CN103193263B - Preparation method of SnO2C hollow nanospheres and its application in lithium-ion batteries - Google Patents
Preparation method of SnO2C hollow nanospheres and its application in lithium-ion batteriesDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103193263B CN103193263BCN201310100899.XACN201310100899ACN103193263BCN 103193263 BCN103193263 BCN 103193263BCN 201310100899 ACN201310100899 ACN 201310100899ACN 103193263 BCN103193263 BCN 103193263B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- sno
- hollow
- add
- lithium
- oven
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000002077nanosphereSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription28
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription7
- 229910001416lithium ionInorganic materials0.000titleabstractdescription21
- HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-NLithium ionChemical compound[Li+]HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000titleabstractdescription20
- 229910006404SnO 2Inorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription36
- XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntin dioxideChemical compoundO=[Sn]=OXOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription33
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription14
- 239000011258core-shell materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription32
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription26
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilicium dioxideChemical compoundO=[Si]=OVYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription19
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription19
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000claimsdescription15
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription15
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-NAmmonium hydroxideChemical compound[NH4+].[OH-]VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription11
- 235000011114ammonium hydroxideNutrition0.000claimsdescription11
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-NIsopropanolChemical compoundCC(C)OKFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription10
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-NTetraethyl orthosilicateChemical compoundCCO[Si](OCC)(OCC)OCCBOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000000377silicon dioxideSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 229920002125Sokalan®Polymers0.000claimsdescription5
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-NUreaChemical compoundNC(N)=OXSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000007864aqueous solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000004202carbamideSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- TVQLLNFANZSCGY-UHFFFAOYSA-Ndisodium;dioxido(oxo)tinChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[O-][Sn]([O-])=OTVQLLNFANZSCGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000003760magnetic stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000011259mixed solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 229940079864sodium stannateDrugs0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000007787solidSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000002244precipitateSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000005119centrifugationMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004584polyacrylic acidSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbonChemical compound[C]OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription8
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000abstractdescription8
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000abstractdescription7
- 229910052799carbonInorganic materials0.000abstractdescription6
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 239000006185dispersionSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000002114nanocompositeSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000abstract1
- 230000003139buffering effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 239000011247coating layerSubstances0.000abstract1
- 239000010410layerSubstances0.000abstract1
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description12
- 239000010405anode materialSubstances0.000description7
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description6
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description5
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-NLithiumChemical compound[Li]WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 239000011149active materialSubstances0.000description4
- 238000009830intercalationMethods0.000description4
- 229910052744lithiumInorganic materials0.000description4
- 239000011734sodiumSubstances0.000description4
- 238000005054agglomerationMethods0.000description3
- 230000002776aggregationEffects0.000description3
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000description3
- 238000001027hydrothermal synthesisMethods0.000description3
- 239000002070nanowireSubstances0.000description3
- 238000010298pulverizing processMethods0.000description3
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-NArgonChemical compound[Ar]XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-NN-MethylpyrrolidoneChemical compoundCN1CCCC1=OSECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000002033PVDF binderSubstances0.000description2
- 239000011230binding agentSubstances0.000description2
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description2
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description2
- 239000003575carbonaceous materialSubstances0.000description2
- 239000002131composite materialSubstances0.000description2
- 239000006258conductive agentSubstances0.000description2
- 238000007599dischargingMethods0.000description2
- 238000000227grindingMethods0.000description2
- 230000002687intercalationEffects0.000description2
- 239000002071nanotubeSubstances0.000description2
- 239000007773negative electrode materialSubstances0.000description2
- 229920002981polyvinylidene fluoridePolymers0.000description2
- 235000012239silicon dioxideNutrition0.000description2
- 239000002002slurrySubstances0.000description2
- OTYYBJNSLLBAGE-UHFFFAOYSA-NCN1C(CCC1)=O.[N]Chemical compoundCN1C(CCC1)=O.[N]OTYYBJNSLLBAGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-NCopperChemical compound[Cu]RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910013870LiPF 6Inorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000004743PolypropyleneSubstances0.000description1
- 239000006230acetylene blackSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052786argonInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000005266castingMethods0.000description1
- 239000012295chemical reaction liquidSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description1
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000description1
- 239000011889copper foilSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description1
- 238000001035dryingMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 238000003487electrochemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 238000005530etchingMethods0.000description1
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description1
- 229910002804graphiteInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000010439graphiteSubstances0.000description1
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description1
- 238000001764infiltrationMethods0.000description1
- 230000008595infiltrationEffects0.000description1
- 238000003780insertionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037431insertionEffects0.000description1
- 238000002955isolationMethods0.000description1
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001000micrographMethods0.000description1
- 239000004570mortar (masonry)Substances0.000description1
- 239000002090nanochannelSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011858nanopowderSubstances0.000description1
- -1polypropylenePolymers0.000description1
- 229920001155polypropylenePolymers0.000description1
- 238000001878scanning electron micrographMethods0.000description1
- 238000000926separation methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000002904solventSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001308synthesis methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
- 229910001887tin oxideInorganic materials0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Battery Electrode And Active Subsutance (AREA)
- Inorganic Compounds Of Heavy Metals (AREA)
- Silicon Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于纳米复合材料及其应用技术领域,具体涉及一种SnO2C空心纳米球的制备方法及其在锂离子电池中的应用。 The invention belongs to the technical field of nanocomposite materials and their applications, and in particular relates to a preparation method of SnO2 C hollow nanospheres and their application in lithium ion batteries.
背景技术Background technique
锂离子电池以其具有充电速度快,循环寿命长,能量密度和工作电压高,安全无污染等优点,已广泛应用于各种便携式电子设备。随着科学技术的进步和人们生活水平的提高,对锂离子电池也提出了更高的要求。就锂离子电池负极材料而言,目前商业化的碳材料存在比容量低、安全性能欠佳等问题,已不能满足新一代高比容量电池负极材料的需求。因此,如何用低电压、可嵌锂的化合物替代目前所用的碳材料,以提高锂离子电池的能量密度和安全性能是一个十分重要的课题。 Lithium-ion batteries have been widely used in various portable electronic devices because of their advantages such as fast charging speed, long cycle life, high energy density and working voltage, safety and pollution-free. With the advancement of science and technology and the improvement of people's living standards, higher requirements are placed on lithium-ion batteries. As far as lithium-ion battery anode materials are concerned, the current commercialized carbon materials have problems such as low specific capacity and poor safety performance, which can no longer meet the needs of a new generation of high specific capacity battery anode materials. Therefore, how to replace the currently used carbon materials with low-voltage, lithium-intercalable compounds to improve the energy density and safety performance of lithium-ion batteries is a very important issue. the
二氧化锡(SnO2)以其约为石墨两倍的高嵌锂容量,得到了研究者们的广泛关注,被认为是最有应用潜力的新型材料。但其循环性能较差,在充放电过程中体积变化较大,易引起电极的“粉化”或“团聚”,从而造成材料比容量衰减,循环性能下降(参考文献:W. M. Zhang, J. S. Hu, Y. Q. Guo, et a1. Tin-nanoparticles encapsulated in elastic hollow carbon spheres for high-performance anode material in lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1160-1164.)。要想将SnO2广泛应用于锂离子电池阳极材料中,就必须减轻SnO2电极的“体积效应”。 Tin dioxide (SnO2 ) has attracted extensive attention from researchers because of its high lithium intercalation capacity which is about twice that of graphite, and is considered to be the most promising new material. However, its cycle performance is poor, and the volume changes greatly during the charging and discharging process, which may easily cause the "powdering" or "agglomeration" of the electrode, resulting in the decay of the specific capacity of the material and the decline in cycle performance (references: W. M. Zhang, J. S. Hu, Y. Q. Guo, et a1. Tin-nanoparticles encapsulated in elastic hollow carbon spheres for high-performance anode material in lithium-ion batteries.Adv. Mater .2008 ,20 , 1160-1164.). IfSnO2 is to be widely used in Li-ion battery anode materials, it is necessary to alleviate the "volume effect" ofSnO2 electrodes.
为了改善SnO2的循环性能,国内外研究人员做了大量的尝试。一种方法是对SnO2进行包覆改性,即将SnO2引入到某些不易发生体积变化的主体框架材料中,使活性中心小颗粒相互之间处于隔离状态,限制其在充放电过程中的体积变化。另一种方法就是减小材料尺寸,当SnO2颗粒为纳米级时,颗粒空隙间也为纳米尺寸,可为锂离子的嵌入提供了很好的纳米通道和嵌锂位置,具有大的嵌锂容量和良好的嵌锂性能,另外纳米化还可以更有效的减缓在充放电过程中带来的体积变化和团聚粉化问题,达到改善循环性能的目的(参考文献:Y. D. Wang, I. Ojerdj, B. Smarsly, et a1. Antimony-Doped SnO2 Nanopowders with High Crystallinity for Lithium-Ion Battery Electrode. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3202-3209.)。各种具有纳米尺寸的SnO2,例如纳米线(参考文献:M. S. Park, G. X. Wang, Y. M. Kang, et a1. Preparation and electrochemical properties of SnO2 nanowires for application in lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 750-753.),纳米颗粒(参考文献:A. Sivashanmugam, T. Premkumar, S. Gopukumar, et a1. Synthesis and electrochemical behaviour of tin oxide for USe as anode in lithium rechargeable batteries, J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 35, 1045-1050.)和纳米管(参考文献:Y. Wang, J. Y. Lee, H. C. Zeng, Polycrystalline SnO2 nanotubes prepared via infiltration casting of nanocrystallites and their electrochemical application. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3899-3903.)等作为锂离子电池材料表现出了很好的循环性能。但到目前为止,还没有文献和专利报道采用本文方法合成高分散、粒径均一的SnO2C空心纳米球。 In order to improve the cycle performance ofSnO2 , researchers at home and abroad have made a lot of attempts. One method is to coat and modify SnO2 , that is, to introduce SnO2 into some main frame materials that are not prone to volume changes, so that the small particles of the active center are in a state of isolation from each other, and limit their separation during charge and discharge. Volume change. Another method is to reduce the size of the material. When the SnO2 particles are nanometer-sized, the interstices between the particles are also nanometer-sized, which can provide good nano-channels and lithium-intercalation sites for the insertion of lithium ions, and have a large lithium-intercalation capacity. Capacity and good lithium intercalation performance, in addition, nanometerization can more effectively slow down the volume change and agglomeration and pulverization problems brought about during the charge and discharge process, and achieve the purpose of improving cycle performance (references: Y. D. Wang, I. Ojerdj, B. Smarsly, et a1. Antimony-Doped SnO2 Nanopowders with High Crystallinity for Lithium-Ion Battery Electrode.Chem. Mater .2009 ,21 , 3202-3209.). Various SnO2 nanowires with nanometer dimensions, such as nanowires (References: M. S. Park, G. X. Wang, Y. M. Kang, et a1. Preparation and electrochemical properties of SnO2 nanowires for application in lithium-ion batteries.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed .2007 ,46 , 750-753.), Nanoparticles (References: A. Sivashanmugam, T. Premkumar, S. Gopukumar, et a1. Synthesis and electrochemical behavior of tin oxide for USe as anode in lithium rechargeable batteries,J . Appl. Electrochem .2005 ,35 , 1045-1050.) and nanotubes (references: Y. Wang, J. Y. Lee, H. C. Zeng, Polycrystalline SnO2 nanotubes prepared via infiltration casting of nanocrystallites and their electrochemical application.Chem. Mater .2005 ,17 , 3899-3903.) etc. have shown good cycle performance as lithium-ion battery materials. But so far, there is no literature or patent report to synthesize SnO2 C hollow nanospheres with high dispersion and uniform particle size by using the method in this paper.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种SnO2C空心纳米球的制备方法及其在锂离子电池中的应用,使用该方法制备的SnO2C复合锂离子电池负极材料具有分散性好、比表面积大、循环性能好、使用寿命长等特点。 The object of the present invention is to provide a preparation method of SnO2 C hollow nanospheres and its application in lithium-ion batteries. The SnO2 C composite lithium-ion battery negative electrode material prepared by the method has good dispersibility, large specific surface area, Good cycle performance and long service life.
本发明SnO2C空心纳米球的制备方法包括如下步骤: The preparation method of SnO2 C hollow nanospheres of the present invention comprises the following steps:
(1) 在100 mL烧瓶中依次加入60 ~ 80 mL乙醇,3 ~ 4 mL氨水和1 ~ 1.3 mL水,搅拌混合均匀,然后缓慢滴加2.0 ~ 3.0 mL正硅酸乙酯(TEOS),20 oC恒温搅拌6 ~ 8 h。(1) Add 60-80 mL of ethanol, 3-4 mL of ammonia water and 1-1.3 mL of water in sequence in a 100-mL flask, stir and mix evenly, then slowly add 2.0-3.0 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) dropwise, 20 Stir at constant temperatureat o C for 6-8 h.
(2) 将步骤(1)得到的溶液进行离心分离(7000 rpm,8 ~ 10 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇交替洗涤数次,所得沉淀在烘箱中50 ~ 80 oC烘干8 ~ 10 h,得到干燥二氧化硅纳米粒子。 (2) Centrifuge the solution obtained in step (1) (7000 rpm, 8 ~ 10 min), and then alternately wash several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol respectively, and dry the obtained precipitate in an oven at 50 ~ 80o C Dry for 8 to 10 h to obtain dry silica nanoparticles.
(3) 将1.0 ~ 1.5 mg步骤(2)得到的二氧化硅纳米粒子分散在6 ~ 7 mL 水和乙醇的混合溶液中(水和乙醇体积比为1:1),然后分别将0.2 ~ 0.3 mL 0.2 M尿素(CH4N2O)和0.4 ~ 0.5 mL 0.08 M锡酸钠(Na2SnO33H2O)添加到反应液中,磁力搅拌0.5 ~1.0 h。 (3) Disperse 1.0 ~ 1.5 mg of silica nanoparticles obtained in step (2) in 6 ~ 7 mL of a mixed solution of water and ethanol (the volume ratio of water and ethanol is 1:1), and then 0.2 ~ 0.3 Add mL 0.2 M urea (CH4 N2 O) and 0.4 ~ 0.5 mL 0.08 M sodium stannate (Na2 SnO3 3H2 O) to the reaction solution, and stir magnetically for 0.5 ~ 1.0 h.
(4) 将步骤(3)得到的溶液转移到15 mL水热反应釜中,于170 oC烘箱中反应1 ~ 2 h。自然冷却至室温,离心分离(7000 rpm,8 ~ 10 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇交替洗涤数次,所得沉淀在烘箱中50 ~ 80 oC烘干8 ~ 10 h,既得到空心SnO2纳米粒子。 (4) Transfer the solution obtained in step (3) to a 15 mL hydrothermal reactor, and react in an oven at 170o C for 1 to 2 h. Naturally cooled to room temperature, centrifuged (7000 rpm, 8-10 min), and then alternately washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol, and the obtained precipitate was dried in an oven at 50-80o C for 8-10 h. HollowSnO2 nanoparticles were obtained.
(5) 将4 ~ 6 mg步骤(4)得到的空心SnO2纳米粒子和8 ~ 12 mL去离子水加入到100 mL烧瓶中,超声分散10 ~ 20 min。 (5) Add 4 ~ 6 mg of the hollowSnO2 nanoparticles obtained in step (4) and 8 ~ 12 mL of deionized water into a 100 mL flask, and ultrasonically disperse for 10 ~ 20 min.
(6) 将60 ~ 100 μL 0.2 g/mL聚丙烯酸水溶液和90 ~ 150 μL 2 mol/L的氨水先后加入步骤(5)得到的溶液中,超声分散10 ~ 30 min。 (6) Add 60 ~ 100 μL 0.2 g/mL polyacrylic acid aqueous solution and 90 ~ 150 μL 2 mol/L ammonia water to the solution obtained in step (5) successively, and ultrasonically disperse for 10 ~ 30 min. the
(7) 在磁力搅拌下将90 ~ 120 mL异丙醇缓慢滴加入步骤(6)得到的溶液中,滴加完毕后进行离心分离(7000 rpm,5 ~ 8 min),所得沉淀在50 ~ 80 oC烘箱中烘干12 ~ 20 h。 (7) Slowly add 90 ~ 120 mL of isopropanol dropwise to the solution obtained in step (6) under magnetic stirring. After the dropwise addition, perform centrifugation (7000 rpm, 5 ~ 8 min).o C drying oven for 12 ~ 20 h.
(8) 将步骤(7)得到的固体置于管式炉中400 ~ 500 oC煅烧4 ~ 5 h,得到SnO2C空心纳米球。 (8) The solid obtained in step (7) was calcined in a tube furnace at 400-500o C for 4-5 h to obtain SnO2 C hollow nanospheres.
本发明具有如下优点:The present invention has the following advantages:
1. 本发明合成方法简单,采用一步法合成高分散、粒径均一的空心SnO2纳米球。在此反应过程中,二氧化锡的生成与二氧化硅模板的刻蚀同步进行,既缩短了反应步骤又保证二氧化硅可以在高温高压下被反应生成的氨水完全除去。1. The synthesis method of the present invention is simple, adopts a one-step method to synthesize highly dispersed, uniform particle size hollowSnO2 nanospheres. During this reaction process, the formation of tin dioxide is carried out simultaneously with the etching of the silicon dioxide template, which not only shortens the reaction steps but also ensures that the silicon dioxide can be completely removed by the ammonia water generated by the reaction under high temperature and high pressure.
2. 本发明得到的核壳结构SnO2C空心纳米球粒径均匀、比表面积大、分散性好,且结构稳定。 2. The SnO2 C hollow nanospheres with core-shell structure obtained by the present invention have uniform particle size, large specific surface area, good dispersion and stable structure.
3. 使用本发明方法制备的空心SnO2C锂离子电池负极材料具有容量大、循环性能好、使用寿命长等特点。首先碳包覆增强了活性物质(SnO2)的导电性,且有碳壳的保护可以有效的减缓在充放电过程中带来的体积变化和团聚粉化问题。其次,SnO2C复合纳米球具有空心结构电解液能进入到空心结构内部,使活性材料的内外两侧都能与电解液充分接触,因此能有效增大电化学反应的活性界面;第三,空心结构还可吸收因体积变化产生的内应力,能有效抑制材料粉化。这些因素决定了该核壳结构SnO2C空心纳米球是具有广阔应用前景的锂离子电池阳极材料。 3. The hollow SnO2 C lithium ion battery anode material prepared by the method of the present invention has the characteristics of large capacity, good cycle performance, and long service life. First of all, the carbon coating enhances the conductivity of the active material (SnO2 ), and the protection of the carbon shell can effectively slow down the volume change and agglomeration and pulverization problems caused by the charging and discharging process. Secondly, the SnO2 C composite nanosphere has a hollow structure, and the electrolyte can enter the hollow structure, so that the inner and outer sides of the active material can fully contact with the electrolyte, so the active interface of the electrochemical reaction can be effectively increased; third, The hollow structure can also absorb the internal stress caused by the volume change, which can effectively suppress the pulverization of the material. These factors determine that the core-shell structure SnO2 C hollow nanosphere is a lithium-ion battery anode material with broad application prospects.
附图说明Description of drawings
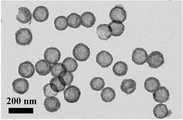
图1、为本发明制备得到的空心二氧化锡纳米球的透射电镜图; Fig. 1, is the transmission electron microscope figure of the hollow tin dioxide nanosphere that the present invention prepares;
图2、为本发明制备得到的SnO2C空心纳米球的透射电镜图;Fig. 2 is a transmission electron microscope image of SnO2 C hollow nanospheres prepared in the present invention;
图3、为本发明制备得到的SnO2C空心纳米球的扫描电镜图;Fig. 3 is a scanning electron micrograph of SnO2 C hollow nanospheres prepared by the present invention;
图4、为本发明制备得到的SnO2C空心纳米球做负极材料的锂离子电池的充放电循环曲线。Fig. 4 is a charge-discharge cycle curve of a lithium-ion battery in which SnO2 C hollow nanospheres prepared by the present invention are used as negative electrode materials.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施例进一步阐述本发明,实施例仅用于说明本发明而不用于限制本发明的保护范围。 The present invention is further described below in conjunction with specific examples, and the examples are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the protection scope of the present invention. the
具体实施例specific embodiment
实施例1: Example 1:
将60 mL乙醇,3 mL氨水和1 mL水先后加入100 mL烧瓶中,搅拌混合均匀,然后缓慢滴加2.3 mL正硅酸乙酯(TEOS),20 oC恒温搅拌6 h。将所得溶液离心分离(7000 rpm,8 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇反复洗涤数次,随后在50 oC下烘干10 h。称取1.0 mg上述烘干二氧化硅纳米粒子分散在3 mL水和3 mL乙醇的混合溶液中,然后分别将0.24 mL 0.2 M尿素(CH4N2O)和0.45 mL 0.08 M 锡酸钠(Na2SnO3H2O)添加到上述反应液中,搅拌0.5 h后将混合物转移到15 mL水热反应釜中。置烘箱中170 oC条件下反应1 h,自然冷却至室温,离心分离(7000 rpm,8 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇反复洗涤数次,所得固体50 oC烘干10 h,得干燥SnO2空心纳米球。再将5 mg已制备好的SnO2和10 mL去离子水加入100 mL烧瓶中,超声分散10 min后,分别加入60 μL 0.2 g/mL PAA水溶液和90 μL 2 mol/L的氨水,超声分散20 min。随后在磁力搅拌下将90 mL 异丙醇缓慢滴入反应液中,滴加完毕,离心分离(7000 rpm,8 min),所得产品在50 oC烘干15 h。最后将产品放在管式炉400 oC,空气氛围中煅烧4 h,得到SnO2C空心纳米球。Add 60 mL of ethanol, 3 mL of ammonia water and 1 mL of water into a 100 mL flask successively, stir and mix evenly, then slowly add 2.3 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) dropwise, and stir at 20o C for 6 h. The obtained solution was centrifuged (7000 rpm, 8 min), washed repeatedly with deionized water and absolute ethanol several times, and then dried at 50o C for 10 h. Weigh 1.0 mg of the above oven-dried silica nanoparticles and disperse them in a mixed solution of 3 mL of water and 3 mL of ethanol, then respectively add 0.24 mL of 0.2 M urea (CH4 N2 O) and 0.45 mL of 0.08 M sodium stannate ( Na2 SnO3 H2 O) was added to the above reaction solution, and after stirring for 0.5 h, the mixture was transferred to a 15 mL hydrothermal reaction kettle. React in an oven at 170o C for 1 h, cool naturally to room temperature, centrifuge (7000 rpm, 8 min), and then wash repeatedly with deionized water and absolute ethanol several times, and dry the obtained solid at 50o C for 10 h, DrySnO2 hollow nanospheres. Add 5 mg of prepared SnO2 and 10 mL of deionized water into a 100 mL flask, ultrasonically disperse for 10 min, add 60 μL of 0.2 g/mL PAA aqueous solution and 90 μL of 2 mol/L ammonia water, and ultrasonically disperse 20 min. Then, 90 mL of isopropanol was slowly dropped into the reaction solution under magnetic stirring. After the addition was completed, centrifuged (7000 rpm, 8 min), the obtained product was dried at 50o C for 15 h. Finally, the product was calcined in a tube furnace at 400o C for 4 h in an air atmosphere to obtain SnO2 C hollow nanospheres.
实施例2:Example 2:
将80 mL乙醇,4 mL氨水和1.3 mL水先后加入100 mL烧瓶中,搅拌混合均匀,然后缓慢滴加3.0 mL正硅酸乙酯(TEOS),20 oC恒温搅拌8 h。将所得溶液离心分离(7000 rpm,10 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇反复洗涤数次,随后在60 oC下烘干10 h。称取1.5 mg上述烘干二氧化硅纳米粒子分散在3.5 mL水和3.5 mL乙醇的混合溶液中,然后分别将0.3 mL 0.2 M尿素(CH4N2O)和0.5 mL 0.08 M 锡酸钠(Na2SnO3H2O)添加到上述反应液中,搅拌1 h后将混合物转移到15 mL水热反应釜中。置烘箱中170 oC条件下反应2 h,自然冷却至室温,离心分离(7000 rpm,10 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇反复洗涤数次,所得固体70 oC烘干8 h,得干燥SnO2空心纳米球。再将6 mg已制备好的SnO2和12 mL去离子水加入100 mL烧瓶中,超声分散20 min后,分别加入100 μL 0.2 g/mL PAA水溶液和150 μL 2 mol/L的氨水,超声分散30 min。随后在磁力搅拌下将120 mL 异丙醇缓慢滴入反应液中,滴加完毕,离心分离(7000 rpm,8 min),所得产品在80 oC烘干15 h。最后将产品放在管式炉450 oC,空气氛围中煅烧4 h,得到SnO2C空心纳米球。Add 80 mL of ethanol, 4 mL of ammonia water and 1.3 mL of water into a 100 mL flask successively, stir and mix evenly, then slowly add 3.0 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) dropwise, and stir at 20o C for 8 h. The obtained solution was centrifuged (7000 rpm, 10 min), washed repeatedly with deionized water and absolute ethanol several times, and then dried at 60o C for 10 h. Weigh 1.5 mg of the above oven-dried silica nanoparticles and disperse them in a mixed solution of 3.5 mL of water and 3.5 mL of ethanol, then add 0.3 mL of 0.2 M urea (CH4 N2 O) and 0.5 mL of 0.08 M sodium stannate ( Na2 SnO3 H2 O) was added to the above reaction solution, and after stirring for 1 h, the mixture was transferred to a 15 mL hydrothermal reaction kettle. React in an oven at 170o C for 2 h, cool naturally to room temperature, centrifuge (7000 rpm, 10 min), wash repeatedly with deionized water and absolute ethanol several times, and dry the obtained solid at 70o C for 8 h, DrySnO2 hollow nanospheres. Add 6 mg of prepared SnO2 and 12 mL of deionized water into a 100 mL flask, ultrasonically disperse for 20 min, add 100 μL of 0.2 g/mL PAA aqueous solution and 150 μL of 2 mol/L ammonia water, and ultrasonically disperse 30 min. Then, 120 mL of isopropanol was slowly dropped into the reaction liquid under magnetic stirring. After the dropwise addition, centrifuged (7000 rpm, 8 min), the obtained product was dried at 80o C for 15 h. Finally, the product was calcined in a tube furnace at 450o C for 4 h in an air atmosphere to obtain SnO2 C hollow nanospheres.
实施例3:Example 3:
将70 mL乙醇,3.5 mL氨水和1.1 mL水先后加入100 mL烧瓶中,搅拌混合均匀,然后缓慢滴加2.0 mL正硅酸乙酯(TEOS),20 oC恒温搅拌7 h。将所得溶液离心分离(7000 rpm,9 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇反复洗涤数次,随后在70 oC下烘干8 h。称取1.2 mg上述烘干二氧化硅纳米粒子分散在3.2 mL水和3.2 mL乙醇的混合溶液中,然后分别将0.22 mL 0.2 M尿素(CH4N2O)和0.4 mL 0.08 M 锡酸钠(Na2SnO3H2O)添加到上述反应液中,搅拌0.6 h后将混合物转移到15 mL水热反应釜中。置烘箱中170 oC条件下反应1.5 h,自然冷却至室温,离心分离(7000 rpm,9 min),再分别用去离子水和无水乙醇反复洗涤数次,所得固体60 oC烘干9 h,得干燥SnO2空心纳米球。再将4 mg已制备好的SnO2和8 mL去离子水加入100 mL烧瓶中,超声分散15 min后,分别加入80 μL 0.2 g/mL PAA水溶液和120 μL 2 mol/L的氨水,超声分散20 min。随后在磁力搅拌下将100 mL 异丙醇缓慢滴入反应液中,滴加完毕,离心分离(7000 rpm,5 min),所得产品在70 oC烘干20 h。最后将产品放在管式炉500 oC,空气氛围中煅烧3 h,得到SnO2C空心纳米球。Add 70 mL of ethanol, 3.5 mL of ammonia water and 1.1 mL of water into a 100 mL flask successively, stir and mix evenly, then slowly add 2.0 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) dropwise, and stir at 20o C for 7 h. The obtained solution was centrifuged (7000 rpm, 9 min), washed repeatedly with deionized water and absolute ethanol several times, and then dried at 70o C for 8 h. Weigh 1.2 mg of the above oven-dried silica nanoparticles and disperse them in a mixed solution of 3.2 mL of water and 3.2 mL of ethanol, then respectively add 0.22 mL of 0.2 M urea (CH4 N2 O) and 0.4 mL of 0.08 M sodium stannate ( Na2 SnO3 H2 O) was added to the above reaction solution, and after stirring for 0.6 h, the mixture was transferred to a 15 mL hydrothermal reaction kettle. React in an oven at 170o C for 1.5 h, naturally cool to room temperature, centrifuge (7000 rpm, 9 min), and then wash repeatedly with deionized water and absolute ethanol several times, and dry the obtained solid at 60o C for 9 h, DrySnO2 hollow nanospheres. Add 4 mg of prepared SnO2 and 8 mL of deionized water into a 100 mL flask, ultrasonically disperse for 15 min, add 80 μL of 0.2 g/mL PAA aqueous solution and 120 μL of 2 mol/L ammonia water, and ultrasonically disperse 20 min. Then, 100 mL of isopropanol was slowly dropped into the reaction solution under magnetic stirring. After the dropwise addition, centrifuged (7000 rpm, 5 min), the obtained product was dried at 70o C for 20 h. Finally, the product was calcined in a tube furnace at 500o C for 3 h in an air atmosphere to obtain SnO2 C hollow nanospheres.
制备出的SnO2C空心纳米球用于锂离子电池。电池组装过程中以合成的核壳结构SnO2C空心纳米球为活性物质,乙炔黑为导电剂,聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)为粘结剂,氮甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)为溶剂。具体过程为:将活性物质、导电剂、粘结剂按85:10:5的重量比准确称量,然后放入玛瑙研钵中充分混合、研磨均匀,然后加入几滴NMP,继续研磨至均匀浆状。将浆料均匀涂于已准确称量过的铜箔上。然后在真空干燥箱中120 oC真空干燥12 h至恒重,30 MPa下压片,再继续干燥2 h,降到室温后取出称重。 The prepared SnO2 C hollow nanospheres are used in lithium ion batteries. During the battery assembly process, the synthesized SnO2 C hollow nanospheres with core-shell structure are used as the active material, acetylene black is used as the conductive agent, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is used as the binder, and nitrogen methylpyrrolidone (NMP) is used as the solvent. The specific process is: accurately weigh the active material, conductive agent, and binder according to the weight ratio of 85:10:5, then put them into an agate mortar and mix thoroughly, grind evenly, then add a few drops of NMP, and continue grinding until uniform Slurry. Spread the slurry evenly on the accurately weighed copper foil. Then vacuum-dry in a vacuum oven at 120o C for 12 h to constant weight, press into tablets at 30 MPa, continue to dry for 2 h, take it out and weigh it after cooling down to room temperature.
电池的组装在无水无氧、充有氩气的手套箱中完成。将烘干的极片、电池壳和隔膜放入手套箱。以金属锂片为对电极,Celgard240聚丙烯多孔膜做隔膜,1.0 mol L-1 LiPF6 的EC-DMC(体积比1:1)溶液做电解液,组装成扣式CR2032模拟电池,进行充放电测试。 The assembly of the cells was done in an anhydrous, oxygen-free, argon-filled glove box. Put the dried pole piece, battery case and separator into the glove box. Using metal lithium sheet as counter electrode, Celgard240 polypropylene porous membrane as diaphragm, 1.0 mol L-1 LiPF6 EC-DMC (volume ratio 1:1) solution as electrolyte, assembled into a button-type CR2032 simulated battery for charge and discharge test.
实验表明所制备的SnO2C空心纳米球做锂离子电池负极材料具有很高的比容量和较好的循环性能。如图4所示,在电流密度为105 mA g-1条件下恒流充放电,其首次放电容量高达1121 mAh g-1,在循环100次后放电比容量仍有808 mAh g-l。 Experiments show that the prepared SnO2 C hollow nanospheres have high specific capacity and good cycle performance as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. As shown in Figure 4, the constant current charge and discharge under the condition of current density of 105 mA g-1 , the initial discharge capacity is as high as 1121 mAh g-1 , and the discharge specific capacity is still 808 mAh g-l after 100 cycles.
Claims (1)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310100899.XACN103193263B (en) | 2013-03-27 | 2013-03-27 | Preparation method of SnO2C hollow nanospheres and its application in lithium-ion batteries |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310100899.XACN103193263B (en) | 2013-03-27 | 2013-03-27 | Preparation method of SnO2C hollow nanospheres and its application in lithium-ion batteries |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103193263A CN103193263A (en) | 2013-07-10 |
| CN103193263Btrue CN103193263B (en) | 2014-07-09 |
Family
ID=48716109
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201310100899.XAExpired - Fee RelatedCN103193263B (en) | 2013-03-27 | 2013-03-27 | Preparation method of SnO2C hollow nanospheres and its application in lithium-ion batteries |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103193263B (en) |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103682272B (en)* | 2013-12-11 | 2016-02-10 | 上海交通大学 | A kind of lithium ion battery cathode material and its preparation method |
| CN104979536B (en)* | 2014-04-10 | 2018-05-29 | 宁德新能源科技有限公司 | Lithium ion battery and its anode strip, the preparation method of active material of positive electrode |
| CN104876259A (en)* | 2015-05-07 | 2015-09-02 | 浙江大学 | Preparation method of open tin dioxide hollow spheres |
| CN105140471B (en)* | 2015-07-23 | 2017-09-12 | 江苏新光环保工程有限公司 | A kind of MoS2/ C composite cathode material of lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof |
| CN106558685B (en)* | 2015-09-30 | 2019-11-22 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | Porous core-shell structure negative electrode material and its preparation method and battery |
| CN105823800B (en)* | 2016-03-23 | 2018-10-12 | 云南大学 | A kind of sensitive material of detection methanol gas |
| CN106025225A (en)* | 2016-07-12 | 2016-10-12 | 天津大学 | Preparation method and application of polymer blend-coated hollow tin dioxide nano-microspheres |
| CN108807935B (en)* | 2016-11-23 | 2021-03-23 | 清华大学 | Silicon-based tin-based composite particles for lithium ion battery, preparation method thereof, negative electrode comprising the same, and lithium ion battery |
| CN107369822B (en)* | 2017-07-19 | 2019-10-29 | 广东工业大学 | A kind of tin oxide as negative electrode of lithium ion battery/C nano hollow ball material and preparation method thereof |
| CN108807912B (en)* | 2018-06-13 | 2021-02-19 | 陕西科技大学 | C @ SnOx(x=0,1,2)Preparation and application of @ C mesoporous nano hollow sphere structure |
| CN109748283A (en)* | 2019-03-07 | 2019-05-14 | 北京科技大学 | A kind of hollow SiOx@C cubic composite negative electrode material for lithium ion battery and preparation method |
| CN110504425A (en)* | 2019-08-16 | 2019-11-26 | 安徽师范大学 | A kind of egg yolk shell structure sulfur particle/polypyrrole conductive hydrogel composite material and its preparation method, lithium-sulfur battery positive electrode and battery |
| CN110707285A (en)* | 2019-08-29 | 2020-01-17 | 东莞力朗电池科技有限公司 | SnO (stannic oxide)2Negative electrode material lithium battery and positive plate thereof |
| CN112687858B (en)* | 2020-12-25 | 2023-04-07 | 武汉工程大学 | An iron-doped tin oxide@carbon double-shell hollow sphere and its preparation method |
| CN112811463B (en)* | 2021-01-28 | 2022-10-18 | 沈阳化工大学 | Preparation method of tin dioxide hollow microspheres with controllable shell thickness |
| CN113135588A (en)* | 2021-04-19 | 2021-07-20 | 合肥工业大学 | Carbon-coated SnO2Preparation method of hollow nanosphere |
| CN113745491B (en)* | 2021-08-10 | 2022-11-29 | 扬州大学 | SnO with double-wall hollow ball structure 2 @ C material and preparation method thereof |
| CN115881935B (en)* | 2022-11-24 | 2025-06-06 | 吉林工程技术师范学院 | Preparation method and application of carbon fiber/SnO2 hollow nanosphere composite material |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100386905C (en)* | 2006-05-26 | 2008-05-07 | 清华大学 | Preparation method of activated carbon microsphere inclusion mixed metal composite negative electrode material |
| JP2011253620A (en)* | 2009-09-30 | 2011-12-15 | K & W Ltd | Negative electrode active material, its manufacturing method, and lithium ion secondary battery using negative electrode active material |
| JP5676907B2 (en)* | 2010-02-17 | 2015-02-25 | 石原産業株式会社 | Method for treating lithium titanate particles |
| CN102054973A (en)* | 2010-11-17 | 2011-05-11 | 安徽师范大学 | Preparation method and application of a multipurpose SnO2@C composite nanomaterial |
- 2013
- 2013-03-27CNCN201310100899.XApatent/CN103193263B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103193263A (en) | 2013-07-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103193263B (en) | Preparation method of SnO2C hollow nanospheres and its application in lithium-ion batteries | |
| CN102790217B (en) | Carbon cladded ferriferrous oxide negative electrode material of lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof | |
| CN103367719B (en) | Preparation method of egg yolk-shell structure tin dioxide-nitrogen doped carbon material | |
| CN104466142B (en) | A kind of silicon/silica carbon/composite cathode material of silicon/carbon/graphite for lithium ion battery | |
| CN106784714A (en) | A kind of silicon-based composite anode material for Li-ion battery and preparation method thereof | |
| CN107256961B (en) | A preparation method and application of lithium titanate hierarchical structure microspheres | |
| CN103227324A (en) | Preparation method of iron oxide cathode material for lithium ion battery | |
| CN104852028A (en) | Lithium titanate/graphene composite cathode material for lithium ion battery | |
| CN101593825B (en) | Negative pole made of nanometer antimony/graphite nanosheet composite material of lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof | |
| CN112174220B (en) | Titanium dioxide coated cobalt tetroxide honeycomb nanowire material and its preparation and application | |
| CN103972497A (en) | Lithium-ion battery Co2SnO4/C nanocomposite negative electrode material and its preparation and application | |
| CN110120516A (en) | A kind of preparation method of antimony/redox graphene composite material | |
| CN105514375B (en) | A kind of carbon coating Na0.55Mn2O4·1.5H2O nanocomposite and preparation method thereof | |
| CN108281625A (en) | A kind of nanometer of compound nucleocapsid of stannic disulfide/carbosphere and preparation method thereof | |
| CN107317011A (en) | A kind of preparation method of the ordered porous carbon coating silicon nano composite material of N doping | |
| CN105702958A (en) | Preparation method and application of a tin dioxide (SnO2) quantum dot solution and its composite material | |
| CN106099066B (en) | A kind of germanium dioxide/graphene composite material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106025180A (en) | Core-shell structure lithium ion battery negative electrode material GeO2/C and its preparation method | |
| CN114976211A (en) | A kind of preparation method of sodium ion soft pack battery | |
| CN103682348A (en) | Preparation method of carbon nano tube filled/coated stannic oxide composite negative material | |
| CN103094572B (en) | Lithium vanadate anode material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106532108A (en) | Porous-structured lithium iron phosphate/carbon nanotube composite microsphere and preparation method therefor | |
| CN103208624A (en) | Preparation method of monodisperse core-shell structure Fe3O4@C nanocomposite lithium battery anode material | |
| CN104157856B (en) | Core-shell LaFeO 3 @ C lithium battery cathode material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106784722B (en) | A kind of lithium titanate/titanium dioxide composite electrode material and preparation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20140709 Termination date:20150327 | |
| EXPY | Termination of patent right or utility model |