CN102512161A - Intraoperative motor area function localization system based on cortex electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis - Google Patents
Intraoperative motor area function localization system based on cortex electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysisDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102512161A CN102512161ACN2011104291958ACN201110429195ACN102512161ACN 102512161 ACN102512161 ACN 102512161ACN 2011104291958 ACN2011104291958 ACN 2011104291958ACN 201110429195 ACN201110429195 ACN 201110429195ACN 102512161 ACN102512161 ACN 102512161A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- rhythm
- intraoperative
- motor
- system based
- electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000033764rhythmic processEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription55
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription22
- 230000004807localizationEffects0.000titleclaimsdescription21
- 230000001054cortical effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription35
- 210000004556brainAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription26
- 238000000354decomposition reactionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription20
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription18
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 230000003321amplificationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 238000003199nucleic acid amplification methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 210000003710cerebral cortexAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 230000033001locomotionEffects0.000claimsdescription15
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsdescription14
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-NplatinumChemical compound[Pt]BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000010410layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000002356single layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 229910052697platinumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000001914filtrationMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 210000001951dura materAnatomy0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000abstractdescription17
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000abstractdescription13
- 230000007659motor functionEffects0.000abstractdescription8
- 238000004422calculation algorithmMethods0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000003491arrayMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 238000007635classification algorithmMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000008569processEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000003902lesionEffects0.000description11
- 238000005070samplingMethods0.000description10
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000description9
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description7
- 206010015037epilepsyDiseases0.000description6
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description6
- 230000002739subcortical effectEffects0.000description6
- 206010028980NeoplasmDiseases0.000description5
- 230000003925brain functionEffects0.000description5
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description4
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description4
- 238000002566electrocorticographyMethods0.000description4
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description4
- 238000002271resectionMethods0.000description4
- 230000002269spontaneous effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000011282treatmentMethods0.000description3
- 208000001654Drug Resistant EpilepsyDiseases0.000description2
- 230000003920cognitive functionEffects0.000description2
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 238000003384imaging methodMethods0.000description2
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description2
- 238000002600positron emission tomographyMethods0.000description2
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description2
- 238000011895specific detectionMethods0.000description2
- 230000001052transient effectEffects0.000description2
- 208000022211Arteriovenous MalformationsDiseases0.000description1
- 208000003163Cavernous HemangiomaDiseases0.000description1
- 241001269524DuraSpecies0.000description1
- 206010027476MetastasesDiseases0.000description1
- 208000012902Nervous system diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 208000009443Vascular MalformationsDiseases0.000description1
- 230000005744arteriovenous malformationEffects0.000description1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description1
- 230000007321biological mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000036770blood supplyEffects0.000description1
- 210000005013brain tissueAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000003727cerebral blood flowEffects0.000description1
- 230000002490cerebral effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002591computed tomographyMethods0.000description1
- 238000013480data collectionMethods0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001037epileptic effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000003292glueSubstances0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 208000030173low grade gliomaDiseases0.000description1
- 238000002582magnetoencephalographyMethods0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001537neural effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002610neuroimagingMethods0.000description1
- 230000000926neurological effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007658neurological functionEffects0.000description1
- 210000002569neuronAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000008520organizationEffects0.000description1
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002980postoperative effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000004393prognosisMethods0.000description1
- 230000035807sensationEffects0.000description1
- 230000001953sensory effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002603single-photon emission computed tomographyMethods0.000description1
- 230000004083survival effectEffects0.000description1
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000008733traumaEffects0.000description1
- 238000004148unit processMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及医疗电子器械领域,具体涉及一种基于皮质脑电mu节律小波分析的术中运动区功能定位系统。The invention relates to the field of medical electronic equipment, in particular to an intraoperative motor zone function positioning system based on cortical EEG mu rhythm wavelet analysis.
背景技术Background technique
大脑功能区病变,主要指位于运动、感觉和语言区的肿瘤,血管畸形和癫痫灶,其发病率由世界卫生组织在我国组织的大规模的调查报告仅仅癫痫的患病率就有8‰,我国现有癫痫病人1000多万人,其中药物难治性癫痫占癫痫病人的30%左右,我国目前有300万的难治性癫痫病人需要手术治疗,这还不包括位于功能区的低级别胶质瘤,转移瘤,原发良性肿瘤,海绵状血管瘤和动静脉畸形等。大脑功能区病变不仅严重威胁人的生命,而且严重影响病人的生存和生活质量,同时造成的个人、社会和经济负担都是长久且巨大的,已成为严重的社会、经济和人文关怀问题。Lesions in functional areas of the brain mainly refer to tumors, vascular malformations, and epileptic foci located in the motor, sensory, and language areas. The prevalence of epilepsy alone is 8‰, according to a large-scale survey reportorganized by the World Health Organization in China. There are more than 10 million epilepsy patients in China, of which drug-refractory epilepsy accounts for about 30% of epilepsy patients. At present, 3 million intractable epilepsy patients in China need surgical treatment, which does not include low-grade glue located in functional areas. Tumors, metastases, primary benign tumors, cavernous hemangiomas, and arteriovenous malformations. Lesions in functional areas of the brain not only seriously threaten human life, but also seriously affect the survival and quality of life of patients. At the same time, they cause long-term and huge personal, social and economic burdens, and have become serious social, economic and humanistic care problems.
神经外科手术治疗是大脑功能区病变首选治疗方法之一,通过功能区定位确定大脑神经脑功能区边界, 帮助医生最大限度地切除病灶而控制肿瘤的生长和复发,同时尽可能地保护病灶周围的正常脑组织,避免神经功能损害,保留正常的神经功能,关系到病人术后的生存质量。如何术中准确实时“脑功能区”定位就是此类手术的关键。Neurosurgery is one of the first-choice treatments for lesions in the functional areas of the brain. The boundaries of the functional areas of the brain are determined through the positioning of the functional areas, helping doctors to maximize the removal of lesions and control the growth and recurrence of tumors, while protecting the surrounding areas of the lesions as much as possible. Normal brain tissue, avoiding neurological damage, and preserving normal neurological function are related to the quality of life of patients after surgery. How to locate the "brain function area" accurately and in real time during the operation is the key to this type of operation.
目前,神经皮质(运动区)功能定位的方法主要包括显微神经外科技术、神经影像技术、神经电生理技术等方法。At present, methods for functional localization of the neurocortex (motor area) mainly include microneurosurgery techniques, neuroimaging techniques, and neurophysiological techniques.
经典解剖功能定位对于临床医学具有重要意义,但有一定误差,由于个体差异及肿瘤的占位效应,引起功能区推移和重塑,经典解剖功能定位误差可达20mm。Classical anatomical function positioning is of great significance to clinical medicine, but there are certain errors. Due to individual differences and the mass effect of tumors, functional areas are shifted and reshaped, and the classic anatomical function positioning error can reach 20mm.
依靠影像技术的高分辨率螺旋CT及功能型磁共振(f-MRI),以及单光子发射计算机断层扫描(SPECT)、正电子发射计算机断层扫描(PET)、脑磁图(MEG)及手术导航系统多可以做到皮质生理解剖定位,但影像学方法存在一定假阳性,尚不能实时监测手术进程以及确定脑功能的状态。功能型磁共振(f-MRI)是依靠脑血流中血氧水平进行功能定位,病变影响脑皮层的血液供应会出现最大可达20mm的误差。正电子发射计算机断层扫描(PET)系统也可以对脑代谢活跃的区域进行定位,但是它与电生理刺激所显示的功能区,仅有65%的符合率。Relying on high-resolution spiral CT and functional magnetic resonance (f-MRI) imaging technology, as well as single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission computed tomography (PET), magnetoencephalography (MEG) and surgical navigation Most of the systems can achieve cortical physiological and anatomical positioning, but there are some false positives in imaging methods, and it is not yet possible to monitor the surgical process in real time and determine the state of brain function. Functional magnetic resonance (f-MRI) relies on the blood oxygen level in the cerebral blood flow for functional positioning, and the lesion affects the blood supply of the cerebral cortex, and there will be a maximum error of up to 20mm. The positron emission tomography (PET) system can also locate the metabolically active areas of the brain, but it has only a 65% coincidence rate with the functional areas shown by electrophysiological stimulation.
基于电生理技术的术中皮质或皮质下直接电刺激术可实时确定运动、感觉、语言甚至记忆等脑功能的皮质和皮质下功能区定位,是目前最准确、可信的常用脑功能区定位方法,基于电生理技术的术中皮质或皮质下直接电刺激术的精确度可达5 mm左右;但是存在电刺激可能损伤大脑皮质、触发癫痫和二次手术等问题,而且操作时间长达0.5至数小时。Intraoperative cortical or subcortical direct electrical stimulation based on electrophysiological technology can determine the location of cortical and subcortical functional areas of brain functions such as motor, sensation, language, and even memory in real time. It is currently the most accurate and reliable location of commonly used brain functional areas. Methods, the accuracy of intraoperative cortical or subcortical direct electrical stimulation based on electrophysiological technology can reach about 5 mm; however, there are problems such as electrical stimulation may damage the cerebral cortex, trigger epilepsy and secondary surgery, and the operation time is as long as 0.5 mm. to several hours.
上述功能区定位方法的缺陷已表现在神经外科手术治疗实践中,传统手术的功能定位技术不能完全分辨和掌握功能结构与病变的关系,极易在切除病灶时导致大脑功能结构损害,据统计传统手术的永久性神经功能损害并发症为13-27%。另外,由于功能区病变手术容易出现严重并发症,也使得手术医生手术切除不积极,常常进行姑息性切除,如低级别胶质瘤的完全切除和次全切除率仅为43%。这样不仅使病变术后治疗变得困难,而且容易造成疾病的复发或症状难以控制,严重影响治疗预后。The defects of the above-mentioned functional area positioning method have been manifested in the practice of neurosurgery. The traditional surgical functional positioning technology cannot fully distinguish and grasp the relationship between the functional structure and the lesion, and it is very easy to cause damage to the brain’s functional structure when the lesion is removed. According to statistics, traditional The permanent neurological impairment complication of surgery is 13-27%. In addition, severe complications are prone to occur in functional zone lesions, which also makes surgeons inactive in surgical resection and often performs palliative resection. For example, the complete resection and subtotal resection rate of low-grade gliomas are only 43%. This not only makes the postoperative treatment of the lesion difficult, but also easily causes the recurrence of the disease or the symptoms are difficult to control, which seriously affects the prognosis of the treatment.
由此可见,目前的神经皮质(运动区)功能定位方法在速度、准确和安全性方面不能完全满足脑功能区手术需要。如何能在术中准确、快速、无创,甚至非唤醒状态下定位脑功能区是一直困扰临床和神经医学研究的基础理论问题,亟待解决。It can be seen that the current neurocortical (motor area) function localization method cannot fully meet the needs of brain functional area surgery in terms of speed, accuracy and safety. How to locate brain functional areas accurately, quickly, non-invasively, and even in a non-awakened state is a basic theoretical problem that has plagued clinical and neuromedical research and needs to be resolved urgently.
目前国内外尚未见有一种基于皮质脑电mu节律小波分析的术中运动区功能定位系统的报道;同时,国内外也尚无在临床上应用的基于皮质脑电mu节律小波分析的术中运动区功能定位系统。因此研发具有自主知识产权的基于皮质脑电mu节律小波分析的术中运动区功能定位系统,实现准确、快速、无创的脑运动区功能定位,将帮助医生最大限度地切除病灶,同时尽可能地保护正常脑功能,提高患者术后生存质量,对未来大脑外科手术具有重大的应用价值。同时,为下一步皮质脑电定位高级认知功能皮质的生物机理科学研究提供新的技术方法手段,对未来大脑高级认知功能科学研究具有重大意义。具有巨大的社会和经济效应前景。At present, there is no report of an intraoperative motor area function localization system based on cortical EEG mu rhythm wavelet analysis at home and abroad; at the same time, there is no clinical application of intraoperative motor function localization system based on cortical EEG mu rhythm wavelet analysis at home and abroad. District function positioning system. Therefore, the development of an intraoperative motor area function positioning system based on cortical EEG mu rhythm wavelet analysis with independent intellectual property rights to achieve accurate, fast, and non-invasive brain motor area function positioning will help doctors to remove lesions to the greatest extent and at the same time Protecting normal brain function and improving the quality of life of patients after surgery has great application value for future brain surgery. At the same time, it provides new technical methods for the next step of cortical EEG localization of the biological mechanism of the cortex of advanced cognitive functions, which is of great significance to the scientific research of advanced cognitive functions of the brain in the future. Has a huge social and economic effect prospect.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于针对现有技术的缺陷,以运动区特异性脑电mu节律为原理,结合小波变换,公开一种基于皮质脑电mu节律小波分析的术中运动区功能定位系统。该系统能够准确、快速、无创地检测运动功能区脑电信号输入,并完成脑运动区功能定位图的输出,通过脑运动区皮质脑电信号mu节律的特异性分析,实现人体神经系统大脑皮质运动区功能定位的准确、快速、无创临床应用。The purpose of the present invention is to aim at the defects of the prior art, based on the principle of motor area specific EEG mu rhythm, combined with wavelet transform, to disclose an intraoperative motor area function positioning system based on cortical EEG mu rhythm wavelet analysis. The system can accurately, quickly and non-invasively detect the input of EEG signals in the motor function area, and complete the output of the functional location map of the brain motor area. Accurate, rapid and non-invasive clinical application of motor zone function localization.
mu 节律是大脑的感觉运动区皮质的特异性脑电节律,肢体的真实运动或想象运动会在感觉运动皮层区域引起mu 和beta节律的事件相关去同步化(ERD)和事件相关同步化(ERS),而且不同肢体运动的ERD/ERS 在皮质运动区上的空间分布也符合躯体特定区域分布的特征。因此,通过检测皮质运动功能区中存在着的特异性脑电mu 节律,及其在肢体运动时产生的ERD/ERS 在皮质上的空间分布,可以静态和动态检测定位皮质运动功能区的空间分布。小波变换具有多分辨特性,利用 Mallat的分解与重构快速算法可以从运动区脑电中提取出mu节律,为运动区特异性脑电信号mu 节律检测提供了有力工具。The mu rhythm is a specific EEG rhythm in the sensorimotor cortex of the brain. The real or imagined movement of the limbs will cause the event-related desynchronization (ERD) and event-related synchronization (ERS) of the mu and beta rhythms in the sensorimotor cortex. , and the spatial distribution of ERD/ERS in different limb movements on the cortical motor area also conforms to the characteristics of the distribution of specific regions of the body. Therefore, by detecting the specific EEG mu rhythm in the cortical motor function area and the spatial distribution of the ERD/ERS generated during limb movement, the spatial distribution of the cortical motor function area can be detected statically and dynamically . Wavelet transform has multi-resolution characteristics, and the mu rhythm can be extracted from the motor area EEG by using Mallat's decomposition and reconstruction fast algorithm, which provides a powerful tool for the mu rhythm detection of the motor area-specific EEG signal.
基于上述原理,本发明所采用的技术方案如下所述:Based on above-mentioned principle, the technical scheme that the present invention adopts is as follows:
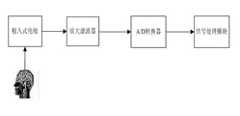
一种基于皮质脑电mu节律小波分析的术中运动区功能定位系统,包括脑电信号采集模块,信号处理模块,功能定位地图输出模块,所述信号处理模块包括脑电信号预处理单元、mu节律特征提取单元和模式分类单元;脑电信号采集模块采集的脑电信号,经由脑电信号预处理单元进行预处理滤波,传送至mu节律特征提取单元提取特异性mu节律特征,再通过模式分类单元进行分类,最后通过功能区定位地图输出模块反馈定位结果。An intraoperative motor zone function positioning system based on cortical EEG mu rhythm wavelet analysis, comprising an EEG signal acquisition module, a signal processing module, and a function localization map output module, the signal processing module including an EEG signal preprocessing unit, a mu Rhythm feature extraction unit and pattern classification unit; the EEG signals collected by the EEG signal acquisition module are preprocessed and filtered by the EEG signal preprocessing unit, and then sent to the mu rhythm feature extraction unit to extract specific mu rhythm features, and then pass pattern classification The units are classified, and finally the positioning results are fed back through the functional area positioning map output module.
所述脑电信号采集模块包括植入式电极、放大滤波器和A/D 转换器,植入式电极采集脑电信号,经由放大滤波器进行放大滤波处理,然后通过A/D转换器将脑电信号转换为数字信号,最后输入到信号处理模块。The EEG signal acquisition module includes implantable electrodes, amplification filters and A/D converters, the implantable electrodes collect EEG signals, amplifies and filters through the amplification filters, and then converts the brain signals through the A/D converters. The electrical signal is converted into a digital signal and finally input to the signal processing module.
所述植入式电极为硬膜铂电极,包括铂6*8或8*8电极阵列,电极直径为4mm,相邻电极间距为10mm。植入式电极安放在人的大脑皮质上。放大滤波器和A/D 转换器采用Synamps2 放大器,用于电极检测信号的放大和数字化。The implantable electrode is a dura mater platinum electrode, including a platinum 6*8 or 8*8 electrode array, the electrode diameter is 4mm, and the distance between adjacent electrodes is 10mm. Implantable electrodes are placed on the human cerebral cortex. Amplification filter and A/D converter adopt Synamps2 amplifier for amplification and digitization of electrode detection signal.
所述脑电信号预处理单元的预处理滤波包括多尺度分解。所述多尺度分解利用离散db3小波变换进行7层小波分解,采用的小波Mallat 算法的分解和重构算法见公式(3)。所述mu节律特征提取单元提取d6单层细节系数,然后进行全点数重构,其重构后的信号Sd6作为mu节律输出。所述模式分类单元以40%为特征阈值对mu节律进行是/否分类,识别特异性电极。The preprocessing filtering of the EEG signal preprocessing unit includes multi-scale decomposition. The multi-scale decomposition uses discrete db3 wavelet transform to perform 7-layer wavelet decomposition, and the decomposition and reconstruction algorithm of the wavelet Mallat algorithm used is shown in formula (3). The mu rhythm feature extraction unit extracts d6 single-layer detail coefficients, and then performs full-point reconstruction, and the reconstructed signal Sd6 is output as mu rhythm. The pattern classification unit performs yes/no classification on the mu rhythm with 40% as the characteristic threshold, and identifies specific electrodes.
(3); (3);
其中,H、G为时域中的小波分解滤波器,h、g为时域中的小波重构滤波器;t为离散时间序列,t=1,2,……,N;j为分解层数,j=1,2,……,J,J为分解深度,f(t)为原始信号。aj为f (t)在第j层近似部分的小波系数;dj为f(t)在第j层细节部分的小波系数。Among them,H ,G are wavelet decomposition filters in time domain,h ,g are wavelet reconstruction filters in time domain; t is discrete time series,t =1, 2,...,N ;j is decomposition layer number,j =1, 2,...,J ,J is the decomposition depth,f (t ) is the original signal.aj is the wavelet coefficient of the approximation part off (t ) in thejth layer;dj is the wavelet coefficient of the detail part off (t ) in thejth layer.
重构各单子频带信号时,只提取单层近似或细节系数,其余系数置0,然后对该单层系数进行全点数重构。重构信号特征量(运动事件发生前后ERD时间内能量比ERD)的计算见公式(4)。When reconstructing each single sub-band signal, only the single-layer approximation or detail coefficients are extracted, and the remaining coefficients are set to 0, and then the single-layer coefficients are reconstructed with all points. The calculation of the reconstructed signal feature quantity (the energy ratio ERD within the ERD time before and after the motion event) is calculated in formula (4).
(4) (4)
其中,ER为运动事件前ERD时间窗口内的各子频带重构信号的每个采样点值的平方和,EA为计算运动事件后ERD时间窗口内的各子频带重构信号的每个采样点值的平方和。Among them, ER is the sum of the squares of each sampling point value of each sub-band reconstructed signal in the ERD time window before the motion event, and EA is the calculation of each sub-band reconstructed signal in the ERD time window after the motion event. Each sampling point The sum of squares of the value.
所述功能区定位地图输出模块输出的运动特异性功能区定位图,是以模式分类单元识别的特异性电极坐标为边界点拟合边界曲线,即:运动特异性功能区定位图,闭合曲线围成的区域为运动特异性功能区。The motion-specific functional area positioning map output by the functional area positioning map output module uses the specific electrode coordinates identified by the pattern classification unit as boundary points to fit the boundary curve, that is: the motion-specific functional area positioning map, and the closed curve surrounds The resulting area is a motor-specific functional area.
本发明相对现有技术具有如下优点和效果:The present invention has following advantage and effect relative to prior art:
(1)特异性检出正确率高:本发明基于运动功能区mu节律的事件ERD特异性,选择了合理的特征频带、特征值,以及特征提取和分类算法具有可靠的检测原理,从根本上保证了特异性检出正确率,其特异性检出正确率达到78%-100%。(1) High specificity detection accuracy rate: the present invention is based on the event ERD specificity of mu rhythm in the motor functional area, selects reasonable characteristic frequency bands and characteristic values, and has reliable detection principles for feature extraction and classification algorithms, fundamentally The correct rate of specific detection is guaranteed, and the correct rate of specific detection reaches 78%-100%.
(2)电极检测精度高:系统采用的电极具有4mm直径和10mm的植入式电极间距离,具有较高的空间和频率分辨率,能提供电极中心点附近5mm半径范围内神经元的电活动信息。特征阈值的实质是在电极中心点附近5mm半径范围内检测到的最小有效特征量。因此计算本系统的定位空间微观精确度可达5 mm。与术中皮质或皮质下直接电刺激术相比,本系统进一步提高了检测精确度。(2) High accuracy of electrode detection: The electrodes used in the system have a diameter of 4mm and an implanted electrode distance of 10mm, which has high spatial and frequency resolution and can provide electrical activity of neurons within a radius of 5mm near the center of the electrode. information. The essence of the feature threshold is the minimum effective feature detected within a radius of 5mm near the center point of the electrode. Therefore, the microcosmic accuracy of the positioning space of the calculation system can reach 5 mm. Compared with intraoperative cortical or subcortical direct electrical stimulation, this system further improves the detection accuracy.
(3)检测速度快:本系统以自发脑电mu节律为运动功能区的特异性脑电为检测对象,自发脑电mu节律的ERD的采样实验周期和时间窗口为4秒,因此,理论上采样速度为4秒。考虑可靠性采用10次采样实验结果共同判断的方法,再加上计算机处理的时间,本系统一次功能定位检测时间为60秒。与术中皮质或皮质下直接电刺激术操作时间长达0.5至数小时相比,本系统极大提高了检测速度,极大减少了医生手术时间和病人的痛苦,节省巨大的人力和物力,具有良好的经济和人文关怀价值。(3) Fast detection speed: This system takes the specific EEG of the motor function area as the spontaneous EEG mu rhythm as the detection object, and the sampling experiment period and time window of the ERD of the spontaneous EEG mu rhythm are 4 seconds. Therefore, in theory The sampling rate is 4 seconds. Considering the reliability, the method of judging the results of 10 sampling experiments together, plus the time of computer processing, the system's one-time function positioning detection time is 60 seconds. Compared with the intraoperative cortical or subcortical direct electrical stimulation, which takes 0.5 to several hours, this system greatly improves the detection speed, greatly reduces the doctor's operation time and the patient's pain, and saves huge manpower and material resources. It has good economic and humanistic care value.
(4)检测无创性:本系统提取自发脑电mu节律采用脑电信号的被动检测方式,无主动刺激造成的创伤。避免了术中皮质或皮质下直接电刺激术可能损伤大脑皮质、触发癫痫等问题。极大减少了医生手术时间和病人的痛苦,节省巨大的人力和物力,具有良好的经济和人文关怀价值。(4) Non-invasive detection: The system extracts spontaneous EEG mu rhythm using the passive detection method of EEG signals without trauma caused by active stimulation. It avoids problems such as cortical or subcortical direct electrical stimulation that may damage the cerebral cortex and trigger epilepsy. It greatly reduces the doctor's operation time and the patient's pain, saves huge manpower and material resources, and has good economic and humanistic care value.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为运动区脑功能定位系统结构图。Figure 1 is a structural diagram of the brain function localization system in the motor area.
图2为脑电信号采集系统模块结构图。Figure 2 is a block diagram of the EEG signal acquisition system.
图3为原始信号的小波分解与重构。Figure 3 shows the wavelet decomposition and reconstruction of the original signal.
图4为原始信号的小波变换滤波。Figure 4 shows the wavelet transform filtering of the original signal.
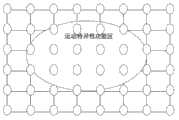
图5为运动特异性功能区定位图。Figure 5 is a map of the location of motor-specific functional areas.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
以下结合附图和实施例对本发明作进一步说明,但本发明的实施不限于此。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, but the implementation of the present invention is not limited thereto.
一种基于皮质脑电mu节律小波分析的术中运动区功能定位系统,如图1所示,包括脑电信号采集模块,信号处理模块,功能区定位地图输出模块,信号处理模块包括脑电信号预处理单元、mu节律特征提取单元和模式分类单元。脑电信号采集模块的组成如图2所示,包括植入式电极、放大滤波器和A/D 转换器。该系统通过植入式电极的硬膜下电极阵列采集皮质脑电信号ECoG,经由放大滤波器进行放大滤波处理,然后通过A/D转换器将脑电信号转换为数字信号,再输入到信号处理模块;信号处理模块的脑电信号预处理单元通过小波分析的分解与重构算法,对各电极采集的数据进行预处理滤波,传送至mu节律特征提取单元提取特异性mu节律特征,再通过模式分类单元进行分类,最后通过功能区定位地图输出模块完成功能区定位图处理输出。An intraoperative motor area function positioning system based on cortical EEG mu rhythm wavelet analysis, as shown in Figure 1, includes an EEG signal acquisition module, a signal processing module, and a function area positioning map output module, and the signal processing module includes EEG signal Preprocessing unit, mu rhythm feature extraction unit and pattern classification unit. The composition of the EEG signal acquisition module is shown in Figure 2, including implanted electrodes, amplification filters and A/D converters. The system collects ECoG cortical EEG signals through the subdural electrode array of implanted electrodes, amplifies and filters them through the amplification filter, and then converts the EEG signals into digital signals through the A/D converter, and then inputs them into the signal processing. Module; the EEG signal preprocessing unit of the signal processing module preprocesses and filters the data collected by each electrode through the decomposition and reconstruction algorithm of wavelet analysis, and sends it to the mu rhythm feature extraction unit to extract specific mu rhythm features, and then passes the pattern The classification unit performs classification, and finally completes the processing and output of the functional area positioning map through the functional area positioning map output module.
在每位病人的大脑皮质上安放硬膜下电极阵列提取ECoG数据,为病人植入硬膜铂6*8或8*8电极阵列(subdural electrode arrays (Ad-Tech, Racine, WI), 每个电极直径为4mm,相邻电极间的距离为10mm;Synamps2放大器(Neuroscan,ElPaso,TX)用于电极检测信号的放大和数字化,ECoG数据采样率为1000Hz,通过0.05-200Hz通带滤波。A subdural electrode array was placed on the cerebral cortex of each patient to extract ECoG data, and the patient was implanted with dura platinum 6*8 or 8*8 electrode arrays (subdural electrode arrays (Ad-Tech, Racine, WI), each The electrode diameter is 4mm, and the distance between adjacent electrodes is 10mm; Synamps2 amplifier (Neuroscan, ElPaso, TX) is used to amplify and digitize the electrode detection signal, and the ECoG data sampling rate is 1000Hz, which is filtered by 0.05-200Hz passband.
信号处理模块由综合计算机处理系统提供,向病人提供运动指示并储存指示时间,接收并储存Synamps2 放大器的脑电信号数据。The signal processing module is provided by a comprehensive computer processing system, which provides motion instructions to the patient and stores the instruction time, and receives and stores the EEG signal data of the Synamps2 amplifier.
每次实验时,根据计算机显示屏的“运动—休息”指示,病人先运动手指2秒,然后休息2秒;再重复多次上述相同实验。采集位于大脑神经皮质运动功能区的特定皮质区域ECoG数据,共进行10次采集数据,用于计算机系统的处理工作。During each experiment, according to the "exercise-rest" instruction on the computer screen, the patient first moved his finger for 2 seconds, and then rested for 2 seconds; then repeated the same experiment many times. The ECoG data of a specific cortical area located in the motor function area of the cerebral neurocortex was collected, and a total of 10 data collections were performed for the processing of the computer system.
根据mu节律和工频干扰的频带确定分解层次:本发明所研究的脑电信号包含mu节律(8 - 12 Hz)、一些瞬变信号以及工频干扰(50 Hz),经表1频带频率计算公式确定分解层次为7。Decomposition levels are determined according to the frequency bands of mu rhythm and power frequency interference: the EEG signals studied in this invention include mu rhythm (8-12 Hz), some transient signals and power frequency interference (50 Hz), calculated by the frequency bands in Table 1 The formula determines that the decomposition level is 7.
表1:各单子频带重构信号的ERD指标特征值Table 1: ERD indicator eigenvalues of reconstructed signals in each single frequency band
脑电信号与处理单元利用小波变换的多分辨率特性,将含有噪声的脑电信号进行多尺度分解,得到不同频带的子带信号。具体如下:将单次试验带有背景噪声的原始皮层脑电数据输入matlab软件应用程序,利用离散db3小波变换进行七层小波分解,结果见图3。图中横坐标表示时间,单位是采样点数(采样频率为 1000Hz),纵轴表示幅度,单位为μV。横坐标的零时刻对应实验开始的时刻。d1-d7是尺度1-6上小波分解的细节信号,a6是尺度6上的小波分解的逼近信号。The EEG signal and processing unit uses the multi-resolution characteristics of wavelet transform to decompose the noise-containing EEG signal on multiple scales to obtain sub-band signals of different frequency bands. The details are as follows: Input the original cortical EEG data with background noise in a single test into the Matlab software application program, and use the discrete db3 wavelet transform to perform seven-layer wavelet decomposition. The results are shown in Figure 3. The abscissa in the figure represents time, and the unit is the number of sampling points (the sampling frequency is 1000Hz), and the vertical axis represents the amplitude, and the unit is μV. The zero time of the abscissa corresponds to the start time of the experiment. d1-d7 are the detail signals of the wavelet decomposition on scales 1-6, and a6 is the approximation signal of the wavelet decomposition on scale 6.
mu节律特征提取单元对含有噪声的频带进行处理,然后重构去除工频干扰等噪声后的脑电信号,并提取出mu节律运动区特异性脑电信号。具体如下:提取出mu节律(频率范围8-12 Hz),只提取d6(频率范围7.812-15.625 Hz)单层细节系数,其余系数置0,然后对该单层系数进行全点数重构,其重构信号Sd6作为mu节律输出,见图4。同时,消除了工频干扰等噪声和其他一些瞬变干扰信号。图中横坐标表示时间,单位是采样点数(采样频率为1000Hz),纵轴表示幅度,单位为μV。横坐标的零时刻对应实验开始的时刻。The mu rhythm feature extraction unit processes the frequency band containing noise, and then reconstructs the EEG signal after removing noise such as power frequency interference, and extracts the specific EEG signal of the mu rhythm motor area. The details are as follows: extract the mu rhythm (frequency range 8-12 Hz), only extract the d6 (frequency range 7.812-15.625 Hz) single-layer detail coefficients, and set the other coefficients to 0, and then reconstruct the single-layer coefficients with full points. The reconstructed signal Sd6 is output as the mu rhythm, see Figure 4. At the same time, noise such as power frequency interference and other transient interference signals are eliminated. The abscissa in the figure represents time, and the unit is the number of sampling points (the sampling frequency is 1000Hz), and the vertical axis represents the amplitude, and the unit is μV. The zero time of the abscissa corresponds to the start time of the experiment.
模式分类单元根据运动区脑电的特异性mu节律特征,以d6(7.812~15.625 Hz)特征频带重构信号的ERD/ERS指标为特征值,以40%为特征阈值进行“是/否”分类,识别各电极的特异性属性。The pattern classification unit uses the ERD/ERS index of the reconstructed signal in the d6 (7.812-15.625 Hz) characteristic frequency band as the characteristic value and 40% as the characteristic threshold to classify "yes/no" according to the specific mu rhythm characteristics of the EEG in the motor area , identifying the specific properties of each electrode.
运动特异性功能区定位图输出模块以硬膜下电极阵列的结构形成坐标系,以全部48个特异性电极的坐标为边界点拟合边界曲线,形成闭合曲线图就是输出地运动特异性功能区定位图,闭合曲线内围成的区域为运动特异性功能区,如图5所示。应用于医学临床手术功能区定位时,与其它方法(如皮质电刺激法等)配合二次功能区定位,确定运动特异性功能区的边界,形成最后的精确运动功能区定位图。根据mu节律特征提取与分类的结果,实现脑运动功能区定位图输出。The output module of the positioning map of the motion-specific functional area uses the structure of the subdural electrode array to form a coordinate system, and uses the coordinates of all 48 specific electrodes as boundary points to fit the boundary curve to form a closed curve map, which is the output motion-specific functional area In the positioning map, the area enclosed by the closed curve is the movement-specific functional area, as shown in Figure 5. When applied to the positioning of functional areas in medical clinical operations, it can be combined with other methods (such as cortical electrical stimulation, etc.) for secondary functional area positioning to determine the boundaries of motor-specific functional areas and form the final precise positioning map of motor functional areas. According to the results of mu rhythm feature extraction and classification, the brain motor function area localization map output is realized.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011104291958ACN102512161A (en) | 2011-12-20 | 2011-12-20 | Intraoperative motor area function localization system based on cortex electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011104291958ACN102512161A (en) | 2011-12-20 | 2011-12-20 | Intraoperative motor area function localization system based on cortex electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102512161Atrue CN102512161A (en) | 2012-06-27 |
Family
ID=46283460
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011104291958APendingCN102512161A (en) | 2011-12-20 | 2011-12-20 | Intraoperative motor area function localization system based on cortex electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102512161A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106725463A (en)* | 2017-01-18 | 2017-05-31 | 浙江大学 | Using the method and system that Cortical ECoG signal is positioned to cerebral cortex hand function area |
| CN109284659A (en)* | 2017-07-22 | 2019-01-29 | 上海谷米实业有限公司 | A kind of positioning of mobile object is rectified a deviation and the method for noise filtering |
| CN109875555A (en)* | 2019-03-05 | 2019-06-14 | 浙江中医药大学 | A kind of non-invasive electroencephalogram recording electrode and its manufacturing method |
| CN116595321A (en)* | 2023-06-01 | 2023-08-15 | 北京航空航天大学 | A Method for Separating the Rhythm of Magnetic Brain Signal Based on Genetic Algorithm and Wavelet Transform |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5638826A (en)* | 1995-06-01 | 1997-06-17 | Health Research, Inc. | Communication method and system using brain waves for multidimensional control |
| WO2009051638A1 (en)* | 2007-10-16 | 2009-04-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Therapy control based on a patient movement state |
| CN101980106A (en)* | 2010-10-15 | 2011-02-23 | 华南理工大学 | A two-dimensional cursor control method and device for a brain-computer interface |
| CN202397464U (en)* | 2011-12-20 | 2012-08-29 | 华南理工大学 | Intraoperative motion area functional localization system based on cortical electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis |
- 2011
- 2011-12-20CNCN2011104291958Apatent/CN102512161A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5638826A (en)* | 1995-06-01 | 1997-06-17 | Health Research, Inc. | Communication method and system using brain waves for multidimensional control |
| WO2009051638A1 (en)* | 2007-10-16 | 2009-04-23 | Medtronic, Inc. | Therapy control based on a patient movement state |
| CN101980106A (en)* | 2010-10-15 | 2011-02-23 | 华南理工大学 | A two-dimensional cursor control method and device for a brain-computer interface |
| CN202397464U (en)* | 2011-12-20 | 2012-08-29 | 华南理工大学 | Intraoperative motion area functional localization system based on cortical electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 姜涛: "基于皮质脑电的脑运动区功能定位原理与算法研究", 《中国博士学位论文全文数据库 医药卫生科技辑》* |
| 黄思娟 等: "基于Mu/Beta节律想象运动脑电信号特征的提取", 《中国组织工程研究与临床康复》* |
| 黄思娟 等: "基于能量特征的脑电信号特征提取与分类", 《传感技术学报》* |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106725463A (en)* | 2017-01-18 | 2017-05-31 | 浙江大学 | Using the method and system that Cortical ECoG signal is positioned to cerebral cortex hand function area |
| CN106725463B (en)* | 2017-01-18 | 2020-02-21 | 浙江大学 | Method and system for localization of hand functional area in cerebral cortex using cortical EEG signals |
| CN109284659A (en)* | 2017-07-22 | 2019-01-29 | 上海谷米实业有限公司 | A kind of positioning of mobile object is rectified a deviation and the method for noise filtering |
| CN109875555A (en)* | 2019-03-05 | 2019-06-14 | 浙江中医药大学 | A kind of non-invasive electroencephalogram recording electrode and its manufacturing method |
| CN116595321A (en)* | 2023-06-01 | 2023-08-15 | 北京航空航天大学 | A Method for Separating the Rhythm of Magnetic Brain Signal Based on Genetic Algorithm and Wavelet Transform |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN105520732B (en) | For assessing the method and Portable Automatic brain function assessment equipment of brain function | |
| Jiang et al. | An automatic analysis method for detecting and eliminating ECG artifacts in EEG | |
| US9826914B2 (en) | Functional analysis of neurophysiological data | |
| Manshanden et al. | Source localization of MEG sleep spindles and the relation to sources of alpha band rhythms | |
| EP2575608B1 (en) | Detector for identifying physiological artifacts from physiological signals and method | |
| CN102429658A (en) | Intraoperative motion area function locating system based on electroencephalogram slow cortex potential wavelet analysis | |
| Turnip et al. | An application of modified filter algorithm fetal electrocardiogram signals with various subjects | |
| CN102512162A (en) | Intraoperative motor area function localization system based on multi-mode electroencephalogram wavelet analysis | |
| CN102512161A (en) | Intraoperative motor area function localization system based on cortex electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis | |
| Brazdzionis et al. | A swine model of changes in the neuronal electromagnetic field after traumatic brain injury: a pilot study | |
| CN202397462U (en) | Intraoperative motor area function positioning system based on brain wave slow cortical potential (SCP) wavelet analysis | |
| CN202397463U (en) | Intra-operative motor area function positioning system based on multi-mode electroencephalogram wavelet analysis | |
| CN202397464U (en) | Intraoperative motion area functional localization system based on cortical electroencephalogram mu rhythm wavelet analysis | |
| CN114081507B (en) | Method and system for locating brain functional areas combined with spectral clustering and event correlation detection | |
| CN116746880A (en) | Stimulation parameter modulation sleep curative effect evaluation method and device based on cerebral cortex brain power supply | |
| Brázdil et al. | Interhemispheric EEG coherence after corpus callosotomy | |
| Kim et al. | Study of biosignal response during acupuncture points stimulations | |
| Ye-Lin et al. | Combined method for reduction of high frequency interferences in surface electroenterogram (EEnG) | |
| CN114983441B (en) | Brain wave forward induction feedback regulation system | |
| Kose et al. | A Review on Biomedical Signals with Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing | |
| Jiang et al. | Functional localization of the cortical motor area in the brain based on wavelet analysis of slow cortical potential | |
| Swaminathan et al. | Analysis of ECG signal processing for smart medical technologies | |
| Kumar et al. | EEG signal processing for monitoring depth of anesthesia | |
| CN107811635A (en) | A kind of health status sorting technique and device based on physiology signal | |
| Wilson et al. | Discrete wavelet analysis of the auditory brainstem response: Effects of subject age, gender and test ear |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20120627 |