CN106924227B - The use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of atherosclerosis medicine - Google Patents
The use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of atherosclerosis medicineDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN106924227B CN106924227BCN201710093813.3ACN201710093813ACN106924227BCN 106924227 BCN106924227 BCN 106924227BCN 201710093813 ACN201710093813 ACN 201710093813ACN 106924227 BCN106924227 BCN 106924227B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- cinnamaldehyde
- plaque
- atherosclerosis
- content
- expression
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- KJPRLNWUNMBNBZ-QPJJXVBHSA-N(E)-cinnamaldehydeChemical compoundO=C\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1KJPRLNWUNMBNBZ-QPJJXVBHSA-N0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription54
- 229940117916cinnamic aldehydeDrugs0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription51
- KJPRLNWUNMBNBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncinnamic aldehydeNatural productsO=CC=CC1=CC=CC=C1KJPRLNWUNMBNBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription51
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription23
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription7
- 201000001320AtherosclerosisDiseases0.000titleabstractdescription28
- 210000002540macrophageAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 102000008186CollagenHuman genes0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 108010035532CollagenProteins0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 229920001436collagenPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 210000000329smooth muscle myocyteAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 230000000087stabilizing effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription5
- 208000037260Atherosclerotic PlaqueDiseases0.000claimsdescription12
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000claimsdescription12
- 210000004322M2 macrophageAnatomy0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000002844meltingMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000008018meltingEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- APFRIPBQCVUZNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N2-phenylprop-1-en-1-oneChemical groupO=C=C(C)C1=CC=CC=C1APFRIPBQCVUZNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription24
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000abstractdescription9
- MZOFCQQQCNRIBI-VMXHOPILSA-N(3s)-4-[[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-[[(1s)-1-carboxy-2-hydroxyethyl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-[[2-[[(2s)-2,6-diaminohexanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acidChemical compoundOC[C@@H](C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(O)=O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCCCNMZOFCQQQCNRIBI-VMXHOPILSA-N0.000abstractdescription6
- 108060008682Tumor Necrosis FactorProteins0.000abstractdescription6
- 102000000852Tumor Necrosis Factor-alphaHuman genes0.000abstractdescription6
- 102100029438Nitric oxide synthase, inducibleHuman genes0.000abstractdescription5
- 101710089543Nitric oxide synthase, inducibleProteins0.000abstractdescription5
- 231100000331toxicToxicity0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000002588toxic effectEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000003285pharmacodynamic effectEffects0.000abstractdescription3
- 229940126680traditional chinese medicinesDrugs0.000abstractdescription3
- 206010061218InflammationDiseases0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000004054inflammatory processEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000007365immunoregulationEffects0.000abstract1
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description16
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description15
- 241000699670Mus sp.Species0.000description12
- 102000013918Apolipoproteins EHuman genes0.000description8
- 108010025628Apolipoproteins EProteins0.000description8
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description7
- WZUVPPKBWHMQCE-UHFFFAOYSA-NHaematoxylinChemical compoundC12=CC(O)=C(O)C=C2CC2(O)C1C1=CC=C(O)C(O)=C1OC2WZUVPPKBWHMQCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NO-XyleneChemical compoundCC1=CC=CC=C1CCTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 210000003690classically activated macrophageAnatomy0.000description6
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description6
- 150000002632lipidsChemical class0.000description6
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description6
- 238000010186stainingMethods0.000description6
- 238000007619statistical methodMethods0.000description6
- 239000008096xyleneSubstances0.000description6
- 206010062717Increased upper airway secretionDiseases0.000description5
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description5
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description5
- 210000002216heartAnatomy0.000description5
- 235000009200high fat dietNutrition0.000description5
- 208000026435phlegmDiseases0.000description5
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description5
- AXMVYSVVTMKQSL-UHFFFAOYSA-NUNPD142122Natural productsOC1=CC=C(C=CC=O)C=C1OAXMVYSVVTMKQSL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 230000000879anti-atherosclerotic effectEffects0.000description4
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description4
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-NcholesterolChemical compoundC1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N0.000description4
- 230000004069differentiationEffects0.000description4
- 230000008506pathogenesisEffects0.000description4
- 230000037361pathwayEffects0.000description4
- 210000002966serumAnatomy0.000description4
- 150000003626triacylglycerolsChemical class0.000description4
- 206010028851NecrosisDiseases0.000description3
- 230000003110anti-inflammatory effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000003143atherosclerotic effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description3
- 210000000497foam cellAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000036571hydrationEffects0.000description3
- 238000006703hydration reactionMethods0.000description3
- 238000011532immunohistochemical stainingMethods0.000description3
- 238000003364immunohistochemistryMethods0.000description3
- 230000002757inflammatory effectEffects0.000description3
- 210000003734kidneyAnatomy0.000description3
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000description3
- 230000017074necrotic cell deathEffects0.000description3
- 230000001681protective effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000013424sirius red stainingMethods0.000description3
- 206010067484Adverse reactionDiseases0.000description2
- 208000024172Cardiovascular diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 241000723347CinnamomumSpecies0.000description2
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 108010023302HDL CholesterolProteins0.000description2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrochloric acidChemical compoundClVEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 108010028554LDL CholesterolProteins0.000description2
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000description2
- 230000006838adverse reactionEffects0.000description2
- 239000003963antioxidant agentSubstances0.000description2
- 230000003078antioxidant effectEffects0.000description2
