CN109237677B - Heat collection-radiation device and refrigerating system thereof - Google Patents
Heat collection-radiation device and refrigerating system thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN109237677B CN109237677BCN201811130130.1ACN201811130130ACN109237677BCN 109237677 BCN109237677 BCN 109237677BCN 201811130130 ACN201811130130 ACN 201811130130ACN 109237677 BCN109237677 BCN 109237677B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- heat
- radiation
- radiating
- collecting
- solution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription76
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription73
- 230000005855radiationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription70
- 238000005057refrigerationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription54
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription14
- 238000010438heat treatmentMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000claimsdescription39
- 239000006096absorbing agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription15
- 239000003507refrigerantSubstances0.000claimsdescription15
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000002834transmittanceMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000006193liquid solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 229920002799BoPETPolymers0.000claims1
- 239000005041Mylar™Substances0.000claims1
- 239000004809TeflonSubstances0.000claims1
- 229920006362Teflon®Polymers0.000claims1
- 238000005187foamingMethods0.000claims1
- 238000005265energy consumptionMethods0.000abstractdescription15
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription13
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description12
- 229920001343polytetrafluoroethylenePolymers0.000description8
- 239000004810polytetrafluoroethyleneSubstances0.000description8
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-NCopperChemical compound[Cu]RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 229910052802copperInorganic materials0.000description6
- 239000010949copperSubstances0.000description6
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-NaluminiumChemical compound[Al]XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description5
- 229910052782aluminiumInorganic materials0.000description5
- 239000011888foilSubstances0.000description5
- 238000002955isolationMethods0.000description5
- 238000004378air conditioningMethods0.000description4
- -1polytetrafluoroethylenePolymers0.000description4
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-NEtheneChemical compoundC=CVGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 229920001684low density polyethylenePolymers0.000description3
- 239000004702low-density polyethyleneSubstances0.000description3
- 230000005499meniscusEffects0.000description3
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description3
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description3
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbon dioxideChemical compoundO=C=OCURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000002745absorbentEffects0.000description2
- 239000002250absorbentSubstances0.000description2
- 238000009835boilingMethods0.000description2
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description2
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 230000002708enhancing effectEffects0.000description2
- AMXOYNBUYSYVKV-UHFFFAOYSA-Mlithium bromideChemical compound[Li+].[Br-]AMXOYNBUYSYVKV-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- 229920006267polyester filmPolymers0.000description2
- 238000002310reflectometryMethods0.000description2
- 230000003595spectral effectEffects0.000description2
- CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-NOzoneChemical compound[O-][O+]=OCBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229920005830Polyurethane FoamPolymers0.000description1
- 239000000853adhesiveSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001070adhesive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description1
- 230000036760body temperatureEffects0.000description1
- 229910002092carbon dioxideInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000001569carbon dioxideSubstances0.000description1
- JJWKPURADFRFRB-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncarbonyl sulfideChemical compoundO=C=SJJWKPURADFRFRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000000295complement effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000012141concentrateSubstances0.000description1
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description1
- 238000005485electric heatingMethods0.000description1
- 239000003822epoxy resinSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012530fluidSubstances0.000description1
- 239000004519greaseSubstances0.000description1
- 238000009413insulationMethods0.000description1
- 229920000647polyepoxidePolymers0.000description1
- 229920001296polysiloxanePolymers0.000description1
- 239000011496polyurethane foamSubstances0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 230000001932seasonal effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000005437stratosphereSubstances0.000description1
- 230000005514two-phase flowEffects0.000description1
- 238000009834vaporizationMethods0.000description1
- 230000008016vaporizationEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F5/00—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater
- F24F5/0007—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater cooling apparatus specially adapted for use in air-conditioning
- F24F5/0014—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater cooling apparatus specially adapted for use in air-conditioning using absorption or desorption
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F13/00—Details common to, or for air-conditioning, air-humidification, ventilation or use of air currents for screening
- F24F13/30—Arrangement or mounting of heat-exchangers
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F5/00—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater
- F24F5/0046—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater using natural energy, e.g. solar energy, energy from the ground
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F5/00—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater
- F24F5/0046—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater using natural energy, e.g. solar energy, energy from the ground
- F24F2005/0064—Air-conditioning systems or apparatus not covered by F24F1/00 or F24F3/00, e.g. using solar heat or combined with household units such as an oven or water heater using natural energy, e.g. solar energy, energy from the ground using solar energy
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Sorption Type Refrigeration Machines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于可再生能源与空调技术领域,更具体地,涉及一种集热-辐射装置及其制冷系统。The invention belongs to the technical field of renewable energy and air conditioning, and more particularly, relates to a heat collecting-radiation device and a refrigeration system thereof.
背景技术Background technique
目前,大力发展新能源和可再生能源是我国当今和未来发展的主要目标,在我国的社会总能耗中,建筑能耗约占1/3,而建筑能耗中的空调能耗高达42%,那么,空调能耗占我国总能耗的14%。因此,空调系统的节能性研究就有着十分重要的经济效益和社会意义。At present, vigorously developing new energy and renewable energy is the main goal of my country's current and future development. In my country's total social energy consumption, building energy consumption accounts for about 1/3, and air conditioning energy consumption in building energy consumption is as high as 42%. , then, air-conditioning energy consumption accounts for 14% of my country's total energy consumption. Therefore, the research on energy saving of air-conditioning system has very important economic and social significance.
广袤的太空中蕴含着无限的能量,太阳是一个温度高达5800k的热源,而宇宙空间则是一个温度只有3K的完美冷源,地球的均温为300K,处于两者之间。太阳每时每刻都在加热着地球,而地球也在向外太空散热;如果能够将两种能源合理利用,可大幅度降低空调能耗。如今太阳能制冷技术发展已经相对成熟,其最大的优点在于季节适应性好:一方面,夏季天气炎热,人们对制冷量要求更高;另一方面,夏季太阳辐射强度大,利用太阳能驱动制冷机可以产生更多的冷量。这正好与夏季人们对空调的需求相匹配。一般太阳能制冷技术是利用太阳能集热器产生热水,产生的热水用来驱动吸收式制冷机工作,它具有对大气无污染、无运动部件、运转安静等优点。但是却存在太阳能夜间无法使用的问题。The vast space contains infinite energy. The sun is a heat source with a temperature of 5800K, while the cosmic space is a perfect cold source with a temperature of only 3K. The average temperature of the earth is 300K, which is in between. The sun is heating the earth all the time, and the earth is also dissipating heat from outer space; if the two energy sources can be used reasonably, the energy consumption of air conditioners can be greatly reduced. Today, the development of solar refrigeration technology is relatively mature, and its biggest advantage lies in its good seasonal adaptability: on the one hand, the weather is hot in summer, and people have higher requirements for cooling capacity; produce more cooling. This just matches the demand for air conditioners in summer. The general solar refrigeration technology uses solar collectors to generate hot water, which is used to drive the absorption refrigerator to work. It has the advantages of no pollution to the atmosphere, no moving parts, and quiet operation. However, there is a problem that solar energy cannot be used at night.
虽然宇宙空间的温度接近绝对零度,大气层的存在却阻碍了地面物体向它直接散热,但在8~13μm波段内,大气层中水蒸汽、二氧化碳和臭氧对辐射的吸收能力很弱,因此,大气在这个波段的透明度很高,通常这个波段称为“大气窗口”,地球上物体在常温下发出的红外辐射,恰好能透过“大气窗口”辐射到外太空,因此可以寻找一种材料作为辐射体,其在8~13μm波段的发射率接近1,而在其余波段的反射率接近1,则物体在常温下发出的辐射将透过大气层辐射到外太空,而来自外界的辐射将被反射掉,从而把物体表面降到比环境更低的温度。虽然太空辐射制冷可以在不消耗能源或者消耗少量能源的条件下,将热量辐射到外太空,从而达到制冷的目的,但是由于选择性辐射材料不够理想,在白天会吸收较多的太阳辐射能量,导致太空辐射制冷白天效果不佳。Although the temperature of the universe is close to absolute zero, the existence of the atmosphere prevents the ground objects from directly dissipating heat to it. However, in the 8-13 μm band, the absorption capacity of water vapor, carbon dioxide and ozone in the atmosphere for radiation is very weak. The transparency of this band is very high. Usually this band is called the "atmospheric window". The infrared radiation emitted by objects on the earth at room temperature can just pass through the "atmospheric window" and radiate to outer space. Therefore, a material can be found as a radiator. , the emissivity in the 8-13μm band is close to 1, and the reflectivity in the other bands is close to 1, the radiation emitted by the object at room temperature will be radiated to outer space through the atmosphere, and the radiation from the outside will be reflected. This lowers the surface of the object to a lower temperature than the environment. Although space radiation cooling can radiate heat to outer space without consuming energy or consume a small amount of energy, so as to achieve the purpose of cooling, but because the selective radiation material is not ideal, it will absorb more solar radiation energy during the day. As a result, the effect of space radiative cooling during the day is not good.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对现有技术的以上缺陷或改进需求,本发明提供了一种集热-辐射装置及其制冷系统,其中通过对集热-辐射装置的关键组件集热部分和辐射热部分的结构设计和布局,以及通过与辅助组件制冷装置的配合连接,一方面充分利用集热辐射装置在太阳光充足的时候吸收太阳光的能量,从而驱动吸收式制冷装置制冷,另一方面,考虑到夜间太阳光不充足的情况,巧妙地利用选择性辐射薄膜向外太空发射电磁波辐射热量的原理降低集热-辐射装置中冷却管中液态介质的温度,从而相互弥补了夜间无法利用太阳光和白天太空辐射制冷效果差的缺陷,实现近零能耗的制冷过程,由此解决制冷系统能耗高和效果差的技术问题。In view of the above defects or improvement needs of the prior art, the present invention provides a heat collection-radiation device and a refrigeration system thereof, wherein through the structural design and layout of the heat collection part and the radiant heat part of the key components of the heat collection and radiation device , and through the cooperative connection with the auxiliary component refrigeration device, on the one hand, the heat collecting and radiating device fully utilizes the energy absorbed by the solar radiation when the sunlight is sufficient, thereby driving the absorption refrigeration device for refrigeration. In sufficient circumstances, the principle of selective radiation film emitting electromagnetic wave radiation heat to outer space is cleverly used to reduce the temperature of the liquid medium in the cooling pipe in the heat collector-radiation device, thereby compensating for the inability to use sunlight at night and the cooling effect of space radiation during the day. It can realize the refrigeration process with nearly zero energy consumption, thereby solving the technical problems of high energy consumption and poor effect of the refrigeration system.
为实现上述目的,按照本发明的一个方面,提供了一种集热-辐射装置,该装置包括支架和集热-辐射单元,其特征在于,In order to achieve the above object, according to an aspect of the present invention, a heat collection-radiation device is provided, the device includes a support and a heat collection-radiation unit, and is characterized in that:
所述支架与集热-辐射单元连接,用于支撑该集热-辐射单元;所述集热-辐射单元呈瓦片状,包括集热部分和辐射热部分,其绕支架与所述集热辐射单元的连接点旋转,当所述集热部分面向太阳光时,所述集热部分工作,当所述集热部分背向太阳光使得所述辐射热部分向上时,所述辐射热部分工作;The bracket is connected to the heat collection-radiation unit for supporting the heat collection-radiation unit; the heat collection-radiation unit is in the shape of a tile, including a heat collection part and a radiant heat part, which surround the bracket and the heat collection The connection point of the radiation unit rotates, when the heat collecting part faces the sunlight, the heat collecting part works, and when the heat collecting part faces away from the sunlight so that the radiant heat part is upward, the radiant heat part works ;
所述集热部分包括瓦片状的反光镜和设置在该反光镜焦点处的集热管,所述反光镜反射太阳光热量并将热量聚集在所述集热管上,以此使得所述集热管中的液体介质被加热;所述辐射热部分设置在所述集热部分的背面,包括冷却管和选择性辐射薄膜,所述冷却管设置在所述反光镜的背面,所述选择性辐射薄膜贴附在所述冷却管的表面,吸收该冷却管中液体介质的热量,然后发射频率为8μm~13μm波段的电磁波,该波段的电磁波穿透大气窗口向外太空辐射热量,从而降低所述冷却管中的液体介质的温度。The heat collecting part includes a tile-shaped reflector and a heat collector tube arranged at the focal point of the reflector, the reflector reflects sunlight heat and collects the heat on the heat collector tube, so that the heat collector tube is The liquid medium in the radiator is heated; the radiant heat part is arranged on the back of the heat collecting part, including a cooling pipe and a selective radiation film, the cooling pipe is arranged on the back of the reflector, and the selective radiation film It is attached to the surface of the cooling pipe, absorbs the heat of the liquid medium in the cooling pipe, and then emits electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 8 μm to 13 μm, which penetrate the atmospheric window and radiate heat to outer space, thereby reducing the cooling effect. The temperature of the liquid medium in the tube.
进一步优选地,所述辐射热部分还包括设置在所述冷却管和选择性辐射薄膜之间的反光导热膜,一方面用于反射外界的电磁波避免外界向冷却管传导热量,另一方面通过包覆在所述冷却管的外部增加所述冷却管与选择性辐射薄膜之间的接触面积,从而增强所述冷却管与选择性辐射薄膜之间的导热。Further preferably, the radiant heat part also includes a light-reflecting heat-conducting film arranged between the cooling pipe and the selective radiation film. Coating the outside of the cooling pipe increases the contact area between the cooling pipe and the selective radiation film, thereby enhancing the heat conduction between the cooling pipe and the selective radiation film.
进一步优选地,所述辐射热部分还包括设置在选择性辐射薄膜上方的全透性隔离薄膜,一方面对全波段有很高的辐射透过率,另一方面用于将辐射热部分隔离空气,减少空气与选择性辐射薄膜之间的对流换热。Further preferably, the radiant heat part also includes a fully transparent isolation film arranged above the selective radiation film, on the one hand, it has a high radiation transmittance for the whole waveband, and on the other hand, it is used to isolate the radiant heat part from air. , reducing the convective heat transfer between the air and the selective radiation film.
进一步优选地,所述选择性辐射薄膜优选采用聚四氟乙烯薄膜或聚酯薄膜。Further preferably, the selective radiation film is preferably a polytetrafluoroethylene film or a polyester film.
进一步优选地,相邻的所述冷却管之间的间隙,所述冷却管和反光镜之间的间隙中填充有发泡材料,用于保持冷却管的温度。Further preferably, the gap between the adjacent cooling tubes, the gap between the cooling tube and the reflector, is filled with foamed material for maintaining the temperature of the cooling tubes.
按照本发明的另一方面,提供了一种制冷系统,包括上述的所述集热-辐射装置,以及分别与该集热-辐射装置两端连接的吸收式制冷装置和冷水箱,其特征在于,According to another aspect of the present invention, a refrigeration system is provided, comprising the above-mentioned heat collection-radiation device, an absorption refrigeration device and a cold water tank respectively connected to both ends of the heat collection-radiation device, characterized in that ,
白天时,所述集热-辐射装置通过反射太阳光热量加热集热管中的液体介质,被加热后的所述液态介质循环流入所述制冷装置中不断与该制冷装置中的工质进行热交换,从而驱动制冷装置,该吸收式制冷装置制冷并获得冷却的水,该冷却后的水流向所述冷水箱中,通过该冷水箱与外界的热交换降低外界的温度,以此实现制冷过程;During the day, the heat collection-radiation device heats the liquid medium in the heat collection tube by reflecting the heat of sunlight, and the heated liquid medium circulates into the refrigeration device to continuously exchange heat with the working medium in the refrigeration device. , thereby driving the refrigeration device, the absorption refrigeration device refrigerates and obtains cooled water, the cooled water flows into the cold water tank, and the temperature of the outside is reduced through the heat exchange between the cold water tank and the outside world, so as to realize the refrigeration process;
夜间时,所述集热-辐射装置断开与制冷装置的连接,而通过所述冷却管与冷水箱连接,所述集热-辐射装置中的辐射部分向外太空辐射热量降低所述冷却管中液态介质的温度从而降低所述冷水箱中水的温度,该冷水箱与外界进行热交换降低外界温度,以此实现制冷过程。At night, the heat collection-radiation device is disconnected from the refrigeration device, and is connected to the cold water tank through the cooling pipe. The radiation part of the heat collection-radiation device radiates heat to outer space to reduce the cooling pipe. The temperature of the liquid medium in the cold water tank can be lowered to reduce the temperature of the water in the cold water tank, and the cold water tank can exchange heat with the outside to reduce the outside temperature, thereby realizing the refrigeration process.
进一步优选地,所述吸收式制冷装置包括气液分离器、冷凝器、布液板、吸收器、蒸发器、U形管、储液桶、溶液热交换器、溶液加热套筒和弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管,Further preferably, the absorption refrigeration device includes a gas-liquid separator, a condenser, a liquid distribution plate, an absorber, an evaporator, a U-shaped pipe, a liquid storage tank, a solution heat exchanger, a solution heating sleeve and a meniscus channel Thermosiphon solution riser,
所述集热-辐射装置与所述溶液加热套筒和所述弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管相连,被加热的所述液态介质进入所述溶液加热套筒和所述弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管中后,所述弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管中的工质温度升高沸腾,并进入所述气液分离器中,所述气液分离器用于将所述工质分为蒸汽和液态溶液,其中,The heat collection-radiation device is connected with the solution heating sleeve and the crescent-shaped channel thermosiphon solution riser, and the heated liquid medium enters the solution heating sleeve and the crescent-shaped channel heat. After siphoning the solution in the riser, the temperature of the working medium in the thermosiphon solution riser of the crescent-shaped channel increases and boils, and enters the gas-liquid separator, which is used to separate the working medium. are vapor and liquid solutions, where,
所述蒸汽进入所述冷凝器中,并依次经过所述U形管、布液板和蒸发器中形成冷剂水,该蒸发器与所述冷水箱连接,所述蒸发器中的冷剂水与所述冷水箱中的水进行热交换,一方面降低所述冷水箱中水的温度实现制冷过程,另一方面在所述蒸发器中的吸收热量形成水蒸汽进入所述吸收器中;The steam enters the condenser, and sequentially passes through the U-shaped pipe, the liquid distribution plate and the evaporator to form refrigerant water, the evaporator is connected to the cold water tank, and the refrigerant water in the evaporator Carry out heat exchange with the water in the cold water tank, on the one hand reduce the temperature of the water in the cold water tank to realize the refrigeration process, and on the other hand absorb heat in the evaporator to form water vapor into the absorber;
所述液态溶液经过所述溶液交换器进入所述吸收器,其吸收所述吸收器中的水蒸汽后从所述吸收器流出,经所述溶液交换器后回到所述弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管中。The liquid solution enters the absorber through the solution exchanger, absorbs the water vapor in the absorber and flows out from the absorber, and returns to the crescent-shaped channel after passing through the solution exchanger. Siphon the solution into the riser.
进一步优选地,所述弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管包括内管和外管,内管和外管之间形成弦月形通道,所述集热管中被加热的所述液态介质流入溶液加热套筒和溶液提升管内管中,将热量传递给所述弦月形通道中的工质。Further preferably, the meniscus channel thermosiphon solution riser includes an inner tube and an outer tube, a meniscus channel is formed between the inner tube and the outer tube, and the heated liquid medium in the heat collecting tube flows into the solution for heating. In the inner tube of the sleeve and the solution riser, heat is transferred to the working medium in the crescent-shaped channel.
总体而言,通过本发明所构思的以上技术方案与现有技术相比,能够取得下列有益效果:In general, compared with the prior art, the above technical solutions conceived by the present invention can achieve the following beneficial effects:
1、本发明将太阳能和太空冷源优势互补,用太空辐射制冷解决了太阳能夜间无法使用的问题,用太阳能吸收式制冷弥补太空辐射制冷白天效果差的不足,从而保证了全天候互补制冷;1. The present invention complements the advantages of solar energy and space cold sources, solves the problem that solar energy cannot be used at night by using space radiation refrigeration, and uses solar energy absorption refrigeration to make up for the lack of space radiation refrigeration in the daytime, thereby ensuring all-weather complementary refrigeration;
2、本发明中集热-辐射装置中的集热部分,除了在夏天起制冷作用,在不需要冷气的冬天,可以作为太阳能热水器进行供暖,提供热水;2. The heat collecting part in the heat collecting-radiation device of the present invention can be used as a solar water heater for heating and providing hot water in winter when cold air is not required, in addition to cooling in summer;
3、本发明采用的两种制冷方式均为被动制冷方式,并且采用弦月型通道热虹吸提升管代替机械泵获得吸收式制冷系统流动压头,进一步降低能耗,从而实现了近零能耗制冷效果;3. The two refrigeration methods adopted in the present invention are both passive refrigeration methods, and a crescent-shaped channel thermosiphon riser is used instead of a mechanical pump to obtain the flow head of the absorption refrigeration system, further reducing energy consumption, thereby achieving near zero energy consumption cooling effect;
4、本发明中利用的能量来自于自然界中的太阳能和太空超低温冷源,能耗极低,可以大幅的降低空调能耗,并且以水为制冷工质,清洁无污染,该系统可广泛应用于居民楼、学校、办公大楼、医院、机场等建筑,尤其适合在日照充足的炎热干燥地区使用,在阴雨天可以用电加热丝辅助;4. The energy used in the present invention comes from the solar energy in nature and the ultra-low temperature cold source in space, and the energy consumption is extremely low, which can greatly reduce the energy consumption of the air conditioner, and the water is used as the refrigerant, which is clean and pollution-free, and the system can be widely used It is suitable for residential buildings, schools, office buildings, hospitals, airports and other buildings, especially suitable for use in hot and dry areas with sufficient sunshine, and electric heating wires can be used to assist in cloudy and rainy days;
5、本发明中提供的集热-辐射装置和制冷系统兼容性强,改装成本低,该装置可与传统空调和空气能空调兼容使用,不需要很大的改装费用,之前的空调也可以作为辅助制冷继续使用,在冬季,本系统一天内产生的热水可以满足一个普通家庭冬季的热水需求,填补了制冷的“空档期”。5. The heat collector-radiation device provided in the present invention has strong compatibility with the refrigeration system, and the modification cost is low. The device can be compatible with traditional air conditioners and air energy air conditioners, and does not require a large modification cost. The previous air conditioners can also be used as Auxiliary refrigeration continues to be used. In winter, the hot water produced by this system in one day can meet the hot water demand of an ordinary family in winter, filling the "vacant period" of refrigeration.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的集热-辐射单元的结构示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a heat collection-radiation unit constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图2是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的集热-辐射装置的结构示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a heat collection-radiation device constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图3是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的大气光谱透射曲线;Fig. 3 is the atmospheric spectral transmission curve constructed according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图4是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的选择性辐射体的辐射制冷示意图;Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of radiation cooling of a selective radiator constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图5是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的理想辐射体的能量示意图;Fig. 5 is the energy schematic diagram of the ideal radiator constructed according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图6是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的制冷系统的结构示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a refrigeration system constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图7是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管截面结构示意图。7 is a schematic cross-sectional structural diagram of a crescent-shaped channel thermosiphon solution riser constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
在所有附图中,相同的附图标记用来表示相同的元件或结构,其中:Throughout the drawings, the same reference numbers are used to refer to the same elements or structures, wherein:
1-集热-辐射装置 2-热水泵 3-气液分离器 4-冷凝器 5-布液板 6-吸收器 7-蒸发器 8-减压阀 9-U形管 10-贮液桶 11-溶液热交换器 12-溶液加热套筒 13-弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管 14-冷水箱 15-水泵 16-毛细管网辐射空调 17-冷水泵 18-全透性隔离薄膜 19-选择性辐射薄膜 20-反光导热膜 21-冷却管 22-反光镜 23-集热管 24-内管25-外管-26-弦月通道1-Heat collector-radiation device 2-Hot water pump 3-Gas-liquid separator 4-Condenser 5-Liquid distribution plate 6-Absorber 7-Evaporator 8-Reducing valve 9-U-shaped pipe 10-Liquid storage tank 11 -Solution heat exchanger 12-Solution heating sleeve 13-Crescent channel thermosiphon solution riser 14-Cold water tank 15-Water pump 16-Capillary network radiant air conditioner 17-Cold water pump 18-Permeable isolation membrane 19-Selective Radiation film 20 - Reflective heat conduction film 21 - Cooling tube 22 - Reflector 23 - Collector tube 24 - Inner tube 25 - Outer tube - 26 - Crescent channel
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。此外,下面所描述的本发明各个实施方式中所涉及到的技术特征只要彼此之间未构成冲突就可以相互组合。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below can be combined with each other as long as they do not conflict with each other.
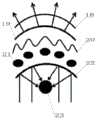
图1是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的集热辐射单元的结构示意图,FIG. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a heat collecting and radiating unit constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
图2是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的集热辐射装置的结构示意图,如图1和2所示,一种集热辐射装置,该装置包括支架和集热辐射单元,其特征在于,Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a heat collecting and radiating device constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Figs. 1 and 2, a heat collecting and radiating device includes a bracket and a heat collecting and radiating unit, characterized in that:
支架与集热辐射单元连接,用于支撑该集热辐射单元;集热辐射单元呈瓦片状,包括集热部分和辐射热部分,其绕支架与集热辐射单元的连接点旋转,当集热部分面向太阳光时,集热部分工作,当集热部分背向太阳光使得辐射热部分向上时,辐射热部分工作;The bracket is connected with the heat collecting and radiating unit for supporting the heat collecting and radiating unit; the heat collecting and radiating unit is in the shape of a tile, including a heat collecting part and a radiating heat part, and it rotates around the connection point between the bracket and the heat collecting and radiating unit. When the hot part faces the sunlight, the heat collecting part works, and when the heat collecting part faces away from the sunlight so that the radiant heat part is upward, the radiant heat part works;
集热部分包括瓦片状的反光镜22和设置在该反光镜焦点处的集热管23,反光镜22反射太阳光热量并将热量聚集在集热管23上,以此使得集热管中的液体介质被加热;The heat collecting part includes a tile-shaped
辐射热部分设置在集热部分的下方,包括冷却管21、选择性辐射薄膜19、全透性隔离薄膜18和反光导热膜20,冷却管21设置在反光镜22的背面,选择性辐射薄膜19贴附在冷却管21的表面,吸收该冷却管21中液体介质的热量,然后发射频率为8μm~13μm波段的电磁波,该波段的电磁波穿透大气窗口向外太空辐射热量,从而降低冷却管中的液体介质的温度;反光导热膜20设置在冷却管21和选择性辐射薄膜19之间,需采用反光性能好和延展性好的薄膜,一方面用于反射外界的电磁波避免外界向冷却管传导热量,另一方面通过包覆在冷却管的外部增加冷却管与选择性辐射薄膜之间的接触面积,从而增强所述冷却管与选择性辐射薄膜之间的导热;全透性隔离薄膜设置在选择性辐射薄膜上方,用于将辐射热部分隔离空气,减少空气与选择性辐射薄膜之间的对流换热;选择性辐射薄膜优选采用聚四氟乙烯薄膜或聚酯薄膜;相邻的冷却管之间的间隙中填充有发泡材料,用于保持冷却管的温度。The radiant heat part is arranged below the heat collecting part, including a
图3是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的大气光谱透射曲线,如图3所示,大气层对不同波长的辐射有不同的透过率,在透过率较高的区间,如8~13μm波段,该波段的电磁波可以较为自由地穿透大气层,气象学上把这些区间称为大气的“窗口”,太空辐射制冷正是基于“大气窗口”的现象,利用一种选择性辐射体通过辐射换热的方式,这种辐射体在8~13μm波段有非常高的发射率,而在其他波长段的辐射将全部反射,在不消耗或消耗少量能源的情况下,把热量辐射到外太空,从而达到制冷的目的。基于此原理,本发明提供的集热辐射装置,通过其中的选择性辐射薄膜发射8~13μm波段的电磁波将热量辐射到外太空,从而达到制冷目的。Fig. 3 is an atmospheric spectral transmittance curve constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 3, the atmosphere has different transmittances for radiation of different wavelengths. The electromagnetic wave in this band can penetrate the atmosphere relatively freely. In meteorology, these intervals are called "windows" of the atmosphere. Space radiative cooling is based on the phenomenon of "atmospheric windows", using a selective radiator to pass radiation In the way of heat exchange, this radiator has a very high emissivity in the 8-13μm band, while the radiation in other wavelength bands will be fully reflected, radiating heat to outer space without consuming or consuming a small amount of energy, So as to achieve the purpose of refrigeration. Based on this principle, the heat collection and radiation device provided by the present invention emits electromagnetic waves in the 8-13 μm band through the selective radiation film therein to radiate heat to outer space, thereby achieving the purpose of cooling.
图4是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的选择性辐射体的辐射制冷示意图,图5是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的理想辐射体的能量示意图,如图4和5所示,理想情况下,选择性辐射体不断向外太空辐射热量,而太阳辐射仅有一小部分能量被辐射体吸收,总的结果是辐射体辐射出去的热量大于吸收的能量,辐射体的温度不断降低,从而达到制冷的目的。太空辐射制冷能够在夜晚取得理想的制冷效果,但现阶段由于材料的限制(白天对太阳光的反射率做不到100%),即使辐射体材料对短波长的太阳光仅有0.1的吸收率,吸收的太阳辐射能量已经足以抵消大部分的辐射制冷量,故太空辐射制冷的效果在白天不够理想。基于此原有,本发明采用集热部分和辐射部分想结合,在白天利用太阳光的热量产生热量驱动制冷装置,从而降低温度达到制冷效果,而夜间利用太空辐射降低冷却管中的温度,从而达到制冷效果。Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of radiation cooling of a selective radiator constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of the energy of an ideal radiator constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, as shown in Figures 4 and 5, Ideally, the selective radiator continuously radiates heat to outer space, while only a small portion of the solar radiation is absorbed by the radiator. The overall result is that the heat radiated by the radiator is greater than the absorbed energy, and the temperature of the radiator continues to decrease So as to achieve the purpose of refrigeration. Space radiative cooling can achieve an ideal cooling effect at night, but at this stage due to material limitations (the reflectivity of sunlight cannot be 100% during the day), even if the radiator material has only a 0.1 absorption rate for short-wavelength sunlight , the absorbed solar radiation energy is enough to offset most of the radiation cooling capacity, so the effect of space radiation cooling is not ideal during the day. Based on this originality, the present invention adopts the combination of the heat collecting part and the radiating part, and uses the heat of sunlight to generate heat to drive the refrigeration device during the day, thereby reducing the temperature to achieve the cooling effect, and using space radiation to reduce the temperature in the cooling pipe at night, thereby reducing the temperature in the cooling pipe. achieve cooling effect.
在本发明的一个实施例中,集热管23采用真空管,冷却管21采用紫铜管,反光导热膜20采用铝箔,选择性辐射薄膜19采用聚四氟乙烯薄膜,全透性隔离薄膜18采用LDPE薄膜。In one embodiment of the present invention, the
集热辐射装置自凸面到凸凹面依次为LDPE薄膜、聚四氟乙烯薄膜、铝箔、紫铜管、槽式反光镜、真空管。其中,真空管位于槽式反光镜的焦点处;LDPE薄膜在8~13μm波段有很高的透射率,隔绝空气,减少空气与聚四氟乙烯薄膜对流换热;聚四氟乙烯薄膜在8~13μm波段有非常高的发射率,通过大气窗口向太空辐射热量;聚四氟乙烯薄膜与铝箔之间涂抹导热硅脂,增强导热,减小接触热阻;铝箔半包裹于铜管上,增强紫铜管与聚四氟乙烯薄膜的导热性能;铝箔与铜管之间涂抹环氧树脂导热胶固定,减少接触热阻;铜管下方采用聚氨酯发泡材料填充保温。From the convex surface to the convex and concave surface, the heat collecting and radiating device is LDPE film, polytetrafluoroethylene film, aluminum foil, copper tube, trough reflector, and vacuum tube. Among them, the vacuum tube is located at the focal point of the trough reflector; the LDPE film has a high transmittance in the 8-13 μm band, which isolates the air and reduces the convection heat transfer between the air and the PTFE film; the PTFE film is in the 8-13 μm band The band has a very high emissivity and radiates heat to space through the atmospheric window; thermally conductive silicone grease is applied between the PTFE film and the aluminum foil to enhance heat conduction and reduce contact thermal resistance; the aluminum foil is semi-wrapped on the copper tube to enhance the red copper The thermal conductivity of the tube and the PTFE film; the epoxy resin thermal adhesive is applied between the aluminum foil and the copper tube to fix it to reduce the contact thermal resistance; the underside of the copper tube is filled with polyurethane foam for insulation.
图6是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的制冷系统的结构示意图,如图6所示,一种采用集热辐射装置的制冷系统,包括集热辐射装置1、弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管13、气液分离器3、冷凝器4、溶液热交换器11、贮液桶10、U形管9、蒸发器7、吸收器6、冷水箱14和毛细管网辐射空调16。图7是按照本发明的优选实施例所构建的套管截面结构示意图,如图7所示,弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管13套在溶液加热套筒12之中。Figure 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a refrigeration system constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Figure 6, a refrigeration system using a heat collection and radiation device includes a heat collection and
集热辐射装置1凹面的集热管路经过热水泵后,分别与溶液加热套筒和弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管连通构成热源水回路。After the concave heat collecting pipeline of the heat collecting
弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管13、气液分离器3、溶液热交换器11、吸收器6、减压阀8构成吸收式制冷系统中吸收剂回路。The crescent-shaped channel
冷凝器4、U形管9与蒸发器7连通,构成制冷剂管路。The
集热辐射装置1凸面的冷却管路经过冷水泵与冷水箱相连,构成冷媒水回路。The cooling pipeline of the convex surface of the heat collecting and radiating
热源水回路、吸收剂回路、制冷剂管路构成白天工作的太阳能吸收式制冷系统;The heat source water circuit, the absorbent circuit and the refrigerant pipeline constitute a solar absorption refrigeration system that works during the day;
冷媒水回路构成夜间太空辐射制冷系统。The refrigerant water circuit constitutes a nighttime space radiative cooling system.
弦月形通道热虹吸溶液提升管13代替机械泵,降低系统能耗。The crescent-shaped channel
白天工作的太阳能吸收式制冷系统和夜间工作的太空辐射制冷系统共用同一个冷水箱,并且冷水箱与毛细管网辐射空调连通。The solar absorption refrigeration system that works during the day and the space radiant refrigeration system that works at night share the same cold water tank, and the cold water tank is connected with the capillary network radiant air conditioner.
本发明的制冷系统工作流程如下:在白天,集热-辐射装置1凹面向上,太阳光经集热-辐射装置凹面反射后聚焦到集热管23上。集热管23内的常温水,被加热到90℃左右后,分为两路经热水泵2分别从底部送入沿提升管全程加热的套筒12与弦月型通道提升管13内,用于由内而外同时加热通道内的LiBr稀溶液。在提升管通道13内,由于弦月型通道尖角处可自然形成强化溶液沸腾的汽化核心,稀溶液很容易被管外的热水连续加热至沸腾,形成两相流,然后靠贮液桶10与热虹吸管中流体密度不同产生的推动力提升到汽液分离器3,分离出来的蒸汽经隔板通道进入冷凝器4冷凝成冷剂水,而溶液部分浓度提高,形成浓溶液。冷剂循环中,冷剂水经过U型管9进入蒸发器6蒸发,浓溶液经过热交换器11后进入吸收器吸收蒸发的冷剂水,吸收后的稀溶液又进入贮液桶10,循环运行。在夜间,集热-辐射装置1自动翻转变为凸面工作,选择性辐射体可将冷却管21中冷媒水的热量通过大气窗口辐射到太空,从而产生温度较低的冷水。白天和夜晚两种模式共用同一套冷媒水系统,获得的冷水均用于室内的毛细管网辐射空调,为房间送去冷量。The working process of the refrigeration system of the present invention is as follows: During the day, the concave surface of the heat collecting-
另外,除制冷外,该系统还可在冬天通过槽的凹面汇聚太阳能,产生的热水可满足用户的部分热需求。In addition to cooling, the system can concentrate solar energy through the concave surface of the trough in winter, producing hot water that can meet part of the user's thermal needs.
白天工作的太阳能吸收式制冷系统和夜间工作的太空辐射制冷系统共用同一个冷水箱14,并且冷水箱14与毛细管网辐射空调16连通,通过冷水箱与毛细管网辐射空调16之间进行热交换,毛细管网辐射空调16与外界进行热交换,当冷水箱中的温度降低时,外界温度被降低,由此达到制冷效果。The solar absorption refrigeration system that works during the day and the space radiation refrigeration system that works at night share the same
下面将结合具体的参数进一步介绍本发明的实际应用效果。The practical application effect of the present invention will be further introduced below in conjunction with specific parameters.
白天制冷过程中,表1是集热辐射装置的部分结构的具体参数,表2是制冷装置中某个时刻测量的部分组件的不同参数值,根据表1和表2中参数值计算可得各换热设备热负荷以及各工作介质的流量,具体见表3。During the daytime cooling process, Table 1 shows the specific parameters of the partial structure of the heat collecting and radiating device, and Table 2 shows the different parameter values of some components measured at a certain time in the cooling device. The heat load of the heat exchange equipment and the flow rate of each working medium are shown in Table 3 for details.
表1集热辐射装置参数值Table 1 Parameter values of collector and radiation device
表2某个时刻部分组件的参数值表Table 2 Parameter value table of some components at a certain time
表3性能参数值Table 3 Performance parameter values
夜间制冷过程中,集热辐射装置的凸面结构使用材料及相关参数分别如表4和表5所示。During the nighttime cooling process, the materials and related parameters of the convex structure of the heat collecting and radiating device are shown in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively.
表4选择性辐射槽相关材料Table 4 Selective Radiation Slot Related Materials
表5选择性辐射槽相关参数Table 5 Selective Radiation Slot Related Parameters
计算夜晚制冷量时,设黑体温度为300K,太空温度为0K,根据斯蒂芬定律,可近似算出黑体单位面积的辐射功率,When calculating the cooling capacity at night, set the black body temperature as 300K and the space temperature as 0K. According to Stephen's law, the radiation power per unit area of the black body can be approximately calculated.
P总=αT4=5.67×108×3004W/m2=459.27W/m2Ptotal=αT4 =5.67×108 ×3004 W/m2 =459.27W /m2
由于选择性辐射体在8~13μm波长的发射率为1,其余波长的发射率为0,因此对此波段进行积分,可得:Since the emissivity of the selective radiator at the wavelength of 8 to 13 μm is 1, and the emissivity of the other wavelengths is 0, this band is integrated to obtain:
高层大气(平流层)的温度为220K,因此选择性辐射体吸收大气的辐射量为:The upper atmosphere (the stratosphere) has a temperature of 220K, so the amount of radiation absorbed by the selective radiator from the atmosphere is:
两者相减得到其净制冷量,Subtract the two to get the net cooling capacity,
P净=147.9W/m2-27.4W/m2=120.5W/m2Pnet = 147.9W/m2 -27.4W/m2 =120.5W/m2
即理想状态下夜间选择性辐射体单位面积制冷量为120.5W/m2。在考虑了各种冷损失之后,实验测得的制冷量为74.5W/m2,由此可见采用本发明提供的制冷系统制冷效果极好,且与理论计算的制冷量接近。That is, under ideal conditions, the cooling capacity per unit area of the selective radiator at night is 120.5W/m2 . After considering various cooling losses, the experimentally measured refrigerating capacity is 74.5W/m2 . It can be seen that the refrigeration system provided by the present invention has an excellent refrigerating effect and is close to the theoretically calculated refrigerating capacity.
本领域的技术人员容易理解,以上仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并不用以限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内所作的任何修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。Those skilled in the art can easily understand that the above are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent replacements and improvements made within the spirit and principles of the present invention should be Included in the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (8)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811130130.1ACN109237677B (en) | 2018-09-27 | 2018-09-27 | Heat collection-radiation device and refrigerating system thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811130130.1ACN109237677B (en) | 2018-09-27 | 2018-09-27 | Heat collection-radiation device and refrigerating system thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN109237677A CN109237677A (en) | 2019-01-18 |
| CN109237677Btrue CN109237677B (en) | 2020-06-30 |
Family
ID=65057008
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811130130.1AActiveCN109237677B (en) | 2018-09-27 | 2018-09-27 | Heat collection-radiation device and refrigerating system thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN109237677B (en) |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109714938A (en)* | 2019-02-28 | 2019-05-03 | 威海云山科技有限公司 | A kind of radiant heat transfer radiator |
| CN109945363B (en)* | 2019-03-21 | 2021-01-12 | 齐鲁工业大学 | Radiation refrigeration system with temperature adaptability and regulation and control method |
| CN110274397B (en)* | 2019-06-13 | 2020-09-11 | 河南五方合创建筑设计有限公司 | Cylindrical tile with refrigerating and heat collecting capabilities and solar tile roof system |
| CN110608548B (en)* | 2019-10-21 | 2024-04-23 | 浙江耀伏能源管理有限公司 | Flat plate type ground space radiation cooler with air flow passage |
| CN111811161B (en)* | 2020-07-13 | 2021-05-07 | 湖南大学 | A combined cold and heat collection and storage device and method based on advanced sky radiation |
| CN112097414A (en)* | 2020-09-10 | 2020-12-18 | 苏州融睿纳米复材科技有限公司 | Indoor radiation refrigeration assisting device |
| CN112361645B (en)* | 2020-11-05 | 2021-10-26 | 中国科学院广州能源研究所 | Solar energy utilization and radiation refrigeration combined system |
| CN112523303B (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2021-12-17 | 南京大学 | A new type of air water intake device and its application |
| CN112524721B (en)* | 2020-12-18 | 2022-02-08 | 南京工业大学 | Novel passive energy storage type air conditioning system |
| CN113587458B (en)* | 2021-06-16 | 2022-09-06 | 东南大学 | Device capable of simultaneously obtaining heat source from sun and cold source from deep space |
| CN113531921B (en)* | 2021-08-17 | 2025-05-27 | 苏州大学 | A reverse differential optical path optical thermal multiplexing device based on band division |
| CN113899109B (en)* | 2021-11-16 | 2023-02-07 | 南京索乐优节能科技有限公司 | Efficient integrated system for medium-temperature heating and sky radiation refrigeration by utilizing solar radiation |
| CN115264992B (en)* | 2022-05-27 | 2024-08-06 | 东南大学 | Heat collecting refrigerating plate capable of automatically adjusting heat radiation emission and receiving and heat flow rectifier |
| CN115264974B (en)* | 2022-08-08 | 2025-02-11 | 四川长虹空调有限公司 | A radiation refrigerator |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100494818C (en)* | 2003-04-15 | 2009-06-03 | 北京环能海臣科技有限公司 | A solar thermal energy lithium bromide absorption type central air-conditioning seawater desalination device |
| EP2169331A3 (en)* | 2008-09-30 | 2010-07-28 | Aeteba GmbH | Solar cooling unit |
| DE102009022059A1 (en)* | 2009-05-20 | 2010-11-25 | Schott Solar Ag | Radiation-selective absorber coating and absorber tube with radiation-selective absorber coating |
| CN102207344A (en)* | 2011-03-17 | 2011-10-05 | 王珏 | Bimirror focusing solar refrigeration device |
| CN103776196B (en)* | 2014-02-25 | 2016-03-30 | 中国科学技术大学 | A kind of solar energy heating and radiation refrigeration integrated application device |
| CN205174878U (en)* | 2015-11-03 | 2016-04-20 | 广东五星太阳能股份有限公司 | Composite parabolic concentrating radiator with daytime heat collection and nighttime radiative cooling |
| CN205070939U (en)* | 2015-11-03 | 2016-03-02 | 广东五星太阳能股份有限公司 | A flat-panel photovoltaic photothermal comprehensive utilization device with night-time radiation cooling function |
| AU2017225866B2 (en)* | 2016-02-29 | 2021-10-07 | The Regents Of The University Of Colorado, A Body Corporate | Radiative cooling structures and systems |
| CN205897607U (en)* | 2016-07-01 | 2017-01-18 | 中国科学技术大学 | Novel solar energy refrigerator |
| CN106524358B (en)* | 2016-12-07 | 2022-07-15 | 中国科学技术大学 | A comprehensive device for solar photovoltaic power generation and radiation cooling |
- 2018
- 2018-09-27CNCN201811130130.1Apatent/CN109237677B/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN109237677A (en) | 2019-01-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109237677B (en) | Heat collection-radiation device and refrigerating system thereof | |
| US4083490A (en) | Solar supplemental heating system | |
| CN210154106U (en) | A heat pipe photovoltaic photothermal system based on dual condensers | |
| CN111811161B (en) | A combined cold and heat collection and storage device and method based on advanced sky radiation | |
| JP6556691B2 (en) | Solar power system | |
| CN103486760B (en) | Solar heat collection-radiation refrigeration integration device | |
| CN204373270U (en) | PV air-conditioner Teat pump boiler | |
| CN103940020B (en) | Superconductive heat storage type solar air conditioner and achieving method thereof | |
| WO2021249576A1 (en) | Solar energy utilization and radiative cooling composite system | |
| CN114135954A (en) | Heat pipe heat exchange air conditioning system | |
| CN101929765A (en) | A kind of solar absorption refrigeration system of separate type | |
| CN202382476U (en) | Three-in-one solar air conditioning system | |
| CN103470460A (en) | Tank-surface-evaporation solar thermal power generation system | |
| CN207230959U (en) | Air source heat pump equipped with solar energy heating structure | |
| CN216693691U (en) | Solar heat pipe wall body radiation heating device | |
| CN103398436B (en) | Solar energy diffusion-absorption refrigeration formula air-conditioning system based on radiation temperature adjustment | |
| CN102589192A (en) | Three-in-one solar air-conditioning system | |
| CN115200111A (en) | Passive ventilation system combining solar chimney structure and radiation refrigeration | |
| CN109737612B (en) | Infrared radiation air conditioner | |
| CN107218734A (en) | A kind of solar powered heating cooling combined supply system | |
| CN111750417A (en) | Heat pipe type photovoltaic photothermal module-heat pump-phase change floor coupling system and method | |
| CN115949986B (en) | Solar-driven heating curtain wall system for summer heat and winter | |
| CN119309264B (en) | Building energy-saving roof system and method with heat flow automatic regulation capability | |
| CN218570138U (en) | A photovoltaic cell cooling roof based on the integration of heat pipe and sky radiation cooling | |
| CN222364043U (en) | All-weather high-temperature cold water circulation preparation system based on building envelope |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |