CN102217237B - Media streaming performance monitoring method and device - Google Patents
Media streaming performance monitoring method and deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102217237B CN102217237BCN2011800007594ACN201180000759ACN102217237BCN 102217237 BCN102217237 BCN 102217237BCN 2011800007594 ACN2011800007594 ACN 2011800007594ACN 201180000759 ACN201180000759 ACN 201180000759ACN 102217237 BCN102217237 BCN 102217237B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- media stream
- sending
- data
- performance monitoring
- sequence number
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/08—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/10—Active monitoring, e.g. heartbeat, ping or trace-route
- H04L43/106—Active monitoring, e.g. heartbeat, ping or trace-route using time related information in packets, e.g. by adding timestamps
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/60—Network streaming of media packets
- H04L65/61—Network streaming of media packets for supporting one-way streaming services, e.g. Internet radio
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/80—Responding to QoS
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明实施例涉及通信技术,尤其涉及一种媒体流性能监控方法及设备。Embodiments of the present invention relate to communication technologies, and in particular to a method and device for monitoring media stream performance.
背景技术Background technique
媒体流的数据包通过网络传输通常存在网络丢包和抖动,网络在实际的运营中,若某段链路或者是某个节点发生故障,需要快速定位出故障发生的链路和设备,修复设备和链路,保障业务的正常进行。为了得到用户体验的客观情况,需要对用户所请求的媒体流实施监测,监测该媒体流的丢包、抖动和时延,当出现较大的异常(丢包率增大、时延值偏大或抖动值偏大)时需要监测网络传输设备是否存在故障。There are usually network packet loss and jitter in the transmission of media stream data packets through the network. In the actual operation of the network, if a certain link or a certain node fails, it is necessary to quickly locate the faulty link and equipment and repair the equipment. and links to ensure the normal operation of services. In order to obtain the objective situation of user experience, it is necessary to monitor the media stream requested by the user, and monitor the packet loss, jitter and delay of the media stream. or the jitter value is too large), it is necessary to monitor whether the network transmission equipment is faulty.
在媒体流传输过程中,为监测网络丢包和抖动情况,一种方法是,根据TS(Transport Stream,传输流)包中的CC(continuity counter,连续计数器)来计算网络丢包。CC是TS头部的一个字段,占用4位,可表示0到15。根据CC的不连续,可以判定丢失了多少个TS包。另一种方法是对RTP(Real TimeTransport Protocol,实时传输协议)包使用RTP头部的序列号和时间戳来计算网络丢包和抖动。RTP序列号为RTP头部的1个16位的字段,通常每发送一个RTP包该数值加一。RTP时间戳为RTP头部的一个32位字段,用来记录时间,时间精度为微秒。In the process of media stream transmission, in order to monitor network packet loss and jitter, one method is to calculate network packet loss according to the CC (continuity counter) in the TS (Transport Stream, transport stream) packet. CC is a field in the TS header, which occupies 4 bits and can represent 0 to 15. According to the discontinuity of the CC, it can be determined how many TS packets are lost. Another method is to use the serial number and timestamp of the RTP header to calculate the network packet loss and jitter for the RTP (Real TimeTransport Protocol, real-time transport protocol) packet. The RTP sequence number is a 16-bit field in the RTP header, and usually increases by one each time an RTP packet is sent. The RTP timestamp is a 32-bit field in the RTP header, used to record the time, and the time precision is microseconds.
然而,根据TS流中的CC计算网络丢包依赖于应用层的TS信息,根据RTP包中的序列号和时间戳来计算网络丢包和抖动依赖于应用层的RTP信息,如果网络应用没有使用RTP或TS来封装数据包,则无法通过上述两种方法实现媒体流性能的监控。However, the calculation of network packet loss based on the CC in the TS stream depends on the TS information of the application layer, and the calculation of network packet loss and jitter based on the sequence number and timestamp in the RTP packet depends on the RTP information of the application layer. If the network application does not use If RTP or TS is used to encapsulate data packets, the monitoring of media stream performance cannot be realized through the above two methods.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例提供一种媒体流性能监控方法及设备,用以解决现有的媒体流性能监控方法依赖于数据包应用层封装信息的缺陷,提供了通用的媒体流性能监控方法。The embodiments of the present invention provide a media stream performance monitoring method and equipment, which are used to solve the defect that the existing media stream performance monitoring method relies on encapsulation information of the data packet application layer, and provide a general media stream performance monitoring method.
本发明实施例提供一种媒体流性能监控方法,包括:An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for monitoring media stream performance, including:
在IP数据包中填充媒体流性能监控数据;所述媒体流性能监控数据包括所述IP数据包的时间戳和所述IP数据包的序列号;Filling media stream performance monitoring data in the IP data packet; the media stream performance monitoring data includes the timestamp of the IP data packet and the sequence number of the IP data packet;
向下游节点发送所述填充了媒体流性能监控数据的IP数据包。Send the IP data packet filled with the media stream performance monitoring data to the downstream node.
本发明实施例还提供一种媒体流性能监控方法,包括:The embodiment of the present invention also provides a media stream performance monitoring method, including:
接收上游节点发送的包括媒体流性能监控数据的IP数据包;所述媒体流性能监控数据包括所述IP数据包的发送时间戳和所述IP数据包的发送序列号;Receiving an IP packet sent by an upstream node that includes media stream performance monitoring data; the media stream performance monitoring data includes a sending timestamp of the IP data packet and a sending sequence number of the IP data packet;
根据所述媒体流性能监控数据,监控媒体流的性能。The performance of the media stream is monitored according to the media stream performance monitoring data.
本发明实施例还提供一种媒体流传输设备,包括:The embodiment of the present invention also provides a media stream transmission device, including:
填充模块,用于在IP数据包中填充媒体流性能监控数据;所述媒体流性能监控数据包括所述IP数据包的发送时间戳和所述IP数据包的发送序列号;A filling module, configured to fill media stream performance monitoring data in the IP data packet; the media stream performance monitoring data includes the sending timestamp of the IP data packet and the sending sequence number of the IP data packet;
发送器,用于向下游节点发送所述填充了媒体流性能监控数据的IP数据包。A sender, configured to send the IP data packet filled with media stream performance monitoring data to a downstream node.
本发明实施例还提供一种媒体流性能监控设备,包括:The embodiment of the present invention also provides a media stream performance monitoring device, including:
接收器,用于接收上游节点发送的包括媒体流性能监控数据的IP数据包;所述媒体流性能监控数据包括所述IP数据包的发送时间戳和所述IP数据包的发送序列号;The receiver is configured to receive an IP packet sent by an upstream node and includes media stream performance monitoring data; the media stream performance monitoring data includes a sending timestamp of the IP data packet and a sending sequence number of the IP data packet;
性能监控模块,用于根据所述媒体流性能监控数据,监控媒体流的性能。A performance monitoring module, configured to monitor the performance of the media stream according to the media stream performance monitoring data.
本发明实施例媒体流中,发送IP数据包的节点在IP数据包中封装了媒体流性能监控数据,接收到IP数据包的网络节点根据其中的媒体流性能监控数据,监控网络的媒体流性能,例如网络的丢包数、时延和抖动等。由于本发明实施例采用了通用的IP封装来封装媒体流,能够在缺少应用层封装信息时实现媒体流性能监控。In the media stream of the embodiment of the present invention, the node sending the IP data packet encapsulates the media stream performance monitoring data in the IP data packet, and the network node receiving the IP data packet monitors the media stream performance of the network according to the media stream performance monitoring data therein , such as packet loss, delay, and jitter of the network. Since the embodiment of the present invention adopts the general IP encapsulation to encapsulate the media stream, the performance monitoring of the media stream can be realized when the encapsulation information of the application layer is lacking.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作一简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动性的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention or the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description These are some embodiments of the present invention. For those skilled in the art, other drawings can also be obtained according to these drawings without any creative effort.
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图;Fig. 1 is a flow chart of a method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2为本发明实施例提供的另一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图;FIG. 2 is a flowchart of another media stream performance monitoring method provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
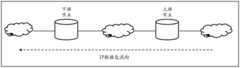
图3为图2的应用场景图;FIG. 3 is an application scenario diagram of FIG. 2;
图4为本发明实施例提供的再一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图;FIG. 4 is a flow chart of another media stream performance monitoring method provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图5为本发明实施例提供的又一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图;FIG. 5 is a flow chart of another method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图6为本发明实施例提供的还一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图;FIG. 6 is a flow chart of another method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图7为图6的应用场景图;FIG. 7 is an application scenario diagram of FIG. 6;
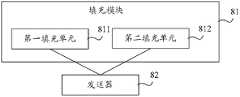
图8A为本发明实施例提供的一种媒体流传输设备结构示意图;FIG. 8A is a schematic structural diagram of a media stream transmission device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图8B为本发明实施例提供的另一种媒体传输设备结构示意图;FIG. 8B is a schematic structural diagram of another media transmission device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图8C为本发明实施例提供的又一种媒体传输设备结构示意图;FIG. 8C is a schematic structural diagram of another media transmission device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图8D为本发明实施例提供的再一种媒体传输设备结构示意图;FIG. 8D is a schematic structural diagram of another media transmission device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
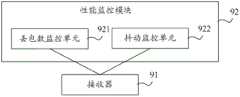
图9A为本发明实施例提供的一种媒体流性能监控设备结构示意图;FIG. 9A is a schematic structural diagram of a media stream performance monitoring device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图9B为本发明实施例提供的另一种媒体流性能监控设备结构示意图。FIG. 9B is a schematic structural diagram of another media stream performance monitoring device provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments It is a part of embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图。本实施例主要从发送IP数据包的节点角度说明媒体流性能监控方法的技术方案。发送IP数据包的节点可为终端设备或网络侧设备。如图1所示,本实施例包括:FIG. 1 is a flow chart of a method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment mainly illustrates the technical solution of the media stream performance monitoring method from the perspective of the node sending the IP data packet. The node sending the IP data packet may be a terminal device or a network side device. As shown in Figure 1, this embodiment includes:
步骤11:在IP数据包中填充媒体流性能监控数据;媒体流性能监控数据包括IP数据包的发送时间戳和IP数据包的发送序列号。Step 11: filling the IP data packet with media stream performance monitoring data; the media stream performance monitoring data includes the sending timestamp of the IP data packet and the sending sequence number of the IP data packet.
步骤12:向下游节点发送填充了媒体流性能监控数据的IP数据包。Step 12: Send the IP data packet filled with the media stream performance monitoring data to the downstream node.
终端设备或网络侧设备向下游节点发送IP数据包之前,将媒体流性能监控数据填充到IP数据包中。在填充媒体流性能监控数据时,可在媒体流的每个IP数据包中都填充媒体流性能监控数据。为提高系统性能,也可以每间隔几个IP数据包填充一次媒体流性能监控数据。例如,对媒体流进行采样,在采样出的IP数据包中填充媒体流性能监控数据。其中,IP数据包的发送时间戳可为发送IP数据包时的系统时间。IP数据包的发送序列号可为IP数据包被发送的次序。Before the terminal device or the network side device sends the IP data packet to the downstream node, the media flow performance monitoring data is filled into the IP data packet. When filling the media stream performance monitoring data, the media stream performance monitoring data may be filled in each IP data packet of the media stream. In order to improve system performance, the media flow performance monitoring data can also be filled every few IP data packets. For example, the media stream is sampled, and the media stream performance monitoring data is filled in the sampled IP data packet. Wherein, the sending timestamp of the IP data packet may be the system time when the IP data packet is sent. The sending sequence numbers of the IP data packets may be the order in which the IP data packets are sent.
为统计媒体流中已发送IP数据包的个数,可为待监控的媒体流设置计数器,IP数据包的发送序列号可为计数器的值。该媒体流每发送一个IP数据包计数器累加一。计数器的初始值可任意设置,例如初始值为0。另外,计数器也可以只统计媒体流中已发送的、填充有发送序列号的IP数据包的个数。In order to count the number of sent IP data packets in the media stream, a counter can be set for the media stream to be monitored, and the sending sequence number of the IP data packet can be the value of the counter. The counter is incremented by one each time an IP data packet is sent by the media stream. The initial value of the counter can be set arbitrarily, for example, the initial value is 0. In addition, the counter may only count the number of IP data packets sent in the media stream and filled with the sending sequence number.
如表1所示,IP首部中包括16位标识字段和选项字段。可将媒体流性能监控数据复用在IP首部的16标识字段中,也可将媒体流性能监控数据填充到IP首部的选项字段中。IP首部的选项字段,是IP首部中一个可变长的可选字段,最大长度为40字节。As shown in Table 1, the IP header includes a 16-bit identification field and an option field. The media stream performance monitoring data can be multiplexed in the 16 identification fields of the IP header, and the media stream performance monitoring data can also be filled into the option field of the IP header. The option field of the IP header is a variable-length optional field in the IP header, with a maximum length of 40 bytes.
表1为IP首部结构Table 1 shows the IP header structure
将媒体流性能监控数据复用在IP首部的16标识字段中时,可将发送时间戳和发送序列号同时复用在IP首部的16位标识字段,发送时间戳和发送序列号各占用IP标识字段的若干位。也可将发送时间戳和发送序列号分时复用在IP首部的16标识字段,即将发送时间戳和发送序列号分别填充到两个IP数据包的IP标识字段中。When the media stream performance monitoring data is multiplexed in the 16-bit identification field of the IP header, the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number can be multiplexed in the 16-bit identification field of the IP header at the same time, and the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number each occupy the IP identifier bits of the field. The sending time stamp and the sending sequence number can also be time-division-multiplexed in the 16 identification fields of the IP header, that is, the sending time stamp and the sending sequence number are respectively filled in the IP identification fields of the two IP data packets.
将媒体流性能监控数据复用在IP首部的选项字段时,可将发送时间戳和发送序列号同时复用在IP首部的选项字段,发送时间戳和发送序列号各占用IP首部的选项字段的若干位。也可将发送时间戳和发送序列号分时复用在IP首部的IP首部的选项字段,即将发送时间戳和发送序列号分别填充到两个IP数据包的IP首部的选项字段。When the media stream performance monitoring data is multiplexed in the option field of the IP header, the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number can be multiplexed in the option field of the IP header at the same time, and the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number each occupy 20% of the option field of the IP header. several bits. It is also possible to time-multiplex the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number in the option field of the IP header of the IP header, that is, to fill the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number into the option fields of the IP header of the two IP data packets respectively.
可有多种方法分时复用IP首部的16位标识字段或选项字段,例如,在第1个IP数据包中填充发送序列号,在第2个IP数据包中填充发送时间戳,第3个IP数据包中填充发送序列号,在第4个IP数据包中填充发送时间戳......依次类推,每间隔1个IP数据包填充一次发送时间戳。又例如,在第1个IP数据包中填充发送序列号,在第2、3和4个IP数据包中分别填充发送时间戳,在第5个IP数据包中填充发送序列号,在第6、7和8个IP数据包中分别填充发送时间戳......依次类推,每间隔3个IP数据包填充一次发送序列号。其中,分时复用可以通过多种方法标识当前IP数据包中填充的是发送时间戳还是发送序列号,一种方法是使用16位标识字段的最高位标识当前IP首部的标识字段的低15位填充的是发送时间戳还是发送序列号。例如最高位为0时,表示低15位填充的是发送时间戳;最高位为1时,表示低15位填充的是发送序列号。另一种方法是通过消息分时复用,一段时间复用为序列号,另一段时间复用为时间戳。网络节点之间约定,在某段时间内的IP数据包,其中IP首部的标识字段中复用的是发送时间戳,在另一段时间内的IP数据包,其中IP首部的标识字段中复用的是发送序列号。There are many ways to time-multiplex the 16-bit identification field or option field of the IP header, for example, filling the sending sequence number in the first IP data packet, filling the sending time stamp in the second IP data packet, and filling the sending time stamp in the third IP data packet. Fill the sending sequence number in the first IP data packet, fill the sending time stamp in the fourth IP data packet...and so on, fill in the sending time stamp every IP data packet. For another example, the sending sequence number is filled in the first IP data packet, the sending timestamp is filled in the second, third and fourth IP data packets respectively, the sending sequence number is filled in the fifth IP data packet, and the sending sequence number is filled in the sixth IP data packet. , 7 and 8 IP data packets are respectively filled with sending time stamps...and so on, and the sending sequence number is filled every 3 IP data packets. Among them, time-division multiplexing can identify whether the current IP data packet is filled with a transmission time stamp or a transmission sequence number through various methods. One method is to use the highest bit of the 16-bit identification field to identify the lower 15 bits of the identification field of the current IP header. Whether the bits are filled with a send timestamp or a send sequence number. For example, when the highest bit is 0, it means that the lower 15 bits are filled with the sending timestamp; when the highest bit is 1, it means that the lower 15 bits are filled with the sending sequence number. Another method is to use time-division multiplexing of messages, a period of time is multiplexed as a serial number, and another period of time is multiplexed as a timestamp. It is agreed between network nodes that for IP data packets within a certain period of time, the identification field of the IP header is multiplexed with the sending timestamp, and for IP data packets within another period of time, the identification field of the IP header is multiplexed with is to send the serial number.
本发明实施例的媒体流性能监控方法中,发送IP数据包的节点在IP数据包中封装媒体流性能监控数据,接收到IP数据包的下游节点根据其中的媒体流性能监控数据,监控网络的媒体流性能,例如网络的丢包数、时延和抖动等。由于本发明实施例采用了通用的IP封装来封装媒体流,能够在缺少应用层封装信息时实现媒体流性能监控。本发明实施例可以用于媒体流的性能监控,也可用于网络设备的故障定界和定位。In the media stream performance monitoring method of the embodiment of the present invention, the node sending the IP data packet encapsulates the media stream performance monitoring data in the IP data packet, and the downstream node receiving the IP data packet monitors the network according to the media stream performance monitoring data therein. Media stream performance, such as packet loss, delay, and jitter of the network. Since the embodiment of the present invention adopts the general IP encapsulation to encapsulate the media stream, the performance monitoring of the media stream can be realized when the encapsulation information of the application layer is lacking. The embodiments of the present invention can be used for performance monitoring of media streams, and can also be used for delimiting and locating faults of network equipment.
图2为本发明实施例提供的另一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图。图3为图2的应用场景图。如图3所示,为了检测从上游节点到下游节点的两个设备间的网络抖动和丢包数,可在上游节点的出接口板上,对某条媒体流进行IP首部的标识字段复用,即在IP首部的标识字段复用发送序列号和发送时间戳。本实施例主要说明上游节点如何采用消息分时复用方法在IP首部的标识字段中填充发送序列号和发送时间戳。FIG. 2 is a flow chart of another method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3 is an application scenario diagram of FIG. 2 . As shown in Figure 3, in order to detect the network jitter and packet loss between the two devices from the upstream node to the downstream node, the identification field of the IP header can be multiplexed for a certain media stream on the outgoing interface board of the upstream node , that is, multiplex the sending sequence number and sending timestamp in the identification field of the IP header. This embodiment mainly explains how the upstream node fills the sending sequence number and the sending time stamp in the identification field of the IP header by using the message time-division multiplexing method.
如图2所示,本实施例包括:As shown in Figure 2, this embodiment includes:
步骤21:接收待监控媒体流的IP数据包。Step 21: Receive the IP data packet of the media stream to be monitored.
步骤22:判断是否在该IP数据包中填充发送时间戳。如果是,执行步骤23,否则执行步骤24。Step 22: judging whether to fill the sending timestamp in the IP data packet. If yes, go to step 23, otherwise go to step 24.
本实施例采用的标识字段复用策略是:每间隔一个IP数据包填充一次发送时间戳,未填充发送时间戳的IP数据包填充发送序列号。步骤22中,根据上述标识字段复用策略判断是否在该IP数据包中填充发送时间戳。The identification field multiplexing strategy adopted in this embodiment is: fill in the sending time stamp every other IP data packet, and fill the sending sequence number in the IP data packet not filled with the sending time stamp. In
步骤23:将当前的系统时间作为该IP数据包的发送时间戳填充到IP首部的标识字段。Step 23: Fill the identification field of the IP header with the current system time as the sending timestamp of the IP data packet.
填充到标识字段中的系统时间的位数可根据系统对时间精度的要求而定。发送时间戳占用的数据位数越多,表示的时间精度越高。因此,在时间精度要求较高时,可从系统时间中提取更多数据位填充到标识字段中。The number of digits of the system time filled in the identification field can be determined according to the system's requirements for time precision. The more data bits occupied by the sending timestamp, the higher the precision of the expressed time. Therefore, when the time precision is required to be high, more data bits can be extracted from the system time and filled into the identification field.
步骤24:将计数器的值作为该IP数据包的发送序列号填充到IP首部的标识字段,并将计数器累加一。Step 24: Fill the value of the counter into the identification field of the IP header as the sending sequence number of the IP data packet, and add one to the counter.
为待监控的媒体流设置16位的计数器,用于统计媒体流中已发送的、填充有发送序列号的IP数据包的个数。填充到标识字段中的计数器的位数可根据系统的流密度而定。因此,可取出计数器的若干位填充到IP首部的标识字段。发送序列号占用的数据位数越多,表示的流密度越高。在流密度较高时,表示数据包数越多,可从计数器中提取更多数据位填充到IP标识字段中。A 16-bit counter is set for the media stream to be monitored, which is used to count the number of IP data packets sent in the media stream and filled with the sending sequence number. The number of bits of the counter that is filled into the identification field can vary depending on the flow density of the system. Therefore, several bits of the counter can be taken out and filled into the identification field of the IP header. The more data bits occupied by the sending serial number, the higher the flow density represented. When the flow density is high, it means that the number of data packets is more, and more data bits can be extracted from the counter and filled into the IP identification field.
步骤25:计算IP首部校验和,并填充到IP数据包中的相应字段。Step 25: Calculate the IP header checksum and fill it into the corresponding field in the IP data packet.
步骤26:在该IP数据包中添加链路层信息,计算CRC(循环冗余校验),并将计算得到的CRC填充到IP数据包中的相应字段。Step 26: Add link layer information in the IP data packet, calculate CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check), and fill the calculated CRC into corresponding fields in the IP data packet.
步骤27:向下游节点发送填充了媒体流性能监控数据、链路层信息和CRC的数据包。Step 27: Send a data packet filled with media stream performance monitoring data, link layer information and CRC to the downstream node.
由于IP首部的标识字段是IP数据包中必有的字段,因而将发送时间戳和发送序列号填充到IP首部的标识字段的方法具有通用性,网络节点可监控任何媒体流的性能。Since the identification field of the IP header is a necessary field in the IP data packet, the method of filling the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number into the identification field of the IP header is universal, and the network node can monitor the performance of any media flow.
图4为本发明实施例提供的再一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图。本实施例主要说明上游节点如何将发送序列号和发送时间戳同时填充到IP首部的选项字段。如表1所示,IP首部含有选项字段。可在IP首部的选项字段中携带发送时间戳和发送序列号。IP首部的选项字段的一般格式是1个字节的代码(code),一个字节的长度(len),一个字节的指针(ptr)。长度包括前面3字节在内的整个IP首部的选项字段最大值为40个字节。FIG. 4 is a flow chart of another method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment mainly describes how the upstream node simultaneously fills the sending sequence number and the sending time stamp into the option field of the IP header. As shown in Table 1, the IP header contains an option field. The sending timestamp and sending sequence number can be carried in the option field of the IP header. The general format of the option field in the IP header is a 1-byte code (code), a 1-byte length (len), and a 1-byte pointer (ptr). The maximum length of the option field of the entire IP header including the first 3 bytes is 40 bytes.
如图4所示,本实施例包括:As shown in Figure 4, this embodiment includes:
步骤41:接收待监控媒体流的IP数据包。Step 41: Receive the IP data packet of the media stream to be monitored.
步骤42:判断是否可在IP首部的选项字段中填充媒体流性能监控数据。如果是,执行步骤43,否则执行步骤46。Step 42: Determine whether the option field of the IP header can be filled with media stream performance monitoring data. If yes, go to step 43, otherwise go to step 46.
根据IP首部的选项字段的结构,在其中填充数据时需相应添加数据的类型和长度等信息,且填充数据所占用的字节数必须是4的整数倍。在IP首部的选项字段中填充媒体流性能监控数据时,在其中添加的类型和长度等信息至少需占用2至3个字节的空间,而类型和长度等信息占用的字节数还需满足4的整数倍的要求,因此,在IP首部的选项字段中填充媒体流性能监控数据时,至少需占用8个字节的空间。如表1所示,除IP首部的选项字段之外,IP首部的其它字段的固定长度为20个字节,IP首部的选项字段和IP首部的其它字段的总长度为60个字节。因而,填充媒体流性能监控数据之前IP首部长度小于等于52个字节时,才能在选项字段中填充媒体流性能监控数据。如果在填充之前IP首部长度大于52字节,则不能在选项字段填充媒体流性能监控数据。According to the structure of the option field in the IP header, information such as the type and length of the data needs to be added when filling the data, and the number of bytes occupied by the filling data must be an integer multiple of 4. When filling the media stream performance monitoring data in the option field of the IP header, the type and length and other information added in it need to occupy at least 2 to 3 bytes of space, and the number of bytes occupied by the type and length and other information needs to meet Therefore, at least 8 bytes of space are required when filling the media stream performance monitoring data in the option field of the IP header. As shown in Table 1, except for the option field of the IP header, the fixed length of other fields of the IP header is 20 bytes, and the total length of the option field of the IP header and other fields of the IP header is 60 bytes. Therefore, the media stream performance monitoring data can only be filled in the option field when the length of the IP header before filling the media stream performance monitoring data is less than or equal to 52 bytes. If the IP header length is greater than 52 bytes before filling, the media stream performance monitoring data cannot be filled in the option field.
步骤43:将当前的系统时间作为该IP数据包的发送时间戳填充到IP首部的选项字段中时间戳位置,将计数器的值作为该IP数据包的发送序列号填充到IP首部的选项字段中序列号位置,并将计数器累加一。Step 43: Fill the current system time as the sending timestamp of the IP packet into the timestamp position in the option field of the IP header, and fill the value of the counter into the option field of the IP header as the sending sequence number of the IP packet serial number position and increment the counter by one.
步骤44:修改IP数据包首部的长度和IP数据包的总长度。Step 44: Modify the length of the header of the IP data packet and the total length of the IP data packet.
在IP首部的选项字段中填充发送序列号和发送时间戳后,计算IP首部的长度,根据计算结果修改IP首部的4位首部长度字段的值。并计算IP数据包的总长度,根据计算结果修改IP首部的16位总长度字段的值。After filling the sending sequence number and sending time stamp in the option field of the IP header, calculate the length of the IP header, and modify the value of the 4-bit header length field of the IP header according to the calculation result. And calculate the total length of the IP data packet, and modify the value of the 16-bit total length field of the IP header according to the calculation result.
步骤45:根据MTU(最大传输单元,Maximum Transmission Unit)实施IP分片处理。Step 45: Implement IP fragmentation processing according to MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit, Maximum Transmission Unit).
MTU的长度表示一次能传输的最大字节数。在选项字段中填充发送时间戳和发送序列号后,IP数据包的总长度增加。当IP数据包的总长度大于MTU的长度时,对IP数据包进行分片,即将一个IP数据包分成多个IP数据包发送。The length of MTU indicates the maximum number of bytes that can be transmitted at one time. After filling the send timestamp and send sequence number in the option field, the total length of the IP packet is increased. When the total length of the IP data packet is greater than the length of the MTU, the IP data packet is fragmented, that is, one IP data packet is divided into multiple IP data packets and sent.
步骤46:计算IP首部校验和,并填充到IP数据包中的相应字段。Step 46: Calculate the IP header checksum and fill it into the corresponding field in the IP data packet.
步骤47:在该IP数据包中添加链路层信息,计算CRC,并将计算得到的CRC填充到IP数据包中的相应字段。Step 47: Add link layer information to the IP data packet, calculate CRC, and fill the calculated CRC into corresponding fields in the IP data packet.
步骤48:向下游节点发送填充了媒体流性能监控数据、链路层信息和CRC的数据包。Step 48: Send a data packet filled with media stream performance monitoring data, link layer information and CRC to the downstream node.
由于每一个IP数据包都可以包含选项字段,因而上游节点可以在IP首部的选项字段中填充发送序列号和发送时间戳,下游节点根据IP数据包中的发送序列号和发送时间戳计算网络抖动和丢包的方法,能够实现缺少应用层封装信息时的媒体流性能监控,具有通用性。Since each IP packet can contain an option field, the upstream node can fill the sending sequence number and sending timestamp in the option field of the IP header, and the downstream node calculates the network jitter according to the sending sequence number and sending timestamp in the IP packet The method of packet loss and packet loss can realize the performance monitoring of the media flow when the encapsulation information of the application layer is lacking, and has universality.
图5为本发明实施例提供的又一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图。本实施例主要从接收IP数据包的节点的角度说明媒体流性能监控方法的技术方案。如图5所示,本实施例包括:FIG. 5 is a flow chart of another method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment mainly illustrates the technical solution of the media stream performance monitoring method from the perspective of the node receiving the IP data packet. As shown in Figure 5, this embodiment includes:
步骤51:接收上游节点发送的包括媒体流性能监控数据的IP数据包;媒体流性能监控数据包括IP数据包的发送时间戳和IP数据包的发送序列号。Step 51: Receive an IP data packet including media flow performance monitoring data sent by an upstream node; the media flow performance monitoring data includes a sending time stamp of the IP data packet and a sending sequence number of the IP data packet.
上游节点将媒体流性能监控数据复用在IP首部的16位标识字段中时,可将发送时间戳和发送序列号同时复用在IP首部的16位标识字段,发送时间戳和发送序列号各占用IP位标识字段的若干位。也可将发送时间戳和发送序列号分时复用在IP首部的16位标识字段。When the upstream node multiplexes the media stream performance monitoring data in the 16-bit identification field of the IP header, it can simultaneously multiplex the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number in the 16-bit identifying field of the IP header, and the sending timestamp and sending sequence number are respectively Occupies several bits of the IP bit identification field. The sending time stamp and sending sequence number can also be time-division multiplexed in the 16-bit identification field of the IP header.
步骤52:根据IP数据包中的媒体流性能监控数据,监控媒体流的性能。Step 52: Monitor the performance of the media stream according to the media stream performance monitoring data in the IP data packet.
监控媒体流的性能包括监控媒体流的丢包数、时延和抖动等。Monitoring the performance of media streams includes monitoring the number of lost packets, delay, and jitter of media streams.
具体地,对于媒体流的丢包数,在发送时间戳和发送序列号分时填充到两个IP数据包中的IP位标识字段时,根据接收到的最大发送序列号、最小发送序列号、已接收到的包括有发送序列号的IP数据包的个数,监控媒体流的丢包数。对于媒体流的抖动,可根据两个IP数据包中的发送时间戳和两个IP数据包的到达时间,监控媒体流的抖动。Specifically, for the number of lost packets of the media stream, when the sending time stamp and the sending sequence number are filled into the IP bit identification field in the two IP data packets, according to the received maximum sending sequence number, minimum sending sequence number, The number of received IP data packets including the sending sequence number, and the number of packet loss in the monitoring media stream. For the jitter of the media stream, the jitter of the media stream can be monitored according to the sending time stamps in the two IP data packets and the arrival time of the two IP data packets.
以下对媒体流性能监控数据:丢包数、抖动和时延的概念进行说明。丢包数是媒体流中被丢失的数据包的个数。时延是一个数据包在传输过程中消耗的时间。通常用一个数据包的实际到达时间与实际发送时间的差值来表示该数据包的时延。媒体流在传输过程中,各种原因(例如大量P2P流量、文件下载和VoIP通话)都可引起网络瞬时拥塞,导致数据包通过网络节点的时延发生变化,这就是所谓的抖动。抖动反映两个数据包的时延变化。通常情况下,抖动的参考值为200ms,即抖动允许的范围是0~200ms。在抖动达到200ms时,表明传输抖动开始出现明显的变化。虽还没有立刻造成媒体流播放质量问题,但应对媒体流进行监控。The following describes the concepts of media stream performance monitoring data: packet loss, jitter, and delay. Lost Packets is the number of lost data packets in the media stream. Latency is the time a packet takes in transit. Usually, the difference between the actual arrival time and the actual sending time of a data packet is used to represent the delay of the data packet. During the transmission of media streams, various reasons (such as a large amount of P2P traffic, file downloads, and VoIP calls) can cause instantaneous network congestion, resulting in changes in the delay of data packets passing through network nodes, which is the so-called jitter. Jitter reflects the variation in the delay between two packets. Usually, the reference value of jitter is 200ms, that is, the allowed range of jitter is 0-200ms. When the jitter reaches 200ms, it indicates that the transmission jitter begins to change significantly. Although there is no immediate problem with the playback quality of the media stream, the media stream should be monitored.
本发明实施例的媒体流性能监控方法中,接收到IP数据包的下游节点根据其中的媒体流性能监控数据,监控网络的媒体流性能,例如网络的丢包数、时延和抖动等。由于本发明实施例采用了通用的IP封装来封装媒体流,能够在缺少应用层封装信息时实现媒体流性能监控本发明实施例可以用于媒体流的性能监控,也可用于网络设备的故障定界和定位。In the media stream performance monitoring method of the embodiment of the present invention, the downstream node receiving the IP data packet monitors the media stream performance of the network, such as the number of lost packets, time delay and jitter of the network, according to the media stream performance monitoring data therein. Since the embodiment of the present invention adopts the general IP encapsulation to encapsulate the media stream, the performance monitoring of the media stream can be realized when the encapsulation information of the application layer is lacking. boundaries and positioning.
图6为本发明实施例提供的还一种媒体流性能监控方法流程图。图7为图6的应用场景图。如图7所示,路径上包括三个网络侧设备:网络侧设备R3、网络侧设备R2和网络侧设备R1。在该路径上的传输质量变差时,为定位路径上发生故障的设备,上游节点在该路径上传输的媒体流的IP数据包中添加IP数据包的发送时间戳和发送序列号,在路径上的下游节点依次监控网络的丢包数、时延和抖动。出现丢包的网络设备就可能是发生故障的设备。FIG. 6 is a flow chart of another method for monitoring media stream performance provided by an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 7 is an application scenario diagram of FIG. 6 . As shown in FIG. 7 , the path includes three network-side devices: network-side device R3 , network-side device R2 , and network-side device R1 . When the transmission quality on the path deteriorates, in order to locate the faulty device on the path, the upstream node adds the sending time stamp and the sending sequence number of the IP data packet to the IP data packet of the media stream transmitted on the path. The downstream nodes on the network monitor the packet loss, delay and jitter of the network in turn. A network device experiencing packet loss could be a malfunctioning device.
如图6所示,本实施例包括:As shown in Figure 6, this embodiment includes:
步骤60:R3接收填充有发送时间戳和发送序列号的媒体流的IP数据包。Step 60: R3 receives the IP data packet of the media stream filled with the sending time stamp and the sending sequence number.
步骤61:R3根据IP数据包中的发送时间戳和发送序列号,计算媒体流的丢包数、时延和抖动。Step 61: R3 calculates the number of lost packets, time delay and jitter of the media stream according to the sending time stamp and sending sequence number in the IP data packet.
丢包数可根据公式1和公式2计算。The number of lost packets can be calculated according to Formula 1 and Formula 2.
pkt_num_expected=max_seq-base_seq (公式1)pkt_num_expected=max_seq-base_seq (Formula 1)
pkt_num_lost=pkt_num_expected-pkt_num_received (公式2)pkt_num_lost=pkt_num_expected-pkt_num_received (Formula 2)
其中,pkt_num_expected表示期望接收到的填充有发送序列号的IP数据包的个数,pkt_num_received表示实际接收到的填充有发送序列号的IP数据包的个数,max_seq表示接收到的最大序列号,pkt_num_lost表示丢包数,base_seq表示接收到的最小序列号。通过公式2可监控媒体流中已填充发送序列号的IP数据包在传输过程中的丢包数。Among them, pkt_num_expected indicates the expected number of received IP packets filled with sending sequence numbers, pkt_num_received indicates the number of actually received IP packets filled with sending sequence numbers, max_seq indicates the maximum sequence number received, and pkt_num_lost Indicates the number of lost packets, and base_seq indicates the minimum sequence number received. The number of lost packets in the transmission process of the IP data packets filled with the sending sequence number in the media stream can be monitored by formula 2.
时延可根据公式3,抖动可根据公式4计算。The time delay can be calculated according to Equation 3, and the jitter can be calculated according to Equation 4.
Di=Ri-Si (公式3)Di =Ri -Si (Formula 3)
J(i,j)=Di-Dj=(Ri-Si)-(Rj-Sj)=(Ri-Rj)-(Si-Sj) (公式4)J(i,j)=Di -Dj =(Ri -Si )-(Rj -Sj )=(Ri -Rj )-(Si -Sj ) (Formula 4)
其中,R表示包的接收时间,S是复用在IP数据包中的发送时间戳。i,j是包的实际到达序号。Di表示第i个包的时延。J(i,j)表示第i个包和第j个包的抖动。Wherein, R represents the receiving time of the packet, and S is the sending timestamp multiplexed in the IP data packet. i, j is the actual arrival sequence number of the packet. Di represents the delay of the i-th packet. J(i, j) represents the jitter of the i-th packet and the j-th packet.
步骤62:R3修改IP数据包中的发送时间戳和发送序列号。Step 62: R3 modifies the sending time stamp and sending sequence number in the IP data packet.
步骤63:R3向下游节点R2转发修改后的IP数据包。Step 63: R3 forwards the modified IP data packet to the downstream node R2.
步骤64:R2根据IP数据包中的发送时间戳和发送序列号,计算媒体流的丢包数、时延和抖动。Step 64: R2 calculates the number of lost packets, time delay and jitter of the media stream according to the sending time stamp and sending sequence number in the IP data packet.
步骤65:R3修改IP数据包中发送时间戳和发送序列号。Step 65: R3 modifies the sending time stamp and sending sequence number in the IP data packet.
步骤66:R3向下游节点R1转发修改后的IP数据包。Step 66: R3 forwards the modified IP data packet to the downstream node R1.
步骤67:R1根据IP数据包中的发送时间戳和发送序列号,计算媒体流的丢包数、时延和抖动。Step 67: R1 calculates the number of packet loss, delay and jitter of the media stream according to the sending time stamp and sending sequence number in the IP data packet.
假设R3、R2和R1上的丢包数和时延情况如表2所示,从丢包情况可以看出,R2的入接口上没有出现丢包,R2的出接口上开始丢包,因此可以初步断定R2内部出现了故障。从抖动情况可以看出,R2的入接口上抖动小于200ms,在抖动允许范围内,R2的出接口上抖动变长,超出抖动允许范围。根据抖动情况也可以初步断定R2内部出现了故障。Assume that the number of packet loss and delay on R3, R2, and R1 are shown in Table 2. From the packet loss situation, it can be seen that there is no packet loss on the inbound interface of R2, and packet loss begins on the outbound interface of R2. Therefore, it can be It is preliminarily concluded that there is a malfunction inside R2. It can be seen from the jitter situation that the jitter on the incoming interface of R2 is less than 200ms, and within the allowable jitter range, the jitter on the outgoing interface of R2 becomes longer and exceeds the allowable jitter range. According to the jitter situation, it can also be preliminarily concluded that there is a fault inside R2.
表2为R3、R2和R1上的丢包数和抖动Table 2 shows the packet loss and jitter on R3, R2 and R1
本实施例,发送端在IP数据包中填充发送时间戳和发送序列号,接收端接收到该IP数据包后根据IP数据包中发送时间戳和发送序列号,计算丢包数、时延和抖动。同时接收端向下游节点转发该IP数据包之前,修改其中的发送时间戳和发送序列号,使下游节点可根据IP数据包中发送时间戳和发送序列号计算网络的丢包数、时延和抖动。In this embodiment, the sending end fills the sending timestamp and the sending sequence number in the IP data packet, and after receiving the IP data packet, the receiving end calculates the number of packet loss, delay and shake. At the same time, before the receiving end forwards the IP data packet to the downstream node, it modifies the sending timestamp and sending sequence number, so that the downstream node can calculate the number of packet loss, delay and shake.
图8A为本发明实施例提供的一种媒体流传输设备结构示意图。如图8A所示本实施例包括:填充模块81和发送器82。FIG. 8A is a schematic structural diagram of a media stream transmission device provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 8A , this embodiment includes: a filling
填充模块81,用于在IP数据包中填充媒体流性能监控数据;所述媒体流性能监控数据包括所述IP数据包的发送时间戳和所述IP数据包的发送序列号。A filling
在IP数据包中填充媒体流性能监控数据时,可在每个IP数据包中都填充媒体流性能监控数据。为提高系统性能,也可以每间隔几个IP数据包填充一次媒体流性能监控数据。例如,填充模块81具体用于对媒体流进行采样,在采样出的IP数据包中填充媒体流性能监控数据。填充媒体流性能监控数据时。可将媒体流性能监控数据复用在IP首部的16标识字段中,也可将媒体流性能监控数据填充到IP首部的IP首部的选项字段中。When the media stream performance monitoring data is filled in the IP data packet, the media stream performance monitoring data may be filled in each IP data packet. In order to improve system performance, the media flow performance monitoring data can also be filled every few IP data packets. For example, the filling
发送器82,用于向下游节点发送填充模块81填充媒体流性能监控数据后的IP数据包。The
如图8B所示,在图8A基础上本实施例还包括:累加模块83。As shown in FIG. 8B , on the basis of FIG. 8A , this embodiment further includes: an
累加模块83,用于在发送器82向下游节点发送IP数据包之前,将计数器累加一。计数器用于统计媒体流中已发送IP数据包的个数,或用于统计媒体流中已发送的、填充有发送序列号的IP数据包的个数。The accumulating
如图8C所示,填充模块81包括:第一填充单元811和第二填充单元812。As shown in FIG. 8C , the filling
第一填充单元811,用于在一个IP数据包中IP首部的标识字段同时填充所述发送时间戳和所述发送序列号。The
第二填充单元812,用于在两个IP数据包中IP首部的标识字段分时填充所述发送时间戳和所述发送序列号。The
如图8D所示,填充模块81包括:第三填充单元813和第四填充单元814。As shown in FIG. 8D , the filling
第三填充单元813,用于在一个IP数据包中IP首部的选项字段同时填充所述发送时间戳和所述发送序列号。The third filling unit 813 is configured to simultaneously fill the sending time stamp and the sending sequence number in the option field of the IP header in an IP data packet.
第四填充单元814,用于在两个IP数据包中IP首部的选项字段分时填充所述发送时间戳和所述发送序列号。The fourth filling unit 814 is configured to time-divisionally fill the sending time stamp and the sending sequence number in the option field of the IP header in the two IP data packets.
另外,填充模块81也可同时包括有第一填充单元811、第二填充单元812、第三填充单元813和第四填充单元814。上述各模块实现的功能可参见图1、图2和图4对应实施例的描述,在此不再赘述。In addition, the filling
本发明实施例媒体流传输设备中填充模块81在IP数据包中封装媒体流性能监控数据,发送器82将填充模块81填充媒体流性能监控数据后的IP数据包发送给下游节点。接收到IP数据包的下游节点根据其中的媒体流性能监控数据,监控网络的媒体流性能,例如网络的丢包数、时延和抖动等。由于本发明实施例中,媒体流传输设备采用了通用的IP封装来封装媒体流,下游节点能够在缺少应用层封装信息时实现媒体流性能监控。The filling
图9A为本发明实施例提供的一种媒体流性能监控设备结构示意图。如图9A所示,本实施例包括:接收器91和性能监控模块92。FIG. 9A is a schematic structural diagram of a media stream performance monitoring device provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 9A , this embodiment includes: a
接收器91,用于接收上游节点发送的包括媒体流性能监控数据的IP数据包;所述媒体流性能监控数据包括所述IP数据包的发送时间戳和所述IP数据包的发送序列号。The
性能监控模块92,用于根据所述媒体流性能监控数据,监控媒体流的性能。The
如图9B所示,性能监控模块92包括:丢包数监控单元921和抖动监控单元922。As shown in FIG. 9B , the
丢包数监控单元921,用于根据接收到的最大发送序列号、最小发送序列号和已接收到的包括有发送序列号的IP数据包的个数,监控媒体流的丢包数。The packet
抖动监控单元922,用于根据两个IP数据包中的发送时间戳和两个IP数据包的到达时间,监控媒体流的抖动。The
上述各模块所实现的功能可参见图5和图6对应实施例的描述,在此不再赘述。For the functions implemented by the above modules, reference may be made to the descriptions of the corresponding embodiments in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6 , and details are not repeated here.
本发明实施例上游节点在IP数据包中封装了媒体流性能监控数据,媒体流性能监控设备中接收器91接收到IP数据包时,性能监控模块92根据其中的媒体流性能监控数据,监控网络的媒体流性能,例如网络的丢包数、时延和抖动等。由于本发明实施例中,媒体流传输设备采用了通用的IP封装来封装媒体流,性能监控模块92能够在缺少应用层封装信息时实现媒体流性能监控。In the embodiment of the present invention, the upstream node encapsulates the media stream performance monitoring data in the IP data packet. When the
本领域普通技术人员可以理解:实现上述方法实施例的全部或部分步骤可以通过程序指令相关的硬件来完成,前述的程序可以存储于一计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,执行包括上述方法实施例的步骤;而前述的存储介质包括:ROM、RAM、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps for realizing the above-mentioned method embodiments can be completed by hardware related to program instructions, and the aforementioned program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. When the program is executed, the It includes the steps of the above method embodiments; and the aforementioned storage medium includes: ROM, RAM, magnetic disk or optical disk and other various media that can store program codes.
最后应说明的是:以上实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的精神和范围。Finally, it should be noted that: the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, rather than to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: it can still be Modifications are made to the technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments, or equivalent replacements are made to some of the technical features; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions of the various embodiments of the present invention.
Claims (13)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2011/073825WO2011120470A2 (en) | 2011-05-09 | 2011-05-09 | Method and device for medium stream performance monitoring |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102217237A CN102217237A (en) | 2011-10-12 |
| CN102217237Btrue CN102217237B (en) | 2013-12-04 |
Family
ID=44712680
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011800007594AExpired - Fee RelatedCN102217237B (en) | 2011-05-09 | 2011-05-09 | Media streaming performance monitoring method and device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102217237B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011120470A2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017132911A1 (en)* | 2016-02-03 | 2017-08-10 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and apparatus |
| CN109842856A (en)* | 2017-11-29 | 2019-06-04 | 成都鼎桥通信技术有限公司 | A kind of method and apparatus shielding uplink packet loss |
| CN108683555A (en)* | 2018-04-17 | 2018-10-19 | 上海电力学院 | A kind of RTP method for detecting packet loss |
| CN112134747A (en)* | 2019-06-24 | 2020-12-25 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for detecting transmission delay and related equipment |
| CN113382437A (en)* | 2020-03-10 | 2021-09-10 | 华为技术有限公司 | Follow-up flow detection method and device |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1223192C (en)* | 2003-10-17 | 2005-10-12 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Video data network ditter elimlating method for H.323 conference television system |
| CN101674228B (en)* | 2008-09-08 | 2011-10-05 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method, device and system for realizing streaming media communication |
| EP2197153B1 (en)* | 2008-12-15 | 2012-07-04 | Koninklijke KPN N.V. | Method and device for reliable multicast using UDP |
| CN101888310B (en)* | 2009-05-11 | 2012-02-22 | 黑龙江大学 | A method for active measurement of IP path based on UDP packets |
| CN102026221B (en)* | 2009-09-17 | 2014-05-07 | 华为技术有限公司 | Measuring method, device and system |
| CN101848396B (en)* | 2009-11-30 | 2012-10-17 | 深圳市华曦达科技股份有限公司 | Audio/video synchronization and anti-shaking method of transport stream |
| CN101902370A (en)* | 2010-07-21 | 2010-12-01 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Device, system and method for measuring frame delay |
| CN101944982B (en)* | 2010-08-11 | 2013-04-10 | 南昌市恒鑫电子技术有限公司 | Real-time stream media transmitting method based on time-driven sliding window protocol |
| CN101924625A (en)* | 2010-08-23 | 2010-12-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data packet retransmission control method and network side device |
- 2011
- 2011-05-09CNCN2011800007594Apatent/CN102217237B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2011-05-09WOPCT/CN2011/073825patent/WO2011120470A2/enactiveApplication Filing
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2011120470A3 (en) | 2012-04-19 |
| WO2011120470A2 (en) | 2011-10-06 |
| CN102217237A (en) | 2011-10-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101298407B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting data packet, and method and apparatus for receiving data packet | |
| CN102263697B (en) | Method and device for sharing aggregated link traffic | |
| CN102035718B (en) | Method, device and system for protection switching of packet transport network | |
| CN103975551B (en) | Network QoS control system, communication equipment and network QoS control method end to end end to end | |
| CN101488912B (en) | A method and device for IP fragmentation | |
| CN102217237B (en) | Media streaming performance monitoring method and device | |
| CN108882008B (en) | A kind of method and apparatus of data conversion | |
| KR101521897B1 (en) | Feedback protocol for end-to-end multiple path network systems | |
| EP2515481A1 (en) | Transmission control method, access equipment and transmission system | |
| CN109120540B (en) | Method for transmitting message, proxy server and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN105071897B (en) | A kind of network real-time audio conversation media data multi-path redundancy transmission method | |
| EP3547690B1 (en) | Real-time video transmission method of multipath network | |
| CN109672929A (en) | A kind of detection method and equipment of video traffic message | |
| KR101567991B1 (en) | Data transport container for transferring data in a high speed internet protocol network | |
| CN102255808A (en) | Congestion notification method, device, system and network equipment | |
| CN110224887B (en) | Method and device for automatically identifying Ethernet Y.1564 test frame | |
| EP2600569A1 (en) | Method, apparatus and system for processing a tunnel packet | |
| CN101714951A (en) | Method and equipment for transmitting and receiving service data in CES | |
| CN102624746B (en) | Detect the method for two ends, tunnel GRE head configuration, source, destination and system | |
| CN103210625B (en) | The processing method of TCP business and VoIP business, equipment and system | |
| WO2023206165A1 (en) | Multicast data message sending method and apparatus, and device and storage medium | |
| Dai et al. | An adaptive forward error correction method for TDM over Ethernet | |
| Epple et al. | Implementation concepts for a bridging protocol for the high data rate slow-fading Free-Space Optical Channel | |
| CN104601382A (en) | Multi-protocol transmission device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20131204 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |