CN102676479A - Preparation method of hybrid xylanase atxb - Google Patents
Preparation method of hybrid xylanase atxbDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102676479A CN102676479ACN2012101841611ACN201210184161ACN102676479ACN 102676479 ACN102676479 ACN 102676479ACN 2012101841611 ACN2012101841611 ACN 2012101841611ACN 201210184161 ACN201210184161 ACN 201210184161ACN 102676479 ACN102676479 ACN 102676479A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- atxb
- xylanase
- atx
- pbs
- ppic9k
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 101710121765Endo-1,4-beta-xylanaseProteins0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription75
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription8
- 229920001221xylanPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription30
- 150000004823xylansChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription30
- 241000588724Escherichia coliSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 241000203780Thermobifida fuscaSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 239000012634fragmentSubstances0.000claimsdescription17
- 239000013613expression plasmidSubstances0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000003259recombinant expressionMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000010079rubber tappingMethods0.000claimsdescription11
- 238000012408PCR amplificationMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- 101000702488Rattus norvegicus High affinity cationic amino acid transporter 1Proteins0.000claimsdescription8
- 230000029087digestionEffects0.000claimsdescription8
- 108091008146restriction endonucleasesProteins0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000012216screeningMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000012141concentrateSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 241000235648PichiaSpecies0.000claims2
- 230000003321amplificationEffects0.000claims2
- 238000003199nucleic acid amplification methodMethods0.000claims2
- 230000003248secreting effectEffects0.000claims1
- 108090000790EnzymesProteins0.000abstractdescription20
- 102000004190EnzymesHuman genes0.000abstractdescription18
- 108010001817Endo-1,4-beta XylanasesProteins0.000abstractdescription10
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000abstractdescription10
- 230000014509gene expressionEffects0.000abstractdescription10
- 241000235058Komagataella pastorisSpecies0.000abstractdescription9
- LGQKSQQRKHFMLI-SJYYZXOBSA-N(2s,3r,4s,5r)-2-[(3r,4r,5r,6r)-4,5,6-trihydroxyoxan-3-yl]oxyoxane-3,4,5-triolChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)OC1LGQKSQQRKHFMLI-SJYYZXOBSA-N0.000abstractdescription4
- JCSJTDYCNQHPRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N20-hydroxyecdysone 2,3-acetonideNatural productsOC1C(O)C(O)COC1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC2C(C(O)C(O)OC2)O)OC1JCSJTDYCNQHPRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription4
- LGQKSQQRKHFMLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N4-O-beta-D-xylopyranosyl-beta-D-xylopyranoseNatural productsOC1C(O)C(O)COC1OC1C(O)C(O)C(O)OC1LGQKSQQRKHFMLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription4
- SQNRKWHRVIAKLP-UHFFFAOYSA-ND-xylobioseNatural productsO=CC(O)C(O)C(CO)OC1OCC(O)C(O)C1OSQNRKWHRVIAKLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription4
- JCSJTDYCNQHPRJ-FDVJSPBESA-Nbeta-D-Xylp-(1->4)-beta-D-Xylp-(1->4)-D-XylpChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](O)C(O)OC2)O)OC1JCSJTDYCNQHPRJ-FDVJSPBESA-N0.000abstractdescription4
- ABKNGTPZXRUSOI-UHFFFAOYSA-NxylotrioseNatural productsOCC(OC1OCC(OC2OCC(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C1O)C(O)C(O)C=OABKNGTPZXRUSOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription4
- 235000018185Betula X alpestrisNutrition0.000abstractdescription3
- 235000018212Betula X uliginosaNutrition0.000abstractdescription3
- 238000000855fermentationMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 230000004151fermentationEffects0.000abstractdescription3
- 210000004102animal cellAnatomy0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000003053toxinSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-NGQZWQHPSA-Nd-xylitolChemical compoundOC[C@H](O)C(O)[C@H](O)COHEBKCHPVOIAQTA-NGQZWQHPSA-N0.000abstract4
- 230000000529probiotic effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 230000028327secretionEffects0.000abstract1
- 239000013598vectorSubstances0.000description25
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description17
- 229940088598enzymeDrugs0.000description15
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description14
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description13
- 239000001913celluloseSubstances0.000description12
- 229920002678cellulosePolymers0.000description12
- 235000010980celluloseNutrition0.000description12
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000description12
- 108010059892CellulaseProteins0.000description11
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description11
- 229940106157cellulaseDrugs0.000description11
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description11
- 230000007062hydrolysisEffects0.000description10
- 238000006460hydrolysis reactionMethods0.000description10
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description10
- 239000006228supernatantSubstances0.000description10
- 240000004808Saccharomyces cerevisiaeSpecies0.000description9
- 238000001976enzyme digestionMethods0.000description9
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description9
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterChemical compoundOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description9
- 108020004414DNAProteins0.000description8
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description7
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description7
- 241001506991Komagataella phaffii GS115Species0.000description6
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description6
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000description6
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000description5
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000description5
- 241000203640ThermomonosporaSpecies0.000description5
- 125000003275alpha amino acid groupChemical group0.000description5
- 238000010353genetic engineeringMethods0.000description5
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description5
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description5
- 238000000746purificationMethods0.000description5
- 102000012410DNA LigasesHuman genes0.000description4
- 108010061982DNA LigasesProteins0.000description4
- 239000000872bufferSubstances0.000description4
- 230000003197catalytic effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description4
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000description4
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-ND-GlucitolNatural productsOC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)COFBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N0.000description3
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethanolChemical compoundOCOKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 229920000168Microcrystalline cellulosePolymers0.000description3
- 241001249784ThermomonasSpecies0.000description3
- 230000001580bacterial effectEffects0.000description3
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description3
- 238000001962electrophoresisMethods0.000description3
- 229920005610ligninPolymers0.000description3
- 239000003550markerSubstances0.000description3
- 239000002609mediumSubstances0.000description3
- 235000019813microcrystalline celluloseNutrition0.000description3
- 239000008108microcrystalline celluloseSubstances0.000description3
- 229940016286microcrystalline celluloseDrugs0.000description3
- 239000013612plasmidSubstances0.000description3
- 229920001282polysaccharidePolymers0.000description3
- 239000005017polysaccharideSubstances0.000description3
- 150000004804polysaccharidesChemical class0.000description3
- 239000000600sorbitolSubstances0.000description3
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description3
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-NChloroformChemical compoundClC(Cl)ClHEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- SRBFZHDQGSBBOR-IOVATXLUSA-ND-xylopyranoseChemical compoundO[C@@H]1COC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1OSRBFZHDQGSBBOR-IOVATXLUSA-N0.000description2
- TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-LMagnesium chlorideChemical compound[Mg+2].[Cl-].[Cl-]TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- 229920002472StarchPolymers0.000description2
- 108010006785Taq PolymeraseProteins0.000description2
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000description2
- 150000001413amino acidsChemical class0.000description2
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 235000005911dietNutrition0.000description2
- 230000037213dietEffects0.000description2
- 238000004520electroporationMethods0.000description2
- 230000003301hydrolyzing effectEffects0.000description2
- PHTQWCKDNZKARW-UHFFFAOYSA-NisoamylolChemical compoundCC(C)CCOPHTQWCKDNZKARW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description2
- 238000012163sequencing techniqueMethods0.000description2
- 238000001179sorption measurementMethods0.000description2
- 239000008107starchSubstances0.000description2
- 235000019698starchNutrition0.000description2
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description2
- 102000009027AlbuminsHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010088751AlbuminsProteins0.000description1
- 244000153158Ammi visnagaSpecies0.000description1
- 235000010585Ammi visnagaNutrition0.000description1
- 244000063299Bacillus subtilisSpecies0.000description1
- 235000014469Bacillus subtilisNutrition0.000description1
- 108010084185CellulasesProteins0.000description1
- 102000005575CellulasesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108091026890Coding regionProteins0.000description1
- 108010014303DNA-directed DNA polymeraseProteins0.000description1
- 102000016928DNA-directed DNA polymeraseHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010031186Glycoside HydrolasesProteins0.000description1
- 102000005744Glycoside HydrolasesHuman genes0.000description1
- 102000006833Multifunctional EnzymesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010047290Multifunctional EnzymesProteins0.000description1
- 240000007594Oryza sativaSpecies0.000description1
- 235000007164Oryza sativaNutrition0.000description1
- 240000000220Panda oleosaSpecies0.000description1
- 235000016496Panda oleosaNutrition0.000description1
- 108010002747Pfu DNA polymeraseProteins0.000description1
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhenolChemical compoundOC1=CC=CC=C1ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 241000589540Pseudomonas fluorescensSpecies0.000description1
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-NSerineNatural productsOCC(N)C(O)=OMTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000007984Tris EDTA bufferSubstances0.000description1
- PYMYPHUHKUWMLA-UHFFFAOYSA-NarabinoseNatural productsOCC(O)C(O)C(O)C=OPYMYPHUHKUWMLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- KCXMKQUNVWSEMD-UHFFFAOYSA-Nbenzyl chlorideChemical compoundClCC1=CC=CC=C1KCXMKQUNVWSEMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229940073608benzyl chlorideDrugs0.000description1
- SRBFZHDQGSBBOR-UHFFFAOYSA-Nbeta-D-Pyranose-LyxoseNatural productsOC1COC(O)C(O)C1OSRBFZHDQGSBBOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 239000007844bleaching agentSubstances0.000description1
- 235000008429breadNutrition0.000description1
- 229940041514candida albicans extractDrugs0.000description1
- 108010089934carbohydraseProteins0.000description1
- 239000013592cell lysateSubstances0.000description1
- 239000006285cell suspensionSubstances0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 210000000349chromosomeAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000005352clarificationMethods0.000description1
- 238000010367cloningMethods0.000description1
- 238000007621cluster analysisMethods0.000description1
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000description1
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000012217deletionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037430deletionEffects0.000description1
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000033629detection of yeastEffects0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 239000003480eluentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000013604expression vectorSubstances0.000description1
- 235000013305foodNutrition0.000description1
- 235000015203fruit juiceNutrition0.000description1
- 239000001963growth mediumSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002209hydrophobic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000003780insertionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037431insertionEffects0.000description1
- 229930027917kanamycinNatural products0.000description1
- SBUJHOSQTJFQJX-NOAMYHISSA-NkanamycinChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CN)O[C@@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)[C@H](N)C[C@@H]1NSBUJHOSQTJFQJX-NOAMYHISSA-N0.000description1
- 229960000318kanamycinDrugs0.000description1
- 229930182823kanamycin ANatural products0.000description1
- 229910001629magnesium chlorideInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 239000006225natural substrateSubstances0.000description1
- 239000013642negative controlSubstances0.000description1
- 230000003472neutralizing effectEffects0.000description1
- 235000016709nutritionNutrition0.000description1
- 239000013641positive controlSubstances0.000description1
- 235000013406prebioticsNutrition0.000description1
- 239000002244precipitateSubstances0.000description1
- 238000005215recombinationMethods0.000description1
- 230000006798recombinationEffects0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 239000011347resinSubstances0.000description1
- 229920005989resinPolymers0.000description1
- 235000009566riceNutrition0.000description1
- 239000013605shuttle vectorSubstances0.000description1
- 239000007974sodium acetate bufferSubstances0.000description1
- 239000010902strawSubstances0.000description1
- 238000006467substitution reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000001131transforming effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000012137tryptoneSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012795verificationMethods0.000description1
- 235000015099wheat bransNutrition0.000description1
- 239000012138yeast extractSubstances0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinesethe
技术领域technical field
本发明涉及基因工程领域中利用基因工程或蛋白质工程技术对酶分子进行改造,获得底物结合能力强、水解性能好的重组酶基因,生产重组木聚糖酶的方法。The invention relates to a method for transforming enzyme molecules by using genetic engineering or protein engineering technology in the field of genetic engineering to obtain a recombinant enzyme gene with strong substrate binding ability and good hydrolysis performance, and to produce recombinant xylanase.
the
背景技术Background technique
木聚糖酶具有广泛的工业应用价值(Subramaniyan S et al. 2002)。木聚糖酶应用在饲料工业中,可提高饲料(尤其是糠麸类)的营养价值,促进动物生长;在造纸和纸浆工业中,木聚糖酶的使用可减少化学漂白剂的使用量,有利于环境保护;在食品工业中,木聚糖酶可用于面包制作、果汁澄清、酿造业和制备功能性低聚木糖。但是在这些实际应用中,木聚糖酶的底物并不是单一的木聚糖而是多糖复合物。如在糠麸类饲料原料中,除了可溶性木聚糖外,还有大量的不溶性木聚糖、淀粉、木质素和纤维素等其它物质(Coughlan et al., 1993)。 因此如何提高木聚糖酶吸附在多糖复合体上尤其是不溶性木聚糖、淀粉、木质素和纤维素等上,高效发挥木聚糖酶水解性能使其适应工业应用至关重要。Xylanase has a wide range of industrial applications (Subramaniyan Set al . 2002). The application of xylanase in the feed industry can improve the nutritional value of feed (especially bran) and promote animal growth; in the paper and pulp industry, the use of xylanase can reduce the use of chemical bleaching agents, It is beneficial to environmental protection; in the food industry, xylanase can be used in bread making, fruit juice clarification, brewing industry and preparation of functional xylooligosaccharides. However, in these practical applications, the substrate of xylanase is not a single xylan but a polysaccharide complex. For example, in bran-based feed materials, in addition to soluble xylan, there are also a large amount of other substances such as insoluble xylan, starch, lignin and cellulose (Coughlanet al ., 1993). Therefore, how to improve the adsorption of xylanase on polysaccharide complexes, especially on insoluble xylan, starch, lignin and cellulose, etc., and how to efficiently exert the hydrolysis performance of xylanase to adapt to industrial applications is very important.
在工业应用上,木聚糖酶的理想特性是同时具有较宽的最适温度和pH、良好的热稳定性和pH稳定性,以及具备较好的底物结合、水解性能,然而此类理想型的木聚糖酶很难从自然界直接获取,需要利用基因工程或蛋白质工程技术对酶分子进行改造,使木聚糖酶的性质更好适应相关产业的发展需要。In industrial applications, the ideal characteristics of xylanase are wide optimum temperature and pH, good thermostability and pH stability, and good substrate binding and hydrolysis performance. It is difficult to obtain the xylanase type directly from nature, and it is necessary to use genetic engineering or protein engineering technology to modify the enzyme molecule, so that the properties of xylanase can better meet the development needs of related industries.
木聚糖酶是可以将木聚糖降解成低聚木糖(xylooligosaccharides, XOs)和木糖(xylose)一类水解酶的总称。根据催化结构域氨基酸同源性和疏水簇分析法,木聚糖酶属于糖苷水解酶第10和第11家族(family)。一些F/10家族木聚糖酶和纤维素酶在水解过程中,首先通过其底物结合域(木聚糖结合域、纤维素结合域)或结合位点锚定在多糖复合体上,使其催化中心更容易靠近底物,便于发挥水解功能(Kuno et al., 2000)。F/10 家族的Pseudomonas fluorescens XylA含一个催化结构域和一个木聚糖结合域,二者由一段富含丝氨酸的连接序列相连,将木聚糖结合域和连接序列分别除去后所得的截短型木聚糖酶对可溶木聚糖的水解能力无明显变化,但它们对不溶性底物的结合、水解能力显著降低(Kulkarni et al.,1999)。Xylanase is a general term for a class of hydrolytic enzymes that can degrade xylan into xylooligosaccharides (XOs) and xylose. According to the amino acid homology and hydrophobic cluster analysis of the catalytic domain, xylanase belongs to the 10th and 11th families of glycoside hydrolases. Some F/10 family xylanases and cellulases are first anchored to the polysaccharide complex through their substrate-binding domains (xylan-binding domains, cellulose-binding domains) or binding sites during hydrolysis, making Its catalytic center is more accessible to the substrate, which facilitates the hydrolysis function (Kunoet al ., 2000). Pseudomonas fluorescens XylA of the F/10 family contains a catalytic domain and a xylan-binding domain, which are connected by a linker sequence rich in serine, and the truncated form obtained by removing the xylan-binding domain and linker sequence The ability of xylanases to hydrolyze soluble xylan did not change significantly, but their ability to bind and hydrolyze insoluble substrates was significantly reduced (Kulkarniet al ., 1999).
国内外关于木聚糖结合域的研究报道多集中在F/10家族木聚糖酶上(Din et al.,2000;刘明启等,2003)。F/10家族木聚糖酶的木聚糖结合域可以结合不溶性木聚糖和微晶纤维素,其功能和纤维素酶的纤维素结合域类似,但绝多数G/11家族木聚糖酶不具备木聚糖结合域,因此在水解天然底物(如麦麸、稻谷和秸杆等)时,酶分子与纤维素和木质素之间存在空间位阻作用,妨碍酶分子的水解作用(Sunna et al., 2000)。木聚糖酶的进化可能是通过酶蛋白分子结构域之间的随机拼接重组而实现的(Gilkes et al., 1991;Kulkarni et al.,1999),酶蛋白分子中结构域的插入,剔除和置换都有可能导致酶蛋白结构功能的显著变化(Shen et al.,1991;Black et al.,1996;Black et al.,1997;Sunna et al.,2000; Lemos et al.,2003;Mangala et al.,2003;Latorre-Garcia et al.,2005)。因此,利用基因工程或蛋白质工程技术对酶分子进行改造,使木聚糖酶能优先吸附于纤维素上,就可使其与底物靠近,从而可以更有效地发挥水解作用。The domestic and foreign research reports on the xylan binding domain mostly focus on the F/10 family xylanase (Dinet al. , 2000; Liu Mingqi et al., 2003). The xylan-binding domain of F/10 family xylanases can bind insoluble xylan and microcrystalline cellulose, and its function is similar to the cellulose-binding domain of cellulase, but most of the G/11 family xylanases It does not have a xylan binding domain, so when hydrolyzing natural substrates (such as wheat bran, rice and straw, etc.), there is a steric hindrance between the enzyme molecule and cellulose and lignin, which hinders the hydrolysis of the enzyme molecule ( Sunnaet al ., 2000). The evolution of xylanase may be achieved through random splicing and recombination between enzyme protein molecular domains (Gilkeset al. , 1991; Kulkarniet al ., 1999), the insertion, deletion and Substitutions may lead to significant changes in enzyme protein structure and function (Shenet al ., 1991; Blacket al ., 1996; Blacket al ., 1997; Sunnaet al ., 2000; Lemoset al ., 2003; Mangalaet al. al ., 2003; Latorre-Garciaet al ., 2005). Therefore, genetic engineering or protein engineering technology is used to modify the enzyme molecule so that the xylanase can be preferentially adsorbed on the cellulose, so that it can be closer to the substrate, so that the hydrolysis can be performed more effectively.
褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A(Thermomonospora fusca xylanase, tfx)是G/11家族中为数不多存在木聚糖结合域和连接序列的酶分子。褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A虽然不具备水解纤维素的能力,但对其具有较高的吸附结合性能(Irwin et al.,1994)。综上所述,利用基因工程或蛋白质工程技术对酶分子进行改造,获得较强底物结合力和水解性能的杂合木聚糖酶是可行的。在饲料工业中,这种人工构建的杂合木聚糖酶兼备木聚糖酶和纤维素酶活性具有特殊优势,单胃动物日粮中纤维素酶和木聚糖酶可以协同作用提高饲料(尤其是糠麸类)消化吸收率,促进动物生长,大大降低成本,提高经济效益。Thermomonospora fusca xylanase A (Thermomonospora fusca xylanase,tfx ) is one of the few enzyme molecules in the G/11 family that has a xylan-binding domain and a linker sequence. Although Xylanase A from Thermomonas variegata does not have the ability to hydrolyze cellulose, it has high adsorption and binding properties (Irwinet al ., 1994). To sum up, it is feasible to obtain hybrid xylanase with strong substrate binding ability and hydrolysis performance by using genetic engineering or protein engineering technology to modify enzyme molecules. In the feed industry, this artificially constructed hybrid xylanase has special advantages in both xylanase and cellulase activities. Cellulase and xylanase in the diet of monogastric animals can synergistically improve feed ( Especially bran) digestion and absorption rate, promote animal growth, greatly reduce costs and improve economic benefits.
the
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明目的是解决以上提出的问题,提供一种杂合木聚糖酶atxb的制备方法。The purpose of the present invention is to solve the above problems and provide a preparation method of hybrid xylanase atxb.
本发明是通过以下技术方案来实现的:The present invention is achieved through the following technical solutions:
一种杂合木聚糖酶atxb的制备方法,包括将来源于褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A的连接序列和木聚糖结合域融合在杂合木聚糖酶atx的C-末端,获得杂合木聚糖酶atxb(SED ID NO:2)。A method for preparing a hybrid xylanase atxb, comprising fused to the C-terminus of the hybrid xylanase atx, a linker sequence and a xylan binding domain derived from Thermomonospora variegata xylanase A, A hybrid xylanase atxb (SED ID NO:2) was obtained.
作为优选,本发明还包括以下步骤:As preferably, the present invention also includes the following steps:
(1)杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb的构建(1) Construction of hybrid xylanase gene atxb
以pBS-T/ atx载体(T-载体购自Promega公司)为模板,X1和X2为引物扩增atx片段;以pBS-T /tfx载体(T-载体购自Promega公司)为模板,X3和X4为引物扩增xbd片段;以上述atx和xbd为模板,X1和X4为引物,PCR扩增得到杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb(SED ID NO:1); Using the pBS-T/atx vector (T-vector was purchased from Promega) as a template, X1 and X2 were used as primers to amplify the atx fragment; using the pBS-T/tfx vector (T-vector was purchased from Promega) as a template, X3 and X4 is the primer to amplify the xbd fragment; using the above atx and xbd as templates, X1 and X4 as primers, PCR amplifies to obtain the hybrid xylanase geneatxb (SED ID NO: 1);
X1:5’- CG?AATTCGCTGTTACATCCAACGAGACCG-3’X1: 5’-CG?AATTCGCTGTTACATCCAACGAGACCG-3’
X2:5’-GTTGTCACCGCCGCTGGTGCCAGAGGAAATCGTGACACTGGC-3’X2: 5'-GTTGTCACCGCCGCTGGTGCCAGAGGAAATCGTGACACTGGC-3'
X3:5’-GGCACCAGCGGCGGTGACAACCCCG-3’X3: 5'-GGCACCAGCGGCGGTGACAACCCCG-3'
X4:5’-GC?GGCCGCGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCT-3’;X4: 5'-GC?GGCCGCGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCT-3';
(2)采用pBS-T载体体系试剂盒(购自Promega公司)将割胶回收的atxb片段与T载体连接,得到pBS-T/ atxb 载体;(2) The pBS-T vector system kit (purchased from Promega) was used to connect the atxb fragment recovered from rubber tapping with the T vector to obtain the pBS-T/ atxb vector;
(3)杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb在毕赤酵母(购自Invitrogen公司)中分泌表达:(3) The hybrid xylanase gene atxb is secreted and expressed in Pichia pastoris (purchased from Invitrogen):
pBS-T/ atxb 载体经EcoR、Not双酶切、割胶回收目的条带,回收的atxb与同样经过双酶切的pPIC9K连接,并转化大肠杆菌,获得的重组表达质粒命名为pPIC9K/atxb;大量提取重组表达质粒,用Bgl限制性内切酶将重组表达质粒pPIC9K/atxb线性化,浓缩线性化重组表达质粒pPIC9K/atxb,电击转化毕赤酵母GS115感受态细胞(购自Invitrogen公司),筛选阳性转化子,阳性转化子分泌表达杂合木聚糖酶atxb(SED ID NO:2)。pBS-T/ atxb vector wasEcoR、Not The target band was recovered by double enzyme digestion and rubber tapping. The recovered atxb was connected with pPIC9K, which had also been double enzyme digested, and transformed into Escherichia coli. The obtained recombinant expression plasmid was namedpPIC9K /atxb; Linearize the recombinant expression plasmid pPIC9K/atxb with restriction endonucleases, concentrate the linearized recombinant expression plasmid pPIC9K/atxb, transform Pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells (purchased from Invitrogen) by electric shock, screen positive transformants, and secrete the positive transformants Expresses the hybrid xylanase ATXB (SED ID NO:2).
本发明的有益效果(优点)如下:Beneficial effect (advantage) of the present invention is as follows:
(1) 采用SOE实现atx基因片段和褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A的连接序列和木聚糖结合域的连接,该方法在构建杂合基因构建过程中不额外引入氨基酸序列,这是其最大的优势;现在绝大多数杂合酶的构建采用限制性内切酶识别位点的粘性末端连接,这样会引入额外的碱基。(1) SOE is used to connect the atx gene fragment with the linker sequence and xylan-binding domain of Thermomonospora variegata xylanase A. This method does not introduce additional amino acid sequences during the construction of hybrid genes, which is Its biggest advantage; most hybrid enzymes are now constructed using cohesive end ligation of restriction endonuclease recognition sites, which introduces additional bases.
(2) 获得的杂合酶对不溶性底物有较强的结合能力,且能够水解纤维素,具备多功能酶的特征;现发现的绝大多数野生木聚糖酶不具备结合、水解纤维素的能力。(2) The obtained hybrid enzyme has a strong binding ability to insoluble substrates, and can hydrolyze cellulose, which has the characteristics of multifunctional enzymes; most of the wild xylanases found now do not have the ability to bind and hydrolyze cellulose Ability.
(3) 该杂合酶水解桦木木聚糖所得的主要为低聚木糖,主要产物为木二糖和木三糖。木二糖和木三糖是功能性低聚木糖的主要成分,其益生作用显著高于其他低聚木糖。(3) The hybrid enzyme hydrolyzes birch xylan to obtain mainly xylooligosaccharides, and the main products are xylobiose and xylotriose. Xylobiose and xylotriose are the main components of functional xylooligosaccharides, and their prebiotic effects are significantly higher than other xylooligosaccharides.
(4) 该杂合基因表达采用的毕赤酵母表达系统,该系统具备安全,不分泌毒性代谢产物且易培养的特点,较大肠杆菌表达系统、动物细胞表达系统具有明显的优势。该特点使得杂合酶atxb的发酵生产具有明显优势。(4) The Pichia pastoris expression system used for the expression of the hybrid gene is safe, does not secrete toxic metabolites, and is easy to cultivate. The expression system of L. coli and animal cells has obvious advantages. This feature makes the fermentation production of the hybrid enzyme atxb have obvious advantages.
the
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb序列及其推译的氨基酸序列。Figure 1 is the hybrid xylanase gene atxb sequence and its deduced amino acid sequence.
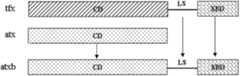
图2是本发明实施例的杂合木聚糖酶atx和atxb、木聚糖酶tfx分子结构示意图。Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the molecular structure of hybrid xylanase atx and atxb and xylanase tfx according to an embodiment of the present invention.
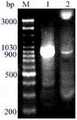
图3是本发明实施例的是木聚糖酶基因片段atx及atxb的PCR扩增。Fig. 3 is the PCR amplification of xylanase gene fragments atx and atxb according to the embodiment of the present invention.
图4是本发明实施例的TOP10F’/pPIC9K-atxb转化子PCR鉴定。Fig. 4 is the PCR identification of the TOP10F'/pPIC9K-atxb transformant of the embodiment of the present invention.
图5是本发明实施例的 pPIC9K-atxb双酶切电泳图。Fig. 5 is the pPIC9K-atxb double restriction electrophoresis diagram of the embodiment of the present invention.
图1中,方框氨基酸序列为连接序列,下画线的氨基酸序列为木聚糖结合域,其余氨基酸序列(303-314除外)来自atx。In Figure 1, the boxed amino acid sequence is the connecting sequence, the underlined amino acid sequence is the xylan binding domain, and the rest of the amino acid sequences (except 303-314) are from atx.
图2中,CD为催化结构域,LS为连接序列,XBD为木聚糖结合域。In Figure 2, CD is the catalytic domain, LS is the linker sequence, and XBD is the xylan binding domain.
图3中,M为DNA Marker,1以pBS-T/ atx 载体为模板PCR扩增产物(atx),2以pBS-T /tfx 载体为模板PCR扩增产物(XBD),3杂合木聚糖酶基因PCR扩增产物(atxb)。In Figure 3, M is DNA Marker, 1 uses the pBS-T/atx vector as the template PCR amplification product (atx), 2 uses the pBS-T/tfx vector as the template PCR amplification product (XBD ), 3 heterozygous xylem Carbohydrase gene PCR amplification product (atxb).
图4中,M为DNA Marker,1-3为不同转化子的PCR扩增产物。In Fig. 4, M is a DNA Marker, and 1-3 are PCR amplification products of different transformants.
图5中,M为DNA Marker,1为杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb的PCR产物,2为 pPIC9K-atxb经EcoR 和Not双酶切。In Fig. 5, M is DNA Marker, 1 is the PCR product of heterozygous xylanase gene atxb, 2 is pPIC9K-atxb throughEcoR and Not Double digestion.
the
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面通过具体实施方式对本发明作进一步详细说明:The present invention is described in further detail below by specific embodiment:
木聚糖结合域在酶分子与不溶底物结合中起至关重要的作用。在已成功构建能编码优良性能木聚糖酶的重组基因基础上(GenBank Accession No. AY858101),为了提高杂合木聚糖酶atx对纤维素类不溶性底物的结合和水解能力,将来源于褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A的连接序列和木聚糖结合域融合在杂合木聚糖酶atx的C-末端,并在毕赤酵母中分泌表达,获得杂合木聚糖酶atxb,其具备结合水解纤维素的能力。The xylan-binding domain plays a crucial role in the binding of enzyme molecules to insoluble substrates. On the basis of the successful construction of a recombinant gene that can encode xylanase with excellent performance (GenBank Accession No. AY858101), in order to improve the binding and hydrolysis ability of the hybrid xylanase atx to cellulose insoluble substrates, the xylanase derived from The linker sequence and xylan-binding domain of Thermomonas variegata xylanase A were fused to the C-terminus of the hybrid xylanase atx and secreted in Pichia pastoris to obtain the hybrid xylanase atxb , which has the ability to bind hydrolyzed cellulose.
本发明获得高底物结合和水解性能的重组木聚糖酶atxb的方法,包括以下步骤:The present invention obtains the method for the recombinant xylanase ATXB of high substrate binding and hydrolysis performance, comprises the following steps:
构建融合木聚糖酶结合域的杂合木聚糖酶基因;Constructing a hybrid xylanase gene fused with a xylanase binding domain;
本发明的木聚糖酶基因是来源于褐色单孢菌和枯草芽孢杆菌的重组基因atx,重组基因能较好耐受饲料制粒等的高温,重组基因GenBank登录号为AY858101。 The xylanase gene of the present invention is a recombinant gene atx derived from Phaemonospora and Bacillus subtilis, and the recombinant gene can better withstand high temperatures such as feed pelleting, and the GenBank accession number of the recombinant gene is AY858101. the
在分子结构上,褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A(Genebank U01242)的显着特征之一就是存在连接序列和木聚糖结合域(Ghangas et al.,1989;Irwin et al.,1994)。在已获得的杂合木聚糖酶基因atx中引入褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A的连接序列木聚糖结合域编码序列,获得另外一个杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb(图1,2)。为了便于atxb在毕赤酵母中的表达,在全长基因PCR扩增的外侧引物中(X1和X4)分别引入EcoR和Not限制性内切酶识别位点。In terms of molecular structure, one of the distinctive features of Thermomonas variegata xylanase A (Genebank U01242) is the presence of a linker sequence and a xylan-binding domain (Ghangaset al. , 1989; Irwinet al. , 1994) . Introduce the linker sequence xylan binding domain coding sequence of Thermomonospora variegata xylanase A into the obtained hybrid xylanase gene atx, and obtain another hybrid xylanase gene atxb (Fig. 1, 2). In order to facilitate the expression of atxb in Pichia pastoris,EcoR was introduced into the outer primers (X1 and X4) of the PCR amplification of the full-length gene, respectively. andNot Restriction enzyme recognition sites.
以pBS-T/ atx 载体为模板,X1和X2为引物扩增atx片段,得到约600 bp条带,理论长度为601 bp(图3);以pBS-T /tfx 载体为模板,X3和X4为引物扩增xbd片段,得到约300 bp条带,理论长度为362 bp(图3);以上述atx和XBD为模板,X1和X4为引物,PCR扩增得到杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb,长度为942 bp,其编码314个氨基酸(图3)。Using the pBS-T/atx vector as a template, X1 and X2 as primers to amplify the atx fragment, a band of about 600 bp was obtained with a theoretical length of 601 bp (Figure 3); using the pBS-T/tfx vector as a template, X3 and X4 The xbd fragment was amplified with primers, and a band of about 300 bp was obtained, with a theoretical length of 362 bp (Figure 3). Using the above atx and XBD as templates, X1 and X4 as primers, PCR amplification obtained the hybrid xylanase gene atxb , with a length of 942 bp, which encodes 314 amino acids (Fig. 3).
杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb在毕赤酵母中分泌表达。The hybrid xylanase gene atxb is secreted and expressed in Pichia pastoris.
pBS-T atxb载体经EcoR、Not双酶切、割胶回收目的条带。回收的atxb与同样经过双酶切的pPIC9K连接,并转化并转化大肠杆菌,获得的重组表达质粒命名为pPIC9K- atxb。大量提取重组表达质粒,用Bgl限制性内切酶将重组表达质粒pPIC9K- atxb线性化,浓缩线性化重组表达质粒pPIC9K- atxb,电击转化毕赤酵母GS115感受态细胞,筛选阳性转化子。pBS-T atxb vector byEcoR、Not Double enzyme digestion and rubber tapping to recover the target band. The recovered atxb was ligated with pPIC9K which had also undergone double enzyme digestion, and transformed into Escherichia coli, and the obtained recombinant expression plasmid was named pPIC9K-atxb. A large number of recombinant expression plasmids were extracted withBgl Linearize the recombinant expression plasmid pPIC9K-atxb with restriction endonucleases, concentrate the linearized recombinant expression plasmid pPIC9K-atxb, transform the competent cells of Pichia pastoris GS115 by electroporation, and screen for positive transformants.
酵母中表达产物的木聚糖酶和纤维素酶活性测定。Determination of xylanase and cellulase activity of products expressed in yeast.
atxb木聚糖酶的最适温度和最适pH分别为60℃和pH5.0;木聚糖酶在pH4.0-9.0范围内稳定性较好。atxb能够结合微晶纤维素并具有纤维素酶的活性,纤维素酶的最适温度和最适pH分别为60℃和pH6.0。The optimum temperature and optimum pH of atxb xylanase were 60℃ and pH5.0 respectively; the stability of xylanase was better in the range of pH4.0-9.0. atxb can bind to microcrystalline cellulose and has cellulase activity. The optimal temperature and pH of cellulase are 60℃ and pH6.0, respectively.
以下三个实施例详细阐明了本发明的具体实施方式。The following three examples illustrate the specific implementation of the present invention in detail.
实施例1:杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb的构建Embodiment 1: Construction of hybrid xylanase gene atxb
1、材料的准备:1. Preparation of materials:
基因材料:杂合木聚糖酶基因atx和褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A基因, 分别位于pBS-T /atx 载体 和pBS-T /tfx 载体中。Genetic material: the hybrid xylanase gene atx and the thermomonospora brown xylanase A gene are located in the pBS-T /atx vector and the pBS-T /tfx vector respectively.
菌种:大肠杆菌 TOP10F’购自Invitrogen公司。穿梭载体:pPIC9K,购自Invitrogen公司,表达宿主菌:毕赤酵母 GS115,购自Invitrogen公司。Strains: Escherichia coli TOP10F' was purchased from Invitrogen. Shuttle vector: pPIC9K, purchased from Invitrogen Company, expression host bacteria: Pichia pastoris GS115, purchased from Invitrogen Company.
高保真DNA聚合酶、平端DNA片段加A试剂盒:购自上海Sangon公司,各种限制性内切酶和T-载体购自Promega公司。High-fidelity DNA polymerase, blunt-ended DNA fragment plus A kit: purchased from Shanghai Sangon Company, and various restriction enzymes and T-vectors were purchased from Promega Company.
化学试剂:酵母浸膏和胰蛋白胨购自OXOID公司,组织培养用试剂和桦木木聚糖购自Sigma公司。其他化学试剂均为国产分析纯。引物合成:上海Sangon公司或上海博亚生物技术有限公司,测序:由上海博亚生物技术有限公司完成。Chemical reagents: Yeast extract and tryptone were purchased from OXOID Company, tissue culture reagents and birch xylan were purchased from Sigma Company. All other chemical reagents were of domestic analytical grade. Primer synthesis: Shanghai Sangon Company or Shanghai Boya Biotechnology Co., Ltd., sequencing: completed by Shanghai Boya Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
2、杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb的构建2. Construction of hybrid xylanase gene atxb
根据杂合木聚糖酶基因atx序列和褐色高温单孢菌木聚糖酶A木聚糖结合域序列设计4条引物,由上海Sangon公司合成。X1、X4为外侧引物,X2、X3为嵌合引物,为了后续目的基因能够定向插入到表达载体上,在外侧引物X1和X4中分别引入EcoR和Not限制性内切酶识别位点。Four primers were designed according to the atx sequence of the hybrid xylanase gene and the xylan-binding domain sequence of Thermomonospora variegata xylanase A, and were synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Company. X1 and X4 are outer primers, and X2 and X3 are chimeric primers. In order to insert the gene of interest into the expression vector,EcoR is introduced into the outer primers X1 and X4 respectively. andNot Restriction enzyme recognition sites.
the
3、以pBS-T/ atx 载体为模板,X1和X2为引物扩增atx片段;以pBS-T/ tfx 载体为模板,X3和X4为引物扩增XBD片段;以上述atx和XBD为模板,X1和X4为引物,PCR扩增得到杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb(图2)。3. Use the pBS-T/ atx vector as a template, X1 and X2 as primers to amplify the atx fragment; use the pBS-T/ tfx vector as a template, and X3 and X4 as primers to amplifythe XBD fragment; use the above atx and XBD as templates, X1 and X4 were used as primers, and the hybrid xylanase gene atxb was amplified by PCR (Figure 2).
4、atx、XBD和杂合基因atxb的TD-PCR扩增体系4. TD-PCR amplification system of atx,XBD and heterozygous gene atxb
atx基因片段TD-PCR条件TD-PCR conditions of atx gene fragment
木聚糖结合域基因XBD片段TD-PCR条件TD-PCR Conditions of Xylan Binding Domain GeneXBD Fragment
杂合木聚糖酶基因(atxb)TD-PCR条件TD-PCR conditions for heterozygous xylanase gene (atxb)
5、杂合酶基因atxb平末端加A5. Add A to the blunt end of the hybrid enzyme gene atxb
高保真Pfu聚合酶(上海Sangon公司)扩增得到基因片段为平末端,直接克隆比较困难。在T/A克隆时,需要在在其末端添加碱基A,反应体系如下表:The high-fidelity Pfu polymerase (Shanghai Sangon Company) amplifies the gene fragments with blunt ends, and it is difficult to clone directly. In T/A cloning, base A needs to be added at the end, and the reaction system is as follows:
稍离心,PCR反应条件为72℃,10 min。Slightly centrifuge, and the PCR reaction conditions are 72°C, 10 min.
6、atxb与T载体连接6. Atxb is connected with T carrier
采用pBS-T载体系统试剂盒将割胶回收的atxb片段与T载体连接。连接反应体系如下:The atxb fragment recovered from rubber tapping was connected to the T vector using the pBS-T vector system kit. The connection reaction system is as follows:
混匀稍离心,4℃,过夜(以上操作均在冰盒上完成)。Mix and centrifuge slightly, 4 ℃, overnight (the above operations are completed on the ice box).
实施例2:杂合木聚糖酶基因atxb 在毕赤酵母中表达Embodiment 2: hybrid xylanase gene atxb is expressed in Pichia pastoris
1、pPIC9K-atxb的构建1. Construction of pPIC9K-atxb
测序验证后,pBS-T/ atxb 载体经EcoR、Not双酶切、割胶回收目的条带。回收的atxb与同样经过双酶切的pPIC9K连接,并转化并转化大肠杆菌TOP10F’感受态细胞,在含卡那霉素的LB平板上挑取单菌落培养,经过PCR检测(图4)和双酶切鉴定(图5)获得重组转化子,命名为TOP10F’/pPIC9K-atxb,获得的重组表达质粒命名为pPIC9K-atxb。After sequencing verification, the pBS-T/ atxb vector wasEcoR、Not Double enzyme digestion and rubber tapping to recover the target band. The recovered atxb was ligated with pPIC9K that had also undergone double enzyme digestion, and transformed into Escherichia coli TOP10F'competent cells, picked a single colony on the LB plate containing kanamycin, and tested by PCR (Figure 4) and double Recombinant transformants were obtained after enzyme digestion identification (Figure 5), named TOP10F'/pPIC9K-atxb, and the obtained recombinant expression plasmid was named pPIC9K-atxb.
1.1 pPIC9K载体双酶切1.1 Double digestion of pPIC9K vector
酶切体系: Enzyme digestion system:
混匀,37℃,过夜。电泳,割胶回收目的片段。Mix well, overnight at 37°C. Electrophoresis, gel tapping to recover the target fragment.
1.2 pBS-T atxb 载体双酶切1.2 Digestion of pBS-T atxb vector
酶切体系: Enzyme digestion system:
混匀,37℃,过夜。电泳,割胶回收目的片段。Mix well, overnight at 37°C. Electrophoresis, gel tapping to recover the target fragment.
1.3 pPIC9K-atxb的构建1.3 Construction of pPIC9K-atxb
将酶切回收的atxb基因与同样经EcoR,Not双酶切回收的pPIC9K进行连接。连接体系如下:The atxb gene recovered by enzyme digestion and the same EcoR , Not The recovered pPIC9K was double digested for ligation. The connection system is as follows:
混匀,稍离心,4℃,过夜(以上操作均在冰盒上完成)。Mix well, centrifuge slightly, and keep overnight at 4°C (the above operations are all done on an ice box).
2、pPIC9K-atxb的大量提取和纯化2. Massive extraction and purification of pPIC9K-atxb
2.1 pPIC9K-atxb质粒的大量提取2.1 Mass extraction of pPIC9K-atxb plasmid
2.1.1阳性克隆子接种于3 ml LB液体培养基中(Kana, 10 μg/ml),37℃,150rpm震荡培养过夜;2.1.1 Positive clones were inoculated in 3 ml LB liquid medium (Kana, 10 μg/ml), cultured overnight at 37°C with shaking at 150 rpm;
2.1.2吸取300 μl菌液接种于300 ml LB培养液中,37℃,150 rpm培养过夜;2.1.2
2.1.3然后5000 rpm离心3 min收集菌体,弃尽上清,加15 ml细胞重悬液(购自Promega公司),充分悬浮菌体;2.1.3 Then centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 3 minutes to collect the cells, discard the supernatant, add 15 ml of cell suspension (purchased from Promega), and fully suspend the cells;
2.1.4加入15 ml细胞裂解液(购自Promega公司),立即温和上下颠倒使溶液变清;2.1.4 Add 15 ml of cell lysate (purchased from Promega), and immediately turn it upside down gently to make the solution clear;
2.1.5加入15 ml中和液(购自Promega公司),立即混匀使之充分中和;2.1.5 Add 15 ml of neutralizing solution (purchased from Promega), and mix immediately to fully neutralize;
2.1.6室温下12000 rpm,离心15 min;2.1.6 Centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 15 min at room temperature;
2.1.7移上清于一灭菌的50 ml量筒,量取体积,再移入另一灭菌的离心管中;2.1.7 Transfer the supernatant to a sterilized 50 ml graduated cylinder, measure the volume, and then transfer it to another sterilized centrifuge tube;
2.1.8加3体积的乙醇,混合;2.1.8
2.1.9室温下12000 rpm,离心10 min;2.1.9 Centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 10 min at room temperature;
2.1.10弃上清,加2 ml TE Buffer溶解DNA。2.1.10 Discard the supernatant, add 2 ml TE Buffer to dissolve the DNA.
2.2 pPIC9K-atxb质粒的纯化2.2 Purification of pPIC9K-atxb plasmid
2.2.1加10 ml Wizard 大量DNA 纯化体系(购自Promega公司)于上述的2.1.10 DNA溶液中,混合;2.2.1 Add 10 ml of Wizard large-scale DNA purification system (purchased from Promega) to the DNA solution in 2.1.10 above, and mix;
2.2.2将Wizard 大量柱子(购自Promega公司),插入真空器,将上步骤的Resin/DNA混合液移入Maxicolumn,打开真空泵,抽干液体后关上;2.2.2 Insert a large number of Wizard columns (purchased from Promega) into the vacuum, transfer the Resin/DNA mixture in the previous step into the Maxicolumn, turn on the vacuum pump, drain the liquid and then close it;
2.2.3加25 ml已加乙醇的柱子洗脱液(购自Promega公司),于Maxicolumn,打开真空泵,抽干液体后关上;2.2.3 Add 25 ml of ethanol-added column eluent (purchased from Promega), to the Maxicolumn, turn on the vacuum pump, drain the liquid and turn it off;
2.2.4加5 ml 80%乙醇于Maxicolumn,打开真空泵,抽干液体后关上。再加1 ml 80%乙醇重复此步骤;2.2.4 Add 5 ml of 80% ethanol to the Maxicolumn, turn on the vacuum pump, drain the liquid and turn it off. Add 1
2.2.5将Maxicolumn放入50 ml配套的螺帽管(购自Promega公司),中,于水平转离心机2500 rpm,离心5 min,再将Maxicolumn放入真空器,打开真空泵,抽滤5 min,关上泵;2.2.5 Put the Maxicolumn into a 50 ml matching screw-cap tube (purchased from Promega), centrifuge in a horizontal centrifuge at 2500 rpm for 5 minutes, then put the Maxicolumn into a vacuum, turn on the vacuum pump, and filter for 5 minutes , turn off the pump;
2.2.6将Maxicolumn放入清洁的50 ml的螺帽管,加1.5 ml预热(65-70℃)去离子灭菌水,于水平转离心机2500 rpm,离心5min;2.2.6 Put the Maxicolumn into a clean 50 ml screw cap tube, add 1.5 ml of preheated (65-70°C) deionized sterilized water, and centrifuge at 2500 rpm in a horizontal centrifuge for 5 minutes;
2.2.7连接已移去活塞的注射器和0.2 μm滤膜,,将上一步骤的液体移入注射器,与1.5ml离心管相连,推进活塞,使液体进入离心管内;20000 rpm,离心1min;2.2.7 Connect the syringe with the piston removed and the 0.2 μm filter membrane, transfer the liquid from the previous step into the syringe, connect it to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, push the piston to make the liquid enter the centrifuge tube; centrifuge at 20,000 rpm for 1 min;
2.2.9将上清移到另一新1.5ml离心管内,获得重组表达质粒,命名为pPIC9K-atxb,-20℃保存备用。2.2.9 Transfer the supernatant to another new 1.5ml centrifuge tube to obtain the recombinant expression plasmid, named pPIC9K-atxb, and store it at -20°C for future use.
3、pPIC9K-atxb质粒线性化及纯化浓缩。3. Linearization, purification and concentration of pPIC9K-atxb plasmid.
3.1pPIC9K-atxb的线性化3.1 Linearization of pPIC9K-atxb
pPIC9K-atxb线性化体系:pPIC9K-atxb linearization system:
混匀,37℃过夜。Mix well, overnight at 37°C.
3.2纯化浓缩3.2 Purification and concentration
3.2.1向上述酶切后的溶液中加入等体积的酚:氯仿:异戊醇,混匀,10000 rpm,离心10 min;3.2.2吸上清于清洁离心管中,加入1/10体积乙酸钠缓冲液(3 mol/L, pH5.2),2.5体积的无水乙醇,混匀,10000 rpm,离心10 min;3.2.1 Add an equal volume of phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol to the solution after digestion, mix well, centrifuge at 10000 rpm for 10 min; 3.2.2 suck the supernatant into a clean centrifuge tube, add 1/10 volume Sodium acetate buffer (3 mol/L, pH5.2), 2.5 volumes of absolute ethanol, mix well, centrifuge at 10000 rpm for 10 min;
3.2.3弃上清,加80%乙醇清洗;3.2.3 Discard the supernatant, add 80% ethanol to wash;
3.2.4在空气中待乙醇挥发后加10 μl TE Buffer,-20℃保存备用。3.2.4 Add 10 μl TE Buffer after ethanol volatilizes in the air, and store at -20°C for later use.
4、毕赤酵母GS115感受态细胞的制备4. Preparation of Pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells
4.1毕赤酵母GS115菌株的筛选4.1 Screening of Pichia pastoris GS115 strain
4.1.1-80℃保存的GS115菌种(购自Invitrogen公司),在YPD平板上划线30℃培养,直至长出菌落;4.1.1 GS115 strains (purchased from Invitrogen) stored at -80°C were streaked on YPD plates and cultured at 30°C until colonies grew;
4.1.2准备MD和MDH平板各一个,画上小方格,作好标记;4.1.2 Prepare one MD and one MDH plate, draw a small square, and make a mark;
4.1.3用无菌牙签挑取GS115菌落,先后点到MD和MDH平板上,使同一菌落在两个平板上的位置一一对应,如此点满所有小方格;4.1.3 Use a sterile toothpick to pick up GS115 colonies, and place them on the MD and MDH plates successively, so that the positions of the same colony on the two plates correspond one by one, so that all the small squares are filled;
4.1.430℃培养箱培养2-5天,观察菌落生长情况,挑取在MD平板上生长缓慢或不生长,而在MDH平板上生长良好的菌落做酵母感受态细胞。4.1. Cultivate in a 430°C incubator for 2-5 days, observe the growth of the colonies, and pick the colonies that grow slowly or do not grow on the MD plate but grow well on the MDH plate as yeast competent cells.
4.2毕赤酵母GS115感受态细胞的制备4.2 Preparation of Pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells
4.2.1挑所筛选的毕赤酵母单菌落于5 mlYPD液体培养基(购自Sigma)中,30℃,200 rpm震荡培养过夜;4.2.1 Pick the single colony of Pichia pastoris selected in 5 ml YPD liquid medium (purchased from Sigma), 30 ° C, 200 rpm shaking culture overnight;
4.2.2取上述培养液0.15 ml于500 ml新鲜YPD(2L长颈瓶),30℃,200 rpm震荡培养至OD600=1.3-1.5(培养8-10h);4.2.2 Take 0.15 ml of the above culture solution in 500 ml of fresh YPD (2L flask), culture at 30°C with shaking at 200 rpm until OD600 =1.3-1.5 (culture for 8-10 hours);
离心5 min,4℃,4500 rpm,收集菌体,加500 ml 0℃灭菌水悬浮;Centrifuge for 5 min, 4°C, 4500 rpm, collect the bacteria, add 500 ml 0°C sterilized water to suspend;
离心5 min,4℃,4500 rpm,收集菌体,加250 ml 0℃灭菌水悬浮;Centrifuge for 5 min, 4°C, 4500 rpm, collect the bacteria, add 250 ml 0°C sterilized water to suspend;
离心5 min,4℃,4500 rpm,收集菌体,加20 ml 0℃ 1M 山梨醇悬浮;Centrifuge for 5 min, 4°C, 4500 rpm, collect the bacteria, add 20 ml 0°C 1M sorbitol to suspend;
离心5 min,4℃,4500 rpm,收集菌体,加1 ml 0℃ 1M 山梨醇悬浮,放于冰上(24h内使用)。Centrifuge for 5 min at 4°C, 4500 rpm, collect the cells, add 1 ml of 0°C 1M sorbitol to suspend, and place on ice (use within 24 hours).
5、电击转化5. Electric shock conversion
将80 μl酵母感受态细胞与10 μl经过线性化和浓缩的pPIC9K-atxb混合,移入0℃转化杯内,冰浴5 min,搽干杯体,放入电击转化仪(Eppendorf, 2510, USA),电压为1800V,电击时间为4.4毫秒,电击结束后,立即用1 ml 0℃的山梨醇(1M)冲出杯内细胞,并转移到已灭菌的离心管内。
6、酵母转化子的筛选和培养6. Screening and cultivation of yeast transformants
取上述转化液200 μl涂于MD平板,30℃下培养至菌苔出现(约2天);Take 200 μl of the above transformation solution and spread it on MD plate, and cultivate it at 30°C until the bacterial lawn appears (about 2 days);
取2 ml无菌去离子水冲洗菌苔,悬浮菌体并保存到新离心管中,涡旋振荡,取200μl到YPD平板(含G418 250 μg/ml),30℃培养2-5天,直至单菌落出现;Take 2 ml of sterile deionized water to wash the bacterial lawn, suspend the bacteria and save it in a new centrifuge tube, vortex, take 200 μl to a YPD plate (containing G418 250 μg/ml), and culture at 30°C for 2-5 days until A single colony appears;
挑取抗G418的单菌落,进行MD/MM快慢斑筛选(挑取单菌落,先点于MM平板,再点于MD平板,30℃下培养3-5天),并设阳性对照GS115 Albumin (His+ MutS)和阴性对照GS115 LacZ (His- Mut+);Pick a single colony resistant to G418, and perform MD/MM fast and slow spot screening (pick a single colony, first spot it on the MM plate, then spot it on the MD plate, and culture it at 30°C for 3-5 days), and set a positive control GS115 Albumin ( His+ MutS ) and negative control GS115 LacZ (His- Mut+ );
在MM上生长慢而在MD上生长正常的菌落初步认定为阳性菌落。Colonies that grow slowly on MM but grow normally on MD were initially identified as positive colonies.
挑酵母转化子接种于3 ml YPM液体培养基中,30℃,250 rpm培养24h。用于提取基因组。The picked yeast transformants were inoculated in 3 ml YPM liquid medium, and cultured at 30°C, 250 rpm for 24 hours. for genome extraction.
实施例3:酵母阳性转化子的检测Example 3: Detection of Yeast Positive Transformants
1、酵母转化子基因组提取1. Genome extraction of yeast transformants
取1.5 ml酵母转化子菌液,4℃,5000 rpm,离心5 min,尽弃上清;Take 1.5 ml yeast transformant culture liquid, centrifuge at 4°C, 5000 rpm for 5 min, and discard the supernatant;
加入500 μl提取液,充分吹打悬浮;Add 500 μl extract solution, fully pipette to suspend;
加100 μl 10% SDS溶液和300 μl氯化苄,剧烈振荡;Add 100 μl 10% SDS solution and 300 μl benzyl chloride, shake vigorously;
50℃保温1h,期间间隔10 min 振荡混匀一次;Incubate at 50°C for 1 hour, shake and mix once every 10 minutes;
加300 μl 3M NaAC(pH5.2),冰浴15 min;Add 300 μl 3M NaAC (pH5.2), ice bath for 15 min;
4℃,10000 rpm离心15 min,取上清;Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C, and take the supernatant;
加入两倍体积冰预冷的无水乙醇,沉淀20 min;Add twice the volume of ice-cooled absolute ethanol, and precipitate for 20 min;
室温10000 rpm,离心15 min,弃上清,70%乙醇清洗一次;Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm at room temperature for 15 min, discard the supernatant, and wash once with 70% ethanol;
自然干燥,加100 μl TE buffer溶解,即为基因组样品,-20℃保存。Naturally dry, add 100 μl TE buffer to dissolve, that is, the genome sample, and store at -20°C.
2、PCR检测2. PCR detection
以提取的酵母重组表达子基因组为模板,分别以X1、X4和5AOX1、3AOX1为引物进行PCR扩增,5AOX1、3AOX1为Invitrogen公司商品化毕赤酵母表达系统自带的特异性引物,用以检测外源基因是否整合到酵母染色体上。PCR体系如下:Using the extracted yeast recombinant expressor genome as a template, PCR amplification was carried out with primers X1, X4, 5AOX1, and 3AOX1 respectively. 5AOX1 and 3AOX1 are specific primers that come with the commercial Pichia pastoris expression system from Invitrogen to detect Whether the exogenous gene is integrated into the yeast chromosome. The PCR system is as follows:
以5AOX1和3AOX1为引物的PCR反应体系:PCR reaction system using 5AOX1 and 3AOX1 as primers:
稍离心,置于PCR仪中。Slightly centrifuge and place in a PCR machine.
PCR反应条件:PCR reaction conditions:
阳性表达子经过0.25%甲醇诱导培养96h,其发酵上清液中的木聚糖酶和纤维素酶活性分别为452.1 U/mg和19.3 U/mg。这种人工构建的杂合木聚糖酶atxb的最适温度和最适pH分别为60℃和pH5.0;木聚糖酶在pH4.0-9.0范围内稳定性较好。atxb能够结合微晶纤维素并具有纤维素酶的活性,纤维素酶的最适温度和最适pH分别为60℃和pH6.0。The positive expressors were induced by 0.25% methanol for 96 hours, and the activities of xylanase and cellulase in the fermentation supernatant were 452.1 U/mg and 19.3 U/mg, respectively. The optimal temperature and pH of this artificially constructed hybrid xylanase atxb are 60°C and pH 5.0, respectively; the xylanase has better stability in the range of pH 4.0-9.0. atxb can bind to microcrystalline cellulose and has cellulase activity. The optimal temperature and pH of cellulase are 60℃ and pH6.0, respectively.
通过在酶分子中引入来自于tfx的连接序列和木聚糖结合域,使杂合木聚糖酶atxb具备了结合和水解纤维素的能力。在饲料工业中,这种人工构建的杂合木聚糖酶兼备纤维素酶活性具有特殊优势,单胃动物日粮中纤维素酶和木聚糖酶可以协同作用提高饲料(尤其是糠麸类)消化吸收率,促进动物生长,大大降低成本,提高经济效益。By introducing linker sequence and xylan binding domain from tfx into the enzyme molecule, the hybrid xylanase atxb has the ability to bind and hydrolyze cellulose. In the feed industry, this artificially constructed hybrid xylanase with cellulase activity has special advantages. Cellulase and xylanase in the diet of monogastric animals can synergistically improve feed (especially bran) ) digestion and absorption rate, promote animal growth, greatly reduce costs and improve economic benefits.
以上所述的仅是本发明的优选实施方式,应当指出,对于本技术领域中的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本发明核心技术特征的前提下,还可以做出若干改进和润饰,这些改进和润饰也应视为本发明的保护范围。What has been described above is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention. It should be pointed out that for those of ordinary skill in the art, some improvements and modifications can be made without departing from the core technical features of the present invention. Improvements and retouches should also be considered within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (2)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012101841611ACN102676479A (en) | 2012-06-02 | 2012-06-02 | Preparation method of hybrid xylanase atxb |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012101841611ACN102676479A (en) | 2012-06-02 | 2012-06-02 | Preparation method of hybrid xylanase atxb |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102676479Atrue CN102676479A (en) | 2012-09-19 |
Family
ID=46809032
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012101841611APendingCN102676479A (en) | 2012-06-02 | 2012-06-02 | Preparation method of hybrid xylanase atxb |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102676479A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108715892A (en)* | 2018-06-14 | 2018-10-30 | 浙江农林大学 | A kind of rareness species DNA information acquisition methods |
| WO2025113531A1 (en)* | 2023-11-28 | 2025-06-05 | 南京百斯杰生物工程有限公司 | Xylanase with improved enzyme activity and preparation method therefor |
- 2012
- 2012-06-02CNCN2012101841611Apatent/CN102676479A/enactivePending
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| 《中国博士学位论文全文数据库 农业科技辑 》 20110515 刘明启 提高木聚糖酶热稳定性、催化活性和结合水解纤维素能力的研究 130-172 1-2 , 第5期* |
| XIAO-YAN WENG ,JIAN-YI SUN: "Construction, Expression, and Characterization of a Thermostable Xylanase", 《CURRENT MICROBIOLOGY》* |
| 刘明启: "提高木聚糖酶热稳定性、催化活性和结合水解纤维素能力的研究", 《中国博士学位论文全文数据库 农业科技辑 》* |
| 江正强 等: "耐热木聚糖酶研究进展", 《中国生物工程杂志》* |
| 石军,陈安国: "木聚糖酶的应用研究进展", 《中国饲料》* |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108715892A (en)* | 2018-06-14 | 2018-10-30 | 浙江农林大学 | A kind of rareness species DNA information acquisition methods |
| WO2025113531A1 (en)* | 2023-11-28 | 2025-06-05 | 南京百斯杰生物工程有限公司 | Xylanase with improved enzyme activity and preparation method therefor |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102304540B (en) | An expression device and its application for secreting and expressing foreign protein in Trichoderma reesei | |
| CN105018448B (en) | The heat-resisting acidic cellulase and its gene of a kind of originated from fungus and application | |
| CN102268448B (en) | Expression equipment for expressing heterologous protein in Trichoderma reesei cell, and gene engineering bacteria | |
| CN105907775B (en) | The mutated gene TlXynA_1 of zytase TlXynA a kind of and its application | |
| CN105238704A (en) | Method for rapidly improving enzyme activity of Trichoderma reesei cellulase | |
| CN109402087A (en) | A kind of Novel ferulic acid esterase and its preparation method and application | |
| CN112553227B (en) | Heat-resistant multifunctional glycoside hydrolase, and encoding gene and application thereof | |
| CN101469325B (en) | Secretory expression method for exoinulinase from Kluyveromyces marxianus | |
| CN104004760B (en) | A kind of expression equipment and its aspergillus oryzae genetic engineering bacterium being used in Aspergillus oryzae cell secreting, expressing foreign protein | |
| CN116515656A (en) | Kluyveromyces marxianus strain capable of efficiently expressing biological enzyme and application thereof | |
| CN105296451B (en) | Method for obtaining high-activity trichoderma reesei fusion cellulase and recombinant strain | |
| CN104630184B (en) | A kind of alkalescent xylanase and its encoding gene and application | |
| CN102719414A (en) | Novel ferulic acid esterase and applications thereof | |
| CN102676479A (en) | Preparation method of hybrid xylanase atxb | |
| CN105969783B (en) | The mutated gene TlXynA_3 of zytase TlXynA a kind of and its application | |
| CN104560833B (en) | A kind of basophilic micrococcus luteus and its alkalescent xylanase and the application of generation | |
| CN105154417B (en) | The acidic cellulase and its gene of a kind of originated from fungus and application | |
| CN108192903A (en) | A kind of alkalescent xylanase and its encoding gene and application | |
| CN109355274B (en) | A beta-glucosidase enzyme with improved resistance to trypsin and pepsin | |
| CN107236692B (en) | Termite Paenibacillus cellulolyticus NP1, xylanase PtXyn1 and their encoding genes and applications | |
| CN102719415B (en) | A kind of β-1,3-1,4-glucanase and its coding gene | |
| CN110184291A (en) | A kind of building and its application of the non-methanol induction of Pichia pastoris expression vector of sequestered | |
| CN111733169B (en) | Elements regulating the expression of fungal lignocellulose-degrading enzymes and their applications | |
| CN116640792A (en) | Method for improving xylanase yield in Trichoderma reesei and application thereof | |
| CN105886520B (en) | The mutated gene TlXynA_2 of zytase TlXynA a kind of and its application |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20120919 |