- 208000026106cerebrovascular diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 235000012000cholesterolNutrition0.000description2
- 235000017803cinnamonNutrition0.000description2
- RGJOEKWQDUBAIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncoenzime ANatural productsOC1C(OP(O)(O)=O)C(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OCC(C)(C)C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCS)OC1N1C2=NC=NC(N)=C2N=C1RGJOEKWQDUBAIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000005516coenzyme ASubstances0.000description2
- 229940093530coenzyme aDrugs0.000description2
- KDTSHFARGAKYJN-UHFFFAOYSA-Ndephosphocoenzyme ANatural productsOC1C(O)C(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OCC(C)(C)C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCS)OC1N1C2=NC=NC(N)=C2N=C1KDTSHFARGAKYJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 238000007490hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stainingMethods0.000description2
- 229940088592immunologic factorDrugs0.000description2
- 239000000367immunologic factorSubstances0.000description2
- 239000003550markerSubstances0.000description2
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description2
- -1methylglutaryl coenzyme AChemical compound0.000description2
- 230000007935neutral effectEffects0.000description2
- 210000000056organAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000010287polarizationEffects0.000description2
- 230000008439repair processEffects0.000description2
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description2
- 210000000952spleenAnatomy0.000description2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VPUBHVLGSA-N(-)-beta-SitosterolNatural productsO[C@@H]1CC=2[C@@](C)([C@@H]3[C@H]([C@H]4[C@@](C)([C@H]([C@H](CC[C@@H](C(C)C)CC)C)CC4)CC3)CC=2)CC1KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VPUBHVLGSA-N0.000description1
- CSVWWLUMXNHWSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N(22E)-(24xi)-24-ethyl-5alpha-cholest-22-en-3beta-olNatural productsC1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)C=CC(CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2CSVWWLUMXNHWSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- HSINOMROUCMIEA-FGVHQWLLSA-N(2s,4r)-4-[(3r,5s,6r,7r,8s,9s,10s,13r,14s,17r)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-methylpentanoic acidChemical compoundC([C@@]12C)C[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1[C@@H](CC)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]([C@H](C)C[C@H](C)C(O)=O)CC[C@H]21HSINOMROUCMIEA-FGVHQWLLSA-N0.000description1
- CABVTRNMFUVUDM-VRHQGPGLSA-N(3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoAChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H](COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSC(=O)C[C@@](O)(CC(O)=O)C)O[C@H]1N1C2=NC=NC(N)=C2N=C1CABVTRNMFUVUDM-VRHQGPGLSA-N0.000description1
- KLEXDBGYSOIREE-UHFFFAOYSA-N24xi-n-propylcholesterolNatural productsC1C=C2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(CCC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2KLEXDBGYSOIREE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 206010002383Angina PectorisDiseases0.000description1
- 206010003210ArteriosclerosisDiseases0.000description1
- 241000283707CapraSpecies0.000description1
- 244000037364Cinnamomum aromaticumSpecies0.000description1
- 235000014489Cinnamomum aromaticumNutrition0.000description1
- 235000021511Cinnamomum cassiaNutrition0.000description1
- LPZCCMIISIBREI-MTFRKTCUSA-NCitrostadienolNatural productsCC=C(CC[C@@H](C)[C@H]1CC[C@H]2C3=CC[C@H]4[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@]12C)C(C)CLPZCCMIISIBREI-MTFRKTCUSA-N0.000description1
- ARVGMISWLZPBCH-UHFFFAOYSA-NDehydro-beta-sitosterolNatural productsC1C(O)CCC2(C)C(CCC3(C(C(C)CCC(CC)C(C)C)CCC33)C)C3=CC=C21ARVGMISWLZPBCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 208000030453Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse reactionDiseases0.000description1
- 206010014513Embolism arterialDiseases0.000description1
- 241000196324EmbryophytaSpecies0.000description1
- 102000010834Extracellular Matrix ProteinsHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010037362Extracellular Matrix ProteinsProteins0.000description1
- 229920002683GlycosaminoglycanPolymers0.000description1
- 208000031226HyperlipidaemiaDiseases0.000description1
- 206010061216InfarctionDiseases0.000description1
- 108010007622LDL LipoproteinsProteins0.000description1
- 102000007330LDL LipoproteinsHuman genes0.000description1
- 241000218195LauraceaeSpecies0.000description1
- 208000017170Lipid metabolism diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-NNiacinChemical compoundOC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 102000004316OxidoreductasesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000854OxidoreductasesProteins0.000description1
- 208000002193PainDiseases0.000description1
- 102000016387Pancreatic elastaseHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010067372Pancreatic elastaseProteins0.000description1
- DJWYOLJPSHDSAL-UHFFFAOYSA-NPantethineNatural productsOCC(C)(C)C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSSCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)CODJWYOLJPSHDSAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 102000003992PeroxidasesHuman genes0.000description1
- 208000007536ThrombosisDiseases0.000description1
- 230000003213activating effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001154acute effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000010171animal modelMethods0.000description1
- 230000000947anti-immunosuppressive effectEffects0.000description1
- 208000011775arteriosclerosis diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- MJVXAPPOFPTTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-Nbeta-SistosterolNatural productsCCC(CCC(C)C1CCC2C3CC=C4C(C)C(O)CCC4(C)C3CCC12C)C(C)CMJVXAPPOFPTTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-UHFFFAOYSA-Nbeta-SitostanolNatural productsC1CC2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCC(CC)C(C)C)C1(C)CC2LGJMUZUPVCAVPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- NJKOMDUNNDKEAI-UHFFFAOYSA-Nbeta-sitosterolNatural productsCCC(CCC(C)C1CCC2(C)C3CC=C4CC(O)CCC4C3CCC12C)C(C)CNJKOMDUNNDKEAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000003613bile acidSubstances0.000description1
- 230000017531blood circulationEffects0.000description1
- 210000001124body fluidAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000010839body fluidSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004556brainAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000030833cell deathEffects0.000description1
- 230000001413cellular effectEffects0.000description1
- 206010008118cerebral infarctionDiseases0.000description1
- 239000008139complexing agentSubstances0.000description1
- 235000009508confectioneryNutrition0.000description1
- 239000006071creamSubstances0.000description1
- 239000013078crystalSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description1
- 208000035475disorderDiseases0.000description1
- 239000012153distilled waterSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002526effect on cardiovascular systemEffects0.000description1
- 230000002124endocrineEffects0.000description1
- YQGOJNYOYNNSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-NeosinChemical compound[Na+].OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C1=C2C=C(Br)C(=O)C(Br)=C2OC2=C(Br)C(O)=C(Br)C=C21YQGOJNYOYNNSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- IDGUHHHQCWSQLU-UHFFFAOYSA-Nethanol;hydrateChemical compoundO.CCOIDGUHHHQCWSQLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000description1
