CN101828917B - Method and system for extracting electrocardiosignal characteristic - Google Patents
Method and system for extracting electrocardiosignal characteristicDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101828917B CN101828917BCN2010101656819ACN201010165681ACN101828917BCN 101828917 BCN101828917 BCN 101828917BCN 2010101656819 ACN2010101656819 ACN 2010101656819ACN 201010165681 ACN201010165681 ACN 201010165681ACN 101828917 BCN101828917 BCN 101828917B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- wave
- threshold
- wavelet
- following formula
- coefficient
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7235—Details of waveform analysis
- A61B5/7253—Details of waveform analysis characterised by using transforms
- A61B5/726—Details of waveform analysis characterised by using transforms using Wavelet transforms
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/318—Heart-related electrical modalities, e.g. electrocardiography [ECG]
- A61B5/346—Analysis of electrocardiograms
- A61B5/349—Detecting specific parameters of the electrocardiograph cycle
- A61B5/352—Detecting R peaks, e.g. for synchronising diagnostic apparatus; Estimating R-R interval
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及心电信号分析技术,更具体地说,涉及一种心电信号特征提取的方法和系统。The present invention relates to electrocardiographic signal analysis technology, more specifically, to a method and system for extracting electrocardiographic signal features.
背景技术Background technique
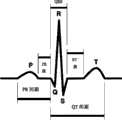
心电信号(electrocardiogram)是由体表电极随时间所记录的,反映心脏电活动的记录,是最早研究并应用于临床的生物电信号。ECG因为在心血管疾病的诊断、药物疗效评估等有重要临床应用,因而时至今日依然是医学界和生物医疗工程学界的研究热点。ECG具体可用于诊断心律失常、反映电解质紊乱、判断血钾、血钙浓度。评定起搏器共工作状况、手术后心脏状况的检查和提示必要的药物处理等等。标准的ECG如图1所示。心电信号由4个基本波形所组成,分别是QRS波、P波、T波和正常情况下出现几率75%的U波,该特征划分由Willem Einthoven提出并沿用至今。心电信号的产生与各个特征对应关系如图1所示。Electrocardiogram (electrocardiogram) is recorded by body surface electrodes over time, reflecting the recording of cardiac electrical activity, and is the earliest bioelectrical signal studied and applied clinically. Because ECG has important clinical applications in the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases and the evaluation of drug efficacy, it is still a research hotspot in the medical and biomedical engineering fields. ECG can be used to diagnose arrhythmia, reflect electrolyte disturbance, and judge blood potassium and blood calcium concentration. Evaluate the working condition of the pacemaker, check the heart condition after operation and prompt the necessary drug treatment, etc. A standard ECG is shown in Figure 1. The ECG signal is composed of 4 basic waveforms, which are QRS wave, P wave, T wave and U wave with a probability of 75% under normal circumstances. This feature division was proposed by Willem Einthoven and is still in use today. The corresponding relationship between the generation of ECG signal and each feature is shown in Figure 1.
心电信号的特征提取一直是心电信号自动分析的主要研究方向,主要包括了QRS波、P波、T波和ST段的检测。所谓特征提取即检测出各个特征的位置、起始点、终止点以及幅度等参数。特征提取的准确性以及稳定性会对临床诊断起到重要的影响,因此是心电信号处理系统研发中的关键问题之一。The feature extraction of ECG signal has always been the main research direction of ECG signal automatic analysis, mainly including the detection of QRS wave, P wave, T wave and ST segment. The so-called feature extraction is to detect parameters such as the position, starting point, ending point and amplitude of each feature. The accuracy and stability of feature extraction will have an important impact on clinical diagnosis, so it is one of the key issues in the development of ECG signal processing system.
1)、P波:表示心房从右至左除极。其幅度、宽度、形状以及持续时间可作为诊断心房扩大、心肌梗塞的依据。1) P wave: Indicates that the atrium is depolarized from right to left. Its amplitude, width, shape and duration can be used as the basis for diagnosing atrial enlargement and myocardial infarction.
2)、QRS波:表示左右心室除极。QRS波所包含的关于心脏健康情况信息最为丰富,Q波的状况可用于诊断心房肥大、心室扩大和心肌梗塞;R波和S波可用于诊断心肌炎。2), QRS wave: Indicates the depolarization of the left and right ventricles. The QRS wave contains the most information about the health of the heart. The condition of the Q wave can be used to diagnose atrial hypertrophy, ventricular enlargement and myocardial infarction; the R wave and S wave can be used to diagnose myocarditis.
3)、ST段与T波:表示左右心室复极。可用于诊断急性心肌梗塞和心室肥大。3), ST segment and T wave: represent left and right ventricular repolarization. Can be used to diagnose acute myocardial infarction and ventricular hypertrophy.
4)、U波:产生机制未明,正常情况下极性同T波;通常可用于判断血钾浓度,诊断心室肥大和心肌梗塞。4), U wave: The mechanism of generation is unknown, and the polarity is the same as T wave under normal circumstances; it can usually be used to judge blood potassium concentration, diagnose ventricular hypertrophy and myocardial infarction.
5)、PR间期:表示心房去极化到心室除极的时间间隔。用于诊断房室传导阻滞。5), PR interval: It means the time interval from atrial depolarization to ventricular depolarization. Used to diagnose atrioventricular block.
5)、QT间期:表示心室由除极到复极的时间间隔。反映了心率的快慢。5), QT interval: Indicates the time interval from depolarization to repolarization of the ventricle. Reflects the speed of the heart rate.
对上述ECG信号特征参数的检测和提取是ECG信号处理的关键所在,其准确性和稳定性会影响到对患者状况进行诊断和治疗的效果。心电信号的特征提取是对心电进行分析的基础,其研究主要集中在检测QRS波、P波、T波和ST段等几项特征上面。其中,QRS波的提取是提取其他特征的基础。对QRS波进行检测的方法中,较常见的有由Jackson和Ahlstrom提出差分阈值法,Pan和Tompkins在此基础上引入了可变阈值和不应期等策略,使得错检率降低至0.675%以下。The detection and extraction of the aforementioned ECG signal characteristic parameters is the key to ECG signal processing, and its accuracy and stability will affect the effect of diagnosis and treatment of the patient's condition. The feature extraction of ECG signal is the basis of ECG analysis, and its research mainly focuses on the detection of several features such as QRS wave, P wave, T wave and ST segment. Among them, the extraction of QRS wave is the basis for extracting other features. Among the methods for detecting QRS complexes, the differential threshold method proposed by Jackson and Ahlstrom is more common. On this basis, Pan and Tompkins introduced strategies such as variable threshold and refractory period, which reduced the false detection rate to less than 0.675%. .
另外,还有一种基于第一代小波变换的检测方法,能够有效地降低由工频、肌电噪声和呼吸基线漂移等噪声带来的干扰,使得检测准确率得到进一步的提升,错检率减至0.2%以下。In addition, there is a detection method based on the first-generation wavelet transform, which can effectively reduce the interference caused by power frequency, myoelectric noise, and respiratory baseline drift, which further improves the detection accuracy and reduces the false detection rate. to below 0.2%.
但是,不管是差分阈值法还是基于第一代小波变换的检测方法,都存在缺陷。However, both the differential threshold method and the detection method based on the first generation of wavelet transform have defects.
差分阈值法缺点主要在于以下方面:The disadvantages of the differential threshold method mainly lie in the following aspects:
1)特征提取的检测准确率较低,通常R波错检率在0.4%以上;1) The detection accuracy rate of feature extraction is low, usually the R-wave false detection rate is above 0.4%;
2)在时域进行检测,必须进行各类信号预处理,易受到心电信号采集过程中产生的各类噪声的干扰,鲁棒性差;2) Detection in the time domain requires various signal preprocessing, which is susceptible to interference from various noises generated during the acquisition of ECG signals, and has poor robustness;
基于第一代小波变换的方法缺点主要在于以下方面:The shortcomings of the method based on the first generation wavelet transform mainly lie in the following aspects:
1)运算量大,对实时性要求较高的便携式设备平台上并不适合,应用范围有限;1) The amount of calculation is large, and it is not suitable for portable device platforms with high real-time requirements, and the application range is limited;
2)对存储空间要求高,对比其他方法如差分阈值法,所占用的存储空间要多出至少30%,限制了对其他功能的扩展。2) The storage space requirement is high. Compared with other methods such as the differential threshold method, the storage space occupied is at least 30%, which limits the expansion of other functions.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明要解决的技术问题在于,针对现有技术的上述准确率低、运算量大、鲁棒性差、存储空间要求高的缺陷,提供一种心电信号特征提取方法和系统。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a method and system for extracting ECG signal features in view of the defects of the prior art, such as low accuracy, large amount of computation, poor robustness, and high storage space requirements.
本发明解决其技术问题所采用的技术方案是:构造一种心电信号特征提取方法,包括:The technical scheme that the present invention adopts to solve the technical problem is: construct a kind of electrocardiogram feature extraction method, comprise:
A、基于自适应提升方法对经采样的心电信号x(n)进行多次小波变换直至达到预设尺度值;A. Perform multiple wavelet transformations on the sampled ECG signal x(n) based on an adaptive lifting method until reaching a preset scale value;
B、依据小波系数d(n)计算阈值;B. Calculate the threshold according to the wavelet coefficient d(n);
C、依据所述阈值检测所述心电信号中R波的位置;C. Detecting the position of the R wave in the ECG signal according to the threshold;
D、依据尺度系数c(n)判断所述R波的位置是否正确,若否,则以预设步长调整所述阈值并返回步骤C。D. Judging whether the position of the R wave is correct according to the scale coefficient c(n), if not, adjusting the threshold with a preset step size and returning to step C.
在本发明所述的方法中,基于自适应提升方法进行小波变换的步骤包括:In the method of the present invention, the step of carrying out wavelet transformation based on the adaptive lifting method comprises:
分裂步骤,对经采样的心电信号x(n)分裂为奇数序列xo(n)和偶数序列xe(n),可由下式表示:In the splitting step, the sampled ECG signal x(n) is split into an odd sequence xo (n) and an even sequence xe (n), which can be expressed by the following formula:
xo(n)=x(2n+1) xe(n)=x(2n);xo (n)=x(2n+1) xe (n)=x(2n);
预测步骤,基于所述偶数序列xe(n)预测所述奇数序列xo(n),得到小波系数d(n);可由下式表示:The prediction step is to predict the odd sequence xo (n) based on the even sequence xe (n) to obtain the wavelet coefficient d (n); it can be expressed by the following formula:
d(n)=xo(n)-P(xe(n)),其中P为预测算子;d(n)=xo (n)-P(xe (n)), where P is the prediction operator;
更新步骤,基于所述小波系数d(n)更新所述偶数序列xe(n),得到尺度系数c(n);可用下式表示:The update step is to update the even sequence xe (n) based on the wavelet coefficient d (n) to obtain the scale coefficient c (n); it can be expressed by the following formula:
c(n)=xe(n)+U(xo(n)),其中U为更新算子。c(n)=xe (n)+U(xo (n)), where U is an update operator.
在本发明所述的方法中,所述预测算子P由如下公式表示:In the method of the present invention, the predictor P is represented by the following formula:
所述更新算子U由如下公式表示:The update operator U is represented by the following formula:
ΔL=|c(n)-d(n-1)| ΔR=|c(n)-d(n)|ΔL =|c(n)-d(n-1)|ΔR =|c(n)-d(n)|
在本发明所述的方法中,所述步骤B包括:In the method of the present invention, said step B comprises:
B1、将小波系数d(n)划分为多个等长区间;B1, dividing the wavelet coefficient d(n) into multiple equal-length intervals;
B2、计算每一等长区间的极大值;B2. Calculate the maximum value of each interval of equal length;
B3、计算所述多个等长区间的极大值的均值;B3. Calculating the mean value of the maximum values of the plurality of equal-length intervals;
B4、选取所述均值的一半作为阈值。B4. Select half of the mean value as the threshold.
在本发明所述的方法中,所述预设尺度值为4,所述等长区间为fs/4,其中fs为心电信号x(n)的采样频率。In the method of the present invention, the preset scale value is 4, and the equal-length interval is fs/4, where fs is the sampling frequency of the ECG signal x(n).
在本发明所述的方法中,所述步骤C包括:In the method of the present invention, said step C comprises:
依据所述阈值检测所述心电信号,并依据检测结果定位R波的位置并判断R波间距是否大于1/150s,若是,则进入步骤D。Detect the ECG signal according to the threshold, locate the position of the R wave according to the detection result, and judge whether the distance between the R waves is greater than 1/150s, and if so, go to step D.
在本发明所述的方法中,所述步骤D包括:In the method of the present invention, said step D comprises:
依据尺度系数c(n)判断R波的位置是否满足c1(n)<c2(n),c1(n)<c3(n),c1(n)<c4(n),若否,则以预设步长调整所述阈值并返回步骤C;According to the scale coefficient c(n), judge whether the position of the R wave satisfies c1 (n)<c2 (n), c1 (n)<c3 (n), c1 (n)<c4 (n), If not, then adjust the threshold with a preset step size and return to step C;
其中c1(n)为第1次小波变换的尺度系数,c2(n)为第2次小波变换的尺度系数,c3(n)为第3次小波变换的尺度系数,c4(n)为第4次小波变换的尺度系数。where c1 (n) is the scale coefficient of the first wavelet transform, c2 (n) is the scale coefficient of the second wavelet transform, c3 (n) is the scale coefficient of the third wavelet transform, c4 (n ) is the scale coefficient of the fourth wavelet transform.
在本发明所述的方法中,还包括:In the method of the present invention, also include:
E、计算预设尺度值为4的尺度系数c(n)的差分信号diff(n),可由下式表不:E. Calculate the differential signal diff(n) of the scale coefficient c(n) whose preset scale value is 4, which can be represented by the following formula:
diff(n)=(-2)×c(n-2)-c(n-1)+c(n+1)+2×c(n+2);diff(n)=(-2)×c(n-2)-c(n-1)+c(n+1)+2×c(n+2);
F、计算差分阈值diff_thresh,可由下式表示:F. Calculate the difference threshold diff_thresh, which can be expressed by the following formula:
其中,thresh_param为可选参数,取值为2、4、8或16,max的初始值为划分为多个等长区间的小波系数的模极大值;Among them, thresh_param is an optional parameter, the value is 2, 4, 8 or 16, and the initial value of max is the modulus maximum value of the wavelet coefficient divided into multiple intervals of equal length;
G、依据所述差分阈值diff_thresh从R波的位置向前检测QRS波的起始点位置,若连续检测到差分信号diff(n)大于所述差分阈值diff_thresh,则可定位心电信号中QRS波的起始点;否则,进入步骤H;或者,G. According to the difference threshold diff_thresh, the starting point position of the QRS wave is detected forward from the position of the R wave. If the differential signal diff(n) is continuously detected to be greater than the difference threshold diff_thresh, the location of the QRS wave in the ECG signal can be located. starting point; otherwise, go to step H; or,
依据所述差分阈值diff_thresh从R波的位置向后检测QRS波的终止点位置,若连续检测到差分信号diff(n)大于所述差分阈值diff_thresh,则可定位心电信号中QRS波的终止点;否则,进入步骤I;According to the difference threshold diff_thresh, the position of the end point of the QRS wave is detected backward from the position of the R wave. If the differential signal diff(n) is continuously detected to be greater than the difference threshold diff_thresh, the end point of the QRS wave in the ECG signal can be located. ; Otherwise, enter step I;
H、由下式更新所述差分阈值diff_thresh,并进入步骤G重新定位QRS波的起始点;H, update the differential threshold diff_thresh by the following formula, and enter step G to relocate the starting point of the QRS wave;
其中,first_max为对应R波的幅度与对应的QRS波的起始点的幅度的差值,filter_param为可选参数,取值为2、4、8或16;Among them, first_max is the difference between the amplitude of the corresponding R wave and the amplitude of the starting point of the corresponding QRS wave, filter_param is an optional parameter, and the value is 2, 4, 8 or 16;
I、由下式更新所述差分阈值diff_thresh,并进入步骤G重新定位QRS波的终止点;1, update the differential threshold diff_thresh by the following formula, and enter step G to relocate the termination point of the QRS wave;
其中,first_max为对应R波的幅度与对应的QRS波的终止点的幅度的差值,filter_param为可选参数,取值为2、4、8或16。Among them, first_max is the difference between the amplitude of the corresponding R wave and the amplitude of the corresponding end point of the QRS wave, filter_param is an optional parameter, and the value is 2, 4, 8 or 16.
本发明还提供一种心电信号特征提取的系统,包括:The present invention also provides a system for extracting ECG signal features, including:
小波变换单元,用于基于自适应提升方法对经采样的心电信号x(n)进行多次小波变换直至达到预设尺度值;A wavelet transform unit, used for performing multiple wavelet transforms on the sampled ECG signal x(n) based on an adaptive lifting method until reaching a preset scale value;
阈值计算单元,用于依据小波系数d(n)计算阈值;a threshold calculation unit, configured to calculate a threshold according to the wavelet coefficient d(n);
检测单元,用于依据所述阈值检测所述心电信号中R波的位置;a detection unit, configured to detect the position of the R wave in the ECG signal according to the threshold;
判断单元,用于依据尺度系数c(n)判断所述R波的位置是否正确,若否,则以预设步长调整所述阈值并由检测单元重新检测R波的位置。The judging unit is used to judge whether the position of the R wave is correct according to the scale coefficient c(n), if not, adjust the threshold with a preset step size and re-detect the position of the R wave by the detection unit.
在本发明所述的系统中,小波变换单元包括:In the system of the present invention, the wavelet transform unit includes:
分裂单元,用于对经采样的心电信号x(n)分裂为奇数序列xo(n)和偶数序列xe(n),可由下式表示:The splitting unit is used to split the sampled ECG signal x(n) into an odd sequence xo (n) and an even sequence xe (n), which can be represented by the following formula:
xo(n)=x(2n+1) xe(n)=x(2n);xo (n)=x(2n+1) xe (n)=x(2n);
预测单元,用于基于所述偶数序列xe(n)预测所述奇数序列xo(n),得到小波系数d(n);可由下式表示:A prediction unit, for predicting the odd sequence xo (n) based on the even sequence xe (n), to obtain the wavelet coefficient d (n); it can be represented by the following formula:
d(n)=xo(n)-P(xe(n)),其中P为预测算子;d(n)=xo (n)-P(xe (n)), where P is the prediction operator;
更新单元,用于基于所述小波系数d(n)更新所述偶数序列xe(n),得到尺度系数c(n);可用下式表示:An update unit, configured to update the even sequence xe (n) based on the wavelet coefficient d (n), to obtain the scale coefficient c (n); it can be represented by the following formula:
c(n)=xe(n)+U(xo(n)),其中U为更新算子。c(n)=xe (n)+U(xo (n)), where U is an update operator.
本发明的有益效果是,基于自适应提升的特征提取方法相对于基于差分阈值的特征提取方法具有以下优点:The beneficial effect of the present invention is that the feature extraction method based on adaptive promotion has the following advantages relative to the feature extraction method based on differential threshold:
1)检测准确率与差分阈值法相比较提升至少0.2%;1) The detection accuracy rate is improved by at least 0.2% compared with the differential threshold method;
2)具有更强的抗干扰能力,受到心电信号采集过程中各类噪声如基线漂移等噪声的影响较小;2) It has stronger anti-interference ability and is less affected by various noises such as baseline drift during the acquisition of ECG signals;
相对于基于第一代小波变换的特征提取方法具有如下优点:Compared with the feature extraction method based on the first generation wavelet transform, it has the following advantages:
1)原位运算,在当前内存位置即可完成分解而不必占据额外的存储空间,可以有效降低对内存空间的需求,对比第一代小波所占据的内存空间可降低至少50%;1) In-situ operation, the decomposition can be completed in the current memory location without occupying additional storage space, which can effectively reduce the demand for memory space, which can be reduced by at least 50% compared with the memory space occupied by the first generation wavelet;
2)不依赖傅立叶变换,可在时域上完成小波变换分解;2) It does not rely on Fourier transform, and can complete wavelet transform decomposition in the time domain;
3)运算量低,对比第一代小波运算量可降低至少1/3,至多可降低50%;且不需要进行运算量较大的算术操作,如乘法、除法;3) The amount of calculation is low, compared with the first generation wavelet, the amount of calculation can be reduced by at least 1/3, and can be reduced by 50% at most; and there is no need to perform arithmetic operations with a large amount of calculation, such as multiplication and division;
4)理论上任何第一代小波变换都可以转到第二代小波的形式来实现;4) In theory, any first-generation wavelet transform can be implemented in the form of second-generation wavelet;
5)可以实现可逆的整数变换。5) Reversible integer transformation can be realized.
这些优点使得能够在对实时性要求高的应用场合以及嵌入式系统平台上进行准确率较高的特征提取,并有效的节约了系统资源,同时对心电信号处理系统进行功能扩展也带来了便利。These advantages make it possible to perform feature extraction with high accuracy in applications with high real-time requirements and embedded system platforms, and effectively save system resources. At the same time, the function expansion of the ECG signal processing system also brings convenient.
附图说明Description of drawings
下面将结合附图及实施例对本发明作进一步说明,附图中:The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment, in the accompanying drawing:
图1是标准心电信号示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of a standard ECG signal;
图2是依据本发明一实施例的心电信号特征提取方法流程示意图;2 is a schematic flow chart of a method for extracting features of an electrocardiographic signal according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是基于自适应提升方法的第二代小波变换架构示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the second-generation wavelet transform architecture based on the adaptive lifting method;
图4是依据本发明一实施例的基于自适应提升方法的R波检测流程示意图;4 is a schematic diagram of an R-wave detection process based on an adaptive lifting method according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图5和图6为MIT-BIH数据库样本示例;Figure 5 and Figure 6 are examples of MIT-BIH database samples;
图7是Marr小波的尺度函数示意图;Fig. 7 is a schematic diagram of the scaling function of Marr wavelet;
图8是基于ALS和基于Marr小波的R波检测算法运行时间和检测准确率对比示意图;Figure 8 is a schematic diagram of the comparison of the running time and detection accuracy of the R-wave detection algorithm based on ALS and Marr wavelet;
图9是使用本发明的自适应提升方法定位的R波位置对QRS波的起始点进行定位的示意图;Fig. 9 is a schematic diagram of positioning the starting point of the QRS wave using the R wave position of the self-adaptive lifting method of the present invention;
图10是使用本发明的自适应提升方法定位的R波位置对QRS波的终止点进行定位的示意图;Fig. 10 is the schematic diagram that uses the R wave position of self-adaptive lifting method location of the present invention to locate the terminal point of QRS wave;
图11是依据本发明一实施例的心电信号特征提取系统结构示意图。Fig. 11 is a schematic structural diagram of an ECG signal feature extraction system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
图2是依据本发明一实施例的心电信号特征提取方法流程示意图。图2所示的方法200用于心电信号R波的特征提取。FIG. 2 is a schematic flowchart of a method for extracting ECG signal features according to an embodiment of the present invention. The
在步骤201中,基于自适应提升方法对经采样的心电信号x(n)进行多次小波变换直至达到预设尺度值;In
在步骤202中,依据小波系数d(n)计算阈值;In
在步骤203中,依据所述阈值检测所述心电信号中R波的位置;In
在步骤204中,依据尺度系数c(n)判断所述R波的位置是否正确,若否,则进入步骤205以预设步长调整阈值并返回步骤204重新检测R波的位置。若是,则说明已正确定位R波,因此结束R波的检测。In
通过方法200可以准确地定位R波的位置。The location of the R-wave can be accurately located by the
图3是基于自适应提升方法(Adaptive Lifting Scheme,ALS)的第二代小波变换架构示意图。基于提升方法的第二代小波变换包括3个步骤:分裂、预测和更新。具体方法如下:Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of the second-generation wavelet transform architecture based on Adaptive Lifting Scheme (ALS). The second-generation wavelet transform based on the lifting method includes three steps: splitting, prediction and updating. The specific method is as follows:
1)分裂:将信号x(n)分裂为不相交的奇数索引序列xo(n)和偶数索引序列xe(n),如式(1)所示。1) Split: split the signal x(n) into disjoint odd index sequence xo (n) and even index sequence xe (n), as shown in formula (1).
xo(n)=x(2n+1) xe(n)=x(2n)xo (n)=x(2n+1) xe (n)=x(2n)
2)预测:通过预测算子P基于序列xe(n)预测序列xo(n),预测值误差即小波系数d(n)。2) Prediction: The sequence xo (n) is predicted based on the sequence x e( n) through the prediction operator P, and the error of the predicted value is the wavelet coefficient d(n).
d(n)=xo(n)-P(xe(n))d(n)=xo (n)-P(xe (n))
3)更新:通过更新算子U基于预测误差d(n)更新序列xe(n),所得结果即尺度系数c(n)。3) Update: The sequence xe (n) is updated based on the prediction error d(n) through the update operator U, and the obtained result is the scale coefficient c(n).
c(n)=xe(n)+U(xo(n))c(n)=xe (n)+U(xo (n))
其中,在本发明一实施例中,使用的更新算子U如下式表示:Wherein, in an embodiment of the present invention, the update operator U used is represented by the following formula:
ΔL=|c(n)-d(n-1)| ΔR=|c(n)-d(n)|ΔL =|c(n)-d(n-1)|ΔR =|c(n)-d(n)|
使用的预测算子P如下式表示:The prediction operator P used is expressed as follows:
上述使用的更新算子U和预测算子P是经实验证实,获取的检测性能较好,当然也不排除其他可能的实现方法,本发明并不限于此,只要是基于本发明的思想来实现特征的提取都属于本发明的保护范围。The update operator U and prediction operator P used above are verified by experiments, and the obtained detection performance is better. Of course, other possible implementation methods are not excluded. The present invention is not limited thereto, as long as it is realized based on the idea of the present invention The extraction of features all belongs to the protection scope of the present invention.
图4是依据本发明一实施例的基于自适应提升方法的R波检测流程示意图。Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of an R-wave detection process based on an adaptive lifting method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
首先,在步骤401中,对输入的经采样的心电信号(采样频率表示为fs)进行分裂,分裂为不相交的奇数索引序列xo(n)和偶数索引序列xe(n),然后经过步骤402-404对分裂后的信号进行预测和更新(详见图3关于小波变化的描述),直至达到预设的分解尺度值。在该实施例中,设置该分解尺度值为4,当然也可以设置为其他数值,可根据要求的精确程度以及运算速度来进行权衡,本发明并不限制于此。如果在步骤404中,判断分解已经完成,则进入下一步骤405。否则,计算进行小波变换,直至达到分解尺度4。First, in
在步骤405中,计算阈值。将小波系数d(n)划分为多个等长区间,并选取每一等长区间的极大值,求出所选出的一系列极大值的均值,选取该均值的一半(50%)作为阈值。在本实施例中,等长区间的长度为fs/4,本发明并不限于此,只要是能够保证本方法正常运作的数值都是可以的。In
在步骤406中,依据阈值进行R波检测。通常情况标准心搏数每秒低于150下,在基于标准心搏数的前提下检测R波间距是否大于1/150s,若是,则进入步骤407,若否则说明心跳很不正常。In
在步骤407中,在尺度系数c(n)上基于李氏指数(李雅普洛夫指数,Lyapunov指数)判断R波位置是否满足c1(n)<c2(n),c1(n)<c3(n),c1(n)<c4(n),其中c1(n)为第1次小波变换的尺度系数,c2(n)为第2次小波变换的尺度系数,c3(n)为第3次小波变换的尺度系数,c4(n)为第4次小波变换的尺度系数。若满足,则说明已正确检测到R波的位置。若不满足,说明存在漏检、误检(错检),这时进入步骤408,调整阈值,这里以初始阈值的10%为步长调整阈值大小并进入步骤406在指定区间重新检测R波的位置。这里的步长可依据实际情况进行选定,此处仅作为示例。所述的指定区间可以是检测出的R波间距内的区间或者包含R波间距的区间,减少了R波的检测时间。当然,也可重新依据新的阈值对整个小波系数进行检测。In
在对本发明的自适应提升方法的准确率进行验证时采用了麻省理工(Massachusetts Institute of Technology)和Beth Israel医院联合建立的MIT-BIH心律失常数据库。MIT-BIH数据库中数据样本丰富、类型特征突出并有详细注释,在ECG信号自动分析处理的研究领域均使用该数据库中的样本进行实验验证。MIT-BIH心律失常数据库中共48组样本,每组样本长度30分钟,采样频率360Hz,总标准心搏数103891,并详细标明了ECG信号各个特征起始点终止点等特征信息。The MIT-BIH arrhythmia database jointly established by MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) and Beth Israel Hospital was adopted when the accuracy rate of the self-adaptive promotion method of the present invention was verified. The data samples in the MIT-BIH database are rich, with prominent type features and detailed annotations. In the research field of automatic analysis and processing of ECG signals, the samples in the database are used for experimental verification. The MIT-BIH arrhythmia database has a total of 48 groups of samples, each group of samples is 30 minutes long, the sampling frequency is 360Hz, the total standard heart rate is 103891, and the characteristic information such as the starting point and ending point of each characteristic of the ECG signal is marked in detail.
图5和图6为MIT-BIH数据库样本示例。Figure 5 and Figure 6 are examples of MIT-BIH database samples.
采用MIT-BIH数据并基于ALS方法对R波进行检测的结果统计如表1所示。其中,错检数=漏检数+误检数。Table 1 shows the statistical results of R wave detection using MIT-BIH data and based on the ALS method. Among them, the number of false detections = the number of missed detections + the number of false detections.
表1Table 1
如表1中所示,由于部分样本,如105、108和228号样本受干扰较为严重,共出现错漏检99个,占到总错检数将近33%,总体上漏检数123、误检数164、总错检数287,检验的准确率达到99.724%,可以满足正常使用的需要。为了对比与其他方法性能上的优劣,本文中实现了基于第一代小波变换的Marr小波的R波检测方法。Marr小波又被称为墨西哥草帽小波,是高斯函数的二阶导数,主要优点在于其小波变换尺度系数上的模极大值点与原始序列上模极大值点有一一对应的关系,对比此前使用小波变换方法进行QRS波检测的Sahambi等所使用的一阶微分小波原始序列上极大值点对应尺度系数上的过零点,具有抗干扰能力更强的特点,且更便于检测和实现。Marr小波的母函数表达式如下式所示,尺度函数图形如图7所示。As shown in Table 1, due to some samples, such as samples No. 105, 108 and 228, which were seriously disturbed, there were 99 missed detections, accounting for nearly 33% of the total number of false detections. Overall, the number of missed detections was 123. The number is 164, the total number of false detections is 287, and the accuracy rate of the inspection reaches 99.724%, which can meet the needs of normal use. In order to compare the advantages and disadvantages of other methods in performance, this paper implements the R-wave detection method based on the first-generation wavelet transform Marr wavelet. The Marr wavelet, also known as the Mexican straw hat wavelet, is the second-order derivative of the Gaussian function. Its main advantage is that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the modulus maximum points on the wavelet transform scale coefficients and the modulus maximum points on the original sequence. Sahambi et al. used the wavelet transform method to detect QRS waves before. The maximum points on the original sequence of the first-order differential wavelet correspond to the zero-crossing points on the scale coefficients, which has stronger anti-interference ability and is easier to detect and implement. The expression of the generating function of the Marr wavelet is shown in the following formula, and the graph of the scaling function is shown in Figure 7.
在Marr小波变换尺度4的尺度系数上,分等长区间分别求局部极大值,再对这组极大值求均值,将该均值二分之一作为阈值,求出过阈值的连续区间中极大值为R波的相应位置,再修正时移,此时与尺度4相应时延为20点,即与原始信号中R波位置有20点的延时,所采取的检错策略与基于ALS的方法相同。On the scale coefficient of Marr
基于第一代小波和第二代小波变换检测方法结果对比如表2和图8所示。图8示出了基于ALS和基于Marr小波的R波检测算法运行时间和检测准确率对比。虽然基于ALS的R波检测方法对比基于Marr小波的方法漏检多出52个,误检多出55个,总计107个,错检率高出0.106%,但检测准确率依然达到了99.724%,可以满足在嵌入式系统上对ECG信号进行实时R波检测的需要。对相同长度向量进行检测所花费的时间仅为基于Marr小波方法的11.49%,且不必进行定点化处理,大大降低了实现的难度。The results of detection methods based on the first-generation wavelet and the second-generation wavelet transform are compared as shown in Table 2 and Figure 8. Figure 8 shows the comparison of the running time and detection accuracy of the R-wave detection algorithm based on ALS and Marr wavelet. Although the ALS-based R-wave detection method has 52 more missed detections and 55 more false detections than the Marr wavelet-based method, a total of 107 detections, the false detection rate is 0.106% higher, but the detection accuracy still reaches 99.724%. It can meet the needs of real-time R-wave detection of ECG signals on the embedded system. The time spent on detecting vectors of the same length is only 11.49% of that based on the Marr wavelet method, and no fixed-point processing is required, which greatly reduces the difficulty of implementation.
表2Table 2
在定位R波后,为了便于进一步定位其他特征如P波和T波等,必须对QRS波的起始点以及终止点进行定位,具体方法可结合差分阈值的方法来实现,图9示出了使用本发明的自适应提升方法定位的R波位置对QRS波的起始点进行定位的示意图900,步骤描述如下:After locating the R wave, in order to further locate other features such as P wave and T wave, etc., it is necessary to locate the starting point and the ending point of the QRS wave. The specific method can be realized by combining the differential threshold method. Figure 9 shows the The R wave position positioned by the adaptive lifting method of the present invention is a schematic diagram 900 of positioning the starting point of the QRS wave, and the steps are described as follows:
在步骤901中,计算预设尺度值为4的尺度系数c(n)的差分信号diff(n),可由下式表示:In
diff(n)=(-2)×c(n-2)-c(n-1)+c(n+1)+2×c(n+2);diff(n)=(-2)×c(n-2)-c(n-1)+c(n+1)+2×c(n+2);
在步骤902中,计算差分阈值diff_thresh,可由下式表示:In
其中,thresh_param为可选参数,取值为2、4、8或16,max的初始值为划分为多个等长区间的小波系数的模极大值;Among them, thresh_param is an optional parameter, the value is 2, 4, 8 or 16, and the initial value of max is the modulus maximum value of the wavelet coefficient divided into multiple intervals of equal length;
在步骤903中,依据所述差分阈值diff_thresh从R波的位置向前检测QRS波的起始点位置;In
随后在步骤904中判断是否连续检测到差分信号diff(n)大于所述差分阈值diff_thresh,若是,则可定位心电信号中QRS波的起始点;否则,进入步骤904;Then in
在步骤904中,由下式更新所述差分阈值diff_thresh,并进入步骤903重新定位QRS波的起始点;In
其中,first_max为对应R波的幅度与对应的QRS波的起始点的幅度的差值,filter_param为可选参数,取值为2、4、8或16。Among them, first_max is the difference between the amplitude of the corresponding R wave and the amplitude of the starting point of the corresponding QRS wave, filter_param is an optional parameter, and the value is 2, 4, 8 or 16.
图10是使用本发明的自适应提升方法定位的R波位置对QRS波的终止点进行定位的示意图1000。步骤描述如下:FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram 1000 of locating the termination point of the QRS wave by using the position of the R wave located by the adaptive lifting method of the present invention. The steps are described as follows:
在步骤1001中,计算预设尺度值为4的尺度系数c(n)的差分信号diff(n),可由下式表示:In
diff(n)=(-2)×c(n-2)-c(n-1)+c(n+1)+2×c(n+2);diff(n)=(-2)×c(n-2)-c(n-1)+c(n+1)+2×c(n+2);
在步骤1002中,计算差分阈值diff_thresh,可由下式表示:In
其中,thresh_param为可选参数,取值为2、4、8或16,max的初始值为划分为多个等长区间的小波系数的模极大值;Among them, thresh_param is an optional parameter, the value is 2, 4, 8 or 16, and the initial value of max is the modulus maximum value of the wavelet coefficient divided into multiple intervals of equal length;
在步骤1003中,依据所述差分阈值diff_thresh从R波的位置向后检测QRS波的终止点位置;In
随后在步骤1004中判断是否连续检测到差分信号diff(n)大于所述差分阈值diff_thresh,若是,则可定位心电信号中QRS波的终止点;否则,进入步骤1004;Then in
在步骤1004中,由下式更新所述差分阈值diff_thresh,并进入步骤903重新定位QRS波的终止点;In
其中,first_max为对应R波的幅度与对应的QRS波的终止点的幅度的差值,filter_param为可选参数,取值为2、4、8或16。Among them, first_max is the difference between the amplitude of the corresponding R wave and the amplitude of the corresponding end point of the QRS wave, filter_param is an optional parameter, and the value is 2, 4, 8 or 16.
图11是依据本发明一实施例的心电信号特征提取系统1100结构示意图。由图11可知,心电信号特征提取系统1100包括:小波变换单元1101、阈值计算单元1102、检测单元1103、判断单元1104。FIG. 11 is a schematic structural diagram of an ECG signal feature extraction system 1100 according to an embodiment of the present invention. It can be seen from FIG. 11 that the ECG signal feature extraction system 1100 includes: a wavelet transform unit 1101 , a
小波变换单元1101,用于基于自适应提升方法对经采样的心电信号x(n)进行多次小波变换直至达到预设尺度值;A wavelet transform unit 1101, configured to perform multiple wavelet transforms on the sampled ECG signal x(n) based on an adaptive lifting method until reaching a preset scale value;
阈值计算单元1102,用于依据小波系数d(n)计算阈值;
检测单元1103,用于依据所述阈值检测所述心电信号中R波的位置;A
判断单元1104,用于依据尺度系数c(n)判断所述R波的位置是否正确,若否,则以预设步长调整所述阈值并由检测单元重新检测R波的位置。The
其中,小波变换单元1101包括分裂单元1101a、预测单元1101b、更新单元1101c。Wherein, the wavelet transform unit 1101 includes a split unit 1101a, a prediction unit 1101b, and an update unit 1101c.
分裂单元1101a,用于对经采样的心电信号x(n)分裂为奇数序列xo(n)和偶数序列xe(n),可由下式表示:The splitting unit 1101a is used to split the sampled ECG signal x(n) into an odd sequence xo (n) and an even sequence xe (n), which can be represented by the following formula:
xo(n)=x(2n+1) xe(n)=x(2n);xo (n)=x(2n+1) xe (n)=x(2n);
预测单元1101b,用于基于所述偶数序列xe(n)预测所述奇数序列xo(n),得到小波系数d(n);可由下式表示:The prediction unit 1101b is used to predict the odd sequence xo (n) based on the even sequence xe (n) to obtain the wavelet coefficient d (n); it can be represented by the following formula:
d(n)=xo(n)-P(xe(n)),其中P为预测算子;d(n)=xo (n)-P(xe (n)), where P is the prediction operator;
更新单元1101c,用于基于所述小波系数d(n)更新所述偶数序列xe(n),得到尺度系数c(n);可用下式表示:The update unit 1101c is used to update the even sequence xe (n) based on the wavelet coefficient d (n) to obtain the scale coefficient c (n); it can be expressed by the following formula:
c(n)=xe(n)+U(xo(n)),其中U为更新算子。c(n)=xe (n)+U(xo (n)), where U is an update operator.
上述关于心电信号特征提取系统的详细描述同样适用于动态编组的方法,类似地关于心电信号特征提取方法的详细描述同样适用于心电信号特征提取系统,此处不再赘述。The above detailed description about the ECG signal feature extraction system is also applicable to the dynamic grouping method, similarly the detailed description about the ECG signal feature extraction method is also applicable to the ECG signal feature extraction system, and will not be repeated here.
以上所述仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并不用以限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内所作的任何修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The above descriptions are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent replacements and improvements made within the spirit and principles of the present invention should be included in the protection of the present invention. within range.
Claims (6)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010101656819ACN101828917B (en) | 2010-05-07 | 2010-05-07 | Method and system for extracting electrocardiosignal characteristic |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010101656819ACN101828917B (en) | 2010-05-07 | 2010-05-07 | Method and system for extracting electrocardiosignal characteristic |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101828917A CN101828917A (en) | 2010-09-15 |
| CN101828917Btrue CN101828917B (en) | 2011-09-14 |
Family
ID=42713244
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010101656819AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101828917B (en) | 2010-05-07 | 2010-05-07 | Method and system for extracting electrocardiosignal characteristic |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101828917B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2589332A1 (en)* | 2011-11-03 | 2013-05-08 | Imec | System and method for the analysis of electrocardiogram signals |
| CN107361764A (en)* | 2017-06-16 | 2017-11-21 | 华南理工大学 | A kind of rapid extracting method of electrocardiosignal signature waveform R ripples |
Families Citing this family (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102670196A (en)* | 2011-01-18 | 2012-09-19 | 王卫东 | R-wave singularity analyzing method |
| CN102247143B (en)* | 2011-06-03 | 2013-05-15 | 吉林大学珠海学院 | Integratable fast algorithm for denoising electrocardiosignal and identifying QRS waves |
| CN102551687B (en)* | 2012-01-18 | 2014-02-05 | 华韵之 | Extraction method of pulse signal feature points based on second-generation wavelets |
| CN102626310A (en)* | 2012-04-23 | 2012-08-08 | 天津工业大学 | Electrocardiogram signal feature detection algorithm based on wavelet transformation lifting and approximate envelope improving |
| CN102885621B (en)* | 2012-10-19 | 2015-04-22 | 深圳邦健生物医疗设备股份有限公司 | Signal processing method and circuit for R-wave detection and defibrillator |
| CN103006208B (en)* | 2012-12-29 | 2014-05-28 | 重庆邮电大学 | Method and device for calibrating R wave of electrocardiosignal |
| CN103222864B (en)* | 2013-04-07 | 2015-03-25 | 广东工业大学 | Self-adaption electrocardiograph (ECG) detection method and monitoring system thereof |
| CN103815897B (en)* | 2014-02-28 | 2015-07-15 | 吉林大学 | Electrocardiogram characteristic extraction method |
| CN105212922A (en)* | 2014-06-11 | 2016-01-06 | 吉林大学 | The method and system that R wave of electrocardiosignal detects automatically are realized towards FPGA |
| CN104042191A (en)* | 2014-07-09 | 2014-09-17 | 北京惠仁康宁科技发展有限公司 | Wrist watch type multi-parameter biosensor |
| CN105310688B (en)* | 2015-11-02 | 2018-07-10 | 广东工业大学 | One kind is based on non-negative blind separation Fetal ECG characteristic signal extraction method |
| CN105748066B (en)* | 2016-03-03 | 2018-03-16 | 深圳竹信科技有限公司 | A kind of extracting method and device of electro-cardiologic signal waveforms characteristic point |
| CN107273827B (en)* | 2017-05-31 | 2020-01-07 | 江苏斯坦德利医疗科技有限公司 | Electrocardiosignal R wave detection method and device |
| CN109009071A (en)* | 2018-07-11 | 2018-12-18 | 上海夏先机电科技发展有限公司 | A kind of method and apparatus identifying electrocardio wave image characteristic point |
| CN111772617B (en)* | 2019-04-04 | 2023-08-04 | 成都心吉康科技有限公司 | ECG display filtering method, device and storage medium |
| CN110420022B (en)* | 2019-07-29 | 2020-12-11 | 浙江大学 | P wave detection method based on dual-density wavelet transform |
| CN111345815B (en)* | 2020-02-11 | 2023-05-02 | 广州视源电子科技股份有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and storage medium for detecting QRS waves in electrocardiographic signals |
| CN111281373A (en)* | 2020-03-06 | 2020-06-16 | 何乐 | Method and device for quantitatively evaluating cardiac function based on electrocardiogram U wave and T wave |
| CN112774033B (en)* | 2021-02-05 | 2024-08-02 | 杭州诺为医疗技术有限公司 | Method, device and system for determining detection parameters of implanted closed-loop system |
| CN112842362B (en)* | 2021-02-05 | 2023-04-07 | 杭州诺为医疗技术有限公司 | Self-response detection parameter optimization method and system for implantable electrical stimulation device |
| CN113951893B (en)* | 2021-12-02 | 2023-02-03 | 清华大学 | Multi-lead electrocardiosignal characteristic point extraction method combining deep learning and electrophysiological knowledge |
| CN118924304A (en)* | 2023-05-09 | 2024-11-12 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | Training method of electrocardiogram reconstruction model, electrocardiogram reconstruction method and system |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006524546A (en)* | 2003-04-23 | 2006-11-02 | ヘムチャンドラ・シャートゥクド | Apparatus and method for non-invasive diagnosis of coronary artery disease |
| ES2272196B1 (en)* | 2006-08-04 | 2008-03-01 | Gem-Med, S.L. | PROCEDURE FOR THE PROCESSING OF CARDIOLECTRIC SIGNS AND CORRESPONDING DEVICE. |
| CN100536765C (en)* | 2007-07-13 | 2009-09-09 | 天津大学 | ECG feature extraction method based on evolutionary wavelet domain Wiener deconvolution |
| CN101632587A (en)* | 2009-08-05 | 2010-01-27 | 南京大学 | Tread signal extracting method based on wavelet transformation |
- 2010
- 2010-05-07CNCN2010101656819Apatent/CN101828917B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2589332A1 (en)* | 2011-11-03 | 2013-05-08 | Imec | System and method for the analysis of electrocardiogram signals |
| US8886299B2 (en) | 2011-11-03 | 2014-11-11 | Imec | System and method for the analysis of electrocardiogram signals |
| CN107361764A (en)* | 2017-06-16 | 2017-11-21 | 华南理工大学 | A kind of rapid extracting method of electrocardiosignal signature waveform R ripples |
| CN107361764B (en)* | 2017-06-16 | 2020-05-22 | 华南理工大学 | A Rapid Extraction Method of ECG Signal Characteristic Waveform R Wave |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101828917A (en) | 2010-09-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101828917B (en) | Method and system for extracting electrocardiosignal characteristic | |
| US7412282B2 (en) | Algorithms for detecting cardiac arrhythmia and methods and apparatuses utilizing the algorithms | |
| Kathirvel et al. | An efficient R-peak detection based on new nonlinear transformation and first-order Gaussian differentiator | |
| CN103083013B (en) | Electrocardio signal QRS complex wave detection method based on morphology and wavelet transform | |
| CN113499079B (en) | Atrial fibrillation detection method in electrocardiogram | |
| US8437839B2 (en) | Electrocardiographic assessment of arrhythmia risk | |
| CN115828056B (en) | Electrocardiogram characteristic signal extraction method and terminal | |
| CN111643070B (en) | A method, device, storage medium and electronic equipment for determining the starting point of T wave | |
| Manriquez et al. | An algorithm for QRS onset and offset detection in single lead electrocardiogram records | |
| CN102626310A (en) | Electrocardiogram signal feature detection algorithm based on wavelet transformation lifting and approximate envelope improving | |
| CN113440145B (en) | Automatic detection method for electrocardiosignal T wave and end point thereof | |
| CN111920407B (en) | Electrocardiogram feature extraction method, system, device and medium based on wavelet transformation | |
| CN102579039B (en) | Method for detecting TWA (T wave alternans) in electrocardiogram | |
| CN110090016B (en) | Method and system for locating R-wave position, and automatic R-wave detection method using LSTM neural network | |
| CN113786202B (en) | Electrocardiogram characteristic starting point and ending point detection method, system, device and medium | |
| CN108720832A (en) | A kind of ECG's data compression method and device | |
| CN111166322A (en) | ECG Signal Feature Wave Extraction Method | |
| CN115486854B (en) | Single-lead electrocardiograph ventricular premature beat identification method for dry electrode acquisition | |
| CN112438735B (en) | Electrocardiogram P wave detection method, analysis device and storage medium | |
| Alcaraz et al. | A novel application of sample entropy to the electrocardiogram of atrial fibrillation | |
| CN103750835A (en) | Electrocardiosignal characteristic detection algorithm | |
| CN1393204A (en) | Cardioelectric spectrometer | |
| Reklewski et al. | Real time ECG R-peak detection by extremum sampling | |
| Li et al. | An approach of heartbeat segmentation in seismocardiogram by matched-filtering | |
| CN111166325B (en) | ECG signal QRS complex detection method and system based on IPCMM algorithm |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20110914 |