CN101838740A - Method for removing soluble heavy metal ions in situ - Google Patents
Method for removing soluble heavy metal ions in situDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101838740A CN101838740ACN201010147868ACN201010147868ACN101838740ACN 101838740 ACN101838740 ACN 101838740ACN 201010147868 ACN201010147868 ACN 201010147868ACN 201010147868 ACN201010147868 ACN 201010147868ACN 101838740 ACN101838740 ACN 101838740A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- pulse
- electrode
- heavy metal
- power supply
- metal ions
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription261
- 229910001385heavy metalInorganic materials0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription183
- 150000002500ionsChemical class0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription173
- 238000011065in-situ storageMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription37
- 239000002689soilSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription94
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription73
- 230000002441reversible effectEffects0.000claimsdescription116
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000claimsdescription29
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000002347injectionMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000007924injectionSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000007789sealingMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000010287polarizationEffects0.000abstractdescription38
- 230000005684electric fieldEffects0.000abstractdescription19
- 230000005520electrodynamicsEffects0.000abstractdescription17
- 230000005012migrationEffects0.000abstractdescription14
- 238000013508migrationMethods0.000abstractdescription14
- 239000002699waste materialSubstances0.000abstractdescription6
- 239000000843powderSubstances0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description70
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description31
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description26
- 239000010949copperSubstances0.000description20
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description20
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description17
- 239000010802sludgeSubstances0.000description14
- 238000005067remediationMethods0.000description9
- 239000013049sedimentSubstances0.000description9
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000description9
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000description9
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description8
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description7
- 238000005265energy consumptionMethods0.000description7
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description7
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description7
- JPVYNHNXODAKFH-UHFFFAOYSA-NCu2+Chemical compound[Cu+2]JPVYNHNXODAKFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhenolChemical compoundOC1=CC=CC=C1ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 229910001431copper ionInorganic materials0.000description6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description6
- 239000012153distilled waterSubstances0.000description6
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description6
- 238000009434installationMethods0.000description6
- 230000009191jumpingEffects0.000description6
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description6
- 238000009825accumulationMethods0.000description5
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description4
- 238000004140cleaningMethods0.000description4
- 238000003487electrochemical reactionMethods0.000description4
- 238000005370electroosmosisMethods0.000description4
- 238000002386leachingMethods0.000description4
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000description4
- 230000000737periodic effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000description4
- 239000008399tap waterSubstances0.000description4
- 235000020679tap waterNutrition0.000description4
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000description4
- VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethyl methacrylateChemical compoundCOC(=O)C(C)=CVVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 229920005372Plexiglas®Polymers0.000description3
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-LSulfateChemical compound[O-]S([O-])(=O)=OQAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description3
- 238000004090dissolutionMethods0.000description3
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description3
- 239000003344environmental pollutantSubstances0.000description3
- 231100000719pollutantToxicity0.000description3
- 230000002829reductive effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000003860storageMethods0.000description3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-NCopperChemical compound[Cu]RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000description2
- 150000001450anionsChemical group0.000description2
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000description2
- 230000015556catabolic processEffects0.000description2
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description2
- 239000004927claySubstances0.000description2
- 238000002485combustion reactionMethods0.000description2
- 229910052802copperInorganic materials0.000description2
- 230000007797corrosionEffects0.000description2
- 238000005260corrosionMethods0.000description2
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description2
- 238000009713electroplatingMethods0.000description2
- 230000008030eliminationEffects0.000description2
- 238000003379elimination reactionMethods0.000description2
- 229920006351engineering plasticPolymers0.000description2
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000011066ex-situ storageMethods0.000description2
- 239000004744fabricSubstances0.000description2
- 238000005188flotationMethods0.000description2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-NgoldChemical compound[Au]PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000010931goldSubstances0.000description2
- 229910052737goldInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000003864humusSubstances0.000description2
- 150000004679hydroxidesChemical class0.000description2
- 238000003780insertionMethods0.000description2
- 230000037431insertionEffects0.000description2
- 238000009413insulationMethods0.000description2
- 238000010979pH adjustmentMethods0.000description2
- 230000008439repair processEffects0.000description2
- 150000003839saltsChemical class0.000description2
- 229920006395saturated elastomerPolymers0.000description2
- 239000010865sewageSubstances0.000description2
- 239000007787solidSubstances0.000description2
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description2
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000description2
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000description1
- 238000003556assayMethods0.000description1
- 230000002238attenuated effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001580bacterial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000013043chemical agentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000003749cleanlinessEffects0.000description1
- 238000013329compoundingMethods0.000description1
- 229910000365copper sulfateInorganic materials0.000description1
- ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-Lcopper(II) sulfateChemical compound[Cu+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-]ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 238000005520cutting processMethods0.000description1
- 230000018044dehydrationEffects0.000description1
- 238000006297dehydration reactionMethods0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 238000002848electrochemical methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001962electrophoresisMethods0.000description1
- 238000009393electroremediationMethods0.000description1
- 238000003912environmental pollutionMethods0.000description1
- 239000012530fluidSubstances0.000description1
- 230000005484gravityEffects0.000description1
- 239000003673groundwaterSubstances0.000description1
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description1
- 230000005764inhibitory processEffects0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description1
- 238000000691measurement methodMethods0.000description1
- 229910021645metal ionInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000000813microbial effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description1
- 238000002161passivationMethods0.000description1
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000011241protective layerSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000746purificationMethods0.000description1
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description1
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description1
- 238000006722reduction reactionMethods0.000description1
- 239000012266salt solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 238000013341scale-upMethods0.000description1
- 230000035939shockEffects0.000description1
- 239000002910solid wasteSubstances0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000002352surface waterSubstances0.000description1
- 230000003313weakening effectEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P10/00—Technologies related to metal processing
- Y02P10/20—Recycling
Landscapes
- Processing Of Solid Wastes (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种从土壤中或者从泥状粉状堆积物中原位脱除可溶性重金属离子的方法。The invention relates to a method for in-situ removal of soluble heavy metal ions from soil or muddy powder deposits.
背景技术Background technique
当今,环境污染问题日益严重,被重金属污染的耕地越来越多,从土壤中有效清除污染重金属离子就成为土壤生态修复的关键问题。对被重金属污染的土壤进行电动力学原位修复,是国内外近十多年才发展起来的一种成本较低、对环境二次损害最小的土壤原位修复方法。Nowadays, the problem of environmental pollution is becoming more and more serious, and more and more arable land is polluted by heavy metals. Effective removal of polluted heavy metal ions from soil has become a key issue for soil ecological restoration. Electrokinetic in-situ remediation of soil contaminated by heavy metals is a soil in-situ remediation method with low cost and minimal secondary damage to the environment that has only been developed in the past ten years at home and abroad.
目前人类工业及生活活动以及环境修复活动中所排出的大量泥状及粉状物料堆积如山,占用了不少耕地。而且,这些废料大都含有大量可溶性重金属离子,因此在露天堆放过程中,大量重金属离子被溶出而污染土壤和地下水乃至地面水,造成严重的生态污染;而欲对这些泥状或粉状物料进行大规模减量化式的资源化利用时,也因为重金属含量超标而限制了其利用范围。因此,为保护环境和对这些废弃物进行资源化利用,从其中脱除重金属离子成为首当其冲的重要技术措施。这类泥状及粉状废弃物包括各种工业泥质或粉质废料,污水处理厂剩余活性污泥,以及水体修复过程中大规模清理而出的底泥等等。然而,迄今为止,从如上物料中脱除重金属离子,总是将该物料部分挖出并运输至专门的设备中进行脱除处理(可称为异位处理);而直接在物料堆上进行原地脱除处理(可称原位处理)的方法未见公开报道。At present, a large amount of muddy and powdery materials discharged from human industrial and living activities and environmental restoration activities are piled up like mountains, occupying a lot of cultivated land. Moreover, most of these waste materials contain a large amount of soluble heavy metal ions, so in the open-air stacking process, a large amount of heavy metal ions are dissolved and pollute the soil, groundwater and even surface water, causing serious ecological pollution; When the resource utilization is reduced in scale, the scope of its utilization is also limited because the content of heavy metals exceeds the standard. Therefore, in order to protect the environment and utilize these wastes as resources, removing heavy metal ions from them has become an important technical measure that bears the brunt. Such muddy and powdery wastes include various industrial muddy or powdery wastes, residual activated sludge from sewage treatment plants, and sediments from large-scale cleaning during water body restoration, etc. However, so far, to remove heavy metal ions from the above materials, the materials are always partially excavated and transported to special equipment for removal treatment (can be called ex-situ treatment); There is no public report on the method of ground removal treatment (can be called in-situ treatment).
目前,从大规模堆积的泥质或粉状物料中脱除可溶性重金属离子的方法主要是异位脱除处理方法,而且大都效果不佳或对环境造成二次污染,属淘汰之列。重金属离子污染土壤的原位修复,目前对环境二次污染最小且具有真正实用价值的方法有两类,即生物修复方法和电动力学修复方法。At present, the methods for removing soluble heavy metal ions from large-scale accumulation of muddy or powdery materials are mainly ex-situ removal treatment methods, and most of them are not effective or cause secondary pollution to the environment, so they are eliminated. In situ remediation of soil contaminated by heavy metal ions, there are currently two types of methods that minimize secondary pollution to the environment and have real practical value, namely bioremediation methods and electrokinetic remediation methods.
1生物原位修复方法:1 Biological in situ restoration method:
该法的原理是:或者在土壤上种植特殊植物,利用植物吸收可溶性重金属离子,或者用特殊微生物制剂液体浸汲物料,让可溶性重金属离子被细菌吸收或吸附,最后又对植物或者细菌浸出液进行焚烧或化学处理,从中回收重金属。这种方法虽很有应用前景,但是其处理进程缓慢,难以在短时间达到清除重金属离子的目的。The principle of this method is: either plant special plants on the soil, use plants to absorb soluble heavy metal ions, or use special microbial preparation liquid to soak materials, let soluble heavy metal ions be absorbed or adsorbed by bacteria, and finally incinerate the plants or bacterial leachate Or chemical treatment, from which heavy metals are recovered. Although this method has great application prospects, its processing process is slow, and it is difficult to achieve the purpose of removing heavy metal ions in a short time.
2直流电动力学原位修复方法:2 Direct current electrodynamic in situ repair method:
污染土壤的电动力学原位修复方法,是国内外近十多年才出现的一种新方法。该法的一般原理是:在土壤被液体介质浸汲,重金属离子已经溶入介质液体中的条件下,在物料堆中一定距离的两端分别建立阳电极液室和阴电极液室,并插入阳电极和阴电极,用外部恒定直流电源正负极通过阳电极和阴电极向物料中施加电场力,使得土壤内部发生导电离子的电迁移和电渗等电化学作用,最后将可溶性重金属离子由土壤内部驱至阴电极室液内,从而达到将可溶性重金属离子从土壤中去除的目的。这种方法最大的优点是修复速度比生物原位修复快得多,效率较高而且对环境不产生二次污染。基于如上优点,土壤电动力学修复将会发展为一类今后应用会日益广泛的绿色技术。The electrokinetic in-situ remediation method of polluted soil is a new method that has only appeared in the past ten years at home and abroad. The general principle of this method is: under the condition that the soil is soaked by the liquid medium and the heavy metal ions have been dissolved in the medium liquid, a positive electrode liquid chamber and a negative electrode liquid chamber are respectively established at both ends of a certain distance in the material pile, and inserted into the The positive and negative electrodes of the external constant DC power supply apply an electric field force to the material through the positive and negative electrodes, so that electromigration and electroosmosis of conductive ions occur in the soil, and finally the soluble heavy metal ions are released from the The interior of the soil is driven into the cathode chamber solution, so as to achieve the purpose of removing soluble heavy metal ions from the soil. The biggest advantage of this method is that the remediation speed is much faster than biological in situ remediation, the efficiency is higher and the environment does not produce secondary pollution. Based on the above advantages, soil electrodynamic remediation will develop into a kind of green technology that will be widely used in the future.
但是,目前已有的这种重金属污染土壤的直流电动力学修复方法,存在处理效率较低能耗较大的缺点,这一缺点使之目前尚难获得广泛的实际应用,因而亟待改善。究其原因,是因为:在恒稳直流电源驱动的条件下,其电动力在物料或土壤中所形成的离子迁移作用和电渗作用脱除可溶性重金属离子时,电极会逐渐产生“活化极化”、“电阻极化”以及“浓差极化”三种极化现象。而电极的极化现象将使整个系统呈现出越来越大的导电阻力,致使同样大小的电场力迁移可溶性重金属离子的效率越来越低;而要保证维持一定的效率,就必须提高所施加的直流电压以增大电场力,于是造成电能的耗费增大。不仅如此,这种以提高直流电源电压来造成更大的电位梯度以克服电极极化现象造成的电压降的措施,不仅增加了电耗而且收效甚微,而且还会加速改变土壤的PH值,产生大量OH-离子,使可溶性重金属离子形成不可溶氢氧化物或盐类,反而更降低了重金属离子的脱除率,其结果造成一种恶性循环。然而,对于直接从土壤中(或者从其他泥状粉状物料堆中)原位脱除可溶性重金属离子而言,电能消耗的增大就意味着处理成本的大幅度增高,直接影响到了该方法应用的经济可行性。所以,解决电极极化问题是降低该方法处理成本和大幅度提高该方法处理效率的关键问题。However, the existing direct current electrodynamic repair method for heavy metal-contaminated soil has the disadvantage of low treatment efficiency and high energy consumption. The reason is because: under the condition of constant and stable DC power supply, when the ion migration and electroosmosis formed by its electromotive force in the material or soil remove soluble heavy metal ions, the electrode will gradually produce "activation polarization". ", "resistance polarization" and "concentration polarization". The polarization phenomenon of the electrodes will make the whole system show more and more conductive resistance, resulting in lower and lower efficiency of the same electric field force to migrate soluble heavy metal ions; and to ensure a certain efficiency, it is necessary to increase the applied The DC voltage is used to increase the electric field force, thus resulting in an increase in the consumption of electric energy. Not only that, this method of increasing the DC power supply voltage to cause a larger potential gradient to overcome the voltage drop caused by the electrode polarization phenomenon not only increases power consumption but has little effect, but also accelerates the change of the pH value of the soil. A large amount of OH- ions are produced, so that soluble heavy metal ions form insoluble hydroxides or salts, which reduces the removal rate of heavy metal ions, resulting in a vicious circle. However, for the in-situ removal of soluble heavy metal ions directly from soil (or from other muddy powder material piles), the increase in power consumption means a significant increase in processing costs, which directly affects the application of this method. economic feasibility. Therefore, solving the problem of electrode polarization is a key issue to reduce the processing cost of this method and greatly improve the processing efficiency of this method.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是为解决在重金属污染土壤电动力学原位修复过程中,现有的恒定直流方法迁移可溶性重金属离子时,因三种电极极化钝化现象而造成处理能耗过大及可溶性重金属离子被OH-“固化”于土壤中或物料中,结果造成该方法高能耗低效率的难题,针对性地提供一种用以消除电极极化现象的脉冲电动力学原位脱除可溶性重金属离子的方法。The purpose of the present invention is to solve the problem of excessive energy consumption and soluble heavy metal ions caused by three kinds of electrode polarization and passivation phenomena when the existing constant direct current method migrates soluble heavy metal ions during the electrodynamic in-situ restoration process of heavy metal polluted soil. The ions are "solidified" in the soil or materials by OH- , resulting in the problem of high energy consumption and low efficiency of the method, and it is targeted to provide a pulse electrokinetic in-situ removal of soluble heavy metal ions to eliminate electrode polarization. method.
本发明的技术解决方案是:一种原位脱除可溶性重金属离子的方法,在含有可溶性重金属离子的土壤或物料堆上直接插入阴电极和阳电极,阴电极和阳电极的驱动电源为脉冲电源,脉冲电源输出的脉冲电压正极接阳电极,负极接阴电极。脉冲电源交替产生单一正向脉冲波和单一反向脉冲波电压输出,正向脉冲波施加时段与反向脉冲波施加时段自动周期性交替倒换。利用单向正脉冲电流(指脉冲电源输出的脉冲电压其正极接阳电极,负极接阴电极)跳跃式地高速电迁移脱除土壤或物料内可溶性重金属离子;利用单向负脉冲电流(即指脉冲电源输出的脉冲电压其正极接电阴极,电源负极接电阳极)强烈的电冲击作用消耗、击穿并溶解电极极化物质,彻底消除电极上的阻碍电迁移的极化现象。The technical solution of the present invention is: a method for removing soluble heavy metal ions in situ, directly inserting the negative electrode and the positive electrode on the soil or material pile containing soluble heavy metal ions, and the driving power of the negative electrode and the positive electrode is a pulse power supply , The positive pole of the pulse voltage output by the pulse power supply is connected to the anode electrode, and the negative pole is connected to the cathode electrode. The pulse power supply alternately generates a single positive pulse wave and a single reverse pulse wave voltage output, and the forward pulse wave application period and the reverse pulse wave application period are automatically and periodically switched alternately. Use one-way positive pulse current (referring to the pulse voltage output by the pulse power supply, the positive pole is connected to the positive electrode, and the negative pole is connected to the negative electrode) to remove soluble heavy metal ions in soil or materials by jumping high-speed electromigration; use one-way negative pulse current (that is, refer to The pulse voltage output by the pulse power supply (the positive pole is connected to the cathode, and the negative pole of the power supply is connected to the anode) has a strong electric impact to consume, break down and dissolve the electrode polarized substances, and completely eliminate the polarization phenomenon on the electrode that hinders electromigration.
脉冲电源运行参数的设定方式如下:The setting method of pulse power supply operating parameters is as follows:
在参数设定中,我们称用于迁移重金属离子至阴电极的单向电脉冲为“正向脉冲”,而将与之反向以消除电极极化现象为工作目的的单向电脉冲称之为“反向脉冲”。参数设定的步骤是:首先设定正向脉冲工作电压、正向电脉冲频率、占空比,正向脉冲电流的连续工作时间,然后设定反向脉冲脉冲工作电压、反向电脉冲频率、占空比,反向脉冲电流的连续工作时间。当设备系统硬软件都连接调适妥当之后,再开动电源。实施对土壤中或者物料中可溶性重金属离子的脉冲电动力学原位脱除。此后,在正向脉冲电流工作到达所设定的迁移重金属离子的连续工作时间之后,电源将自动切换,向电极反向施加用以清除电极极化膜的反向脉冲电流;而当反向脉冲电流工作时间达到设定值之后,电源又自动切换为正脉冲工作方式;正反脉冲连续工作时间的周期性切换交替,构成了脉冲电源的运行模式。In the parameter setting, we call the one-way electric pulse used to transfer heavy metal ions to the negative electrode as "forward pulse", and the one-way electric pulse for the purpose of eliminating electrode polarization in the opposite direction is called For "reverse pulse". The steps of parameter setting are: first set the forward pulse working voltage, forward electric pulse frequency, duty ratio, and the continuous working time of forward pulse current, then set the reverse pulse working voltage, reverse electric pulse frequency , Duty cycle, continuous working time of reverse pulse current. When the hardware and software of the device system are connected and adjusted properly, turn on the power. Implement pulse electrokinetic in-situ removal of soluble heavy metal ions in soil or materials. Afterwards, after the forward pulse current work reaches the set continuous working time for the migration of heavy metal ions, the power supply will automatically switch, and reversely apply the reverse pulse current to the electrode to remove the polarized film of the electrode; and when the reverse pulse After the current working time reaches the set value, the power supply will automatically switch to positive pulse working mode; the periodic switching of positive and negative pulse continuous working time constitutes the operation mode of pulse power supply.
脉冲电源的特征和功能如下:The characteristics and functions of the pulse power supply are as follows:
(1)脉冲电源供电输入端具有交流220V/380V输入,以及直流12V/24V输入两个端口可供选择;前者为在紧靠市电地区直接接电使用、或者为在远离市电地区使用由其他动力(内燃机、水力、风力、)所拖动的220V/380V50HZ交流发电机现场直接供电而设,后者则为远离市电地区使用蓄电池供电或者使用太阳能充电/蓄电系统直接供电、或者使用由其他动力(内燃机、水力、风力)所拖动的直流发电机现场直接供电而设。(1) The input terminal of the pulse power supply has two ports of AC 220V/380V input and DC 12V/24V input; The 220V/380V50HZ alternator driven by other power (internal combustion engine, hydraulic power, wind power, etc.) is designed for direct power supply on site, and the latter is used for power supply by batteries or solar charging/storage systems for direct power supply in areas far away from mains power, or by using It is designed for direct power supply on site by a DC generator driven by other power (internal combustion engine, hydraulic power, wind power).
(2)脉冲电源输出端不仅可以交替输出单一正向脉冲和单一反向脉冲,而且正向脉冲施加时段与反向脉冲施加时段可以自动周期性交替倒换;(2) The output terminal of the pulse power supply can not only alternately output a single forward pulse and a single reverse pulse, but also the forward pulse application period and the reverse pulse application period can be automatically and periodically alternately switched;
(3)用正向脉冲电场力的冲击跳跃性能,以较小的电能消耗,快速跳跃式电迁移脱除可溶性重金属离子;(3) Use the impact jumping performance of the positive pulse electric field force to remove soluble heavy metal ions by fast jumping electromigration with less power consumption;
(4)用反向脉冲电场力的逆向冲击性电化学反应,在不添加任何化学药剂的条件下自动周期性消耗、击穿并溶解清除电极上的极化物并且动态调整土壤或者物料内PH值,以确保电迁移重金属离子工作的持续低能耗性和高效率性;(4) Use the reverse impact electrochemical reaction of the reverse pulse electric field force to automatically periodically consume, break down and dissolve the polarized substances on the electrodes without adding any chemical agents, and dynamically adjust the pH value in the soil or materials , to ensure continuous low energy consumption and high efficiency of electromigration of heavy metal ions;
(5)为了使用安全,设有空载保护电路:空载开不了机;而开机后一旦出现空载或者低电阻事故(电极线断路或短路)即自动切断电源并报警。(5) For the safety of use, there is a no-load protection circuit: the machine cannot be turned on without a load; and once no-load or low resistance accidents (electrode wire breakage or short circuit) occur after starting up, the power supply will be automatically cut off and an alarm will be issued.
脉冲电源的特征技术参数如下:The characteristic technical parameters of the pulse power supply are as follows:
(1)电源输入选择端口的输入电压特征:(1) The input voltage characteristics of the power input selection port:
市电输入选择端口 交流220VMains input selection port AC 220V
蓄电池或太阳能充电/蓄电系统供电端口 直流12V/24VBattery or solar charging/storage system power supply port DC 12V/24V
(2)电源输出端电压特征:(2) The voltage characteristics of the output terminal of the power supply:
正向脉冲电工作电压:0-200V连续可调(可施加最大电压梯度200V/M)Forward pulse electric working voltage: 0-200V continuously adjustable (maximum voltage gradient 200V/M can be applied)
正向电脉冲频率: 0-100HZ连续可调Forward electrical pulse frequency: 0-100HZ continuously adjustable
正向电脉冲波形 正单向方波/正单向正弦半波(可选择设定)Positive electrical pulse waveform Positive one-way square wave/positive one-way half-sine wave (optional setting)
正向电脉冲占空比 50-98%可调Positive electrical pulse duty cycle 50-98% adjustable
正向电脉冲电流连续工作时间: 0-48h连续可调Continuous working time of positive electric pulse current: 0-48h continuously adjustable
反向脉冲工作电压: 0-200V连续可调Reverse pulse working voltage: 0-200V continuously adjustable
反向电脉冲频率: 0-100HZ连续可调Reverse electrical pulse frequency: 0-100HZ continuously adjustable
反向电脉冲波形 负单向方波/负单向正弦半波(可选择设定)Reverse electrical pulse waveform Negative one-way square wave/negative one-way sine half wave (optional setting)
反向电脉冲占空比 50-98%可调Reverse electrical pulse duty cycle 50-98% adjustable
反向脉冲电流连续工作时间: 0-24h连续可调Reverse pulse current continuous working time: 0-24h continuously adjustable
脉冲电源可设定最长一次连续工作总时间: 0-100天 连续可调The pulse power supply can set the longest continuous working time: 0-100 days, continuously adjustable
脉冲电源启停工作方式: 手动/自动(电子定时)Pulse power supply start and stop working mode: Manual/automatic (electronic timing)
正向脉冲工作电流与反向脉冲电流的交替方式:Alternate mode of forward pulse working current and reverse pulse current:
操作人员事先在电源上对正反向脉冲的运行参数进行事先设定,然后开机由电源自动切换;The operator pre-sets the operating parameters of the forward and reverse pulses on the power supply in advance, and then the power supply automatically switches when the power is turned on;
反向脉冲工作时段总是夹在正向电脉冲的两个连续工作时间段之间;电源以自动控制方式实现正反脉冲的周期性交替切换。The reverse pulse working period is always sandwiched between two continuous working periods of the positive electric pulse; the power supply realizes the periodic alternate switching of positive and negative pulses in an automatic control mode.
本脉冲电源所具有的独特的输出脉冲工作模式,其实质可概括为:The essence of the unique output pulse working mode of this pulse power supply can be summarized as:
所谓“正脉冲”与“反脉冲”,实质上它们都属于具有一定脉冲频率的单向方波脉冲或者单向正弦半波脉冲,只不过它们施加于电极的方向相反而已;The so-called "positive pulse" and "reverse pulse" are essentially one-way square wave pulses or one-way sine half-wave pulses with a certain pulse frequency, but they are applied to the electrodes in opposite directions;
正脉冲与反脉冲的连续工作时段自动周期性交替切换。The continuous working period of positive pulse and negative pulse is automatically switched periodically.
正脉冲与反脉冲有各自独立可调的工作电压、脉冲频率、占空比、以及连续工作时间范围,以供运用时灵活设定。The positive pulse and reverse pulse have their own adjustable working voltage, pulse frequency, duty cycle, and continuous working time range for flexible setting during use.
脉冲电源具有脉冲方波和正弦半波的输出波形转换功能The pulse power supply has the output waveform conversion function of pulse square wave and sine half wave
本方法依据电极布局的方式不同分为二种实施方案This method is divided into two implementations according to the different ways of electrode layout
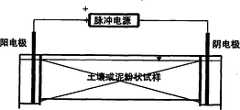
(1)在土壤中或者物料堆上直接开挖沟槽作为阴电极室和阳电极室(1) Dig trenches directly in the soil or on the material pile as the cathode electrode chamber and the anode electrode chamber
在含有可溶性重金属离子的物料堆上或土壤中相隔一定距离两端分别开挖沟槽作为阴电极室和阳电极室,并在其中分别插入阳电极和阴电极,电极形状不论,但至少要有一对电极,开挖沟槽的距离依据实验所得的“最佳电压梯度”所计算确定,然后在土壤或物料堆上加一定量的水,使之渗透入颗粒间隙溶解重金属离子形成导电液并浸满电极室,再在电极上接上脉冲电源并设定好运行参数,继而开机进行重金属脱除作业。此后,脉冲电源将会自动按正反脉冲工作时段反复交替的模式运行,直至将土壤内或者物料内重金属离子脱至允许含量为止,或者直至达到设定运行总时间为止。On the pile of materials containing soluble heavy metal ions or in the soil with a certain distance apart, trenches are excavated at both ends as the cathode electrode chamber and the anode electrode chamber, and the anode electrode and the cathode electrode are respectively inserted in it. Regardless of the shape of the electrodes, there must be at least one For the opposite electrode, the distance of the excavated trench is calculated and determined according to the "optimum voltage gradient" obtained from the experiment, and then a certain amount of water is added to the soil or material pile to penetrate into the particle gap to dissolve heavy metal ions to form a conductive liquid and soak it. When the electrode chamber is full, connect the pulse power supply to the electrode and set the operating parameters, and then start the machine to remove heavy metals. After that, the pulse power supply will automatically operate in the mode of alternating positive and negative pulse working periods until the heavy metal ions in the soil or materials are removed to the allowable content, or until the total set operating time is reached.
(2)直接在土壤中或物料堆上插入组合式电极(2) Insert the combined electrode directly in the soil or on the material pile
直接使用一种其电极与电极室一体化组合而成的“组合式电极”的电极布局的实施方案,至少应当有一对组合式电极分别作阴阳电极。而将若干组合式电极按一种最佳的节能布点方式插入,将之连接成阴阳电极点阵的布局方式则最为理想;即以一个阴电极为中心,周围布置若干电阳极,所有阳电极与阴电极保持与最佳电位梯度相应的最佳距离,然后将所有作阴电极用的组合式电极并联于脉冲电源负极,将所有作阳电极用的组合式电极并联于脉冲电源正极,由此方式而构成电极点阵,并且在土壤或物料堆上加一定量的水,使之渗透入颗粒间隙内并溶解重金属离子形成导电液并浸满各组合式电极室,之后开动运行参数已经设定好的脉冲电源进行重金属脱除作业。此后,脉冲电源将会全自动按正反脉冲工作时段反复交替的模式运行,直至将土壤内或者物料内重金属离子脱至允许含量为止,或者直至达到设定运行总时间为止。In the embodiment of electrode layout directly using a "combined electrode" in which electrodes and electrode chambers are integrated, at least one pair of combined electrodes should be used as cathode and anode electrodes respectively. However, it is most ideal to insert several combined electrodes according to an optimal energy-saving layout method and connect them into a matrix of cathode and anode electrodes; Keep the optimal distance corresponding to the optimal potential gradient for the negative electrode, then connect all combined electrodes used as negative electrodes in parallel to the negative pole of the pulse power supply, and connect all combined electrodes used as anode electrodes in parallel to the positive pole of the pulse power supply, in this way To form an electrode lattice, and add a certain amount of water to the soil or material pile, so that it penetrates into the particle gap and dissolves heavy metal ions to form a conductive liquid and fill each combined electrode chamber, and then the operating parameters have been set. The pulse power supply for heavy metal removal. After that, the pulse power supply will automatically operate in the mode of alternating positive and negative pulse working periods, until the heavy metal ions in the soil or materials are removed to the allowable content, or until the total running time is reached.
本发明的有益效果是:本方法提供了一种能产生强冲击电场力的脉冲电源,该电源不仅输出电压为脉冲波形,并且其输出的脉冲波电压的极性自动周期性反相。即该电源能按事先设定,自动产生单一正向脉冲连续工作时段与单一反向脉冲连续工作时段周期性交替的工作模式。这一特点使之能彻底消除原有直流电动力学法无法克服的三种电极极化现象:首先是在脉冲条件下,电迁移及电渗过程中电极上的电阻膜不易形成,或易被冲击电流击穿而破坏,并最终被周期性反向电流在电极上所产生的逆向电化学反应的溶解作用而彻底从电极上脱落。周期性被彻底动态清洁后的电极又进一步促进反向脉冲电流对活化极化及浓差极化现象的抑制和削弱,继而使得土壤或物料内的PH值被周期性调整,由活化极化产生的OH-与重金属离子生成不溶性氢氧化物的几率大大降低,从而彻底克服了直流电动力学方法无法消除电极极化的致命缺点,使以脉冲电源为关键设备的“脉冲电动力学法”原位脱出重金属离子方法的获得了低能耗和高效率。The beneficial effects of the invention are: the method provides a pulse power supply capable of generating a strong impact electric field force, the power supply not only outputs a pulse waveform, but also automatically and periodically reverses the polarity of the output pulse wave voltage. That is to say, the power supply can automatically generate a working mode in which a single positive pulse continuous working period and a single reverse pulse continuous working period alternate periodically according to the preset setting. This feature enables it to completely eliminate three kinds of electrode polarization phenomena that cannot be overcome by the original DC electrodynamic method: firstly, under pulse conditions, the resistance film on the electrode is not easy to form during the electromigration and electroosmosis process, or is easily impacted. The current breaks down and is destroyed, and finally it is completely detached from the electrode by the dissolution of the reverse electrochemical reaction generated by the periodic reverse current on the electrode. The electrodes that are periodically thoroughly and dynamically cleaned further promote the inhibition and weakening of the reverse pulse current on activation polarization and concentration polarization, and then make the pH value in the soil or material be periodically adjusted, resulting in activation polarization The probability of OH- and heavy metal ions forming insoluble hydroxides is greatly reduced, thus completely overcoming the fatal shortcoming that the direct current electrokinetic method cannot eliminate electrode polarization, and making the "pulse electrokinetic method" with pulse power supply as the key equipment in-situ protrude Low energy consumption and high efficiency were obtained by the heavy metal ion method.
本发明具有独特优越性的最本质原理在于:脉冲电源所造成的单向脉冲波工作电场,其能量在时间上高强度集中并短促释放时会产生能量冲击效应,其结果造成一种比同等消耗的恒流直流电场力强大数倍的瞬间冲击电场力;在这种冲击电场力的作用下,造成物料堆内的电离子迁移和电渗现象以一种跳跃式(或称浪涌式)的方式快速进行,其结果使得可溶性重金属离子被冲击电场力以一种“跳跃式”(或称“浪涌式”)的方式所迁移,因而大大提高了其迁移速度和迁移效率,而且这种冲击电场力打破了电极极化现象极易形成的静态环境,使得电极的极化现象不易形成或被有效击穿。另一方面,由于电源施加于电极上的脉冲电压极性周期性倒换,所施加的反向脉冲电流又对阳阴电极施加与正向脉冲电流完全相反的电化学反应,其结果产生了对正向脉冲电流所产生的极化物质的针锋相对的消除和溶解作用,高速动态溶解了电极上的极化物,从而使电极得以清洗,并且周期性动态调正了土壤或物料中的PH值,其最终结果是彻底消除了电极极化现象。本脉冲电源可以自动控制,用作金属离子电迁移工作的正向(单向)脉冲电流(电源正极接阳电极、负极接阴电极)与用作清除电极极化工作的反向(单向)脉冲电流(电源正极接阴电极、负极接阳电极)按各自的设定脉冲频率和设定时间,相互进行周期性倒换,从而形成本脉冲电源的“电迁移-清除电极极化”工作自动交错连续运行的独特模式和独特功能,正是本脉冲电源的这一独特功能,决定了以之为核心的本脉冲电动力学法脱除土壤中或者其他泥质或粉质物料堆中可溶性重金属离子的高效率性和低能耗特性,而且,本脉冲电动力学法是采用反向电流的反向电化学反应来消除电极极化现象,对环境无二次污染,这一点比之于目前很多改善直流电动力学法研究中采用添加化学试剂消除电极极化而不顾及对环境的二次污染的做法,具有不可比拟的环保意义。以上特性使本“脉冲电动力学法”极具广泛实用前景的高效绿色处理技术。The most essential principle of the unique superiority of the present invention is that the unidirectional pulse wave working electric field caused by the pulse power supply will produce an energy shock effect when its energy is concentrated in a high intensity in time and released in a short time, which results in a power consumption higher than the same consumption. The constant current DC electric field force is several times stronger than the instantaneous impact electric field force; under the action of this impact electric field force, the ion migration and electroosmosis in the material pile are caused in a jumping (or surge) manner. As a result, the soluble heavy metal ions are migrated in a "jump" (or "surge") manner by the impact electric field force, thus greatly improving their migration speed and migration efficiency, and this impact The electric field force breaks the static environment where the electrode polarization phenomenon is easy to form, making the electrode polarization phenomenon difficult to form or effectively broken down. On the other hand, due to the periodic reversal of the polarity of the pulse voltage applied to the electrode by the power supply, the applied reverse pulse current exerts an electrochemical reaction completely opposite to the forward pulse current on the anode and cathode electrodes, resulting in positive The tit-for-tat elimination and dissolution of the polarized substances generated by the pulse current, the high-speed dynamic dissolution of the polarized substances on the electrodes, so that the electrodes can be cleaned, and the pH value in the soil or materials is dynamically adjusted periodically, and finally The result is a complete elimination of electrode polarization. This pulse power supply can be automatically controlled, and it is used as a positive (one-way) pulse current for metal ion electromigration work (the positive pole of the power supply is connected to the anode electrode, and the negative pole is connected to the cathode electrode) and the reverse (one-way) pulse current used for cleaning electrode polarization work. The pulse current (the positive electrode of the power supply is connected to the cathode electrode, and the negative electrode is connected to the anode electrode) is periodically switched with each other according to the respective set pulse frequency and set time, thus forming the automatic interleaving of the "electromigration-clearing electrode polarization" work of this pulse power supply The unique mode and unique function of continuous operation, it is this unique function of this pulse power supply, which determines the efficiency of this pulse electrokinetic method, which is based on it, to remove soluble heavy metal ions in soil or other muddy or powdery material piles. High efficiency and low energy consumption, and this pulse electrokinetic method uses the reverse electrochemical reaction of the reverse current to eliminate the electrode polarization phenomenon, and has no secondary pollution to the environment. This is compared with many current improved DC electrodynamics. The method of adding chemical reagents to eliminate electrode polarization without regard to the secondary pollution to the environment in the study of the law has incomparable environmental protection significance. The above characteristics make the "pulse electrokinetic method" a highly efficient green processing technology with extensive practical prospects.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1脉冲电源方波输出示意图Figure 1 Schematic diagram of square wave output of pulse power supply
图2脉冲电源正弦半波输出示意图Figure 2 Schematic diagram of pulse power supply half-sine wave output
图3实施方案一:在土壤或泥状粉状物料堆上开挖沟槽作电极室的示意图Figure 3 Embodiment 1: Schematic diagram of excavating trenches on soil or muddy powder material piles as electrode chambers
图4实施方案二:采用组合式电极插入方案示意图Figure 4 Embodiment 2: Schematic diagram of the combined electrode insertion scheme
图5组合式电极的构造示意图Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the structure of the combined electrode
图6图5的俯视图Top view of Figure 6 and Figure 5
图7组合式电极点阵接法示意图Figure 7 Schematic diagram of combined electrode dot matrix connection
图8本发明方法实施方案一的模拟试验装置Fig. 8 the simulated test device of the method embodiment one of the present invention
图9本发明方法实施方案二的模拟试验装置The simulation test device of Fig. 9 method embodiment two of the present invention
具体实施方式Detailed ways
一种原位脱除可溶性重金属离子的方法,在含有可溶性重金属离子的土壤或物料堆上直接插入阴电极和阳电极,采用脉冲电源为驱动电源,电极布局的方式分为二种,实施方案一是在土壤中或者物料堆上直接开挖沟槽作为阴电极室和阳电极室,实施方案二是在土壤中或物料堆上插入组合式电极。A method for in-situ removal of soluble heavy metal ions, directly inserting negative electrodes and positive electrodes on the soil or material pile containing soluble heavy metal ions, using pulse power as the driving power, and the electrode layout is divided into two types,
组合式电极是由不锈钢柱状或管状电极3和由孔管状外壳7所包围空间形成的电极室8的组合体。在电极室8内中上部设置有电极室液注入/抽取管道11和电极室液电导传感器12、底部设置有电极钉入锥10。The combined electrode is a combination of a stainless steel columnar or tubular electrode 3 and an
组合式电极部件装配结构以不锈钢柱状或管状电极3、过滤膜6安装用孔管状支架5、过滤膜6、孔管状外壳7、及兼作电极3和电导传感器12及电极室液注入/抽取管道11以及过滤膜安装孔管状支架5的安装定位上骨架的上螺旋端盖4、以及底部呈圆锥型的钉入锥10、并兼作电极3及过滤膜6安装孔管状支架5的安装定位下骨架的不锈钢下螺旋端盖9按图5组装而成;其上螺旋端盖4、下螺旋端盖9与孔管状外壳7之间以螺纹连接,三者共同构成组合式电极的封闭和保护层;The assembly structure of combined electrode parts is made of stainless steel columnar or tubular electrodes 3,
组合式电极的过滤膜6、孔管状支架5、孔管状外壳7、上螺旋端盖4既可以用不锈钢材质制造,也可以用高强度耐腐蚀耐磨蚀绝缘工程塑料制造;The
组合式电极,当上螺旋端盖4用不锈钢制造时,其上的电极定位安装孔与电极3之间必须加装绝缘击穿电压大于2000V的绝缘环;For combined electrodes, when the upper
组合式电极,不锈钢柱状或管状电极3的上密封绝缘盖2和下定位绝缘盖13由高强度绝缘工程塑料制造,且绝缘击穿电压必须大于2000VCombined electrode, the upper sealing insulating cover 2 and the lower
组合式电极,其过滤膜6的材质既可选用高强度耐腐蚀透水布料也可选用透水薄毛毯,过滤膜剪裁及安装方式,既可将布料或薄毯剪裁成与过滤膜6的孔管状支架5的直径和长度相当的长方形料,然后将之卷贴于孔管状支架5的外壁,以形成封闭筒状过滤膜,或者直接使用已经事先按相应尺寸加工好的封闭筒状过滤膜;Combined electrode, the
组合式电极各部件的作用说明如下:The function of each component of the combined electrode is described as follows:
(1)组合式电极的上螺旋端盖4和下螺旋端盖9与多孔管状外壳7不仅起封闭保护组合电极作用,而且三者为其他所有部件的组合装配提供了安装定位骨架。(1) The upper
(2)组合式电极中,过滤膜6的作用是阻挡固体物悬浮颗粒进入电极室而只让水及可溶性离子进入电极室,从而保证电极室及电极的清洁和正常工作。(2) In the combined electrode, the function of the
(3)组合式电极中,不锈钢螺旋下端盖9与钉入锥10实质上是一个一体化加工的整体;钉入锥10的作用是可以直接轻巧地往土地上或者物料堆上插入并且可即插即用。(3) In the combined electrode, the stainless steel screw lower end cover 9 and the nailing
(4)由于具有电极室液注入/抽取管道11,可以方便地完成注入电解液或者将饱和阴极室液抽出的操作,从而为阴极室液电解还原提纯回收其中的重金属的工作创造了方便条件;(4) Due to the presence of the electrode chamber liquid injection/
(5)由于具有在线监测电导传感器12,可以连续监测并显示重金属离子的脱除情况以及时调整各种工艺参数,从而使脱除工艺更加优化。(5) Due to the on-line
组合式电极直径一般在10-30mm,组合式电极外直径一般在30-100mm,长度一般在0.5-30M,可做成若干尺寸系列,视插入点的污染土壤深度或者物料堆积高度而恰当选用。The diameter of the combined electrode is generally 10-30mm, the outer diameter of the combined electrode is generally 30-100mm, and the length is generally 0.5-30M. It can be made into several size series, depending on the depth of contaminated soil at the insertion point or the height of material accumulation. Proper selection.
电极点阵是指若干阴阳电极在一起工作时所列成的材耗和能耗最小,对脉冲电压要求最低的经济上最合算的排列方式。本方法的电极排列方式见图7。电极点阵的特点是:以阴电极组合式电极为中心,以在实验所确定的“最佳电位梯度”所对应的阴阳电极最佳距离为布置依据,在每一根阴电极周围均匀配置1~50个阳电极,以确保各阳电极与阴电极之间具有相同的最佳的电场梯度。阴电极和阳电极之间的最佳距离,对应着电场在物料或土壤中的最佳的电压梯度数据,它决定了脉冲电源工作的最佳电压。而最佳的电场梯度数据,则依据对于该物料的模拟电迁移实验中直接确定。因为本实验装置中,模拟料样的体积是极其有限的,故其体电阻必大于体积庞大的现场物料堆或大面积土地,故使用该数据进行现场电极布点,实际电迁移效果将总是优于实验效果,故称之为“最佳的电压梯度”。Electrode lattice refers to the economical and most cost-effective arrangement with the least material consumption and energy consumption and the lowest requirement for pulse voltage when several yin and yang electrodes work together. The arrangement of electrodes in this method is shown in FIG. 7 . The characteristics of the electrode lattice are: the combined cathode electrode is the center, and the optimal distance between the cathode and anode electrodes corresponding to the "best potential gradient" determined in the experiment is used as the layout basis, and 1 electrode is evenly arranged around each cathode electrode. ~50 anode electrodes to ensure the same optimal electric field gradient between each anode electrode and cathode electrode. The optimum distance between the cathode electrode and the anode electrode corresponds to the optimum voltage gradient data of the electric field in the material or soil, which determines the optimum working voltage of the pulse power supply. The optimal electric field gradient data is determined directly based on the simulated electromigration experiment for the material. Because in this experimental device, the volume of the simulated material sample is extremely limited, so its volume resistance must be greater than the bulky on-site material pile or large area of land, so using this data for on-site electrode layout, the actual electromigration effect will always be excellent. Because of the experimental effect, it is called "the best voltage gradient".
当阴电极室液的重金属离子达到饱和状态后,有必要抽取饱和室液并替换新室液。该项工作对于实施方案一,采用自吸式微型离心泵来完成;对于实施方案二,则采用具有强劲自动抽吸能力的微型隔膜泵来完成。When the heavy metal ions in the cathode chamber liquid reach saturation, it is necessary to extract the saturated chamber liquid and replace it with a new chamber liquid. The work is completed by using a self-priming micro-centrifugal pump for the first embodiment; for the second embodiment, it is completed by a micro-diaphragm pump with strong automatic suction capability.
由于本专利申请的“脉冲电动力学法”是对已有”直流电动力学法”脱除土壤中重金属离子方式的改进和应用领域的扩展,而这两种方法的主要区别就在于所使用的电源不同。因此,要考察本方法的实施效果,就必须与已有方法进行相同条件下实施效果的实验对比来加以说明。为达到此目的,在每次试验中,皆作了两种方法的平行对比实验。Since the "pulse electrokinetic method" of this patent application is an improvement and application field expansion of the existing "direct current electrokinetic method" for removing heavy metal ions in soil, the main difference between the two methods lies in the power used different. Therefore, to investigate the implementation effect of this method, it is necessary to carry out an experimental comparison of the implementation effect under the same conditions with the existing method to illustrate. In order to achieve this purpose, in each test, a parallel comparative experiment of two methods was carried out.
本发明设计了一个标准模拟工业现场实验装置。该装置既可用以对已有的“直流电动力学法”与本发明的“脉冲电动力学法”进行实验对比,还可以直接通过它确定“最佳电位梯度”,以供工业现场确定最佳阴阳电极间距或者设定电源最佳施加电压值之用。The present invention designs a standard simulated industrial field experiment device. The device can be used to compare the existing "direct current electrokinetic method" with the "pulse electrokinetic method" of the present invention, and can also directly determine the "best potential gradient" through it, so as to determine the best yin and yang in the industrial field It is used for electrode spacing or setting the optimum applied voltage value of the power supply.
本发明模拟工业现场脱除重金属离子的实施方案1的实验装置及其操作是:在一个长1050mm,宽100mm,深150mm,两端分别设有电极室的有机玻璃矩形槽内,首先在阴阳电极室与槽主体之间分别安置好一块多孔挡板,以阻隔实验中槽内试样固体微粒进入电极室,继而在阳阴电极室内并分别插入不锈钢板式电极,然后,均匀装入质量一定的、含有一定的可溶性重金属的某种物料或土壤,以模拟该物料的自然堆积状态。然后,在槽中加入一定量的蒸馏水或者自来水使物料具备一定的有利于电化学迁移重金属离子的含水率,经过一定时间的浸汲后,物料内的重金属离子溶入水中形成一定浓度的重金属浸汲液。而在往槽内加水的同时,也在电极室内加上与物料槽内液体持平的同一蒸馏水或者自来水,之后,将脉冲电源正负极分别接于不锈钢板式阳电极和阴电极上。继而设定好所需要的操作参数,调整到所需脉冲电压、脉冲电压频率及占空时间,开通电源进行重金属离子的电迁移脱除。在正脉冲电迁移脱除工作进行到设定时间之后,脉冲电源电压将自动反向开始施加反向脉冲,在一段设定的反脉冲工作设定时间内以反向脉冲电流清除电极极化现象。之后,电源再自动返回正脉冲状态,开始下一回合的电迁移脱除重金属离子工作。如此反复交替进行,直至达到设定之重金属脱除指标标。实验装置见附图8。The present invention simulates the experimental device of the
在作与“直流电动力学法”对等比较实验时,只要将脉冲电源换成直流电源,而保持其余初始条件完全相同即可;或者使用两个完全相同的实验槽,分别接上脉冲电源和直流电源,同时同初始条件作对等平行运行实验。When doing the equivalent comparison experiment with the "DC electrodynamics method", just replace the pulse power supply with a DC power supply, and keep the rest of the initial conditions exactly the same; or use two identical experimental tanks, respectively connect the pulse power supply and DC power supply, at the same time with the initial conditions for peer-to-peer parallel operation experiments.
本发明模拟工业现场脱除重金属离子的实施方案2的实验装置及其操作是:在一个长1050mm,宽100mm,深150mm,两端分别装有直径为30mm的组合式阴电极和组合式阳电极的有机玻璃矩形槽内,均匀装入质量一定的、含有一定的可溶性重金属的某种物料或土壤,以模拟该物料的自然堆积状态。然后,在槽中加入一定量的蒸馏水或者自来水使物料具备一定的有利于电化学迁移重金属离子的含水率,经过一定时间的浸汲后,物料内的重金属离子溶入水中形成一定浓度的重金属浸汲液。而在往槽内加水的同时,也在组合式电极的电极室内加上与物料槽内液体持平的同一蒸馏水或者自来水,之后,将脉冲电源正负极分别接于组合式阳电极和组合式阴电极上。继而设定好所需要的操作参数,调整到所需脉冲电压、脉冲电压频率及占空时间,开通电源进行重金属离子的电迁移脱除。在正脉冲电迁移脱除工作进行到设定时间之后,脉冲电源电压将自动反向开始施加反向脉冲,在一段设定的反脉冲工作设定时间内以反向脉冲电流清除电极极化现象。之后,电源再自动返回正脉冲状态,开始下一回合的电迁移脱除重金属离子工作。如此反复交替进行,直至达到设定之重金属脱除指标标。而假如电源预设有运行总时间时,脉冲电源会自动按时停止。实验装置图9。The present invention simulates the experimental device and the operation of the embodiment 2 of industrial site removal of heavy metal ions as follows: in a long 1050mm, wide 100mm, deep 150mm, the two ends are respectively equipped with a combined negative electrode and a combined positive electrode with a diameter of 30mm In the plexiglass rectangular tank, a certain material or soil with a certain quality and a certain amount of soluble heavy metals is evenly loaded to simulate the natural accumulation state of the material. Then, add a certain amount of distilled water or tap water into the tank to make the material have a certain water content that is conducive to the electrochemical transfer of heavy metal ions. After a certain period of leaching, the heavy metal ions in the material dissolve into the water to form a certain concentration of heavy metal leaching. draw liquid. While adding water to the tank, the same distilled water or tap water that is equal to the liquid in the material tank is also added to the electrode chamber of the combined electrode, and then the positive and negative electrodes of the pulse power supply are respectively connected to the combined anode electrode and the combined cathode electrode. on the electrode. Then set the required operating parameters, adjust to the required pulse voltage, pulse voltage frequency and duty time, and turn on the power for electromigration removal of heavy metal ions. After the positive pulse electromigration removal work reaches the set time, the pulse power supply voltage will automatically reverse and start to apply the reverse pulse, and the electrode polarization phenomenon will be removed with the reverse pulse current within a set period of reverse pulse work setting time . After that, the power supply will automatically return to the positive pulse state, and start the next round of electromigration to remove heavy metal ions. This is repeated alternately until the set heavy metal removal index is reached. And if the power supply is preset with a total running time, the pulse power supply will automatically stop on time. Figure 9 of the experimental setup.
在作与“直流电动力学法”对等比较实验时,只要将脉冲电源换成直流电源,而保持其余初始条件完全相同即可;或者使用两个完全相同的实验槽,分别接上脉冲电源和直流电源,同时同初始条件作对等平行运行实验。When doing the equivalent comparison experiment with the "DC electrodynamics method", just replace the pulse power supply with a DC power supply, and keep the rest of the initial conditions exactly the same; or use two identical experimental tanks, respectively connect the pulse power supply and DC power supply, at the same time with the initial conditions for peer-to-peer parallel operation experiments.
应当特别指出的是:这个实验室模拟装置是充分考虑了工业放大而设计的,用它进行一系列条件实验后,所确定的对应于该物料的最佳重金属离子的脱除效果的最重要电迁移操作参数——物料中的最佳“电位梯度”量值,其单位是“每米距离上的电位降”这一标准量值,所以可以直接提供作工业现场作业设计之用。之所以称之为“最佳电位梯度”,是因为:实验试样在实验槽中的体积是有限的,因此其相应的体电阻比实际庞大体积的自然堆积物料堆或土壤中都要大;换言之,即:在本实验装置上所获得的“最佳电压梯度”对应1M的阴阳电极距离,也对应着1M电极间距时可能出现的最大的体电阻。而在实际土壤中或者物料堆中,在1M间距的阴阳电极之间,所对应的体电阻都比实验装置的小,因此,能使得实验槽中较高的体电阻试样高效脱除重金属离子的实验电压梯度,用以作实际现场土壤或者物料中阴阳电极的布点间距或者作为设定脉冲电源最佳输出电压的计算依据,必然能获得比实验效果更高的重金属离子脱除效果。It should be pointed out that this laboratory simulation device is designed with full consideration of industrial scale-up. After a series of conditional experiments, the most important electric current corresponding to the best heavy metal ion removal effect of the material is determined. Migration operation parameters - the optimal "potential gradient" value in the material, its unit is the standard value of "potential drop per meter distance", so it can be directly provided for the design of industrial field operations. The reason why it is called "optimum potential gradient" is because: the volume of the experimental sample in the experimental tank is limited, so its corresponding volume resistance is larger than that of the actual bulky natural accumulation material pile or soil; In other words, the "best voltage gradient" obtained on this experimental device corresponds to the distance between the cathode and anode electrodes of 1M, and also corresponds to the maximum bulk resistance that may occur when the distance between the electrodes is 1M. In the actual soil or in the material pile, the corresponding volume resistance between the cathode and anode electrodes with a spacing of 1M is smaller than that of the experimental device. Therefore, the higher volume resistance samples in the experimental tank can efficiently remove heavy metal ions The experimental voltage gradient is used as the spacing between the cathode and anode electrodes in the actual field soil or material or as the calculation basis for setting the optimal output voltage of the pulse power supply. It is bound to obtain a higher heavy metal ion removal effect than the experimental effect.
A)长历时运行探索比较实验实例A) Example of long-duration operation exploration and comparison experiment
为了全面对比性说明“脉冲电动力学法”与已有“直流电动力学法”的脱除重金属离子效率之优劣,提供了“长历时运行对比”与“短历时运行对比”两类实例。In order to comprehensively illustrate the advantages and disadvantages of the removal efficiency of heavy metal ions between the "pulse electrokinetic method" and the existing "direct current electrokinetic method", two examples of "long-duration operation comparison" and "short-duration operation comparison" are provided.
所谓长历时运行,是指两种方法分别使用两个尺寸结构完全相同的电迁移槽,在除了电源不同之外其余初始条件完全相同的条件下,同时分别一次性开机后不停机连续运行5天(120h)或5天以上的运行方式,主要考查两种方法在能有效脱除重金属离子范围内的效果差异和方法的一次性可持久运行性能。The so-called long-duration operation means that the two methods use two electromigration cells with exactly the same size and structure, and under the same initial conditions except for the power supply, they run continuously for 5 days without stopping after starting up at one time. (120h) or more than 5 days of operation, mainly to examine the difference in the effect of the two methods in the range of effective removal of heavy metal ions and the one-time sustainable operation performance of the method.
本系列长历时对比实验采用了本发明实施方案1的模拟实验装置,详见图8。This series of long-duration comparative experiments adopts the simulation experiment device of
长历时运行实例1Long run
两种方法对铜离子污染土壤的120h修复效果对比Comparison of 120h remediation effect of two methods on copper ion polluted soil
为保证对比实验的准确性,特向同一无重金属污染实验土壤内均匀湿态配制入含量为500mg/kg的铜离子,形成Cu+2含量为500mg/kg试验土样再烘干待用,然后在保证除电源不同而其他初始条件及操作步骤完全相同的前提下,以120h的长历时运行时间对脉冲电动力学法和直流电动力学法脱除重金属离子效率进行对比实验。In order to ensure the accuracy of the comparison experiment, copper ions with a content of 500 mg/kg were specially prepared in the same wet state without heavy metal pollution to form a test soil sample with a Cu+2 content of 500 mg/kg, which was then dried for use, and then Under the premise of ensuring that the initial conditions and operation steps are identical except for the different power sources, a comparative experiment was carried out on the removal efficiency of heavy metal ions by the pulse electrokinetic method and the direct current electrokinetic method with a long running time of 120 hours.
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:电压梯度1.0v/cm;第一次开机后保持初始电压梯度不停机连续运行时间120h(5d)。DC power supply: the voltage gradient is 1.0v/cm; after the first start-up, the initial voltage gradient is maintained and the continuous operation time is 120h (5d).
脉冲电源:输入端口选市电输入端口,选用220V市电直接供电;输出为正脉冲峰值电压梯度1.0v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,,正脉冲施加时段600s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度1.0v/cm,反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段10s,第一次开机后保持初始峰值电压梯度不停机连续运行时间120h。Pulse power supply: the input port is the mains input port, and the 220V mains is used for direct power supply; the output is a positive pulse peak voltage gradient of 1.0v/cm, a positive pulse frequency of 25HZ, a positive pulse duty cycle of 50%, and a positive pulse application period of 600s; The reverse pulse peak voltage gradient is 1.0v/cm, the reverse pulse frequency is 25HZ, the reverse pulse duty cycle is 50%, the reverse pulse application period is 10s, and the initial peak voltage gradient is maintained for 120 hours without stopping after the first startup.
2)实验现象及结果:2) Experimental phenomena and results:
在开始24h内,两种方法的极间电流呈逐渐上升趋势,但脉冲法的极间脉冲峰值电流(平均值60mA)总是略大于直流法的极间电流(平均值50mA);In the first 24 hours, the inter-electrode currents of the two methods showed a gradual upward trend, but the inter-electrode pulse peak current (average value 60mA) of the pulse method was always slightly greater than the inter-electrode current (average value 50mA) of the DC method;
当一次性连续运行48h之后,脉冲法的峰值电流稳定在80mA左右,直流法电流稳定在55mA左右;当运行120h后,脉冲峰值电流仍旧稳定在80mA左右,而直流电流法电流锐减至19mA左右,正常有效运行已难以为继,也就是说,“直流法“运行120h之后,电极出现严重的极化现象而导致电阻增大并呈现出低效或无效运行状态;此时若要能再有效运行,必须或者提高直流电源电压,或者停止运行以化学方法清洗电极和调整PH值后再开机。After 48 hours of one-time continuous operation, the peak current of the pulse method is stable at about 80mA, and the current of the direct current method is stable at about 55mA; after 120 hours of operation, the peak current of the pulse is still stable at about 80mA, while the current of the direct current method drops sharply to about 19mA , the normal and effective operation is difficult to sustain, that is to say, after the "DC method" runs for 120 hours, the electrode will have serious polarization phenomenon, which will cause the resistance to increase and show an inefficient or invalid operation state; at this time, if it can be effectively To run, you must either increase the DC power supply voltage, or stop the operation to clean the electrodes chemically and adjust the pH value before restarting.
两种方法运行120h后,分别取处理土并样检测其中可溶性重金属离子残留量,结果是:直流电动力学法处理土样中重金属平均残留含量为234mg/kg,去除率仅为53.2%;而脉冲电动力学法处理土壤中平均残留量为仅为51.5mg/kg,去除率已达89.7%。对比实验说明在120h长历时运行时,脉冲电动力学法迁移重金属离子的效果远优于直流电动力学法。After the two methods were run for 120 hours, the treated soil was taken and sampled to detect the residual amount of soluble heavy metal ions. The results showed that the average residual content of heavy metals in the soil sample treated by DC electrokinetic method was 234 mg/kg, and the removal rate was only 53.2%. The average residual amount in the soil treated by the electrokinetic method is only 51.5mg/kg, and the removal rate has reached 89.7%. The comparison experiment shows that the effect of the pulse electrokinetic method for transferring heavy metal ions is far better than that of the direct current electrokinetic method when the long-duration operation is 120h.
120h以后,直流法若还要继续运行必须重新进行如下操作:或者在停机状态下重新调整土样PH值并清洗一次电极,或者提高供电电压方能再继续运行,然而这两种种状况已经属于其第二次运行了。由此我们可以有一个概括性的结论:对一次性开机后就不停机的长历时连续运行方式而言,脉冲电动力学法可以保持初始电位梯度和较高的重金属离子脱除效率而一直坚持到使脱除重金属指标达标目的为止,而直流法电动力学法则因电极极化致使电阻越来越大而无法一次性开机坚持到底;因此,在长历时原位处理方式之下,脉冲电动力学法具有的优势令直流电动力学法望尘莫及;从这一角度来看,在一次性开机后即不停机的长历时运行条件下,“直流电动力学法”几乎失去了与“脉冲电动力学法”的对等可比性。After 120 hours, if the DC method continues to operate, the following operations must be performed again: either readjust the pH value of the soil sample and clean the electrodes once in the shutdown state, or increase the power supply voltage to continue the operation. Run it for the second time. From this, we can draw a general conclusion: For the long-duration continuous operation mode without stopping after one-time start-up, the pulse electrokinetic method can maintain the initial potential gradient and high heavy metal ion removal efficiency and persist until Until the removal of heavy metals reaches the target, the electrokinetic method of the direct current method cannot be started at one time due to the increasing resistance due to electrode polarization; therefore, under the long-duration in-situ treatment method, the pulse electrokinetic method has the advantages The advantages of the direct current electrodynamics method are far behind; from this point of view, the "direct current electrodynamics method" has almost lost its equivalence with the "pulse electrodynamics method" comparability.
长历时运行实例2Long run instance 2
两种方法对剩余活性污泥中重金属离子的120h脱除效率对比Comparison of 120h removal efficiency of heavy metal ions in excess activated sludge by two methods
同样,为保证对比实验的准确性,特向同一污水厂所取的脱水后剩余活性污泥内均匀湿态配制入一定含量的铜离子,使之形成重金属离子总含量为700mg/kg试验泥样,然后在保证除电源不同而其他初始条件完全相同的前提下,以120h的长历时运行时间对脉冲电动力学法和直流电动力学法脱除重金属离子效率进行对比实验。Similarly, in order to ensure the accuracy of the comparison experiment, a certain amount of copper ions was prepared in the uniform wet state of the remaining activated sludge after dehydration taken from the same sewage plant to form a test mud sample with a total content of heavy metal ions of 700mg/kg. , and then under the premise of ensuring that the initial conditions are identical except for the different power sources, a comparative experiment was carried out on the removal efficiency of heavy metal ions by the pulse electrokinetic method and the direct current electrokinetic method with a long running time of 120 h.
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:电压梯度1.0v/cm;第一次开机后保持初始电压梯度不停机连续运行时间120h(5d)。DC power supply: the voltage gradient is 1.0v/cm; after the first start-up, the initial voltage gradient is maintained and the continuous operation time is 120h (5d).
脉冲电源:输入端口12V/24V直流端口,选择实验室型太阳能充电/蓄电供电器,供电电压直流12V,最大电流200mA;输出正脉冲峰值电压梯度1.0v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,,正脉冲施加时段1200s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度1.0v/cm,反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段20s,第一次开机后保持初始峰值电压梯度不停机连续运行时间120h。Pulse power supply: input port 12V/24V DC port, choose laboratory solar charging/storage power supply, supply voltage DC 12V, maximum current 200mA; output positive pulse peak voltage gradient 1.0v/cm, positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse The duty cycle is 50%, the positive pulse application period is 1200s; the reverse pulse peak voltage gradient is 1.0v/cm, the reverse pulse frequency is 25HZ, the reverse pulse duty cycle is 50%, the reverse pulse application period is 20s, and the initial peak value is maintained after the first power-on The continuous running time of voltage gradient without stopping is 120h.
2)实验现象及结果:2) Experimental phenomena and results:
在开始24h内,两种方法的极间电流呈逐渐上升趋势,但脉冲法的极间脉冲峰值电流(平均值86mA)总是略大于直流法的极间电流(平均值64mA);In the first 24 hours, the inter-electrode currents of the two methods showed a gradual upward trend, but the inter-electrode pulse peak current (average value 86mA) of the pulse method was always slightly greater than the inter-electrode current (average value 64mA) of the DC method;
当一次性连续运行48h之后,脉冲法的峰值电流稳定在95mA左右,直流法电流稳定在78mA左右;当运行120h后,脉冲峰值电流仍旧稳定在95mA左右,而直流电流法电流下降至24mA左右,正常有效运行已难以为继,此时若要能有效运行,必须提高直流电源电压,在更高的电位梯度下方能维持原有78mA左右电流。After 48 hours of one-time continuous operation, the peak current of the pulse method is stable at about 95mA, and the current of the direct current method is stable at about 78mA; after 120 hours of operation, the peak current of the pulse is still stable at about 95mA, while the current of the direct current method drops to about 24mA. Normal and effective operation is difficult to sustain. At this time, in order to operate effectively, the DC power supply voltage must be increased, and the original current of about 78mA can be maintained under a higher potential gradient.
两种方法运行120h后,分别取处理泥样并样检测其中可溶性铜离子残留量,结果是:直流电动力学法处理土样中重金属平均残留含量为302.4mg/kg,去除率仅为56.8%;而脉冲电动力学法处理土壤中平均残留量为仅为87.5mg/kg,去除率已达87.5%。对比实验说明在120h长历时运行时脉冲电动力学法从污泥中脱除可溶性重金属离子的效果也远优于直流电动力学法。而且运行至此,脉冲电动力学法仍能继续高效运行,直流电动力学法因电极极化而电阻越来越大,已经无法继续有效运行而几乎失去与脉冲电动力学法的对等可比性了。After the two methods were run for 120 hours, the treated mud samples were taken and tested for the residual amount of soluble copper ions. The results showed that the average residual content of heavy metals in the soil samples treated by DC electrokinetic method was 302.4mg/kg, and the removal rate was only 56.8%; However, the average residual amount in the soil treated by the pulse electrokinetic method is only 87.5 mg/kg, and the removal rate has reached 87.5%. The comparison experiment shows that the pulse electrokinetic method is far superior to the direct current electrokinetic method in removing soluble heavy metal ions from sludge during 120h long-duration operation. And so far, the pulse electrokinetic method can still continue to operate efficiently. The resistance of the direct current electrokinetic method is getting larger and larger due to electrode polarization.
(二)短历时(24h)脱除重金属离子效率对比:(2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions in short duration (24h):
鉴于电动力学脱除可溶性重金属离子方法若要进行到土壤或者物料中重金属离子低于容许含量,需数百小时甚至数千小时,运行时间很长,而在这样长的时间段内,“直流电动力学法”因电极极化严重和土壤或物料中PH不均衡的问题根本不可能一次性开机后运行到底,而是必须多次中断运行以人工清洗电极和调整PH值,这与本发明提供的因为具有以周期性自动施加的反向脉冲电流动态消除了电极极化现象、而且不加任何药剂不停机自动调适PH值的优点、故可以在一次性开机后即可不停机长时间运行到底的“脉冲电动力学法”难以对等比较,而且做这种比较实验的时间太长,因此,为缩短对等比较实验时间,在往后试验中,我们采用在除电源不同之外的其他初始实验条件完全相同的前提下,比较“直流电动力学法”和“脉冲电动力学法”在相同短历时运行时间段(24h)上的重金属离子脱除率,或者在该时间段内比较在达到相同重金属离子脱除率时各自所用的时间,以此来快速评价并进一步证实这两种方法孰优孰劣。显然,对于运行相同时间后,重金属离子脱除率高者为优,而相应地,对于达到相同去除率,所用时间短者为优。探索实验证实,两种判断方式可能数据上有微小差异,但其所评判的优劣结论却都是一样的。In view of the electrokinetic removal of soluble heavy metal ions, if the heavy metal ions in the soil or material are lower than the allowable content, it takes hundreds or even thousands of hours, and the operation time is very long. In such a long period of time, "DC electric power Because of serious electrode polarization and PH imbalance in soil or materials, it is impossible to run to the end after one-time start-up, but the operation must be interrupted many times to manually clean the electrodes and adjust the PH value, which is different from that provided by the present invention. Because it has the advantages of dynamically eliminating the electrode polarization phenomenon by periodically automatically applying reverse pulse current, and automatically adjusting the pH value without adding any medicine, it can run to the end without stopping for a long time after one-time startup. "Pulse electrodynamics method" is difficult to compare equally, and the time to do this kind of comparison experiment is too long. Therefore, in order to shorten the time of equivalent comparison experiment, in the future test, we use other initial experimental conditions except power supply. Under exactly the same premise, compare the heavy metal ion removal rate of "DC electrokinetic method" and "pulse electrokinetic method" in the same short-duration operation period (24h), or compare the removal rate of heavy metal ions in the same short period of time during this period. The time taken for each removal rate can be used to quickly evaluate and further confirm which of the two methods is better. Obviously, after running for the same time, the one with the higher removal rate of heavy metal ions is the best, and correspondingly, for the same removal rate, the one with the shortest time is the best. Exploratory experiments have confirmed that the two judgment methods may have slight differences in data, but the conclusions of their judgments are the same.
短历时(24h)运行对比实验,采用本专利实施方案2的实验模拟装置,详见图9。For the short-duration (24h) comparative experiment, the experimental simulation device of Embodiment 2 of this patent is used, as shown in FIG. 9 for details.
为保证对比性实验结论的准确性,首先就必须保证实验条件的严格相同。即是除了电源不相同之外,其他实验原始条件都严格相同。这些原始条件包括采用同样重量的含可溶性重金属离子量一定的同一物料的试样、同样的电极和电极间距,同量同种同样方式加入的用以浸融重金属离子的水,以确保试样中均匀分布有等量的含重金属离子浓度相等的水而呈现其含水率的相同。具体作法是:选用两个结构尺寸完全一样的有机玻璃(槽尺寸1060*100*150mm,电极皆为相同结构直径为30mm的组合式电阴极和电阳极,电极间距1000mm)实验槽,分别装入重量精确相等的同一种实验泥样(为准确控制对比实验,该物料事先被人为配制)In order to ensure the accuracy of the conclusions of the comparative experiments, it is first necessary to ensure that the experimental conditions are strictly the same. That is to say, except that the power supply is different, the original conditions of other experiments are strictly the same. These original conditions include the use of the same weight of samples of the same material containing a certain amount of soluble heavy metal ions, the same electrodes and electrode spacing, and the same amount of water added in the same way to immerse heavy metal ions to ensure Evenly distributed with the same amount of water containing the same concentration of heavy metal ions to present the same water content. The specific method is: select two plexiglass with exactly the same structural size (the tank size is 1060*100*150mm, the electrodes are all combined electric cathodes and electric anodes with the same structural diameter of 30mm, and the electrode spacing is 1000mm) experimental tanks, and put them into the experimental tanks respectively. The same experimental mud sample with the exact same weight (in order to accurately control the comparison experiment, the material was artificially prepared in advance)
加入一定量一定浓度的重金属盐类溶液,均匀混合并晾干后待用,因此其可溶性重金属离子含量是已知的,并且分别均匀压实到两槽泥样两端用插入电阻表笔以同样的测量方式所测得的物料体电阻完全相同为止(即保证两个槽中物料的堆比重完全相同),再分向槽中别加入相同体积的蒸馏水,也向阴阳极室加入同样高度的蒸馏水以作电极室液。实施如上措施后,最终形成两个实验槽完全相同的初始实验条件。之后,将其中一套实验装置作为对比实验样接上直流电源,而另一套实验装置作为主实验样接上脉冲电源,并分别调整两电源至相同的电压值,并同时开始各自的脱除可溶性重金属离子的实验。值得一提的是:所谓“相同的电源电压值”,是指:直流恒定电源的电压量值与脉冲电源的峰值电压量值相等;但事实上,在直流恒定电源的恒定电压量值与脉冲电源的峰值电压量值相等相等的条件下,脉冲电源的电耗比直流电源的小,原因是在相同的施加时段内,Add a certain amount of heavy metal salt solution with a certain concentration, mix evenly and dry it before use, so the content of soluble heavy metal ions is known, and they are evenly compacted to both ends of the mud sample in the two tanks. Until the resistance of the material body measured by the measurement method is exactly the same (that is, to ensure that the bulk specific gravity of the material in the two tanks is exactly the same), then add the same volume of distilled water to the tank, and add distilled water of the same height to the anode and cathode chambers. For the electrode chamber fluid. After the above measures are implemented, the two experimental tanks are finally formed with identical initial experimental conditions. Afterwards, one set of experimental devices was connected to a DC power supply as a comparative experimental sample, while the other set of experimental devices was connected to a pulse power supply as a main experimental sample, and the two power supplies were adjusted to the same voltage value, and their respective removal Experiments with soluble heavy metal ions. It is worth mentioning that the so-called "same power supply voltage value" means: the voltage value of the DC constant power supply is equal to the peak voltage value of the pulse power supply; but in fact, the constant voltage value of the DC constant power supply is the same as the pulse power supply Under the condition that the peak voltage magnitude of the power supply is equal, the power consumption of the pulse power supply is smaller than that of the DC power supply, because in the same application period,
脉冲电源的连续施加时间比率必然小于直流恒定电源的连续施加的时间比率;但是由于脉冲电场力具有冲击式的做功特性,因此其对物料中重金属离子呈现跳跃式的迁移,因此,脉冲电源在能耗低于直流恒流电源的情况下,对重金属离子迁移的迁移脱除速度却高于直流恒定电源。这一原理就是本发明的技术本质和创新性之所在。。The continuous application time ratio of the pulse power supply must be less than the continuous application time ratio of the DC constant power supply; however, because the pulse electric field force has an impact-type work characteristic, it shows a jumping migration of heavy metal ions in the material. When the power consumption is lower than that of a DC constant current power supply, the migration and removal speed of the migration of heavy metal ions is higher than that of a DC constant current power supply. This principle is where the technical essence and innovativeness of the present invention are. .
鉴于阴极室液的电导率的增加直接正相关于被电场力从物料中所移出来的重金属离子的量,而当污染物中重金属离子占绝大比重的情况下,可以认为阴极室液的电导率的增加直接正比于被电场力从物料中所移出来的重金属离子的量。因此,为在短时间内获得实时比较实验数据,本实验采用测量阴极室液电导变化的方式来衡量设备系统的重金属离子的脱出效果;又鉴于要证明本发明技术的先进性及优越性的最好办法,莫过于通过与已有的直流电动力学法进行对比性实验以比较出而者重金属离子脱除效果之高低,因此决定以直流电脱除装置的阴极室的电导为计量基准来衡量脉冲电脱除装置阴极室液的电导变化,即是:以直流电脱除实验装置的阴极室液的在某时间点上的相对于初始时间点的实测电导增量为100%,来衡量同一时间点上的脉冲电脱除实验装置阴极室液的电导变化增量,以此获得两种脱除方法效果优劣的相对对比数据。具体计算公式是:In view of the fact that the increase of the conductivity of the cathodic chamber liquid is directly related to the amount of heavy metal ions removed from the material by the electric field force, and when the heavy metal ions account for a large proportion of the pollutants, it can be considered that the conductivity of the cathodic chamber liquid The increase in the rate is directly proportional to the amount of heavy metal ions removed from the material by the electric field force. Therefore, in order to obtain real-time comparative experimental data in a short period of time, this experiment adopts the mode of measuring the catholyte liquid conductance change to measure the detachment effect of the heavy metal ion of the equipment system; A good way is to conduct a comparative experiment with the existing DC electrokinetic method to compare the removal effect of heavy metal ions. Therefore, it is decided to use the conductance of the cathode chamber of the DC removal device as the measurement benchmark to measure the pulse current. The conductance change of the cathodic chamber liquid of the removal device is: the measured conductance increment of the cathodic chamber liquid of the direct current removal experimental device at a certain time point relative to the initial time point is 100%, which is measured at the same time point. The conductance change increment of the cathodic chamber liquid in the pulse electric removal experimental device is used to obtain the relative comparison data of the advantages and disadvantages of the two removal methods. The specific calculation formula is:
换言之也即等同于:In other words it is equivalent to:
以下列出若干“脉冲电动力学法”与“直流电动力学法”脱除重金属离子效果优劣的短历时实验对比系列实例。实例采用24小时连续运行终了时的两种方法对重金属离子的相对脱除率来加以定量比较。A series of short-duration experiments comparing the advantages and disadvantages of the "pulse electrokinetic method" and "direct current electrokinetic method" in removing heavy metal ions are listed below. Example Two methods at the end of 24 hours of continuous operation were used to quantitatively compare the relative removal rates of heavy metal ions.
为了便于比较,更为了比较结论的准确,选用单一Cu+2盐类加入土壤或泥状粉状固废物料中,人工制备成含可溶性Cu+2离子为准确已知的模拟含重金属离子实验样,这样可以使阴极电导率增量基本正比于Cu+2脱除率。For the convenience of comparison and the accuracy of the comparison conclusion, a single Cu+2 salt was selected to be added to soil or muddy powdery solid waste materials, and artificially prepared to simulate experimental samples containing heavy metal ions containing soluble Cu+2 ions. , so that the increase in cathode conductivity is basically proportional to the removal rate of Cu+2 .
短历时(24h)运行对比系列实例1Short duration (24h) operation comparison series example 1
——对不同重金属离子含量土壤重金属离子脱除的短历时运行效果对比汇总——Comparative summary of short-duration operation effects on the removal of heavy metal ions from soils with different heavy metal ion contents
对同一实验土壤均匀配制入不同含量的铜离子,然后分别按上述其他相同初始条件,对含Cu+2量不同的试样进行对比实验。短历时试验中,脉冲电源输入端口的选择一律使用市电输入端口,直接由交流220V市电供电。The same experimental soil was uniformly prepared with different contents of copper ions, and then the comparative experiments were carried out on samples with different amounts of Cu+2 according to the other same initial conditions mentioned above. In the short-duration test, the selection of the input port of the pulse power supply all uses the mains input port, which is directly powered by the AC 220V mains.
【1-1】Cu+2含量为0.002%试验土样【1-1】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.002%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:电压梯度0.5v/cm;连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: voltage gradient 0.5v/cm; continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,,正脉冲施加时段600s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5v/cm,反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段3s,连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5v/cm, positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50%, positive pulse application period 600s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 25HZ, reverse pulse The duty cycle is 50%, the anti-pulse application period is 3s, and the continuous operation time is 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法110%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 110%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高10%The efficiency of the pulse method is 10% higher than that of the DC method
【1-2】Cu+2含量为0.003%试验土样【1-2】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.003%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:电压梯度1.5v/cm;连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: voltage gradient 1.5v/cm; continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度1.5v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,正脉冲施加时段600s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度1.5v/cm,反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉施加时段5s,连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 1.5v/cm, positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50%, positive pulse application period 600s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 1.5v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle The duty ratio is 50%, the reverse pulse application period is 5s, and the continuous operation time is 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法122.6%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 122.6%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高22.6%The efficiency of the pulse method is 22.6% higher than that of the DC method
【1-3】Cu+2含量为0.004%试验土样【1-3】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.004%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:电压梯度2v/cm;连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: voltage gradient 2v/cm; continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度2v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,正向脉冲施加时段600s;反脉冲电压梯度2v/cm,反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段6s,连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 2v/cm, positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50%, forward pulse application period 600s; reverse pulse voltage gradient 2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%, the anti-pulse application period is 6s, and the continuous operation time is 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法128.3%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 128.3%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高28.3%The efficiency of the pulse method is 28.3% higher than that of the DC method
【1-4】Cu+2含量为0.04%试验土样【1-4】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.04%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:直流电压梯度1.5v/cm;连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: DC voltage gradient 1.5v/cm; continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度1.5v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占比50%,正脉冲施加时段600s;反脉冲电压梯度2v/cm,反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段3s,连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 1.5v/cm, positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse proportion 50%, positive pulse application period 600s; reverse pulse voltage gradient 2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50 %, the anti-pulse application period is 3s, and the continuous operation time is 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法120%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 120%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高20%The efficiency of the pulse method is 20% higher than that of the DC method
【1-5】Cu+2含量为0.01%试验土样【1-5】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.01%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:直流电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验);连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: DC voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments); continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验),正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,正脉冲施加时段600s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验),反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段7s,连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments), positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50%, positive pulse application period 600s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments), reverse pulse frequency 25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%, reverse pulse application period 7s, continuous operation time 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法111.2%-124.6%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 111.2%-124.6%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高11.2%-24.6%The efficiency of the pulse method is 11.2%-24.6% higher than that of the DC method
【1-6】Cu+2含量为0.05%试验土样【1-6】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.05%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:直流电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验);连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: DC voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments); continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,正脉冲施加时段600s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验),反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段5s;连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50%, positive pulse application period 600s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 Four groups of experiments), the counter pulse frequency is 25HZ, the counter pulse duty cycle is 50%, the counter pulse application period is 5s; the continuous operation time is 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法110.6%-128.8%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 110.6%-128.8%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高10.6%-28.8%The efficiency of the pulse method is 10.6%-28.8% higher than that of the DC method
【1-7】Cu+2含量为0.1%试验土样【1-7】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.1%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:直流电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验);连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: DC voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments); continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验),正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比,正脉冲施加时段900s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲电流作用时段10s;连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments), positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle, positive pulse application period 900s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5- 2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%, reverse pulse current action period 10s; continuous operation time 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法119.8%-138.8%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 119.8%-138.8%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高19.8%-38.8%The efficiency of the pulse method is 19.8%-38.8% higher than that of the DC method
【1-8】Cu+2含量为0.1%试验土样【1-8】Test soil sample with Cu+2 content of 0.1%
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:直流电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验);连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: DC voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments); continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率25HZ,正脉冲占空比50%,正脉冲施加时段1200s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验),反脉冲频率25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%,反脉冲施加时段5s;连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, positive pulse frequency 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50%, positive pulse application period 1200s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 Four groups of experiments), the counter pulse frequency is 25HZ, the counter pulse duty cycle is 50%, the counter pulse application period is 5s; the continuous operation time is 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法118.1%-131.5%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 118.1%-131.5%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高18.1%-31.5%The efficiency of the pulse method is 18.1%-31.5% higher than that of the DC method
【1-9】Cu+2含量为0.1%试验土样变动电压梯度对比实验【1-9】Cu+2 content of 0.1% test soil sample change voltage gradient comparison experiment
1)电源操作条件:1) Power supply operating conditions:
直流电源:直流电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验);连续运行时间24h。DC power supply: DC voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments); continuous operation time 24h.
脉冲电源:正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0四组实验),正脉冲频率0.017HZ,正脉冲占空比97%,正脉冲施加时段1200s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ,反脉冲占空比95%,反脉冲施加时段30s;连续运行时间24h。Pulse power supply: positive pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 four groups of experiments), positive pulse frequency 0.017HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 97%, positive pulse application period 1200s; reverse pulse peak voltage Gradient 0.5-2v/cm, back pulse frequency 0.017HZ, back pulse duty cycle 95%, back pulse application period 30s; continuous operation time 24h.
2)脱除重金属离子效率对比:2) Comparison of removal efficiency of heavy metal ions:
直流法:100% 脉冲法125%-155,7%,DC method: 100% Pulse method 125%-155, 7%,
脉冲法效率比直流法效率提高25%-55.7%The efficiency of the pulse method is 25%-55.7% higher than that of the DC method
归结【1-1】至【1-9】的系列对比运行实验可以证实,经过24h短历时对比运行,两种方法对重金属污染土壤中可溶性重金属离子的电动力学脱除效果比较而呈现出的规律是:在直流电源工作电压梯度与脉冲电源峰值工作电压梯度量值相同、以及在试样的各种初始条件完全相同的下,脉冲电动力学脱除效果皆优于直流电动力学脱除效果。即:当土壤中Cu+2在含量在0.002%-0.1%之间,所施加直流电源的直流电压梯度为0.5-2v/cm,脉冲电源的正脉冲峰值电压梯度为0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率为0.017-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-97%,正脉冲施加时段600s-1200s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度为0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率为0.017-25HZ,反脉冲占空比为50-95%,反脉冲施加时段3-30s的电源操作条件取值范围内,同时经过24h短历时运行,脉冲法脱除重金属离子效率普遍比直流法提高10%-55%左右。The series of comparative operation experiments concluded from [1-1] to [1-9] can confirm that after 24h short-duration comparative operation, the two methods show the same rule in the comparison of the electrokinetic removal effects of soluble heavy metal ions in heavy metal polluted soil Yes: when the working voltage gradient of the DC power supply is the same as the peak working voltage gradient of the pulse power supply, and under the same initial conditions of the sample, the removal effect of pulse electrokinetics is better than that of DC electrokinetics. That is: when the content of Cu+2 in the soil is between 0.002%-0.1%, the DC voltage gradient of the applied DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, and the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of the pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm. The pulse frequency is 0.017-25HZ, the positive pulse duty ratio is 50-97%, the positive pulse application period is 600s-1200s, the reverse pulse peak voltage gradient is 0.5-2v/cm, the reverse pulse frequency is 0.017-25HZ, the reverse pulse duty cycle It is 50-95%, within the value range of the power supply operating conditions for the counter pulse application period of 3-30s, and after 24h short-duration operation, the efficiency of the pulse method for removing heavy metal ions is generally 10%-55% higher than that of the DC method.
短历(24h)时运行系列对比实验实例2Short-calendar (24h) operation series comparison experiment example 2
对活性污泥中可溶性重金属离子的去除Removal of soluble heavy metal ions in activated sludge
以下实验是一系列不同重金属含量活性污泥试样,并变动不同操作条件的实验结果汇总。The following experiments are a summary of the experimental results of a series of activated sludge samples with different heavy metal contents and different operating conditions.
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法对活性污泥中可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率也总是优于直流电动力学脱除法。具体系列实例为:而当活性污泥中Cu+2含量范围为0.002%-0.1%,电操作参数的设定值取值范围为直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,脉冲占空比50%-98%,正脉冲施加时段600s-1800s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%,反脉冲施加时段1-30s的电源操作条件范围内,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了8%-52%左右。The comparative experiments of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time show that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrokinetic method has no effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in activated sludge is always better than that of direct current electrokinetic removal method. The specific series of examples are: when the Cu+2 content range in the activated sludge is 0.002%-0.1%, the set value range of the electric operation parameter is the DC power supply working voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm; the pulse power supply positive pulse peak value Voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, positive pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, pulse duty cycle 50%-98%, positive pulse application period 600s-1800s, reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ -25HZ, counter-pulse duty cycle 50%-98%, and counter-pulse application period 1-30s within the range of power supply operating conditions, the efficiency of the pulse method is generally 8%-52% higher than that of the DC method.
短历(24h)时系列对比运行实验实例3Short-calendar (24h) time series comparative operation experiment example 3
湖泊清淤底泥中可溶性重金属离子的去除Removal of Soluble Heavy Metal Ions in Lake Dredged Sediment
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法对水体清淤底泥的可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率也皆优于直流电动力学法。具体系列实例为:而当活性污泥中Cu+2含量为0.002%-0.1%,采用直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲施加600s-1800s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%,反脉冲施加时段1-30s的电源操作条件范围内,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了7%-50%左右。The comparative experiments of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time show that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrokinetic method has no effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in the dredged sediment of the water body is also better than that of the direct current electrokinetic method. The specific series of examples are: when the Cu+2 content in the activated sludge is 0.002%-0.1%, the working voltage gradient of the DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm; the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of the pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, and the positive pulse Frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50-98%, positive pulse application 600s-1800s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%- 98%, within the range of power supply operating conditions in which the counter pulse application period is 1-30s, the efficiency of the pulse method is generally improved by about 7%-50% compared with the DC method.
短历时(24h)运行系列对比实验实例4Short duration (24h) operation series comparison experiment example 4
电镀混合污泥中重金属离子的去除Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Electroplating Mixed Sludge
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法对电镀混合污泥的可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率皆优于直流电动力学法。而当活性污泥中各种重金属离子总含量为0.002%-0.1%,采用直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲施加时段600s-3600s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%,反脉冲施加时段1-60s的电源操作条件范围内,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了6%-48%左右。The comparative experiments of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time show that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrokinetic method has no effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in electroplating mixed sludge is better than that of direct current electrokinetic method. And when the total content of various heavy metal ions in the activated sludge is 0.002%-0.1%, the working voltage gradient of the DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm; the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of the pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, and the positive pulse frequency is 0.017HZ -25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50-98%, positive pulse application period 600s-3600s, reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%-98% , within the range of power supply operating conditions where the anti-pulse application period is 1-60s, the efficiency of the pulse method is generally increased by about 6%-48% compared with the DC method.
短历时(24h)运行系列对比实验实例5Short duration (24h) operation series comparison experiment example 5
学校化学实验室排水沟清淤底泥中重金属离子的去除Removal of heavy metal ions in the dredged sediment of drainage ditches in school chemistry laboratory
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法对化学实验室排水沟清淤底泥中的可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率皆优于直流电动力学法。具体实例为:而当活性污泥中各种重金属离子总含量为0.002%-0.1%,采用直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲施加时段600s-3600s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%反脉冲施加时段1-60s的电源操作条件范围内,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了5%-45%左右。The comparative experiments of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time show that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrokinetic method has no effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in the dredged sediment of chemical laboratory drainage ditch is better than that of direct current electrokinetic method. The specific example is: when the total content of various heavy metal ions in the activated sludge is 0.002%-0.1%, the working voltage gradient of the DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm; the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of the pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, and the positive pulse Frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50-98%, positive pulse application period 600s-3600s, reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50% -98% The efficiency of the pulse method is generally increased by about 5%-45% compared with the direct current method within the power supply operating condition range of the application period of -98% counter pulse 1-60s.
短历时(24h)运行系列对比实例6Comparative example of short duration (24h) running
铜矿尾矿矿泥中重金属离子的去除Removal of heavy metal ions in copper ore tailings slime
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法对铜矿尾矿矿泥中的可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率亦皆优于直流电动力学法。而当活性污泥中各种重金属离子总含量为0.002%-0.1%,采用直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲施加时段600s-3600s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%反脉冲施加时段1-60s的电源操作条件范围内,,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了5%-47%左右。The comparative experiments of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time show that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrokinetic method has no effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in copper ore tailings slime is also better than that of direct current electrokinetic method. And when the total content of various heavy metal ions in the activated sludge is 0.002%-0.1%, the working voltage gradient of DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm; the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, and the positive pulse frequency is 0.017HZ- 25HZ, positive pulse duty cycle 50-98%, positive pulse application period 600s-3600s, reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%-98% reverse Within the range of power supply operating conditions for the pulse application period of 1-60s, the efficiency of the pulse method is generally increased by about 5%-47% compared with the DC method.
短历时(24h)运行系列对比实验实例7Short duration (24h) operation series comparison experiment example 7
校医院X光胶片冲洗阴沟清淤底泥中重金属离子去除Removal of heavy metal ions in sewer dredging sediment by X-ray film washing in school hospital
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电化学法对X光胶片冲洗阴沟清淤底泥中的可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率皆优于直流电化学脱除法。而当该底泥中重金属离子总含量为0.002%-0.1%,采用直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲电流连续工作时间600s-3600s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%反脉冲施加时段1-60s的电源操作条件范围内,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了5%-42%左右。The comparison experiment of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time shows that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrochemical method has the best effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in ditch dredging sediment by X-ray film washing is better than that of direct current electrochemical removal method. And when the total content of heavy metal ions in the sediment is 0.002%-0.1%, the working voltage gradient of DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm; the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, and the positive pulse frequency is 0.017HZ-25HZ, Positive pulse duty cycle 50-98%, positive pulse current continuous working time 600s-3600s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%-98% reverse In the range of power supply operating conditions with the pulse application period of 1-60s, the efficiency of the pulse method is generally increased by about 5%-42% compared with the DC method.
短历时(24h)运行系列对比实验实例8Short duration (24h) operation series comparison experiment example 8
金矿浮选尾矿矿泥中重金属离子的去除Removal of heavy metal ions in gold ore flotation tailings slime
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法对金矿浮选尾矿矿泥中的可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率皆优于直流电动力学法。而当该底泥中重金属离子总含量为0.002%-0.1%,采用直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲施加时段600s-3600s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%反脉冲施加时段1-60s的电源操作条件范围内,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了8%-41%左右。The comparative experiments of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time show that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrokinetic method has no effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in gold ore flotation tailings slime is better than that of direct current electrokinetic method. And when the total content of heavy metal ions in the sediment is 0.002%-0.1%, the working voltage gradient of DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm; the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, and the positive pulse frequency is 0.017HZ-25HZ, Positive pulse duty cycle 50-98%, positive pulse application period 600s-3600s, reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%-98% reverse pulse application Within the range of power supply operating conditions for a period of 1-60s, the efficiency of the pulse method is generally increased by about 8%-41% compared with the DC method.
短历时(24h)运行系列对比实验实例9Short duration (24h) operation series comparison experiment example 9
带丰富腐殖质的褐色粘土中重金属离子的去除(亦即电化学修复)Removal of heavy metal ions from brown clay rich in humus (i.e. electrochemical remediation)
两种方法分别同时连续运行24h终了的对比实验表明:在直流电源施加于试样的电压梯度与脉冲电源施加于相同原始条件试样的脉冲峰值电压梯度数值相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法对带丰富腐殖质的褐色粘土中的可溶性重金属离子的脱除效率皆优于直流电动力学法。而当该土壤中重金属离子总含量为0.002%-0.1%,采用直流电源工作电压梯度0.5-2v/cm;脉冲电源正脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲电流连续工作时间600s-3600s;反脉冲峰值电压梯度0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率0.017HZ-25HZ,反脉冲占空比50%-98%反脉冲施加时段1-60s的电源操作条件范围内,脉冲法比直流法效率普遍提高了5%-35%左右。The comparative experiments of the two methods running continuously for 24 hours at the same time show that: under the condition that the voltage gradient applied by the DC power supply to the sample is equal to the value of the pulse peak voltage gradient applied by the pulse power supply to the sample under the same original condition, the pulse electrokinetic method has no effect on the sample. The removal efficiency of soluble heavy metal ions in brown clay rich in humus is better than that of direct current electrokinetic method. And when the total content of heavy metal ions in the soil is 0.002%-0.1%, the working voltage gradient of DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm; the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, the positive pulse frequency is 0.017HZ-25HZ, Pulse duty cycle 50-98%, positive pulse current continuous working time 600s-3600s; reverse pulse peak voltage gradient 0.5-2v/cm, reverse pulse frequency 0.017HZ-25HZ, reverse pulse duty cycle 50%-98% reverse pulse Within the range of power supply operating conditions for an application period of 1-60s, the efficiency of the pulse method is generally increased by about 5%-35% compared with the DC method.
对以上九种物料中的可溶性重金属离子的脱除对比性实验皆显示:对于电动力学方法从物料堆中或者土壤中去除可溶性重金属离子而言,所施于物料中的工作电压梯度是一个重要的电参数;而在直流工作电压梯度与脉冲工作峰值电压梯度在数值上相等的条件下,脉冲电动力学法在重金属离子去除效率上不仅都普遍高于直流电动力学法的效率,而且电耗降低。究其原因,就是因为在直流工作电压梯度与脉冲工作峰值电压梯度在数值上相等的条件下,在同一时间段上脉冲电流的施加时间比率总小于直流电流的施加时间比率;而且,脉冲电化学场所产生的对重金属离子的“跳跃式”迁移方式,比之于直流电化学场产生的平稳迁移方式不仅省电力而且省时间。在达到相同迁移效果(阴极室液电导增量相同)的情况下,脉冲电动力学法在时间上比之于直流电动力法在时间上普遍缩短了大约5%-50%;而从另一种角度来评价,则是在处理时间相同(以上实例皆以24h为连续运行时间)的情况下,脉冲电动力学法在迁移重金属离子效率上比之于直流电动力学法在移出重金属离子的效率(亦即该时间末阴极室液中电导增量的比较)普遍提高了大约5%-50%。The comparative experiments on the removal of soluble heavy metal ions in the above nine materials all show that: for the electrokinetic method to remove soluble heavy metal ions from material piles or soil, the working voltage gradient applied to the material is an important factor. Electrical parameters; and under the condition that the DC working voltage gradient and the pulse working peak voltage gradient are numerically equal, the removal efficiency of heavy metal ions in the pulse electrokinetic method is not only generally higher than that of the DC electrokinetic method, but also reduces the power consumption. The reason is that under the condition that the DC working voltage gradient and the pulse working peak voltage gradient are numerically equal, the application time ratio of the pulse current in the same time period is always smaller than the application time ratio of the DC current; moreover, the pulse electrochemical The "jumping" migration mode of heavy metal ions generated by the field, compared with the smooth migration mode generated by the DC electrochemical field, not only saves power but also saves time. In the case of achieving the same migration effect (the increase in the conductivity of the cathodic chamber liquid is the same), the pulse electrokinetic method generally shortens the time by about 5%-50% compared with the DC electrodynamic method; and from another perspective To evaluate, then under the condition of the same processing time (the above examples all take 24h as the continuous running time), the efficiency of the pulse electrokinetic method in the transfer of heavy metal ions is compared to the efficiency of the direct current electrokinetic method in removing heavy metal ions (that is, Comparison of the increase in conductance in the catholyte at the end of this time) generally increased by about 5% to 50%.
值得提醒的是:随着一次开机即不停机连续运行时间的推移,这两种方法的重金属离子相对脱除率差距将越来越大,实验表明,当连续运行时间大于240h后,直流电动力学方法的电极间电流已经衰减了初始值的90%而使重金属离子脱除绝对量大幅度减少,此时必须停机进行电极极化清除及PH调整,否则只能靠提高处理电压(等同于提高电能损耗)来克服电极极化,以维持能有效脱除重金属离子的极间电流;而相比之下,本发明的“脉冲电动力学法”,则基本保持着初始脉冲峰值电流的幅值,除非土壤中或物料中可溶性重金属离子已经绝大部分被脱除才会产生明显衰减。It is worth reminding that: as the continuous operation time without stopping after one start, the difference in the relative removal rate of heavy metal ions between the two methods will become larger and larger. Experiments show that when the continuous operation time is greater than 240h, the DC electrodynamic The current between the electrodes of the method has attenuated 90% of the initial value and the absolute amount of heavy metal ion removal has been greatly reduced. At this time, the electrode polarization removal and pH adjustment must be stopped. Loss) to overcome the electrode polarization to maintain the inter-electrode current that can effectively remove heavy metal ions; in contrast, the "pulse electrokinetic method" of the present invention basically maintains the amplitude of the initial pulse peak current unless Significant attenuation occurs only when most of the soluble heavy metal ions in the soil or materials have been removed.
对于采用电动力学去除物料堆或者土壤中可溶性重金属离子而言,由于直流电动力学方法不能克服电极极化现象,因此随着电源施加的时间越长,电耗越大,故难于支持长时间(如数十天)一次连续运行达到预期去除目标(即物料或土壤中可溶性重金属离子的含量已经等于或低于容许值),而中途必须多次停下来采取一些物理或化学措施对电极加以清理以及对土壤PH值加以调适才能继续进行;而相比之下,由于脉冲电动力学法具有能及时动态消除并遏制电极极化现象以及自动动态调适土壤PH值的功能,因此它可以做到第一次开机后即可长历时(如数十天乃至数月)不停机处理达到预定去除目标。这不仅体现出本专利所提供的这种脉冲电动力学法比较于已有直流电动力学法有着无可比拟的优越性,而且也同时是本专利大量对比实验中,只将两种方法在短历(24h)时脱除处理时段内进行比较的原因——因为在长历时(例如等于或大于120h以后)脱除处理条件下,直流电动力学法因所需施加电压越来越高而难以一次性进行到底,中途需多次停顿进行电极清理和PH调整再进行第二次运行;而脉冲电动力学法则能长期维持一定的脉冲峰值电压,一次性将脱除作业进行到底。也就是说,脉冲电动力学法可以一次性长期运行直至预设的最终脱除率,而要达到这最终脱除率,直流电动力学要经历数次停顿清理调适,数次停机开机操作才能达到。For electrokinetic removal of soluble heavy metal ions in material piles or soil, since the DC electrokinetic method cannot overcome the electrode polarization phenomenon, the longer the power is applied, the greater the power consumption, so it is difficult to support for a long time (such as Dozens of days) a continuous operation reaches the expected removal target (that is, the content of soluble heavy metal ions in the material or soil has been equal to or lower than the allowable value), but must stop several times in the middle to take some physical or chemical measures to clean the electrodes and to clean the electrodes. The pH value of the soil must be adjusted to continue; in contrast, because the pulse electrokinetic method can dynamically eliminate and contain the electrode polarization in time and automatically adjust the soil pH value, it can be turned on for the first time. After that, it can be processed without stopping for a long time (such as tens of days or even months) to achieve the predetermined removal target. This not only reflects the incomparable superiority of the pulse electrokinetic method provided by this patent over the existing DC electrokinetic method, but also shows that in a large number of comparative experiments in this patent, only the two methods are compared in a short period of time. (24h) The reason for the comparison within the removal treatment period——Because under the long-duration (for example, equal to or greater than 120h) removal treatment conditions, the DC electrokinetic method is difficult to perform at one time because the required applied voltage is getting higher and higher To the end, it needs to stop several times for electrode cleaning and PH adjustment before the second run; while the pulse electrokinetics method can maintain a certain pulse peak voltage for a long time, and the removal operation will be carried out to the end at one time. That is to say, the pulse electrokinetic method can run for a long time at one time until the preset final removal rate, but to achieve this final removal rate, the DC electrokinetics needs to undergo several pauses, cleaning and adjustments, and several shutdowns and start-up operations to achieve it.
(三)脉冲电动力学法与直流电动力学法去除重金属离子以外的其他污染离子的效果对比(3) Comparison of the effect of pulse electrokinetic method and direct current electrokinetic method on removing other polluting ions except heavy metal ions
以下两组对比实验是为了考查脉冲电动力学法相对于直流电动力学法去除重金属以外的其他污染离子的效率。以全面判断脉冲电动力学法相对于直流电动力学法在原位去除土壤或泥状粉状物料中所有污染物离子的相对规律。The following two sets of comparative experiments are to examine the efficiency of the pulse electrokinetic method for removing other polluting ions other than heavy metals compared to the direct current electrokinetic method. To comprehensively judge the relative law of the pulse electrokinetic method compared with the direct current electrokinetic method for in-situ removal of all pollutant ions in soil or muddy powder materials.
1)两种方法从土壤中原位(阳极)脱除硫酸根离子SO4-2的短历时(24h)运行系列比较实验1) Short duration (24h) running series comparison experiment of two methods for in situ (anode) removal of sulfate ion SO4-2 from soil
在电动力学方法将可溶性重金属离子迁移往阴极的同时,土壤内的阴离子基团也电泳往阳极,导致阳极电导也发生正相关变化;当准确配入硫酸根离子的含量而且SO4-2配入量占土壤中其他阴离子比例较大时,可以认为阳极电导增量正比于阳极对SO4-2的脱除量,因此只要测定阳极电导变化的增量比,据此也可以算出脉冲电动力学法相对于直流电动力学法脱除SO4-2的相对效率。While the electrokinetic method migrates the soluble heavy metal ions to the cathode, the anion groups in the soil also electrophoresis to the anode, resulting in a positive correlation change in the conductivity of the anode; when the content of sulfate ions is accurately adjusted and the amount of SO4-2 added When it accounts for a large proportion of other anions in the soil, it can be considered that the increase in anode conductance is proportional to the removal amount of SO4-2 from the anode, so as long as the increase ratio of the change in anode conductance is measured, it can also be calculated accordingly. The relative efficiency ofSO4-2 removal by kinetic method.
入配试剂采用了硫酸铜,当土壤中Cu+2在含量在0.002%-0.1%之间时,土壤中的SO4-2则在0.003-0.15%之间。所施加直流电源的直流电压梯度为0.5-2v/cm,脉冲电源的正脉冲峰值电压梯度为0.5-2v/cm,正脉冲频率为0.017-25HZ,正脉冲占空比50-98%,正脉冲施加时段600s-1200s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度为0.5-2v/cm,反脉冲频率为0.017-25HZ,反脉冲占空比为50-98%,反脉冲施加时段3-30s的电源操作条件取值范围内,运行时间24h后,脉冲法相对于直流法阳极脱除SO4-2的效率普遍为112-153%;也就是说,在运行24h之后,脉冲法比之于直流法其阳极脱除SO4-2的效率普遍提高了12%-53%左右,这基本与阴极脱除铜离子的效率(10-55%)相当。Copper sulfate is used as the compounding reagent, and when the content of Cu+2 in the soil is between 0.002% and 0.1%, the SO4-2 in the soil is between 0.003% and 0.15%. The DC voltage gradient of the applied DC power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of the pulse power supply is 0.5-2v/cm, the positive pulse frequency is 0.017-25HZ, the positive pulse duty cycle is 50-98%, and the positive pulse The application period is 600s-1200s, the reverse pulse peak voltage gradient is 0.5-2v/cm, the reverse pulse frequency is 0.017-25HZ, the reverse pulse duty cycle is 50-98%, and the value of the power supply operating conditions is the reverse pulse application period 3-30s Within the range, after 24 hours of operation, the efficiency of the pulse method for anode removal of SO4-2 compared to the DC method is generally 112-153%; The efficiency of2 is generally increased by about 12%-53%, which is basically equivalent to the efficiency of cathode removal of copper ions (10-55%).
2)两种方法从土壤中原位脱除苯酚的短历时(24h)运行系列比较实验2) Short duration (24h) running series comparison experiment of two methods for in situ removal of phenol from soil
配制土壤样,使其内含苯酚量为500mg/kg。在试样初始条件完全相同,而且直流电源的直流电压梯度为1v/cm,脉冲电源的正脉冲峰值电压梯度为0.5v/cm,正脉冲频率为1HZ,正脉冲占空比60%,正脉冲施加时段1200s,反脉冲峰值电压梯度为1v/cm,反脉冲频率为1HZ,反脉冲占空比为60%,反脉冲施加时段20s的电源操作条件下,同时运行24h之后,分别取处理后土样化验测定其中苯酚的残留量。化验结果是:脉冲电动力学与直流电动力学处理土样中的苯酚残留量分别为121.5mg/kg和246.2mg/kg,即是脉冲法与直流法的苯酚脱除率分别为75.7%和50.76%;也就是说,在运行24h之后,脉冲法比直流法阳极脱除苯酚的效率高出24.94%;Prepare the soil sample so that the amount of phenol contained in it is 500mg/kg. The initial conditions of the sample are exactly the same, and the DC voltage gradient of the DC power supply is 1v/cm, the positive pulse peak voltage gradient of the pulse power supply is 0.5v/cm, the positive pulse frequency is 1HZ, the positive pulse duty cycle is 60%, and the positive pulse The application period is 1200s, the peak voltage gradient of the reverse pulse is 1v/cm, the frequency of the reverse pulse is 1HZ, the duty cycle of the reverse pulse is 60%, and the application period of the reverse pulse is 20s. Sample assay was used to determine the residual amount of phenol in it. The test results are: the phenol residues in the soil samples treated by pulse electrokinetics and direct current electrokinetics are 121.5mg/kg and 246.2mg/kg respectively, that is, the removal rates of phenol by pulse method and direct current method are 75.7% and 50.76% respectively ; That is to say, after running for 24 hours, the efficiency of pulse method for removing phenol by anode is 24.94% higher than that of direct current method;
由数次具体实验归结而得的规律表明:脉冲电动力学法除了对重金属离子脱除效果比直流电动力学法优异之外,对其它污染离子也有着比直流电动力学法优异的的脱除效果。The laws concluded from several specific experiments show that the pulse electrokinetic method has a better removal effect than the direct current electrokinetic method on heavy metal ions, and also has a better removal effect on other pollutant ions than the direct current electrokinetic method.
由上述一系列实例概括出的几点重要结论是:Some important conclusions summarized from the above series of examples are:
1在一次开机后即不停机连续运行时间超过120h(5d)的“长历时”运行模式下,原有直流电动力学法已经不能再坚持有效运行而是必须多次调整电源提高电压或多次停机清洗电极和调整PH值,而脉冲电动力学法则仍能继续保持初始电源参数不变条件下高效运行;因此,对于长历时运行而言,脉冲电动力学法远远胜于直流电动力学法,或者干脆说二者之间几乎失去可比性。1 In the "long-duration" operation mode in which the continuous operation time exceeds 120h (5d) without stopping after one startup, the original DC electrodynamics method can no longer maintain effective operation, but must adjust the power supply multiple times to increase the voltage or shut down multiple times Clean the electrode and adjust the PH value, while the pulse electrokinetic method can still continue to operate efficiently under the condition of maintaining the initial power supply parameters; therefore, for long-term operation, the pulse electrokinetic method is far better than the DC electrokinetic method, or simply It is said that there is almost no comparability between the two.
2在短历时(24h)对比运行模式下,脉冲电动力学法原位脱除重金属离子的效率也总是优于直流电动力学法。2 In the short-duration (24h) comparative operation mode, the efficiency of in-situ removal of heavy metal ions by the pulse electrokinetic method is always better than that of the direct current electrokinetic method.
3实验证实:在去除重金属以外的其他污染离子方面,脉冲电动力学法的效率也是优于直流电动力学法。3 Experiments have confirmed that the efficiency of the pulse electrokinetic method is also better than that of the direct current electrokinetic method in removing other polluting ions other than heavy metals.
4总而言之,实验证实:无论是长历时(大于120h)或者是短历时(24h)对比运行,无论是去除重金属离子或者是其他污染离子,:脉冲电动力学法都比直流电动力学法优异,由此可见本专利方法的先进性。4 All in all, the experiment proves that the pulse electrokinetic method is better than the direct current electrokinetic method whether it is a long-duration (greater than 120h) or a short-duration (24h) comparative operation, whether it is to remove heavy metal ions or other polluting ions. Visible the advanced nature of this patent method.
本发明所提供的方法,以不对环境产生二次污染的方式,彻底克服了原有直流电动力学原位脱除重金属离子方法难以克服或者难以以不产生二次污染的方式克服因而导致其运行高能耗低效率的三种电极极化现象(活化极化、电阻极化、浓差极化),从而极大提高了在土壤中或者泥状粉状废弃物料中采用已有直流电动力学方法原位迁移脱除其中可溶性重金属离子的效率。The method provided by the present invention completely overcomes the difficulty of the original direct current electrodynamic in-situ removal of heavy metal ions in a way that does not cause secondary pollution, which leads to its high-energy operation. Three electrode polarization phenomena (activation polarization, resistance polarization, and concentration polarization) with low consumption efficiency, thus greatly improving the in-situ electrokinetic method used in soil or muddy powdery waste materials. The efficiency of migration to remove soluble heavy metal ions.
实验还证实,本发明方法不仅对原位脱除土壤或物料中重金属离子具有高效低耗性能,而且对其中的其他污染正负离子或基团也同样具有脱除的高效低耗性能。因此,本发明方法作为一种先进的绿色处理技术必将获得日益广泛的应用前景。Experiments also prove that the method of the present invention not only has high efficiency and low consumption performance for in-situ removal of heavy metal ions in soil or materials, but also has high efficiency and low consumption performance for the removal of other polluting positive and negative ions or groups therein. Therefore, as an advanced green processing technology, the method of the present invention will surely obtain increasingly wide application prospects.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201010147868ACN101838740A (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2010-04-09 | Method for removing soluble heavy metal ions in situ |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201010147868ACN101838740A (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2010-04-09 | Method for removing soluble heavy metal ions in situ |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101838740Atrue CN101838740A (en) | 2010-09-22 |
Family
ID=42742414
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201010147868APendingCN101838740A (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2010-04-09 | Method for removing soluble heavy metal ions in situ |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101838740A (en) |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103240268A (en)* | 2013-05-09 | 2013-08-14 | 中国石油大学(华东) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous field experiment device for electrically repairing polluted soil |
| CN103286121A (en)* | 2013-05-09 | 2013-09-11 | 中国石油大学(华东) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous electric field experiment method used for electrokinetic restoration of polluted soil |
| CN103706622A (en)* | 2013-12-25 | 2014-04-09 | 江苏大地益源环境修复有限公司 | Method and device for obtaining uniform electric field for electrically repairing polluted soil |
| CN106192512A (en)* | 2016-07-08 | 2016-12-07 | 湖南农业大学 | Heavy metal pollution district watermelon vine fiber extraction process |
| CN106914486A (en)* | 2017-04-28 | 2017-07-04 | 中南林业科技大学 | The electro reclamation device and electric repair method of heavy-metal contaminated soil |
| CN107008744A (en)* | 2017-04-24 | 2017-08-04 | 广东环境保护工程职业学院 | A kind of method and soil remediation method for removing heavy metal in soil |
| CN108455696A (en)* | 2018-01-10 | 2018-08-28 | 南开大学 | A kind of half-wave AC field method in situ for efficiently removing porous material surface and internal salinity |
| CN113385527A (en)* | 2021-05-31 | 2021-09-14 | 山东大学 | Method and device for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil suspension by adopting pulse current |
| CN114072362A (en)* | 2019-07-08 | 2022-02-18 | 梅特基因有限公司 | Electrochemical soil treatment device and method |
| CN114192567A (en)* | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-18 | 江苏澳洋生态园林股份有限公司 | Process for improving acidified contaminated soil |
| CN114904905A (en)* | 2022-03-10 | 2022-08-16 | 同济大学 | Efficient electric coupling repair equipment for composite contaminated soil |
| CN118997758A (en)* | 2024-08-08 | 2024-11-22 | 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所 | Method and system for mining rare earth ore by adopting transformed direct current electric field |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003290760A (en)* | 2002-03-29 | 2003-10-14 | Babcock Hitachi Kk | Method and apparatus for decontaminating contaminated soil |
| CN1695834A (en)* | 2005-06-09 | 2005-11-16 | 上海交通大学 | Electrokinetic Remediation Method of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil |
- 2010
- 2010-04-09CNCN201010147868Apatent/CN101838740A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003290760A (en)* | 2002-03-29 | 2003-10-14 | Babcock Hitachi Kk | Method and apparatus for decontaminating contaminated soil |
| CN1695834A (en)* | 2005-06-09 | 2005-11-16 | 上海交通大学 | Electrokinetic Remediation Method of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 工程科技Ⅰ辑》 20080515 丁飒 重金属污染土壤的脉冲电泳原位修复研究 59-60 7-9 , 第5期 2* |
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103240268A (en)* | 2013-05-09 | 2013-08-14 | 中国石油大学(华东) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous field experiment device for electrically repairing polluted soil |
| CN103286121A (en)* | 2013-05-09 | 2013-09-11 | 中国石油大学(华东) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous electric field experiment method used for electrokinetic restoration of polluted soil |
| CN103240268B (en)* | 2013-05-09 | 2014-06-11 | 中国石油大学(华东) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous field experiment device for electrically repairing polluted soil |
| CN103286121B (en)* | 2013-05-09 | 2014-07-09 | 中国石油大学(华东) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous electric field experiment method used for electrokinetic restoration of polluted soil |
| CN103706622A (en)* | 2013-12-25 | 2014-04-09 | 江苏大地益源环境修复有限公司 | Method and device for obtaining uniform electric field for electrically repairing polluted soil |
| CN103706622B (en)* | 2013-12-25 | 2015-12-09 | 江苏大地益源环境修复有限公司 | The uniform electric field preparation method of Electrokinetic Remediation of Polluted Soils and device |
| CN106192512A (en)* | 2016-07-08 | 2016-12-07 | 湖南农业大学 | Heavy metal pollution district watermelon vine fiber extraction process |
| CN106192512B (en)* | 2016-07-08 | 2017-12-15 | 湖南农业大学 | Heavy metal pollution area watermelon vine fiber extraction process technology |
| CN107008744A (en)* | 2017-04-24 | 2017-08-04 | 广东环境保护工程职业学院 | A kind of method and soil remediation method for removing heavy metal in soil |
| CN106914486A (en)* | 2017-04-28 | 2017-07-04 | 中南林业科技大学 | The electro reclamation device and electric repair method of heavy-metal contaminated soil |
| CN106914486B (en)* | 2017-04-28 | 2020-04-03 | 中南林业科技大学 | Electric remediation device and electric remediation method for heavy metal contaminated soil |
| CN108455696A (en)* | 2018-01-10 | 2018-08-28 | 南开大学 | A kind of half-wave AC field method in situ for efficiently removing porous material surface and internal salinity |
| CN114072362A (en)* | 2019-07-08 | 2022-02-18 | 梅特基因有限公司 | Electrochemical soil treatment device and method |
| CN113385527A (en)* | 2021-05-31 | 2021-09-14 | 山东大学 | Method and device for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil suspension by adopting pulse current |
| CN113385527B (en)* | 2021-05-31 | 2022-04-01 | 山东大学 | A method and device for repairing heavy metal polluted soil by using pulse current |
| CN114192567A (en)* | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-18 | 江苏澳洋生态园林股份有限公司 | Process for improving acidified contaminated soil |
| CN114904905A (en)* | 2022-03-10 | 2022-08-16 | 同济大学 | Efficient electric coupling repair equipment for composite contaminated soil |
| CN114904905B (en)* | 2022-03-10 | 2024-03-22 | 同济大学 | Efficient electric coupling repair equipment for composite contaminated soil |
| CN118997758A (en)* | 2024-08-08 | 2024-11-22 | 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所 | Method and system for mining rare earth ore by adopting transformed direct current electric field |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101838740A (en) | Method for removing soluble heavy metal ions in situ | |
| CN103008334B (en) | In-situ rainwater leaching repair system for contaminated soil | |
| CN203380185U (en) | Device for restoring polluted soil by using electrodynamic force | |
| CN104368596B (en) | In-situ treatment method for electrically repairing heavy metal contaminated soil based on plastic electrode | |
| CN206083404U (en) | Do you be used for prosthetic horizontal EK of on --spot combined pollution soil PRB device | |
| CN106269835B (en) | Electric-promoted leaching removal device and method for soil heavy metals based on electric geotextiles | |
| CN103406347B (en) | One can be used for heavy metal and organic method in Enriching soil | |
| CN103286119A (en) | Device and method for restoring chlorobenzene-type organism polluted soil and underground water | |
| CN101265007A (en) | A Method for Removing Heavy Metals from Municipal Sludge Using Electric Restoration Technology | |
| CN103286121B (en) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous electric field experiment method used for electrokinetic restoration of polluted soil | |
| CN103240268B (en) | Two-dimensional inhomogeneous field experiment device for electrically repairing polluted soil | |
| CN102896143A (en) | Electric surfactant combined repair contaminated soil experimental device | |
| Abou-Shady et al. | A comprehensive analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of pulsed electric fields during soil electrokinetic remediation | |
| CN206316141U (en) | A kind of processing unit of electro reclamation heavy-metal contaminated soil | |
| CN102989759B (en) | Device and method for remediation of in-situ fracturing aeration auxiliary electrochemical array well | |
| CN1331619C (en) | Cathode acidifying electric power repairing process for heavy metal contaminated soil | |
| CN110185024A (en) | A kind of device and method that MICP consolidation by grouting soil can be achieved at the same time and removes its by-product | |
| CN110369490A (en) | A kind of prosthetic device and restorative procedure of heavy-metal contaminated soil | |
| CN206305191U (en) | Heavy metal-polluted soil electricity based on electronic geotextiles promotees drip washing removal device | |
| CN103232096B (en) | In-situ repairing system and repairing method capable of continuously removing Cr in underground water | |
| Yuan et al. | In situ removal of copper from sediments by a galvanic cell | |
| CN110697968B (en) | Pulse current and permeable reactive barrier cooperative treatment method for removing pollution in soil and underground water | |
| CN201799448U (en) | Combined electrode | |
| CN207204846U (en) | A kind of contaminated soil, underground water reaction in-situ band repair system | |
| CN214391608U (en) | System for electronic restoration unites normal position drip washing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20100922 |