CN102120168A - Multifunctional core-shell structure fluorescent coding magnetic microspheres and preparation method thereof - Google Patents
Multifunctional core-shell structure fluorescent coding magnetic microspheres and preparation method thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102120168A CN102120168ACN2010105765143ACN201010576514ACN102120168ACN 102120168 ACN102120168 ACN 102120168ACN 2010105765143 ACN2010105765143 ACN 2010105765143ACN 201010576514 ACN201010576514 ACN 201010576514ACN 102120168 ACN102120168 ACN 102120168A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- shell structure
- magnetic microspheres
- core
- magnetic
- microspheres
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于纳米材料和生物医学技术领域,具体涉及一种双荧光标记的纳米磁性微球及其制备方法。The invention belongs to the technical fields of nanomaterials and biomedicine, and in particular relates to a double-fluorescent-labeled nano-magnetic microsphere and a preparation method thereof.
背景技术Background technique
目前,磁性纳米硅球复合材料在生物技术研究领域得到了极大地发展,多种磁性微球基于其高效的分离效率,简单的样本处理过程,无害的操作条件和易于功能化修饰等优点,已被广泛应用于蛋白分离,细胞标记,细胞检测,细胞成像等。此外,基于四氧化三铁这一磁性材料的良好顺磁性和易于合成、功能化的性质,使之成为分离、富集、核磁成像、免疫分析的重要研发对象,而硅纳米球颗粒基于其良好的生物适应性,稳定性,水溶性和易于再修饰的能力,也得到了极大地关注与发展。于是,合成的磁性纳米硅球复合材料保存了二者的多种优良性质,比如超顺磁性,大的比表面积,良好的生物适应性,水溶性和易于修饰的性质等。荧光的引入更是极大地拓宽了磁性微球复合纳米材料的应用范围,使得在纳米尺度下的实时检测成为可能。At present, magnetic nano-silicon sphere composite materials have been greatly developed in the field of biotechnology research. A variety of magnetic microspheres are based on their high separation efficiency, simple sample processing process, harmless operating conditions and easy functional modification. It has been widely used in protein separation, cell labeling, cell detection, cell imaging, etc. In addition, based on the good paramagnetism, easy synthesis, and functional properties of the magnetic material of ferric iron tetroxide, it has become an important research and development object for separation, enrichment, nuclear magnetic imaging, and immunoassay, while silicon nanospheres are based on its good The biocompatibility, stability, water solubility and ability to be easily remodified have also received great attention and development. Therefore, the synthesized magnetic nano-silicon sphere composite retains many excellent properties of the two, such as superparamagnetism, large specific surface area, good biocompatibility, water solubility and easy modification properties. The introduction of fluorescence has greatly broadened the application range of magnetic microsphere composite nanomaterials, making real-time detection at the nanoscale possible.
此外,随着生物医学的发展,在生物标记、生物诊断上愈发迫切的需要多种可编码的磁性微球复合材料,荧光编码微球成为一种主要的解决手段。荧光编码微球指的是一种负载了两种或两种以上荧光物质的新型微球,通过调节荧光物质的配比进而实现对微球的光学编码。如此,通过偶联抗体等进一步功能化修饰即可实现对复杂样品中的蛋白质(抗原)、基因、细胞进行特异识别及诊断。目前主要的制备荧光编码微球的方法有:1、通过溶胀的方法,将量子点包裹在微球表面。2、通过层层自组装的方法将量子点吸附于微球表面。3、利用微乳法,正硅酸乙酯水解包裹荧光物质合成复合材料(高明远,涂赤枫,杨云华,CN1948383A.孙康,窦红静,陶可,CN101037205A.洪霞,白玉白,李军等,CN1524925A. 叶玲,于景娴,王楠等,CN101671554A.)。而荧光编码磁性微球的制备是一种集成了磁性和荧光性质的多功能纳米微球,较之传统的荧光编码聚苯乙烯微球(多为微米级),具备了更多的优点,包括纳米比表面积大,超顺磁性,易于功能化修饰等,因而极大地拓宽了复合材料的应用领域。这里,量子点和有机荧光染料均可作为编码磁性微球纳米复合材料的荧光来源,而且量子点也有着诸多优点,如宽的激发光谱,窄的发射光谱,不易光漂白等,然而量子点也有着一些自身的缺点,如对环境的普遍敏感性,固有的生物毒性等(Zhou L, Gao C, Hu X, et al. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2010, 2(4): 1211-1219. King-Heiden T C, Wiecinski P N, Mangham A N, et al. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43(5): 1605-1611.)。相比较而言,有机分子染料有着良好的生物适应性和无毒性,因而仍然表现出良好的应用价值。In addition, with the development of biomedicine, there is an increasingly urgent need for a variety of coded magnetic microsphere composite materials in biomarkers and biodiagnosis, and fluorescently coded microspheres have become a major solution. Fluorescence-encoded microspheres refer to a new type of microspheres loaded with two or more fluorescent substances, and the optical encoding of the microspheres can be realized by adjusting the ratio of fluorescent substances. In this way, specific recognition and diagnosis of proteins (antigens), genes, and cells in complex samples can be achieved through further functional modification such as coupling antibodies. At present, the main methods for preparing fluorescently encoded microspheres include: 1. Wrap quantum dots on the surface of the microspheres by swelling. 2. Quantum dots are adsorbed on the surface of microspheres by layer-by-layer self-assembly. 3. Using the microemulsion method, ethyl orthosilicate is hydrolyzed to wrap fluorescent substances to synthesize composite materials (Gao Mingyuan, Tu Chifeng, Yang Yunhua, CN1948383A. Sun Kang, Dou Hongjing, Tao Ke, CN101037205A. Hong Xia, Bai Yubai, Li Jun, etc., CN1524925A . Ye Ling, Yu Jingxian, Wang Nan, etc., CN101671554A.). The preparation of fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres is a multifunctional nano-microsphere that integrates magnetic and fluorescent properties. Compared with traditional fluorescent-encoded polystyrene microspheres (mostly micron-sized), it has more advantages, including The specific surface area of nanometer is large, superparamagnetic, easy to functional modification, etc., thus greatly broadening the application field of composite materials. Here, both quantum dots and organic fluorescent dyes can be used as the fluorescent source of the encoded magnetic microsphere nanocomposites, and quantum dots also have many advantages, such as wide excitation spectrum, narrow emission spectrum, not easy to photobleaching, etc. However, quantum dots also have However, it has some shortcomings of its own, such as general sensitivity to the environment, inherent biological toxicity, etc. (Zhou L, Gao C, Hu X, et al. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2010, 2(4): 1211-1219. King-Heiden T C, Wiecinski P N, Mangham A N, et al. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43(5): 1605-1611.). In comparison, organic molecular dyes have good biological adaptability and non-toxicity, so they still show good application value.
此外,发展合成多功能化的磁性荧光纳米微球材料的方法依然是生物纳米技术发展的关键。目前报道过的合成方法主要包括以磁性纳米粒子为核心,外包硅层,而后氨基化,再通过有机染料分子的异硫氰根与复合材料外层氨基反应,偶联上有机染料分子,(Jang J H, Lim H B. Microchem. J. 2010, 94(2): 148-158. Zhang Y, Gong S W Y, Jin L, et al. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2009, 20(8): 969-972.) 不过这种偶联方法会造成有机分子占据复合材料的表面功能基团,进而影响进一步的反应,我们提出的原位制备方法很好的解决了这一问题。同时,相对于制备双核壳结构的量子点荧光编码复合材料(苏星光,王冠男. CN 101530766A.),我们实现了荧光一步编码,因而节省了操作步骤,并且,相对于一种或两种荧光素或量子点单独标记(李振奎,赵明行,朴承范等,CN101283276A.邓勇辉,杨武利,高海峰等,CN1523076A.),这种双荧光标记可以制备更多的荧光编码材料。此外,相对于目前正在使用的磁性微球,多采用的是利用预制备的微球对磁粒子进行再吸附而制备(庞代文,谢海燕,王国平等,CN1869692A)。我们制备的磁性微球使用原位合成,因而避免了磁粒子渗漏及不稳定性。另外,我们只使用一种激发光即488nm激发光,即实现了双荧光发射,综上,这种荧光编码磁性微球更具前景优势。In addition, the development of methods for synthesizing multifunctional magnetic fluorescent nanosphere materials is still the key to the development of bionanotechnology. The synthesis method reported so far mainly includes magnetic nanoparticles as the core, outer silicon layer, and then amination, and then through the reaction of the isothiocyanate of the organic dye molecule with the amino group of the outer layer of the composite material, and the coupling of the organic dye molecule, (Jang J H, Lim H B. Microchem. J. 2010, 94(2): 148-158. Zhang Y, Gong S W Y, Jin L, et al. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2009, 20(8): 969- 972.) However, this coupling method will cause organic molecules to occupy the surface functional groups of the composite material, which will affect further reactions. The in situ preparation method we proposed solves this problem well. At the same time, compared to the preparation of double-core-shell quantum dot fluorescent coding composite materials (Su Xingguang, Wang Guannan. CN 101530766A.), we have realized one-step fluorescent coding, thus saving operation steps, and, compared to one or two kinds of fluorescent Single-labeling of prime or quantum dots (Li Zhenkui, Zhao Mingxing, Park Chengfan, etc., CN101283276A. Deng Yonghui, Yang Wuli, Gao Haifeng, etc., CN1523076A.), this double fluorescent labeling can prepare more fluorescent coding materials. In addition, compared with the magnetic microspheres currently in use, most of them are prepared by re-adsorbing magnetic particles with pre-prepared microspheres (Pang Daiwen, Xie Haiyan, Wang Guoping, CN1869692A). The magnetic microspheres we prepared use in-situ synthesis, thus avoiding the leakage and instability of magnetic particles. In addition, we only use one kind of excitation light, that is, 488nm excitation light, to achieve dual fluorescence emission. In summary, this kind of fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres has more promising advantages.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于提供一种可荧光编码的纳米磁性微球及其制备方法。The object of the present invention is to provide a fluorescently encoded nano magnetic microsphere and a preparation method thereof.
本发明提供的可荧光编码的纳米磁性微球,为核壳结构,其内核为四氧化三铁(Fe3O4)磁性纳米颗粒,该纳米颗粒粒径小于250nm ,例如,粒径一般在50—250 nm之间;外壳为二氧化硅层,该二氧化硅层中含有两种荧光素染料分子:异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)和异硫氰酸罗丹明B(RBITC);异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)和异硫氰酸罗丹明B(RBITC)的不同质量比例,构成不同荧光编码的磁性微球;该磁性微球的粒径小于320nm,例如,粒径一般在100—320 nm之间。The fluorescently encoded nano-magnetic microspheres provided by the present invention have a core-shell structure, and the inner core is ferric oxide (Fe3 O4 ) magnetic nanoparticles. The particle size of the nanoparticles is less than 250nm. — between 250 nm; the shell is a layer of silica containing two fluorescein dye molecules: fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and rhodamine B isothiocyanate (RBITC); isothiocyanate Different mass ratios of fluorescein cyanate (FITC) and rhodamine B isothiocyanate (RBITC) constitute magnetic microspheres with different fluorescent codes; the particle size of the magnetic microspheres is less than 320nm, for example, the particle size is generally between 100- between 320 nm.
合成这一功能化荧光编码磁性微球,是在微乳液中将两种具有不同荧光的荧光素:异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)和异硫氰酸罗丹明B(RBITC)以不同质量比例混合,并与3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷(APTMS)偶联反应,而后与正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)在氨水中共水解,在超顺磁性的Fe3O4纳米粒子表面,形成含有两种荧光素的二氧化硅层外壳,即得到粒径小于320nm,荧光强度高,稳定性好的荧光编码磁性微球。The functional fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres were synthesized by mixing two fluoresceins with different fluorescence: fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and rhodamine B isothiocyanate (RBITC) in different mass ratios in microemulsions. Mixed and reacted with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS), and then co-hydrolyzed with tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) in ammonia water, on the surface of superparamagnetic Fe3 O4 nanoparticles, the formation of Two kinds of fluorescein shells with silicon dioxide layer can obtain fluorescent coded magnetic microspheres with a particle size less than 320nm, high fluorescence intensity and good stability.
这种制备方法避免了前述有机染料分子偶联于硅层表面占据反应位点的问题,同时也避免了前述溶胀法中荧光分子渗漏的问题以及在层层组装法中聚电解质削弱荧光分子信号的问题。这里,通过改变FITC和RBITC的配比比例即可达到调节复合微球的荧光变化,从而实现对复合微球进行荧光编码的目的。正是基于这种在制备过程中加入了两种不同的荧光试剂,使得该复合微球在具备了超顺磁性的前提下,可以通过调节荧光素的配比以实现荧光编码,因此可以称之为荧光编码磁性微球。This preparation method avoids the problem that the aforementioned organic dye molecules are coupled to the surface of the silicon layer to occupy the reaction sites, and also avoids the problem of the leakage of fluorescent molecules in the aforementioned swelling method and the weakening of the signal of fluorescent molecules by the polyelectrolyte in the layer-by-layer assembly method. The problem. Here, by changing the proportion of FITC and RBITC, the fluorescence change of the composite microspheres can be adjusted, so as to achieve the purpose of fluorescently encoding the composite microspheres. It is based on the addition of two different fluorescent reagents in the preparation process that the composite microspheres can achieve fluorescence encoding by adjusting the ratio of fluorescein on the premise of superparamagnetism, so it can be called Fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres.
对上述制备的荧光编码磁性微球,通过进一步的表面修饰,可以连接抗体、核酸适配体、多肽、细胞因子等,进而可以广泛应用于免疫检测、核酸识别、核酸杂交、基因分析、细胞识别、细胞成像等。例如通过硅烷化试剂进行修饰,如利用氨基硅烷化试剂进行表面氨基化处理,进一步偶联抗体,实现生物识别、标记功能。For the fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres prepared above, through further surface modification, antibodies, nucleic acid aptamers, polypeptides, cytokines, etc. can be connected, and then can be widely used in immune detection, nucleic acid recognition, nucleic acid hybridization, gene analysis, cell recognition , cell imaging, etc. For example, modification by silylating reagents, such as using amino silylating reagents for surface amination treatment, and further coupling of antibodies to achieve biological recognition and labeling functions.
上述荧光编码磁性微球的制备的具体步骤为:The specific steps for the preparation of the above-mentioned fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres are:
1、制备超顺磁性的四氧化三铁纳米粒子;1. Preparation of superparamagnetic ferric oxide nanoparticles;
2、制备荧光素包括FITC以及RBITC,在二者不同质量配比条件下与APTMS偶联的预聚体;2. Preparation of prepolymers of fluorescein including FITC and RBITC coupled with APTMS under different mass ratio conditions;
3、室温,微乳液条件下,不同配比的荧光素FITC-APTMS以及RBITC-APTMS预聚体与TEOS在氨水条件下共水解于磁性四氧化三铁表面,制备得具有核壳结构的荧光编码的磁性微球;3. Under room temperature and microemulsion conditions, different ratios of fluorescein FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS prepolymers and TEOS were co-hydrolyzed on the surface of magnetic iron tetroxide under the condition of ammonia water, and fluorescent codes with core-shell structure were prepared. magnetic microspheres;
4、用氨基硅烷化试剂(如3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷(APTMS),3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES))对上述方法制备的具有核壳结构的荧光编码的磁性微球进行氨基再修饰,得到可用于多种生物分析的氨基功能化荧光编码磁性微球。4. Use aminosilylating reagents (such as 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS), 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES)) to treat the fluorescently encoded magnetic The microspheres are re-modified with amino groups to obtain amino-functionalized fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres that can be used in various biological analysis.
上述步骤1,可采用水热法制备得到四氧化三铁纳米粒子,该粒径小于250nm。其中,通过调节反应时间及反应温度,可以调节四氧化三铁纳米粒子的粒径。另外,在外加磁铁的辅助下,可方便的进行磁性洗涤,而后真空干燥,备用。In the
上述步骤2,通过调节FITC和RBITC的不同配比,其中FITC和RBITC的质量配比范围为1:1~10:1,即可达到调控荧光强度的目的,从而控制后续合成的核壳结构荧光编码微球的种类。此外,所用反应容器需先经过5%氢氟酸溶液的洗涤,以除去玻璃容器可能带来的成核位点。In the above step 2, by adjusting the different ratios of FITC and RBITC, wherein the mass ratio of FITC and RBITC ranges from 1:1 to 10:1, the purpose of regulating the fluorescence intensity can be achieved, thereby controlling the subsequent synthesis of the core-shell structure fluorescence Types of coded microspheres. In addition, the reaction vessel used must first be washed with 5% hydrofluoric acid solution to remove possible nucleation sites from the glass vessel.
上述步骤3,所用反应容器需先经过5%氢氟酸溶液的洗涤,以除去玻璃容器可能带来的成核位点。此处,可以通过调节荧光素预聚体与TEOS的配比,以及TEOS的用量,还有TEOS与四氧化三铁的用量配比等,可以达到调节最终制备的核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球的硅壳层的厚度、粒径。荧光素预聚体与TEOS的质量配比为0.00215:1~0.0355:1,TEOS与四氧化三铁的质量配比为0.93:1~9.3:1,其中在四氧化三铁量一定的情况下,TEOS的量每增加1μL,颗粒粒径约增加0.04nm。In
上述步骤4,所述制备功能化荧光编码磁性微球,是向核壳结构的荧光编码磁性微球溶液中加入带有氨基的硅烷化试剂,在复合材料表面进行功能化修饰。具体是在20℃~40℃温度下,在步骤3的制得磁性微球溶液(如10~50mg制备的四氧化三铁纳米颗粒,在100~150μL不同浓度配比的FITC-APTMS及RBITC-APTMS混合溶液中,以及50~100μL正硅酸乙酯和30~60μL质量分数为20~30%的氨水条件下制备得到的荧光编码磁性微球溶液)中加入(如10~50μL)氨基硅烷化试剂,继续搅拌19~24h,而后再加入少量丙酮破乳,停止搅拌,在外加磁铁的帮助下,使用乙醇、去离子水磁性洗涤多次,即得到氨基功能化的荧光编码磁性微球。In the
上述步骤中所使用的水均为双蒸去离子水。The water used in the above steps is double distilled deionized water.
在带有氨基的硅烷化试剂对荧光编码磁性微球进行氨基化处理后,可增加该种复合材料的生物适用性,不过由于修饰上的氨基会和二氧化硅表面的硅羟基发生作用,如此会影响到二氧化硅表面的电荷密度,而该种复合材料的分散性能恰恰正是基于这种电荷的排斥性能。于是,过量的氨基化试剂会减少复合微球在水相中的分散性,进而引起聚集。这时,可以考虑加入三羟硅基-3-丙基甲膦酸酯(THPMP),加入的三羟硅基-3-丙基甲膦酸酯与带有氨基的硅烷化试剂的质量比为1:1~2:1即可,这是一种含有甲基磷酸酯的惰性稳定剂,荧光编码磁性微球表面的氨基会和甲基磷酸酯基结合,从而达到阻止复合微球团聚的效果。After amination treatment of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with silylating reagents with amino groups, the biocompatibility of this composite material can be increased, but since the modified amino groups will interact with the silanol groups on the surface of silica, so It will affect the charge density on the surface of silica, and the dispersion performance of this kind of composite material is precisely based on the repulsion performance of this charge. Thus, excessive amination reagents will reduce the dispersibility of the composite microspheres in the aqueous phase, thereby causing aggregation. At this time, it can be considered to add trihydroxysilyl-3-propyl methylphosphonate (THPMP), and the mass ratio of added trihydroxysilyl-3-propyl methylphosphonate to the silylating agent with amino group is 1:1~2:1 is enough, this is an inert stabilizer containing methyl phosphate, the amino group on the surface of the fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres will combine with the methyl phosphate group, so as to prevent the aggregation of the composite microspheres .
本发明的有益效果是,制备的荧光编码磁性微球具有良好的荧光性能和磁性能,以及生物稳定性和水溶性,并可进一步功能化修饰,适用于生物医学领域,如药物研发、悬液芯片、生物标记等,并且通过施加外加磁场,可实现对被分析识别分子、细胞的分离和纯化。The beneficial effect of the present invention is that the prepared fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres have good fluorescent properties and magnetic properties, as well as biological stability and water solubility, and can be further functionalized and modified, and are suitable for biomedical fields, such as drug research and development, suspension Chips, biomarkers, etc., and by applying an external magnetic field, the separation and purification of the analyzed recognition molecules and cells can be realized.
附图说明Description of drawings
下面结合附图和实施例对本发明进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
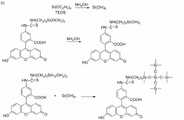
图1是制备多功能核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球所涉及到的化学反应方程式。其中:Fig. 1 is the chemical reaction equation involved in the preparation of multifunctional core-shell fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres. in:
(a)所示为FITC和RBITC分别于APTMS反应制备预聚体;(a) shows the prepolymer prepared by the reaction of FITC and RBITC in APTMS;
(b)所示为FITC与TEOS在氨水条件下发生共水解反应;(b) shows the co-hydrolysis reaction of FITC and TEOS under the condition of ammonia water;
(c)所示为RBITC与TEOS在氨水条件下发生共水解反应;(c) shows the cohydrolysis reaction of RBITC and TEOS under the condition of ammonia water;
(d)所示分别为FITC与TEOS共水解产物与APTES进行氨基功能化修饰,RBITC与TEOS共水解产物与APTES进行氨基功能化修饰。(d) shows the amino-functional modification of FITC and TEOS co-hydrolyzate and APTES, and the amino-functional modification of RBITC and TEOS co-hydrolyzate and APTES, respectively.
图2是水热法合成的四氧化三铁的扫描电子显微镜图。Figure 2 is a scanning electron micrograph of ferric oxide synthesized by hydrothermal method.
图3是核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球的透射电子显微镜图。Fig. 3 is a transmission electron micrograph of the fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure.
图4是四氧化三铁纳米粒子和核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球的各自傅立叶红外光谱图。Fig. 4 is the respective Fourier transform infrared spectrograms of ferric oxide nanoparticles and fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with core-shell structure.
图5是核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球的x-射线衍射图。Fig. 5 is an x-ray diffraction pattern of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure.
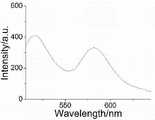
图6是核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球的荧光光谱图。Fig. 6 is a fluorescence spectrum diagram of the fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure.
图1通过化学反应方程式详细的说明了如何制备荧光素-APTMS预聚体,TEOS与FITC-APTMS以及RBITC-APTMS在氨水条件下如何共水解,以及如何实现在荧光编码磁性微球表面进行氨基化修饰这一化学过程。图2说明了本发明用以作为磁性核的四氧化三铁纳米粒子是单分散的,均匀粒径的(250nm)。图3呈现了此核壳结构的荧光编码磁性微球,粒径~300nm,外围硅层很好的包裹了磁性内核。图4通过四氧化三铁纳米粒子的傅立叶红外光谱和荧光编码磁性微球的红外光谱进行比较,不难看出,在582cm-1吸收峰为四氧化三铁中的Fe-O振动峰,二者均具有这一吸收峰,而荧光编码微球的1090cm-1红外吸收峰则为Si-O的伸缩振动峰,由此进一步证明了荧光编码微球中的确含有二氧化硅层。图5是荧光编码磁性微球的x-射线衍射光谱图,从图中的(220),(311),(400),(422),(400)衍射峰,比对文献可以确定此为顺磁性的四氧化三铁晶型的特征峰,而(100)衍射峰则说明有硅层存在,且这一二氧化硅硅层为不定型状态。图6是荧光编码磁性微球的荧光光谱图,在488nm激发光激发下,在515nm,580nm分别有FITC、RBITC的发射光谱。Figure 1 illustrates in detail how to prepare fluorescein-APTMS prepolymer through the chemical reaction equation, how TEOS, FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS are co-hydrolyzed under the condition of ammonia water, and how to achieve amination on the surface of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres Modify this chemical process. Figure 2 illustrates that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles used as magnetic cores in the present invention are monodisperse and uniform in size (250nm). Figure 3 presents the fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure, the particle size is ~300nm, and the outer silicon layer wraps the magnetic core well. Figure 4 compares the Fourier infrared spectrum of ferric oxide nanoparticles with the infrared spectrum of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres. It is not difficult to see that the absorption peak at 582 cm-1 is the Fe-O vibration peak in ferric oxide. All have this absorption peak, while the 1090cm-1 infrared absorption peak of the fluorescent coded microspheres is the stretching vibration peak of Si-O, which further proves that the fluorescent coded microspheres do contain a silicon dioxide layer. Figure 5 is the x-ray diffraction spectrum of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres. From the (220), (311), (400), (422), (400) diffraction peaks in the figure, it can be determined that this is a cis The characteristic peak of the magnetic ferric oxide crystal form, and the (100) diffraction peak indicates the existence of a silicon layer, and this silicon dioxide silicon layer is in an amorphous state. Fig. 6 is a fluorescence spectrum diagram of the fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres. Under the excitation of 488nm excitation light, there are emission spectra of FITC and RBITC at 515nm and 580nm respectively.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
在下文中将对本发明进行更加详细的描述。Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail.
本发明的荧光编码磁性复合纳米材料含有位于材料内部的顺磁性四氧化三铁纳米粒子,以及包裹于其上的二氧化硅外壳,该外壳中含有两种不同配比的有机荧光染料(FITC和RBITC),并可被硅烷化试剂进行表面修饰。因此,本发明的荧光编码磁性纳米复合材料即具备光学性能也具备磁学性能。The fluorescence-encoded magnetic composite nanomaterial of the present invention contains paramagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles inside the material, and a silica shell wrapped thereon, which contains two organic fluorescent dyes (FITC and RBITC), and can be surface modified by silylating reagents. Therefore, the fluorescence-encoded magnetic nanocomposite material of the present invention has both optical properties and magnetic properties.
本发明的荧光编码磁性微球可以通过以下步骤制备:Fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres of the present invention can be prepared by the following steps:
1、制备超顺磁性四氧化三铁纳米颗粒。1. Preparation of superparamagnetic ferric oxide nanoparticles.
四氧化三铁纳米粒子的合成采用水热法。首先,称取六水合三氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)1.35g,溶于40mL乙二醇中,磁力搅拌30min,直到三氯化铁完全溶解,得到黄色透明的溶液。然后依次加入3.6g无水乙酸钠,1.0g聚乙二醇,磁力搅拌30min,而后将所得溶液转入到50mLTeflon-Lined不锈钢反应釜中,在200℃条件下反应8~16h,反应完成后取出反应釜自然冷却至室温。所得纳米材料,利用强磁铁的吸附作用,使用乙醇和去离子水反复清洗多次,以除去乙酸钠和乙二醇等水溶性杂质,而后在60℃条件下真空干燥备用,所得四氧化三铁纳米粒子粒径为~250nm。The synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles was carried out by hydrothermal method. First, weigh 1.35 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3 ·6H2 O), dissolve it in 40 mL of ethylene glycol, and stir for 30 minutes until the ferric chloride is completely dissolved to obtain a yellow transparent solution. Then add 3.6g of anhydrous sodium acetate and 1.0g of polyethylene glycol in sequence, stir magnetically for 30min, then transfer the resulting solution into a 50mL Teflon-Lined stainless steel reactor, and react at 200°C for 8~16h, take it out after the reaction is completed The reactor was naturally cooled to room temperature. The obtained nanomaterials, using the adsorption effect of a strong magnet, are repeatedly washed with ethanol and deionized water several times to remove water-soluble impurities such as sodium acetate and ethylene glycol, and then vacuum-dried at 60°C for later use. The obtained ferric iron tetroxide The nanoparticles have a particle size of ~250 nm.
2、制备FITC-APTMS,RBITC-APTMS预聚体。2. Preparation of FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS prepolymers.
反应所用的反应瓶预先使用5%的氢氟酸清洗5min,而后除去洗液,并使用去离子水冲洗,置于真空干燥箱干燥。The reaction bottle used in the reaction was cleaned with 5% hydrofluoric acid for 5 minutes in advance, then the washing solution was removed, rinsed with deionized water, and dried in a vacuum oven.
取1mL乙醇置于干燥清洁的反应瓶中,而后取不同质量的FITC、RBITC溶于乙醇溶液中,磁力搅拌条件下加入10μLAPTMS,干燥、密闭、避光、搅拌反应24h。得到FITC-APTMS以及RBITC-APTMS预聚体。Take 1mL of ethanol and place it in a dry and clean reaction bottle, then take FITC and RBITC of different qualities and dissolve it in the ethanol solution, add 10μLAPTMS under the condition of magnetic stirring, dry, airtight, avoid light, and stir for 24h. FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS prepolymers were obtained.
3、制备核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球。3. Preparation of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with core-shell structure.
反应前,所用反应瓶同样预先使用5%氢氟酸清洗5min,而后除去洗液,并使用去离子水冲洗,置于真空干燥箱干燥。Before the reaction, the reaction bottle used was also cleaned with 5% hydrofluoric acid for 5 minutes, and then the washing solution was removed, rinsed with deionized water, and dried in a vacuum oven.
在50mL圆底烧瓶中,加入7.5mL环己烷,1.77mLTriton X-100,1.8mL的正己醇,机械强力搅拌30min使之混匀,而后滴加250μL水溶液,继续搅拌使之混匀,而后加入10~50mg前述制备的四氧化三铁纳米颗粒,辅之超声,使得四氧化三铁很好的分散在溶液中,继续搅拌12~15min,然后加入100~150μL不同浓度配比的FITC-APTMS及RBITC-APTMS混合溶液,继续搅拌5~8min,加入50~100μL正硅酸乙酯和30~60μL质量分数为20~30%的氨水,在避光条件下持续搅拌20~24h,之后加入10μL丙酮破乳,停止搅拌。在外加强磁铁的吸附作用下,分别用乙醇和去离子水反复清洗反应产物,即得到核壳结构的荧光编码磁性微球,粒径在~300nm,根据加入TEOS和Fe3O4量比的不同,可调节所得材料的粒径。In a 50mL round bottom flask, add 7.5mL cyclohexane, 1.77mL Triton X-100, 1.8mL n-hexanol, stir vigorously for 30min to mix well, then add 250μL aqueous solution dropwise, continue stirring to mix well, then add 10~50mg of ferric oxide nanoparticles prepared above, supplemented by ultrasound, make ferric oxide well dispersed in the solution, continue to stir for 12~15min, then add 100~150μL of FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS mixed solution, continue to stir for 5~8min, add 50~100μL tetraethyl orthosilicate and 30~60μL ammonia water with a mass fraction of 20~30%, keep stirring for 20~24h under dark conditions, then add 10μL acetone To break the emulsion, stop stirring. Under the adsorption of an external strengthening magnet, the reaction product was washed repeatedly with ethanol and deionized water respectively, and then the fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure were obtained, with a particlesize of ~300nm . , the particle size of the resulting material can be adjusted.
4、制备氨基功能化的荧光编码磁性微球。4. Preparation of amino-functionalized fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres.
前述步骤同上述3,在正硅酸乙酯同荧光素-APTMS预聚体共水解于四氧化三铁表面24h之后,加入氨基硅烷化试剂,如APTES,10~50μLAPTES加入到上述混合溶液,继续搅拌19~24h,而后再加入少量丙酮(10μL)破乳,停止搅拌。在外加磁铁的吸附作用辅助下,分别用乙醇和去离子水反复清洗所得产物,即得到氨基功能化的具有核壳结构的荧光编码磁性微球。为得到良好分散的氨基化荧光编码磁性微球,可在加入APTES时,同时加入30~100μLTHPMP。The aforementioned steps are the same as the above 3. After co-hydrolysis of ethyl tetrasilicate and fluorescein-APTMS prepolymer on the surface of ferric oxide for 24 hours, add aminosilylating reagents, such as APTES, 10~50μLAPTES is added to the above mixed solution, and continue Stir for 19~24h, then add a small amount of acetone (10μL) to break the emulsion, and stop stirring. With the help of the adsorption effect of an external magnet, the obtained product is washed repeatedly with ethanol and deionized water respectively, and the amino-functionalized fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure are obtained. In order to obtain well-dispersed aminated fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres, 30-100 μL THPMP can be added at the same time as APTES is added.
实施例1:Example 1:
制备荧光配比(质量比)FITC:RBITC=1:1的核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球。Prepare fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure with a fluorescent ratio (mass ratio) of FITC:RBITC=1:1.
a、制备超顺磁性四氧化三铁纳米颗粒。a. Preparation of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles.
称取六水合三氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)1.35g,溶于40mL乙二醇中,磁力搅拌30min,三氯化铁完全溶解。然后依次加入3.6g无水乙酸钠,1.0g聚乙二醇,磁力搅拌30min后将所得溶液移至50mLTeflon-Lined不锈钢反应釜中,在200℃条件下反应8~16h,反应完成后取出反应釜自然冷却至室温,使用乙醇和去离子水反复清洗多次,而后在60℃条件下真空干燥备用。Weigh 1.35g of ferric trichloride hexahydrate (FeCl3 ·6H2 O), dissolve it in 40mL of ethylene glycol, stir with magnetic force for 30min, and the ferric chloride is completely dissolved. Then add 3.6g of anhydrous sodium acetate and 1.0g of polyethylene glycol in sequence, and stir the solution for 30 minutes with magnetic force, then transfer the resulting solution to a 50mL Teflon-Lined stainless steel reactor, and react at 200°C for 8-16 hours. After the reaction is completed, take out the reactor Naturally cooled to room temperature, washed repeatedly with ethanol and deionized water, and then vacuum-dried at 60°C for later use.
b、制备FITC-APTMS,RBITC-APTMS预聚体。b. Preparation of FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS prepolymers.
取1mL乙醇置于干燥清洁,5%氢氟酸预处理过的反应瓶中,而后取1mgFITC、1mgRBITC溶于乙醇溶液中,磁力搅拌条件下加入10μLAPTMS,干燥、密闭、避光、搅拌反应24h,得到FITC-APTMS以及RBITC-APTMS混合的预聚体。Take 1mL of ethanol and put it in a dry and clean reaction bottle pretreated with 5% hydrofluoric acid, then take 1mgFITC and 1mgRBITC and dissolve it in the ethanol solution, add 10μLAPTMS under the condition of magnetic stirring, dry, airtight, avoid light, and stir for 24h. A prepolymer mixed with FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS was obtained.
c、制备核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球。c. Preparation of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with core-shell structure.
在50mL圆底烧瓶中,加入7.5mL环己烷,1.77mLTriton X-100,1.8mL的正己醇,机械强力搅拌30min使之混匀,而后滴加250μL水溶液,继续搅拌使之混匀后加入10mg步骤a制备的四氧化三铁纳米颗粒,辅之超声,使四氧化三铁均匀分散在溶液中,继续搅拌15min,加入150μL步骤b制备的FITC-APTMS及RBITC-APTMS混合溶液,继续搅拌5min,而后加入100μL正硅酸乙酯和60μL质量分数为28%的氨水,在避光条件下持续搅拌24h,之后加入10μL丙酮破乳,停止搅拌。在外加强磁铁的吸附作用下,分别用乙醇和去离子水反复清洗反应产物,即得到核壳结构的荧光编码磁性微球。In a 50mL round bottom flask, add 7.5mL cyclohexane, 1.77mL Triton X-100, 1.8mL n-hexanol, stir vigorously for 30min to mix well, then add 250μL aqueous solution dropwise, continue stirring to mix well, then add 10mg The ferric iron tetroxide nanoparticles prepared in step a, supplemented by ultrasound, are used to uniformly disperse ferric ferric oxide in the solution, continue stirring for 15 minutes, add 150 μL of FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS mixed solution prepared in step b, and continue stirring for 5 minutes, Then add 100 μL tetraethyl orthosilicate and 60 μL ammonia water with a mass fraction of 28%, and keep stirring for 24 h under dark conditions, then add 10 μL acetone to break the emulsion, and stop stirring. Under the adsorption effect of an externally strengthened magnet, the reaction product is washed repeatedly with ethanol and deionized water, respectively, to obtain fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure.
实施例2:Example 2:
制备荧光配比(质量比)FITC:RBITC=4:1的氨基功能化的核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球。Amino-functionalized core-shell fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with a fluorescence ratio (mass ratio) of FITC:RBITC=4:1 were prepared.
a、制备超顺磁性四氧化三铁纳米颗粒,同实施样例1步骤a。a. Prepare superparamagnetic ferric oxide nanoparticles, the same as step a of Example 1.
b、制备FITC-APTMS,RBITC-APTMS预聚体。b. Preparation of FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS prepolymers.
取1mL乙醇置于干燥清洁,5%氢氟酸预处理过的反应瓶中,而后取4mgFITC、1mgRBITC溶于乙醇溶液中,磁力搅拌条件下加入10μLAPTMS,干燥、密闭、避光、搅拌反应24h,得到FITC-APTMS以及RBITC-APTMS混合的预聚体。Take 1mL of ethanol and place it in a dry and clean reaction bottle pretreated with 5% hydrofluoric acid, then take 4mgFITC and 1mgRBITC and dissolve it in the ethanol solution, add 10μLAPTMS under the condition of magnetic stirring, dry, airtight, avoid light, and stir for 24h. A prepolymer mixed with FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS was obtained.
c、制备核壳结构荧光编码磁性微球。c. Preparation of fluorescently encoded magnetic microspheres with core-shell structure.
在50mL圆底烧瓶中,加入7.5mL环己烷,1.77mLTriton X-100,1.8mL的正己醇,机械强力搅拌30min使之混匀,而后滴加250μL水溶液,继续搅拌使之混匀后加入10mg步骤a制备的四氧化三铁纳米颗粒,辅之超声,使得四氧化三铁很好的分散在溶液中,继续搅拌15min,然后加入150μL步骤b制备的FITC-APTMS及RBITC-APTMS混合溶液,继续搅拌5min,加入100μL正硅酸乙酯和60μL质量分数为28%的氨水,在避光条件下持续搅拌24h。In a 50mL round bottom flask, add 7.5mL cyclohexane, 1.77mL Triton X-100, 1.8mL n-hexanol, stir vigorously for 30min to mix well, then add 250μL aqueous solution dropwise, continue stirring to mix well, then add 10mg The iron ferric oxide nanoparticles prepared in step a, supplemented by ultrasound, make the iron ferric oxide well dispersed in the solution, continue to stir for 15 minutes, then add 150 μL of the mixed solution of FITC-APTMS and RBITC-APTMS prepared in step b, and continue Stir for 5 min, add 100 μL tetraethyl orthosilicate and 60 μL ammonia water with a mass fraction of 28%, and continue stirring for 24 h under dark conditions.
d、制备氨基功能化的荧光编码磁性微球。d. Preparation of amino-functionalized fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres.
氨基硅烷化试剂,如APTES,10μLAPTES加入到步骤c反应24h后的混合溶液中,继续搅拌19~24h,而后在加入少量丙酮(10μL)破乳,停止搅拌。在外加磁铁的吸附作用辅助下,分别用乙醇和去离子水反复清洗所得产物,即得到氨基功能化的具有核壳结构的荧光编码磁性微球。欲得到良好分散的氨基化荧光编码磁性微球,只需在加入APTES时,同时加入30μLTHPMP。Aminosilylating reagents, such as APTES, 10μLAPTES are added to the mixed solution after 24h of reaction in step c, continue to stir for 19~24h, then add a small amount of acetone (10μL) to break the emulsion, and stop stirring. With the help of the adsorption effect of an external magnet, the obtained product is washed repeatedly with ethanol and deionized water respectively, and the amino-functionalized fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with a core-shell structure are obtained. To obtain well-dispersed aminated fluorescent-encoded magnetic microspheres, only need to add 30 μL THPMP when adding APTES.
Claims (7)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201010576514CN102120168B (en) | 2010-12-07 | 2010-12-07 | Fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with multifunctional core-shell structure and preparation method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201010576514CN102120168B (en) | 2010-12-07 | 2010-12-07 | Fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with multifunctional core-shell structure and preparation method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102120168Atrue CN102120168A (en) | 2011-07-13 |
| CN102120168B CN102120168B (en) | 2013-05-29 |
Family
ID=44248886
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201010576514Expired - Fee RelatedCN102120168B (en) | 2010-12-07 | 2010-12-07 | Fluorescence-encoded magnetic microspheres with multifunctional core-shell structure and preparation method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102120168B (en) |
Cited By (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102676157A (en)* | 2012-05-15 | 2012-09-19 | 泰普生物科学(中国)有限公司 | Fluorescent microsphere marker and preparation method thereof |
| CN103187134A (en)* | 2013-03-21 | 2013-07-03 | 郑州大学 | Ferroferric oxide magnetic nanometer particles decorated with tetraazacalix [2] arene [2] triazine as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN103241776A (en)* | 2012-02-11 | 2013-08-14 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Ferroferric oxide nano-composite particle and preparation method and applications thereof |
| CN103525405A (en)* | 2013-10-21 | 2014-01-22 | 北京理工大学 | Magnetic fluorescent difunctional nano material based on natural polymer and preparation method thereof |
| CN103674947A (en)* | 2013-12-25 | 2014-03-26 | 福州大学 | Trace copper ion visual rapid detection method |
| CN103901198A (en)* | 2012-12-26 | 2014-07-02 | 深圳先进技术研究院 | Immune test paper for detecting group A rotaviruses, and its making method |
| CN103990423A (en)* | 2014-03-27 | 2014-08-20 | 华南师范大学 | Single-stranded DNA aptamer modified SiO2/Fe3O4 magnetic microsphere preparation method |
| CN104781321A (en)* | 2012-11-16 | 2015-07-15 | 首尔大学校产学协力团 | Encoded polymer microparticles |
| CN105363394A (en)* | 2015-09-24 | 2016-03-02 | 济南大学 | Preparation and application of magnetic fluorescent molecule imprinting nano-microspheres for detecting nitrobenzene |
| CN105542750A (en)* | 2015-12-07 | 2016-05-04 | 兰州大学 | Preparation method of HAN-Fe3O4@MSN-based inorganic-organic hybrid fluorescent sensor |
| CN105826805A (en)* | 2016-05-24 | 2016-08-03 | 中国计量大学 | Random fiber laser capable of realizing magnetic regulation |
| CN105854747A (en)* | 2016-04-29 | 2016-08-17 | 南京工程学院 | Monodisperse melamine resin magnetic microsphere and preparation method thereof |
| CN105920620A (en)* | 2016-06-21 | 2016-09-07 | 东南大学 | Magnetic fluorescent multimodal nano biological probe as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN107607506A (en)* | 2017-09-05 | 2018-01-19 | 中山大学 | A kind of quick detection platform based on the micro-nano probe of magnetic coupling and micro-fluidic chip |
| CN109001452A (en)* | 2018-07-26 | 2018-12-14 | 上海纳米技术及应用国家工程研究中心有限公司 | Preparation method of detection probe of alpha-synapse nucleoprotein accumulation and products thereof and application |
| CN106009347B (en)* | 2016-05-24 | 2019-03-12 | 东南大学 | A kind of polymer carrier microspheres encoded by magnetic content and preparation method thereof |
| CN109632920A (en)* | 2018-11-20 | 2019-04-16 | 武汉市农业科学院 | A kind of preparation method of electrochemical signals marker material |
| CN110187115A (en)* | 2019-05-17 | 2019-08-30 | 苏州百源基因技术有限公司 | A kind of fluorescence-encoded magnetic bead and its preparation and application |
| CN113063764A (en)* | 2021-03-23 | 2021-07-02 | 重庆华芯云物联科技有限公司 | Singlet oxygen producing microsphere based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| CN113281317A (en)* | 2021-05-14 | 2021-08-20 | 北京指真生物科技有限公司 | Coded microsphere containing cyanine compounds, and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN113634240A (en)* | 2021-08-26 | 2021-11-12 | 山东交通学院 | Fluorescent magnetic composite nanofiber, its preparation method and application |
| CN113943653A (en)* | 2020-07-16 | 2022-01-18 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | Tannin-based broad-spectrum CTC (CTC) capturing and separating substrate as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN115058010A (en)* | 2022-05-28 | 2022-09-16 | 南昌大学 | Core-shell type high-luminescence aggregation-induced-luminescence nano particle and preparation method thereof |
| CN115184599A (en)* | 2022-06-28 | 2022-10-14 | 军事科学院军事医学研究院环境医学与作业医学研究所 | A kind of detection kit of ricin B chain and preparation method thereof and detection method of ricin B chain |
| CN119320994A (en)* | 2024-12-19 | 2025-01-17 | 武汉理工大学 | Magnetic fluorescent photonic crystal and preparation method and application thereof |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10319502B2 (en) | 2014-10-23 | 2019-06-11 | Corning Incorporated | Polymer-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1312479C (en)* | 2003-08-08 | 2007-04-25 | 清华大学 | Nano fluorescent magnetic particle and its preparing method |
| CN101283276A (en)* | 2005-09-08 | 2008-10-08 | 比特里斯株式会社 | Magnetic nanoparticles with fluorescence, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN101671554A (en)* | 2008-09-10 | 2010-03-17 | 首都医科大学 | Silica-coated fluorescent magnetic nanoparticle, preparation method and application |
- 2010
- 2010-12-07CNCN 201010576514patent/CN102120168B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1312479C (en)* | 2003-08-08 | 2007-04-25 | 清华大学 | Nano fluorescent magnetic particle and its preparing method |
| CN101283276A (en)* | 2005-09-08 | 2008-10-08 | 比特里斯株式会社 | Magnetic nanoparticles with fluorescence, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN101671554A (en)* | 2008-09-10 | 2010-03-17 | 首都医科大学 | Silica-coated fluorescent magnetic nanoparticle, preparation method and application |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| J.H.JANG: "Characterization and analytical application of surfacemodified magnetic nanoparticles", 《MICROCHEMICAL JOURNAL》* |
| YU ZHANG ET AL.: "Magnetic nanocomposites of Fe3O4/SiO2-FITC with pH-dependent fluorescence emission", 《CHINESE CHEMICAL LETTERS》* |
Cited By (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103241776A (en)* | 2012-02-11 | 2013-08-14 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Ferroferric oxide nano-composite particle and preparation method and applications thereof |
| CN103241776B (en)* | 2012-02-11 | 2014-10-01 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Iron ferric oxide nanocomposite particles and its preparation method and application |
| CN102676157A (en)* | 2012-05-15 | 2012-09-19 | 泰普生物科学(中国)有限公司 | Fluorescent microsphere marker and preparation method thereof |
| CN102676157B (en)* | 2012-05-15 | 2014-07-09 | 泰普生物科学(中国)有限公司 | Fluorescent microsphere marker and preparation method thereof |
| CN104781321A (en)* | 2012-11-16 | 2015-07-15 | 首尔大学校产学协力团 | Encoded polymer microparticles |
| CN104781321B (en)* | 2012-11-16 | 2018-01-23 | 昆塔麦特利斯株式会社 | Encoded polymer microparticles |
| US10557846B2 (en) | 2012-11-16 | 2020-02-11 | Quantamatrix Inc. | Encoded polymeric microparticles |
| CN103901198A (en)* | 2012-12-26 | 2014-07-02 | 深圳先进技术研究院 | Immune test paper for detecting group A rotaviruses, and its making method |
| CN103187134A (en)* | 2013-03-21 | 2013-07-03 | 郑州大学 | Ferroferric oxide magnetic nanometer particles decorated with tetraazacalix [2] arene [2] triazine as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN103187134B (en)* | 2013-03-21 | 2016-04-06 | 郑州大学 | The ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticle that four azepine cup [2] aromatic hydrocarbons [2] triazines are modified and preparation method and application |
| CN103525405A (en)* | 2013-10-21 | 2014-01-22 | 北京理工大学 | Magnetic fluorescent difunctional nano material based on natural polymer and preparation method thereof |
| CN103525405B (en)* | 2013-10-21 | 2015-02-18 | 北京理工大学 | Magnetic fluorescent difunctional nano material based on natural polymer and preparation method thereof |
| CN103674947A (en)* | 2013-12-25 | 2014-03-26 | 福州大学 | Trace copper ion visual rapid detection method |
| CN103990423B (en)* | 2014-03-27 | 2016-02-03 | 华南师范大学 | A kind of single stranded DNA nucleic acid aptamers modifies the preparation method of silica/Fe 3 O 4 magnetic microballoon |
| CN103990423A (en)* | 2014-03-27 | 2014-08-20 | 华南师范大学 | Single-stranded DNA aptamer modified SiO2/Fe3O4 magnetic microsphere preparation method |
| CN105363394B (en)* | 2015-09-24 | 2017-11-07 | 济南大学 | A kind of preparation and application of the magnetic fluorescence molecular engram nanoparticle for detecting nitrobenzene |
| CN105363394A (en)* | 2015-09-24 | 2016-03-02 | 济南大学 | Preparation and application of magnetic fluorescent molecule imprinting nano-microspheres for detecting nitrobenzene |
| CN105542750A (en)* | 2015-12-07 | 2016-05-04 | 兰州大学 | Preparation method of HAN-Fe3O4@MSN-based inorganic-organic hybrid fluorescent sensor |
| CN105854747A (en)* | 2016-04-29 | 2016-08-17 | 南京工程学院 | Monodisperse melamine resin magnetic microsphere and preparation method thereof |
| CN105854747B (en)* | 2016-04-29 | 2019-02-15 | 南京工程学院 | A kind of monodisperse melamine resin magnetic microsphere and preparation method thereof |
| CN105826805A (en)* | 2016-05-24 | 2016-08-03 | 中国计量大学 | Random fiber laser capable of realizing magnetic regulation |
| CN106009347B (en)* | 2016-05-24 | 2019-03-12 | 东南大学 | A kind of polymer carrier microspheres encoded by magnetic content and preparation method thereof |
| CN105826805B (en)* | 2016-05-24 | 2023-12-19 | 中国计量大学 | Random fiber laser capable of being magnetically regulated and controlled |
| CN105920620A (en)* | 2016-06-21 | 2016-09-07 | 东南大学 | Magnetic fluorescent multimodal nano biological probe as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN107607506A (en)* | 2017-09-05 | 2018-01-19 | 中山大学 | A kind of quick detection platform based on the micro-nano probe of magnetic coupling and micro-fluidic chip |
| CN109001452A (en)* | 2018-07-26 | 2018-12-14 | 上海纳米技术及应用国家工程研究中心有限公司 | Preparation method of detection probe of alpha-synapse nucleoprotein accumulation and products thereof and application |
| CN109632920B (en)* | 2018-11-20 | 2021-05-14 | 武汉市农业科学院 | A kind of preparation method of electrochemical signal marking material |
| CN109632920A (en)* | 2018-11-20 | 2019-04-16 | 武汉市农业科学院 | A kind of preparation method of electrochemical signals marker material |
| CN110187115A (en)* | 2019-05-17 | 2019-08-30 | 苏州百源基因技术有限公司 | A kind of fluorescence-encoded magnetic bead and its preparation and application |
| CN113943653A (en)* | 2020-07-16 | 2022-01-18 | 中国科学院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所 | Tannin-based broad-spectrum CTC (CTC) capturing and separating substrate as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN113063764A (en)* | 2021-03-23 | 2021-07-02 | 重庆华芯云物联科技有限公司 | Singlet oxygen producing microsphere based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| CN113063764B (en)* | 2021-03-23 | 2023-04-25 | 重庆华芯云物联科技有限公司 | Singlet oxygen-producing microsphere based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| CN113281317A (en)* | 2021-05-14 | 2021-08-20 | 北京指真生物科技有限公司 | Coded microsphere containing cyanine compounds, and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN113634240A (en)* | 2021-08-26 | 2021-11-12 | 山东交通学院 | Fluorescent magnetic composite nanofiber, its preparation method and application |
| CN113634240B (en)* | 2021-08-26 | 2023-10-27 | 宏葵生物(中国)股份有限公司 | Fluorescent magnetic composite nanofiber, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN115058010A (en)* | 2022-05-28 | 2022-09-16 | 南昌大学 | Core-shell type high-luminescence aggregation-induced-luminescence nano particle and preparation method thereof |
| CN115184599A (en)* | 2022-06-28 | 2022-10-14 | 军事科学院军事医学研究院环境医学与作业医学研究所 | A kind of detection kit of ricin B chain and preparation method thereof and detection method of ricin B chain |
| CN119320994A (en)* | 2024-12-19 | 2025-01-17 | 武汉理工大学 | Magnetic fluorescent photonic crystal and preparation method and application thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102120168B (en) | 2013-05-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102120168A (en) | Multifunctional core-shell structure fluorescent coding magnetic microspheres and preparation method thereof | |
| Liu et al. | Magnetic nanocomposites with mesoporous structures: synthesis and applications | |
| JP6788686B2 (en) | A method for producing a superparamagnetic nanocomposite and a superparamagnetic nanocomposite produced using the method. | |
| Sonmez et al. | Synthesis and applications of Fe3O4/SiO2 core-shell materials | |
| Zhang et al. | Preparation of IDA-Cu functionalized core–satellite Fe 3 O 4/polydopamine/Au magnetic nanocomposites and their application for depletion of abundant protein in bovine blood | |
| CN107790075B (en) | A kind of preparation method of magnetic mesoporous SiO2 nanoparticles of core-shell-shell structure | |
| Lu et al. | Synthesis and characteristic of the Fe3O4@ SiO2@ Eu (DBM) 3· 2H2O/SiO2 luminomagnetic microspheres with core-shell structure | |
| CN101670107B (en) | Multifunctional core-shell structure drug carrier material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN104292493B (en) | A kind of magnetic, fluorescent hollow hierarchical porous polymer microsphere and preparation method thereof | |
| CN103310935A (en) | Silicon dioxide nano magnetic microsphere and preparation method thereof | |
| CN104762085B (en) | A kind of magnetic fluorescence composite Nano bioprobe and preparation method thereof | |
| CN1523076A (en) | A magnetic fluorescent bifunctional microsphere with core-shell structure and preparation method thereof | |
| CN105771908B (en) | A kind of magnetic silica core-shell composite material and preparation method thereof for heavy metal adsorption | |
| CN101721964A (en) | Method for preparing shell-core micrometer/nanometer spheres capable of preventing functional materials | |
| CN106970215B (en) | A kind of preparation method of the Fe3O4@PEG@SiO2 artificial antibodies of detection thifensulfuronmethyl | |
| CN1229305C (en) | Method for preparing ferrite-silica core-shell nanoparticles by ultrasonic treatment | |
| CN101694795B (en) | Preparation method of multi-pore canal nuclear shell type magnet gold compound nano-particle | |
| CN102764618B (en) | Method for preparing three-layer core-shell structural gold magnetic nano particles | |
| CN103372407A (en) | Preparation method of magnetic fluorescent composite nanospheres | |
| CN112666140A (en) | Poly (undecylenic acid-divinyl benzene) coated magnetic fluorescent coding microsphere | |
| CN103508461A (en) | Method for preparing hollow silicon dioxide nanometer particles | |
| CN105832699A (en) | Preparation method and application of Fe3O4@SiO2 egg yolk-eggshell structure hollow composite microspheres | |
| CN103400677A (en) | A preparation method of magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 nanospheres | |
| CN110776910A (en) | Preparation method of bifunctional magnetic and fluorescent nanocomposite Fe3O4@CDs microspheres | |
| CN103521237A (en) | Preparation method of Fe3O4/SiO2/Bi2WO6 magnetic microsphere photocatalyst |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20130529 Termination date:20151207 | |
| EXPY | Termination of patent right or utility model |