CN102036177A - Multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipment - Google Patents
Multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102036177A CN102036177ACN200910179903XACN200910179903ACN102036177ACN 102036177 ACN102036177 ACN 102036177ACN 200910179903X ACN200910179903X ACN 200910179903XACN 200910179903 ACN200910179903 ACN 200910179903ACN 102036177 ACN102036177 ACN 102036177A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- service
- multicast
- multicast broadcast
- broadcast service
- mbms
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及通信技术领域,具体涉及组播广播业务流量控制方法及相关设备。The invention relates to the field of communication technology, in particular to a multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipment.
背景技术Background technique
第三代移动通信引入了多媒体组播广播业务(MultiMedia Broadcast Multicast Service,MBMS),实现对天气预报、新闻短片、体育比赛集锦内容的群发。The third-generation mobile communication introduces Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS), which realizes the group distribution of weather forecast, news clips, and sports highlights.
现有技术MBMS业务提供过程为:当一个新的MBMS会话开始的时候,BMSC会通过MBMS GW发送会话开始消息到MME,其中包括会话标识、MBMS业务标识等信息。MME转发会话开始消息到MCE,MCE为新增的MBMS业务预留无线资源,并且告诉给该MBSFN区域下的所有eNB。eNB通过RAN侧的无线资源控制消息(RRC)告诉UE有新的MBMS业务进行传输,对该业务感兴趣的UE会向eNB进行反馈,eNB根据用户的反馈信息决定是否加入该MBMS业务的IP多播组进行该业务的传输。The process of providing MBMS services in the prior art is: when a new MBMS session starts, the BMSC will send a session start message to the MME through the MBMS GW, which includes information such as the session identifier and the MBMS service identifier. The MME forwards the session start message to the MCE, and the MCE reserves radio resources for the newly added MBMS service, and informs all eNBs in the MBSFN area. The eNB tells the UE that there is a new MBMS service to be transmitted through the radio resource control message (RRC) on the RAN side, and the UE interested in the service will give feedback to the eNB, and the eNB decides whether to join the MBMS service according to the feedback information of the user. broadcast group to transmit the service.
在对现有技术的研究和实践过程中,本发明的发明人发现,MCE对于动态调度周期(Dynamic Scheduling Period,DSP)的配置不依赖于BMSC具体传输的业务数据,这就有可能造成在一个调度周期内,需要调度的业务的数据包超出了该调度周期实际能够调度的数据包的数量,尤其是在某段时间出现突发MBMS业务的数据传输时,会最终导致eNB丢弃无法进行调度的数据包,从而影响用户的体验。During the research and practice of the prior art, the inventors of the present invention found that the configuration of the Dynamic Scheduling Period (Dynamic Scheduling Period, DSP) by the MCE does not depend on the specific business data transmitted by the BMSC, which may result in a During the scheduling period, the data packets of the services that need to be scheduled exceed the number of data packets that can actually be scheduled in the scheduling period, especially when there is a burst of data transmission of the MBMS service in a certain period of time, it will eventually cause the eNB to discard the data packets that cannot be scheduled. packets, thereby affecting the user experience.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例提供组播广播业务流量控制方法及相关设备,可以实现对组播广播进行流量控制,降低丢包率,提升用户的业务体验。Embodiments of the present invention provide a multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipment, which can implement flow control on multicast broadcast, reduce packet loss rate, and improve user service experience.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,包括:A method for controlling flow of a multicast broadcast service provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
组播广播业务服务器BMSC接收多小区多播协调实体MCE发送的业务资源分配信息;The multicast broadcast service server BMSC receives the service resource allocation information sent by the multi-cell multicast coordination entity MCE;
根据所述业务资源分配信息对组播广播业务的数据流进行流量整形以实现流量控制。Traffic shaping is performed on the data flow of the multicast broadcast service according to the service resource allocation information to realize flow control.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,包括:A method for controlling flow of a multicast broadcast service provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
BMSC根据MBMS业务服务质量QoS信息,生成组播广播业务的数据流输速率门限值;The BMSC generates the data stream transmission rate threshold value of the multicast broadcast service according to the MBMS service quality of service QoS information;
根据所述门限值对所述组播广播业务的数据流进行流量整形,以实现流量控制。Perform traffic shaping on the data stream of the multicast broadcast service according to the threshold value, so as to realize traffic control.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,包括:A method for controlling flow of a multicast broadcast service provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
BMSC获取复用的多个组播广播业务的业务绑定速率ABBR;The BMSC obtains the service binding rate ABBR of the multiplexed multicast broadcast services;
根据所述ABBR对所复用的多个组播广播业务传输的数据流进行流量整形,以实现流量控制。According to the ABBR, traffic shaping is performed on the data streams transmitted by the multiplexed multicast broadcast services, so as to realize traffic control.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,包括:A method for controlling flow of a multicast broadcast service provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
基站统计组播广播业务数据流的丢包信息;The base station counts the packet loss information of the multicast broadcast service data flow;
当所述统计的丢包信息超出预置的门限时,则基站向BMSC发送流量控制请求,以便于BMSC对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制。When the statistical packet loss information exceeds the preset threshold, the base station sends a flow control request to the BMSC, so that the BMSC can perform flow control on the multicast broadcast service data flow.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,包括:A method for controlling flow of a multicast broadcast service provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
MCE接收BMSC的会话开始请求消息;The MCE receives the session start request message of the BMSC;
MCE根据剩余的MBMS无线资源判断是否可以支持新增的MBMS业务,The MCE judges whether it can support the newly added MBMS service according to the remaining MBMS radio resources,
若不可以支持,则MCE拒绝为新增的MBMS业务分配无线资源,或者用新增的MBMS业务替代已有的MBMS业务的无线资源。If it cannot be supported, the MCE refuses to allocate radio resources for the newly added MBMS service, or replaces the radio resources of the existing MBMS service with the newly added MBMS service.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,包括:A method for controlling flow of a multicast broadcast service provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
MCE接收BMSC发送的QoS信息;MCE receives the QoS information sent by BMSC;
根据同步序列长度SYNC sequence length和/或QoS信息,配置动态周期DSP的长度,并将调整后的DSP长度通知给广播多播单频网MBSFN区域下的基站。Configure the length of the dynamic period DSP according to the synchronization sequence length SYNC sequence length and/or QoS information, and notify the base station under the MBSFN area of the broadcast multicast single frequency network of the adjusted DSP length.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务服务器,包括:A multicast broadcast service server provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
信息接收单元,用于接收多小区多播协调实体MCE发送的业务资源分配信息;An information receiving unit, configured to receive service resource allocation information sent by a multi-cell multicast coordination entity MCE;
流量控制单元,用于根据所述业务资源分配信息对组播广播业务数据流进行流量整形以实现流量控制。The flow control unit is configured to perform flow shaping on the multicast and broadcast service data flow according to the service resource allocation information to realize flow control.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务服务器,包括:A multicast broadcast service server provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
门限值设置单元,根据MBMS业务服务质量QoS信息,生成组播广播业务的数据流输速率门限值;The threshold value setting unit generates the data stream transmission rate threshold value of the multicast broadcast service according to the MBMS service quality of service QoS information;
流量控制单元,用于根据所述门限值对所述组播广播业务的数据流传输进行流量整形。A traffic control unit, configured to perform traffic shaping on the data stream transmission of the multicast broadcast service according to the threshold value.
本发明实施例提供的一种组播广播业务服务器,包括:A multicast broadcast service server provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
速率选择单元,用于获取复用的多个组播广播业务的业务绑定速率ABBR;The rate selection unit is used to obtain the service binding rate ABBR of multiple multicast broadcast services multiplexed;
流量控制单元,用于根据所述ABBR对所述数据传输通道的传输的数据流进行流量整形。A flow control unit, configured to perform traffic shaping on the data flow transmitted by the data transmission channel according to the ABBR.
本发明实施例提供的一种基站,包括:A base station provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
统计单元,用于统计组播广播业务数据流的丢包信息;A statistical unit, used for counting the packet loss information of the multicast broadcast service data flow;
流量控制请求单元,用于当所述统计的丢包信息超出预置的门限时,向BMSC发送流量控制请求,以便于BMSC对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制。A flow control request unit, configured to send a flow control request to the BMSC when the statistical packet loss information exceeds a preset threshold, so that the BMSC can perform flow control on the multicast broadcast service data flow.
本发明实施例提供的一种多小区多播协调实体,包括:A multi-cell multicast coordination entity provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
接收单元,用于接收BMSC的会话开始请求消息;a receiving unit, configured to receive a session start request message of the BMSC;
资源分配控制单元,用于根据剩余的MBMS无线资源判断是否可以支持新增的MBMS业务,若不可以支持,则拒绝为新增的MBMS业务分配无线资源,或者用新增的MBMS业务替代已有的MBMS业务的无线资源。The resource allocation control unit is used to judge whether the newly added MBMS service can be supported according to the remaining MBMS radio resources, and if it cannot be supported, then refuse to allocate radio resources for the newly added MBMS service, or replace the existing MBMS service with the newly added MBMS service Radio resources for MBMS services.
本发明实施例提供的一种多小区多播协调实体,包括:A multi-cell multicast coordination entity provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes:
接收单元,接收BMSC发送的QoS信息;The receiving unit receives the QoS information sent by the BMSC;
周期调整单元,用于根据同步序列长度SYNC sequence length和/或QoS信息,配置动态周期DSP的长度,并将调整后的DSP长度通知给广播多播单频网MBSFN区域下的基站。本发明实施例提供组播广播业务流量控制方法,通过在组播广播业务提供过程中获取相关数据,并根据获取的数据对组播广播业务流进行控制,相对于现有技术,降低了组播广播业务数据包的丢包率,提升了用户的业务体验。The cycle adjustment unit is used to configure the length of the dynamic cycle DSP according to the synchronization sequence length SYNC sequence length and/or QoS information, and notify the base station under the broadcast multicast single frequency network MBSFN area of the adjusted DSP length. The embodiment of the present invention provides a multicast broadcast service flow control method, by obtaining relevant data during the multicast broadcast service provision process, and controlling the multicast broadcast service flow according to the acquired data, compared with the prior art, the multicast broadcast service flow is reduced. The packet loss rate of broadcast service data packets improves the service experience of users.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例中的技术方案,下面将对实施例描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention, the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments will be briefly introduced below. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention. For those skilled in the art, other drawings can also be obtained based on these drawings without creative effort.
图1是现有技术组播广播业务的网络架构示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a network architecture of a multicast broadcast service in the prior art;
图2是本发明实施例一组播广播业务流量控制方法的流程图;FIG. 2 is a flow chart of a method for controlling traffic of a multicast broadcast service according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明实施例二组播广播业务流量控制方法的流程图;FIG. 3 is a flow chart of a method for controlling traffic of multicast and broadcast services according to
图4是本发明实施例三组播广播业务流量控制方法的流程图;FIG. 4 is a flow chart of a method for controlling traffic of a multicast broadcast service according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention;
图5是本发明应用例一的信令流程图;Fig. 5 is a signaling flow chart of application example 1 of the present invention;
图6是本发明实施例四组播广播业务流量控制方法的流程图;FIG. 6 is a flow chart of a method for controlling flow of multicast and broadcast services according to
图7是本发明应用例二的信令流程图;Fig. 7 is a signaling flow chart of the second application example of the present invention;
图8是本发明实施例五组播广播业务流量控制方法的流程图;FIG. 8 is a flow chart of a method for controlling multicast broadcast service traffic according to Embodiment 5 of the present invention;
图9是本发明应用例三的信令流程图;Fig. 9 is a signaling flow chart of application example 3 of the present invention;
图10本发明实施例六组播广播业务流量控制方法的流程图;FIG. 10 is a flow chart of a six-multicast broadcast service flow control method according to Embodiment 6 of the present invention;
图11是本发明应用例四的信令流程图;Fig. 11 is a signaling flowchart of Application Example 4 of the present invention;
图12是本发明实施例七组播广播业务服务器的结构示意图;FIG. 12 is a schematic structural diagram of a multicast broadcast service server according to Embodiment 7 of the present invention;
图13是本发明实施例八组播广播业务服务器的结构示意图;FIG. 13 is a schematic structural diagram of an eighth multicast broadcast service server according to Embodiment 8 of the present invention;
图14是本发明实施例九组播广播业务服务器的结构示意图;FIG. 14 is a schematic structural diagram of a multicast broadcast service server according to Embodiment 9 of the present invention;
图15是本发明实施例十基站的结构示意图;FIG. 15 is a schematic structural diagram of a base station according to Embodiment 10 of the present invention;
图16是本发明实施例十一多小区多播协调实体的结构示意图;FIG. 16 is a schematic structural diagram of a multi-cell multicast coordination entity according to Embodiment 11 of the present invention;
图17是本发明实施例十二多小区多播协调实体的结构示意图。FIG. 17 is a schematic structural diagram of a multi-cell multicast coordination entity according to Embodiment 12 of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
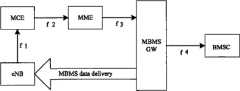
支持演进的通用陆基无线接入网(Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network,E-UTRAN)的组播广播业务的网络架构示意图如图1所示,主要实体和接口功能如下:A schematic diagram of the network architecture supporting the multicast broadcast service of the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN) is shown in Figure 1. The main entities and interface functions are as follows:
组播广播业务服务器(Broadcast Multicast Service Center,BMSC):用于接收来自内容提供商得广播/多播业务数据,通过MBMS网关(Gateway,GW)下发到各个基站(eNB)。首要功能是使用同步(synchronization,SYNC)协议给传输业务的eNB发送/广播MBMS包。使用网际协议(Internet Protocol,IP)组播协议传输MBMS用户面数据。Multicast broadcast service server (Broadcast Multicast Service Center, BMSC): used to receive broadcast/multicast service data from content providers, and send it to each base station (eNB) through the MBMS gateway (Gateway, GW). The primary function is to use a synchronization (SYNC) protocol to send/broadcast MBMS packets to eNBs that transmit services. Use Internet Protocol (Internet Protocol, IP) multicast protocol to transmit MBMS user plane data.
多小区多播协调实体(Multi-cell/multicast Coordination Entity,MCE)是一个逻辑实体,不排除该实体是其他网元的一部分,该实体在广播多播单频网(Multicast/Broadcast single frequency network,MB SFN)传输中给所有参与的eNB分配资源。不仅分配时频资源,还包括确定无线配置的细节,比如调制和编码方案。MCE仅涉及MBMS会话控制信令。不存在MCE和用户设备(User Equipment,UE)交互信令。The multi-cell/multicast coordination entity (Multi-cell/multicast Coordination Entity, MCE) is a logical entity, and it does not exclude that the entity is part of other network elements. All participating eNBs allocate resources during MB SFN) transmission. Not only allocating time-frequency resources, but also determining the details of the radio configuration, such as modulation and coding schemes. MCE only involves MBMS session control signaling. There is no interactive signaling between the MCE and the user equipment (User Equipment, UE).
演进的多媒体广播组播业务(Evolved MultiMedia Broadcast Multicast Service,E-MBMS)提出了广播多播单频网(Multicast/Broadcast single frequency network,MBSFN)的概念,即采用同一个频率在所有小区同时发送相同的数据,这种方式可以极大地提高小区整体信噪比分布,大大节约宝贵的频率资源,提高频谱利用率,并且可通过多点同频发射的办法来解决覆盖盲区问题,获得较好的覆盖率。Evolved Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (E-MBMS) proposes the concept of Multicast/Broadcast single frequency network (MBSFN), which uses the same frequency to transmit the same This method can greatly improve the overall signal-to-noise ratio distribution of the cell, greatly save precious frequency resources, improve spectrum utilization, and solve the problem of coverage blind spots through multi-point co-frequency transmission to obtain better coverage Rate.
实施例一Embodiment one
一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,流程图如图2所示,包括:A flow control method for a multicast broadcast service, the flow chart of which is shown in Figure 2, comprising:
A1,组播广播业务服务器(BMSC)接收多小区多播协调实体MCE发送的业务资源分配信息;A1, the multicast broadcast service server (BMSC) receives the service resource allocation information sent by the multi-cell multicast coordination entity MCE;
A2,根据所述业务资源分配信息对组播广播业务数据流进行流量整形以实现流量控制。A2. Perform traffic shaping on the multicast broadcast service data stream according to the service resource allocation information to implement traffic control.
可以理解,所述BMSC接收多小区多播协调实体发送的业务资源分配信息之前可以包括:MCE根据从BMSC获取的服务质量(Quality of Service,QoS)信息或从基站上获取的资源使用信息进行组播广播业务无线资源的分配。所述从基站上获取的资源使用信息包括:基站上用于单播或者位置业务的资源使用信息。It can be understood that before the BMSC receives the service resource allocation information sent by the multi-cell multicast coordination entity, it may include: MCE performs grouping according to the quality of service (Quality of Service, QoS) information obtained from the BMSC or the resource usage information obtained from the base station. allocation of radio resources for broadcasting and broadcasting services. The resource usage information acquired from the base station includes: resource usage information used for unicast or location services on the base station.
本发明实施例中进行流量整形的粒度可以基于某一业务的,也可以是基于进行业务复用的多个业务(至少两个业务),具体所述业务资源分配信息可以包括:In the embodiment of the present invention, the granularity of traffic shaping can be based on a certain service, and can also be based on multiple services (at least two services) for service multiplexing. Specifically, the service resource allocation information can include:
某一组播广播业务传输的比特率;或者,进行复用的多个组播广播业务传输的总比特率;或者,一个调度周期内某一组播广播业务的传输数据量;或者,一个调度周期内进行复用的多个组播广播业务总的传输数据量。The bit rate of a certain multicast broadcast service transmission; or, the total bit rate of multiple multicast broadcast service transmissions for multiplexing; or, the transmission data volume of a certain multicast broadcast service within a scheduling period; or, a scheduling The total transmission data volume of multiple multicast and broadcast services multiplexed within a period.
本发明实施例中,流量整形一般是指对某一MBMS业务或者进行复用的多个MBMS业务超出一个调度周期内能够调度的数据包进行缓存,并在用后续的调度周期进行调度。即采用延迟调度的方式,使得数据流的传输可以基于资源的使用情况和设备能力进行调配。In the embodiment of the present invention, traffic shaping generally refers to caching the data packets that can be scheduled within one scheduling cycle for a certain MBMS service or multiple multiplexed MBMS services, and scheduling in a subsequent scheduling cycle. That is, the delay scheduling method is adopted, so that the transmission of data streams can be allocated based on resource usage and device capabilities.
本发明实施例还可以基于空口资源占用情况或者QoS参数进行流量整形,参见下述实施例二和三;The embodiment of the present invention can also perform traffic shaping based on air interface resource occupancy or QoS parameters, see the following embodiments two and three;
实施例二,基于空口资源占用情况的流量整形;
一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,流程图如图3所示,包括:A flow control method for a multicast broadcast service, the flow chart of which is shown in Figure 3, comprising:
B1、BMSC根据MBMS业务服务质量QoS信息,生成组播广播业务的数据流输速率门限值;B1, BMSC generates the data stream transmission rate threshold value of the multicast broadcast service according to the MBMS service quality of service QoS information;
可以理解,本发明实施例中,基于业务的优先级不同,MBMS业务可以定义不同的QoS信息,QoS信息可以包括多种参数,如时延、抖动、业务保证速率(Guaranteed Bit Rate,GBR)和最大业务传输速率(Maximal Bit Rate,MBR)等等。It can be understood that, in the embodiment of the present invention, based on different priorities of services, MBMS services can define different QoS information, and the QoS information can include multiple parameters, such as time delay, jitter, service guaranteed rate (Guaranteed Bit Rate, GBR) and Maximum business transmission rate (Maximal Bit Rate, MBR) and so on.
B2、根据所述门限值对所述组播广播业务的数据流进行流量整形。B2. Perform traffic shaping on the data flow of the multicast broadcast service according to the threshold value.
获取QoS信息中的业务保证速率(Guaranteed Bit Rate,GBR)和最大业务传输速率(Maximai Bit Rate,MBR);Get the business guaranteed rate (Guaranteed Bit Rate, GBR) and maximum business transmission rate (Maximai Bit Rate, MBR) in the QoS information;
并根据GMR和MBR生成组播广播业务的数据流输速率门限值;所述门限值大于业务保证速率,小于最大业务传输速率;所述门限值的选择范围一般在业务保证速率和最大业务传输速率之间进行选择;当所述组播广播业务的数据流传输速率超过所述门限值,则把传输速率调整到所述门限值并缓存多余的数据包。And generate the data stream transmission rate threshold value of multicast broadcast service according to GMR and MBR; The threshold value is greater than the service guarantee rate, less than the maximum service transmission rate; The selection range of the threshold value is generally between the service guarantee rate and the maximum service rate. Select between service transmission rates; when the data stream transmission rate of the multicast broadcast service exceeds the threshold value, adjust the transmission rate to the threshold value and buffer redundant data packets.
实施例三、基于QoS参数的流量整形;Embodiment 3, traffic shaping based on QoS parameters;
一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,流程如图4所示,包括:A flow control method for a multicast broadcast service, the process of which is shown in Figure 4, comprising:
C1,BMSC获取复用的多个组播广播业务的业务绑定速率ABBR;C1, the BMSC obtains the service binding rate ABBR of the multiplexed multicast broadcast services;
具体获取复用的多个组播广播业务的业务绑定速率ABBR的过程可以采取多种方式,下面提供两种可行的方式,可以理解以下方式仅仅为本发明举例,不构成对本发明的限制。Specifically, the process of obtaining the service binding rate ABBR of multiple multiplexed multicast broadcast services can be adopted in various ways. Two feasible ways are provided below. It can be understood that the following ways are only examples of the present invention and do not constitute limitations to the present invention.
方式一、获取所述复用的多个组播广播业务的QoS信息内的ABBR;Mode 1, obtaining the ABBR in the QoS information of the multiplexed multicast broadcast services;
方式二、根据所述所述复用的多个组播广播业务中每个业务的QoS信息内的GBR和MBR计算所述ABBR。Mode 2: Calculate the ABBR according to the GBR and MBR in the QoS information of each of the multiple multiplexed multicast broadcast services.
C2,根据所述ABBR对所述复用的多个组播广播业务的数据流进行流量整形。C2. Perform traffic shaping on the data streams of the multiplexed multicast broadcast services according to the ABBR.
本发明实施例中,为了保证服务质量(QoS),可根据不同的组播广播业务的OoS参数,选取对应的业务绑定的传输速率;流量整形的方式参见上述实施例一或二。In the embodiment of the present invention, in order to ensure the quality of service (QoS), the transmission rate of the corresponding service binding can be selected according to the OoS parameters of different multicast broadcast services; refer to the above-mentioned
上述实施例一至三技术方案,BMSC通过依据MCE上报的资源分配信息或者根据获取的空口资源状况信息或者业务的QoS参数对组播广播业务数据流进行流量整形,控制数据流的传输,降低了组播广播业务数据包的丢包率,提升了用户的业务体验。In the technical solutions of Embodiments 1 to 3 above, the BMSC performs traffic shaping on the multicast broadcast service data flow according to the resource allocation information reported by the MCE or according to the obtained air interface resource status information or service QoS parameters to control the transmission of the data flow and reduce the number of groups. The packet loss rate of broadcast service data packets is improved, which improves the user's service experience.
下面结合具体应用场景,提供应用例一对本发明实施例一至三的方法进行描述,信令流程图如图所示5所示,包括:Combining with specific application scenarios, an application example is provided below to describe the methods of Embodiments 1 to 3 of the present invention. The signaling flow chart is shown in Figure 5, including:
步骤d1-d3中,BMSC通过携带业务相关的服务质量参数(QoS)到MCE,其中包括该业务保证比特率(GBR)和/或最大比特率(MBR)等信息。MCE根据获取的业务质量信息为该业务分配无线资源,如计算出该业务在一个调度周期内传的数据量。实现方式是,根据空口资源情况取GBR和MBR之间的一个值作为该业务的传输速率,设为x,调度周期的长度为y,分配的无线资源为z。计算公式为:z=x*y。In steps d1-d3, the BMSC sends service-related quality of service parameters (QoS) to the MCE, including information such as the guaranteed bit rate (GBR) and/or maximum bit rate (MBR) of the service. The MCE allocates wireless resources for the service according to the obtained service quality information, for example, calculates the amount of data transmitted by the service in one scheduling period. The implementation method is to take a value between GBR and MBR as the transmission rate of the service according to the air interface resources, and set it to x, the length of the scheduling cycle to y, and the allocated wireless resources to z. The calculation formula is: z=x*y.
步骤d4中,MCE通过会话请求消息或者其它的M2(MCE和eNB之间)信令告知eNB该业务在空口上的无线资源配置信息,其中包括传输业务的传输信道、业务传输的顺序等。In step d4, the MCE notifies the eNB of the wireless resource configuration information of the service on the air interface through a session request message or other M2 (between the MCE and eNB) signaling, including the transmission channel for transmitting the service, the order of service transmission, etc.
步骤d5、eNB加入IP多播组,主要是为了建立核心网和接入网之间的MBMS用户面的传输通道。In step d5, the eNB joins the IP multicast group mainly to establish the MBMS user plane transmission channel between the core network and the access network.
步骤d6、eNB根据MCE提供的相关信息为该业务进行无线资源的调度,并返回会话开始响应消息或其他的M2信令消息到MCE。步骤五和六没有必然的时间关系。In step d6, the eNB schedules radio resources for the service according to the relevant information provided by the MCE, and returns a session start response message or other M2 signaling messages to the MCE. Steps 5 and 6 do not necessarily have a time relationship.
步骤d7-d9、MCE在会话开始响应消息中携带该业务的资源预留信息到BMSC,该预留信息可以是一个调度周期中分配给该业务的资源信息(如传输的数据量/传输的比特速率),也可以为一个调度周期中分配给该业务所在的传输信道(MCH)的资源信息(如传输信道传输的数据量/传输的比特速率),或者进行业务复用的多个组播广播业务绑定的资源。其中的业务或传输信道或业务绑定的传输数据量一般指的是一个动态调度周期传输的数据包的数量,当使用该参数的时候,MCE还需要告诉BMSC动态调度周期的长度。如果预留资源信息用业务绑定的资源表示,MCE还需要告诉BMSC该业务绑定的传输信道上的业务映射信息,即传输信道上有哪些MBMS业务。另外,本应用例中,步骤d7,可以直接在步骤d3以后就发送,无需等到收到步骤d6的响应消息。Steps d7-d9, MCE carries the resource reservation information of this service to BMSC in the session start response message, and this reservation information can be the resource information (such as the amount of transmitted data/transmitted bits) allocated to this service in a scheduling period Rate), it can also be the resource information allocated to the transport channel (MCH) where the service is located in a scheduling period (such as the amount of data transmitted by the transport channel/transmitted bit rate), or multiple multicast broadcasts for service multiplexing Business-bound resources. The business or transmission channel or the amount of data to be bound for service generally refers to the number of data packets transmitted in a dynamic scheduling period. When using this parameter, the MCE also needs to tell the BMSC the length of the dynamic scheduling period. If the reserved resource information is represented by service-bound resources, the MCE also needs to tell the BMSC the service mapping information on the transport channel bound to the service, that is, which MBMS services are on the transport channel. In addition, in this application example, step d7 can be sent directly after step d3 without waiting for the response message of step d6 to be received.
步骤d10、BMSC根据MCE提供的资源分配信息进行MBMS业务传输的流量整形,该流量整形根据步骤d9的指示可以是基于某个播组广播业务的,也可以是基于进行业务复用的多个组播广播业务的。流量整形的方式是,BMSC根据MCE提供的资源预留信息缓存在一个调度周期无法调度的数据包,在后续的调度周期对缓存的数据包进行调度。Step d10, BMSC performs traffic shaping for MBMS service transmission according to the resource allocation information provided by MCE. According to the instruction of step d9, the traffic shaping can be based on a certain broadcast group broadcast service, or based on multiple groups for business multiplexing broadcast broadcasting business. The way of traffic shaping is that the BMSC caches the data packets that cannot be scheduled in one scheduling period according to the resource reservation information provided by the MCE, and schedules the cached data packets in the subsequent scheduling period.
本应用例MCE还可以通过各个eNB上报的资源使用情况进行资源预留,实现方式是,eNB可以通过步骤d6的会话响应消息或其他的M2信令消息告知MCE该eNB上的资源使用情况,其中包含eNB上用于单播或者其他用途(如位置业务LCS、Relay)等的资源情况。步骤d7-d9、MCE通过该信息决定如何进行无线侧的资源分配,并且通知给BMSC。步骤d10、BMSC根据上述信息进行流量整形。In this application example, the MCE can also reserve resources through the resource usage reported by each eNB. The implementation method is that the eNB can notify the MCE of the resource usage on the eNB through the session response message in step d6 or other M2 signaling messages. Including resources used for unicast or other purposes (such as location service LCS, Relay) on the eNB. In steps d7-d9, the MCE decides how to allocate resources on the wireless side based on the information, and notifies the BMSC. Step d10, the BMSC performs traffic shaping according to the above information.
实施例四、Embodiment four,
一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,流程图如图6所示,包括:A flow control method for a multicast broadcast service, the flow chart of which is shown in Figure 6, comprising:
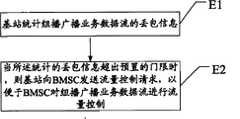
E1,基站统计组播广播业务数据流的丢包信息;E1, the base station counts the packet loss information of the multicast broadcast service data flow;
E2,当所述统计的丢包信息超出预置的门限时,则基站向BMSC发送流量控制请求,以便于BMSC对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制。E2. When the statistical packet loss information exceeds the preset threshold, the base station sends a flow control request to the BMSC, so that the BMSC performs flow control on the multicast broadcast service data flow.
本发明实施例中,所述丢包信息可以采用多方式来表示当前的丢包状况,如:丢失的数据包的数量,或者基于连续丢包的时间间隔或者统计的丢包率等。In the embodiment of the present invention, the packet loss information may use multiple methods to represent the current packet loss situation, such as: the number of lost data packets, or based on the time interval of continuous packet loss or the statistical packet loss rate.
具体的丢包信息的统计对象可以有多种:例如:统计某个组播广播业务的数据流丢包信息;所述BMSC对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制为:对所述组播广播业务的数据流进行控制。或者,统计复用的多个组播广播业务的数据流总的丢包信息;所述BMSC对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制为:对所述复用的多个组播广播业务的数据流进行控制。There can be multiple statistical objects of specific packet loss information: for example: counting the data flow packet loss information of a certain multicast broadcast service; the BMSC performs flow control on the multicast broadcast service data flow as: The data flow of the business is controlled. Or, counting the total packet loss information of the multiplexed multicast broadcast service data streams; the BMSC performs flow control on the multicast broadcast service data stream as: the data of the multiplexed multiple multicast broadcast service flow control.
本发明实施例四、通过在组播广播业务提供过程中统计业务数据流的丢包信息,并根据丢包信息对组播广播业务数据流进行控制,相对于现有技术,降低了组播广播业务数据包的丢包率,提升了用户的业务体验。
下面结合具体应用场景,提供应用例二本发明实施例四的方法进行描述,信令流程图如图所示7所示,本例中,MCE通过会话管理消息(如会话开始请求)为各个eNB配置反馈报告的门限值,或者O&M预先在各个eNB上配置报告反馈的门限值,该门限值可以基于丢失的数据包的数量,或者基于连续丢包的时间间隔,具体流程包括:In the following, combined with specific application scenarios, an application example 2 is provided to describe the method of
步骤f1、当数据包丢失的情况超过设置的门限值的时候,eNB会向MCE发送流量控制请求,该请求可以是基于某业务的(Session ID或Service ID),也可以是基于某个传输信道的,如果是基于传输信道的,eNB需要告知MCE该传输信道所包含的MBMS业务信息,如哪些业务映射在该传输信道上。Step f1, when the data packet loss exceeds the set threshold, the eNB will send a flow control request to the MCE, which can be based on a certain business (Session ID or Service ID), or based on a certain transmission If it is based on the transport channel, the eNB needs to inform the MCE of the MBMS service information contained in the transport channel, such as which services are mapped on the transport channel.
步骤f2-f4、MCE可以直接转发流量控制请求消息到MBMS网关(Gateway,GW);也可以根据eNB上报的流量控制请求决定是否需要进行流量控制,如果是,则转发流量控制请求到MBMS GW。MBMS GW转发流量控制请求消息到BMSC。BMSC根据eNB发送的流量控制请求携带的信息(如丢包率等)进行流量控制,如降低业务或业务绑定的传输速率。In steps f2-f4, the MCE can directly forward the flow control request message to the MBMS gateway (Gateway, GW); it can also decide whether to perform flow control according to the flow control request reported by the eNB, and if so, forward the flow control request to the MBMS GW. MBMS GW forwards the flow control request message to BMSC. The BMSC performs flow control according to the information carried in the flow control request sent by the eNB (such as packet loss rate, etc.), such as reducing the transmission rate of services or service bindings.
另外,eNB也可以直接通过MBMS GW向BMSC发送流量控制请求,不需要通过MCE和MME进行转发。In addition, the eNB can also directly send a flow control request to the BMSC through the MBMS GW without forwarding it through the MCE and MME.
实施例五、一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,流程图如图8所示,包括:Embodiment 5. A flow control method for multicast and broadcast services, the flowchart of which is shown in FIG. 8 , including:
G1,MCE接收BMSC的会话开始请求消息;G1, the MCE receives the session start request message from the BMSC;
G2,MCE根据剩余的MBMS无线资源判断是否可以支持新增的MBMS业务,若不支持,则继续步骤G3;若支持,则继续步骤G4;G2, the MCE judges whether it can support the newly added MBMS service according to the remaining MBMS radio resources, if not supported, proceed to step G3; if supported, proceed to step G4;
G3,MCE拒绝为新增的MBMS业务分配无线资源,或者用新增的MBMS业务替代已有的MBMS业务的无线资源。具体用新增的MBMS业务替代已有的MBMS业务的无线资源可以采取多种实现方式:本实施例中可以根据所述会话开始请求中携带的新增MBMS业务的优先级等信息,将低于所述优先级的MBMS业务占用的无线资源重新分配给所述新增的MBMS业务。当然,在进行业务替换时,也可以随机选择已有的业务进行替换,只是按照优先级替换更加合理,贴近用户需求,具体的替换方方式不构成对本发明的限制。G3. The MCE refuses to allocate radio resources for the newly added MBMS service, or replaces the radio resources of the existing MBMS service with the newly added MBMS service. Specifically, a new MBMS service can be used to replace the radio resources of the existing MBMS service in various ways: in this embodiment, according to the information such as the priority of the new MBMS service carried in the session start request, it will be lower than The radio resource occupied by the priority MBMS service is reallocated to the newly added MBMS service. Of course, when performing service replacement, existing services can also be randomly selected for replacement, but replacement according to priority is more reasonable and close to user needs, and the specific replacement method does not constitute a limitation to the present invention.
本实施例中,将低于所述优先级的MBMS业务占用的无线资源重新分配给所述新增的MBMS业务可以采取以下方式:In this embodiment, the following methods may be adopted for reallocating the radio resources occupied by MBMS services lower than the priority to the newly added MBMS services:
MCE通过M2信令消息通知eNB,使得eNB退出被替换的MBMS业务的多播组,加入所述新增的MBMS业务的多播组;并通过响应消息通知BMSC。The MCE notifies the eNB through the M2 signaling message, so that the eNB exits the multicast group of the replaced MBMS service and joins the multicast group of the newly added MBMS service; and notifies the BMSC through a response message.
G4,MCE向广播多播单频网MBSFN区域下的基站转发会话开始请求消息。G4. The MCE forwards the session start request message to the base station in the MBSFN area of the broadcast multicast single frequency network.
在本发明实施例中,,若MCE拒绝为新增的MBMS业务分配无线资源,则MCE不向广播多播单频网MBSFN区域下的基站转发会话开始请求消息。In the embodiment of the present invention, if the MCE refuses to allocate radio resources for the newly added MBMS service, the MCE does not forward the session start request message to the base station under the MBSFN area of the broadcast multicast single frequency network.
本发明实施例五,通过MCE作为准入控制的接口,基于无线资源的分配情况,决定是否拒绝新的业务资源申请,降低了系统的负载,进而降低了组播广播业务数据包的丢包率,提升了用户的业务体验。Embodiment 5 of the present invention uses the MCE as an interface for admission control to determine whether to reject a new service resource application based on the allocation of wireless resources, thereby reducing the load on the system and further reducing the packet loss rate of multicast broadcast service data packets , which improves the user experience.
下面结合具体应用场景,提供应用例三对本发明实施例五的方法进行描述,信令流程图如图所示9所示,包括:Combining with specific application scenarios, Application Example 3 is provided below to describe the method of Embodiment 5 of the present invention. The signaling flow chart is shown in Figure 9, including:
步骤h1-h3中,BMSC通过携带业务相关的服务质量参数(QoS)到MCE,其中包括该业务保证速率(GBR)和/或最大速率(MBR)等信息。In steps h1-h3, the BMSC sends service-related quality of service parameters (QoS) to the MCE, including the service guaranteed rate (GBR) and/or maximum rate (MBR) and other information.
步骤h4、由于MCE负责为MBSFN区域下的所有eNB分配用于MBMS传输的无线资源,因而MCE知道该MBSFN区域还剩余多少可用的MBMS无线资源;并且根据从BMSC接收到的服务质量(QoS)信息,MCE可以估算出新增的MBMS业务所需的无线资源。Step h4: Since the MCE is responsible for allocating radio resources for MBMS transmission to all eNBs under the MBSFN area, the MCE knows how many available MBMS radio resources are left in the MBSFN area; and according to the quality of service (QoS) information received from the BMSC , the MCE can estimate the radio resources required by the newly added MBMS service.
步骤h5-h7、如果剩余的MBMS无线资源无法支持新增的MBMS业务,MCE不会向该MBSFN区域下的eNB转发会话开始请求消息,而是直接拒绝为新增的MBMS业务分配无线资源,并且向BMSC返回会话拒绝响应;或者MCE会根据MBMS业务中携带的业务优先级等信息,决定是否替代优先级比较低的MBMS业务的无线资源,如需要替换,MCE通过M2信令消息通知eNB,使得eNB退出被替换的MBMS业务的多播组,并通过响应消息通知BMSC。Steps h5-h7, if the remaining MBMS radio resources cannot support the newly added MBMS service, the MCE will not forward the session start request message to the eNB under the MBSFN area, but directly refuses to allocate radio resources for the newly added MBMS service, and Return a session rejection response to the BMSC; or the MCE will decide whether to replace the radio resources of the MBMS service with a lower priority according to the information such as the service priority carried in the MBMS service. If replacement is required, the MCE will notify the eNB through the M2 signaling message, so that The eNB withdraws from the multicast group of the replaced MBMS service, and notifies the BMSC through a response message.
实施例六、Embodiment six,
一种组播广播业务流量控制方法,流程图如图10所示,包括:A flow control method for a multicast broadcast service, the flow chart of which is shown in Figure 10, comprising:
K1,MCE接收BMSC发送的QoS信息;K1, MCE receives the QoS information sent by BMSC;
K2,根据同步序列长度(SYNC sequence length)和/或QoS信息,配置动态周期DSP的长度,并将调整后的DSP长度通知给广播多播单频网MBSFN区域下的基站。K2, configure the length of the dynamic period DSP according to the synchronization sequence length (SYNC sequence length) and/or QoS information, and notify the base station under the MBSFN area of the broadcast multicast single frequency network of the adjusted DSP length.
本实施例中,同步序列(synchronization sequence,SYNC sequence)用于标识在一段时间内的多个数据包的传输,在同一个SYNC sequence下的所有数据包使用相同的时间戳(Timestamp)作为指示。对于不同的MBMS业务根据传输的数据率可能采用不同的SYNC sequence取值,SYNC sequence的取值可以由网管中心(O&M)进行配置,也可以由BMSC进行配置。In this embodiment, a synchronization sequence (synchronization sequence, SYNC sequence) is used to identify the transmission of multiple data packets within a period of time, and all data packets under the same SYNC sequence use the same timestamp (Timestamp) as an indication. For different MBMS services, different SYNC sequence values may be adopted according to the data rate of transmission. The value of SYNC sequence can be configured by the network management center (O&M) or by the BMSC.
本实施例根据同步序列长度(SYNC sequence length)和/或QoS信息对DSP进行动态调整,在原有的业务动态调度周期不能满足调度需求而导致丢包时,则增加DSP,有效的降低了数据传输的丢包率,提高了数据传输的质量,提升了用户的业务体验。This embodiment dynamically adjusts the DSP according to the synchronization sequence length (SYNC sequence length) and/or QoS information. When the original dynamic scheduling period of the business cannot meet the scheduling requirements and causes packet loss, the DSP is added, which effectively reduces the data transmission. The packet loss rate is high, which improves the quality of data transmission and improves the user's service experience.
下面结合具体应用场景,提供应用例四对本发明实施例六的方法进行描述,信令流程图如图所示11所示,包括:Combining with specific application scenarios, Application Example 4 is provided below to describe the method of Embodiment 6 of the present invention. The signaling flow chart is shown in Figure 11, including:
步骤S1-S3中,BMSC通过携带SYNC sequence length和业务相关的服务质量参数(QoS)到MCE,其中SYNC sequence length也可以是直接通过网管系统(O&M)配置在MCE上;QoS包括该业务保证比特率(GBR)和/或最大比特率(MBR)等信息。MCE根据SYNC sequence length和QoS信息配置动态周期(DSP)的长度,为了使得同一个SYNC sequence的业务能够在一个DSP传输完毕,DSP的配置一般为SYNC sequence length的整数倍;MCE在配置DSP的时候还要考虑对应的传输信道(MCH)具体传输的业务数据量的总和,保证在一个DSP中能够使得该传输信道中的所有的业务数据包得到调度。In steps S1-S3, BMSC sends SYNC sequence length and business-related quality of service parameters (QoS) to MCE, wherein SYNC sequence length can also be directly configured on MCE through network management system (O&M); QoS includes the service guarantee bit information such as bit rate (GBR) and/or maximum bit rate (MBR). MCE configures the length of the dynamic period (DSP) according to SYNC sequence length and QoS information. In order to enable the same SYNC sequence business to be transmitted in one DSP, the configuration of DSP is generally an integer multiple of SYNC sequence length; when MCE configures DSP The total amount of service data specifically transmitted by the corresponding transport channel (MCH) should also be considered, so as to ensure that all service data packets in the transport channel can be scheduled in one DSP.
步骤S4中,MCE通过会话请求消息或其他的M2信令消息告知eNB该业务在空口上的无线资源配置信息,其中包括DSP的配置信息、传输业务的传输信道、业务传输的顺序等。eNB根据接收到的相关信息对该传输信道里的业务进行调度。后续步骤和现有技术相同。In step S4, the MCE informs the eNB of the wireless resource configuration information of the service on the air interface through a session request message or other M2 signaling messages, including DSP configuration information, service transmission channel, service transmission sequence, etc. The eNB schedules the services in the transmission channel according to the received related information. Subsequent steps are the same as in the prior art.
下面提供本发明实施例中实现上述方法的设备的基本逻辑结构示意图。为了便于说明,仅示出了与本发明实施例相关的部分,以下设备包含的功能模块/单元可以是硬件模块/单元、软件模块/单元或软硬件相结合的模块/单元。The following provides a schematic diagram of a basic logical structure of a device implementing the above method in an embodiment of the present invention. For ease of description, only parts related to the embodiments of the present invention are shown, and the functional modules/units contained in the following devices may be hardware modules/units, software modules/units, or modules/units combining software and hardware.
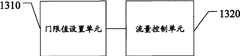
实施例七、一种组播广播业务服务器,结构示意图如图12所示,包括:Embodiment 7. A multicast broadcast service server, as shown in FIG. 12 , includes:
信息接收单元1210,用于接收多小区多播协调实体MCE发送的业务资源分配信息;The
流量控制单元1220,用于根据所述信息接收单元1210接收的业务资源分配信息对组播广播业务流进行流量整形以实现流量控制。The
本实施例中,所述流量控制单元1220进行流量整形的粒度可以基于某一业务的,也可以是基于进行业务复用的多个业务(至少两个业务),具体的所述信息接收单元1210业务资源分配信息可以包括:某一组播广播业务传输的比特率;或者,进行复用的多个组播广播业务传输的总比特率;或者,一个调度周期内某一组播广播业务的传输数据量;或者,一个调度周期内进行复用的多个组播广播业务总的传输数据量。In this embodiment, the granularity of traffic shaping performed by the
本发明实施例中,流量整形一般是指对某一MBMS业务或者进行复用的多个MBMS业务超出一个调度周期内能够调度的数据包进行缓存,并在用后续的调度周期进行调度。即采用延迟调度的方式,使得数据流的传输可以基于资源的使用情况和设备能力进行调配。In the embodiment of the present invention, traffic shaping generally refers to caching the data packets that can be scheduled within one scheduling cycle for a certain MBMS service or multiple multiplexed MBMS services, and scheduling in a subsequent scheduling cycle. That is, the delay scheduling method is adopted, so that the transmission of data streams can be allocated based on resource usage and device capabilities.
本发明实施例七组播广播业务服务器可以但不限于运行实施例一所述的方法。Embodiment 7 of the present invention The multicast broadcast service server may, but is not limited to, run the method described in Embodiment 1.
可以理解,进行流量整形还可以依据其他数据进行,参考实施例八和九和十。It can be understood that traffic shaping can also be performed based on other data, refer to Embodiments 8, 9 and 10.
实施例八、一种组播广播业务服务器,结构示意图如图13所示,包括:Embodiment 8. A multicast broadcast service server, as shown in FIG. 13 , includes:
门限值设置单元1310,根据MBMS业务服务质量QoS信息,生成组播广播业务的数据流输速率门限值;Threshold
本发明实施例中,基于业务的优先级不同,MBMS业务可以定义不同的QoS信息,QoS信息可以包括多种参数,如时延、抖动、业务保证速率(Guaranteed Bit Rate,GBR)和最大业务传输速率(Maximal Bit Rate,MBR)等等。In the embodiment of the present invention, different QoS information can be defined for MBMS services based on different priorities of services, and the QoS information can include various parameters, such as time delay, jitter, service guaranteed rate (Guaranteed Bit Rate, GBR) and maximum service transmission Rate (Maximal Bit Rate, MBR) and so on.
流量控制单元1320,用于根据所述门限值对所述组播广播业务的数据流传输进行流量整形。The
本实施例中所述流量控制单元1320进行流量整形的过程可以采取以下方式:获取QoS信息中的业务保证速率(Guaranteed Bit Rate,GBR)和最大业务传输速率(Maximal Bit Rate,MBR);并根据GMR和MBR生成组播广播业务的数据流输速率门限值;所述门限值大于业务保证速率,小于最大业务传输速率;所述门限值的选择范围一般在业务保证速率和最大业务传输速率之间进行选择;当所述组播广播业务的数据流传输速率超过所述门限值,则把传输速率调整到所述门限值并缓存多余的数据包。The
本实施例提供的组播广播业务服务器可以但不限于运行实施例二所述的方法。The multicast broadcast service server provided in this embodiment can, but is not limited to, run the method described in
实施例九、一种组播广播业务服务器,结构示意图如图14所示,包括:Embodiment 9. A multicast and broadcast service server, the structural diagram of which is shown in FIG. 14 , including:
速率选择单元1410,用于获取复用的多个组播广播业务的业务绑定速率ABBR;The
本实施例中,速率选择单元1410具体获取复用的多个组播广播业务的业务绑定速率ABBR的过程可以采取多种方式,下面提供两种可行的方式,可以理解以下方式仅仅为本发明举例,不构成对本发明的限制。In this embodiment, the process of the
方式一、获取所述复用的多个组播广播业务的QoS信息内的ABBR;Mode 1, obtaining the ABBR in the QoS information of the multiplexed multicast broadcast services;
方式二、根据所述所述复用的多个组播广播业务中每个业务的QoS信息内的GBR和MBR计算所述ABBR。Mode 2: Calculate the ABBR according to the GBR and MBR in the QoS information of each of the multiple multiplexed multicast broadcast services.
流量控制单元1420,用于根据所述ABBR对所述数据传输通道的传输的数据流进行流量整形。流量整形的过程参见实施例七的描述。The
本实施例提供的组播广播业务服务器可以但不限于运行实施例三所述的方法。The multicast broadcast service server provided in this embodiment can, but is not limited to, run the method described in the third embodiment.
为了实现组播广播业务的流量控制,本发明实施例十提供一种基站,结构示意图如图15所示,包括:In order to realize flow control of multicast and broadcast services, Embodiment 10 of the present invention provides a base station, the structural diagram of which is shown in FIG. 15 , including:
统计单元1510,用于统计组播广播业务数据流的丢包信息;Statistical unit 1510, configured to count the packet loss information of the multicast broadcast service data flow;
流量控制请求单元1520,用于当所述统计的丢包信息超出预置的门限时,向BMSC发送流量控制请求,以便于BMSC对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制。The flow control request unit 1520 is configured to send a flow control request to the BMSC when the statistical packet loss information exceeds a preset threshold, so that the BMSC can perform flow control on the multicast broadcast service data flow.
本发明实施例中,所述丢包信息可以采用多方式来表示当前的丢包状况,如:丢失的数据包的数量,或者基于连续丢包的时间间隔或者统计的丢包率等。In the embodiment of the present invention, the packet loss information may use multiple methods to represent the current packet loss situation, such as: the number of lost data packets, or based on the time interval of continuous packet loss or the statistical packet loss rate.
所述统计单元1510具体的丢包信息的统计对象可以有多种:例如:统计某个组播广播业务的数据流丢包信息;所述BMSC收到所述流量控制请求后,对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制为:对所述组播广播业务的数据流进行控制。或者,统计复用的多个组播广播业务的数据流总的丢包信息;所述BMSC对组播广播业务数据流进行流量控制为:对所述复用的多个组播广播业务的数据流进行控制。The statistical object of the specific packet loss information of the statistical unit 1510 can be various: for example: counting the data flow packet loss information of a certain multicast broadcast service; after the BMSC receives the flow control request, the multicast broadcast The flow control of the service data flow is: controlling the data flow of the multicast broadcast service. Or, counting the total packet loss information of the multiplexed multicast broadcast service data streams; the BMSC performs flow control on the multicast broadcast service data stream as: the data of the multiplexed multiple multicast broadcast service flow control.
进行流量控制的还可以在多小区多播协调实体上实现,本发明实施例十五和十六提供一种多小区多播协调实体。Flow control can also be implemented on the multi-cell multicast coordinating entity. Embodiments 15 and 16 of the present invention provide a multi-cell multicast coordinating entity.
本实施例提供的基站可以运行实施例四所述的方法。The base station provided in this embodiment can run the method described in
实施例十一、一种多小区多播协调实体,结构示意图如图16所示,包括:Embodiment 11. A multi-cell multicast coordination entity, as shown in FIG. 16 , including:
接收单元1610,用于接收BMSC的会话开始请求消息;The receiving
资源分配控制单元1620,用于根据剩余的MBMS无线资源判断是否可以支持新增的MBMS业务,若不可以支持,则拒绝为新增的MBMS业务分配无线资源,或者用新增的MBMS业务替代已有的MBMS业务的无线资源。The resource
本实施例中资源分配控制单元1620可以根据所述会话开始请求中携带的新增MBMS业务的优先级等信息,将低于所述优先级的MBMS业务占用的无线资源重新分配给所述新增的MBMS业务。当然,在进行业务替换时,也可以随机选择已有的业务进行替换,只是按照优先级替换更加合理,贴近用户需求,具体的替换方方式不构成对本发明的限制。In this embodiment, the resource
将低于所述优先级的MBMS业务占用的无线资源重新分配给所述新增的MBMS业务可以采取以下方式:The following methods may be adopted for reallocating the radio resources occupied by MBMS services lower than the priority to the newly added MBMS services:
MCE通过M2信令消息通知eNB,使得eNB退出被替换的MBMS业务的多播组,加入所述新增的MBMS业务的多播组;并通过响应消息通知BMSC。The MCE notifies the eNB through the M2 signaling message, so that the eNB exits the multicast group of the replaced MBMS service and joins the multicast group of the newly added MBMS service; and notifies the BMSC through a response message.
本实施例提供的多小区多播协调实体可以但不限于运行实施例五所述的方法。The multi-cell multicast coordination entity provided in this embodiment may, but is not limited to, execute the method described in Embodiment 5.
实施例十二、一种多小区多播协调实体,结构示意图如图17所示,包括:Embodiment 12, a multi-cell multicast coordination entity, a schematic structural diagram as shown in FIG. 17 , including:
接收单元1710,接收BMSC发送的QoS信息;The receiving
周期调整单元1720,用于根据同步序列长度SYNC sequence length和/或QoS信息,配置动态周期DSP的长度,并将调整后的DSP长度通知给广播多播单频网MBSFN区域下的基站。The
本实施例中,同步序列(synchronization sequence,SYNC sequence)用于标识在一段时间内的多个数据包的传输,在同一个SYNC sequence下的所有数据包使用相同的时间戳(Timestamp)作为指示。对于不同的MBMS业务根据传输的数据率可能采用不同的SYNC sequence取值,SYNC sequence的取值可以由网管中心(O&M)进行配置,也可以由BMSC进行配置。In this embodiment, a synchronization sequence (synchronization sequence, SYNC sequence) is used to identify the transmission of multiple data packets within a period of time, and all data packets under the same SYNC sequence use the same timestamp (Timestamp) as an indication. For different MBMS services, different SYNC sequence values may be adopted according to the data rate of transmission. The value of SYNC sequence can be configured by the network management center (O&M) or by the BMSC.
本实施例提供的多小区多播协调实体可以但不限于运行实施例六所述的方法。The multi-cell multicast coordination entity provided in this embodiment may, but is not limited to, execute the method described in Embodiment 6.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解上述实施例的各种方法或者装置中的全部或部分步骤是可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件来完成,该程序可以存储于一计算机可读存储介质中,存储介质可以包括:ROM、RAM、磁盘或光盘等。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps in the various methods or devices of the above embodiments can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program, and the program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium, and the storage medium can be Including: ROM, RAM, disk or CD, etc.
本发明实施例上述各种设备可以运行的方法参照上述方法实施例的描述,此处不再赘述。For the methods that the above various devices can operate in the embodiments of the present invention, refer to the description of the above method embodiments, and details are not repeated here.
以上对本发明实施例所提供的组播广播业务流量控制方法及相关设备进行了详细介绍,其中:The method for controlling the flow of the multicast broadcast service provided by the embodiment of the present invention and related equipment have been introduced in detail above, wherein:
本发明实施例中提供的组播广播业务流量控制方法,通过在组播广播业务提供过程中获取相关数据,并根据获取的数据对组播广播业务数据流进行控制,相对于现有技术,降低了组播广播业务数据包的丢包率,提升了用户的业务体验。The multicast broadcast service flow control method provided in the embodiment of the present invention obtains relevant data during the multicast broadcast service provision process, and controls the multicast broadcast service data flow according to the acquired data, compared with the prior art, it reduces The packet loss rate of multicast and broadcast service data packets is reduced, and the service experience of users is improved.
本文中应用了具体个例对本发明的原理及实施方式进行了阐述,以上实施例的说明只是用于帮助理解本发明的方法及其核心思想;同时,对于本领域的一般技术人员,依据本发明的思想,在具体实施方式及应用范围上均会有改变之处,综上所述,本说明书内容不应理解为对本发明的限制。In this paper, specific examples have been used to illustrate the principle and implementation of the present invention. The description of the above embodiments is only used to help understand the method of the present invention and its core idea; meanwhile, for those of ordinary skill in the art, according to the present invention Thoughts, there will be changes in the specific implementation and application scope. In summary, the contents of this specification should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
Claims (23)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910179903XACN102036177A (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2009-09-29 | Multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipment |
| CN201410333781.6ACN104093130B (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2009-09-29 | Multicast broadcast service flow control methods and relevant device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910179903XACN102036177A (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2009-09-29 | Multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipment |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201410333781.6ADivisionCN104093130B (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2009-09-29 | Multicast broadcast service flow control methods and relevant device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102036177Atrue CN102036177A (en) | 2011-04-27 |
Family
ID=43888363
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910179903XAPendingCN102036177A (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2009-09-29 | Multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102036177A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102355708A (en)* | 2011-11-08 | 2012-02-15 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Method and equipment for processing priority level of multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) |
| CN102790948A (en)* | 2011-05-17 | 2012-11-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and system for indicating interruption of multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) and user equipment (UE) |
| CN102857440A (en)* | 2012-08-17 | 2013-01-02 | 杭州华三通信技术有限公司 | Data processing method and switchboard |
| CN103856970A (en)* | 2012-11-29 | 2014-06-11 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Method and system for counting multicast broadcast service demands |
| WO2018090573A1 (en)* | 2016-11-18 | 2018-05-24 | 深圳市中兴微电子技术有限公司 | Buffer space management method and device, electronic apparatus, and storage medium |
| CN113766514A (en)* | 2020-06-02 | 2021-12-07 | 中国移动通信集团河南有限公司 | Network resource distribution method, device, electronic device, and storage medium |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008153474A1 (en)* | 2007-06-14 | 2008-12-18 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Method of maintaining broadcast service continuity |
| CN101370157A (en)* | 2007-08-15 | 2009-02-18 | 上海贝尔阿尔卡特股份有限公司 | E-MBMS system and method for statistic multiplexing by using AMBR |
| CN102301811A (en)* | 2009-04-28 | 2011-12-28 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | Method, Mce And Base Station For Dynamically Dispatching Wireless Resources For Mbsfn Transmission |
- 2009
- 2009-09-29CNCN200910179903XApatent/CN102036177A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008153474A1 (en)* | 2007-06-14 | 2008-12-18 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Method of maintaining broadcast service continuity |
| CN101370157A (en)* | 2007-08-15 | 2009-02-18 | 上海贝尔阿尔卡特股份有限公司 | E-MBMS system and method for statistic multiplexing by using AMBR |
| CN102301811A (en)* | 2009-04-28 | 2011-12-28 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | Method, Mce And Base Station For Dynamically Dispatching Wireless Resources For Mbsfn Transmission |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| HUAWEI: "《3GPP TSG-RAN WG2 Meeting #67 R2-095354》", 28 August 2009* |
| LG ELECTRONICS INC.: "《3GPP TSG-RAN WG2 #67 R2-094650》", 29 August 2009* |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102790948A (en)* | 2011-05-17 | 2012-11-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and system for indicating interruption of multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) and user equipment (UE) |
| WO2012155408A1 (en)* | 2011-05-17 | 2012-11-22 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method, device and user equipment for indicating service interruption of multimedia broadcast multicast service |
| US9055469B2 (en) | 2011-05-17 | 2015-06-09 | Zte Corporation | Method and device for indicating MBMS service suspension, and user equipment |
| CN102790948B (en)* | 2011-05-17 | 2017-04-05 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A kind of method, device and user equipment for indicating that MBMS is interrupted |
| CN102355708A (en)* | 2011-11-08 | 2012-02-15 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Method and equipment for processing priority level of multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) |
| CN102355708B (en)* | 2011-11-08 | 2015-03-11 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Method and equipment for processing priority level of multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) |
| CN102857440A (en)* | 2012-08-17 | 2013-01-02 | 杭州华三通信技术有限公司 | Data processing method and switchboard |
| CN103856970A (en)* | 2012-11-29 | 2014-06-11 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Method and system for counting multicast broadcast service demands |
| CN103856970B (en)* | 2012-11-29 | 2017-09-12 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | The statistical method and system of multicast broadcast service demand |
| WO2018090573A1 (en)* | 2016-11-18 | 2018-05-24 | 深圳市中兴微电子技术有限公司 | Buffer space management method and device, electronic apparatus, and storage medium |
| CN113766514A (en)* | 2020-06-02 | 2021-12-07 | 中国移动通信集团河南有限公司 | Network resource distribution method, device, electronic device, and storage medium |
| CN113766514B (en)* | 2020-06-02 | 2023-08-01 | 中国移动通信集团河南有限公司 | Network resource offloading method, device, electronic equipment, and storage medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4109671B2 (en) | MBMS data transmission scheduling method in wireless mobile communication system | |
| CN102301811B (en) | Method for dynamically scheduling radio resources used for MBSFN transmission, MCE and base station | |
| US8879457B2 (en) | Method and system for allocating resources to multimedia broadcast multicast control channel | |
| KR101150459B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for handling MBMS dynamic scheduling information | |
| US8705475B2 (en) | Scheduling apparatus considering quality of service (QOS) | |
| CN105635985B (en) | Method and device for determining suspended service and method and device for processing indication information | |
| US8855037B2 (en) | Scheduling processing method for multimedia broadcast and multicast service and lower-layer network element | |
| CN101931881A (en) | Method, device and system for synchronizing business content | |
| CN102036177A (en) | Multicast broadcast service flow control method and related equipment | |
| CN102137336A (en) | Method and device of service transmission | |
| CN101820687B (en) | Self-adaptive allocation system and method for broadcasting multicast radio resources | |
| US9094938B2 (en) | Method and system for transmitting dynamic scheduling information | |
| US20120163274A1 (en) | System and method for receiving mbms broadcasting service | |
| CN100583869C (en) | Dispatching method for service transmission priority in multiple service communication system | |
| JP5349682B2 (en) | Method of multiplexing MBMS service in MBSFN, BM-SC, and base station | |
| CN102045643A (en) | Resource adjustment method and multi-cell/multicast coordination entity | |
| CN104093130B (en) | Multicast broadcast service flow control methods and relevant device | |
| CN104080173A (en) | System for processing MBMS service by base station MAC layer in LTE system | |
| CN101370163B (en) | Method for implementing multimedia broadcast multicast service | |
| EP2466948A1 (en) | Method for trimming traffic in e-mbms system and bm-sc for implementing method | |
| CN101998265A (en) | Data transmission method, base station, multicast coordination entity and user equipment | |
| Ghandri et al. | Dynamic MBSFN subframe allocation algorithm for bursty video traffic in LTE-Advanced network | |
| CN1988717A (en) | Transmitting method for enhanced multimedia broadcast and multicast service | |
| Lai | An Efficient Resource Allocation Approach for Multicast Cellular-Based Services Based on Dynamic eMBMS Configuration | |
| CN102045642B (en) | The shaping preprocess method of Business Stream of multimedia broadcast-multicast service and device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20110427 |