CN107305768B - A typo-prone calibration method in voice interaction - Google Patents
A typo-prone calibration method in voice interactionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN107305768B CN107305768BCN201610248440.8ACN201610248440ACN107305768BCN 107305768 BCN107305768 BCN 107305768BCN 201610248440 ACN201610248440 ACN 201610248440ACN 107305768 BCN107305768 BCN 107305768B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- word
- similarity
- sentence
- corrected
- context
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G10—MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS; ACOUSTICS
- G10L—SPEECH ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES OR SPEECH SYNTHESIS; SPEECH RECOGNITION; SPEECH OR VOICE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES; SPEECH OR AUDIO CODING OR DECODING
- G10L15/00—Speech recognition
- G10L15/22—Procedures used during a speech recognition process, e.g. man-machine dialogue
- G—PHYSICS
- G10—MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS; ACOUSTICS
- G10L—SPEECH ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES OR SPEECH SYNTHESIS; SPEECH RECOGNITION; SPEECH OR VOICE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES; SPEECH OR AUDIO CODING OR DECODING
- G10L15/00—Speech recognition
- G10L15/08—Speech classification or search
- G10L15/18—Speech classification or search using natural language modelling
- G10L15/1815—Semantic context, e.g. disambiguation of the recognition hypotheses based on word meaning
- G—PHYSICS
- G10—MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS; ACOUSTICS
- G10L—SPEECH ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES OR SPEECH SYNTHESIS; SPEECH RECOGNITION; SPEECH OR VOICE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES; SPEECH OR AUDIO CODING OR DECODING
- G10L15/00—Speech recognition
- G10L15/08—Speech classification or search
- G10L15/18—Speech classification or search using natural language modelling
- G10L15/1822—Parsing for meaning understanding
- G—PHYSICS
- G10—MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS; ACOUSTICS
- G10L—SPEECH ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES OR SPEECH SYNTHESIS; SPEECH RECOGNITION; SPEECH OR VOICE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES; SPEECH OR AUDIO CODING OR DECODING
- G10L15/00—Speech recognition
- G10L15/22—Procedures used during a speech recognition process, e.g. man-machine dialogue
- G10L2015/226—Procedures used during a speech recognition process, e.g. man-machine dialogue using non-speech characteristics
- G10L2015/228—Procedures used during a speech recognition process, e.g. man-machine dialogue using non-speech characteristics of application context
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Audiology, Speech & Language Pathology (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Machine Translation (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及易错字校准技术,具体地,涉及语音交互中的易错字校准方法,尤其是将自然语言理解方法应用于语音交互易错字的校准与纠正中,实现了一个可用的语音交互易错字校准方案。The invention relates to a typo-prone calibration technology, in particular, to a typo-prone calibration method in voice interaction, and in particular applies a natural language understanding method to the calibration and correction of typo-prone characters in voice interaction, and realizes a usable typo-prone calibration for voice interaction Program.
背景技术Background technique
语音交互作为一种人机交互的新途径,近年来,获得了突飞猛进的广泛应用。这首先源于语音识别技术的发展,从隐马尔科夫模型(Hidden Markov Model,HMM)、混合高斯模型(Gaussian Mixture Model,GMM)到现在的深度神经网络模型(Deep Neural Network,DNN),语音识别系统的错误率大幅下降;其次,智能设备用户的使用习惯尚未成型,新技术如语音交互容易被大众接受;而云计算、移动互联网的超常规发展使得大量的全新语料资源产生进而助推了语音识别技术的发展。As a new way of human-computer interaction, voice interaction has been widely used by leaps and bounds in recent years. This first stems from the development of speech recognition technology, from Hidden Markov Model (HMM), Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to the current Deep Neural Network (DNN), speech The error rate of the recognition system has dropped significantly; secondly, the usage habits of smart device users have not yet been formed, and new technologies such as voice interaction are easily accepted by the public; and the extraordinary development of cloud computing and mobile Internet has generated a large number of new corpus resources and boosted the The development of speech recognition technology.
在很多场景下,语音交互具有更加现实的实用价值,符合人类的交互习惯。然而,由于语音输入不可避免会受到环境噪声、衰落信道的影响,经常会产生很多错误结果,此外,由于汉语中存在大量的同音字、音近字现象,导致机器无法准确识别用户的语音输入,使语音识别中较易出现错字。换言之,目前的语音识别正确率尚未达到人们期望的水平,语音识别技术也必须在很多方面取得突破性进展。In many scenarios, voice interaction has more realistic practical value, which is in line with human interaction habits. However, since the voice input is inevitably affected by environmental noise and fading channels, many wrong results are often generated. In addition, due to the existence of a large number of homophones and near-phones in Chinese, the machine cannot accurately recognize the user's voice input. Makes speech recognition more prone to typos. In other words, the current speech recognition accuracy rate has not yet reached the level that people expect, and speech recognition technology must also make breakthroughs in many aspects.
经对现有技术文献的检索发现,中国专利文献号CN201210584746.2,公开号CN103021412A,记载了一种“语音识别方法和系统”,该技术包括:对用户输入的语音信号进行语音识别,获得语音识别结果以及语音识别结果中各字符对应的语音片段;接收用户单独输入的纠错信息并生成纠错字符串;根据纠错字符串确定用户输入的语音信号中产生识别错误的语音段;根据语音识别结果中各字符对应的语音片段,确定产生识别错误的语音段在语音识别结果中所对应的字符串,作为错误字符串;利用纠错字符串替换错误字符串。该技术实现一种错误字符串纠错方法,但纠错字符串的录入需要使用特殊按键后方可录入,或使用拼音、手写等其他方式录入。其中语音录入方式仅可重复之前录入内容,以期达到修正错误识别的目的;但若用户录入的字词未被系统所录入,则该方案将无法正确纠正。Through the retrieval of prior art documents, it is found that Chinese Patent Document No. CN201210584746.2, Publication No. CN103021412A, describes a "speech recognition method and system", the technology includes: voice recognition is performed on the voice signal input by the user, and the voice is obtained. The recognition result and the speech segment corresponding to each character in the speech recognition result; receive the error correction information input by the user alone and generate an error correction string; determine the speech segment with the recognition error in the speech signal input by the user according to the error correction string; The speech segment corresponding to each character in the recognition result is determined, and the character string corresponding to the speech segment in the speech recognition result with the recognition error is determined as the error character string; the error character string is replaced with the error correction character string. This technology implements an error correction method for error strings, but the input of error correction strings needs to be entered after using special keys, or by other methods such as pinyin and handwriting. Among them, the voice input method can only repeat the previously entered content, in order to achieve the purpose of correcting the wrong recognition; but if the words entered by the user are not entered by the system, the solution will not be able to correct correctly.
中国专利文献号CN201310589827.6,公开号CN103680505A,记载了一种“语音识别方法及系统”,该方法包括:持续接收录音输入;利用小词汇量语音识别网络对所述录音进行语音识别,以检查所述录音中是否包含预设的关键词;如果所述录音中包含所述关键词,则利用大词汇量语音识别网络对所述关键词后的录音进行识别,得到识别结果。该技术解决了长时间监听命令时的识别准确率问题,可由小词汇量网络顺利过渡至正常的语音识别阶段,即文中所述的大词汇量网络。但该技术并未对大词汇量网络进行优化,如限制语境下的语义增强等,且未提到相关的易错字校准技术。Chinese Patent Document No. CN201310589827.6, Publication No. CN103680505A, describes a "speech recognition method and system", the method comprising: continuously receiving recording input; using a small vocabulary speech recognition network to perform speech recognition on the recording to check Whether the recording contains a preset keyword; if the recording contains the keyword, a large-vocabulary speech recognition network is used to identify the recording after the keyword to obtain a recognition result. This technology solves the problem of recognition accuracy when listening to commands for a long time, and can smoothly transition from a small-vocabulary network to a normal speech recognition stage, that is, the large-vocabulary network described in the article. However, this technique does not optimize large-vocabulary networks, such as semantic enhancement in restricted contexts, and does not mention related typo-prone calibration techniques.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对现有技术中的缺陷,本发明的目的是提供一种语音交互中的易错字校准方法。本发明使用现有语音识别API(Application Programming Interface,应用程序编程接口),完成一个可用的有价值的易错字校准系统。该系统通过与用户语音交互,感知、识别话题语境,从而在受限语义范围内,利用命名实体识别技术,对含有特定意义的实体实现自动纠错功能,并支持通过人工反馈获得附加语义进而纠错,实现比现有语音识别软件更高的输入效率以及更方便的错字修正方式。In view of the defects in the prior art, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for calibrating typo-prone words in voice interaction. The present invention uses the existing speech recognition API (Application Programming Interface, application programming interface) to complete an available and valuable typo-prone calibration system. By interacting with the user's voice, the system perceives and recognizes the topic context, so that within the scope of limited semantics, the named entity recognition technology is used to realize automatic error correction for entities with specific meanings, and supports obtaining additional semantics through manual feedback. Error correction to achieve higher input efficiency and more convenient typo correction than existing speech recognition software.
根据本发明提供的一种语音交互中的易错字校准方法,包括:According to a method for calibrating typo-prone words in voice interaction provided by the present invention, the method includes:
识别语境步骤:针对不同的领域创建相应的语境知识库,构造语境知识库的步骤包括:首先根据领域的关键词,通过搜索引擎得到相关文档,作为该领域的语料库;然后根据语义知识,获取该领域的核心词,按照核心词聚类得到该领域的实例句子,从而构建了语境知识库。The step of identifying the context: creating corresponding context knowledge bases for different fields. The steps of constructing the context knowledge base include: first, according to the keywords of the field, obtain the relevant documents through the search engine as the corpus of the field; then according to the semantic knowledge , obtain the core words in the field, and cluster the example sentences in the field according to the core words, thus constructing a contextual knowledge base.
优选地,在识别语境步骤中,依据文本句子与语境知识库中不同领域的语境相似度来判断,作为自动纠错的前提;其中,语境相似度的具体算法如下:Preferably, in the step of recognizing the context, the judgment is made according to the context similarity between the text sentence and the context knowledge base in different fields, as the premise of automatic error correction; wherein, the specific algorithm of the context similarity is as follows:
S1:统计文本句子A中每个词语出现的次数,并表示成向量形式;S1: Count the number of occurrences of each word in the text sentence A, and express it in the form of a vector;
S2:按照余弦相似度计算公式,计算文本句子A与语境Ci中向量形式的每一个实例句子B这两个向量之间向量夹角的余弦值,作为基于向量的词形相似度;S2: According to the cosine similarity calculation formula, calculate the cosine value of the vector angle between the two vectors of the text sentence A and each instance sentence B in the vector form in the context Ci, as the vector-based morphological similarity;
S3:将文本句子A的所有词语转为拼音形式,统计文本句子A中每个不同拼音序列出现的次数,表示成向量形式,计算以拼音形式表示的文本句子A与语境Ci中向量形式的每一个实例句子B这两个向量之间向量夹角的余弦值,得到基于向量的拼音相似度;S3: Convert all words of text sentence A into pinyin form, count the number of occurrences of each different pinyin sequence in text sentence A, express it in vector form, and calculate the text sentence A expressed in pinyin form and the vector form in context Ci. The cosine value of the vector angle between the two vectors of each instance sentence B, obtains the pinyin similarity based on the vector;
S4:通过对拼音相似度和词形相似度赋予不同权重,计算文本句子A与每一个实例句子B的句子相似度,并选择句子相似度最大的值,作为文本句子A与语境Ci的句子相似度;S4: Calculate the sentence similarity between text sentence A and each instance sentence B by assigning different weights to pinyin similarity and morphological similarity, and select the value with the largest sentence similarity as the sentence between text sentence A and context Ci. similarity;
S5:计算文本句子A与语境Ci的核心词匹配率,即文本句子A中含有语境Ci中所有核心词的数量占文本句子A中所有词语数量的百分比;S5: Calculate the matching rate of the core words between the text sentence A and the context Ci, that is, the percentage of the number of all the core words in the context Ci contained in the text sentence A to the number of all the words in the text sentence A;
S6:通过对句子相似度和核心词匹配率赋予不同权重,计算文本句子A与语境Ci的语境相似度;S6: Calculate the context similarity between text sentence A and context Ci by assigning different weights to sentence similarity and core word matching rate;
S7:计算文本句子A与语境Ci基于前文语境的平滑语境相似度SmoothContextSim(A,Ci):S7: Calculate the smooth context similarity between text sentence A and context Ci based on the previous context SmoothContextSim(A,Ci ):
SmoothContextSim(A,Ci)=λ1·ContextSim(A-2,Ci)SmoothContextSim(A,Ci )=λ1 ·ContextSim(A-2 ,Ci )
+λ2·ContextSim(A-1,Ci)+λ2 ·ContextSim(A-1 ,Ci )
+λ3·ContextSim(A,Ci)+λ3 ·ContextSim(A,Ci )
λ1+λ2+λ3=1λ1 +λ2 +λ3 =1
λ1≤λ2≤λ3λ1 ≤λ2 ≤λ3
其中,A,A-1,A-2分别表示当前文本句子、当前文本句子的前第一句、当前文本句子的前第两句;λ1,λ2,λ3是常数;ContextSim(X,Y)表示文本句子X与语境Y的语境相似度。Among them, A, A-1 , A-2 respectively represent the current text sentence, the first sentence of the current text sentence, and the first two sentences of the current text sentence; λ1 , λ2 , λ3 are constants; ContextSim(X, Y) represents the contextual similarity between text sentence X and context Y.
优选地,还包括:Preferably, it also includes:
基于限制语义的自动纠错步骤:获取用户语音输入的文本句子中的待纠错地名,对待纠错地名进行差错纠错。The automatic error correction step based on restricted semantics: Obtain the place name to be corrected in the text sentence input by the user's voice, and perform error correction on the place name to be corrected.
优选地,所述基于限制语义的自动纠错步骤,包括:Preferably, the automatic error correction step based on restriction semantics includes:
文本句子读取步骤:读入用户语音输入的文本句子P,P=P1P2...Pi...Pn;其中,pi表示文本句子中的第i个汉字,n表示文本句子的长度;Text sentence reading step: read in the text sentence P input by the user's voice, P=P1 P2 ... Pi ... Pn ; wherein, pi represents theith Chinese character in the text sentence, and n represents the text the length of the sentence;
待纠错地名获取步骤:扫描P,根据地名匹配规则进行匹配,得到待纠错地名;The step of obtaining the place name to be corrected: scan P, and match according to the place name matching rule to obtain the place name to be corrected;
差错纠错步骤:将待纠错地名与地名库中的所有地名进行短文本相似度匹配,得到与待纠错地名最相似的地名,作为查错纠错后的正确地名。Error correction step: short text similarity matching is performed between the place name to be corrected and all the place names in the place name database, and the place name most similar to the place name to be corrected is obtained as the correct place name after error checking and correction.