- 210000002744extracellular matrixAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 210000005003heart tissueAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000003384imaging methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000002519immonomodulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007574infarctionEffects0.000description1
- 210000004969inflammatory cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000028709inflammatory responseEffects0.000description1
- 239000003112inhibitorSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000302ischemic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003902lesionEffects0.000description1
- 231100001231less toxicToxicity0.000description1
- 210000004185liverAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 210000000191macrophage derived foam cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000002398materia medicaSubstances0.000description1
- 235000013372meatNutrition0.000description1
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 208000010125myocardial infarctionDiseases0.000description1
- 230000001114myogenic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001338necrotic effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000013642negative controlSubstances0.000description1
- 229960003512nicotinic acidDrugs0.000description1
- 235000001968nicotinic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 239000011664nicotinic acidSubstances0.000description1
- 150000002894organic compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 230000036542oxidative stressEffects0.000description1
- 108010071584oxidized low density lipoproteinProteins0.000description1
- DJWYOLJPSHDSAL-ROUUACIJSA-NpantethineChemical compoundOCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSSCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)[C@H](O)C(C)(C)CODJWYOLJPSHDSAL-ROUUACIJSA-N0.000description1
- 229960000903pantethineDrugs0.000description1
- 235000008975pantethineNutrition0.000description1
- 239000011581pantethineSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001717pathogenic effectEffects0.000description1
- 231100000915pathological changeToxicity0.000description1
- 230000036285pathological changeEffects0.000description1
- 230000001575pathological effectEffects0.000description1
- 108040007629peroxidase activity proteinsProteins0.000description1
- 125000000951phenoxy groupChemical group[H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(O*)C([H])=C1[H]0.000description1
- OXNIZHLAWKMVMX-UHFFFAOYSA-Npicric acidChemical compoundOC1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1[N+]([O-])=OOXNIZHLAWKMVMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 235000020777polyunsaturated fatty acidsNutrition0.000description1
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000description1
- FYPMFJGVHOHGLL-UHFFFAOYSA-NprobucolChemical compoundC=1C(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=CC=1SC(C)(C)SC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1FYPMFJGVHOHGLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229960003912probucolDrugs0.000description1
- 230000000770proinflammatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000035755proliferationEffects0.000description1
- 230000001737promoting effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000005084renal tissueAnatomy0.000description1
- 108010078070scavenger receptorsProteins0.000description1
- 102000014452scavenger receptorsHuman genes0.000description1
- 238000012216screeningMethods0.000description1
- 230000028327secretionEffects0.000description1
- 230000035939shockEffects0.000description1
- KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VJSFXXLFSA-NsitosterolChemical compoundC1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CC[C@@H](CC)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2KZJWDPNRJALLNS-VJSFXXLFSA-N0.000description1
- 229950005143sitosterolDrugs0.000description1
- NLQLSVXGSXCXFE-UHFFFAOYSA-NsitosterolNatural productsCC=C(/CCC(C)C1CC2C3=CCC4C(C)C(O)CCC4(C)C3CCC2(C)C1)C(C)CNLQLSVXGSXCXFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 235000015500sitosterolNutrition0.000description1
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 241000894007speciesSpecies0.000description1
- 239000012192staining solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 150000003431steroidsChemical class0.000description1
- 235000000346sugarNutrition0.000description1
- 150000008163sugarsChemical class0.000description1
- 230000009885systemic effectEffects0.000description1
- 229940126585therapeutic drugDrugs0.000description1
- 238000002604ultrasonographyMethods0.000description1
- 210000004509vascular smooth muscle cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000341volatile oilSubstances0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/11—Aldehydes
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Acyclic And Carbocyclic Compounds In Medicinal Compositions (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及桂皮醛在制备靶器官保护药物中的用途,尤其是桂皮醛在制备治疗动脉粥样硬化药物中的用途,属于中药技术领域。The invention relates to the use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of target organ protection drugs, in particular the use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of drugs for treating atherosclerosis, and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines.
背景技术Background technique
随着社会的进步和生活方式的改变,动脉粥样硬化(AS)等心血管疾病的发病率逐年攀升。据不完全统计,我国的动脉粥样硬化发病率接近10%,60岁以上人群发病率接近80%。现代医学研究显示,动脉粥样硬化是一种与脂质代谢紊乱有关的全身性疾病,其病变特点是血液中的脂质,特别是胆固醇在动脉血管壁内膜沉积,并伴有平滑肌细胞和纤维基质成分的增殖,逐步发展形成动脉粥样硬化斑块,导致动脉硬化。动脉粥样硬化发生于心、脑、肾等重要器官时,将引起组织缺血性改变,造成严重后果,例如心绞痛、心肌梗塞、脑梗塞、肾组织梗塞以及四肢动脉栓塞等,是当今严重危害人类健康和生命的常见疾病。With the progress of society and changes in lifestyle, the incidence of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis (AS) is increasing year by year. According to incomplete statistics, the incidence of atherosclerosis in my country is close to 10%, and the incidence of people over 60 years old is close to 80%. Modern medical research shows that atherosclerosis is a systemic disease related to lipid metabolism disorders. The proliferation of fibrous matrix components gradually develops into atherosclerotic plaques, leading to arteriosclerosis. When atherosclerosis occurs in the heart, brain, kidney and other important organs, it will cause tissue ischemic changes and cause serious consequences, such as angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, renal tissue infarction, and limb arterial embolism. Common diseases of human health and life.
动脉粥样硬化的发病原因十分复杂,发病机制也尚未完全阐释清楚。经典的关于动脉粥样硬化的病因病机为低密度脂蛋白被过氧化形成氧化低密度脂蛋白,进而被巨噬细胞和血管平滑肌细胞吞噬和沉积,形成巨噬源性泡沫细胞和肌源性泡沫细胞,最终导致两种泡沫细胞坏死崩解,形成糜粥样坏死物,粥样斑块形成。高脂血症、氧化应激和炎症等多种因素参与了动脉粥样硬化的发生和发展过程。The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis is very complex, and the pathogenesis has not been fully elucidated. The classic etiology and pathogenesis of atherosclerosis is that low-density lipoprotein is peroxidized to form oxidized low-density lipoprotein, which is then phagocytosed and deposited by macrophages and vascular smooth muscle cells to form macrophage-derived foam cells and myogenic Foam cells eventually lead to the necrosis and disintegration of two types of foam cells, the formation of atheromatous necrosis, and the formation of atheromatous plaques. Various factors such as hyperlipidemia, oxidative stress and inflammation are involved in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis.
目前,防治动脉粥样硬化的药物主要是通过调血脂、抗炎和抗氧化途径稳定易损斑块而发挥作用。现代医学中主要通过调血脂进行治疗,药物按其作用可分为:(1)主要降低血总胆固醇(TC)的药物,包括胆酸络合剂、经甲基戊二酸单酰辅酶A(HMG-CoA)还原酶抑制剂、甾体衍生物谷固醇等。(2)降低血甘油三酯(TG)的药物,包括烟酸类、苯氧酸类、多不饱和脂肪酸类、粘多糖及糖类等。(3)其他调血脂药物,如丙丁酚、泛硫乙胺、弹性酶等。但这些药物在长期使用过程中可出现一些不良反应,造成患者不能耐受,影响了临床疗效和患者的治疗信心。因此,提供一种经济有效、毒副作用小、安全可靠的抗动脉粥样硬化的药物是本领域研究人员函待解决的一个重要问题。此类药物的开发将具有重大的现实意义。At present, drugs for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis mainly work by stabilizing vulnerable plaques through regulating blood lipids, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. In modern medicine, blood lipids are mainly used for treatment, and drugs can be divided into: (1) drugs that mainly lower blood total cholesterol (TC), including bile acid complexing agents, methylglutaryl coenzyme A (methylglutaryl coenzyme A) ( HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors, steroid derivatives sitosterol, etc. (2) Drugs that lower blood triglycerides (TG), including niacin, phenoxy acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, mucopolysaccharides and sugars. (3) Other blood lipid-lowering drugs, such as probucol, pantethine, elastase, etc. However, some adverse reactions may occur in the long-term use of these drugs, resulting in intolerance of patients, affecting clinical efficacy and patients' confidence in treatment. Therefore, to provide a cost-effective, safe and reliable anti-atherosclerosis drug with less toxic and side effects is an important problem to be solved by researchers in the field. The development of such drugs will have great practical significance.
中药治疗动脉粥样硬化已在几千年的临床实践中积累了丰富而成功的经验,为延缓和减轻动脉粥样硬化病变的发展,防治心脑血管疾病提供了客观依据。早在《黄帝内经》中已有关于本病的重要理论依据。如《灵枢·卫失常论》云:“人有肥,有膏,有肉”,“脂者,其血清,气滑少”。中医学认为动脉粥样硬化性疾病属气血津液病变范畴,与痰浊、瘀血等证相似,是以肝、脾、肾三脏之虚为本,痰浊、瘀血为标的病证。可以概括为脾失健运,痰湿内生;肾虚开合不利,水湿内停;肝气郁结,气滞血瘀;痰湿血瘀,留滞脉络;本虚标实,虚实夹杂。本病病机虽错综复杂,但不外虚、痰、瘀、滞四者,基本病理机制可以虚实两端概括,虚以脾虚为主,实即以痰滞为标。现代医家在继承古人治疗经验的同时结合现代人的体质和发病特点不断拓展和延伸了动脉粥样硬化的治疗思路,提出了健脾益气,豁痰化瘀;疏肝健脾,祛瘀化痰;滋补肝肾,益气活血等治法,并通过大量的实验和临床研究证实了大量具有良好临床疗效、无明显毒副作用的中药制剂,给患者带来了福音和光明的治疗前景。Traditional Chinese medicine has accumulated rich and successful experience in clinical practice for thousands of years in the treatment of atherosclerosis, providing an objective basis for delaying and reducing the development of atherosclerotic lesions and preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. As early as the "Huangdi Neijing" has an important theoretical basis for the disease. For example, "Lingshu·wei disorder theory" says: "People have fat, cream, and meat", "the fat, the serum, and the air is less slippery." Traditional Chinese medicine believes that atherosclerotic diseases belong to the category of diseases of qi, blood and body fluids, which are similar to phlegm turbidity and blood stasis. It can be summed up as spleen loses healthy movement, phlegm-damp endogenous; kidney deficiency opens and closes unfavorably, water-dampness stops within; liver-qi stagnation, qi stagnation and blood stasis; Although the pathogenesis of this disease is complicated, it is nothing but deficiency, phlegm, blood stasis, and stagnation. The basic pathological mechanism can be summarized at both ends of deficiency and excess. Deficiency is dominated by spleen deficiency, and in reality, phlegm stagnation is the target. While inheriting the treatment experience of the ancients, modern doctors have continuously expanded and extended the treatment ideas of atherosclerosis in combination with the physique and pathogenic characteristics of modern people. Phlegm; nourishing liver and kidney, nourishing qi and activating blood, etc., and through a large number of experiments and clinical studies, a large number of traditional Chinese medicine preparations with good clinical efficacy and no obvious toxic and side effects have been confirmed, bringing good news and bright treatment prospects to patients.
樟科植物肉桂(Cinnamomum cassia),始载于《神农本草经》,辛甘,大热,具有补火助阳、引火归源、散寒止痛、活血通经的作用功效。桂皮醛(trans-cinnamaldehyde, TCA),是从肉桂树中提取的烯醛类有机化合物,是其挥发油中主要成分。迄今为止,尚未见有关桂皮醛对治疗动脉粥样硬化作用的报道。Cinnamomum cassia, a plant of the Lauraceae family, was first recorded in the "Shen Nong's Materia Medica". It is acrid and sweet, and has the effects of invigorating the yang, igniting the fire and returning to the source, dispelling cold and relieving pain, promoting blood circulation and clearing the meridians. Trans-cinnamaldehyde (TCA) is an alkenal organic compound extracted from cinnamon tree, and it is the main component in its volatile oil. So far, there is no report on the effect of cinnamaldehyde on the treatment of atherosclerosis.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于克服现有技术中治疗动脉粥样硬化的药物毒副作用大、患者不能耐受,影响临床疗效和患者的治疗信心的技术缺陷,提供桂皮醛在制药中的新用途,具体涉及桂皮醛在制备治疗动脉粥样硬化药物中的用途。The object of the present invention is to overcome the large toxic and side effects of drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis in the prior art, the patient cannot tolerate it, and the technical defects that affect the clinical efficacy and the patient's treatment confidence, provide a new use of cinnamaldehyde in pharmacy, specifically related to Use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of atherosclerosis medicament.
本发明中所述桂皮醛的分子式为C9H8O,分子量为132.16,熔点为-7.5℃,其具有式(Ⅰ)的结构:The molecular formula of cinnamaldehyde in the present invention is C9 H8 O, the molecular weight is 132.16, the melting point is -7.5°C, and it has the structure of formula (I):
(Ⅰ)(I)
本发明进行了高脂饲料喂养ApoE-/-小鼠建立动脉粥样硬化动物模型的实验。结果表明,桂皮醛可减小高脂饲料喂养ApoE-/-小鼠主动脉斑块的面积,使斑块稳定;能够减少炎症因子的释放,调控免疫因子的表达。结果表明,所述的桂皮醛可通过抗炎和免疫抑制途径发挥抗动脉粥样硬化,稳定易损斑块的作用,可作为治疗药物应用于治疗动脉粥样硬化。In the present invention, an experiment of establishing an atherosclerosis animal model by feeding ApoE-/- mice with high-fat feed is carried out. The results showed that cinnamaldehyde could reduce the area of aortic plaques in ApoE-/- mice fed with high-fat diet and stabilize the plaques; it could also reduce the release of inflammatory factors and regulate the expression of immune factors. The results show that the cinnamaldehyde can exert anti-atherosclerosis and stabilize vulnerable plaques through anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive pathways, and can be used as a therapeutic drug for the treatment of atherosclerosis.
与现有技术相比,本发明的有益效果为:Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects of the present invention are:
(1)现代医学研究显示,动脉粥样硬化会随着年龄的增长而自然显现,尤其中老年患者常因动脉粥样硬化斑块破裂造成血栓形成而危害生命,因此,稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块更突显出其预防临床急性事件发生的重要性。本发明通过药效学实验证明了本发明所涉及的桂皮醛对改善高脂饲料喂养ApoE-/-小鼠主动脉斑块面积无影响,但能显著减少斑块内巨噬细胞含量,增加平滑肌细胞和胶原含量而显著增强斑块稳定性。研究结果提示了桂皮醛具有良好的稳定动脉粥样硬化易损斑块的作用,明确了桂皮醛干预动脉粥样硬化的方向。本发明关于桂皮醛在制备抗动脉粥样硬化药物用途中的应用为首次公开。(1) Modern medical research shows that atherosclerosis will appear naturally with age, especially in middle-aged and elderly patients, which often endanger life due to thrombosis caused by the rupture of atherosclerotic plaques. Therefore, stable atherosclerotic plaques The block further highlights its importance in preventing clinical acute events. The present invention proves that the cinnamic aldehyde involved in the present invention has no effect on improving the aortic plaque area of ApoE-/- mice fed with high-fat feed through pharmacodynamic experiments, but can significantly reduce the content of macrophages in the plaque and increase smooth muscle Cell and collagen content significantly enhanced plaque stability. The results of the study suggest that cinnamic aldehyde has a good effect on stabilizing vulnerable plaques in atherosclerosis, and clarifies the direction of cinnamic aldehyde to intervene in atherosclerosis. The application of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of anti-atherosclerosis drugs is disclosed for the first time in the present invention.
(2)目前中药多是通过抗炎和抗氧化途径稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块。本发明通过药效学实验证明了本发明所涉及的桂皮醛能显著降低M1型巨噬细胞标志物iNOS、TNF-α的表达,显著升高M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD206、FIZZ-1的表达。结果提示,桂皮醛抑制巨噬细胞向M1型分化,促进巨噬细胞向M2型分化,影响了巨噬细胞极化而稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块,对易损斑块具有保护作用。研究结果表明,桂皮醛是通过免疫调节途径抑制动脉粥样硬化炎症反应稳定斑块。为中药抗动脉粥样硬化提供了新的方向和策略。(2) At present, traditional Chinese medicines mostly stabilize atherosclerotic plaques through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. The present invention proves that the cinnamaldehyde involved in the present invention can significantly reduce the expression of M1 macrophage markers iNOS and TNF-α, and significantly increase the M2 macrophage markers CD206 and FIZZ-1 through pharmacodynamic experiments. Express. The results suggest that cinnamaldehyde inhibits the differentiation of macrophages to M1 type, promotes the differentiation of macrophages to M2 type, affects the polarization of macrophages and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques, and has a protective effect on vulnerable plaques. The findings suggest that cinnamaldehyde is stabilizing plaque by inhibiting the atherosclerotic inflammatory response through an immunomodulatory pathway. It provides a new direction and strategy for the anti-atherosclerosis of traditional Chinese medicine.
(3)桂皮醛入药,无毒副作用和不良反应,安全性高,本发明为动脉粥样硬化的临床治疗提供一种经济有效、无毒副作用、安全可靠的药物。(3) Cinnamaldehyde is used as medicine, has no toxic side effects and adverse reactions, and has high safety. The present invention provides an economical, effective, safe and reliable medicine for the clinical treatment of atherosclerosis.
(4)原料药材肉桂为常见中药材,来源广泛,原料成本低。(4) The raw medicinal material, cinnamon, is a common Chinese medicinal material with wide sources and low cost of raw materials.
附图说明Description of drawings
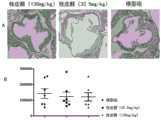
图1为桂皮醛对主动脉斑块的影响结果;其中,图A为HE染色结果,图B为统计分析结果。图中标尺大小为500μm。Figure 1 shows the results of the effect of cinnamaldehyde on aortic plaque; among them, Figure A is the result of HE staining, and Figure B is the result of statistical analysis. The scale bar in the figure is 500 μm.
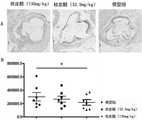
图2为桂皮醛对斑块内巨噬细胞含量的影响结果;其中,图A为免疫组化染色结果,图B为统计分析结果。图中标尺大小为500μm。Figure 2 shows the effect of cinnamaldehyde on the content of macrophages in plaques; among them, Figure A is the result of immunohistochemical staining, and Figure B is the result of statistical analysis. The scale bar in the figure is 500 μm.
图3为桂皮醛对斑块内平滑肌细胞含量的影响结果;其中,图A为免疫组化染色结果,图B为统计分析结果。图中标尺大小为500μm。Figure 3 shows the results of the effect of cinnamaldehyde on the content of smooth muscle cells in the plaque; wherein, Figure A is the result of immunohistochemical staining, and Figure B is the result of statistical analysis. The scale bar in the figure is 500 μm.
图4为桂皮醛对斑块内胶原含量的影响结果;其中,图A为天狼星红染色结果,图B为统计分析结果。图中标尺大小为500μm。Figure 4 shows the effect of cinnamaldehyde on the content of collagen in plaques; wherein, Figure A is the result of Sirius Red staining, and Figure B is the result of statistical analysis. The scale bar in the figure is 500 μm.
图5为桂皮醛对M1型巨噬细胞标志物iNOS、TNF-α和M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD206、FIZZ-1含量影响的免疫组化染色结果。图中标尺大小为500μm。Figure 5 shows the immunohistochemical staining results of the effect of cinnamaldehyde on the contents of M1 macrophage markers iNOS, TNF-α and M2 macrophage markers CD206 and FIZZ-1. The scale bar in the figure is 500 μm.
图6为桂皮醛对M1型巨噬细胞标志物iNOS、TNF-α和M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD206、FIZZ-1含量影响的统计分析结果。Figure 6 is a statistical analysis result of the effect of cinnamaldehyde on the contents of M1 macrophage markers iNOS, TNF-α and M2 macrophage markers CD206 and FIZZ-1.
图7为桂皮醛对血脂水平的影响结果。Figure 7 shows the effect of cinnamaldehyde on blood lipid levels.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
实施例1. 桂皮醛对主动脉斑块的影响Example 1. The effect of cinnamaldehyde on aortic plaque
ApoE-/-小鼠(购于常州卡文斯实验动物有限公司),高脂饲料喂养13周。13周后,影像学筛查去除无主动脉斑块的小鼠,剩余小鼠于第13周起随机分组,给予桂皮醛(购于上海宝曼生物科技有限公司)干预,继续喂养13周。实验分为:①模型组:高脂饲料喂养;②桂皮醛高剂量组:高脂饲料喂养+桂皮醛130mg/kg/day;②桂皮醛低剂量组:高脂饲料喂养+桂皮醛32.5mg/kg/day。实验过程中采用小动物超声仪定时观察和记录小鼠动脉斑块形成情况,并于13、17、21、25周采血、实验结束时心脏组织取材。继而采用HE染色观察基本组织细胞病理结构改变,方法如下:常规二甲苯脱蜡、梯度水化;滴加苏木素染色;过一下1%盐酸酒精,迅速流水返蓝15分钟;滴加1%伊红溶液染色;无水乙醇脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片;显微镜下观察拍照,使用图像分析软件分析。ApoE-/- mice (purchased from Changzhou Cavens Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd.) were fed with high-fat diet for 13 weeks. After 13 weeks, the mice without aortic plaques were removed by imaging screening, and the remaining mice were randomly divided into groups from the 13th week onwards, given cinnamaldehyde (purchased from Shanghai Baoman Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), and continued to feed for 13 weeks. The experiment was divided into: ① model group: fed with high-fat diet; ② high-dose group of cinnamaldehyde: fed with high-fat diet + cinnamaldehyde 130 mg/kg/day; ② low-dose group of cinnamaldehyde: fed with high-fat diet + cinnamaldehyde 32.5 mg/day kg/day. During the experiment, a small animal ultrasound apparatus was used to observe and record the formation of arterial plaque in mice regularly, and blood was collected at 13, 17, 21, and 25 weeks, and heart tissue was collected at the end of the experiment. Then HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of the basic tissue cells. The methods are as follows: routine xylene dewaxing, gradient hydration; drip hematoxylin staining; pass 1% hydrochloric acid alcohol, quickly run water back to blue for 15 minutes;
结果如图1所示,与模型组相比,桂皮醛两个剂量组能改善ApoE-/-小鼠主动脉斑块面积,无显著性差异(p>0.05)。结果表明,桂皮醛不具有显著缩小斑块的作用。The results are shown in Figure 1. Compared with the model group, the two dose groups of cinnamaldehyde can improve the aortic plaque area of ApoE-/- mice, with no significant difference (p>0.05). The results showed that cinnamic aldehyde did not significantly shrink plaque.
实施例2. 桂皮醛对斑块内巨噬细胞含量的影响Example 2. The effect of cinnamaldehyde on the content of macrophages in plaques
巨噬细胞通过细胞表面的多种清道夫受体等内吞斑块的脂质成分形成泡沫细胞,坏死后释放胆固醇结晶和炎症刺激因子,促进坏死核心形成,加速邻近细胞死亡和动脉粥样硬化的进展。Macrophages form foam cells through lipid components of endocytosed plaques such as multiple scavenger receptors on the cell surface, release cholesterol crystals and inflammatory stimulators after necrosis, promote the formation of necrotic cores, and accelerate adjacent cell death and atherosclerosis Progress.
心脏取材后采用免疫组化分析斑块内巨噬细胞含量,方法如下:常规二甲苯脱蜡、梯度水化。3%H202去除内源性过氧化物酶,进行高压修复。正常山羊血清封闭,加相应一抗4℃过夜。加入辣根酶标记的生物素化二抗,室温孵育40 min。DAB显色(阳性结果显示黄色),苏木素复染、二甲苯透明、封片。阳性染色为胞聚或胞核棕色颗粒,阴性对照以PBS或与一抗相同种属来源的正常IgG 代替。用图像分析软件分析每一图像中的阳性信号强度,计算阳性染色面积进行统计分析。The content of macrophages in the plaques was analyzed by immunohistochemistry after the hearts were taken. The methods were as follows: conventional xylene dewaxing and gradient hydration. 3
结果如图2所示,与模型组相比,桂皮醛组能显著减少ApoE-/-小鼠主动脉斑块内巨噬细胞含量(p<0.05),提示桂皮醛能够减少促炎细胞而稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块。The results are shown in Figure 2. Compared with the model group, the cinnamaldehyde group can significantly reduce the content of macrophages in the aortic plaques of ApoE-/- mice (p<0.05), suggesting that cinnamaldehyde can reduce pro-inflammatory cells and stabilize Atherosclerotic plaque.
实施例3. 桂皮醛对斑块内平滑肌细胞含量的影响Example 3. The effect of cinnamaldehyde on the content of smooth muscle cells in plaques
平滑肌细胞可分泌多种细胞基质,是动脉粥样硬化斑块内分泌胶原的唯一细胞源,主要作用是修复被破坏的细胞基质成分从而起到保护作用。Smooth muscle cells can secrete a variety of cell matrices and are the only cell source of endocrine collagen in atherosclerotic plaques. Their main function is to repair the damaged cell matrix components and play a protective role.
心脏取材后采用免疫组化分析斑块内平滑肌细胞含量,方法同实施例2。The content of smooth muscle cells in the plaques was analyzed by immunohistochemistry after the heart was taken, and the method was the same as that in Example 2.
结果如图3所示,与模型组相比,桂皮醛130mg/kg能显著增加ApoE-/-小鼠主动脉斑块内平滑肌细胞含量,增加了胶原分泌的来源,促进了斑块的稳定(p<0.05)。The results are shown in Figure 3. Compared with the model group, cinnamaldehyde 130 mg/kg can significantly increase the content of smooth muscle cells in the aortic plaques of ApoE-/- mice, increase the source of collagen secretion, and promote the stability of the plaque ( p<0.05).
实施例4. 桂皮醛对斑块内胶原组织含量的影响Example 4. The effect of cinnamaldehyde on the content of collagen in plaques
胶原是动脉粥样硬化斑块内最重要的细胞外基质成分,是维持斑块“刚性”成分的最主要成分,而且还是组成纤维帽的主要成分,所以胶原组织有抗血流冲击防止斑块破裂的作用,是维护斑块稳定性的重要评价指标。Collagen is the most important extracellular matrix component in atherosclerotic plaque, the most important component to maintain the "rigid" component of the plaque, and the main component of the fibrous cap, so collagen tissue has anti-blood flow shock to prevent plaque The role of rupture is an important evaluation index for maintaining plaque stability.
心脏取材后采用天狼星红染色分析斑块内胶原组织的含量,方法如下:常规二甲苯脱蜡、梯度水化;置于0.1%苦味酸天狼星红染液中染色;蒸馏水冲洗;Harris’s 苏木素染色;无水乙醇脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片;显微镜下观察拍照。The content of collagen tissue in the plaques was analyzed by Sirius red staining after the heart was harvested. The methods were as follows: conventional xylene dewaxing and gradient hydration; placing in 0.1% picric acid Sirius red staining solution for staining; rinsing with distilled water; Harris's hematoxylin staining; no Dehydrated with water ethanol, transparent with xylene, and sealed with neutral gum; observed and photographed under a microscope.
结果如图4所示,与模型组相比,桂皮醛130mg/kg能显著增加斑块内胶原组织(Collage)含量(p<0.05),表明桂皮醛通过增加斑块基质成分稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块。The results are shown in Figure 4. Compared with the model group, cinnamaldehyde 130 mg/kg can significantly increase the collagen tissue (Collage) content in the plaque (p<0.05), indicating that cinnamaldehyde stabilizes atherosclerosis by increasing the plaque matrix components. plaque.
实施例5.桂皮醛对M1型、M2型巨噬细胞标志物的影响Example 5. Effect of cinnamaldehyde on markers of M1 and M2 macrophages
心脏取材后采用免疫组化分析斑块内M1型、M2型巨噬细胞标志物的表达,方法同实施The expression of M1 type and M2 type macrophage markers in the plaque was analyzed by immunohistochemistry after the heart was taken, and the method was the same as the implementation.
例2。Example 2.
巨噬细胞向M1型分化,斑块不稳定性增加;向M2型分化,斑块稳定性增加。Macrophages differentiate into M1 type, and plaque instability increases; when they differentiate into M2 type, plaque stability increases.
结果如图5和图6所示,与模型组相比,桂皮醛130mg/kg能显著降低M1型巨噬细胞标志物iNOS、TNF-α的表达(p<0.05或p<0.01);显著升高M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD206、FIZZ-1的表达(p<0.05)。桂皮醛32.5mg/kg能显著降低M1型巨噬细胞标志物TNF-α的表达(p<0.05);显著升高M2型巨噬细胞标志物FIZZ-1的表达(p<0.05)。提示桂皮醛能抑制炎症和免疫因子的释放,抑制巨噬细胞向M1型分化,促进巨噬细胞向M2型分化,影响了巨噬细胞极化而稳定动脉粥样硬化斑块,对易损斑块具有保护作用。The results are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, compared with the model group, cinnamaldehyde 130mg/kg can significantly reduce the expression of M1 macrophage markers iNOS and TNF-α (p<0.05 or p<0.01); High expression of M2 macrophage markers CD206 and FIZZ-1 (p<0.05). Cinnamaldehyde 32.5mg/kg can significantly reduce the expression of M1 macrophage marker TNF-α (p<0.05); significantly increase the expression of M2 macrophage marker FIZZ-1 (p<0.05). It is suggested that cinnamaldehyde can inhibit the release of inflammatory and immune factors, inhibit the differentiation of macrophages to M1 type, and promote the differentiation of macrophages to M2 type, which affects the polarization of macrophages and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques. Blocks are protective.
实施例6. 桂皮醛对ApoE-/-小鼠血脂质水平的影响Example 6. Effects of cinnamaldehyde on blood lipid levels in ApoE-/- mice
实验结束后动物空腹取血,分离血清,采用自动生化分析仪测定TC、LDL-C、TG、HDL-C。After the experiment, the animals were fasted to take blood, and the serum was separated, and TC, LDL-C, TG, and HDL-C were determined by an automatic biochemical analyzer.
结果如图7所示,与模型组相比,桂皮醛两个剂量组ApoE-/-小鼠血清TC、TG、LDL-C、HDL-C水平变化无统计学差异,p>0.05。结果表明,桂皮醛对血脂无影响,无降脂作用。The results are shown in Figure 7. Compared with the model group, there was no statistical difference in the changes of serum TC, TG, LDL-C and HDL-C levels of ApoE-/- mice in the two dose groups of cinnamaldehyde, p>0.05. The results showed that cinnamaldehyde had no effect on blood lipids and had no lipid-lowering effect.
Claims (3)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710093813.3ACN106924227B (en) | 2017-02-21 | 2017-02-21 | The use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of atherosclerosis medicine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710093813.3ACN106924227B (en) | 2017-02-21 | 2017-02-21 | The use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of atherosclerosis medicine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN106924227A CN106924227A (en) | 2017-07-07 |
| CN106924227Btrue CN106924227B (en) | 2020-01-24 |
Family
ID=59423432
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710093813.3AActiveCN106924227B (en) | 2017-02-21 | 2017-02-21 | The use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of atherosclerosis medicine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN106924227B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118141068B (en)* | 2024-04-12 | 2024-09-10 | 消感卫士(山东)医疗用品有限公司 | Hawthorn fermentation product and preparation method thereof |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006199647A (en)* | 2005-01-21 | 2006-08-03 | Japan Health Science Foundation | Adipocyte differentiation regulator |
| KR20120122597A (en)* | 2011-04-29 | 2012-11-07 | 영남대학교 산학협력단 | Composition Comprising Extract of Cinnamon for Prevention and Ttreatment of Metabolic Syndrome |
- 2017
- 2017-02-21CNCN201710093813.3Apatent/CN106924227B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006199647A (en)* | 2005-01-21 | 2006-08-03 | Japan Health Science Foundation | Adipocyte differentiation regulator |
| KR20120122597A (en)* | 2011-04-29 | 2012-11-07 | 영남대학교 산학협력단 | Composition Comprising Extract of Cinnamon for Prevention and Ttreatment of Metabolic Syndrome |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Cinnamaldehyde inhibits the tumor necrosis factor-α-induced expression of cell adhesion molecules in endothelial cells by suppressing NF-κB activation: Effects upon IκB and Nrf2;Being-Chyuan Liao et al.;《Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology》;20080205;第229卷;161-171* |
| Water extracts of cinnamon and clove exhibits potent inhibition of protein glycation and anti-atherosclerotic activity in vitro and in vivo hypolipidemic activity in zebrafish;Seori Jin et al.;《Food and Chemical Toxicology》;20110405;第49卷;1521-1529* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106924227A (en) | 2017-07-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Ke et al. | Preventive and therapeutic effects of astaxanthin on depressive-like behaviors in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-treated rats | |
| WO2021164210A1 (en) | Application of gallic acid derivative in prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis disease | |
| Park et al. | Protective activity ethanol extract of the fruits of Illicium verum against atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice | |
| Sun et al. | Yi Mai granule improve energy supply of endothelial cells in atherosclerosis via miRNA-125a-5p regulating mitochondrial autophagy through Pink1-Mfn2-Parkin pathway | |
| Song et al. | LiuweiDihuang improved cognitive functions in SAMP8 mice by inhibiting COX-2 expression and subsequent neuroinflammation | |
| Wang et al. | Dihydromyricetin alleviates inflammatory bowel disease associated intestinal fibrosis by inducing autophagy through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | |
| Adejor et al. | Effects of Garcinia kola biflavonoid fractions on serum lipid profile and kidney function parameters in hyperlipidemic rats | |
| CN110075094A (en) | Pterostilbene is preparing the application in drug or health care product | |
| CN107349190B (en) | The application of aromatic turmeric | |
| US8609163B2 (en) | Herbal formulation advocated for the prevention and management of coronary heart disease | |
| CN106924227B (en) | The use of cinnamaldehyde in the preparation of atherosclerosis medicine | |
| CN105025910A (en) | Pharmaceutical composition and functional food containing natural extract for prevention or treatment of diabetic complications or angioedema | |
| Wang et al. | Effect of Huangdisan grain on improving cognitive impairment in VD rats and its mechanism in immune inflammatory response | |
| WO2022135461A1 (en) | Use of magl inhibitor in preparation of medicament for preventing or treating fatty liver diseases | |
| CN103169694B (en) | Application of n-butenyl phthalide in preparing medicine for treating liver injury and improving liver function and pharmaceutical composition | |
| CN105687178B (en) | Salviandic acid A is individually or multiple medicine combines the application in treatment nephrotic syndrome medicine is prepared | |
| Lu et al. | The role of TFEB-mediated autophagy-lysosome dysfunction in manganese neurotoxicity | |
| CN106176777A (en) | The new application of rhodioside and be used for treating atherosclerotic compositions | |
| CN115887568A (en) | A traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating liver damage caused by lipid metabolism disorder and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110613712B (en) | Chinese medicinal composition and its application in treating vasculitis and endothelial injury | |
| Huang et al. | TJ0113 attenuates fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis by inducing mitophagy | |
| CN111467385B (en) | Use of composition in preventing or treating neurodegenerative disease | |
| EP2606883A1 (en) | Uses of n-Butylidenephthalide in Treating a Liver Injury and Improving Liver Function | |
| CN103908567B (en) | A kind of compound preparation and its application for treating Painful diabetic neuropathy | |
| CN112972440B (en) | Application of muscone in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating depression |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |