CN103442336A - Data distribution method based on link relevance in wireless sensor network - Google Patents
Data distribution method based on link relevance in wireless sensor networkDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103442336A CN103442336ACN2013102993048ACN201310299304ACN103442336ACN 103442336 ACN103442336 ACN 103442336ACN 2013102993048 ACN2013102993048 ACN 2013102993048ACN 201310299304 ACN201310299304 ACN 201310299304ACN 103442336 ACN103442336 ACN 103442336A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- node
- link
- message
- formula
- child
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于无线自组织网络与传感器网络领域,涉及一种链路相关性的数据分发协议的实现方法,用于实现无线传感网络中节点的快速代码更新。 The invention belongs to the field of wireless ad hoc networks and sensor networks, and relates to a method for implementing a data distribution protocol of link correlation, which is used to realize fast code update of nodes in a wireless sensor network. the
背景技术Background technique
随着嵌入式,传感器制造,无线通信技术的不断发展,大规模无线传感器网络技术迅速发展并被广泛应用到军事侦察、公共安全、智能交通、环境检测、医学监控等诸多领域。典型的无线传感器网络由大量微型传感器节点组成,它们被部署在无人的监控的恶劣环境中,并通过无线自组成网,通过拓扑控制和网络协议自动形成多跳网络系统,不受现有有线网络基础设施的限制。感知数据通过无线通信以多跳中继方式汇集到数据处理中心。无线传感器网络使人们在任何时间、地点和环境条件下实时获取大量详实而可靠的信息,仿佛人类将远程神经末梢伸向了外部世界的万物。正因为传感器网络规模之大覆盖范围之广,使得传感器节点上所运程序的代码更新遇到很多挑战。现有的数据分发协议都能完成代码的更新,但忽略了链路相关性存在的客观事实,使得数据分发的效率不高,不能有效的减少完成时间和数据传输开销。 With the continuous development of embedded, sensor manufacturing, and wireless communication technologies, large-scale wireless sensor network technology has developed rapidly and has been widely used in many fields such as military reconnaissance, public safety, intelligent transportation, environmental detection, and medical monitoring. A typical wireless sensor network is composed of a large number of miniature sensor nodes, which are deployed in the harsh environment of unmanned monitoring, and form a multi-hop network system automatically through wireless self-organization, topology control and network protocols, and are not affected by existing wired networks. Network infrastructure limitations. Sensing data is gathered to the data processing center through multi-hop relay through wireless communication. Wireless sensor networks enable people to obtain a large amount of detailed and reliable information in real time at any time, place and environmental conditions, as if human beings have extended their remote nerve endings to all things in the external world. Because of the large scale and wide coverage of the sensor network, the code update of the program running on the sensor nodes encounters many challenges. Existing data distribution protocols can complete code updates, but ignore the objective fact of link dependencies, making data distribution inefficient and unable to effectively reduce completion time and data transmission overhead. the
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种无线传感网络中基于链路相关的数据分发方法,用于实现无线传感网络中节点的快速代码更新。 The purpose of the present invention is to provide a data distribution method based on link correlation in a wireless sensor network, which is used to realize fast code update of nodes in the wireless sensor network. the
为实现上述目的,本发明所采取的技术方案如下: In order to achieve the above object, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is as follows:
本发明无线传感网络中基于链路相关性的数据分发方法包括如下步骤: The data distribution method based on link correlation in the wireless sensor network of the present invention comprises the following steps:
步骤一:由根节点广播一条HOP消息,所述HOP消息只有一个字段跳数,所述字段跳数为非根节点到根节点的跳数,所述字段跳数的初始值为0;非根节点第一次收到所述HOP消息后,将字段跳数的值加1并记下作为该非根节点到根节点的跳数,然后非根节点再将修改后的HOP消息广播出去; Step 1: broadcast a HOP message by the root node, the HOP message has only a field hop count, the field hop count is the hop count from the non-root node to the root node, and the initial value of the field hop count is 0; non-root After the node receives the HOP message for the first time, it adds 1 to the value of the field hop count and records it as the hop count from the non-root node to the root node, and then the non-root node broadcasts the modified HOP message;
各节点互相广播HELLO消息,所述HELLO消息包含发送节点的ID、发送节点到根节点的跳数和递增序号;节点只接收下游节点的HELLO消息,所述下游节点是指到根节点的跳数为本节点到根节点的跳数加1的节点;将听到的下游节点记为本节点的子节点,并使用位向量记录每个子节点的最新10条HELLO消息的接收状态,其中,所述位向量中为1的位表示对应的HELLO消息丢失了,为0的位表示对应的HELLO消息成功接收,每个子节点占用一个位向量; Each node broadcasts the HELLO message to each other, and the HELLO message includes the ID of the sending node, the number of hops from the sending node to the root node, and the incremental sequence number; the node only receives the HELLO message of the downstream node, and the downstream node refers to the number of hops to the root node A node that adds 1 to the number of hops from this node to the root node; record the heard downstream node as a child node of this node, and use a bit vector to record the receiving status of the latest 10 HELLO messages of each child node, wherein the A bit of 1 in the bit vector indicates that the corresponding HELLO message is lost, and a bit of 0 indicates that the corresponding HELLO message is successfully received, and each child node occupies a bit vector;
步骤二:每个节点广播一条CLAIM消息,所述CLAIM消息包含发送节点的ID和一个键值对集合,所述键值对集合的每个键值对由发送节点的子节点的ID、发送节点所记录的表示各对应子节点的HELLO消息的位向量构成; Step 2: each node broadcasts a CLAIM message, and the CLAIM message includes the ID of the sending node and a key-value pair set, and each key-value pair of the key-value pair set is composed of the ID of the child node of the sending node, the sending node The recorded bit vector composition representing the HELLO message of each corresponding child node;
各节点根据所收到的CLAIM消息,根据公式(1)计算节点到各发送节点的链路质量,根据公式(2)计算节点与各发送节点的子节点之间的链路的链路相关性,进而根据公式(3)计算出各发送节点的影响因子,选择影响因子的值最大的发送节点作为父节点,并根据节点间的父子关系建立相关性树; According to the received CLAIM message, each node calculates the link quality from the node to each sending node according to the formula (1), and calculates the link correlation between the node and the child nodes of each sending node according to the formula (2) , and then calculate the influence factor of each sending node according to the formula (3), select the sending node with the largest value of the influence factor as the parent node, and build a correlation tree according to the parent-child relationship between nodes;
mk(i)=αci(k,S)+(1-α)qik (3) mk (i)=αci (k,S)+(1-α)qik (3)
式(1)、(2)和(3)中: In formulas (1), (2) and (3):
i表示发送CLAIM消息的节点, i represents the node sending the CLAIM message,
k表示接收CLAIM消息的节点, k represents the node receiving the CLAIM message,
Bik表示节点i所记录的节点k所发送的HELLO消息的位向量, Bik represents the bit vector of the HELLO message sent by node k recorded by node i,
|Bik|表示位向量的模, |Bik | represents the modulus of the bit vector,
qik表示链路i→k的链路质量, qik represents the link quality of link i→k,
S表示节点i的不包括节点k的剩余子节点的集合(s1,s2...sn), S represents the set (s1 , s2 ...sn ) of the remaining child nodes of node i not including node k,
BiS表示节点i所记录的不包括节点k的剩余子节点发送的HELLO消息的位向量按位与运算后得到的新位向量; BiS represents the new bit vector obtained after the bit vector of the HELLO message sent by the remaining child nodes of node i that is not included in the bitwise AND operation recorded by node i;
Bik(m)表示Bik第m位的值; Bik (m) represents the value of the mth bit of Bik ;
BiS(m)表示BiS第m位的值; BiS (m) represents the value of the mth bit of BiS ;
ci(k,S)表示节点k所计算的链路i→k到链路集合i→S的链路相关性; ci (k, S) represents the link correlation calculated by node k from link i→k to link set i→S;
Pi(S|k)表示公式(2)的条件概率数学表示方式; Pi (S|k) represents the mathematical representation of the conditional probability of formula (2);
α表示加权平均因子,α的取值区间为[0,1]; α represents the weighted average factor, and the value range of α is [0, 1];
mk(i)表示节点k所计算出的节点i的影响因子; mk (i) represents the influence factor of node i calculated by node k;
各非根节点选定父节点后,广播一条PSLT消息通知邻居节点,所述PSLT消息包含本非根节点的ID和选定的父节点的ID; After each non-root node selects a parent node, it broadcasts a PSLT message to notify neighbor nodes, and the PSLT message includes the ID of the non-root node and the ID of the selected parent node;
步骤三:建立如式(4)所示的使用编码的决策模型和式(5)所示的不使用编码的决策模型, Step 3: set up the decision-making model that uses coding shown in formula (4) and the decision-making model that does not use coding shown in formula (5),
其中,
式(6)中的由式(7)和递推式(8)算出: In formula (6) Calculated by formula (7) and recursive formula (8):
式(4)到式(8)中, From formula (4) to formula (8),
N表示单个数据页所包含的数据包的数量; N represents the number of packets contained in a single data page;
τ表示单个数据包的传输时间; τ represents the transmission time of a single packet;
D表示使用网络编码时的解码时间; D represents the decoding time when using network coding;
n表示节点i的子节点的集合S中的节点个数; n represents the number of nodes in the set S of child nodes of node i;
qik表示链路i→k的链路质量; qik represents the link quality of link i→k;
w表示到节点i的链路质量最差的一个子节点,qiw=mink∈S(qik); w represents a child node with the worst link quality to node i, qiw =mink∈S (qik );
tREQ表示请求丢失的数据包的时间; tREQ indicates the time to request the lost packet;
Epkt表示单个数据包要覆盖到n个子节点所需的期望传输值; Epkt represents the expected transmission value required for a single data packet to cover n child nodes;
tcoding表示单个数据页在使用编码时的传输延时; tcoding indicates the transmission delay of a single data page when using encoding;
tnative表示单个数据页在不使用编码时的传输延时; tnative indicates the transmission delay of a single data page when no encoding is used;
r表示单个数据包的传输次数; r represents the transmission times of a single data packet;
表示节点i的单个数据包发送r次能覆盖n个子节点的概率; Indicates the probability that a single data packet sent by node i can cover n child nodes r times;
表示节点i的单个数据包发送r次不能覆盖n个子节点的概率; Indicates the probability that a single data packet sent by node i cannot cover n child nodes r times;
(1-qin)r表示节点i的单个数据包发送r次不能覆盖子节点n的概率; (1-qin )r represents the probability that a single data packet sent by node i cannot cover child node n for r times;
表示节点i的单个数据包发送r次不能覆盖除子节点n之外的n-1个子节点的概率; Indicates the probability that node i's single data packet sent r times cannot cover n-1 child nodes except child node n;
表示在节点n所丢失的数据包被包含在余下的n-1个节点丢失的数据包集合中的概率;根据公式(2)计算得到
表示节点i的单个数据包发送r次,既不能覆盖子节点n,也不能覆盖余下n-1个子节点的概率; Indicates the probability that a single data packet of node i is sent r times, neither can cover child node n, nor can it cover the remaining n-1 child nodes;
分别计算使用编码的编码决策模型和不使用编码的编码决策模型的传输延迟,从中选择传输延迟值较小的编码决策模型作为每个节点的最终编码策略; Calculate the transmission delay of the encoding decision model using encoding and the encoding decision model without encoding respectively, and select the encoding decision model with a smaller transmission delay value as the final encoding strategy of each node;
步骤四:每个节点根据以上步骤所建立的相关性树和所选择的最终编码策略将数据分发出去,整个分发过程由根节点开始。 Step 4: Each node distributes the data according to the correlation tree established in the above steps and the selected final coding strategy, and the whole distribution process starts from the root node. the
进一步地,本发明在步骤四中,当子节点每接收完一轮数据后,如果有数据丢失,就触发一个计时器,由子节点向父节点发送重传丢失的数据的请求;所述计时器的计时间隔如式(9)所示: Further, in step 4 of the present invention, after each round of data is received by the child node, if there is data loss, a timer is triggered, and the child node sends a request for retransmitting the lost data to the parent node; the timer The timing interval of is shown in formula (9):
Δt=Cn×qik+Tr (9) Δt=Cn×qik +Tr (9)
式(9)中,Cn表示大于100的整数,qik表示父节点i到子节点k的链路质量,Tr表示0到8范围内的随机数;子节点到父节点的链路质量越差,计时间隔Δt越短。 In formula (9), Cn represents an integer greater than 100, qik represents the link quality from parent node i to child node k, Tr represents a random number in the range of 0 to 8; the link quality from child node to parent node is higher Poor, the shorter the timing interval Δt.
与现有技术相比,本发明的有益效果是:本发明方法考虑了链路相关性在数据分发过程中的影响,减少了节点的传输开销、能量消耗、整个网络的数据分发的完成时间。 Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effect of the present invention is: the method of the present invention considers the influence of link correlation in the data distribution process, reduces the transmission overhead of nodes, energy consumption, and the completion time of data distribution of the entire network. the
附图说明Description of drawings
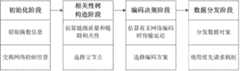
图1是本发明方法的工程流程图。 Fig. 1 is the engineering flowchart of the inventive method. the
图2是一个数据分发拓扑图,图中,节点A和B都发10个数据包给节点C、D和E;其中,灰色矩形表示对应的数据包成功接收,白色矩形表示对应的数据包丢失了,需要下一轮重传;R是根节点。 Figure 2 is a data distribution topology diagram. In the figure, nodes A and B both send 10 data packets to nodes C, D, and E; among them, the gray rectangle indicates that the corresponding data packet is successfully received, and the white rectangle indicates that the corresponding data packet is lost. , the next round of retransmission is required; R is the root node. the
图3是利用本发明方法建立的相关性树。 Fig. 3 is a dependency tree established by the method of the present invention. the
具体实施方式Detailed ways
在嵌入式网络操作系统TinyOS2.1.1中可以实现本发明无线传感网络中基于链路相关性的数据分发方法。本发明的工作流程如图1所示,图2是本发明的一个实施例的数据分发拓扑图,节点A和B的父节点都是根节点R。下面结合图2对本发明作进一步描述。 The data distribution method based on link correlation in the wireless sensor network of the present invention can be realized in the embedded network operating system TinyOS2.1.1. The working process of the present invention is shown in FIG. 1 , and FIG. 2 is a data distribution topology diagram of an embodiment of the present invention, and the parent nodes of nodes A and B are both root nodes R. The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with FIG. 2 . the
(1)初始化阶段。 (1) Initialization stage. the
首先由R开始广播一个HOP消息,所述HOP消息只有一个字段跳数hR=0。A、B第一次听到这个HOP消息后,获取HOP消息中的字段跳数的值,执行计算hA=hR+1=1,作为A到R的跳数,同理B到R的跳数hB=1。A、B分别将修改后的字段跳数的值封装进HOP消息中并广播出去,之后听到任何HOP消息都不再处理。C、D听到了A的HOP的消息,计算出各自到R的跳数hC(hD)=hA+1=2,E听到了B的HOP消息,计算出自己到R的跳数hE=hB+1=2,HOP消息的作用是防止在相关性树构造阶段出现回路。 Firstly, R starts to broadcast a HOP message, and the HOP message has only one field hop count hR =0. After A and B hear the HOP message for the first time, they obtain the value of the field hop count in the HOP message, and perform the calculation hA = hR + 1 = 1, as the hop count from A to R, and similarly from B to R The number of hops hB =1. A and B respectively encapsulate the value of the modified field hop count into a HOP message and broadcast it, and will not process any HOP message after hearing it. C and D heard the HOP message from A, and calculated the number of hops hC (hD )=hA +1=2, and E heard the HOP message from B, and calculated the number of hops to R from hE = hB + 1 = 2, the function of the HOP message is to prevent loops from appearing in the dependency tree construction phase.
各节点互相广播HELLO消息,所述HELLO消息包含发送节点的ID、发送 节点到根节点的跳数和递增序号;C的HELLO消息包含C的ID、C到R的跳数hC和递增序号;递增序号是用来标识HELLO消息的唯一性,比如当前HELLO消息的递增序号为1,那么下一个HELLO消息的递增序号就为2;A、B只接收下游节点C、D、E的HELLO消息;A将听到的下游节点C、D作为A的子节点,B将听到的下游节点D、E作为B的子节点;图2中的四个大矩形分别表示A所记录的C、D的HELLO消息的位向量BAC和BAD,B所记录的D、E的HELLO消息的位向量BBD和BBE。每个大矩形都包含10个小矩形,表示各子节点的最新10条HELLO消息,白色的小矩形表示对应HELLO消息丢失了,其位向量对应位的位值为1,例如位向量BAC={0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1},其第9位的位值BAC(9)=1,表示第9个HELLO消息丢失了。 Each node broadcasts the HELLO message mutually, and described HELLO message comprises the ID of sending node, the hop count and the increment sequence number of sending node to root node; The HELLO message of C comprises the ID of C, the hop count hC and increment sequence number of C to R; The increment sequence number is used to identify the uniqueness of the HELLO message. For example, if the increment sequence number of the current HELLO message is 1, then the increment sequence number of the next HELLO message will be 2; A and B only receive the HELLO messages of downstream nodes C, D, and E; A regards the downstream nodes C and D heard as the child nodes of A, and B regards the downstream nodes D and E heard as the child nodes of B; the four large rectangles in Figure 2 represent the records of C and D recorded by A respectively. Bit vectors BAC and BAD of the HELLO message, bit vectors BBD and BBE of the HELLO messages of D and E recorded by B. Each large rectangle contains 10 small rectangles, which represent the latest 10 HELLO messages of each child node. The small white rectangles indicate that the corresponding HELLO messages are lost, and the bit value of the corresponding bit of the bit vector is 1, for example, the bit vector BAC = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}, its 9th bit value BAC (9)=1, means that the 9th HELLO message is lost.
(2)相关性树构造阶段 (2) Dependency tree construction stage
每个节点广播一条CLAIM消息,所述CLAIM消息包含发送节点的ID和一个键值对集合,所述键值对集合的每个键值对由发送节点的子节点的ID、发送节点所记录的对应HELLO消息的位向量构成;例如图2中A的CLAIM消息表示为<A,{[C,BAC],[D,BAD]}>。 Each node broadcasts a CLAIM message, and the CLAIM message includes the ID of the sending node and a key-value pair set, and each key-value pair of the key-value pair set is recorded by the ID of the child node of the sending node, the sending node The bit vector structure corresponding to the HELLO message; for example, the CLAIM message of A in Figure 2 is expressed as <A, {[C, BAC ], [D, BAD ]}>.
节点D听到了节点B的CLAIM消息,根据公式(1)计算B→D的链路质量: Node D hears the CLAIM message of node B, and calculates the link quality of B→D according to the formula (1):
同理可得其他3条链路的链路质量分别为60%,70%,50%,如图2所示。 Similarly, the link quality of the other three links can be obtained as 60%, 70%, and 50%, respectively, as shown in Figure 2. the
再根据公式(2)计算链路B→D到链路B→S的相关性cB(D,S),S是除子节点D之外的节点B的剩余子节点集合,在附图2中S中只有节点E。 Then calculate the correlation cB (D, S) from link B → D to link B → S according to the formula (2), S is the remaining sub-node set of node B except sub-node D, in Figure 2 There is only node E in S.
同理可得cA(D,S)=0,进而由公式(3)分别计算出发送节点A、B的影响因子,取α=0.5,选择影响因子的值最大的发送节点作为父节点,根据节点间的父子关系建立相关性树。 In the same way, cA (D, S)=0 can be obtained, and then the influence factors of sending nodes A and B are calculated by formula (3), and α=0.5 is selected, and the sending node with the largest value of the influencing factor is selected as the parent node. Build a dependency tree based on the parent-child relationship between nodes.
mD(A)=αcA(D,S)+(1-α)qAD=0.5×0+0.5×0.7=0.35 mD (A)=αcA (D,S)+(1-α)qAD =0.5×0+0.5×0.7=0.35
mD(B)=αcB(D,S)+(1-α)qBD=0.5×1+0.5×0.6=0.8 mD (B)=αcB (D, S)+(1-α)qBD =0.5×1+0.5×0.6=0.8
所以,D选择B作为其父节点,最后建立的相关性树如图3所示。 Therefore, D selects B as its parent node, and the finally established dependency tree is shown in Figure 3. the
(3)编码选择阶段。 (3) Code selection stage. the
在相关性树构造完成后,节点根据公式(4)建立使用编码的决策模型和根据公式(5)建立不使用编码的策略模型,分别计算两种策略下的传输延迟,选择传输延时较小的策略最为最终的编码策略。 After the construction of the correlation tree is completed, the node establishes a decision model using coding according to formula (4) and a policy model without coding according to formula (5), and calculates the transmission delay under the two strategies respectively, and the transmission delay is selected to be smaller The strategy of is the final encoding strategy. the
以图2中B及其子节点D、E为例,假设N=20,τ=1ms,D=570ms,tREQ=20ms,B到E的链路质量较差,所以qiw=qBE=0.5。 Take B and its child nodes D and E in Figure 2 as an example, assuming N=20, τ=1ms, D=570ms, tREQ =20ms, the link quality from B to E is poor, so qiw =qBE = 0.5.
当最终编码策略为使用编码时,单个数据页的传输延迟计算如下: When the final encoding strategy is to use encoding, the transmission delay of a single data page is calculated as follows:
当最终编码策略为不使用编码时,首先计算B的期望传输值 When the final encoding strategy is not to use encoding, first calculate the expected transmission value of B
表示E所丢的数据能够包含D所丢的数据包的概率,表示D和E都丢了同一个数据包的概率,表示D和E至少有一个节点接收到数据包的概率。 Indicates the probability that the data lost by E can contain the data packet lost by D, Indicates the probability that D and E both lost the same packet, Indicates the probability that at least one node in D and E receives the packet.
在图2中,表示D丢失的数据包被包含在E丢失的数据包中,链路B→E的链路质量较差,B的期望传输值是由链路质量最差的子节点所决定的,所以进而单个数据页的传输延迟为 In Figure 2, Indicates that the data packet lost by D is included in the lost data packet of E, the link quality of link B→E is poor, and the expected transmission value of B is determined by the child node with the worst link quality, so Then the transmission delay of a single data page is
因为tnative<tcoding,所以节点B选择不使用编码的策略作为其最终编码策略。 Because tnative <tcoding , node B chooses the strategy of not using coding as its final coding strategy.
(4)数据分发阶段。 (4) Data distribution stage. the
本发明方法根据已建立的相关性树(如图3所示)和最终编码策略进行数据的分发。 The method of the present invention distributes data according to the established correlation tree (as shown in FIG. 3 ) and the final encoding strategy. the
由根节点开始分发数据,数据分发过程中使用以下机制来化解可能的冲突。第一,当节点A要发送数据页n时,如果侦听到网络中节点B在发送数据页n-1,它则延缓数据页n的发送。第二,如果节点A侦听到网络中节点B 正在发送数据页n,且节点B的ID较小,则节点A就延缓数据页n的发送。 The data distribution starts from the root node, and the following mechanisms are used in the data distribution process to resolve possible conflicts. First, when node A wants to send data page n, if it detects that node B in the network is sending data page n-1, it will delay the sending of data page n. Second, if node A detects that node B in the network is sending data page n, and the ID of node B is small, then node A will delay the sending of data page n. the
本发明方法使用一种优先请求机制来减少请求消息和数据包的传输。当子节点D、E每接收完一轮数据后,如果有数据丢失,就触发一个计时器,向父节点发送重传丢失的数据的请求,所述计时器的计时间隔通过式(9)计算得出:假设Cn=128,D、E的计时间隔分别计算如下 The method of the invention uses a priority request mechanism to reduce the transmission of request messages and data packets. After child nodes D and E receive a round of data each time, if there is data loss, a timer is triggered to send a request for retransmission of the lost data to the parent node, and the timing interval of the timer is calculated by formula (9) Draw: suppose Cn=128, the timing interval of D, E is calculated as follows respectively
Δt(D)=Cn×qBD+Tr=128×0.6+5=81(ms) Δt(D)=Cn×qBD +Tr =128×0.6+5=81(ms)
Δt(E)=Cn×qBE+Tr=128×0.5+6=70(ms) Δt(E)=Cn×qBE +Tr =128×0.5+6=70(ms)
所以,E的计时器比D先触发,先向父节点B请求丢失的数据包(序号为0,2,3,5,7),当D的计时器触发时,B可能已经在发送序列号为(0,2,3,5,7)的数据包了,而后四个数据包正好也是D所丢失的,所以D此时就可直接接收数据包,而不再需要发送请求。 Therefore, E's timer fires before D, and requests the lost data packets (sequence numbers 0, 2, 3, 5, 7) from parent node B first. When D's timer fires, B may already be sending the sequence number It is a data packet of (0, 2, 3, 5, 7), and the last four data packets are also lost by D, so D can directly receive the data packet at this time without sending a request. the
Claims (2)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310299304.8ACN103442336B (en) | 2013-07-15 | 2013-07-15 | Data distributing method based on link correlation in a kind of radio sensing network |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310299304.8ACN103442336B (en) | 2013-07-15 | 2013-07-15 | Data distributing method based on link correlation in a kind of radio sensing network |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103442336Atrue CN103442336A (en) | 2013-12-11 |
| CN103442336B CN103442336B (en) | 2016-05-04 |
Family
ID=49695991
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310299304.8AActiveCN103442336B (en) | 2013-07-15 | 2013-07-15 | Data distributing method based on link correlation in a kind of radio sensing network |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103442336B (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103780364A (en)* | 2014-01-08 | 2014-05-07 | 浙江大学 | Sending end selecting method considering link correlation in wireless sensor network |
| CN103780344A (en)* | 2014-01-17 | 2014-05-07 | 浙江大学 | Sensor network data distribution forward selection method based on network coding |
| CN104601306A (en)* | 2014-12-31 | 2015-05-06 | 无锡儒安科技有限公司 | Link retransmission method in wireless sensor network |
| CN109246790A (en)* | 2018-10-15 | 2019-01-18 | 西北工业大学 | A kind of underwater wireless multihop network topology discovery method |
| CN113872868A (en)* | 2020-06-30 | 2021-12-31 | 华为技术有限公司 | Notification message transmission method, device and system and storage medium |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20110079398A (en)* | 2009-12-30 | 2011-07-07 | 경희대학교 산학협력단 | A method for determining a packet transmission path in an ad hoc routing based wireless sensor network transmitting data at multiple transmission rates |
| CN102595505A (en)* | 2012-03-12 | 2012-07-18 | 中国科学技术大学苏州研究院 | Distributed routing method based on node load balancing for wireless sensor network |
- 2013
- 2013-07-15CNCN201310299304.8Apatent/CN103442336B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20110079398A (en)* | 2009-12-30 | 2011-07-07 | 경희대학교 산학협력단 | A method for determining a packet transmission path in an ad hoc routing based wireless sensor network transmitting data at multiple transmission rates |
| CN102595505A (en)* | 2012-03-12 | 2012-07-18 | 中国科学技术大学苏州研究院 | Distributed routing method based on node load balancing for wireless sensor network |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103780364A (en)* | 2014-01-08 | 2014-05-07 | 浙江大学 | Sending end selecting method considering link correlation in wireless sensor network |
| CN103780364B (en)* | 2014-01-08 | 2017-05-03 | 浙江大学 | Sending end selecting method considering link correlation in wireless sensor network |
| CN103780344A (en)* | 2014-01-17 | 2014-05-07 | 浙江大学 | Sensor network data distribution forward selection method based on network coding |
| CN103780344B (en)* | 2014-01-17 | 2017-05-24 | 浙江大学 | Sensor network data distribution forward selection method based on network coding |
| CN104601306A (en)* | 2014-12-31 | 2015-05-06 | 无锡儒安科技有限公司 | Link retransmission method in wireless sensor network |
| CN104601306B (en)* | 2014-12-31 | 2018-04-03 | 无锡儒安科技有限公司 | Wireless sensor network link repeating method |
| CN109246790A (en)* | 2018-10-15 | 2019-01-18 | 西北工业大学 | A kind of underwater wireless multihop network topology discovery method |
| CN109246790B (en)* | 2018-10-15 | 2019-08-09 | 西北工业大学 | A topology discovery method for underwater wireless multi-hop networks |
| CN113872868A (en)* | 2020-06-30 | 2021-12-31 | 华为技术有限公司 | Notification message transmission method, device and system and storage medium |
| CN113872868B (en)* | 2020-06-30 | 2022-11-25 | 华为技术有限公司 | Notification message transmission method, device and system and storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103442336B (en) | 2016-05-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102006625B (en) | System and method for reliable broadcast protocol of vehicle-mounted ad hoc network based on forward error correction | |
| CN102724764B (en) | Adaptive MAC Protocol for Vehicle Wireless Ad Hoc Networks | |
| CN103078795B (en) | Improve the cooperative routing method of throughput of wireless networks | |
| CN101895376B (en) | Transmission method for realizing data broadcasting in multi-hop wireless network | |
| CN103442336B (en) | Data distributing method based on link correlation in a kind of radio sensing network | |
| CN109474897B (en) | Single-hop cooperative broadcast method for safety message of Internet of Vehicles based on hidden Markov model | |
| KR100664953B1 (en) | Multicast Routing Method in Mobile Ad Hoc Network Environment | |
| CN101431784B (en) | Optimized data transmission method based on geographical position in vehicle-mounted network | |
| CN106851765A (en) | A kind of method for optimizing of the transmission trunking node of In-vehicle networking emergency safety message | |
| Palma et al. | A fountain codes-based data dissemination technique in vehicular ad-hoc networks | |
| CN103634868A (en) | Mixed distributing method and device in opportunity network | |
| CN103763172A (en) | Network topology building method | |
| Jeong et al. | A²-Trickle: Adaptive & Aligned Trickle for Rapid and Reliable Dissemination in Low-Power Wireless Networks | |
| Stefanović et al. | Urban infrastructure-to-vehicle traffic data dissemination using UEP rateless codes | |
| CN101883439B (en) | Method for reliably transmitting real-time service in wireless Ad Hoc network | |
| CN103888847B (en) | Vehicular ad hoc network video transmission method based on overlay structure | |
| Uchida et al. | Construction and Maintenance of a Novel Cluster-based Architecture for Ad Hoc Sensor Networks. | |
| CN105979497A (en) | LTE network based D2D device automatic discovery method | |
| Kumar et al. | Design and implementation of a mobility support adaptive trickle algorithm for RPL in vehicular IoT networks | |
| CN103780344B (en) | Sensor network data distribution forward selection method based on network coding | |
| CN115811773A (en) | High-reliability data transmission method of wireless ad hoc network | |
| CN103780364B (en) | Sending end selecting method considering link correlation in wireless sensor network | |
| Tang et al. | Data dissemination based on fuzzy logic and network coding in vehicular networks | |
| Gau et al. | Reliable multimedia broadcasting over dense wireless ad-hoc networks | |
| Dammak et al. | Cycle-based routing protocol for device-to-device group communications |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |