CN107330131B - Interval Optimization Method for Structural Dimensional Parameters and Dimensional Tolerances of Mechanical Parts - Google Patents
Interval Optimization Method for Structural Dimensional Parameters and Dimensional Tolerances of Mechanical PartsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN107330131B CN107330131BCN201610280903.9ACN201610280903ACN107330131BCN 107330131 BCN107330131 BCN 107330131BCN 201610280903 ACN201610280903 ACN 201610280903ACN 107330131 BCN107330131 BCN 107330131B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- interval
- structural
- possibility
- parameters
- optimization
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/10—Geometric CAD
- G06F30/17—Mechanical parametric or variational design
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/20—Design optimisation, verification or simulation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2111/00—Details relating to CAD techniques
- G06F2111/04—Constraint-based CAD
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Computational Mathematics (AREA)
- Other Investigation Or Analysis Of Materials By Electrical Means (AREA)
- Feedback Control In General (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及机械结构优化设计领域,具体是一种基于离散化的区间可能度和加工精度的机械零部件结构尺寸参数及尺寸公差的区间优化方法。The invention relates to the field of mechanical structure optimization design, in particular to an interval optimization method for structural dimension parameters and dimension tolerances of mechanical parts based on discretized interval possibility and machining accuracy.
背景技术Background technique
传统的机械设计问题一般是基于确定的参数和优化模型,并借助于经典的确定性优化问题进行求解,但是在实际的工程问题中结构尺寸、材料特性、载荷、边界条件、元器件参数、测量偏差等的误差或不确定性必然存在,这些误差或不确定性会影响设计的优化目标性能或改变约束的可行性,本发明从结构尺寸的不确定性入手来进行机械结构的优化设计。Traditional mechanical design problems are generally based on determined parameters and optimization models, and are solved with the help of classical deterministic optimization problems, but in practical engineering problems, structural dimensions, material properties, loads, boundary conditions, component parameters, measurement Errors or uncertainties such as deviations must exist, and these errors or uncertainties will affect the optimization target performance of the design or the feasibility of changing constraints. The present invention starts from the uncertainty of the structure size to optimize the mechanical structure design.
传统的结构尺寸优化设计是基于确定性模型得到的最优解,能优化得到设计参数的名义尺寸,再根据实际工程经验给定名义尺寸的公差,实际参数的尺寸会在名义尺寸附近浮动,尺寸误差是由制造、测量、装配和磨损等在现有技术条件下带来的不确定性因素造成,它会使得目标性能和约束条件在一定范围内波动,特别是关键结构尺寸参数误差会影响设计的优化目标性能或改变约束的可行性,此时必须考虑目标性能区间和约束条件区间。关键结构尺寸参数误差的分布可以通过长期的生产实践得到,但是目标性能区间的分布和约束条件区间的分布未知,然而优化过程中要对不同关键结构尺寸参数误差方案的目标性能区间进行比较同时使得约束条件区间得到满足。The traditional structural size optimization design is based on the optimal solution obtained by the deterministic model, which can optimize the nominal size of the design parameters, and then give the tolerance of the nominal size according to the actual engineering experience. The size of the actual parameters will float near the nominal size. Errors are caused by uncertain factors such as manufacturing, measurement, assembly and wear under the existing technical conditions, which will cause the target performance and constraints to fluctuate within a certain range, especially the key structural dimensional parameter errors will affect the design To optimize the target performance or change the feasibility of constraints, the target performance interval and the constraint condition interval must be considered. The distribution of key structural dimension parameter error can be obtained through long-term production practice, but the distribution of target performance interval and the distribution of constraint condition interval are unknown. However, in the optimization process, the target performance interval of different key structural dimension parameter error schemes should be compared while making The constraint interval is satisfied.
近年来国内外学者针对参数不确定性提出了许多方法,一般而言这些方法基于三类模型:概率模型、模糊模型、非概率模型。概率模型以概率论和随机规划为基础,将不确定性参数看成随机变量,通过统计方法构造不确定性参数的精确概率分布。模糊模型以模糊理论和模糊规划为基础,将不确定参数看成模糊数,构造其模糊隶属度函数。非概率模型无需构造精准的概率分布或者模糊隶属度函数,而是用凸集或者区间来描述不确定性参数,只需知道不确定性参数的上下界即可。In recent years, scholars at home and abroad have proposed many methods for parameter uncertainty. Generally speaking, these methods are based on three types of models: probabilistic models, fuzzy models, and non-probabilistic models. The probability model is based on probability theory and stochastic programming, treats uncertain parameters as random variables, and constructs accurate probability distributions of uncertain parameters through statistical methods. Based on fuzzy theory and fuzzy programming, fuzzy model regards uncertain parameters as fuzzy numbers and constructs its fuzzy membership function. Non-probabilistic models do not need to construct accurate probability distributions or fuzzy membership functions, but use convex sets or intervals to describe uncertainty parameters, and only need to know the upper and lower bounds of uncertainty parameters.
C.Jiang,H.C.Xie,Z.G.Zhang提出了一种考虑公差的区间不确定性优化方法,定义了一个无量纲的设计公差指标,采用服从均匀分布的区间可能度模型处理约束函数,这种方法得到了名义尺寸及公差,但它仅用设计变量区间中点求得平均目标性能,没有将目标性能考虑成区间,更没有考虑目标性能的区间分布,同时定义的无量纲设计公差指标局限于数学意义。C.Jiang, H.C.Xie, Z.G.Zhang proposed an interval uncertainty optimization method considering tolerances, defined a dimensionless design tolerance index, and used a uniformly distributed interval probability model to process the constraint function. This method obtains The nominal size and tolerance are not considered, but it only uses the midpoint of the design variable interval to obtain the average target performance. It does not consider the target performance as an interval, nor does it consider the interval distribution of the target performance. At the same time, the defined dimensionless design tolerance index is limited to mathematical meaning. .
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明为解决结构尺寸参数和尺寸公差不能同步优化,关键结构尺寸参数误差会影响结构设计的优化目标性能或改变约束的可行性问题,提供了一种机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化方法,将关键结构尺寸参数区间离散化为离散型随机变量,来得到目标性能区间分布,以加工精度为评价指标构建平均公差等级系数评价函数,建立考虑目标性能区间分布、约束条件区间分布和加工精度的不确定性优化模型同时优化关键结构尺寸参数的名义尺寸和尺寸公差。In order to solve the feasibility problem that the structural dimension parameters and the dimensional tolerance cannot be optimized synchronously, and the error of the key structural dimension parameter will affect the optimization target performance of the structural design or change the constraints, the invention provides a mechanical component structural dimension parameter and its dimensional tolerance. The interval optimization method discretizes the interval of key structural size parameters into discrete random variables to obtain the interval distribution of target performance, and uses the machining accuracy as the evaluation index to construct an evaluation function of the average tolerance grade coefficient, and establishes the interval distribution considering the target performance and constraints. And the uncertainty optimization model of machining accuracy simultaneously optimizes the nominal dimensions and dimensional tolerances of key structural dimensional parameters.
本发明技术解决方案:一种机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化方法,包括以下步骤:The technical solution of the present invention: an interval optimization method for structural dimension parameters of mechanical parts and their dimension tolerances, comprising the following steps:
步骤一、确定需要进行区间优化设计的机械零部件的结构尺寸参数集合X=[x1,x2,...,xm],m为参数的个数,含尺寸公差的结构尺寸参数xj为:
步骤二、假设结构尺寸参数服从正态分布,建立结构尺寸参数xj小于等于尺寸a的区间可能度;将结构尺寸参数离散化,得到离散型结构尺寸参数的取值和取值对应的概率;再把离散型结构尺寸参数代入函数f(X),实现函数f(X)的离散化;建立基于离散化的区间可能度模型;通过基于离散化的区间可能度模型建立关于结构尺寸参数区间方案两两比较的可能度矩阵;
步骤三、用区间中点和区间半径描述结构尺寸参数区间,建立平均公差等级系数A;Step 3: Use the interval midpoint and interval radius to describe the structural dimension parameter interval, and establish the average tolerance grade coefficient A;
步骤四、以基于离散化的区间可能度模型和平均公差等级系数A转化不确定性优化问题为确定性优化问题,建立机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化模型;Step 4: Taking the discretization-based interval possibility model and the average tolerance grade coefficient A transforming the uncertainty optimization problem as a deterministic optimization problem, establish an interval optimization model of the structural dimension parameters of mechanical parts and their dimension tolerances;
步骤五、用罚函数法将步骤四的有约束的区间优化模型转化为无约束的区间优化模型;Step 5: Convert the constrained interval optimization model in step 4 into an unconstrained interval optimization model by using the penalty function method;
步骤六、用多目标遗传算法求解步骤五的无约束的区间优化模型。Step 6, use multi-objective genetic algorithm to solve the unconstrained interval optimization model of
本发明与现有技术相比,其显著优点为:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following significant advantages:
(1)与传统的结构优化问题相比较,所建立的区间优化方法不仅仅得到结构尺寸的名义尺寸,而且还得到了其尺寸公差,大大缩短设计周期节约成本。(1) Compared with the traditional structural optimization problem, the established interval optimization method not only obtains the nominal size of the structure size, but also obtains its dimensional tolerance, which greatly shortens the design cycle and saves costs.
(2)与传统区间优化相比较,所建立的优化方法考虑了目标函数区间分布、约束条件区间分布,得到的优化设计方案在实际情况下目标性能更优,约束的可行性更可靠。(2) Compared with the traditional interval optimization, the established optimization method considers the interval distribution of the objective function and the interval distribution of the constraint conditions, and the obtained optimization design scheme has better objective performance and more reliable constraints in the actual situation.
(3)考虑加工精度建立的平均公差等级系数工程意义明显,使得优化模型在考虑目标性能和约束条件的基础上,考虑了实际加工精度因素,使得优化的结果更满足实际情况。(3) The average tolerance grade coefficient established by considering the machining accuracy has obvious engineering significance, so that the optimization model takes into account the actual machining accuracy factors on the basis of considering the target performance and constraints, so that the optimization results are more suitable for the actual situation.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1本发明区间优化方法的流程图。Fig. 1 is a flow chart of the interval optimization method of the present invention.
图2结合本发明区间优化方法的NGSA-Ⅱ遗传算法流程图。Fig. 2 is a flow chart of the NGSA-II genetic algorithm combined with the interval optimization method of the present invention.
图3实施例1的目标函数的最佳区间的期望随迭代次数的曲线。FIG. 3 is a curve of the expectation of the optimal interval of the objective function in
图4实施例1的平均公差等级评价函数的最佳值随迭代次数的曲线。FIG. 4 is a graph of the optimal value of the average tolerance level evaluation function of the
图5实施例1的最优Pareto解集的目标性能和平均公差等级系数。Figure 5. Target performance and average tolerance class coefficients for the optimal Pareto solution set of Example 1.
图6实施例2的目标函数的最佳区间的期望随迭代次数的曲线。FIG. 6 is a graph of the expectation of the optimal interval of the objective function in
图7实施例2的平均公差等级评价函数的最佳值随迭代次数的曲线。FIG. 7 is a graph of the optimum value of the mean tolerance level evaluation function of the second embodiment as a function of the number of iterations.
图8实施例2的最优Pareto解集的目标性能和平均公差等级系数。Figure 8. Target performance and mean tolerance class coefficients for the optimal Pareto solution set for Example 2.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明基于离散化区间可能度和平均公差等级系数构建了一种机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化方法。The invention constructs an interval optimization method for structural dimension parameters of mechanical parts and their dimension tolerances based on the discretization interval possibility and the average tolerance grade coefficient.
下面结合附图和实施例对本发明做进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
结合图1本实施方式所述的一种机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化方法的建立具体步骤如下:The specific steps for establishing an interval optimization method for structural dimension parameters of mechanical parts and their dimensional tolerances described in this embodiment in conjunction with FIG. 1 are as follows:
步骤一、确定需要进行区间优化设计的机械零部件的结构尺寸参数m个X=[x1,x2,...,xm],结构尺寸参数xj考虑尺寸公差后表示为:
步骤二、假设结构尺寸参数服从正态分布,建立结构尺寸参数xj小于等于尺寸a的区间可能度;将结构尺寸参数离散化,得到离散型结构尺寸参数的取值和取值对应的概率;再把离散型结构尺寸参数代入函数f(X),实现函数f(X)的离散化;建立基于离散化的区间可能度模型;通过基于离散化的区间可能度模型建立关于结构尺寸参数区间方案两两比较的可能度矩阵;
步骤二(一)、假设结构尺寸参数服从以为均值,为标准差的正态分布,服从正态分布的区间小于等于尺寸a的区间可能度模型表示如下:Step 2 (1), assuming that the structural size parameters obey the following is the mean, is the normal distribution with standard deviation, and obeys the interval of the normal distribution The interval probability model less than or equal to size a is expressed as follows:
式中Φ(x)是μ=0,σ=1的标准正态分布的分布函数;where Φ(x) is the distribution function of the standard normal distribution with μ=0 and σ=1;
步骤二(二)、将结构尺寸参数区间分成n等份,每份为一个单元,每个单元有两个节点同时包含一个单元中点用单元中点来代替每个单元,单元对应的概率就是单元中点的概率,表示如下:Step 2 (2), set the structure size parameter range Divided into n equal parts, each part is a unit, each unit has two nodes Also contains a cell midpoint Replacing each unit with the midpoint of the unit, the probability corresponding to the unit is the probability of the midpoint of the unit, which is expressed as follows:
每个水平值对应的可能度,由式(4)可能度模型得到:The probability corresponding to each level value is obtained from the probability model of equation (4):
结构尺寸参数离散为离散型随机变量后记作<xj>、p(<xj>);Structural dimension parameters Discrete is a discrete random variable and denoted as <xj >, p(<xj >);
假设结构尺寸参数之间相互独立,每个结构尺寸参数离散化时的取值水平个数均为n,构成一个m维设计参数矩阵<X>n×n×...×n,每个元素记为Assuming that the structure size parameters are independent of each other, the number of value levels when each structure size parameter is discretized is n, forming an m-dimensional design parameter matrix <X>n×n×...×n , each element marked as
m维设计参数矩阵<X>n×n×...×n每个元素对应的可能度构成m维可能度矩阵<P>n×n×...×n,每个元素对应的可能度采用相互独立的离散型变量的联合分布公式有:The m-dimensional design parameter matrix<X>n×n×...×n The possibility corresponding to each element constitutes the m-dimensional possibility matrix<P>n×n×...×n , the possibility corresponding to each element The joint distribution formula using independent discrete variables is:
将代入函数f(X)得到形成m维函数矩阵f(<X>)n×n×...×n,其对应的m维可能度矩阵依然为<P>n×n×...×n;Will Substitute into the function f(X) to get An m-dimensional function matrix f(<X>)n×n×...×n is formed, and the corresponding m-dimensional possibility matrix is still <P>n×n×...×n;
步骤二(三)、建立基于离散化的区间可能度模型:Step 2 (3), establish a discretization-based interval possibility model:
f(<Xj>)n×n×...×n的元素小于等于f(<Xz>)n×n×...×n的元素可能度为:The element probability of f(<Xj >)n×n×...×n is less than or equal to f(<Xz >)n×n×...×n is:
将f(<Xj>)n×n×...×n的每一个元素与f(<Xz>)n×n×...×n的所有元素按式(6)计算,然后求和,f(Xj)I小于等于f(Xz)I的区间可能度模型为:Calculate each element of f(<Xj >) n×n×...×n and all elements of f(<Xz >) n×n×...×n according to formula (6), and then find And, the interval possibility model of f(Xj )I less than or equal to f(Xz )I is:
步骤二(四)、建立结构尺寸参数区间方案两两比较的可能度矩阵;Step 2 (4), establishing a possibility matrix for pairwise comparison of structural size parameter interval schemes;
结构尺寸参数区间方案对应的目标函数分别形成m维函数矩阵f(<X1>)n×n×...×n,f(<X2>)n×n×...×n,…,f(<Xq>)n×n×...×n;结构尺寸参数区间方案两两比较的可能度矩阵为:Structural dimension parameter interval scheme The corresponding objective functions respectively form m-dimensional function matrices f(<X1 >)n×n×...×n , f(<X2 >)n×n×...×n ,..., f(<Xq >)n×n×...×n ; the possibility matrix for the pairwise comparison of the structure size parameter interval scheme is:
其中pjk=p(f(Xj)I≤f(Xk)I);j,k=1,2,...,q。where pjk =p(f(Xj )I ≤f(Xk )I ); j, k=1, 2, . . . , q.
将式(8)的每一行元素加起来得到:Adding up the elements of each row of equation (8), we get:
Pi=pi1+pi2+...+pi(j-1)+pi(j+1)+...+piq;i,j=1,2,...,q. (9)Pi = pi1 +pi2 +...+pi(j-1) +pi(j+1) +...+piq ; i,j=1,2,...,q. (9)
当优化问题求函数f(X)的最小值时,以-Pj作为排序依据。When the optimization problem seeks the minimum value of the function f(X), -Pj is used as the sorting basis.
步骤三、用区间中点和区间半径描述结构尺寸参数区间,建立平均公差等级系数A;Step 3: Use the interval midpoint and interval radius to describe the structural dimension parameter interval, and establish the average tolerance grade coefficient A;
步骤三(一)、用区间中点和区间半径描述结构尺寸参数区间:Step 3 (1), use the interval midpoint and interval radius to describe the structural size parameter interval:
式中为区间中点,为区间半径;in the formula is the midpoint of the interval, is the interval radius;
步骤三(二)、建立平均公差等级系数评价函数:Step 3 (2), establish the average tolerance grade coefficient evaluation function:
先建立连续型的公差等级系数:First establish the continuous tolerance class coefficient:
式中其中D为直径,单位mm;i为公差单位,单位mm;in the formula Where D is the diameter, in mm; i is the tolerance unit, in mm;
平均公差等级系数评价函数为:The evaluation function of the average tolerance level coefficient is:
步骤四、以基于离散化的区间可能度模型和平均公差等级系数A转化不确定性优化问题为确定性优化问题,建立机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化模型;Step 4: Taking the discretization-based interval possibility model and the average tolerance grade coefficient A transforming the uncertainty optimization problem as a deterministic optimization problem, establish an interval optimization model of the structural dimension parameters of mechanical parts and their dimension tolerances;
一般的结构优化问题转化为如下区间优化问题,由于优化问题求最小值,在平均公差等级系数前加负号,则机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化模型为:The general structural optimization problem is transformed into the following interval optimization problem. Since the optimization problem seeks the minimum value, a minus sign is added before the average tolerance grade coefficient, and the interval optimization model of the structural dimension parameters of mechanical parts and their dimension tolerances is:
式中l为约束函数的个数。where l is the number of constraint functions.
步骤五、用罚函数法将步骤四有约束的区间优化模型转化为无约束的区间优化模型:
将第一部分目标函数min f(<XC,XW>)n×n×...×n和约束函数gj(<XC,XW>)n×n×...×n对应位置的元素采用罚函数来处理得到增广目标函数1:The first part of the objective function min f(<XC , XW >)n×n×...×n and the constraint function gj (<XC , XW >)n×n×...×n correspond to the position The elements of are processed with a penalty function to obtain the augmented objective function 1:
式中M为惩罚因子;where M is the penalty factor;
将约束函数离散化后的所有元素用罚函数法全部惩罚到第二部分平均公差等级系数评价函数A上,得到增广目标函数2:All the elements after the discretization of the constraint function are all penalized to the second part of the average tolerance grade coefficient evaluation function A by the penalty function method, and the augmented
通过式(14)、(15)将有约束区间优化问题(13)转化为如下无约束区间优化问题:The constrained interval optimization problem (13) is transformed into the following unconstrained interval optimization problem by equations (14) and (15):
步骤六、用多目标遗传算法求解步骤五的无约束的机械零部件结构尺寸参数及其尺寸公差的区间优化模型。In step 6, the multi-objective genetic algorithm is used to solve the interval optimization model of the unconstrained mechanical component structural dimension parameters and dimension tolerances of the
实施例1:Example 1:
如下含有两个设计参数的确定性优化问题:The following is a deterministic optimization problem with two design parameters:
根据式(5),n取10,得到的m维可能度矩阵<P>10×10为:According to formula (5), n is taken as 10, and the obtained m-dimensional possibility matrix <P>10×10 is:
根据式(13),上述优化问题转化为:According to formula (13), the above optimization problem is transformed into:
上式中的优化设计参数为The optimized design parameters in the above formula are
用式(16)转化为无约束优化问题,结合图2,采用NSGA-Ⅱ遗传算法编程计算,种群数为100,迭代400代,算数交叉的交叉概率为0.8,高斯变异的变异概率为0.1。Using equation (16) to transform into an unconstrained optimization problem, combined with Figure 2, using NSGA-II genetic algorithm programming calculation, the population number is 100, the iteration is 400 generations, the crossover probability of arithmetic crossover is 0.8, and the mutation probability of Gaussian mutation is 0.1.
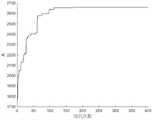
结合图3、图4知遗传算法迭代220代前有多次明显跳跃,说明寻找到了更优个体,220代后目标性能和平均公差等级系数基本没有变化,说明算法收敛。Combined with Figure 3 and Figure 4, it can be seen that there are many obvious jumps before the genetic algorithm iteration 220 generations, indicating that a better individual has been found. After 220 generations, the target performance and the average tolerance grade coefficient basically did not change, indicating that the algorithm converged.
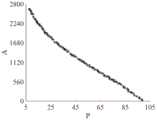
结合图4,得到的最优Pareto解集,反映了目标性能的最优区间会随着平均公差等级系数的增大而逐渐变差,两者成负相关。Combined with Figure 4, the obtained optimal Pareto solution set reflects that the optimal interval of target performance will gradually deteriorate with the increase of the average tolerance level coefficient, and the two are negatively correlated.
结合表1,关键设计参数不再是一个确定的值,而是包含误差的一个区间;得到了目标函数的区间及分布,每个设计方案的平均公差等级系数。Combining with Table 1, the key design parameter is no longer a definite value, but an interval containing the error; the interval and distribution of the objective function and the average tolerance grade coefficient of each design scheme are obtained.
表1实施例1的部分Pareto最优解。Table 1 Partial Pareto optimal solutions of Example 1.
实施例2Example 2
针对某大口径火炮的制退机径向尺寸大,结构不够紧凑的问题,本文采用上述优化模型来获得其参数误差方案。制退机主要结构参数有制退机工作长度L、活塞工作面积A0、制退筒内径DT、制退杆外径dT、制退杆内腔直径d1、节制环直径dp、制退筒外径D1,其中其他参数均依赖制退筒内径DT和制退杆外径dT得到,选取DT和dT为关键设计参数[x1,x2]=[DT,dT];目标函数为考虑实际结构得到的活塞工作面积与考虑制退机液量温升得到的活塞工作面积之差的绝对值最小,可获得最小的活塞工作面积,使得制退机径向尺寸尽量小,结构更加紧凑;约束条件1为满足制退杆复进时受内腔压力的强度条件,按受内压的厚壁圆筒公式;约束条件2为满足节制杆稳定性条件,按压杆稳定的欧拉公式;边界条件为关键设计参数的上下限值。Aiming at the problem of large radial size and not compact structure of the braking machine of a large-caliber artillery, this paper adopts the above optimization model to obtain its parameter error scheme. The main structural parameters of the braking machine include the working length L of the braking machine, the working area of the piston A0 , the inner diameter of the braking cylinder DT , the outer diameter of the braking rod dT , the diameter of the inner cavity of the braking rod d1 , the diameter of the control ring dp , The outer diameter D1 of the braking cylinder, among which other parameters are obtained from the inner diameter DT of the braking cylinder and the outer diameter dT of the braking rod, and DT and dT are selected as the key design parameters [x1 , x2 ]=[DT , dT ]; the objective function is that the absolute value of the difference between the working area of the piston obtained by considering the actual structure and the working area of the piston obtained by considering the fluid volume and temperature rise of the braking machine is the smallest, so that the minimum working area of the piston can be obtained, so that the diameter of the braking machine can be minimized. The size of the direction is as small as possible, and the structure is more compact;
该优化数学模型写为:The optimization mathematical model is written as:
其中E为自由后坐能量,α为估算系数,λmax为最大后坐长度,e为考虑装配误差及射击条件而保留的余量;hm为复进节制器沟槽最大深度,σs为制退杆材料的屈服极限;n为安全系数,λjx为极限后坐长,FΦfmax为复进节制器最大液压阻力,K为与杆两端固定情况有关的系数,节制杆视为一端固定一端铰接K=2π,Es为节制杆材料弹性模量。Among them, E is the free recoil energy, α is the estimation coefficient, λmax is the maximum recoil length, e is the margin reserved considering the assembly error and shooting conditions; hm is the maximum depth of the recoil controller groove, σs is the braking retreat The yield limit of the rod material; n is the safety factor, λjx is the limit recoil length, FΦfmax is the maximum hydraulic resistance of the recoil controller, K is the coefficient related to the fixed condition of both ends of the rod, and the control rod is regarded as one end fixed and the other end hinged K =2π, Es is the elastic modulus of the control rod material.
根据式(13),同时n取10,上述优化问题转化为:According to formula (13), and at the same time n is 10, the above optimization problem is transformed into:
上式中的优化设计变量为The optimal design variables in the above formula are
用式(16)转化为无约束优化问题,结合图2,并采用NSGA-Ⅱ遗传算法编程计算。It is transformed into an unconstrained optimization problem with formula (16), combined with Fig. 2, and is calculated by NSGA-II genetic algorithm programming.
结合图6、图7知遗传算法迭代150代前有多次明显跳跃,说明寻找到了更优个体,150代后目标性能和平均公差等级系数基本没有变化,说明算法收敛。Combined with Figure 6 and Figure 7, it can be seen that there are many obvious jumps before the 150-generation iteration of the genetic algorithm, indicating that a better individual has been found. After 150 generations, the target performance and the average tolerance level coefficient have basically remained unchanged, indicating that the algorithm has converged.
结合图4,得到的最优Pareto解集,反映了目标性能的最优区间会随着平均公差等级系数的增大而逐渐变差,两者成负相关。Combined with Figure 4, the obtained optimal Pareto solution set reflects that the optimal interval of target performance will gradually deteriorate with the increase of the average tolerance level coefficient, and the two are negatively correlated.
结合表2,制退筒内径和制退杆外径不再是一个确定的值,而是包含误差的一个区间;得到了目标函数的区间及分布,每个设计方案的平均公差等级系数。Combined with Table 2, the inner diameter of the braking cylinder and the outer diameter of the braking rod are no longer a definite value, but an interval containing the error; the interval and distribution of the objective function, and the average tolerance grade coefficient of each design scheme are obtained.
表2实施例2的部分Pareto最优解Table 2 Partial Pareto Optimal Solutions of Example 2
Claims (2)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610280903.9ACN107330131B (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Interval Optimization Method for Structural Dimensional Parameters and Dimensional Tolerances of Mechanical Parts |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610280903.9ACN107330131B (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Interval Optimization Method for Structural Dimensional Parameters and Dimensional Tolerances of Mechanical Parts |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN107330131A CN107330131A (en) | 2017-11-07 |
| CN107330131Btrue CN107330131B (en) | 2020-10-20 |
Family
ID=60193282
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610280903.9AActiveCN107330131B (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Interval Optimization Method for Structural Dimensional Parameters and Dimensional Tolerances of Mechanical Parts |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN107330131B (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108595841B (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2022-04-01 | 中国航发沈阳发动机研究所 | Method for establishing vent hole flow model |
| CN109446601B (en)* | 2018-10-12 | 2022-11-04 | 南京理工大学 | Uncertain optimization method for projectile initial disturbance |
| CN109885061B (en)* | 2019-03-14 | 2021-11-23 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | Improved NSGA-II-based dynamic positioning multi-objective optimization method |
| CN113987717B (en)* | 2021-11-16 | 2024-03-26 | 重庆大学 | Planetary roller screw tolerance optimization design method |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102622483A (en)* | 2012-03-09 | 2012-08-01 | 北京工业大学 | Robust design method based on functional characteristic parameter volatility boundary optimization |
| CN104484531A (en)* | 2014-12-18 | 2015-04-01 | 大连理工大学 | Stiffened plate shell structure reliability optimization method with multisource uncertainty being considered |
| CN105162116A (en)* | 2015-09-10 | 2015-12-16 | 大连理工大学 | Non-linear dual optimization method for figuring out section economic dispatch containing wind power |
| CN105389450A (en)* | 2015-12-24 | 2016-03-09 | 电子科技大学 | Uncertain factor-correlated four-high mill multidisciplinary reliability design optimization method |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6434265B1 (en)* | 1998-09-25 | 2002-08-13 | Apple Computers, Inc. | Aligning rectilinear images in 3D through projective registration and calibration |
- 2016
- 2016-04-29CNCN201610280903.9Apatent/CN107330131B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102622483A (en)* | 2012-03-09 | 2012-08-01 | 北京工业大学 | Robust design method based on functional characteristic parameter volatility boundary optimization |
| CN104484531A (en)* | 2014-12-18 | 2015-04-01 | 大连理工大学 | Stiffened plate shell structure reliability optimization method with multisource uncertainty being considered |
| CN105162116A (en)* | 2015-09-10 | 2015-12-16 | 大连理工大学 | Non-linear dual optimization method for figuring out section economic dispatch containing wind power |
| CN105389450A (en)* | 2015-12-24 | 2016-03-09 | 电子科技大学 | Uncertain factor-correlated four-high mill multidisciplinary reliability design optimization method |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| A new interval optimization method considering tolerance design;C. Jiang;《Engineering Optimization》;20141213;第47卷(第13期);第37-41页* |
| PROBABILISTIC APPROACH FOR DIGITAL HUMAN KINEMATIC AND DYNAMIC RELIABILITIES;Jared Gragg;《Proceedings of the ASME 2012 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference》;20120812;第1-12页* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107330131A (en) | 2017-11-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107330131B (en) | Interval Optimization Method for Structural Dimensional Parameters and Dimensional Tolerances of Mechanical Parts | |
| CN110046408B (en) | Interval uncertainty optimization method based on BP neural network differentiation and interval analysis | |
| CN103366065B (en) | A kind of size optimization design method for aircraft thermal protection system based on section reliability | |
| CN106650934B (en) | The method that thermal process state-space model parameter is accurately recognized using improved genetic Optimization Algorithm | |
| CN119066937A (en) | Method and system for calculating mold structure strength based on digital design | |
| CN113868966A (en) | An optimal design method for the structural parameters of the economizer of a biomass boiler | |
| CN106709133A (en) | Method for soft measurement of nuclear power station reactor core temperature fields on basis of neutral network surface fitting | |
| CN114153180B (en) | Method for predicting thermal error of main shaft of grinding machine | |
| CN112632728A (en) | Turbine mechanical blade profile design and performance prediction method based on deep learning | |
| CN108090293A (en) | A kind of blast furnace hearth and bottom corrodes enveloping surface and determines method | |
| CN117093836A (en) | Last-stage reheater steam temperature early warning method and system based on VMD-EWOA-LSTM | |
| CN120257837A (en) | An optimization method for embedded optical fiber composites based on adaptive genetic algorithm | |
| CN110727987B (en) | A Closed-loop Control Intelligent String Beam Structure Based on Genetic Gradient Algorithm | |
| CN110751173B (en) | Prediction method of critical heat flux density based on deep learning support vector machine | |
| CN111274624B (en) | Multi-working-condition special-shaped node topology optimization design method based on RBF proxy model | |
| CN106503456B (en) | An Ensemble Kalman Filter Reservoir Dynamics History Matching Method Based on Hypersphere Transformation | |
| CN113435080A (en) | Method and system for predicting pipe connection stress of nuclear power equipment | |
| CN111576350B (en) | Automatic optimization method for arch dam body shape | |
| CN110210724B (en) | Water supply network node water demand checking method capable of coupling multiple prior probability distributions simultaneously | |
| CN108197738A (en) | A kind of process parameter optimizing method of polyester filament melt conveying process | |
| Li et al. | Modeling and applying of RBF neural network based on fuzzy clustering and pseudo-inverse method | |
| JP2020183049A (en) | Cooling device design method, cooling device manufacturing method and program | |
| CN108763624B (en) | Method for calculating bounded uncertain structure buckling safety margin | |
| CN113154404A (en) | Intelligent setting method for secondary air volume in urban domestic garbage incineration process | |
| Freitas et al. | CCWI2017: F119'WDNs Calibration Using k-means Algorithm for Pipes Clustering and a Hybrid Model for Optimization' |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |