CN108409988B - A kind of preparation method of spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel - Google Patents
A kind of preparation method of spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogelDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN108409988B CN108409988BCN201810356499.8ACN201810356499ACN108409988BCN 108409988 BCN108409988 BCN 108409988BCN 201810356499 ACN201810356499 ACN 201810356499ACN 108409988 BCN108409988 BCN 108409988B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- polyvinyl alcohol
- hydrogel
- polyethylene glycol
- mixed solution
- macroporous
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004372Polyvinyl alcoholSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription76
- 229920002451polyvinyl alcoholPolymers0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription76
- 239000000017hydrogelSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription67
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription10
- 239000002202Polyethylene glycolSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription46
- 229920001223polyethylene glycolPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription46
- 239000011259mixed solutionSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription37
- 229910052588hydroxylapatiteInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription32
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription27
- 238000007710freezingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription26
- 230000008014freezingEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription26
- 238000002844meltingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription24
- 230000008018meltingEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription24
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- XYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-Dpentacalcium;hydroxide;triphosphateChemical compound[OH-].[Ca+2].[Ca+2].[Ca+2].[Ca+2].[Ca+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OXYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-D0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterChemical compoundOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription33
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000claimsdescription23
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription23
- 239000000499gelSubstances0.000claimsdescription16
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000006136alcoholysis reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000005352clarificationMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000claims1
- 125000004122cyclic groupChemical group0.000abstractdescription15
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000abstractdescription6
- 238000005191phase separationMethods0.000abstractdescription6
- 239000011148porous materialSubstances0.000abstractdescription4
- 238000004132cross linkingMethods0.000description9
- 230000008961swellingEffects0.000description9
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene glycolChemical compoundOCCOLYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 239000012456homogeneous solutionSubstances0.000description6
- 238000010382chemical cross-linkingMethods0.000description4
- 231100000135cytotoxicityToxicity0.000description3
- 230000003013cytotoxicityEffects0.000description3
- 108010087230SincalideProteins0.000description2
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000description2
- 238000010609cell counting kit-8 assayMethods0.000description2
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description2
- 231100000263cytotoxicity testToxicity0.000description2
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 229910052739hydrogenInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000001257hydrogenSubstances0.000description2
- 229920001477hydrophilic polymerPolymers0.000description2
- 238000010309melting processMethods0.000description2
- 239000002861polymer materialSubstances0.000description2
- IZTQOLKUZKXIRV-YRVFCXMDSA-NsincalideChemical compoundC([C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CC=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O)C1=CC=C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C=C1IZTQOLKUZKXIRV-YRVFCXMDSA-N0.000description2
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description2
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description2
- 102000004190EnzymesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000790EnzymesProteins0.000description1
- 238000012925biological evaluationMethods0.000description1
- 239000003519biomedical and dental materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000013270controlled releaseMethods0.000description1
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000description1
- 238000007334copolymerization reactionMethods0.000description1
- 239000003431cross linking reagentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000002242deionisation methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description1
- 238000001493electron microscopyMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000004108freeze dryingMethods0.000description1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-NgoldChemical compound[Au]PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000010931goldSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052737goldInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000023597hemostasisEffects0.000description1
- 230000002209hydrophobic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000000338in vitroMethods0.000description1
- 229920002521macromoleculePolymers0.000description1
- 229920005615natural polymerPolymers0.000description1
- 102000039446nucleic acidsHuman genes0.000description1
- 108020004707nucleic acidsProteins0.000description1
- 150000007523nucleic acidsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000011056performance testMethods0.000description1
- 238000006068polycondensation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000006116polymerization reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description1
- 230000005855radiationEffects0.000description1
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002441reversible effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004083survival effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000002522swelling effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000010998test methodMethods0.000description1
- 231100000419toxicityToxicity0.000description1
- 230000001988toxicityEffects0.000description1
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000description1
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description1
- 238000000844transformationMethods0.000description1
- 238000001291vacuum dryingMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J3/00—Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances
- C08J3/02—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques
- C08J3/03—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques in aqueous media
- C08J3/075—Macromolecular gels
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J9/00—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof
- C08J9/26—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof by elimination of a solid phase from a macromolecular composition or article, e.g. leaching out
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J9/00—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof
- C08J9/28—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof by elimination of a liquid phase from a macromolecular composition or article, e.g. drying of coagulum
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2201/00—Foams characterised by the foaming process
- C08J2201/04—Foams characterised by the foaming process characterised by the elimination of a liquid or solid component, e.g. precipitation, leaching out, evaporation
- C08J2201/044—Elimination of an inorganic solid phase
- C08J2201/0444—Salts
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2201/00—Foams characterised by the foaming process
- C08J2201/04—Foams characterised by the foaming process characterised by the elimination of a liquid or solid component, e.g. precipitation, leaching out, evaporation
- C08J2201/046—Elimination of a polymeric phase
- C08J2201/0464—Elimination of a polymeric phase using water or inorganic fluids
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2205/00—Foams characterised by their properties
- C08J2205/04—Foams characterised by their properties characterised by the foam pores
- C08J2205/044—Micropores, i.e. average diameter being between 0,1 micrometer and 0,1 millimeter
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2329/00—Characterised by the use of homopolymers or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by an alcohol, ether, aldehydo, ketonic, acetal, or ketal radical; Hydrolysed polymers of esters of unsaturated alcohols with saturated carboxylic acids; Derivatives of such polymer
- C08J2329/02—Homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated alcohols
- C08J2329/04—Polyvinyl alcohol; Partially hydrolysed homopolymers or copolymers of esters of unsaturated alcohols with saturated carboxylic acids
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Colloid Chemistry (AREA)
- Processes Of Treating Macromolecular Substances (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶的制备方法,属于生物化工领域。The invention relates to a preparation method of a novel spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel, which belongs to the field of biochemical industry.
背景技术Background technique
水凝胶是通过化学或物理交联产生的具有三维网络结构的亲水性聚合物。它能吸收大量水溶胀并保持一定的形状。典型的水凝胶常常呈果冻状,柔软而且富有弹性。良好的吸水、保水及缓释特性使其在组织工程,伤口敷料和药物缓控释等领域都展现了良好的应用前景。Hydrogels are hydrophilic polymers with a three-dimensional network structure produced by chemical or physical cross-linking. It absorbs a lot of water to swell and maintain a certain shape. Typical hydrogels are often jelly-like, soft and elastic. The good water absorption, water retention and slow release properties make it have good application prospects in the fields of tissue engineering, wound dressings and drug slow and controlled release.
制备水凝胶的材料可分为天然高分子材料和化学合成高分子材料两大类,制备方法通常为物理交联和化学交联,其中物理交联指通过离子键、氢键及疏水键相互作用使分子相互缠结而形成的网络结构。物理交联在自然界中非常普遍,尤其在维持生物大分子(如蛋白质、酶及核酸等)的三维空间结构、参与很多生物学反应过程均发挥着非常重要的作用。物理交联常常是动态的、可逆的,对维护水凝胶的强度和韧性方面具有显著作用。化学交联是指运用化学交联剂或光聚合、辐射聚合等技术,引发共聚或缩聚反应产生共价键从而形成的共价交联网络。与物理交联方式相比,化学交联形成的水凝胶力学强度好但韧性差,并且会引入其他物质,因此其生物相容性不如物理交联方法制备的水凝胶。The materials for preparing hydrogels can be divided into two categories: natural polymer materials and chemically synthesized polymer materials. The preparation methods are usually physical cross-linking and chemical cross-linking, where physical cross-linking refers to ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic bonds. A network structure formed by entanglement of molecules with each other. Physical cross-linking is very common in nature, and plays a very important role in maintaining the three-dimensional structure of biological macromolecules (such as proteins, enzymes and nucleic acids) and participating in many biological reaction processes. Physical crosslinking is often dynamic and reversible and plays a significant role in maintaining the strength and toughness of hydrogels. Chemical cross-linking refers to the covalent cross-linking network formed by the use of chemical cross-linking agents or photopolymerization, radiation polymerization and other technologies to initiate a copolymerization or polycondensation reaction to generate covalent bonds. Compared with the physical cross-linking method, the hydrogel formed by chemical cross-linking has good mechanical strength but poor toughness, and will introduce other substances, so its biocompatibility is not as good as the hydrogel prepared by the physical cross-linking method.
聚乙烯醇是一种高分子亲水性聚合物,由于其良好的水溶性及生物相容性而被广泛研究用于生物医学领域。聚乙烯醇溶液在低温和室温下反复冷冻-解冻,形成由氢键为主要作用的物理交联,具有优异的机械性能。但该方法制备的水凝胶通常不具有大孔结构,限制了其应用范围。Polyvinyl alcohol is a kind of macromolecular hydrophilic polymer, which has been widely studied in the field of biomedicine due to its good water solubility and biocompatibility. The polyvinyl alcohol solution is repeatedly frozen-thawed at low temperature and room temperature to form a physical cross-linking with hydrogen bonding as the main function, and has excellent mechanical properties. However, the hydrogels prepared by this method usually do not have a macroporous structure, which limits their application range.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明目的是提供一种具有大孔结构、孔隙率高、生物相容性优异的新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶及其制备方法。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a novel spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel with macroporous structure, high porosity and excellent biocompatibility and a preparation method thereof.
本发明实现过程如下:The implementation process of the present invention is as follows:
一种海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶的制备方法:向聚乙烯醇溶液加入聚乙二醇,搅拌至聚乙二醇充分溶解,于室温静置,当混合溶液由澄清变浑浊时,加入纳米羟基磷灰石,搅拌,使纳米羟基磷灰石均匀地分散在混合溶液中,将混合好的溶液转移到模具中常温放置,通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成水凝胶,用去离子水洗涤除去聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石以获得具有大孔结构的聚乙烯醇水凝胶。A preparation method of a spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel: adding polyethylene glycol to a polyvinyl alcohol solution, stirring until the polyethylene glycol is fully dissolved, standing at room temperature, and when the mixed solution changes from clarification to turbidity, Add nano-hydroxyapatite, stir to make nano-hydroxyapatite evenly dispersed in the mixed solution, transfer the mixed solution to the mold and place at room temperature, prepare hydrogel by cyclic freezing/melting method, use deionization Water washing removes polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite to obtain polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel with macroporous structure.
上述大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶的制备方法,包括以下步骤:The preparation method of above-mentioned macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel, comprises the following steps:
(1)将聚乙烯醇溶解在85-98℃去离子水,得到质量体积比浓度为8-12%的聚乙烯醇溶液;(1) Dissolving polyvinyl alcohol in deionized water at 85-98 °C to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass-volume ratio of 8-12%;
(2)将质量体积比浓度为3-10%的聚乙二醇溶液加至步骤(1)的聚乙烯醇溶液中,在常温放置0.5-1 h;(2) adding a polyethylene glycol solution with a mass volume ratio of 3-10% to the polyvinyl alcohol solution in step (1), and placing it at room temperature for 0.5-1 h;
(3)待聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇澄清混合溶液变浑浊时,将纳米羟基磷灰石以质量体积比浓度6-10%的含量溶于步骤(3)的聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇混合溶液中;(3) When the clear mixed solution of polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol becomes turbid, the nano-hydroxyapatite is dissolved in the polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol of step (3) at a concentration of 6-10% by mass and volume. in solution;
(4)将步骤(3)混合溶液于常温放置1-1.5 h;通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度为-18℃至-20℃,熔融温度为室温,循环次数3-7次;(4) The mixed solution of step (3) is placed at room temperature for 1-1.5 h; the gel is prepared by a cyclic freezing/melting method, wherein the freezing temperature is -18°C to -20°C, the melting temperature is room temperature, and the number of cycles is 3-7 Second-rate;
(5)将制备好的水凝胶在去离子水中除去聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石,获得海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶。(5) Remove polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite from the prepared hydrogel in deionized water to obtain a sponge-like macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
上述步骤(1)中,聚乙烯醇的分子量为80,000-120,000Da,醇解度大于99%。In the above step (1), the molecular weight of polyvinyl alcohol is 80,000-120,000 Da, and the alcoholysis degree is greater than 99%.
上述步骤(1)中,将聚乙烯醇溶解在95℃去离子水中。In the above step (1), the polyvinyl alcohol was dissolved in deionized water at 95°C.
上述步骤(2)中,聚乙二醇的分子量为1000-4000 Da。In the above step (2), the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is 1000-4000 Da.
上述步骤(3)中,纳米羟基磷灰石的粒径为10-30 nm。In the above step (3), the particle size of the nano-hydroxyapatite is 10-30 nm.
本发明具有以下优点:本发明将乙二醇溶于聚乙烯醇溶液中后,通过降低温度使混合溶液发生相分离,然后向已发生相分离的混合溶液中添加纳米羟基磷灰石以稳定相分离体系。通过循环冷冻/熔融方法使水凝胶成型,洗涤出聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石,获得具有大孔结构的聚乙烯醇水凝胶。与不添加羟基磷灰石而仅通过循环冷冻/熔融方法制备的聚乙烯醇水凝胶相比,本发明所制备的水凝胶具有类似海绵的外观及弹性、三维贯通的多孔结构,高孔隙率(孔径为30~100μm),良好的机械性能及生物相容性。本发明中的海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶在烧烫伤敷料、止血等生物医用材料领域具有良好的应用潜力。The invention has the following advantages: after dissolving ethylene glycol in the polyvinyl alcohol solution, the mixed solution is phase-separated by lowering the temperature, and then nano-hydroxyapatite is added to the phase-separated mixed solution to stabilize the phase separation system. The hydrogel was formed by cyclic freezing/melting method, and polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite were washed out to obtain polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel with macroporous structure. Compared with the polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel prepared only by the cyclic freezing/melting method without adding hydroxyapatite, the hydrogel prepared by the present invention has a sponge-like appearance and elasticity, a three-dimensional through-hole porous structure, and high porosity. ratio (pore size is 30~100μm), good mechanical properties and biocompatibility. The spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel in the present invention has good application potential in the fields of biomedical materials such as burn dressings and hemostasis.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为实例1聚乙烯醇水凝胶湿样外观图;Fig. 1 is the appearance diagram of the wet sample of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel of Example 1;
图2为实例1聚乙烯醇水凝胶湿样冷冻干燥后的样品图;Fig. 2 is the sample diagram after freeze-drying of the wet sample of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel of Example 1;
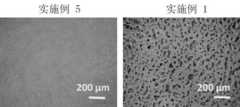
图3为实例1聚乙烯醇水凝胶样品的扫描电镜图;Fig. 3 is the scanning electron microscope picture of example 1 polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel sample;
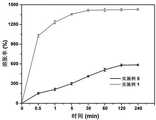
图4为实例1聚乙烯醇水凝胶样品在去离子水中的溶胀率;Fig. 4 is the swelling ratio of example 1 polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel sample in deionized water;
图5为实例1聚乙烯醇水凝胶样品在25℃下的保水率;Figure 5 is the water retention rate of the polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel sample of Example 1 at 25°C;
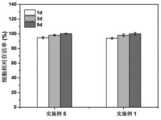
图6为实例1聚乙烯醇水凝胶样品的CCK-8细胞毒性检验结果。FIG. 6 is the CCK-8 cytotoxicity test result of the polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel sample of Example 1. FIG.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施方式对本发明进行详细的说明。The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to specific embodiments.
本发明所涉及的以聚乙烯醇、聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石为原料,制备新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝的制备方法,通过循环冷冻熔融过程获得,其中聚乙烯醇与聚乙二醇混合溶液通过冷却造成相分离,纳米羟基磷灰石的加入稳定了混合溶液的相分离,这种相分离是形成大孔水凝胶的原因。溶液通过循环冷冻/熔融过程形成具有三维结构的水凝胶,使用去离子水洗去纳米羟基磷灰石,聚乙二醇最终得到具有大孔、高孔隙率的水凝胶。具体制备方法由以下步骤实现:The invention relates to a preparation method for preparing a new type of sponge-like macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydraulically by using polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite as raw materials, which is obtained through a cyclic freezing and melting process, wherein polyvinyl alcohol and polyvinyl alcohol are The phase separation of the ethylene glycol mixed solution was caused by cooling, and the addition of nano-hydroxyapatite stabilized the phase separation of the mixed solution, which was the reason for the formation of macroporous hydrogels. The solution forms a hydrogel with a three-dimensional structure through a cyclic freezing/melting process, and deionized water is used to wash off the nano-hydroxyapatite, and polyethylene glycol finally obtains a hydrogel with macropores and high porosity. The specific preparation method is realized by the following steps:
步骤一:将聚乙烯醇溶解在95℃去离子水得到质量体积比浓度为8-12%的聚乙烯醇溶液;Step 1: dissolving polyvinyl alcohol in deionized water at 95°C to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass-volume ratio of 8-12%;
步骤二:将聚乙二醇以质量体积比浓度3-10%的含量溶于步骤一的聚乙烯醇溶液;Step 2: dissolving polyethylene glycol in the polyvinyl alcohol solution of
步骤三:将步骤二的聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇混合溶液于常温放置0.5-1 h;Step 3: place the mixed solution of polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol in step 2 at room temperature for 0.5-1 h;
步骤四:待步骤三的聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇澄清混合溶液变浑浊将纳米羟基磷灰石以质量体积比浓度6-10%的含量溶于步骤三的聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇混合溶液中;Step 4: When the clarified mixed solution of polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol in step 3 becomes cloudy, dissolve nano-hydroxyapatite in the mixed solution of polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol in step 3 at a concentration of 6-10% by mass and volume middle;
步骤五:将步骤四中混合好的溶液于常温放置1-1.5 h;之后通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度为-18℃至-20℃,熔融温度室温,循环次数3-7次。制备好的混合凝胶在去离子水中除去聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石,获得所述的新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶。Step 5: Put the solution mixed in Step 4 at room temperature for 1-1.5 h; then prepare the gel by a cyclic freezing/melting method, wherein the freezing temperature is -18°C to -20°C, the melting temperature is room temperature, and the number of cycles is 3- 7 times. The prepared mixed gel is removed in deionized water to remove polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite to obtain the novel spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
步骤一中,聚乙烯醇分子量为80,000-120,000Da,醇解度大于99%。In
步骤二中,聚乙二醇的分子量为1000-4000 Da。In the second step, the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is 1000-4000 Da.
步骤四中,纳米羟基磷灰石的粒径为20 nm。In step 4, the particle size of the nano-hydroxyapatite is 20 nm.
步骤五中,通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度为-18℃至-20℃,熔融温度为室温,循环次数3-7次。In
实施例1Example 1
步骤一:称量分子量为89000Da的聚乙烯醇溶于20 ml去离子水中,得到质量体积比浓度为10%的聚乙烯醇溶液,置于95℃水浴锅中搅拌使其充分溶解;Step 1: Weigh polyvinyl alcohol with a molecular weight of 89000Da and dissolve it in 20 ml of deionized water to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass-volume ratio of 10%, which is then stirred in a 95°C water bath to fully dissolve;
步骤二:向上述溶液中加入分子量为1500 Da的聚乙二醇使其充分混合均匀,形成均一溶液,使聚乙二醇质量体积比浓度为8%;Step 2: adding polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 1500 Da to the above solution to make it fully mixed to form a homogeneous solution, so that the mass volume ratio of polyethylene glycol is 8%;
步骤三:将上述聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇混合溶液于常温放置1 h;Step 3: place the above-mentioned polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol mixed solution at room temperature for 1 h;
步骤四:待上述混合溶液变浑浊将纳米羟基磷灰石以质量体积比浓度10%的含量溶于该浑浊混合溶液中;Step 4: when the above mixed solution becomes turbid, the nano-hydroxyapatite is dissolved in the turbid mixed solution with a concentration of 10% by mass and volume;
步骤五:将上述混匀的溶液于常温放置1 h;之后通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度-20℃,熔融温度为室温,循环次数5次。制备好的混合凝胶在去离子水中除去聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石,获得所述的新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶。Step 5: The mixed solution was placed at room temperature for 1 hour; then the gel was prepared by a cyclic freezing/melting method, wherein the freezing temperature was -20°C, the melting temperature was room temperature, and the number of cycles was 5 times. The prepared mixed gel is removed in deionized water to remove polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite to obtain the novel spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
实施例2Example 2
步骤一:称量分子量为98000 Da的聚乙烯醇溶于20ml去离子水中,得到质量分数为10 %的聚乙烯醇溶液,置于95℃水浴锅中搅拌使其充分溶解;Step 1: Weigh polyvinyl alcohol with a molecular weight of 98,000 Da and dissolve it in 20 ml of deionized water to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 10%, which is then stirred in a 95°C water bath to fully dissolve;
步骤二:向上述溶液中加入分子量为1500 Da的聚乙二醇使其充分混合均匀,形成均一溶液,使聚乙二醇质量体积比浓度为8%;Step 2: adding polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 1500 Da to the above solution to make it fully mixed to form a homogeneous solution, so that the mass volume ratio of polyethylene glycol is 8%;
步骤三:将上述聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇混合溶液于常温放置1 h;Step 3: place the above-mentioned polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol mixed solution at room temperature for 1 h;
步骤四:待上述混合溶液变浑浊将纳米羟基磷灰石以质量体积比浓度6%的含量溶于该浑浊混合溶液中;Step 4: when the above mixed solution becomes turbid, the nano-hydroxyapatite is dissolved in the turbid mixed solution with a concentration of 6% by mass and volume;
步骤五:将上述混匀的溶液于常温放置1 h;之后通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度-20℃,熔融温度为室温,循环次数5次。制备好的混合凝胶在去离子水中除去聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石,获得所述的新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶。Step 5: The mixed solution was placed at room temperature for 1 hour; then the gel was prepared by a cyclic freezing/melting method, wherein the freezing temperature was -20°C, the melting temperature was room temperature, and the number of cycles was 5 times. The prepared mixed gel is removed in deionized water to remove polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite to obtain the novel spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
实施例3Example 3
步骤一:称量分子量为98000 Da的聚乙烯醇溶于20ml去离子水中,得到质量分数为8%的聚乙烯醇溶液,置于95℃水浴锅中搅拌使其充分溶解;Step 1: Weigh polyvinyl alcohol with a molecular weight of 98,000 Da and dissolve it in 20 ml of deionized water to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 8%, which is then stirred in a 95°C water bath to fully dissolve;
步骤二:向上述溶液中加入分子量为3000 Da聚乙二醇使其充分混合均匀,形成均一溶液,使聚乙二醇质量体积比浓度为4%;Step 2: adding polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 3000 Da to the above solution to make it fully mixed to form a homogeneous solution, so that the mass volume ratio of polyethylene glycol is 4%;
步骤三:将上述聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇混合溶液于常温放置1h;Step 3: place the above-mentioned polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol mixed solution at room temperature for 1h;
步骤四:待上述混合溶液变浑浊将纳米羟基磷灰石以质量体积比浓度10%的含量溶于该浑浊混合溶液中;Step 4: when the above mixed solution becomes turbid, the nano-hydroxyapatite is dissolved in the turbid mixed solution with a concentration of 10% by mass and volume;
步骤五:将上述混匀的溶液于常温放置1h;之后通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度-20℃,熔融温度为室温,循环次数5次。制备好的混合凝胶在去离子水中除去聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石,获得所述的新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶。Step 5: The mixed solution was placed at room temperature for 1 hour; then the gel was prepared by a cyclic freezing/melting method, wherein the freezing temperature was -20°C, the melting temperature was room temperature, and the number of cycles was 5 times. The prepared mixed gel is removed in deionized water to remove polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite to obtain the novel spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
实施例4Example 4
步骤一:称量分子量为89000 Da的聚乙烯醇溶于20ml去离子水中,得到质量分数为8%的聚乙烯醇溶液,置于95℃水浴锅中搅拌使其充分溶解;Step 1: Weigh the polyvinyl alcohol with a molecular weight of 89000 Da and dissolve it in 20 ml of deionized water to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 8%, which is then stirred in a 95°C water bath to fully dissolve;
步骤二:向上述溶液中加入分子量为4000 Da聚乙二醇使其充分混合均匀,形成均一溶液,使聚乙二醇质量体积比浓度为3%;Step 2: adding polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 4000 Da to the above solution to make it fully mixed to form a homogeneous solution, so that the mass volume ratio of polyethylene glycol is 3%;
步骤三:将上述聚乙烯醇和聚乙二醇混合溶液于常温放置1 h;Step 3: place the above-mentioned polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol mixed solution at room temperature for 1 h;
步骤四:待上述混合溶液变浑浊将纳米羟基磷灰石以质量体积比浓度10%的含量溶于该浑浊混合溶液中;Step 4: when the above mixed solution becomes turbid, the nano-hydroxyapatite is dissolved in the turbid mixed solution with a concentration of 10% by mass and volume;
步骤五:将上述混匀的溶液于常温放置1 h;之后通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度-20℃,熔融温度为室温,循环次数5次。制备好的混合凝胶在去离子水中除去聚乙二醇和纳米羟基磷灰石,获得所述的新型海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶。Step 5: The mixed solution was placed at room temperature for 1 hour; then the gel was prepared by a cyclic freezing/melting method, wherein the freezing temperature was -20°C, the melting temperature was room temperature, and the number of cycles was 5 times. The prepared mixed gel is removed in deionized water to remove polyethylene glycol and nano-hydroxyapatite to obtain the novel spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
实施例5Example 5
步骤一:称量分子量为89000 Da聚乙烯醇溶于20 ml去离子水中,得到质量分数为10%的聚乙烯醇溶液,置于95℃水浴锅中搅拌使其充分溶解;Step 1: Weigh the polyvinyl alcohol with a molecular weight of 89000 Da and dissolve it in 20 ml of deionized water to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 10%, which is then stirred in a 95°C water bath to fully dissolve;
步骤二:向上述溶液中加入分子量为1500 Da聚乙二醇使其充分混合均匀,形成均一溶液,使聚乙二醇质量体积比浓度为8%。Step 2: Add polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 1500 Da to the above solution to make it fully mixed to form a homogeneous solution, so that the concentration of polyethylene glycol is 8% by mass/volume.
步骤三:上述均一溶液通过循环冷冻/熔融法制备成胶,其中冷冻温度-20℃,熔融温度为室温,循环次数5次。制备好的混合凝胶在去离子水中除去聚乙二醇,获得聚乙烯醇水凝胶。Step 3: The above homogeneous solution is prepared into a gel by a cyclic freezing/melting method, wherein the freezing temperature is -20° C., the melting temperature is room temperature, and the number of cycles is 5 times. The prepared mixed gel was deionized water to remove polyethylene glycol to obtain polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel.
上述实施例中,实施例5为对比实施例,对上述本发明的实施例1和实例5中制备的海绵状大孔聚乙烯醇水凝胶的各项性能参数进行测定,包括微观结构、溶胀性能、保水性能、细胞毒性,结果参见附图3-6。Among the above-mentioned examples, Example 5 is a comparative example. Various performance parameters of the spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel prepared in Example 1 and Example 5 of the present invention were measured, including microstructure, swelling Performance, water retention performance, cytotoxicity, the results are shown in Figures 3-6.
1、本发明中的水凝胶湿样如图1所示,水凝胶类似于海绵状的半透明凝胶。1. The wet sample of the hydrogel in the present invention is shown in Figure 1, and the hydrogel is similar to a sponge-like translucent gel.
2、本发明中的水凝胶样品经冷冻干燥的形貌如图2所示,材料呈白色并且表面平整。2. The freeze-dried morphology of the hydrogel sample in the present invention is shown in Figure 2, the material is white and the surface is flat.
3、水凝胶微观结构检测。3. Hydrogel microstructure detection.
将所制备的样品切成大约2µm的薄片,采用冷冻真空干燥进行干燥并在其表面喷金。在电子显微镜下进行水凝胶的微观结构研究。The prepared samples were cut into thin slices of approximately 2 µm, dried by freeze-vacuum drying and sprayed with gold on the surface. Microstructural studies of the hydrogels were performed under electron microscopy.
如图3所示,由图可以看出,与实施例5相比实施例1中本发明水凝胶,其微观结果呈多孔状,孔径分布均匀且孔径大小在30-100µm之间。As shown in Figure 3, it can be seen from the figure that, compared with Example 5, the microscopic result of the hydrogel of the present invention in Example 1 is porous, the pore size distribution is uniform, and the pore size is between 30-100µm.
4、水凝胶溶胀性能检测。4. Testing of hydrogel swelling properties.
在37℃的去离子水中测定水凝胶的溶胀率。称取冷冻干燥后的水凝胶样品,其质量记为M0。浸入去离子水中并在设定时间点取出,用滤纸擦去表面水分后,称重并记为M1。(M1-M0) 为水凝胶吸水后的质量,M0为水凝胶的干重,比值即为溶胀率。The swelling ratio of the hydrogels was determined in deionized water at 37°C. The freeze-dried hydrogel sample was weighed, and its mass was recorded as M0 . It was immersed in deionized water and taken out at a set time point, and after wiping off surface moisture with filter paper, it was weighed and recorded as M1 . (M1 -M0 ) is the mass of the hydrogel after water absorption, M0 is the dry weight of the hydrogel, and the ratio is the swelling ratio.
如图4所示,与实施例5相比实施例1中本发明水凝胶,经过30min后就能达到溶胀平衡,溶胀率大约为1500%;而实例5中的水凝胶经过120min后才能达到溶胀平衡,溶胀率仅大约为500%。As shown in Figure 4, compared with Example 5, the hydrogel of the present invention in Example 1 can reach swelling equilibrium after 30 minutes, and the swelling rate is about 1500%; and the hydrogel in Example 5 can only be achieved after 120 minutes. The swelling equilibrium is reached, and the swelling ratio is only about 500%.
5、水凝胶保水性能检测。5. Water retention performance test of hydrogel.
将达到溶胀平衡的湿水凝胶M0置于每个烧杯中,然后放置在37℃环境下测定重量随时间的变化。在预定的时间点,将水凝胶取出并称重M。M和M0的比值即为保水率。The wet hydrogel M0 that reached the swelling equilibrium was placed in each beaker, and then placed in a 37°C environment to measure the change in weight over time. At predetermined time points, the hydrogels were removed and weighed. The ratio of M and M0 is the water retention rate.
如图5所示37℃下,两种水凝胶的保水率随时间的变化,经过48h保水率仍大于50%,并且实施例1和实施例5与对比实例差别不大。As shown in Figure 5, at 37 °C, the water retention rate of the two hydrogels changes with time, and the water retention rate is still greater than 50% after 48h, and there is little difference between Example 1 and Example 5 and the comparative example.
6、水凝胶细胞毒性检测。6. Hydrogel cytotoxicity detection.
按照 GB/T16886.5-2003(《 医疗器械生物学评价第 5 部分:体外细胞毒性试验》)中规定的试验方法进行试验。Carry out the test according to the test method specified in GB/T16886.5-2003 ("Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices Part 5: In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test").
图6结果表明:采用L929细胞CCK-8法检验材料浸提液的细胞毒性。培养五天后,细胞存活率大于90%,本实验结果表明:根据国家标准,材料毒性等级均为1级,属于可放心使用的生物医用材料。The results in Figure 6 show that the cytotoxicity of the material extract was tested by L929 cell CCK-8 method. After five days of culture, the cell survival rate was greater than 90%. The results of this experiment showed that according to the national standard, the toxicity grade of the material was all
本发明的内容不限于实施例所列举,本领域普通技术人员通过阅读本发明说明书而对本发明技术方案采取的任何等效的变换,均为本发明的权利要求所涵盖。The content of the present invention is not limited to those listed in the embodiments, and any equivalent transformations taken by those of ordinary skill in the art to the technical solutions of the present invention by reading the description of the present invention are covered by the claims of the present invention.
Claims (2)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810356499.8ACN108409988B (en) | 2018-04-20 | 2018-04-20 | A kind of preparation method of spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810356499.8ACN108409988B (en) | 2018-04-20 | 2018-04-20 | A kind of preparation method of spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN108409988A CN108409988A (en) | 2018-08-17 |
| CN108409988Btrue CN108409988B (en) | 2020-10-30 |
Family
ID=63136039
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201810356499.8AActiveCN108409988B (en) | 2018-04-20 | 2018-04-20 | A kind of preparation method of spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN108409988B (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111494701B (en)* | 2019-01-31 | 2021-07-02 | 西北大学 | Polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels with asymmetric pore size |
| CN110698719A (en)* | 2019-10-30 | 2020-01-17 | 陕西巨子生物技术有限公司 | Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogel |
| CN112094418B (en)* | 2020-09-27 | 2023-04-25 | 河南省科学院同位素研究所有限责任公司 | A hydrogel composite material with photothermal conversion shape memory effect and preparation method thereof |
| CN113813436B (en)* | 2021-08-18 | 2022-08-05 | 西北大学 | Preparation method of visual antibacterial anti-inflammatory dressing for treating bacterial infection type wound |
| CN113773462A (en)* | 2021-08-19 | 2021-12-10 | 华东理工大学 | Invisible orthodontic polyurethane film, preparation method and application |
| CN117143427A (en)* | 2023-09-12 | 2023-12-01 | 上海应用技术大学 | Molecular sieve-tea tree essential oil antibacterial hydrogel, preparation method and application thereof |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1527860A (en)* | 2001-05-11 | 2004-09-08 | ������ϵ�о���˾ | Methods for the preparation of cellular hydrogels |
| CN1651506A (en)* | 2003-10-31 | 2005-08-10 | 四川大学 | Preparation method of nano-hydroxyapatite/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel |
| WO2012118662A2 (en)* | 2011-02-28 | 2012-09-07 | The General Hospital Corporation | Highly porous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels for cartilage resurfacing |
| CN107126583A (en)* | 2017-05-03 | 2017-09-05 | 中国矿业大学 | The preparation technology of multilayer heterogeneous bionic joint cartilage material |
- 2018
- 2018-04-20CNCN201810356499.8Apatent/CN108409988B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1527860A (en)* | 2001-05-11 | 2004-09-08 | ������ϵ�о���˾ | Methods for the preparation of cellular hydrogels |
| CN1651506A (en)* | 2003-10-31 | 2005-08-10 | 四川大学 | Preparation method of nano-hydroxyapatite/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel |
| WO2012118662A2 (en)* | 2011-02-28 | 2012-09-07 | The General Hospital Corporation | Highly porous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels for cartilage resurfacing |
| CN107126583A (en)* | 2017-05-03 | 2017-09-05 | 中国矿业大学 | The preparation technology of multilayer heterogeneous bionic joint cartilage material |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| "Morphological and swelling behavior of cellulose nanofiber (CNF)/poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) hydrogels: poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) as porogen";Zhaoyang Xu等;《RSC Adv.》;20160503;第6卷;第43626-43633页* |
| "多孔纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇复合水凝胶的表征";许凤兰等;《化学研究与应用》;20051031(第5期);第599-602页* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN108409988A (en) | 2018-08-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108409988B (en) | A kind of preparation method of spongy macroporous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel | |
| Xu et al. | Morphological and swelling behavior of cellulose nanofiber (CNF)/poly (vinyl alcohol)(PVA) hydrogels: poly (ethylene glycol)(PEG) as porogen | |
| Kundu et al. | Silk sericin/polyacrylamide in situ forming hydrogels for dermal reconstruction | |
| Cui et al. | Mechanical, microstructural, and rheological characterization of gelatin-dialdehyde starch hydrogels constructed by dual dynamic crosslinking | |
| Qi et al. | Investigation of Salecan/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freeze/thaw method | |
| CN106832422B (en) | Bacterial nanocellulose composite material with temperature response and its preparation method and application | |
| Yang et al. | Natural self-healing injectable hydrogels loaded with exosomes and berberine for infected wound healing | |
| CN106674562B (en) | A kind of polyvinyl alcohol film with loose structure and preparation method thereof | |
| Wei et al. | One‐step preparation of hydrogel based on different molecular weights of chitosan with citric acid | |
| CN114702704B (en) | Functional polymer membrane/hydrogel membrane based on unidirectional nano-pore dehydration, preparation method and device | |
| CN107200855A (en) | A kind of preparation method of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel | |
| Gümüşderelioğlu et al. | Superporous polyacrylate/chitosan IPN hydrogels for protein delivery | |
| Wu et al. | The study of double-network carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate based cryogels for rapid hemostasis in noncompressible hemorrhage | |
| CN110698719A (en) | Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogel | |
| US7420024B2 (en) | Partially biodegradable temperature and pH sensitive hydrogel | |
| CN110016160A (en) | A kind of preparation method of polysaccharide-based hydrogel | |
| CN119925680A (en) | Wound repair hydrogel dressing and preparation method thereof | |
| CN104874017B (en) | Collagen-chitosan tissue engineering scaffold compounded with Tβ4 and its preparation method and application | |
| CN112704765A (en) | Chitosan-graphene oxide composite gel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN111973803A (en) | Chitosan-based antibacterial wound dressing with excellent mechanical property and antibacterial property | |
| Luthfianti et al. | Tunable Physical Properties of Starch-Based Hydrogels Synthesized by Freeze-Thaw Technique | |
| Barbalata-Mandru et al. | Preparation and surface characterization of polyurethane hydrogels | |
| Zhang et al. | pH-responsive swelling behavior of collagen complex materials | |
| Bonakdara et al. | Comparison of the Effect of Hydrophilicity on Biocompatibilityand Platelet Adhesion of Two Different Kinds of Biomaterials: Effect of hydrophilicity on biocompatibility of biomaterialsRoswell | |
| CN118063690B (en) | Acrylophenylalanine-acrylic ester chiral copolymerization macromolecule hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |