as to quickly assess the risk of current aneurysm rupture. patient's diagnosis.
作为一种可选的实施方式,形态学测量模块502可以包括模型分割子模块5021以及形态学确定子模块5022,此时,颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图可以如图6所示,图6是本发明实施例公开的另一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图,其中:As an optional implementation, the
模型分割子模块5021,用于基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割上述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型。The
形态学确定子模块5022,用于基于上述分割后的三维模型确定目标形态学参数。
其中,模型分割子模块5021基于预先确定的模型分割算法分割上述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型的方式具体为:Wherein, the model segmentation sub-module 5021 segments the above-mentioned 3D model based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm, and obtains the segmented 3D model specifically as follows:
基于预先确定的模型分割算法确定上述虚拟载瘤动脉上的某一像素点所在位置作为第一模拟波的第一波源点,以及确定上述虚拟动脉瘤上的某一像素点所在位置作为第二模拟波的第二波源点,该第一模拟波和该第二模拟波为同一类型的模拟波;Based on a predetermined model segmentation algorithm, determine the position of a certain pixel point on the above-mentioned virtual parent artery as the first wave source point of the first simulation wave, and determine the position of a certain pixel point on the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm as the second simulation wave The second wave source point of the wave, the first analog wave and the second analog wave are analog waves of the same type;
同时发射上述第一模拟波以及上述第二模拟波,并记录该第一模拟波和该第二模拟波的传播时长,该传播时长的起始传播时刻为发射第一模拟波和第二模拟波的时刻,该传播时长的终止传播时刻为第一模拟波的波峰和第二模拟波的波峰第一次重叠的时刻;Simultaneously transmit the above-mentioned first analog wave and the above-mentioned second analog wave, and record the propagation time of the first analog wave and the second analog wave, the initial propagation time of the propagation time is when the first analog wave and the second analog wave are emitted , the end propagation time of this propagation duration is the moment when the peak of the first analog wave and the peak of the second analog wave overlap for the first time;
确定在上述传播时长内上述第一模拟波传播所覆盖的区域和上述第二模拟波传播所覆盖的区域之和,作为与上述虚拟载瘤动脉以及上述虚拟动脉瘤相对应的分割区域,并根据该分割区域分割所述三维模型,得到分割后的三维模型。Determining the sum of the area covered by the first simulated wave propagation and the area covered by the second simulated wave within the propagation time as the segmented area corresponding to the virtual parent artery and the virtual aneurysm, and according to The segmentation area divides the 3D model to obtain the divided 3D model.
作为另一种可选的实施例,如图6或图7所示,颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统还可以包括影像质量判断模块505以及影像预处理模块506,其中:As another optional embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6 or FIG. 7 , the assessment system for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk may further include an image
影像质量判断模块505,用于在上述三维重建模块基于颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和该载瘤动脉上动脉瘤的三维模型之前,判断颅内影像数据的影像质量指标是否达到预设影像质量指标;The image
三维重建模块501,具体用于:The three-
当影像质量判断模块505判断出颅内影像数据的影像质量指标达到预设影像质量指标时,根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和该载瘤动脉上动脉瘤的三维模型的操作。When the image
影像预处理模块506,用于当影像质量判断模块505判断出颅内影像数据的影像质量指标未达到预设影像质量指标时,基于预设影像算法对颅内影像数据进行预处理,直至该颅内影像数据的影像质量指标达到预设影像质量指标,并触发三维重建模块501执行上述的根据颅内影像数据建立包括载瘤动脉和该载瘤动脉上动脉瘤的三维模型的操作。The
可见,实施图6所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统还通过在建立载瘤动脉以及载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型之前,判断颅内影像数据的影像质量指标是否达到预设标准,当没有达到预设标准时,将颅内影像数据的影像质量指标进行预处理,直至达到预设影像质量指标才建立载瘤动脉以及载瘤动脉上的动脉瘤的三维模型,能够降低因影像质量指标不达标而导致建立载瘤动脉以及动脉瘤的三维模型不精准的可能性。It can be seen that the implementation of the assessment system for the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture described in Figure 6 also determines whether the image quality index of the intracranial image data reaches the preset level before establishing the three-dimensional model of the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery. When the preset standard is not met, the image quality index of the intracranial image data is preprocessed until the preset image quality index is reached before the three-dimensional model of the parent artery and the aneurysm on the parent artery is established, which can reduce the The possibility of inaccurate establishment of 3D models of parent artery and aneurysm due to substandard quality indicators.
作为另一种可选的实施例,如图7所示,形态学测量模块502包括中心线提取子模块5023、区域区分子模块5024以及形态学计算子模块5025,其中:As another optional embodiment, as shown in FIG. 7 , the
中心线提取子模块5023,用于基于预先确定的中心线提取算法以及上述三维模型提取上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉中心线。The
区域区分子模块5024,用于基于预先确定的区域区分算法对上述三维模型进行区域区分,得到目标区域,该目标区域包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域、该虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域、该虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域。The area area sub-module 5024 is configured to perform area area division on the above three-dimensional model based on a predetermined area area identification algorithm to obtain a target area, the target area includes the arterial inlet area of the virtual parent artery and the arterial outlet area of the virtual parent artery , the arterial wall area of the virtual parent artery and the aneurysm wall area of the virtual aneurysm.
形态学计算子模块5025,用于基于预先确定的形态学参数算法对上述目标区域包括的内容进行计算几何分析,得到目标形态学参数。The
该可选的实施例中,作为一种可选的实施方式,区域区分子模块1024基于预先确定的区域区分算法对上述三维模型进行区域区分,得到目标区域的方式具体为:In this optional embodiment, as an optional implementation manner, the region distinguishing submodule 1024 performs region distinction on the above-mentioned 3D model based on a predetermined region distinguishing algorithm, and the method of obtaining the target region is specifically as follows:
基于预先确定的区域区分算法确定上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口横截面、动脉出口横截面以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的瘤颈平面;Determining the arterial inlet cross-section, the arterial outlet cross-section, and the neck plane of the virtual aneurysm based on a predetermined area discrimination algorithm;
根据上述动脉入口横截面切割上述三维模型,得到上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口区域,以及根据上述出口横截面切割所述三维模型,得到上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口区域,以及根据上述瘤颈平面切割上述三维模型,得到上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉壁区域以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的动脉瘤壁区域。Cutting the above three-dimensional model according to the above-mentioned arterial inlet cross-section to obtain the artery inlet area of the virtual parent artery, and cutting the three-dimensional model according to the above-mentioned outlet cross-section to obtain the arterial outlet area of the above-mentioned virtual parent artery, and according to the above-mentioned aneurysm neck Cutting the three-dimensional model in a plane to obtain the artery wall area of the virtual parent artery and the aneurysm wall area of the virtual aneurysm.
作为一种可选的实施方式,血流动力学计算模块503基于所述三维模型确定目标血流动力学参数的方式具体为:As an optional implementation manner, the manner in which the
基于预先确定的网格划分算法划分上述三维模型,得到多个目标体网格模型,所有目标体网格模型均为多面体网格模型;Divide the above three-dimensional model based on a predetermined grid division algorithm to obtain a plurality of target volume grid models, and all target volume grid models are polyhedral grid models;
确定上述三维模型的目标边界条件,该目标边界条件至少包括上述虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉入口边界的边界条件、该虚拟载瘤动脉的动脉出口边界的边界条件;Determining the target boundary conditions of the three-dimensional model, the target boundary conditions at least including the boundary conditions of the artery inlet boundary of the virtual parent artery and the boundary conditions of the artery outlet boundary of the virtual parent artery;
基于所有上述目标体网格模型以及上述目标边界条件模拟上述虚拟载瘤动脉的血液流动以及上述虚拟动脉瘤的血液流动,得到目标血流动力学参数。The blood flow of the above-mentioned virtual parent artery and the blood flow of the above-mentioned virtual aneurysm are simulated based on all the above-mentioned target body mesh models and the above-mentioned target boundary conditions to obtain target hemodynamic parameters.
作为另一种可选的实施例,如图6或图7所示,该颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统还可以包括模型构建模块507,其中:As another optional embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6 or FIG. 7, the system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture may also include a
模型构建模块507,用于在综合风险计算模块504基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果之前,构建机器学习模型,该机器学习模型用于确定上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果;The
其中,模型构建模块507构建机器学习模型的方式具体为:Wherein, the manner of constructing the machine learning model by the
获取多个样本颅内影像数据,每个样本颅内影像数据对应一个动脉瘤患者;Acquire multiple samples of intracranial image data, each sample of intracranial image data corresponds to a patient with aneurysm;
确定每个样本颅内影像数据的样本特征参数,每个样本特征参数包括样本形态学参数、与该样本形态学参数对应的样本血流动力参数以及与该样本形态学参数对应的样本临床参数;Determine the sample characteristic parameters of the intracranial image data of each sample, where each sample characteristic parameter includes a sample morphological parameter, a sample hemodynamic parameter corresponding to the sample morphological parameter, and a sample clinical parameter corresponding to the sample morphological parameter;
标记每个样本特征参数,得到标记后的样本特征参数以及该标记后的样本特征参数对应的标记值;Mark each sample characteristic parameter, obtain the marked sample characteristic parameter and the marked value corresponding to the marked sample characteristic parameter;
基于预先确定的训练算法训练每个标记后的样本特征参数,得到机器学习模型;Train each marked sample feature parameter based on a predetermined training algorithm to obtain a machine learning model;
其中,模型构建模块507标记每个样本特征参数,得到标记后的样本特征参数对应的标记值的方式具体为:Wherein, the
当上述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为破裂动脉瘤,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第一预设值;When the aneurysm included in the sample intracranial image data is a ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is a first preset value;
当上述样本颅内影像数据包括的动脉瘤为非破裂动脉瘤,则标记与该样本颅内影像数据对应的样本特征参数的标记值为第二预设值;When the aneurysm included in the sample intracranial image data is a non-ruptured aneurysm, the flag value of the sample characteristic parameter corresponding to the sample intracranial image data is a second preset value;
其中,该第一预设值与该第二预设值不相同。Wherein, the first preset value is different from the second preset value.
该可选的实施例中,当模型构建模块507执行完上述的构建机器学习模型的操作之后,可以触发综合风险计算模块504执行上述的基于预先训练好的机器学习模型对上述目标形态学参数、上述目标血流动力学参数以及目标临床参数进行运算,得到上述虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果的操作。In this optional embodiment, after the
可见,实施图6或图7所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统还通过预先建立好用于确定虚拟动脉瘤的评估结果的机器学习模型,能够在确定患者的形态学参数、血流动力学参数以及临床参数后,直接利用该机器学习模型进行运算,从而快速确定患者的动脉瘤的破裂风险,进而进一步快速为患者提供有效的治疗方案。It can be seen that the implementation of the assessment system for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk described in Figure 6 or Figure 7 can also determine the patient's morphological parameters, blood flow After the kinetic parameters and clinical parameters are calculated, the machine learning model is directly used for calculation, so as to quickly determine the rupture risk of the patient's aneurysm, and further provide effective treatment options for the patient.
实施例三Embodiment three
请参阅图8,图8是本发明实施例公开的又一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统的结构示意图。如图8所示,该颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估系统可以包括:Please refer to FIG. 8 . FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of another system for assessing the rupture risk of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Figure 8, the assessment system for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk may include:
存储有可执行程序代码的存储器701;A
与存储器701耦合的处理器702;a
处理器702调用存储器701中存储的可执行程序代码,执行实施例一中所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法中的步骤。The
实施例四Embodiment Four
本发明实施例公开了一种计算机可读存储介质,其存储用于电子数据交换的计算机程序,其中,该计算机程序使得计算机执行实施例一中所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法中的步骤。The embodiment of the present invention discloses a computer-readable storage medium, which stores a computer program for electronic data exchange, wherein the computer program enables the computer to execute the method for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture described in Embodiment 1 A step of.
实施例五Embodiment five
本发明实施例公开了一种计算机程序产品,该计算机程序产品包括存储了计算机程序的非瞬时性计算机可读存储介质,且该计算机程序可操作来使计算机执行实施例一中所描述的颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法中的步骤。The embodiment of the present invention discloses a computer program product, the computer program product includes a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing a computer program, and the computer program is operable to make the computer execute the intracranial described in the first embodiment Steps in a method for assessing the risk of aneurysm rupture.
以上所描述的装置实施例仅是示意性的,其中所述作为分离部件说明的模块可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为模块显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理模块,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个网络模块上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部模块来实现本实施例方案的目的。本领域普通技术人员在不付出创造性的劳动的情况下,即可以理解并实施。The device embodiments described above are only illustrative, and the modules described as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and the components shown as modules may or may not be physical modules, that is, they may be located in One place, or it can be distributed to multiple network modules. Part or all of the modules can be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution of this embodiment. It can be understood and implemented by those skilled in the art without any creative efforts.
通过以上的实施例的具体描述,本领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到各实施方式可借助软件加必需的通用硬件平台的方式来实现,当然也可以通过硬件。基于这样的理解,上述技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品可以存储在计算机可读存储介质中,存储介质包括只读存储器(Read-Only Memory,ROM)、随机存储器(Random Access Memory,RAM)、可编程只读存储器(Programmable Read-only Memory,PROM)、可擦除可编程只读存储器(ErasableProgrammable Read Only Memory,EPROM)、一次可编程只读存储器(One-timeProgrammable Read-Only Memory,OTPROM)、电子抹除式可复写只读存储器(Electrically-Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory,EEPROM)、只读光盘(CompactDisc Read-Only Memory,CD-ROM)或其他光盘存储器、磁盘存储器、磁带存储器、或者能够用于携带或存储数据的计算机可读的任何其他介质。Through the specific description of the above embodiments, those skilled in the art can clearly understand that each implementation manner can be implemented by means of software plus a necessary general-purpose hardware platform, and of course also by hardware. Based on this understanding, the above-mentioned technical solution essentially or the part that contributes to the prior art can be embodied in the form of a software product, and the computer software product can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium, and the storage medium includes a read-only memory (Read-Only Memory, ROM), random access memory (Random Access Memory, RAM), programmable read-only memory (Programmable Read-only Memory, PROM), erasable programmable read-only memory (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory, EPROM) , One-time Programmable Read-Only Memory (OTPROM), Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM), Compact Disc Read-Only Memory , CD-ROM) or other optical disk storage, magnetic disk storage, magnetic tape storage, or any other computer-readable medium that can be used to carry or store data.
最后应说明的是:本发明实施例公开的一种颅内动脉瘤破裂风险的评估方法及系统所揭露的仅为本发明较佳实施例而已,仅用于说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解;其依然可以对前述各项实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或替换,并不使相应的技术方案的本质脱离本发明各项实施例技术方案的精神和范围。Finally, it should be noted that: the method and system for assessing the risk of rupture of an intracranial aneurysm disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and is only used to illustrate the technical solution of the present invention, not to It is limited; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the aforementioned embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that it can still modify the technical solutions described in the aforementioned embodiments, or modify some of the technical features thereof. Equivalent replacement; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions of the various embodiments of the present invention.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910280012.7ACN109907732B (en) | 2019-04-09 | 2019-04-09 | A method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910280012.7ACN109907732B (en) | 2019-04-09 | 2019-04-09 | A method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN109907732A CN109907732A (en) | 2019-06-21 |
| CN109907732Btrue CN109907732B (en) | 2022-12-02 |
Family
ID=66969088
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910280012.7AActiveCN109907732B (en) | 2019-04-09 | 2019-04-09 | A method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN109907732B (en) |
Families Citing this family (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110353639B (en)* | 2019-07-16 | 2022-04-01 | 脑玺(上海)智能科技有限公司 | Blood supply area quantification method and system based on blood vessel enhanced radiography |
| CN110517780A (en)* | 2019-09-02 | 2019-11-29 | 强联智创(北京)科技有限公司 | A kind of aneurysm rupture methods of risk assessment and system |
| CN110534193A (en)* | 2019-09-02 | 2019-12-03 | 强联智创(北京)科技有限公司 | A kind of aneurysm rupture methods of risk assessment and system |
| CN110739078B (en)* | 2019-09-02 | 2024-03-26 | 北京市神经外科研究所 | Aneurysm rupture risk assessment method and system |
| CN110706808A (en)* | 2019-09-12 | 2020-01-17 | 北京深睿博联科技有限责任公司 | Aneurysm rupture state prediction method and device |
| CN114340498A (en)* | 2019-10-30 | 2022-04-12 | 未艾医疗技术(深圳)有限公司 | Aneurysm Ai processing method and product based on VRDS 4D medical image |
| CN110742689B (en)* | 2019-10-31 | 2021-11-23 | 北京理工大学 | Method and device for evaluating arterial dissection operation, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN110782988B (en)* | 2019-11-04 | 2022-11-01 | 北京理工大学 | Intracranial aneurysm virtual support simulation method |
| CN110866914B (en)* | 2019-11-21 | 2023-10-03 | 北京冠生云医疗技术有限公司 | Evaluation method, system, equipment and medium for cerebral aneurysm hemodynamic index |
| CN111081378B (en)* | 2019-11-22 | 2022-05-20 | 强联智创(北京)科技有限公司 | Aneurysm rupture risk assessment method and system |
| CN110974415B (en)* | 2019-12-19 | 2020-10-30 | 向欣 | A method for establishing aneurysm morphological database based on three-dimensional angiography of aneurysm volume |
| CN111462047B (en)* | 2020-03-06 | 2024-03-12 | 深圳睿心智能医疗科技有限公司 | Vascular parameter measurement method, vascular parameter measurement device, vascular parameter measurement computer device and vascular parameter measurement storage medium |
| CN111584076A (en)* | 2020-04-08 | 2020-08-25 | 北京市神经外科研究所 | Aneurysm rupture risk assessment method and system |
| CN111584077A (en)* | 2020-04-08 | 2020-08-25 | 北京市神经外科研究所 | A kind of aneurysm rupture risk assessment method and system |
| CN111671556A (en)* | 2020-04-14 | 2020-09-18 | 北京市神经外科研究所 | Aneurysm stent and method of construction thereof |
| CN113887146B (en)* | 2020-07-02 | 2025-02-11 | 复旦大学附属华山医院 | An automated cerebral aneurysm rupture risk analysis system based on cerebral hemodynamics |
| CN112365473A (en)* | 2020-11-12 | 2021-02-12 | 同心医联科技(北京)有限公司 | AI medical image processing system, equipment and storage medium |
| CN112617770A (en)* | 2020-12-28 | 2021-04-09 | 首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院 | Intracranial aneurysm risk prediction method based on artificial intelligence and related device |
| CN112826457A (en)* | 2020-12-31 | 2021-05-25 | 苏州爱琴生物医疗电子有限公司 | Brain-based sign information detection device and method and related equipment |
| CN113143458A (en)* | 2021-03-15 | 2021-07-23 | 北京理工大学 | Method and device for evaluating aortic dissection distal laceration occlusion treatment scheme |
| CN113077435B (en)* | 2021-03-30 | 2025-02-18 | 昆明同心医联科技有限公司 | Aneurysm analysis method and device based on hemodynamics |
| CN113143306B (en)* | 2021-03-31 | 2023-01-24 | 广东医科大学附属医院 | Be used for intracranial aneurysm CFD diagnosis visual equipment |
| CN113192004B (en)* | 2021-04-01 | 2022-01-18 | 温州医科大学附属第二医院(温州医科大学附属育英儿童医院) | Simplified calculation method based on coronary artery multimode image crack formation and expansion and plaque rupture risk quantitative evaluation system |
| CN113133827B (en)* | 2021-04-07 | 2022-08-05 | 昆明同心医联科技有限公司 | Preoperative prediction method, system, terminal and medium for intracranial aneurysm operation |
| CN114121262A (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2022-03-01 | 北京市神经外科研究所 | A model and method for evaluating the stability of intracranial aneurysm based on machine learning |
| CN114145843B (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2023-07-04 | 北京市神经外科研究所 | Novel intracranial aneurysm weak area assessment method |
| CN114287954A (en)* | 2021-12-13 | 2022-04-08 | 杭州脉流科技有限公司 | Methods, systems, electronic devices and media for functional assessment of intracranial vascular stenosis |
| CN114299021B (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2024-08-16 | 北京理工大学 | Aneurysm region positioning method of tumor-carrying blood vessel |
| CN114972165B (en)* | 2022-03-24 | 2024-03-15 | 中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院 | A method and device for measuring time-averaged shear force |
| CN115546123B (en)* | 2022-09-20 | 2025-07-08 | 同心智医科技(北京)股份有限公司 | Prediction system of abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture risk based on machine learning |
| CN116485800B (en)* | 2023-06-26 | 2023-09-08 | 杭州脉流科技有限公司 | Automatic acquisition method, device, equipment and storage medium for morphological parameters of aneurysms |
| CN116919374B (en)* | 2023-07-19 | 2024-04-12 | 西安交通大学 | Intracranial aneurysm and method and system for evaluating blood flow dynamics parameters in aneurysm-carrying artery |
| CN117438092B (en)* | 2023-12-20 | 2024-03-22 | 杭州脉流科技有限公司 | Intracranial aneurysm rupture risk prediction device, computer device, and storage medium |
| CN120236770B (en)* | 2025-05-26 | 2025-07-25 | 杭州脉流科技有限公司 | Intracranial aneurysm rupture risk assessment method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7986822B2 (en)* | 2006-04-24 | 2011-07-26 | Siemens Medical Solutions Usa, Inc. | System and method for X-ray based assessment of aneurysm pulsation |
| US8170304B2 (en)* | 2007-04-03 | 2012-05-01 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Modeling cerebral aneurysms in medical images |
| US8315812B2 (en)* | 2010-08-12 | 2012-11-20 | Heartflow, Inc. | Method and system for patient-specific modeling of blood flow |
| US9220418B2 (en)* | 2013-12-18 | 2015-12-29 | Heartflow, Inc. | Systems and methods for predicting coronary plaque vulnerability from patient-specific anatomic image data |
| CN105096388B (en)* | 2014-04-23 | 2019-02-05 | 北京冠生云医疗技术有限公司 | Coronary flow analogue system and method based on Fluid Mechanics Computation |
| CN106127819B (en)* | 2016-06-30 | 2019-10-08 | 上海联影医疗科技有限公司 | The method and device thereof of vessel centerline are extracted in medical image |
| US10402976B2 (en)* | 2017-05-16 | 2019-09-03 | Siemens Healthcare Gmbh | Isolation of aneurysm and parent vessel in volumetric image data |
| EP3404667B1 (en)* | 2017-05-19 | 2024-02-28 | Siemens Healthineers AG | Learning based methods for personalized assessment, long-term prediction and management of atherosclerosis |
| IT201700059572A1 (en)* | 2017-05-31 | 2018-12-01 | Fond Ri Med | METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF THE RISK OF AN ANEURISM OF THE ASCENDING THORACIC AORTA |
| JP6487001B2 (en)* | 2017-08-23 | 2019-03-20 | キヤノンメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Aneurysm rupture risk analysis program and system |
| CN108133478B (en)* | 2018-01-11 | 2021-11-23 | 苏州润迈德医疗科技有限公司 | Method for extracting coronary artery blood vessel central line |
| CN109493348B (en)* | 2018-10-26 | 2021-11-26 | 强联智创(北京)科技有限公司 | Method and system for measuring morphological parameters of intracranial aneurysm image |
| CN109584997B (en)* | 2018-10-26 | 2023-07-25 | 首都医科大学宣武医院 | Method and system for measuring morphological parameters of intracranial aneurysm image |
| CN109961850A (en)* | 2019-03-19 | 2019-07-02 | 肖仁德 | A kind of method, apparatus, computer equipment for assessing rupture of intracranial aneurysm risk |
- 2019
- 2019-04-09CNCN201910280012.7Apatent/CN109907732B/enactiveActive
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 颅内动脉瘤破裂的血流动力学和形态学因素;江国权等;《介入放射学杂志》;20141225(第12期);全文* |
| 颅内动脉瘤破裂风险和动脉瘤形态学参数的关系;刘超博等;《中国临床神经外科杂志》;20180225(第02期);全文* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN109907732A (en) | 2019-06-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109907732B (en) | A method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture | |
| CN109924956B (en) | Method and device for measuring morphological parameters of intracranial aneurysm images | |
| US11583187B2 (en) | Method and system for monitoring a condition of cerebral aneurysms | |
| CN108261176B (en) | Fetal heart monitoring data processing method, device, system, storage medium and computer equipment | |
| EP3457413B1 (en) | Method for classifying a risk for thrombus formation in an organ, system for classifying a risk for thrombus formation in an organ, a computer program product and a computer readable medium | |
| WO2017047819A1 (en) | Blood vessel shape analysis device, method for same, and computer software program for same | |
| CN109635669B (en) | Image classification method and device and classification model training method and device | |
| CN113313715B (en) | Method, device, apparatus and medium for segmenting cardiac artery blood vessel | |
| US20170323587A1 (en) | Blood-vessel-shape construction device for blood-flow simulation, method therefor, and computer software program | |
| CN110522449B (en) | Plaque parting method and device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| KR20230052967A (en) | Method and apparatus for determining imaging quality control of fetal ultrasound images | |
| CN117373070B (en) | Method and device for labeling blood vessel segments, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| EP4225146B1 (en) | Aortic aneurysm growth rate prediction from geometric analysis | |
| CN114096993A (en) | Image segmentation confidence determination | |
| WO2021190656A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for localizing center of macula in fundus image, server, and storage medium | |
| Nouri et al. | Characterization of 3D bifurcations in micro-scan and MRA-TOF images of cerebral vasculature for prediction of intra-cranial aneurysms | |
| CN112434807B (en) | Deep learning model performance verification method and device based on fundus images | |
| Kohout et al. | Aneurysm identification by analysis of the blood-vessel skeleton | |
| CN117635635A (en) | Interactive segmentation method and device for medical image, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| KR102796118B1 (en) | Device and method for detecting lesions of disease related to body component that conveyes fluid from medical image | |
| CN113506270B (en) | Method, system and storage medium for processing inferior vena cava image | |
| US20230015122A1 (en) | Aortic stenosis classification | |
| KR102000615B1 (en) | A method for automatically extracting a starting point of coronary arteries, and an apparatus thereof | |
| CN118824520A (en) | A risk assessment method for arterial cone evolution based on GBDT decision tree | |
| CN120105319B (en) | Quality control methods, devices, computer equipment and media for pulmonary function test reports |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20230113 Address after:1301, Floor 13, Building 3, Block 2, Heyang Plaza, No. 13, Changjiang Road, Guicheng Street, Nanhai District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province, 528000 Patentee after:Weizhi medical technology (Foshan) Co.,Ltd. Address before:510000 room 3025, No. 95, Jinling North Road, Nansha street, Nansha District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province Patentee before:GUANGZHOU XINMAI TECHNOLOGY Co.,Ltd. | |
| PE01 | Entry into force of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | ||
| PE01 | Entry into force of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | Denomination of invention:A method and system for assessing the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture Granted publication date:20221202 Pledgee:Shenyang Aimu Trading Co.,Ltd. Pledgor:GUANGDONG WEIREN MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY Co.,Ltd.|Weiren medical (Foshan) Co.,Ltd.|Weizhi medical technology (Foshan) Co.,Ltd. Registration number:Y2024980047105 |