CN103302092A - Rapid passivation and repair process for pollution of soil heavy metals Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn - Google Patents
Rapid passivation and repair process for pollution of soil heavy metals Cr, Cu, Pb and ZnDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103302092A CN103302092ACN201310287811XACN201310287811ACN103302092ACN 103302092 ACN103302092 ACN 103302092ACN 201310287811X ACN201310287811X ACN 201310287811XACN 201310287811 ACN201310287811 ACN 201310287811ACN 103302092 ACN103302092 ACN 103302092A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- soil
- passivation
- heavy metal
- bioavailability
- pollution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Processing Of Solid Wastes (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及的是一种土壤重金属污染修复中降低污染重金属元素生物有效性的一种修复方法,能在不影响土壤物理化学性状情况下、在较短时间内使土壤中重金属元素向难溶或不溶化合物类型转化,进而使其生物有效性迅速降低。The present invention relates to a remediation method for reducing the bioavailability of polluted heavy metal elements in soil heavy metal pollution remediation, which can make heavy metal elements in the soil refractory to insoluble or The insoluble compound species shifts, thereby rapidly reducing its bioavailability.
背景技术Background technique
土壤重金属污染已成为当前严重的环境问题,对污染的修复治理需求在日益增大。目前的修复治理方法主要可概括为两个方面:1、通过给被污染土壤中加入其它物质降低重金属的生物有效性,使其不进入或少进入在土壤中生长的植物体;2、通过工程手段和生物吸收转移等手段把重金属从土壤中移除。上述治理方法从具体作用角度可划分为物理修复、化学修复和生物修复三大类别。Soil heavy metal pollution has become a serious environmental problem at present, and the demand for pollution remediation and treatment is increasing day by day. The current restoration and treatment methods can be summarized in two aspects: 1. Reduce the bioavailability of heavy metals by adding other substances to the contaminated soil so that they do not enter or less enter the plants growing in the soil; 2. Through engineering Heavy metals are removed from the soil by means of bioabsorption and transfer. The above treatment methods can be divided into three categories: physical restoration, chemical restoration and biological restoration from the perspective of specific effects.
重金属的物理修复方法主要包括稀释法和热解吸法。稀释修复主要包括客土换土、去表土和深耕翻土等;热解吸修复是利用高频电压产生电磁波,产生热能对土壤加热,使污染物从土壤颗粒内解吸出来,进而去除。物理修复方法可使土壤中的重金属元素得到一定程度的稀释或去除,但具有明显的操作条件要求高、程序繁琐复杂、耗能和过程中易造成有害元素向其它生态系统的转移的缺陷。如换土、深耕工作量大,并会使土壤的自然性状受到影响;而给土壤加热时在使有害易气化元素(Hg)挥发脱离土壤的同时,会导致其向大气的迁移,造成对大气环境的污染,此外,还会对土壤的自然性状如微生物条件等受到破坏。The physical restoration methods of heavy metals mainly include dilution method and thermal desorption method. Dilution restoration mainly includes replacing soil with foreign soil, topsoil removal and deep plowing, etc. Thermal desorption restoration uses high-frequency voltage to generate electromagnetic waves, which generate heat energy to heat the soil, so that pollutants are desorbed from the soil particles and then removed. Physical remediation methods can dilute or remove heavy metal elements in the soil to a certain extent, but they have the obvious defects of demanding operating conditions, cumbersome and complicated procedures, energy consumption, and the transfer of harmful elements to other ecosystems during the process. For example, the workload of soil replacement and deep plowing is heavy, which will affect the natural properties of the soil; while heating the soil, the harmful gasifiable elements (Hg) will be volatilized from the soil, and at the same time, it will cause its migration to the atmosphere, causing damage to the soil. The pollution of the atmospheric environment, in addition, will also damage the natural properties of the soil such as microbial conditions.
化学修复方法主要包括向污染土壤中投入填加剂(修复剂),使污染土壤中的重金属元素生物有效性降低或环境迁移活性减弱。修复中使用的修复剂可分为无机钝化修复剂、有机钝化修复剂和有机、无机复合修复剂。其中,无机钝化修复剂可分为以下几个主要类别:磷酸盐类(羟基磷灰石、磷矿粉、磷酸、磷肥和骨炭等)、粘土矿物类(膨润土、粗面棕闪石和沸石等)、工业副产品类(飞灰、磷石膏和白云石残渣等)等。此外,还有一些纯化学制品,如硫酸亚铁等。这类钝化修复剂通常对重金属元素的作用具有一定的选择性。有机钝化修复剂主要包括有机堆肥、畜禽粪便、市政污泥等。有机物质作为重金属络合剂可通过形成不溶性金属、有机复合物增加土壤阳离子交换量(CEC)和降低土壤中重金属的水溶态及可交换态组分含量的方式,降低其生物有效性。由于这类修复剂其修复效果的不确定性和常常会将自身(如市政污泥)含有的重金属元素带入土壤,其实际应用都非常有限。复合材料钝化修复剂是用几种材料混合共同作用使土壤中的重金属发生钝化,其可避免单独使用一种修复剂所带来的显著改变土壤pH值、作用单一等的不利影响;该方向工作目前多尚停留在实验室研究阶段。而且据文献报导情况看,对需要的填加物质有较大的量要求。The chemical remediation method mainly includes adding additives (remedial agents) to the polluted soil to reduce the bioavailability of heavy metal elements in the polluted soil or weaken the environmental migration activity. Restoration agents used in restoration can be divided into inorganic passivation restoration agents, organic passivation restoration agents and organic-inorganic composite restoration agents. Among them, inorganic passivation repair agents can be divided into the following main categories: phosphates (hydroxyapatite, phosphate rock powder, phosphoric acid, phosphate fertilizer and bone char, etc.), clay minerals (bentonite, amphibole and zeolite, etc.) ), industrial by-products (fly ash, phosphogypsum and dolomite residue, etc.), etc. In addition, there are some pure chemicals, such as ferrous sulfate. This kind of passivation repair agent usually has a certain selectivity to the action of heavy metal elements. Organic passivation restoration agents mainly include organic compost, livestock and poultry manure, municipal sludge, etc. Organic substances as heavy metal complexing agents can reduce their bioavailability by forming insoluble metals, organic complexes, increasing soil cation exchange capacity (CEC) and reducing the content of water-soluble and exchangeable components of heavy metals in soil. Due to the uncertainty of the remediation effect of this kind of remediation agent and the heavy metal elements contained in itself (such as municipal sludge) are often brought into the soil, its practical application is very limited. Composite material passivation repair agent is to passivate heavy metals in soil by mixing several materials together, which can avoid the adverse effects of significantly changing soil pH value and single effect caused by using one repair agent alone; Most of the direction work is still in the laboratory research stage. And according to the situation reported in the literature, there is a relatively large quantity requirement for the required additives.
生物修复主要分植物修复和微生物修复两种情况。植物修复是利用某些植物能忍耐和在生长过程中能超量积累某种重金属元素的特性来清除土壤中的金属元素。植物修复要求被修复土壤所处的气候条件要与用于修复的重金属超累积植物的生长条件相适应,并且由于目前人们发现的超累积植物一般都是植株较小、生长周期较长的种类,这些都使其应用范围和修复效率受到严重限制。微生物修复是利用土壤中的某些微生物类群对重金属元素具有吸收、沉淀、氧化还原等作用的特性,降低污染土壤中重金属生物有效性或毒性的修复方法。这种修复方法的作用机制是利用一些菌类的特殊功效,通过其对土壤中重金属元素化合物结构中电子行为的影响促使土壤中重金属元素发生转化,进而使土壤环境中重金属产生沉淀析出,进而达到降低其生物有效性或环境活性的目的;如硫酸盐还原细菌可将硫酸盐还原成硫化物,使重金属硫酸盐的生物有效性大大降低等。微生物修复受微生物生物量、种类及存活周期的影响,要求被修复土壤的性状如质地、含水率、有机质含量以及pH、Eh值等与用于修复的微生物类群的正常存活条件相适应,土壤条件要满足能保证微生物活性和足够数量存在。这些情况都是对土壤重金属污染微生物修复方法的制约因素,使其应用范围受到限制。Bioremediation is mainly divided into phytoremediation and microbial remediation. Phytoremediation is to remove metal elements in the soil by using the characteristics of certain plants that can tolerate and over-accumulate certain heavy metal elements during the growth process. Phytoremediation requires that the climatic conditions of the soil to be remediated should be compatible with the growth conditions of the heavy metal superaccumulative plants used for remediation, and since the superaccumulative plants found so far are generally species with small plants and long growth cycles, These have severely limited its application range and repair efficiency. Microbial remediation is a remediation method to reduce the bioavailability or toxicity of heavy metals in polluted soil by using the characteristics of certain microbial groups in the soil that have absorption, precipitation, redox and other effects on heavy metal elements. The mechanism of this repair method is to use the special effects of some fungi to promote the transformation of heavy metal elements in the soil through its influence on the electronic behavior of the heavy metal element compound structure in the soil, and then cause the heavy metal in the soil environment to precipitate and precipitate, thereby achieving The purpose of reducing its bioavailability or environmental activity; for example, sulfate reducing bacteria can reduce sulfate to sulfide, greatly reducing the bioavailability of heavy metal sulfate, etc. Microbial remediation is affected by microbial biomass, species, and survival cycle, and requires that the properties of the remediated soil, such as texture, moisture content, organic matter content, pH, and Eh values, be compatible with the normal survival conditions of the microbial groups used for remediation. It must be satisfied to ensure the existence of microbial activity and sufficient quantity. These conditions are the restrictive factors for the microbial remediation method of soil heavy metal pollution, which limits its application range.
概括起来,目前存在的上述重金属污染修复方法大都存在修复成本高或修复效率低两个缺点,并且修复后还可能对环境造成次生影响。寻求修复效果好、效率高和最小次生污染风险的修复方法是土壤重金属污染修复中力图达到的目标。化学钝化修复是一个就达到上述目标而言相对较为理想的方向。但是,由于在修复过程并未改变土壤中重金属含量、只是通过各种作用暂时性地降低了重金属的有效形态含量基本情况下,上述诸种钝化修复剂对土壤中的重金属钝化效果的时效作用以及可能的环境风险尚存在疑虑。如一些钝化剂在一定时间内起到钝化效果后,随着体系物理化学条件变化其效果是否会发生反弹以至使其生物毒性恢复等问题。另外,在一般情况下以含磷物质钝化修复土壤时的磷素施入量往往是在远高于土壤正常磷素需要量时才能达到理想的钝化效果,这无疑会引起磷素的水体富营养化风险。另外,大量施用石灰等化学钝化修复剂除了会引起土壤pH值显著改变外,还会向土壤中带入其他有害重金属元素,造成二次污染。To sum up, most of the above-mentioned heavy metal pollution remediation methods currently exist have two shortcomings of high remediation cost or low remediation efficiency, and may cause secondary impacts on the environment after remediation. Seeking a remediation method with good remediation effect, high efficiency and minimum secondary pollution risk is the goal to be achieved in the remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil. Chemical passivation repair is a relatively ideal direction in terms of achieving the above goals. However, since the remediation process does not change the heavy metal content in the soil, but only temporarily reduces the effective form content of heavy metals through various actions, the timeliness of the above-mentioned passivation remediation agents for the passivation effect of heavy metals in the soil There are still doubts about its role and possible environmental risks. For example, after some passivating agents have a passivating effect within a certain period of time, as the physical and chemical conditions of the system change, whether their effects will rebound and restore their biological toxicity. In addition, in general, the amount of phosphorus applied when repairing soil with phosphorus-containing substances passivation is often much higher than the normal phosphorus requirement of the soil to achieve the ideal passivation effect, which will undoubtedly cause phosphorus pollution in water bodies. Eutrophication risk. In addition, extensive application of chemical passivation restoration agents such as lime will not only cause significant changes in soil pH, but also bring other harmful heavy metal elements into the soil, causing secondary pollution.
经过对现有技术的检索发现,中国专利文献号CN101362009,公开日2009-02-11,公开了一种垃圾焚化飞灰、底渣或土壤的重金属安定方法。该技术使用硅酸盐类物质作为安定剂,利用喷洒或直接添加混合等方式,于垃圾焚化底渣、飞灰或土壤中加入安定剂,利用安定剂中的硅酸盐物质及其溶解性硅酸根离子与底渣、飞灰或土壤中的重金属形成稳定物,使底渣、飞灰或土壤中的重金属(尤其是铅)在自然环境的条件下不易溶出,使的符合相关溶出标准或可降低、并符合再利用的相关规范。但该技术的缺陷或不足在于:1)其只针对Pb元素有稳定效果,对其它元素的正负面环境行为影响都不明确;这些情况对当前土壤重金属污染多见的是多元素综合型污染问题的针对性相对局限;2)该技术硅酸钠填加量最低为被处理土壤量的0.8%时,被处理土壤中的Pb可溶出含量由8.98mg/kg(L)降低为5.23mg/kg(L),即处理后其有效态含量较之未处理时可减小41.76%;相当于被处理土壤量0.8%的硅酸钠填加量已远远超出微量范畴(0.1%),如此量比的硅酸钠水解作用会引起被处理土壤pH值显著增高,进而会严重影响农作物对土壤的正常生长需求;3)该技术填加剂量过高,性价比限制导致其难以广泛应用;4)该技术处理土壤需要时间(填加剂与土壤作用时间)没有明确;这对于对被处理土壤正常功能的恢复和利用统筹都是明显的缺陷。After searching the prior art, it is found that Chinese Patent Document No. CN101362009, published on 2009-02-11, discloses a method for stabilizing heavy metals in waste incineration fly ash, bottom slag or soil. This technology uses silicate substances as stabilizers, and adds stabilizers to waste incineration bottom slag, fly ash or soil by spraying or directly adding and mixing. The acid radical ions form stabilizers with the heavy metals in the bottom slag, fly ash or soil, so that the heavy metals (especially lead) in the bottom slag, fly ash or soil are not easy to dissolve under natural environment conditions, so that they meet the relevant dissolution standards or can reduce and comply with the relevant norms of reuse. However, the defects or deficiencies of this technology are: 1) It only has a stabilizing effect on the Pb element, and the positive and negative environmental behavior effects on other elements are not clear; these situations are mostly multi-element comprehensive pollution problems in the current soil heavy metal pollution 2) When the sodium silicate filling amount of this technology is at least 0.8% of the treated soil, the soluble Pb content in the treated soil is reduced from 8.98mg/kg (L) to 5.23mg/kg (L), that is, the effective state content after treatment can be reduced by 41.76% compared with that without treatment; the amount of sodium silicate added, which is equivalent to 0.8% of the treated soil, is far beyond the trace range (0.1%), such an amount The specific sodium silicate hydrolysis will cause the pH value of the treated soil to increase significantly, which will seriously affect the normal growth requirements of crops on the soil; 3) The dosage of this technology is too high, and the cost-effectiveness limit makes it difficult to be widely used; 4) The technology The time required for technical treatment of soil (action time between additives and soil) is not clear; this is an obvious defect in the restoration and utilization of the normal function of the treated soil.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明针对现有技术存在的上述不足,提出一种土壤重金属Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn污染快速钝化修复工艺,着眼于土壤体系中重金属成分生物有效性降低的本质作用是含金属成分的化合物向环境活性更低、在环境中稳定性更强进而既不易迁移也不易为生物(主要是植物)吸收的化学形态转化这一根本机制,强化化学作用过程在金属形态转化中的贡献,直接选用硅酸盐作为钝化作用剂,在既不使被作用土壤的物理化学性状发生明显改变,又起到能与土壤体系中的金属成分快速作用并形成环境活性更低、在环境中稳定性更强进而既不易迁移也不易为生物吸收的化合物类型,以此达到降低金属成分生物有效性——使其钝化的目的。The present invention aims at the above-mentioned deficiencies existing in the prior art, and proposes a rapid passivation restoration process for soil heavy metal Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn pollution, focusing on the essential role of the reduction in the bioavailability of heavy metal components in the soil system is the compound containing metal components The fundamental mechanism of chemical form conversion to a chemical form with lower environmental activity and stronger stability in the environment, which is neither easy to migrate nor absorbed by organisms (mainly plants), strengthens the contribution of chemical processes in metal form conversion, and directly selects As a passivating agent, silicate does not significantly change the physical and chemical properties of the affected soil, but also acts quickly with the metal components in the soil system to form a less active environment and a more stable environment. A type of compound that is strong and thus neither migratable nor bioabsorbable, in order to reduce the bioavailability of the metal component - to passivate it.
本发明是通过以下技术方案实现的:The present invention is achieved through the following technical solutions:
本发明涉及一种土壤重金属Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn污染快速钝化修复剂,其成分为九水合硅酸钠,即偏硅酸钠,化学式为Na2SiO3·9H2O。The invention relates to a rapid passivation repairing agent for soil heavy metal Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn pollution. The composition is sodium silicate nonahydrate, ie sodium metasilicate, and its chemical formula is Na2 SiO3 ·9H2 O.
本发明涉及上述土壤修复剂的应用,通过将上述修复剂溶液喷洒于土壤中得以实现;作用的条件为:土壤含水率20-25%,温度为15-22℃,钝化作用时间为15天。The present invention relates to the application of the above-mentioned soil remediation agent, which is realized by spraying the above-mentioned remediation agent solution in the soil; the conditions of action are: the soil moisture content is 20-25%, the temperature is 15-22°C, and the passivation time is 15 days .
所述的喷洒是指:将修复剂按被处理土壤重量的0.5‰的剂量溶于水,以溶液形式均匀喷洒于被修复土壤中。The spraying refers to: dissolving the restoration agent in water at a dose of 0.5‰ of the weight of the soil to be treated, and spraying evenly in the soil to be repaired in the form of a solution.
所述的喷洒的用量保持在使土壤含水率小于等于25%。The amount of spraying is kept to make the soil moisture content less than or equal to 25%.
该应用通过诱导土壤中的有效态重金属元素向硅酸盐态转化。在被处理土壤含水率(20%±)、pH值(7±)正常情况下喷洒加入含钝化药剂的溶液后作用15天,即可使Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn几个金属元素的有效态含量显著降低,残渣态(硅酸盐态)含量相应升高。钝化作用对被处理土壤的基本性状(pH值、质地、有机质含量、微生物状况)无明显改变。This application induces the conversion of available heavy metal elements in soil to silicate state. Under the normal conditions of soil moisture content (20%±) and pH value (7±), the solution containing passivation agent is sprayed and acted for 15 days, and the metal elements such as Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn can be effectively deactivated. The state content decreased significantly, and the residue state (silicate state) content increased correspondingly. Passivation did not significantly change the basic properties (pH value, texture, organic matter content, microbial status) of the treated soil.
技术效果technical effect
与现有技术相比,本发明避免了目前试验或试行的土壤重金属污染修复中使用的作用剂筛选、处理、加工等复杂环节,而且具有在不改变土壤原来性状条件下快速见效的显著优势。符合成本低、操作简便、效果体现时间周期短等当前土壤重金属污染治理中的实际形势需求。该措施通过适当更次重叠操作,可明显抑制以至消除重金属对处理土壤中的生物负面效应,过程中被钝化重金属元素生成硅酸盐化合物后,从理论上讲,其生物毒性反弹可能性在地表正常条件下几乎没有。Compared with the prior art, the present invention avoids the complex steps of agent screening, treatment, and processing used in the current tests or trials of remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil, and has the remarkable advantage of quick results without changing the original properties of the soil. It meets the actual situation needs in the current soil heavy metal pollution control such as low cost, simple operation, and short period of time for effect manifestation. This measure can significantly suppress or even eliminate the biological negative effects of heavy metals on the treated soil through appropriate overlapping operations. After the passivated heavy metal elements form silicate compounds during the process, theoretically speaking, the possibility of biological toxicity rebound is within Almost none under normal conditions on the surface.
本发明快速钝化修复技术修复成本较低,修复周期较短,并且能够对几个重金属元素同时起到生物有效性钝化作用,能较好的满足重金属污染土壤修复的条件要求。通过诱导硅酸盐盐中的硅酸根(SiO32-)与土壤中重金属元素作用,使重金属与之结合形成硅酸盐化合物——即重金属生物有效性评价中所指残渣态形态,使土壤中的重金属元素生物有效性恢复的可能性变得较小或较彻底消失,进而起到对重金属污染土壤的快速、永久性修复。The rapid passivation repair technology of the present invention has lower repair cost and shorter repair period, and can play a biologically effective passivation effect on several heavy metal elements at the same time, and can better meet the condition requirements of heavy metal contaminated soil repair. By inducing the silicate radical (SiO32- ) in the silicate salt to interact with the heavy metal elements in the soil, the heavy metals combine with it to form a silicate compound—that is, the residue form referred to in the evaluation of the bioavailability of heavy metals, so that the soil The possibility of recovery of the bioavailability of heavy metal elements in the soil becomes smaller or disappears more completely, and then it can quickly and permanently repair the heavy metal contaminated soil.
附图说明Description of drawings
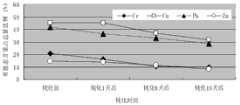
图1为实施例中不同钝化作用时间重金属有效态量变化图。Fig. 1 is a graph showing the changes in the effective state of heavy metals for different passivation times in the examples.
图2为实施例中Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn在土壤中的硅酸盐态量随时间的变化图。Fig. 2 is a diagram showing the variation of Silicate state of Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn in soil with time in the embodiment.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面对本发明的实施例作详细说明。本实施例在以本发明技术方案为前提下进行实施,给出了详细的实施方式和具体的操作过程,但本发明的保护范围不限于下述的实施例。Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below. This embodiment is carried out on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and the detailed implementation and specific operation process are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
实施例1Example 1
在实验室以内蒙古河套地区农田黄棕壤为实验对象,实验土壤含水率为25%,pH值为7.0。在22℃下给实验土壤均匀喷洒加入钝化剂重量为实验土壤重量0.5‰的九水合硅酸钠(Na2SiO3·9H2O)溶液与之作用。溶液加入量以不使土壤含水率大于25%为限——通过调节实验土壤含水率或钝化剂溶液浓度实现。在保持实验条件作用不同时间后取样分别测量土壤中Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn有效态含量,以了解其Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn生物有效性变化情况。以该方法实现的重金属生物有效性钝化作用在不影响土壤正常条件情况下可使Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn四个元素的有效态含量快速(15天)显著降低,结果见表1。In the laboratory, the farmland yellow-brown soil in the Hetao area of Inner Mongolia was used as the experimental object. The experimental soil moisture content was 25%, and the pH value was 7.0. At 22°C, uniformly spray the experimental soil and add a solution of sodium silicate nonahydrate (Na2 SiO3 ·9H2 O) whose weight of passivator is 0.5‰ of the experimental soil weight to act on it. The amount of solution to be added should not make the soil moisture content greater than 25% - by adjusting the experimental soil moisture content or passivator solution concentration. After keeping the experimental conditions for different periods of time, samples were taken to measure the available content of Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn in the soil, so as to understand the changes in the bioavailability of Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn. The heavy metal bioavailability passivation achieved by this method can quickly (15 days) significantly reduce the available content of the four elements of Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn without affecting the normal conditions of the soil. The results are shown in Table 1.
表1九水合硅酸钠(Na2SiO3·9H2O)对Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn生物有效性钝化实验数据(有效态变化)Table 1 Experimental data of sodium silicate nonahydrate (Na2 SiO3 9H2 O) bioavailability passivation on Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn (effective state change)
实施例2Example 2
在实验室以内蒙古河套地区农田黄棕壤为实验对象,实验土壤含水率为25%,pH值为7.0。在22℃下给实验土壤加入钝化剂重量为实验土壤重量0.5‰的九水合硅酸钠(Na2SiO3·9H2O)与之作用。溶液加入量以不使土壤含水率大于25%为限——通过调节实验土壤含水率或钝化剂溶液浓度实现。在保持实验条件作用不同时间后分别取样测量土壤中Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn残渣态含量,以了解其Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn生物有效性变化情况。以该方法实现的重金属生物有效性钝化作用在不影响土壤正常条件情况下可使Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn四个元素的残渣态含量快速(15天)显著升高,结果见表2。In the laboratory, the farmland yellow-brown soil in the Hetao area of Inner Mongolia was used as the experimental object. The experimental soil moisture content was 25%, and the pH value was 7.0. At 22°C, add sodium silicate nonahydrate (Na2 SiO3 ·9H2 O) whose passivating agent weight is 0.5‰ of the experimental soil weight to the experimental soil to act on it. The amount of solution to be added should not make the soil moisture content greater than 25% - by adjusting the experimental soil moisture content or passivator solution concentration. After maintaining the experimental conditions for different periods of time, samples were taken to measure the residual content of Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn in the soil, so as to understand the changes in the bioavailability of Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn. The bioavailable passivation of heavy metals achieved by this method can rapidly (15 days) significantly increase the residual content of Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn without affecting the normal conditions of the soil. The results are shown in Table 2.
表2九水合硅酸钠(Na2SiO3·9H2O)对Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn生物有效性钝化实验数据(残渣态变化)Table 2 Experimental data of sodium silicate nonahydrate (Na2 SiO3 9H2 O) bioavailability passivation on Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn (residue state change)
本实施例对重金属Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn具有明显的快速钝化效果。经实验室模拟实验,在土壤含水率24%、土壤pH值7.0、作用温度22℃、不同作用时间后的作用效果(有效态含量降低、硅酸盐态含量相应升高)对比,15天后可使上述五个金属元素有效态含量降低6.54-13.78%,如图1、2。因为其既有操作简便、成本低、见效快优点,又不明显影响土壤自身物理化学性状,这对于一些重金属含量超标但并不严重的污染治理情况是非常有价值的处理方案。This embodiment has obvious rapid passivation effect on heavy metals Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn. According to the laboratory simulation experiment, the effect (the effective state content decreases and the silicate state content increases correspondingly) is compared after the soil moisture content is 24%, the soil pH value is 7.0, the action temperature is 22°C, and the action time is different. After 15 days, it can be Reduce the effective state content of the above five metal elements by 6.54-13.78%, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. Because it has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, and quick results, and does not significantly affect the physical and chemical properties of the soil itself, it is a very valuable treatment plan for some pollution control situations where the heavy metal content exceeds the standard but is not serious.
本实施例对污染土壤的处理方法为针对Cr污染土壤的Cr生物有效性的快速钝化,兼具对Cu、Pb、Zn的生物有效性钝化作用(钝化效率见表1)。The treatment method of the polluted soil in this example is the rapid passivation of the Cr bioavailability of the Cr polluted soil, as well as the passivation of the bioavailability of Cu, Pb, and Zn (see Table 1 for passivation efficiency).
本实施例对污染土壤的处理方法为针对Cu污染土壤的Cu生物有效性的快速钝化,兼具对Cr、Pb、Zn的生物有效性钝化作用(钝化效率见表1)。The treatment method of the polluted soil in this embodiment is the rapid passivation of Cu bioavailability for the Cu polluted soil, and also has the bioavailability passivation of Cr, Pb, and Zn (see Table 1 for passivation efficiency).
本实施例对污染土壤的处理方法为针对Pb污染土壤的Pb生物有效性的快速钝化,兼具对Cr、Cu、Zn的生物有效性钝化作用(钝化效率见表1)。The treatment method of the polluted soil in this example is the rapid passivation of the Pb bioavailability of the Pb polluted soil, as well as the passivation of the bioavailability of Cr, Cu, and Zn (see Table 1 for passivation efficiency).
本实施例对污染土壤的处理方法为针对Zn污染土壤的Zn生物有效性的快速钝化,兼具对Cu、Pb、Cr的生物有效性钝化作用(钝化效率见表1)。The treatment method of the polluted soil in this example is the rapid passivation of the Zn bioavailability of the Zn polluted soil, and also has the passivation of the bioavailability of Cu, Pb, and Cr (see Table 1 for passivation efficiency).
表1钝化作用后土壤体系中重金属生物有效性(形态含量)变化情况Table 1 Changes in the bioavailability (species content) of heavy metals in the soil system after passivation
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310287811XACN103302092A (en) | 2013-07-10 | 2013-07-10 | Rapid passivation and repair process for pollution of soil heavy metals Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310287811XACN103302092A (en) | 2013-07-10 | 2013-07-10 | Rapid passivation and repair process for pollution of soil heavy metals Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103302092Atrue CN103302092A (en) | 2013-09-18 |
Family
ID=49128061
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310287811XAPendingCN103302092A (en) | 2013-07-10 | 2013-07-10 | Rapid passivation and repair process for pollution of soil heavy metals Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103302092A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103965919A (en)* | 2014-05-10 | 2014-08-06 | 复旦大学 | Heavy metal composite passivant suitable for northern farmland soil and preparing and using method thereof |
| CN105368455A (en)* | 2015-12-08 | 2016-03-02 | 江苏盖亚环境工程有限公司 | Heavy metal contaminated acidic soil remediation agent, and preparation method and application method thereof |
| CN106269827A (en)* | 2016-11-01 | 2017-01-04 | 南通圆平农业科技有限公司 | A kind of Soil structure condenses restorative procedure |
| CN106424123A (en)* | 2016-12-06 | 2017-02-22 | 重庆理工大学 | Remediation composition and remediation method for lead-polluted soil |
| CN106699387A (en)* | 2016-12-28 | 2017-05-24 | 贵州省贵福生态肥业有限公司 | Multifunctional soil remediation fertilizer |
| CN106753414A (en)* | 2016-12-29 | 2017-05-31 | 广东万山土壤修复技术有限公司 | A kind of heavy metal deactivator and its preparation method and application |
| CN106903158A (en)* | 2017-03-03 | 2017-06-30 | 武汉大学 | A kind of Soil oxidation solidification and stabilization repairs medicament and its application method |
| CN108070382A (en)* | 2017-12-22 | 2018-05-25 | 苏州艾捷尔斯生物科技有限公司 | A kind of heavy metal cadmium soil-repairing agent and its preparation method and application |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101331835A (en)* | 2008-08-01 | 2008-12-31 | 广东省生态环境与土壤研究所 | Method for reducing lead content in Chinese cabbage |
| CN101921144A (en)* | 2010-08-06 | 2010-12-22 | 广东省农业科学院土壤肥料研究所 | Nutrient regulation and control agent for reducing lead and cadmium content of leaf vegetables and using method thereof |
- 2013
- 2013-07-10CNCN201310287811XApatent/CN103302092A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101331835A (en)* | 2008-08-01 | 2008-12-31 | 广东省生态环境与土壤研究所 | Method for reducing lead content in Chinese cabbage |
| CN101921144A (en)* | 2010-08-06 | 2010-12-22 | 广东省农业科学院土壤肥料研究所 | Nutrient regulation and control agent for reducing lead and cadmium content of leaf vegetables and using method thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (6)
| Title |
|---|
| 于勤勤、牛漫兰: "改性硅酸盐在修复土壤重金属污染中的应用", 《安徽农学通报》, vol. 14, no. 9, 31 December 2008 (2008-12-31)* |
| 徐超等: "硅酸盐和磷酸盐矿物对土壤重金属化学固定的研究进展", 《环境科学与管理》, vol. 37, no. 5, 31 May 2012 (2012-05-31), pages 164 - 168* |
| 李淑仪等: "施硅对污染土壤中铬形态及其生物有效性的影响", 《生态环境》, vol. 17, no. 1, 31 December 2008 (2008-12-31), pages 227 - 231* |
| 梁媛等: "基于磷酸盐、碳酸盐和硅酸盐材料化学钝化修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展", 《环境化学》, vol. 31, no. 1, 31 January 2012 (2012-01-31), pages 16 - 25* |
| 王晨: ""硅对重金属复合污染土壤中草坪草生理生化性质和重金属吸收的影响", 《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库-农业科技辑》, no. 7, 15 July 2010 (2010-07-15), pages 048 - 105* |
| 董敬娜等: "硅对小麦吸收金属铜和土壤性质的影响", 《水土保持学报》, vol. 26, no. 2, 30 April 2012 (2012-04-30), pages 111 - 115* |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103965919A (en)* | 2014-05-10 | 2014-08-06 | 复旦大学 | Heavy metal composite passivant suitable for northern farmland soil and preparing and using method thereof |
| CN105368455A (en)* | 2015-12-08 | 2016-03-02 | 江苏盖亚环境工程有限公司 | Heavy metal contaminated acidic soil remediation agent, and preparation method and application method thereof |
| CN106269827A (en)* | 2016-11-01 | 2017-01-04 | 南通圆平农业科技有限公司 | A kind of Soil structure condenses restorative procedure |
| CN106424123A (en)* | 2016-12-06 | 2017-02-22 | 重庆理工大学 | Remediation composition and remediation method for lead-polluted soil |
| CN106424123B (en)* | 2016-12-06 | 2019-07-30 | 重庆理工大学 | Remediation composition and restorative procedure for lead-contaminated soil |
| CN106699387A (en)* | 2016-12-28 | 2017-05-24 | 贵州省贵福生态肥业有限公司 | Multifunctional soil remediation fertilizer |
| CN106753414A (en)* | 2016-12-29 | 2017-05-31 | 广东万山土壤修复技术有限公司 | A kind of heavy metal deactivator and its preparation method and application |
| CN106903158A (en)* | 2017-03-03 | 2017-06-30 | 武汉大学 | A kind of Soil oxidation solidification and stabilization repairs medicament and its application method |
| CN108070382A (en)* | 2017-12-22 | 2018-05-25 | 苏州艾捷尔斯生物科技有限公司 | A kind of heavy metal cadmium soil-repairing agent and its preparation method and application |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103302092A (en) | Rapid passivation and repair process for pollution of soil heavy metals Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn | |
| CN102389776B (en) | Metal heavy absorbent and preparation method and use thereof | |
| CN103464101B (en) | A kind of method of repairing the plant giantreed recycling of heavy-metal contaminated soil | |
| CN103788959B (en) | A kind of heavy-metal contaminated soil renovation agent and preparation method thereof | |
| CN108130087A (en) | A kind of soil conditioner and application process for repairing cadmium-arsenic combined pollution | |
| CN106978191A (en) | It is a kind of to be used to repair lead in acid soil, cadmium, the compound stabilizer of arsenic pollution | |
| CN104845626A (en) | Passivating agent for governing heavy metal contaminated soil and preparation and use method of passivating agent | |
| CN104556342B (en) | The reparation medicament of hexavalent chromium polluted soil and underground water and preparation method | |
| CN104117529B (en) | An in-situ remediation method for acidic soil containing heavy metals | |
| CN104194795A (en) | Novel in-situ passivation modifier and preparing method thereof | |
| CN106623400A (en) | Method for remedying heavy metal contaminated soil through passivation | |
| CN105582638A (en) | Liquid stabilizer for treatment of waste incineration fly ash high in lead and cadmium content and application thereof | |
| CN109078972A (en) | Heavy metal contaminated soil remediation material and application method thereof | |
| CN103551375A (en) | Preparation method of ion mineralization blocking agent for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation | |
| CN110976506A (en) | Curing and stabilizing repairing agent for polluted soil and repairing method thereof | |
| CN105598156A (en) | Heavy metal curing agent and method for treating heavy metal compound contaminated soil by same | |
| CN111704905A (en) | A kind of soil remediation agent and its preparation method and application | |
| Zong et al. | Research status of soda residue in the field of environmental pollution control | |
| CN109652079A (en) | A kind of flyash modified method and application for mercury pollution original position soil reparation | |
| CN107721297B (en) | Solidification stabilization composition agent suitable for heavy metal slag | |
| CN104479686A (en) | Curing agent and method for heavy metal | |
| CN113372920B (en) | Composite conditioner for soil cadmium pollution remediation and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN104531158A (en) | Curing agent and curing method thereof | |
| Yingying et al. | Application of clay minerals in remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil | |
| CN110436728B (en) | A method for in-situ stabilization of iron-based materials and microorganisms for remediation of lead-contaminated sediment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20130918 |