CN103049035A - Reconfiguration optimizing method of photovoltaic cell array local reconfigurable electrical system - Google Patents
Reconfiguration optimizing method of photovoltaic cell array local reconfigurable electrical systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103049035A CN103049035ACN201210558810XACN201210558810ACN103049035ACN 103049035 ACN103049035 ACN 103049035ACN 201210558810X ACN201210558810X ACN 201210558810XACN 201210558810 ACN201210558810 ACN 201210558810ACN 103049035 ACN103049035 ACN 103049035A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- photovoltaic
- photovoltaic module
- array
- reconstruction
- group
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/56—Power conversion systems, e.g. maximum power point trackers
Landscapes
- Photovoltaic Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及光伏发电技术领域,尤其是一种光伏电池阵列的运行控制方法。The invention relates to the technical field of photovoltaic power generation, in particular to an operation control method of a photovoltaic cell array.
背景技术Background technique
随着传统能源的枯竭和环保意识的觉醒,太阳能的开发利用日益受到重视,光伏发电是利用太阳能的主要方式。由于单个光伏电池的输出电压和电流都较小,无法直接满足并网或大部分用电负载的用电要求,所以需要将多个光伏电池通过串并联组成光伏组件。光伏发电站中需要用大量的光伏组件来组成光伏阵列,从而获取所需的光伏输出电压和功率。为了防止热斑现象出现损坏光伏电池,光伏阵列中还装设有旁路二极管和防逆二极管。当光伏组件输出特性一致且光照均匀时,光伏阵列的输出功率-电压(P-U)特性曲线呈现单峰现象,此时传统的最大功率点跟踪(MPPT)方法可以很容易跟踪到最大功率点(MPP)。With the depletion of traditional energy sources and the awakening of environmental awareness, the development and utilization of solar energy has been paid more and more attention. Photovoltaic power generation is the main way to utilize solar energy. Since the output voltage and current of a single photovoltaic cell are small, it cannot directly meet the electricity requirements of grid-connected or most electric loads, so it is necessary to connect multiple photovoltaic cells in series and parallel to form a photovoltaic module. A large number of photovoltaic modules are required to form a photovoltaic array in a photovoltaic power station to obtain the required photovoltaic output voltage and power. In order to prevent hot spots from damaging photovoltaic cells, bypass diodes and anti-reverse diodes are also installed in the photovoltaic array. When the output characteristics of the photovoltaic modules are consistent and the illumination is uniform, the output power-voltage (P-U) characteristic curve of the photovoltaic array presents a single-peak phenomenon. At this time, the traditional maximum power point tracking (MPPT) method can easily track the maximum power point (MPP). ).
当光伏阵列中存在光照条件不均匀、温度差、组件特性不一致等影响光伏电池组件输出特性差异的因素时,光伏阵列的输出P-U特性曲线极有可能呈现多峰值现象,此时光伏阵列的最大输出功率损失通常明显大于因光照、温度等外部环境因素引起的光伏组件功率损失之和。这是因为光伏阵列运行于MPP并不等同于其内部的每个光伏电池组件都运行于MPP,其中存在较大的失配功率损失。When there are factors in the photovoltaic array that affect the output characteristics of photovoltaic cell components such as uneven lighting conditions, temperature differences, and inconsistent module characteristics, the output P-U characteristic curve of the photovoltaic array is likely to show a multi-peak phenomenon. At this time, the maximum output of the photovoltaic array The power loss is usually significantly greater than the sum of the power losses of photovoltaic modules caused by external environmental factors such as light and temperature. This is because the operation of the photovoltaic array on MPP is not equivalent to the operation of every photovoltaic cell module inside it on MPP, and there is a large mismatch power loss.
改进MPPT方法对于减少失配功率损失显然是无能为力,降低或消除失配功率损失必须从光伏阵列的电气连接结构出发寻找解决办法。有学者提出通过对光伏阵列的电气连接结构进行重构来消除失配功率损失,无奈重构系统结构过于繁杂、重构优化算法计算复杂度过大,所以光伏阵列重构技术目前仍停留在理论研究阶段。在确保调节能力的前提下,简化光伏阵列重构系统的结构,并建立相应的低计算复杂度的重构优化策略,对于改善光伏阵列发电效率,减少功率损失具有重要意义。Improving the MPPT method is obviously powerless to reduce the mismatch power loss. To reduce or eliminate the mismatch power loss, a solution must be found from the electrical connection structure of the photovoltaic array. Some scholars proposed to eliminate the mismatch power loss by reconstructing the electrical connection structure of the photovoltaic array, but the reconstruction system structure is too complicated, and the calculation complexity of the reconstruction optimization algorithm is too large, so the photovoltaic array reconstruction technology is still in the theoretical field. research stage. On the premise of ensuring the regulation ability, simplifying the structure of the photovoltaic array reconfiguration system and establishing a corresponding low computational complexity reconfiguration optimization strategy are of great significance for improving the power generation efficiency of the photovoltaic array and reducing power loss.
发明内容Contents of the invention
为了克服已有光伏电池阵列的由于光伏电池组件输出特性不匹配而引入的失配功率损失、发电效率较低的不足,本发明提供一种有效减少由于光伏电池组件输出特性不匹配而引入的失配功率损失、发电效率较高的光伏电池阵列局部可重构电气系统的重构优化方法。In order to overcome the mismatch power loss and low power generation efficiency of the existing photovoltaic cell array due to the mismatch of the output characteristics of the photovoltaic cell components, the present invention provides a method to effectively reduce the mismatch caused by the mismatch of the output characteristics of the photovoltaic cell components. A reconfiguration optimization method for locally reconfigurable electrical systems of photovoltaic cell arrays with high power loss distribution and high power generation efficiency.
本发明解决其技术问题所采用的技术方案是:The technical solution adopted by the present invention to solve its technical problems is:
一种光伏电池阵列局部可重构电气系统的重构优化方法,所述光伏电池阵列包括由固定结构部分与可重构部分组成,A reconfiguration optimization method for a local reconfigurable electrical system of a photovoltaic cell array, the photovoltaic cell array is composed of a fixed structure part and a reconfigurable part,
所述固定结构部分的光伏阵列包含M组串联着的光伏组件组,每组光伏组件组的两端接口并联可重构部分的任意若干个光伏组件;所述可重构部分包括N块光伏组件,N块光伏组件将被分成M组后分别并联到与之对应的固定结构的M组光伏组件组的外部接口上;The photovoltaic array of the fixed structure part includes M groups of photovoltaic module groups connected in series, and the two ends of each group of photovoltaic module groups are connected in parallel to any number of photovoltaic modules of the reconfigurable part; the reconfigurable part includes N pieces of photovoltaic modules , N pieces of photovoltaic modules will be divided into M groups and connected in parallel to the external interfaces of M groups of photovoltaic module groups with corresponding fixed structures;
每个光伏组件串联有一个防逆二极管,固定结构部分的光伏阵列中每组并联光伏组件组先串联一个电流互感器后并联一个旁路二极管和一个电压互感器,可重构部分的光伏阵列中每个光伏组件串联一个电流互感器;Each photovoltaic module has an anti-reverse diode in series. In the photovoltaic array of the fixed structure part, each group of parallel photovoltaic module groups is first connected in series with a current transformer and then connected in parallel with a bypass diode and a voltage transformer. In the photovoltaic array of the reconfigurable part Each photovoltaic module is connected in series with a current transformer;
光伏阵列运行过程中,对于可重构部分光伏阵列中的光伏组件,通过实时测量光伏组件的端电压以及流过的电流,根据光伏组件的数学模型快速估算出每个光伏组件的短路电流Isci,i=1,2,3,……,N;对于固定结构部分光伏阵列中的光伏组件,通过实时测量每组并联光伏组件组的端电压和总电流,根据并联光伏组件组的等效模型快速估算出每组光伏组件组的合成短路电流Iscj,j=1,2,3,……,M;During the operation of the photovoltaic array, for the photovoltaic modules in the reconfigurable part of the photovoltaic array, the short-circuit current Isci of each photovoltaic module is quickly estimated according to the mathematical model of the photovoltaic module by measuring the terminal voltage of the photovoltaic module and the current flowing in real time , i=1, 2, 3,..., N; For the photovoltaic modules in the photovoltaic array of the fixed structure part, by measuring the terminal voltage and total current of each parallel photovoltaic module group in real time, according to the equivalent model of the parallel photovoltaic module group Quickly estimate the combined short-circuit current Iscj of each group of photovoltaic modules, j=1, 2, 3, ..., M;
所述重构优化方法包括以下步骤:The reconstruction optimization method includes the following steps:
(1)采集电压和电流信号;当重构优化启动时间到或者串联光伏组件组的端电压之间出现超出预设差值时,启动光伏阵列重构优化;(1) Collect voltage and current signals; when the start-up time of reconstruction optimization is reached or when the terminal voltage of the series photovoltaic module group exceeds the preset difference, start the reconstruction optimization of the photovoltaic array;
(2)根据固定结构部分光伏组件组的端电压及通过每组并联光伏组件的总电流测量值,计算每组光伏组件组的短路电流值Iscj,j=1,2,3,……,M,并按短路电流从大到小的顺序对光伏组件组进行排序;(2) Calculate the short-circuit current value Iscj of each photovoltaic module group according to the terminal voltage of the photovoltaic module group in the fixed structure and the total current measurement value passing through each group of parallel photovoltaic modules, j=1, 2, 3,..., M, and sort the photovoltaic module groups in the order of short-circuit current from large to small;
(3)根据可重构部分光伏组件的端电压和电流测量值,计算每个光伏组件的短路电流值Isci,i=1,2,3,……,N,并按短路电流从大到小的顺序对光伏组件进行排序;(3) Calculate the short-circuit current value Isci of each photovoltaic module according to the terminal voltage and current measurement values of some reconfigurable photovoltaic modules, i=1, 2, 3, ..., N, and calculate the short-circuit current value from large to Sort PV modules in small order;
(4)计算重构后光伏阵列中串联着的每组并联光伏组件组的短路电流目标值Isc,计算公式为重构的目标是使每组光伏组件的短路电流之和尽可能接近该目标值Isc;(4) Calculate the short-circuit current target value Isc of each group of parallel photovoltaic module groups connected in series in the photovoltaic array after reconstruction, and the calculation formula is The goal of reconstruction is to make the sum of the short-circuit current of each group of photovoltaic modules as close as possible to the target value Isc ;
(5)检查固定结构部分是否有光伏组件组的短路电流之和超过重构后的目标值Isc,如果是,则取消对该组光伏组件组继续分配可重构部分的光伏组件,设定下次启动重构优化程序的时间T为第一时间阈值,否则设定下次启动重构优化程序的时间T为第二时间阈值,即下次重构程序由光伏组件端电压差值过大这个条件来启动,所述第二时间阈值比所述第一时间阈值大;(5) Check whether the sum of the short-circuit current of the photovoltaic module group in the fixed structure exceeds the target value Isc after reconstruction, and if so, cancel the distribution of photovoltaic modules in the reconfigurable part of the group of photovoltaic module groups, and set The time T for starting the reconstruction optimization program next time is the first time threshold, otherwise, set the time T for the next start of the reconstruction optimization program as the second time threshold, that is, the next time the reconstruction program is caused by the excessive voltage difference between the photovoltaic module terminals This condition is activated, the second time threshold is greater than the first time threshold;
(6)每次为固定结构部分的短路电流之和尚未达到目标值Isc的光伏组件组分别分配一块从可重构部分挑选的待分配的光伏组件;分配过程中,如果有光伏组件组的短路电流之和超过设定的目标值,则采取两种措施:1) 保持此次分配不变,但立即停止下一次对该光伏组件组再分配光伏组件;2) 撤销最近分配的一块光伏组件,替代为剩余待分配光伏组件中使该光伏组件组短路电流超过目标值Isc的短路电流最小的光伏组件,此后立即停止下一次对该光伏组件组再分配光伏组件;上述分配过程循环进行,直至所有可重构光伏阵列部分的光伏组件分配完毕。(6) Every time, a photovoltaic module group selected from the reconfigurable part is assigned to the photovoltaic module group whose short-circuit current sum of the fixed structure part has not yet reached the target value Isc ; during the distribution process, if there is a photovoltaic module group If the sum of the short-circuit current exceeds the set target value, two measures will be taken: 1) Keep this allocation unchanged, but immediately stop the next allocation of PV modules to the PV module group; 2) Cancel the most recently allocated PV module , replace it with the photovoltaic module with the smallest short-circuit current of the photovoltaic module group whose short-circuit current exceeds the target value Isc in the remaining photovoltaic modules to be allocated, and then immediately stop the next distribution of photovoltaic modules to the photovoltaic module group; the above-mentioned distribution process is carried out cyclically, Until all the photovoltaic modules of the reconfigurable photovoltaic array are allocated.
(7)形成当前运行条件下的光伏阵列重构优化策略,并将重构信号释放到电力连接开关的切换控制系统中,将可重构部分光伏组件准确并联到固定结构光伏阵列中对应的光伏组件组两端。(7) Form the photovoltaic array reconstruction optimization strategy under the current operating conditions, release the reconstruction signal to the switching control system of the power connection switch, and accurately parallel connect the reconfigurable part of the photovoltaic modules to the corresponding photovoltaic array in the fixed structure photovoltaic array. Component groups at both ends.
本发明的有益效果主要表现在:本发明无需测量每个组件所处的外部环境量(辐照度、温度等),也无需求解复杂的优化问题,只需要采集少量的几个电压信号以及每个组件的电流信号,通过简单的短路电流计算和排序即可获得令人满意的光伏阵列重构优化策略,可以有效提高光伏阵列在复杂运行条件下的发电效率,降低发电成本。光伏阵列部分采用固定结构、部分采用可重构结构,在提高发电效率的同时,也大大降低了重构开关设备的投资成本并提高了系统运行可靠性。The beneficial effects of the present invention are mainly manifested in: the present invention does not need to measure the external environment quantity (irradiance, temperature, etc.) A satisfactory photovoltaic array reconstruction optimization strategy can be obtained through simple short-circuit current calculation and sorting of the current signal of each component, which can effectively improve the power generation efficiency of the photovoltaic array under complex operating conditions and reduce power generation costs. Part of the photovoltaic array adopts a fixed structure and part adopts a reconfigurable structure. While improving power generation efficiency, it also greatly reduces the investment cost of reconfiguring switchgear and improves system operation reliability.
附图说明Description of drawings
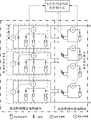
图1是局部可重构光伏阵列的结构及测量控制系统的示意图。Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the structure of a locally reconfigurable photovoltaic array and a measurement control system.
图2是局部可重构光伏阵列的重构优化算法流程图。Fig. 2 is a flow chart of the reconstruction optimization algorithm of the locally reconfigurable photovoltaic array.
图3是光伏阵列重构方案重构过程举例的示意图,,其中,(a)为光伏阵列运行状态(一),(b)为光伏阵列运行状态(二),(c)为光伏阵列运行状态(三)。Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of an example of the reconstruction process of the photovoltaic array reconfiguration scheme, where (a) is the operating state of the photovoltaic array (1), (b) is the operating state of the photovoltaic array (2), and (c) is the operating state of the photovoltaic array (three).
图4是光伏阵列在重构前后的输出功率-电压特性曲线的示意图。Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of output power-voltage characteristic curves of a photovoltaic array before and after reconstruction.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图对本发明作进一步描述。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
参照图1~图4,一种光伏电池阵列局部可重构电气系统的重构优化方法,Referring to Figures 1 to 4, a reconfiguration optimization method for a partially reconfigurable electrical system of a photovoltaic cell array,
可重构光伏阵列的系统结构及测量控制系统如图1所示,光伏阵列由固定结构部分和可重构部分两块组成,其中:固定结构部分由M组串联着的并联光伏组件组构成,其结构固定不可调节;可重构部分由N块光伏组件及其切换开关组成,每块光伏组件可以选择固定结构部分任意一组光伏组件组进行并联电气连接,具体连接方案由重构优化算法决定。The system structure and measurement control system of the reconfigurable photovoltaic array are shown in Figure 1. The photovoltaic array is composed of a fixed structure part and a reconfigurable part. Among them, the fixed structure part is composed of M groups of parallel photovoltaic modules connected in series. Its structure is fixed and cannot be adjusted; the reconfigurable part is composed of N pieces of photovoltaic modules and their switches. Each photovoltaic module can choose any group of photovoltaic module groups in the fixed structure part for parallel electrical connection. The specific connection scheme is determined by the reconstruction optimization algorithm. .
本系统中,每个光伏组件串联有一个防逆二极管,固定结构光伏阵列中每组并联光伏组件组先串联一个电流互感器后并联一个旁路二极管和一个电压互感器,可重构部分光伏阵列中每个光伏组件串联一个电流互感器。防逆二极管可以防止光伏组件并联时由于每个光伏组件端电压不同产生的电流环流。电流互感器则可以感知流过每个组件或每组并联组件组的电流,电压互感器可以感知每组并联光伏组件的端电压,电流信号和电压信号输出到信号调理电路进行预处理,然后输入到光伏阵列重构优化控制中心(单片机、数字处理器(DSP)等),为光伏阵列重构优化提供基础数据。In this system, each photovoltaic module is connected in series with an anti-reverse diode, and each group of parallel photovoltaic module groups in a fixed structure photovoltaic array first connects a current transformer in series, and then connects a bypass diode and a voltage transformer in parallel, so that part of the photovoltaic array can be reconfigured Each photovoltaic module is connected in series with a current transformer. The anti-reverse diode can prevent the current circulation caused by the different terminal voltage of each photovoltaic module when the photovoltaic modules are connected in parallel. The current transformer can sense the current flowing through each component or each group of parallel components, and the voltage transformer can sense the terminal voltage of each group of parallel photovoltaic components. The current signal and voltage signal are output to the signal conditioning circuit for preprocessing, and then input Go to the photovoltaic array reconstruction optimization control center (single chip microcomputer, digital processor (DSP), etc.) to provide basic data for photovoltaic array reconstruction optimization.
光伏阵列运行过程中,对于可重构部分光伏阵列中的光伏组件,通过实时测量光伏组件的端电压以及流过的电流,可以根据光伏组件的数学模型(单二极管模型、双二极管模型、工程模型等)快速估算出每个光伏组件的短路电流Isci,i=1,2,3,……,N;对于固定结构部分光伏阵列中的光伏组件,通过实时测量每组并联光伏组件组的端电压和总电流,根据并联光伏组件组的等效模型可以快速估算出每组光伏组件组的合成短路电流Iscj,j=1,2,3,……,M。短路电流很好地反映了每时每刻光伏组件的光照条件和温度等环境情况,不仅避免了成本相对较高的辐照度和温度的测量,而且可以获得精度更高的适用于重构优化算法的测量数据。During the operation of the photovoltaic array, for the photovoltaic modules in the reconfigurable part of the photovoltaic array, by measuring the terminal voltage of the photovoltaic module and the current flowing in real time, according to the mathematical model of the photovoltaic module (single diode model, double diode model, engineering model etc.) quickly estimate the short-circuit current Isci of each photovoltaic module, i=1, 2, 3, ..., N; Voltage and total current, according to the equivalent model of parallel photovoltaic module groups, the combined short-circuit current Iscj of each group of photovoltaic module groups can be quickly estimated, j=1, 2, 3, ..., M. The short-circuit current well reflects the environmental conditions such as the lighting conditions and temperature of photovoltaic modules at every moment, which not only avoids the relatively high-cost irradiance and temperature measurement, but also obtains higher-precision measurements suitable for reconstruction optimization. Algorithm measurement data.
光伏阵列运行过程中,测量到的信息汇集到重构优化控制中心。本实施案例中,控制中心的对光伏阵列的重构优化策略流程图如图2所示,具体步骤如下:During the operation of the photovoltaic array, the measured information is collected to the reconstruction optimization control center. In this implementation case, the flow chart of the control center’s reconstruction and optimization strategy for the photovoltaic array is shown in Figure 2, and the specific steps are as follows:
(1)光伏阵列按重构优化方案运行,有M组光伏组件组串联后形成光伏阵列的固定结构部分;有N块光伏组件位于光伏阵列的可重构部分,可以随时响应重构优化方案调整其接入端口。采集图1中电压互感器和电流互感器传送到控制中心的电压和电流信号。(1) The photovoltaic array operates according to the reconfiguration optimization scheme. There are M groups of photovoltaic modules connected in series to form a fixed structural part of the photovoltaic array; its access port. Collect the voltage and current signals sent to the control center by the voltage transformer and current transformer in Figure 1.
(2)如果光伏阵列持续运行(中间无重构操作)时间大于设定时间T或者串联光伏组件组的端电压之间出现较大差值时,启动光伏阵列重构优化程序,进入下一步;否则跳转至步骤(1)。(2) If the continuous operation of the photovoltaic array (without reconfiguration operation in the middle) is longer than the set time T or there is a large difference between the terminal voltages of the series-connected photovoltaic module groups, start the photovoltaic array reconfiguration optimization program and enter the next step; Otherwise go to step (1).
(3)根据固定结构部分光伏组件组的端电压及通过每组并联光伏组件组的总电流测量值,计算每组光伏组件组的短路电流值Iscj,j=1,2,3,……,M,并按短路电流从大到小的顺序对光伏组件组进行排序,排序后Isc1>Isc2>Isc3>……>IscM;根据可重构部分光伏组件的端电压和电流测量值,计算每个光伏组件的短路电流值Isci,i=1,2,3,……,N,并按短路电流从大到小的顺序对光伏组件进行排序,排序后Isc1>Isc2>Isc3>……>IscN。(3) Calculate the short-circuit current value Iscj of each photovoltaic module group according to the terminal voltage of the photovoltaic module group in the fixed structure and the total current measurement value passing through each group of parallel photovoltaic module groups, j=1, 2, 3, ... , M, and sort the photovoltaic module groups in descending order of short-circuit current, after sorting, Isc1 >Isc2 >Isc3 >…>IscM ; according to the terminal voltage and current measurement of the reconfigurable part of the photovoltaic module Value, calculate the short-circuit current value Isci of each photovoltaic module, i=1, 2, 3, ..., N, and sort the photovoltaic modules according to the order of short-circuit current from large to small, after sorting, Isc1 >Isc2 >Isc3 >…>IscN .
(4)计算重构后光伏阵列中串联着的每组光伏组件的短路电流的目标值为重构的目标是使每组光伏组件的短路电流之和尽可能接近该目标值Isc。(4) Calculate the short-circuit current target value of each group of photovoltaic modules connected in series in the photovoltaic array after reconstruction The goal of the reconstruction is to make the sum of the short-circuit currents of each group of photovoltaic modules as close as possible to the target value Isc .
(5)如果固定结构部分有光伏组件组的短路电流超过重构后的目标值Isc,则剔除该组光伏组件组继续参与重构光伏组件的分配,记录参与重构的光伏组件组数量m(m<M),令T=5分钟(较短的时间皆可),否则参与重构的光伏组件组数量m=M,令T=4小时(较长的时间皆可)。(5) If the short-circuit current of a photovoltaic module group in the fixed structure exceeds the target value Isc after reconstruction, then remove this group of photovoltaic module groups and continue to participate in the distribution of reconstructed photovoltaic modules, and record the number m of photovoltaic module groups participating in the reconstruction (m<M), let T=5 minutes (shorter time is acceptable), otherwise, the number of photovoltaic module groups participating in the reconstruction is m=M, and T=4 hours (longer time is acceptable).
(6)令可重构部分光伏组件的计数器i=1,固定结构部分光伏组件组的分配轮数(参与分配的每组光伏组件组分配到一块光伏组件记为一轮)计数器k=1。(6) Make the counter i=1 of the photovoltaic module of the reconfigurable part, and the number of distribution rounds of the photovoltaic module group of the fixed structure part (each group of photovoltaic module groups participating in the distribution is assigned to a photovoltaic module as a round) counter k=1.
(7)每一轮分配中固定结构部分光伏组件组的计数器j=1+(m-1)*mod(k/2),其含义为:在奇数轮分配中,j从m开始倒数,在偶数轮分配中,j从1开始顺数,mod为取余数符号。(7) The counter j=1+(m-1)*mod(k/2) of the photovoltaic module group with a fixed structure in each round of distribution, which means: in odd-numbered rounds of distribution, j starts counting down from m, and in In the even-numbered round allocation, j counts up from 1, and mod is the symbol for taking the remainder.
(8)将可重构部分第i个的光伏组件分配并联到第j组光伏组件组的两端。(8) Assign the i-th photovoltaic module of the reconfigurable part to the two ends of the j-th photovoltaic module group in parallel.
(9)计算加入重构光伏组件后第j组光伏组件组的短路电流之和Iscj。(9) Calculate the sum of the short-circuit current Iscj of the jth photovoltaic module group after adding the reconstructed photovoltaic module.
(10)如果Iscj大于或等于Isc,则第i块光伏组件的分配,在待重构光伏组件中选择使第j组短路电流和超过Isc的短路电流最小的光伏组件(序号n)加入第j组。可重构部分短路电流排序介于(包括)i和n之间的光伏组件编号均加1。剔除第j组光伏组件参与接下来的重构,且令下一轮参与可重构光伏组件分配的光伏组件组数量tp=m-1。如果Iscj小于Isc,则直接转入下一步。(10) If Iscj is greater than or equal to Isc , then the assignment of the i-th photovoltaic module, among the photovoltaic modules to be reconfigured, select the photovoltaic module (number n) that minimizes the short-circuit current of the j-th group and the short-circuit current exceeding Isc Join group j. The number of PV modules whose reconfigurable partial short-circuit current sort is between (including) i and n is increased by 1. Eliminate the jth group of photovoltaic modules to participate in the next reconstruction, and make the number of photovoltaic module groups participating in the distribution of reconfigurable photovoltaic modules in the next round tp=m-1. If Iscj is smaller than Isc , go directly to the next step.
(11)令i=i+1,j=j+(-1)k,即:奇数轮中,j递减,偶数轮中,j递增。(11) Set i=i+1, j=j+(-1)k , that is, in odd-numbered rounds, j decreases, and in even-numbered rounds, j increases.
(12)如果i大于N,说明光伏阵列中可重构光伏组件分配完毕,则直接转步骤(14),否则转下一步。(12) If i is greater than N, it means that the reconfigurable photovoltaic modules in the photovoltaic array have been allocated, then directly go to step (14), otherwise go to the next step.
(13)如果j大于m或者j小于1,则令下一轮参与重构分配的光伏组件组数量m=tp,轮数计数器k=k+1,然后跳转至步骤(7);否则跳转至步骤(8),继续本轮光伏组件的分配。(13) If j is greater than m or j is less than 1, then set the number of photovoltaic module groups participating in the next round of reconstruction allocation m=tp, the number of rounds counter k=k+1, and then jump to step (7); otherwise, jump to Go to step (8) to continue the distribution of photovoltaic modules in this round.
(14)形成新的重构方案,并将重构控制命令发送给每个光伏组件的切换开关,然后跳转至步骤(1),等待下一次重构优化程序的启动。(14) Form a new reconfiguration scheme, and send a reconfiguration control command to the switching switch of each photovoltaic module, then jump to step (1), and wait for the start of the next reconfiguration optimization program.
上述重构优化流程是基于本发明中局部可重构光伏阵列的系统结构和测量系统布局,根据光伏阵列重构优化的基本思想(即确保重构后光伏阵列中串联着的M组并联光伏组件组的总短路电流尽可能相等),而设计出来的。通过对上述重构优化流程或者参数进行修改,还可以衍生出来多种重构优化流程,只要其使用了本发明所提出的光伏阵列重构结构或者重构优化思想,均受本发明专利的保护。The above-mentioned reconfiguration optimization process is based on the system structure and measurement system layout of the partially reconfigurable photovoltaic array in the present invention, and according to the basic idea of photovoltaic array reconfiguration optimization (that is, to ensure that the M groups of parallel photovoltaic modules connected in series in the photovoltaic array after reconfiguration The total short-circuit current of the group is as equal as possible), and it is designed. By modifying the above reconfiguration optimization process or parameters, a variety of reconfiguration optimization processes can also be derived, as long as they use the photovoltaic array reconfiguration structure or reconfiguration optimization idea proposed by the present invention, they are all protected by the patent of the present invention .
将上述重构优化算法应用于一个包含15块光伏组件的光伏阵列系统,其中固定结构部分包含9块光伏组件(分为三组,每组由3块并联的光伏组件构成),可重构部分包含6块光伏组件(编号分别为①②③④⑤⑥)。图3中,运行状态(一)为光伏阵列的初始运行状态,其中可重构部分的6块光伏组件分为[(①②)、(③④)、(⑤⑥)]三组分别并联在固定结构部分的三组光伏组件组两端;当运行条件改变后,部分光伏组件的短路电流(标于图中)发生了变化,重构前的光伏阵列如图3中运行状态(二)所示,可重构光伏组件的分组与接入方案同运行状态(一);重构后的光伏阵列如图3中运行状态(三)所示,可重构部分的光伏组件根据重构优化策略被分为[(①④)、(⑥)、(②③⑤)]三组,然后分别并联在固定结构部分的三组光伏组件组两端。采用上述重构优化算法对光伏阵列的结构进行优化调整后,每组光伏组件组的短路电流之和较重构前更接近相等。Apply the above reconstruction optimization algorithm to a photovoltaic array system containing 15 photovoltaic modules, in which the fixed structure part contains 9 photovoltaic modules (divided into three groups, each group is composed of 3 parallel photovoltaic modules), and the reconfigurable part Contains 6 photovoltaic modules (numbered ①②③④⑤⑥). In Figure 3, the operating state (1) is the initial operating state of the photovoltaic array, in which the 6 photovoltaic modules in the reconfigurable part are divided into three groups [(①②), (③④), (⑤⑥)] and connected in parallel in the fixed structure part The two ends of the three groups of photovoltaic modules; when the operating conditions change, the short-circuit current of some photovoltaic modules (marked in the figure) has changed, and the photovoltaic array before reconstruction is shown in the operating state (2) in Figure 3. The grouping and access scheme of the reconstructed photovoltaic modules is the same as the operating state (1); the reconstructed photovoltaic array is shown in the operating state (3) in Figure 3, and the photovoltaic modules in the reconfigurable part are divided into [(①④), (⑥), (②③⑤)] three groups, and then connected in parallel at both ends of the three groups of photovoltaic modules in the fixed structure part. After using the above reconstruction optimization algorithm to optimize and adjust the structure of the photovoltaic array, the sum of the short-circuit current of each photovoltaic module group is closer to equal than before the reconstruction.
图4画出了上述三种运行状态下,光伏阵列的输出端功率-电压特性曲线。当光伏阵列中所有光伏组件的短路电流相等时,光伏阵列的输出端功率-电压特性曲线(运行状态(一))呈现单峰状态,输出最大功率约为4000W。当运行条件改变后,部分光伏组件的短路电流发生了变化,如果原光伏阵列结构不进行重构调整,则此时的光伏阵列输出端功率-电压特性曲线如图4中曲线(运行状态(二))所示,呈现多个峰值,此时光伏阵列的最大输出功率约1750W,而且最大功率点跟踪(MPPT)算法可能受困于局部最大功率点从而引入更大的功率损失。如果此时根据上述重构优化算法对光伏阵列的结构进行优化调整,与其对应的光伏阵列输出端功率-电压曲线如图4中曲线(运行状态(三))所示,基本呈现单峰状态,其最大输出功率约为2350W,明显高于运行状态(二)的最大输出功率1750W,此外单峰功率-电压曲线也降低了对MPPT算法的要求,提高了MPPT算法的跟踪准确度。Fig. 4 shows the power-voltage characteristic curves of the output end of the photovoltaic array under the above three operating states. When the short-circuit current of all photovoltaic modules in the photovoltaic array is equal, the output power-voltage characteristic curve of the photovoltaic array (operating state (1)) presents a single-peak state, and the maximum output power is about 4000W. When the operating conditions change, the short-circuit current of some photovoltaic modules changes. If the original photovoltaic array structure is not reconfigured and adjusted, the power-voltage characteristic curve of the output terminal of the photovoltaic array at this time is shown in the curve in Figure 4 (operating state (two )) shows multiple peaks, at this time the maximum output power of the photovoltaic array is about 1750W, and the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm may be trapped in the local maximum power point and thus introduce greater power loss. If the structure of the photovoltaic array is optimized and adjusted according to the above-mentioned reconstruction optimization algorithm at this time, the corresponding power-voltage curve at the output end of the photovoltaic array is shown in the curve (running state (3)) in Figure 4, which basically presents a single-peak state. Its maximum output power is about 2350W, which is significantly higher than the maximum output power of 1750W in the running state (2). In addition, the single-peak power-voltage curve also reduces the requirements for the MPPT algorithm and improves the tracking accuracy of the MPPT algorithm.
由此可见,通过采用本发明所提出的部分可重构光伏阵列系统结构及重构优化算法,可以显著改善光伏阵列的输出功率-电压特性曲线,使其更接近于单峰状态,便于MPPT方法跟踪到全局最大功率点。此外,由于光伏组件失配功率损失减少,大大提高了同样运行条件下光伏阵列的输出功率。与完全可重构光伏阵列相比,本发明减少了参与重构的光伏组件数量,系统结构更简单、所需测量设备数量减少、优化算法速度更快。It can be seen that by adopting the partially reconfigurable photovoltaic array system structure and the reconstruction optimization algorithm proposed by the present invention, the output power-voltage characteristic curve of the photovoltaic array can be significantly improved, making it closer to the single-peak state, which is convenient for the MPPT method track to the global maximum power point. In addition, due to the reduction of mismatch power loss of photovoltaic modules, the output power of photovoltaic arrays under the same operating conditions is greatly improved. Compared with the fully reconfigurable photovoltaic array, the invention reduces the number of photovoltaic components involved in reconfiguration, the system structure is simpler, the number of required measuring devices is reduced, and the optimization algorithm is faster.
Claims (1)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210558810.XACN103049035B (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2012-12-20 | Reconfiguration optimizing method of photovoltaic cell array local reconfigurable electrical system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210558810.XACN103049035B (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2012-12-20 | Reconfiguration optimizing method of photovoltaic cell array local reconfigurable electrical system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103049035Atrue CN103049035A (en) | 2013-04-17 |
| CN103049035B CN103049035B (en) | 2014-11-12 |
Family
ID=48061710
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210558810.XAActiveCN103049035B (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2012-12-20 | Reconfiguration optimizing method of photovoltaic cell array local reconfigurable electrical system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103049035B (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103353716A (en)* | 2013-05-16 | 2013-10-16 | 河海大学 | Topological structure capable of realizing photovoltaic array reconstruction and method for solving maximum power point |
| CN107423501A (en)* | 2017-07-17 | 2017-12-01 | 南京邮电大学 | A kind of array automatic detection and method for numbering serial based on photovoltaic plant logic chart |
| CN109067358A (en)* | 2018-08-06 | 2018-12-21 | 浙江工业大学 | Photovoltaic array reconstruction optimization method based on shading battery number |
| CN109842155A (en)* | 2019-03-05 | 2019-06-04 | 协鑫能源工程有限公司 | The series-parallel loss appraisal method, apparatus of photovoltaic module and computer equipment |
| CN112332517A (en)* | 2020-10-16 | 2021-02-05 | 许继电源有限公司 | Photovoltaic charging MPPT control circuit |
| CN117154853A (en)* | 2023-10-27 | 2023-12-01 | 兰州理工大学 | A dual reconstruction strategy for photovoltaic arrays based on static reconstruction and local reconstruction |
| CN117239742A (en)* | 2023-11-14 | 2023-12-15 | 成都量芯集成科技有限公司 | Photovoltaic array global reconstruction device and method based on improved ant colony algorithm |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090079412A1 (en)* | 2007-09-24 | 2009-03-26 | Yao Hsien Kuo | Apparatus and method for controlling the output of a photovoltaic array |
| CA2747684A1 (en)* | 2008-12-18 | 2010-06-24 | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique | Electronic management system for photovoltaic cells |
| US20110140532A1 (en)* | 2009-12-16 | 2011-06-16 | Nagendra Srinivas Cherukupalli | Systems, Circuits, and Methods For Generating a Solar Cell String of an Adaptive Solar Power System |
| WO2012006723A1 (en)* | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Mohamed Zakaria Mohamed Ahmed Shamseldein | Reconfigurable photovoltaic structure |
| WO2012122131A2 (en)* | 2011-03-04 | 2012-09-13 | Paceco Corp | Measurement of insulation resistance of configurable photovoltaic panels in a photovoltaic array |
- 2012
- 2012-12-20CNCN201210558810.XApatent/CN103049035B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090079412A1 (en)* | 2007-09-24 | 2009-03-26 | Yao Hsien Kuo | Apparatus and method for controlling the output of a photovoltaic array |
| CA2747684A1 (en)* | 2008-12-18 | 2010-06-24 | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique | Electronic management system for photovoltaic cells |
| US20110140532A1 (en)* | 2009-12-16 | 2011-06-16 | Nagendra Srinivas Cherukupalli | Systems, Circuits, and Methods For Generating a Solar Cell String of an Adaptive Solar Power System |
| WO2012006723A1 (en)* | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Mohamed Zakaria Mohamed Ahmed Shamseldein | Reconfigurable photovoltaic structure |
| WO2012122131A2 (en)* | 2011-03-04 | 2012-09-13 | Paceco Corp | Measurement of insulation resistance of configurable photovoltaic panels in a photovoltaic array |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| DZUNG NGUYN,BRAD LEHMAN: "An Adaptive Solar Photovoltaic Array Using Model-Based Reconfiguration Algoithm", 《IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS》* |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103353716A (en)* | 2013-05-16 | 2013-10-16 | 河海大学 | Topological structure capable of realizing photovoltaic array reconstruction and method for solving maximum power point |
| CN103353716B (en)* | 2013-05-16 | 2015-09-16 | 河海大学 | Topological structure and the maximum power point method for solving of photovoltaic array reconstruction can be realized |
| CN107423501A (en)* | 2017-07-17 | 2017-12-01 | 南京邮电大学 | A kind of array automatic detection and method for numbering serial based on photovoltaic plant logic chart |
| CN107423501B (en)* | 2017-07-17 | 2020-05-19 | 南京邮电大学 | Array automatic detection and numbering method based on photovoltaic power station logic diagram |
| CN109067358A (en)* | 2018-08-06 | 2018-12-21 | 浙江工业大学 | Photovoltaic array reconstruction optimization method based on shading battery number |
| CN109067358B (en)* | 2018-08-06 | 2019-11-29 | 浙江工业大学 | Photovoltaic array reconstruction optimization method based on shading battery number |
| CN109842155A (en)* | 2019-03-05 | 2019-06-04 | 协鑫能源工程有限公司 | The series-parallel loss appraisal method, apparatus of photovoltaic module and computer equipment |
| CN112332517A (en)* | 2020-10-16 | 2021-02-05 | 许继电源有限公司 | Photovoltaic charging MPPT control circuit |
| CN117154853A (en)* | 2023-10-27 | 2023-12-01 | 兰州理工大学 | A dual reconstruction strategy for photovoltaic arrays based on static reconstruction and local reconstruction |
| CN117154853B (en)* | 2023-10-27 | 2024-01-09 | 兰州理工大学 | Photovoltaic array double-reconstruction strategy based on static reconstruction and partial reconstruction |
| CN117239742A (en)* | 2023-11-14 | 2023-12-15 | 成都量芯集成科技有限公司 | Photovoltaic array global reconstruction device and method based on improved ant colony algorithm |
| CN117239742B (en)* | 2023-11-14 | 2024-01-26 | 成都量芯集成科技有限公司 | Photovoltaic array global reconstruction device and method based on improved ant colony algorithm |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103049035B (en) | 2014-11-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103049035B (en) | Reconfiguration optimizing method of photovoltaic cell array local reconfigurable electrical system | |
| Bajpai et al. | Hybrid renewable energy systems for power generation in stand-alone applications: A review | |
| CN103064459B (en) | Reconfiguration optimization method of photovoltaic cell array completely reconfigurable electrical system | |
| CN104319768B (en) | A kind of micro-capacitance sensor is powered and method for supervising | |
| CN105576677B (en) | A kind of photovoltaic energy storage system capacity management control method | |
| CN108521140A (en) | A kind of distributed photovoltaic and from energy storage inversion system | |
| JP6236582B2 (en) | Electronic management system for solar cells with matching thresholds. | |
| CN114069774B (en) | Photovoltaic energy storage system for tracking maximum power generated by photovoltaic cell and photovoltaic power generation system based on system | |
| CN105739595B (en) | Device and method for tracking maximum power point in partial shadow of photovoltaic power generation system | |
| CN105811461A (en) | Photovoltaic power generation system and control method of photovoltaic power generation system | |
| CN102608413A (en) | Method and device for detecting maximum power point of photovoltaic power generation | |
| CN111817350A (en) | Voltage fluctuation adjustment method of distributed photovoltaic energy storage microgrid system | |
| CN106779374A (en) | Photovoltaic generation transmits peak power energy storage Optimization Modeling method | |
| CN102624284A (en) | Solar cell photovoltaic array adjustment output control method | |
| CN205622241U (en) | Photovoltaic power generation system | |
| CN119582293A (en) | A hybrid photovoltaic energy storage optimization method based on PerturbandObserve algorithm | |
| CN111585322B (en) | Mobile online photovoltaic charging MPPT device based on variable-step disturbance approximation method | |
| Chen et al. | Scheduling of energy storage in a grid-connected PV/battery system via SIMPLORER | |
| Barote et al. | Renewable hybrid system with battery storage for safe loads supply | |
| CN114784942A (en) | A power self-matching high-efficiency intelligent photovoltaic charging control algorithm and system | |
| Doan et al. | Development of Controller Hardware-in-the-Loop Platform-based Battery Management System for Hybrid PV/Battery System | |
| CN101609999B (en) | Automatic control system for solar energy and wind power combined generation | |
| CN110994671B (en) | A Simulation Model of Small Independent Photovoltaic Power Generation Based on MATLAB | |
| Ghoshal et al. | Performance Analysis of a Storage-Based PV System | |
| An et al. | Design of Household Photovoltaic Power Generation System |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |