CN102752173A - Distributed simulation system and method supporting large-scale complicated delay tolerant network (DTN) - Google Patents
Distributed simulation system and method supporting large-scale complicated delay tolerant network (DTN)Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102752173A CN102752173ACN2012102504579ACN201210250457ACN102752173ACN 102752173 ACN102752173 ACN 102752173ACN 2012102504579 ACN2012102504579 ACN 2012102504579ACN 201210250457 ACN201210250457 ACN 201210250457ACN 102752173 ACN102752173 ACN 102752173A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- node
- simulator
- simulation
- emulation
- network
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于计算机网络仿真技术领域,具体涉及一种支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统和仿真方法。 The invention belongs to the technical field of computer network simulation, and in particular relates to a distributed simulation system and simulation method supporting a large-scale complex DTN network.
背景技术Background technique
DTN网络,即时延容忍网络(Delay Tolerant NetWorks)。在一些特定的网络环境下(如军事Ad hoc网络,传感器网络),会经常出现由于节点不断移动造成网络断开的现象,导致报文在传输过程中不能确保端到端的路径,这类网络被称为时延容忍网络。DTN network, instant delay tolerant network (Delay Tolerant NetWorks). In some specific network environments (such as military Ad hoc networks, sensor networks), it often occurs that the network is disconnected due to the continuous movement of nodes, resulting in the inability to ensure the end-to-end path of the message during transmission. This type of network is called It is called a delay tolerant network.
目前仿真(simulation)在DTN网络的路由协议设计和分析中发挥着重要作用。在DTN网络路由协议的验证过程中,出于成本的考虑,不可能在现实世界中搭建出一套具备一定规模的DTN网络,因此大部分DTN网络路由协议的设计、验证和分析,都依赖于仿真工具。目前简单易用的DTN网络仿真工具有ONE、DTNSim2。DTNSim2是一个架构简单的单机单线程的DTN网络仿真工具,支持脚本控制。ONE是一个架构完善,可扩展性好的单机单线程的DTN网络仿真工具,支持创建节点运动模型、创建消息分发路由协议,同时支持导入现实世界中的GPS和经纬度等地理数据。ONE是目前使用最多的DTN网络仿真工具。At present, simulation plays an important role in the design and analysis of routing protocols in DTN networks. In the verification process of DTN network routing protocols, due to cost considerations, it is impossible to build a set of DTN networks with a certain scale in the real world, so most of the design, verification and analysis of DTN network routing protocols rely on simulation tools. Currently, the easy-to-use DTN network simulation tools include ONE and DTNSim2. DTNSim2 is a single-machine single-thread DTN network simulation tool with simple architecture, and supports script control. ONE is a well-structured, scalable single-machine and single-threaded DTN network simulation tool that supports the creation of node motion models, creation of message distribution routing protocols, and supports the import of geographic data such as GPS and latitude and longitude in the real world. ONE is currently the most used DTN network simulation tool.
但是现有的DTN网络仿真工具都只能在单机上运行,由于单机的运算能力有限,导致仿真工具的仿真能力小,可以支持的仿真节点规模小,可以支持的消息分发路由协议简单。上述缺陷导致使用现有仿真器进行仿真无法高效快速的完成实验仿真。However, the existing DTN network simulation tools can only run on a single machine. Due to the limited computing power of the single machine, the simulation ability of the simulation tool is small, the scale of the simulation nodes that can be supported is small, and the message distribution routing protocol that can be supported is simple. The above defects lead to the inability to complete the experimental simulation efficiently and quickly by using the existing simulator for simulation.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种能提高仿真速度、可扩展性和通用性更好的支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统和仿真方法,用以解决DTN网络仿真系统的仿真能力问题,特别是解决仿真节点规模大、消息分发路由协议复杂的大规模复杂DTN网络仿真的性能问题。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a distributed simulation system and simulation method that can improve the simulation speed, scalability and versatility better support large-scale complex DTN network, in order to solve the simulation capability problem of the DTN network simulation system, especially It solves the performance problem of large-scale and complex DTN network simulation with large-scale simulation nodes and complex message distribution routing protocols.
本发明采用的技术方案是:The technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统,其特征在于:A distributed simulation system supporting large-scale and complex DTN networks, characterized by:
设置有同在一个局域网的一台主控制器和若干台仿真器;Set up a main controller and several emulators in the same local area network;
所述的主控制器中设置有节点初始化模块、主控制器模块和仿真时钟同步模块;The main controller is provided with a node initialization module, a main controller module and an emulation clock synchronization module;
所述的仿真器中设置有仿真器状态更新模块、仿真器状态同步模块和节点初始化模块。The emulator is provided with an emulator state update module, an emulator state synchronization module and a node initialization module.
所述的节点初始化模块在系统启动时初始化所有仿真节点;The node initialization module initializes all simulation nodes when the system starts;
所述的主控制器模块统一管理仿真时钟和仿真事件;在每次仿真时钟的推进后,将仿真时钟同步到所有仿真器上并给仿真器发送仿真命令;根据仿真时钟处理仿真事件,并把状态有变化的节点同步到相应的仿真器,最后推进时钟; The main controller module uniformly manages the simulation clock and the simulation event; after each simulation clock advances, the simulation clock is synchronized to all simulators and sends simulation commands to the simulators; the simulation event is processed according to the simulation clock, and the The nodes whose state has changed are synchronized to the corresponding emulator, and finally the clock is advanced;
所述的仿真时钟同步模块保证仿真时钟的一致性;主控制器模块将仿真时钟同步到所有仿真器并发送仿真命令,仿真器根据仿真命令完成节点状态更新,之后通知仿真时钟同步模块命令执行完毕;仿真时钟同步模块收到所有仿真器的命令执行完毕消息后,通知主控制器模块分发下一条仿真命令或者推进时钟;The emulation clock synchronization module guarantees the consistency of the emulation clock; the master controller module synchronizes the emulation clock to all emulators and sends emulation commands, and the emulator completes the node state update according to the emulation commands, and then notifies the emulation clock synchronization module that the command execution is completed ; After the emulation clock synchronization module receives the message that all emulators' commands have been executed, it notifies the main controller module to distribute the next emulation command or advance the clock;
所述的仿真器状态更新模块接收主控制器模块的仿真命令,根据仿真命令更新仿真器上节点的状态;The emulator state updating module receives the emulation command of the main controller module, and updates the state of the nodes on the emulator according to the emulation order;
所述的仿真器状态同步模块将相邻的仿真器上的节点状态同步到本地仿真器。The emulator state synchronization module synchronizes the node states on adjacent emulators to the local emulator.
所述的主控制器和仿真器均为个人计算机或高性能服务器。Both the main controller and the emulator are personal computers or high-performance servers.
支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真方法,其特征在于:A distributed simulation method supporting large-scale complex DTN networks, characterized in that:
由以下步骤实现:Achieved by the following steps:
步骤一:将若干台机器搭建成局域网,并指定其中一台机器为主控制器,其他机器为仿真器;Step 1: Build several machines into a local area network, and designate one of the machines as the master controller, and the other machines as emulators;
步骤二:启动主控制器和仿真器,创建并初始化仿真网络中的所有节点,为每个节点分配唯一的ID;Step 2: Start the main controller and the emulator, create and initialize all nodes in the emulation network, and assign a unique ID to each node;
步骤三:将整个仿真网络分割成大小一致的网格,同时为每个网格分配唯一的ID;Step 3: Divide the entire simulation network into grids of the same size, and assign a unique ID to each grid;
步骤四:主控制器初始化节点后等待仿真器连接,当所有仿真器都连接到主控制器并进行注册登记后,主控制器检测到所有仿真器都已经连接,则分割仿真网络并给仿真器分配管辖区域;Step 4: After the main controller initializes the nodes, it waits for the emulator to connect. When all the emulators are connected to the main controller and registered, the main controller detects that all the emulators have been connected, then divides the emulation network and gives the emulator assign jurisdiction;
步骤五:主控制器在节点初始化后初始化仿真时钟并初始化事件模型,然后向各个仿真器发送仿真命令;Step 5: After the node is initialized, the main controller initializes the simulation clock and the event model, and then sends simulation commands to each simulator;
步骤六:主控制器处理仿真事件,将状态有变化的节点同步到相应的仿真器,然后推进仿真时钟,再次向仿真器发送仿真命令,之后继续处理后续仿真事件,如此往复直到仿真结束;仿真器收到仿真命令后执行相应的仿真命令。Step 6: The main controller processes the simulation events, synchronizes the nodes with changed states to the corresponding simulator, then advances the simulation clock, sends simulation commands to the simulator again, and then continues to process subsequent simulation events, and so on until the simulation ends; the simulation After receiving the simulation command, the device executes the corresponding simulation command.
步骤三中,主控制器分割仿真网络的方法为:In step 3, the method for the main controller to divide the simulation network is as follows:
将仿真网络分割成大小一致的网格,选定的网格尺寸必须大于节点的辐射直径;将网格按照水平或垂直方向划分为与仿真器等数量的区域,将所有区域一对一分配给每个仿真器,并告知每个仿真器与自己的管辖区域相邻的仿真器的通信地址;主控制器与各个仿真器保持套接字连接,仿真器与相邻仿真器保持套接字连接。Divide the simulated network into grids of the same size, the selected grid size must be larger than the radiation diameter of the node; divide the grid into areas equal to the number of simulators horizontally or vertically, and assign all areas one-to-one to Each emulator, and inform each emulator of the communication address of the emulator adjacent to its own jurisdiction; the main controller maintains a socket connection with each emulator, and the emulator maintains a socket connection with the adjacent emulator .
步骤五中,所述的仿真命令有MOVE、SIM_SYN、CONNECT、UPDATE;In step five, the simulation commands include MOVE, SIM_SYN, CONNECT, UPDATE;
其中,MOVE命令,即通知各仿真器移动管辖范围内的节点;SIM_SYN命令,即通知各仿真器将移动出管辖范围的节点的状态同步到相邻仿真器;CONNECT命令,即通知各仿真器尝试连接管辖范围内所有节点;UPDATE命令,即通知仿真器更新管辖范围内所有节点状态,包括发送仿真消息、链路建立和断开。Among them, the MOVE command informs the emulators to move the nodes within the jurisdiction; the SIM_SYN command informs the emulators to synchronize the state of the nodes that move out of the jurisdiction to the adjacent emulator; the CONNECT command informs the emulators to try Connect all nodes within the jurisdiction; UPDATE command, which notifies the emulator to update the status of all nodes within the jurisdiction, including sending simulation messages, link establishment and disconnection.
步骤六中,处理仿真命令中,节点因为运动离开仿真器的管辖范围时的节点迁移过程为:In step six, when processing the simulation command, the node migration process when the node leaves the jurisdiction of the simulator due to motion is:
确定节点迁移的目的仿真器,将离开管辖范围的节点打包成数据包发送给目的仿真器;目的仿真器根据数据包将节点状态同步到同ID的节点上,在同步之前,具有同ID的节点不在目的仿真器的管辖范围,节点状态同步之后该节点处于仿真器的管辖范围。Determine the destination emulator for node migration, pack the nodes leaving the jurisdiction into data packets and send them to the destination emulator; the destination emulator will synchronize the node status to the node with the same ID according to the data packet, before synchronization, the nodes with the same ID Not under the jurisdiction of the target emulator, the node is under the jurisdiction of the emulator after the node state is synchronized.
步骤六中,处理仿真命令中,链路状态同步过程为:In step six, in processing the simulation command, the link state synchronization process is:
拷贝相邻仿真器上边界网格中的节点位置信息到本地仿真器;对于管辖范围内的所有节点,取出节点周围八个相邻网格内的所有节点逐一判断;若节点间距离小于节点辐射半径,则在节点间尝试建立链路连接;若节点间距离不小于节点辐射半径,则判断节点间是否已经存在链路连接,如果是,则删除链路。Copy the node position information in the upper boundary grid of the adjacent simulator to the local simulator; for all nodes within the jurisdiction, take out all the nodes in the eight adjacent grids around the node and judge one by one; if the distance between nodes is less than the node radiation Radius, then try to establish a link connection between nodes; if the distance between nodes is not less than the node radiation radius, then judge whether there is already a link connection between nodes, and if so, delete the link.
步骤六中,处理仿真命令中,仿真消息的分发过程为:In step six, in processing the simulation command, the distribution process of the simulation message is:
将节点上已有的仿真消息发送到已有链路的对端节点;判断对端节点是否在仿真器的管辖范围;如果否,则对端节点将仿真消息发送给与自己同ID且位于相邻仿真器上的节点;在建立链路连接时,处于管辖范围的节点有可能和不处于管辖范围的节点建立连接,该不处于管辖范围的节点称为代理节点,代理节点是相邻仿真器上某节点的代理;代理节点和被代理节点即目的节点通过节点ID来确定关系;当代理节点收到仿真消息,则将仿真消息转发给实际应该接收该消息的目的节点。Send the existing simulation message on the node to the peer node of the existing link; judge whether the peer node is under the jurisdiction of the emulator; if not, then the peer node sends the simulation message to the The node on the adjacent emulator; when establishing a link connection, the node under the jurisdiction may establish a connection with the node not under the jurisdiction. The node outside the jurisdiction is called the proxy node, and the proxy node is the adjacent emulator. The proxy of a certain node; the proxy node and the proxy node, that is, the destination node, determine the relationship through the node ID; when the proxy node receives the simulation message, it forwards the simulation message to the destination node that should actually receive the message.
本发明将DTN网络仿真时的计算需求分布到不同仿真器,同时保证仿真的有效性,它主要具有以下优点:The present invention distributes the calculation requirements of DTN network simulation to different simulators, and at the same time ensures the validity of the simulation. It mainly has the following advantages:
(1)提高仿真速度:本发明将DTN网络仿真时的巨大计算需求分布到不同仿真器,相对于现有仿真工具,本发明的DTN网络仿真速度有明显的提升。特别是在DTN网络规模大、消息分发路由协议复杂的情况下,本发明的优势更为突出。(1) Improving the simulation speed: the present invention distributes the huge computing requirements during DTN network simulation to different emulators. Compared with the existing simulation tools, the DTN network simulation speed of the present invention is significantly improved. Especially in the case of large DTN network scale and complex message distribution routing protocol, the advantages of the present invention are more prominent.
(2)可扩展性:本发明采用一个主控制器多个仿真器的基础网络拓扑结构,可扩展性强;与此同时,仿真网络支持线性分割,可以很方便的在已有仿真系统上添加仿真器。一般情况下,仿真器的增加将促使仿真速度的进一步增加。(2) Scalability: The present invention adopts the basic network topology structure of multiple emulators for one master controller, which has strong scalability; at the same time, the emulation network supports linear segmentation, which can be easily added to the existing emulation system Emulator. In general, the addition of emulators will lead to further increases in simulation speed.
(3)通用性:本发明对DTN网络仿真方案要求少,只需要仿真方案支持仿真网络的线性分割即可使用本发明来实现分布式仿真。本发明与DTN网络仿真协议无关,对上层仿真系统几乎透明,对于已有的DTN网络仿真工具,可以很方便的利用本发明改造成分布式的仿真系统。(3) Versatility: the present invention has few requirements on the DTN network simulation scheme, and only needs the simulation scheme to support the linear segmentation of the simulation network, and the present invention can be used to realize distributed simulation. The invention has nothing to do with the DTN network emulation protocol, and is almost transparent to the upper layer emulation system. For the existing DTN network emulation tool, the invention can be conveniently transformed into a distributed emulation system.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统结构图。Figure 1 is a structural diagram of a distributed simulation system supporting large-scale and complex DTN networks.
图2为支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统方法流程图。Fig. 2 is a flowchart of a method for a distributed simulation system supporting a large-scale complex DTN network.
图3为仿真网络分割流程图。Figure 3 is a flow chart of simulation network segmentation.
图4为仿真时节点移动流程图。Figure 4 is a flow chart of node movement during simulation.
图5为仿真时节点链路状态同步流程图。Fig. 5 is a flow chart of node link state synchronization during simulation.
图6为仿真时仿真消息分发流程图。Fig. 6 is a flow chart of simulation message distribution during simulation.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施方式对本发明进行详细的说明。The present invention will be described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments.
研究和分析DTN网络的仿真行为和仿真过程时,可以发现距离相距比较远的节点存在长时间的状态无关性,即距离相距比较远的两个节点,其中一个节点的状态变化,在很长一段时间内不影响另外一个节点的状态。进而可以发现DTN网络中节点存在区域相关性,即位于两个不同的区域的节点,它们之间相互影响的概率比较小。本发明的技术方案就是基于上述指导思想完成的。When researching and analyzing the simulation behavior and simulation process of the DTN network, it can be found that there is a long-term state independence between nodes that are far apart, that is, two nodes that are far apart, the state change of one of the nodes, in a long period of time Time does not affect the state of another node. Furthermore, it can be found that the nodes in the DTN network have regional correlation, that is, nodes located in two different regions have a relatively small probability of mutual influence. The technical solution of the present invention is completed based on the above guiding thought.
本发明所述的支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统,由同在一个局域网的一台主控制器和若干台仿真器组成。所有机器通过以太网进行数据交换,均为个人计算机或高性能服务器。如图1,主控制器中设置有节点初始化模块、主控制器模块和仿真时钟同步模块;仿真器中设置有仿真器状态更新模块、仿真器状态同步模块和节点初始化模块。这五类功能模块的具体作用为:The distributed emulation system supporting large-scale complex DTN network described in the present invention is composed of a main controller and several emulators in the same local area network. All machines exchange data through Ethernet, all of which are personal computers or high-performance servers. As shown in Figure 1, the main controller is provided with a node initialization module, the main controller module and an emulation clock synchronization module; the emulator is provided with an emulator state update module, an emulator state synchronization module and a node initialization module. The specific functions of these five types of functional modules are:
(1)节点初始化模块在系统启动时初始化所有仿真节点;(1) The node initialization module initializes all simulation nodes when the system starts;
(2)主控制器模块统一管理仿真时钟和仿真事件;在每次仿真时钟的推进后,将仿真时钟同步到所有仿真器上并给仿真器发送仿真命令;根据仿真时钟处理仿真事件,并把状态有变化的节点同步到相应的仿真器,最后推进时钟;(2) The main controller module manages the simulation clock and simulation events in a unified manner; after each simulation clock advances, the simulation clock is synchronized to all simulators and sends simulation commands to the simulators; the simulation events are processed according to the simulation clock, and the The nodes whose state has changed are synchronized to the corresponding emulator, and finally the clock is advanced;
(3)所述的仿真时钟同步模块保证仿真时钟的一致性。主控制器模块将仿真时钟同步到所有仿真器并发送仿真命令,仿真器根据仿真命令完成节点状态更新,之后通知仿真时钟同步模块命令执行完毕;仿真时钟同步模块收到所有仿真器的命令执行完毕消息后,通知主控制器模块分发下一条仿真命令或者推进时钟;(3) The simulation clock synchronization module ensures the consistency of the simulation clock. The main controller module synchronizes the simulation clock to all simulators and sends simulation commands. The simulator completes the node status update according to the simulation commands, and then notifies the simulation clock synchronization module that the command execution is completed; the simulation clock synchronization module receives all the simulator commands and completes the execution After the message, notify the main controller module to distribute the next simulation command or advance the clock;
(4)仿真器状态更新模块接收主控制器模块的仿真命令,根据仿真命令更新仿真器上节点的状态;(4) The simulator status update module receives the simulation command from the main controller module, and updates the status of the nodes on the simulator according to the simulation command;
(5)仿真器状态同步模块将相邻的仿真器上的节点状态同步到本地仿真器。(5) The emulator state synchronization module synchronizes the node state on the adjacent emulator to the local emulator.
其中,节点初始化为仿真系统初始化流程,主控制器和仿真器都需要完成节点初始化流程,后面的四部分构成仿真运行时环境。Among them, node initialization is the simulation system initialization process, both the main controller and the emulator need to complete the node initialization process, and the following four parts constitute the simulation runtime environment.
本发明所述的支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真方法如图2所示:The distributed emulation method supporting large-scale complex DTN network described in the present invention is as shown in Figure 2:
(1)将若干台机器搭建成局域网,并指定其中一台机器为主控制器,其他机器为仿真器。所述机器为个人计算机或者高性能服务器。(1) Build several machines into a local area network, and designate one of the machines as the master controller, and the other machines as emulators. The machine is a personal computer or a high-performance server.
(2)在主控制器和仿真器上构造节点初始化模块,将所有节点初始化。(2) Construct a node initialization module on the main controller and emulator to initialize all nodes.
(3)在主控制器上构造主控制器模块,该主控制器模块统一管理仿真时钟和仿真事件。(3) A main controller module is constructed on the main controller, and the main controller module uniformly manages the simulation clock and simulation events.
(4)在仿真器上构造仿真器状态更新模块,该仿真器状态更新模块接收主控制器模块的仿真命令,根据仿真命令更新仿真器上节点的状态。(4) Build a simulator status update module on the simulator, which receives the simulation command from the main controller module, and updates the status of the nodes on the simulator according to the simulation command.
(5)在仿真器上构造仿真器状态同步模块,该仿真器状态同步模块将相邻的仿真器上的节点状态同步到本地仿真器。(5) A simulator state synchronization module is constructed on the simulator, and the simulator state synchronization module synchronizes the node states on the adjacent simulators to the local simulator.
(6)在主控制器上构造仿真时钟同步模块,该仿真时钟同步模块保证仿真时钟的一致性。主控制器模块将仿真时钟同步到所有仿真器并发送仿真命令,仿真器根据仿真命令完成节点状态更新,之后通知仿真时钟同步模块命令执行完毕;仿真时钟同步模块收到所有仿真器的命令执行完毕消息后,通知主控制器模块分发下一条仿真命令或者推进时钟;(6) A simulation clock synchronization module is constructed on the main controller, and the simulation clock synchronization module ensures the consistency of the simulation clock. The main controller module synchronizes the simulation clock to all simulators and sends simulation commands. The simulator completes the node status update according to the simulation commands, and then notifies the simulation clock synchronization module that the command execution is completed; the simulation clock synchronization module receives all the simulator commands and completes the execution After the message, notify the main controller module to distribute the next simulation command or advance the clock;
主控制器和仿真器刚刚启动时创建并初始化仿真网络中的所有节点,为每个节点分配唯一的ID,该ID值代表了节点在仿真系统中的身份,为后面节点状态同步和节点状态迁移做好基础。最后,在水平方向和垂直方向上将整个仿真网络分割成大小一致的网格,同时为每个网格分配唯一的ID。主控制器初始化节点后等待仿真器连接,当所有仿真器都连接主控制器后,主控制器将所有网格按照水平方向或者垂直方向划分为与仿真器等数量的区域,将所有区域一对一分配给每个仿真器,并告知每个仿真器与自己的管辖区域相邻的仿真器的地址,即相邻仿真器的地址。主控制器与所有仿真器保持套接字连接,连接主要用于发送仿真命令和回馈仿真状态;仿真器1与仿真器2在管辖范围上是相邻的,仿真器1与仿真器2保持套接字连接,连接主要用于同步节点状态。When the main controller and the emulator are just started, all nodes in the simulation network are created and initialized, and a unique ID is assigned to each node. The ID value represents the identity of the node in the simulation system, and is used for subsequent node state synchronization and node state migration. Do the basics. Finally, the entire simulated network is divided into grids of uniform size in the horizontal and vertical directions, and a unique ID is assigned to each grid. After the main controller initializes the nodes, it waits for the emulator to connect. When all the emulators are connected to the main controller, the main controller divides all the grids into areas equal to the number of emulators in the horizontal or vertical direction, and divides all the areas into one pair. One is assigned to each emulator, and each emulator is notified of the address of the emulator adjacent to its own jurisdiction, that is, the address of the adjacent emulator. The main controller maintains socket connections with all emulators, and the connection is mainly used to send simulation commands and feedback simulation status; emulator 1 and emulator 2 are adjacent in jurisdiction, and emulator 1 and emulator 2 maintain a socket connection. Socket connection, the connection is mainly used to synchronize the node state.
主控制器在节点初始化后初始化仿真时钟并初始化事件模型,然后向各个仿真器发送一个仿真命令,仿真命令有MOVE、SIM_SYN、CONNECT、UPDATE。MOVE命令,即通知各仿真器移动管辖范围内的节点;SIM_SYN命令,即通知各仿真器将移动出管辖范围的节点的状态同步到相邻仿真器;CONNECT命令,即通知各仿真器尝试连接管辖范围内所有节点;UPDATE命令,即通知仿真器更新管辖范围内所有节点状态,包括发送仿真消息、链路建立和断开。After the node is initialized, the main controller initializes the simulation clock and the event model, and then sends a simulation command to each simulator. The simulation commands include MOVE, SIM_SYN, CONNECT, and UPDATE. The MOVE command is to notify each emulator to move the node within the jurisdiction; the SIM_SYN command is to inform each emulator to synchronize the state of the node that has moved out of the jurisdiction to the adjacent emulator; the CONNECT command is to notify each emulator to try to connect to the jurisdiction All nodes within the scope; UPDATE command, which notifies the emulator to update the status of all nodes within the jurisdiction, including sending simulation messages, link establishment and disconnection.
主控制器处理仿真事件,将状态有变化的节点同步到相应的仿真器,然后推进仿真时钟,依次发送MOVE、SIM_SYN、CONNECT、UPDATE命令,之后继续处理后续仿真事件,如此往复直到仿真结束。仿真器收到仿真命令后执行相应的仿真命令。The main controller processes the simulation events, synchronizes the nodes with changed states to the corresponding simulator, then advances the simulation clock, sends MOVE, SIM_SYN, CONNECT, and UPDATE commands in sequence, and then continues to process subsequent simulation events, and so on until the end of the simulation. The emulator executes the corresponding simulation command after receiving the simulation command.
如图3所示,本发明所述的仿真方法中,分割仿真网络的方法如下:As shown in Figure 3, in the emulation method described in the present invention, the method for dividing emulation network is as follows:
S201 将DTN网络分割成一定数量的大小一致的网格。选定一个网格尺寸,要求网格尺寸必须大于节点的辐射直径。根据选定的网格尺寸将DTN网络分割成网格。这样,每个节点必须在且仅在某一个网格中。S201 Divide the DTN network into a certain number of grids with the same size. To select a grid size, it is required that the grid size must be larger than the radial diameter of the node. Divide the DTN network into grids according to the selected grid size. In this way, each node must be in one and only one grid.
S202 在主控制器端,将所有网格分割成与仿真器等数量的规则区域。一般的,可以将网格在水平方向上均匀划分为等大小的矩形网格区。S202 On the main controller side, divide all grids into regular areas equal to the number of simulators. Generally, the grid can be evenly divided into rectangular grid areas of equal size in the horizontal direction.
S104 在主控制器端,将划分后的网格分配给仿真器。将划分后的网格区域一一分配给仿真器,同时告知其相邻仿真器的地址。所述相邻仿真器指的是管辖区域相邻的仿真器。S104 On the main controller side, distribute the divided grids to the simulator. Allocate the divided grid areas to the emulator one by one, and inform the address of its adjacent emulator at the same time. The adjacent simulators refer to simulators with neighboring jurisdictions.
S30 在主控制器上构造主控制器模块。该模块统一管理仿真时钟和仿真事件。主控制器模块推进仿真时钟,处理仿真事件,管理各个仿真器的仿真与状态同步。S30 constructs the main controller module on the main controller. This module manages the simulation clock and simulation events in a unified manner. The main controller module advances the simulation clock, handles simulation events, and manages the synchronization of the simulation and state of each simulator.
S40 在仿真器上构造仿真器状态更新模块。仿真器在仿真过程中,需要接收主控制器的命令,然后执行命令。执行命令的过程,即为更新管辖区域内所有节点的状态,包括MOVE节点位置、节点之间建立CONNECT、UPDATE节点状态。S40 constructs a simulator status update module on the simulator. During the emulation process, the emulator needs to receive commands from the main controller and then execute the commands. The process of executing the command is to update the status of all nodes in the jurisdiction, including the position of MOVE nodes, the establishment of CONNECT between nodes, and the status of UPDATE nodes.
S50 在仿真器上构造仿真器状态同步模块。由于节点存在运动,节点有可能会离开仿真器的管辖范围而进入相邻仿真器的管辖范围。节点在仿真器之间迁移,会引起仿真器之间状态同步。仿真器在接收到主控制器的SIM_SYN命令后,检查是否有节点因为移动而离开了管辖范围,如果有则将节点打包成数据包并发送给相邻仿真器。S50 constructs a simulator state synchronization module on the simulator. Due to the movement of nodes, nodes may leave the jurisdiction of the simulator and enter the jurisdiction of adjacent simulators. Migration of nodes between emulators will cause state synchronization between emulators. After the emulator receives the SIM_SYN command from the main controller, it checks whether any node has left the jurisdiction due to movement, and if so, packs the node into a data packet and sends it to the adjacent emulator.
S60 在主控制器上构造仿真时钟同步模块。主控制器管理仿真时钟。每当主控制器向所有仿真器发送一个仿真命令后,则由仿真时钟同步模块等待仿真器的回馈状态。等待所有仿真器都执行完仿真命令,通知主控制器模块发送下一个仿真命令。在发送仿真命令之前,检查是否需要推进时钟。如果时钟发送变更,则在发送命令的时候以参数的形式传递仿真时钟信息。S60 constructs a simulation clock synchronization module on the main controller. The master controller manages the emulation clock. Whenever the master controller sends a simulation command to all simulators, the simulation clock synchronization module waits for the feedback status of the simulators. Wait for all emulators to finish executing the emulation command, and notify the main controller module to send the next emulation command. Before sending a simulation command, check whether the clock needs to be advanced. If the clock transmission is changed, the simulated clock information is passed in the form of parameters when sending the command.
基于上述支持大规模复杂仿真节点的DTN网络分布式仿真系统的仿真过程为:The simulation process based on the above-mentioned DTN network distributed simulation system supporting large-scale complex simulation nodes is as follows:
主控制器处理仿真事件,把状态有更变的节点的状态同步到相应的仿真器。由前面所述的仿真网络分割过程可以发现,节点在任何时刻只可能处于某一个仿真器的管辖范围。处理完仿真事件后,向所有仿真器发送MOVE命令,所有仿真器执行MOVE命令移动管辖范围内所有节点的位置,然后向主控制器回馈命令执行结果。主控制器检测到所有仿真器执行完MOVE命令后向所有仿真器发送SIM_SYN命令,所有仿真器在这个时刻将刚刚离开管辖范围的节点迁移到相邻仿真器。同样,主控制器检测到所有仿真器执行完SIM_SYN命令后发送CONNECT命令,仿真器将管辖范围内所有节点尝试建立链路连接。主控制器检测到所有仿真器执行完CONNECT命令后发送UPDATE命令,仿真器执行UPDATE命令,对于管辖范围内所有节点,在节点之间已有链路的基础上,将节点上已有的仿真消息发送到链路的另端节点。The main controller handles the simulation events, and synchronizes the status of the nodes whose status has changed to the corresponding simulator. From the simulation network segmentation process mentioned above, it can be found that a node can only be under the jurisdiction of a certain simulator at any time. After processing the simulation event, send the MOVE command to all simulators, and all simulators execute the MOVE command to move the positions of all nodes within the jurisdiction, and then feedback the command execution result to the main controller. After the master controller detects that all emulators have executed the MOVE command, they send SIM_SYN commands to all emulators, and all emulators migrate the nodes that have just left their jurisdiction to adjacent emulators at this moment. Similarly, the main controller sends a CONNECT command after detecting that all emulators have executed the SIM_SYN command, and the emulator will try to establish a link connection with all nodes within the jurisdiction. The main controller detects that all emulators have executed the CONNECT command and sends the UPDATE command. The emulator executes the UPDATE command. For all nodes within the jurisdiction, on the basis of the existing links between the nodes, the existing emulation messages on the nodes sent to the other end of the link.
主控制器检测到所有节点执行完UPDATE命令后,重复上述仿真过程,直到仿真结束。After the main controller detects that all nodes have executed the UPDATE command, it repeats the above simulation process until the simulation ends.
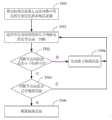
基于上述支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统的仿真时节点迁移过程如图4所示:The simulation node migration process based on the above-mentioned distributed simulation system supporting large-scale and complex DTN networks is shown in Figure 4:
T401 仿真节点运动。节点因为运动有可能离开仿真器的管辖范围。T401 simulates nodal motion. Nodes may leave the jurisdiction of the simulator due to movement.
T402 仿真器判断节点是否离开了管辖范围。The T402 emulator judges whether the node has left the jurisdiction.
T403 如果是,则将离开管辖范围的节点打包成数据包。数据包格式在仿真器之间相互约定好。T403 If yes, pack the nodes leaving the jurisdiction into data packets. The packet format is mutually agreed between emulators.
T404 确定目的仿真器。离开管辖范围的节点,必定处于相邻仿真器的管辖范围。根据节点的当前位置可以确定节点当前所在的管辖范围,从而确定目的仿真器。T404 Determine the target emulator. A node that leaves the jurisdiction must be under the jurisdiction of the adjacent emulator. According to the current location of the node, the current jurisdiction of the node can be determined, so as to determine the destination emulator.
T405 将数据包发送给目的仿真器。T405 sends the packet to the destination emulator.
T406 目的仿真器根据数据包将节点状态同步到同ID的节点上。在同步之前,具有同ID的节点不在目的仿真器的管辖范围,节点状态同步之后该节点处于仿真器的管辖范围。T406 The purpose emulator synchronizes the node status to the node with the same ID according to the data packet. Before the synchronization, the node with the same ID is not under the jurisdiction of the target emulator, and after the node state is synchronized, the node is under the jurisdiction of the emulator.
至此,节点已经从源仿真器迁移到目的仿真器。At this point, the node has been migrated from the source emulator to the destination emulator.
基于上述支持大规模复杂仿真DTN网络的分布式仿真系统的仿真时节点链路状态同步过程如图5所示:Based on the above-mentioned distributed simulation system supporting large-scale and complex simulation DTN networks, the node link state synchronization process during simulation is shown in Figure 5:
T501 拷贝相邻仿真器上边界网格中的节点位置信息到本地仿真器。所述边界网格为,仿真器管辖范围内边界上的所有网格。在两个节点之间建立连接的时候,需要两个节点的位置信息,而边界网格内的节点有可能跨仿真器建立连接,本发明解决跨仿真器建立连接的做法是将相邻仿真器上边界网格内节点的位置信息同步到本地。T501 copies the node position information in the boundary grid on the adjacent simulator to the local simulator. The boundary grids are all grids on the boundary within the jurisdiction of the simulator. When a connection is established between two nodes, the position information of the two nodes is needed, and the nodes in the boundary grid may establish connections across emulators. The method of the present invention to solve the establishment of connections across emulators is to connect adjacent The position information of the nodes in the upper boundary grid is synchronized to the local.
T502 对于管辖范围内的所有节点,取出节点周围八个相邻网格内的所有节点逐一判断。由于之前已经同步相邻仿真器上边界网格中的节点位置信息到本地,于是边界网格内的节点的八个相邻的网格内的所有节点的位置信息都是有效的,包括不在仿真器管辖范围的节点的位置信息。T502 For all nodes within the jurisdiction, take out all nodes in the eight adjacent grids around the node and judge one by one. Since the node position information in the boundary grid on the adjacent simulator has been synchronized to the local, the position information of all nodes in the eight adjacent grids of the node in the boundary grid is valid, including those that are not in the simulation The location information of the nodes under the jurisdiction of the server.
T503 判断节点间距离是否小于节点辐射半径。T503 Determine whether the distance between nodes is less than the node radiation radius.
T504 如果是,则在节点间尝试建立链路连接。T504 If yes, try to establish link connection between nodes.
T505 如果节点间距离不小于节点辐射半径,则判断节点间是否已经存在链路连接。T505 If the distance between nodes is not less than the node radiation radius, judge whether there is a link connection between nodes.
T506 如果是,则删除链路。T506 If yes, delete the link.
基于上述支持大规模复杂DTN网络的分布式仿真系统的仿真时仿真消息分发过程如图6所示:The simulation message distribution process during simulation based on the above-mentioned distributed simulation system supporting large-scale and complex DTN networks is shown in Figure 6:
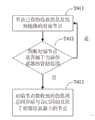
T411 将节点上已有的仿真消息发送到已有链路的对端节点。所述对端节点为,链路中消息的接收节点。仿真器在执行UPDATE命令时,逐一更新管辖范围内的所有节点。把所有节点上的仿真消息通过链路发送到对端节点;T411 Send the existing simulation message on the node to the peer node of the existing link. The peer node is a receiving node of the message in the link. When the emulator executes the UPDATE command, it updates all the nodes within its jurisdiction one by one. Send the simulation messages on all nodes to the peer node through the link;
T412 判断对端节点是否在仿真器的管辖范围;T412 Determine whether the peer node is within the jurisdiction of the emulator;
T413 如果否,则对端节点将仿真消息发送给与自己同ID且位于相邻仿真器上的节点。在建立链路连接时,处于管辖范围的节点有可能和不处于管辖范围的节点建立连接,该不处于管辖范围的节点称为代理节点,代理节点是相邻仿真器上某节点的代理。代理节点和被代理节点(目的节点)通过节点ID来确定关系。当代理节点收到仿真消息,则将仿真消息转发给实际应该接收该消息的目的节点。T413 If not, the peer node sends the emulation message to the node with the same ID as itself and located on the adjacent emulator. When establishing a link connection, a node in the jurisdiction may establish a connection with a node not in the jurisdiction. The node not in the jurisdiction is called a proxy node, and the proxy node is an agent of a node on the adjacent emulator. The proxy node and the proxy node (destination node) determine the relationship through the node ID. When the proxy node receives the simulation message, it forwards the simulation message to the destination node that should actually receive the message.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210250457.9ACN102752173B (en) | 2012-07-19 | 2012-07-19 | Distributed simulation system and method supporting large-scale complicated delay tolerant network (DTN) |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210250457.9ACN102752173B (en) | 2012-07-19 | 2012-07-19 | Distributed simulation system and method supporting large-scale complicated delay tolerant network (DTN) |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102752173Atrue CN102752173A (en) | 2012-10-24 |
| CN102752173B CN102752173B (en) | 2014-08-13 |
Family
ID=47032079
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210250457.9AExpired - Fee RelatedCN102752173B (en) | 2012-07-19 | 2012-07-19 | Distributed simulation system and method supporting large-scale complicated delay tolerant network (DTN) |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102752173B (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103152380A (en)* | 2012-12-31 | 2013-06-12 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十八研究所 | Distributed type simulation communication framework and communication effectiveness calculating method |
| CN103763142A (en)* | 2014-01-23 | 2014-04-30 | 电子科技大学 | Multimode heterogeneous DTN simulation verification system and method |
| CN103825761A (en)* | 2014-02-26 | 2014-05-28 | 武汉大学 | On-board router simulation method of delay-tolerant network |
| CN108989218A (en)* | 2018-07-11 | 2018-12-11 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Data forwarding device and method based on network convergence architecture |
| CN117591232A (en)* | 2023-10-31 | 2024-02-23 | 厦门渊亭信息科技有限公司 | Data parallel deduction simulation method and system |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101587446A (en)* | 2009-06-30 | 2009-11-25 | 中国运载火箭技术研究院 | Simulation Model Conversion Method Based on Distributed Interactive Simulation Platform |
| CN101873233A (en)* | 2009-04-22 | 2010-10-27 | 电子科技大学 | A Simulation Method Compatible with PeerCast Network |
- 2012
- 2012-07-19CNCN201210250457.9Apatent/CN102752173B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101873233A (en)* | 2009-04-22 | 2010-10-27 | 电子科技大学 | A Simulation Method Compatible with PeerCast Network |
| CN101587446A (en)* | 2009-06-30 | 2009-11-25 | 中国运载火箭技术研究院 | Simulation Model Conversion Method Based on Distributed Interactive Simulation Platform |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| ZHENJING ZHANG 等: "Design and Implementation of a Delay-Tolerant Network Emulator Based in QualNet Simulator", 《WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, NETWORKING AND MOBILE COMPUTING, 2009. WICOM"09. 5TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON》, 26 September 2009 (2009-09-26), pages 1 - 4, XP031553456* |
| 王朕 等: "机会网络模拟器ONE及其扩展研究", 《计算机应用研究》, 15 January 2012 (2012-01-15), pages 272 - 276* |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103152380A (en)* | 2012-12-31 | 2013-06-12 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十八研究所 | Distributed type simulation communication framework and communication effectiveness calculating method |
| CN103152380B (en)* | 2012-12-31 | 2017-02-22 | 中国电子科技集团公司第二十八研究所 | Distributed type simulation communication framework and communication effectiveness calculating method |
| CN103763142A (en)* | 2014-01-23 | 2014-04-30 | 电子科技大学 | Multimode heterogeneous DTN simulation verification system and method |
| CN103763142B (en)* | 2014-01-23 | 2016-10-26 | 电子科技大学 | Multimode isomery DTN simulation verification system and method |
| CN103825761A (en)* | 2014-02-26 | 2014-05-28 | 武汉大学 | On-board router simulation method of delay-tolerant network |
| CN103825761B (en)* | 2014-02-26 | 2017-06-27 | 武汉大学 | A Simulation Method of On-Star Router for Delay Tolerant Network |
| CN108989218A (en)* | 2018-07-11 | 2018-12-11 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Data forwarding device and method based on network convergence architecture |
| CN108989218B (en)* | 2018-07-11 | 2021-04-06 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Data forwarding device and method based on network convergence architecture |
| CN117591232A (en)* | 2023-10-31 | 2024-02-23 | 厦门渊亭信息科技有限公司 | Data parallel deduction simulation method and system |
| CN117591232B (en)* | 2023-10-31 | 2024-10-25 | 厦门渊亭信息科技有限公司 | Data parallel deduction simulation method and system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102752173B (en) | 2014-08-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107404350B (en) | Satellite network simulation method, device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| CN114363021B (en) | Network target range system, virtual network implementation method and device of network target range system | |
| CN105763570A (en) | Virtualization-technology-based distributed real-time network simulation system | |
| CN106571956B (en) | Satellite networking routing protocol simulation system and method | |
| CN114244449B (en) | Satellite network simulation verification method, system, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN108768685A (en) | Extensive communication network real-time analog simulation system | |
| CN102752173B (en) | Distributed simulation system and method supporting large-scale complicated delay tolerant network (DTN) | |
| Looga et al. | Mammoth: A massive-scale emulation platform for internet of things | |
| CN101626383A (en) | Route test method of aeronautical telecommunication network and router virtual machine | |
| CN104954166A (en) | Hardware based network simulation system and method | |
| CN114422010B (en) | A protocol testing method for satellite communication simulation platform based on network virtualization | |
| CN101610275B (en) | Supporting large-scale distributed P2P simulation system and its implementation method and device | |
| CN105472632B (en) | A method, device and system for constructing a simulated wireless network | |
| CN116233133B (en) | A method for digital twin-assisted data center network load balancing | |
| CN103414612A (en) | Communication network real-time simulation method based on OPNET | |
| CN114285458B (en) | Ground simulation method, system, device and medium for progressive deployment of satellite network | |
| CN103036934A (en) | Wide area network clustered deployment system and method based on mirror image | |
| CN101094112A (en) | Method, device and system for testing performance of route protocol of network device | |
| CN103763142B (en) | Multimode isomery DTN simulation verification system and method | |
| Tello et al. | SDN controllers scalability and performance study | |
| CN105488288A (en) | NS3 (Network Simulator Version-3) parallel analog simulation system | |
| CN108259232A (en) | A kind of spatial network analogy method and system | |
| CN103634290B (en) | Network (WSN) emulation system | |
| CN105471634B (en) | A kind of simulated maneuver communication network construction method, device and system | |
| Chen et al. | Multiscale emulation technology based on the integration of virtualization, physical and simulation networks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20140813 Termination date:20190719 |