CN106932829B - Radiation body examination method and radiation body examination system - Google Patents
Radiation body examination method and radiation body examination systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN106932829B CN106932829BCN201610818922.2ACN201610818922ACN106932829BCN 106932829 BCN106932829 BCN 106932829BCN 201610818922 ACN201610818922 ACN 201610818922ACN 106932829 BCN106932829 BCN 106932829B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- dose
- radiation
- human body
- examination
- examinee
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01V—GEOPHYSICS; GRAVITATIONAL MEASUREMENTS; DETECTING MASSES OR OBJECTS; TAGS
- G01V5/00—Prospecting or detecting by the use of ionising radiation, e.g. of natural or induced radioactivity
- G01V5/20—Detecting prohibited goods, e.g. weapons, explosives, hazardous substances, contraband or smuggled objects
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/54—Control of apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis
- A61B6/542—Control of apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis involving control of exposure
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B6/00—Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis; Apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment
- A61B6/54—Control of apparatus or devices for radiation diagnosis
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01T—MEASUREMENT OF NUCLEAR OR X-RADIATION
- G01T1/00—Measuring X-radiation, gamma radiation, corpuscular radiation, or cosmic radiation
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- General Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Geophysics (AREA)
- Measurement Of Radiation (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明的实施例涉及放射线人体检查方法和放射线人体检查系统,例如用于机场、车站、海关等涉及安全检查的领域和/或医院等涉及人体医学辐射诊疗的领域。Embodiments of the present invention relate to a radiation body examination method and a radiation body examination system, for example, for airports, stations, customs and other fields involving security inspection and/or hospitals and other fields involving human medical radiation diagnosis and treatment.
背景技术Background technique
放射线人体安全检查广泛地用于机场、海关、车站等场所。常用的放射线检查技术包括放射线透视成像及放射线背散射成像。放射线透射成像技术是指利用放射线穿过被检查人体,由计算机分析处理穿过人体之后的放射线信号,形成人体透视图像,这是目前检查人体体内藏匿物品的主要技术手段。放射线背散射技术则是使用微量放射线扫描被检人,通过接收人体表面散射回的射线信号,获取人体表面轮廓图像,这一技术能够有效的检测人体随身携带的危险品。Radiation human safety inspection is widely used in airports, customs, stations and other places. Commonly used radiographic techniques include fluoroscopic imaging and radiation backscatter imaging. Radiation transmission imaging technology refers to the use of radiation passing through the human body to be inspected, and the radiation signal after passing through the human body is analyzed and processed by a computer to form a fluoroscopic image of the human body. Radiation backscattering technology uses trace radiation to scan the subject, and obtains the contour image of the human body surface by receiving the ray signal scattered back from the surface of the human body. This technology can effectively detect the dangerous goods carried by the human body.
人体受照剂量限值是单个人体可接收的受照剂量的上限值,或者单个人体不可接收的受照剂量的下限值。不同放射防护体系,都制定了相应的剂量限值。剂量限值通常包括单次扫描受照剂量限值和年度累积受照剂量限值。放射线人体检查设备需要满足放射防护体系对于剂量限值的要求,以保障被检查者的人体安全。The human exposure dose limit is the upper limit of the exposure dose acceptable to a single human body, or the lower limit value of the unacceptable exposure dose to a single human body. Different radiation protection systems have formulated corresponding dose limits. Dose limits usually include a single scan exposure dose limit and an annual cumulative exposure dose limit. The radiation human body inspection equipment needs to meet the requirements of the radiation protection system for the dose limit to ensure the human safety of the inspected.
但是,目前在使用的放射线类人体检查设备,设计时一般都只考虑了人体单次放射线受照剂量满足放射线防护要求;而对于被检人一定时期内的累积放射线受照剂量,则没有办法提供直接的衡量和控制。而随着现代社会人们被迫接受放射线检查的情况越来越多,累积放射线受照剂量对于人体健康的影响不容忽视。However, the radiation-type human body inspection equipment currently in use is generally only designed to meet the radiation protection requirements for a single dose of radiation exposure to the human body. Direct measurement and control. With more and more cases of people being forced to undergo radiological examinations in modern society, the impact of cumulative radiation dose on human health cannot be ignored.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于提供一种对被检查者来说更安全的放射线人体检查系统和方法,其能够对被检人的单次放射线受照剂量和一定时期内在不同设备上受照的放射线累积剂量总值进行监控和管理,避免放射线受照剂量超限对人体健康带来的危害。An object of the present invention is to provide a system and method for a radiation human body examination that is safer for the examinee, which can measure the single radiation dose of the examinee and the cumulative dose of radiation irradiated on different equipment within a certain period of time. Monitor and manage the total value of radiation exposure to avoid the harm to human health caused by excessive radiation dose.
根据本发明实施例的一个方面,提出一种放射线人体检查方法,包括步骤:对待检查者进行个人身份识别;根据身份识别结果调取被检查者已往的累积放射线受照剂量;获取进行本次检查的放射线人体检查设备的预计单次放射线扫描剂量;计算被检查者已往的累积放射线受照剂量和放射线人体检查设备的所述预计单次放射线受照剂量的累加值;和根据所述累加值是否超过剂量限值来确定是否对被检查者执行本次放射线检查。According to an aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a method for a radiation human body inspection is proposed, which includes the steps of: performing personal identification of the person to be inspected; retrieving the past cumulative radiation dose of the inspected person according to the identification result; obtaining and performing the current inspection The estimated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination equipment; calculate the cumulative value of the past cumulative radiation exposure dose of the examinee and the estimated single radiation exposure dose of the radiation body examination equipment; and according to whether the accumulated value Exceed the dose limit to determine whether to perform this radiation examination on the subject.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,其中,其中,放射线人体检查设备的预计单次放射线扫描剂量是该放射线人体检查设备的额定单次放射线扫描剂量。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, wherein, the estimated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination apparatus is a rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination apparatus.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,其中,所述已往的累积放射线受照剂量是个人在一年内已经接受的放射线受照剂量的累积值,所述剂量限值是个人一年内可以接受的放射线受照剂量的上限值。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, wherein the past cumulative radiation dose is a cumulative value of radiation doses that the individual has received within one year, and the dose limit is the radiation that the individual can receive within one year The upper limit of the exposure dose.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,根据所述累加值是否超过剂量限值来确定是否对被检查者执行本次放射线检查包括:According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, determining whether to perform this radiation examination on the subject according to whether the accumulated value exceeds a dose limit value includes:
当被检查者已往的累积放射线受照剂量和放射线人体检查设备的额定单次放射线受照剂量的累加值超过剂量限值时,确定不对被检查者进行放射线检查;和When the cumulative value of the past cumulative radiation dose of the examinee and the rated single radiation exposure dose of the radiation human examination equipment exceeds the dose limit, it is determined that the examinee will not be subjected to a radiological examination; and
当被检查者已往的累积放射线受照剂量和放射线人体检查设备的额定单次放射线受照剂量的累加值不超过剂量限值时,确定对被检查者执行放射线检查。When the cumulative value of the past cumulative radiation exposure dose of the examinee and the rated single radiation exposure dose of the radiation human examination equipment does not exceed the dose limit, it is determined that the radiation examination is performed on the examinee.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,其中,在对被检查者执行放射线检查的过程中,实时监测放射线人体检查设备的输出参数,如果输出参数异常则中止检查工作;已经执行完成部分的放射线检查受照剂量,按已执行时间与完整执行检查所需时间比例折算本次非完整检查对被检查人员造成的放射线受照剂量。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, in the process of performing the radiological examination on the subject, the output parameters of the radiation human body examination apparatus are monitored in real time, and the examination work is terminated if the output parameters are abnormal; the completed part of the radiological examination has been performed For exposure dose, the radiation exposure dose caused by this incomplete inspection to the inspected personnel is converted according to the ratio of the executed time to the time required for the complete inspection.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,所述的放射线人体检查方法,还包括步骤:在对被检查者执行放射线检查之后,获取被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量,并将本次放射线受照剂量的数据传送至云端剂量信息服务器,以更新被检查者的年度累积放射线受照剂量的值。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the radiation human body examination method further includes the steps of: obtaining the current radiation exposure dose of the examinee after performing the radiation examination on the examinee, and applying the current radiation exposure to the subject. The dose data is transmitted to the cloud dose information server to update the annual cumulative radiation dose value of the examinee.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,获取被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量包括:According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, acquiring the current radiation dose of the subject includes:
获取被检查者本次检查的放射线扫描图像;以及Obtain a radiographic scan of the examinee for this examination; and
对所述放射线扫描图像进行处理,根据所述放射线扫描图像中除人体影像以外的残余像素区域的单像素平均亮度值,经转换系数转换后获得被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量的值,其中,所述单像素亮度值是所述放射线扫描图像中除人体影像以外的残余像素区域的各像素亮度的平均亮度值。Process the radiation scan image, and obtain the current radiation exposure dose value of the examinee after conversion by a conversion coefficient according to the single pixel average luminance value of the residual pixel region in the radiation scan image except for the human body image, The single-pixel brightness value is an average brightness value of the brightness of each pixel in the residual pixel region other than the human body image in the radiographic scan image.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量Y按如下公式计算:According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the current radiation dose Y of the examinee is calculated according to the following formula:
Y=Y1·X/X1Y=Y1·X/X1
其中,X是放射线扫描图像中残余像素区域的单像素平均亮度值,Y1是放射线人体检查设备在本次人体检查时的额定单次放射线扫描剂量的值,X1是对应本次人体检查时的额定单次放射线扫描剂量的值,在无任何遮挡物时得到的扫描图像中的单像素亮度值。Among them, X is the single-pixel average brightness value of the residual pixel area in the radiation scan image, Y1 is the value of the rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination equipment during this body examination, and X1 is the rated value corresponding to this body examination. The value of a single radiation scan dose, the brightness value of a single pixel in the scanned image obtained when there is no obstruction.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,获取被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量包括:获取放射线人体检查设备在本次人体检查时的额定单次放射线扫描剂量,作为被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, acquiring the current dose of radiation exposure of the examinee includes: acquiring the rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation human body examination equipment during the current human body examination, as the current radiation dose of the examinee exposure dose.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,获取被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量包括:被检查者携带个人放射线剂量计同步接受放射线检查,通过个人计量计测量被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, acquiring the current radiation exposure of the examinee includes: the examinee carries a personal radiation dosimeter to receive the radiation examination synchronously, and the current radiation exposure of the examinee is measured by the personal dosimeter. dose.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,所述剂量限值被可变化地配置。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the dose limit is variably configurable.
根据本发明的另一方面,提供一种放射线人体检查系统,一种放射线人体检查系统,包括:According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a radiation body examination system, a radiation body examination system, comprising:
至少一台放射线人体检查设备,构造用于利用放射线对人体进行检查;At least one radiological human examination device constructed to examine the human body using radiation;
个人身份识别设备,所述个人身份识别设备识别被检查者的身份信息,并将该身份信息发送至所述至少一台放射线人体检查设备;Personal identification equipment, the personal identification equipment recognizes the identity information of the examinee, and sends the identity information to the at least one radiological human body examination equipment;
云端剂量信息服务器,构造用于存储该被检查者年度内每次进行放射线检查时的单次放射线受照剂量信息以及年度累积放射线受照剂量;和a cloud dose information server, configured to store the single radiation exposure dose information and the annual cumulative radiation exposure dose of the examinee each time a radiation examination is performed within the year; and
数据处理器,所述数据处理器构造用于从所述至少一台放射线人体检查设备获得额定单次放射线受照剂量和从云端剂量信息服务器获得被检查者的年度已往累积放射线受照剂量,并计算二者的累加值,根据所述累加值是否超过剂量限值来判断是否对被检查者进行本次放射线检查。a data processor configured to obtain a rated single dose of radiation exposure from the at least one radiation human body examination apparatus and to obtain an annual past cumulative radiation dose of the examinee from the cloud dose information server, and Calculate the cumulative value of the two, and determine whether to perform the current radiological examination on the subject according to whether the cumulative value exceeds the dose limit.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,其中,所述放射线人体检查系统包括多台放射线人体检查设备,所述多台放射线人体检查设备与所述云端剂量信息服务器通讯,以将被检查者每次在每台放射线人体检查设备上进行检查时的单次放射线受照剂量的数据传送给云端服务器,并进行年度已受照剂量累加,从而建立个人年度内每次放射线受照剂量信息以及年度累积放射线受照剂量的数据库。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, wherein the radiation body examination system includes a plurality of radiation body examination apparatuses, and the plurality of radiation body examination apparatuses communicate with the cloud dose information server so as to The data of the single radiation exposure dose during the inspection on each radiation human body examination equipment is transmitted to the cloud server, and the annual exposure dose is accumulated, so as to establish the individual annual radiation exposure dose information and the annual cumulative radiation exposure dose. Database of doses.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,其中,所述多台放射线人体检查设备是相同或不同型号的放射线人体检查设备。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, wherein the plurality of radiological human examination apparatuses are the same or different models of radiological human examination apparatuses.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,所述剂量限值存储在云端剂量信息服务器中,所述云端剂量信息服务器可变化地配置所述剂量限值。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the dose limits are stored in a cloud dose information server, which is variably configurable for the dose limits.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,所述数据处理器集成到每台放射线人体检查设备中或集成到所述云端剂量信息服务器中。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the data processor is integrated into each radiation human body inspection apparatus or integrated into the cloud dose information server.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,所述个人身份识别设备集成到每台放射线人体检查设备中。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the personal identification device is integrated into each radiological body examination device.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,所述放射线人体检查系统包括单台放射线人体检查设备,所述个人身份识别设备、所述云端剂量信息服务器和所述数据处理器集成到所述单台放射线人体检查设备中。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the radiation body examination system includes a single radiation body examination device, and the personal identification device, the cloud dose information server and the data processor are integrated into the single radiation body Human body examination equipment.
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,所述的放射线人体检查系统,还包括个人放射线剂量计,所述个人放射线计量计由被检查者携带,用于测量被检查者的单次放射线受照剂量。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the radiation human body inspection system further includes a personal radiation dosimeter, which is carried by the examinee and is used to measure the single dose of radiation exposure of the examinee .
根据本发明的一个示例性实施例,其中,所述放射线人体检查设备包括:According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, wherein the radiation human body inspection apparatus includes:
放射线机或放射源,所述放射线机或放射源用于发射放射线,a radiation machine or source for emitting radiation,
探测器组,所述探测器组构造成接收放射线并产生电信号;和a set of detectors configured to receive radiation and generate electrical signals; and
图像生成装置,构造成将探测器组的电信号转换成放射线扫描图像;以及an image generating device configured to convert the electrical signals of the detector group into a radiographic scan image; and
剂量确定装置,构造成提取所述放射线扫描图像中除人体影像以外的残余像素区域像素的亮度值,并计算所述残余像素区域像素的亮度平均值作为单像素平均亮度值,根据所述单像素平均亮度值经转换系数转换后获得被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量。A dose determination device configured to extract luminance values of pixels in the residual pixel area other than the human body image in the radiation scan image, and calculate an average luminance value of the pixels in the residual pixel area as a single-pixel average luminance value, according to the single-pixel average luminance value The average brightness value is converted by the conversion coefficient to obtain the current radiation dose of the examinee.
根据本发明实施例的放射线人体检查方法和系统,能够全面监控和管理被检人的单次放射线受照剂量和多次累积、年度累积放射线受照剂量,确保被检人接受的放射线剂量不超标,防止辐射事故的发生。The radiation human body inspection method and system according to the embodiments of the present invention can comprehensively monitor and manage the single radiation exposure dose, multiple cumulative and annual cumulative radiation exposure doses of the examinee, and ensure that the radiation dose received by the examinee does not exceed the standard , to prevent the occurrence of radiation accidents.
另外,由于根据残余像素区域单像素平均亮度值实时换算被检查者的当次实际放射线受照剂量,或者采有个人放射线剂量计实时测量被检查者的当次实际放射线受照剂量,因此,可以准确地获得被检查者的当次实际放射线受照剂量,进一步提高放射线人体检查的安全性。In addition, since the current actual radiation dose of the examinee is converted in real time according to the average brightness value of a single pixel in the residual pixel area, or a personal radiation dosimeter is used to measure the actual radiation dose of the examinee in real time, therefore, it is possible to Accurately obtain the current actual radiation dose of the examinee, and further improve the safety of the radiation body examination.
为了使本发明的目的、特征及优点能更加明显易懂,下面结合附图和具体实施例对本发明作进一步说明。In order to make the objects, features and advantages of the present invention more clearly understood, the present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是根据本发明的一个实施例的放射线人体检查系统的示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of a radiation human body inspection system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图2是放射线人体检查设备的基本构成的方框图;Fig. 2 is a block diagram showing the basic configuration of the radiation human body inspection apparatus;
图3是被检查者接受检查的放射线扫描图像的示意图;和3 is a schematic diagram of a radiographic scan image of an examinee undergoing examination; and
图4是利用如图1所示的放射线人体检查系统进行放射线人体检查的方法的流程图。FIG. 4 is a flowchart of a method of performing a radiological human examination using the radiological human examination system shown in FIG. 1 .
具体实施方式Detailed ways
在下面的详细描述中,为便于解释,阐述了许多具体的细节以提供对本披露实施例的全面理解。然而明显地,一个或多个实施例在没有这些具体细节的情况下也可以被实施。在其他情况下,公知的结构和装置被省略以简化附图。并且,在所有附图中,相同的附图标记用于表示相同的部件。In the following detailed description, for convenience of explanation, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the disclosed embodiments. Obviously, however, one or more embodiments may be practiced without these specific details. In other instances, well-known structures and devices are omitted to simplify the drawings. Also, the same reference numerals are used for the same components throughout the drawings.
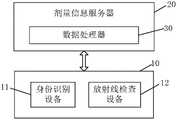
图1是根据本发明的一个实施例的放射线人体检查系统的示意图。如图1所示,放射线人体检查系统总的来说包括用户端10的个人身份识别设备11和放射线人体检查设备12以及网络端(云端)的剂量信息服务器20。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a radiation human body inspection system according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1 , the radiation body examination system generally includes a
个人身份识别设备10在检查前登记或识别被检查者的身份信息,并将该身份信息发送至放射线人体检查设备12。个人身份识别设备10的例子包括身份证阅读器、指纹识别设备、二维码扫码枪、M1读卡器等设备。The
放射线人体检查设备12利用放射线对人体进行安全或医学检查。放射线人体检查设备12能够与云端剂量信息服务器20交互通讯,将个人身份识别设备10识别的被检查者的身份信息传送到云端剂量信息服务器20,并从云端剂量信息服务器20获得该被检查者的年度放射线受照剂量信息、年度累积放射线受照剂量的值。The radiation human
云端剂量信息服务器20能够和放射线人体检查设备12通讯,以从放射线人体检查设备12接受个人每次接受放射线检查时接受的单次放射线扫描剂量的数据,并自动将所述数据进行累加,以得到对应个人的累积放射线受照剂量的数据,例如年度累积放射线受照剂量的值,并存储在云端剂量信息服务器20的存储器中。云端剂量信息服务器20还可以存储包括个人ID、放射线扫描设备ID、扫描时间、单次剂量值、年度累计剂量限值等信息。The cloud
虽然图1示意地示出了一台放射线人体检查设备12。但是,根据其它实施例,放射线人体检查系统可包括多台放射线人体检查设备12,该多台放射线人体检查设备12均与所述云端剂量信息服务器20通讯,形成剂量监控网络。云端剂量信息服务器负责管理所有联网的放射线人体检查设备12。这个网络可大可小,最小的网络就是只有一台设备。一个应用的实例是一座监狱,只有一台设备对人员进行检查。并且,云端剂量信息服务器20中保存的剂量限值是可变化地配置的,具体值根据当地放射防护相关法律法规、行业规范等决定。在某些使用场合,不同性别、不同年龄的使用者,也有不同的剂量限值,这些信息可以通过配置到云端服务器里进行使用。Although FIG. 1 schematically shows a radiation
当有多台放射线人体检查设备12联网时,多台放射线人体检查设备12均与所述云端剂量信息服务器20通讯,以将被检查者每次在每台放射线人体检查设备12上进行检查时的单次放射线受照剂量的数据传送给云端服务器,从而建立个人年度内每次接受放射线检查的放射线受照剂量信息和年度累积放射线受照剂量的数据库。所述多台放射线人体检查设备可以是相同或不同型号的放射线人体检查设备。每台放射线人体检查设备根据其参数配置可以具有不同的额定单次放射线扫描剂量。When a plurality of radiation
所述多台放射线人体检查设备12可以与云端剂量信息服务器20进行远程或近程通讯。多台放射线人体检查设备12与云端剂量信息服务器20之间的网络连接可以通过有线或者无线的方式完成。可以是几台设备组成的局域网,也可以是跨地域的公众网络。因此,因此,本申请的放射线人体检查系统可以实现多台设备的信息共享和管理,最大限度地保护个人辐射防护剂量的安全。The plurality of radiation human body inspection apparatuses 12 can perform long-distance or short-distance communication with the cloud
此外,根据本发明的上述实施例的放射线人体检查系统还包括数据处理器30。图1示出了数据处理器30集成到云端剂量信息服务器20中的例子。所述数据处理器30构造用于从所述至少一台放射线人体检查设备12获得额定单次放射线扫描剂量和从云端剂量信息服务器20获得被检查者的年度累积放射线受照剂量,并计算二者的累加值,根据所述累加值是否超过剂量限值来判断是否对被检查者进行本次放射线检查。Furthermore, the radiation human body inspection system according to the above-described embodiment of the present invention further includes the
具体地,当被检查者的累积放射线受照剂量和放射线人体检查设备的额定单次放射线扫描剂量的累加值超过剂量限值时,确定不对被检查者进行放射线检查;和Specifically, when the cumulative value of the cumulative radiation exposure dose of the examinee and the rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation human body examination apparatus exceeds the dose limit, it is determined that the examinee is not to be subjected to the radiation examination; and
当被检查者的累积放射线受照剂量和放射线人体检查设备的额定单次放射线扫描剂量的累加值不超过剂量限值时,确定对被检查者执行本次放射线检查。When the cumulative value of the cumulative radiation exposure dose of the examinee and the rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation human examination equipment does not exceed the dose limit, it is determined that the current radiation examination is performed on the examinee.
在图1的例子中,所述数据处理器30集成到云端剂量信息服务器20中。这样,当对人体进行检查时,云端剂量信息服务器20可以从放射线人体检查设备12处获得当前被检查者的个人身份信息和当前放射线人体检查设备12的额定单次放射线扫描剂量,然后在云端剂量信息服务器20处数据处理器30将当前放射线人体检查设备12的额定单次放射线扫描剂量和被检查者的年度累积放射线受照剂量相加,得到累加值;并根据累加值是否超过云端剂量信息服务器20设定的剂量限值,来决定是否对被检查者执行当前的放射线检查,并将决定的结果发送给放射线人体检查设备12。In the example of FIG. 1 , the
根据另外的实施例,当有多台放射线人体检查设备时,所述数据处理器30也可以集成到每台放射线人体检查设备12中。这样,当对人体进行安全检查时,放射线人体检查设备12可以将个人身份识别设备10识别的被检查者的身份信息传送到云端剂量信息服务器20,并从云端剂量信息服务器20获得该被检查者的年度累积放射线受照剂量的值。然后,集成到放射线人体检查设备12中的数据处理器可以将当前放射线人体检查设备12的额定单次放射线扫描剂量和被检查者的年度累积放射线受照剂量相加,得到累加值;并根据累加值是否超过云端剂量信息服务器20设定的剂量限值,来决定是否对被检查者执行当前的放射线检查。According to another embodiment, the
此外,所述个人身份识别设备11可以是独立于放射线人体检查设备的设备,例如可以单独放置于操作台、或由操作人员手持;或者,所述个人身份识别设备11也可以集成到每台放射线人体检查设备12中,例如固定在放射线人体检查设备12的表面上。In addition, the
当所述放射线人体检查系统包括单台放射线人体检查设备12时,云端剂量信息服务器20可以放置于服务器机房,也可以集成于单台放射线人体检查设备12中。并且,所述个人身份识别设备11和所述数据处理器30也可以集成到单台放射线人体检查设备12中。When the radiation body examination system includes a single radiation
如果有多台放射线人体检查设备12时,云端剂量信息服务器20可以放置于机房,也可以集成于联网的某一台放射线人体检查设备12中。If there are multiple radiation human body inspection apparatuses 12 , the cloud
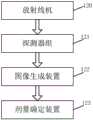
如图2所示,每台放射线人体检查设备12具体可以包括:放射线机或放射源120,所述放射线机或放射源用于发射放射线,探测器组121,所述探测器组构造成接收放射线并产生电信号,探测器组121可以由排成阵列的多个探测器构成;图像生成装置122,构造成将探测器组的电信号转换成放射线扫描图像;以及剂量确定装置123,构造成提取所述放射线扫描图像中除人体影像以外的残余像素区域的各像素的亮度值,并计算所述残余像素区域的各像素的亮度值的平均值作为单像素平均亮度值,根据所述单像素平均亮度值确定被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量。As shown in FIG. 2 , each radiographic human
本领域技术人员可以理解,放射线人体检查设备12还可以包括机械传动装置、电控装置、存储装置、软件程序等,每台放射线人体检查设备12可以具有不同的输出参数、扫描速度、单次扫描人体受照剂量、探测器信号与剂量转换系数等,这里不再赘述。Those skilled in the art can understand that the radiation
对于每台放射线人体检查设备,其探测器信号强度反应接受的放射线剂量大小,探测器信号强度在放射线扫描图像中反映为像素亮度,因此,对设定完成的放射线人体检查设备,其像素亮度与放射线剂量直接相关,像素亮度高,则表明放射线剂量大。对于同一台放射线设备,在特定参数设置下其扫描剂量应当是稳定的,但受环境、设备状态等因素的影响,实际进行放射线检查时放射线扫描剂量会发生波动,而不同于额定放射线扫描剂量。但是,每台设备经出厂校正后其无遮挡物时的平均单像素亮度和扫描剂量的转换系数是固定的,并且存储在设备中。因此,根据无遮挡物时的扫描图像中的平均单像素亮度值,经过转换系数的转换,可以得到实际的扫描剂量值,反映实际的当次个人放射线受照剂量。For each radiation human body inspection equipment, the detector signal intensity reflects the received radiation dose, and the detector signal intensity is reflected in the radiation scan image as the pixel brightness. The radiation dose is directly related, and the pixel brightness is high, indicating that the radiation dose is large. For the same radiation equipment, its scanning dose should be stable under certain parameter settings, but affected by factors such as environment and equipment status, the radiation scanning dose will fluctuate during actual radiological inspection, which is different from the rated radiation scanning dose. However, the conversion factor of the average single-pixel brightness and scanning dose when each device is factory-corrected without obstructions is fixed and stored in the device. Therefore, according to the average single-pixel brightness value in the scanned image when there is no obstruction, the actual scanning dose value can be obtained through the conversion of the conversion coefficient, reflecting the actual current personal radiation dose.
图3是被检查者接受检查的扫描图像的示意图。如图3所示,放射线扫描图像包括人体影像区51和除人体影像区51以外的残余像素区52。人体影像区51对应放射线被人体遮挡的区域(如果存在其它物体,也包括被其它物体遮挡的区域),残余像素区52是无遮挡物时射线直接照射到探测器的区域。因为残余像素区52和人体同步被放射线照射,通过测量残余像素区52的单像素亮度,再根据执行检查的放射线检查设备的转换系数转换成对应的放射线剂量值,即可获得人体受照剂量值。FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of a scanned image of an examinee undergoing examination. As shown in FIG. 3 , the radiographic scan image includes a human
进一步地,因为探测器组中的不同的探测器的测量值可能存在误差,因此,可以计算残余像素区52的各个像素的单像素亮度的平均值,将该单像素平均亮度值再转换成对应的放射线剂量。由于有足够多的残余像素参与平均,使得该均值非常稳定,可以正确地反映当次扫描的放射线输出剂量,因此能够精确反映当次扫描被检人员的受照剂量,避免因各种因素可能造成的设备输出剂量的波动带来的被检人员受照剂量的不正确记录。Further, since there may be errors in the measurement values of different detectors in the detector group, the average value of the single-pixel brightness of each pixel in the
根据另外的实施例,如图1所示,放射线人体检查系统还可以包括个人放射线剂量计40,所述个人放射线计量计40在被检查者接收放射线检查时由被检查者同步携带,用于直接测量被检查者的单次放射线受照剂量。所述个人放射线计量计40可以和放射线人体检查设备12有线或无线通信,以将测量得到的单次放射线受照剂量发送给放射线人体检查设备12;或者,所述个人放射线计量计40可以和云端剂量信息服务器20直接通信,以将测量得到的单次放射线受照剂量直接上传至云端剂量信息服务器。具体地,可以在被检查者胸口或身旁与胸口相齐的位置放置一个个人放射线剂量计,个人放射线剂量计与被检人员同步接受放射线扫描,以直接测量被检查者的单次放射线受照剂量。According to another embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1 , the radiation human body examination system may further include a personal radiation dosimeter 40 , which is carried by the examinee synchronously when the examinee receives the radiation examination, and is used for direct Measure the single dose of radiation exposure of the examinee. The personal radiation meter 40 may communicate with the radiation human
图4是利用如图1所示的放射线人体检查系统进行放射线人体检查的方法的流程图。如图4所示,根据本发明的一个实施例的检查过程包括:FIG. 4 is a flowchart of a method of performing a radiological human examination using the radiological human examination system shown in FIG. 1 . As shown in FIG. 4 , the inspection process according to an embodiment of the present invention includes:
在被检查者准备进入放射线人体检查设备的扫描通道时,首先,对待检查者进行个人身份登记或识别;When the examinee prepares to enter the scanning channel of the radiation human body examination equipment, firstly, register or identify the personal identity of the examinee;
根据身份识别结果调取被检查者的累积放射线受照剂量,例如年度累积放射线受照剂量;Obtain the cumulative radiation dose of the examinee according to the identification result, such as the annual cumulative radiation dose;
根据放射线人体检查设备类型获得如果进行本次检查将产生的预计举次放射线扫描剂量,该预计单次放射线扫描剂量可以是当前进行检查的放射线人体检查设备的额定放射线扫描剂量;Obtain the estimated radiation scan dose that will be generated if this examination is carried out according to the type of radiation body examination equipment, and the estimated single radiation scan dose may be the rated radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination equipment currently performing the examination;
将被检者本年度累积放射线受照剂量和预计单次放射线扫描剂量相加得到累加剂量值,根据所述累加值是否超过剂量限值来确定是否对被检查者执行本次放射线检查。The cumulative dose of radiation exposure of the subject in the current year and the expected dose of a single radiation scan are added to obtain a cumulative dose value, and whether to perform the current radiological examination on the subject is determined according to whether the cumulative value exceeds the dose limit.
具体地,如果累加剂量值超过预先设定的累计剂量限值,则决定不对被检查者进行当前放射线检查,以免被检查者接受过量的放射线辐射而损害身体健康。另一方面,如果被检者本年度累积放射线受照剂量和预计单次放射线扫描剂量相加得到的累加剂量值不超过预先设定的累计剂量限值,则确定开始对被检查者进行单次放射线检查。Specifically, if the accumulated dose value exceeds a preset accumulated dose limit, it is decided not to perform the current radiation examination on the examinee, so as to prevent the examinee from receiving excessive radiation radiation and damage to his health. On the other hand, if the cumulative dose value obtained by adding the cumulative radiation dose of the subject in the current year and the expected single radiation scan dose does not exceed the preset cumulative dose limit, it is determined to start a single dose of radiation on the subject. examine.
根据一个例子,所述累积放射线受照剂量可以是个人在一年内已经接受的放射线受照剂量的累积值,所述剂量限值可以是个人一年内可以接受的放射线受照剂量的上限值。According to an example, the cumulative radiation dose may be a cumulative value of radiation doses that an individual has received in one year, and the dose limit may be an upper limit of the radiation dose that an individual can receive in one year.
当确定对被检查者执行本次放射线检查时,在对被检查者执行放射线检查的过程中,可以实时监测放射线人体检查设备的输出参数,如果输出参数异常则中止检查工作;已经执行完成部分的放射线检查受照剂量,按已执行时间与完整执行检查所需时间比例折算本次非完整检查对被检查人员造成的放射线受照剂量。所述输出参数例如可以是放射线机的电压、电流、扫描速度等源项参数。如果在扫描过程中由于操作员操作失误或者设备故障等意外原因源项参数超出了设计值(异常),则可能导致单次扫描剂量超出个人单次受照剂量限值,对人体造成危害,因此,在这种情况下,放射线检查设备停止发射放射线以中断扫描操作,并记录当次已经受照的剂量。否则,放射线检查设备正常完成本次扫描,并记录当次受照的剂量。When it is determined to perform this radiological examination on the subject, the output parameters of the radiation human body examination equipment can be monitored in real time during the process of performing the radiological examination on the subject. If the output parameters are abnormal, the examination will be terminated; The radiation dose of the radiation inspection shall be converted into the radiation dose of the inspected personnel caused by this incomplete inspection according to the proportion of the time that has been performed and the time required for the complete inspection. The output parameters may be, for example, source term parameters such as voltage, current, and scanning speed of the radiation machine. If the source item parameter exceeds the design value (abnormal) due to unexpected reasons such as operator error or equipment failure during the scanning process, the single scanning dose may exceed the individual single exposure dose limit, causing harm to the human body. Therefore, , in this case, the radiation inspection equipment stops emitting radiation to interrupt the scanning operation, and records the dose that has been irradiated at that time. Otherwise, the radiological examination equipment normally completes the scan and records the dose received at that time.
具体地,根据一个实施例,获取被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量包括:获取被检查者本次检查的放射线扫描图像;以及对所述放射线扫描图像进行处理,根据所述放射线扫描图像中除人体影像以外的残余像素区域的单像素平均亮度值,经转换系数转换后获得被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量。所述转换系数预先存储在放射线检查设备中。所述单像素平均亮度值是所述放射线扫描图像中除人体影像以外的残余像素区域的各像素的像素亮度值的平均值。Specifically, according to one embodiment, acquiring the current radiation exposure dose of the examinee includes: acquiring the radiographic scan image of the examinee for the current examination; and processing the radiographic scan image, according to the radiographic scan image The single-pixel average brightness value of the residual pixel area other than the human image is converted by the conversion coefficient to obtain the current radiation dose of the examinee. The conversion coefficients are stored in the radiation inspection apparatus in advance. The single-pixel average luminance value is an average value of pixel luminance values of each pixel in the residual pixel region other than the human body image in the radiographic scan image.
因为探测器组中的不同的探测器的测量值可能存在误差,因此,通过计算残余像素区的各个像素的单像素亮度的平均值,将该单像素平均亮度值再转换成对应的放射线剂量。由于有足够多的残余像素参与平均,使得该均值非常稳定,可以正确地反映当次扫描的放射线输出剂量,因此能够精确反映当次扫描被检人员的受照剂量,避免因各种因素可能造成的设备输出剂量的波动带来的被检人员受照剂量的不正确记录。Because there may be errors in the measurement values of different detectors in the detector group, by calculating the average value of the single-pixel brightness of each pixel in the residual pixel area, the single-pixel average brightness value is converted into a corresponding radiation dose. Since there are enough residual pixels to participate in the averaging, the average value is very stable and can correctly reflect the radiation output dose of the current scan, so it can accurately reflect the radiation dose of the inspected person in the current scan, avoiding the possible cause by various factors. The fluctuation of the output dose of the equipment brings about the incorrect recording of the dose of the inspected person.
根据该实施例的一个简化的例子,被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量Y可以按如下公式计算:According to a simplified example of this embodiment, the current radiation dose Y of the examinee can be calculated according to the following formula:
Y=Y1·X/X1Y=Y1·X/X1
其中,X是放射线扫描图像中残余像素区域的单像素平均亮度值,Y1是放射线人体检查设备在本次人体检查时的额定单次放射线扫描剂量的值,X1是对应本次人体检查时的额定单次放射线扫描剂量的值,在无任何遮挡物时得到的扫描图像中的单像素亮度值。其中,X1和Y1可以是作为设备参数被预先存储在设备中的。Among them, X is the single-pixel average brightness value of the residual pixel area in the radiation scan image, Y1 is the value of the rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination equipment during this body examination, and X1 is the rated value corresponding to this body examination. The value of a single radiation scan dose, the brightness value of a single pixel in the scanned image obtained when there is no obstruction. Wherein, X1 and Y1 may be pre-stored in the device as device parameters.
根据另外的实施例,获取被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量包括:简单地获取放射线人体检查设备在本次人体检查时的额定单次放射线扫描剂量,作为被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量。According to another embodiment, acquiring the current radiation exposure dose of the examinee includes: simply acquiring the rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination equipment during the current body examination, as the current radiation exposure of the examinee dose.
根据另外的实施例,获取被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量包括:被检查者携带个人放射线剂量计同步接受放射线检查,通过个人计量计测量被检查者的本次放射线受照剂量。例如,在被检人员胸口或身傍与胸口相齐区位放置一个个人剂量计,个人剂量计与被检人员同步通过检查通道,并通过有线或无线与X线设备通信,个人放射线剂量计将每次扫描人体后受照剂量直接精确记录下来。According to another embodiment, acquiring the current dose of radiation exposure of the examinee includes: the subject carries a personal dosimeter to receive a radiation examination synchronously, and the personal dose meter is used to measure the current dose of radiation exposure of the examinee. For example, a personal dosimeter is placed on the subject's chest or at the same position as the chest. The personal dosimeter and the subject pass through the examination channel synchronously, and communicate with the X-ray equipment through wired or wireless communication. After the first scan of the human body, the exposure dose is directly and accurately recorded.
上述几种测量、计算被检人员受照剂量的方法可以单独使用,也可以几种方法同时使用;如几种方法同时使用,为保护被检人的健康,个人剂量管理统计时采用最大值计算。The above-mentioned methods for measuring and calculating the exposure dose of the inspected person can be used alone or at the same time; if several methods are used at the same time, in order to protect the health of the inspected person, the maximum value is used for the calculation of personal dose management statistics. .
最后,将上述方式测量、计算得到的被检人员的本次放射线受照剂量信息上传至云端剂量信息服务器,与剂量信息服务器中存储的个人累积放射线受照剂量值累加,以更新该被检人的个人累积放射线受照剂量。Finally, upload the current radiation exposure dose information of the inspected person measured and calculated in the above method to the cloud dose information server, and accumulate with the personal cumulative radiation exposure dose value stored in the dose information server to update the inspected person. individual cumulative radiation exposure.
以上实施例提出的放射线人体检查方法和检查系统,一方面可以防止误操作和设备故障导致的单次辐射剂量超标,更重要的是可以在年度累积剂量上进行监控和防护,因此,提高了放射线人体检查的安全性。The radiation human body inspection method and inspection system proposed in the above embodiments, on the one hand, can prevent the single radiation dose from exceeding the standard caused by misoperation and equipment failure, and more importantly, can monitor and protect the annual cumulative dose, therefore, the radiation dose is improved. Safety of human examination.
另外,由于根据单像素平均亮度值实时换算被检查者的当次实际放射线受照剂量,或者采用个人放射线剂量计实时测量被检查者的当次实际放射线受照剂量,因此,可以准确地获得被检查者的当次实际放射线受照剂量,进一步提高放射线人体检查的安全性。In addition, since the current actual radiation dose of the examinee is converted in real time according to the average brightness value of a single pixel, or the actual radiation dose of the examinee is measured in real time by using a personal radiation dosimeter, the current actual radiation dose of the examinee can be accurately obtained. The actual radiation dose received by the examiner at that time further improves the safety of the radiation body examination.
以上实施例中,所述年度累积放射线受照剂量是个人在一年内已经接受的放射线扫描剂量的累积值。所述剂量限值是个人一年内可以接受的放射线扫描剂量的上限值。放射线人体检查设备的预计单次放射线扫描剂量可取该放射线人体检查设备的额定单次放射线扫描剂量。但是,以上规定不是限制性的。例如,累积放射线扫描剂量可是个人在一个季度内已经接受的放射线扫描剂量的累积值。所述剂量限值是个人一个季度内可以接受的放射线扫描剂量的上限值。放射线人体检查设备的预计单次放射线扫描剂量可以取不同于额定单次放射线扫描剂量的其它适当的剂量值。本发明实施例的放射线人体检查系统可以用于多种类型的放射线人体检查领域,例如X射线、γ射线等需要进行健康监测的放射线。In the above embodiment, the annual cumulative radiation dose is the cumulative value of the radiation scanning dose that the individual has received within one year. The dose limit is the upper limit of the radiation scan dose that an individual can receive in one year. The estimated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination apparatus may take the rated single radiation scan dose of the radiation body examination apparatus. However, the above provisions are not restrictive. For example, the cumulative radiation scan dose may be the cumulative value of the radiation scan dose an individual has received over a quarter. The dose limit is the upper limit of the radiation scan dose that an individual can accept in a quarter. The estimated single radiation scan dose of the radiation human body examination apparatus may take other appropriate dose values other than the rated single radiation scan dose. The radiation human body inspection system of the embodiment of the present invention can be used in various types of radiation human body inspection fields, such as X-rays, gamma rays, and other radiations that require health monitoring.
因此,本发明的上述实施例仅示例性的说明了本发明的原理及构造,而非用于限制本发明,本领域的技术人员应明白,在不偏离本发明的总体构思的情况下,对本发明所作的任何改变和改进都在本发明的范围内。本发明的保护范围,应如本申请的权利要求书所界定的范围为准。Therefore, the above-mentioned embodiments of the present invention merely illustrate the principle and structure of the present invention, but are not intended to limit the present invention. Those skilled in the art should understand that, without departing from the general concept of the present invention, the Any changes and improvements made by the invention are within the scope of the invention. The protection scope of the present invention shall be as defined by the claims of the present application.
Claims (12)
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2016/099548WO2017113894A1 (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2016-09-21 | Method and system for performing radiation-based examination on human body |
| SG10202006052TASG10202006052TA (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2016-09-21 | Human body radiation examining method and human body radiation examining system |
| SG11201709738WASG11201709738WA (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2016-09-21 | Human body radiation examining method and human body radiation examining system |
| CA2942792ACA2942792C (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2016-09-22 | Human body radiation examining method and human body radiation examining system |
| BR102016022520-5ABR102016022520B1 (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2016-09-28 | METHOD FOR EXAMINING THE HUMAN BODY WITH RADIATION AND SYSTEM FOR EXAMINING THE HUMAN BODY WITH RADIATION |
| US15/282,485US20170184727A1 (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2016-09-30 | Human body radiation examining method and system |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2015110089586 | 2015-12-29 | ||
| CN201521116652 | 2015-12-29 | ||
| CN2015211166528 | 2015-12-29 | ||
| CN201511008958.6ACN105652331A (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2015-12-29 | Ray-utilized human body security checking method and ray-utilized human body security checking system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN106932829A CN106932829A (en) | 2017-07-07 |
| CN106932829Btrue CN106932829B (en) | 2020-10-30 |
Family
ID=59444574
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610818922.2AActiveCN106932829B (en) | 2015-12-29 | 2016-09-12 | Radiation body examination method and radiation body examination system |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN106932829B (en) |
| SG (2) | SG11201709738WA (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109045477A (en)* | 2018-08-28 | 2018-12-21 | 西安大医集团有限公司 | A kind of radiation therapy clinic monitoring system |
| CN114849089B (en)* | 2022-06-08 | 2024-09-10 | 上海联影医疗科技股份有限公司 | Radiation therapy guiding method and system |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7557353B2 (en)* | 2001-11-30 | 2009-07-07 | Sicel Technologies, Inc. | Single-use external dosimeters for use in radiation therapies |
| US8538776B2 (en)* | 2006-10-25 | 2013-09-17 | Bruce Reiner | Method and apparatus of providing a radiation scorecard |
| US8412544B2 (en)* | 2007-10-25 | 2013-04-02 | Bruce Reiner | Method and apparatus of determining a radiation dose quality index in medical imaging |
| AU2010237616A1 (en)* | 2009-04-17 | 2011-10-20 | Dosimetry & Imaging Pty Ltd | Apparatus and method for detecting radiation exposure levels |
| CN102033075B (en)* | 2009-09-25 | 2013-05-01 | 清华大学 | Radiation inspection device for object safety inspection and inspection method using radiation inspection device |
| US20120065994A1 (en)* | 2010-09-13 | 2012-03-15 | Carter Jeffrey D | Methods and systems for utilizing electronic medical records to track and manage radiation doses |
| JP5706269B2 (en)* | 2011-08-16 | 2015-04-22 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Apparatus and method for sharing dose information of radiation imaging system |
| US9314646B2 (en)* | 2011-08-17 | 2016-04-19 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Skin dose evaluation support apparatus and treatment planning apparatus |
| JP5774447B2 (en)* | 2011-10-28 | 2015-09-09 | ジーイー・メディカル・システムズ・グローバル・テクノロジー・カンパニー・エルエルシー | X-ray CT apparatus, dose calculation method and program |
| JP6004464B2 (en)* | 2012-03-19 | 2016-10-05 | 国立大学法人北海道大学 | Radiotherapy control apparatus and radiotherapy control program |
| WO2014096993A1 (en)* | 2012-12-17 | 2014-06-26 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Real-time adaptive dose computation radiation therapy |
| CN203802482U (en)* | 2013-12-19 | 2014-09-03 | 上海西门子医疗器械有限公司 | X-ray dose information informing device and X-ray scanning device |
| CN104865281B (en)* | 2014-02-24 | 2017-12-12 | 清华大学 | Human body back scattering inspection method and system |
- 2016
- 2016-09-12CNCN201610818922.2Apatent/CN106932829B/enactiveActive
- 2016-09-21SGSG11201709738WApatent/SG11201709738WA/enunknown
- 2016-09-21SGSG10202006052TApatent/SG10202006052TA/enunknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| SG10202006052TA (en) | 2020-07-29 |
| BR102016022520A2 (en) | 2017-07-04 |
| SG11201709738WA (en) | 2017-12-28 |
| CN106932829A (en) | 2017-07-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10061043B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for the evaluation of gamma radiation events | |
| US10786222B2 (en) | Methods, systems, and apparatus for automatically assessing quality of imaging systems | |
| US20160320466A1 (en) | Density guided attenuation map generation in pet/mr systems | |
| CN103505228B (en) | X-ray imaging equipment and X-ray imaging systems | |
| US11083423B2 (en) | Image processing device and method for operating image processing device | |
| JP2015500121A (en) | Dose optimization based on result quality | |
| US9055923B2 (en) | Computed radiography positioning method and system | |
| US10806419B2 (en) | X-ray CT apparatus, X-ray CT system, and injector | |
| WO2021064194A1 (en) | Magnetic resonance (mr) image artifact determination using texture analysis for image quality (iq) standardization and system health prediction | |
| US20140276029A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for data selection for positron emission tomogrpahy (pet) image reconstruction | |
| US11426138B2 (en) | Radiographing apparatus, radiographing system, and dose index management method | |
| CN106932829B (en) | Radiation body examination method and radiation body examination system | |
| JP7678056B2 (en) | X-ray CT device | |
| CN107252353B (en) | Control method of medical imaging equipment and medical imaging equipment | |
| US9773318B2 (en) | Systems and methods for detecting camera defect caused by exposure to radiation | |
| US20160349195A1 (en) | Image processing devices, image processing system, image processing method, and non-transitory recording medium | |
| US7460640B2 (en) | Radiotherapy monitoring apparatus | |
| CN112673396B (en) | Detecting object motion in medical imaging | |
| JP2000275757A (en) | Method and device for evaluating image | |
| CA2942792C (en) | Human body radiation examining method and human body radiation examining system | |
| US8837799B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for selecting a reference gate | |
| TWI813684B (en) | Image management system and computer program product | |
| CN105652331A (en) | Ray-utilized human body security checking method and ray-utilized human body security checking system | |
| JP2020096646A (en) | Radiographic apparatus, radiographic system, radiographic method and program | |
| JP7669322B2 (en) | System and method for collimator screening in computed tomography systems - Patents.com |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |