CN102499759A - Multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgery - Google Patents
Multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgeryDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102499759A CN102499759ACN2011103384851ACN201110338485ACN102499759ACN 102499759 ACN102499759 ACN 102499759ACN 2011103384851 ACN2011103384851 ACN 2011103384851ACN 201110338485 ACN201110338485 ACN 201110338485ACN 102499759 ACN102499759 ACN 102499759A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- freedom
- degree
- arm
- joint
- degrees
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Manipulator (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种医疗手术器械,具体涉及的是一种用于腹腔微创手术的多自由度的机械手。The invention relates to a medical operation instrument, in particular to a multi-degree-of-freedom manipulator used for abdominal minimally invasive surgery.
背景技术Background technique
为了避免传统的腹腔开腹手术带来的创口大、失血多、脏器暴露于空气中的危险,目前的腹腔微创手术通常要在腹腔开三个孔径为8mm左右孔。不过对于手术精度要求和康复角度来说,三个孔对病人的康复甚至手术后美观等方面还会有很大影响。因此,单孔腹腔镜手术受到了广泛的关注。In order to avoid the risk of large wounds, blood loss, and exposure of organs to the air brought about by traditional abdominal laparotomy, the current minimally invasive abdominal surgery usually requires three holes with a diameter of about 8 mm in the abdominal cavity. However, in terms of surgical accuracy requirements and rehabilitation perspective, the three holes will have a great impact on the patient's rehabilitation and even post-operative aesthetics. Therefore, single-port laparoscopic surgery has received extensive attention.
经对现有技术的文献检索发现,发明专利201110007611.5(公开日2011-04-27,公开号102028548A)发明了一种腹腔微创手术机器人用夹钳式手术器械,以解决现有腹腔微创手术机器人左指和右指的多余运动得不到补偿,导致驱动左指和右指的钢丝易拉断的问题。After searching the literature of the prior art, it was found that the invention patent 201110007611.5 (publication date 2011-04-27, publication number 102028548A) invented a clamp-type surgical instrument for a minimally invasive abdominal surgery robot to solve the problem of the existing minimally invasive abdominal surgery. The redundant movement of the left and right fingers of the robot cannot be compensated, resulting in the problem that the steel wires driving the left and right fingers are easily broken.
国外发明专利PCT/KR2010/007314(SURGICAL INSTRUMENT ANDADAPTER FOR SINGLE PORT SURGERY)发明了一种外科手术仪器,用管形轴在纵向方向延伸,为制成更薄的仪器结构提供了一种方法。The foreign invention patent PCT/KR2010/007314 (SURGICAL INSTRUMENT ANDADAPTER FOR SINGLE PORT SURGERY) invented a surgical instrument, which extends in the longitudinal direction with a tubular shaft, providing a method for making a thinner instrument structure.
检索中还发现,根据姜海军等在《中国微创外科杂志》2010年第10卷第1期上发表的“单孔腹腔镜手术进展与未来”和徐大华在《腹腔镜外科杂志》2010年1月第15卷第1期发表的“单孔腹腔镜手术器械的研发与应用”,现有的腹腔镜手术仍存在如下缺点:During the search, it was also found that according to Jiang Haijun et al.’s “Progress and Future of Single-port Laparoscopic Surgery” published in “Chinese Journal of Minimally Invasive Surgery”, Vol. In the "Development and Application of Single-port Laparoscopic Surgical Instruments" published in Issue 1 of Volume 15 of July, the existing laparoscopic surgery still has the following shortcomings:
1)在单孔条件下,所有器械都几乎平行进入病人腹腔内完成手术,无法形成医师习惯的三角形的操作空间,使得器械间容易造成干涉,加大了操作的难度;1) Under the condition of a single hole, all the instruments are almost parallel to enter the patient's abdominal cavity to complete the operation, and it is impossible to form a triangular operating space that doctors are accustomed to, which makes it easy to cause interference between instruments and increases the difficulty of operation;
2)现有最尖端的微创手术机器人在进行复杂手术时需要在病人身上定位并开三个创口实施手术,如此一来对病人的康复以及日后皮肤的美观都有很大影响;2) The existing cutting-edge minimally invasive surgical robot needs to locate and open three wounds on the patient when performing complex operations, which will have a great impact on the patient's recovery and the appearance of the skin in the future;
3)借助电子摄像设备代替人眼使手术视野失去三维真实视觉,使医师对距离和位置的判断产生困难;3) With the help of electronic camera equipment instead of human eyes, the surgical field of view loses three-dimensional real vision, making it difficult for doctors to judge distance and position;
4)为了使手术过程更接近于传统的手术,通常需要研制专用器械,如多通道、可变形的穿刺套管等,使成本增高。4) In order to make the operation process closer to the traditional operation, it is usually necessary to develop special instruments, such as multi-channel, deformable puncture cannula, etc., which increases the cost.
腹腔镜器械是由众多复杂的高科技器械所组成的一整套医疗仪器设备,包括光源、气腹机,动力系统、摄录像系统、麻醉机、监护仪以及手术工具等。多自由度单孔腹腔微创手术机器人是基于腹腔镜器械手术工具的改进,它是用机械臂代替原来的手工操作。在实际应用中,单孔腹腔镜手术中必需的仪器是是开口器。开口器是一个带有多个操作孔道的套管。Laparoscopic instruments are a complete set of medical instruments and equipment composed of many complex high-tech instruments, including light sources, insufflation machines, power systems, video recording systems, anesthesia machines, monitors, and surgical tools. The multi-degree-of-freedom single-hole minimally invasive abdominal surgery robot is based on the improvement of laparoscopic instruments and surgical tools. It uses a mechanical arm to replace the original manual operation. In practical application, the necessary instrument in single-port laparoscopic surgery is a gag. The gag is a sleeve with multiple operating channels.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于针对上述现有技术中的不足,提出了一种单孔操作的多自由度机构,即多自由度单创孔腹腔微创手术机器人灵巧手,可以置入开口器中的一个12mm直径的孔道,以代替原先人工操作的手术刀,从而改进手术的可操作性和精确度。The object of the present invention is to address the deficiencies in the above-mentioned prior art, and propose a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanism for single-hole operation, that is, the dexterous hand of the multi-degree-of-freedom single-hole minimally invasive surgery robot, which can be placed in one of the gags. 12mm diameter hole to replace the original manually operated scalpel, thereby improving the operability and accuracy of the operation.
本发明是通过如下技术方案实现的,本发明包括:两个末端安装手术刀的7自由度的机械手臂,一个末端安装摄像头的5自由度的机械手臂。The present invention is realized through the following technical solutions. The present invention includes: two robotic arms with 7 degrees of freedom installed with scalpels at the ends, and a robotic arm with 5 degrees of freedom installed at the ends with a camera.
所述7自由度的机械手臂,所述7个自由度从根部算起,依次为:绕手臂中心轴旋转自由度、手臂前后伸缩自由度、水平摆动自由度、竖直摆动自由度、水平摆动自由度、竖直摆动自由度、工具自由度,从根部算起第二个自由度后,五个自由度都在开口器内部(即人体内)完成,每个自由度都由一根钢丝控制。手臂在开口器内部有5个自由度,整条手臂处于伸直状态时,由靠近开口器处算起,分别为连续两个关节、第一手臂、第三关节、第二手臂、第四关节、可更换的专用工具。每两个相邻关节间形成的自由度方向空间垂直。所述7自由度的机械手臂完全伸直时长度约为70mm,每个摆动自由度关节的摆角可达180°加上整个手臂在开口器外部的旋转和伸缩自由度,整个手臂的工作空间可以达到现今医用腹腔手术的要求。For the mechanical arm with 7 degrees of freedom, the 7 degrees of freedom are counted from the root, and they are: the degree of freedom of rotation around the central axis of the arm, the degree of freedom of the arm's front and rear telescopic movement, the degree of freedom of horizontal swing, the degree of freedom of vertical swing, and the degree of freedom of horizontal swing Degree of freedom, vertical swing degree of freedom, tool degree of freedom, after the second degree of freedom counted from the root, the five degrees of freedom are all completed inside the opener (that is, inside the human body), and each degree of freedom is controlled by a steel wire . The arm has 5 degrees of freedom inside the opener. When the whole arm is in a straight state, counting from the position close to the opener, there are two consecutive joints, the first arm, the third joint, the second arm, and the fourth joint. , Replaceable special tools. The degree of freedom direction space formed between every two adjacent joints is vertical. The length of the mechanical arm with 7 degrees of freedom is about 70mm when it is fully extended, and the swing angle of each swing degree of freedom joint can reach 180°. It can meet the requirements of today's medical abdominal surgery.
所述5自由度的机械手臂,工作时与开口器接触的末端手臂有前后伸缩和绕手臂中心线旋转2个自由度,深入开口器内部,从根部开始有3个平面摆动自由度,前端为摄像头。手臂在开口器内部有3个自由度,整条手臂处于伸直状态时,由靠近开口器处算起,分别为第五关节和第六关节、第三手臂、第七关节、第四手臂、摄像头。每两个相邻关节间形成的自由度方向空间垂直。所述5自由度的机械手臂完全伸直时长度约为55mm,每个摆动自由度关节的摆角可达180°,加上整个手臂在开口器外部的旋转和伸缩自由度,整个手臂的工作空间可以达到手术中的视野要求。The mechanical arm with 5 degrees of freedom, the end arm in contact with the opener has 2 degrees of freedom for front and back expansion and rotation around the center line of the arm during work, and goes deep into the inside of the opener. There are 3 plane swing degrees of freedom from the root, and the front end is Camera. The arm has 3 degrees of freedom inside the opener. When the whole arm is in a straight state, counting from the position close to the opener, they are the fifth joint and the sixth joint, the third arm, the seventh joint, the fourth arm, Camera. The degree of freedom direction space formed between every two adjacent joints is vertical. The length of the mechanical arm with 5 degrees of freedom is about 55mm when it is fully extended, and the swing angle of each swing degree of freedom joint can reach 180°, plus the rotation and telescopic degrees of freedom of the entire arm outside the opener, the working of the entire arm The space can meet the visual field requirements in the operation.
所述7自由度的机械手臂和所述5自由度的机械手臂,它们包含的每个关节结构相同,主要由根部零件和摆动零件组成,根部零件和摆动零件之间由刚性轴连接,主传动钢丝从根部零件中穿入,带动摆动零件中的主滑轮。钢丝拉紧后,摆动零件便可绕刚性轴摆动,两零件间相互摆动形成摆动自由度。由于每条7自由度的机械手臂在开口器内部部分有5个自由度,故需要5组钢丝,这样靠近末端的关节零件中,就会穿入靠近前端关节零件传动所需的钢丝,为了保证钢丝之间不形成干涉,并且在末端关节摆动时前端钢丝仍为收紧状态,所以在根部零件和摆动零件中各装入两个小滑轮组。滑轮组用来使前端自由度传动的钢丝沿滑轮位置穿过关节,两排滑轮位置与关节传动主轴相切以保证各个关节的摆动对其他关节的钢丝传动没有影响。随着关节逐步靠近机械臂前端,每个滑轮组上的小滑轮将以1个为单位,整个关节的小滑轮数量将以4个为单位,逐步递减,随着滑轮的减少,滑轮原有的位置将由垫片来取代。The 7-DOF robotic arm and the 5-DOF robotic arm have the same structure of each joint, mainly composed of a root part and a swing part, the root part and the swing part are connected by a rigid shaft, and the main drive The steel wire passes through the root part and drives the main pulley in the swing part. After the steel wire is tensioned, the swinging part can swing around the rigid axis, and the two parts swing with each other to form a swinging degree of freedom. Since each mechanical arm with 7 degrees of freedom has 5 degrees of freedom in the inner part of the opener, 5 sets of steel wires are required, so that the joint parts near the end will penetrate the steel wires required for the transmission of the joint parts near the front end, in order to ensure No interference is formed between the steel wires, and the front end steel wire is still in a tightened state when the end joint is swinging, so two small pulley blocks are respectively loaded into the root part and the swing part. The pulley block is used to make the steel wire of the front-end degree of freedom transmission pass through the joint along the position of the pulley, and the position of the two rows of pulleys is tangent to the main shaft of the joint transmission to ensure that the swing of each joint has no influence on the transmission of the steel wire of other joints. As the joints gradually approach the front end of the mechanical arm, the number of small pulleys on each pulley block will be 1, and the number of small pulleys in the entire joint will be 4, gradually decreasing. With the reduction of the pulleys, the original position of the pulleys Will be replaced by spacers.
上述的机械手臂为钢丝传动方式,每个自由度都由钢丝来负责传动操控,在外部手术台架上设有驱动钢丝的电机盒,每台电机对应一根钢丝。The above-mentioned mechanical arm is driven by steel wires, and each degree of freedom is controlled by steel wires. A motor box for driving the steel wires is installed on the external operating table, and each motor corresponds to a steel wire.
本发明在工作时,首先,在开口器中插入本发明的末端机构,即三个机械手臂,在机械手臂伸入病人体内后,由电机驱动钢丝旋转带动机械手臂,实现机械手臂的姿态变换。另外,5自由的机械手臂是用于观察体内情况的,因此,通过变换其不同的姿态以达到不同角度的立体视角,方便医师诊断病情和实施手术。When the present invention is working, at first, insert the terminal mechanism of the present invention into the gag, that is, three mechanical arms. After the mechanical arms are inserted into the patient's body, the motor drives the steel wire to rotate and drive the mechanical arms to realize the posture transformation of the mechanical arms. In addition, the 5 free mechanical arms are used to observe the internal conditions, therefore, by changing their different postures to achieve different angles of stereoscopic viewing angles, it is convenient for doctors to diagnose diseases and perform operations.
综上,本发明机器人能够实现切割、拉扯、缝线等手术操作来替代原始的手工操作,其主要驱动方式是通过电机带动钢丝,再由钢丝拉动末端构件来实现姿态的变换和末端手术刀的操作。In summary, the robot of the present invention can perform surgical operations such as cutting, pulling, and suturing to replace the original manual operation. Its main driving mode is to drive the steel wire through the motor, and then pull the end member by the steel wire to realize the transformation of posture and the operation of the end scalpel. operate.
与现有技术相比,本发明有如下特点和有益效果:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following characteristics and beneficial effects:
(1)近乎全自动的手术操作,除更换手术刀具时需要人工升降电机控制台架,其余手术过程全部可在PC上进行操控。(1) Nearly fully automatic surgical operation, except for the need to manually lift the motor control frame when replacing surgical knives, the rest of the surgical process can be controlled on the PC.
(2)实现单创口手术,最大创口直径也只有12mm,除此以外无需在病人身体上再开任何创口。(2) Single-incision surgery is realized, and the maximum incision diameter is only 12mm, and there is no need to open any incision on the patient's body.
(3)多自由度灵活操作,在单创口中同时伸入三支直径各为5mm的机器手臂,其中两支工具手臂各自包含7个自由度,第三支摄像头手臂包含5个自由度,三支手臂可以到达人体胸腹腔内工作空间位置。(3) Flexible operation with multiple degrees of freedom. Three robotic arms with a diameter of 5mm are inserted into the single wound at the same time. Two of the tool arms each contain 7 degrees of freedom, and the third camera arm contains 5 degrees of freedom. The supporting arm can reach the position of the working space in the thorax and abdominal cavity of the human body.
(4)手术工具更换,两支7自由度手臂上的工具可在手术中按需求更换,以便增强手术的便捷性、多样性等。(4) Replacement of surgical tools. The tools on the two 7-DOF arms can be replaced as needed during the operation, so as to enhance the convenience and diversity of the operation.
附图说明Description of drawings
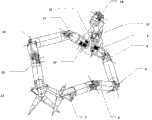
图1是本发明的前端机械臂工具手臂部分自由度分配示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the distribution of degrees of freedom of the tool arm of the front-end mechanical arm of the present invention;
图2是本发明的前端机械臂摄像头手臂部分自由度分配示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the distribution of degrees of freedom of the camera arm of the front-end robotic arm of the present invention;
图3是本发明的前端机械手臂装配总成图;Fig. 3 is an assembly assembly diagram of the front-end mechanical arm of the present invention;
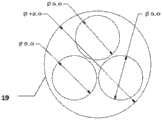
图4是本发明的腹腔开口器孔径分配图;Fig. 4 is an aperture distribution diagram of the abdominal cavity gag of the present invention;
图5是本发明的摆动自由度关节结构原理及钢丝走线图。Fig. 5 is a structural principle of the swing degree of freedom joint and a wire routing diagram of the present invention.
图中:绕轴旋转自由度关节1、8,伸缩自由度关节2、9,开口器内部两支手臂共8个摆动自由度3、4、5、6、10、11、12、13,前端工具关节7、14,开口器外部的旋转自由度15、伸缩自由度16,患者体内手臂根部的摆动自由度17、18,开口器19,前端关节传回钢丝20,关节传动钢丝绳21,小滑轮组20、22、23、24、25,根部关节26,前端关节27。In the figure: joints 1 and 8 for rotational degrees of freedom around the axis, joints 2 and 9 for telescopic degrees of freedom, and a total of 8 swing degrees of freedom for the two arms inside the
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图对本发明的实施例作详细说明:本实施例在以本发明技术方案为前提下进行实施,给出了详细的实施方式和具体的操作过程,但本发明的保护范围不限于下述的实施例。The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings: this embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following the described embodiment.
如图1、2所示,本实施例包括:两个末端安装手术刀的7自由度的机械手臂,一个末端安装摄像头的5自由度的机械手臂。每个自由度均由钢丝绳拉动。这三个手臂设置在同一个升降平台上。当然,在实际使用的时候还可以根据需要进行安放。As shown in Figures 1 and 2, this embodiment includes: two mechanical arms with 7 degrees of freedom with a scalpel installed at the ends, and a robotic arm with 5 degrees of freedom with a camera installed at the end. Each degree of freedom is pulled by a wire rope. These three arms are set on the same lifting platform. Of course, it can also be placed as needed during actual use.
如图1所示,所述7自由度的机械手臂,为圆柱形塑料手臂、不锈钢关节和几个专用工具构成,另包括钢丝、滑轮关节等。两只手臂各自的7个自由度从根部算起,分别为:绕手臂中心轴旋转自由度1和8、手臂前后伸缩自由度2和9、水平摆动自由度3和10、竖直摆动自由度4和11、水平摆动自由度5和12、竖直摆动自由度6和13、工具自由度7和14。As shown in Fig. 1, the mechanical arm with 7 degrees of freedom is composed of a cylindrical plastic arm, stainless steel joints and several special tools, and also includes steel wires, pulley joints and the like. The 7 degrees of freedom of the two arms are counted from the root, respectively: 1 and 8 degrees of freedom of rotation around the central axis of the arm, 2 and 9 degrees of freedom of the front and back stretching of the arm, 3 and 10 degrees of freedom of horizontal swing, and 3 and 10 degrees of freedom of
本实施例中,所述7自由度的机械手臂,每个关节为一个自由度,每个自由度都由一根钢丝控制。手臂在开口器内部有5个自由度,整条手臂处于伸直状态时,由靠近开口器处算起,分别为连续两个长度为8mm的关节、长度为15mm的塑料手臂、8mm的关节、13mm的塑料手臂、8mm的关节、可更换的专用工具。每两个相邻关节间形成的自由度方向空间垂直。手臂完全伸直时长度约为70mm,每个摆动自由度关节的摆角可达180°,加上手臂在开口器外部的旋转和伸缩自由度,手臂的工作空间可以达到现今医用腹腔手术的要求。In this embodiment, for the mechanical arm with 7 degrees of freedom, each joint is a degree of freedom, and each degree of freedom is controlled by a steel wire. The arm has 5 degrees of freedom inside the opener. When the whole arm is in a straight state, counting from the position close to the opener, there are two consecutive joints with a length of 8mm, a plastic arm with a length of 15mm, a joint with 8mm, 13mm plastic arms, 8mm joints, and replaceable special tools. The degree of freedom direction space formed between every two adjacent joints is vertical. When the arm is fully straightened, the length is about 70mm, and the swing angle of each swing degree of freedom joint can reach 180°, plus the degree of freedom of rotation and expansion of the arm outside the gag, the working space of the arm can meet the requirements of today's medical abdominal surgery .
前端工具关节7、14包含1个自由度,由钢丝绳带动实现闭合。根部手臂的伸缩自由度关节2、9和绕轴旋转自由度关节1、8在开口器的外部实现,通过电机带动钢丝绳实现伸缩旋转运动。The front
如图2所示,所述5自由度的机械手臂,由圆柱形塑料手臂、不锈钢关节和摄像头构成,另包括钢丝、滑轮关节等。工作时与开口器接触的末端手臂有前后伸缩和绕手臂中心线旋转2个自由度,深入开口器内部,从根部开始有3个平面摆动自由度,前端为直径5mm的摄像头装置。As shown in Fig. 2, the mechanical arm with 5 degrees of freedom is composed of a cylindrical plastic arm, stainless steel joints and a camera, and also includes steel wires, pulley joints and the like. The end arm that is in contact with the opener has 2 degrees of freedom of forward and backward expansion and rotation around the center line of the arm. It penetrates into the opener and has 3 plane swing degrees of freedom from the root. The front end is a camera device with a diameter of 5mm.
本实施例中,所述5自由度的机械手臂在开口器内部有3个自由度,整条手臂处于伸直状态时,由靠近开口器处算起,分别为连续两个长度为8mm的关节、长度为15mm的塑料手臂、8mm的关节、8mm的塑料手臂、摄像头。每两个相邻关节间形成的自由度方向空间垂直。手臂完全伸直时长度约为55mm,每个摆动自由度关节的摆角可达180°,加上手臂在开口器外部的旋转和伸缩自由度,手臂的工作空间可以达手术中的视野要求。In this embodiment, the robotic arm with 5 degrees of freedom has 3 degrees of freedom inside the opener. When the whole arm is in a straight state, counting from the position close to the opener, there are two consecutive joints with a length of 8 mm. , a plastic arm with a length of 15mm, a joint of 8mm, a plastic arm of 8mm, and a camera. The degree of freedom direction space formed between every two adjacent joints is vertical. The length of the arm is about 55mm when it is fully extended, and the swing angle of each swing degree of freedom joint can reach 180°. In addition to the degree of freedom of rotation and expansion of the arm outside the gag, the working space of the arm can meet the requirements of the field of view during surgery.
开口镜外部操作结果与图1手臂相同,内部两个摆动自由度的操作也与机械手臂相同,前端为5mm的摄像头使手术室随时观测情况。The external operation result of the open mirror is the same as that of the arm in Figure 1, and the operation of the two internal swing degrees of freedom is also the same as that of the mechanical arm. The 5mm camera at the front allows the operating room to observe the situation at any time.
本实施例中,上述的7自由度的机械手臂和所述5自由度的机械手臂,它们包含的每个关节结构相同,主要由根部零件和摆动零件组成,根部零件和摆动零件之间由刚性轴连接,主传动钢丝从根部零件中穿入,带动摆动零件中的主滑轮。钢丝拉紧后,摆动零件便可绕刚性轴摆动,两零件间相互摆动形成摆动自由度。In this embodiment, the mechanical arm with 7 degrees of freedom and the mechanical arm with 5 degrees of freedom mentioned above have the same structure of each joint, mainly composed of root parts and swing parts. The shaft is connected, and the main drive steel wire passes through the root part to drive the main pulley in the swing part. After the steel wire is tensioned, the swinging part can swing around the rigid axis, and the two parts swing with each other to form a swinging degree of freedom.
由于机械手臂的设计受工作环境所制约,每只手臂的最大外径只有5mm,为了实现每支机械臂各个自由度的操控,选择钢丝传动方式,每个自由度都由钢丝来负责传动操控,在外部手术台架上会附有驱动钢丝的电机盒,每台电机对应一根钢丝,机械臂部分加起来共有17个自由度,故需配备17台电机。Since the design of the robot arm is restricted by the working environment, the maximum outer diameter of each arm is only 5mm. In order to realize the control of each degree of freedom of each robot arm, the steel wire transmission mode is selected, and each degree of freedom is controlled by the steel wire. A motor box for driving steel wires is attached to the external operating table. Each motor corresponds to a steel wire. The mechanical arm has 17 degrees of freedom in total, so 17 motors are required.
如图4所示,本实施例使用的腹腔开口器孔径分配,是基于一个直径为12mm的开口器上均布3个直径为5mm的小孔,用来插入三支机械手臂。工作时会往开口器内部充气,使人体腹腔内形成合适的工作空间。As shown in Figure 4, the aperture distribution of the abdominal cavity gag used in this embodiment is based on the fact that three small holes with a diameter of 5 mm are uniformly distributed on a gag with a diameter of 12 mm for inserting three robotic arms. When working, it will inflate the inside of the gag to form a suitable working space in the abdominal cavity of the human body.
如图5所示,开口器内部每支手臂的4个摆动自由度通过滑轮关节来实现,由钢丝绳21从靠根部关节26伸出,套过靠近前端关节27上的滑轮,钢丝拉紧后,拉动钢丝便可使前端关节与后端关节间形成摆动自由度。对于靠近末端的关节而言,关节中会穿入的前端零件摆动所需的钢丝组20,把钢丝组20以此套在小滑轮组22、23、24、25上,由于小滑轮组和摆动轴之间相切(也可以近似相切),所以钢丝之间不形成干涉,并且在末端关节摆动时前端钢丝仍为收紧状态,如此实现了摆动自由度的钢丝传动。As shown in Figure 5, the 4 swing degrees of freedom of each arm inside the opener are realized by the pulley joints. The
利用上述手臂进行操作过程中,三只手臂全部处于伸平状态,将每只手臂末端扣在前端控制机构(即上述驱动电机、滑轮组、牵引钢丝等组成的)上,准备工作完毕,调整手术台架位置、高度,再调整三只手臂的角度,对准已经在肚脐位置安置的开口器19,手动操作将安置三只手臂的小升降台向下滑动,使三只机械手臂沿开口器上三个口插入患者体内。先通过开口器外部的旋转自由度15、伸缩自由度16以及患者体内手臂根部的摆动自由度17、18来调整手臂使其确定大致的手术位置,然后依从末端至前端的顺序逐一调节各自由度使摄像头、两只操作手臂精确达到手术操作点,一只手臂负责抓取,一只手臂负责工具操作,进行手术。In the process of using the above-mentioned arms for operation, all three arms are in a flat state, and the end of each arm is buckled on the front-end control mechanism (that is, the above-mentioned drive motor, pulley block, traction wire, etc.), and the preparation work is completed. Adjust the operating platform position, height, and then adjust the angles of the three arms to align with the
手术中涉及更换刀具的时候,需将该手臂调节成伸直状态,随前端控制机构上电机盒一并抽出,进行刀具的更换。When the operation involves changing the knives, the arm needs to be adjusted to a straight state, and the motor box on the front control mechanism is pulled out together to replace the knives.
本实施例中,两支7自由度的机械工具手臂和一支5自由度的摄像头手臂,操作时共同通过一个在病人身体脐部、直径12mm的圆形开口器进入病人体内,由一直手臂上摄像头抓取的视频来进行观测,三手臂能够实现180°摆动以到达各种工作点,三只手臂全部由电机带动钢丝操作,电机控制端将连接PC,整个手术过程可在PC上操作完成。In this embodiment, two mechanical tool arms with 7 degrees of freedom and a camera arm with 5 degrees of freedom enter into the patient's body through a circular mouthpiece with a diameter of 12 mm at the navel of the patient's body during operation. The video captured by the camera is used for observation. The three arms can swing 180° to reach various working points. The three arms are all driven by motors with steel wires. The motor control end will be connected to the PC. The entire operation process can be completed on the PC.
综上,本发明能实现单创口,以实现美观、低感染风险。全自动化操作,手术过程中除更换刀具外,无需人工操作。机械手臂进入开口器后展开,器械之间基本没有干涉,保证操作安全可靠。To sum up, the present invention can achieve a single wound to achieve aesthetic appearance and low risk of infection. Fully automatic operation, no manual operation is required except for changing the knife during the operation. After the mechanical arm enters the opener, it unfolds, and there is basically no interference between the instruments, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
尽管本发明的内容已经通过上述优选实施例作了详细介绍,但应当认识到上述的描述不应被认为是对本发明的限制。在本领域技术人员阅读了上述内容后,对于本发明的多种修改和替代都将是显而易见的。因此,本发明的保护范围应由所附的权利要求来限定。Although the content of the present invention has been described in detail through the above preferred embodiments, it should be understood that the above description should not be considered as limiting the present invention. Various modifications and alterations to the present invention will become apparent to those skilled in the art upon reading the above disclosure. Therefore, the protection scope of the present invention should be defined by the appended claims.
Claims (8)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011103384851ACN102499759B (en) | 2011-10-31 | 2011-10-31 | Multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgery |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011103384851ACN102499759B (en) | 2011-10-31 | 2011-10-31 | Multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgery |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102499759Atrue CN102499759A (en) | 2012-06-20 |
| CN102499759B CN102499759B (en) | 2013-11-20 |
Family
ID=46211938
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011103384851AExpired - Fee RelatedCN102499759B (en) | 2011-10-31 | 2011-10-31 | Multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgery |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102499759B (en) |
Cited By (55)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103006329A (en)* | 2012-12-03 | 2013-04-03 | 上海交通大学 | Multi-joint single-wound abdominal cavity minimally-invasive surgery robot and operating mechanism thereof |
| CN103519772A (en)* | 2013-10-29 | 2014-01-22 | 上海交通大学 | Single-port laparoscopic imaging system for minimally invasive surgery |
| CN103536364A (en)* | 2013-10-18 | 2014-01-29 | 江苏艾迪尔医疗科技股份有限公司 | Intelligent orthopaedic system |
| CN103948435A (en)* | 2014-05-15 | 2014-07-30 | 上海交通大学 | Single-port laparoscopy minimally invasive surgery robot system |
| CN104490477A (en)* | 2014-12-29 | 2015-04-08 | 天津大学 | Multi-degree-of-freedom single-incision surgical robot for laparoscopic surgery |
| CN104758059A (en)* | 2015-04-07 | 2015-07-08 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Wrist threading barrel for multi-degree-of-freedom flexible robot for single-incision laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery |
| CN105361951A (en)* | 2015-12-14 | 2016-03-02 | 山东科技大学 | Endoscope-holding robot for minimally invasive abdominal operation |
| CN105455902A (en)* | 2015-11-23 | 2016-04-06 | 微创(上海)医疗机器人有限公司 | Wrist of robot and surgical robot |
| CN105963017A (en)* | 2016-04-12 | 2016-09-28 | 浙江大学 | Spatial multi-degree-of-freedom surgery assisting arm mechanism |
| CN106377316A (en)* | 2016-09-18 | 2017-02-08 | 上海交通大学 | Thyroid minimally invasive surgery operation equipment |
| CN106901835A (en)* | 2017-03-15 | 2017-06-30 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A kind of main hand of five degree of freedom with position retaining function |
| CN107536642A (en)* | 2017-08-24 | 2018-01-05 | 胡荣 | A kind of multiple degrees of freedom multifunction surgical manipulator |
| CN107708597A (en)* | 2015-07-09 | 2018-02-16 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Operation robot |
| CN108175511A (en)* | 2018-02-26 | 2018-06-19 | 路要武 | A kind of single-hole laparoscopic robot system |
| CN108309455A (en)* | 2018-02-26 | 2018-07-24 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of surgical instrument with running fix joint for single hole operating robot |
| CN108366836A (en)* | 2015-10-16 | 2018-08-03 | 医疗显微器具股份公司 | Operation tool |
| CN108391416A (en)* | 2015-12-11 | 2018-08-10 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Surgical system |
| CN108420533A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2018-08-21 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | With mobile and rotation positioning joint single hole operating robot integral layout structure |
| CN108433811A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2018-08-24 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of integral layout structure of the single hole operating robot with rotation positioning joint |
| CN108433812A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2018-08-24 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of integral layout structure of the single hole operating robot with running fix joint |
| CN108524002A (en)* | 2018-03-02 | 2018-09-14 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of mechanically decoupled single hole surgical robot quick replacement mechanism with linear joint |
| CN108567487A (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2018-09-25 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | With adjustable link from operation equipment and operating robot |
| CN108814713A (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2018-11-16 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | Minimally Invasive Surgery motion arm, from operation equipment and operating robot |
| CN108836480A (en)* | 2014-04-22 | 2018-11-20 | 香港生物医学工程有限公司 | Surgical device |
| CN108839047A (en)* | 2018-03-28 | 2018-11-20 | 江苏求恒医疗器械有限公司 | A kind of Medical instrument fixture with clamp device |
| CN108882969A (en)* | 2016-04-15 | 2018-11-23 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Surgical system |
| CN108969106A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2018-12-11 | 微创(上海)医疗机器人有限公司 | Telescopic device and operating robot |
| CN109330697A (en)* | 2018-07-31 | 2019-02-15 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | Minimally Invasive Surgery is from operation apparatus assembly and operating robot |
| CN109567943A (en)* | 2016-11-01 | 2019-04-05 | 香港生物医学工程有限公司 | Surgical system for performing intracorporeal surgical procedures |
| CN109715081A (en)* | 2016-05-18 | 2019-05-03 | 虚拟切割有限公司 | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| CN109770966A (en)* | 2019-01-23 | 2019-05-21 | 吉林大学 | A multi-degree-of-freedom integrated single-port endoscopic surgical instrument |
| CN110063791A (en)* | 2014-08-13 | 2019-07-30 | 柯惠Lp公司 | The clamping with mechanical dominance of robot control |
| CN110522517A (en)* | 2019-09-16 | 2019-12-03 | 西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院 | A robotic arm for minimally invasive surgery in a single-port laparoscopic environment |
| CN111407411A (en)* | 2020-03-27 | 2020-07-14 | 南京航空航天大学 | A micro manipulator system and its control method |
| CN111991084A (en)* | 2020-10-08 | 2020-11-27 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | Surgical robot, virtual imaging control method thereof and virtual imaging control device thereof |
| CN112638316A (en)* | 2020-11-24 | 2021-04-09 | 曹庆恒 | Oral cavity robot and using method thereof |
| CN113440258A (en)* | 2021-07-12 | 2021-09-28 | 曹庆恒 | Ear-nose robot and using method thereof |
| CN113855287A (en)* | 2021-07-06 | 2021-12-31 | 上海优医基医疗影像设备有限公司 | Oral implant surgical robot with implant precision evaluation function and control method |
| US11246614B2 (en) | 2014-08-13 | 2022-02-15 | Covidien Lp | Robotically controlling mechanical advantage gripping |
| CN114271948A (en)* | 2021-12-07 | 2022-04-05 | 南京航空航天大学 | A compact single-hole surgical robot from the hand |
| CN114851245A (en)* | 2022-04-15 | 2022-08-05 | 郑州大学 | A kind of robot telescopic swing mechanism and bionic robot |
| CN116725693A (en)* | 2023-07-13 | 2023-09-12 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | Six-degree-of-freedom wire transmission micro manipulator with analytic inverse solution and operation triangle |
| US11819299B2 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2023-11-21 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Single site robotic device and related systems and methods |
| US11826032B2 (en) | 2013-07-17 | 2023-11-28 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
| US11832902B2 (en) | 2012-08-08 | 2023-12-05 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| US11872090B2 (en) | 2015-08-03 | 2024-01-16 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| US11909576B2 (en) | 2011-07-11 | 2024-02-20 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| US11903658B2 (en) | 2019-01-07 | 2024-02-20 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotically assisted surgical system and related devices and methods |
| US11950867B2 (en) | 2018-01-05 | 2024-04-09 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Single-arm robotic device with compact joint design and related systems and methods |
| US11974824B2 (en) | 2017-09-27 | 2024-05-07 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices with tracking camera technology and related systems and methods |
| US12070282B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2024-08-27 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Methods, systems, and devices relating to force control surgical systems |
| US12096999B2 (en) | 2014-11-11 | 2024-09-24 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic device with compact joint design and related systems and methods |
| US12156710B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2024-12-03 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
| US12274517B2 (en) | 2016-08-30 | 2025-04-15 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic device with compact joint design and an additional degree of freedom and related systems and methods |
| US12295680B2 (en) | 2012-08-08 | 2025-05-13 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050272977A1 (en)* | 2004-04-14 | 2005-12-08 | Usgi Medical Inc. | Methods and apparatus for performing endoluminal procedures |
| CN101500470A (en)* | 2006-06-13 | 2009-08-05 | 直观外科手术公司 | Minimally invasive surgery system |
| CN102186396A (en)* | 2008-08-14 | 2011-09-14 | M.S.T.医疗手术技术有限公司 | N DOF Laparoscopic Operating System |
- 2011
- 2011-10-31CNCN2011103384851Apatent/CN102499759B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050272977A1 (en)* | 2004-04-14 | 2005-12-08 | Usgi Medical Inc. | Methods and apparatus for performing endoluminal procedures |
| CN101500470A (en)* | 2006-06-13 | 2009-08-05 | 直观外科手术公司 | Minimally invasive surgery system |
| CN102186396A (en)* | 2008-08-14 | 2011-09-14 | M.S.T.医疗手术技术有限公司 | N DOF Laparoscopic Operating System |
Cited By (83)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11909576B2 (en) | 2011-07-11 | 2024-02-20 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| US12323289B2 (en) | 2011-07-11 | 2025-06-03 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| US12156710B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2024-12-03 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
| US11819299B2 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2023-11-21 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Single site robotic device and related systems and methods |
| US12171512B2 (en) | 2012-05-01 | 2024-12-24 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Single site robotic device and related systems and methods |
| US12295680B2 (en) | 2012-08-08 | 2025-05-13 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
| US11832902B2 (en) | 2012-08-08 | 2023-12-05 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| CN103006329A (en)* | 2012-12-03 | 2013-04-03 | 上海交通大学 | Multi-joint single-wound abdominal cavity minimally-invasive surgery robot and operating mechanism thereof |
| US12070282B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2024-08-27 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Methods, systems, and devices relating to force control surgical systems |
| US11826032B2 (en) | 2013-07-17 | 2023-11-28 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
| CN103536364A (en)* | 2013-10-18 | 2014-01-29 | 江苏艾迪尔医疗科技股份有限公司 | Intelligent orthopaedic system |
| CN103519772B (en)* | 2013-10-29 | 2016-03-16 | 上海交通大学 | Single-port laparoscopic minimally-invasive surgery imaging system |
| CN103519772A (en)* | 2013-10-29 | 2014-01-22 | 上海交通大学 | Single-port laparoscopic imaging system for minimally invasive surgery |
| CN108836480A (en)* | 2014-04-22 | 2018-11-20 | 香港生物医学工程有限公司 | Surgical device |
| CN103948435B (en)* | 2014-05-15 | 2016-04-13 | 上海交通大学 | Single-port laparoscopic minimally-invasive surgery robot system |
| CN103948435A (en)* | 2014-05-15 | 2014-07-30 | 上海交通大学 | Single-port laparoscopy minimally invasive surgery robot system |
| CN110063791B (en)* | 2014-08-13 | 2022-04-15 | 柯惠Lp公司 | Robotically controlled clamping with mechanical advantage |
| US11246614B2 (en) | 2014-08-13 | 2022-02-15 | Covidien Lp | Robotically controlling mechanical advantage gripping |
| CN110063791A (en)* | 2014-08-13 | 2019-07-30 | 柯惠Lp公司 | The clamping with mechanical dominance of robot control |
| US11957371B2 (en) | 2014-08-13 | 2024-04-16 | Covidien Lp | Robotically controlling mechanical advantage gripping |
| US12096999B2 (en) | 2014-11-11 | 2024-09-24 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic device with compact joint design and related systems and methods |
| CN104490477A (en)* | 2014-12-29 | 2015-04-08 | 天津大学 | Multi-degree-of-freedom single-incision surgical robot for laparoscopic surgery |
| CN104758059B (en)* | 2015-04-07 | 2017-03-01 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | The multiple degrees of freedom flexible robot of single hole abdominal-cavity minimal-invasion surgery wrist threading bucket |
| CN104758059A (en)* | 2015-04-07 | 2015-07-08 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Wrist threading barrel for multi-degree-of-freedom flexible robot for single-incision laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery |
| CN107708597A (en)* | 2015-07-09 | 2018-02-16 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Operation robot |
| CN107708597B (en)* | 2015-07-09 | 2021-02-05 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Robot for operation |
| US11872090B2 (en) | 2015-08-03 | 2024-01-16 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| CN108366836A (en)* | 2015-10-16 | 2018-08-03 | 医疗显微器具股份公司 | Operation tool |
| CN108366836B (en)* | 2015-10-16 | 2021-08-27 | 医疗显微器具股份公司 | Surgical tool |
| CN105455902A (en)* | 2015-11-23 | 2016-04-06 | 微创(上海)医疗机器人有限公司 | Wrist of robot and surgical robot |
| CN108391416A (en)* | 2015-12-11 | 2018-08-10 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Surgical system |
| CN105361951A (en)* | 2015-12-14 | 2016-03-02 | 山东科技大学 | Endoscope-holding robot for minimally invasive abdominal operation |
| CN105361951B (en)* | 2015-12-14 | 2017-11-14 | 山东科技大学 | A kind of minimally invasive abdominal operation Chi Jing robots |
| CN105963017B (en)* | 2016-04-12 | 2018-08-24 | 浙江大学 | A kind of space multiple degrees of freedom operation nondominant hand arm mechanism |
| CN105963017A (en)* | 2016-04-12 | 2016-09-28 | 浙江大学 | Spatial multi-degree-of-freedom surgery assisting arm mechanism |
| CN108882969B (en)* | 2016-04-15 | 2021-07-06 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | surgical system |
| CN108882969A (en)* | 2016-04-15 | 2018-11-23 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Surgical system |
| US12383355B2 (en) | 2016-05-18 | 2025-08-12 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
| US11826014B2 (en) | 2016-05-18 | 2023-11-28 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices, systems and related methods |
| CN109715081A (en)* | 2016-05-18 | 2019-05-03 | 虚拟切割有限公司 | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| CN109715081B (en)* | 2016-05-18 | 2021-11-09 | 虚拟切割有限公司 | Robotic surgical devices, systems, and related methods |
| US12274517B2 (en) | 2016-08-30 | 2025-04-15 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Robotic device with compact joint design and an additional degree of freedom and related systems and methods |
| CN106377316A (en)* | 2016-09-18 | 2017-02-08 | 上海交通大学 | Thyroid minimally invasive surgery operation equipment |
| CN109567943A (en)* | 2016-11-01 | 2019-04-05 | 香港生物医学工程有限公司 | Surgical system for performing intracorporeal surgical procedures |
| CN109567943B (en)* | 2016-11-01 | 2023-01-10 | 香港生物医学工程有限公司 | Surgical system for performing intracorporeal surgical procedures |
| CN106901835A (en)* | 2017-03-15 | 2017-06-30 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A kind of main hand of five degree of freedom with position retaining function |
| CN107536642A (en)* | 2017-08-24 | 2018-01-05 | 胡荣 | A kind of multiple degrees of freedom multifunction surgical manipulator |
| US11974824B2 (en) | 2017-09-27 | 2024-05-07 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices with tracking camera technology and related systems and methods |
| US12343098B2 (en) | 2017-09-27 | 2025-07-01 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotic surgical devices with tracking camera technology and related systems and methods |
| US12303221B2 (en) | 2018-01-05 | 2025-05-20 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Single-arm robotic device with compact joint design and related systems and methods |
| US11950867B2 (en) | 2018-01-05 | 2024-04-09 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Nebraska | Single-arm robotic device with compact joint design and related systems and methods |
| CN108175511A (en)* | 2018-02-26 | 2018-06-19 | 路要武 | A kind of single-hole laparoscopic robot system |
| CN108309455A (en)* | 2018-02-26 | 2018-07-24 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of surgical instrument with running fix joint for single hole operating robot |
| CN108524002A (en)* | 2018-03-02 | 2018-09-14 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of mechanically decoupled single hole surgical robot quick replacement mechanism with linear joint |
| CN108433812B (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2024-08-20 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | Integral layout structure of single-hole surgical robot with movable positioning joint |
| CN108420533B (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2024-08-20 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | Single-hole surgical robot integral layout structure with movable and autorotation positioning joints |
| CN108420533A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2018-08-21 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | With mobile and rotation positioning joint single hole operating robot integral layout structure |
| CN108433811B (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2024-10-01 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | Integral layout structure of single-hole surgical robot with autorotation positioning joint |
| CN108433812A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2018-08-24 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of integral layout structure of the single hole operating robot with running fix joint |
| CN108433811A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2018-08-24 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | A kind of integral layout structure of the single hole operating robot with rotation positioning joint |
| CN108814713A (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2018-11-16 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | Minimally Invasive Surgery motion arm, from operation equipment and operating robot |
| CN108567487A (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2018-09-25 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | With adjustable link from operation equipment and operating robot |
| CN108839047A (en)* | 2018-03-28 | 2018-11-20 | 江苏求恒医疗器械有限公司 | A kind of Medical instrument fixture with clamp device |
| CN108969106B (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2020-06-16 | 微创(上海)医疗机器人有限公司 | Telescoping device and surgical robot |
| CN108969106A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2018-12-11 | 微创(上海)医疗机器人有限公司 | Telescopic device and operating robot |
| CN109330697A (en)* | 2018-07-31 | 2019-02-15 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | Minimally Invasive Surgery is from operation apparatus assembly and operating robot |
| CN109330697B (en)* | 2018-07-31 | 2023-09-22 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技股份有限公司 | Minimally invasive surgery slave operation equipment assembly and surgery robot |
| US11903658B2 (en) | 2019-01-07 | 2024-02-20 | Virtual Incision Corporation | Robotically assisted surgical system and related devices and methods |
| CN109770966A (en)* | 2019-01-23 | 2019-05-21 | 吉林大学 | A multi-degree-of-freedom integrated single-port endoscopic surgical instrument |
| CN109770966B (en)* | 2019-01-23 | 2021-11-09 | 吉林大学 | Integrated single-port endoscopic surgical instrument with multiple degrees of freedom |
| CN110522517A (en)* | 2019-09-16 | 2019-12-03 | 西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院 | A robotic arm for minimally invasive surgery in a single-port laparoscopic environment |
| CN111407411A (en)* | 2020-03-27 | 2020-07-14 | 南京航空航天大学 | A micro manipulator system and its control method |
| CN111991084A (en)* | 2020-10-08 | 2020-11-27 | 深圳市精锋医疗科技有限公司 | Surgical robot, virtual imaging control method thereof and virtual imaging control device thereof |
| CN112638316A (en)* | 2020-11-24 | 2021-04-09 | 曹庆恒 | Oral cavity robot and using method thereof |
| WO2022109760A1 (en)* | 2020-11-24 | 2022-06-02 | 曹庆恒 | Oral cavity robot and method for use thereof |
| CN113855287A (en)* | 2021-07-06 | 2021-12-31 | 上海优医基医疗影像设备有限公司 | Oral implant surgical robot with implant precision evaluation function and control method |
| CN113855287B (en)* | 2021-07-06 | 2023-09-26 | 上海优医基医疗影像设备有限公司 | Oral implantation operation robot with evaluation of implantation precision and control method |
| CN113440258A (en)* | 2021-07-12 | 2021-09-28 | 曹庆恒 | Ear-nose robot and using method thereof |
| CN114271948A (en)* | 2021-12-07 | 2022-04-05 | 南京航空航天大学 | A compact single-hole surgical robot from the hand |
| CN114271948B (en)* | 2021-12-07 | 2024-03-26 | 南京航空航天大学 | A compact, single-hole surgical robot emerges from the hand |
| CN114851245A (en)* | 2022-04-15 | 2022-08-05 | 郑州大学 | A kind of robot telescopic swing mechanism and bionic robot |
| CN114851245B (en)* | 2022-04-15 | 2024-02-06 | 郑州大学 | A kind of robot telescopic swing mechanism and bionic robot |
| CN116725693A (en)* | 2023-07-13 | 2023-09-12 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | Six-degree-of-freedom wire transmission micro manipulator with analytic inverse solution and operation triangle |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102499759B (en) | 2013-11-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102499759B (en) | Multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgery | |
| US11172958B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus for controlling surgical instruments using a port assembly | |
| US10856943B2 (en) | Surgical system and methods for mimicked motion | |
| CN104814792B (en) | Separable multi-arm soft robotic arm device | |
| CN111437036A (en) | Serpentine surgical robot applied to minimally invasive surgery | |
| CN107820412A (en) | robotic surgery assembly | |
| JP4856109B2 (en) | Surgical instrument and surgical instrument | |
| US20130085509A1 (en) | Methods and devices for remotely controlling movement of surgical tools | |
| JP2009528150A (en) | Surgical instruments for endoscopic surgery | |
| CN104490477A (en) | Multi-degree-of-freedom single-incision surgical robot for laparoscopic surgery | |
| JPWO2014103096A1 (en) | Surgical instruments | |
| KR101151738B1 (en) | Tubular type manipulator with multi-articulated end-effector for surgical robot | |
| CN210095849U (en) | Multifunctional laparoscope grasping forceps | |
| CN108175511A (en) | A kind of single-hole laparoscopic robot system | |
| CN114795476A (en) | Surgical execution device and surgical robot | |
| JP2020115968A (en) | Surgical system and support equipment | |
| US20150045620A1 (en) | Curved manual surgical equipment | |
| CN203789996U (en) | Separating forceps with suction function for laparoscopic operations | |
| TWI770509B (en) | Multi-segment-rotation robotic arm | |
| US20160270868A1 (en) | Thread Handling Tool | |
| US11406254B2 (en) | Surgical devices and systems for minimally-invasive vessel-harvesting and other surgical procedures | |
| CN106377316A (en) | Thyroid minimally invasive surgery operation equipment | |
| JP6111320B2 (en) | In vivo introduction device | |
| RU114835U1 (en) | LAPAROLIFT | |
| CN203790036U (en) | Dual-electrode electrocoagulator with suction function for laparoscopic operations |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20131120 |