CN101810470A - Physiological signal measurement module and method - Google Patents
Physiological signal measurement module and methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101810470A CN101810470ACN200910006994ACN200910006994ACN101810470ACN 101810470 ACN101810470 ACN 101810470ACN 200910006994 ACN200910006994 ACN 200910006994ACN 200910006994 ACN200910006994 ACN 200910006994ACN 101810470 ACN101810470 ACN 101810470A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- delay time
- initial
- physiological signal
- blood pressure
- pulse wave
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明是有关于一种生理信号测量模块,特别是有关于一种移动式血压信号测量模块。The invention relates to a physiological signal measurement module, in particular to a mobile blood pressure signal measurement module.
背景技术Background technique
随着社会的高龄化,年老人口逐渐增加,对于医疗设备的需求亦大幅增加,使得医疗资源供不应求大型医院经常人满为患。再者,生活压力的增加使得现代人罹患心血管疾病机率也提高,其中,高血压更是造成中风的主要因子。因此,生理信号自我测量设备已逐渐成为医疗产业发展的重要目标。通过生理信号自我测量的方式,个人能够随时监控自己的生理状况,并能减少医疗资源浪费。With the aging of the society, the elderly population is gradually increasing, and the demand for medical equipment has also increased significantly, making the supply of medical resources in short supply and large hospitals are often overcrowded. Furthermore, the increase in life pressure has increased the risk of cardiovascular diseases in modern people, among which high blood pressure is the main factor causing stroke. Therefore, physiological signal self-measurement equipment has gradually become an important goal of the development of the medical industry. Through self-measurement of physiological signals, individuals can monitor their own physiological conditions at any time and reduce the waste of medical resources.
已知的血压测量设备是利用腕带式气囊感测技术,其通过气囊的充放气来测量血压。但是,此感测技术无法连续地测量血压,且气囊的充放气需花费较长时间。此外,腕带式的血压测量设备会因为手腕与心脏的高度差而造成测量误差。Known blood pressure measuring devices utilize wristband airbag sensing technology, which measures blood pressure through inflation and deflation of the airbag. However, this sensing technology cannot continuously measure blood pressure, and it takes a long time to inflate and deflate the airbag. In addition, wrist-worn blood pressure measurement equipment will cause measurement errors due to the height difference between the wrist and the heart.
因此,期望提供一种生理信号测量模块,其可随身携带,且能补偿测量部位与心脏间的高度差所造成的误差。Therefore, it is desired to provide a physiological signal measurement module, which can be carried around and can compensate the error caused by the height difference between the measurement site and the heart.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明所要解决的技术问题在于提供一种生理信号测量模块及方法,其可随身携带,且能补偿测量部位与心脏间的高度差所造成的误差。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a physiological signal measurement module and method, which can be carried around and can compensate the error caused by the height difference between the measurement site and the heart.
本发明提供一种生理信号测量模块,包括生理信号感测单元、姿势感测单元、以及处理单元。生理信号感测单元测量受测者的心电信号与脉搏信号。姿势感测单元感测生理信号测量模块的位置,并输出多个位置信号。处理单元接收心电信号、脉搏信号、与位置信号,用以根据位置信号来产生表示生理信号测量模块与参考位置间的高度差的变化参数。处理单元还根据心电信号与脉搏信号来计算当前脉波延迟时间,且根据高度变化参数来补偿当前脉波延迟时间以获得补偿脉波延迟时间,并根据补偿脉波延迟时间来获得血压信号。The present invention provides a physiological signal measurement module, which includes a physiological signal sensing unit, a posture sensing unit, and a processing unit. The physiological signal sensing unit measures the ECG signal and pulse signal of the subject. The posture sensing unit senses the position of the physiological signal measuring module and outputs a plurality of position signals. The processing unit receives the electrocardiographic signal, the pulse signal, and the position signal, and generates a change parameter representing the height difference between the physiological signal measurement module and the reference position according to the position signal. The processing unit also calculates the current pulse wave delay time according to the ECG signal and the pulse signal, and compensates the current pulse wave delay time according to the altitude change parameter to obtain the compensated pulse wave delay time, and obtains the blood pressure signal according to the compensated pulse wave delay time.
本发明另提供一种生理信号测量方法,首先,以一生理信号测量模块来测量受测者的心电信号与脉搏信号,接着测量生理信号测量模块与参考位置之间的高度,以产生高度变化参数。根据心电信号与脉搏信号来计算当前脉波延迟时间。根据高度变化参数来补偿当前脉波延迟时间以获得补偿脉波延迟时间。最后,根据补偿脉波延迟时间来获得血压信号。The present invention also provides a physiological signal measurement method. Firstly, a physiological signal measurement module is used to measure the ECG signal and pulse signal of the subject, and then the height between the physiological signal measurement module and the reference position is measured to generate a height change. parameter. Calculate the current pulse wave delay time according to the ECG signal and the pulse signal. Compensate the current pulse delay time according to the altitude change parameter to obtain the compensated pulse delay time. Finally, the blood pressure signal is obtained according to the compensated pulse wave delay time.
本发明的生理信号测量模块可随身携带,且能补偿测量部位与心脏间的高度差所造成的误差。The physiological signal measurement module of the present invention can be carried around, and can compensate the error caused by the height difference between the measurement site and the heart.
为使本发明能更明显易懂,下文特举一较佳实施例,并配合所附附图,作详细说明如下。In order to make the present invention more comprehensible, a preferred embodiment will be described in detail below together with the accompanying drawings.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1表示根据本发明实施例的生理信号测量模块架构;FIG. 1 shows a physiological signal measurement module architecture according to an embodiment of the present invention;
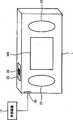
图2表示生理信号测量模块1的外观示意图;FIG. 2 shows a schematic diagram of the appearance of the physiological signal measurement module 1;
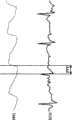
图3表示脉波延迟时间的示意图;以及Fig. 3 represents the schematic diagram of pulse wave delay time; And
图4表示根据本发明实施例的生理信号测量流程图。Fig. 4 shows a flowchart of physiological signal measurement according to an embodiment of the present invention.
【主要组件符号说明】[Description of main component symbols]
1~生理信号测量模块;1~physiological signal measurement module;
10~生理信号感测单元;10~physiological signal sensing unit;
11~姿势感测单元;11~posture sensing unit;
12~处理单元;12 ~ processing unit;
13~内存;13 ~ memory;
14~显示单元;14 ~ display unit;
15~外部装置;15 ~ external device;
20~输入端口;20 ~ input port;
21、22、23~感测电极;21, 22, 23~sensing electrodes;
24~光传感器;24 ~ light sensor;
140~显示面板。140~display panel.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
图1是表示根据本发明实施例的生理信号测量模块架构。参阅图1,生理信号测量模块1包括生理信号感测单元10、姿势感测单元11、处理单元12、内存13、以及显示单元14。图2是表示生理信号测量模块1的外观示意图。生理信号测量模块操作在初始参数设定模式或测量模式下。FIG. 1 shows the architecture of a physiological signal measurement module according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1 , the physiological signal measurement module 1 includes a physiological signal sensing unit 10 , a posture sensing unit 11 , a processing unit 12 , a memory 13 , and a display unit 14 . FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram showing the appearance of the physiological signal measurement module 1 . The physiological signal measurement module operates in the initial parameter setting mode or the measurement mode.
在初始参数设定模式下,将一外部装置15连接至生理信号测量模块1的输入端口20。外部装置15可以是已知的血压计,例如电子式气囊血压计。由外部装置15来测量受测者在数秒内的平均舒张压与收缩压,并透过输入端口20将所测得的舒张压与收缩压输入至内存13,作为初始舒张压参数DBP0与初始收缩压参数SBP0。In the initial parameter setting mode, an
参阅图2,生理信号测量模块1具有三个感测电极21-23与一个光传感器24。受测者的三只手指分别触碰感测电极21-23,借以撷取心电信号(例如,左手的食指触碰感测电极23、左手的大拇指触碰感测电极21、以及右手的大拇指触碰感测电极22)。用来撷取脉搏信号的光传感器24可与感测电极23结合,因此,受测者的左手食指是同时触碰感测电极23与光传感器24。在此数秒内的血压测量期间,生理信号测量模块1的生理信号感测单元10同时透过感测电极21-23与光传感器24来测量数秒的心电信号与脉搏信号,以作为初始心电信号ECG0与初始脉搏信号PPG0。处理单元12接收初始心电信号ECG0与初始脉搏信号PPG0,并根据初始心电信号ECG0与初始脉搏信号PPG0来计算脉波延迟时间(Pulse Transit Time,PTT)。此技术领域的人员已知,如图3所示,脉波延迟时间是心电信号与脉搏信号之间的时间差(例如,心电信号R波与脉波信号位准开始上升的时间点)。在初始参数设定模式下,处理单元12计算获得此数秒内多个脉波延迟时间的值,且将这些值做平均运算以获得初始脉波延迟时间PTT0。在获得初始脉波延迟时间PTT0后,处理单元12根据式(1)来计算关系常数K:Referring to FIG. 2 , the physiological signal measurement module 1 has three sensing electrodes 21 - 23 and one
K=SBP0×PTT0 式(1)K=SBP0 ×PTT0 Equation (1)
根据式(1)可得知,关系常数K是有关于初始收缩压参数SBP0与初始脉波延迟时间PTT0。According to formula (1), it can be known that the relationship constant K is related to the initial systolic blood pressure parameter SBP0 and the initial pulse delay time PTT0 .
在此数秒的血压测量期间,姿势感测单元11同时来测量此时的生理信号测量模块1与受测者的心脏间的初始高度差H0。姿势感测单元11依据生理信号测量模块1的位置来获得重力(G)在X轴、Y轴、与Z轴方向的分量,以产生对应的初始位置信号,即X0、Y0及Z0信号。处理单元12根据Y0与Z0来计算受测者此时下臂倾斜角度θ0,如式(2)During the several-second blood pressure measurement, the posture sensing unit 11 simultaneously measures the initial height difference H0 between the physiological signal measurement module 1 and the subject's heart. The posture sensing unit 11 obtains the components of gravity (G) in the X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis directions according to the position of the physiological signal measurement module 1, so as to generate corresponding initial position signals, that is, X0 , Y0 , and Z0 Signal. The processing unit 12 calculates the inclination angle θ0 of the lower arm of the subject at this time according to Y0 and Z0 , as shown in formula (2)
在获得下臂倾斜角度θ0后,处理单元12根据式(3)来计算生理信号测量模块1与受测者的心脏间的初始高度差H0:After obtaining the inclination angle θ0 of the lower arm, the processing unit 12 calculates the initial height difference H0 between the physiological signal measurement module 1 and the heart of the subject according to formula (3):
H0=L0-L1+L2sinθ0 式(3)H0 =L0 -L1 +L2 sinθ0 Formula (3)
其中,L0表示受测者的心脏至肩膀高度、L1表示受测者的上臂长度、而L2表示受测者的下臂长度。受测者可透过生理信号测量模块1的输入单元(未显示)来预先输入其身高,且处理单元12根据受测者的身高由标准身材比例(stand body proportion)公式来求出数值L0、L1、与L2,并将获得的数值L0、L1、与L2储存至内存13。Wherein, L0 represents the height from the heart to the shoulder of the test subject, L1 represents the length of the upper arm of the test subject, and L2 represents the length of the lower arm of the test subject. The subject can pre-input his height through the input unit (not shown) of the physiological signal measurement module 1, and the processing unit 12 calculates the value L according to the subject's height by a standard body ratio (stand body proportion) formula. , L1 , and L2 , and store the obtained values L0 , L1 , and L2 into the memory 13 .
当处理单元12完成计算初始脉波延迟时间PTT0、关系常数K、以及初始高度差H0后,将这些初始参数传送至内存13储存。在上述初始参数设定模式完成后,内存13已储存个体化的血压校正所需的初始参数,即初始舒张压参数DBP0、初始收缩压参数SBP0、初始脉波延迟时间PTT0、关系常数K、以及初始高度差H0。之后,可移除外部装置15与输入端口20的连接。After the processing unit 12 finishes calculating the initial pulse delay time PTT0 , the relation constant K, and the initial height difference H0 , these initial parameters are sent to the memory 13 for storage. After the above initial parameter setting mode is completed, the memory 13 has stored the initial parameters required for individualized blood pressure correction, namely the initial diastolic blood pressure parameter DBP0 , the initial systolic blood pressure parameter SBP0 , the initial pulse wave delay time PTT0 , and the relationship constant K, and the initial height difference H0 . Afterwards, the connection of the
在初始参数设定模式结束后,若随时欲测量受测者的血压信号时,生理信号测量模块1则进入测量模式。参阅图1及2,在测量模式下,受测者的相同三只手指(即左手的食指与大拇指、以及右手的大拇指)分别触碰感测电极21-23,同时,左手的食指也触碰光传感器24。生理信号感测单元10同时透过感测电极21-23与光传感器24来测量当前的心电信号ECGN与脉搏信号PPGN。处理单元12接收当前的心电信号ECGN与脉搏信号PPGN,并根据当前的心电信号ECGN与脉搏信号PPGN来计算当前脉波延迟时间PTTN。After the initial parameter setting mode ends, if the blood pressure signal of the subject is to be measured at any time, the physiological signal measurement module 1 enters the measurement mode. Referring to Figures 1 and 2, in the measurement mode, the subject's same three fingers (ie, the index finger and thumb of the left hand, and the thumb of the right hand) touch the sensing electrodes 21-23 respectively, and at the same time, the index finger of the left hand also touches the sensing electrodes 21-23. Touch
在此测量模式中,姿势感测单元11同时测量此时的生理信号测量模块1与受测者的心脏间的高度差HN。同样地,姿势感测单元11依据生理信号测量模块1的位置来获得重力(G)在X轴、Y轴、与Z轴方向的分量,以产生对应的位置信号,即XN、YN、及ZN信号。处理单元12根据YN信号与ZN信号来计算受测者此时下臂倾斜角度θN,如式(4)In this measurement mode, the posture sensing unit 11 simultaneously measures the height difference HN between the physiological signal measurement module 1 and the heart of the subject at this time. Similarly, the posture sensing unit 11 obtains the components of gravity (G) in the X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis directions according to the position of the physiological signal measurement module 1 to generate corresponding position signals, that is, XN , YN , and ZN signal. The processing unit 12 calculates the inclination angle θN of the lower arm of the subject at this time according to the YN signal and the ZN signal, as shown in formula (4)
在获得下臂倾斜角度θN后,处理单元12根据式(4)来计算生理信号测量模块1与受测者的心脏间的高度差HN:After obtaining the inclination angle θN of the lower arm, the processing unit 12 calculates the height difference HN between the physiological signal measurement module 1 and the heart of the subject according to formula (4):
HN=L0-L1+L2sinθN 式(5)HN =L0 -L1 +L2 sinθN formula (5)
在处理单元12计算出在测量模式下生理信号测量模块1与受测者的心脏间的高度差HN后,根据在初始参数设定模式下的高度差H0(读取自内存13)与在测量模式下的高度差HN,则可以得到生理信号测量模块1在测量模式下与在初始参数设定模式下的高度差ΔH,以作为高度变化参数。换句话说,在初始参数设定模式下生理信号测量模块1的位置视为参考位置,而在测量模式下处理单元12则是依据YN信号与ZN信号来计算生理信号测量模块1与参考位置的高度差ΔH(高度变化参数)。After the processing unit 12 calculates the height differenceHN between the physiological signal measurement module 1 and the heart of the subject in the measurement mode, according to the height differenceH0 (read from the memory 13) and For the height difference HN in the measurement mode, the height difference ΔH of the physiological signal measurement module 1 in the measurement mode and the initial parameter setting mode can be obtained as the height change parameter. In other words, in the initial parameter setting mode, the position of the physiological signal measurement module 1 is regarded as the reference position, while in the measurement mode, the processing unit 12 calculates the position of the physiological signal measurement module 1 and the reference position according to the YN signal and the ZN signal. The height difference ΔH of the position (altitude change parameter).
在获得高度变化参数ΔH后,处理单元12根据高度变化参数ΔH来补偿与当前脉波延迟时间PTTN,以获得补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC,如式(6):After obtaining the height change parameter ΔH, the processing unit 12 compensates the current pulse wave delay time PTTN according to the height change parameter ΔH to obtain the compensated pulse wave delay time PTTC , as shown in formula (6):
在获得补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC后,处理单元12自内存13读取在初始参数设定模式下获得的关系常数K,且根据补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC与关系常数K来计算血压信号的收缩压值SBPC,如式(7):After obtaining the compensated pulse wave delay time PTTC , the processing unit 12 reads the relationship constant K obtained in the initial parameter setting mode from the memory 13, and calculates the value of the blood pressure signal according to the compensated pulse wave delay time PTTC and the relationship constant K Systolic blood pressure value SBPC , such as formula (7):
SBPC=K[PTTC]-1 式(7)SBPC =K[PTTTC ]-1 Formula (7)
在获得收缩压值SBPC后,处理单元12自内存13读取初始舒张压参数DBP0、初始收缩压参数SBP0、及初始脉波延迟时间PTT0,并根据缩压值SBPC、初始舒张压参数DBP0、初始收缩压参数SBP0、初始脉波延迟时间PTT0、以及补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC来计算该血压信号中的舒张压值SBPC,如式(8)After the systolic blood pressure value SBPC is obtained, the processing unit 12 reads the initial diastolic blood pressure parameter DBP0 , the initial systolic blood pressure parameter SBP0 , and the initial pulse wave delay time PTT0 from the memory 13, and according to the systolic blood pressure valueSBPC , the initial diastolic Blood pressure parameter DBP0 , initial systolic blood pressure parameter SBP0 , initial pulse wave delay time PTT0 , and compensated pulse wave delay time PTTC to calculate the diastolic blood pressure value SBPC in the blood pressure signal, as shown in formula (8)
根据上述,在测量模式下,假使生理信号测量模块1的高度偏离参考位置的高度时,可通过姿势传感器11来计算此高度差ΔH(高度变化参数),并透过高度变化参数ΔH来对当前脉波延迟时间PTTN进行补偿,以进一步精准地计算收缩压值与舒张压值,避免因受测者下臂位置的变换所导致的血压值误差。According to the above, in the measurement mode, if the height of the physiological signal measurement module 1 deviates from the height of the reference position, the height difference ΔH (altitude change parameter) can be calculated by the posture sensor 11, and the current The pulse delay time PTTN is compensated to further accurately calculate the systolic and diastolic blood pressure values, avoiding blood pressure value errors caused by changes in the position of the lower arm of the subject.
根据本发明的实施例,在生理信号测量模块1每次进行测量模式前,不需一定要进行初始参数设定模式。当内存13已储存了上述初始参数后,使用者可随时使用生理信号测量模块1的测量模式来测量血压。可定时或在必要时再将外部装置15连接至生理信号测量模块1,以进行初始参数设定模式。According to the embodiment of the present invention, before the physiological signal measurement module 1 performs the measurement mode every time, it is not necessary to perform the initial parameter setting mode. After the memory 13 has stored the above initial parameters, the user can use the measurement mode of the physiological signal measurement module 1 to measure blood pressure at any time. The
本发明的生理信号测量模块1可整合在个人数字助理、移动电话、数字相机、全球定位系统等移动式电子设备,以方便使用者能随身携带,以达到居家照护与实时自我生理测量的目的。The physiological signal measurement module 1 of the present invention can be integrated in mobile electronic devices such as personal digital assistants, mobile phones, digital cameras, global positioning systems, etc., so that users can carry it with them, so as to achieve the purpose of home care and real-time self-physiological measurement.
在本发明的实施例中,姿势感测单元11可包括加速度计、陀螺仪、或磁力计。此外,生理信号测量模块1可包括显示单元14,其可接收来自内存13的初始参数初始舒张压参数DBP0、初始收缩压参数SBP0、初始脉波延迟时间PTT0、关系常数K、以及/或高度差H0,也可接收由处理单元12所计算获得的高度变化参数ΔH、补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC、收缩压值SBPC、以及/或舒张压值SBPC,并将接收的参数或信号透过显示面板140来显示给受测者。In an embodiment of the present invention, the posture sensing unit 11 may include an accelerometer, a gyroscope, or a magnetometer. In addition, the physiological signal measurement module 1 may include a display unit 14, which may receive the initial parameters from the memory 13, the initial diastolic pressure parameter DBP0 , the initial systolic blood pressure parameter SBP0 , the initial pulse wave delay time PTT0 , the relationship constant K, and/or or altitude difference H0 , can also receive the altitude change parameter ΔH calculated by the processing unit 12, the compensated pulse wave delay time PTTC , the systolic blood pressure valueSBPC , and/or the diastolic blood pressure valueSBPC , and the received parameters Or the signal is displayed to the subject through the
在本发明的实施例中,光传感器24可与感测电极21-23中的一个结合,例如,光传感器24与感测电极23结合。在其它实施例中,光传感器24接近于感测电极23。In an embodiment of the present invention, the
图4是表示根据本发明实施例的生理信号测量流程图。参阅图1与2以及图4,首先,以生理信号测量模块11的感测电极21-23与光传感器24来测量受测者的心电信号ECGN与脉搏信号PPGN(步骤S40)。接着,处理单元12测量生理信号测量模块1与参考位置之间的高度,以产生高度变化参数ΔH(步骤S41)。处理单元12根据心电信号ECGN与该脉搏信号PPGN来计算当前脉波延迟时间PTTN(步骤S42)。处理单元12根据高度变化参数ΔH来补偿当前脉波延迟时间PTTN以获得补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC,如式(6)(步骤S43)。由外部装置15提供初始舒张压参数DBP0与初始收缩压参数SBP0,且由内存13提供预先储存的初始脉波延迟时间PTT0与以及关系常数K(步骤S44)。在此实施例中,外部装置15测量初始舒张压参数DBP0初始收缩压参数SBP0的操作,以及初始脉波延迟时间PTT0与以及关系常数K的获得如前图1的实施例所述。处理单元12根据关系常数K与补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC来计算血压信号的收缩压值SBPC,如式(7)(步骤S45)。在获得收缩压值SBPC之后,处理单元12根据收缩压值SBPC、初始收缩压参数SBP0、该初始舒张压参数DBP0、初始脉波延迟时间PTT0、与补偿脉波延迟时间PTTC来计算血压信号的舒张压值DBPC(步骤S46)。Fig. 4 is a flow chart showing a physiological signal measurement according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2 and FIG. 4 , first, use the sensing electrodes 21 - 23 and the
在本发明的实施例中,步骤S44不限定在步骤S43之后,其可在执行步骤S45之前完成即可。In the embodiment of the present invention, step S44 is not limited to be performed after step S43, it can be completed before step S45 is executed.
虽然本发明已以较佳实施例揭露如上,然其并非用以限制本发明,任何熟悉此项技术的人员,在不脱离本发明的精神和范围内,当可做更动与润饰,因此本发明的保护范围当视后附的权利要求书所界定的范围为准。Although the present invention has been disclosed above with preferred embodiments, it is not intended to limit the present invention. Any person familiar with the art may make changes and modifications without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Therefore, this The scope of protection of the invention should depend on the scope defined by the appended claims.
Claims (23)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910006994ACN101810470B (en) | 2009-02-23 | 2009-02-23 | Physiological signal measurement module and physiological signal error compensation method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910006994ACN101810470B (en) | 2009-02-23 | 2009-02-23 | Physiological signal measurement module and physiological signal error compensation method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101810470Atrue CN101810470A (en) | 2010-08-25 |
| CN101810470B CN101810470B (en) | 2012-09-05 |
Family
ID=42617953
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910006994AActiveCN101810470B (en) | 2009-02-23 | 2009-02-23 | Physiological signal measurement module and physiological signal error compensation method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101810470B (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102525434A (en)* | 2012-01-04 | 2012-07-04 | 安阳工学院 | Remote electronic monitoring device |
| CN103582451A (en)* | 2011-05-31 | 2014-02-12 | 株式会社村田制作所 | Pulse wave sensor device |
| WO2016055356A1 (en)* | 2014-10-10 | 2016-04-14 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Non-invasive blood pressure monitors, methods and computer program product of operating the same |
| CN107847153A (en)* | 2015-07-03 | 2018-03-27 | 深圳市长桑技术有限公司 | A system and method for monitoring physiological parameters |
| CN107960998A (en)* | 2018-01-02 | 2018-04-27 | 广东乐心医疗电子股份有限公司 | Blood pressure measuring method and blood pressure measuring device |
| CN108852413A (en)* | 2018-08-31 | 2018-11-23 | 华南理工大学 | Ultrasound pulse detection probe and detection method based on multiple aperture male part |
| WO2020154835A1 (en)* | 2019-01-28 | 2020-08-06 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for measurement compensation |
| US10799127B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2020-10-13 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for physiological parameter monitoring |
| US11672430B2 (en) | 2015-01-04 | 2023-06-13 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for health monitoring |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1127939C (en)* | 1995-07-28 | 2003-11-19 | 北京新兴生物医学工程研究发展中心 | Method for measuring arterial blood pressure by using pulse wave and apparatus thereof |
| CN100418471C (en)* | 2000-11-14 | 2008-09-17 | 欧姆龙健康医疗事业株式会社 | Electronic sphygmomanometer |
| CN100512750C (en)* | 2006-06-16 | 2009-07-15 | 香港中文大学 | Method for calibrating cuff-free arterial blood pressure measuring device |
| CN101248989B (en)* | 2007-02-25 | 2011-10-12 | 香港中文大学 | A monitoring system for physiological parameters |
- 2009
- 2009-02-23CNCN200910006994Apatent/CN101810470B/enactiveActive
Cited By (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10149623B2 (en) | 2011-05-31 | 2018-12-11 | Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Pulse wave sensor device |
| CN103582451A (en)* | 2011-05-31 | 2014-02-12 | 株式会社村田制作所 | Pulse wave sensor device |
| CN103582451B (en)* | 2011-05-31 | 2016-01-06 | 株式会社村田制作所 | Pulse wave sensor device |
| CN102525434A (en)* | 2012-01-04 | 2012-07-04 | 安阳工学院 | Remote electronic monitoring device |
| US10595733B2 (en) | 2014-10-10 | 2020-03-24 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Non-invasive blood pressure monitors, methods and computer program product of operating the same |
| US11298033B2 (en) | 2014-10-10 | 2022-04-12 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Non-invasive blood pressure monitors and methods of operating the same |
| WO2016055356A1 (en)* | 2014-10-10 | 2016-04-14 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Non-invasive blood pressure monitors, methods and computer program product of operating the same |
| US11672430B2 (en) | 2015-01-04 | 2023-06-13 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for health monitoring |
| US11957440B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2024-04-16 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for physiological parameter monitoring |
| US11712168B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2023-08-01 | Vita-Course Technoloaies (Hainan) Co., Ltd. | System and method for physiological feature derivation |
| US12076125B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2024-09-03 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for blood pressure monitoring |
| US10799127B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2020-10-13 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for physiological parameter monitoring |
| US11540735B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2023-01-03 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for physiological parameter monitoring |
| US10932680B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2021-03-02 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for physiological parameter monitoring |
| CN112754445A (en)* | 2015-03-31 | 2021-05-07 | 深圳市长桑技术有限公司 | System and method for monitoring physiological parameters |
| US11134853B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2021-10-05 | Vita-Course Technologies Co., Ltd. | System and method for blood pressure monitoring |
| US11185242B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2021-11-30 | Vita-Course Technologies (Hainan) Co., Ltd. | System and method for physiological feature derivation |
| CN107847153B (en)* | 2015-07-03 | 2020-12-04 | 深圳市长桑技术有限公司 | A system and method for monitoring physiological parameters |
| CN107847153A (en)* | 2015-07-03 | 2018-03-27 | 深圳市长桑技术有限公司 | A system and method for monitoring physiological parameters |
| CN107960998B (en)* | 2018-01-02 | 2021-12-07 | 广东乐心医疗电子股份有限公司 | Blood pressure measuring device |
| CN107960998A (en)* | 2018-01-02 | 2018-04-27 | 广东乐心医疗电子股份有限公司 | Blood pressure measuring method and blood pressure measuring device |
| CN108852413A (en)* | 2018-08-31 | 2018-11-23 | 华南理工大学 | Ultrasound pulse detection probe and detection method based on multiple aperture male part |
| CN108852413B (en)* | 2018-08-31 | 2023-10-24 | 华南理工大学 | Ultrasonic pulse detection probe and detection method based on multi-aperture coupling piece |
| CN112040842A (en)* | 2019-01-28 | 2020-12-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Measurement compensation method and device |
| WO2020154835A1 (en)* | 2019-01-28 | 2020-08-06 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for measurement compensation |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101810470B (en) | 2012-09-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI425934B (en) | Biosignal measurement modules and methods | |
| CN101810470A (en) | Physiological signal measurement module and method | |
| US10952624B2 (en) | Blood pressure related information display apparatus | |
| JP5471337B2 (en) | Blood pressure measuring device and blood pressure measuring method | |
| US10729338B2 (en) | Blood pressure measurement device and calibration method thereof | |
| CN109893110B (en) | Method and device for calibrating dynamic blood pressure | |
| US8795185B2 (en) | Portable device for measuring blood pressure and method therefor | |
| US9918645B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for measuring change in blood pressure by respiration control | |
| CN112890790B (en) | Wearable noninvasive dynamic blood pressure tracking and monitoring method | |
| EP2967392B1 (en) | Improved ecg calculation method for use in generating 12 lead ecg measurements from devices that have less than 10 electrodes | |
| EP1369081A1 (en) | Visceral fat meter provided with tonometer | |
| CN201767961U (en) | Wrist band sphygmomanometer | |
| WO2017119187A1 (en) | Blood pressure correction information generating device, blood pressure measurement device, blood pressure correction information generating method, and blood pressure correction information generating program | |
| Edwan et al. | Blood pressure monitoring using arduino-android platform | |
| TWI584781B (en) | Blood pressure measurement device and method of blood pressure measurement | |
| WO2018168804A1 (en) | Device and method for displaying blood pressure-related information | |
| WO2023016326A1 (en) | Blood pressure calibration method and apparatus, blood pressure measurement system, and electronic device | |
| CN104665801B (en) | Wrist-cuff device based on motion capture | |
| CN107137066A (en) | A kind of portable terminal | |
| US20240197248A1 (en) | Biometric information measurement device, control method of biometric information measurement device, and program | |
| JP2006192052A (en) | Blood pressure measurement device | |
| US20240197194A1 (en) | Biological information measurement device, control method for biological information measurement device, and program | |
| JP2020018558A (en) | Blood pressure measurement device, method and program | |
| CN119908691A (en) | A blood pressure measurement method and related device | |
| JP2023002975A (en) | Venous pressure measurement device, venous pressure measurement method, and venous pressure measurement program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |