CN102251131A - Method for preparing injection-molding nickel-base ODS (oxide dispersion strengthened) alloy - Google Patents
Method for preparing injection-molding nickel-base ODS (oxide dispersion strengthened) alloyDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102251131A CN102251131ACN2011101807442ACN201110180744ACN102251131ACN 102251131 ACN102251131 ACN 102251131ACN 2011101807442 ACN2011101807442 ACN 2011101807442ACN 201110180744 ACN201110180744 ACN 201110180744ACN 102251131 ACN102251131 ACN 102251131A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- powder
- alloy
- injection
- nickel
- based ods
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Powder Metallurgy (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于粉末注射成形技术领域,特别提供了一种以预处理机械合金化粉末为原料制备注射成形镍基氧化物弥散强化(Oxide Dispersion Strengthening,ODS)合金的方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of powder injection molding, and in particular provides a method for preparing an injection-molded nickel-based oxide dispersion strengthening (Oxide Dispersion Strengthening, ODS) alloy by using pretreated mechanically alloyed powder as a raw material.
背景技术Background technique
镍基ODS合金在1000℃以上仍具有优异的高温蠕变性能、疲劳性能和抗氧化性能。镍基合金的中温(700~900℃)强度较低,通过Al、Ti和Nb等元素的添加形成L12结构的γ′[Ni3(Al,Ti)]析出相能够有效提高中温强度。在更高温度(>1000℃)下,γ′相由于溶解而失去强化作用,此时稳定氧化物的弥散强化机制占主导。γ′相和氧化物弥散相共强化的镍基ODS合金是一种重要的高温结构材料,它可以用作燃气涡轮发动机、航空发动机以及汽车涡轮增压器中的一些关键高温部件。在燃气涡轮发动机中,为了提高效率,涡轮前端进口温度已由初期的600-700℃增至1500℃左右,这对高温组件材料(特别是叶片材料)的性能提出了更高的要求。在车用领域,涡轮增压技术是提高汽车发动机功率、降低能耗和汽车工业实现节能减排目标的最有效手段之一。涡轮是汽车涡轮增压器中的核心部件。目前,涡轮增压技术正逐步向汽油机普及,汽油机增压后发动机的排气温度高达1050℃,普通镍基合金已经不能满足使用要求。Nickel-based ODS alloys still have excellent high-temperature creep properties, fatigue properties and oxidation resistance above 1000 °C. The medium-temperature (700-900℃) strength of nickel-based alloys is low, and the addition of elements such as Al, Ti, and Nb to form γ′[Ni3 (Al, Ti)] precipitates with L12 structure can effectively improve the medium-temperature strength. At higher temperatures (>1000°C), the γ′ phase loses its strengthening effect due to dissolution, and the dispersion strengthening mechanism of stable oxides dominates at this time. The nickel-based ODS alloy strengthened by γ′ phase and oxide disperse phase is an important high-temperature structural material, which can be used as some key high-temperature components in gas turbine engines, aeroengines and automotive turbochargers. In gas turbine engines, in order to improve efficiency, the inlet temperature at the front end of the turbine has increased from the initial 600-700°C to about 1500°C, which puts forward higher requirements on the performance of high-temperature component materials (especially blade materials). In the field of vehicles, turbocharging technology is one of the most effective means to increase the power of automobile engines, reduce energy consumption and achieve the goal of energy saving and emission reduction in the automobile industry. Turbine is the core component in automobile turbocharger. At present, turbocharging technology is gradually being popularized in gasoline engines. After gasoline engines are supercharged, the exhaust temperature of the engine is as high as 1050°C, and ordinary nickel-based alloys can no longer meet the use requirements.
镍基ODS合金是先进燃气轮机中的叶片和汽车涡轮增压器中涡轮的潜在替代材料,但是镍基ODS合金的硬度高、塑性低和加工成形性差,很难通过传统机加工方法制备出形状复杂的叶片或涡轮等零件,这严重制约了镍基ODS合金的推广应用。国际上一直致力于镍基ODS高温合金的开发及其先进成形技术的研究。粉末注射成形技术适合于制备燃气轮机中的高压叶片和车用涡轮增压器中的涡轮等尺寸适中、形状复杂的零件,它具有近终成形、组织均匀、性能高、精度高和成本低等一系列优点,还能够有效避免铸造镍基合金存在的非金属夹杂、成分偏析和疏松等缺陷。Nickel-based ODS alloys are potential substitute materials for blades in advanced gas turbines and turbines in automotive turbochargers. However, nickel-based ODS alloys have high hardness, low plasticity, and poor formability, making it difficult to prepare complex shapes by traditional machining methods. Parts such as blades or turbines, which seriously restrict the popularization and application of nickel-based ODS alloys. The world has been committed to the development of nickel-based ODS superalloys and research on advanced forming technology. Powder injection molding technology is suitable for the preparation of high-pressure blades in gas turbines and turbines in automotive turbochargers with moderate size and complex shapes. It has near-net shape, uniform structure, high performance, high precision and low cost. A series of advantages can also effectively avoid defects such as non-metallic inclusions, composition segregation and porosity in cast nickel-based alloys.
机械合金化是制备注射成形镍基ODS合金粉末原料必不可少的工艺,但是机械合金粉末由于形状不规则、粉末团聚和粒径粗大而不适合进行注射成形。因此,必须对机械合金粉末进行预处理,以制得粒径和形状都适合注射成形的粉末。利用对喷式气流磨和射频等离子体球化技术可以对机械合金化粉末的粒径和形状进行改性。对喷式气流磨利用超音速喷嘴将高压气体加速后射入粉碎区,物料颗粒在高速气体巨大动能的作用下被加速并在喷嘴交汇处碰撞而达到粉碎的目的。射频等离子体球化技术是将形状不规则的粉末颗粒由携带气体通过加料枪喷入等离子体炉中,在辐射、对流、传导和化学四种传热机制作用下被迅速加热而熔化,熔融颗粒在表面张力作用下形成球形液滴,并在极高的温度梯度下迅速凝固,从而获得球形粉末。Mechanical alloying is an essential process for preparing nickel-based ODS alloy powder raw materials for injection molding, but mechanical alloy powders are not suitable for injection molding due to irregular shape, powder agglomeration and coarse particle size. Therefore, mechanical alloy powders must be pretreated to produce powders with particle sizes and shapes suitable for injection molding. The particle size and shape of mechanically alloyed powders can be modified by counter-jet jet milling and radio frequency plasma spheroidization. The counter-jet jet mill uses a supersonic nozzle to accelerate the high-pressure gas and inject it into the crushing area. The material particles are accelerated under the action of the huge kinetic energy of the high-speed gas and collide at the intersection of the nozzles to achieve the purpose of crushing. The radio frequency plasma spheroidization technology is to spray irregularly shaped powder particles into the plasma furnace through the feeding gun through the carrying gas, and is rapidly heated and melted under the action of four heat transfer mechanisms of radiation, convection, conduction and chemistry, and the molten particles Spherical droplets are formed under the action of surface tension and rapidly solidified under extremely high temperature gradients to obtain spherical powders.
可见,机械合金粉末通过气流磨细化和等离子体球化处理后能够获得适合注射成形工艺的细颗粒球形粉末,注射成形成功解决了镍基ODS合金近终成形的难题。注射成形镍基ODS合金的研制将大大促进镍基ODS合金的推广应用。It can be seen that the fine-grained spherical powder suitable for the injection molding process can be obtained after the mechanical alloy powder is refined by jet milling and plasma spheroidization, and the injection molding successfully solves the problem of near net forming of the nickel-based ODS alloy. The development of injection molding nickel-based ODS alloy will greatly promote the popularization and application of nickel-based ODS alloy.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于提供一种制备注射成形镍基ODS合金的方法,旨在解决镍基ODS合金近终成形的难题,具有显微组织均匀、性能高、精度高、材料利用率高和成本低等优点。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloys, which aims to solve the problem of near-net forming of nickel-based ODS alloys, and has the advantages of uniform microstructure, high performance, high precision, high material utilization rate and low cost. low merit.
本发明首先采用机械合金化工艺制备氧化物弥散强化镍基合金粉末,然后对机械合金化粉末进行预处理(气流磨细化和等离子体球化)以得到粒径细小和球形的注射成形用粉末原料,接着将预处理过的机械合金化粉末进行注射成形、热等静压及热处理,最后得到注射成形镍基ODS合金,制备工艺如图1所示,具体工艺步骤为:The present invention first adopts the mechanical alloying process to prepare oxide dispersion strengthened nickel-based alloy powder, and then performs pretreatment (jet milling and plasma spheroidization) on the mechanical alloying powder to obtain fine and spherical powder for injection molding Raw materials, then the pretreated mechanically alloyed powder is subjected to injection molding, hot isostatic pressing and heat treatment, and finally an injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloy is obtained. The preparation process is shown in Figure 1, and the specific process steps are:
1、机械合金化:将镍基合金粉末、Y2O3颗粒和Hf元素颗粒预混合均匀,然后在高纯Ar气氛中通过高能球磨将0.8-1.5wt%Y2O3颗粒和0.8-3.0wt%的Hf元素颗粒均匀分散在基体中。球磨机的转速为380~500转/分,球磨时间为36-72小时。机械合金化粉末的形貌如图2所示;1. Mechanical alloying: pre-mix nickel-based alloy powder, Y2 O3 particles and Hf element particles evenly, and then mix 0.8-1.5wt% Y2 O3 particles and 0.8-3.0 The wt% Hf element particles are uniformly dispersed in the matrix. The rotating speed of the ball mill is 380-500 rpm, and the ball milling time is 36-72 hours. The morphology of the mechanically alloyed powder is shown in Figure 2;
所述的镍基合金粉末的成分为各种标准牌号的镍基高温合金,或者是根据实际工况设计的非标准合金。镍基高温合金选自:Nimonic 90(美国标准)、Inconel718(美国标准)、Inconel 713C(美国标准)、HastelloyX(美国标准)、GH4195(国标)或GH4195(国标);原料粉末以元素粉末的形式添加,或者采用高压气雾化或水雾化法工艺制备的预合金粉末。The composition of the nickel-based alloy powder is various standard grades of nickel-based superalloys, or non-standard alloys designed according to actual working conditions. Nickel-based superalloys are selected from: Nimonic 90 (US standard), Inconel718 (US standard), Inconel 713C (US standard), HastelloyX (US standard), GH4195 (national standard) or GH4195 (national standard); raw material powder is in the form of elemental powder Addition, or pre-alloyed powder prepared by high-pressure gas atomization or water atomization process.
2、对喷式气流磨:将机械合金化粉末通过对喷式气流磨进行粉碎细化处理。通过控制气体流量、工作压力、分选能频率来控制粉末的粒径。气体压力为3~8MPa,分选轮频率为40~60Hz,气流磨处理后的粉末粒径为10-40μm。图3是对喷式气流磨处理后的粉末形貌图。由图可见,气流磨处理后的粉末明显细化,团聚粉末消失;2. Counter-jet jet mill: The mechanically alloyed powder is pulverized and refined by the counter-jet jet mill. The particle size of the powder is controlled by controlling the gas flow, working pressure and sorting energy frequency. The gas pressure is 3-8 MPa, the frequency of the sorting wheel is 40-60 Hz, and the particle size of the powder after jet milling is 10-40 μm. Fig. 3 is a powder morphology diagram after being treated by jet jet milling. It can be seen from the figure that the powder treated by the jet mill is obviously refined, and the agglomerated powder disappears;
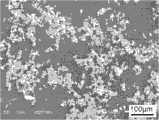
3、等离子体球化:对气流磨细化后的粉末进行等离子球化处理,通过控制送粉速率和气体输送量等参数,使粉末球形度尽可能高。送粉速率为30~200g·min-1,等离子输出功率为50~90KW,负压为7000~12000Pa。图4为等离子球化粉末的SEM形貌图,可以看出粉末的球化效果显著;3. Plasma spheroidization: Plasma spheroidization is performed on the powder refined by jet mill, and the powder sphericity is as high as possible by controlling parameters such as powder feeding rate and gas delivery volume. The powder feeding rate is 30-200g·min-1 , the plasma output power is 50-90KW, and the negative pressure is 7000-12000Pa. Figure 4 is the SEM image of the plasma spheroidized powder, it can be seen that the spheroidization effect of the powder is remarkable;
4、混炼:气流磨细化粉末和等离子球化粉末与粘结剂混合均匀后在双行星混炼机中于145-170℃、转速为30-50转/分的条件下混炼0.5-1.5h制成均匀喂料,其中粉末装载量为55-65vol%。4. Mixing: Mix the jet mill fine powder and plasma spheroidized powder with the binder evenly, then mix 0.5- 1.5h to make a uniform feed, where the powder loading is 55-65vol%.
所述的粘结剂采用蜡基多组元聚合物体系,各组元的比例为:50-70wt%石蜡、10-20%高密度聚乙烯、10-20%聚丙烯和余量硬脂酸;The binder adopts a wax-based multi-component polymer system, and the ratio of each component is: 50-70% by weight of paraffin, 10-20% of high-density polyethylene, 10-20% of polypropylene and the balance of stearic acid ;
5、注射成形:在注射成形机上进行注射成形,得到所需形状零件。注射温度为150-175℃、注射压力为75-125MPa;5. Injection molding: Injection molding is performed on an injection molding machine to obtain parts of the desired shape. The injection temperature is 150-175°C, and the injection pressure is 75-125MPa;
6、脱脂:注射坯采用溶剂脱脂和热脱脂两步脱脂工艺,先在三氯乙烯或三氯乙烷等有机溶剂中于45-60℃浸泡5-12h;然后在高纯氩气气氛中于25-1100℃进行热脱脂;6. Degreasing: The injection base adopts two-step degreasing process of solvent degreasing and thermal degreasing. Thermal degreasing at 25-1100°C;
7、烧结:脱脂坯在真空气氛或高纯氩气保护气氛中进行烧结,烧结温度为1270-1360℃,保温时间为1-3h;7. Sintering: The degreased billet is sintered in a vacuum atmosphere or a high-purity argon protective atmosphere, the sintering temperature is 1270-1360°C, and the holding time is 1-3h;
8、热等静压:烧结坯在1000-1200℃的温度范围内进行热等静压,压力为100-200MPa,保温时间为1-3h,得到全致密镍基ODS合金;8. Hot isostatic pressing: The sintered billet is hot isostatic pressed in the temperature range of 1000-1200 °C, the pressure is 100-200 MPa, and the holding time is 1-3 hours to obtain a fully dense nickel-based ODS alloy;
9、热处理:热等静压后的制品在1100-1250℃进行固溶处理,保温2-6h后水冷,然后在650-850℃时效处理8-24h,最终得到注射成形镍基ODS合金。9. Heat treatment: The product after hot isostatic pressing is subjected to solution treatment at 1100-1250°C, kept warm for 2-6h, then water-cooled, then aged at 650-850°C for 8-24h, and finally an injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloy is obtained.
本发明的优点是气流磨细化和等离子球化后的机械合金化粉末的粒径小、球形度高,适合进行注射成形。热等静压进一步提高了材料的综合力学性能,从而制备出高性能、高精度、形状复杂的零件,成功解决了镍基ODS合金难成形加工的难题,此外还避免了铸造镍基合金存在的非金属夹杂、成分偏析和疏松缺陷等问题。γ′析出相强化和氧化物弥散强化机制相结合大幅度拓展了镍基ODS合金的高温力学性能。The invention has the advantages that the mechanical alloying powder after jet milling and plasma spheroidization has small particle size and high sphericity, and is suitable for injection molding. Hot isostatic pressing further improves the comprehensive mechanical properties of the material, thereby preparing high-performance, high-precision, and complex-shaped parts, successfully solving the problem of difficult forming and processing of nickel-based ODS alloys, and avoiding the problems of casting nickel-based alloys. Problems such as non-metallic inclusions, composition segregation and loose defects. The combination of γ′ precipitation strengthening and oxide dispersion strengthening mechanisms greatly expands the high-temperature mechanical properties of nickel-based ODS alloys.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明的工艺流程图Fig. 1 is a process flow diagram of the present invention
图2为机械合金化粉末SEM图Figure 2 is the SEM image of mechanical alloying powder
图3为气流磨细化粉末SEM图Figure 3 is the SEM image of jet milling fine powder
图4为等离子球化粉末SEM图Figure 4 is the SEM image of plasma spheroidized powder
图5(a)为注射成形镍基ODS合金中γ′相SEM图Figure 5(a) is the SEM image of the γ′ phase in the injection molded nickel-based ODS alloy
和氧化物弥散相TEM图(b)and oxide dispersed phase TEM images (b)
具体实施方式Detailed ways
实施例1:以气流磨细粉为原料制备无γ′相强化注射成形镍基ODS合金Example 1: Preparation of Injection Molded Nickel-based ODS Alloy Without γ′ Phase Reinforcement Using Jet Milled Powder as Raw Material
以粒度为20-30nm的Y2O3颗粒、以及高纯Ni粉、Cr粉、Co粉、Mo粉、W粉、Fe粉、Si粉、Hf粉和C粉为原料,按如下质量百分含量配制混合粉末:21%Cr、1.5%Co、9%Mo、0.5%W、18%Fe、0.8%Si、0.09%C、1%Y2O3、1.2%Hf和余量Ni。首先将混合粉末在高纯Ar气氛中进行高能球磨使Y2O3颗粒均匀分散在Ni基体中,球磨机转速为380转/分,球磨时间为40小时;机械合金粉末采用气流磨进行破碎细化处理,气压为6MPa,分选能频率为45Hz,得到平均粒径约20μm的粉末;气流磨细颗粒粉末与粘结剂混合均匀后在双行星混炼机上于150℃混炼1h制得均匀喂料,其中粘结剂由63%石蜡、13%高密度聚乙烯、17%聚丙烯、7%硬脂酸组成,粉末装载量为56vol.%;喂料在CJ80-E型注射成形机上注射成形,注射温度为155℃,注射压力为90MPa;注射坯在三氯乙烯溶液中溶脱10h后,在高纯氩气气氛中进行热脱脂,热脱脂温度为900℃;脱脂坯在真空气氛中于1300℃烧结,保温1h;烧结坯在1100℃热等静压,压力为100MPa,保温2h。所得注射成形镍基ODS合金的致密度为98.4%,氧化物颗粒平均粒径为14.5nm。UseY2O3 particles with a particle size of 20-30nm, and high- purity Ni powder, Cr powder, Co powder, Mo powder, W powder, Fe powder, Si powder, Hf powder and C powder as raw materials, according to the following mass percentages The content of mixed powder is formulated: 21% Cr, 1.5% Co, 9% Mo, 0.5% W, 18% Fe, 0.8% Si, 0.09% C, 1% Y2 O3 , 1.2% Hf and the balance of Ni. First, the mixed powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling in a high-purity Ar atmosphere to uniformly disperse the Y2 O3 particles in the Ni matrix. The ball mill speed is 380 rpm, and the ball milling time is 40 hours; the mechanical alloy powder is crushed and refined by a jet mill. Treatment, the air pressure is 6MPa, the sorting energy frequency is 45Hz, and the powder with an average particle size of about 20μm is obtained; the airflow milled fine particle powder is mixed with the binder evenly, and then mixed on a double planetary mixer at 150°C for 1h to obtain a uniform feed. Material, wherein the binder is composed of 63% paraffin, 13% high-density polyethylene, 17% polypropylene, 7% stearic acid, and the powder loading is 56vol.%. The feeding is injection molded on a CJ80-E injection molding machine , the injection temperature is 155°C, and the injection pressure is 90MPa; after the injection billet is dissolved in the trichlorethylene solution for 10 hours, it is thermally degreased in a high-purity argon atmosphere, and the thermal degreasing temperature is 900°C; the degreasing billet is heated in a vacuum atmosphere at 1300 ℃ sintering, heat preservation 1h; sintered billet hot isostatic pressing at 1100 ℃, pressure 100MPa, heat preservation 2h. The density of the obtained injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloy is 98.4%, and the average particle size of oxide particles is 14.5nm.
实施例2:以等离子球化粉末为原料制备无γ′相强化注射成形镍基ODS合金Example 2: Using plasma spheroidized powder as raw material to prepare injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloy without γ′ phase reinforcement
以粒度为20-30nm的Y2O3颗粒、以及高纯Ni粉、Cr粉、Co粉、Mo粉、W粉、Fe粉、Si粉、Hf粉和C粉为原料,按如下质量百分含量配制混合粉末:19%Cr、2%Co、8%Mo、1%W、19%Fe、0.6%Si、0.08%C、1%Y2O3、1.2%Hf和余量Ni。首先将混合粉末在高纯Ar气氛中进行高能球磨使Y2O3颗粒均匀分散在Ni基体中,球磨机转速为450转/分,球磨时间为48小时;机械合金粉末采用气流磨进行破碎细化处理,气压为8MPa,分选能频率为50Hz,得到平均粒径约30μm的粉末;将气流磨细化后的粉末进行等离子体球化处理,送粉速率为50g·min-1,等离子输出功率为70KW,腔内负压为7000Pa;球化后的粉末与粘结剂混合均匀后在双行星混炼机上于155℃混炼1.5h制得均匀喂料,其中粘结剂由55%石蜡、20%高密度聚乙烯、15%聚丙烯、10%硬脂酸组成,粉末装载量为64vol.%;喂料在CJ80-E型注射成形机上注射成形,注射温度为160℃,注射压力为90MPa;注射坯在三氯乙烯溶液中溶脱12h后,在高纯氩气气氛中进行热脱脂,热脱脂温度为1000℃;脱脂坯在高纯氩气气氛中于1320℃烧结,保温2h;烧结坯在1150℃热等静压,压力为150MPa,保温2h。所得注射成形镍基ODS合金的致密度为99.1%,氧化物颗粒平均粒径为11.1nm。UseY2O3 particles with a particle size of 20-30nm, and high- purity Ni powder, Cr powder, Co powder, Mo powder, W powder, Fe powder, Si powder, Hf powder and C powder as raw materials, according to the following mass percentages The mixed powder is formulated as follows: 19% Cr, 2% Co, 8% Mo, 1% W, 19% Fe, 0.6% Si, 0.08% C, 1% Y2 O3 , 1.2% Hf and the balance Ni. First, the mixed powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling in a high-purity Ar atmosphere to uniformly disperse the Y2 O3 particles in the Ni matrix. The ball mill speed is 450 rpm, and the ball milling time is 48 hours; the mechanical alloy powder is crushed and refined by a jet mill. Treatment, the air pressure is 8MPa, the sorting energy frequency is 50Hz, and the powder with an average particle size of about 30μm is obtained; the powder after jet milling is subjected to plasma spheroidization treatment, the powder feeding rate is 50g·min-1 , and the plasma output power It is 70KW, and the negative pressure in the chamber is 7000Pa; after the spheroidized powder and the binder are mixed evenly, they are mixed on a double planetary mixer at 155°C for 1.5h to obtain a uniform feed, in which the binder is made of 55% paraffin, Composition of 20% high-density polyethylene, 15% polypropylene, 10% stearic acid, powder loading is 64vol.%; feeding is injection molded on a CJ80-E injection molding machine, the injection temperature is 160°C, and the injection pressure is 90MPa ; After the injection billet is dissolved in the trichlorethylene solution for 12 hours, it is thermally degreased in a high-purity argon atmosphere, and the thermal degreasing temperature is 1000°C; the degreased billet is sintered at 1320°C in a high-purity argon atmosphere and kept for 2 hours; the sintered billet Hot isostatic pressing at 1150°C, pressure 150MPa, heat preservation 2h. The density of the obtained injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloy is 99.1%, and the average particle diameter of oxide particles is 11.1 nm.
实施例3:用气流磨细粉制备γ′和氧化物共强化型注射成形镍基ODS合金Example 3: Preparation of γ′ and oxide co-reinforced nickel-based ODS alloy for injection molding with jet mill fine powder
以粒度为20-30nm的Y2O3颗粒、以及高纯Ni粉、Cr粉、Nb粉、Mo粉、Ti粉、Al粉、Fe粉、Si粉、Hf粉和C粉为原料,按如下质量百分含量配制混合粉末:18%Cr、5%Nb、3%Mo、0.4%Al、1%Ti、19%Fe、0.3%Si、0.36%C、1%Y2O3、1.2%Hf和余量Ni。首先将混合粉末在高纯Ar气氛中进行高能球磨使Y2O3颗粒均匀分散在Ni基体中,球磨机转速为400转/分,球磨时间为60小时;机械合金粉末采用气流磨进行破碎细化处理,气压为5MPa,分选能频率为40Hz,得到平均粒径约35μm的粉末;气流磨细颗粒粉末与粘结剂混合均匀后在双行星混炼机上于160℃混炼1.5h制得均匀喂料,其中粘结剂由60%石蜡、15%高密度聚乙烯、15%聚丙烯、10%硬脂酸组成,粉末装载量为57vol.%;喂料在CJ80-E型注射成形机上注射成形,注射温度为160℃,注射压力为90MPa;注射坯在三氯乙烯溶液中溶脱8h后,在高纯氩气气氛中进行热脱脂,热脱脂温度为1100℃;脱脂坯在真空气氛中于1340℃烧结,保温1h;烧结坯在1100℃热等静压,压力为200MPa,保温2h;热等静压样品在1250℃固溶处理2h,然后在700℃时效处理12h。所得注射成形镍基ODS合金的致密度为99.2%,γ′相的体积分数为45%,粒径为100nm,氧化物颗粒平均粒径为12.8nm。UseY2O3 particles with a particle size of 20-30nm, and high- purity Ni powder, Cr powder, Nb powder, Mo powder, Ti powder, Al powder, Fe powder, Si powder, Hf powder and C powder as raw materials, as follows Mass percentage content to prepare mixed powder: 18% Cr, 5% Nb, 3% Mo, 0.4% Al, 1% Ti, 19% Fe, 0.3% Si, 0.36% C, 1% Y2 O3 , 1.2% Hf and the balance Ni. First, the mixed powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling in a high-purity Ar atmosphere to uniformly disperse the Y2 O3 particles in the Ni matrix. The ball mill speed is 400 rpm, and the ball milling time is 60 hours; the mechanical alloy powder is crushed and refined by a jet mill. Treatment, the air pressure is 5MPa, the sorting energy frequency is 40Hz, and the powder with an average particle size of about 35μm is obtained; the jet-milled fine particle powder is mixed with the binder evenly, and then mixed on a double planetary mixer at 160°C for 1.5h to obtain a uniform Feeding, wherein binder is made up of 60% paraffin, 15% high-density polyethylene, 15% polypropylene, 10% stearic acid, powder loading is 57vol.%; Feeding is injected on CJ80-E type injection molding machine Forming, the injection temperature is 160°C, and the injection pressure is 90MPa; after the injection billet is dissolved in the trichlorethylene solution for 8 hours, it is thermally degreased in a high-purity argon atmosphere, and the thermal degreasing temperature is 1100°C; the degreasing billet is in a vacuum atmosphere at Sintering at 1340°C, heat preservation for 1h; hot isostatic pressing at 1100°C, pressure 200MPa, heat preservation for 2h; hot isostatic pressing samples were solution treated at 1250°C for 2h, and then aged at 700°C for 12h. The density of the obtained injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloy is 99.2%, the volume fraction of γ' phase is 45%, the particle size is 100nm, and the average particle size of oxide particles is 12.8nm.
实施例4:用等离子球化粉末制备γ′和氧化物共强化注射成形镍基ODS合金Example 4: Preparation of γ′ and oxide co-reinforced injection molded nickel-based ODS alloy with plasma spheroidized powder
以粒度为20-30nm的Y2O3颗粒、以及高纯Ni粉、Cr粉、Nb粉、Mo粉、Ti粉、Al粉、Fe粉、Si粉、Hf粉和C粉为原料,按如下质量百分含量配制混合粉末:16%Cr、16%Co、1.9%Ti、0.85%Al、2%Fe、0.7%Si、0.065%C、1%Y2O3、1.2%Hf和余量Ni。首先将混合粉末在高纯Ar气氛中进行高能球磨使Y2O3颗粒均匀分散在Ni基体中,球磨机转速为400转/分,球磨时间为48小时;机械合金粉末采用气流磨进行破碎细化处理,气压为7MPa,分选能频率为55Hz,得到平均粒径约19μm的粉末;将气流磨细化后的粉末进行等离子体球化处理,送粉速率为60g·min-1,等离子输出功率为80KW,腔内负压为6000Pa;球化后的粉末与粘结剂混合均匀后在双行星混炼机上于155℃混炼2h制得均匀喂料,其中粘结剂由55%石蜡、20%高密度聚乙烯、10%聚丙烯、15%硬脂酸组成,粉末装载量为65vol.%;喂料在CJ80-E型注射成形机上注射成形,注射温度为160℃,注射压力为90MPa;注射坯在三氯乙烯溶液中溶脱10h后,在高纯氩气气氛中进行热脱脂,热脱脂温度为1000℃;脱脂坯在真空或高纯氩气气氛中于1290℃烧结,保温2h;烧结坯在1200℃热等静压,压力为150MPa,保温2h;热等静压样品在1200℃固溶处理3h,然后在750℃时效处理10h。所得注射成形镍基ODS合金的致密度为99.1%,γ′相的体积分数为45%,粒径为100nm,氧化物颗粒平均粒径为8.8nm。UseY2O3 particles with a particle size of 20-30nm, and high- purity Ni powder, Cr powder, Nb powder, Mo powder, Ti powder, Al powder, Fe powder, Si powder, Hf powder and C powder as raw materials, as follows Mixed powder prepared in mass percent: 16% Cr, 16% Co, 1.9% Ti, 0.85% Al, 2% Fe, 0.7% Si, 0.065% C, 1% Y2 O3 , 1.2% Hf and the balance Ni . First, the mixed powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling in a high-purity Ar atmosphere to uniformly disperse the Y2 O3 particles in the Ni matrix. The ball mill speed is 400 rpm, and the ball milling time is 48 hours; the mechanical alloy powder is crushed and refined by a jet mill. Processing, the air pressure is 7MPa, the sorting energy frequency is 55Hz, and the powder with an average particle size of about 19μm is obtained; the powder after jet milling is subjected to plasma spheroidization treatment, the powder feeding rate is 60g·min-1 , and the plasma output power It is 80KW, and the negative pressure in the cavity is 6000Pa; after the spheroidized powder and the binder are mixed evenly, they are mixed on a double planetary mixer at 155°C for 2 hours to obtain a uniform feed, in which the binder is made of 55% paraffin, 20 % high-density polyethylene, 10% polypropylene, 15% stearic acid, the powder loading is 65vol.%; the feed is injection molded on a CJ80-E injection molding machine, the injection temperature is 160 ° C, and the injection pressure is 90 MPa; After the injection billet is dissolved in the trichlorethylene solution for 10 hours, thermal degreasing is carried out in a high-purity argon atmosphere, and the thermal degreasing temperature is 1000°C; the degreasing billet is sintered at 1290°C in a vacuum or high-purity argon atmosphere, and kept for 2 hours; sintering The billets were hot isostatically pressed at 1200°C with a pressure of 150MPa and held for 2 hours; the hot isostatic pressed samples were solution treated at 1200°C for 3 hours, and then aged at 750°C for 10 hours. The density of the obtained injection-molded nickel-based ODS alloy is 99.1%, the volume fraction of γ' phase is 45%, the particle size is 100nm, and the average particle size of oxide particles is 8.8nm.
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011101807442ACN102251131B (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2011-06-30 | Method for preparing injection-molding nickel-base ODS (oxide dispersion strengthened) alloy |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011101807442ACN102251131B (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2011-06-30 | Method for preparing injection-molding nickel-base ODS (oxide dispersion strengthened) alloy |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102251131Atrue CN102251131A (en) | 2011-11-23 |
| CN102251131B CN102251131B (en) | 2012-11-28 |
Family
ID=44978696
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011101807442AExpired - Fee RelatedCN102251131B (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2011-06-30 | Method for preparing injection-molding nickel-base ODS (oxide dispersion strengthened) alloy |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102251131B (en) |
Cited By (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103008657A (en)* | 2013-01-13 | 2013-04-03 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing oxide dispersion strengthened alloy by rapid forming |
| CN103060591A (en)* | 2013-01-08 | 2013-04-24 | 北京科技大学 | Method for near-net shaping of porous Ni-based ODS (oxide dispersion strengthening) alloy |
| CN103121105A (en)* | 2013-03-19 | 2013-05-29 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing micro spherical niobium (Nb)-wolfram (W)-molybdenum (Mo)-zirconium (Zr) alloy powder |
| CN103122420A (en)* | 2013-02-28 | 2013-05-29 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing porous nickel-based ODS ( Oxide Dispersion Strengthened) alloy |
| CN103834831A (en)* | 2014-03-11 | 2014-06-04 | 武汉理工大学 | Nanometer yttrium oxide dispersion-stiffened nickel base composite material in crystalline grain and preparation method thereof |
| CN104263998A (en)* | 2014-09-18 | 2015-01-07 | 中国华能集团公司 | Heat treatment process for nickel-iron-chromium-boron high-temperature alloy |
| WO2015058534A1 (en)* | 2013-10-22 | 2015-04-30 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | Hot isostatic pressing process for high-temperature alloy powder |
| CN105821359A (en)* | 2016-04-11 | 2016-08-03 | 西安欧中材料科技有限公司 | Heat-treatment technology of high-plasticity nickel base alloy |
| CN106834870A (en)* | 2017-02-15 | 2017-06-13 | 江苏省海洋资源开发研究院(连云港) | Ni‑Al2O3Composite near-net-shape method |
| CN107052345A (en)* | 2016-12-28 | 2017-08-18 | 江苏精研科技股份有限公司 | Copper alloy injection molding process |
| CN107127348A (en)* | 2017-06-15 | 2017-09-05 | 北京康普锡威科技有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of MIM metal dusts |
| CN107775005A (en)* | 2017-11-29 | 2018-03-09 | 安徽恒利增材制造科技有限公司 | A kind of injection molding method of high-strength aluminum alloy turbine wheel |
| CN108161275A (en)* | 2018-01-08 | 2018-06-15 | 河北工业大学 | A kind of nickel-base alloy seam organization crystal fining method and its application |
| CN108461748A (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2018-08-28 | 格林美(无锡)能源材料有限公司 | A kind of lithium ion battery class monocrystalline positive electrode and preparation method thereof |
| CN108611507A (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2018-10-02 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of hot isostatic pressing near-net-shape method based on powder reprocessing |
| CN110014145A (en)* | 2019-04-18 | 2019-07-16 | 北京科技大学 | A kind of preparation method of spherical iron-based powder |
| CN110343908A (en)* | 2019-08-30 | 2019-10-18 | 江苏奇纳新材料科技有限公司 | The hip moulding and heat treatment process of IN718 alloy powder and its alloy |
| WO2019211534A1 (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2019-11-07 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | Ods alloy powder, method for producing same by means of plasma treatment, and use thereof |
| US10702923B2 (en) | 2014-07-23 | 2020-07-07 | Ihi Corporation | Method of manufacturing ni alloy part |
| CN111926207A (en)* | 2020-08-27 | 2020-11-13 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing nickel-based alloy |
| CN112453413A (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2021-03-09 | 中科院过程工程研究所南京绿色制造产业创新研究院 | Preparation method of oxide dispersion strengthened steel spherical powder for 3D printing |
| CN112632716A (en)* | 2020-11-17 | 2021-04-09 | 北京科技大学 | Defect visualization analysis method for preparing turbine through powder injection molding and preparation method of titanium-aluminum alloy turbine |
| CN114015908A (en)* | 2021-09-28 | 2022-02-08 | 深圳艾利门特科技有限公司 | Nickel-phosphorus alloy and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN114058895A (en)* | 2021-11-16 | 2022-02-18 | 陕西宝锐金属有限公司 | Double nozzle spray forming Y2O3Process for particle reinforced Monel 400 alloy plate |
| CN117020204A (en)* | 2023-08-22 | 2023-11-10 | 钢研昊普科技有限公司 | 20CrNiMo bearing piece and preparation method and application thereof |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1814379A (en)* | 2006-03-07 | 2006-08-09 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing Al2O3 dispersion-strengthened Ni Al base composite material |
| CN101948970A (en)* | 2010-10-13 | 2011-01-19 | 北京科技大学 | Mechanical alloying method for preparing strengthened dispersion alloy of nickel-based oxide |
| CN101979691A (en)* | 2010-10-13 | 2011-02-23 | 北京科技大学 | A preparation method of oxide dispersion strengthened cobalt-based superalloy |
- 2011
- 2011-06-30CNCN2011101807442Apatent/CN102251131B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1814379A (en)* | 2006-03-07 | 2006-08-09 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing Al2O3 dispersion-strengthened Ni Al base composite material |
| CN101948970A (en)* | 2010-10-13 | 2011-01-19 | 北京科技大学 | Mechanical alloying method for preparing strengthened dispersion alloy of nickel-based oxide |
| CN101979691A (en)* | 2010-10-13 | 2011-02-23 | 北京科技大学 | A preparation method of oxide dispersion strengthened cobalt-based superalloy |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 陈嵩等: "《球磨时间对镍基ODS合金拉伸性能的影响》", 《材料科学与工艺》* |
Cited By (45)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103060591A (en)* | 2013-01-08 | 2013-04-24 | 北京科技大学 | Method for near-net shaping of porous Ni-based ODS (oxide dispersion strengthening) alloy |
| CN103008657A (en)* | 2013-01-13 | 2013-04-03 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing oxide dispersion strengthened alloy by rapid forming |
| CN103122420A (en)* | 2013-02-28 | 2013-05-29 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing porous nickel-based ODS ( Oxide Dispersion Strengthened) alloy |
| CN103122420B (en)* | 2013-02-28 | 2015-01-07 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing porous nickel-based ODS ( Oxide Dispersion Strengthened) alloy |
| CN103121105B (en)* | 2013-03-19 | 2015-04-01 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing micro spherical niobium (Nb)-wolfram (W)-molybdenum (Mo)-zirconium (Zr) alloy powder |
| CN103121105A (en)* | 2013-03-19 | 2013-05-29 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing micro spherical niobium (Nb)-wolfram (W)-molybdenum (Mo)-zirconium (Zr) alloy powder |
| WO2015058534A1 (en)* | 2013-10-22 | 2015-04-30 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | Hot isostatic pressing process for high-temperature alloy powder |
| CN103834831B (en)* | 2014-03-11 | 2016-03-30 | 武汉理工大学 | In crystal grain, nano yttrium oxide disperse strengthens nickel-base composite material and preparation method thereof |
| CN103834831A (en)* | 2014-03-11 | 2014-06-04 | 武汉理工大学 | Nanometer yttrium oxide dispersion-stiffened nickel base composite material in crystalline grain and preparation method thereof |
| US11273493B2 (en) | 2014-07-23 | 2022-03-15 | Ihi Corporation | Method of manufacturing Ni alloy part |
| US10702923B2 (en) | 2014-07-23 | 2020-07-07 | Ihi Corporation | Method of manufacturing ni alloy part |
| CN104263998A (en)* | 2014-09-18 | 2015-01-07 | 中国华能集团公司 | Heat treatment process for nickel-iron-chromium-boron high-temperature alloy |
| CN104263998B (en)* | 2014-09-18 | 2016-06-22 | 中国华能集团公司 | A kind of Technology for Heating Processing of ni-fe-cr-boron system high temperature alloy |
| CN105821359A (en)* | 2016-04-11 | 2016-08-03 | 西安欧中材料科技有限公司 | Heat-treatment technology of high-plasticity nickel base alloy |
| CN107052345A (en)* | 2016-12-28 | 2017-08-18 | 江苏精研科技股份有限公司 | Copper alloy injection molding process |
| CN106834870A (en)* | 2017-02-15 | 2017-06-13 | 江苏省海洋资源开发研究院(连云港) | Ni‑Al2O3Composite near-net-shape method |
| CN106834870B (en)* | 2017-02-15 | 2018-05-11 | 江苏省海洋资源开发研究院(连云港) | Ni-Al2O3Composite material near-net-shape method |
| CN107127348A (en)* | 2017-06-15 | 2017-09-05 | 北京康普锡威科技有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of MIM metal dusts |
| CN107775005A (en)* | 2017-11-29 | 2018-03-09 | 安徽恒利增材制造科技有限公司 | A kind of injection molding method of high-strength aluminum alloy turbine wheel |
| CN107775005B (en)* | 2017-11-29 | 2019-08-02 | 安徽恒利增材制造科技有限公司 | A kind of injection molding method of high-strength aluminum alloy turbine wheel |
| CN108161275A (en)* | 2018-01-08 | 2018-06-15 | 河北工业大学 | A kind of nickel-base alloy seam organization crystal fining method and its application |
| CN108461748A (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2018-08-28 | 格林美(无锡)能源材料有限公司 | A kind of lithium ion battery class monocrystalline positive electrode and preparation method thereof |
| CN108461748B (en)* | 2018-03-23 | 2020-09-15 | 格林美(无锡)能源材料有限公司 | A kind of lithium ion battery-like single crystal positive electrode material and preparation method thereof |
| CN108611507A (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2018-10-02 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of hot isostatic pressing near-net-shape method based on powder reprocessing |
| CN108611507B (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2020-06-05 | 北京航空航天大学 | A near-net-shaping method for hot isostatic pressing based on powder reprocessing |
| JP2021521344A (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2021-08-26 | コミッサリア ア レネルジー アトミーク エ オ ゼネルジ ザルタナテイヴ | ODS alloy powder, its production method by plasma treatment, and its use |
| KR102432787B1 (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2022-08-12 | 꼼미사리아 아 레네르지 아토미끄 에뜨 옥스 에너지스 앨터네이티브즈 | ODS alloy powder, production method thereof by plasma treatment, and use thereof |
| WO2019211534A1 (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2019-11-07 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | Ods alloy powder, method for producing same by means of plasma treatment, and use thereof |
| JP7589048B2 (en) | 2018-05-03 | 2024-11-25 | コミッサリア ア レネルジー アトミーク エ オ ゼネルジ ザルタナテイヴ | ODS alloy powder, its production method by plasma treatment and its use |
| KR20200131906A (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2020-11-24 | 꼼미사리아 아 레네르지 아토미끄 에뜨 옥스 에너지스 앨터네이티브즈 | ODS alloy powder, its manufacturing method by plasma treatment, and its use |
| CN112469520A (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2021-03-09 | 原子能与替代能源委员会 | ODS alloy powder, use thereof, and method for producing same by plasma treatment |
| US12123079B2 (en) | 2018-05-03 | 2024-10-22 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | ODS alloy powder, method for producing same by means of plasma treatment, and use thereof |
| JP7562613B2 (en) | 2018-05-03 | 2024-10-07 | コミッサリア ア レネルジー アトミーク エ オ ゼネルジ ザルタナテイヴ | ODS alloy powder, its production method by plasma treatment and its use |
| JP2022192063A (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2022-12-28 | コミッサリア ア レネルジー アトミーク エ オ ゼネルジ ザルタナテイヴ | ODS alloy powder, method for its production by plasma treatment, and use thereof |
| FR3080786A1 (en)* | 2018-05-03 | 2019-11-08 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | ODS ALLOY POWDER AND PROCESS FOR PRODUCING THE SAME BY PLASMA PROCESSING |
| CN110014145A (en)* | 2019-04-18 | 2019-07-16 | 北京科技大学 | A kind of preparation method of spherical iron-based powder |
| CN110343908A (en)* | 2019-08-30 | 2019-10-18 | 江苏奇纳新材料科技有限公司 | The hip moulding and heat treatment process of IN718 alloy powder and its alloy |
| CN111926207B (en)* | 2020-08-27 | 2021-12-14 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing nickel-based alloy |
| CN111926207A (en)* | 2020-08-27 | 2020-11-13 | 北京科技大学 | Method for preparing nickel-based alloy |
| CN112632716A (en)* | 2020-11-17 | 2021-04-09 | 北京科技大学 | Defect visualization analysis method for preparing turbine through powder injection molding and preparation method of titanium-aluminum alloy turbine |
| CN112453413B (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2023-05-12 | 中科南京绿色制造产业创新研究院 | Preparation method of oxide dispersion strengthening steel spherical powder for 3D printing |
| CN112453413A (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2021-03-09 | 中科院过程工程研究所南京绿色制造产业创新研究院 | Preparation method of oxide dispersion strengthened steel spherical powder for 3D printing |
| CN114015908A (en)* | 2021-09-28 | 2022-02-08 | 深圳艾利门特科技有限公司 | Nickel-phosphorus alloy and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN114058895A (en)* | 2021-11-16 | 2022-02-18 | 陕西宝锐金属有限公司 | Double nozzle spray forming Y2O3Process for particle reinforced Monel 400 alloy plate |
| CN117020204A (en)* | 2023-08-22 | 2023-11-10 | 钢研昊普科技有限公司 | 20CrNiMo bearing piece and preparation method and application thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102251131B (en) | 2012-11-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102251131B (en) | Method for preparing injection-molding nickel-base ODS (oxide dispersion strengthened) alloy | |
| CN103240412B (en) | Method for preparing powder super-alloy by near net shape | |
| CN100464905C (en) | Method for preparing adjustable nozzle blades for engine turbocharger using powder as raw material | |
| CN107400802B (en) | A kind of increasing material manufacturing titanium aluminium base alloy dusty material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN103233182B (en) | Forming method for nanometer beta' phase element and nanometer oxide composite reinforced Fe-based ODS alloy | |
| CN103121105B (en) | Method for preparing micro spherical niobium (Nb)-wolfram (W)-molybdenum (Mo)-zirconium (Zr) alloy powder | |
| CN101948970A (en) | Mechanical alloying method for preparing strengthened dispersion alloy of nickel-based oxide | |
| CN102127713B (en) | Oxide dispersion-strengthening ferrite steel with bicrystal structure and production method thereof | |
| JP2011122246A (en) | Method for processing nanostructured ferritic alloy and article produced thereby | |
| CN104004942B (en) | TiC particle-reinforced nickel-based composite material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110014145B (en) | Preparation method of spherical ferrite-based powder | |
| CN102127712A (en) | Micro alloyed oxide dispersion-strengthening ferrite steel and preparation method | |
| CN113458402A (en) | Method for preparing high-temperature alloy powder by using nickel-based high-temperature alloy powder return material | |
| CN104388788A (en) | Low-cost method for preparing niobium-base alloy | |
| CN109897991B (en) | High-entropy grain boundary modified nanocrystalline alloy powder and preparation method thereof | |
| CN111266571B (en) | Adhesive, TiAl alloy turbine injection molding preparation method and product | |
| CN116676504A (en) | A kind of nano oxide dispersion strengthening CoCrFeNi base high entropy alloy and its preparation method | |
| CN101979691B (en) | Method for preparing oxide dispersion strengthened cobalt-based super alloy | |
| CN110039062B (en) | Method for preparing spherical nickel-based powder | |
| CN113020605B (en) | In-situ toughened high-performance spherical tungsten powder for laser 3D printing and preparation method thereof | |
| CN109877312B (en) | A kind of preparation method of spherical ferrite-based ODS alloy powder | |
| CN104451225A (en) | Preparation method of superalloy composite material with double interconnected structure | |
| CN115044793B (en) | Manufacturing method for preparing two-phase high-entropy alloy by powder injection molding | |
| CN110512119A (en) | A kind of injection moulding nickel-base alloy powder, ejection forming method and nickel-based alloy articles | |
| CN113618068B (en) | Laser additive manufacturing method of high-performance GH3536 nickel-based superalloy without thermal cracks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20121128 |