CN102214255A - Method for simulating and optimizing numerical value of anti-corrosion system of naval architecture and ocean engineering - Google Patents
Method for simulating and optimizing numerical value of anti-corrosion system of naval architecture and ocean engineeringDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102214255A CN102214255ACN 201110120406CN201110120406ACN102214255ACN 102214255 ACN102214255 ACN 102214255ACN 201110120406CN201110120406CN 201110120406CN 201110120406 ACN201110120406 ACN 201110120406ACN 102214255 ACN102214255 ACN 102214255A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- current
- potential
- anode
- node
- corrosion
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription25
- 238000005260corrosionMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription19
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription46
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription26
- 238000013461designMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription3
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000claimsdescription30
- 238000004210cathodic protectionMethods0.000claimsdescription21
- 230000010287polarizationEffects0.000claimsdescription8
- 230000007797corrosionEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000010405anode materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000002596correlated effectEffects0.000claims1
- 230000000007visual effectEffects0.000claims1
- 230000002035prolonged effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 238000007667floatingMethods0.000description9
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description7
- 238000013528artificial neural networkMethods0.000description6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description6
- 238000009826distributionMethods0.000description5
- 230000008878couplingEffects0.000description4
- 238000010168coupling processMethods0.000description4
- 238000005859coupling reactionMethods0.000description4
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description3
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description3
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description3
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000description2
- 239000013535sea waterSubstances0.000description2
- 238000012795verificationMethods0.000description2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000004422calculation algorithmMethods0.000description1
- 238000005553drillingMethods0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description1
- 210000002569neuronAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000012549trainingMethods0.000description1
- 238000009827uniform distributionMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Prevention Of Electric Corrosion (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于船舶与海洋工程防腐技术领域,涉及到复杂耦合防腐系统的数值模拟及设计方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of anticorrosion of ships and ocean engineering, and relates to numerical simulation and design methods of complex coupled anticorrosion systems.
背景技术Background technique
阴极保护系统的数值模拟计算方法研究始于上个世纪七十年代末,研究者们起初选择牺牲阳极阴极保护系统作为计算对象,尝试了有限差分法、有限元法和边界远法。经过二十多年的发展,针对海洋工程防腐系统的数值模拟计算问题,边界元法显示出了最强的适应性,也获得了最好的发展。在牺牲阳极阴极保护系统、外加电流阴极保护系统、电偶腐蚀以及杂散电流腐蚀等数值模拟计算研究方面均有学术论文发表了相应的研究成果。The research on numerical simulation calculation method of cathodic protection system began in the late 1970s. Researchers initially chose sacrificial anode cathodic protection system as the calculation object, and tried finite difference method, finite element method and boundary distance method. After more than 20 years of development, the boundary element method has shown the strongest adaptability and achieved the best development for the numerical simulation calculation of marine engineering anticorrosion systems. Corresponding research results have been published in academic papers on the numerical simulation calculation research of sacrificial anode cathodic protection system, impressed current cathodic protection system, galvanic corrosion and stray current corrosion.
在英国的“BEASY Software”公司推出的工程模拟计算软件“BEASY Software”中,“BEASY Corrosion Control”部分能够提供基于数值模拟计算的阴极保护系统优化设计功能,其中集成了国外在船舶与海洋工程防腐系统数值模拟计算方法研究方面的最新研究成果。在“BEASY Software”公司网页“http://www.beasy.com”中,介绍了阴极保护系统数值模拟计算方法研究的代表性学术论文。In the engineering simulation calculation software "BEASY Software" launched by the "BEASY Software" company in the UK, the "BEASY Corrosion Control" part can provide the optimal design function of cathodic protection system based on numerical simulation calculation, which integrates foreign anticorrosion in ships and marine engineering. The latest research results in the research of system numerical simulation calculation methods. In the "BEASY Software" company web page "http://www.beasy.com", representative academic papers on the research of numerical simulation calculation methods for cathodic protection systems are introduced.
①船舶与海洋工程牺牲阳极阴极保护系统的数值模拟计算技术,趋于成熟,可以用于求解电偶体系导致的腐蚀问题,但针对船舶或浮式海洋结构物中的压载水舱防腐系统的数值模拟计算尚存在局限性。① The numerical simulation calculation technology of sacrificial anode cathodic protection system in ships and marine engineering is becoming mature, and can be used to solve the corrosion problem caused by galvanic couple system, but for the anticorrosion system of ballast water tank in ships or floating marine structures Numerical simulation calculations still have limitations.
②船舶与海洋工程外加电流阴极保护系统的数值模拟计算技术,能够针对由单一外加电流阴极保护装置(直流电源、参比电极、辅助阳极)构成的防腐系统实施数值模拟计算,但针对由多个外加电流阴极保护装置构成的复杂防 腐系统,在计算方法的论述中,只体现了电流平衡条件,而未体现外加电流阴极保护装置之间的耦合问题,所以不能期待实现正确的数值模拟计算。②Numerical simulation calculation technology of impressed current cathodic protection system for ships and ocean engineering can carry out numerical simulation calculation for anticorrosion system composed of a single impressed current cathodic protection device (DC power supply, reference electrode, auxiliary anode), but for multiple For the complex anti-corrosion system composed of impressed current cathodic protection devices, in the discussion of the calculation method, only the current balance condition is reflected, but the coupling problem between impressed current cathodic protection devices is not reflected, so the correct numerical simulation calculation cannot be expected.
本发明针对船舶或浮式海洋结构物中的压载水舱防腐系统的数值模拟计算问题,采用分块边界元法,使得“屏蔽效应”问题获得完美解决;不仅能够针对由单一外加电流阴极保护装置(直流电源、参比电极、辅助阳极)构成的防腐系统实施数值模拟计算,而且针对由多个外加电流阴极保护装置构成的复杂防腐系统,在考虑了电流平衡条件的同时,解决了外加电流阴极保护装置之间的耦合问题,所以能够实现正确的数值模拟计算;在基于边界元法建立的方程系统中,列入了每一个独立的结构(或防腐)系统的电流平衡条件,同时解决了各独立防腐系统所产生的子电场之间的干涉耦合问题,因此可以期待确切地求解复杂海洋工程中的杂散电流腐蚀问题。The present invention aims at the numerical simulation calculation problem of the anticorrosion system of the ballast water tank in the ship or floating marine structure, and adopts the block boundary element method, so that the problem of "shielding effect" is perfectly solved; The anti-corrosion system composed of devices (DC power supply, reference electrode, auxiliary anode) implements numerical simulation calculations, and for the complex anti-corrosion system composed of multiple impressed current cathodic protection devices, while considering the current balance conditions, the applied current problem is solved. The coupling problem between cathodic protection devices, so the correct numerical simulation calculation can be realized; in the equation system established based on the boundary element method, the current balance condition of each independent structure (or anti-corrosion) system is included, and at the same time it solves the The interference coupling problem between the sub-electric fields generated by each independent anti-corrosion system, so it can be expected to solve the stray current corrosion problem in complex marine engineering exactly.
通过建立一整套阴极保护体系的边界元数值计算模型,可实现数值模拟计算与仿真,得到阴极保护电位和保护电流密度等有关结果。By establishing a set of boundary element numerical calculation models of the cathodic protection system, numerical simulation calculations and simulations can be realized, and relevant results such as cathodic protection potential and protection current density can be obtained.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明提供了一种海洋结构物防腐系统数值模拟仿真计算方法,能够综合考虑环境、防腐涂层损伤状态等因素的变化,考虑由电偶体系、杂散电流体系、牺牲阳极系统以及外加电流阴极保护系统等共同形成的复杂耦合体系问题,真实反应海洋结构物的实际防腐状态,以环境参数等为变量,通过边界元分析计算,形成复杂海洋工程防腐系统数值模拟设计的核心技术。The invention provides a numerical simulation calculation method for the anticorrosion system of marine structures, which can comprehensively consider the changes in factors such as the environment and the damage state of the anticorrosion coating, and consider the galvanic couple system, stray current system, sacrificial anode system and applied current cathode The complex coupling system problem jointly formed by the protection system and so on truly reflects the actual anti-corrosion state of the marine structure, and the core technology of the numerical simulation design of the complex marine engineering anti-corrosion system is formed through boundary element analysis and calculation with environmental parameters as variables.
本发明数值模型的基本要素包括:The essential elements of the numerical model of the present invention include:
(1)网格:是对阴极(被保护对象)和阳极(牺牲阳极或外加电流辅助阳极)表面进行离散后的边界元网格模型;(1) Grid: It is a boundary element grid model after discretizing the surface of the cathode (protected object) and anode (sacrificial anode or external current assisted anode);
(2)电流流经的体系周围介质的电性能参数;(2) The electrical performance parameters of the surrounding medium of the system through which the current flows;
(3)边界条件:主要是阴、阳极的电化学特性(极化曲线描述)。(3) Boundary conditions: mainly the electrochemical characteristics of cathode and anode (described by polarization curve).
对于均一、各向同性的体系而言,域内满足Laplace方程,用域内方程去逼近边界条件,并经格林公式降阶以及对研究对象网格划分后,即可得到阴极表面电位、阳极表面电位、阴极表面电流密度以及阳极表面电流密度的相关的方程组。For a homogeneous and isotropic system, the Laplace equation is satisfied in the domain, and the boundary conditions are approximated by the equation in the domain, and after the Green's formula is used to reduce the order and the research object is meshed, the cathode surface potential, anode surface potential, The related equations for the cathode surface current density and the anode surface current density.
因此,该数值模型的计算过程分为两个阶段。第一阶段利用边界元法形成离散化的边界积分方程组,可表示为:Therefore, the calculation process of this numerical model is divided into two stages. In the first stage, the boundary element method is used to form a discretized boundary integral equation system, which can be expressed as:
[H]{Φ}=[G]{Q}[H]{Φ}=[G]{Q}
式中,[Φ]={ф1,ф2,…фn,ф∞},表示复杂海洋结构物湿表面(阴极)及阳极的n个网格节点上的电位,以及距离复杂海洋结构物足够远处的电位;[Q]={q1,q2,…qn}表示n个网格节点上的电流密度;[H]、[G]为在此阶段中计算出来的系数矩阵,与网格模型的几何特征有关。In the formula, [Φ]={ф1, ф2, ...фn, ф∞}, which means the potential on the n grid nodes of the wet surface (cathode) and anode of the complex marine structure, and the potential far enough away from the complex marine structure potential; [Q]={q1, q2,...qn} represents the current density on n grid nodes; [H], [G] are the coefficient matrices calculated in this stage, and the geometry of the grid model feature related.
由于电位ф和电流密度q之间通过边界条件存在一定的关系,因此可以将ф∞设为0以作为参考电位,然后对方程组进行求解。这是计算过程的第二阶段。Since there is a certain relationship between the potential ф and the current density q through boundary conditions, it is possible to set ф∞ to 0 as the reference potential, and then solve the equations. This is the second stage of the calculation process.
在边界条件为材料极化曲线描述的部位,ф和q之间的关系是非线性的。为了有效地求解这个非线性方程组,可采用分段拟线性方法来处理非线性边界条件。即将极化曲线分为若干区段,对每一区段进行线性拟合,从而求得相应的线性关系。在求解方程组时,首先根据当前的电位值来判断其所在的区间,然后用该区间的线性关系带入线性方程组,对方程组进行求解得到待求的电位,并对求出的电位进行判断,如果与求解前所在区间不同,则重复上述步骤直至 区间完全相同为止。Where the boundary condition is described by the polarization curve of the material, the relationship between ф and q is nonlinear. In order to efficiently solve this nonlinear equation system, a piecewise quasi-linear method can be used to deal with the nonlinear boundary conditions. That is to say, the polarization curve is divided into several sections, and each section is linearly fitted to obtain the corresponding linear relationship. When solving a system of equations, first judge the interval it is in according to the current potential value, and then use the linear relationship of the interval to bring it into the system of linear equations, solve the system of equations to obtain the potential to be sought, and perform a calculation on the obtained potential Judgment, if it is different from the interval before solving, repeat the above steps until the interval is exactly the same.
为了实现上述目的,本发明的技术方案包括以下步骤:In order to achieve the above object, the technical solution of the present invention comprises the following steps:
A、几何建模:采用计算机对所要计算的结构进行几何建模,利用计算机进行建模所使用的建模软件包括ANSYS、PANTRAN等商用软件;A. Geometric modeling: use computer to carry out geometric modeling of the structure to be calculated, and the modeling software used for modeling by computer includes commercial software such as ANSYS and PANTRAN;
B、建立边界元模型:对建立的几何模型进行网格划分,根据实际项目,对阳极屏,开孔附近进行加密;每一个网格是一个单元,然后确立模型各单元与网格节点的编号和空间坐标;如果需要加入螺旋桨,则需要利用建模软件导出螺旋桨节点和单元数据文件。B. Establish boundary element model: divide the established geometric model into grids, and encrypt the anode screen and the vicinity of the opening according to the actual project; each grid is a unit, and then establish the number of each unit and grid node of the model and space coordinates; if a propeller needs to be added, it is necessary to use the modeling software to export the propeller node and element data files.
C、在边界元模型的基础上加载数字化后的牺牲阳极信息,如如牺牲阳极材料、相关几何数据等;首次加载依据经验公式,以后均根据下述计算结果进行调整:C. Load the digitized sacrificial anode information on the basis of the boundary element model, such as sacrificial anode material, relevant geometric data, etc.; the first loading is based on empirical formulas, and subsequent adjustments are made according to the following calculation results:
计算系数矩阵,初始化各节点电位和电流密度之间的分段线性关系,求解线性方程组,判断各节点处电位和电流密度是否符合分段线性的极化曲线,是否存在不符合原线性关系的节点,并调整这些电位和电流密度,最终得到阳极输出电流等整体计算结果,以及各节点处的点位和电流密度等;Calculate the coefficient matrix, initialize the piecewise linear relationship between the potential and current density of each node, solve the linear equation system, and judge whether the potential and current density at each node conform to the piecewise linear polarization curve, and whether there is a polarization curve that does not conform to the original linear relationship nodes, and adjust these potentials and current densities, and finally obtain the overall calculation results such as the anode output current, as well as the points and current densities at each node;
E、以云图或曲线的形式可视化计算结果;E. Visualize the calculation results in the form of cloud diagrams or curves;
F、将牺牲阳极等重新布置,得到最优的阴极保护系统。F. Rearrange sacrificial anodes to obtain an optimal cathodic protection system.
本发明的有益效果是通过本发明可以计算得出被保护对象表面上的保护电位、保护电流的分布状态及其随时间变化情况、牺牲阳极的消耗状态和随时间变化情况、外加电源的容量及控制参数等信息,可以更加全面地说明海洋结构物的总体防腐性能,从而全面评估海洋结构物在役期间的生存能力,并给出优化设计方案,以使被保护对象表面上的保护电位分布在全保护周期内始终处于所要求的基准范围内,从而提升海洋结构物的使用寿命;同时根据此计算方法编制软件,使其在短时间能完成所有的计算,实现整个计算过程的全自动化,使这一方法具有实际工程使用意义。The beneficial effect of the present invention is that the protection potential on the surface of the protected object, the distribution state of the protection current and its change with time, the consumption state of the sacrificial anode and the change with time, the capacity of the external power supply and the change with time can be obtained through the present invention. Information such as control parameters can more comprehensively explain the overall anti-corrosion performance of marine structures, so as to comprehensively evaluate the survivability of marine structures during service, and provide an optimal design plan so that the protection potential on the surface of the protected object is distributed between It is always within the required reference range during the full protection period, thereby improving the service life of marine structures; at the same time, the software is compiled according to this calculation method, so that it can complete all calculations in a short time and realize the full automation of the entire calculation process. This method has practical engineering application significance.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明的边界元算法流程图。Fig. 1 is a flowchart of the boundary element algorithm of the present invention.
图2是本发明的系统结构图。Fig. 2 is a system structure diagram of the present invention.
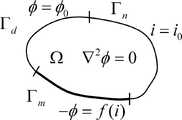
图3阴极保护体系的边界条件示意图。Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of the boundary conditions of the cathodic protection system.
图4.1是半潜平台外加电流阴极保护系统示意图。Figure 4.1 is a schematic diagram of an impressed current cathodic protection system for a semi-submersible platform.
图4.2是边界元网格划分示意图。Figure 4.2 is a schematic diagram of boundary element meshing.
图4.3是优化后的1至4号阳极位置示意图。Figure 4.3 is a schematic diagram of the positions of
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图以某一半潜式钻井平台为例对本发明进行进一步地描述。The present invention will be further described below by taking a certain semi-submersible drilling platform as an example in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
计算对象及初始设计主要参数Calculation object and main parameters of initial design
某半潜平台的主尺度如下:The main dimensions of a semi-submersible platform are as follows:
浮体长:115.4mLength of floating body: 115.4m
浮体宽:18mFloating body width: 18m
浮体高:10mFloat height: 10m
工作吃水:19mWorking draft: 19m
平台浮体以及动力定位系统等水下部分采用了外加电流阴极保护系统。该系统的初始设计在每个浮体上布置了4个辅助阳极,在立柱上各布置2个辅助阳极,共16(8×2)个阳极,阳极屏半径均为4m。平台结构湿表面模型及阳极布置如图4.1所示。Impressed current cathodic protection system is adopted for the underwater part of platform floating body and dynamic positioning system. In the initial design of the system, 4 auxiliary anodes are arranged on each floating body, and 2 auxiliary anodes are arranged on each column, a total of 16 (8×2) anodes, and the radius of the anode screen is 4m. The wet surface model of the platform structure and the anode arrangement are shown in Figure 4.1.
网格划分meshing
根据对称性,取一半建立模型。划分边界元网格后,共有68716个三角形单元和34964个节点。整体网格划分、阳极以及螺旋桨局部网格划分如图4.2所示。According to symmetry, take half to build the model. After dividing the boundary element mesh, there are 68716 triangle elements and 34964 nodes in total. The overall meshing, anode and propeller local meshing are shown in Figure 4.2.
边界条件及介质参数Boundary conditions and medium parameters
半潜平台防腐涂层损伤表面(Sc)、外加电流辅助阳极表面(Sa)以及螺旋桨表面(Sp)的电位状态和电流状态之间的关系满足极化曲线;在水线面处为海水电解质区域边界(Sw),在垂直方向上满足电流密度为“0”的边界条件;距离 海洋结构物足够远处(S∞)为物理模型的外边界,电位设为常数,电流密度为“0”。其中,Sc边界的极化曲线根据阴极保护系统到达10年设计寿命时的涂层破损情况选取。电解质(海水)的电阻率取为0.25Ωm。The relationship between the potential state and current state of the semi-submersible platform anti-corrosion coating damaged surface (Sc ), the surface of the applied current auxiliary anode (Sa ) and the surface of the propeller (Sp ) satisfies the polarization curve; The boundary of the seawater electrolyte area (Sw ) satisfies the boundary condition that the current density is "0" in the vertical direction; the distance far enough from the marine structure (S∞ ) is the outer boundary of the physical model, the potential is set as a constant, and the current density is "0". Among them, the polarization curve of the Sc boundary is selected according to the coating damage when the cathodic protection system reaches the design life of 10 years. The resistivity of the electrolyte (seawater) was taken as 0.25Ωm.
计算结果Calculation results
当通过外加电流装置给辅助阳极与被保护对象之间施加的电压为13.5V时,计算得到的保护电位范围为823.1mV~1106.5mV。最低保护电位出现在浮体底部靠近螺旋桨的区域,最高保护电位则出现在立柱上靠近7号阳极屏下端的区域。保护电位均值和方差为别为930.925mV和2352.512mV2。When the voltage applied between the auxiliary anode and the protected object by the external current device is 13.5V, the calculated protection potential ranges from 823.1mV to 1106.5mV. The lowest protection potential appears in the area near the propeller at the bottom of the floating body, and the highest protection potential appears in the area near the lower end of No. 7 anode screen on the column. The mean value and variance of the protection potential were 930.925mV and 2352.512mV2 .
被保护对象表面的平均电流密度为-12.366mA/m2。1~8号阳极输出电流为{13649,13648,13635,13636,13494,13474,13477,13489},单位:A。总的阳极输出电流为108501mA,外加电流装置输出功率为1.465kW。The average current density on the surface of the protected object is -12.366mA/m2 . The output current of
从数值模拟计算的结果来看,该半潜平台ICCP系统的初始设计能够基本满足10年设计寿命的使用要求。但由于其阳极屏的总面积太大、整体保护电位水平过高、保护电位分布较不均匀等问题的存在,针对该初始设计还可以做进一步的优化。From the results of numerical simulation calculations, the initial design of the ICCP system of the semi-submersible platform can basically meet the service requirements of the 10-year design life. However, due to the existence of problems such as the total area of the anode screen is too large, the overall protection potential level is too high, and the protection potential distribution is uneven, further optimization can be made for this initial design.
阳极位置优化Anode position optimization
若选择每个阳极在三维方向上的位置作为优化变量,则变量的个数达到3×8=24个。根据实际情况对优化变量的个数进行简化,可大大提高优化效率。在本问题中,考虑到阳极屏的覆盖面积和屏蔽效果,立柱上的阳极的可移动范围有限,故将其位置固定。浮体上的四个阳极在船高方向上不便于做调整,但在船长方向是可以灵活布置。因此可选择1~4号阳极的x方向位置作为优化变量,则将优化变量简化为P={x1,x2,x3,x4}。If the position of each anode in the three-dimensional direction is selected as the optimization variable, the number of variables reaches 3×8=24. Simplifying the number of optimization variables according to the actual situation can greatly improve the optimization efficiency. In this problem, considering the coverage area and shielding effect of the anode screen, the movable range of the anode on the column is limited, so its position is fixed. The four anodes on the floating body are not easy to adjust in the direction of ship height, but they can be arranged flexibly in the direction of ship length. Therefore, the x-direction positions of No. 1 to No. 4 anodes can be selected as optimization variables, and then the optimization variables are simplified as P={x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 }.
针对可能对保护电位分布影响较大的阳极分布区域,选择坐标值的合理可变范 围为:Pmin={10,85,10,85},Pmax={30,105,30,105},Pmin≤P≤Pmax(单位:m)。For the anode distribution area that may have a greater impact on the protection potential distribution, the reasonable variable range of the selected coordinate values is: Pmin = {10, 85, 10, 85}, Pmax = {30, 105, 30, 105}, Pmin ≤ P ≤ Pmax (unit: m).
本问题相应的优化模型为:The corresponding optimization model for this problem is:
MinMin
S.T.S.T.
800≤Ei≤1150on ΓC i=1,2,…,n (4.2)800≤Ei ≤1150on ΓC i=1, 2,..., n (4.2)
{10,85,10,85}≤{x1,x2,x3,x4}≤{30,105,30,105} (4.3){10, 85, 10, 85} ≤ {x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 } ≤ {30, 105, 30, 105} (4.3)
优化过程如下:The optimization process is as follows:
(1)在每个阳极的移动范围以内,每隔2m取一个样本点,而其它阳极保持在初始设计位置。共有44种阳极位置的组合。(1) Within the moving range of each anode, take a sample point every 2m, while other anodes remain at the initial design position. There are 44 combinations of anode positions.
(2)相应地进行44次数值模拟计算。(2) Carry out 44 numerical simulation calculations accordingly.
(3)设计BP神经网络的隐层神经元数目为18,对样本进行训练,建立优化变量与目标函数值之间的关系:(3) The number of neurons in the hidden layer of the BP neural network is designed to be 18, and the samples are trained to establish the relationship between the optimization variable and the objective function value:
(4)经过9次迭代搜索,得到了最终的收敛值:Ψ=2032.9,即电位方差。对应的优化变量值为:P={23.73,110,19.55,102.48}。通过数值计算验证得到的目标函数值为:Ψtrue=2212.3。最优设计方案的电位方差的神经网络仿真误差为:δS=8.11%。(4) After 9 iterations of searching, the final convergence value is obtained: Ψ=2032.9, which is the potential variance. The corresponding optimized variable value is: P={23.73, 110, 19.55, 102.48}. The value of the objective function verified by numerical calculation is: Ψtrue = 2212.3. The neural network simulation error of the potential variance of the optimal design scheme is: δS =8.11%.
(5)认为上述误差过于偏大。将数值验证计算结果加入样本重新进行优化。重复此过程3次后,得到了一个比较满意的结果。神经网络仿真值为:Ψ=2086.3,数值计算验证值为:Ψtrue=2092.9,误差δS=0.32%。对应的优化变量值为: P={27.76,86.48,10.86,103.47}。优化后的1~4号阳极位置如图4.3所示。(5) It is believed that the above error is too large. The numerical verification calculation results are added to the sample for re-optimization. After repeating this process 3 times, a satisfactory result was obtained. The neural network simulation value is: Ψ=2086.3, the numerical calculation verification value is: Ψtrue =2092.9, and the error δS =0.32%. The corresponding optimized variable values are: P={27.76, 86.48, 10.86, 103.47}. The optimized positions of No. 1 to No. 4 anodes are shown in Figure 4.3.
经过阳极位置优化后的整体保护电位方差比初始设计时减小了11.04%,因此结构物表面获得了一个更均匀保护电位分布。此时的保护电位均值为930.2mV,保护电位范围为:829.4mV~1102.5mV。可以考虑减小阳极屏的覆盖面积,并适当降低外加电流装置的工作电压。将每个阳极的阳极屏半径由4m改为3m,工作电压由13.5改为13.2V,重新进行数值模拟计算。此时得到的保护电位均值和方差分别为911.2mV和2122.9mV2,保护电位范围为809.7mV~1113.7mV,满足防腐要求。The overall protection potential variance after the anode position optimization is reduced by 11.04% compared with the initial design, so a more uniform protection potential distribution is obtained on the surface of the structure. At this time, the average value of the protection potential is 930.2mV, and the protection potential range is: 829.4mV~1102.5mV. It can be considered to reduce the coverage area of the anode screen and appropriately reduce the working voltage of the impressed current device. Change the anode screen radius of each anode from 4m to 3m, and the working voltage from 13.5 to 13.2V, and re-calculate the numerical simulation. The mean value and variance of the protection potential obtained at this time are 911.2mV and 2122.9mV2 respectively, and the protection potential range is 809.7mV-1113.7mV, meeting the anticorrosion requirements.
阳极输出电流优化Anode output current optimization
将经过阳极位置优化后的方案作为初始设计,总的输阳极出电流为108787.6mA。取所有8个阳极的输出电流作为优化变量:I={i1,i2,i3,i4,i5,i6,i7,i8}。初始值为:Iinit={13598,13598,13598,13598,13598,13598,13598,13598}(平均分配初始设计时的总阳极输出电流)。设计每个阳极的输出电流在10598mA~16598mA范围内变化。The scheme after optimizing the anode position is taken as the initial design, and the total output current of the anode is 108787.6mA. Take the output currents of all 8 anodes as optimization variables: I={i1 , i2 , i3 , i4 , i5 , i6 , i7 , i8 }. The initial value is: Iinit ={13598, 13598, 13598, 13598, 13598, 13598, 13598, 13598} (total anode output current in the initial design is evenly distributed). The output current of each anode is designed to vary within the range of 10598mA ~ 16598mA.
选择a1=a2=0.5,Eopt=910(mV),则本问题相应的优化模型为:Choose a1 =a2 =0.5, Eopt =910(mV), then the corresponding optimization model for this problem is:
MinMin
S.T.S.T.
800≤Ei≤1150on ΓCi=1,2,…,n (4.6)800≤Ei ≤1150on ΓC i=1, 2,..., n (4.6)
优化过程如下:The optimization process is as follows:
(1)在使得保护电位都在允许范围以内的情况下,将每个阳极的工作电流从10598mA到16598mA每隔1000mA取一个样本点,而其他阳极的工作电流保持在13598mA不变,有49种组合。再将所有阳极的工作电流一并从12598mA到14598mA 每隔500mA取一个样本点,又有4种组合。(1) In the case that the protection potential is within the allowable range, take a sample point every 1000mA for the working current of each anode from 10598mA to 16598mA, while the working current of other anodes remains unchanged at 13598mA, there are 49 kinds combination. Then, the working current of all anodes is taken together from 12598mA to 14598mA, and a sample point is taken every 500mA, and there are 4 combinations.
(2)相应地进行53次数值模拟计算。(2) Carry out 53 numerical simulation calculations accordingly.
(3)采用BP神经网络对样本进行训练,建立优化变量与目标函数值之间的关系:(3) Use the BP neural network to train the samples, and establish the relationship between the optimization variables and the objective function value:
(4)经过25次迭代搜索,得到了最终的收敛值:Ψ=851.8,对应的电位均值和电位方差分别为:907.2mV和1688.1mV2。对应的优化变量(阳极输出电流)为:I={16145,15627,15754,16598,10598,10598,10598,10598}。通过数值计算验证此设计方案,得到的电位均值和方差分别为905.6mV和1614.7mV2,目标函数值为:Ψtrue=817.0。最优设计方案的电位均值和电位方差的神经网络仿真误差分别为:δE=0.18%,δS=4.54%。(4) After 25 iterations of search, the final convergence value is obtained: Ψ=851.8, and the corresponding potential mean value and potential variance are respectively: 907.2mV and 1688.1mV2 . The corresponding optimization variable (anode output current) is: I={16145, 15627, 15754, 16598, 10598, 10598, 10598, 10598}. The design scheme is verified by numerical calculation, and the obtained potential mean value and variance are 905.6mV and 1614.7mV2 respectively, and the objective function value is: Ψtrue =817.0. The neural network simulation errors of the potential mean value and potential variance of the optimal design scheme are: δE = 0.18%, δS = 4.54%.
经过本轮阳极电流的优化之后,结构物表面获得了更均匀的结构物表面保护电位分布和理想的目标电位均值。同时发现,立柱上的5至8号阳极的输出电流在寻优的过程中一直保持最小值10598mV不变。这说明初始设计的5至8号阳极输出电流过大。After this round of optimization of the anode current, the surface of the structure has obtained a more uniform distribution of protection potential on the surface of the structure and an ideal average value of the target potential. At the same time, it was found that the output currents of No. 5 to No. 8 anodes on the column kept the minimum value of 10598mV during the optimization process. This shows that the output current of the anodes 5 to 8 in the initial design is too large.
返回第一步,重新设计训练样本。将1至4号阳极输出电流的变化范围改为16598mA到20598mA,5至8号阳极输出电流的变化范围改为6598mA到10598mA,每隔1000mA取一个样本点,共有33个新样本点。相应地进行33次数值模拟计算。重新对53+33=86个样本进行训练,然后进行迭代搜索寻优。经过58次迭代,得到最终的收敛目标函数值为:Ψ=658.9,对应的电位均值和电位方差分别为: 909.8和1217.7,对应的优化变量(阳极输出电流)为:I={19628,19148,19558,20238,7598,6968,6598,7248}。通过数值计算验证此设计方案,得到的电位均值和方差分别为908.7mV和1234.1mV2,目标函数值为:Ψtrue=617.9。最优设计方案的电位均值和电位方差的神经网络仿真误差分别为:δE=0.12%,δS=1.33%。Go back to the first step and redesign the training samples. Change the variation range of the output current of No. 1 to No. 4 anodes to 16598mA to 20598mA, and the variation range of the output current of No. 5 to No. 8 anodes to 6598mA to 10598mA. Take a sample point every 1000mA, and there are 33 new sample points in total. Correspondingly, 33 numerical simulation calculations were carried out. Retrain 53+33=86 samples, and then perform iterative search for optimization. After 58 iterations, the final convergence objective function value is obtained: Ψ=658.9, the corresponding potential mean value and potential variance are respectively: 909.8 and 1217.7, and the corresponding optimization variable (anode output current) is: I={19628, 19148, 19558, 20238, 7598, 6968, 6598, 7248}. The design scheme is verified by numerical calculation, and the obtained potential mean value and variance are 908.7mV and 1234.1mV2 , respectively, and the objective function value is: Ψtrue =617.9. The neural network simulation errors of the potential mean value and potential variance of the optimal design scheme are: δE = 0.12%, δS = 1.33%.
阳极电流优化的结果实际上是通过减小立柱上5至8号阳极的输出电流,同时增大浮体上1至4号阳极的输出电流,使最低保护电位和最高保护电位之间的范围缩小。因此可以考虑减小5至8号阳极某些不必要的阳极屏面积。将5至8号阳极的阳极屏的半径由3m改为2m,重新计算得到电位均值和方差则分别为905.3mV和1306.8mV2,保护电位范围为815.4mV~1118.1mV。The result of anode current optimization is actually to reduce the range between the lowest protection potential and the highest protection potential by reducing the output current of anodes 5 to 8 on the column and increasing the output current of
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201110120406CN102214255A (en) | 2011-05-10 | 2011-05-10 | Method for simulating and optimizing numerical value of anti-corrosion system of naval architecture and ocean engineering |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201110120406CN102214255A (en) | 2011-05-10 | 2011-05-10 | Method for simulating and optimizing numerical value of anti-corrosion system of naval architecture and ocean engineering |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102214255Atrue CN102214255A (en) | 2011-10-12 |
Family
ID=44745561
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201110120406PendingCN102214255A (en) | 2011-05-10 | 2011-05-10 | Method for simulating and optimizing numerical value of anti-corrosion system of naval architecture and ocean engineering |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102214255A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104674228A (en)* | 2015-02-02 | 2015-06-03 | 深圳市燃气集团股份有限公司 | Detection method for cathode protection of directionally drilled and crossed pipeline |
| CN105154887A (en)* | 2015-09-16 | 2015-12-16 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for optimally designing of impressed current cathodic corrosion control system of steel-concrete structures |
| CN110208764A (en)* | 2019-05-05 | 2019-09-06 | 南京航空航天大学 | Dynamic sea large scene echo simulation method based on electromagnetism Scattering Calculation |
| CN111876785A (en)* | 2020-08-05 | 2020-11-03 | 上海外高桥造船有限公司 | Current cathode protection system for FPSO outer plate corrosion prevention and setting method thereof |
| CN112538632A (en)* | 2020-11-18 | 2021-03-23 | 广东工业大学 | Marine structure protection method based on cathode protection and sacrificial anode block service life prediction |
| CN113673076A (en)* | 2021-07-09 | 2021-11-19 | 华南理工大学 | A Dynamic Response Solution Applicable to Marine Floating Structures |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080105562A1 (en)* | 2006-11-07 | 2008-05-08 | Marine Project Management, Inc. | Systems and methods for underwater impressed current cathodic protection |
- 2011
- 2011-05-10CNCN 201110120406patent/CN102214255A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080105562A1 (en)* | 2006-11-07 | 2008-05-08 | Marine Project Management, Inc. | Systems and methods for underwater impressed current cathodic protection |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 工程科技I辑》 20100715 何其昀 海洋工程防腐系统数值模拟优化设计技术研究 第38-47页 1 ,* |
| 《海军工程大学学报》 20110228 李俊等 优化ICCP系统的船舶静电场隐身研究 全文 1 第23卷, 第1期* |
| 《腐蚀研究》 20110331 刘极莉等 压载水舱牺牲阳极优化布置研究 全文 1 第25卷, 第3期* |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104674228A (en)* | 2015-02-02 | 2015-06-03 | 深圳市燃气集团股份有限公司 | Detection method for cathode protection of directionally drilled and crossed pipeline |
| CN104674228B (en)* | 2015-02-02 | 2018-01-23 | 深圳市燃气集团股份有限公司 | A kind of detection method of directional drilling crossing pipeline cathode protection |
| CN105154887A (en)* | 2015-09-16 | 2015-12-16 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for optimally designing of impressed current cathodic corrosion control system of steel-concrete structures |
| CN105154887B (en)* | 2015-09-16 | 2017-06-16 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Steel and concrete structure impressed current cathodic corrosion control system Optimization Design |
| CN110208764A (en)* | 2019-05-05 | 2019-09-06 | 南京航空航天大学 | Dynamic sea large scene echo simulation method based on electromagnetism Scattering Calculation |
| CN111876785A (en)* | 2020-08-05 | 2020-11-03 | 上海外高桥造船有限公司 | Current cathode protection system for FPSO outer plate corrosion prevention and setting method thereof |
| CN112538632A (en)* | 2020-11-18 | 2021-03-23 | 广东工业大学 | Marine structure protection method based on cathode protection and sacrificial anode block service life prediction |
| CN113673076A (en)* | 2021-07-09 | 2021-11-19 | 华南理工大学 | A Dynamic Response Solution Applicable to Marine Floating Structures |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102214255A (en) | Method for simulating and optimizing numerical value of anti-corrosion system of naval architecture and ocean engineering | |
| CN110110413B (en) | A Structural Topology Optimization Method Based on Reduced Series Expansion of Material Field | |
| Amaya et al. | Effective boundary element methods in corrosion analysis | |
| CN116090293A (en) | DC resistivity inversion method and system based on unsupervised deep learning | |
| CN112347678A (en) | Novel multi-scale finite element method for simultaneously simulating underground water flow and Darcy speed | |
| CN115691708A (en) | Neutronics Simulation Method for Axial Linear Section Variation of Pressurized Water Reactor CRUD | |
| Zamani et al. | BEM simulation of cathodic protection systems employed in infinite electrolytes | |
| CN108376208A (en) | A kind of impressed current anode system optimization method of grounded screen cathodic protection | |
| Adey et al. | Applications of Boundary Elements in corrosion engineering | |
| Bortels et al. | Three-dimensional boundary element method and finite element method simulations applied to stray current interference problems. A unique coupling mechanism that takes the best of both methods | |
| Montoya et al. | Using the right side of Poisson’s equation to save on numerical calculations in FEM simulation of electrochemical systems | |
| CN110096819B (en) | A Simulation Analysis Method for Electric Field of Aluminum Electrolyzer Considering the Change Process of Anode Shape | |
| Santos et al. | An application of genetic algorithms and the method of fundamental solutions to simulate cathodic protection systems | |
| Bojarevics et al. | MHD stability for irregular and disturbed aluminium reduction cells | |
| Zhang et al. | Optimization of ICCP anode configuration based on multi objective genetic algorithm | |
| Mujezinović et al. | Calculation of the protective current density distribution of a cathodic protection system with galvanic anodes in terms of double-layer electrolyte | |
| Zhang et al. | Research on Optimization of Cathodic Protection Effect of Buried Pipeline | |
| Martinez | Evaluation of the uniform current density assumption in cathodic protection systems with close anode‐to‐cathode arrangement | |
| Ma et al. | A Cartesian ghost‐cell multigrid Poisson solver for incompressible flows | |
| CN119989822B (en) | Corrosion solver construction method based on boundary element-finite element coupling algorithm | |
| Mujezinović et al. | Modelling of the cathodic protection system with dynamic non-linear polarization characteristics | |
| Young et al. | Locally corrected Nyström discretization for impressed current cathodic protection systems | |
| Purcar et al. | Electroforming simulations based on the level set method | |
| CN114547935B (en) | A method for evaluating interference of high voltage DC double grounding electrodes on buried metal structures | |
| Huang et al. | Numerical Simulation with Parallel Computation for Anti-Corrosion System of Ocean Structure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20111012 |