CN102547716A - Wireless communication system and method for flat network architecture and extend unit - Google Patents
Wireless communication system and method for flat network architecture and extend unitDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102547716A CN102547716ACN2012100050891ACN201210005089ACN102547716ACN 102547716 ACN102547716 ACN 102547716ACN 2012100050891 ACN2012100050891 ACN 2012100050891ACN 201210005089 ACN201210005089 ACN 201210005089ACN 102547716 ACN102547716 ACN 102547716A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- subsystem
- speed signal
- high speed
- baseband
- sent
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及无线通信技术领域,尤其涉及一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统、方法及扩展装置。The present invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, in particular to a wireless communication system, method and extension device of a flat network architecture.
背景技术Background technique
目前在无线通信技术领域,如第二代移动通信技术(2nd Generation,2G)和第三代移动通信技术(3rd Generation,3G)领域,一般采用宏基站的方式部署无线通信系统,辅助以室内分布式天线系统以及直放站来实现无线信号的覆盖,如对于全球移动通信系统(Global System for Mobile Communications,GSM)来说,一般采用基站控制器(Base Station Controller,BSC)和基站收发台(BaseTransceiver Station,BTS)的无线覆盖方式;而在3G领域,则一般采用基带处理单元(Base Band Unit,BBU)和射频拉远单元(Radio Remote Unit,RRU)的无线覆盖方式。At present, in the field of wireless communication technology, such as the second generation mobile communication technology (2nd Generation, 2G) and the third generation mobile communication technology (3rd Generation, 3G), the wireless communication system is generally deployed in the form of a macro base station to assist Indoor distributed antenna system and repeater to achieve wireless signal coverage, such as for the Global System for Mobile Communications (Global System for Mobile Communications, GSM), generally use the base station controller (Base Station Controller, BSC) and base transceiver station (Base Transceiver Station, BTS) wireless coverage; in the 3G field, the base band processing unit (Base Band Unit, BBU) and radio remote unit (Radio Remote Unit, RRU) are generally used for wireless coverage.
如图1所示,为现有3G领域中无线通信系统的结构示意图,所述系统主要由无线网络控制器(Radio Network Controller,RNC)、BBU、RRU等组成。As shown in FIG. 1 , it is a schematic structural diagram of a wireless communication system in the existing 3G field, and the system is mainly composed of a radio network controller (Radio Network Controller, RNC), BBU, RRU, and the like.
所述系统的BBU主要用来完成Uu接口(Interface between the NodeB andthe UE)的基带处理功能(如编码、复用、调制和扩频等)、RNC的Iub接口(Interface between the RNC and the BBU)功能、信令处理、本地和远程操作维护功能,以及NodeB系统的工作状态监控和告警信息上报功能。The BBU of the system is mainly used to complete the baseband processing functions (such as encoding, multiplexing, modulation and spread spectrum, etc.) of the Uu interface (Interface between the NodeB and the UE), the Iub interface (Interface between the RNC and the BBU) of the RNC functions, signaling processing, local and remote operation and maintenance functions, as well as the working status monitoring and alarm information reporting functions of the NodeB system.
所述系统的RRU集成了数字中频模块、收发信机模块、功放和滤波模块,其中数字中频模块用于光传输的调制解调、数字上下变频、A/D、D/A转换等,收发信机模块用于完成中频信号到射频信号的变换,功放和滤波模块则用于将射频信号经过功放和滤波后,通过天线口发射出去。The RRU of the system integrates a digital intermediate frequency module, a transceiver module, a power amplifier and a filtering module, wherein the digital intermediate frequency module is used for modulation and demodulation of optical transmission, digital up-down conversion, A/D, D/A conversion, etc. The machine module is used to complete the conversion of the intermediate frequency signal to the radio frequency signal, and the power amplifier and filter module is used to transmit the radio frequency signal through the antenna port after the power amplifier and filter.
如图1所示的无线通信系统中,所述RNC通过Iu接口(Interface betweenthe Core Network and the RNC)实现与核心网的互联,通过Iub接口实现与BBU的互联,并通过Iub接口实现对BBU的管理和控制;所述BBU通过光纤等高速传输链路实现与RRU的互联,如可采用标准的通信协议IR(Interface betweenthe RRU and the BBU)/CPRI(Common Public Radio Interface)/OBASI(OpenBase Station Architecture Initiative)等接口协议;所述RRU通过Uu接口实现与用户终端的互联。In the wireless communication system shown in Figure 1, the RNC realizes the interconnection with the core network through the Iu interface (Interface between the Core Network and the RNC), realizes the interconnection with the BBU through the Iub interface, and realizes the BBU through the Iub interface Management and control; the BBU is interconnected with the RRU through high-speed transmission links such as optical fibers, such as standard communication protocols IR (Interface between the RRU and the BBU)/CPRI (Common Public Radio Interface)/OBASI (OpenBase Station Architecture Initiative) and other interface protocols; the RRU realizes the interconnection with the user terminal through the Uu interface.
在上述无线通信系统中,由于BBU和RRU之间是基于光纤等高速传输链路连接的,因此,需要有光纤部署的地方才能安装RRU,网络系统部署困难,成本较高。In the above-mentioned wireless communication system, since the BBU and the RRU are connected based on high-speed transmission links such as optical fibers, the RRU needs to be deployed where optical fibers are deployed, making network system deployment difficult and costly.
另外,由于GSM是目前应用最为广泛、效益最好的通信网络,在很长一段时间内将长期存在,而随着GSM网络用户数量的不断增加和业务的不断扩展,现有的GSM网络需要不断地扩容和优化,以满足业务发展的需要和不断增加的GSM网络用户的需求。但是,GSM网络扩容面临着基站选址难、室内信号覆盖接入复杂等诸多困境,而且随着移动通信的快速发展,移动通信系统的网络架构正在逐步演进,从GSM复杂的开放式网络架构逐渐演变为全IP化的长期演进(Long Term Evolution,LTE)扁平化网络架构,因此,在现有技术的基础上,需要提供一种符合未来移动通信的发展趋势的新的无线通信系统,来解决上述2G、3G通信系统中存在的诸多问题。In addition, because GSM is currently the most widely used communication network with the best benefits, it will exist for a long time for a long time. With the continuous increase in the number of GSM network users and the continuous expansion of services, the existing GSM network needs to continue Capacity expansion and optimization to meet the needs of business development and the ever-increasing demands of GSM network users. However, GSM network expansion faces many difficulties such as difficult base station location selection and complex indoor signal coverage and access. Moreover, with the rapid development of mobile communications, the network architecture of mobile communication systems is gradually evolving. From the complex open network architecture of GSM to Evolved into an all-IP long-term evolution (Long Term Evolution, LTE) flat network architecture. Therefore, on the basis of existing technologies, it is necessary to provide a new wireless communication system that conforms to the development trend of future mobile communications to solve the problem. There are many problems in the above-mentioned 2G and 3G communication systems.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例提供了一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统、方法及扩展装置,用以解决现有技术中存在的网络系统部署困难的问题。Embodiments of the present invention provide a wireless communication system, method and extension device with a flat network architecture to solve the problem of difficult network system deployment in the prior art.
一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统,包括接入(Access Unit,AU)子系统、扩展装置(Extend Unit,EU)以及与EU连接的至少一个射频拉远装置(RadioRemote Unit,RU),其中:A wireless communication system with a flat network architecture, including an access unit (AU) subsystem, an extension unit (Extend Unit, EU) and at least one radio remote unit (RadioRemote Unit, RU) connected to the EU, wherein :
所述AU子系统,用于将网关(Gateway,GW)子系统发送的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号并发送到EU,以及,将EU发送的上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据并通过GW子系统传输到核心网;The AU subsystem is used to convert the GW downlink data sent by the gateway (Gateway, GW) subsystem into a downlink baseband high-speed signal and send it to the EU, and convert the uplink baseband high-speed signal sent by the EU into the GW uplink data and pass the The GW subsystem transmits to the core network;
所述EU,用于将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并将所述下行子基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号后,发送到所述RU,以及,将RU发送的上行子基带低速信号汇聚并转换为上行基带高速信号后发送到AU子系统;The EU is configured to decompose the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU subsystem to obtain multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, convert the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal into a downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal, and send it to the RU, and, aggregate and convert the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signals sent by RU into uplink baseband high-speed signals and send them to the AU subsystem;
所述RU,用于将EU发送的下行子基带低速信号变频为远端下行射频信号,并发送给用户终端,以及,接收用户终端发送的远端上行射频信号,并将该远端上行射频信号变频为上行子基带低速信号后发送到EU。The RU is configured to convert the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal sent by the EU into a remote downlink radio frequency signal and send it to the user terminal, and receive the remote uplink radio frequency signal sent by the user terminal and transmit the remote uplink radio frequency signal The frequency is converted into an uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal and sent to the EU.
一种EU,包括处理单元和转换单元:An EU, including processing units and conversion units:
所述处理单元,用于对接收到的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并发送给转换单元,以及,将接收到的上行子基带低速信号汇聚为上行基带低速信号后,发送给转换单元;The processing unit is configured to decompose the received downlink baseband high-speed signals to obtain multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, and send them to the conversion unit, and to gather the received uplink sub-baseband low-speed signals into uplink baseband low-speed signals After that, it is sent to the conversion unit;
所述转换单元,用于将处理单元发送的下行子基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号后输出,以及,将处理单元发送的上行基带低速信号转换为上行基带高速信号后输出。The converting unit is configured to convert the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal sent by the processing unit into a downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal and output it, and convert the uplink baseband low-speed signal sent by the processing unit into an uplink baseband high-speed signal and output it.
一种AU子系统,包括:An AU subsystem, comprising:
接收单元,用于接收GW下行数据以及上行基带高速信号;The receiving unit is used to receive GW downlink data and uplink baseband high-speed signals;
转换单元,用于将接收单元接收到的所述GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号,以及将接收单元接收到的所述上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据;A conversion unit, configured to convert the GW downlink data received by the receiving unit into a downlink baseband high-speed signal, and convert the uplink baseband high-speed signal received by the receiving unit into GW uplink data;
发送单元,用于发送转换单元转换得到的下行基带高速信号和GW上行数据。The sending unit is configured to send the downlink baseband high-speed signal and the GW uplink data converted by the conversion unit.
一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信方法,所述方法包括:A wireless communication method of a flat network architecture, the method comprising:
AU子系统将GW子系统发送的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号后发送到EU;The AU subsystem converts the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem into a downlink baseband high-speed signal and sends it to the EU;
EU将所述下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并将所述下行子基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号后,发送到RU;The EU decomposes the downlink baseband high-speed signal to obtain multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, converts the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal into a downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal, and sends it to the RU;
RU将所述下行子基带低速信号变频为远端下行射频信号后发送给用户终端。The RU converts the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal into a remote downlink radio frequency signal and sends it to the user terminal.
一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信方法,所述方法包括:A wireless communication method of a flat network architecture, the method comprising:
RU将用户终端发送的远端上行射频信号变频为上行子基带低速信号后发送到EU;The RU converts the remote uplink radio frequency signal sent by the user terminal into an uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal and sends it to the EU;
EU将所述上行子基带低速信号汇聚并转换为上行基带高速信号后发送到AU子系统;The EU aggregates and converts the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signals into uplink baseband high-speed signals and sends them to the AU subsystem;
AU子系统将所述上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据后,通过GW子系统传输到核心网。After the AU subsystem converts the uplink baseband high-speed signal into GW uplink data, it transmits to the core network through the GW subsystem.
本发明的有益效果为:The beneficial effects of the present invention are:
本发明实施例提供了一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统、方法及扩展装置,所述无线通信系统包括AU子系统、EU和与EU连接的至少一个RU,通过利用EU将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号并发送给RU,使得EU和RU之间可以采用五类线等低速传输链路连接,便于室内覆盖,降低了网络部署的难度和成本。Embodiments of the present invention provide a wireless communication system, method, and extension device of a flat network architecture. The wireless communication system includes an AU subsystem, an EU, and at least one RU connected to the EU. By using the EU, the AU subsystem sends The downlink baseband high-speed signal is converted into a downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal and sent to the RU, so that the EU and RU can be connected by a low-speed transmission link such as a Category 5 line, which is convenient for indoor coverage and reduces the difficulty and cost of network deployment.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1所示为现有3G无线通信系统的结构示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of an existing 3G wireless communication system;
图2所示为本发明实施例一中扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统结构示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a wireless communication system with a flat network architecture in Embodiment 1 of the present invention;
图3所示为本发明实施例二中采用AU子系统级联的组网方式的无线通信系统结构示意图;FIG. 3 is a schematic structural diagram of a wireless communication system using a cascaded networking mode of AU subsystems in Embodiment 2 of the present invention;
图4所示为本发明实施例三中采用AU子系统堆叠的组网方式的无线通信系统结构示意图;FIG. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a wireless communication system using a networking mode of AU subsystem stacking in Embodiment 3 of the present invention;
图5所示为本发明实施例四中扩展装置的结构示意图;FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of an expansion device in Embodiment 4 of the present invention;
图6所示为采用EU级联的组网方式的无线通信系统结构示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a wireless communication system adopting EU cascade networking;
图7所示为本发明实施例五中AU子系统的结构示意图;FIG. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of the AU subsystem in Embodiment 5 of the present invention;
图8所示为本发明实施例六中扁平化网络架构的无线通信方法流程示意图;FIG. 8 is a schematic flowchart of a wireless communication method in a flat network architecture in Embodiment 6 of the present invention;
图9所示为传输数据在单个子帧中的数据结构示意图;FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram of a data structure of transmission data in a single subframe;
图10所示为CPRI封包方式数据结构示意图。FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram of the data structure of the CPRI packet mode.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明实施例提供了一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统、方法及扩展装置,将现有的无线网络通信系统结构进一步分解和简化,将RNC的功能下移到GW子系统和AU子系统,并增加了EU,利用所述EU将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号后发送给RU,使得EU和RU之间可以采用五类线等低速传输链路连接,无需基于大容量的光纤等回传网络,便于室内覆盖,降低了网络部署的难度和成本;进一步地,通过本发明实施例的方案可以支持AU子系统的级联及组叠模式,提高了系统的可扩容性。Embodiments of the present invention provide a wireless communication system, method and extension device with a flat network architecture, which further decomposes and simplifies the structure of the existing wireless network communication system, and moves the function of the RNC down to the GW subsystem and the AU subsystem , and an EU is added, using the EU to convert the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU subsystem into a downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal and then send it to the RU, so that the EU and the RU can be connected by a low-speed transmission link such as a five-category line, There is no need for backhaul networks based on large-capacity optical fibers, which facilitates indoor coverage and reduces the difficulty and cost of network deployment; furthermore, the scheme of the embodiment of the present invention can support the cascading and stacking modes of the AU subsystem, improving the system scalability.
下面结合说明书附图对本发明实施例作进一步说明,但本发明不局限于下面的实施例。The embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
实施例一:Embodiment one:
如图2所示,为本发明实施例一中扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统结构示意图,所述无线通信系统包括:AU子系统11、EU12和与EU12连接的至少一个RU13,所述无线通信系统还可以包括GW子系统14。As shown in Figure 2, it is a schematic structural diagram of a wireless communication system with a flat network architecture in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The wireless communication system includes: an
所述无线通信系统可以支持多种无线传输制式,包括全球移动通讯系统(Global System of Mobile communication,GSM)、宽带码分多址(WidebandCode Division Multiple Access,WCDMA)、时分同步码分多址(TimeDivision-Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access,TD-SCDMA)、长期演进(Long Term Evolution,LTE)、无线局域网络(Wireless Local Area Networks,WLAN)等;所述无线通信系统可以支持以上任一制式的信号处理,也可以同时支持以上多种制式的多种信号的混合处理,也即,所述无线通信系统可以支持单模或多模信号的处理;具体地,所述无线通信系统的GW子系统14、AU子系统11、EU12和RU13可以支持以上任一制式的信号处理,也可以同时支持以上多种制式的信号处理,即所述GW子系统14、AU子系统11、EU12和RU13为可以支持单模或多模的无线通信子系统。The wireless communication system can support multiple wireless transmission systems, including Global System of Mobile Communication (GSM), Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA), Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access (TimeDivision -Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access, TD-SCDMA), Long Term Evolution (Long Term Evolution, LTE), Wireless Local Area Networks (Wireless Local Area Networks, WLAN), etc.; the wireless communication system can support signal processing of any of the above standards, It can also support the mixed processing of multiple signals of the above multiple formats at the same time, that is, the wireless communication system can support the processing of single-mode or multi-mode signals; specifically, the
所述AU子系统11用于将GW子系统14发送的GW下行数据(包括信令面和用户面)转换为下行基带高速信号并发送到EU12,以及,将EU12发送的上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据并通过GW子系统14传输到核心网。The
具体地,所述AU子系统11包含BBU和上层控制单元,相当于集成了部分RNC和NodeB的功能,或者部分BSC和BTS的功能;其中所述BBU包括编解码、调制解调、交织解交织、加密解密、跳频、定时控制、组帧解帧等功能,主要用于将接收到的GW下行数据进行基带处理,得到下行基带高速信号,以及将接收到的上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据;所述上层控制单元包括无线资源管理、移动性管理、媒体接入控制(Media Access Control,MAC)、无线链路控制(Radio Link Control,RLC)等功能;同时,所述AU子系统11还具有Iuh接口功能、本地和远程操作维护功能以及AU子系统11的工作状态监控和告警信息上报等功能。Specifically, the
所述EU12用于将AU子系统11发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并将所述下行子基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号后,发送到所述RU13,以及将RU13发送的上行子基带低速信号汇聚并转换为上行基带高速信号后发送到AU子系统11。The EU12 is used to decompose the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU
具体地,所述EU12包括处理单元和转换单元:Specifically, the EU12 includes a processing unit and a conversion unit:
所述处理单元用于将AU子系统11发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并发送给转换单元,以及,将RU13发送的上行子基带低速信号汇聚为上行基带低速信号后,发送给转换单元;所述转换单元用于将处理单元发送的下行子基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号,并发送到所述RU13,以及,将处理单元发送的上行基带低速信号转换为上行基带高速信号后,发送到AU子系统11。The processing unit is used to decompose the downlink baseband high-speed signals sent by the
进一步地,所述处理单元还用于分别针对所述RU13的负载能力,将多路下行子基带高速信号进行组合,得到多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号,并发送给转换单元;所述转换单元具体用于将处理单元发送的多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号转换为多组下行子基带低速信号,并发送到所述RU13,其中,属于同一小区的RU13接收同一组下行子基带低速信号,任意两个属于不同小区的RU13接收不同组的下行子基带低速信号;所述多路下行子基带高速信号可以是同一制式的信号,也可以是多种制式的信号;所述叠加后的下行子基带高速信号可以为所述一路或多路的下行子基带高速信号的任意组合叠加。Further, the processing unit is also used to combine multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals according to the load capacity of the RU13 to obtain multiple superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, and send them to the conversion unit; The conversion unit is specifically used to convert multiple sets of superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals sent by the processing unit into multiple sets of downlink sub-baseband low-speed signals, and send them to the RU13, wherein the RU13 belonging to the same cell receives the same set of downlink sub-baseband signals For low-speed signals, any two RU13 belonging to different cells receive different groups of downlink sub-baseband low-speed signals; the multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals can be signals of the same system or signals of multiple systems; after the superposition The downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal can be superimposed for any combination of the one or more downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals.
具体地,以WCDMA和GSM双模为例,所述处理单元将AU子系统11发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解后,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,假设每路下行子基带高速信号均包括3路WCDMA的I/Q信号和8路GSM的I/Q信号,处理单元针对所述RU13的负载能力,对所述多路下行子基带高速信号进行组合,得到多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号,假设EU12对应3个RU13。Specifically, taking WCDMA and GSM dual-mode as an example, the processing unit decomposes the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the
(1)对于分裂小区模式,即各RU13属于不同小区时:(1) For the split cell mode, that is, when each RU13 belongs to different cells:
EU12待发送给第一个RU13的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a包括:1路WCDMA I/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a to be sent by EU12 to the first RU13 includes: 1 WCDMA I/Q signal and 3 GSM I/Q signals;
EU12待发送给第二个RU13的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b包括:2路WCDMA I/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b to be sent by EU12 to the second RU13 includes: 2-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 3-way GSM I/Q signals;
EU12待发送给第三个RU13的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c包括:2路GSM I/Q信号。The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c to be sent by EU12 to the third RU13 includes: 2 GSM I/Q signals.
(2)对于同一小区模式,即各RU13属于同一小区时:(2) For the same cell mode, that is, when each RU13 belongs to the same cell:
EU12待发送给第一个RU13的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a包括:3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a to be sent to the first RU13 by EU12 includes: 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals;
EU12待发送给第二个RU13的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b包括:3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b to be sent by EU12 to the second RU13 includes: 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals;
EU13待发送给第三个RU13的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c包括:3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号。The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c to be sent by EU13 to the third RU13 includes: 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals.
需要说明的是,上述下行子基带高速信号的叠加方式仅为本发明实施例的举例说明,在实际应用中,可以根据小区情况进行调整。It should be noted that, the superimposition manner of the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal is only an illustration of the embodiment of the present invention, and may be adjusted according to the conditions of the cell in practical application.
进一步地,所述转换单元将所述叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a、叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b和叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c按照同步以太网协议分别进行封装,得到下行子基带低速信号a、下行子基带低速信号b和下行子基带低速信号c,并把所述下行子基带低速信号a发送到第一个RU13,把下行子基带低速信号b发送到第二个RU13,把下行子基带低速信号c发送到第三个RU13。Further, the conversion unit encapsulates the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a, the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b, and the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol to obtain the downlink Sub-baseband low-speed signal a, downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b, and downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal c, and send the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal a to the first RU13, and send the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b to the second RU13 , sending the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal c to the third RU13.
需要说明的是,本发明实施例中不限于采用其他协议对所述叠加后的下行子基带低速信号进行封装,如还可以采用支持五类线、超五类线或网线的接口协议对所述叠加后的下行子基带低速信号进行封装。It should be noted that, in the embodiment of the present invention, other protocols are not limited to encapsulating the superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal. The superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signals are packaged.
所述RU13用于将EU12发送的下行子基带低速信号变频为远端下行射频信号,并发送给用户终端,以及,接收用户终端发送的远端上行射频信号,并将该远端上行射频信号变频为上行子基带低速信号后发送到EU12。The RU13 is used to convert the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal sent by the EU12 into a remote downlink radio frequency signal, and send it to the user terminal, and receive the remote uplink radio frequency signal sent by the user terminal, and convert the remote uplink radio frequency signal It is an uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal and sent to EU12.
所述EU12和与其连接的至少一个RU13可以称为覆盖子系统或多模分布式天线系统(Multi-mode Distribution Antanna System,MDAS)子系统;所述覆盖子系统用于将AU子系统11发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解、重组并上变频为至少一路的远端下行射频信号,实现对覆盖区域的信号覆盖;以及将覆盖区域的用户终端发送的至少一路的远端上行射频信号下变频,并重新汇聚组合为上行基带高速信号后发送到AU子系统11。The EU12 and at least one RU13 connected thereto may be referred to as a coverage subsystem or a multi-mode distributed antenna system (Multi-mode Distribution Antanna System, MDAS) subsystem; the coverage subsystem is used to send the
具体地,所述叠加后的下行子基带低速信号及上行子基带低速信号为适应五类线、超五类线或网线等低速传输链路的信号,所述下行基带高速信号及上行基带高速信号为适应光纤或数据总线等高速传输链路的信号。Specifically, the superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal and uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal are signals suitable for low-speed transmission links such as Category 5 lines, Super Category 5 lines, or network cables, and the downlink baseband high-speed signals and uplink baseband high-speed signals In order to adapt to the signal of high-speed transmission links such as optical fiber or data bus.
所述AU子系统11与EU12可以通过光纤或数据总线等高速传输链路连接,当AU子系统11与EU12为两个不同的设备时,两者之间采用光纤等高速传输链路连接,采用的标准通信协议可以为IR/CPRI/OBSAI等接口协议;当AU子系统11与EU12为同一设备时,两者之间可以通过数据总线连接。The
由于EU12实现了对下行基带高速信号与下行子基带低速信号,以及上行子基带低速信号与上行基带高速信号之间的转变,因此在AU子系统11与EU12之间采用光纤或数据总线进行连接传输高速信号的时候,EU12与RU13之间可以采用五类线、超五类线或网线等低速传输链路连接,有别于传统的BBU和RRU之间采用的光纤等高速传输链路的连接方式,能够很好的依托现有部署完备的驻地网资源,不需布放光纤线缆、入户简单,便于室内覆盖,可以低成本快速建网。Since EU12 realizes the transition between the downlink baseband high-speed signal and the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal, as well as the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal and the uplink baseband high-speed signal, an optical fiber or a data bus is used for connection and transmission between the
所述RU13通过标准接口(如3G的Uu接口或GSM的Um接口)与用户终端进行连接。The RU13 is connected to the user terminal through a standard interface (such as the Uu interface of 3G or the Um interface of GSM).
所述GW子系统14处于AU子系统11和核心网之间,通过网关接口(如Iuh接口,Interface between the Gateway and the AU)与AU子系统11相连,用于实现AU子系统11与核心网之间信令和数据的汇聚和转发;GW子系统14完成信令和数据的汇聚后通过标准的通信接口接入核心网,如可以通过标准的通信接口(如3GPP的Iu-PS)接入CN的分组域、通过标准的通信接口(如3GPP的Iu-CS)接入CN的电路域。The
进一步地,所述GW子系统14还包含部分RNC的功能,包括支持用户终端的移动性切换用户面数据的功能、空闲模式下行分组数据缓存和寻呼支持等功能;还包含了安全网关处理功能,包括支持建立和管理Internet协议安全性(IPSec)通道、为AU子系统11及GW子系统14之间提供安全可靠的通信传输及接入认证等。Further, the
进一步地,所述无线通信系统还包括网管子系统15:Further, the wireless communication system also includes a network management subsystem 15:
所述网管子系统15通过网管接口(如基于TR-069协议的网管接口)与GW子系统14、AU子系统11、EU12和RU13相连,实现对GW子系统14、AU子系统11、EU12和RU13的管理和控制处理;所述网管子系统15还可以实现对GW子系统14、AU子系统11、EU12和RU13的用户界面管理、用户管理、用户组管理、软件管理、日志管理、系统维护、参数设置、告警上报等功能。Described
实施例二:Embodiment two:
本发明实施例所述无线通信系统中,所述AU子系统可以采用级联的方式组网,如图3所示,为采用AU子系统级联的组网方式的无线通信系统结构示意图,所述无线通信系统包括GW子系统、多个EU、与各EU相连的至少一个RU以及多个AU子系统,各AU子系统还包括级联接口。In the wireless communication system described in the embodiment of the present invention, the AU subsystems may be networked in a cascaded manner, as shown in FIG. The wireless communication system includes a GW subsystem, multiple EUs, at least one RU connected to each EU, and multiple AU subsystems, and each AU subsystem also includes a cascade interface.
具体地,各AU子系统通过本地的级联接口依次相连,其中,排列在第一位的AU子系统与排列在最后一位的AU子系统通过本地的级联接口与一个AU子系统相连,其余AU子系统通过本地的级联接口分别与两个AU子系统相连,同时各AU子系统还分别与其对应的EU相连,一般情况下,各AU子系统均与GW子系统相连。Specifically, each AU subsystem is connected sequentially through a local cascading interface, wherein the AU subsystem arranged first and the last AU subsystem are connected to one AU subsystem through a local cascading interface, The remaining AU subsystems are respectively connected to the two AU subsystems through local cascading interfaces, and each AU subsystem is also connected to its corresponding EU. Generally, each AU subsystem is connected to the GW subsystem.
如图3所示,所述无线通信系统中包括三个AU子系统,分别为AU子系统1、AU子系统2和AU子系统3;所述AU子系统1通过本地级联接口与AU子系统2相连;所述AU子系统2通过本地级联接口分别与AU子系统1、AU子系统3同时相连;所述AU子系统3通过本地级联接口与AU子系统2相连;同时,AU子系统1、AU子系统2和AU子系统3均通过网关接口与GW子系统相连,且AU子系统1、AU子系统2和AU子系统3分别通过光纤等高速传输链路与对应的EU1、EU2和EU3相连。As shown in Figure 3, the wireless communication system includes three AU subsystems, respectively AU subsystem 1, AU subsystem 2 and AU subsystem 3; the AU subsystem 1 communicates with the AU subsystem through a local cascade interface The system 2 is connected; the AU subsystem 2 is connected to the AU subsystem 1 and the AU subsystem 3 respectively through the local cascade interface; the AU subsystem 3 is connected to the AU subsystem 2 through the local cascade interface; at the same time, the AU subsystem Subsystem 1, AU Subsystem 2 and AU Subsystem 3 are all connected to the GW Subsystem through a gateway interface, and AU Subsystem 1, AU Subsystem 2 and AU Subsystem 3 are respectively connected to the corresponding EU1 through high-speed transmission links such as optical fibers. , EU2 and EU3 are connected.
针对任一AU子系统,具体用于在其相邻的下一AU子系统与GW子系统的连接中断时,接收GW子系统发送给相邻的下一AU子系统的GW下行数据,并将其发送至相邻的下一AU子系统,以及,通过接收相邻的下一AU子系统待发送的GW上行数据,并将其发送至GW子系统。For any AU subsystem, it is specifically used to receive the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem to the adjacent next AU subsystem when the connection between the adjacent next AU subsystem and the GW subsystem is interrupted, and send It is sent to the adjacent next AU subsystem, and the GW uplink data to be sent by the adjacent next AU subsystem is received and sent to the GW subsystem.
若AU子系统到GW子系统的连接中断,如图3所示,AU子系统2到GW子系统的链路出现故障时(以虚线表示AU子系统2与GW子系统的链路出现故障),通过本发明实施例二的方案,AU子系统1可以转发AU子系统2到GW子系统的GW上行数据和GW子系统到AU子系统2的GW下行数据,从而保证了链路的通畅,具体流程如下所述:If the connection between the AU subsystem and the GW subsystem is interrupted, as shown in Figure 3, when the link between the AU subsystem 2 and the GW subsystem fails (the broken line indicates that the link between the AU subsystem 2 and the GW subsystem fails) , through the solution of the second embodiment of the present invention, the AU subsystem 1 can forward the GW uplink data from the AU subsystem 2 to the GW subsystem and the GW downlink data from the GW subsystem to the AU subsystem 2, thereby ensuring the smoothness of the link, The specific process is as follows:
AU子系统1接收GW子系统发送给AU子系统2的GW下行数据,并通过级联接口将其发送至AU子系统2,以及通过级联接口接收AU子系统2待发送的GW上行数据,并将其发送至GW子系统。The AU subsystem 1 receives the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem to the AU subsystem 2, and sends it to the AU subsystem 2 through the cascading interface, and receives the GW uplink data to be sent by the AU subsystem 2 through the cascading interface, and send it to the GW subsystem.
本发明实施例二的方案中,各AU子系统之间可以通过光纤进行连接。In the solution of the second embodiment of the present invention, the AU subsystems may be connected through optical fibers.
实施例三:Embodiment three:
本发明实施例所述无线通信系统中,所述AU子系统还可以采用堆叠的方式组网,如图4所示,为采用AU子系统堆叠的组网方式的无线通信系统结构示意图,所述无线通信系统包括GW子系统、EU、与EU相连的至少一个RU和多个AU子系统,其中一个AU子系统为主AU子系统,其余AU子系统为从AU子系统,各AU子系统还包括堆叠接口。In the wireless communication system described in the embodiment of the present invention, the AU subsystems can also be networked in a stacked manner, as shown in FIG. The wireless communication system includes a GW subsystem, an EU, at least one RU connected to the EU, and multiple AU subsystems. One of the AU subsystems is the master AU subsystem, and the remaining AU subsystems are slave AU subsystems. Includes stacking interface.
所述主AU子系统分别与GW子系统和EU相连,从AU子系统通过本地的堆叠接口依次相连,其中第一个从AU子系统通过堆叠接口与主AU子系统连接。The master AU subsystem is connected to the GW subsystem and the EU respectively, and the slave AU subsystems are connected to each other through a local stacking interface in turn, wherein the first slave AU subsystem is connected to the master AU subsystem through a stacking interface.
如图4所示,所述无线通信系统中包括三个AU子系统,分别为AU子系统1、AU子系统2和AU子系统3,所述AU子系统1通过网关接口与GW子系统相连,通过光纤等高速传输链路与EU相连;所述AU子系统2通过堆叠接口与AU子系统1和AU子系统3分别相连;所述AU子系统3通过堆叠接口与AU子系统2相连。As shown in Figure 4, the wireless communication system includes three AU subsystems, namely AU subsystem 1, AU subsystem 2 and AU subsystem 3, and the AU subsystem 1 is connected to the GW subsystem through a gateway interface , connected to the EU through a high-speed transmission link such as an optical fiber; the AU subsystem 2 is connected to the AU subsystem 1 and the AU subsystem 3 respectively through a stacking interface; the AU subsystem 3 is connected to the AU subsystem 2 through a stacking interface.
所述主AU子系统,用于接收GW子系统发送的GW下行数据,并根据本地能够处理的载波数量,将所述GW下行数据中包含的超出所述载波数量的载波信号通过堆叠接口发送至从AU子系统,并将未发送给从AU子系统的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号,接收从AU子系统返回的转换后的下行基带高速信号,将下行基带高速信号发送到EU,以及,接收EU发送的上行基带高速信号,并根据本地能够处理的载波数量,将所述上行基带高速信号中包含的超出所述载波数量的载波信号通过堆叠接口发送至从AU子系统,并将未发送给从AU子系统的上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据,接收从AU子系统返回的转换后的GW上行数据,将GW上行数据发送到GW子系统;The main AU subsystem is used to receive the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem, and according to the number of carriers that can be processed locally, send the carrier signals contained in the GW downlink data that exceed the number of carriers to the From the AU subsystem, convert the GW downlink data not sent to the slave AU subsystem into a downlink baseband high-speed signal, receive the converted downlink baseband high-speed signal returned from the AU subsystem, and send the downlink baseband high-speed signal to the EU, and , receive the uplink baseband high-speed signal sent by the EU, and according to the number of carriers that can be processed locally, send the carrier signal contained in the uplink baseband high-speed signal that exceeds the number of carriers to the slave AU subsystem through the stack interface, and send the remaining Convert the uplink baseband high-speed signal sent to the slave AU subsystem into GW uplink data, receive the converted GW uplink data returned from the AU subsystem, and send the GW uplink data to the GW subsystem;
所述从AU子系统,用于接收主AU子系统或上一从AU子系统发送的GW下行数据,并根据本地能够处理的载波数量,将所述GW下行数据中包含的超出本地能够处理的载波数量的载波信号通过堆叠接口发送至相邻的下一从AU子系统,并将未发送给下一从AU子系统的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号,接收下一从AU子系统返回的转换后的下行基带高速信号,将下行基带高速信号发送到主AU子系统或上一从AU子系统,以及,接收主AU子系统或上一从AU子系统发送的上行基带高速信号,并根据本地能够处理的载波数量,将所述上行基带高速信号中包含的超出本地能够处理的载波数量的载波信号通过堆叠接口发送至相邻的下一从AU子系统,并将未发送给下一从AU子系统的上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据,接收下一从AU子系统返回的转换后的GW上行数据,将GW上行数据发送到主AU子系统或上一从AU子系统。The slave AU subsystem is used to receive the GW downlink data sent by the master AU subsystem or the last slave AU subsystem, and according to the number of carriers that can be processed locally, the GW downlink data contained in the GW downlink data that exceeds the local processable The carrier signal of the number of carriers is sent to the adjacent next slave AU subsystem through the stack interface, and the GW downlink data not sent to the next slave AU subsystem is converted into a downlink baseband high-speed signal, and the next slave AU subsystem returns the converted downlink baseband high-speed signal, send the downlink baseband high-speed signal to the master AU subsystem or the last slave AU subsystem, and receive the uplink baseband high-speed signal sent by the master AU subsystem or the last slave AU subsystem, and According to the number of carriers that can be processed locally, the carrier signals contained in the uplink baseband high-speed signal that exceed the number of carriers that can be processed locally are sent to the adjacent next slave AU subsystem through the stack interface, and are not sent to the next Convert the uplink baseband high-speed signal from the AU subsystem into GW uplink data, receive the converted GW uplink data returned from the next AU subsystem, and send the GW uplink data to the master AU subsystem or the last slave AU subsystem.
具体地,如图4所示,假设AU子系统1、AU子系统2和AU子系统3预设的能够处理的载波数量阈值均为10,则当GW子系统向AU子系统1发送的GW下行数据所包括的载波数量为30时,AU子系统1将把超过阈值的剩余20个载波信号通过堆叠接口转发到AU子系统2,并将未发送给AU子系统2的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号;AU子系统2判断出20个载波信号也超出其预设阈值10,因此把20个载波信号中的10个载波信号发送到AU子系统3,并将未发送给AU子系统3的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号;AU子系统3处理AU子系统2发送的10个载波信号,并把经过处理后得到的AU子系统3的下行基带高速信号通过堆叠接口转发给AU子系统2,AU子系统2把自身处理后得到的下行基带高速信号以及AU子系统3发送的下行基带高速信号转发给AU子系统1,由AU子系统1将AU子系统1、AU子系统2和AU子系统3处理的下行基带高速信号发送到EU;Specifically, as shown in FIG. 4 , assuming that AU subsystem 1, AU subsystem 2, and AU subsystem 3 preset the thresholds for the number of carriers that can be processed to be 10, then when the GW subsystem transmits to AU subsystem 1, the GW When the number of carriers included in the downlink data is 30, AU subsystem 1 will forward the remaining 20 carrier signals exceeding the threshold to AU subsystem 2 through the stack interface, and convert the GW downlink data not sent to AU subsystem 2 into Downlink baseband high-speed signal; AU subsystem 2 judges that 20 carrier signals also exceed its preset threshold of 10, so 10 carrier signals out of 20 carrier signals are sent to AU subsystem 3, and will not be sent to AU subsystem The GW downlink data of 3 is converted into a downlink baseband high-speed signal; AU subsystem 3 processes the 10 carrier signals sent by AU subsystem 2, and forwards the processed downlink baseband high-speed signal of AU subsystem 3 to AU through the stack interface Subsystem 2, AU subsystem 2 forwards the downlink baseband high-speed signal obtained after its own processing and the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by AU subsystem 3 to AU subsystem 1, and AU subsystem 1 transfers AU subsystem 1, AU subsystem The downlink baseband high-speed signal processed by 2 and AU subsystem 3 is sent to EU;
当EU向AU子系统1发送的上行基带高速信号为20个载波时,AU子系统1将把超过阈值10的剩余10个载波信号通过堆叠接口转发到AU子系统2,AU子系统2将接收到的10个载波信号进行处理后得到GW上行数据,并将所述GW上行数据通过堆叠接口转发给AU子系统1,AU子系统1把自身处理的GW上行数据和AU子系统2处理的GW上行数据发送到GW子系统。When the uplink baseband high-speed signal sent by the EU to AU subsystem 1 is 20 carriers, AU subsystem 1 will forward the remaining 10 carrier signals exceeding the threshold of 10 to AU subsystem 2 through the stack interface, and AU subsystem 2 will receive After processing the received 10 carrier signals, GW uplink data is obtained, and the GW uplink data is forwarded to AU subsystem 1 through the stack interface. AU subsystem 1 combines the GW uplink data processed by itself with the GW uplink data processed by AU subsystem 2. The uplink data is sent to the GW subsystem.
采用本发明实施例三中AU子系统堆叠的方式组网时,若系统需要扩容,则只需要在原来架设AU子系统的机房内简单增加多个AU子系统,系统的处理能力就会成倍增长,且用户完全不会受到影响,从而使得系统的扩容更加简单、扩容成本也得到较大幅度地降低。When using the AU subsystem stacking method in the third embodiment of the present invention to form a network, if the system needs to be expanded, it is only necessary to simply add multiple AU subsystems in the computer room where the AU subsystem was originally installed, and the processing capacity of the system will be doubled growth, and users will not be affected at all, which makes the expansion of the system easier and the cost of expansion is greatly reduced.
现有技术中存在多个BBU直接连接到RNC的分布式BBU的技术方案,在这种网络架构系统中,当系统需要扩容时,需要在RRU和RNC中进行配置,以建立载波与对应的BBU的关系,也就是说,假如RRU上支持100个载波,且所述系统中有两个分布式BBU,则需要将前50个载波配置在第一个BBU上处理,将后50个载波配置在第二个BBU上处理;而在本发明实施例三中,当AU子系统发现无法满足当前载波要求时,将自动把载波数据分配到从AU子系统上处理,无需对GW子系统或者EU、RU等进行设置,因此,组网方式更加灵活、方便系统扩容;同时,从工程架设角度来看,本发明实施例三中AU子系统堆叠的组网方式,各从AU子系统无需与GW子系统、EU或RU连接,从而减少了网络架设难度以及资源的浪费。In the prior art, there is a technical solution in which multiple BBUs are directly connected to the distributed BBU of the RNC. In this network architecture system, when the system needs to be expanded, it needs to be configured in the RRU and RNC to establish the carrier and the corresponding BBU. In other words, if the RRU supports 100 carriers and there are two distributed BBUs in the system, the first 50 carriers need to be configured on the first BBU for processing, and the last 50 carriers should be configured on the Processing on the second BBU; and in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, when the AU subsystem finds that it cannot meet the requirements of the current carrier, it will automatically allocate the carrier data to the secondary AU subsystem for processing, without the need for GW subsystem or EU, RU etc. are set, therefore, the networking mode is more flexible and convenient for system expansion; at the same time, from the perspective of engineering erection, the networking mode of AU subsystem stacking in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, each slave AU subsystem does not need to communicate with the GW subsystem System, EU or RU connection, thus reducing the difficulty of network construction and the waste of resources.
实施例四:Embodiment four:
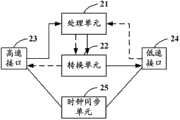
如图5所示,为本发明实施例四中EU的结构示意图,所述EU包括处理单元21和转换单元22。As shown in FIG. 5 , it is a schematic structural diagram of an EU in Embodiment 4 of the present invention, and the EU includes a
所述处理单元21用于对接收到的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并发送给转换单元22,以及,将接收到的上行子基带低速信号汇聚为上行基带低速信号后,发送给转换单元22;The
所述转换单元22用于将处理单元21发送的下行子基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号后输出,以及,将处理单元21发送的上行基带低速信号转换为上行基带高速信号后输出。The
具体地,转换单元22将处理单元21发送的下行子基带高速信号进行协议转换,从高速协议转换为低速协议,得到下行子基带低速信号后输出,以及,将处理单元21发送的上行基带低速信号进行协议转换,从低速协议转换为高速协议,得到上行基带高速信号后输出;所述高速协议包括IR/CPRI/OBSAI等支持光纤链路通讯的接口协议,所述低速协议包括以太网传输协议等支持五类线、超五类线或网线等链路通讯的接口协议。Specifically, the
所述高速协议转换为低速协议即把原来使用高速协议封装的信号数据转换为使用低速协议封装;所述低速协议转换为高速协议即把原来使用低速协议封装的信号数据转换为使用高速协议封装。The conversion of the high-speed protocol to the low-speed protocol is to convert the signal data originally encapsulated by the high-speed protocol into the low-speed protocol; the conversion of the low-speed protocol to the high-speed protocol is to convert the signal data originally encapsulated by the low-speed protocol to be encapsulated by the high-speed protocol.
进一步地,所述处理单元21还用于分别针对所述RU的负载能力,将多路下行子基带高速信号进行组合,得到多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号,并发送给转换单元22;所述转换单元22具体用于将处理单元21发送的多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号转换为多组下行子基带低速信号,并发送到所述RU,其中,属于同一小区的RU接收同一组下行子基带低速信号,任意两个属于不同小区的RU接收不同组的下行子基带低速信号。Further, the
所述多路下行子基带高速信号可以是同一制式的信号,也可以是多种制式的信号;所述叠加后的下行子基带高速信号可以为所述一路或多路的下行子基带高速信号的任意组合叠加。The multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals may be signals of the same system, or signals of multiple systems; the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals may be the one or more downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals. Stack in any combination.
具体地,以WCDMA和GSM双模为例,所述处理单元将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解后,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,假设每路下行子基带高速信号均包括3路WCDMA的I/Q信号和8路GSM的I/Q信号,处理单元针对所述RU的负载能力,对所述多路下行子基带高速信号进行组合,得到多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号,假设EU对应3个RU。Specifically, taking WCDMA and GSM dual-mode as an example, the processing unit decomposes the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU subsystem to obtain multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, assuming that each downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal includes 3 The I/Q signal of WCDMA and the I/Q signal of 8 GSM. The processing unit combines the multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals according to the load capacity of the RU to obtain multiple superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals. Signal, assuming EU corresponds to 3 RUs.
(1)对于分裂小区模式,即各RU属于不同小区时:(1) For the split cell mode, that is, when each RU belongs to a different cell:
EU待发送给第一个RU的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a包括:1路WCDMA I/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a to be sent to the first RU by the EU includes: 1 WCDMA I/Q signal and 3 GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给第二个RU的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b包括:2路WCDMA I/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b to be sent by the EU to the second RU includes: 2 WCDMA I/Q signals and 3 GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给第三个RU的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c包括:2路GSMI/Q信号。The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c to be sent by the EU to the third RU includes: two GSMI/Q signals.
(2)对于同一小区模式,即各RU属于同一小区时:(2) For the same cell mode, that is, when each RU belongs to the same cell:
EU待发送给第一个RU的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a包括:3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a to be sent to the first RU by the EU includes: 3 WCDMA I/Q signals and 8 GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给第二个RU的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b包括:3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b to be sent by the EU to the second RU includes: 3 WCDMA I/Q signals and 8 GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给第三个RU的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c包括:3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号。The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c to be sent by the EU to the third RU includes: 3 WCDMA I/Q signals and 8 GSM I/Q signals.
需要说明的是,上述下行子基带高速信号的叠加方式仅为本发明实施例的举例说明,在实际应用中,可以根据小区情况进行调整。It should be noted that, the superimposition manner of the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal is only an illustration of the embodiment of the present invention, and may be adjusted according to the conditions of the cell in practical application.
进一步地,所述转换单元将所述叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a、叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b和叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c按照同步以太网协议分别进行封装,得到下行子基带低速信号a、下行子基带低速信号b和下行子基带低速信号c,并把所述下行子基带低速信号a发送到第一个RU,把下行子基带低速信号b发送到第二个RU,把下行子基带低速信号c发送到第三个RU。Further, the conversion unit encapsulates the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a, the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b, and the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol to obtain the downlink Sub-baseband low-speed signal a, downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b, and downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal c, and send the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal a to the first RU, and send the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b to the second RU , to send the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal c to the third RU.
需要说明的是,本发明实施例中不限于采用其他协议对所述叠加后的下行子基带低速信号进行封装,如还可以采用支持五类线、超五类线或网线的接口协议对所述叠加后的下行子基带低速信号进行封装。It should be noted that, in the embodiment of the present invention, other protocols are not limited to encapsulating the superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal. The superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signals are packaged.
进一步地,所述EU还包括高速接口23和低速接口24:Further, the EU also includes a high-
所述高速接口23支持高速传输协议,用于接收下行基带高速信号并将其发送至处理单元21,以及输出转换单元22转换后的上行基带高速信号。The high-
所述低速接口24支持低速传输协议,用于接收上行子基带低速信号并将其发送至处理单元21,以及输出转换单元22转换后的下行子基带低速信号。The low-
优选地,所述EU还包括时钟同步单元25,所述时钟同步单元25用于从高速接口23中抽取同步时钟源,并传送到低速接口24,以进行高速接口23与低速接口24的时钟同步。Preferably, the EU also includes a
所述EU可以作为一个独立的装置存在,也可以作为子系统应用在本发明实施例一至实施例三所述扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统中。The EU can exist as an independent device, and can also be used as a subsystem in the wireless communication system of the flat network architecture described in Embodiment 1 to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
当所述EU作为子系统应用在本发明实施例一至实施例三任一所述的无线通信系统中时,可以采用以下所述级联的组网模式:When the EU is used as a subsystem in any of the wireless communication systems described in Embodiment 1 to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, the following cascading networking mode can be adopted:
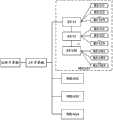
如图6所示为本发明实施例四中采用EU级联的组网方式的无线通信系统结构示意图,所述无线通信系统包括GW子系统、AU子系统和至少一个MDAS,所述MDAS包括至少一个EU和与各EU相连的至少一个RU,所述EU包括两个高速接口。Figure 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a wireless communication system using EU cascade networking in Embodiment 4 of the present invention. The wireless communication system includes a GW subsystem, an AU subsystem, and at least one MDAS. The MDAS includes at least One EU and at least one RU connected to each EU, the EU includes two high-speed interfaces.
具体地,对于任一MDAS,各EU通过本地的高速接口依次相连,其中,排列在第一位的EU与排列在最后一位的EU通过本地的一个高速接口与一个EU相连,其余EU通过本地的两个高速接口分别与两个EU相连,同时各EU还分别与其对应的至少一个RU相连,且排列在第一位的EU还通过另一高速接口与AU子系统相连。Specifically, for any MDAS, each EU is connected in turn through a local high-speed interface. Among them, the EU ranked first and the last EU are connected to one EU through a local high-speed interface, and the remaining EUs are connected through a local high-speed interface. The two high-speed interfaces are connected to two EUs, and each EU is also connected to at least one corresponding RU, and the EU ranked first is also connected to the AU subsystem through another high-speed interface.
如图6所示,所述无线通信系统包括MDAS1、MDAS2、MDAS3以及MDAS4,且各MDAS均通过光纤等高速传输链路与AU子系统相连;对于MDAS1来说,其包含M个EU,分别为EU11、EU12…以及EU1M,各EU分别与N个RU相连,如对应EU11,与其相连的RU为RU111、RU112…以及RU11N,所述M和N均为正整数。As shown in Figure 6, the wireless communication system includes MDAS1, MDAS2, MDAS3, and MDAS4, and each MDAS is connected to the AU subsystem through a high-speed transmission link such as an optical fiber; for MDAS1, it includes M EUs, respectively EU11, EU12... and EU1M are respectively connected to N RUs. For example, corresponding to EU11, the RUs connected to it are RU111, RU112... and RU11N, and M and N are both positive integers.
其中,EU11通过第一高速接口与AU子系统相连,通过第二高速接口与EU12的第一高速接口相连;EU12的第二高速接口与……EU1M的第一高速接口连接,从而形成EU的级联。Among them, EU11 is connected to the AU subsystem through the first high-speed interface, and connected to the first high-speed interface of EU12 through the second high-speed interface; the second high-speed interface of EU12 is connected to the first high-speed interface of ... EU1M, thus forming the level of EU couplet.
具体地,在下行链路中,AU子系统将GW子系统发送的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号后,从EU11的第一高速接口输入到EU11,一部分下行基带高速信号经过EU11的处理单元和转换单元转换为多路叠加下行子基带信号后,从低速接口输出,另一部分下行基带高速信号直接从EU11的第二高速接口输出到EU12;Specifically, in the downlink, the AU subsystem converts the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem into a downlink baseband high-speed signal, and then inputs it to the EU11 from the first high-speed interface of EU11, and a part of the downlink baseband high-speed signal passes through the processing unit of EU11 After the conversion unit is converted into a multi-channel superimposed downlink sub-baseband signal, it is output from the low-speed interface, and another part of the downlink baseband high-speed signal is directly output from the second high-speed interface of EU11 to EU12;
在上行链路中,RU121至RU12N发送的上行子基带低速信号从EU12的低速接口输入,经过处理单元和转换单元转换为上行基带高速信号后,从第一高速接口输入到EU11的第二高速接口并通过EU11的第一高速接口发送到AU子系统;同时,EU11还将与其连接的各RU发送的上行子基带低速信号转换为上行基带高速信号后通过第一高速接口发送到AU子系统。In the uplink, the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal sent by RU121 to RU12N is input from the low-speed interface of EU12, and after being converted into an uplink baseband high-speed signal by the processing unit and conversion unit, it is input from the first high-speed interface to the second high-speed interface of EU11 And send it to the AU subsystem through the first high-speed interface of EU11; at the same time, EU11 also converts the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal sent by each RU connected to it into an uplink baseband high-speed signal and sends it to the AU subsystem through the first high-speed interface.
对于同一小区模式,不同EU之间的上行数据为或的关系,而对于分裂小区模式,不同EU之间的上行数据为与的关系。For the same cell mode, the uplink data between different EUs has an OR relationship, while for the split cell mode, the uplink data between different EUs has an AND relationship.
需要说明的是,本发明实施例所述无线通信系统还可以支持EU的星型组网,RU的菊花链、星型以及混合组网等组网模式。It should be noted that the wireless communication system described in the embodiment of the present invention may also support EU star networking, RU daisy chain, star and hybrid networking and other networking modes.
实施例五:Embodiment five:
如图7所示,为本发明实施例五中AU子系统的结构示意图,所述AU子系统包括接收单元31、转换单元32以及发送单元33。As shown in FIG. 7 , it is a schematic structural diagram of the AU subsystem in Embodiment 5 of the present invention. The AU subsystem includes a receiving
所述接收单元31用于接收GW下行数据以及上行基带高速信号;所述转换单元32用于将接收单元31接收到的所述GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号,以及将接收单元31接收到的所述上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据;所述发送单元33用于发送转换单元32转换得到的下行基带高速信号和GW上行数据。The receiving
具体地,所述转换单元32相当于基带处理单元,包括编解码、调制解调、交织解交织、加密解密、跳频、定时控制、组帧解帧等功能;所述发送单元33还具有工作状态监控和告警信息上报等功能;所述接收单元31还具有Iuh接口功能、本地和远程操作维护功能。Specifically, the
进一步地,所述AU子系统还包括上层控制单元34,所述上层控制单元34包括无线资源管理、移动性管理、MAC、RLC等功能。Further, the AU subsystem further includes an upper
需要说明的是,本发明实施例五中所述AU子系统可以为实施例二和实施例三中的任一AU子系统,例如当应用在实施例三中的无线通信系统中时,所述AU子系统可以为主AU子系统,也可以为任一从AU子系统。It should be noted that the AU subsystem in Embodiment 5 of the present invention may be any AU subsystem in Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 3. For example, when applied to the wireless communication system in Embodiment 3, the The AU subsystem can be the master AU subsystem or any slave AU subsystem.
实施例六:Embodiment six:
如图8所示,为本发明实施例六中扁平化网络架构的无线通信方法流程示意图,所述方法包括以下步骤:As shown in FIG. 8 , it is a schematic flowchart of a wireless communication method in a flat network architecture in Embodiment 6 of the present invention, and the method includes the following steps:
步骤101:AU子系统将GW子系统发送的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号后发送到EU。Step 101: The AU subsystem converts the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem into a downlink baseband high-speed signal and sends it to the EU.
具体地,AU子系统将GW子系统发送的GW下行数据(包括信令面和用户面)进行信令处理和物理层基带处理,得到下行基带高速信号并发送到EU。Specifically, the AU subsystem performs signaling processing and physical layer baseband processing on the GW downlink data (including the signaling plane and the user plane) sent by the GW subsystem to obtain a downlink baseband high-speed signal and send it to the EU.
所述下行基带高速信号采用帧形式传输,每个帧包括一个或多个模式的基带信号。The downlink baseband high-speed signal is transmitted in the form of frames, and each frame includes one or more modes of baseband signals.
步骤102:EU将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并将所述下行子基带高速信号转换下行子基带低速信号后,发送到RU。Step 102: The EU decomposes the downlink baseband high-speed signals sent by the AU subsystem to obtain multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, converts the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals into downlink sub-baseband low-speed signals, and sends them to the RU.
具体地,EU用于将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,针对所述RU的负载能力,将所述多路下行子基带高速信号进行组合,得到多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号,将所述多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号转换为多组叠加后的下行子基带低速信号后分别路由并发送到所述一个或多个RU。Specifically, the EU is used to decompose the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU subsystem to obtain multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, and according to the load capacity of the RU, combine the multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals to obtain Multiple sets of superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals are converted into multiple sets of superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signals, respectively routed and sent to the one or more RUs.
所述多路下行子基带高速信号可以是同一制式的信号,也可以是多种制式的信号;所述叠加后的下行子基带高速信号可以为所述一路或多路的下行子基带高速信号的任意组合叠加。The multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals may be signals of the same system, or signals of multiple systems; the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals may be the one or more downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals. Stack in any combination.
步骤103:RU将EU发送的下行子基带低速信号变频为远端下行射频信号后发送给用户终端。Step 103: The RU converts the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal sent by the EU into a remote downlink radio frequency signal and sends it to the user terminal.
具体地,RU将EU发送的叠加下行子基带低速信号进行解帧操作,得到对应的一个或多个模式的基带信号,并对不同模式的基带信号分别执行相应的上变频操作,将其转变为一个或多个模式的远端下行射频信号并发送给用户终端。Specifically, the RU deframes the superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal sent by the EU to obtain the corresponding baseband signals of one or more modes, and performs corresponding up-conversion operations on the baseband signals of different modes to convert them into One or more patterns of remote downlink radio frequency signals are sent to the user terminal.
以上所述是本发明实施例六的下行传输过程,其上行传输过程为其逆过程,具体可以包括:The above is the downlink transmission process of Embodiment 6 of the present invention, and its uplink transmission process is its inverse process, which may specifically include:
RU将用户终端发送的远端上行射频信号变频为上行子基带低速信号后发送到EU,由EU将所述上行子基带低速信号汇聚并转换为上行基带高速信号后发送到AU子系统,由AU子系统将所述上行基带高速信号转换为GW上行数据后,通过GW子系统传输到核心网。The RU converts the remote uplink radio frequency signal sent by the user terminal into an uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal and sends it to the EU. The EU aggregates and converts the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal into an uplink baseband high-speed signal and sends it to the AU subsystem. The AU After the subsystem converts the uplink baseband high-speed signal into GW uplink data, it transmits to the core network through the GW subsystem.
需要说明的是,本发明实施例六中所述无线通信方法可以支持多种无线传输模式,包括GSM、WCDMA、TD-SCDMA、LTE以及WLAN等。It should be noted that the wireless communication method described in Embodiment 6 of the present invention can support multiple wireless transmission modes, including GSM, WCDMA, TD-SCDMA, LTE, and WLAN.
实施例七:Embodiment seven:
本发明实施例七通过具体的实例对实施例六所述无线通信方法进行详细说明,以WCDMA和GSM双模为例,假设GW子系统向AU子系统发送的GW下行数据包括8个GSM载波以及3个WCDMA载波,则所述无线通信方法包括以下步骤:Embodiment 7 of the present invention describes the wireless communication method described in Embodiment 6 in detail through specific examples. Taking WCDMA and GSM dual-mode as an example, it is assumed that the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem to the AU subsystem includes 8 GSM carriers and 3 WCDMA carriers, then the wireless communication method comprises the following steps:
步骤一:AU子系统将GW子系统发送的GW下行数据转换为下行基带高速信号后发送到EU。Step 1: The AU subsystem converts the GW downlink data sent by the GW subsystem into a downlink baseband high-speed signal and sends it to the EU.
具体地,AU子系统对接收到的包括8个GSM载波和3个WCDMA载波的GW混合下行数据(即所述GW下行数据)分别进行基带处理,得到GSM的I/Q信号以及WCDMA的I/Q信号,并对所述GSM的I/Q信号以及WCDMA的I/Q信号进行成帧操作,得到下行基带高速信号。Specifically, the AU subsystem performs baseband processing on the received GW mixed downlink data (that is, the GW downlink data) including 8 GSM carriers and 3 WCDMA carriers to obtain GSM I/Q signals and WCDMA I/Q signals. Q signal, and perform a framing operation on the I/Q signal of the GSM and the I/Q signal of the WCDMA to obtain a downlink baseband high-speed signal.
所述下行基带高速信号采用具有多个子帧的复帧形式传输,子帧传送的内容由3部分构成,包括开销字节、GSM制式I/Q信号和WCDMA制式I/Q信号、空闲字节;如图9所示,为下行基带高速信号传输数据在单个子帧中的数据结构示意图,包括开销字节、GSM制式的8路I/Q信号、WCDMA的3路I/Q信号,以及空闲字节,需要说明的是,图8所示的数据结构为针对本实施例七特定传输方式所采用的数据结构,当本发明实施例七采用其他传输方式时,可对所述数据结构做适应性调整。The downlink baseband high-speed signal is transmitted in a multi-frame form with multiple subframes, and the content transmitted by the subframe is composed of 3 parts, including overhead bytes, GSM standard I/Q signals and WCDMA standard I/Q signals, and idle bytes; As shown in Figure 9, it is a schematic diagram of the data structure of the downlink baseband high-speed signal transmission data in a single subframe, including overhead bytes, 8-way I/Q signals for GSM, 3-way I/Q signals for WCDMA, and idle words Section, it should be noted that the data structure shown in Figure 8 is the data structure adopted for the specific transmission mode of the seventh embodiment. When other transmission modes are used in the seventh embodiment of the present invention, the data structure can be adapted Adjustment.
所述下行基带高速信号传输数据一帧接一帧传送,多个子帧组成一个复帧,复帧再按照通用公共无线接口(The Common Public Radio Interface,CPRI)协议封装,如图10所示,为614.4Mbit/s线速率的CPRI封包方式;需要说明的是,本发明实施例七中采用CPRI协议对下行基带高速信号传输数据进行封装,但本发明实施例七不限于采用其他协议对所述下行基带高速信号传输数据进行封装,例如,采用包括IR/OBSAI等支持光纤链路通讯的接口协议对数据进行封装,数据速率可以为其他适合系统应用的速率要求。The downlink baseband high-speed signal transmission data is transmitted frame by frame, and multiple subframes form a multiframe, and the multiframe is encapsulated according to the Common Public Radio Interface (The Common Public Radio Interface, CPRI) protocol, as shown in Figure 10. 614.4Mbit/s line rate CPRI encapsulation method; It should be noted that, in the seventh embodiment of the present invention, the CPRI protocol is used to encapsulate the downlink baseband high-speed signal transmission data, but the seventh embodiment of the present invention is not limited to the use of other protocols for the downlink The baseband high-speed signal transmission data is encapsulated, for example, the data is encapsulated by using an interface protocol including IR/OBSAI that supports optical fiber link communication, and the data rate can be other rate requirements suitable for system applications.
步骤二:EU将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号进行分解,得到多路下行子基带高速信号,并将所述下行子基带高速信号转换下行子基带低速信号后,发送到RU。Step 2: The EU decomposes the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU subsystem to obtain multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals, converts the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal into a downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal, and sends it to the RU.
具体地,EU的处理单元按照CPRI协议将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号进行解帧处理,得到多路WCDMA和GSM的I/Q信号,即下行子基带高速信号;由于在步骤一中形成的各子帧包含3路WCDMA的I/Q信号和8路GSM的I/Q信号,因此,在本步骤二中,通过解帧处理后可以得到3路的WCDMA的I/Q信号和8路的GSM的I/Q信号。Specifically, the processing unit of the EU deframes the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU subsystem according to the CPRI protocol to obtain multiple I/Q signals of WCDMA and GSM, that is, the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal; Each subframe of 3 includes I/Q signals of No. 3 WCDMA and I/Q signals of No. 8 GSM. Therefore, in this step 2, the I/Q signals of No. 3 WCDMA and the I/Q signals of No. 8 GSM can be obtained after deframing processing. GSM I/Q signal.
进一步地,EU的处理单元针对所述RU的负载能力,对所述多路下行子基带高速信号进行组合,得到多组叠加后的下行子基带高速信号,假设EU对应3个RU,分别为RU1、RU2和RU3。Further, the processing unit of the EU combines the multiple downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals according to the load capacity of the RUs to obtain multiple sets of superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signals. It is assumed that the EU corresponds to 3 RUs, namely RU1 , RU2 and RU3.
(1)对于分裂小区模式:(1) For split cell mode:
EU待发送给RU1的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a包括:1路WCDMAI/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a to be sent to RU1 by the EU includes: 1 WCDMA I/Q signal and 3 GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给RU2的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b包括:2路WCDMAI/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b to be sent by the EU to RU2 includes: 2-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 3-way GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给RU3的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c包括:2路GSM I/Q信号。The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c to be sent by the EU to RU3 includes: 2 GSM I/Q signals.
(2)对于同一小区模式:(2) For the same cell mode:
EU待发送给RU1的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a包括:3路WCDMAI/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a to be sent to RU1 by the EU includes: 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给RU2的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b包括:3路WCDMAI/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号;The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b to be sent by the EU to RU2 includes: 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals;
EU待发送给RU3的叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c包括:3路WCDMAI/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号。The superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c to be sent by the EU to RU3 includes: 3 WCDMA I/Q signals and 8 GSM I/Q signals.
需要说明的是,上述下行子基带高速信号的叠加方式仅为本发明实施例七的举例说明,在实际应用中,可以根据小区情况进行调整。It should be noted that the superimposition manner of the downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal is only an example of Embodiment 7 of the present invention, and may be adjusted according to the conditions of the cell in practical applications.
进一步地,EU的转换单元将所述叠加后的下行子基带高速信号a、叠加后的下行子基带高速信号b和叠加后的下行子基带高速信号c按照同步以太网协议分别进行封装,得到下行子基带低速信号a、下行子基带低速信号b和下行子基带低速信号c,并把所述下行子基带低速信号a发送到RU1,把下行子基带低速信号b发送到RU2,把下行子基带低速信号c发送到RU3。Further, the conversion unit of the EU encapsulates the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal a, the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal b, and the superimposed downlink sub-baseband high-speed signal c according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol to obtain the downlink The sub-baseband low-speed signal a, the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b and the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal c, and the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal a is sent to RU1, the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b is sent to RU2, and the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b is sent to RU2. Signal c is sent to RU3.
需要说明的是,本发明实施例七中不限于采用其他协议对所述叠加下行子基带低速信号进行封装,如还可以采用支持五类线、超五类线或网线的接口协议对所述叠加下行子基带低速信号进行封装。It should be noted that Embodiment 7 of the present invention is not limited to using other protocols to encapsulate the superimposed downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal. The downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal is encapsulated.
步骤三:RU将EU发送的下行子基带低速信号变频为远端下行射频信号后发送给用户终端。Step 3: The RU converts the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal sent by the EU into a remote downlink radio frequency signal and sends it to the user terminal.
(1)对于分裂小区模式:(1) For split cell mode:
RU1将EU发送的下行子基带低速信号a按照同步以太网协议进行解帧处理,得到1路WCDMA I/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号后进行上变频操作,得到WCDMA射频信号和GSM射频信号,并将其发送给用户终端;RU1 deframes the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal a sent by the EU according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol, obtains 1 channel of WCDMA I/Q signal and 3 channels of GSM I/Q signal, and performs up-conversion operation to obtain WCDMA radio frequency signal and GSM radio frequency signal and send it to the user terminal;
RU2将EU发送的下行子基带低速信号b按照同步以太网协议进行解帧处理,得到2路WCDMA I/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号后对其进行上变频操作,得到WCDMA射频信号和GSM射频信号,并将其发送给用户终端;RU2 deframes the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal b sent by the EU according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol, obtains 2 channels of WCDMA I/Q signals and 3 channels of GSM I/Q signals, and performs up-conversion operations on them to obtain WCDMA radio frequency signals and GSM radio frequency signal and send it to the user terminal;
RU3将EU发送的下行子基带低速信号c按照同步以太网协议进行解帧处理,得到2路GSM I/Q信号后进行上变频操作,得到GSM射频信号,并将其发送给用户终端。RU3 deframes the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal c sent by the EU according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol, obtains 2 GSM I/Q signals, performs up-conversion operation, obtains GSM radio frequency signals, and sends them to the user terminal.
(2)对于同一小区模式:(2) For the same cell mode:
RU1、RU2和RU3分别将EU发送的下行子基带低速信号a、b和c按照同步以太网协议进行解帧处理,得到3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号后对其进行上变频操作,得到WCDMA射频信号和GSM射频信号,并将其发送给用户终端。RU1, RU2, and RU3 respectively deframe the downlink sub-baseband low-speed signals a, b, and c sent by the EU according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol, obtain 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals, and then process them Up-conversion operation to obtain WCDMA radio frequency signal and GSM radio frequency signal, and send them to the user terminal.
以上所述是本发明实施例七的下行传输过程,其上行传输过程为其逆过程,具体可以包括如下步骤:The above is the downlink transmission process of Embodiment 7 of the present invention, and its uplink transmission process is its inverse process, which may specifically include the following steps:
第一步:RU接收用户终端发送的远端上行射频信号,将该远端上行射频信号下变频为一个或多个模式的基带信号,按照图9所示数据结构对所述基带信号进行组帧后,采用同步以太网协议将其封装为上行子基带低速信号并发送到EU。Step 1: The RU receives the remote uplink radio frequency signal sent by the user terminal, down-converts the remote uplink radio frequency signal into one or more modes of baseband signals, and frames the baseband signals according to the data structure shown in Figure 9 Afterwards, it is encapsulated into an uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal using the synchronous Ethernet protocol and sent to the EU.
具体地,当本发明实施例采用其他传输方式时,可对图9所示数据结构做适应性调整;另外,本步骤中不限于采用其他协议对所述组帧后的上行子基带低速信号进行封装,如还可以采用支持五类线、超五类线或网线的接口协议对其进行封装。Specifically, when the embodiment of the present invention adopts other transmission methods, adaptive adjustments can be made to the data structure shown in FIG. Encapsulation, for example, it can also be encapsulated by using an interface protocol that supports Category 5, Super Category 5 or network cables.
第二步:EU的处理单元将RU1、RU2和RU3发送的上行子基带低速信号a’、b’和c’按照同步以太网协议进行解帧处理,得到WCDMA I/Q信号和GSM I/Q信号,并按照图9所示数据结构将其重新组合为子帧,多个子帧组合为复帧,形成采用复帧形式的上行基带低速信号后发送到转换单元,转换单元对所述上行基带低速信号按照CPRI协议进行封装后得到上行基带高速信号,并将其发送到AU子系统。Step 2: The EU processing unit deframes the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signals a', b' and c' sent by RU1, RU2 and RU3 according to the synchronous Ethernet protocol to obtain WCDMA I/Q signals and GSM I/Q signal, and recombine it into subframes according to the data structure shown in Figure 9, and multiple subframes are combined into multiframes to form an uplink baseband low-speed signal in the form of a multiframe and then send it to the conversion unit, and the conversion unit converts the uplink baseband low-speed signal After the signal is encapsulated according to the CPRI protocol, the uplink baseband high-speed signal is obtained and sent to the AU subsystem.
(1)对于分裂小区模式:(1) For split cell mode:
上行子基带低速信号a’的1路WCDMA I/Q信号和2路GSM I/Q信号、上行子基带低速信号b’的2路WCDMA I/Q信号和3路GSM I/Q信号、上行子基带低速信号c’的2路GSM I/Q信号,组成3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号的上行基带低速信号。1 WCDMA I/Q signal and 2 GSM I/Q signals of uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal a', 2 WCDMA I/Q signals and 3 GSM I/Q signals of uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal b', uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal b' The 2-way GSM I/Q signal of the baseband low-speed signal c' forms the uplink baseband low-speed signal of 3-way WCDMA I/Q signal and 8-way GSM I/Q signal.
(2)对于同一小区模式:(2) For the same cell mode:
上行子基带低速信号a’的3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号、上行子基带低速信号b’的3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号、上行子基带低速信号c’的3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号,组成3路WCDMA I/Q信号和8路GSM I/Q信号的上行基带低速信号;对于同一小区模式,上行子基带低速信号与上行基带低速信号之间为或关系,即上行子基带低速信号a’的I信号+上行子基带低速信号b’的I信号+上行子基带低速信号c’的I信号=上行基带低速信号的I信号;上行子基带低速信号a’的Q信号+上行子基带低速信号b’的Q信号+上行子基带低速信号c’的Q信号=上行基带低速信号的Q信号,符号“+”表示“或”的关系。3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals of uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal a', 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals of uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal b', uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal b' 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals of the baseband low-speed signal c' form an uplink baseband low-speed signal of 3-way WCDMA I/Q signals and 8-way GSM I/Q signals; for the same cell mode, the uplink There is an OR relationship between the sub-baseband low-speed signal and the uplink baseband low-speed signal, that is, the I signal of the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal a' + the I signal of the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal b' + the I signal of the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal c' = uplink The I signal of the baseband low-speed signal; the Q signal of the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal a' + the Q signal of the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal b' + the Q signal of the uplink sub-baseband low-speed signal c' = the Q signal of the uplink baseband low-speed signal, symbol " +" means "or" relationship.
转换单元对所述上行基带低速信号按照CPRI协议进行封装后得到上行基带高速信号,并将其发送到AU子系统。The conversion unit encapsulates the uplink baseband low-speed signal according to the CPRI protocol to obtain an uplink baseband high-speed signal, and sends it to the AU subsystem.
第三步:AU子系统按照CPRI协议对EU发送的采用复帧形式传输的上行基带高速信号进行解帧处理,得到WCDMA和GSM的I/Q信号,并分别将其转换为WCDMA和GSM的GW上行数据。Step 3: According to the CPRI protocol, the AU subsystem deframes the uplink baseband high-speed signal sent by the EU in the form of multi-frame transmission, obtains the I/Q signal of WCDMA and GSM, and converts it into the GW of WCDMA and GSM respectively upstream data.
由于本实施例七的下行传输过程中采用CPRI协议对下行基带高速信号传输数据进行成帧操作,因此本步骤中采用CPRI协议对上行基带高速信号进行解帧,实际上,还可以采用包括IR/OBSAI等支持光纤链路通讯的接口协议对数据进行成帧以及解帧处理。Since the CPRI protocol is used to frame the downlink baseband high-speed signal transmission data in the downlink transmission process of the seventh embodiment, the CPRI protocol is used in this step to deframe the uplink baseband high-speed signal. Interface protocols such as OBSAI that support optical fiber link communication perform framing and deframing processing on data.
本发明实施例提供了一种扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统、方法及扩展装置,所述扁平化网络架构的无线通信系统包括GW子系统、AU子系统、EU以及与EU连接的至少一个RU,通过将无线网络控制器RNC的功能下移到GW子系统和AU子系统,使得整个通信系统的结构进一步分解和简化,降低了网络处理时延和传输时延,改善了用户体验,同时,信令传输节点减少,从而有效提高了业务接入效率和切换效率;同时,利用所述EU将AU子系统发送的下行基带高速信号转换为下行子基带低速信号后发送给RU,使得EU和RU之间可以采用五类线等低速传输链路连接,有别于传统的BBU和RRU之间采用的光纤传输的方式,便于室内覆盖,降低了网络部署的难度,同时所述无线通信系统支持多种回传方式,包括xDSL(各种类型Digital Subscribe Line数字用户线路,包括ADSL、VDSL、RADSL等)、GPON、EPON、Cable等,建设维护方便,费用较低;且所述无线覆盖系统可以支持AU子系统的级联及组叠模式,提高了系统的可扩容性、降低了系统扩容的成本。Embodiments of the present invention provide a wireless communication system, method, and extension device of a flat network architecture. The wireless communication system of the flat network architecture includes a GW subsystem, an AU subsystem, an EU, and at least one RU connected to the EU , by moving the function of the radio network controller RNC down to the GW subsystem and the AU subsystem, the structure of the entire communication system is further decomposed and simplified, the network processing delay and transmission delay are reduced, and the user experience is improved. At the same time, Signaling transmission nodes are reduced, thereby effectively improving service access efficiency and switching efficiency; at the same time, using the EU to convert the downlink baseband high-speed signal sent by the AU subsystem into a downlink sub-baseband low-speed signal and sending it to the RU, so that the EU and RU CAT5 lines and other low-speed transmission links can be used to connect between them, which is different from the traditional optical fiber transmission method used between BBU and RRU, which is convenient for indoor coverage and reduces the difficulty of network deployment. At the same time, the wireless communication system supports multiple A variety of backhaul methods, including xDSL (various types of Digital Subscribe Line digital subscriber lines, including ADSL, VDSL, RADSL, etc.), GPON, EPON, Cable, etc., are convenient for construction and maintenance, and the cost is low; and the wireless coverage system can support The cascading and stacking modes of the AU subsystem improve the scalability of the system and reduce the cost of system expansion.
以上所述仅是本发明的优选实施方案,显然,本领域的技术人员可以对本发明进行各种改动和变型而不脱离本发明的精神和范围。这样,倘若本发明的这些修改和变型属于本发明权利要求及其等同技术的范围之内,则本发明也意图包含这些改动和变型在内。The above descriptions are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, obviously, those skilled in the art can make various changes and modifications to the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Thus, if these modifications and variations of the present invention fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention and their equivalent technologies, the present invention also intends to include these modifications and variations.
Claims (13)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210005089.1ACN102547716B (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2012-01-06 | Wireless communication system and method for flat network architecture and extend unit |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210005089.1ACN102547716B (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2012-01-06 | Wireless communication system and method for flat network architecture and extend unit |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102547716Atrue CN102547716A (en) | 2012-07-04 |
| CN102547716B CN102547716B (en) | 2015-06-10 |
Family
ID=46353421
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210005089.1AActiveCN102547716B (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2012-01-06 | Wireless communication system and method for flat network architecture and extend unit |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102547716B (en) |
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013102368A1 (en)* | 2012-01-06 | 2013-07-11 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | Wireless communication system and method and expansion unit of flat network architecture |
| CN103369616A (en)* | 2013-07-09 | 2013-10-23 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | Data transmission method and data transmission device under dual-mode networking |
| CN103379674A (en)* | 2013-07-24 | 2013-10-30 | 三维通信股份有限公司 | Multimode digital DAS supporting multi-information-source access |
| CN103384385A (en)* | 2013-07-17 | 2013-11-06 | 三维通信股份有限公司 | Automatic antenna feed fault detection system for distributed antenna system |
| CN103475418A (en)* | 2013-10-10 | 2013-12-25 | 南京云恒瑞通网络科技有限责任公司 | Wireless-coverage active light distribution system and working method thereof |
| CN104703279A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Software-defined distributed wireless system |
| CN104703122A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Communication control method for software-defined distributed wireless system |
| CN104703278A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Software-defined distributed wireless system and downlink data communication method thereof |
| CN104703285A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Software-defined distributed wireless system and uplink data communication method thereof |
| CN105430666A (en)* | 2015-11-02 | 2016-03-23 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | A cell access method and optical fiber distribution system |
| CN106301923A (en)* | 2016-08-18 | 2017-01-04 | 上海肯汀通讯科技有限公司 | MDAS System Architecture |
| CN107396390A (en)* | 2017-08-30 | 2017-11-24 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | A communication method, device and system |
| CN107612714A (en)* | 2017-08-23 | 2018-01-19 | 武汉虹信通信技术有限责任公司 | A kind of automated topology structure realization method and system |
| CN108243493A (en)* | 2016-12-26 | 2018-07-03 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A kind of device and method of antenna data packetizing transmission |
| CN108834153A (en)* | 2018-09-27 | 2018-11-16 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | A kind of cell wireless coverage system and method |
| CN109474934A (en)* | 2018-11-02 | 2019-03-15 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | A base station system and base station capacity expansion method |
| CN110049512A (en)* | 2019-04-22 | 2019-07-23 | 武汉虹信通信技术有限责任公司 | A kind of forward pass network data processing device and method |
| CN110113762A (en)* | 2019-05-23 | 2019-08-09 | 江阴辰光通讯科技有限公司 | A method of it is wirelessly communicated for 5G network high-frequency section |
| CN115189784A (en)* | 2022-06-30 | 2022-10-14 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Delay-based processing method and device, electronic device, and storage medium |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101166064A (en)* | 2006-10-17 | 2008-04-23 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Conversion device for RF remote distribution system in communication system |
| CN101442756A (en)* | 2007-11-22 | 2009-05-27 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method and apparatus for recognizing baseband zooming unit logic topology structure |
| CN101453799A (en)* | 2007-11-30 | 2009-06-10 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | Multi-carrier digital frequency-selection radio frequency pulling system and signal processing method thereof |
- 2012
- 2012-01-06CNCN201210005089.1Apatent/CN102547716B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101166064A (en)* | 2006-10-17 | 2008-04-23 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Conversion device for RF remote distribution system in communication system |
| CN101442756A (en)* | 2007-11-22 | 2009-05-27 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method and apparatus for recognizing baseband zooming unit logic topology structure |
| CN101453799A (en)* | 2007-11-30 | 2009-06-10 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | Multi-carrier digital frequency-selection radio frequency pulling system and signal processing method thereof |
Cited By (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9838885B2 (en) | 2012-01-06 | 2017-12-05 | Comba Telecom Systems (China) Ltd. | Wireless communication system and method and expansion unit of flat network architecture |
| WO2013102368A1 (en)* | 2012-01-06 | 2013-07-11 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | Wireless communication system and method and expansion unit of flat network architecture |
| CN103369616A (en)* | 2013-07-09 | 2013-10-23 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | Data transmission method and data transmission device under dual-mode networking |
| CN103369616B (en)* | 2013-07-09 | 2016-08-10 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | Data transmission method under a kind of alternative working mode and device |
| CN103384385A (en)* | 2013-07-17 | 2013-11-06 | 三维通信股份有限公司 | Automatic antenna feed fault detection system for distributed antenna system |
| CN103379674B (en)* | 2013-07-24 | 2016-04-20 | 三维通信股份有限公司 | A kind of multimode numeral DAS system supporting multiple source to access |
| CN103379674A (en)* | 2013-07-24 | 2013-10-30 | 三维通信股份有限公司 | Multimode digital DAS supporting multi-information-source access |
| CN103475418A (en)* | 2013-10-10 | 2013-12-25 | 南京云恒瑞通网络科技有限责任公司 | Wireless-coverage active light distribution system and working method thereof |
| CN104703278A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Software-defined distributed wireless system and downlink data communication method thereof |
| CN104703285A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Software-defined distributed wireless system and uplink data communication method thereof |
| CN104703122A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Communication control method for software-defined distributed wireless system |
| CN104703279A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2015-06-10 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | Software-defined distributed wireless system |
| CN104703279B (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2018-08-07 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | A kind of distributed wireless system of software definition |
| CN104703278B (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2018-04-17 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | The distributed wireless system and its downlink data communication method of a kind of software definition |
| CN104703285B (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2018-04-17 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | The distributed wireless system and its upstream data communication method of a kind of software definition |
| CN104703122B (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2018-04-17 | 上海宽带技术及应用工程研究中心 | A kind of communication control method of the distributed wireless system of software definition |
| CN105430666A (en)* | 2015-11-02 | 2016-03-23 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | A cell access method and optical fiber distribution system |
| CN105430666B (en)* | 2015-11-02 | 2019-03-15 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | A method for cell access and optical fiber distribution system |
| CN106301923A (en)* | 2016-08-18 | 2017-01-04 | 上海肯汀通讯科技有限公司 | MDAS System Architecture |
| CN108243493A (en)* | 2016-12-26 | 2018-07-03 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A kind of device and method of antenna data packetizing transmission |
| CN107612714A (en)* | 2017-08-23 | 2018-01-19 | 武汉虹信通信技术有限责任公司 | A kind of automated topology structure realization method and system |
| CN107396390A (en)* | 2017-08-30 | 2017-11-24 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | A communication method, device and system |
| CN108834153A (en)* | 2018-09-27 | 2018-11-16 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | A kind of cell wireless coverage system and method |
| CN109474934A (en)* | 2018-11-02 | 2019-03-15 | 京信通信系统(中国)有限公司 | A base station system and base station capacity expansion method |
| CN109474934B (en)* | 2018-11-02 | 2021-12-14 | 京信网络系统股份有限公司 | A base station system and base station capacity expansion method |
| CN110049512A (en)* | 2019-04-22 | 2019-07-23 | 武汉虹信通信技术有限责任公司 | A kind of forward pass network data processing device and method |
| CN110049512B (en)* | 2019-04-22 | 2022-08-02 | 武汉虹信科技发展有限责任公司 | Forward-transmission network data processing device and method |
| CN110113762A (en)* | 2019-05-23 | 2019-08-09 | 江阴辰光通讯科技有限公司 | A method of it is wirelessly communicated for 5G network high-frequency section |
| CN115189784A (en)* | 2022-06-30 | 2022-10-14 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Delay-based processing method and device, electronic device, and storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102547716B (en) | 2015-06-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102547716B (en) | Wireless communication system and method for flat network architecture and extend unit | |
| CN102547778B (en) | Wireless communication system of flat network architecture, method and expansion unit | |
| CN110049512B (en) | Forward-transmission network data processing device and method | |
| CN107925471B (en) | Telecommunication system with distributed base station functionality | |
| CN101562900B (en) | System and method based on shared baseband pool and distributed radio frequency units | |
| CN104602200B (en) | A kind of fusion method of arrowband group service for timesharing long term evolution base station | |
| KR101472100B1 (en) | Base station apparatus and data processing method in wireless communication system | |
| CN101730279B (en) | Wireless local area network and 3G cellular network cooperative working method based on AP forwarding mechanism | |
| CN101686578B (en) | Family evolution base station system and access method of wireless device | |
| CN101309442B (en) | Wireless communication apparatus and data transmission method | |
| KR20160040595A (en) | Transmission and scheduling schemes for wireless fronthaul | |
| CN103199975B (en) | Associating base station system in a kind of distributed carrier aggregation multicell | |
| EP2652986A1 (en) | Mode switching | |
| US20160204974A1 (en) | Communications System, Control Apparatus, and Network Management Server | |
| JP2015525541A (en) | Method for realizing data transmission of convergence network, UE and 3GPP access network apparatus | |
| CN113543151A (en) | 4G/5G signal wireless coverage method | |
| CN104579479B (en) | Distributed base station system and E1 signal and Ethernet signal transmitting method thereof | |
| Artuso et al. | Cloudification of mmwave-based and packet-based fronthaul for future heterogeneous mobile networks | |
| CN102932849B (en) | Based on the wireless communication system of Femto framework, method and gateway subsystem | |
| CN101742695B (en) | Data transmission method, base station and data transmission system | |
| WO2009049496A1 (en) | Data interaction method, device and system in a base radio station | |
| CN101420260B (en) | Radio electric device node, distributed radio communication base station and communication method therefor | |
| CN109150592B (en) | System of LTE-D2D wireless private network | |
| CN116636284A (en) | IAB hierarchical DU resource configuration | |
| CN116456483A (en) | Wireless communication method, network node and equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right | Owner name:JINGXIN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM CO LTD (GUANGZHOU) Free format text:FORMER OWNER: COMBA TELECOM SYSTEMS (CHINA) CO., LTD. Effective date:20150821 | |
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20150821 Address after:510663 Guangdong city of Guangzhou province Guangzhou economic and Technological Development Zone Jinbi Road No. 6 Patentee after:Comba Telecom Systems (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd. Address before:510663 Guangzhou Science City, Guangdong Shenzhou Road, No. 10 Patentee before:Comba Telecom System (China) Co., Ltd. | |
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20200107 Address after:510663 No. 10, Shenzhou Road, Science City, Guangzhou, economic and Technological Development Zone, Huangpu District, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province Patentee after:Jingxin Communication System (China) Co., Ltd. Address before:510663, No. 6, Jin Lu, Guangzhou economic and Technological Development Zone, Guangdong, Guangzhou Patentee before:Jingxin Communication System (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd. | |
| CP01 | Change in the name or title of a patent holder | Address after:510663 No.10, Shenzhou Road, Guangzhou Science City, economic and Technological Development Zone, Huangpu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province Patentee after:Jingxin Network System Co.,Ltd. Address before:510663 No.10, Shenzhou Road, Guangzhou Science City, economic and Technological Development Zone, Huangpu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province Patentee before:Comba Telecom System (China) Ltd. | |
| CP01 | Change in the name or title of a patent holder |