优选地,地名匹配规则包括如下任一个规则:Preferably, the place name matching rules include any one of the following rules:
规则一:如果Wl属于左边界字的集合,Wr属于右边界字的集合,Wp的字数Wp.len大于1,则将Wp识别为待纠错地名;Rule 1: If Wl belongs to the set of left boundary words, Wr belongs to the set of right boundary words, and the number of words Wp .len of Wp is greater than 1, then Wp is identified as the place name to be corrected;
规则二:如果Wl于左边界字的集合,Wr属于地名后缀的集合,则将由Wp、Wr构成的字串识别为待纠错地名;Rule 2: If Wl belongs to the set of left boundary words, and Wr belongs to the set of place name suffixes, then the string composed of Wp and Wr will be Identify the place name to be corrected;
规则三:如果Wl属于地名后缀的集合,Wr属于右边界字的集合,Wp的字数大于1,则将Wp识别为待纠错地名;Rule 3: If Wl belongs to the set of place name suffixes, Wr belongs to the set of right boundary words, and the number of words of Wp is greater than 1, then Wp is identified as the place name to be corrected;
规则四:如果Wl属于地名后缀的集合,Wr地名后缀的集合,则将由Wp、Wr构成的字串识别为待纠错地名;Rule 4: If Wl belongs to the set of place name suffixes and Wr is the set of place name suffixes, then the string composed of Wp and Wr will be Identify the place name to be corrected;
其中,Wl是待纠错词的前一个词,Wp是待纠错词,Wr是待纠错词的后一个词。Among them, Wl is the word before the word to be corrected, Wp is the word to be corrected, and Wr is the word after the word to be corrected.
优选地,在基于限制语义的自动纠错步骤中,采用带权重的最长公共子序列算法来计算短文本相似度匹配;所述带权重的最长公共子序列算法,是指:两序列的任意两元素之间存在相似度函数,寻找两序列中相似度之和最大的公共子序列,其中,相似度函数定义为两拼音之间的拼音相似度。Preferably, in the automatic error correction step based on restricted semantics, a weighted longest common subsequence algorithm is used to calculate short text similarity matching; the weighted longest common subsequence algorithm refers to: two sequences of There is a similarity function between any two elements, and the common subsequence with the largest sum of similarity in the two sequences is found, where the similarity function is defined as the similarity between two pinyin.
优选地,所述拼音相似度,是指:分别计算两拼音中声母的相似度、两拼音中韵母的相似度,并对音节混用的情况分别赋予相应的相似度。Preferably, the similarity of pinyin refers to calculating the similarity of initials in the two pinyin and the similarity of finals in the two pinyin respectively, and assigning the corresponding similarity to the mixed use of syllables.
优选地,还包括:Preferably, it also includes:
基于语义反馈的人工纠错步骤:根据语音输入的更正句式进行纠错;其中,更正句式的形式包括:Manual error correction step based on semantic feedback: Correct the error according to the corrected sentence pattern of the voice input; wherein, the form of the corrected sentence pattern includes:
第一形式:修改,字A是词B的字C;First form: modification, word A is word C of word B;
第二形式:修改,第N个字A是词B的字C;The second form: modification, the Nth word A is the word C of word B;
其中,字A与字C为同一个字,记为指示字;词B是包含字A与字C的一个成语或词组,记为更正词;Wherein, word A and word C are the same word, denoted as indicative word; word B is an idiom or phrase comprising word A and word C, denoted as correction word;
指示字的拼音与已输入文本中的错字拼音相同,也与更正词中正确字的拼音相同;The pinyin of the indicator word is the same as that of the typo in the entered text and the pinyin of the correct word in the corrected word;
根据指示字,从更正词中提取正确字作为更正字进行替换。According to the indicator, the correct word is extracted from the corrected word as the corrected word for replacement.
与现有技术相比,本发明具有如下的有益效果:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following beneficial effects:
第一,本发明三阶段的易错字校准技术可广泛适用于各类语音识别系统和语音交互设备,既可共同使用,也可单独应用,以增强单一方面的易错字纠正能力。First, the three-stage typo-prone calibration technology of the present invention can be widely used in various speech recognition systems and voice interaction devices, and can be used together or independently to enhance the typo-prone correction capability in one aspect.
第二,本发明的语境识别功能可应用于通用化语音录入系统中,可根据用户输入上下文,识别相应语境,并提高该语境下的各类词语权重,以提高识别正确率。Second, the context recognition function of the present invention can be applied to a generalized voice input system, and can recognize the corresponding context according to the user input context, and increase the weights of various words in the context to improve the recognition accuracy.
第三,本发明的基于语音车载导航语境下的自动纠错功能可提高道路名称、地点等命令实体的识别正确率,减少司机与导航设备的交互、修正频率,提高驾驶安全性。Third, the automatic error correction function based on the voice-based vehicle navigation context of the present invention can improve the recognition accuracy rate of command entities such as road names and locations, reduce the interaction and correction frequency between the driver and the navigation device, and improve driving safety.
第四,本发明的人工语义反馈的自动纠错功能可应用于长时间、大量文本录入的场景下,使用自然流畅的命令语音,实现前文录入信息的纠错。该功能符合国人语言文化习惯,无需额外的点击,即可实现纯语音的文本录入。Fourth, the automatic error correction function of artificial semantic feedback of the present invention can be applied to the scenario of long time and a large amount of text input, using natural and smooth command voice to realize the error correction of the preceding input information. This function is in line with the Chinese language and cultural habits, and it can realize the text input of pure voice without additional clicks.
附图说明Description of drawings
通过阅读参照以下附图对非限制性实施例所作的详细描述,本发明的其它特征、目的和优点将会变得更明显:Other features, objects and advantages of the present invention will become more apparent by reading the detailed description of non-limiting embodiments with reference to the following drawings:
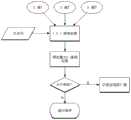
图1为本发明的基本框架示意图。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of the basic framework of the present invention.
图2为本发明的整体校准流程示意图。FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the overall calibration flow of the present invention.
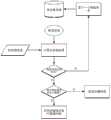
图3为本发明的识别语境流程示意图。FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of a context recognition process flow of the present invention.
图4为本发明的自动纠错流程示意图。FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of the automatic error correction process of the present invention.
图5为本发明的人工纠错流程示意图。FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of the manual error correction process of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施例对本发明进行详细说明。以下实施例将有助于本领域的技术人员进一步理解本发明,但不以任何形式限制本发明。应当指出的是,对本领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本发明构思的前提下,还可以做出若干变化和改进。这些都属于本发明的保护范围。The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to specific embodiments. The following examples will help those skilled in the art to further understand the present invention, but do not limit the present invention in any form. It should be noted that, for those skilled in the art, several changes and improvements can be made without departing from the inventive concept. These all belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
本发明提出了一系列语音交互中的易错字校准技术,将自然语言理解方法应用于语音交互易错字的校准和纠正中,实现一个综合性语音交互易错字校准系统。系统包括如下功能:The invention proposes a series of typo-prone calibration technologies in voice interaction, applies the natural language understanding method to the calibration and correction of typo-prone words in voice interaction, and realizes a comprehensive voice interaction-prone typo-prone calibration system. The system includes the following functions:
第一,基于上下文语境的语义增强。在特定的数个语境下,系统通过分析用户录入的语音,感知、识别话题语境,理解用户的交互需求。First, context-based semantic enhancement. In a number of specific contexts, the system perceives and recognizes the topic context and understands the user's interaction needs by analyzing the voice entered by the user.
第二,基于限制语义的自动纠错。系统通过对语音交互的情景加以限制,在受限语义的上下文环境中,利用语言特征来针对性地提高语音识别的正确率。Second, automatic error correction based on restriction semantics. The system restricts the context of speech interaction and uses language features to improve the accuracy of speech recognition in the context of restricted semantics.
