CN102740519A - Radio-frequency heating method and radio-frequency heating device for biological thanosomes - Google Patents
Radio-frequency heating method and radio-frequency heating device for biological thanosomesDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102740519A CN102740519ACN2012102305594ACN201210230559ACN102740519ACN 102740519 ACN102740519 ACN 102740519ACN 2012102305594 ACN2012102305594 ACN 2012102305594ACN 201210230559 ACN201210230559 ACN 201210230559ACN 102740519 ACN102740519 ACN 102740519A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- radio frequency
- heating
- resonant cavity
- biological
- frequency heating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Thermotherapy And Cooling Therapy Devices (AREA)
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属射频加热技术,具体涉及一种将射频应用于生物大体的热疗和均匀加热处理的技术。The invention belongs to radio frequency heating technology, and specifically relates to a technology of applying radio frequency to thermal therapy and uniform heating treatment of living organisms.
背景技术Background technique
微波是频率在300MHz-300GHz范围内的电磁波。微波加热的物理基础是电介质在电磁场中存在介质损耗,所消耗的能量以热的形式沉积在介质中,微波加热是一种直接与介质进行能量传递的加热原理。因此,微波加热广泛应用于工业加热处理、食品加工、药材处理和医疗等方面。目前微波加热主要采用的频率是915MHz和2450MHz,加热的方式是通过散射多角度辐照对加热区的物料进行整体加热。与其它加热方式相比,微波加热的主要优点是相关组织内部加热时间快和热流分布均匀,加热过程无污染、零排放,直接加热高效率和加热功率精确可控等显著优势。但是,由于微波加热涉及微波的传输耦合以及功率耗散等问题,因此,微波频率不同,对不同材料的加热效果有所不同。一般来讲微波频率越高,能有效穿透生物有机材料的深度下降,能量的损耗效率(吸收率)增加。特别是2450MHz的微波对水分子存在共振吸收效应,对含水物质的加热效率高,速度快。但是随着微波频率的升高,对大尺寸物体的加热均匀性下降,中心部位的耗散功率存在低谷,如图1所示,不适合大尺寸物体的加热应用。而当微波频率太低,一方面对加热工作区域尺寸要求很大,否则,微波无法传播;另一方面,材料对微波的吸收率下降,加热效率和速度下降,不适合小尺寸材料的加热。综合起来,微波加热领域主要采用的频段集中在900MHz~3GHz之间。Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies in the range of 300MHz-300GHz. The physical basis of microwave heating is that there is a dielectric loss in the dielectric in the electromagnetic field, and the consumed energy is deposited in the medium in the form of heat. Microwave heating is a heating principle that directly transfers energy to the medium. Therefore, microwave heating is widely used in industrial heating, food processing, medicinal material processing and medical treatment. At present, the main frequencies used for microwave heating are 915MHz and 2450MHz, and the heating method is to heat the materials in the heating zone as a whole by scattering multi-angle radiation. Compared with other heating methods, the main advantages of microwave heating are fast heating time and uniform heat flow distribution inside the relevant tissues, no pollution and zero emissions during the heating process, high efficiency of direct heating, and precise and controllable heating power. However, since microwave heating involves problems such as microwave transmission coupling and power dissipation, different microwave frequencies have different heating effects on different materials. Generally speaking, the higher the microwave frequency, the lower the depth that can effectively penetrate bio-organic materials, and the higher the energy loss efficiency (absorption rate). In particular, the 2450MHz microwave has a resonant absorption effect on water molecules, and has high heating efficiency and fast speed for water-containing substances. However, as the microwave frequency increases, the heating uniformity of large-sized objects decreases, and the dissipated power at the center has a low valley, as shown in Figure 1, which is not suitable for heating applications of large-sized objects. When the microwave frequency is too low, on the one hand, the size of the heating working area is required to be large, otherwise, the microwave cannot propagate; on the other hand, the absorption rate of the material to the microwave decreases, and the heating efficiency and speed decrease, which is not suitable for heating small-sized materials. Taken together, the frequency bands mainly used in the field of microwave heating are concentrated between 900MHz and 3GHz.
近年来,生物医学对热处理,尤其是热疗产生了浓厚的兴趣。而基于生物活体的加热处理及热疗对加热过程的可控性和安全性有极高的要求,生物大体加热及热疗不同于通常的工业加热和食品加热,生物大体的热疗是对生物活体整体进行加热,对加热过程有其特有的要求。首先是安全性及副作用控制,对生物活体的加热首要的问题是确保加热过程的安全,同时尽量减少副作用的产生。这就对加热方式提出了很高的要求,主要包括:加热过程的功率精确可控,对关键部位可有效隔离防护等。其次是对生物大体加热部位和加热功率分布均匀性要严格控制。这就要求加热的功率可有效深入生物大体内部,也可以根据需要在特定的区域形成强加热区域或不加热区,还可以对生物大体整体从里到外均匀加热等。最后是加热设备不能有能量泄露,确保周边工作人员的安全。传统微波的加热方法难以直接采用。存在的问题包括:1、生物大体的尺寸一般在分米~米量级,常用的微波加热仍然难以深入生物体内部,难以满足加热均匀性要求;2、传统微波加热采用散射腔的方式加热,不能按要求稳定可靠控制加热功率的分布;3、微波加热腔无法开孔保护生物体部分重点部位,不能满足高安全性的要求。In recent years, biomedicine has developed a strong interest in heat treatment, especially hyperthermia. The heating treatment and hyperthermia based on living organisms have extremely high requirements on the controllability and safety of the heating process. The general heating and hyperthermia of living organisms are different from the usual industrial heating and food heating. The living body is heated as a whole, which has its unique requirements for the heating process. The first is safety and side effect control. The primary issue for heating living organisms is to ensure the safety of the heating process while minimizing side effects. This puts forward high requirements on the heating method, mainly including: the power of the heating process is accurately and controllable, and the key parts can be effectively isolated and protected. The second is to strictly control the heating part of the organism and the uniformity of heating power distribution. This requires that the heating power can effectively penetrate deep into the organism, and can also form a strong heating area or a non-heating area in a specific area according to needs, and can evenly heat the organism from the inside to the outside. Finally, the heating equipment must not have energy leakage to ensure the safety of surrounding staff. The traditional microwave heating method is difficult to directly adopt. Existing problems include: 1. The general size of organisms is generally in the order of decimeters to meters. It is still difficult for the commonly used microwave heating to penetrate into the interior of organisms and meet the requirements of heating uniformity; 2. Traditional microwave heating adopts the method of scattering cavity heating, The distribution of heating power cannot be controlled stably and reliably as required; 3. The microwave heating chamber cannot open holes to protect some important parts of the living body, which cannot meet the requirements of high safety.
发明内容Contents of the invention
为了克服现有技术的不足,本发明提供一种生物大体射频加热方法,改善生物大体加热的均匀性、可控性和安全性。In order to overcome the deficiencies of the prior art, the present invention provides a biological body radio frequency heating method to improve the uniformity, controllability and safety of the biological body heating.
本发明解决其技术问题所采用的技术方案是:采用频率为150MHz-200MHz的射频对生物大体进行加热。The technical scheme adopted by the present invention to solve the technical problem is: adopt the radio frequency with a frequency of 150MHz-200MHz to heat the living organisms.
所述的加热采用谐振腔式加热。The heating adopts resonant cavity heating.
本发明还提供一种实现上述方法的装置,包括射频源和谐振腔,谐振腔为一个封闭腔体,谐振腔电磁场分布可调节,射频源安装在谐振腔一端,射频源频率为150MHz-200MHz,生物大体置于射频谐振腔内。The present invention also provides a device for implementing the above method, including a radio frequency source and a resonant cavity, the resonant cavity is a closed cavity, the electromagnetic field distribution of the resonant cavity can be adjusted, the radio frequency source is installed at one end of the resonant cavity, and the frequency of the radio frequency source is 150MHz-200MHz, The living being is generally placed inside the radio frequency resonant cavity.
所述的射频源输出功率为50W-2000W。The output power of the radio frequency source is 50W-2000W.
所述的射频源频率连续可调;功率连续可调。The frequency of the radio frequency source is continuously adjustable; the power is continuously adjustable.
所述的谐振腔开有一个直径在15cm以内的通孔,通孔与射频源关于谐振腔体积中心对称分布。The resonant cavity has a through hole with a diameter within 15cm, and the through hole and the radio frequency source are distributed symmetrically about the volume center of the resonant cavity.
所述的谐振腔为一面对称腔体,开有两个直径在15cm以内的通孔,两个通孔关于对称平面对称分布,且射频源位于谐振腔的对称平面内。The resonant cavity is a one-sided symmetrical cavity with two through holes with a diameter within 15 cm. The two through holes are symmetrically distributed about the symmetry plane, and the radio frequency source is located in the symmetry plane of the resonant cavity.
本发明的有益效果是:本发明提出采用频率为150MHz-200MHz的射频加热人体或其他动物大体,进行生物大体的射频热疗或整体均匀加热处理。150MHz-200MHz的射频对生物大体加热采用了电磁场对生物大体介质极化反转振荡吸能机理,与微波加热的不同之处在于,射频加热中水分子共振吸收效应很弱,生物介质对该频段的适度低吸收率带来了更好的穿透力和更均匀的能量耗散分布等优势。该频段对牛、羊和人等生物大体的有效透射深度可达10cm以上,可更好地实现里外同时加热,加热功率分布更均匀,综合加热效果比915MHz、2450MHz等微波加热更优、更安全。The beneficial effects of the present invention are: the present invention proposes to use radio frequency with a frequency of 150MHz-200MHz to heat the human body or other animal bodies, so as to carry out radio frequency hyperthermia or overall uniform heating treatment of the biological body. The 150MHz-200MHz radio frequency heating of the biological body adopts the electromagnetic field to the biological medium polarization reversal oscillation energy absorption mechanism. The difference from microwave heating is that the resonance absorption effect of water molecules in radio frequency heating is very weak, and the biological medium has a very weak absorption effect on the frequency band. The moderately low absorption rate brings advantages such as better penetration and more uniform energy dissipation distribution. The effective transmission depth of this frequency band to cattle, sheep and human organisms can reach more than 10cm, which can better realize simultaneous heating inside and outside, and the heating power distribution is more uniform. Safety.
本发明采用150MHz-200MHz射频进行加热,加热方式改为谐振腔式加热。该波段的波长为1.5m~2m,该波长与人体或其它动物如猪、牛、羊等生物大体的外形尺寸相当,采用封闭谐振腔后,可以形成电磁场稳定的均匀分布,由于动物大体对该频段的电磁波吸收率适度,使电磁波能量具有较好的穿透力和更均匀的能量吸收耗散分布,使动物大体得到从里到外更均匀的加热处理,有利于改善热疗效果和提高生物大体加热的安全性。同时该波段的谐振腔尺度适当,工程实现更经济可行,也便于开适当大小的孔对生物体关键部位(如头部)进行监测和保护,而不会导致射频能量的泄露。The present invention uses 150MHz-200MHz radio frequency for heating, and the heating method is changed to resonant cavity heating. The wavelength of this band is 1.5m~2m, which is equivalent to the general dimensions of the human body or other animals such as pigs, cattle, sheep, etc. After the closed resonant cavity is used, a stable and uniform distribution of the electromagnetic field can be formed. The electromagnetic wave absorption rate in the frequency band is moderate, so that the electromagnetic wave energy has better penetrating power and more uniform energy absorption and dissipation distribution, so that animals can generally be heated more uniformly from the inside to the outside, which is conducive to improving the effect of hyperthermia and improving biological General heating safety. At the same time, the scale of the resonant cavity in this band is appropriate, and the project is more economical and feasible, and it is also convenient to open holes of appropriate size to monitor and protect key parts of the organism (such as the head) without causing leakage of radio frequency energy.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是微波与射频透射功率分布与物料厚度关系图;Figure 1 is a diagram of the relationship between microwave and radio frequency transmission power distribution and material thickness;
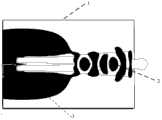
图2是带等效人体模型的谐振腔内180MHz射频瞬态场分布图;Figure 2 is a 180MHz radio frequency transient field distribution diagram in a resonant cavity with an equivalent human body model;
图中,1—射频谐振腔,2—人体,3—射频电场;In the figure, 1—radio frequency resonant cavity, 2—human body, 3—radio frequency electric field;
图3(a)是射频加热谐振腔结构图,图3(b)是射频加热谐振腔结构图,Figure 3(a) is the structural diagram of the radio frequency heating resonant cavity, and Figure 3(b) is the structural diagram of the radio frequency heating resonant cavity,
图中,4—射频传输线L40波导,5—射频天线,6—活动支架,7—屏蔽门,8—圆柱射频腔观察孔,9—射频电磁波,10—屏蔽门间隙,11—谐振腔支撑体,12—谐振腔滚动轮,13—屏蔽门扶手,14—电磁屏蔽门,15—圆柱谐振腔开孔,16—生物大体头部支撑,17—谐振腔支撑,18—圆柱谐振腔直径,19—圆柱谐振腔开孔直径。In the figure, 4—radio frequency transmission line L40 waveguide, 5—radio frequency antenna, 6—movable bracket, 7—shield door, 8—cylindrical radio frequency cavity observation hole, 9—radio frequency electromagnetic wave, 10—shield door gap, 11—resonant cavity support body , 12—resonant cavity rolling wheel, 13—shield door handrail, 14—electromagnetic shielded door, 15—cylindrical resonant cavity opening, 16—biological general head support, 17—resonant cavity support, 18—cylindrical resonant cavity diameter, 19 —The opening diameter of the cylindrical resonator.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明包括以下内容:The present invention includes the following contents:
(1)加热射频源频段为150MHz-200MHz,射频源频率可调。在不同加热负载情况下,可调节射频源频率,满足谐振加热要求;(2)采用谐振腔式加热方式,可调节控制场分布。人体或其它动物大体置于射频谐振腔内,可以调节射频场的分布来改善动物大体对射频的吸收。也可以开直径在15cm以内的孔用作其它目的而不会导致射频能量泄露。(3)加热射频源功率为50W-2000W,连续波,功率可调。调节射频源输出功率,可控制加热速度和加热时间;(1) The frequency band of the heating RF source is 150MHz-200MHz, and the frequency of the RF source is adjustable. Under different heating load conditions, the frequency of the radio frequency source can be adjusted to meet the requirements of resonance heating; (2) The resonant cavity heating method can be used to adjust the control field distribution. The human body or other animals are generally placed in the radio frequency resonant cavity, and the distribution of the radio frequency field can be adjusted to improve the animal's general absorption of radio frequency. It is also possible to open holes within 15 cm in diameter for other purposes without causing leakage of radio frequency energy. (3) The power of the heating radio frequency source is 50W-2000W, continuous wave, and the power is adjustable. Adjust the output power of the RF source to control the heating speed and heating time;
采用150MHz-200MHz射频加热,主要是由于该波段的波长为1.5m~2m,该波长与人体或其它动物如猪、牛、羊等生物大体的外形尺寸相当,由于共振效应从而可以形成电磁场的均匀分布和有效穿透,由于动物大体对该频段的电磁波吸收率适度,使电磁波能量具有较好的穿透力和更均匀的能量吸收耗散分布,使生物大体得到从里到外更均匀的加热处理,有利于改善热疗效果和提高生物大体加热的安全性。此外,生物大体的个体形状和重量差异,加热时工作频率存在漂移现象。因此,采用150MHz-200MHz射频源加热,射频源频率可调,可满足不同生物大体谐振加热的要求。射频源工作频率的调节步长为0.25MHz。150MHz-200MHz radio frequency heating is used, mainly because the wavelength of this band is 1.5m~2m, which is equivalent to the general shape and size of human body or other animals such as pigs, cattle, sheep, etc. Due to the resonance effect, it can form a uniform electromagnetic field. Distribution and effective penetration, because animals generally have a moderate absorption rate of electromagnetic waves in this frequency band, so that electromagnetic wave energy has better penetration and more uniform energy absorption and dissipation distribution, so that organisms generally get more uniform heating from the inside to the outside Treatment is conducive to improving the effect of hyperthermia and improving the safety of biological general heating. In addition, due to the individual shape and weight differences of organisms, the operating frequency drifts when heated. Therefore, a 150MHz-200MHz radio frequency source is used for heating, and the frequency of the radio frequency source is adjustable, which can meet the requirements for general resonance heating of different organisms. The adjustment step size of the working frequency of the RF source is 0.25MHz.
采用谐振腔式加热方式,主要是为了调节控制谐振腔内电磁场分布,满足不同的生物大体加热要求。150MHz-200MHz的谐振腔尺寸与生物大体尺寸相当,对生物大体加热时腔内能量分布较均匀,谐振腔内部空间得到合理充分应用。同时,谐振腔所占空间较小,有利于医疗设备的产品化。最后,150MHz-200MHz谐振腔便于开适当大小的孔对生物体关键部位(如头部)进行观察和保护,而不会导致射频能量的泄露,有利于屏蔽电磁污染和生物大体敏感部位的局部保护等。谐振腔结构采用圆柱谐振腔,圆柱谐振腔长度1750mm,圆柱谐振腔直径1100mm,圆柱谐振腔开孔尺寸300mm和150mm。The resonant cavity heating method is mainly used to adjust and control the electromagnetic field distribution in the resonant cavity to meet the general heating requirements of different organisms. The size of the resonant cavity of 150MHz-200MHz is equivalent to the general size of the living being, and the energy distribution in the cavity is relatively uniform when the living being is generally heated, and the internal space of the resonant cavity is reasonably and fully utilized. At the same time, the space occupied by the resonant cavity is small, which is conducive to the commercialization of medical equipment. Finally, the 150MHz-200MHz resonant cavity is convenient to open holes of appropriate size to observe and protect key parts of the organism (such as the head) without causing leakage of radio frequency energy, which is conducive to shielding electromagnetic pollution and partial protection of biologically sensitive parts wait. The resonant cavity structure adopts a cylindrical resonant cavity, the length of the cylindrical resonant cavity is 1750mm, the diameter of the cylindrical resonant cavity is 1100mm, and the opening size of the cylindrical resonant cavity is 300mm and 150mm.
采用射频源功率为50W-2000W,连续波,功率可调,主要控制加热速度和加热时间,满足不同生物大体的加热要求。加热生物大体时,功率过大,会导致生物大体的表面灼伤;功率过小,满足不了生物大体的加热需求。射频源输出功率的调节步长为20W。根据生物大体在加热过程的反应,实时调节射频源输出功率,满足加热安全性和有效性要求。The power of the radio frequency source is 50W-2000W, continuous wave, and the power is adjustable. It mainly controls the heating speed and heating time to meet the heating requirements of different organisms. When heating the living organisms, if the power is too high, the surface of the living organisms will be burned; if the power is too small, the heating needs of the living organisms cannot be met. The adjustment step size of the output power of the RF source is 20W. According to the response of the organism in the heating process, the output power of the RF source is adjusted in real time to meet the safety and effectiveness requirements of heating.
下面结合附图和实施例对本发明进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
⑴射频源频率为150MHz-200MHz,且频率连续可调。在生物大体形状和重量不同情况下,可调节射频源输出频率,满足谐振要求。(1) The frequency of the radio frequency source is 150MHz-200MHz, and the frequency is continuously adjustable. In the case of different shapes and weights of organisms, the output frequency of the RF source can be adjusted to meet the resonance requirements.
⑵采用谐振腔式加热方式,可调节控制场分布。人体或其它动物大体置于射频谐振腔内,可以调节射频场的分布来改善动物大体对射频的吸收。也可以开直径在15cm以内的孔用作其它目的而不会导致射频能量泄露。⑵Using resonant cavity heating method, the distribution of control field can be adjusted. The human body or other animals are generally placed in the radio frequency resonant cavity, and the distribution of the radio frequency field can be adjusted to improve the animal's general absorption of radio frequency. It is also possible to open holes within 15 cm in diameter for other purposes without causing leakage of radio frequency energy.
⑶射频源输出功率为50W-2000W,连续波,功率连续可调。调节射频源输出功率,可控制加热速度和加热时间。⑶ The output power of the RF source is 50W-2000W, continuous wave, and the power is continuously adjustable. Adjust the output power of the RF source to control the heating speed and heating time.
这里给出人体吸收180MHz射频的仿真结果,如图2所示,表示某一时刻射频在带有人体负载的谐振腔内电场分布。仿真结果表明:150MHz-200MHz射频场强分布相对较均匀,易于整体均匀加热。Here is the simulation result of human body absorbing 180MHz radio frequency, as shown in Figure 2, which shows the electric field distribution of radio frequency in the resonant cavity with human body load at a certain moment. The simulation results show that the distribution of 150MHz-200MHz radio frequency field strength is relatively uniform, and it is easy to heat uniformly as a whole.
图3(a)中,射频天线采用单极子天线结构,既能高效激励电磁波,又不占用谐振腔空间。图3(a)中,圆柱谐振腔内有绝缘介质材料做成的自由活动架,便于固定生物大体。图3(a)中,圆柱谐振腔开两个直径为100mm观察孔,便于观察生物大体在加热过程中的反应,开孔采用透明的电磁屏蔽布覆盖,保证射频电磁波不泄露。图3(b)中,谐振腔开孔直径为300mm,开孔的主要目的是保护生物大体头部,使其不受射频电磁波辐照加热。图3(b)中,在开孔周围采用电磁屏蔽布做成电磁屏蔽护套,其功能是防止电磁波泄露。In Figure 3(a), the RF antenna adopts a monopole antenna structure, which can efficiently excite electromagnetic waves without occupying the resonant cavity space. In Figure 3(a), there is a freely movable frame made of insulating dielectric material in the cylindrical resonator cavity, which is convenient for fixing the biological body. In Figure 3(a), the cylindrical resonator has two observation holes with a diameter of 100 mm, which is convenient for observing the reaction of the organism during the heating process. The openings are covered with transparent electromagnetic shielding cloth to ensure that the radio frequency electromagnetic waves do not leak. In Figure 3(b), the opening diameter of the resonant cavity is 300 mm, and the main purpose of the opening is to protect the general head of the living being from being heated by radio frequency electromagnetic waves. In Figure 3(b), the electromagnetic shielding sheath is made of electromagnetic shielding cloth around the opening, and its function is to prevent the leakage of electromagnetic waves.
本发明的创新点是:Innovation point of the present invention is:
⑴采用150MHz-200MHz射频加热新方法,射频电磁波透射深度深,加热体内外同时加热。⑴Using a new method of 150MHz-200MHz radio frequency heating, the radio frequency electromagnetic wave has a deep penetration depth, heating inside and outside the body at the same time.
⑵采用射频谐振腔加热新方式,电磁场场强分布可控,也更均匀,加热腔大小合适,适合用于生物大体整体均匀加热。⑵Using a new method of radio frequency resonant cavity heating, the distribution of electromagnetic field strength is controllable and more uniform, and the size of the heating cavity is appropriate, which is suitable for uniform heating of organisms.
⑶采用150MHz-200MHz射频谐振腔加热,局部电磁场较容易屏蔽,也可以开合适的窗口,用于保护头、手等敏感部位,更有利于保证加热过程中生物大体的安全性。⑶Using 150MHz-200MHz radio frequency resonant cavity heating, the local electromagnetic field is easier to shield, and a suitable window can also be opened to protect sensitive parts such as the head and hands, which is more conducive to ensuring the general safety of organisms during the heating process.
⑷射频谐振加热腔结构与生物大体尺寸相当,结构紧凑,易于加热设备的工程化,易于推广应用到医疗设备和其它射频加热设备。(4) The structure of the radio frequency resonant heating chamber is equivalent to the general size of the living body, the structure is compact, and it is easy to engineer the heating equipment, and it is easy to popularize and apply to medical equipment and other radio frequency heating equipment.
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012102305594ACN102740519A (en) | 2012-07-05 | 2012-07-05 | Radio-frequency heating method and radio-frequency heating device for biological thanosomes |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012102305594ACN102740519A (en) | 2012-07-05 | 2012-07-05 | Radio-frequency heating method and radio-frequency heating device for biological thanosomes |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102740519Atrue CN102740519A (en) | 2012-10-17 |
Family
ID=46995045
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012102305594APendingCN102740519A (en) | 2012-07-05 | 2012-07-05 | Radio-frequency heating method and radio-frequency heating device for biological thanosomes |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102740519A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104486856A (en)* | 2014-12-15 | 2015-04-01 | 西北核技术研究所 | Feeding frequency stabilization structure for biological thanosome radio frequency heating device |
| CN108702817A (en)* | 2016-02-15 | 2018-10-23 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Method and apparatus for delivering radio frequency electromagnetic energy for cooking food |
| CN113891512A (en)* | 2021-08-26 | 2022-01-04 | 电子科技大学长三角研究院(湖州) | Radio frequency heating method based on frequency selection technology |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5163446A (en)* | 1989-02-16 | 1992-11-17 | Omron Corporation | Electromagnetic heating device |
| US20020047009A1 (en)* | 1998-04-21 | 2002-04-25 | The State Of Or Acting By And Through The State Board Of Higher Edu. On Behalf Of Or State Univ. | Variable frequency automated capacitive radio frequency (RF) dielectric heating system |
| CN101226119A (en)* | 2008-01-30 | 2008-07-23 | 吉林大学 | Dynamic cycle microwave assisted digestion device |
| CN202679682U (en)* | 2012-07-05 | 2013-01-16 | 西北核技术研究所 | Radio frequency heating apparatus for large living organism |
- 2012
- 2012-07-05CNCN2012102305594Apatent/CN102740519A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5163446A (en)* | 1989-02-16 | 1992-11-17 | Omron Corporation | Electromagnetic heating device |
| US20020047009A1 (en)* | 1998-04-21 | 2002-04-25 | The State Of Or Acting By And Through The State Board Of Higher Edu. On Behalf Of Or State Univ. | Variable frequency automated capacitive radio frequency (RF) dielectric heating system |
| CN101226119A (en)* | 2008-01-30 | 2008-07-23 | 吉林大学 | Dynamic cycle microwave assisted digestion device |
| CN202679682U (en)* | 2012-07-05 | 2013-01-16 | 西北核技术研究所 | Radio frequency heating apparatus for large living organism |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104486856A (en)* | 2014-12-15 | 2015-04-01 | 西北核技术研究所 | Feeding frequency stabilization structure for biological thanosome radio frequency heating device |
| CN104486856B (en)* | 2014-12-15 | 2016-03-02 | 西北核技术研究所 | A kind of biological frequency stabilization of radio frequency heating apparatus feed substantially structure |
| CN108702817A (en)* | 2016-02-15 | 2018-10-23 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Method and apparatus for delivering radio frequency electromagnetic energy for cooking food |
| CN113891512A (en)* | 2021-08-26 | 2022-01-04 | 电子科技大学长三角研究院(湖州) | Radio frequency heating method based on frequency selection technology |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Leonelli et al. | Microwave and ultrasonic processing: Now a realistic option for industry | |
| NO20023819D0 (en) | Heater with microwaves | |
| CN201625531U (en) | A Multifunctional Ultrasonic Microwave Synergistic Chemical Reactor | |
| Gong et al. | Superficial tumor hyperthermia with flat left-handed metamaterial lens | |
| Ragaini et al. | Simultaneous ultrasound and microwave new reactor: detailed description and energetic considerations | |
| CN102740519A (en) | Radio-frequency heating method and radio-frequency heating device for biological thanosomes | |
| CN202679682U (en) | Radio frequency heating apparatus for large living organism | |
| CN100459951C (en) | Radio-frequency thermotherapy apparatus for eliminating defect of subcutaneous fat superheat | |
| Sandhu et al. | The development of microwave hyperthermia applicators | |
| Chou | Application of electromagnetic energy in cancer treatment | |
| Fiser et al. | Waveguide applicator system for head and neck hyperthermia treatment | |
| CN210675148U (en) | Spiral coil type microwave reactor | |
| CN209405498U (en) | A device for magnetic induction hyperthermia in animals | |
| Debnath et al. | Breast cancer treatment by combining microwave hyperthermia and radiation brachytherapy | |
| Rashed | Multi-Physical Field Simulation of Radiofrequency Therapy for Alzheimer’s | |
| CN100542629C (en) | Horizontal electric field RF heat therapy equipment | |
| Tang et al. | Passive Beamforming Metasurfaces for Microwave-induced Thermoacoustic Imaging | |
| Tullius et al. | Relaxation time effect on the human head using the thermal wave model | |
| Chen et al. | Electromagnetic field exposure may influence the apoptosis rate of human cell cultures | |
| Dubost et al. | Morphological transformations of human cancer cells and microtubules caused by frequency specific pulsed electric fields broadcast by an enclosed gas plasma antenna | |
| Morega et al. | Optimal design for microwave hyperthermia applicator | |
| Maini et al. | Comparison of coaxial choke and extended tip choke antenna for interstitial microwave ablation of HCC | |
| CN108434601A (en) | A kind of MM wave therapeutic instrument based on photonic crystal fiber | |
| CN201044768Y (en) | Horizontal electric field radio frequency thermotherapy instrument | |
| Huang et al. | The study of SAR distribution in microwave ablation for tumours |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20121017 |