CN101827137A - Hash table-based and extended memory-based high-performance IPv6 address searching method - Google Patents
Hash table-based and extended memory-based high-performance IPv6 address searching methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101827137A CN101827137ACN201010145939ACN201010145939ACN101827137ACN 101827137 ACN101827137 ACN 101827137ACN 201010145939 ACN201010145939 ACN 201010145939ACN 201010145939 ACN201010145939 ACN 201010145939ACN 101827137 ACN101827137 ACN 101827137A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- hash
- prefix
- search
- extended
- item
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 230000015654memoryEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription54
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription79
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription58
- 238000009826distributionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsdescription42
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription28
- 238000003780insertionMethods0.000claimsdescription14
- 230000037431insertionEffects0.000claimsdescription14
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description18
- 230000008520organizationEffects0.000description10
- 238000012217deletionMethods0.000description8
- 230000037430deletionEffects0.000description8
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description8
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description8
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description7
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description6
- 238000010845search algorithmMethods0.000description3
- 230000006835compressionEffects0.000description2
- 238000007906compressionMethods0.000description2
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 238000004064recyclingMethods0.000description2
- 235000008694Humulus lupulusNutrition0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 238000013467fragmentationMethods0.000description1
- 238000006062fragmentation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000003672processing methodMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种在高速IPv6路由器中查找路由表项的方法,准确地说,涉及一种采用哈希表和扩展存储器的IPv6地址查找方法,属于IPv6网络设备路由转发技术领域。The invention relates to a method for searching routing table items in a high-speed IPv6 router. Specifically, it relates to a method for searching an IPv6 address using a hash table and an extended memory, and belongs to the technical field of routing and forwarding of IPv6 network equipment.
背景技术Background technique
IP路由器在网络中起着桥梁作用,可将多个小网络连接成大网络,通过IP(Internet Protocol)协议相互通信。而路由器最主要功能是IP数据包的转发,即从输入接口接收IP数据包,并根据IP包首部中的目标地址,从路由信息表RIB(Routing Information Base)中查找出相应的输出接口信息,然后将IP包转发到相应的输出接口,从而完成分组转发功能。The IP router acts as a bridge in the network, which can connect multiple small networks into a large network and communicate with each other through the IP (Internet Protocol) protocol. The main function of the router is the forwarding of IP data packets, that is, it receives IP data packets from the input interface, and finds out the corresponding output interface information from the routing information table RIB (Routing Information Base) according to the destination address in the IP packet header. Then forward the IP packet to the corresponding output interface, thus completing the packet forwarding function.
为了解决路由信息表中路由前缀数目快速增长的问题,无分类域间路由CIDR(Classless Inter-Domain Routing)的IP地址编址方案被正式采用,从而,必须采用最长前缀匹配LPM(Longest Prefix Matching)算法解决IP地址查找问题,因此,大大增加了IP地址查找的复杂性。In order to solve the problem of rapid increase in the number of routing prefixes in the routing information table, the IP addressing scheme of CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) is officially adopted. Therefore, the Longest Prefix Matching LPM (Longest Prefix Matching) must be used. ) algorithm solves the IP address lookup problem, therefore, greatly increases the complexity of IP address lookup.
随着网络用户和通信业务的日益增长,导致IPv4地址分配面临枯竭,以及IPv4网络安全性及灵活性等问题的限制,于是IETF(Internet Engineering TaskForce)提出了IPv6(Internet Protocol Version 6)编址方案,但是,由于IP地址从IPv4的32位变成IPv6的128位,很多IPv4查找算法已经不能满足IPv6的128位地址查找。现在是IPv6发展的初期,还有很多不确定性因素:IPv6路由表中前缀分布规律及表项增长规律,IPv6地址查找算法的设计只能依据IPv4地址查找的经验,从而,IPv6地址查找算法的效率及实现代价等问题需要设计者来解决。With the increasing number of network users and communication services, IPv4 address allocation is facing exhaustion, and the limitations of IPv4 network security and flexibility issues, so IETF (Internet Engineering TaskForce) proposed IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) addressing scheme However, since the IP address changes from 32 bits in IPv4 to 128 bits in IPv6, many IPv4 lookup algorithms can no longer satisfy the 128 bit address lookup in IPv6. Now is the initial stage of IPv6 development, and there are still many uncertain factors: the distribution of prefixes in the IPv6 routing table and the growth of table entries, the design of the IPv6 address lookup algorithm can only be based on the experience of IPv4 address lookup, thus, the IPv6 address lookup algorithm Issues such as efficiency and implementation cost need to be solved by designers.
现有的IPv6地址查找方法都是直接或者间接利用传统的IPv4地址查找方案进行设计的,由于查找关键字从32位增长到128位,所以这种设计思路会存在很多问题,例如,使用TCAM进行IPv6地址查找会在很大程度上提高设计成本和系统功耗,同样表项数量的路由表,要使用多级TCAM进行级联才能完成查找工作,这样在工程系统设计时,其高昂的成本和大的功耗使该方案不会被直接应用;使用Trie树及其衍生算法(比如:层压缩Trie树、路径压缩Trie树、多比特Trie树等)在地址查找时,会使存储器访问次数成倍增加,从而导致查找延迟更大,系统查找效率降低;使用基于存储器扩展的查找方法会使存储成本成指数级的增加,在IPv6地址中,分布数量最多的是长度为32位的路由前缀,直接利用存储器扩展的方法进行设计,将其作为第一级查找,需要的存储器大小为232bit,再加上第二级更大空间的存储器,使得直接应用该方案对IPv6地址查找是不可实现的。The existing IPv6 address lookup methods are designed directly or indirectly by using the traditional IPv4 address lookup scheme. Since the lookup keyword increases from 32 bits to 128 bits, there are many problems in this design idea. For example, using TCAM to IPv6 address lookup will greatly increase the design cost and system power consumption. The routing table with the same number of entries must be cascaded with multi-level TCAM to complete the lookup work. In this way, the high cost and The large power consumption prevents this scheme from being directly applied; using the Trie tree and its derivative algorithms (for example: layer compression Trie tree, path compression Trie tree, multi-bit Trie tree, etc.) will make the number of memory accesses become Doubling, resulting in greater lookup delay and reduced system lookup efficiency; using a memory expansion-based lookup method will increase storage costs exponentially. In IPv6 addresses, the most distributed number is the routing prefix with a length of 32 bits. Directly use the method of memory expansion to design, and use it as the first level of search, the required memory size is232 bits, plus the second level of larger memory, making it impossible to directly apply this solution to IPv6 address lookup of.
总之,IPv4地址查找方法直接用于IPv6地址查找是难以实现高性能IPv6地址查找的,所以在IPv6地址查找方法设计时,要利用IPv6本身的特点(比如IPv6前缀分布规律、IPv6路由表项增长趋势等)和传统的IPv4地址查找思路进行设计,会使IPv6地址查找方法具有可实现性和高效性。In short, it is difficult to achieve high-performance IPv6 address lookup by using the IPv4 address lookup method directly for IPv6 address lookup, so when designing the IPv6 address lookup method, it is necessary to use the characteristics of IPv6 itself (such as the distribution of IPv6 prefixes, the growth trend of IPv6 routing entries etc.) and the traditional IPv4 address lookup idea, the IPv6 address lookup method will be feasible and efficient.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种采用哈希表和扩展存储器两级结构的IPv6地址查找方法,该方法具有高速查找效率、可扩展性强、存储利用率高等特点,可用于高性能IPv6核心路由器中。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a kind of IPv6 address search method that adopts two-level structure of hash table and extended memory, this method has the characteristics of high-speed search efficiency, strong scalability, high storage utilization rate, etc., and can be used in high-performance IPv6 core routers .
(1)为描述方便,首先做如下定义:(1) For the convenience of description, first define as follows:
定义1哈希前缀HP(i)(Hashing Prefix):表示长度i可以被8整除的前缀项,该方法中所指的哈希前缀为:HP(16)、HP(24)、HP(32)、HP(40)、HP(48)、HP(56)和HP(64);
定义2扩展前缀EP(j,k)(Expanded Prefix):两个能被8整除哈希前缀项之间的所有前缀,j=8i+1,i为整数且0≤i≤7,k=j+m,m为整数且1≤m≤6该方法中所指的扩展前缀包括:EP(17,23)、EP(25,31)、EP(33,39)、EP(41,47)、EP(49,55)和EP(57,63)等。在IPv6路由表中,哈希前缀HP和扩展前缀EP构成了整个路由表;
定义3扩展前缀哈希项EPH(n)(Expanded Prefix Hashing Segment)与扩展前缀扩展项EPE(n)(Expanded Prefix Expanded Segment):长度为n的扩展前缀可以分为两个部分:1~i和i+1~n,i是小于n且最大可以被8整除的整数。将扩展前缀中1~i比特之间的值称为EPH(n),而i+1~n称为扩展前缀扩展项EPE(n)。例如,长度为20比特的扩展前缀2a01:c*/20,其扩展前缀哈希项EPH(20)为2a01,其扩展前缀扩展项EPE(20)为c。
在该方法中用Hashm表示长度为m比特的哈希前缀所存储的哈希表。其中m=16,24,32,40,48,56和64,即有Hash16、Hash24、Hash32、Hash40、Hash48、Hash56、Hash64分别存放长度为16,24,32,40,48,56和64比特哈希前缀的哈希值;用RAMp_q表示存放扩展前缀项所对应值的存储器块,RAM存储地址用扩展前缀扩展项EPE计算,其中包括RAM17_23、RAM25_31、RAM33_39、RAM41_47、RAM49_55、RAM57_63;用CPEs_t表示哈希冲突处理单元(Collision Processing Element),在该方法中包括CPE16_23、CPE24_31、CPE32_39、CPE40_47、CPE48_55、CPE56_63、CPE64。In this method, Hashm is used to represent the hash table stored by the hash prefix with a length of m bits. Where m=16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, and 64, that is, Hash16, Hash24, Hash32, Hash40, Hash48, Hash56, and Hash64 store lengths of 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, and 64 bits respectively The hash value of the hash prefix; use RAMp_q to represent the memory block that stores the value corresponding to the extended prefix item, and the RAM storage address is calculated with the extended prefix extension item EPE, including RAM17_23, RAM25_31, RAM33_39, RAM41_47, RAM49_55, RAM57_63; represented by CPEs_t A hash conflict processing unit (Collision Processing Element), including CPE16_23, CPE24_31, CPE32_39, CPE40_47, CPE48_55, CPE56_63, CPE64 in this method.
注:在描述时将Hashm、RAMp_q、CPEs_t看成模块名,下面的描述过程同理。Note: When describing, Hashm, RAMp_q, and CPEs_t are regarded as module names, and the following description process is the same.
(2)本发明的思路及总体结构如下所述:(2) thinking and overall structure of the present invention are as follows:
随着IPv6网络的发展,IPv6路由表项数目逐渐增加,并呈现出一定的分布规律,如图2(Potaroo上核心路由器中的路由表),通过分析路由表中IPv6路由前缀长度的分布规律,可以发现IPv6路由表前缀分布有如下特点:With the development of the IPv6 network, the number of IPv6 routing entries gradually increases, and presents a certain distribution law, as shown in Figure 2 (routing table in the core router on Potaroo), by analyzing the distribution law of the length of the IPv6 routing prefix in the routing table, It can be found that the IPv6 routing table prefix distribution has the following characteristics:
①IPv6路由前缀长度全部小于64比特;①The IPv6 routing prefix length is all less than 64 bits;
②长度可以被8整除的前缀分布比例非常大,占总共路由表的93%以上。例如,长度为32比特的前缀占整个路由表的65.44%,长度为48比特的前缀占整个路由表的24.15%等等;② The proportion of prefixes whose length can be divisible by 8 is very large, accounting for more than 93% of the total routing table. For example, prefixes with a length of 32 bits account for 65.44% of the entire routing table, prefixes with a length of 48 bits account for 24.15% of the entire routing table, etc.;
③根据Potaroo网站统计的数据,长度可以被8整除的前缀增长速度特别快,而且整个IPv6路由器表项数目的增长这部分前缀数量占很大比例,例如,08年1月到09年6月期间,长度为32比特的前缀从600多项增加到了1176项,长度为64比特的前缀从10多项增加到30多项;③According to the statistical data of the Potaroo website, prefixes whose length can be divisible by 8 are growing very fast, and the number of prefixes in this part of the entire IPv6 router accounted for a large proportion of the increase in the number of entries. For example, during the period from January 2008 to June 2009 , the prefixes with a length of 32 bits have increased from more than 600 items to 1176 items, and the prefixes with a length of 64 bits have increased from more than 10 items to more than 30 items;
④长度不能被8整除的前缀在整个路由表中所占的比例非常小,仅有6%,而且增长速度缓慢。④ The proportion of prefixes whose length is not divisible by 8 in the entire routing table is very small, only 6%, and the growth rate is slow.
本发明根据以上的分析结果,利用局部性原理对长度可以被8整除和不可以被8整除的前缀项用不同的处理方法进行处理。According to the above analysis results, the present invention uses the principle of locality to process the prefix items whose length is divisible by 8 and which is not divisible by 8 with different processing methods.
将绝大多数前缀(长度可以被8整除的前缀)作为第一级哈希表中的数据,这样可以使绝大多数地址在第一级就可以完成查找,而将其它前缀(长度不可以被8整除的前缀)作为第二级扩展存储器的数据,少数地址需要查找第二级可以完成查找。为了提高整个查找系统的性能,该方法利用所统计的前缀分布规律,将长度为16比特,24比特,32比特,40比特,48比特,56比特和64比特的前缀作为第一级查找数据,其它前缀作为第二级查找。同时由于16比特和24比特,24比特和32比特,32比特和40比特,40比特和48比特,48比特和56比特,56比特和64比特之间都相差7位,可以对其它长度的前缀用扩展存储器进行处理,如图4和图11。Hash函数存在冲突,所以用哈希冲突处理模块解决冲突。这就是本文提出的基于哈希和扩展存储器的IPv6地址查找的主要思路。Most of the prefixes (prefixes whose length can be divisible by 8) are used as the data in the first-level hash table, so that most addresses can be searched at the first level, while other prefixes (lengths that cannot be divided by 8 divisible prefix) as the data of the second-level extended memory, a small number of addresses need to be searched and the second level can complete the search. In order to improve the performance of the entire search system, this method utilizes the statistical prefix distribution rules, and uses prefixes with a length of 16 bits, 24 bits, 32 bits, 40 bits, 48 bits, 56 bits and 64 bits as the first-level search data. Other prefixes are used as second-level lookups. At the same time, since there is a difference of 7 bits between 16 bits and 24 bits, 24 bits and 32 bits, 32 bits and 40 bits, 40 bits and 48 bits, 48 bits and 56 bits, and 56 bits and 64 bits, prefixes of other lengths can be Process with extended memory, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 11. There is a conflict in the Hash function, so the hash conflict processing module is used to resolve the conflict. This is the main idea of IPv6 address lookup based on hash and extended memory proposed in this paper.
图3给出了哈希表和扩展RAM的存储结构。为了表述方便,在图中将各种哈希表Hashi(i=16,24,32,40,48,56)的存储结构统一起来描述,每种哈希表都是17位的宽度和65535项的深度(216)的存储器;也将各种扩展RAMp_q的存储结构统一起来描述,但是在具体实现时,应该考虑到哈希冲突的影响,对存储器的地址宽度W(也为存储器深度D的对数值W=log2D)应该做适当调整。Figure 3 shows the storage structure of the hash table and extended RAM. For the convenience of expression, the storage structures of various hash tables Hashi (i=16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56) are unified and described in the figure. Each hash table has a width of 17 bits and 65535 items memory with a depth of (216 ); also describe the storage structures of various extended RAMp_q together, but in the specific implementation, the impact of hash collisions should be taken into account, the address width W of the memory (also the memory depth D The log value W=log2 D) should be properly adjusted.
●哈希表项存储结构(i=16,24,32,40,48,56和64)如图3(a)所示:●Hash table item storage structure (i=16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56 and 64) as shown in Figure 3(a):
①E:表示有扩展前缀扩展项EPE,即长度为i+1~i+7比特的前缀,E=1,表示该项存在扩展前缀扩展项EPE,E=0,表示该项不存在扩展前缀扩展项;①E: Indicates that there is an extended prefix extension item EPE, that is, a prefix with a length of i+1~i+7 bits, E=1, indicating that the item has an extended prefix extension item EPE, and E=0, indicating that the item does not have an extended prefix extension item;
②Block_addr:是扩展前缀扩展项EPE所对应扩展RAM块的编号。②Block_addr: It is the number of the extended RAM block corresponding to the extended prefix extension item EPE.
例如,如果一条前缀项所对应Block_addr的值为“x”,扩展前缀扩展项EPE的低位扩展可化成十进制数“y”,则该前缀所对应的下一跳值应该存放在第二级存储器的第128*x+y个地址单元中;For example, if the value of Block_addr corresponding to a prefix item is "x", the low-order extension of the extended prefix extension item EPE can be transformed into a decimal number "y", then the next hop value corresponding to the prefix should be stored in the second-level storage In the 128th*x+y address unit;
③F:表示哈希表此项为有效匹配前缀项。当F=0时,Nh(i)为全零;F=1时,输出Nh(i),即为下一跳值;当对扩展RAM的某项插入前缀对应信息时,F字段则设为1;③F: Indicates that the item in the hash table is a valid matching prefix item. When F=0, Nh(i) is all zeros; when F=1, output Nh(i), which is the next hop value; when inserting prefix corresponding information to an item in the extended RAM, the F field is then set to 1;
④Nh(i)字段为该前缀项所对应的下一跳值。④Nh(i) field is the next hop value corresponding to the prefix item.
●扩展部分的表项存储结构,如图3(b)所示:●The table item storage structure of the extension part, as shown in Figure 3(b):
①H:表示此项为有效匹配的前缀项,可以将此项所对应的下一跳值Nh(i+1,i+7)输出。H=1时,Nh(i+1,i+7)为全零,F=1时,输出Nh(i+1,i+7);当对该项插入前缀信息时,F字段则设为1;①H: Indicates that this item is a valid matching prefix item, and the next-hop value Nh(i+1, i+7) corresponding to this item can be output. When H=1, Nh(i+1, i+7) is all zeros, when F=1, output Nh(i+1, i+7); when inserting prefix information to this item, the F field is then set to 1;
②Nh(i+1,i+7)字段为该前缀项所对应的下一跳值。②Nh(i+1, i+7) field is the next hop value corresponding to the prefix item.
上面所定义的哈希表存储结构和扩展RAM的存储结构在本文中的组织如图4所示,哈希表存放哈希前缀HP和扩展前缀哈希项EPH的信息,第二级的扩展RAM存放扩展前缀扩展项EPE的信息,这两级查找之间通过信号“E”进行连接。在查找过程中,如果哈希项中的“F”为“1”,则表示该项即为匹配项;如果哈希表项中的“E”为“1”,则表示所查找的地址还需要在扩展RAM中查找更长的匹配项;如果扩展RAM项中的“H”为“1”,则表示该扩展RAM项中的值为匹配的下一跳索引值。The storage structure of the hash table defined above and the storage structure of the extended RAM are organized in this paper as shown in Figure 4. The hash table stores the information of the hash prefix HP and the extended prefix hash item EPH, and the second-level extended RAM It stores the information of the extended prefix extension item EPE, and the two levels of search are connected through the signal "E". During the search process, if the "F" in the hash item is "1", it means that the item is a match; if the "E" in the hash table item is "1", it means that the address you are looking for is still A longer matching item needs to be searched in the extended RAM; if "H" in the extended RAM item is "1", it means that the value in the extended RAM item is the matching next-hop index value.
(3)本发明采用的技术方案描述如下:(3) The technical scheme adopted in the present invention is described as follows:
一种基于哈希表查找和扩展存储器查找的IPv6地址查找方法,包括1个查找分类器,1个更新分类器,7个并行的哈希处理单元Hash16、Hash24、Hash32、Hash40、Hash48、Hash56、Hash64,6个扩展存储器处理单元RAM17_23、RAM25_31、RAM33_39、RAM41_47、RAM49_55、RAM57_63,7个哈希冲突处理单元CPE16_23、CPE24_31、CPE32_39、CPE40_47、CPE48_55、CPE56_63、CPE64,1个优先级比较单元;其特征在于对IPv6地址进行查找,并对IPv6路由表项进行更新,具体步骤为:An IPv6 address search method based on hash table search and extended memory search, including 1 search classifier, 1 update classifier, 7 parallel hash processing units Hash16, Hash24, Hash32, Hash40, Hash48, Hash56, The features It is to look up the IPv6 address and update the IPv6 routing table entry. The specific steps are:
a.根据IPv6路由表分布规律的统计,将路由表项分为两种:一种是长度可以被8整除的前缀,一种是长度不能被8整除的前缀;a. According to the statistics of the distribution rules of the IPv6 routing table, the routing table entries are divided into two types: one is the prefix whose length is divisible by 8, and the other is the prefix whose length is not divisible by 8;
b.对两种路由表项分别用哈希表和扩展存储器进行存储,用哈希冲突处理单元处理哈希冲突项;b. Store the two routing table items with a hash table and an extended memory respectively, and process the hash conflict items with a hash conflict processing unit;
c.优先级比较器可以选择出最长匹配前缀所对应的下一跳信息;c. The priority comparator can select the next hop information corresponding to the longest matching prefix;
d.在查找过程中,以目的IPv6地址为查找对象在7路查找模块中并行查找,最长匹配前缀所对应的下一跳信息为查找结果;d. In the search process, use the destination IPv6 address as the search object to search in parallel in the 7-way search module, and the next-hop information corresponding to the longest matching prefix is the search result;
本方法的具体查找过程如图6所示:The specific search process of this method is shown in Figure 6:
要进行IPv6地址查找,必须先将路由表进行初始化,初始化具体过程下文所述;To perform IPv6 address lookup, the routing table must be initialized first, and the initialization process is described below;
如果路由表初始化工作已完成,则可以对IPv6地址进行查找:先对IPv6做第一级哈希查找,然后根据情况判断是否要进行第二级查找。查找过程可以分为三个步骤完成:第一级哈希表查找,第二级扩展RAM查找和优先级比较。If the initialization of the routing table has been completed, the IPv6 address can be searched: first perform a first-level hash search on IPv6, and then judge whether to perform a second-level search according to the situation. The search process can be divided into three steps to complete: first-level hash table search, second-level extended RAM search and priority comparison.
具体描述如下:The specific description is as follows:
第一步:将目的IPv6地址做7种hash查找,即分别在Hash16、Hash24、Hash32、Hash40、Hash48、Hash56、Hash64哈希查找单元中,对目的IPv6地址的前16bits、24bits、32bits、40bits、48bits、56bits和64bits做并行查找操作。如果查找到匹配项,则将对应的下一跳索引值输出到优先级比较器中准备比较。Step 1: Do 7 kinds of hash lookups on the destination IPv6 address, that is, in Hash16, Hash24, Hash32, Hash40, Hash48, Hash56, Hash64 hash lookup units, the first 16bits, 24bits, 32bits, 40bits, 48bits, 56bits and 64bits do parallel search operations. If a matching item is found, the corresponding next-hop index value is output to the priority comparator for comparison.
第二步:如果第一级查找指示在第二级查找单元中还有更长的前缀需要做匹配计算,则需要进行第二级查找,在第二级中利用存储器扩展技术,扩展前缀扩展项EPE可以插入到有128个地址的块RAM中。设前缀的对应位为[i+1:i+7](i为哈希前缀的长度),查找时,则根据目的地址的第(i+1~i+7)位计算出索引值,利用该值在扩展RAM存储器中寻址,匹配地址单元所对应的值即为下一跳值Nh(i+1,i+7),将该下一跳值输出到优先级比较器中进行比较。Step 2: If the first-level search indicates that there are still longer prefixes to be calculated in the second-level search unit, then a second-level search is required, and the prefix expansion item is expanded by using the memory expansion technology in the second level EPE can be inserted into block RAM with 128 addresses. Let the corresponding bits of the prefix be [i+1:i+7] (i is the length of the hash prefix), and when searching, calculate the index value according to the (i+1~i+7)th bits of the destination address, and use This value is addressed in the extended RAM memory, and the value corresponding to the matching address unit is the next hop value Nh(i+1, i+7), and the next hop value is output to the priority comparator for comparison.
第三步:将输入到优先级比较器的寄存器中的值进行优先比较,“next hop”输出优先级最高的值(即最长匹配前缀所对应的下一跳值)作为该IPv6目的地址所匹配的下一跳值,即为所查到的值。Step 3: compare the values in the registers of the priority comparator first, and "next hop" outputs the value with the highest priority (that is, the next hop value corresponding to the longest matching prefix) as the IPv6 destination address. The matched next hop value is the found value.
e.在更新过程中,通过哈希计算和扩展存储器地址计算可以进行路由表项更新,包括路由表初始化(构造路由表)、插入表项、删除表项和修改表项,具体如下:e. During the update process, routing table entries can be updated through hash calculations and extended memory address calculations, including routing table initialization (routing table construction), inserting entries, deleting entries and modifying entries, as follows:
●路由表初始化及表项插入步骤为:●The routing table initialization and entry insertion steps are:
①通过需要更新的路由表项确定需要更新表项的位置:先判断需要更新路由前缀的长度是否可以被8整除;① Determine the position of the entry to be updated through the routing table entry that needs to be updated: first determine whether the length of the routing prefix that needs to be updated is divisible by 8;
②如果可以被8整除,通过更新分类器选择出对应的处理模块,将此前缀进行哈希计算,用所得哈希值索引哈希表,如果索引到的哈希表项已经放入其它路由信息,则将该前缀所对应的路由信息放入哈希冲突处理单元中进行处理,如果索引到的哈希表项是空项,则将对应的路由信息放入该项中;② If it can be divisible by 8, select the corresponding processing module by updating the classifier, perform hash calculation on this prefix, and use the obtained hash value to index the hash table. If the indexed hash table item has been put into other routing information , put the routing information corresponding to the prefix into the hash conflict processing unit for processing, and if the indexed hash table entry is empty, put the corresponding routing information into this entry;
③如果前缀长度不可以被8整除,通过更新分类器选择出对应的处理模块,先将该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项做哈希计算,用所得哈希值索引哈希表,若该表项为空,则将所分配的第二级存储单元的首地址存入该表项,然后将所对应的路由信息放入所分配存储单元的对应位置,若该表项不为空且该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项不同于已插入前缀的扩展前缀哈希项,则将该前缀所对应的路由信息插入到已分配的第二级存储单元中,如该表项不为空且该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项和已插入前缀的扩展前缀哈希项相同,则将该前缀放入哈希冲突处理单元中进行处理。③ If the length of the prefix is not divisible by 8, select the corresponding processing module by updating the classifier, first perform hash calculation on the extended prefix hash item of the prefix, and use the obtained hash value to index the hash table. is empty, then store the first address of the allocated second-level storage unit into the entry, and then put the corresponding routing information into the corresponding location of the allocated storage unit, if the entry is not empty and the address of the prefix If the extended prefix hash item is different from the extended prefix hash item that has already been inserted, insert the routing information corresponding to the prefix into the allocated second-level storage unit. If the entry is not empty and the extension of the prefix If the prefix hash item is the same as the extended prefix hash item with the inserted prefix, the prefix is put into the hash conflict processing unit for processing.
如图5所示,路由表构造及表项插入的具体过程描述如下:As shown in Figure 5, the specific process of routing table construction and entry insertion is described as follows:
第一步:将哈希表和扩展RAM初始化为空;Step 1: Initialize the hash table and extended RAM to be empty;
第二步:根据待插入前缀长度来判断此前缀属于哈希前缀HP还是扩展前缀EP,如果是HP,则将此前缀进行哈希计算,用所得哈希值索引哈希表,如果索引到的哈希表项中“F”字段为“0”,则将该项的“F”字段设为“1”,“Nh(i)”字段设为该前缀所对应的下一跳值;如果对应项中“F”字段为“1”,表明该前缀项产生哈希冲突,则用CPE进行哈希冲突处理。Step 2: Determine whether the prefix belongs to the hash prefix HP or the extended prefix EP according to the length of the prefix to be inserted. If it is HP, perform hash calculation on this prefix, and use the obtained hash value to index the hash table. If the index is If the "F" field in the hash table entry is "0", then the "F" field of the item is set to "1", and the "Nh(i)" field is set to the next hop value corresponding to the prefix; if the corresponding The "F" field in the entry is "1", indicating that the prefix entry generates a hash collision, and the CPE is used to handle the hash collision.
如果是EP,则将此前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH做哈希计算,用所得哈希值索引哈希表,判断索引到的哈希表项“E”字段是否为“0”,如果“E”字段为“0”,则将哈希表对应项的“E”字段设为“1”,“Block_addr”字段是为扩展前缀扩展项EPE所分配块RAM的编号,用扩展前缀扩展项EPE计算出块RAM的块内相对地址,并将下一跳值放入对应的存储单元中;如果“E”字段为“1”且该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH部分和已插入该项的前缀的扩展前缀哈希项相同,则将该前缀的下一跳值放入该哈希表项“Block_addr”字段所指示的已分配块RAM中,用扩展前缀扩展项EPE计算出块RAM的块内相对地址,并将下一跳值放入对应的存储单元中;如果“E”字段为“1”且该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH部分和已插入该项的前缀的扩展前缀哈希项不同,表明该前缀项产生哈希冲突,则用CPE进行哈希冲突处理。If it is EP, perform hash calculation on the extended prefix hash item EPH of this prefix, use the obtained hash value to index the hash table, and judge whether the "E" field of the indexed hash table item is "0", if " If the "E" field is "0", set the "E" field of the hash table corresponding item to "1", and the "Block_addr" field is the number of the block RAM allocated for the extended prefix extension item EPE, and the extended prefix extension item EPE is used Calculate the relative address in the block RAM block, and put the next hop value into the corresponding storage unit; if the "E" field is "1" and the extended prefix hash item EPH part of the prefix and the EPH part of the item have been inserted If the extended prefix hash items of the prefix are the same, put the next hop value of the prefix into the allocated block RAM indicated by the "Block_addr" field of the hash table item, and use the extended prefix extension item EPE to calculate the block of the block RAM Inner relative address, and put the next hop value into the corresponding storage unit; if the "E" field is "1" and the EPH part of the extended prefix hash item of the prefix and the extended prefix hash of the prefix of the item have been inserted Items are different, indicating that the prefix item generates a hash collision, and the CPE is used to handle the hash collision.
在此用一个例子说明以上路由表的构造过程:现有三个待插入的路由表项,分别为2001:2abc::/32,下一跳值为A,2001:2abc:9::/36,下一跳值为B,2abc:2001:9::/36,下一跳值为C。当插入前缀2001:2abc::/32时,先判断出这个前缀长度为32比特,可以知道该前缀为哈希前缀,经过哈希计算得到结果为16’h0abd,然后判断Hash32第16’h0abd个单元中的“F”字段设是否为“0”,如果为“0”,则将该单元中的“F”字段设为“1”,“Nh(32)”字段设置为“A”,其余字段都不改变;如果为“1”,则将前缀项2001:2abc::/32放入CPE(32,39)中进行处理,这样就完成了第一个表项的插入;Here is an example to illustrate the construction process of the above routing table: there are three routing table entries to be inserted, respectively 2001:2abc::/32, the next hop value is A, 2001:2abc:9::/36, The next hop value is B, 2abc:2001:9::/36, and the next hop value is C. When inserting the prefix 2001:2abc::/32, first determine that the prefix length is 32 bits, you can know that the prefix is a hash prefix, and the result of hash calculation is 16'h0abd, and then judge the 16'h0abd of Hash32 Whether the "F" field in the unit is set to "0", if it is "0", then the "F" field in the unit is set to "1", the "Nh(32)" field is set to "A", and the rest None of the fields are changed; if it is "1", the prefix item 2001:2abc::/32 is put into the CPE (32, 39) for processing, thus completing the insertion of the first table item;
当插入前缀2001:2abc:9::/36时,将其前32位做哈希计算得到的结果为16’h0abd,然后判断Hash32第16’h0abd个单元中的“E”字段为“0”,则将该项的“E”字段设为“1”,再给此扩展前缀扩展项9(二进制可表示为1001000)分配一块8位宽,128个存储单元的块扩展RAM,将此块RAM的编号填充到该哈希表项的“Block_addr”字段,将下一跳值存入扩展RAM的第72(二进制1001000转换为十进制为72)个存储单元中(绝对地址则为该块扩展RAM的编号乘以128,再加上72所得的值),并将该单元的最高位“H”设置为1,这样就完成了路由表项的插入;When the prefix 2001:2abc:9::/36 is inserted, the result obtained by hashing the first 32 bits is 16'h0abd, and then the "E" field in the 16'h0abd unit of Hash32 is judged to be "0" , then the "E" field of the item is set to "1", and then an 8-bit wide block expansion RAM with 128 storage units is allocated to the extension prefix extension item 9 (binary can be expressed as 1001000), and this block RAM Fill in the "Block_addr" field of the hash table entry, and store the next hop value in the 72nd (binary 1001000 converted to decimal is 72) storage unit of the extended RAM (the absolute address is the block of the extended RAM The number is multiplied by 128, plus the value obtained by 72), and the highest bit "H" of the unit is set to 1, thus completing the insertion of the routing table entry;
当插入第三项前缀2abc:2001:9::/36时,将其前32位做哈希计算得到的结果为16’h0abd,然后判断Hash32第16’h0abd个单元中的“E”字段为“1”,但是该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH和已插入前缀的扩展前缀哈希项不同,所以将该前缀放入哈希冲突处理模块CPE中进行处理。When the third prefix 2abc:2001:9::/36 is inserted, the result obtained by hashing the first 32 bits is 16'h0abd, and then the "E" field in the 16'h0abd unit of Hash32 is judged as "1", but the extended prefix hash item EPH of the prefix is different from the extended prefix hash item of the inserted prefix, so the prefix is put into the hash collision processing module CPE for processing.
这样,将所有的路由表项进行插入就完成了路由表的构建。In this way, all routing table entries are inserted to complete the construction of the routing table.
●表项删除及修改步骤为:●The steps to delete and modify entries are as follows:
①通过更新分类器选择出对应的处理模块;① Select the corresponding processing module by updating the classifier;
②利用查找方法,查找到待更新的路由表项,然后将该表项的路由信息进行删除或者修改。② Use the search method to find the routing entry to be updated, and then delete or modify the routing information of the entry.
路由表项删除及修改的具体情况描述如下:The details of deleting and modifying routing table entries are described as follows:
路由表项的更新主要包括三种操作,插入、删除和修改,分别要根据待更新项的前缀值确定更新表项的位置。对于前缀插入操作,可以按照路由表的创建算法进行插入。对于前缀修改和删除操作,则类似于地址查找的过程,首先利用查找算法,找到该前缀表项,然后再执行相应的修改和删除操作,可以分为以下两种情况:The update of the routing table entry mainly includes three operations, insert, delete and modify, and respectively determine the location of the updated table entry according to the prefix value of the entry to be updated. For the prefix insertion operation, the insertion can be performed according to the creation algorithm of the routing table. For prefix modification and deletion operations, it is similar to the process of address search. First, use the search algorithm to find the prefix entry, and then perform the corresponding modification and deletion operations, which can be divided into the following two cases:
第1种情况:当要修改或删除的前缀为哈希前缀时,则将“F”字段设置为“0”,清空其它字段的值;Case 1: When the prefix to be modified or deleted is a hash prefix, set the "F" field to "0" and clear the values of other fields;
第2种情况:当要修改或删除的前缀为扩展前缀时,则将“E”字段和“Block_addr”字段设置为全“0”,然后收回扩展RAM的存储空间。Case 2: When the prefix to be modified or deleted is an extended prefix, the "E" field and the "Block_addr" field are set to all "0", and then the storage space of the extended RAM is reclaimed.
其实也可以将路由表的更新看成地址查找的另一种功能,就是找到特定的位置,在该位置上进行插入操作或者删除操作。In fact, the update of the routing table can also be regarded as another function of address search, which is to find a specific location and perform an insert or delete operation on that location.
将长度可以被8整除的路由前缀用哈希表进行存储,将长度不能被8整除的前缀用哈希表和扩展存储器做两级存储。The routing prefix whose length is divisible by 8 is stored in a hash table, and the prefix whose length is not divisible by 8 is stored in two levels using a hash table and an extended memory.
将长度为n的前缀(n不能被8整除)可以分为两个部分:1~i和i+1~n,i是小于n且最大可以被8整除的整数。将前缀中1~i比特之间的值所对应的信息存储到哈希表中,而i+1~n之间的值所对应的信息存放到扩展存储器中,两级之间有相互联系的字段。如图4所示,哈希表存放哈希前缀HP和扩展前缀哈希项EPH的信息,第二级的扩展RAM存放扩展前缀扩展项EPE的信息,这两级查找之间通过信号“E”进行连接。在查找过程中,如果哈希项中的“F”为“1”,则表示该项即为匹配项;如果哈希表项中的“E”为“1”,则表示所查找的地址还需要在扩展RAM中查找更长的匹配项;如果扩展RAM项中的“H”为“1”,则表示该扩展RAM项中的值为匹配的下一跳索引值。A prefix with a length of n (n cannot be divisible by 8) can be divided into two parts: 1~i and i+1~n, where i is an integer smaller than n and at most divisible by 8. The information corresponding to the value between 1 and i bits in the prefix is stored in the hash table, and the information corresponding to the value between i+1 and n is stored in the extended memory, and there is a relationship between the two levels field. As shown in Figure 4, the hash table stores the information of the hash prefix HP and the extended prefix hash item EPH, and the second-level extended RAM stores the information of the extended prefix extension item EPE, and the signal "E" is passed between the two levels of search to connect. During the search process, if the "F" in the hash item is "1", it means that the item is a match; if the "E" in the hash table item is "1", it means that the address you are looking for is still A longer matching item needs to be searched in the extended RAM; if "H" in the extended RAM item is "1", it means that the value in the extended RAM item is the matching next-hop index value.
按照前缀长度从长到短,在优先级比较器中设置优先级从高到低的13个寄存器,实现最长前缀匹配结果。According to the prefix length from long to short, 13 registers with priority from high to low are set in the priority comparator to achieve the longest prefix matching result.
优先级比较器的流程图如图13所示,工作过程如下:The flowchart of the priority comparator is shown in Figure 13, and the working process is as follows:
第一步:定义13个寄存器,分别表示各查找结果的优先级,设置其优先级从高到低依次为:“Nh64”,“Nh57-63”,“Nh56”,“Nh49-55”,“Nh48”,“Nh41-47”,“Nh40”,“Nh 33-39”,“Nh 32”,“Nh 25-31”,“Nh 24”,“Nh 17-23”,“Nh 16”,并将这13个寄存器初始化为零。Step 1: Define 13 registers, which respectively represent the priority of each search result, and set their priority from high to low as follows: "Nh64", "Nh57-63", "Nh56", "Nh49-55", " Nh48", "Nh41-47", "Nh40", "Nh 33-39", "
第二步:如果哪一个寄存器内的值不为零,则该寄存器中所存的值为待查目的地址所匹配的一个下一跳,而该目的地址的最长匹配前缀所对应的下一跳值为优先级最高的寄存器里的值,将该值作为下一跳值输出,即为所查。Step 2: If the value in any register is not zero, the value stored in the register is a next hop matched by the destination address to be checked, and the next hop corresponding to the longest matching prefix of the destination address The value is the value in the register with the highest priority, and the value is output as the next jump value, which is the value to be checked.
将哈希处理单元Hash16、Hash24、Hash32、Hash40、Hash48、Hash56、Hash64所计算的16位值直接作为哈希值在哈希表中进行索引,;The 16-bit values calculated by the hash processing units Hash16, Hash24, Hash32, Hash40, Hash48, Hash56, and Hash64 are directly indexed in the hash table as hash values;
哈希处理单元Hash16、Hash24、Hash32、Hash40、Hash48、Hash56与对应的扩展存储器RAM17_23、RAM25_31、RAM33_39、RAM41_47、RAM49_55、RAM57_63进行两级关联,并和对应的哈希冲突处理单元CPE16_23、CPE24_31、CPE32_39、CPE40_47、CPE48_55、CPE56_63分别构成6路处理模块,第7个哈希处理单元hash64和其对应的哈希冲突处理单元CPE64构成1路处理模块,7路模块并行对IPv6地址进行查找以确定其匹配前缀项,在7路查找出的结果中,通过优先级比较器进行比较以实现最长前缀匹配。The hash processing units Hash16, Hash24, Hash32, Hash40, Hash48, Hash56 are associated with the corresponding extended memory RAM17_23, RAM25_31, RAM33_39, RAM41_47, RAM49_55, RAM57_63 in two levels, and are associated with the corresponding hash conflict processing units CPE16_23, CPE24_31, CPE32_39 , CPE40_47, CPE48_55, and CPE56_63 respectively constitute 6-way processing modules, the seventh hash processing unit hash64 and its corresponding hash conflict processing unit CPE64 constitute 1-way processing modules, and the 7-way modules search IPv6 addresses in parallel to determine their matching Prefix items, among the results of the 7-way search, are compared by the priority comparator to achieve the longest prefix match.
通过哈希计算和扩展存储器地址计算完成路由表项更新工作,路由表项的更新主要包括三种操作,插入、删除和修改,分别要根据待更新项的前缀值确定更新表项的位置,对于前缀插入操作,可以按照路由表的创建算法进行插入。对于前缀修改和删除操作,则类似于地址查找的过程,首先利用查找算法,找到该前缀表项,然后再执行相应的修改和删除操作,可以分为以下两种情况:The update of routing table items is completed through hash calculation and extended memory address calculation. The update of routing table items mainly includes three operations, insertion, deletion and modification. The location of the updated table item should be determined according to the prefix value of the item to be updated. For The prefix insertion operation can be performed according to the creation algorithm of the routing table. For prefix modification and deletion operations, it is similar to the process of address search. First, use the search algorithm to find the prefix entry, and then perform the corresponding modification and deletion operations, which can be divided into the following two cases:
第1种情况:当要修改或删除的前缀为哈希前缀时,则将“F”字段设置为“0”,清空其它字段的值;Case 1: When the prefix to be modified or deleted is a hash prefix, set the "F" field to "0" and clear the values of other fields;
第2种情况:当要修改或删除的前缀为扩展前缀时,则将“E”字段和“Block_addr”字段设置为全“0”,然后收回扩展RAM的存储空间。Case 2: When the prefix to be modified or deleted is an extended prefix, the "E" field and the "Block_addr" field are set to all "0", and then the storage space of the extended RAM is reclaimed.
有益效果:Beneficial effect:
本发明是采用基于哈希表和扩展存储器的两级结构查找方案,有93%以上的IPv6地址可以使用一个存储周期即可完成查找,不到7%的IPv6地址只需要两个存储周期即可完成查找,所以本发明具有很高的查找效率。The present invention adopts a two-level structure search scheme based on hash table and extended memory, more than 93% of IPv6 addresses can be searched in one storage cycle, and less than 7% of IPv6 addresses only need two storage cycles Complete the search, so the present invention has very high search efficiency.
由于地址查找方案会占用相对较大的存储空间,存储空间也是衡量地址查找方案优劣的主要性能之一,所以按照65536项的IPv6路由表的规模,将该方法所占的存储空间大小进行统计,如下:Since the address lookup scheme will occupy a relatively large storage space, and storage space is also one of the main performances to measure the pros and cons of the address lookup scheme, so according to the size of the IPv6 routing table with 65536 items, the storage space occupied by this method is counted ,as follows:
按照定义,对哈希表Hash16、Hash24、Hash32、Hash40、Hash48、Hash56、Hash64用20位宽的地址总线,17位宽的数据总线,这样,哈希表总共所占的存储为:220×(24+1)×7=14.875(MB);According to the definition, the hash table Hash16, Hash24, Hash32, Hash40, Hash48, Hash56, and Hash64 use a 20-bit wide address bus and a 17-bit wide data bus. In this way, the total storage occupied by the hash table is: 220 × (24 +1)×7=14.875(MB);
设扩展前缀按7%计算,65536项路由表中有4587项扩展前缀,且每个扩展前缀所占的存储空间为27×8=1k(7位宽的地址总线,8位宽的数据总线)可以求出总共需要的存储空间为:4587×1k=4587k(b)=0.4587(MB);Assuming that the extended prefix is calculated by 7%, there are 4587 extended prefixes in the 65536 routing table, and the storage space occupied by each extended prefix is 27 * 8 = 1k (7-bit wide address bus, 8-bit wide data bus ) can find that the total required storage space is: 4587*1k=4587k(b)=0.4587(MB);
设冲突率是按前缀分布比例分布的,如果按9.86%的冲突率来计算(该冲突率是统计得到的,会随着哈希表深度增加而减小),总共有6462项会发生哈希冲突,在处理哈希冲突时,所需要的CAM为:28.75kB;Assuming that the conflict rate is distributed according to the proportion of the prefix distribution, if it is calculated according to the conflict rate of 9.86% (the conflict rate is obtained from statistics and will decrease as the depth of the hash table increases), a total of 6462 items will be hashed Conflict, when dealing with hash conflicts, the required CAM is: 28.75kB;
可以得到,如果65536项的路由表,使用本方案总共需要RAM为15.33MB,需要CAM 28.75kB。It can be obtained that if there are 65536 entries in the routing table, using this solution requires a total of 15.33MB of RAM and 28.75kB of CAM.
由于预先设定大小的RAM和CAM还能存放更多路由表项,且哈希表的深度可以增加,所以本发明的扩展性强且容易实现。Since the pre-set RAM and CAM can store more routing table items, and the depth of the hash table can be increased, the present invention has strong expansibility and is easy to implement.
因此,本发明方法的优点是查找效率高、存储利用率高、可扩展性强且实现简单。Therefore, the method of the present invention has the advantages of high search efficiency, high storage utilization, strong scalability and simple implementation.
附图说明Description of drawings
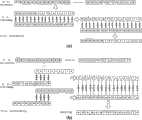
图1是基于哈希表和扩展存储器的高性能IPv6地址查找方法总体结构图;Fig. 1 is the overall structural diagram of the high-performance IPv6 address search method based on hash table and extended memory;
图2是IPv6路由表的前缀分布规律;Fig. 2 is the prefix distribution law of IPv6 routing table;
图3:a是哈希表存储结构,b是扩展存储器的存储结构;Figure 3: a is the hash table storage structure, b is the storage structure of the extended memory;
图4是哈希表和扩展存储器的组织方式;Fig. 4 is the organization mode of hash table and extended memory;
图5是路由表构造及前缀插入流程图;Fig. 5 is a flowchart of routing table construction and prefix insertion;
图6是查找过程流程图;Fig. 6 is a search process flowchart;
图7:a是48比特值的哈希计算过程示意图,b是40比特值哈希计算过程示意图;Figure 7: a is a schematic diagram of the hash calculation process of a 48-bit value, and b is a schematic diagram of the hash calculation process of a 40-bit value;
图8是1-16比特值的哈希组织过程;Fig. 8 is the hash organization process of 1-16 bit value;
图9是扩展前缀在扩展存储器中的组织;Fig. 9 is the organization of the extension prefix in the extension memory;
图10是第二级扩展存储器地址分配实例示意图;Fig. 10 is a schematic diagram of an example of second-level extended memory address allocation;
图11是块RAM分配的一种特例;Figure 11 is a special case of block RAM allocation;
图12是哈希单元与扩展存储器的组织关系示意图;Fig. 12 is a schematic diagram of the organizational relationship between the hash unit and the extended memory;
图13是优先级比较流程图;Fig. 13 is a priority comparison flowchart;
图14是哈希冲突处理原理图。Fig. 14 is a schematic diagram of hash collision processing.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明的具体实现方式描述如下:The specific implementation of the present invention is described as follows:
(1)总体实现结构(1) Overall implementation structure
该方法使用7路哈希表并行查找,如图1所示。总体设计可以分为四部分:哈希表的设计,扩展RAM的设计,哈希冲突处理单元的设计以及优先级比较器的设计。而且还需要考虑到每种哈希表的结构都不同,第一级哈希表和第二级扩展RAM如何进行组织。The method uses a 7-way hash table for parallel lookup, as shown in Figure 1. The overall design can be divided into four parts: the design of the hash table, the design of the extended RAM, the design of the hash conflict processing unit and the design of the priority comparator. Moreover, it is also necessary to consider that the structure of each hash table is different, how to organize the first-level hash table and the second-level extended RAM.
由于哈希表和扩展RAM之间存在一定的关系:哈希表Hashi可以存放哈希前缀HP(i)和扩展前缀哈希项EPH(i+1,i+7)的信息,所以将具体方案划分为:Hash16和RAM17_23查找单元、Hash24和RAM25_31查找单元、Hash32和RAM33_39查找单元、Hash40和RAM41_47查找单元、Hash48和RAM49_55查找单元、Hash56和RAM57_63查找单元、Hash64查找单元以及优先级比较器。Since there is a certain relationship between the hash table and the extended RAM: the hash table Hashi can store the information of the hash prefix HP(i) and the extended prefix hash item EPH(i+1, i+7), so the specific scheme Divided into: Hash16 and RAM17_23 search unit, Hash24 and RAM25_31 search unit, Hash32 and RAM33_39 search unit, Hash40 and RAM41_47 search unit, Hash48 and RAM49_55 search unit, Hash56 and RAM57_63 search unit, Hash64 search unit and priority comparator.
按照这样的单元划分,Hash16和RAM17_23查找单元、Hash24和RAM25_31查找单元、Hash32和RAM33_39查找单元、Hash40和RAM41_47查找单元、Hash48和RAM49_55查找单元、Hash56和RAM57_63查找单元的实现方法及结构组织类似,即第一级哈希查找和第二级扩展RAM查找,只需要将不同单元的哈希函数改变即可,Hash64查找单元仅仅是哈希查找,而没有扩展RAM,实现更加简单,而且第一级哈希表和第二级扩展RAM的组织容易实现。According to this unit division, the implementation methods and structural organization of Hash16 and RAM17_23 search unit, Hash24 and RAM25_31 search unit, Hash32 and RAM33_39 search unit, Hash40 and RAM41_47 search unit, Hash48 and RAM49_55 search unit, Hash56 and RAM57_63 search unit are similar, namely The first-level hash lookup and the second-level extended RAM lookup only need to change the hash function of different units. The Hash64 search unit is only a hash lookup without expanding RAM, which is simpler to implement, and the first level hash The organization of Greek tables and second-level extended RAM is easy to implement.
所以按照这样的划分,具体实现的有这几部分:哈希单元的设计,扩展RAM单元的设计,哈希单元和扩展RAM的组织,哈希冲突处理单元的设计以及优先级比较器的设计。Therefore, according to this division, there are several parts to be implemented specifically: the design of the hash unit, the design of the extended RAM unit, the organization of the hash unit and the extended RAM, the design of the hash conflict processing unit, and the design of the priority comparator.
为了减少哈希冲突的发生,每个哈希表都是独立编址,但哈希表存储的数据结构都相同。将Hash16和RAM17_23查找单元、Hash24和RAM25_31查找单元、Hash32和RAM33_39查找单元、Hash40和RAM41_47查找单元、Hash48和RAM49_55查找单元、Hash56和RAM57_63查找单元、Hash64查找单元所产生的哈希冲突都分别用CAM进行处理,因为在不影响系统性能的情况下,CAM可以使用一个存储周期完成一次查找,并且CAM的设计复杂度及功耗比TCAM低。In order to reduce the occurrence of hash collisions, each hash table is independently addressed, but the data structures stored in the hash tables are the same. The hash collisions generated by Hash16 and RAM17_23 search units, Hash24 and RAM25_31 search units, Hash32 and RAM33_39 search units, Hash40 and RAM41_47 search units, Hash48 and RAM49_55 search units, Hash56 and RAM57_63 search units, and Hash64 search units are all used in CAM For processing, because without affecting the system performance, CAM can use one storage cycle to complete a search, and the design complexity and power consumption of CAM are lower than that of TCAM.
(2)查找分类器和更新分类器的设计与实现(2) Design and implementation of search classifier and update classifier
查找分类器取待查IPv6地址的前16位、24位、32位、40位、48位、56位、64位,分别送入7路模块中并行查找。例如,待查目的IPv6地址为2001:4500:5a6b:44f9:0:0:0:0(16进制表示法),则将2001、2001:45、2001:4500、2001:4500:5a、2001:4500:5a6b、2001:4500:5a6b:44、2001:4500:5a6b:44f9分别送入到如图1中的7路模块中进行处理。The search classifier takes the first 16 bits, 24 bits, 32 bits, 40 bits, 48 bits, 56 bits, and 64 bits of the IPv6 address to be checked, and sends them to the 7-way module for parallel search. For example, if the destination IPv6 address to be checked is 2001:4500:5a6b:44f9:0:0:0:0 (in hexadecimal notation), then 2001, 2001:45, 2001:4500, 2001:4500:5a, :4500:5a6b, 2001:4500:5a6b:44, 2001:4500:5a6b:44f9 are respectively sent to the 7-channel module as shown in Figure 1 for processing.
更新分类器将待更新数据进行判断发送到对应的7路模块中进行更新。例如,待插入的路由表项为2001:2abc::/32,则将该表项所对应的路由信息送入到Hash32模块中进行插入操作;待删除的路由表项为2001:2abc:ba5::/44,则将Hash40和RAM41_47查找单元的对应表项进行删除即可。The update classifier judges the data to be updated and sends it to the corresponding 7-way module for update. For example, if the routing entry to be inserted is 2001:2abc::/32, then the routing information corresponding to the entry is sent to the Hash32 module for insertion; the routing entry to be deleted is 2001:2abc:ba5: :/44, delete the corresponding entries of the Hash40 and RAM41_47 search units.
(3)哈希单元的设计与实现(3) Design and implementation of hash unit
利用基于折叠XOR算法的哈希函数进行哈希计算,为了降低哈希冲突率,对7种不同长度的数据采用7种不同的折叠XOR哈希算法,在描述时,我们将所有的哈希索引值都设置成16位宽,但是在具体实现时,可以根据不同前缀分布设置不同的位宽。对本文所涉及到的XOR Folding算法分为以下两种情况:Use the hash function based on the folded XOR algorithm for hash calculation. In order to reduce the hash collision rate, 7 different folded XOR hash algorithms are used for data of 7 different lengths. When describing, we index all the hashes The values are all set to 16-bit width, but in actual implementation, different bit widths can be set according to different prefix distributions. The XOR Folding algorithm involved in this article is divided into the following two situations:
第一种情况:直接折叠法,若数据可以划分为相等长度的子数据,且子数据长度和所要求的哈希索引值位宽相等,则将数据做直接划分为相等长度的若干个子数据,然后将子数据对应位进行异或操作。The first case: direct folding method, if the data can be divided into sub-data of equal length, and the length of the sub-data is equal to the required bit width of the hash index value, then the data is directly divided into several sub-data of equal length, Then XOR operation is performed on the corresponding bits of the sub-data.
例如,若有一个48位的二进制数B[47:0],需要计算得到的索引值为16位宽的Index[15:0],则Index计算公式为:过程如以下例子:For example, if there is a 48-bit binary number B[47:0], the index value to be calculated is Index[15:0] with a width of 16 bits, and the index calculation formula is: The process is like the following example:
48比特的值利用XOR Folding计算哈希索引值的过程,如图7(a)所示:The 48-bit value uses XOR Folding to calculate the hash index value process, as shown in Figure 7(a):
第一步:对输入的48比特值B[47:0]进行哈希计算,B[47:0]是IPv6地址的前48位或者48比特长度的前缀。Step 1: Perform hash calculation on the input 48-bit value B[47:0]. B[47:0] is the first 48 bits of the IPv6 address or a 48-bit prefix.
第二步:对此值进行折半异或操作,可以得到中间值B1[15:0]:Step 2: Execute the halved XOR operation on this value to get the intermediate value B1[15:0]:
第三步:对中间值B1[15:0]和B[47:32]进行位异或操作,得出哈希索引值index[15:0]:Step 3: Execute a bit-exclusive OR operation on the intermediate values B1[15:0] and B[47:32] to obtain the hash index value index[15:0]:
在该方案中,对长度为64比特,48比特和32比特的值使用直接折叠法进行哈希计算。In this scheme, the hash calculation is performed using the direct folding method for values of length 64 bits, 48 bits and 32 bits.
第二种情况:错位折叠法,若数据可以划分为相等长度的子数据,但子数据长度和所要求的哈希索引值位宽不相等,则将数据做直接划分为相等长度的若干个子数据,然后将子数据之间进行错位,凑成和索引值位宽相等后再进行异或操作。The second case: dislocation folding method, if the data can be divided into sub-data of equal length, but the length of the sub-data is not equal to the required bit width of the hash index value, then the data is directly divided into several sub-data of equal length , and then misplace the sub-data to make it equal to the bit width of the index value before performing the XOR operation.
若有一个40位的二进制数B[39:0]。需要计算得到的索引值为16位宽的Index[15:0],则Index计算公式为:0<i,j,p,q<40。If there is a 40-bit binary number B[39:0]. The index value that needs to be calculated is Index[15:0] with a width of 16 bits, and the formula for calculating Index is: 0<i, j, p, q<40.
例如,40比特的值利用XOR Folding计算哈希索引值的过程,如图7(b)所示:For example, the 40-bit value uses XOR Folding to calculate the hash index value process, as shown in Figure 7(b):
第一步:对输入的40比特值B[39:0]进行哈希计算,B[39:0]是IPv6地址的前40位或者40比特长度的前缀。Step 1: Perform hash calculation on the input 40-bit value B[39:0]. B[39:0] is the first 40 bits of the IPv6 address or the 40-bit prefix.
第二步:对此值进行折半异或操作,可以得到中间值B1[15:0]和B2[15:0]:Step 2: Execute the halved XOR operation on this value to get the intermediate values B1[15:0] and B2[15:0]:
第三步:得出哈希索引值index[15:0]:Step 3: Get the hash index value index[15:0]:
在该方案中,对长度为56比特,40比特和24比特的值使用错位折叠法进行哈希计算。In this scheme, values of length 56 bits, 40 bits, and 24 bits are hashed using the misfolding method.
对1-16比特值进行组织过程如下:The 1-16 bit values are organized as follows:
可以直接将16位的值作为哈希索引,如图8所示,其实hash16可以对0-16比特的值直接进行处理,例如,10比特长的二进制数“1000110110”(转换成十进制数为566),其哈希表索引地址为16’d566,那么,哈希表中16’d566单元即为所查找到的单元。因此,可以用一次访问存储时间解决1-16位长数据的查找,而且该单元不会发生哈希冲突情况。The 16-bit value can be directly used as a hash index, as shown in Figure 8, in fact, hash16 can directly process the value of 0-16 bits, for example, the 10-bit long binary number "1000110110" (converted to a decimal number is 566 ), the index address of the hash table is 16'd566, then the unit 16'd566 in the hash table is the found unit. Therefore, the lookup of 1-16-bit long data can be solved with one access storage time, and there will be no hash collision in this unit.
(4)扩展存储器的实现(4) Implementation of extended memory
A.扩展前缀扩展项EPE在扩展RAM中地址的计算A. Calculation of the address of the extended prefix extension item EPE in the extended RAM
已知一扩展前缀EP,可以获得它的扩展前缀扩展项EPE(i,n),其中n是EP的长度,而i是小于n的能被8整除的最大整数,n-i+1<7。用EPE可以形成一个7位的二进制数δ,用δ作为索引,将该前缀所对应的下一跳信息插入到给其所分配块RAM的第δ个存储单元中,这样就可以完成该前缀的组织。EPE所形成的二进制数δ用Verilog语言描述为:Given an extended prefix EP, its extended prefix extension item EPE(i, n) can be obtained, where n is the length of EP, and i is the largest integer smaller than n that can be divisible by 8, n-
{E P E,j{0}},其中j=n-i+1。{E P E, j{0}}, where j=n-
以32到39位长度前缀组织为例说明扩展前缀在扩展RAM中的组织方式,如图9所示,32位长的前缀为哈希前缀HP(32),则其信息可以直接存储在哈希表Hash32中,而33到39位长的前缀为扩展前缀,其高32位扩展前缀哈希项EPH的有效信息存储到哈希表Hash32中,低位信息存储于扩展RAM3339中。Take the 32- to 39-bit length prefix organization as an example to illustrate the organization of the extended prefix in the extended RAM. As shown in Figure 9, the 32-bit long prefix is the hash prefix HP(32), and its information can be directly stored in the hash In the table Hash32, the 33 to 39-bit long prefix is an extended prefix, and the effective information of the high-order 32-bit extended prefix hash item EPH is stored in the hash table Hash32, and the low-order information is stored in the extended RAM3339.
B.扩展RAM的分配及回收B. Allocation and recycling of extended RAM
这一小节主要描述块RAM的分配以及回收。This section mainly describes the allocation and recycling of block RAM.
块RAM的分配分为以下几种情况,如图10所示:The allocation of block RAM is divided into the following situations, as shown in Figure 10:
情况1:待插入前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH和已插入前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH都不相同。如果已经插入了4条都不同的前缀,且4条前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH都不相同,所以给每条前缀都分配一个128个存储单元的块RAM,各自的前缀信息分别存储到不同块RAM中。第5条前缀待插入,先判断其扩展前缀哈希项与已分配前缀的扩展前缀哈希项是否相同,如果不同,则重新分配一个128个存储单元的块RAM;Case 1: The extended prefix hash item EPH to be inserted with the prefix is different from the extended prefix hash item EPH with the prefix inserted. If four different prefixes have been inserted, and the extended prefix hash items EPH of the four prefixes are different, a block RAM of 128 storage units is allocated to each prefix, and the respective prefix information is stored in different block RAM.
情况2:待插入前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH和已插入前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH有相同的情况。第5条前缀待插入,先判断其扩展前缀哈希项EPH与已分配前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH是否相同,如果相同,例如和第二条前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH相同,则将第5条前缀的路由信息插入到第2个已分配的块RAM中,而不需要重新分配块RAM,这样不会发生冲突。因为,如果有两条不同的前缀P1和P2,当P1和P2的扩展前缀哈希项EPH相同时,其扩展前缀扩展项EPE一定不相同,而这两条前缀的路由信息一定存储在所分配的同一块RAM中,由于扩展前缀扩展项EPE不相同,所以在同一块RAM中所计算得到的地址肯定不同。Case 2: The extended prefix hash item EPH to be inserted with a prefix has the same situation as the extended prefix hash item EPH with a prefix inserted. The fifth prefix is to be inserted, first judge whether the extended prefix hash item EPH is the same as the extended prefix hash item EPH of the assigned prefix, if they are the same, for example, the same as the extended prefix hash item EPH of the second prefix, then the The routing information of the fifth prefix is inserted into the second allocated block RAM without reallocating the block RAM, so that no conflicts will occur. Because, if there are two different prefixes P1 and P2, when the extended prefix hash items EPH of P1 and P2 are the same, the extended prefix extension items EPE must be different, and the routing information of these two prefixes must be stored in the allocated In the same block of RAM, the addresses calculated in the same block of RAM must be different because the extended prefix extension EPE is different.
扩展前缀在扩展RAM中绝对地址的计算过程为:当分配的块RAM的编号为block_addr,扩展前缀扩展项EPE转换成的十进制数为V(epe),则该前缀所对应信息应该存储的单元绝对地址ram_addr为:The calculation process of the absolute address of the extended prefix in the extended RAM is: when the number of the allocated block RAM is block_addr, and the decimal number converted from the extended prefix extension item EPE is V(epe), then the unit where the information corresponding to the prefix should be stored is absolutely The address ram_addr is:
ram_addr=128×block_addr+V(epe)。(公式1)ram_addr=128×block_addr+V(epe). (Formula 1)
当进行表项删除时,就需要回收已分配的块RAM,由于该方案对每个扩展前缀所分配的块RAM都是128个存储单元,所以在块RAM回收时,整个扩展RAM存储器不会产生存储碎片。如果要给该空闲块插入表项,只需要得到对该空闲块所分配的编号即可。When the table entry is deleted, the allocated block RAM needs to be reclaimed. Since the block RAM allocated for each extended prefix in this scheme is 128 storage units, when the block RAM is reclaimed, the entire extended RAM memory will not be generated. Storage fragmentation. If you want to insert an entry into the free block, you only need to obtain the number allocated to the free block.
(5)哈希单元和扩展存储器的组织(5) Organization of hash unit and extended memory
第一级哈希单元与第二级扩展RAM单元的组织关系如图12所示,其中有任意四个前缀prefix1,prefix2,prefix3,prefix4,下一跳分别为AA,BB,CC,DD,prefix1和prefix3为哈希前缀HP,prefix2和prefix4为扩展前缀EP,prefix3的值和prefix4扩展前缀哈希项EPH的值相同。The organizational relationship between the first-level hash unit and the second-level extended RAM unit is shown in Figure 12, in which there are any four prefixes prefix1, prefix2, prefix3, prefix4, and the next hops are AA, BB, CC, DD, prefix1 And prefix3 is the hash prefix HP, prefix2 and prefix4 are the extended prefix EP, and the value of prefix3 is the same as the value of prefix4 extended prefix hash item EPH.
哈希表的第16’h00fi+1个单元存储prefix1的路由信息,其下一跳值为AA;第16’h00ff+2个单元存储prefix2扩展前缀哈希项EPH的信息,给其扩展前缀扩展项EPE分配了第69个块RAM;第16’h0fff+3个单元存储prefix3的路由信息,其下一跳为BB,同时也存储prefix4扩展前缀哈希项EPH的信息,给其扩展前缀扩展项EPE分配了第115个块RAM。The 16'h00fi+1 unit of the hash table stores the routing information of prefix1, and its next hop value is AA; the 16'h00ff+2 unit stores the information of the prefix2 extended prefix hash item EPH, and extends the prefix extension to it The item EPE allocates the 69th block of RAM; the 16'h0fff+3 unit stores the routing information of prefix3, and its next hop is BB, and also stores the information of prefix4 extended prefix hash item EPH, giving it an extended prefix extension item EPE allocates the 115th block of RAM.
根据公式1,第69个块RAM的首地址为69*128+0,而prefix2的扩展前缀扩展项EPE进行低位补零扩展成7位二进制数,最后转换成十进制数为85,则将prefix2的下一跳信息CC插入到扩展RAM的第69*128+85个地址单元中。同样,第115个块RAM的首地址为115*128+0,而prefix4的扩展前缀扩展项EPE进行低位补零扩展成7位二进制数,最后转换成十进制数为42,则将prefix4的下一跳信息DD插入到扩展RAM的第115*128+42个地址单元中。According to
以上过程为第一级哈希单元和第二级扩展RAM之间的组织关系,图12中的灰色项表示有效前缀项,用虚线括起来的扩展RAM为被分配的块RAM。该方案中,所有扩展前缀EP的第一级哈希表和第二级扩展RAM都是以这种方式组织的。The above process is the organizational relationship between the first-level hash unit and the second-level extended RAM. The gray items in Figure 12 represent effective prefix items, and the extended RAM enclosed by dotted lines is the allocated block RAM. In this scheme, the first-level hash tables and second-level extended RAMs of all extended prefix EPs are organized in this way.
(6)优先级比较器的实现(6) Implementation of Priority Comparator
优先级比较器的流程图如图13所示,工作过程如下:The flowchart of the priority comparator is shown in Figure 13, and the working process is as follows:
第一步:定义13个寄存器,分别表示各查找结果的优先级,设置其优先级从高到低依次为:“Nh64”,“Nh57-63”,“Nh56”,“Nh49-55”,“Nh48”,“Nh41-47”,“Nh40”,“Nh 33-39”,“Nh 32”,“Nh 25-31”,“Nh 24”,“Nh 17-23”,“Nh 16”,并将这13个寄存器初始化为零。Step 1: Define 13 registers, which respectively represent the priority of each search result, and set their priority from high to low as follows: "Nh64", "Nh57-63", "Nh56", "Nh49-55", " Nh48", "Nh41-47", "Nh40", "Nh 33-39", "
第二步:如果哪一个寄存器内的值不为零,则该寄存器中所存的值为待查目的地址所匹配的一个下一跳,而该目的地址的最长匹配前缀所对应的下一跳值为优先级最高的寄存器里的值,将该值作为下一跳值输出,即为所查。Step 2: If the value in any register is not zero, the value stored in the register is a next hop matched by the destination address to be checked, and the next hop corresponding to the longest matching prefix of the destination address The value is the value in the register with the highest priority, and the value is output as the next jump value, which is the value to be checked.
举例说明:在一条目的地址查找过程中,如果优先级比较器中,寄存器“Nh48”的值为8’h0a,寄存器“Nh32”的值为8’h0b,寄存器“Nh17-23”的值为8’h0c,其余寄存器的值依然为8’h00,则可以看出该地址有三个匹配项,而这三个匹配项中,所对应的下一跳值为分别为8’h0a,8’h0b,8’h0c,由于寄存器“Nh 48”的优先级高于寄存器“Nh 32”和寄存器“Nh17-23”,所以寄存器“Nh48”中的值8’h0a即为该地址最长匹配前缀所对应的下一跳值。For example: In the process of searching for an entry address, if the value of the register "Nh48" is 8'h0a, the value of the register "Nh32" is 8'h0b, and the value of the register "Nh17-23" is 8 in the priority comparator 'h0c, the value of the other registers is still 8'h00, it can be seen that the address has three matching items, and among these three matching items, the corresponding next-hop values are 8'h0a, 8'h0b, 8'h0c, since the priority of the register "Nh 48" is higher than that of the register "
(7)哈希冲突处理模块的实现(7) Implementation of the hash collision processing module
在哈希计算过程中,会发生哈希冲突情况,所以就要进行哈希冲突处理。During the hash calculation process, hash collisions will occur, so hash collisions must be handled.
哈希冲突处理模块的设计必须考虑到以下几个问题:The design of the hash collision processing module must take into account the following issues:
第一,快速查找及更新性能。如果哈希冲突处理模块的查找能力不高,则会影响整个系统的处理能力。First, fast lookup and update performance. If the search capability of the hash collision processing module is not high, the processing capability of the entire system will be affected.
第二,要保证可以处理所有冲突情况,这样才可以保证整个查找系统的功能完备性。Second, ensure that all conflict situations can be handled so that the entire lookup system is functionally complete.
第三,在哈希函数的选择时,必须考虑到要保证尽量少发生冲突。Third, when choosing a hash function, it must be considered to ensure that collisions occur as little as possible.
基于以上几个问题,本文用CAM查找模块来处理哈希冲突。在设计时,对不同前缀利用不同的CAM进行哈希冲突处理,总共需要6种宽度的CAM,即24位宽,32位宽,40位宽,48位宽,56位宽和64位宽的CAM,分别处理24-31位,32-39位,40-47位,48-55位,56-63位和64位长的前缀。CAM的具体组织与第一级哈希和第二级扩展RAM的组织方式相同。如图14所示,CAM处理哈希前缀HP和扩展前缀哈希项EPH,扩展前缀扩展项EPE的信息存储于块RAM中。扩展前缀在扩展RAM中绝对地址的计算过程为:当分配的块RAM的编号为block_addr,扩展前缀扩展项EPE低位补零形成7位二进制数,再将该7位二进制数转换成的十进制数V(epe),则该前缀所对应信息应该存储的单元绝对地址ram_addr为:Based on the above problems, this paper uses the CAM lookup module to deal with hash collisions. At design time, use different CAMs for different prefixes for hash collision processing. A total of 6 widths of CAMs are required, namely 24-bit wide, 32-bit wide, 40-bit wide, 48-bit wide, 56-bit wide and 64-bit wide. CAM, respectively handles 24-31, 32-39, 40-47, 48-55, 56-63 and 64-bit long prefixes. The specific organization of the CAM is the same as that of the first-level hash and the second-level extended RAM. As shown in Figure 14, the CAM processes the hash prefix HP and the extended prefix hash item EPH, and the information of the extended prefix extension item EPE is stored in the block RAM. The calculation process of the absolute address of the extended prefix in the extended RAM is: when the number of the allocated block RAM is block_addr, the extended prefix extension item EPE is filled with zeros to form a 7-bit binary number, and then the 7-bit binary number is converted into a decimal number V (epe), then the absolute address ram_addr of the unit where the information corresponding to the prefix should be stored is:
ram_addr=128×block_addr+V(epe)。ram_addr=128×block_addr+V(epe).
(8)整体工作过程(8) Overall working process
●路由表构造及表项插入的具体过程如图5所示,具体描述如下:●The specific process of routing table construction and entry insertion is shown in Figure 5, and the specific description is as follows:
第一步:将哈希表和扩展RAM初始化为空;Step 1: Initialize the hash table and extended RAM to be empty;
第二步:根据待插入前缀长度来判断此前缀属于哈希前缀HP还是扩展前缀EP,如果是HP,则将此前缀进行哈希计算,用所得哈希值索引哈希表,如果索引到的哈希表项中“F”字段为“0”,则将该项的“F”字段设为“1”,“Nh(i)”字段设为该前缀所对应的下一跳值;如果对应项中“F”字段为“1”,表明该前缀项产生哈希冲突,则用CPE进行哈希冲突处理。Step 2: Determine whether the prefix belongs to the hash prefix HP or the extended prefix EP according to the length of the prefix to be inserted. If it is HP, perform hash calculation on this prefix, and use the obtained hash value to index the hash table. If the index is If the "F" field in the hash table entry is "0", then the "F" field of the item is set to "1", and the "Nh(i)" field is set to the next hop value corresponding to the prefix; if the corresponding The "F" field in the entry is "1", indicating that the prefix entry generates a hash collision, and the CPE is used to handle the hash collision.
如果是EP,则将此前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH做哈希计算,用所得哈希值索引哈希表,判断索引到的哈希表项“E”字段是否为“0”,如果“E”字段为“0”,则将哈希表对应项的“E”字段设为“1”,“Block_addr”字段是为扩展前缀扩展项EPE所分配块RAM的编号,用扩展前缀扩展项EPE计算出块RAM的块内相对地址,并将下一跳值放入对应的存储单元中;如果“E”字段为“1”且该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH部分和已插入该项的前缀的扩展前缀哈希项相同,则将该前缀的下一跳值放入该哈希表项“Block_addr”字段所指示的已分配块RAM中,用扩展前缀扩展项EPE计算出块RAM的块内相对地址,并将下一跳值放入对应的存储单元中;如果“E”字段为“1”且该前缀的扩展前缀哈希项EPH部分和已插入该项的前缀的扩展前缀哈希项不同,表明该前缀项产生哈希冲突,则用CPE进行哈希冲突处理。If it is EP, perform hash calculation on the extended prefix hash item EPH of this prefix, use the obtained hash value to index the hash table, and judge whether the "E" field of the indexed hash table item is "0", if " If the "E" field is "0", set the "E" field of the hash table corresponding item to "1", and the "Block_addr" field is the number of the block RAM allocated for the extended prefix extension item EPE, and the extended prefix extension item EPE is used Calculate the relative address in the block RAM block, and put the next hop value into the corresponding storage unit; if the "E" field is "1" and the extended prefix hash item EPH part of the prefix and the EPH part of the item have been inserted If the extended prefix hash items of the prefix are the same, put the next hop value of the prefix into the allocated block RAM indicated by the "Block_addr" field of the hash table item, and use the extended prefix extension item EPE to calculate the block of the block RAM Inner relative address, and put the next hop value into the corresponding storage unit; if the "E" field is "1" and the EPH part of the extended prefix hash item of the prefix and the extended prefix hash of the prefix of the item have been inserted Items are different, indicating that the prefix item generates a hash collision, and the CPE is used to handle the hash collision.
●IPv6地址查找过程如图6所示:●The IPv6 address lookup process is shown in Figure 6:
要进行IPv6地址查找,必须先将路由表进行初始化,初始化具体过程下文所述;To perform IPv6 address lookup, the routing table must be initialized first, and the initialization process is described below;
如果路由表初始化工作已完成,则可以对IPv6地址进行查找:先对IPv6做第一级哈希查找,然后根据情况判断是否要进行第二级查找。查找过程可以分为三个步骤完成:第一级哈希表查找,第二级扩展RAM查找和优先级比较。具体描述如下:If the initialization of the routing table has been completed, the IPv6 address can be searched: first perform a first-level hash search on IPv6, and then judge whether to perform a second-level search according to the situation. The search process can be divided into three steps to complete: first-level hash table search, second-level extended RAM search and priority comparison. The specific description is as follows:
第一步:将目的IPv6地址做7种hash查找,即分别在Hash16、Hash24、Hash32、Hash40、Hash48、Hash56、Hash64哈希查找单元中,对目的IPv6地址的前16bits、24bits、32bits、40bits、48bits、56bits和64bits做并行查找操作。如果查找到匹配项,则将对应的下一跳索引值输出到优先级比较器中准备比较。Step 1: Do 7 kinds of hash lookups on the destination IPv6 address, that is, in Hash16, Hash24, Hash32, Hash40, Hash48, Hash56, Hash64 hash lookup units, the first 16bits, 24bits, 32bits, 40bits, 48bits, 56bits and 64bits do parallel search operations. If a matching item is found, the corresponding next-hop index value is output to the priority comparator for comparison.
第二步:如果第一级查找指示在第二级查找单元中还有更长的前缀需要做匹配计算,则需要进行第二级查找:在第二级中利用存储器扩展技术,扩展前缀扩展项EPE可以插入到有128个地址的块RAM中。设前缀的对应位为[i+1:i+7](i为哈希前缀的长度),查找时,则根据目的地址的第(i+1~i+7)位计算出索引值,利用该值在扩展RAM存储器中寻址,匹配地址单元所对应的值即为下一跳值Nh(i+1,i+7),将该下一跳值输出到优先级比较器中进行比较。Step 2: If the first-level search indicates that there is still a longer prefix to be calculated in the second-level search unit, then a second-level search is required: use the memory expansion technology in the second level to expand the prefix expansion item EPE can be inserted into block RAM with 128 addresses. Let the corresponding bits of the prefix be [i+1:i+7] (i is the length of the hash prefix), and when searching, calculate the index value according to the (i+1~i+7)th bits of the destination address, and use This value is addressed in the extended RAM memory, and the value corresponding to the matching address unit is the next hop value Nh(i+1, i+7), and the next hop value is output to the priority comparator for comparison.
第三步:将输入到优先级比较器的寄存器中的值进行优先比较,“next hop”输出优先级最高的值(即最长匹配前缀所对应的下一跳值)作为该IPv6目的地址所匹配的下一跳值,即为所查到的值。Step 3: compare the values in the registers of the priority comparator first, and "next hop" outputs the value with the highest priority (that is, the next hop value corresponding to the longest matching prefix) as the IPv6 destination address. The matched next hop value is the found value.
●路由表项删除及修改的具体情况描述如下:●The details of deletion and modification of routing table entries are described as follows:
路由表项的更新主要包括三种操作,插入、删除和修改,分别要根据待更新项的前缀值确定更新表项的位置。对于前缀插入操作,可以按照路由表的创建算法进行插入。对于前缀修改和删除操作,则类似于地址查找的过程,首先利用查找算法,找到该前缀表项,然后再执行相应的修改和删除操作,可以分为以下两种情况:The update of the routing table entry mainly includes three operations, insert, delete and modify, and respectively determine the location of the updated table entry according to the prefix value of the entry to be updated. For the prefix insertion operation, the insertion can be performed according to the creation algorithm of the routing table. For prefix modification and deletion operations, it is similar to the process of address search. First, use the search algorithm to find the prefix entry, and then perform the corresponding modification and deletion operations, which can be divided into the following two cases:
第1种情况:当要修改或删除的前缀为哈希前缀时,则将“F”字段设置为“0”,清空其它字段的值;Case 1: When the prefix to be modified or deleted is a hash prefix, set the "F" field to "0" and clear the values of other fields;
第2种情况:当要修改或删除的前缀为扩展前缀时,则将“E”字段和“Block_addr”字段设置为全“0”,然后收回扩展RAM的存储空间。Case 2: When the prefix to be modified or deleted is an extended prefix, the "E" field and the "Block_addr" field are set to all "0", and then the storage space of the extended RAM is reclaimed.
Claims (7)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010101459399ACN101827137B (en) | 2010-04-13 | 2010-04-13 | A High Performance IPv6 Address Lookup Method Based on Hash Table and Extended Memory |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010101459399ACN101827137B (en) | 2010-04-13 | 2010-04-13 | A High Performance IPv6 Address Lookup Method Based on Hash Table and Extended Memory |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101827137Atrue CN101827137A (en) | 2010-09-08 |
| CN101827137B CN101827137B (en) | 2013-01-30 |
Family
ID=42690833
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010101459399AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101827137B (en) | 2010-04-13 | 2010-04-13 | A High Performance IPv6 Address Lookup Method Based on Hash Table and Extended Memory |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101827137B (en) |
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103051543A (en)* | 2012-11-01 | 2013-04-17 | 广州微仕科信息技术有限公司 | Route prefix processing, lookup, adding and deleting method |
| CN103414603A (en)* | 2013-07-31 | 2013-11-27 | 清华大学 | Ipv6 deep packet inspection method based on Hash folding method |
| CN104917852A (en)* | 2015-05-29 | 2015-09-16 | 中国科学院信息工程研究所 | Data rapid processing method aiming at IPv6 address |
| CN105978814A (en)* | 2015-03-13 | 2016-09-28 | 联发科技股份有限公司 | Network device and method for querying data in network device |
| CN106844233A (en)* | 2016-12-07 | 2017-06-13 | 深圳市德传技术有限公司 | A kind of router service data caching method and system based on Hash table |
| CN106878185A (en)* | 2017-04-13 | 2017-06-20 | 济南浪潮高新科技投资发展有限公司 | A packet IP address matching circuit and method |
| CN109039911A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2018-12-18 | 烽火通信科技股份有限公司 | It is a kind of to search the method and system that mode shares RAM based on HASH |
| CN109582598A (en)* | 2018-12-13 | 2019-04-05 | 武汉中元华电软件有限公司 | A kind of preprocess method for realizing efficient lookup Hash table based on external storage |
| CN109656832A (en)* | 2017-10-11 | 2019-04-19 | 深圳市中兴微电子技术有限公司 | A kind of look-up method, computer readable storage medium |
| CN110753133A (en)* | 2018-07-23 | 2020-02-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for processing address and network equipment |
| CN111291058A (en)* | 2020-03-17 | 2020-06-16 | 芯启源(南京)半导体科技有限公司 | Method for optimizing storage LPM (low power management) rule based on hierarchical pc-trie structure |
| CN111352931A (en)* | 2018-12-21 | 2020-06-30 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Hash collision processing method and device and computer readable storage medium |
| CN111835359A (en)* | 2019-04-22 | 2020-10-27 | 深圳捷誊技术有限公司 | Compression device, storage medium, and method and device for repeating information query and update |
| CN111935021A (en)* | 2020-09-27 | 2020-11-13 | 翱捷智能科技(上海)有限公司 | Method and system for quickly matching network data packets |
| CN112769704A (en)* | 2021-02-09 | 2021-05-07 | 芯河半导体科技(无锡)有限公司 | High-speed extensible IP route lookup hardware device based on hash table |
| CN112818185A (en)* | 2021-04-20 | 2021-05-18 | 芯启源(南京)半导体科技有限公司 | Method for searching longest prefix matching hardware system based on SRAM |
| CN113726660A (en)* | 2021-08-27 | 2021-11-30 | 西安微电子技术研究所 | Route finder and method based on perfect hash algorithm |
| CN114629669A (en)* | 2020-11-27 | 2022-06-14 | 国家计算机网络与信息安全管理中心 | A method for constructing an anonymous network channel |
| CN115687344A (en)* | 2022-10-14 | 2023-02-03 | 西安电子科技大学 | Acceleration device and acceleration method based on FPGA-based perfect hash construction |
| CN115987888A (en)* | 2022-12-20 | 2023-04-18 | 苏州盛科通信股份有限公司 | Routing address storage method, device, network equipment and storage medium |
| CN117093881A (en)* | 2023-10-19 | 2023-11-21 | 深圳大普微电子股份有限公司 | Data compression method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN117221224A (en)* | 2023-11-09 | 2023-12-12 | 格创通信(浙江)有限公司 | Table item construction and search method and device, network equipment and storage medium |
| CN117997834A (en)* | 2024-04-03 | 2024-05-07 | 格创通信(浙江)有限公司 | Lookup table updating and table item searching methods, device, network equipment and medium |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050141519A1 (en)* | 2003-12-31 | 2005-06-30 | Stmicroelectronics, Inc. | Apparatus and method using hashing for efficiently implementing an IP lookup solution in hardware |
| CN1655533A (en)* | 2004-02-09 | 2005-08-17 | 阿尔卡特公司 | Filters based on longest prefix matching algorithm |
| CN1863169A (en)* | 2006-03-03 | 2006-11-15 | 清华大学 | Route searching result cache method based on network processor |
| CN101350788A (en)* | 2008-08-25 | 2009-01-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for mixed loop-up table of network processor inside and outside |
- 2010
- 2010-04-13CNCN2010101459399Apatent/CN101827137B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050141519A1 (en)* | 2003-12-31 | 2005-06-30 | Stmicroelectronics, Inc. | Apparatus and method using hashing for efficiently implementing an IP lookup solution in hardware |
| CN1655533A (en)* | 2004-02-09 | 2005-08-17 | 阿尔卡特公司 | Filters based on longest prefix matching algorithm |
| CN1863169A (en)* | 2006-03-03 | 2006-11-15 | 清华大学 | Route searching result cache method based on network processor |
| CN101350788A (en)* | 2008-08-25 | 2009-01-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for mixed loop-up table of network processor inside and outside |
Cited By (35)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103051543B (en)* | 2012-11-01 | 2015-09-09 | 广州键智桥网络技术有限公司 | A kind of process of route prefix, search, increase and delet method |
| CN103051543A (en)* | 2012-11-01 | 2013-04-17 | 广州微仕科信息技术有限公司 | Route prefix processing, lookup, adding and deleting method |
| CN103414603A (en)* | 2013-07-31 | 2013-11-27 | 清华大学 | Ipv6 deep packet inspection method based on Hash folding method |
| CN103414603B (en)* | 2013-07-31 | 2016-08-10 | 清华大学 | Ipv6 deep packet inspection method based on Hash method for folding |
| CN105978814A (en)* | 2015-03-13 | 2016-09-28 | 联发科技股份有限公司 | Network device and method for querying data in network device |
| CN104917852B (en)* | 2015-05-29 | 2019-01-18 | 中国科学院信息工程研究所 | A kind of data quick-processing method for the address IPv6 |
| CN104917852A (en)* | 2015-05-29 | 2015-09-16 | 中国科学院信息工程研究所 | Data rapid processing method aiming at IPv6 address |
| CN106844233A (en)* | 2016-12-07 | 2017-06-13 | 深圳市德传技术有限公司 | A kind of router service data caching method and system based on Hash table |
| CN106878185A (en)* | 2017-04-13 | 2017-06-20 | 济南浪潮高新科技投资发展有限公司 | A packet IP address matching circuit and method |
| CN106878185B (en)* | 2017-04-13 | 2020-04-07 | 浪潮集团有限公司 | Message IP address matching circuit and method |
| CN109656832A (en)* | 2017-10-11 | 2019-04-19 | 深圳市中兴微电子技术有限公司 | A kind of look-up method, computer readable storage medium |
| US11570106B2 (en) | 2018-07-23 | 2023-01-31 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Address processing method and network device |
| CN110753133A (en)* | 2018-07-23 | 2020-02-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for processing address and network equipment |
| CN109039911A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2018-12-18 | 烽火通信科技股份有限公司 | It is a kind of to search the method and system that mode shares RAM based on HASH |
| CN109582598A (en)* | 2018-12-13 | 2019-04-05 | 武汉中元华电软件有限公司 | A kind of preprocess method for realizing efficient lookup Hash table based on external storage |
| CN109582598B (en)* | 2018-12-13 | 2023-05-02 | 武汉中元华电软件有限公司 | Preprocessing method for realizing efficient hash table searching based on external storage |
| CN111352931A (en)* | 2018-12-21 | 2020-06-30 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Hash collision processing method and device and computer readable storage medium |
| CN111835359A (en)* | 2019-04-22 | 2020-10-27 | 深圳捷誊技术有限公司 | Compression device, storage medium, and method and device for repeating information query and update |
| CN111291058A (en)* | 2020-03-17 | 2020-06-16 | 芯启源(南京)半导体科技有限公司 | Method for optimizing storage LPM (low power management) rule based on hierarchical pc-trie structure |
| CN111291058B (en)* | 2020-03-17 | 2023-06-16 | 芯启源(南京)半导体科技有限公司 | LPM rule storage method based on layered pc-trie structure |
| CN111935021A (en)* | 2020-09-27 | 2020-11-13 | 翱捷智能科技(上海)有限公司 | Method and system for quickly matching network data packets |
| CN111935021B (en)* | 2020-09-27 | 2020-12-25 | 翱捷智能科技(上海)有限公司 | Method and system for quickly matching network data packets |
| CN114629669A (en)* | 2020-11-27 | 2022-06-14 | 国家计算机网络与信息安全管理中心 | A method for constructing an anonymous network channel |
| CN112769704A (en)* | 2021-02-09 | 2021-05-07 | 芯河半导体科技(无锡)有限公司 | High-speed extensible IP route lookup hardware device based on hash table |
| CN112818185A (en)* | 2021-04-20 | 2021-05-18 | 芯启源(南京)半导体科技有限公司 | Method for searching longest prefix matching hardware system based on SRAM |
| CN113726660B (en)* | 2021-08-27 | 2022-11-15 | 西安微电子技术研究所 | Route finder and method based on perfect hash algorithm |
| CN113726660A (en)* | 2021-08-27 | 2021-11-30 | 西安微电子技术研究所 | Route finder and method based on perfect hash algorithm |
| CN115687344A (en)* | 2022-10-14 | 2023-02-03 | 西安电子科技大学 | Acceleration device and acceleration method based on FPGA-based perfect hash construction |
| CN115987888A (en)* | 2022-12-20 | 2023-04-18 | 苏州盛科通信股份有限公司 | Routing address storage method, device, network equipment and storage medium |
| CN117093881A (en)* | 2023-10-19 | 2023-11-21 | 深圳大普微电子股份有限公司 | Data compression method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN117093881B (en)* | 2023-10-19 | 2024-01-12 | 深圳大普微电子股份有限公司 | Data compression method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN117221224A (en)* | 2023-11-09 | 2023-12-12 | 格创通信(浙江)有限公司 | Table item construction and search method and device, network equipment and storage medium |
| CN117221224B (en)* | 2023-11-09 | 2024-02-06 | 格创通信(浙江)有限公司 | Table item construction and search method and device, network equipment and storage medium |
| CN117997834A (en)* | 2024-04-03 | 2024-05-07 | 格创通信(浙江)有限公司 | Lookup table updating and table item searching methods, device, network equipment and medium |
| CN117997834B (en)* | 2024-04-03 | 2024-07-26 | 格创通信(浙江)有限公司 | Lookup table updating and table item searching methods, device, network equipment and medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101827137B (en) | 2013-01-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101827137B (en) | A High Performance IPv6 Address Lookup Method Based on Hash Table and Extended Memory | |
| US7418505B2 (en) | IP address lookup using either a hashing table or multiple hash functions | |
| US6985483B2 (en) | Methods and systems for fast packet forwarding | |
| US6434144B1 (en) | Multi-level table lookup | |
| US7146371B2 (en) | Performance and memory bandwidth utilization for tree searches using tree fragmentation | |
| CN101594319B (en) | Entry lookup method and entry lookup device | |
| CN103107945B (en) | A kind of system and method for fast finding IPV6 route | |
| Pao et al. | Efficient hardware architecture for fast IP address lookup | |
| US20040230696A1 (en) | Bounded index extensible hash-based IPv6 address lookup method | |
| CN104462144A (en) | Search method and device of packet classification rules | |
| CN113315705B (en) | Flexible IP addressing method and device based on single Hash bloom filter | |
| CN114884877B (en) | IPv6 route searching method combining hash table and HOT | |
| CN105978814A (en) | Network device and method for querying data in network device | |
| CN101556610B (en) | Table creating and searching method used by network processor | |
| CN100496019C (en) | A Method for Rapid Search and Update of IPv6 Routing Table | |
| CN115086221B (en) | Message processing method, device, forwarding equipment and storage medium | |
| CN110191057B (en) | Route searching method and route equipment | |
| CN1312890C (en) | Method for generating a trie having a reduced number of trie blocks | |
| CN113328947B (en) | Variable-length route searching method and device based on application of controllable prefix extension bloom filter | |
| Li et al. | An IPv6 routing lookup algorithm based on hash table and HOT | |
| US10476785B2 (en) | IP routing search | |
| CN100401723C (en) | A Fast Indexing Method | |
| Li et al. | Address lookup algorithms for IPv6 | |
| CN107204926B (en) | Rapid route searching method for preprocessing cache | |
| US7376657B1 (en) | Fast IPv6 address lookup using skip level processing on multi-bit tries |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C17 | Cessation of patent right | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20130130 Termination date:20130413 |