CN103400123A - Gait type identification method based on three-axis acceleration sensor and neural network - Google Patents
Gait type identification method based on three-axis acceleration sensor and neural networkDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103400123A CN103400123ACN2013103673511ACN201310367351ACN103400123ACN 103400123 ACN103400123 ACN 103400123ACN 2013103673511 ACN2013103673511 ACN 2013103673511ACN 201310367351 ACN201310367351 ACN 201310367351ACN 103400123 ACN103400123 ACN 103400123A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- gait
- neural network
- data
- acceleration
- identification
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000005021gaitEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription213
- 238000013528artificial neural networkMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription94
- 230000001133accelerationEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription91
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription48
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 230000011218segmentationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 230000005484gravityEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 230000001360synchronised effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription3
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000claimsdescription46
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsdescription35
- 238000012549trainingMethods0.000claimsdescription34
- 238000005070samplingMethods0.000claimsdescription20
- 238000004422calculation algorithmMethods0.000claimsdescription17
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000claimsdescription14
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000claimsdescription11
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000001537neural effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000002441reversible effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000013461designMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000012216screeningMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000abstract1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description8
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000description5
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description3
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description3
- 239000002390adhesive tapeSubstances0.000description2
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description2
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000description2
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000description2
- 230000002411adverseEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000007405data analysisMethods0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 238000012850discrimination methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 210000000653nervous systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000description1
- 238000003672processing methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000029058respiratory gaseous exchangeEffects0.000description1
- 238000005303weighingMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于生物医学信号处理技术领域,涉及一种步态类型鉴别方法,具体涉及一种基于三轴加速度传感器及神经网络的步态类型鉴别方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical signal processing, and relates to a gait type identification method, in particular to a gait type identification method based on a triaxial acceleration sensor and a neural network.
背景技术Background technique
步态是指人步行时的姿态,是一种复杂的生物特征。它具有以下优点:对系统分辨率要求不高、适应于远距离识别、不易受侵犯、难于隐藏等等。因此对步态的研究成为国内外研究机构和大学的研究热点之一。Gait refers to the posture of a person when walking, and is a complex biological characteristic. It has the following advantages: low requirements for system resolution, suitable for long-distance identification, not easy to be violated, difficult to hide and so on. Therefore, the research on gait has become one of the research hotspots of domestic and foreign research institutions and universities.
国外对步态类型鉴别的研究和关注起步较早,方式方法主要是在基于视频图像和传感器两种模式。The research and attention on gait type identification in foreign countries started earlier, and the methods are mainly based on video images and sensors.
基于视频图像的研究方法,其实验数据来源于摄像头监测个体运动状况而来。这种研究方法一般包括:对序列图像的分割、图像二值化、图像空间特征提取、识别算法应用等过程。它的缺点就是资金投入大、易受环境影响、个体隐私得不到保证、而且实验数据量大,二维的图像数据处理起来较为麻烦。Based on the research method of video images, the experimental data comes from the monitoring of individual movement conditions by cameras. This research method generally includes: segmentation of sequence images, image binarization, image space feature extraction, recognition algorithm application and other processes. Its disadvantages are large capital investment, easy to be affected by the environment, individual privacy cannot be guaranteed, and the amount of experimental data is large, and the processing of two-dimensional image data is more troublesome.
另一种研究方法是通过个体佩戴传感器进行检测采集某种生理信号数据,再传输到上位机进行数据的分析处理。传感器类型有呼吸、心跳、能量、加速度等等作为步态类型鉴别的应用。加速度信号具有易获取、数据准确、环境干扰因素少等优点。加速度传感器被广泛应用到这一课题。Another research method is to detect and collect certain physiological signal data through individual wearing sensors, and then transmit it to the host computer for data analysis and processing. Sensor types include respiration, heartbeat, energy, acceleration, etc. as applications for gait type identification. The acceleration signal has the advantages of easy acquisition, accurate data, and less environmental interference factors. Accelerometers are widely used in this topic.
利用步态加速度信号进行类型鉴别就是要对获取的人体自然运动的加速度信号进行分析处理,通常包含运动信号获取、信号周期分割、信号特征提取、鉴别算法4个过程。Using the gait acceleration signal for type identification is to analyze and process the acquired acceleration signal of human natural motion, which usually includes four processes: motion signal acquisition, signal period segmentation, signal feature extraction, and identification algorithm.
其中信号特征提取这过程直接影响最终的鉴别性能。近来许多研究者集中将样本熵、小波能量值、小波多尺度熵、傅里叶描述子作为步态类型分析鉴别的特征,然后再将检测数据的特征与样本特征应用各类识别算法完成最终的鉴别任务。这种处理方法的缺点在于缺乏高准确性和可靠性,步态信号的一种或两种时频特征在区分两种相似的步态时,会出现鉴别失败的情况。也有研究者采取混合时频域特征匹配的方法进行步态鉴别,却容易忽视不同特征可能存在相关性的问题,出现事倍功半的不良效果。The signal feature extraction process directly affects the final discrimination performance. Recently, many researchers focus on sample entropy, wavelet energy value, wavelet multi-scale entropy, and Fourier descriptors as features for gait type analysis and identification, and then apply various recognition algorithms to the features of the detection data and sample features to complete the final analysis. identification task. The disadvantage of this processing method is that it lacks high accuracy and reliability, and one or two time-frequency features of the gait signal may fail to distinguish two similar gaits. Some researchers also adopt the method of mixed time-frequency domain feature matching for gait identification, but it is easy to ignore the possible correlation of different features, and the adverse effect of getting twice the result with half the effort occurs.
综上所述,按传统加速度方法存在的局限性有:In summary, the limitations of traditional acceleration methods are:
(1)在传感器佩戴位置方面,佩戴位置都必须确定统一,且附着在衣物上,这会使有的实验者在实验时不适,使步态缺乏自然性;(1) In terms of the wearing position of the sensor, the wearing position must be determined uniformly and attached to the clothing, which will make some experimenters uncomfortable during the experiment and make the gait unnatural;
(2)按时间顺序分割信号,会使某个时刻的突变动作信号被单独分离开,影响误判;(2) Segmenting the signal in chronological order will separate the sudden action signal at a certain moment, which will affect misjudgment;
(3)提取的有些特征它们之间存在很大的相关性,完全可以通过降维选取最具代表的特征代替所有特征;(3) There is a great correlation between some extracted features, and it is entirely possible to select the most representative features through dimensionality reduction to replace all features;
(4)有些特征降维方法对筛选步态信号特征效果不佳,鉴别率不高。(4) Some feature dimensionality reduction methods are not effective in screening gait signal features, and the discrimination rate is not high.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是为克服上述现有技术的不足,提供一种基于三轴加速度传感器及神经网络的步态类型鉴别方法,通过三轴加速度传感器获取人体步态加速度信号,本发明基于获取人体步态加速度信号,采用分阶段鉴别的方法,能够鉴别6种人体步态类型(坐、站立、慢走、快走、上楼、下楼),包括2种静态步态和4种动态步态。The purpose of the present invention is to overcome above-mentioned deficiencies in the prior art, provide a kind of gait type discrimination method based on three-axis acceleration sensor and neural network, obtain human body gait acceleration signal by three-axis acceleration sensor, the present invention is based on obtaining human body gait It can identify 6 types of human gait (sitting, standing, walking slowly, briskly walking, going up stairs, going downstairs) by adopting the method of stage identification, including 2 types of static gaits and 4 types of dynamic gaits.
为实现上述目的,本发明采用下述技术方案:To achieve the above object, the present invention adopts the following technical solutions:
基于三轴加速度传感器及神经网络的步态类型鉴别方法,具体步骤如下:The gait type identification method based on the triaxial acceleration sensor and the neural network, the specific steps are as follows:
步骤1):建立步态加速度信号数据库,这里得到的称作原始步态数据;Step 1): Establish a gait acceleration signal database, which is called the original gait data;
步骤2):将原始步态数据通过滤波去除重力因素,获取的信号数据称作运动加速度数据样本;Step 2): The original gait data is filtered to remove the gravity factor, and the obtained signal data is called the motion acceleration data sample;
步骤3):信号同期分割阶段:将步骤1)中的原始步态数据和步骤2)中的运动加速度样本进行切割得到原始步态数据样本块和运动加速度数据样本块,分别均从分割的两类数据样本块中间隔抽取得到检测样本和训练样本,此时检测样本包括原始步态检测样本和运动加速度检测样本,训练样本包括原始步态训练样本和运动加速度训练样本;Step 3): Signal synchronous segmentation stage: Cut the original gait data in step 1) and the motion acceleration sample in step 2) to obtain the original gait data sample block and the motion acceleration data sample block, respectively from the two divided The class data sample block is extracted at intervals to obtain detection samples and training samples. At this time, the detection samples include the original gait detection samples and the motion acceleration detection samples, and the training samples include the original gait training samples and the motion acceleration training samples;
步骤4):步态特征提取阶段:从运动加速度训练样本和运动加速度检测样本中提取特征值,从原始步态检测样本和原始步态训练样本中提取特征值;Step 4): Gait feature extraction stage: extract feature values from motion acceleration training samples and motion acceleration detection samples, and extract feature values from original gait detection samples and original gait training samples;
步骤5):步态预分类阶段:利用步骤4)得到的运动加速度训练样本的特征值训练第一神经网络,利用训练好的第一神经网络对步骤4)得到的运动加速度检测样本进行预分类;Step 5): Gait pre-classification stage: use the eigenvalues of the motion acceleration training samples obtained in step 4) to train the first neural network, and use the trained first neural network to pre-classify the motion acceleration detection samples obtained in step 4) ;
步骤6):步态特征集降维操作:分别进行静态步态特征集的降维和动态步态特征集的降维;Step 6): Dimensionality reduction operation of gait feature set: perform dimensionality reduction of static gait feature set and dimensionality reduction of dynamic gait feature set respectively;
步骤7):步态具体鉴别阶段:Step 7): Gait specific identification stage:
训练第二神经网络,并用训练好的第二神经网络对预分类为静态类型的原始步态检测样本进行类型的鉴别;Train the second neural network, and use the trained second neural network to carry out type discrimination to the original gait detection samples pre-classified as the static type;
训练第三神经网络,并用训练好的第三神经网络对预分类为动态类型的原始步态检测样本进行类型的鉴别。The third neural network is trained, and the trained third neural network is used to discriminate the type of the original gait detection samples pre-classified as dynamic types.
所述步骤1)的具体方法是:The specific method of the step 1) is:
11)三轴加速度传感器佩戴的位置都统一在胸前,且用强力胶布加以固定,采集来的XYZ三轴的数据代表了实验者竖直方向、左右方向、前后方向上的加速度数据;步态信号的采集使用三轴加速度传感器MMA7260Q,加速度测试量程为±4g,g为自由落体速度,1g=9.8m/s2,系统采样频率为200Hz;11) The wearing position of the three-axis acceleration sensor is unified on the chest, and fixed with strong adhesive tape. The collected XYZ three-axis data represents the acceleration data of the experimenter in the vertical direction, left and right directions, and front and rear directions; gait The signal acquisition uses a three-axis acceleration sensor MMA7260Q, the acceleration test range is ±4g, g is the free fall speed, 1g=9.8m/s2 , and the system sampling frequency is 200Hz;
12)实验者人数为若干名,穿平底鞋以自然步速进行坐、站、慢走、快走、上楼、下楼6种不同步态的实验,每名实验者进行每种步态实验持续若干分钟,从而建立了步态加速度信号数据库,所得数据称作原始步态信号。12) The number of experimenters is several. They wear flat shoes and carry out 6 different gait experiments of sitting, standing, walking slowly, briskly, going upstairs, and going downstairs at a natural pace. Each experimenter performs each gait experiment continuously. Several minutes, thereby establishing the gait acceleration signal database, the obtained data is called the original gait signal.
所述步骤2)为将运动加速度从原始步态信号中分离开来,将原始步态信号经过截止频率为0.5Hz,波纹为0.01db的三阶巴特沃斯低通滤波器,把重力因素去除,得到运动加速度数据。Step 2) To separate the motion acceleration from the original gait signal, pass the original gait signal through a third-order Butterworth low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 0.5Hz and a ripple of 0.01db to remove the gravity factor , to get the motion acceleration data.
所述步骤3)的具体方法是:将采样频率从200Hz降为100Hz,每个数据使用5秒的重叠率为50%矩形时间窗分割成48段数据样本,在保存数据样本时,为每个数据样本加上标签1~6,分别代表坐、站、慢走、快走、上楼、下楼6种不同步态,间隔选取每人每种步态25%的数据作为检测样本,剩余的75%作为训练样本,所述间隔抽取是每四个数据样本块中选取第一个数据样本块。The specific method of step 3) is: reduce the sampling frequency from 200Hz to 100Hz, divide each data into 48 segments of data samples using a rectangular time window with an overlap rate of 50% for 5 seconds, and save the data samples for each Data samples plus labels 1 to 6 represent six different gaits of sitting, standing, walking slowly, briskly, going upstairs, and going downstairs, respectively. 25% of the data of each gait of each person is selected as the detection sample at intervals, and the remaining 75 % is used as a training sample, and the interval sampling is to select the first data sample block in every four data sample blocks.
所述步骤4)的步骤如下:The steps of step 4) are as follows:
步骤41):分别从步骤3)的运动加速度训练样本和运动加速度检测样本中提取信号幅度面积SMA和平均能量值AE两个特征值;Step 41): extract two eigenvalues of the signal amplitude area SMA and the average energy value AE from the motion acceleration training sample and the motion acceleration detection sample in step 3) respectively;
步骤42):从步骤3)的原始步态检测样本和原始步态训练样本中提取X、Y、Z三个轴数据的特征值,每一个轴的特征值包括均值、轴相关系数、能量值、四分位差、平均绝对差、平方根、标准差和方差8个特征值,由于有三个轴共计24个特征值。Step 42): Extract the eigenvalues of X, Y, and Z axis data from the original gait detection samples and original gait training samples in step 3), and the eigenvalues of each axis include mean value, axis correlation coefficient, and energy value , quartile difference, mean absolute difference, square root, standard deviation and variance 8 eigenvalues, since there are three axes a total of 24 eigenvalues.
所述步骤5)的步骤如下:The steps of step 5) are as follows:
建立第一BP神经网络,将步骤41)获得的运动加速度训练样本的两个特征值合并为它的特征集作为神经网络输入,训练能够鉴别动态步态与静态步态的第一BP神经网络,使其误差率满足要求:误差率小于0.02,然后将运动加速度检测样本的特征集作为输入用训练好的第一BP神经网络进行预分类。Establish the first BP neural network, combine the two eigenvalues of the motion acceleration training sample obtained in step 41) into its feature set as the input of the neural network, and train the first BP neural network capable of distinguishing dynamic gait and static gait, Make the error rate meet the requirements: the error rate is less than 0.02, and then use the feature set of the motion acceleration detection sample as input to pre-classify with the trained first BP neural network.
所述步骤6)的步骤如下:The steps of step 6) are as follows:
步骤61)静态步态特征集降维:将步骤3)中标签属于静态的原始步态训练样本的24个特征值进行平均影响值MIV方法降维,对步态鉴别影响越大的特征值的MIV值越大,选取8个MIV值最大的特征值合并作为静态步态神经网络输入特征集;Step 61) Dimensionality reduction of static gait feature set: Perform average influence value MIV method on the 24 eigenvalues of the original gait training samples whose labels belong to static in step 3), and reduce the dimensionality of the eigenvalues that have a greater impact on gait identification The larger the MIV value, select the 8 feature values with the largest MIV value and combine them as the input feature set of the static gait neural network;
步骤62)动态步态特征集降维:将步骤3)中标签属于动态的原始步态训练样本的24个特征值同样进行平均影响值MIV方法降维,选取8个MIV值最大的特征值合并作为动态步态神经网络输入特征集。Step 62) Dimensionality reduction of the dynamic gait feature set: the 24 eigenvalues of the original gait training samples whose labels belong to the dynamics in step 3) are also reduced by the average influence value MIV method, and the 8 eigenvalues with the largest MIV value are selected to be combined As the input feature set to the dynamic gait neural network.
所述步骤7)的步骤如下:Described step 7) the step is as follows:
步骤71)静态步态的具体鉴别:建立第二BP神经网络用于对静态步态进行具体类型鉴别,利用步骤61)的静态步态神经网络输入特征集作为输入训练第二BP神经网络,训练完成后,步骤5)中预分类为静态类型的原始步态检测样本进入第二BP神经网络中进行具体鉴别,鉴别类型结果有两种:站立、坐;Step 71) Specific identification of static gait: establish a second BP neural network for specific type identification of static gait, use the static gait neural network input feature set in step 61) as input to train the second BP neural network, train After completion, the original gait detection samples pre-classified as static type in step 5) enter the second BP neural network for specific identification. There are two types of identification results: standing and sitting;
步骤72)动态步态的具体鉴别:建立第三BP神经网络用于对动态步态进行具体类型鉴别,利用步骤62)的动态步态神经网络输入特征集作为输入训练第三BP神经网络,训练完成后步骤5)中预分类为动态类型的原始步态检测样本进入第三BP神经网络中进行具体鉴别,鉴别类型结果有四种:快走、慢走、上楼、下楼。Step 72) Specific identification of dynamic gait: establish a third BP neural network for specific type identification of dynamic gait, use the dynamic gait neural network input feature set in step 62) as input to train the third BP neural network, train After completion, the original gait detection samples pre-classified as dynamic types in step 5) enter the third BP neural network for specific identification. There are four types of identification results: fast walking, slow walking, going upstairs, and going downstairs.
所述步骤4)步态特征的提取是运用特征计算公式从步态数据中计算而来:The step 4) extracting the gait feature is calculated from the gait data by using the feature calculation formula:
步骤41)用于预分类阶段的计算公式分别为:Step 41) The calculation formulas used in the pre-classification stage are respectively:
其中w、N均为为时间窗长度,xiyizi代表一个窗的xyz三轴上的运动加速度数据,Ak是一个窗的xyz三轴上的运动加速度数据进行离散FFT变换的系数;Among them, w and N are the length of the time window, xi yi zi represents the motion acceleration data on the xyz three axes of a window, and Ak is the coefficient of discrete FFT transformation of the motion acceleration data on the xyz three axes of a window ;
步骤42)用于具体鉴别类型阶段的部分计算公式为:Step 42) Part of the calculation formula used in the stage of specific identification type is:
均值式中,ai为第i时刻加速度的采样值,w为窗口长度;轴相关系数式中,aibi分别代表两个不同轴的加速度采样信号,此式用于计算xy,xz和yz三轴之间的相关系数;能量值方差式中ai为第i时刻加速度的采样值,u为ai的平均值;标准差式中ai为第i时刻加速度的采样值,u为ai的平均值。average In the formula, ai is the sampling value of the acceleration at the i-th moment, w is the window length; the axis correlation coefficient In the formula, ai bi represent the acceleration sampling signals of two different axes respectively, and this formula is used to calculate the correlation coefficient between the xy, xz and yz axes; the energy value variance In the formula, ai is the sampling value of acceleration at the i-th moment, u is the average value of ai ; standard deviation In the formula, ai is the sampling value of the acceleration at the i-th moment, and u is the average value of ai .
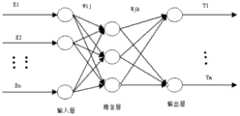
所述步骤5)在步态预分类阶段,第一BP神经网络结构是:2-5-2,即输入层有2个节点,隐含层有5个节点,输出层有2个节点;这里隐含层和输出层的神经网络激活函数均选择S型激活函数神经网络的期望误差设定为0.02,使用的神经网络算法为Levnberg_Marquardt的BP算法;用运动加速度数据样本训练神经网络时,信号幅度面积SMA和平均能量值AE作为预分类神经网络区分静态或动态步态的输入特征集,输出结果为1、2的将转化为[10]T用来表示静态步态,输出结果为3、4、5、6将转化为为[01]T用来表示动态步态;3层BP神经系统的扑拓结构图表达的是n×1维的特征集列向量Xn=(x1,x2,...,xn)T(Xn∈X)到m×1维鉴别结果列向量Ym=(Y1,Y2,...,Ym)T(Ym∈Y)的非线性函数映射关系,BP神经网络通过信息正向传播和误差反向传播2个训练过程,反复调节神经网络权值和阈值,使神经网络输出值与期望值的误差达到要求。Step 5) In the gait pre-classification stage, the first BP neural network structure is: 2-5-2, that is, the input layer has 2 nodes, the hidden layer has 5 nodes, and the output layer has 2 nodes; here The neural network activation functions of the hidden layer and the output layer both choose the S-type activation function The expected error of the neural network is set to 0.02, and the neural network algorithm used is the BP algorithm of Levnberg_Marquardt; when the neural network is trained with motion acceleration data samples, the signal amplitude area SMA and the average energy value AE are used as the pre-classified neural network to distinguish static or dynamic steps. The input feature set of the state, the output result is 1, 2 will be converted into [10]T to represent the static gait, the output result is 3, 4, 5, 6 will be converted into [01]T to represent the dynamic gait state; the topological structure diagram of the 3-layer BP neural system expresses the n×1-dimensional feature set column vector Xn =(x1 ,x2 ,...,xn )T (Xn ∈X) to m ×1-dimensional identification result column vector Ym = (Y1 ,Y2 ,...,Ym )T (Ym ∈ Y) nonlinear function mapping relationship, BP neural network through information forward propagation and error reverse Propagate two training processes, adjust the weights and thresholds of the neural network repeatedly, so that the error between the output value of the neural network and the expected value meets the requirements.
所述步骤6)静态/动态步态分类器的输入特征集的维数为24。对输入特征集的维数降低,去除冗余的特征,选择出最能反映神经网络的非线性映射关系的特征集。平均影响值(MIV)方法主要是在用所有步态信号特征集训练一个正确的神经网络后,再对各个输入特征集进行差值运算即每个输入变量分别±10%生成新样本p1、p2(p1p2=原特征值×(1±10%)),再分别作为仿真样本的神经网络输入用建好的网络进行仿真,得到网络输出仿真值A1、A2。再取其差值的算术平方根即平均影响值。经过平均影响值计算后,选取平均影响值前8最大的特征作为优化的动态步态神经网络分类器的输入自变量。用相同的平均影响值方法,选取平均影响值最大的这8个特征作为优化的静态步态神经网络分类器的输入自变量。The dimensionality of the input feature set of the step 6) static/dynamic gait classifier is 24. The dimensionality of the input feature set is reduced, redundant features are removed, and the feature set that best reflects the nonlinear mapping relationship of the neural network is selected. The mean influence value (MIV) method is mainly to use all gait signal feature sets to train a correct neural network, and then perform a difference operation on each input feature set, that is, each input variable is ±10% to generate new samples p1 , p2 (p1 p2 = original eigenvalue × (1±10%)), and then used as the neural network input of the simulation sample to simulate with the built network to obtain the simulated network output values A1 and A2 . Then take the arithmetic square root of the difference That is the average influence value. After the average influence value is calculated, the top 8 features with the largest average influence value are selected as the input variables of the optimized dynamic gait neural network classifier. Using the same average influence value method, the eight features with the largest average influence value are selected as the input variables of the optimized static gait neural network classifier.
所述步骤7)在步态类型具体鉴别阶段,在具体鉴别其步态类型阶段,均值、轴相关系数、能量值、四位分差、平均绝对差、方根、标准差、方差这8个特征则作为静态/动态步态分类器的输入特征集,由于有3个轴,因此静态/动态动作分类器的输入特征集的维数为24。The step 7) in the stage of specific identification of gait type, in the stage of specific identification of its gait type, the 8 parameters of mean value, axial correlation coefficient, energy value, quartile difference, mean absolute difference, square root, standard deviation, and variance The features are used as the input feature set of the static/dynamic gait classifier. Since there are 3 axes, the dimensionality of the input feature set of the static/dynamic action classifier is 24.
需要进行步态标签提取转化为二维输出结果操作:在动态步态具体分类时,标签为3、4、5、6将输出结果分别定为[1000]T、[0100]T、[0010]T、[0001]T;在静态步态分类时,标签为1的将输出结果定为[10]T,标签为2将输出结果定为[01]T。动态步态神经网络结构是:8-30-4。静态步态神经网络结构是:8-10-2。这里隐含层和输出层的激活函数均选择S型激活函数:网络的期望误差设定为0.02。使用的神经网络算法为Levnberg_Marquardt的BP算法。Levnberg_Marquardt的BP算法的简要说明:设W(k)表示第k次迭代的网络权值向量,维数为M,新的权值向量W(k+1)可根据下面的规则求得:W(k+1)=W(k)+ΔW(k)(ΔW为权值增量);在Levnberg_Marquardt的算法中,其ΔW形式为:ΔW=-[JT(W)J(W)+uI]-1J(W)e(W),式中u为比例系数,是正的常数;I是单位矩阵;J(W)为Jacobian矩阵;e(W)为期望输出与实际输出的误差向量。Levnberg_Marquardt的BP算法每次迭代效率很高,可大大改善神经网络的整体性能。It is necessary to extract the gait label and convert it into a two-dimensional output result operation: in the specific classification of dynamic gait, the labels are 3, 4, 5, and 6, and the output results are respectively set as [1000]T , [0100]T , [0010]T , [0001]T ; in static gait classification, if the label is 1, the output result is set as [10]T , and if the label is 2, the output result is set as [01]T . The dynamic gait neural network structure is: 8-30-4. The static gait neural network structure is: 8-10-2. Here, the activation functions of the hidden layer and the output layer all choose the S-type activation function: The expected error of the network is set to 0.02. The neural network algorithm used is the BP algorithm of Levnberg_Marquardt. A brief description of Levnberg_Marquardt's BP algorithm: Let W(k) represent the network weight vector of the kth iteration, the dimension is M, and the new weight vector W(k+1) can be obtained according to the following rules: W( k+1)=W(k)+ΔW(k) (ΔW is the weight increment); in the algorithm of Levnberg_Marquardt, the form of ΔW is: ΔW=-[JT (W)J(W)+uI]-1 J(W)e(W), where u is a proportional coefficient, which is a positive constant; I is the unit matrix; J(W) is the Jacobian matrix; e(W) is the error vector between the expected output and the actual output. The BP algorithm of Levnberg_Marquardt is very efficient in each iteration, which can greatly improve the overall performance of the neural network.
本发明的有益效果:Beneficial effects of the present invention:
1、本发明所用数据由随身佩戴三轴加速度传感器即时获取并处理,成本更低,更易于集成到其他便携医疗监护设备中。佩戴加速度传感器选在胸前,避免受试者佩戴不适,保证了步态的自然性。每种步态数据用5秒的50%重叠时间矩形窗进行分割出的数据样本提取的特征延续性好,能良好保持彼此的共性。1. The data used in the present invention is acquired and processed in real time by the three-axis acceleration sensor worn by the person, which has lower cost and is easier to integrate into other portable medical monitoring equipment. The acceleration sensor is worn on the chest to avoid discomfort for the subjects and ensure the naturalness of the gait. Each kind of gait data is segmented with a 50% overlapping time rectangular window of 5 seconds. The feature continuity of the data sample extraction is good, and the commonality of each other can be well maintained.
2、本发明利用神经网络在区分非线性可分类上有较强的学习能力及自主学习复杂映射的能力,通过信息正向传播和误差反向传播2个训练过程,反复调节网络权值和阈值,使网络预测值与期望值的误差达到要求。2. The present invention utilizes the neural network to have strong learning ability in distinguishing non-linear and classifiable and the ability to learn complex mapping independently, through two training processes of information forward propagation and error back propagation, repeatedly adjust network weights and thresholds , so that the error between the network prediction value and the expected value meets the requirements.
3、本发明利用分阶段MIV法筛选步态特征,结合BP神经网络进行步态类型鉴别工作,将提取的特征作为神经网络输入自变量,依次经步态预分类、步态具体鉴别两阶段,实现了坐、站立、慢走、快走、上楼、下楼6种步态类型的有效鉴别,且通过今后对步态数据容量范围的增大及神经网络的优化设计,将会具有较高的准确性和可靠性。3. The present invention utilizes the staged MIV method to screen the gait features, combines the BP neural network to carry out the gait type identification work, uses the extracted feature as the input variable of the neural network, and successively undergoes two stages of gait pre-classification and gait specific identification, Realize the effective identification of 6 gait types: sitting, standing, slow walking, fast walking, going upstairs and downstairs, and through the increase of the gait data capacity range and the optimized design of the neural network in the future, it will have a higher accuracy and reliability.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为用50%重叠矩形时间窗分割受试者慢走步态信号;Fig. 1 is to use 50% overlapping rectangular time window to divide subject's slow walking gait signal;
图2为BP神经系统的扑拓结构图;Figure 2 is a topological structure diagram of the BP nervous system;
图3为受试者静态/动态两类步态在SMA/AE特征上的对比图;Figure 3 is a comparison chart of subjects' static/dynamic gait on SMA/AE characteristics;
图4(a)为受试者的四种动态步态(慢走、快走)在X轴标准差和X轴能量值特征对比图;Figure 4(a) is a comparison chart of the standard deviation of the subject's four dynamic gaits (slow walking, fast walking) on the X-axis and the energy value of the X-axis;
图4(b)为受试者的四种动态步态(上楼、下楼)在X轴标准差和X轴能量值特征对比图;Figure 4(b) is a comparison chart of the standard deviation of the subject's four dynamic gaits (upstairs, downstairs) on the X-axis and the energy value of the X-axis;
图5为受试者的坐与站立两种静态步态在X轴均方根和X轴能量值特征对比图;Figure 5 is a comparison chart of the X-axis root mean square and X-axis energy value characteristics of the subject's sitting and standing two static gaits;
图6为步态类型鉴别仿真算法流程图。Fig. 6 is a flow chart of the gait type identification simulation algorithm.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图与实施例对本发明作进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
如图6所示,实施例1:As shown in Figure 6, embodiment 1:
本发明根据便携式心电监护系统的统一要求,通过人体佩戴,获取人体自然步态加速度信号基础上,进行步态类型鉴别。According to the uniform requirements of the portable ECG monitoring system, the invention carries out the gait type identification on the basis of obtaining the natural gait acceleration signal of the human body through wearing on the human body.
1)受试者步态数据的采集1) Collection of gait data of subjects
11)步态信号的采集使用Freescale公司的三轴加速度传感器MMA7260Q,加速度测试量程为±4g,系统采样频率为200Hz。传感器佩戴的位置都统一在胸前,且用强力胶布加以固定,采集来的XYZ三轴的数据代表了实验者竖直方向、左右方向、前后方向上的加速度数据。11) The acquisition of gait signals uses a three-axis acceleration sensor MMA7260Q from Freescale, the acceleration test range is ±4g, and the system sampling frequency is 200Hz. The wearing positions of the sensors are unified on the chest and fixed with strong adhesive tape. The collected XYZ three-axis data represents the acceleration data of the experimenter in the vertical direction, left and right directions, and front and rear directions.
12)受试者人数为10名,4名男性6名女性(年龄在22~28岁之间,体重介于45~75kg之间),穿平底鞋以自然步速进行坐、站、慢走、快走、上楼、下楼6种不同步态的实验,每名实验者进行每种步态实验持续2分钟。这样就建立了一个容量为60组的步态加速度信号数据库,所得的数据称为原始步态数据。12) The number of subjects is 10, 4 males and 6 females (aged between 22 and 28, weighing between 45 and 75 kg), who sit, stand and walk slowly at a natural pace in flat shoes , brisk walking, going upstairs, and downstairs 6 different gait experiments, and each experimenter performed each gait experiment for 2 minutes. In this way, a gait acceleration signal database with a capacity of 60 groups is established, and the obtained data is called the original gait data.
2)数据的分割与预处理2) Data segmentation and preprocessing
21)由其他研究结果可知,人体所受重力的频率在0.5Hz以下,为将运动加速度从步态加速度信号中分离开来,设计截止频率为0.5Hz,0.01db波纹的三阶巴特沃斯低通滤波器,把步态数据样本经过滤波器,就可将重力因素去除,得到的则是运动加速度数据便可用于预分类的信号提取。在动态/静态动作分类时,使用的是原始步态数据。21) According to other research results, the frequency of gravity on the human body is below 0.5Hz. In order to separate the motion acceleration from the gait acceleration signal, a third-order Butterworth low frequency with a cutoff frequency of 0.5Hz and 0.01db ripple is designed. The gravity factor can be removed by passing the gait data samples through the filter, and the obtained motion acceleration data can be used for signal extraction of pre-classification. For dynamic/static motion classification, raw gait data is used.
22)采用二间隔抽值(按顺序两个数据抽取第一个)的方法,将采样频率从200Hz降为100Hz,来消除部分噪声。降频后,每人每种步态数据量为12000,且有两类对应的数据形式:运动加速度数据和原始步态数据。每种步态的两种数据形式均使用5秒50%重叠率矩形时间窗分割成48段数据样本块,分割后在保存数据样本块时,为每种步态数据加上标签,标签为数字1~6,用来代表站、坐、慢走、快走、上楼、下楼六种不同步态,标签位置放在步态信号数据的第一位。所有实验者的步态数据样本总和为2880组(48×6×10),图1表示的是如何对慢走步态信号进行时间窗分割。每一类数据的每种步态数据样本有480组,间隔选取每人每种步态25%的数据作为检测样本,剩余的75%作为训练样本,注:检测样本包括原始步态检测样本和运动加速度检测样本,训练样本包括原始步态训练样本和运动加速度训练样本。22) Use the method of two-interval extraction (extract the first of the two data in sequence), and reduce the sampling frequency from 200Hz to 100Hz to eliminate part of the noise. After frequency reduction, the amount of each gait data per person is 12,000, and there are two types of corresponding data forms: motion acceleration data and original gait data. The two data forms of each gait are divided into 48 data sample blocks using a rectangular time window with a 50% overlap rate of 5 seconds. After the segmentation, when saving the data sample block, add a label to each gait data, and the label is a number. 1 to 6, used to represent six different gaits: standing, sitting, walking slowly, walking fast, going upstairs, and going downstairs. The label position is placed first in the gait signal data. The sum of the gait data samples of all experimenters is 2880 groups (48×6×10). Figure 1 shows how to perform time window segmentation on the slow walking gait signal. There are 480 groups of gait data samples for each type of data, and 25% of the data of each gait of each person is selected as the detection sample at intervals, and the remaining 75% is used as the training sample. Note: the detection samples include the original gait detection samples and Motion acceleration detection samples, training samples include original gait training samples and motion acceleration training samples.
3)提取用于鉴别的步态特征3) Extract gait features for identification
步态特征的提取是运用特征计算公式从步态数据中计算而来。在步态预分类阶段,信号幅度面积(SMA)和平均能量值(AE)作为预分类器区分静态/动态步态的输入特征集,计算公式分别为:其中w、N均为为时间窗长度,xiyizi代表一个窗的xyz三轴上的运动加速度数据,Ak是一个窗的xyz三轴上的运动加速度数据进行离散FFT变换的系数。由图3可看出,从运动加速度数据提取的这两个特征能容易区分静态/动态步态,因为静态步态的这两个特征值绝对小于动态的。而步态类型具体鉴别阶段,均值、轴相关系数、能量值、四位分差、平均绝对差、方根、标准差、方差这8个特征则作为静态/动态步态分类器的输入特征集,这8个特征值部分计算公式为:均值式中,ai为第i时刻加速度的采样值,w为窗口长度;轴相关系数式中,aibi分别代表两个不同轴的加速度采样信号,此式用于计算xy,xz和yz三轴之间的相关系数;能量值式中Ak是一个窗的xyz三轴上的运动加速度数据进行离散FFT变换的系数,N为为时间窗长度;方差式中ai为第i时刻加速度的采样值,u为ai的平均值;标准差式中ai为第i时刻加速度的采样值,u为ai的平均值;由于有3个轴,因此静态/动态动作分类器的输入特征集的维数为24。The extraction of gait features is calculated from gait data by using the feature calculation formula. In the gait pre-classification stage, the signal magnitude area (SMA) and average energy value (AE) are used as the input feature set for the pre-classifier to distinguish static/dynamic gait, and the calculation formulas are: Among them, w and N are the length of the time window, xi yi zi represents the motion acceleration data on the xyz three axes of a window, and Ak is the coefficient of discrete FFT transformation of the motion acceleration data on the xyz three axes of a window . It can be seen from Figure 3 that the two features extracted from the motion acceleration data can easily distinguish static/dynamic gait, because the two feature values of static gait are definitely smaller than dynamic ones. In the specific identification stage of the gait type, the mean, axis correlation coefficient, energy value, quartile difference, mean absolute difference, square root, standard deviation, and variance are used as the input feature set of the static/dynamic gait classifier , the calculation formula of these 8 eigenvalues is: mean In the formula, ai is the sampling value of the acceleration at the i-th moment, w is the window length; the axis correlation coefficient In the formula, ai bi represent the acceleration sampling signals of two different axes respectively, and this formula is used to calculate the correlation coefficient between the xy, xz and yz axes; the energy value In the formula, Ak is the coefficient of the discrete FFT transformation of the motion acceleration data on the xyz three axes of a window, and N is the length of the time window; the variance In the formula, ai is the sampling value of acceleration at the i-th moment, u is the average value of ai ; standard deviation where ai is the sampling value of the acceleration at the i-th moment, and u is the average value of ai ; since there are 3 axes, the dimensionality of the input feature set of the static/dynamic action classifier is 24.
4)步态预分类阶段4) Gait pre-classification stage
在步态预分类阶段,首先将步态动作标签提取转化为输出结果操作是:标签为1、2的将输出结果定为[10]T用来代表静态类型步态;标签为3、4、5、6将输出结果定为[01]T用来代表动态类型步态。In the gait pre-classification stage, the first step is to convert the gait action label extraction into the output result: the output result is set as [10] if the label is 1, 2T is used to represent the static type gait; the label is 3, 4, 5, 6 set the output result as [01]T to represent the dynamic type of gait.
本文使用3层BP神经网络实现的是(n×1)维的特征集列向量Xn=(x1,x2,...,xn)T(Xn∈X)到(m×1)维鉴别结果列向量Ym=(Y1,Y2,...,Ym)T(Ym∈Y)的非线性函数映射。BP神经网络的结构图如图2所示,构建的步态预分类神经网络结构是:2-5-2,即输入层有2个节点,隐含层有5个节点,输出层有2个节点(作为输入的特征有两个,故输入层节点数为2;输出的步态类型有两种,故输出层节点数为2)。这里隐含层和输出层的激活函数均选择S型激活函数:网络的期望误差设定为0.02。使用的神经网络算法为Levnberg_Marquardt的BP算法。This paper uses a 3-layer BP neural network to realize (n×1)-dimensional feature set column vector Xn =(x1 ,x2 ,...,xn )T (Xn ∈X) to (m×1 )-dimensional identification result column vector Ym = (Y1 , Y2 ,...,Ym )T (Ym ∈ Y) nonlinear function mapping. The structure diagram of the BP neural network is shown in Figure 2. The structure of the gait pre-classification neural network constructed is: 2-5-2, that is, there are 2 nodes in the input layer, 5 nodes in the hidden layer, and 2 nodes in the output layer. Nodes (there are two input features, so the number of input layer nodes is 2; there are two output gait types, so the number of output layer nodes is 2). Here, the activation functions of the hidden layer and the output layer all choose the S-type activation function: The expected error of the network is set to 0.02. The neural network algorithm used is the BP algorithm of Levnberg_Marquardt.
首先训练样本特征集作为输入往前传输到隐含层,经激活函数f(u)作用会有输出结果产生;隐含层的结果再向后传输到输出层,会有输出结果产生,其中上述两式中wijwjk为BP神经网络各层连接处的权值,θHjθOk为隐含层和输出层的阈值,f为S型激活函数,Hjp、Ykp分别为隐含层输出结果、输出层输出结果。如果最终输出结果Ykp和期望值存在不符合要求的误差,再向前反复调节网络权值wijwjk和阈值θHjθOk,使网络预测值与期望值的误差达到要求。First, the training sample feature set is transmitted forward to the hidden layer as input, and the activation function f(u) will have an output result Generated; the result of the hidden layer is then transmitted to the output layer, and there will be an output result In the above two formulas, wij wjk is the weight of the connection of each layer of the BP neural network, θHj θOk is the threshold of the hidden layer and the output layer, f is the S-type activation function, Hjp and Ykp respectively Output results for the hidden layer and output results for the output layer. If there is an error between the final output Ykp and the expected value that does not meet the requirements, then repeatedly adjust the network weight wij wjk and the threshold θHj θOk to make the error between the network prediction value and the expected value meet the requirements.
5)原始步态特征集MIV法降维5) Original gait feature set MIV method for dimensionality reduction
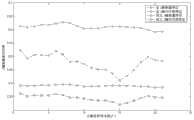
静态/动态步态分类器的输入特征集的维数为24。为了防止神经网络的过拟合,提高建模精度,需要对输入特征集的维数降低,去除冗余的特征,选择出最能反映神经网络的非线性映射关系的特征集。平均影响值(MIV)方法主要是在用所有步态信号特征集训练一个正确的神经网络后,再对各个输入特征集进行差值运算即每个输入变量分别±10%生成新样本p1p2,p1p2再分别作为仿真样本用建好的网络进行仿真,得到仿真值A1A2,再取其差值的算术平方根,即MIV值。经过MIV法降维后,选取MIV值前8最大的特征:X轴标准差、X轴能量值、X轴均方根、XZ轴相关系数、YZ轴相关系数、Y轴能量值、Y轴均方根、X轴方差作为优化的动态步态神经网络分类器的输入自变量。用相同的MIV方法,选取Y轴均方根、Y轴能量值、X轴均方根、Z轴均方根、YZ轴相关系数、Z轴能量值、X轴能量值、Z轴四位分差MIV值最大的这8个特征作为优化的静态步态神经网络分类器的输入自变量。The dimensionality of the input feature set for the static/dynamic gait classifier is 24. In order to prevent the over-fitting of the neural network and improve the modeling accuracy, it is necessary to reduce the dimensionality of the input feature set, remove redundant features, and select the feature set that best reflects the nonlinear mapping relationship of the neural network. The mean influence value (MIV) method is mainly to use all gait signal feature sets to train a correct neural network, and then perform a difference operation on each input feature set, that is, each input variable is ±10% to generate a new sample p1 p2 , p1 p2 are then used as simulation samples to simulate with the built network to obtain the simulated value A1 A2 , and then take the arithmetic square root of the difference, that is, the MIV value. After dimensionality reduction by the MIV method, select the top 8 features of the MIV value: X-axis standard deviation, X-axis energy value, X-axis root mean square, XZ-axis correlation coefficient, YZ-axis correlation coefficient, Y-axis energy value, Y-axis average The square root and X-axis variance are used as input variables of the optimized dynamic gait neural network classifier. Using the same MIV method, select Y-axis root mean square, Y-axis energy value, X-axis root mean square, Z-axis root mean square, YZ-axis correlation coefficient, Z-axis energy value, X-axis energy value, and Z-axis quartiles The 8 features with the largest difference MIV value are used as the input variables of the optimized static gait neural network classifier.
从图4(a)和图4(b)可看出四种动态步态在由MIV筛选出的最大前2个特征值X轴标准差、X轴能量值上有很好的区分度,同时从图5中看出两种静态步态在X轴均方根和X轴能量值2个特征上差异性比较明显,这表明MIV法能选择出最能反映神经网络的非线性映射关系的特征集。From Figure 4(a) and Figure 4(b), it can be seen that the four dynamic gaits have a good degree of discrimination in the X-axis standard deviation and X-axis energy value of the largest first two eigenvalues screened out by MIV, and at the same time It can be seen from Figure 5 that the two static gaits have obvious differences in the two features of the X-axis root mean square and the X-axis energy value, which shows that the MIV method can select the features that best reflect the nonlinear mapping relationship of the neural network set.
6)步态类型具体鉴别阶段6) Specific identification stage of gait type
在步态类型具体鉴别阶段,需要进行步态标签提取转化为二维输出结果操作:在动态步态具体分类时,标签为3、4、5、6将输出结果分别定为[1000]T、[0100]T、[0010]T、[0001]T;在静态步态分类时,标签为1的将输出结果定为[10]T,标签为2将输出结果定为[01]T。动态步态神经网络结构是:8-30-4,因为选取8个最具代表性的特征集,要鉴别的动态动作有4种。静态步态神经网络结构是:8-10-2,因为选取8个最具代表性的特征集,要鉴别的静态动作有2种。这里隐含层和输出层的激活函数均选择S型:网络的期望误差设定为0.02。使用的神经网络算法为Levnberg_Marquardt的BP算法。In the specific identification stage of the gait type, it is necessary to extract the gait label and convert it into a two-dimensional output result operation: in the specific classification of the dynamic gait, the labels are 3, 4, 5, and 6, and the output results are set as [1000]T , [0100]T , [0010]T , [0001]T ; during static gait classification, if the label is 1, the output result will be defined as [10]T , and if the label is 2, the output result will be defined as [01]T . The dynamic gait neural network structure is: 8-30-4, because the 8 most representative feature sets are selected, and there are 4 dynamic actions to be identified. The static gait neural network structure is: 8-10-2, because the 8 most representative feature sets are selected, and there are 2 static actions to be identified. Here, the activation functions of the hidden layer and the output layer are both selected to be S-type: The expected error of the network is set to 0.02. The neural network algorithm used is the BP algorithm of Levnberg_Marquardt.
上述虽然结合附图对本发明的具体实施方式进行了描述,但并非对本发明保护范围的限制,所属领域技术人员应该明白,在本发明的技术方案的基础上,本领域技术人员不需要付出创造性劳动即可做出的各种修改或变形仍在本发明的保护范围以内。Although the specific implementation of the present invention has been described above in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, it does not limit the protection scope of the present invention. Those skilled in the art should understand that on the basis of the technical solution of the present invention, those skilled in the art do not need to pay creative work Various modifications or variations that can be made are still within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013103673511ACN103400123A (en) | 2013-08-21 | 2013-08-21 | Gait type identification method based on three-axis acceleration sensor and neural network |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013103673511ACN103400123A (en) | 2013-08-21 | 2013-08-21 | Gait type identification method based on three-axis acceleration sensor and neural network |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103400123Atrue CN103400123A (en) | 2013-11-20 |
Family
ID=49563741
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013103673511APendingCN103400123A (en) | 2013-08-21 | 2013-08-21 | Gait type identification method based on three-axis acceleration sensor and neural network |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103400123A (en) |
Cited By (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104269025A (en)* | 2014-09-29 | 2015-01-07 | 南京信息工程大学 | Wearable type single-node feature and position selecting method for monitoring outdoor tumble |
| WO2015120824A1 (en)* | 2014-02-17 | 2015-08-20 | Hong Kong Baptist University | Gait measurement with 3-axes accelerometer/gyro in mobile devices |
| CN105125220A (en)* | 2015-10-20 | 2015-12-09 | 重庆软汇科技股份有限公司 | Falling-down detection method |
| CN105760819A (en)* | 2016-01-28 | 2016-07-13 | 西南大学 | Daily activity recognition method based on acceleration signal |
| CN106101060A (en)* | 2016-05-24 | 2016-11-09 | 杭州华三通信技术有限公司 | A kind of information detecting method and device |
| CN106295680A (en)* | 2016-07-29 | 2017-01-04 | 深圳云智优泊科技有限公司 | Low-power consumption is driven and ambulatory status identification system |
| CN106344031A (en)* | 2016-08-29 | 2017-01-25 | 常州市钱璟康复股份有限公司 | Sound feedback-based gait training and estimating system |
| CN107016346A (en)* | 2017-03-09 | 2017-08-04 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | gait identification method and system |
| CN107016411A (en)* | 2017-03-28 | 2017-08-04 | 北京犀牛数字互动科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device |
| CN107277222A (en)* | 2016-12-20 | 2017-10-20 | 浙江从泰网络科技有限公司 | User behavior state judging method based on mobile phone built-in sensors |
| CN107316052A (en)* | 2017-05-24 | 2017-11-03 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | A kind of robust Activity recognition method and system based on inexpensive sensor |
| CN107403154A (en)* | 2017-07-20 | 2017-11-28 | 四川大学 | A kind of gait recognition method based on dynamic visual sensor |
| CN107958221A (en)* | 2017-12-08 | 2018-04-24 | 北京理工大学 | A kind of human motion Approach for Gait Classification based on convolutional neural networks |
| CN108073154A (en)* | 2016-11-11 | 2018-05-25 | 横河电机株式会社 | Information processing unit, information processing method and recording medium |
| CN108563939A (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2018-09-21 | 常州大学 | Human body identification based on gait geometric locus feature |
| CN108814585A (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2018-11-16 | 深圳竹信科技有限公司 | ECG's data compression method, apparatus and computer readable storage medium |
| CN109009143A (en)* | 2018-07-12 | 2018-12-18 | 杭州电子科技大学 | A method of ecg information is predicted by body gait |
| CN109325428A (en)* | 2018-09-05 | 2019-02-12 | 周军 | Mankind's activity gesture recognition method based on multi-level end-to-end neural network |
| CN109512643A (en)* | 2017-09-20 | 2019-03-26 | 三星电子株式会社 | Device of walking aid and the method for controlling the device |
| TWI657800B (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2019-05-01 | 國立成功大學 | Method and system for analyzing gait |
| CN109753172A (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2019-05-14 | 矽统科技股份有限公司 | Classification method and system of touch panel tap event, and touch panel product |
| CN110705584A (en)* | 2019-08-21 | 2020-01-17 | 深圳壹账通智能科技有限公司 | Emotion recognition method, emotion recognition device, computer device and storage medium |
| CN111512178A (en)* | 2017-12-08 | 2020-08-07 | 认知系统公司 | Motion Detection Based on Machine Learning of Wireless Signal Properties |
| CN111870248A (en)* | 2020-06-05 | 2020-11-03 | 安徽建筑大学 | Motion state feature extraction and identification method based on 3D acceleration signal |
| CN112932469A (en)* | 2021-01-26 | 2021-06-11 | 山西三友和智慧信息技术股份有限公司 | CNN + Transformer-based triaxial acceleration activity identification method |
| CN112946318A (en)* | 2021-03-24 | 2021-06-11 | 苏州康旺聚贤智能科技有限公司 | Calibration algorithm of acceleration sensor |
| CN119279571A (en)* | 2024-11-07 | 2025-01-10 | 南方科技大学 | A gait feature extraction and analysis method and device |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101807245A (en)* | 2010-03-02 | 2010-08-18 | 天津大学 | Artificial neural network-based multi-source gait feature extraction and identification method |
| WO2011026001A2 (en)* | 2009-08-28 | 2011-03-03 | Allen Joseph Selner | Characterizing a physical capability by motion analysis |
| CN201812295U (en)* | 2010-10-09 | 2011-04-27 | 天津职业技术师范大学 | Human gait data extraction device based on zigbee and accelerometer |
- 2013
- 2013-08-21CNCN2013103673511Apatent/CN103400123A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011026001A2 (en)* | 2009-08-28 | 2011-03-03 | Allen Joseph Selner | Characterizing a physical capability by motion analysis |
| CN101807245A (en)* | 2010-03-02 | 2010-08-18 | 天津大学 | Artificial neural network-based multi-source gait feature extraction and identification method |
| CN201812295U (en)* | 2010-10-09 | 2011-04-27 | 天津职业技术师范大学 | Human gait data extraction device based on zigbee and accelerometer |
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| 刘蓉: ""人体运动信息获取及物理活动识别研究"", 《中国博士学位论文全文数据库 社会科学II辑》* |
| 戴永,等: ""基于RBF神经网络的手绘电气草图分类研究"", 《湘谭大学自然科学学报》* |
| 王科俊等: ""步态识别中的步态检测与序列预处理"", 《模式识别与仿真》* |
| 王美,等: ""改进的BP神经网络在糖尿病危险因素分析中的应用"", 《软件导刊》* |
| 顾姚媛: ""基于MIV特征筛选和BP神经网络的三维人体参数转换"", 《上海工程技术大学学报》* |
Cited By (37)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015120824A1 (en)* | 2014-02-17 | 2015-08-20 | Hong Kong Baptist University | Gait measurement with 3-axes accelerometer/gyro in mobile devices |
| CN104269025A (en)* | 2014-09-29 | 2015-01-07 | 南京信息工程大学 | Wearable type single-node feature and position selecting method for monitoring outdoor tumble |
| CN104269025B (en)* | 2014-09-29 | 2016-09-28 | 南京信息工程大学 | Wearable single node feature and the position choosing method of monitoring is fallen down towards open air |
| CN105125220A (en)* | 2015-10-20 | 2015-12-09 | 重庆软汇科技股份有限公司 | Falling-down detection method |
| CN105760819A (en)* | 2016-01-28 | 2016-07-13 | 西南大学 | Daily activity recognition method based on acceleration signal |
| CN105760819B (en)* | 2016-01-28 | 2019-03-26 | 西南大学 | A kind of daily routines recognition methods based on acceleration signal |
| CN106101060A (en)* | 2016-05-24 | 2016-11-09 | 杭州华三通信技术有限公司 | A kind of information detecting method and device |
| CN106295680A (en)* | 2016-07-29 | 2017-01-04 | 深圳云智优泊科技有限公司 | Low-power consumption is driven and ambulatory status identification system |
| CN106344031A (en)* | 2016-08-29 | 2017-01-25 | 常州市钱璟康复股份有限公司 | Sound feedback-based gait training and estimating system |
| CN108073154A (en)* | 2016-11-11 | 2018-05-25 | 横河电机株式会社 | Information processing unit, information processing method and recording medium |
| CN108073154B (en)* | 2016-11-11 | 2021-05-18 | 横河电机株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and recording medium |
| CN107277222B (en)* | 2016-12-20 | 2020-12-15 | 浙江斑智科技有限公司 | A method for judging user behavior status based on built-in sensors in mobile phones |
| CN107277222A (en)* | 2016-12-20 | 2017-10-20 | 浙江从泰网络科技有限公司 | User behavior state judging method based on mobile phone built-in sensors |
| CN107016346A (en)* | 2017-03-09 | 2017-08-04 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | gait identification method and system |
| CN107016411B (en)* | 2017-03-28 | 2020-09-29 | 北京犀牛数字互动科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device |
| CN107016411A (en)* | 2017-03-28 | 2017-08-04 | 北京犀牛数字互动科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device |
| CN107316052A (en)* | 2017-05-24 | 2017-11-03 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | A kind of robust Activity recognition method and system based on inexpensive sensor |
| CN107403154A (en)* | 2017-07-20 | 2017-11-28 | 四川大学 | A kind of gait recognition method based on dynamic visual sensor |
| CN109512643A (en)* | 2017-09-20 | 2019-03-26 | 三星电子株式会社 | Device of walking aid and the method for controlling the device |
| TWI657800B (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2019-05-01 | 國立成功大學 | Method and system for analyzing gait |
| CN109753172A (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2019-05-14 | 矽统科技股份有限公司 | Classification method and system of touch panel tap event, and touch panel product |
| CN107958221A (en)* | 2017-12-08 | 2018-04-24 | 北京理工大学 | A kind of human motion Approach for Gait Classification based on convolutional neural networks |
| CN111512178B (en)* | 2017-12-08 | 2024-06-04 | 认知系统公司 | Motion detection based on machine learning of wireless signal properties |
| CN111512178A (en)* | 2017-12-08 | 2020-08-07 | 认知系统公司 | Motion Detection Based on Machine Learning of Wireless Signal Properties |
| CN108563939A (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2018-09-21 | 常州大学 | Human body identification based on gait geometric locus feature |
| CN108563939B (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2022-05-20 | 常州大学 | Human body identity recognition based on gait track curve characteristics |
| CN108814585B (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2021-05-28 | 深圳竹信科技有限公司 | Electrocardiosignal processing method and device and computer readable storage medium |
| CN108814585A (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2018-11-16 | 深圳竹信科技有限公司 | ECG's data compression method, apparatus and computer readable storage medium |
| CN109009143A (en)* | 2018-07-12 | 2018-12-18 | 杭州电子科技大学 | A method of ecg information is predicted by body gait |
| CN109009143B (en)* | 2018-07-12 | 2021-01-29 | 杭州电子科技大学 | Method for predicting electrocardio information through human gait |
| CN109325428A (en)* | 2018-09-05 | 2019-02-12 | 周军 | Mankind's activity gesture recognition method based on multi-level end-to-end neural network |
| CN109325428B (en)* | 2018-09-05 | 2020-11-27 | 周军 | Human activity posture recognition method based on multilayer end-to-end neural network |
| CN110705584A (en)* | 2019-08-21 | 2020-01-17 | 深圳壹账通智能科技有限公司 | Emotion recognition method, emotion recognition device, computer device and storage medium |
| CN111870248A (en)* | 2020-06-05 | 2020-11-03 | 安徽建筑大学 | Motion state feature extraction and identification method based on 3D acceleration signal |
| CN112932469A (en)* | 2021-01-26 | 2021-06-11 | 山西三友和智慧信息技术股份有限公司 | CNN + Transformer-based triaxial acceleration activity identification method |
| CN112946318A (en)* | 2021-03-24 | 2021-06-11 | 苏州康旺聚贤智能科技有限公司 | Calibration algorithm of acceleration sensor |
| CN119279571A (en)* | 2024-11-07 | 2025-01-10 | 南方科技大学 | A gait feature extraction and analysis method and device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103400123A (en) | Gait type identification method based on three-axis acceleration sensor and neural network | |
| Javeed et al. | Wearable sensors based exertion recognition using statistical features and random forest for physical healthcare monitoring | |
| Abdulhay et al. | Gait and tremor investigation using machine learning techniques for the diagnosis of Parkinson disease | |
| CN112472048B (en) | Method for realizing neural network for identifying pulse condition of cardiovascular disease patient | |
| CN111401435B (en) | Human body motion mode identification method based on motion bracelet | |
| CN104598880A (en) | Behavior identification method based on fuzzy support vector machine | |
| CN110197235B (en) | Human body activity recognition method based on unique attention mechanism | |
| CN102567715B (en) | Hierarchical recognition method of human action based on pyroelectric infrared detection | |
| CN110084286A (en) | A kind of human motion recognition method of sensor-based ECOC technology | |
| CN112580486B (en) | Human behavior classification method based on radar micro-Doppler signal separation | |
| CN115393956A (en) | CNN-BiLSTM fall detection method with improved attention mechanism | |
| Wu et al. | Recognizing activities of the elderly using wearable sensors: a comparison of ensemble algorithms based on boosting | |
| CN104269025A (en) | Wearable type single-node feature and position selecting method for monitoring outdoor tumble | |
| Jiang et al. | Recent progress in wearable tactile sensors combined with algorithms based on machine learning and signal processing | |
| Li et al. | Human activity recognition based on LPA | |
| Aydemir et al. | A new method for activity monitoring using photoplethysmography signals recorded by wireless sensor | |
| CN110522455A (en) | A WD tremor grade assessment method based on deep learning | |
| CN110032987B (en) | A surface electromyographic signal classification method based on cerebellar neural network model | |
| Bayat et al. | Human gait recognition using bag of words feature representation method | |
| CN109271889A (en) | A kind of action identification method based on the double-deck LSTM neural network | |
| Ren et al. | PDCHAR: human activity recognition via multi-sensor wearable networks using two-channel convolutional neural networks | |
| Krassnig et al. | User-friendly system for recognition of activities with an accelerometer | |
| Ning et al. | Fall detection algorithm based on gradient boosting decision tree | |
| Kuduz et al. | A deep learning approach for human gait recognition from time-frequency analysis images of inertial measurement unit signal | |
| Cao et al. | An Approach for Human Posture Recognition Based on the Fusion PSE-CNN-BiGRUModel. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20131120 |