第三,基于语音交互的人工语义增强。要求用户主动通过附加语义与系统语音交互,在交互系统中对重点词语进行语义技术增强,从而引导计算机准确理解用户意图并做出相应的反馈。Third, artificial semantic enhancement based on speech interaction. The user is required to actively interact with the system voice through additional semantics, and the key words are enhanced with semantic technology in the interactive system, so as to guide the computer to accurately understand the user's intention and give corresponding feedback.
具体地,本发明基于现有的语音识别API,完成一个可用的有价值的语音交互易错字校准系统。该系统通过与用户语音交互,感知、识别话题语境,从而在受限语义范围内,利用命名实体识别技术,对含有特定意义的实体实现自动纠错功能,并支持通过人工反馈获得附加语义进而纠错,实现比现有语音识别软件更高的输入效率以及更方便的错字修正方式。图1描述了本发明的基本框架,图2描述了本发明的整体校准流程。Specifically, based on the existing speech recognition API, the present invention completes an available and valuable typo-prone calibration system for speech interaction. By interacting with the user's voice, the system perceives and recognizes the topic context, so that within the scope of limited semantics, the named entity recognition technology is used to realize automatic error correction for entities with specific meanings, and supports obtaining additional semantics through manual feedback. Error correction to achieve higher input efficiency and more convenient typo correction than existing speech recognition software. Figure 1 depicts the basic framework of the present invention, and Figure 2 depicts the overall calibration flow of the present invention.
本发明提供的语音交互中的易错字校准方法,包括步骤:The typo-prone word calibration method in the voice interaction provided by the present invention includes the steps:
第一步,识别语境步骤The first step is to identify the context step
识别语境的首要前提在于针对不同的领域创建相应的语境知识库。构造每个领域的语境知识库的流程如下:首先根据选定领域的关键词,通过搜索引擎得到大量相关文档,作为该领域的语料库。然后根据语义知识,人工获取该领域的核心词,按照核心词手工聚类得到该领域的实例句子,从而构建了语境知识库。The first premise of identifying context is to create corresponding context knowledge bases for different fields. The process of constructing the contextual knowledge base in each field is as follows: Firstly, according to the keywords of the selected field, a large number of relevant documents are obtained through the search engine as the corpus of this field. Then, according to the semantic knowledge, the core words in the field are manually obtained, and the instance sentences in the field are obtained by manual clustering according to the core words, thereby constructing a contextual knowledge base.
在识别语境步骤中,主要依据文本句子与语境知识库中不同领域的语境相似度来判断,作为自动纠错的前提。In the step of recognizing the context, the judgment is mainly based on the similarity between the text sentence and the context in different fields in the context knowledge base, as the premise of automatic error correction.
其中,语境相似度的具体算法如下:Among them, the specific algorithm of context similarity is as follows:
S1:统计文本句子A中每个词语出现的次数,并表示成向量形式;S1: Count the number of occurrences of each word in the text sentence A, and express it in the form of a vector;
S2:按照余弦相似度计算公式,计算文本句子A与语境Ci中每一个向量形式的实例句子B这两个向量之间向量夹角的余弦值,作为基于向量的词形相似度;S2: According to the cosine similarity calculation formula, calculate the cosine value of the vector angle between the two vectors of the text sentence A and the instance sentence B in the form of each vector in the context Ci, as the vector-based morphological similarity;
S3:将文本句子A的所有词语转为拼音形式,统计文本句子A中每个不同拼音序列出现的次数,表示成向量形式,计算文本句子A与语境Ci中每一个向量形式的实例句子B这两个向量之间向量夹角的余弦值,得到基于向量的拼音相似度;S3: Convert all words in text sentence A into pinyin form, count the number of occurrences of each different pinyin sequence in text sentence A, express it in vector form, and calculate text sentence A and context Ci in each vector form instance sentence B The cosine value of the vector angle between these two vectors, to get the vector-based pinyin similarity;
S4:通过对拼音相似度和词形相似度赋予不同权重,计算文本句子A与每一个实例句子B的句子相似度,并选择相似度最大的值,作为文本句子A与语境Ci的句子相似度;S4: Calculate the sentence similarity between text sentence A and each instance sentence B by assigning different weights to pinyin similarity and morphological similarity, and select the value with the largest similarity as the similarity between text sentence A and context Ci. Spend;
S5:计算文本句子A与语境Ci的核心词匹配率,即文本句子A中含有语境Ci中所有核心词的数量占文本句子A中所有词语数量的百分比;S5: Calculate the matching rate of the core words between the text sentence A and the context Ci, that is, the percentage of the number of all the core words in the context Ci contained in the text sentence A to the number of all the words in the text sentence A;
S6:通过对句子相似度和核心词匹配率赋予不同权重,计算文本句子A与语境Ci的语境相似度;S6: Calculate the context similarity between text sentence A and context Ci by assigning different weights to sentence similarity and core word matching rate;
S7:计算文本句子A与语境Ci基于前文语境的平滑语境相似度SmoothContextSim(A,Ci):S7: Calculate the smooth context similarity between text sentence A and context Ci based on the previous context SmoothContextSim(A,Ci ):
SmoothContextSim(A,Ci)=λ1·ContextSim(A-2,Ci)SmoothContextSim(A,Ci )=λ1 ·ContextSim(A-2 ,Ci )
+λ2·ContextSim(A-1,Ci)+λ2 ·ContextSim(A-1 ,Ci )
+λ3·ContextSim(A,Ci)+λ3 ·ContextSim(A,Ci )
λ1+λ2+λ3=1λ1 +λ2 +λ3 =1
λ1≤λ2≤λ3λ1 ≤λ2 ≤λ3
其中,A,A-1,A-2分别表示当前文本句子、当前文本句子的前第一句、当前文本句子的前第两句;λ1,λ2,λ3是常数;ContextSim(X,Y)表示文本句子X与语境Y的语境相似度;Among them, A, A-1 , A-2 respectively represent the current text sentence, the first sentence of the current text sentence, and the first two sentences of the current text sentence; λ1 , λ2 , λ3 are constants; ContextSim(X, Y) represents the context similarity between text sentence X and context Y;
在本发明测试中,选取λ1=0.1,λ2=0.2,λ3=0.7。图3给出了识别语境的大体流程。In the test of the present invention, λ1 =0.1, λ2 =0.2, and λ3 =0.7 are selected. Figure 3 shows the general process of identifying the context.
第二步,基于限制语义的自动纠错步骤The second step, the automatic error correction step based on restriction semantics
本发明优选地将语音交互情景应用在车载导航系统中,因此,在本发明的优选例中,语料库是一个保存着正确路名、地名、机构名的细胞词库。The present invention preferably applies the voice interaction scene to the vehicle navigation system. Therefore, in the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the corpus is a cellular thesaurus storing correct road names, place names, and institution names.
首先,本发明基于对车载导航系统中地名构成、语境规律的分析,定义了下列集合:First of all, the present invention defines the following sets based on the analysis of the structure of place names and the rules of context in the vehicle navigation system:
地名后缀的集合PlaceTailWord,如“市”、“县”、“路”、“区”、“村”等。PlaceTailWord, a collection of place name suffixes, such as "city", "county", "road", "district", "village", etc.
左边界字的集合LeftBorderWord:如“到”、“去”、“往”、“从”、“位于”、“距离”、“靠近”等。The set of left border words LeftBorderWord: such as "to", "go", "to", "from", "located", "distance", "close to" and so on.
右边界字的集合RightBorderWord:如“附近”、“周围”、“旁边”等。A collection of right border words RightBorderWord: such as "nearby", "around", "next to", etc.
AsPlace(S)表示将S识别为待纠错地名。AsPlace(S) means to identify S as the place name to be corrected.
将由Wl、Wp、Wr构成的字串记为Wl是待纠错词的前一个词,Wp是待纠错词,Wr是待纠错词的后一个词。Denote the string composed of Wl , Wp , and Wr as Wl is the word before the word to be corrected, Wp is the word to be corrected, and Wr is the word after the word to be corrected.
具体的地名匹配规则定义如下:The specific place name matching rules are defined as follows:
规则一:如果Wl属于左边界字的集合,Wr属于右边界字的集合,Wp的字数Wp.len大于1,则将Wp识别为待纠错地名;Rule 1: If Wl belongs to the set of left boundary words, Wr belongs to the set of right boundary words, and the number of words Wp .len of Wp is greater than 1, then Wp is identified as the place name to be corrected;
即(Wl∈LeftBorderWord)&&(Wr∈RightBorderWord)&&(Wp.len>1)→AsPlace(Wp)That is (Wl ∈ LeftBorderWord)&&(Wr ∈RightBorderWord)&&(Wp .len>1)→AsPlace(Wp )
规则二:如果Wl于左边界字的集合,Wr属于地名后缀的集合,则将由Wp、Wr构成的字串识别为待纠错地名;Rule 2: If Wl belongs to the set of left boundary words, and Wr belongs to the set of place name suffixes, then the string composed of Wp and Wr will be Identify the place name to be corrected;
即which is
规则三:如果Wl属于地名后缀的集合,Wr属于右边界字的集合,Wp的字数大于1,则将Wp识别为待纠错地名;Rule 3: If Wl belongs to the set of place name suffixes, Wr belongs to the set of right boundary words, and the number of words of Wp is greater than 1, then Wp is identified as the place name to be corrected;
即(Wl∈PlaceTailWord)&&(Wr∈RightBorderWord)&&(Wp.len>1)→AsPlace(Wp)That is (Wl ∈PlaceTailWord)&&(Wr ∈RightBorderWord)&&(Wp .len>1)→AsPlace(Wp )
规则四:如果Wl属于地名后缀的集合,Wr地名后缀的集合,则将由Wp、Wr构成的字串识别为待纠错地名;Rule 4: If Wl belongs to the set of place name suffixes and Wr is the set of place name suffixes, then the string composed of Wp and Wr will be Identify the place name to be corrected;
即which is
命名实体的识别建立在分词结果的基础上,一旦没有正确地分词,命名实体识别的正确率将会大大降低。为了解决分词带来的错误识别,本发明将每一个词切分为一个个字,以字为单位进行命名实体识别。The recognition of named entities is based on the result of word segmentation. Once the word segmentation is not performed correctly, the correct rate of named entity recognition will be greatly reduced. In order to solve the erroneous recognition caused by word segmentation, the present invention divides each word into characters, and performs named entity recognition in units of characters.
具体算法如下:The specific algorithm is as follows:
文本句子读取步骤:读入用户语音输入的文本句子P,P=P1P2...Pi...Pn;其中,pi表示文本句子中的第i个汉字,n表示文本句子的长度;Text sentence reading step: read in the text sentence P input by the user's voice, P=P1 P2 ... Pi ... Pn ; wherein, pi represents theith Chinese character in the text sentence, and n represents the text the length of the sentence;
待纠错地名获取步骤:扫描P,根据地名匹配规则进行匹配,得到待纠错地名;The step of obtaining the place name to be corrected: scan P, and match according to the place name matching rule to obtain the place name to be corrected;
差错纠错步骤:将待纠错地名与地名库中的所有地名进行短文本相似度匹配,得到与待纠错地名最相似的地名,作为查错纠错后的正确地名。Error correction step: short text similarity matching is performed between the place name to be corrected and all the place names in the place name database, and the place name most similar to the place name to be corrected is obtained as the correct place name after error checking and correction.
在自动纠错阶段,本发明主要利用常见地名库中的地名对语音识别结果进行校准和确认。换句话说,将按规则提取出的待纠错地名与常见地名库中的地名进行短文本比较,得到相同或最相似的一个用来进行替换待纠错地名以实现查错纠错。In the automatic error correction stage, the present invention mainly uses the place names in the common place name database to calibrate and confirm the speech recognition result. In other words, the place names to be corrected extracted according to the rules are compared with the place names in the common place names database in short text, and the same or the most similar one is obtained to replace the place names to be corrected to realize error checking and correction.
在基于限制语义的自动纠错步骤中,采用带权重的最长公共子序列算法来计算短文本相似度匹配;所述带权重的最长公共子序列算法,是指:两序列的任意两元素之间存在相似度函数,寻找两序列中相似度之和最大的公共子序列,其中,相似度函数定义为两拼音之间的拼音相似度。In the automatic error correction step based on restricted semantics, the weighted longest common subsequence algorithm is used to calculate the short text similarity matching; the weighted longest common subsequence algorithm refers to: any two elements of the two sequences There is a similarity function between the two sequences, and the common subsequence with the largest sum of similarity in the two sequences is found, where the similarity function is defined as the similarity between the two pinyin.
本发明的短文本比较算法是以拼音为单位实现的,考虑到拼音中声母、韵母的组成结构差别较大,在进行拼音相似度计算时,需要对声母、韵母两部分分别计算相似度。两个不同拼音中,一旦声母或韵母完全相同,则赋予0.5的相似度;若声母或韵母相似(如平翘舌音、前后鼻音等),即赋予0.25的相似度。The short text comparison algorithm of the present invention is implemented in units of pinyin. Considering that the composition and structure of initials and finals in pinyin are quite different, when calculating the similarity of pinyin, it is necessary to calculate the similarity of the initials and finals respectively. In two different pinyin, once the initials or finals are exactly the same, a similarity of 0.5 is given; if the initials or finals are similar (such as flattened tongue, front and rear nasal, etc.), a similarity of 0.25 is given.
在此基础上,本发明采用带权重的最长公共子序列算法,以字为单位计算候选地名A与常见地名库中地名B的拼音相似度,利用动态规划思想,计算A与B的最长公共子序列。On this basis, the present invention adopts the longest common subsequence algorithm with weight, calculates the phonetic similarity between the candidate place name A and the place name B in the common place name database in units of words, and uses the dynamic programming idea to calculate the longest distance between A and B. public subsequence.
设用二维数组WLCS[i,j]表示字符串A=a0a1...an中第i位字符和字符串B=b0b1...bm中第j位字符之前带权重的最长公共子序列,则有Let a two-dimensional array WLCS[i,j] be used to represent the i-th character in the string A=a0 a1 ... an and the string B=b0 b1 ...bm before the j-th character longest common subsequence with weight, then
其中,0≤i≤n,0≤j≤m。SimPY(ai,bj)表示字符串A的第i位字符与字符串B的第j位字符的拼音相似度,利用前文的拼音相似度算法计算得到。Among them, 0≤i≤n, 0≤j≤m. SimPY(ai,bj ) represents the pinyin similarity between the i-th character of the string A and the j-th character of the string B, which is calculated by using the above-mentioned pinyin similarity algorithm.
字符串A和B的相似度SimWLCS(A,B)可由下述公式计算得来:The similarity of strings A and B, SimWLCS(A,B), can be calculated by the following formula:
其中,WLCS(A,B)表示字符串A、B中各相应位最长公共子序列相似度之和;maxlan(A,B)表示字符串A、B中字符长度的最大值。Among them, WLCS(A, B) represents the sum of the longest common subsequence similarity of each corresponding bit in strings A and B; maxlan(A, B) represents the maximum character length in strings A and B.
第三步,基于语义反馈的人工纠错步骤The third step, manual error correction based on semantic feedback
人工语义反馈的语音交互方案的基本模式为,语音识别系统持续地接收用户发出的语音,并进行识别、处理。在一般情况下,用户正常使用语音进行文字录入,当用户认为某个字出现识别错误时,则可以使用语音进行修正,修正的简单句式为“修改,吴是口天吴的吴”,系统则会自动识别该语音录入模式为更正模式,进入本系统的反馈、更正流程,从更正句式中提取更正信息,并修改之前对应的错字。如果还有其它错字,用户可以重复上述反馈流程,直至更正满意,再进行之后的录入,那么之前录入的文本默认地被用户所确认,不再接受修正。The basic mode of the voice interaction scheme of artificial semantic feedback is that the voice recognition system continuously receives the voice sent by the user, and performs recognition and processing. Under normal circumstances, users normally use voice for text input. When the user thinks that a certain word has a recognition error, he can use voice to correct it. The simple sentence format for correction is "Modify, Wu is the Wu of Wu Tianwu", the system It will automatically recognize the voice input mode as the correction mode, enter the feedback and correction process of the system, extract the correction information from the correction sentence pattern, and modify the previous corresponding typos. If there are other typos, the user can repeat the above feedback process until the correction is satisfied, and then make subsequent entries, then the previously entered text will be confirmed by the user by default and will no longer be corrected.
具体地,用户进行语音输入文本句子时,当输入文本与用户所期待的结果不一致时,用户可以继续通过语音,讲出更正句式,更正句式有两种形式:Specifically, when the user enters a text sentence by voice, when the input text is inconsistent with the result expected by the user, the user can continue to speak the corrected sentence through voice. There are two forms of the corrected sentence:
第一种形式:修改,A是B的C。The first form: modification, A is C of B.
第二种形式:修改,第N个A是B的C。The second form: modification, the Nth A is the C of B.
其中,A与C理应为同一个字,称为“指示字”;B是包含A与C的一个成语或词组,称为“更正词”。指示字在通常情况下,其拼音与已输入文本中的错字拼音相同,也与更正词中正确字的拼音相同。指示字的存在建立起错误字与更正字之间的联系,根据指示字,可以从更正词中提取正确的更正字,在前文中查找错误字,并使用更正字进行替换。例如:Among them, A and C should be the same word, called "indicative word"; B is an idiom or phrase containing A and C, called "correction word". In general, pointers have the same pinyin as the typo in the entered text, and the same pinyin as the correct word in the corrected word. The existence of the pointer establishes the connection between the wrong word and the corrected word. According to the pointer, the correct corrected word can be extracted from the corrected word, the wrong word can be found in the previous text, and the corrected word can be used to replace it. E.g:
用户语音输入:我叫黄亦睿。User voice input: My name is Huang Yirui.
语音识别结果:我叫黄一睿。Speech recognition result: My name is Huang Yirui.
其中“一”字被用户认为是错误录入。用户可以继续使用语音,说出更正句式“修改,亦是不亦乐乎的亦”。此时,A、C部分的亦字为指示字,“不亦乐乎”为更正词。系统将启动纠错流程,使用“亦”字,替换错误的“一”,从而在屏幕上显示正确的结果“我叫黄亦睿”。Among them, the word "one" is considered to be wrongly entered by the user. The user can continue to use the voice and say the correction sentence "modification, it is also a pleasure". At this time, the words in parts A and C are indicative words, and "pleasure" is the correction word. The system will start the error correction process and use the word "Yi" to replace the wrong "One", so that the correct result "My name is Huang Yirui" will be displayed on the screen.
为了避免用户录入文本出现多个发音相同的字而无法选择对其中之一进行修正,需要用户主动说出出错字的具体次序。可以借助第二种形式的更正句式,使用N部分提供的数字,如“第二个A是B的C”,精确出错字的位置,避免多个同音字带来混淆,来修正前文第二个与指示字同音的汉字。In order to avoid that multiple words with the same pronunciation appear in the text entered by the user and cannot choose to correct one of them, the user needs to take the initiative to say the specific order of the erroneous words. With the help of the second form of corrected sentence pattern, use the numbers provided in the N part, such as "the second A is the C of B", to accurately position the wrong word and avoid confusion caused by multiple homophones, to correct the second sentence above. A Chinese character with the same pronunciation as the indicator word.
在修改句式中,指示字部分,一方面,通过拼音,在更正词部分查找拼音对应的汉字,作为正确的更正字;另一方面,通过拼音,在前文中寻找对应的汉字位置,使用更正字进行替换,从而完成错误文本的修正。In the modified sentence pattern, the indicator part, on the one hand, through the pinyin, find the corresponding Chinese character in the pinyin in the correction word part, as the correct correction word; Words are replaced, so as to complete the correction of the erroneous text.
查找更正字的具体步骤如下:The specific steps to find the correct word are as follows:
步骤(1):将更正句子转换为拼音序列,并根据关键字切分得到指示字与更正字。如将“亦是不亦乐乎的亦”转换为拼音序列[yi shi bu yi le hu de yi],通过“shi”,“de”这些关键字切分得到指示字A、更正词B、指示字C的内容,分别为“yi”,[bu yi le hu],“yi”。Step (1): Convert the corrected sentence into a pinyin sequence, and segment it according to the keyword to obtain the indicative word and the corrected word. For example, converting "also a joyful yi" into a sequence of pinyin [yi shi bu yi le hu de yi], through the keywords of "shi" and "de", we can obtain the indicative word A, the corrected word B, the indication word The content of word C is "yi", [bu yi le hu], "yi".
步骤(2):判断指示字A与C是否相同,若相同则查找指示字在更正词中的位置。即“yi”在[bu yi le hu]中的位置下标为2(从1开始)。Step (2): determine whether the pointers A and C are the same, and if they are the same, find the position of the pointer in the corrected word. That is, the position subscript of "yi" in [bu yi le hu] is 2 (starting from 1).
步骤(3):在进行专用知识库或API匹配的过程中,根据位置信息得到指示字拼音在更正词中对应的汉字,作为正确的更正字。这里,不亦乐乎中的“亦”为更正字。Step (3): In the process of matching the special knowledge base or API, the Chinese characters corresponding to the pinyin of the indicator word in the corrected word are obtained according to the position information, as the correct corrected word. Here, the "also" in the ecstasy is a corrected word.
步骤(4):根据更正字的拼音查找上一句中出错字的位置,将出错字替换为更正字,从而达到纠正出错字的功能。Step (4): Find the position of the erroneous word in the previous sentence according to the pinyin of the corrected word, and replace the erroneous word with the corrected word, so as to achieve the function of correcting the erroneous word.
在进行语音反馈与修正中,人们常常采用不易重复的词语对更正字进行组词,如常见词语、成语、名人姓名或专为描述汉字的常用词组。In the process of voice feedback and correction, people often use words that are not easy to repeat to form words for the corrected characters, such as common words, idioms, celebrity names or common phrases specially designed to describe Chinese characters.
汉语中存在不少专有名词,其中各字都是一些词语的缩写,如“编程”,可用“编写的编”,“路程的程”来描述。There are many proper nouns in Chinese, each of which is an abbreviation of some words, such as "programming", which can be described by "writing the program" and "the course of the journey".
同时,汉语中还有一个常见现象,即使用偏旁部首来描述一个字,常见于姓氏或不易组词的描述中,如“草头黄”、“古月胡”等。At the same time, there is a common phenomenon in Chinese, that is, the use of radicals to describe a word, which is often used in the description of surnames or difficult-to-form words, such as "grass head yellow", "guyuehu" and so on.
下表列举了描述汉字的几种情况:The following table lists several situations that describe Chinese characters:
表1描述汉字的几种情况Table 1 describes several situations of Chinese characters
对于成语、名人姓名和常见词语,现有语音识别API均可以正确识别,即可以得到准确的更正词。但对于描述汉字型词语,由于不属于常用词,现有语音识别API并不能全部正确识别。对此,本发明引入了基于惯用语的专用知识库,以提高这类词语的识别正确率。For idioms, celebrity names, and common words, existing speech recognition APIs can correctly identify them, that is, get accurate corrected words. However, for words describing Chinese characters, because they are not commonly used words, existing speech recognition APIs cannot all correctly recognize them. In this regard, the present invention introduces a special knowledge base based on idioms to improve the recognition accuracy of such words.
知识库的每一条记录所代表的待纠错字,都属于常见易错字范畴,储存着专有名词与其拼音的映射,如:The words to be corrected represented by each record in the knowledge base belong to the category of common typos and store the mapping of proper nouns and their pinyin, such as:
li zao zhang:立早章li zao zhang: Li Zao Zhang
gong chang zhang:弓长张gong chang zhang: bow long Zhang
在使用语音识别API识别用户输入,得到修正句式后,系统提取更正词部分的汉字,将其转换为拼音序列,使用该拼音序列,在知识库中寻找匹配的拼音序列,将拼音序列对应的汉字词语,替换更正词部分原有的识别结果,作为新的更正词部分。如果用户的更正词无法匹配到本地知识库时,系统将根据原有的API识别结果来提取,假如,用户的修改语句为“瞿是瞿秋白的瞿”,若本地知识库中不存在对应的记录,而API又能准确识别出瞿秋白时,系统也能做到用“瞿”来纠正错字。After using the speech recognition API to identify the user input and get the corrected sentence pattern, the system extracts the Chinese characters in the corrected word part, converts them into a pinyin sequence, uses the pinyin sequence to find a matching pinyin sequence in the knowledge base, For Chinese characters, replace the original recognition result of the corrected word part as a new corrected word part. If the user's correction words cannot be matched to the local knowledge base, the system will extract them according to the original API recognition results. , and when the API can accurately identify Qu Qiubai, the system can also use "Qu" to correct the typo.
另外,在语音识别中,由于录入者的口音或噪声干扰,识别结果并非用户所想,尤其在单字录入时。即使用户字正腔圆地录入单字,由于口音的存在,加之单字没有上下文词语的辅助,往往很难识别为用户实际说出的字,如“牛”与“刘”,“胡”与“福”,以及平卷舌音和前后鼻音的误差问题。在本发明中,指示字部分就是单字识别的结果,根据更正字提取的流程,如果更正词部分识别正确,但指示字部分被识别成常见的模糊音别字,如“牛奶的刘”等,此时使用拼音liu在拼音序列[niu,nai]中查找,无法匹配到结果。这需要在查找时加入模糊音,以提高更正成功率。In addition, in speech recognition, the recognition result is not what the user expects due to the accent or noise of the input person, especially when inputting a single character. Even if the user enters a single word in a eloquent manner, due to the existence of accents and the lack of contextual words, it is often difficult to recognize the words actually spoken by the user, such as "Niu" and "Liu", "Hu" and "Fu" ”, as well as the error problem of flat roll and front-to-back nasal. In the present invention, the indicator part is the result of single-character recognition. According to the process of correcting word extraction, if the correcting word part is recognized correctly, but the indicator part is recognized as a common fuzzy phonetic word, such as "Liu of milk", etc., this When using the pinyin liu to search in the pinyin sequence [niu, nai], the result cannot be matched. This requires adding ambiguity to the search to improve the success rate of correction.
以上段中的“牛奶的刘”为例,我们构造了拼音liu的模糊音数组[liu,niu],依次使用数据中的元素在拼音序列[niu,nai]中进行查找。对于存在多种模糊音的情况如zhen,模糊音数组按照与原声音相似度排序,即[zhen,zen,zheng,zeng]。系统将依次遍历数组,并在拼音序列中查找匹配。Take "Liu of milk" as an example in the above paragraph, we constructed the fuzzy sound array [liu, niu] of Pinyin liu, and used the elements in the data in turn to search in the Pinyin sequence [niu, nai]. For the case where there are multiple fuzzy sounds such as zhen, the fuzzy sound array is sorted according to the similarity with the original sound, namely [zhen,zen,zheng,zeng]. The system will iterate through the array in turn and look for a match in the pinyin sequence.
使用模糊音能够提高更正词中提取更正字的成功率。同样,当将更正结构应用到前文中,即寻找错误的字并进行替换时,也需要模糊音匹配,以找到错误的字。具体实现,是将正确的字对应的拼音,展开为模糊音数组,使用数组中各元素在前文的拼音序列进行查找,然后再对找到的汉字进行替换。The use of fuzzy sounds can improve the success rate of extracting corrected words from corrected words. Likewise, when applying the correction structure to the preceding text, i.e. finding the wrong word and replacing it, fuzzy sound matching is also required to find the wrong word. The specific implementation is to expand the pinyin corresponding to the correct word into a fuzzy sound array, use each element in the array to search for the previous pinyin sequence, and then replace the found Chinese characters.
以上对本发明的具体实施例进行了描述。需要理解的是,本发明并不局限于上述特定实施方式,本领域技术人员可以在权利要求的范围内做出各种变化或修改,这并不影响本发明的实质内容。在不冲突的情况下,本申请的实施例和实施例中的特征可以任意相互组合。Specific embodiments of the present invention have been described above. It should be understood that the present invention is not limited to the above-mentioned specific embodiments, and those skilled in the art can make various changes or modifications within the scope of the claims, which do not affect the essential content of the present invention. The embodiments of the present application and features in the embodiments may be combined with each other arbitrarily, provided that there is no conflict.
Claims (6)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610248440.8ACN107305768B (en) | 2016-04-20 | 2016-04-20 | A typo-prone calibration method in voice interaction |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610248440.8ACN107305768B (en) | 2016-04-20 | 2016-04-20 | A typo-prone calibration method in voice interaction |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN107305768A CN107305768A (en) | 2017-10-31 |
| CN107305768Btrue CN107305768B (en) | 2020-06-12 |
Family
ID=60152309
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610248440.8AExpired - Fee RelatedCN107305768B (en) | 2016-04-20 | 2016-04-20 | A typo-prone calibration method in voice interaction |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN107305768B (en) |
Families Citing this family (36)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107909996B (en)* | 2017-11-02 | 2020-11-10 | 威盛电子股份有限公司 | Voice recognition method and electronic device |
| CN109785842B (en)* | 2017-11-14 | 2023-09-05 | 蔚来(安徽)控股有限公司 | Speech recognition error correction method and speech recognition error correction system |
| CN108133706B (en)* | 2017-12-21 | 2020-10-27 | 深圳市沃特沃德股份有限公司 | Semantic recognition method and device |
| EP3544001B8 (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2022-01-12 | Articulate.XYZ Ltd | Processing speech-to-text transcriptions |
| CN108664467B (en)* | 2018-04-11 | 2022-09-06 | 广州视源电子科技股份有限公司 | Candidate word evaluation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN108647202B (en)* | 2018-04-11 | 2022-09-06 | 广州视源电子科技股份有限公司 | Candidate word evaluation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN108628826B (en)* | 2018-04-11 | 2022-09-06 | 广州视源电子科技股份有限公司 | Candidate word evaluation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN108694167B (en)* | 2018-04-11 | 2022-09-06 | 广州视源电子科技股份有限公司 | Candidate word evaluation method, candidate word ordering method and device |
| CN108733646B (en)* | 2018-04-11 | 2022-09-06 | 广州视源电子科技股份有限公司 | Candidate word evaluation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN109102797B (en)* | 2018-07-06 | 2024-01-26 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Speech recognition test method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN109040481A (en)* | 2018-08-09 | 2018-12-18 | 武汉优品楚鼎科技有限公司 | The automatic error-correcting smart phone inquiry method, system and device of field of securities |
| CN109036424A (en)* | 2018-08-30 | 2018-12-18 | 出门问问信息科技有限公司 | Audio recognition method, device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium |
| CN109166581A (en)* | 2018-09-26 | 2019-01-08 | 出门问问信息科技有限公司 | Audio recognition method, device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium |
| CN109065056B (en)* | 2018-09-26 | 2021-05-11 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Method and device for controlling air conditioner through voice |
| CN110135879B (en)* | 2018-11-17 | 2024-01-16 | 华南理工大学 | Customer service quality automatic scoring method based on natural language processing |
| CN111462748B (en)* | 2019-01-22 | 2023-09-26 | 北京猎户星空科技有限公司 | Speech recognition processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN110288985B (en)* | 2019-06-28 | 2022-03-08 | 北京猎户星空科技有限公司 | Voice data processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN110880316A (en)* | 2019-10-16 | 2020-03-13 | 苏宁云计算有限公司 | Audio output method and system |
| CN111028834B (en)* | 2019-10-30 | 2023-01-20 | 蚂蚁财富(上海)金融信息服务有限公司 | Voice message reminding method and device, server and voice message reminding equipment |
| CN110807319B (en)* | 2019-10-31 | 2023-07-25 | 北京奇艺世纪科技有限公司 | Text content detection method, detection device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN111144101B (en)* | 2019-12-26 | 2021-12-03 | 北大方正集团有限公司 | Wrongly written character processing method and device |
| CN111209737B (en)* | 2019-12-30 | 2022-09-13 | 厦门市美亚柏科信息股份有限公司 | Method for screening out noise document and computer readable storage medium |
| CN111541904B (en)* | 2020-04-15 | 2024-03-22 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Information prompting method, device, equipment and storage medium in live broadcast process |
| CN111554295B (en)* | 2020-04-24 | 2021-06-22 | 科大讯飞(苏州)科技有限公司 | Text error correction method, related device and readable storage medium |
| CN111581970B (en)* | 2020-05-12 | 2023-01-24 | 厦门市美亚柏科信息股份有限公司 | Text recognition method, device and storage medium for network context |
| CN111782896B (en)* | 2020-07-03 | 2023-12-12 | 深圳市壹鸽科技有限公司 | Text processing method, device and terminal after voice recognition |
| CN114079797A (en)* | 2020-08-14 | 2022-02-22 | 阿里巴巴集团控股有限公司 | Live subtitle generation method and device, server, live client and live system |
| CN112016305B (en)* | 2020-09-09 | 2023-03-28 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Text error correction method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN111931490B (en)* | 2020-09-27 | 2021-01-08 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Text error correction method, device and storage medium |
| CN114678027B (en)* | 2020-12-24 | 2024-12-03 | 深圳Tcl新技术有限公司 | Speech recognition result error correction method, device, terminal equipment and storage medium |
| CN112863516B (en)* | 2020-12-31 | 2024-07-23 | 竹间智能科技(上海)有限公司 | Text error correction method and system and electronic equipment |
| CN112331191B (en)* | 2021-01-07 | 2021-04-16 | 广州华源网络科技有限公司 | Voice recognition system and method based on big data |
| CN112767924A (en)* | 2021-02-26 | 2021-05-07 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Voice recognition method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN112905026B (en)* | 2021-03-30 | 2024-04-16 | 完美世界控股集团有限公司 | Method, device, storage medium and computer equipment for showing word suggestion |
| CN118865955B (en)* | 2024-07-07 | 2025-04-04 | 苏州工业职业技术学院 | A mutual information processing method for language recognition model |
| CN118588065B (en)* | 2024-08-02 | 2024-12-10 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | Intention recognition method, electronic device, vehicle and medium |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001273293A (en)* | 2000-03-23 | 2001-10-05 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Word estimation method and apparatus, and recording medium storing word estimation program |
| CN101655837A (en)* | 2009-09-08 | 2010-02-24 | 北京邮电大学 | Method for detecting and correcting error on text after voice recognition |
| JP2014035361A (en)* | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-24 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Speech recognition device and method and program thereof |
| CN105183848A (en)* | 2015-09-07 | 2015-12-23 | 百度在线网络技术(北京)有限公司 | Human-computer chatting method and device based on artificial intelligence |
| CN105869634A (en)* | 2016-03-31 | 2016-08-17 | 重庆大学 | Field-based method and system for feeding back text error correction after speech recognition |
- 2016
- 2016-04-20CNCN201610248440.8Apatent/CN107305768B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001273293A (en)* | 2000-03-23 | 2001-10-05 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Word estimation method and apparatus, and recording medium storing word estimation program |
| CN101655837A (en)* | 2009-09-08 | 2010-02-24 | 北京邮电大学 | Method for detecting and correcting error on text after voice recognition |
| JP2014035361A (en)* | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-24 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Speech recognition device and method and program thereof |
| CN105183848A (en)* | 2015-09-07 | 2015-12-23 | 百度在线网络技术(北京)有限公司 | Human-computer chatting method and device based on artificial intelligence |
| CN105869634A (en)* | 2016-03-31 | 2016-08-17 | 重庆大学 | Field-based method and system for feeding back text error correction after speech recognition |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 基于实例语境的语音识别后文本检错与纠错研究;龙丽霞;《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 信息科技辑》;20110315(第3期);第22、36页* |
| 基于生物实体语境的语音识别后文本纠错算法研究;姜俊;《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 信息科技辑》;20120815(第8期);第27-29页* |
| 龙丽霞.基于实例语境的语音识别后文本检错与纠错研究.《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 信息科技辑》.2011,(第3期),第I136-164页.* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107305768A (en) | 2017-10-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107305768B (en) | A typo-prone calibration method in voice interaction | |
| CN112149406B (en) | A Chinese text error correction method and system | |
| KR102390940B1 (en) | Context biasing for speech recognition | |
| CN113692616B (en) | Phoneme-based contextualization for cross-language speech recognition in an end-to-end model | |
| Schuster et al. | Japanese and korean voice search | |
| US8892420B2 (en) | Text segmentation with multiple granularity levels | |
| KR102417045B1 (en) | Method and system for robust tagging of named entities | |
| CN107016994B (en) | Voice recognition method and device | |
| CN103578464B (en) | Language model building method, speech recognition method and electronic device | |
| CN107729313B (en) | Deep neural network-based polyphone pronunciation distinguishing method and device | |
| CN103578465B (en) | Speech recognition method and electronic device | |
| CN103578467B (en) | Acoustic model building method, speech recognition method and electronic device thereof | |
| CN105404621B (en) | A kind of method and system that Chinese character is read for blind person | |
| CN109637537B (en) | Method for automatically acquiring annotated data to optimize user-defined awakening model | |
| CN109032375A (en) | Candidate text sort method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| US20100180199A1 (en) | Detecting name entities and new words | |
| US10290299B2 (en) | Speech recognition using a foreign word grammar | |
| Sitaram et al. | Speech synthesis of code-mixed text | |
| CN108124477A (en) | Segmenter is improved based on pseudo- data to handle natural language | |
| Kumar et al. | A knowledge graph based speech interface for question answering systems | |
| CN103678684A (en) | Chinese word segmentation method based on navigation information retrieval | |
| CN104166462A (en) | Input method and system for characters | |
| CN101415259A (en) | System and method for searching information of embedded equipment based on double-language voice enquiry | |
| KR20130126570A (en) | Apparatus for discriminative training acoustic model considering error of phonemes in keyword and computer recordable medium storing the method thereof | |
| JP5097802B2 (en) | Japanese automatic recommendation system and method using romaji conversion |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20200612 |