CN102908204A - Establishing method for rabbit sinus node chronic injury model and special electrode for implementing establishing method - Google Patents
Establishing method for rabbit sinus node chronic injury model and special electrode for implementing establishing methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102908204A CN102908204ACN2012104109714ACN201210410971ACN102908204ACN 102908204 ACN102908204 ACN 102908204ACN 2012104109714 ACN2012104109714 ACN 2012104109714ACN 201210410971 ACN201210410971 ACN 201210410971ACN 102908204 ACN102908204 ACN 102908204A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- rabbit
- heart rate
- reservoir
- sinoatrial node
- formaldehyde solution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 210000001013sinoatrial nodeAnatomy0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription80
- 241000283973Oryctolagus cuniculusSpecies0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription71
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription58
- 230000009693chronic damageEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription14
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-NFormaldehydeChemical compoundO=CWSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription74
- 210000002216heartAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription69
- 239000008098formaldehyde solutionSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription32
- HOBWAPHTEJGALG-JKCMADFCSA-N[(1r,5s)-8-methyl-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl] 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate;sulfateChemical compound[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O.C([C@H]1CC[C@@H](C2)[NH+]1C)C2OC(=O)C(CO)C1=CC=CC=C1.C([C@H]1CC[C@@H](C2)[NH+]1C)C2OC(=O)C(CO)C1=CC=CC=C1HOBWAPHTEJGALG-JKCMADFCSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 229960002028atropine sulfateDrugs0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 210000000038chestAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 210000002615epidermisAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 210000001370mediastinumAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 210000003205muscleAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 210000003516pericardiumAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 210000000115thoracic cavityAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 238000002347injectionMethods0.000claimsdescription28
- 239000007924injectionSubstances0.000claimsdescription28
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription27
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000claimsdescription27
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000claimsdescription23
- 235000009161Espostoa lanataNutrition0.000claimsdescription6
- 240000001624Espostoa lanataSpecies0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000claimsdescription5
- 210000003462veinAnatomy0.000claimsdescription4
- 206010002091AnaesthesiaDiseases0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000037005anaesthesiaEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 229960001412pentobarbitalDrugs0.000claimsdescription3
- 210000003491skinAnatomy0.000claimsdescription3
- 210000001562sternumAnatomy0.000claimsdescription3
- 241000221377AuriculariaSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000005484gravityEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000010253intravenous injectionMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000000149penetrating effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- WEXRUCMBJFQVBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NpentobarbitalChemical compoundCCCC(C)C1(CC)C(=O)NC(=O)NC1=OWEXRUCMBJFQVBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- 210000005247right atrial appendageAnatomy0.000abstractdescription9
- 230000000630rising effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description21
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description16
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description9
- 101150024326Csn1s2b geneProteins0.000description8
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description8
- 229920000742CottonPolymers0.000description6
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000description6
- 206010040639Sick sinus syndromeDiseases0.000description6
- 230000004083survival effectEffects0.000description6
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description5
- 230000008595infiltrationEffects0.000description5
- 238000001764infiltrationMethods0.000description5
- 201000003144pneumothoraxDiseases0.000description5
- 208000032843HemorrhageDiseases0.000description4
- 206010003119arrhythmiaDiseases0.000description4
- 230000006793arrhythmiaEffects0.000description4
- QGMRQYFBGABWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-MPentobarbital sodiumChemical compound[Na+].CCCC(C)C1(CC)C(=O)NC(=O)[N-]C1=OQGMRQYFBGABWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description3
- 241000700159RattusSpecies0.000description3
- 210000001744T-lymphocyteAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000description3
- 238000010171animal modelMethods0.000description3
- 230000001746atrial effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000036770blood supplyEffects0.000description3
- 230000001684chronic effectEffects0.000description3
- 210000004457myocytus nodalisAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000035515penetrationEffects0.000description3
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description3
- 238000012353t testMethods0.000description3
- 210000002620vena cava superiorAnatomy0.000description3
- 210000001367arteryAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000008827biological functionEffects0.000description2
- 230000000747cardiac effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000005779cell damageEffects0.000description2
- 208000037887cell injuryDiseases0.000description2
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description2
- 210000004351coronary vesselAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000034994deathEffects0.000description2
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description2
- 210000002837heart atriumAnatomy0.000description2
- 238000007490hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stainingMethods0.000description2
- 208000015181infectious diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description2
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-NJFSPNSNSA-NmethanoneChemical compoundO=[14CH2]WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-NJFSPNSNSA-N0.000description2
- 230000000877morphologic effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000002980postoperative effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000000718qrs complexMethods0.000description2
- 238000007674radiofrequency ablationMethods0.000description2
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description2
- 230000033764rhythmic processEffects0.000description2
- 230000008961swellingEffects0.000description2
- 210000001631vena cava inferiorAnatomy0.000description2
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229930040373ParaformaldehydeNatural products0.000description1
- 229930182555PenicillinNatural products0.000description1
- JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-NPenicillin GChemical compoundN([C@H]1[C@H]2SC([C@@H](N2C1=O)C(O)=O)(C)C)C(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N0.000description1
- 208000033248Sanjad-Sakati syndromeDiseases0.000description1
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilverChemical compound[Ag]BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 206010040736Sinoatrial blockDiseases0.000description1
- 206010040738Sinus arrestDiseases0.000description1
- 208000027418Wounds and injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 238000002679ablationMethods0.000description1
- 230000009692acute damageEffects0.000description1
- 238000000540analysis of varianceMethods0.000description1
- FCPVYOBCFFNJFS-LQDWTQKMSA-Mbenzylpenicillin sodiumChemical compound[Na+].N([C@H]1[C@H]2SC([C@@H](N2C1=O)C([O-])=O)(C)C)C(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1FCPVYOBCFFNJFS-LQDWTQKMSA-M0.000description1
- 230000000740bleeding effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000009395breedingMethods0.000description1
- 230000001488breeding effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009089cytolysisEffects0.000description1
- 210000000805cytoplasmAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000007850degenerationEffects0.000description1
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 230000000857drug effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004064dysfunctionEffects0.000description1
- 210000005069earsAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000description1
- 230000008014freezingEffects0.000description1
- 238000007710freezingMethods0.000description1
- 244000144993groups of animalsSpecies0.000description1
- 208000008541hypoparathyroidism-retardation-dysmorphism syndromeDiseases0.000description1
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 238000003780insertionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037431insertionEffects0.000description1
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description1
- 210000000056organAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000012188paraffin waxSubstances0.000description1
- 229920002866paraformaldehydePolymers0.000description1
- 230000008506pathogenesisEffects0.000description1
- 229940049954penicillinDrugs0.000description1
- 229960002275pentobarbital sodiumDrugs0.000description1
- 210000004224pleuraAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 229910052709silverInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000004332silverSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011780sodium chlorideSubstances0.000description1
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007619statistical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000004936stimulating effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000description1
- 230000001629suppressionEffects0.000description1
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description1
- 208000011580syndromic diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 238000005303weighingMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于医学领域中的动物模型领域,具体涉及一种兔窦房结慢性损伤模型的建立方法。The invention belongs to the field of animal models in the medical field, and in particular relates to a method for establishing a rabbit sinoatrial node chronic injury model.
背景技术Background technique
病态窦房结综合征(Sick Sinus Syndrome,SSS)是一种临床常见的难治性心律失常疾病,其发病机制尚未明确,已有研究表明,窦房结细胞损伤导致起搏及传导功能障碍是其直接原因。建立稳定、可重复的窦房结慢性损伤(ChronicSinus Node Dysfunction,CSND)模型是对SSS进行实验研究的前提。Sick sinus syndrome (Sick Sinus Syndrome, SSS) is a common clinical refractory arrhythmia disease, its pathogenesis is not yet clear, studies have shown that sinoatrial node cell damage leads to pacing and conduction dysfunction its immediate cause. Establishing a stable and reproducible chronic sinus node damage (Chronic Sinus Node Dysfunction, CSND) model is a prerequisite for experimental research on SSS.
CSND模型成功的关键是在尽可能减少动物窦房结周围组织及其他组织器官损伤的前提下,造成窦房结慢性损伤,使心脏电生理各项指标在造模后一段时间内趋于稳定,符合临床SSS的特征。目前CSND模型的建立方法主要通过冰冻消融窦房结区法、射频消融窦房结区法、结扎窦房结血供动脉法、甲醛湿敷窦房结区法等造成窦房结细胞损伤来实现。这些方法存在较难精确定位窦房结区、损伤范围较大、存活率较低的弊端。例如,冰冻消融窦房结区法及射频消融法依赖于大型设备,操作难度较大,不适宜建立类似兔这样较小动物的CSND模型;结扎窦房结血供动脉法可成功建立窦房结急性损伤模型,兔窦房结主要血供来源于右冠脉,但兔窦房结区面积较小,暴露右冠脉部位欠佳,使用该法易造成心脏其他组织损伤,对建立CSND模型难度较大;甲醛湿敷法虽然能够建立CSND模型,但需在体表进行3~5cm切口并钳断2根肋骨,损伤较大,此外,甲醛湿敷法难以精确定位窦房结区,容易造成心脏其他组织的损伤,并易造成右心耳出血及胸膜破裂导致气胸,不利于模型动物术后存活。The key to the success of the CSND model is to cause chronic damage to the sinus node on the premise of reducing the damage to the tissues around the sinus node and other tissues and organs as much as possible, so that the electrophysiological indicators of the heart tend to be stable for a period of time after the model is established. Consistent with the characteristics of clinical SSS. At present, the methods of establishing the CSND model are mainly through freezing and ablation of the sinus node area, radiofrequency ablation of the sinus node area, ligation of the blood supply artery of the sinoatrial node, and wet dressing of the sinus node area with formaldehyde, etc. to cause sinus node cell damage. . These methods have the disadvantages of difficulty in accurately locating the sinoatrial node area, large damage range, and low survival rate. For example, cryoablation of the sinus node area and radiofrequency ablation rely on large-scale equipment and are difficult to operate, so they are not suitable for establishing CSND models in smaller animals such as rabbits; ligation of sinus node blood supply arteries can successfully establish the sinus node In the acute injury model, the main blood supply of the rabbit sinus node comes from the right coronary artery, but the area of the rabbit sinus node area is small, and the exposure of the right coronary artery is not good. Using this method can easily cause damage to other tissues of the heart, which is difficult for the establishment of CSND models Larger; although the formaldehyde wet compress method can establish a CSND model, it needs to make a 3-5cm incision on the body surface and clamp off two ribs, which causes relatively large damage. Damage to other tissues of the heart can easily cause right atrial appendage hemorrhage and pleural rupture leading to pneumothorax, which is not conducive to the postoperative survival of model animals.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于提供一种兔窦房结慢性损伤模型的建立方法。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for establishing a rabbit sinoatrial node chronic injury model.
本发明采用的技术方案是:The technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
一种兔窦房结慢性损伤模型的建立方法,包括以下步骤:A method for establishing a rabbit sinoatrial node chronic injury model, comprising the following steps:
(一)将兔麻醉后,背位固定于兔台上,记录体表心电图;(1) After the rabbit is anesthetized, the dorsal position is fixed on the rabbit platform, and the surface electrocardiogram is recorded;
(二)胸前区备皮,沿胸骨右缘第三肋处纵行开胸1.5-2.5cm,逐层分离表皮及肌肉组织,钳断右侧第三肋,经纵膈打开心包,暴露右心耳;(2) Prepare the skin in the chest area, open the chest 1.5-2.5 cm longitudinally along the third rib on the right edge of the sternum, separate the epidermis and muscle tissue layer by layer, cut off the third rib on the right side with forceps, open the pericardium through the mediastinum, and expose the right side Auricularia;
(三)将连接心电图v1导联的电极置于兔心脏的近窦房结区表面并缓慢移动,根据心电图的特征(即心电图显示出窦房结区电图特征)定位窦房结区的准确位置,向该位置施加20%的甲醛溶液,待兔心率下降至原心率的50%~70%时,停止施加甲醛溶液,静脉注射硫酸阿托品2mg,如兔心率稳定于原心率的50%~70%,则可实施步骤(四);如注射硫酸阿托品后兔心率回升到原心率的70%以上,则需再次施加甲醛溶液,当兔心率又下降至原心率的50%~70%时,停止施加甲醛溶液,再次静脉注射硫酸阿托品2mg,如此交替施加两种药物,直至静脉注射硫酸阿托品后兔心率仍稳定于原心率的50%~70%;(3) Place the electrode connected to the V1 lead of the electrocardiogram on the surface of the near sinoatrial node area of the rabbit heart and move it slowly, and accurately locate the sinoatrial node area according to the characteristics of the electrocardiogram (that is, the electrocardiogram shows the electrogram characteristics of the sinoatrial node area) position, apply 20% formaldehyde solution to this position, and stop applying formaldehyde solution when the heart rate of the rabbit drops to 50%-70% of the original heart rate, and inject 2mg of atropine sulfate intravenously, if the rabbit heart rate is stable at 50%-70% of the original heart rate %, then step (4) can be implemented; if the heart rate of the rabbit rises to more than 70% of the original heart rate after the injection of atropine sulfate, formaldehyde solution needs to be applied again, and when the heart rate of the rabbit drops to 50% to 70% of the original heart rate, stop Apply formaldehyde solution, and inject 2 mg of atropine sulfate intravenously again, so that the two drugs are applied alternately until the heart rate of the rabbit is still stable at 50% to 70% of the original heart rate after intravenous injection of atropine sulfate;
(四)冲洗胸腔,逐层关胸,饲养备用。(4) Flush the chest cavity, close the chest layer by layer, and keep them for later use.
优选地,所述兔为大耳白兔。Preferably, the rabbit is a white rabbit with big ears.
优选地,所述步骤(一)中,所述麻醉采用以3%戊巴比妥钠按30mg/kg剂量耳缘静脉麻醉实施。Preferably, in the step (1), the anesthesia is implemented by auricular vein anesthesia with 3% sodium pentobarbital at a dose of 30 mg/kg.
优选地,所述步骤(三)中,所述向窦房结区施加甲醛溶液的方法是通过注射器向窦房结区表面推注甲醛溶液。这样可以根据需要随时启动或停止施加甲醛溶液,并且便于准确控制甲醛溶液的用量和推注速度。更优选地,所述甲醛溶液通过直径不超过4mm的无菌棉球施加至窦房结区表面。这样的设计不仅使甲醛溶液对窦房结区的浸润位置更加准确,而且可以将甲醛溶液锁住而不致外流,以减少甲醛溶液对周围组织的损伤。Preferably, in the step (3), the method of applying the formaldehyde solution to the sinoatrial node area is to inject the formaldehyde solution onto the surface of the sinoatrial node area through a syringe. In this way, the application of formaldehyde solution can be started or stopped at any time according to needs, and it is convenient to accurately control the dosage and injection speed of formaldehyde solution. More preferably, the formaldehyde solution is applied to the surface of the sinoatrial node region through a sterile cotton ball with a diameter not exceeding 4 mm. This design not only makes the infiltration position of the formaldehyde solution to the sinoatrial node area more accurate, but also can lock the formaldehyde solution from outflow, so as to reduce the damage of the formaldehyde solution to the surrounding tissues.
优选地,在完成步骤(三)后,应待兔心率稳定于原心率的50%~70%达2小时后再实施步骤(四)。Preferably, after completing step (3), the rabbit's heart rate should be stabilized at 50%-70% of the original heart rate for 2 hours before implementing step (4).
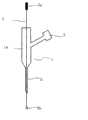
为了更好地实施本发明兔窦房结慢性损伤模型的建立方法,本发明同时还提供一种用于实施步骤(三)的窦房结定位注射渗透电极装置。一种窦房结定位注射渗透电极装置,所述装置包括储液器(1)、注液接口(2)、金属电极针(3);其中储液器(1)包括储液器主体(1a)和储液器颈(1b);储液器主体(1a)一端封闭,另一端与储液器颈(1b)连通;储液器颈(1b)一端与储液器主体(1a)连通,另一端开放;注液接口(2)的一端与储液器主体(1a)连通,另一端开放,且该开放端可与医用注射器实现密闭连接;金属电极针(3)从内部贯穿储液器主体(1a)和储液器颈(1b),且其两端从储液器(1)中伸出;金属电极针(3)从储液器主体(1a)伸出的一端用于连接心电图v1导联,金属电极针(3)从储液器颈(1b)伸出的一端用于将储液器(1)内的液体导至窦房结区。In order to better implement the establishment method of the rabbit sinoatrial node chronic injury model of the present invention, the present invention also provides a sinoatrial node locating injection permeable electrode device for implementing step (3). A sinoatrial node positioning injection penetrating electrode device, the device includes a liquid reservoir (1), a liquid injection interface (2), a metal electrode needle (3); wherein the liquid reservoir (1) includes a liquid reservoir body (1a ) and the reservoir neck (1b); one end of the reservoir body (1a) is closed, and the other end communicates with the reservoir neck (1b); one end of the reservoir neck (1b) communicates with the reservoir body (1a), The other end is open; one end of the liquid injection interface (2) communicates with the liquid reservoir main body (1a), and the other end is open, and the open end can be connected to a medical syringe in a sealed manner; the metal electrode needle (3) penetrates the liquid reservoir from the inside The main body (1a) and the liquid reservoir neck (1b), and its two ends protrude from the liquid reservoir (1); the end of the metal electrode needle (3) protruding from the liquid reservoir main body (1a) is used to connect the electrocardiogram Lead v1, the end of the metal electrode needle (3) protruding from the reservoir neck (1b) is used to lead the liquid in the reservoir (1) to the sinoatrial node area.
优选地,金属电极针(3)与所述储液器颈(1b)内壁之间的空隙使储液器主体(1a)中的液体仅凭重力作用不能流出,需在所述注射器的推力作用下沿金属电极针(3)的下端流出。这样不仅可以用注射器精确控制施加液体的用量,而且可以控制液体流出的速度。Preferably, the gap between the metal electrode needle (3) and the inner wall of the reservoir neck (1b) prevents the liquid in the reservoir body (1a) from flowing out only by the action of gravity, and it needs to be under the action of the thrust of the syringe. Flow out along the lower end of the metal electrode needle (3). This allows precise control not only of the amount of liquid applied with the syringe, but also of the rate at which the liquid flows out.
优选地,金属电极针(3)从储液器颈(1b)端伸出的一端的末端缠绕无菌棉。这样可将多余甲醛溶液锁住而不致外流,减小了对周围组织的损伤;且电极一直固定于窦房结区,确保了窦房结区定位的一致性。优选地,所述金属电极针(3)从储液器颈(1b)端伸出的一端的末端弯成圆环(3b)或爪钩,所述圆环(3b)或爪钩的内径不超过4mm。Preferably, the end of the end of the metal electrode needle (3) protruding from the neck (1b) of the reservoir is wrapped with sterile cotton. In this way, the excess formaldehyde solution can be locked without outflow, reducing the damage to the surrounding tissue; and the electrodes are always fixed in the sinoatrial node area, ensuring the consistency of the sinoatrial node area positioning. Preferably, the end of the metal electrode needle (3) extending from the end of the reservoir neck (1b) is bent into a ring (3b) or a hook, and the inner diameter of the ring (3b) or the hook is not larger than more than 4mm.
以本发明窦房结定位注射渗透电极的上述优选实施方式实施制备兔窦房结慢性损伤模型的步骤(三)时,金属电极针下端的金属圆环(3b)缠绕有无菌棉,棉球有效直径不超过4mm,将所述金属电极针的上端(3a)连接心电图v1导联,然后将金属圆环(3b)置于近窦房结区并缓慢移动,当心电图显示出窦房结区电图特征时,停止移动金属圆环(3b)并固定位置,使用注射器(例如规格为1ml的注射器)与注液接口(2)密闭连接并缓慢向储液器主体(1a)中注入20%的甲醛溶液,在注射压力的作用下,甲醛溶液进入储液器颈(1b),并沿金属电极针(3)到达金属圆环(3b)上的无菌棉球,从而在窦房结区直径4mm的局部位置内发挥药效。When implementing the step (3) of preparing the rabbit sinus node chronic injury model with the above-mentioned preferred embodiment of sinoatrial node positioning injection permeable electrode of the present invention, the metal ring (3b) at the lower end of the metal electrode needle is wrapped with sterile cotton, cotton balls The effective diameter does not exceed 4mm. Connect the upper end (3a) of the metal electrode needle to the V1 lead of the electrocardiogram, and then place the metal ring (3b) in the area near the sinoatrial node and move it slowly. When the electrocardiogram shows the sinoatrial node area When the electrogram is characterized, stop moving the metal ring (3b) and fix the position, use a syringe (such as a syringe with a specification of 1ml) to tightly connect with the liquid injection port (2) and slowly inject 20% into the main body of the liquid reservoir (1a) Formaldehyde solution, under the action of injection pressure, the formaldehyde solution enters the reservoir neck (1b), and reaches the sterile cotton ball on the metal ring (3b) along the metal electrode needle (3), thus in the sinoatrial node area The drug effect is exerted in a local area with a diameter of 4mm.
与现有的各种兔窦房结慢性损伤模型建立方法相比,本发明的方法具有如下优点:Compared with various existing rabbit sinoatrial node chronic injury model establishment methods, the method of the present invention has the following advantages:
1.方法简单,易于操作,不依赖于大型设备;1. The method is simple, easy to operate, and does not depend on large equipment;
2.采用注射器进行甲醛溶液的推注,易于控制甲醛溶液的使用量;2. Use a syringe to inject formaldehyde solution, which is easy to control the amount of formaldehyde solution used;
3.金属圆环(3b)上缠绕的直径不超过4mm的无菌棉球,可将多余甲醛溶液锁住而不致外流,减小了对周围组织的损伤;且电极一直固定于窦房结区,避免了因直接使用注射器注射药物时反复插拔而感染的机会及窦房结定位的不一致性;3. A sterile cotton ball with a diameter of no more than 4mm wrapped around the metal ring (3b) can lock excess formaldehyde solution from outflow, reducing damage to surrounding tissues; and the electrode is always fixed in the sinoatrial node area , to avoid the chance of infection and the inconsistency of sinoatrial node positioning due to repeated insertion and extraction when directly using the syringe to inject drugs;
4.通过窦房结电图准确定位窦房结区,使甲醛溶液的施加靶位更加准确、具体,相比于甲醛湿敷法中直接用棉球敷药,可显著降低因窦房结周围组织及心脏其他组织损伤而造成心脏出血的几率;4. Accurately locate the sinus node area through the sinoatrial node electrogram, so that the application target of the formaldehyde solution is more accurate and specific. The chance of bleeding from the heart due to damage to tissue and other tissues in the heart;
5.相比于甲醛湿敷法,由于施药靶位准确,因此可将胸部切口的长度由原来的3-5cm减小到2cm左右,需钳断的肋骨也由原来的2根减少到1根,从而可有效避免手术造成的右心耳出血及胸膜破裂导致的气胸,提高了模型动物的术后存活率;5. Compared with the formaldehyde wet compress method, due to the accurate target position of the drug application, the length of the chest incision can be reduced from the original 3-5cm to about 2cm, and the ribs to be clamped are also reduced from the original 2 to 1 root, which can effectively avoid right atrial appendage hemorrhage caused by surgery and pneumothorax caused by pleural rupture, and improve the postoperative survival rate of model animals;
6.造模成功率高,且模型较稳定;6. The success rate of modeling is high, and the model is relatively stable;
7.可行性、重复性好。7. Good feasibility and repeatability.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为兔窦房结电图;图中所示信息包括:心率为164次/分、最大值0.79mV、最小值-0.99mV、峰峰值1.78mV;特征为出现深大负向之P波及相对较小的QRS波群。Figure 1 is the electrogram of the sinus node in rabbits; the information shown in the figure includes: heart rate 164 beats/min, maximum value 0.79mV, minimum value -0.99mV, peak-to-peak value 1.78mV; characterized by deep and large negative P waves Relatively small QRS complexes.
图2为窦房结定位注射渗透电极装置的纵向剖面图的简化示意图。Fig. 2 is a simplified schematic diagram of a longitudinal section view of a sinoatrial node locating injectable permeable electrode device.
附图标记列表List of reference signs
1储液器1 reservoir
1a储液器主体1a reservoir body
1b储液器颈1b Reservoir Neck
2储液器上的注液接口2 Injection port on the reservoir
3金属电极针(全针通常用不锈钢制成)3 metal electrode needles (full needles are usually made of stainless steel)
3a金属电极针的上端3a The upper end of the metal electrode needle
3b金属电极针下端的金属圆环3b The metal ring at the lower end of the metal electrode needle
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施例对本发明做进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
实施例1甲醛湿敷法和甲醛加压注射渗透法制造兔窦房结慢性损伤模型的比较材料与方法Embodiment 1 Formaldehyde wet compress method and formaldehyde pressurized injection infiltration method make the comparative material and method of rabbit sinoatrial node chronic injury model
1实验动物1 experimental animal
大耳白兔35只,普通级,体重2.5±0.5kg,雌雄不拘,广安门医院实验动物中心提供(许可证号:SCXK(京)2005-0009)。35 big-eared white rabbits, ordinary grade, weighing 2.5±0.5kg, male or female, were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Guang'anmen Hospital (permit number: SCXK (Beijing) 2005-0009).
2实验分组2 experimental groups
实验动物按随机数字表随机分为甲醛湿敷组(以下简称为“湿敷组”)和甲醛加压注射渗透组(即使用本发明方法组,以下简称为“新方法组”),每组15只;另有5只做为假手术组(即按甲醛加压注射渗透组方法实施手术,但以生理盐水代替甲醛溶液)。The experimental animals are randomly divided into formaldehyde wet compress group (hereinafter referred to as "wet compress group") and formaldehyde pressurized injection infiltration group (i.e. using the method group of the present invention, hereinafter referred to as "new method group") by random number table, each group 15 rats; the other 5 rats were used as a sham operation group (that is, the operation was performed according to the method of the formaldehyde pressurized injection penetration group, but with normal saline instead of formaldehyde solution).
3实验仪器3 experimental equipment
BL-420F生物机能实验仪(成都泰盟科技有限公司);DF-4A心脏电生理刺激仪(东方电子仪器厂);自制窦房结定位注射渗透电极。BL-420F biological function experiment instrument (Chengdu Taimeng Technology Co., Ltd.); DF-4A cardiac electrophysiological stimulator (Dongfang Electronic Instrument Factory); self-made sinoatrial node positioning injection penetration electrode.
4实验试剂4 experimental reagents
3%戊巴比妥钠(sigma,批号:018k0754),20%甲醛溶液(国药集团,批号:20091015),硫酸阿托品注射液(天津金耀氨基酸有限公司,批号:H12020382),注射用青霉素钠(80万单位,华北制药,批号:Y0909210)3% sodium pentobarbital (sigma, batch number: 018k0754), 20% formaldehyde solution (Sinopharm Group, batch number: 20091015), atropine sulfate injection (Tianjin Jinyao Amino Acid Co., Ltd., batch number: H12020382), penicillin sodium for injection ( 800,000 units, North China Pharmaceuticals, batch number: Y0909210)
5实验方法5 Experimental methods
5.1窦房结慢性损伤模型的建立5.1 Establishment of sinus node chronic injury model
取健康大耳白兔,以3%戊巴比妥钠按30mg/kg剂量耳缘静脉麻醉,背位固定于兔台上,记录体表心电图。胸前区备皮,沿胸骨右缘2~3mm第三肋处纵行开胸(开口长度:湿敷组3-5cm、新方法组约2cm),逐层分离表皮及肌肉组织,钳断右侧部分肋骨(湿敷组钳断第三、四肋,新方法组钳断第三肋),经纵膈打开心包(避免损伤右胸膜),暴露右心耳,然后,Healthy big-eared white rabbits were anesthetized with 3% pentobarbital sodium at a dose of 30mg/kg in the ear vein, fixed on the rabbit table in the dorsal position, and the surface electrocardiogram was recorded. Prepare the skin in the chest area, open the chest longitudinally along the third rib 2-3mm from the right edge of the sternum (opening length: 3-5cm in the wet compress group, about 2cm in the new method group), separate the epidermis and muscle tissue layer by layer, and cut off the right Part of the side ribs (the third and fourth ribs were clamped in the wet compress group, and the third rib was clamped in the new method group), the pericardium was opened through the mediastinum (to avoid damage to the right pleura), and the right atrial appendage was exposed.
湿敷组,以直径5mm棉签蘸取20%甲醛溶液湿敷近窦房结区(上腔静脉与右心耳之间);In the wet compress group, wet compress the area near the sinoatrial node (between the superior vena cava and the right atrial appendage) with 20% formaldehyde solution dipped in a cotton swab with a diameter of 5 mm;
新方法组,将自制窦房结定位注射渗透电极的上端(3a)连接心电图v1导联,将金属圆环(3b)上缠绕少量无菌棉后(不要影响导电性)置于兔心脏近窦房结区的表面并缓慢移动,当心电图显示出窦房结区电图特征时(即出现深大负向之P波及相对较小的QRS波群),停止移动电极并固定位置,于注液接口(2)处密闭连接微量注射器,推注20%甲醛溶液0.01-0.02ml,使之经棉球作用于窦房结区;In the new method group, the upper end (3a) of the self-made sinoatrial node positioning injection penetration electrode is connected to the V1 lead of the ECG, and a small amount of sterile cotton is wrapped around the metal ring (3b) (do not affect the conductivity) and placed near the sinus of the rabbit heart The surface of the atrial node area moves slowly. When the electrocardiogram shows the characteristics of the electrogram of the sinoatrial node area (that is, there are deep and large negative P waves and relatively small QRS complexes), stop moving the electrodes and fix the position. The interface (2) is airtightly connected to a micro-syringe, and 0.01-0.02 ml of 20% formaldehyde solution is injected to make it act on the sinoatrial node area through the cotton ball;
两组均待兔心率下降至原心率的50%~70%时,静脉注射硫酸阿托品2mg,观察兔心率变化情况。如兔心率回升到原心率的70%以上,则再次施加甲醛溶液,当兔心率又下降至原心率的50%~70%时,停止施加甲醛溶液,再次静脉注射硫酸阿托品2mg,如此交替施加两种药物,直至注射硫酸阿托品后兔心率仍稳定于原心率的50%~70%。当兔心率稳定于原心率的50%~70%达2小时,则以青霉素生理盐水冲洗胸腔,逐层关胸,精心饲养备用。When the heart rate of the rabbits dropped to 50%-70% of the original heart rate, both groups were injected with 2 mg of atropine sulfate intravenously, and the heart rate changes of the rabbits were observed. If the rabbit's heart rate rises to more than 70% of the original heart rate, apply formaldehyde solution again. When the rabbit's heart rate drops to 50% to 70% of the original heart rate, stop applying formaldehyde solution and inject 2 mg of atropine sulfate intravenously again. After the injection of atropine sulfate, the rabbit's heart rate remained stable at 50% to 70% of the original heart rate. When the rabbit's heart rate was stable at 50% to 70% of the original heart rate for 2 hours, the chest cavity was washed with penicillin saline, the chest was closed layer by layer, and carefully reared for use.
剔除动物:1.实验过程中造成气胸者。2.饲养过程中出现感染及死亡者。Exclude animals: 1. Those who caused pneumothorax during the experiment. 2. Infection and death occurred during the breeding process.
5.2观察指标5.2 Observation indicators
5.2.1心率及心律5.2.1 Heart rate and rhythm
兔四肢皮下插入电极连接BL-420F生物机能实验仪,实验仪与电脑相连输出,记录体表心电图,以连续10个AA间期的均值计算心率,分别于造模前及造模后2h、24h、1w、2w测定并观察心律失常情况。Electrodes were inserted subcutaneously into the limbs of rabbits and connected to the BL-420F biological function experiment instrument. The experiment instrument was connected to the computer for output, and the body surface electrocardiogram was recorded. The heart rate was calculated by the average value of 10 consecutive AA intervals, and the heart rate was calculated before and after 2 hours and 24 hours after modeling. , 1w, 2w measurement and observation of arrhythmia.
5.2.2电生理指标5.2.2 Electrophysiological indicators
采用心外膜调搏法,以银针电极两根作为心外膜调搏电极,一根作为刺激电极,置于右心耳高位,另一根作为参考电极置于右心耳,电极另一端连接心脏电生理刺激仪。以体表心电图记录电生理变化,分别于造模前及造模后2h、2w测定以下指标:The epicardial pacing method is adopted, and two silver needle electrodes are used as epicardial pacing electrodes, one is used as a stimulating electrode, placed at the high position of the right atrial appendage, and the other is placed as a reference electrode at the right atrial appendage, and the other end of the electrode is connected to the heart Electrophysiological Stimulator. Electrophysiological changes were recorded by body surface electrocardiogram, and the following indicators were measured before modeling and 2 hours and 2 weeks after modeling:
(1)SACT(窦房传导时间):设置输出电压为3v,选择高于兔心脏基础心率的10%~15%的频率周期。(1) SACT (sinus atrial conduction time): set the output voltage to 3v, and select a frequency cycle that is 10% to 15% higher than the basic heart rate of the rabbit heart.
短阵起搏心房,步长-10ms,S1∶S2为8∶1反扫,以Narula法计算SACT。The atrium was paced in short bursts, the step length was -10ms, S1:S2 was 8:1 backsweep, and SACT was calculated by Narula method.
(2)SNRT(窦房恢复时间):采用超速抑制分级递增法刺激心房,间隔1min,以最后一个心房刺激到恢复第一个窦性周期之间的最长间歇作为SNRT记录。(2) SNRT (sinus recovery time): the atrium was stimulated by the overspeed suppression step-by-step method with an interval of 1 min, and the longest interval between the last atrial stimulation and the recovery of the first sinus cycle was recorded as the SNRT.
(3)cSNRT(校正窦房恢复时间):cSNRT=SNRT-SCL(窦性周期)。(3) cSNRT (corrected sinus recovery time): cSNRT=SNRT-SCL (sinus cycle).
5.2.3造模成功率及兔死亡率5.2.3 Modeling success rate and rabbit mortality rate
记录两组动物造模后兔存活情况,计算两组造模成功率及兔死亡率。The survival of the rabbits after modeling was recorded in the two groups of animals, and the success rate of modeling and the mortality rate of the rabbits in the two groups were calculated.
5.2.4窦房结组织细胞形态观察5.2.4 Morphological observation of sinoatrial node tissue cells
从两实验组中每组取3只兔行窦房结组织细胞形态观察,分别于第2w完成电生理指标的测量后安乐处死,迅速取出心脏并用生理盐水冲洗,分离右心耳及上、下腔静脉,剪开上、下腔静脉,于上腔静脉入口以下至下腔静脉口以上界嵴的腔静脉侧切取窦房结组织。将切取的窦房结组织经生理盐水冲洗干净后立即置入4%多聚甲醛固定48h,梯度酒精脱水、透明、石蜡包埋、各组织采用横向连续切片,片厚6μm,隔10取1,做HE染色,以确定窦房结组织具体起始位置,随后各组织选取相对一致的层面间取5张白片继续行HE染色,使用Olympus IX-70倒置荧光显微镜观察窦房结组织形态结构的改变。Three rabbits were taken from each of the two experimental groups to observe the morphology of sinoatrial node tissue cells. They were euthanized after the measurement of electrophysiological indicators on the 2nd week, and the heart was quickly taken out and washed with normal saline, and the right atrial appendage and the upper and lower chambers were separated. Vein, cut the superior and inferior vena cava, and cut the sinoatrial node tissue from the vena cava side below the entrance of the superior vena cava to the crest above the ostium of the inferior vena cava. The excised sinoatrial node tissue was rinsed with normal saline and immediately fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 48 hours, dehydrated with gradient alcohol, transparent, embedded in paraffin, and each tissue was sliced horizontally with a thickness of 6 μm, and 1 was taken every 10. Perform HE staining to determine the specific starting position of the sinoatrial node tissue, and then select 5 white slices from relatively consistent layers of each tissue to continue HE staining, and use an Olympus IX-70 inverted fluorescence microscope to observe the morphology and structure of the sinoatrial node tissue Change.
6统计分析6 Statistical analysis
所有数据以均数±标准差表示。采用spss16.0软件,做t检验及方差分析,以P<0.05为差异有显著性。All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Using spss16.0 software, do t test and analysis of variance, with P<0.05 as the difference is significant.
结果之一两组的共同之处Findings 1 What the two groups have in common
1心率及节律变化1 Heart rate and rhythm changes
湿敷组及新方法组造模后2h、24h、1w、2w心率均较造模前明显下降,经t检验与造模前有明显差异(P<0.01)。18只造模成功兔中有14只出现窦性停搏、窦房阻滞、结性逸搏等心律失常。湿敷组与新方法组造模后2h、24h、1w、2w心率组间比较无统计学差异(P>0.05),且均与造模前不同,证实两种手术方法均可成功建立窦房结慢性损伤模型。见表1。The heart rates of the wet compress group and the new method group at 2h, 24h, 1w, and 2w after modeling were significantly lower than those before modeling, and there was a significant difference from before modeling by t test (P<0.01). Among the 18 successful rabbits, 14 had arrhythmias such as sinus arrest, sinoatrial block, and nodal escape. There was no statistical difference between the wet compress group and the new method group after 2h, 24h, 1w, and 2w heart rate after modeling (P>0.05), and they were all different from those before modeling, which confirmed that both surgical methods can successfully establish sinus chambers Chronic injury model. See Table 1.
表1两组兔造模前后心率变化(x±s,次/分)Table 1 Changes in heart rate of two groups of rabbits before and after modeling (x±s, times/min)
*P<0.01,与造模前比较;△P>0.05,造模后各时间点之间比较* P<0.01, compared with before modeling;△ P>0.05, compared with each time point after modeling
2电生理指标变化2 Changes in electrophysiological indicators
两组兔造模后2h、2w SACT、SNRT及cSNRT均较造模前明显延长(P<0.01),且两组兔上述指标无明显差异(P>0.05),两种方法均可制备较稳定的窦房结慢性损伤模型。见表2。The 2h, 2w SACT, SNRT and cSNRT of the two groups of rabbits after modeling were significantly longer than those before modeling (P<0.01), and there was no significant difference in the above indicators between the two groups of rabbits (P>0.05). The two methods can be prepared more stable sinus node chronic injury model. See Table 2.
表2两组家兔造模前后电生理指标变化(x±s,ms)Table 2 Changes of electrophysiological indicators in two groups of rabbits before and after modeling (x±s, ms)
*P<0.01,与造模前比较;△P>0.05,与造模后2h比较;▲P>0.05,与造模后2h比较* P<0.01, compared with before modeling;△ P>0.05, compared with 2 hours after modeling;▲ P>0.05, compared with 2 hours after modeling
3窦房结组织细胞形态观察3 Morphological observation of sinoatrial node tissue cells
发明人在研究中切取正常兔窦房结组织观察其形态,光镜下正常兔窦房结细胞排列有序,无肿胀及充血,结区主要由P细胞和T细胞组成,胞质淡染。P细胞核大,呈圆形或椭圆形,细胞界限不清,常成团分布;T细胞散在分布于窦房结区中心及边缘,呈长形或梭形。实验中,假手术组兔窦房结组织细胞排列清楚、有序,与正常组大致一致,湿敷组及新方法组兔窦房结细胞间质疏松,排列紊乱,P细胞和T细胞难以区分,细胞肿胀明显,可见核固缩、裂解及脂肪变性,可见两组均造成窦房结细胞形态结构一定程度的破坏。In the research, the inventor cut out the normal rabbit sinus node tissue to observe its shape. Under the light microscope, the cells of the normal rabbit sinus node are arranged in an orderly manner without swelling and congestion. The nodal area is mainly composed of P cells and T cells, and the cytoplasm is lightly stained. P cells have large nuclei, round or oval, with unclear cell boundaries, and are often distributed in clusters; T cells are scattered in the center and edge of the sinoatrial node area, and are elongated or spindle-shaped. In the experiment, the sinoatrial node tissue cells in the sham operation group were clearly and orderly arranged, which was roughly the same as that in the normal group. The sinoatrial node cells in the wet compress group and the new method group were loose and disordered, and it was difficult to distinguish P cells from T cells. , cell swelling was obvious, and nuclear pyknosis, lysis and fatty degeneration could be seen. It can be seen that both groups caused a certain degree of damage to the morphology and structure of sinoatrial node cells.
结果之二新方法组的优势Result 2 Advantages of the new method group
4一般情况4 general situation
湿敷组兔在使用甲醛棉签湿敷窦房结后平均3-5min内心率下降到原心率的50%-70%;新方法组兔心率下降到原有心率50%-70%的平均时间为加压注射渗透后1-2min,假手术组加压注射生理盐水后心率无明显变化,且湿敷组与新方法组兔心率在施加甲醛0.5-2h内心率略有波动,其中湿敷组有2只心率回复到原有心率70%,重复使用甲醛棉签湿敷窦房结2min,继续观察2h心率稳定,新方法组作用甲醛后心率基本在原有心率50%-70%间波动,没有重复施加甲醛。The heart rate of the rabbits in the wet compress group dropped to 50%-70% of the original heart rate in an average of 3-5 minutes after using formaldehyde cotton swabs to wet the sinus node; the average time for the heart rate of the rabbits in the new method group to drop to 50%-70% of the original heart rate was 1-2 minutes after pressurized injection infiltration, the heart rate of the sham operation group had no significant change after pressurized injection of normal saline, and the heart rate of the rabbits in the wet compress group and the new method group fluctuated slightly after 0.5-2 hours of formaldehyde application, and the wet compress group had The heart rate of the 2 rats returned to 70% of the original heart rate, repeated use of formaldehyde cotton swabs to wet the sinus node for 2 minutes, and continued to observe the heart rate stability for 2 hours. The heart rate of the new method group basically fluctuated between 50% and 70% of the original heart rate after the application of formaldehyde, without repeated application formaldehyde.
5兔存活情况和造模成功率、兔死亡率5 Rabbit Survival and Modeling Success Rate, Rabbit Mortality Rate
假手术组5只兔全部存活,成功完成实验,其余30只实验兔18只成功完成实验,其中湿敷组6只、新方法组12只。湿敷组手术中死亡4只,其中因窦房结损伤过重死亡3只,湿敷中损伤右心耳造成心脏出血死亡1只;手术中造成气胸3只;手术后饲养中死亡2只;新方法组手术中因窦房结损伤过重死亡1只;因气胸1只;手术后饲养中死亡1只。模型成功率湿敷组53.3%,新方法组86.7%,经t检验两者有显著性差异(P<0.01);兔死亡率湿敷组46.7%,新方法组13.3%,差异具显著性(P<0.01),可见新方法组造模成功率高于湿敷组,且死亡率低于湿敷组。见表3。All 5 rabbits in the sham operation group survived and successfully completed the experiment, and 18 of the remaining 30 experimental rabbits successfully completed the experiment, including 6 in the wet compress group and 12 in the new method group. In the wet compress group, 4 died during the operation, of which 3 died due to excessive damage to the sinus node, 1 died of cardiac hemorrhage due to damage to the right atrial appendage during the wet compress; 3 died of pneumothorax during the operation; 2 died during the feeding after the operation; In the method group, one died due to overweight sinus node injury during operation; one died due to pneumothorax; and one died during feeding after operation. Model success rate wet compress group 53.3%, new method group 86.7%, both have significant difference (P<0.01) through t test; Rabbit death rate wet compress group 46.7%, new method group 13.3%, difference is significant ( P<0.01), it can be seen that the modeling success rate of the new method group was higher than that of the wet compress group, and the mortality rate was lower than that of the wet compress group. See Table 3.
表3两组动物存活情况、造模成功情况比较表Table 3 Comparison of animal survival and modeling success in the two groups
*P<0.01,与湿敷组相比。* P<0.01, compared with wet compress group.
结论in conclusion
甲醛加压注射渗透法可成功建立兔CSND模型,建模后其电生理等相关指标符合缓慢性心率失常病窦综合征的特征,该方法具有如下优势:1.通过窦房结电图准确定位窦房结区;2.甲醛药物推注的剂量好控制;3.对窦房结周围组织损伤小;4.兔胸部切口相对较小;5.造模成功率高、动物死亡率低;6.模型较稳定。本方法具有良好的可行性、重复性,为CSND模型的建立提供一种新的方法。The formaldehyde pressurized injection infiltration method can successfully establish the rabbit CSND model. After modeling, its electrophysiological and other related indicators conform to the characteristics of sinus syndrome in chronic arrhythmia disease. This method has the following advantages: 1. Accurate positioning through sinoatrial node electrogram sinoatrial node area; 2. The dose of formaldehyde drug injection is well controlled; 3. The damage to the tissue around the sinoatrial node is small; 4. The rabbit chest incision is relatively small; 5. The success rate of modeling is high and the mortality rate of animals is low; 6. . The model is more stable. This method has good feasibility and repeatability, and provides a new method for the establishment of CSND model.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012104109714ACN102908204A (en) | 2012-10-25 | 2012-10-25 | Establishing method for rabbit sinus node chronic injury model and special electrode for implementing establishing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012104109714ACN102908204A (en) | 2012-10-25 | 2012-10-25 | Establishing method for rabbit sinus node chronic injury model and special electrode for implementing establishing method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102908204Atrue CN102908204A (en) | 2013-02-06 |
Family
ID=47606948
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012104109714APendingCN102908204A (en) | 2012-10-25 | 2012-10-25 | Establishing method for rabbit sinus node chronic injury model and special electrode for implementing establishing method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102908204A (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6766190B2 (en)* | 2001-10-31 | 2004-07-20 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for developing a vectorcardiograph in an implantable medical device |
| CN1703257A (en)* | 2002-11-16 | 2005-11-30 | 加利福尼亚大学董事会 | Cardiac stimulation system and method |
| US20060111626A1 (en)* | 2003-03-27 | 2006-05-25 | Cvrx, Inc. | Electrode structures having anti-inflammatory properties and methods of use |
| CN201572089U (en)* | 2010-01-12 | 2010-09-08 | 耿乃志 | Mapping electrode component |
| CN102551705A (en)* | 2012-01-19 | 2012-07-11 | 赖珩莉 | Auricular tachycardia mapping catheter and preparation method thereof |
| CN102579037A (en)* | 2012-01-19 | 2012-07-18 | 洪浪 | Coronary vein mapping catheter and preparation method thereof |
- 2012
- 2012-10-25CNCN2012104109714Apatent/CN102908204A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6766190B2 (en)* | 2001-10-31 | 2004-07-20 | Medtronic, Inc. | Method and apparatus for developing a vectorcardiograph in an implantable medical device |
| CN1703257A (en)* | 2002-11-16 | 2005-11-30 | 加利福尼亚大学董事会 | Cardiac stimulation system and method |
| US20060111626A1 (en)* | 2003-03-27 | 2006-05-25 | Cvrx, Inc. | Electrode structures having anti-inflammatory properties and methods of use |
| CN201572089U (en)* | 2010-01-12 | 2010-09-08 | 耿乃志 | Mapping electrode component |
| CN102551705A (en)* | 2012-01-19 | 2012-07-11 | 赖珩莉 | Auricular tachycardia mapping catheter and preparation method thereof |
| CN102579037A (en)* | 2012-01-19 | 2012-07-18 | 洪浪 | Coronary vein mapping catheter and preparation method thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 刘如秀 等: ""强心复脉颗粒对兔慢性窦房结损伤模型心律的影响"", 《中国中医药信息杂志》* |
| 贾绍华: "《常用动物模型的复制方法》", 31 July 2012* |
| 赵效国 等: "《新编医学动物实验设计与方法》", 31 August 2009* |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69325364T2 (en) | DEVICE FOR ABLATION TREATMENT OF VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA | |
| Hashimoto et al. | Adrenergic mechanism participating in induction of atrial fibrillation by ACh | |
| BRPI1014628B1 (en) | INJECTION CATHETER TO ADMINISTER A THERAPEUTIC AGENT WITHIN A SUBSTRATE | |
| Powers et al. | Canine model of pacing-induced heart failure | |
| Yang et al. | Keeping donor hearts in completely beating status with normothermic blood perfusion for transplants | |
| Antz et al. | Electrophysiology of the right anterior approach to the atrioventricular node: studies in vivo and in the isolated perfused dog heart | |
| RUFFY et al. | Electrophysiological effects of ethmozin on canine myocardium | |
| CN114848577A (en) | Double-layer conductive microneedle patch for treating subcutaneous tumors and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN111544757A (en) | A kind of anti-angioma drug-loaded microneedle patch and preparation method thereof | |
| CN113317272A (en) | Rabbit liver transplantation tumor model of VX2 | |
| CN102908204A (en) | Establishing method for rabbit sinus node chronic injury model and special electrode for implementing establishing method | |
| CN203075346U (en) | Infant intra-arterial infusion syringe needle | |
| Crawford et al. | Localization of experimental ventricular myocardial lesions by the electrocardiogram | |
| CN108939052A (en) | Purposes of the Exenatide in the drug of preparation prevention or treatment atrial fibrillation | |
| Liu et al. | Comparative study between original and traditional method in establishing a chronic sinus node damage model in rabbit | |
| CN114917181A (en) | A detachable microneedle patch and its preparation method and application | |
| CN108653880A (en) | A kind of liquid SMAS deep layers separation anti-wrinkle special equipment and anti-wrinkle method | |
| CN203154560U (en) | Biatrial catheter | |
| CN211024568U (en) | A triple puncture needle device | |
| Hu et al. | Ligation of the left circumflex coronary artery with subsequent MRI and histopathology in rabbits | |
| CN111345917A (en) | Myocardial injection molding method and device after myocardial infarction of mouse | |
| CN113855299A (en) | Method for making rat myocardial infarction model | |
| CN110279486A (en) | Myocardial injection modeling method and device after murine myocardial infarction | |
| CN207838011U (en) | Double horizontal balloon occlusions pressurization infusion systems in aorta lumen | |
| CN101947223B (en) | Compound anesthetic and its preparation method and application in animal model of myocardial infarction |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20130206 |