CN103152697A - Method for realizing automatic floor positioning by using intelligent mobile phone Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) function - Google Patents
Method for realizing automatic floor positioning by using intelligent mobile phone Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) functionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103152697A CN103152697ACN2013100955198ACN201310095519ACN103152697ACN 103152697 ACN103152697 ACN 103152697ACN 2013100955198 ACN2013100955198 ACN 2013100955198ACN 201310095519 ACN201310095519 ACN 201310095519ACN 103152697 ACN103152697 ACN 103152697A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- user
- building
- floor
- signals
- elevator
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Navigation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinesethe
技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种新的定位技术,具体是一种智能手机Wi-Fi功能自动定位用户在建筑物中的哪一层楼的方法。 The invention relates to a new positioning technology, in particular to a method for automatically locating which floor a user is in a building with the Wi-Fi function of a smart phone. the
背景技术Background technique
在当今飞速发展的基于位置的应用领域,利用智能手机进行定位占据着很重要的地位。目前,绝大多数的定位技术都需要一定的基础设施的支持,如蜂窝网络,Wi-Fi无线网络和全球定位系统(GPS)。而这些技术各有各的优缺点,在精度、使用场景上都有限制。在定位技术领域中,如何定位一个用户在一栋建筑物中的哪一层,是一个很热门的问题,因为如果知道了此类信息,就可以据此给用户提供相关的服务,如广告,指路,以及救援搜寻。 In today's rapidly developing field of location-based applications, positioning with a smartphone plays an important role. At present, most positioning technologies require the support of certain infrastructure, such as cellular network, Wi-Fi wireless network and Global Positioning System (GPS). Each of these technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages, and has limitations in accuracy and usage scenarios. In the field of positioning technology, how to locate which floor a user is in a building is a very hot issue, because if such information is known, relevant services can be provided to the user, such as advertisements, Guidance, and rescue search. the
目前,公知的定位技术有如下几类: At present, the well-known positioning technologies include the following categories:
第一类:基于GPS、GSM、WI-FI等信号The first category: based on GPS, GSM, WI-FI and other signals
GPS是比较通用的定位技术,他通过卫星定位手机在地球上的经度纬度及高度信息,精度能够达到5米以内,但是这是在室外的情况,在室内情况由于受到建筑物干扰,精度降低很多,无法用来定位用户处于哪一层上。GPS is a relatively common positioning technology. It uses satellites to locate the longitude, latitude, and altitude information of mobile phones on the earth. The accuracy can reach within 5 meters, but this is in the outdoor situation. In the indoor situation, due to the interference of buildings, the accuracy is much lower. , cannot be used to locate which layer the user is on.
基于GSM的定位技术不管在室内室外的情况,精度都很低,不能定位用户的楼层; The positioning technology based on GSM has low accuracy regardless of indoor and outdoor situations, and cannot locate the user's floor;
基于WI-FI的定位技术主要是这样工作的,用户在室内的不同位置手机检测到周围的WI-FI信号强度是不同的,如果预先在室内的每个位置都采集一下WI-FI的信号强度,得到WI-FI信号强度和对应位置的二元组,存储到一个数据库中。当一个新的用户要定位时,只要检测一下当前周围的WI-FI信号强度,然后与数据库中的做对比,找到最接近的,这个最接近的WI-FI信号所对应的位置就是该用户的当前位置。这种技术的缺点在于它需要室内有足够多的WI-FI热点,并且需要一个学习的过程,那就是预先到室内的每个位置采集一下数据,存储到数据库中,这样的工作量是巨大的;还有个缺点就是WI-FI信号强度受到周围环境的影响较大,同一地点不同时候的WI-FI信号强度可能变化,影响定位精度。The positioning technology based on WI-FI mainly works like this. The mobile phone of the user detects that the surrounding WI-FI signal strength is different in different locations indoors. If the WI-FI signal strength is collected in advance at each location in the room , get the 2-tuple of WI-FI signal strength and corresponding location, and store it in a database. When a new user wants to locate, just check the current surrounding WI-FI signal strength, and then compare it with the one in the database to find the closest one. The location corresponding to the closest WI-FI signal is the user’s current location. The disadvantage of this technology is that it requires enough WI-FI hotspots in the room, and requires a learning process, that is, to collect data from each location in the room in advance and store it in the database. This kind of workload is huge. Another disadvantage is that the WI-FI signal strength is greatly affected by the surrounding environment, and the WI-FI signal strength may change at different times in the same place, which affects the positioning accuracy.
第二类:通过手机传感器辅助定位技术 The second category: Auxiliary positioning technology through mobile phone sensors
该类技术利用用户手机的感知能力辅助定位,通过手机自带传感器获得的数据可以大致追踪用户的运动路径,如走了多少步,有没有上下楼等可以通过手机的加速度传感器获得加速度数据,再依赖行为识别技术进行识别;由于这种识别方法精度不是很好,现有的技术都是需要在建筑物内安装一些校准装置,称为校准点,校准点会发出一些特殊的信号,用户的手机可以检测到这样的信号,从而校准自己的位置;这样该技术的实现就要预先在建筑物中部署大量的校准点,耗费大量人力物力,而且后期需要较多的维护工作,并不经济实用。This type of technology uses the perception ability of the user's mobile phone to assist positioning. The data obtained by the mobile phone's built-in sensor can roughly track the user's movement path, such as how many steps have been taken, whether there are stairs, etc. Acceleration data can be obtained through the acceleration sensor of the mobile phone, and then Rely on behavior recognition technology for identification; because the accuracy of this identification method is not very good, the existing technology needs to install some calibration devices in the building, called calibration points, which will send out some special signals, and the user's mobile phone Such a signal can be detected to calibrate its own position; in this way, the realization of this technology requires the deployment of a large number of calibration points in the building in advance, which consumes a lot of manpower and material resources, and requires more maintenance work later, which is not economical and practical.
第三类:基于RFID的定位技术 The third category: RFID-based positioning technology
基于RFID的定位技术原理很简单,利用读卡器和标签,当它们彼此之间相互接近的时候,读卡器可以读取到标签,如果这两者中有一方位置是已知的,当读卡动作发生时另一方的位置就知道了。 通常有两种方式:1、标签固定,读卡器移动;首先大量标签被部署在建筑物的不同位置,用户携带者便携式的读卡器,由于标签的位置是已知的,所以当用户读到标签时,标签的位置就是用户当前的位置。 2、读卡器固定,标签移动,与上一种方法相反,用户手机上贴有标签,而建筑物内部署了许多读卡器,一旦读卡器读到用户的标签,那用户的位置就在该读卡器附近,从而实现了定位。The principle of RFID-based positioning technology is very simple. Using a card reader and a tag, when they are close to each other, the card reader can read the tag. If one of the two positions is known, when the reader The position of the other party is known when the card action occurs. There are usually two ways: 1. The tags are fixed, and the card readers move; first, a large number of tags are deployed in different locations of the building, and the user carries a portable card reader. Since the location of the tags is known, when the user reads When a tab is reached, the tab's location is the user's current location. 2. The card reader is fixed and the label moves. Contrary to the previous method, the user's mobile phone has a label, and many card readers are deployed in the building. Once the card reader reads the user's label, the user's location will be determined. In the vicinity of the card reader, positioning is thus achieved.
基于RFID的定位技术精度高,但是有很多缺点,部署大量的读卡器和标签很耗时耗力,且非常昂贵。用户手机使用RFID定位技术必须贴着标签,因为一般手机不具有读卡器的功能,由于读卡器成本高,在建筑物部署到一定密度的读卡器很不经济。 RFID-based positioning technology has high accuracy, but it has many disadvantages. Deploying a large number of readers and tags is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and very expensive. The user's mobile phone must be attached with a label when using RFID positioning technology, because the general mobile phone does not have the function of a card reader. Due to the high cost of the card reader, it is not economical to deploy a certain density of card readers in buildings. the
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明所要解决的技术问题是利用智能手机本身加速度感知功能和Wi-Fi功能功能进行用户的楼层定位,这种方法不需要在建筑物内部署任何软硬件设施,就能够提供高精度的定位服务。 The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to use the smart phone's own acceleration sensing function and Wi-Fi function to locate the user's floor. This method can provide high-precision positioning services without deploying any hardware and software facilities in the building. . the
本发明所述的利用智能手机Wi-Fi功能实现楼层自动定位的方法,该智能手机具有加速度传感器,其包括以下步骤: The method for realizing floor automatic positioning utilizing the smart phone Wi-Fi function of the present invention, the smart phone has an acceleration sensor, and it comprises the following steps:
1)在同一建筑物内,利用加速度传感器收集的加速度数据识别某用户乘坐电梯的行为,同时收集该用户上下电梯时电梯口的Wi-Fi信息,形成一组对应楼层的Wi-Fi信号;1) In the same building, use the acceleration data collected by the acceleration sensor to identify the behavior of a user taking the elevator, and at the same time collect the Wi-Fi information at the elevator entrance when the user gets on and off the elevator to form a set of Wi-Fi signals for the corresponding floors;
2)通过步骤1)收集该建筑物内所有手机用户的Wi-Fi信息,利用聚类的方法对这些信号进行聚类,这样,聚类后获得的类的个数就是这栋楼的层数,然后根据Wi-Fi信号的高低关系对聚类的结果进行排序,排序之后就能够得到某个楼层与类之间的一一映射关系;将所有用户的Wi-Fi轨迹融合起来,获得整个建筑物的Wi-Fi地图;2) Through step 1), collect the Wi-Fi information of all mobile phone users in the building, and use the clustering method to cluster these signals, so that the number of clusters obtained after clustering is the number of floors of the building , and then sort the clustering results according to the high-low relationship of the Wi-Fi signal. After sorting, you can get the one-to-one mapping relationship between a certain floor and the class; combine the Wi-Fi trajectories of all users to get the whole building Wi-Fi map of objects;
3)将Wi-Fi地图建立起来存储在云端服务器中,当用户在建筑物内运动时,定位系统收集几个周围Wi-Fi信息的样本,上传到服务器中,服务器通过与Wi-Fi地图的对比匹配,即可获的用户当前的楼层位置。3) The Wi-Fi map is established and stored in the cloud server. When the user moves in the building, the positioning system collects several samples of the surrounding Wi-Fi information and uploads them to the server. The server communicates with the Wi-Fi map. Compare and match to obtain the current floor location of the user.
所述步骤1)收集的每组对应楼层的Wi-Fi信号均被实时传输到一个云端服务器,云端服务器执行步骤2)的聚类工作,并形成完整的建筑物的Wi-Fi地图。 The Wi-Fi signals of each group of corresponding floors collected in step 1) are transmitted to a cloud server in real time, and the cloud server performs the clustering work in step 2) to form a complete Wi-Fi map of the building. the
本发明的有益效果:本发明无需知道建筑物本身的信息,如楼层高度,层数等;无需在建筑物中部署设备,如校准设备,读卡设备等,这样就极大减少了实施成本及开销;无需预先游历整个建筑物来建立地图,节省了大量人力物力;且一旦Wi-Fi地图建立以后,无需再重新计算即可提供高精度的楼层定位,定位实施非常简便。 Beneficial effects of the present invention: the present invention does not need to know the information of the building itself, such as the height of the floor, the number of floors, etc.; it does not need to deploy equipment in the building, such as calibration equipment, card reading equipment, etc., thus greatly reducing the implementation cost and cost; there is no need to travel the entire building in advance to build a map, which saves a lot of manpower and material resources; and once the Wi-Fi map is established, it can provide high-precision floor positioning without recalculation, and the positioning implementation is very simple. the
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是用户坐垂直电梯时手机加速度传感器获得的数据; Figure 1 is the data obtained by the acceleration sensor of the mobile phone when the user takes the vertical elevator;
图2是获取用户进电梯前和出电梯后较短时间的一组Wi-Fi信号;Figure 2 is a set of Wi-Fi signals obtained for a short period of time before the user enters the elevator and after exiting the elevator;
图3是获取每个用户进出电梯前后较短时间的一组Wi-Fi信号;Figure 3 is a set of Wi-Fi signals obtained for a short time before and after each user enters and exits the elevator;
图4是利用聚类技术对Wi-Fi信号进行聚类,再根据Wi-Fi信号所在楼层高低关系把类进行排序;Figure 4 uses clustering technology to cluster Wi-Fi signals, and then sorts the classes according to the relationship between the floors where the Wi-Fi signals are located;
图5是把每个类的大小从包含楼梯口区域到包含整个楼层的Wi-Fi信号;Figure 5 shows the size of each class from the area containing the stairway to the Wi-Fi signal containing the entire floor;
图6是本发明的系统总体框架图。Fig. 6 is a general frame diagram of the system of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和实施例对本发明进一步说明。 The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. the
要实现本发明,要解决如下几个问题,1)识别用户上下电梯的行为;2)用户轨迹的获取与分析;3)聚类算法的设计及Wi-Fi地图的生成。 To implement the present invention, the following problems must be solved: 1) Identify the behavior of users getting on and off the elevator; 2) Acquisition and analysis of user trajectories; 3) Design of clustering algorithms and generation of Wi-Fi maps. the
经过加速度数据采样,我们发现上下电梯在加速度数据上具有明显的特性,利用简单的方法进行识别就达到了较好的效果,在行为识别领域,此类的行为识别方法已经较为成熟,本发明可以使用现有的识别算法进行识别。图1展示的是加速度数据,该数据是电梯上行时(图1a)和电梯下行时(图1b)在电梯中的手机的加速计读数。利用这个加速度曲线的特性,我们可以识别出用户是否乘坐了一次电梯。 After sampling the acceleration data, we found that the up and down elevators have obvious characteristics on the acceleration data, and a simple method for identification has achieved better results. In the field of behavior recognition, this type of behavior recognition method has been relatively mature. The present invention can Use existing recognition algorithms for recognition. Figure 1 shows the acceleration data, which is the accelerometer reading from a mobile phone in an elevator when the elevator is going up (Figure 1a) and when the elevator is going down (Figure 1b). Using the characteristics of this acceleration curve, we can identify whether the user has taken an elevator. the
用户在建筑物中活动时,通过打开手机的Wi-Fi功能,采集周围的Wi-Fi信号,这些Wi-Fi信号构成了用户连续的Wi-Fi轨迹,如果用户在不同楼层间移动,那Wi-Fi信号也是分段的,每段属于不同的楼层。本发明先通过手机加速度识别用户上下电梯的行为,再利用用户乘坐电梯的行为以将收集的Wi-Fi轨迹进行分段,并且能够根据电梯往上或者往下知道每个段的高低关系。图2中展示了一个用户从一楼到四楼的过程,中间乘坐了一次电梯,通过行为识别能够识别出用户乘坐了电梯,在进电梯前和出电梯后的较短时间内的Wi-Fi数据可以被获取,我们称为一组Wi-Fi信号,这组Wi-Fi信号前半部分LowerGroup是比后半部分UpperGroup要低,因为用户是坐电梯往上走的。 When the user is active in the building, by turning on the Wi-Fi function of the mobile phone, the surrounding Wi-Fi signals are collected. These Wi-Fi signals constitute the continuous Wi-Fi trajectory of the user. If the user moves between different floors, the Wi-Fi -Fi signal is also segmented, and each segment belongs to a different floor. The invention first recognizes the user's behavior of getting on and off the elevator through the acceleration of the mobile phone, and then uses the user's behavior of taking the elevator to segment the collected Wi-Fi trajectory, and can know the height relationship of each segment according to the up or down of the elevator. Figure 2 shows the process of a user going from the first floor to the fourth floor, and took an elevator in the middle. Through behavior recognition, it can be recognized that the user took the elevator. The data can be obtained. We call it a set of Wi-Fi signals. The LowerGroup in the first half of this set of Wi-Fi signals is lower than the UpperGroup in the second half, because the user is going up by elevator. the
本发明选取用户在上电梯前和下电梯后短时间的Wi-Fi信号,这个信号应该是在电梯口获得的。收集多个用户在电梯口获得的Wi-Fi信号,图3展示当多个用户在建筑物内运动时,利用图2展示的方法我们可以获得许多组Wi-Fi信号;每组Wi-Fi信号前后两部分都有高低关系。之后利用聚类的方法对这些信号进行聚类,这样,聚类后获得的类的个数就是这栋楼的层数,然后根据Wi-Fi信号的高低关系对聚类的结果进行排序,排序之后就能够得到一个楼层与类的一一映射。图4是利用聚类的方法将许多用户的Wi-Fi信号进行聚类,比较接近的会被放在同一个类中,由于每个用户的每组Wi-Fi信号时有高低关系的,这样包含这些Wi-Fi信号的类也有高低关系,我们利用这个高低关系对类进行排序,就得到了所有类的高低关系;而且每一层都会有一个类出现,虽然我们不知道该建筑物有多少层,也不知道每个类再哪一层;但是由于聚类的特性,我们知道有多少个类就有多少个楼层,根据类的高低关系,就获得了类和楼层的一一映射。至此,我们就知道这栋建筑物有多少层和每层电梯口的Wi-Fi信号地图。利用之前的Wi-Fi轨迹段,我们将所有用户的Wi-Fi轨迹融合起来,获得整个建筑物的Wi-Fi地图。图5中,由于需要的是整个楼层的Wi-Fi信号,所以这里就是将类一步一步扩大,使其包含整个楼层的Wi-Fi信号。 The present invention selects the short-term Wi-Fi signal of the user before getting on the elevator and after getting off the elevator, and this signal should be obtained at the elevator entrance. Collect the Wi-Fi signals obtained by multiple users at the elevator entrance. Figure 3 shows that when multiple users are moving in the building, we can obtain many sets of Wi-Fi signals using the method shown in Figure 2; each set of Wi-Fi signals There is a high-low relationship between the front and back parts. Then use the clustering method to cluster these signals. In this way, the number of classes obtained after clustering is the number of floors of the building, and then sort the clustering results according to the relationship between the Wi-Fi signals. Then you can get a one-to-one mapping between floors and classes. Figure 4 uses the clustering method to cluster the Wi-Fi signals of many users, and the closer ones will be placed in the same class. Since each group of Wi-Fi signals of each user has a high-low relationship, this The class containing these Wi-Fi signals also has a high-low relationship. We use this high-low relationship to sort the classes to get the high-low relationship of all classes; and each floor will have a class, although we don’t know how many buildings there are. We don't know which floor each class is on; but due to the characteristics of clustering, we know that there are as many floors as there are classes. According to the high-low relationship of the classes, we can obtain a one-to-one mapping between classes and floors. So far, we know how many floors the building has and the Wi-Fi signal map of the elevator entrance on each floor. Using previous Wi-Fi trajectory segments, we fuse all users' Wi-Fi trajectories to obtain a Wi-Fi map of the entire building. In Figure 5, since the Wi-Fi signal of the entire floor is needed, the class is expanded step by step to include the Wi-Fi signal of the entire floor. the
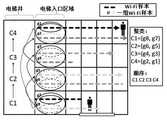
从上面介绍的方法可以发现,我们不需要游历整个建筑物来建立Wi-Fi信号地图,而是利用了一种后台自动的方法,在不干预用户正常活动的情况下,利用本来就在建筑物中活动的用户采集到的信息生成了Wi-Fi地图。在图6中:是整个系统的运行过程,看实线箭头,首先:用户在建筑物内运动的时候,手机采集加速度和Wi-Fi信号数据,利用加速度识别出乘坐电梯的行为,然后上传到服务器,服务器利用聚类的方法进行聚类,获得每个楼层的类,然后排序,再扩大类,最后获得整个建筑物的Wi-Fi地图。再进行定位时,看虚线箭头,一个用户的手机采集周围的Wi-Fi信号,上传到服务器,服务器根据Wi-Fi地图对比就知道该用户在哪个楼层了,然后把楼层信息告知该用户。 From the method introduced above, we can find that we do not need to travel the entire building to build a Wi-Fi signal map, but use an automatic method in the background, without interfering with the normal activities of the user, using the Wi-Fi signals already in the building A Wi-Fi map is generated from the information collected by active users. In Figure 6: it is the running process of the whole system, see the solid arrow, first: when the user is moving in the building, the mobile phone collects the acceleration and Wi-Fi signal data, uses the acceleration to identify the behavior of taking the elevator, and then uploads it to The server uses the clustering method to perform clustering, obtains the class of each floor, then sorts, expands the class, and finally obtains the Wi-Fi map of the entire building. When positioning, look at the dotted arrow. A user's mobile phone collects the surrounding Wi-Fi signal and uploads it to the server. The server knows which floor the user is on based on the Wi-Fi map comparison, and then informs the user of the floor information. the
总体来说,用户手机在后台运行着本方案的服务,不停收集加速度传感器数据和Wi-Fi信号,并且识别用户行为,生成用户运行的轨迹。这些轨迹被实时传输到一个云端服务器,在云端服务器上运行着本方案算法,它将不同用户的轨迹通过聚类的方法合并到一起,这样生成了一张Wi-Fi信号地图,在这图中可以识别出该建筑的楼层数量,以及定位用户的楼层。当一个用户需要定位自己的楼层时,打开手机Wi-Fi收集周围的Wi-Fi信号,然后到存储着Wi-Fi地图的服务器进行查询,根据Wi-Fi信号的对比就能确定该用户现在处于哪个楼层。 Generally speaking, the user's mobile phone runs the service of this solution in the background, continuously collects acceleration sensor data and Wi-Fi signals, and recognizes user behavior to generate user running trajectories. These trajectories are transmitted to a cloud server in real time, and the algorithm of this solution is run on the cloud server, which merges the trajectories of different users together by clustering, thus generating a Wi-Fi signal map, in this figure It is possible to identify the number of floors of the building and locate the floor of the user. When a user needs to locate his or her own floor, turn on the Wi-Fi of the mobile phone to collect the surrounding Wi-Fi signals, and then query the server storing the Wi-Fi map. According to the comparison of the Wi-Fi signals, it can be determined that the user is currently in which floor. the
通过采集的真实Wi-Fi数据对该方法进行了充分的软件模拟,并在三栋不同建筑物的真实场景下进行了实验。实验证明该方案能够达到95%的精度将用户定位在正确的楼层上,98%的精度保证定位误差在1层以内。之后又组织了20个志愿者进行了5天的实地实验,实验表明定位到正确楼层的精度达到98%。 The method is fully simulated in software by collecting real Wi-Fi data, and experiments are carried out in real scenarios of three different buildings. Experiments have proved that the scheme can achieve 95% accuracy to locate the user on the correct floor, and 98% accuracy ensures that the positioning error is within 1 floor. After that, 20 volunteers were organized to conduct a field experiment for 5 days. The experiment showed that the accuracy of positioning to the correct floor reached 98%. the
本发明具体应用途径很多,以上所述仅是本发明的优选实施方式,应当指出,对于本技术领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本发明原理的前提下,还可以作出若干改进,这些改进也应视为本发明的保护范围。 There are many specific application approaches of the present invention, and the above description is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention. It should be pointed out that for those of ordinary skill in the art, some improvements can also be made without departing from the principles of the present invention. Improvements should also be regarded as the protection scope of the present invention. the
Claims (2)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013100955198ACN103152697A (en) | 2013-03-25 | 2013-03-25 | Method for realizing automatic floor positioning by using intelligent mobile phone Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) function |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013100955198ACN103152697A (en) | 2013-03-25 | 2013-03-25 | Method for realizing automatic floor positioning by using intelligent mobile phone Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) function |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103152697Atrue CN103152697A (en) | 2013-06-12 |
Family
ID=48550521
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013100955198APendingCN103152697A (en) | 2013-03-25 | 2013-03-25 | Method for realizing automatic floor positioning by using intelligent mobile phone Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) function |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103152697A (en) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104268481A (en)* | 2014-10-10 | 2015-01-07 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Method and device for realizing early warning of smart phone |
| CN104573859A (en)* | 2014-12-31 | 2015-04-29 | 合肥城市云数据中心有限公司 | Human traffic prediction method based on Wifi positioning and cloud data processing technology |
| CN108780137A (en)* | 2016-03-24 | 2018-11-09 | 高通股份有限公司 | For the selective crowdsourcing of multilayer positioning |
| WO2019071762A1 (en)* | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | 深圳数位传媒科技有限公司 | Floor positioning method and system, server and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN109996179A (en)* | 2017-12-30 | 2019-07-09 | 中国移动通信集团贵州有限公司 | Positioning and optimizing method, system, device and equipment, medium |
| CN112229411A (en)* | 2020-10-15 | 2021-01-15 | 广州小鹏自动驾驶科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device |
| CN112423383A (en)* | 2020-10-29 | 2021-02-26 | 南京大学 | Positioning method based on positioning base station and positioning label in multi-floor environment |
| WO2022042655A1 (en)* | 2020-08-31 | 2022-03-03 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for constructing fingerprint map of multi-floor building, positioning method, and apparatus |
| CN115924664A (en)* | 2022-12-23 | 2023-04-07 | 泰州雷德波达定位导航科技有限公司 | Vertical elevator identification method, system, medium, equipment, terminal and application |
| CN116456406A (en)* | 2022-01-10 | 2023-07-18 | 荣耀终端有限公司 | Network switching method, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN118116066A (en)* | 2022-11-30 | 2024-05-31 | 荣耀终端有限公司 | Behavior recognition method, generation method of behavior recognition model and behavior recognition system |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101742545A (en)* | 2009-12-15 | 2010-06-16 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | Positioning method and system in WiFi environment |
| CN102791025A (en)* | 2011-05-20 | 2012-11-21 | 盛乐信息技术(上海)有限公司 | Wireless fidelity (WIFI) based layered positioning system and implementing method |
- 2013
- 2013-03-25CNCN2013100955198Apatent/CN103152697A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101742545A (en)* | 2009-12-15 | 2010-06-16 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | Positioning method and system in WiFi environment |
| CN102791025A (en)* | 2011-05-20 | 2012-11-21 | 盛乐信息技术(上海)有限公司 | Wireless fidelity (WIFI) based layered positioning system and implementing method |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 叶海波等: "FTrack: Infrastructure-free Floor Localization via Mobile Phone Sensing", 《IEEE》, 23 March 2012 (2012-03-23), pages 2 - 10, XP032180712, DOI: doi:10.1109/PerCom.2012.6199843* |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104268481A (en)* | 2014-10-10 | 2015-01-07 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Method and device for realizing early warning of smart phone |
| CN104573859A (en)* | 2014-12-31 | 2015-04-29 | 合肥城市云数据中心有限公司 | Human traffic prediction method based on Wifi positioning and cloud data processing technology |
| CN108780137A (en)* | 2016-03-24 | 2018-11-09 | 高通股份有限公司 | For the selective crowdsourcing of multilayer positioning |
| WO2019071762A1 (en)* | 2017-10-10 | 2019-04-18 | 深圳数位传媒科技有限公司 | Floor positioning method and system, server and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN109996179A (en)* | 2017-12-30 | 2019-07-09 | 中国移动通信集团贵州有限公司 | Positioning and optimizing method, system, device and equipment, medium |
| WO2022042655A1 (en)* | 2020-08-31 | 2022-03-03 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for constructing fingerprint map of multi-floor building, positioning method, and apparatus |
| CN112229411A (en)* | 2020-10-15 | 2021-01-15 | 广州小鹏自动驾驶科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device |
| CN112229411B (en)* | 2020-10-15 | 2021-12-07 | 广州小鹏自动驾驶科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device |
| CN112423383A (en)* | 2020-10-29 | 2021-02-26 | 南京大学 | Positioning method based on positioning base station and positioning label in multi-floor environment |
| CN116456406A (en)* | 2022-01-10 | 2023-07-18 | 荣耀终端有限公司 | Network switching method, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN118116066A (en)* | 2022-11-30 | 2024-05-31 | 荣耀终端有限公司 | Behavior recognition method, generation method of behavior recognition model and behavior recognition system |
| CN115924664A (en)* | 2022-12-23 | 2023-04-07 | 泰州雷德波达定位导航科技有限公司 | Vertical elevator identification method, system, medium, equipment, terminal and application |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103152697A (en) | Method for realizing automatic floor positioning by using intelligent mobile phone Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) function | |
| Abdelnasser et al. | SemanticSLAM: Using environment landmarks for unsupervised indoor localization | |
| Kang et al. | Extracting places from traces of locations | |
| Alzantot et al. | Crowdinside: Automatic construction of indoor floorplans | |
| CN104483658B (en) | Based on Wi-Fi and the indoor orientation method in earth's magnetic field | |
| CN105025440B (en) | Indoor and outdoor scene detection method and equipment | |
| Xiao et al. | Transportation activity analysis using smartphones | |
| Kjærgaard et al. | Detecting pedestrian flocks by fusion of multi-modal sensors in mobile phones | |
| CN106248107B (en) | A track inference calibration method and device based on indoor geomagnetic track matching | |
| CN111698774B (en) | Indoor positioning method and device based on multi-source information fusion | |
| CN106714102A (en) | Method of using intelligent mobile phone to assist indoor positioning | |
| US11337031B2 (en) | Systems and methods for tracking a location of a mobile device | |
| Biczok et al. | Navigating MazeMap: indoor human mobility, spatio-logical ties and future potential | |
| CN103152487A (en) | Method for performing floor positioning by utilizing intelligent mobile | |
| Ryoo et al. | Geo-fencing: Geographical-fencing based energy-aware proactive framework for mobile devices | |
| CN104717744A (en) | Indoor positioning method based on wireless local area network and hierarchical clustering | |
| CN104931051A (en) | Indoor electronic map drawing and navigating method and system based on big data | |
| CN110049441B (en) | WiFi indoor positioning method based on deep ensemble learning | |
| Raychoudhury et al. | Crowd-pan-360: Crowdsourcing based context-aware panoramic map generation for smartphone users | |
| Wang et al. | Indoor PDR Positioning Assisted by Acoustic Source Localization, and Pedestrian Movement Behavior Recognition, Using a Dual‐Microphone Smartphone | |
| Elhamshary et al. | Towards ubiquitous indoor spatial awareness on a worldwide scale | |
| Ye et al. | Infrastructure-free floor localization through crowdsourcing | |
| US20150278705A1 (en) | Control method to be executed by information processing device, information processing device, and storage medium | |
| Matos et al. | Wi-Fi fingerprint similarity in collaborative radio maps for indoor positioning | |
| KR20160072361A (en) | The method and device for protecting infant and evaluating bevavior of infant and The method and device for tracking infant based on network |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20130612 |