CN101753253B - Method, equipment and system for encoding and decoding of GSM (global system for mobile communications) packet-switched domain - Google Patents
Method, equipment and system for encoding and decoding of GSM (global system for mobile communications) packet-switched domainDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101753253B CN101753253BCN 200810182901CN200810182901ACN101753253BCN 101753253 BCN101753253 BCN 101753253BCN 200810182901CN200810182901CN 200810182901CN 200810182901 ACN200810182901 ACN 200810182901ACN 101753253 BCN101753253 BCN 101753253B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- length
- data
- rlc
- encoding
- decoding
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/0078—Avoidance of errors by organising the transmitted data in a format specifically designed to deal with errors, e.g. location
- H04L1/009—Avoidance of errors by organising the transmitted data in a format specifically designed to deal with errors, e.g. location arrangements specific to transmitters
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/004—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using forward error control
- H04L1/0041—Arrangements at the transmitter end
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及网络通信技术领域,特别涉及一种GSM分组域编解码的方法、设备及系统。The invention relates to the technical field of network communication, in particular to a method, device and system for encoding and decoding in the GSM packet domain.
背景技术Background technique
现有全球移动通讯系统(GSM,Global System for Mobile Communications)分组域(PS,Packet Switched domain)采用固定的无线链路控制或媒介接入控制(RLC/MAC,Radio Link Control/Medium Access Control)编码方式来承载逻辑链路控制分组数据单元(LLC PDU,Logical Link Control Packet DataUnit)。例如增强型数据速率GSM演进技术(EDGE,Enhanced Data Rates forGSM Evolution)网络中有调制编码方式MCS-1~MCS-9(MCS,Modulation andCoding Scheme)共九种RLC/MAC编码方式,每种RLC/MAC编码方式具有固定的长度。LLC PDU数据采用分段级联的方式承载在所述RLC/MAC块中。The existing GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) packet domain (PS, Packet Switched domain) adopts fixed radio link control or medium access control (RLC/MAC, Radio Link Control/Medium Access Control) coding way to carry the logical link control packet data unit (LLC PDU, Logical Link Control Packet DataUnit). For example, in the Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE, Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution) network, there are nine kinds of RLC/MAC coding methods, MCS-1~MCS-9 (MCS, Modulation and Coding Scheme), each RLC/MAC The MAC encoding method has a fixed length. The LLC PDU data is carried in the RLC/MAC block in a segmented and concatenated manner.
GSM EDGE无线接入网(GERAN,GSM EDGE Radio Access Network)承载电路域(CS,Circuit Switched domain)语音业务是利用RLC/MAC块承载CS帧。由于CS域的自适应多速率编解码(AMR,Adaptive Multi-Rate codec)速率与分组域(PS,Packet Switched Domain)的RLC速率不匹配,所以通常情况下,LLC PDU数据长度总和无法填满当前的RLC/MAC块。GSM EDGE Radio Access Network (GERAN, GSM EDGE Radio Access Network) bears circuit domain (CS, Circuit Switched domain) voice services and uses RLC/MAC blocks to carry CS frames. Since the Adaptive Multi-Rate Codec (AMR, Adaptive Multi-Rate codec) rate of the CS domain does not match the RLC rate of the Packet Switched Domain (PS, Packet Switched Domain), usually, the total length of LLC PDU data cannot fill the current RLC/MAC block.
现有技术中,当所有剩余的LLC PDU数据长度总和无法填满当前的RLC/MAC块时,采用填充0x2B无效字节的方式填满整个RLC/MAC块。但是采用现有技术中的0x2B无效字节填充剩余空间,将浪费有限的带宽资源。在信道编码时,无法利用剩余空间进一步增加冗余。尤其在当前业务数据流量小,并且LLC PDU数据长度较小时,RLC/MAC块中出现填充无效字节的几率很大,利用现有的填充技术无法提升链路传输性能。In the prior art, when the sum of the data lengths of all remaining LLC PDUs cannot fill the current RLC/MAC block, the entire RLC/MAC block is filled by filling 0x2B invalid bytes. However, filling the remaining space with 0x2B invalid bytes in the prior art will waste limited bandwidth resources. In channel coding, the remaining space cannot be used to further increase redundancy. Especially when the current business data flow is small and the LLC PDU data length is small, the probability of filling invalid bytes in the RLC/MAC block is very high, and the existing filling technology cannot improve link transmission performance.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例提供一种GSM分组域编解码的方法、设备及系统,节省有限的带宽资源,提高了链路传输性能。Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, device and system for GSM packet domain encoding and decoding, which save limited bandwidth resources and improve link transmission performance.
本发明实施例提供一种GSM分组域编解码的方法,包括:判断无线链路控制/媒介接入控制RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中是否存在指示承载的有效数据长度的信息,所述有效数据长度为编码前输入数据的长度;当所述RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中存在所述有效数据长度的信息时,根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度,进行变长信道编码。An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for GSM packet domain encoding and decoding, including: judging whether there is information indicating the effective data length of the bearer in the control field of the radio link control/medium access control RLC/MAC block header, the effective The data length is the length of the input data before encoding; when the information of the effective data length exists in the control field in the RLC/MAC block header, according to the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after encoding, the length is changed channel coding.
本发明实施例还提供一种GSM分组域编码设备,包括:判断单元和变长信道编码单元。所述判断单元,用于判断无线链路控制/媒介接入控制RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中是否存在指示承载的有效数据长度的信息,所述有效数据长度为编码前输入数据的长度;所述变长信道编码单元,用于当所述判断单元的判断结果为所述RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中存在所述有效数据长度的信息时,根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道编码。The embodiment of the present invention also provides a GSM packet domain coding device, including: a judging unit and a variable-length channel coding unit. The judging unit is used to judge whether there is information indicating the effective data length carried in the control field in the radio link control/medium access control RLC/MAC block header, and the effective data length is the length of the input data before encoding; The variable-length channel coding unit is configured to, when the judging result of the judging unit is that the effective data length information exists in the control field in the RLC/MAC block header, according to the length of the input data before coding and the length of the data after coding The length of the output data is variable-length channel coded.
本发明实施例还提供一种GSM分组域编解码的系统,所述系统包括上述编码设备,还包括接收端;所述接收端,用于在接收到所述设备发送的数据后,根据所述解码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道解码。The embodiment of the present invention also provides a GSM packet domain encoding and decoding system, the system includes the above-mentioned encoding device, and also includes a receiving end; the receiving end is configured to, after receiving the data sent by the device, The length of the input data before decoding and the length of the output data after decoding are subjected to variable-length channel decoding.
以上技术方案,在RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中增加指示RLC/MAC块承载的有效数据的长度的信息,编码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度均与所述有效数据的长度相同。发送端根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道编码。接收端根据所述解码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道解码。本发明提供的方法由于在控制域中增加了指示有效数据的长度信息,发送端可以根据有效数据长度进行变长编码,接收端根据有效数据长度进行变长解码。由于RLC/MAC块中承载的数据长度是可变的,避免承载的帧中出现空闲比特或无效的填充字节,从而节省了有限的带宽资源,提高了链路性能。In the above technical scheme, the information indicating the length of the effective data carried by the RLC/MAC block is added in the control field in the RLC/MAC block header, and the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after decoding are all the same as the length of the effective data same. The sending end performs variable-length channel coding according to the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after encoding. The receiving end performs variable-length channel decoding according to the length of the input data before decoding and the length of the output data after decoding. Because the method provided by the invention adds length information indicating effective data in the control field, the sending end can perform variable-length encoding according to the effective data length, and the receiving end can perform variable-length decoding according to the effective data length. Since the length of the data carried in the RLC/MAC block is variable, idle bits or invalid filling bytes in the carried frame are avoided, thereby saving limited bandwidth resources and improving link performance.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是基于本发明方法第一实施例流程图;Fig. 1 is a flow chart based on the first embodiment of the method of the present invention;
图2是基于本发明实施例GMSK下行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the GMSK downlink CS over GERAN of the embodiment of the present invention;
图3是基于本发明实施例8PSK下行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the embodiment of the present invention 8PSK downlink CS over GERAN;
图4是基于本发明实施例GMSK上行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the GMSK uplink CS over GERAN of the embodiment of the present invention;
图5是基于本发明实施例8PSK上行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the embodiment of the present invention 8PSK uplink CS over GERAN;
图6是基于本发明方法第二实施例示意图;Fig. 6 is a schematic diagram based on the second embodiment of the method of the present invention;
图7是基于本发明实施例CS over GERAN承载两个5.9kb/s AMR帧的变长信道编解码示意图;Fig. 7 is a schematic diagram of variable-length channel encoding and decoding based on CS over GERAN carrying two 5.9kb/s AMR frames according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图8是基于本发明设备第一实施例结构图;Fig. 8 is a structural diagram of the first embodiment of the device based on the present invention;
图9是基于本发明设备第二实施例结构图;Fig. 9 is a structural diagram of the second embodiment of the device based on the present invention;
图10是基于本发明系统第一实施例结构图;Fig. 10 is a structural diagram of the first embodiment of the system based on the present invention;
图11是基于本发明系统第二实施例结构图。Fig. 11 is a structural diagram of the second embodiment of the system based on the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
首先对本发明实施例实现一种GSM分组域编解码的方法进行说明,包括:First, the embodiment of the present invention realizes a method for GSM packet domain encoding and decoding, including:
判断无线链路控制/媒介接入控制RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中是否存在指示承载的有效数据长度的信息,所述有效数据长度为编码前输入数据的长度;当所述RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中存在所述有效数据长度的信息时,根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度,进行变长信道编码。下面结合附图,对本发明的实施例进行详细描述。Judging whether there is information indicating the effective data length carried in the control field in the radio link control/medium access control RLC/MAC block header, the effective data length is the length of the input data before encoding; when the RLC/MAC block header If there is information about the effective data length in the control field in , variable-length channel coding is performed according to the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after encoding. Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
方法实施例一:Method embodiment one:
参见图1,该图为基于本发明方法第一实施例流程图。Referring to Fig. 1, this figure is a flowchart of the first embodiment of the method based on the present invention.
本发明一种GSM分组域编解码的方法第一实施例包括以下步骤:A first embodiment of a method for GSM packet domain encoding and decoding of the present invention comprises the following steps:
S101:在RLC/MAC块的头中的控制域中增加指示所述RLC/MAC块中承载的有效数据的长度的信息。S101: Add information indicating the length of valid data carried in the RLC/MAC block to the control field in the header of the RLC/MAC block.
其中,编码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度均与所述有效数据的长度相同。Wherein, the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after decoding are both the same as the length of the valid data.
指示RLC/MAC块中承载的有效数据的长度的信息具体可以用两种指示信息来表示,比如:用于指示AMR的编码模式指示(CMI,Code Mode Indicator)和帧的个数帧数(FN,Frame Number)。其中,CMI用于指示当前RLC/MAC块中各个CS帧的AMR模式,由每个帧的AMR模式可以得到每个帧的长度。FN用于指示当前RLC/MAC块中承载的CS帧的个数。The information indicating the length of the valid data carried in the RLC/MAC block can be specifically represented by two kinds of indication information, such as: a code mode indication (CMI, Code Mode Indicator) for indicating AMR and a number of frames (FN , Frame Number). Wherein, the CMI is used to indicate the AMR mode of each CS frame in the current RLC/MAC block, and the length of each frame can be obtained from the AMR mode of each frame. The FN is used to indicate the number of CS frames carried in the current RLC/MAC block.
需要说明的是,RLC/MAC块中的各个CS帧可以使用不同的AMR模式,也可以使用相同的AMR模式。RLC/MAC块中承载的CS帧个数可以为一个或多个。It should be noted that each CS frame in the RLC/MAC block may use different AMR modes, or may use the same AMR mode. The number of CS frames carried in the RLC/MAC block can be one or more.
每个帧的长度乘以FN指示的有效帧的个数便是RLC/MAC块中承载的有效数据的长度。The length of each frame multiplied by the number of valid frames indicated by FN is the length of valid data carried in the RLC/MAC block.
由CMI指示的AMR模式和FN指示的帧的个数就可以计算出RLC/MAC块中承载的数据的长度。所以,通过CMI和FN的组合,可以指示有效数据的长度。当然,除了使用CMI和FN的组合的方式之外,还可以有其他表示有效数据长度信息的标识方式。The length of the data carried in the RLC/MAC block can be calculated from the AMR mode indicated by the CMI and the number of frames indicated by the FN. Therefore, through the combination of CMI and FN, the length of valid data can be indicated. Certainly, besides the combined manner of using CMI and FN, there may be other identification manners representing the effective data length information.
需要说明的是,所述CMI和FN在RLC/MAC头中的位置是可以选择的。It should be noted that the positions of the CMI and FN in the RLC/MAC header are optional.
S102:根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道编码。S102: Perform variable-length channel coding according to the length of input data before encoding and the length of output data after encoding.
具体的,根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度,选择信道编码方法和速率。然后根据变长打孔算法或填充冗余算法,通过打孔或填充冗余进行变长信道编码。Specifically, the channel coding method and rate are selected according to the length of input data before encoding and the length of output data after encoding. Then according to the variable-length puncturing algorithm or padding redundancy algorithm, variable-length channel coding is performed by puncturing or padding redundancy.
例如,当编码前输入数据的长度与编码后输出数据的长度的差值在一定范围内时,所述信道编码速率可以选择1/2或1/3卷积码。For example, when the difference between the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after encoding is within a certain range, the channel encoding rate can be 1/2 or 1/3 convolutional code.
需要说明的是,编码前输入数据的长度与编码后输出数据的长度的差值变化时,所述信道编码也可以选择其他速率的卷积码。It should be noted that when the difference between the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after encoding changes, the channel encoding may also select convolutional codes of other rates.
在接收端,还可以包括解码的步骤:On the receiving end, the decoding step can also be included:
S103:根据所述解码前输入的长度和解码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道解码。S103: Perform variable-length channel decoding according to the length of the input data before decoding and the length of the output data after decoding.
根据RLC/MAC块的头中的控制域,获得解码后输出数据的长度,解码后输出数据的长度与有效数据的长度相同。根据解码前输入数据的长度和所述解码后输出数据的长度,推算出编码时使用的打孔或填充冗余的方法,进行正确的变长信道解码。According to the control field in the header of the RLC/MAC block, the length of the decoded output data is obtained, and the length of the decoded output data is the same as the length of the valid data. According to the length of the input data before decoding and the length of the output data after decoding, the method of puncturing or filling redundancy used in encoding is calculated to perform correct variable-length channel decoding.
本发明实施例提供的GSM分组域编解码方法,由于控制域增加了指示有效数据的长度的信息,发送端可以根据有效数据长度进行变长信道编码,接收端根据有效数据长度进行变长解码。由于采用变长信道编码,因此RLC/MAC块中承载的数据不会出现空闲比特,进而避免出现无效的填充字节,从而区别传统的PS域的RLC/MAC编码方法(例如,MCS-1~MCS-9),节省了有限的带宽资源,提高了链路性能。In the GSM packet field encoding and decoding method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, since the control field adds information indicating the length of valid data, the sending end can perform variable-length channel coding according to the effective data length, and the receiving end can perform variable-length decoding according to the effective data length. Due to the use of variable-length channel coding, there will be no idle bits in the data carried in the RLC/MAC block, thereby avoiding invalid padding bytes, thereby distinguishing the traditional RLC/MAC coding method of the PS domain (for example, MCS-1~ MCS-9), which saves limited bandwidth resources and improves link performance.
下面结合附图详细说明本发明实施例所述CS over GERAN变长编解码的上下行RLC/MAC的头格式。所述RLC/MAC的头类型与调制方式有关。调制方式不同,所述RLC/MAC的头类型的长度不同。The header format of the uplink and downlink RLC/MAC of the CS over GERAN variable-length codec described in the embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The header type of the RLC/MAC is related to the modulation mode. The modulation modes are different, and the lengths of the RLC/MAC header types are different.
参见图2,该图为基于本发明实施例GMSK下行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图。Referring to Fig. 2, this figure is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the GMSK downlink CS over GERAN of the embodiment of the present invention.
下面以高斯滤波最小移频键控(GMSK,Gaussian Minimum Shift-frequencyKeying)下行CS over GERAN为例说明RLC/MAC头格式。The following takes Gaussian Minimum Shift-frequency Keying (GMSK, Gaussian Minimum Shift-frequency Keying) downlink CS over GERAN as an example to illustrate the RLC/MAC header format.
从图2中可以看出,RLC/MAC头格式中增加了指示有效数据长度的CMI和FN。It can be seen from Figure 2 that CMI and FN indicating the effective data length are added to the RLC/MAC header format.
需要说明的是,图2中所示为一个RLC/MAC的头格式中包含四个CMI,分别是CMI1、CMI2、CMI3和CMI4,用于指示一个RLC/MAC块中承载4个CS帧,并且每个CMI代表不同的AMR模式。当然,一个RLC/MAC块中承载的各个CS帧的AMR模式可以相同,即四个CMI的数值相同。It should be noted that, as shown in FIG. 2, an RLC/MAC header format includes four CMIs, namely CMI1, CMI2, CMI3, and CMI4, which are used to indicate that one RLC/MAC block carries 4 CS frames, and Each CMI represents a different AMR mode. Of course, the AMR modes of the CS frames carried in one RLC/MAC block may be the same, that is, the values of the four CMIs are the same.
需要说明的是,一个RLC/MAC块中承载的CS帧的个数是可以选择的,图2中所示为一个RLC/MAC块中承载了4个CS帧的数据。It should be noted that the number of CS frames carried in one RLC/MAC block can be selected. As shown in FIG. 2 , one RLC/MAC block carries data of 4 CS frames.
FN表示一个RLC/MAC块中承载的CS帧的有效个数,例如FN是3,则表示CMI1、CMI2和CMI3是有效的帧模式,即RLC/MAC块中承载的有效数据的长度仅包括CMI1、CMI2和CMI3代表的帧的长度。同理,如果FN是2,则有效数据的长度仅包括CMI1和CMI2代表的帧的长度。FN indicates the effective number of CS frames carried in an RLC/MAC block. For example, if FN is 3, it means that CMI1, CMI2, and CMI3 are valid frame modes, that is, the length of valid data carried in an RLC/MAC block only includes CMI1. , CMI2 and CMI3 represent the length of the frame. Similarly, if FN is 2, the length of valid data only includes the length of frames represented by CMI1 and CMI2.
需要说明的是,RLC/MAC的头格式中其他的编码与传统的PS编码可以是相同的,例如图2中的上行状态标识(USF,Uplink State Flag)和临时流标识(TFI,Temporary Flow Identity)编码可以与原来的PS编码相同。其中,USF用于调度各用户的上行。It should be noted that other encodings in the header format of RLC/MAC can be the same as traditional PS encodings, such as the uplink state flag (USF, Uplink State Flag) and temporary flow identity (TFI, Temporary Flow Identity) in Figure 2 ) encoding can be the same as the original PS encoding. Wherein, the USF is used for scheduling the uplink of each user.
参见图3,该图为基于本发明实施例8PSK下行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图。Referring to Fig. 3, this figure is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the 8PSK downlink CS over GERAN of the embodiment of the present invention.
与图2类型,图3所示是以相移相键控(8PSK,8Phase Shift Keying 8)的下行CS over GERAN为例介绍RLC/MAC头格式。Similar to Figure 2, Figure 3 shows the RLC/MAC header format using the downlink CS over GERAN of phase shift keying (8PSK, 8Phase Shift Keying 8) as an example.
比较图2和图3的RLC/MAC头格式,可以看出GMSK和8PSK的头中仅数据的长度不同。GMSK的第四个字节有7位,而8PSK的第四个字节仅有4位。Comparing the RLC/MAC header format in Figure 2 and Figure 3, it can be seen that only the length of the data in the header of GMSK and 8PSK is different. The fourth byte of GMSK has 7 bits, while the fourth byte of 8PSK has only 4 bits.
参见图4,该图为基于本发明实施例GMSK上行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图。Referring to Fig. 4, this figure is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the GMSK uplink CS over GERAN according to the embodiment of the present invention.
图4与图2类似,上行的RLC/MAC头中也包括TFI、CMI和FN。Fig. 4 is similar to Fig. 2, and the uplink RLC/MAC header also includes TFI, CMI and FN.
参见图5,该图为基于本发明实施例所述8PSK上行CS over GERAN的RLC/MAC头格式示意图。Referring to FIG. 5, this figure is a schematic diagram of the RLC/MAC header format based on the 8PSK uplink CS over GERAN described in the embodiment of the present invention.
图5与图4表示的RLC/MAC头格式类似,可以看出GMSK和8PSK的头中仅数据的长度不同,GMSK的第四个字节有7位,而8PSK的第五个字节有5位。Figure 5 is similar to the RLC/MAC header format shown in Figure 4. It can be seen that only the length of the data in the header of GMSK and 8PSK is different. The fourth byte of GMSK has 7 bits, while the fifth byte of 8PSK has 5 bits. bit.
方法实施例二:Method embodiment two:
参见图6,该图为基于本发明方法第二实施例流程图。Referring to FIG. 6 , this figure is a flowchart of the second embodiment of the method based on the present invention.
下面以CS over GERAN为例介绍本发明的变长信道编码流程。The following takes CS over GERAN as an example to introduce the variable-length channel coding process of the present invention.
S601:根据RLC/MAC头中的TFI判断当前RLC/MAC头格式是变长信道编解码的CS over GERAN头格式时,读取控制域中的CMI和FN,确定当前数据RLC/MAC块的有效数据的长度。S601: When judging from the TFI in the RLC/MAC header that the current RLC/MAC header format is the CS over GERAN header format of the variable-length channel codec, read the CMI and FN in the control field to determine the validity of the current data RLC/MAC block The length of the data.
需要说明的是,由TFI的数值可以判断当前RLC/MAC头格式是传统的PS头格式还是变长信道编码头格式。It should be noted that the value of the TFI can determine whether the current RLC/MAC header format is the traditional PS header format or the variable-length channel coding header format.
由CMI和FN可以得到有效数据的长度。The length of valid data can be obtained from CMI and FN.
S602:对RLC/MAC块中承载的各个帧的重要比特进行循环冗余校验(CRC,Cyclic Redundancy Check)。S602: Perform a cyclic redundancy check (CRC, Cyclic Redundancy Check) on important bits of each frame carried in the RLC/MAC block.
需要说明的是,所谓各个帧的重要比特可以是各个帧的Ia类最重要比特,而且,校验位可以选择加在每个帧之后,也可以选择加在帧的其他位置。校验位的长度也可以根据实际需要选择,例如可以为3bit,也可以为6bit。It should be noted that the so-called important bits of each frame may be the most important bits of class Ia of each frame, and the parity bit may be added after each frame or at other positions of the frame. The length of the parity bit can also be selected according to actual needs, for example, it can be 3 bits or 6 bits.
需要说明的是,与传统的AMR模式相比,本发明可以省去块校验序列(BCS,Block Check Sequence),从而增加CRC的长度,对重要数据进行保护。It should be noted that, compared with the traditional AMR mode, the present invention can save the Block Check Sequence (BCS, Block Check Sequence), thereby increasing the length of the CRC and protecting important data.
需要说明的是,该CRC校验的步骤是可选的。It should be noted that the step of CRC checking is optional.
S603:对USF和RLC/MAC头进行编码,其编码形式与传统的PS编码相同,在此不再赘述。S603: Encode the USF and RLC/MAC headers, the encoding format of which is the same as that of traditional PS encoding, and will not be repeated here.
S604:为RLC/MAC块承载的每个帧加上尾比特(TB,Tail Bits)。S604: Add tail bits (TB, Tail Bits) to each frame carried by the RLC/MAC block.
需要说明的是,本发明中的RLC/MAC头格式中去掉了传统PS编码中的BCS、末块指示(FBI,Final Block Indication)和扩充比特(E,Extension bit)。It should be noted that the BCS, Final Block Indication (FBI, Final Block Indication) and extension bit (E, Extension bit) in the traditional PS encoding are removed from the RLC/MAC header format in the present invention.
S605:对上述加上TB的每个帧进行独立的信道编码。S605: Perform independent channel coding on each frame added with the TB.
每个帧可以利用变长打孔或填充冗余算法进行空口速率的适配。Each frame can use variable-length puncturing or padding redundancy algorithm to adapt the air interface rate.
S606:编码的同时,在承载的CS帧最前端增加窃取比特(SB,Steal Bits),SB用于指示当前RLC/MAC的头类型。S606: At the same time of encoding, steal bits (SB, Steal Bits) are added to the head of the carried CS frame, and the SB is used to indicate the header type of the current RLC/MAC.
由SB的数值可以得知当前的RLC/MAC的头类型,例如是GMSK还是8PSK。The current RLC/MAC header type can be known from the value of SB, such as GMSK or 8PSK.
需要说明的是,GMSK调制方式时,SB是12bits;8PSK调制方式下,SB是8bits。RLC/MAC的头类型不同,则SB所指示的比特长度不同。It should be noted that, in the GMSK modulation mode, the SB is 12 bits; in the 8PSK modulation mode, the SB is 8 bits. The header types of RLC/MAC are different, and the bit lengths indicated by the SB are different.
S607:接收端首先读取SB获得RLC/MAC的头类型。S607: The receiver first reads the SB to obtain the RLC/MAC header type.
本步骤中,接收端在接收到发送端编码后发送的数据后,可以首先读取SB获得RLC/MAC的头类型。In this step, after receiving the encoded data sent by the sending end, the receiving end may first read the SB to obtain the RLC/MAC header type.
S608:接收端读取TFI判断RLC/MAC头格式是变长信道编码格式时,读取控制域中的CMI和FN,得到有效数据的长度,即解码后输出数据的长度。S608: When the receiving end reads the TFI and judges that the RLC/MAC header format is a variable-length channel coding format, it reads the CMI and FN in the control field to obtain the length of valid data, that is, the length of the decoded output data.
S609:根据解码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度,对RLC/MAC承载的CS帧进行变长信道解码。S609: Perform variable-length channel decoding on the CS frame carried by the RLC/MAC according to the length of the input data before decoding and the length of the output data after decoding.
接收端根据FN的值确定RLC/MAC块中承载的有效帧的个数,并根据CMI指示的AMR模式得到各个帧的长度。接收端可以只解码有效帧,得到有效数据的长度。The receiving end determines the number of effective frames carried in the RLC/MAC block according to the value of FN, and obtains the length of each frame according to the AMR mode indicated by the CMI. The receiving end can only decode valid frames to obtain the length of valid data.
本发明所述变长信道编解码的方法,有效利用了RLC/MAC块承载CS帧后的剩余空间,在信道编解码时进一步增加冗余,从而提升链路传输性能。而且,本发明实施例所述CS over GERAN利用变长信道编解码,对RLC/MAC块承载CS帧中最重要的比特进行CRC校验,提高了数据传输的精度。The variable-length channel encoding and decoding method of the present invention effectively utilizes the remaining space after the RLC/MAC block bears the CS frame, and further increases redundancy during channel encoding and decoding, thereby improving link transmission performance. Moreover, the CS over GERAN described in the embodiment of the present invention uses variable-length channel codec to perform CRC check on the most important bits in the CS frame carried by the RLC/MAC block, which improves the accuracy of data transmission.
下面以CS over GERAN承载两个5.9kb/s AMR帧为例来详细介绍本发明的变长信道编解码。The following takes CS over GERAN as an example to carry two 5.9kb/s AMR frames to introduce the variable-length channel codec of the present invention in detail.
参见图7,该图为基于本发明实施例CS over GERAN承载两个5.9kb/sAMR帧的变长信道编解码示意图。Referring to FIG. 7, this figure is a schematic diagram of variable-length channel encoding and decoding based on CS over GERAN carrying two 5.9kb/s AMR frames according to an embodiment of the present invention.
由图7中可以看出,卷积编码之前CS over GERAN块承载的数据包括USF、RLC/MAC头、HCS、CRC、TB,以及两个5.9kb/s AMR帧(即Data数据部分)。It can be seen from Figure 7 that the data carried by the CS over GERAN block before convolutional encoding includes USF, RLC/MAC header, HCS, CRC, TB, and two 5.9kb/s AMR frames (that is, the Data data part).
每个AMR帧之后均加CRC和TB。CRC and TB are added after each AMR frame.
由于各个帧是独立编码的,所以每个帧后可以添加TB,用于帧与帧之间的间隔保护,以便进行卷积编码。Since each frame is encoded independently, TB can be added after each frame for interval protection between frames for convolutional encoding.
各个指示的长度举例如下:其中USF可以是3bits;RLC/MAC头和HCS共36bits,CRC可以是6bits或3bits、TB可以是6bits。The length of each indication is as follows: the USF can be 3 bits; the RLC/MAC header and HCS can be 36 bits in total, the CRC can be 6 bits or 3 bits, and the TB can be 6 bits.
每个5.9kb/s AMR帧包括118bits的数据。Each 5.9kb/s AMR frame includes 118bits of data.
对除了USF之外的所有数据进行1/3卷积编码(Rate 1/3 convolutionalcoding),进行速率的适配,得到如图7所示的卷积编码后的数据格式。
其中USF是12bits;RLC/MAC头和HCS共108bits。Among them, USF is 12 bits; RLC/MAC header and HCS are 108 bits in total.
对卷积编码后的数据通过打孔算法进行打孔(puncturing),如图7所示,得到打孔后的数据格式。The convolutionally encoded data is puncturing through a puncturing algorithm, as shown in FIG. 7 , to obtain a puncturing data format.
另外,由图7看出,打孔的同时在最前端加上窃取比特SB,该SB用于指示当前RLC/MAC的头类型。In addition, it can be seen from FIG. 7 that a steal bit SB is added at the front end while puncturing, and the SB is used to indicate the header type of the current RLC/MAC.
需要说明的是,GMSK调制方式时,SB是12bits;8PSK调制方式下,SB是8bits。本实施例采用的是GMSK调制,因此SB是12bits。It should be noted that, in the GMSK modulation mode, the SB is 12 bits; in the 8PSK modulation mode, the SB is 8 bits. This embodiment adopts GMSK modulation, so the SB is 12 bits.
经过打孔以后,RLC/MAC头和HCS共68bits;CRC、TB和一个AMR帧共186bits。After punching, the RLC/MAC header and HCS have a total of 68 bits; CRC, TB and an AMR frame have a total of 186 bits.
由此可得,采用本发明实施例所述的变长信道编码后,有效数据的码率为118bits/186bits=63.4%。如果采用传统的MCS-3承载两个5.9kb/s的AMR帧,则码率为80%。可以看出,针对CS over GERAN业务的变长信道编码方式,大大提高了链路的传输性能。It can be obtained from this that after adopting the variable length channel coding described in the embodiment of the present invention, the code rate of effective data is 118bits/186bits=63.4%. If the traditional MCS-3 is used to carry two 5.9kb/s AMR frames, the code rate is 80%. It can be seen that the variable-length channel coding method for CS over GERAN service greatly improves the transmission performance of the link.
上述实施例仅以CS over GERAN承载两个5.9kb/s AMR帧为例对变长信道编解码进行了说明。需要说明的是,CS over GERAN可以承载一个或多个帧,其中帧的AMR模式可以选择。当CS over GERAN承载多个AMR帧时,每个帧的AMR模式可以相同,也可以不相同。如果每个帧的AMR模式不同,由于各帧都是独立编码,因此当各帧模式即长度不同时,可以按其长度比例对每帧增加不同长度的冗余。这样,在接收端也可以根据长度比例,对每帧进行独立解码。The above-mentioned embodiment only takes CS over GERAN carrying two 5.9kb/s AMR frames as an example to describe the variable-length channel coding and decoding. It should be noted that CS over GERAN can carry one or more frames, and the AMR mode of the frame can be selected. When CS over GERAN carries multiple AMR frames, the AMR mode of each frame can be the same or different. If the AMR mode of each frame is different, since each frame is encoded independently, when each frame mode is different in length, redundancy of different lengths can be added to each frame according to its length ratio. In this way, each frame can be independently decoded according to the length ratio at the receiving end.
本发明实施例提供的CS over GERAN承载两个5.9kb/s AMR帧的变长信道编解码的方法,由于增加控制域指示有效数据的长度,发送端可以根据有效数据长度进行变长编码,接收端根据有效数据长度进行变长解码。RLC/MAC块中承载的数据不会出现空闲比特,进而避免出现无效的填充字节,从而区别传统的PS域的RLC/MAC编码方法(例如,MCS-1~MCS-9),节省了有限的带宽资源,提高了链路性能。需要说明的是,本发明所述GSM分组域编解码的方法不仅适用于CS over GERAN业务,而且适用于传统的PS业务。当本发明所述方法运用在传统PS业务中时,由于传统PS业务中数据的长度是固定的,因此,可以利用本发明所述变长信道编码方法将固定数据长度中除了有效数据以外的空余空间进行冗余,进而提高链路性能。The CS over GERAN method provided by the embodiment of the present invention carries two 5.9kb/s AMR frame variable-length channel encoding and decoding methods. Since the length of the effective data indicated by the control field is increased, the sending end can perform variable-length encoding according to the effective data length, and the receiving end The terminal performs variable-length decoding according to the effective data length. The data carried in the RLC/MAC block will not have idle bits, thereby avoiding invalid padding bytes, thereby distinguishing the traditional RLC/MAC coding methods of the PS domain (for example, MCS-1~MCS-9), saving limited bandwidth resources, improving link performance. It should be noted that the GSM packet domain encoding and decoding method described in the present invention is not only applicable to CS over GERAN services, but also applicable to traditional PS services. When the method of the present invention is used in the traditional PS service, since the length of the data in the traditional PS service is fixed, the variable length channel coding method of the present invention can be used to convert the vacant data in the fixed data length except valid data Space for redundancy, thereby improving link performance.
本发明实施例提供一种GSM分组域编码设备。An embodiment of the present invention provides a GSM packet domain encoding device.
设备实施例一:Equipment embodiment one:
参见图8,该图为基于本发明设备第一实施例示意图。Referring to Fig. 8, this figure is a schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the device based on the present invention.
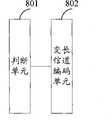
本发明提供一种GSM分组域编码设备,包括:判断单元801和变长信道编码单元802。The present invention provides a GSM packet domain encoding device, including: a judging
所述判断单元801,用于判断无线链路控制/媒介接入控制RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中是否存在指示承载的有效数据长度的信息,所述有效数据长度为编码前输入数据的长度。The judging
变长信道编码单元802,用于当判断单元801的判断结果为RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中存在上述有效数据长度的信息时,根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道编码。The variable-length
在RLC/MAC块头的控制域中增加指示RLC/MAC块中承载的有效数据长度的信息,其中,有效数据的长度与编码前输入数据的长度相同。而且,解码后输出数据的长度也是该有效数据的长度,即,其长度与有效数据长度相同。具体的,有效数据长度的信息可以包括CMI和FN。其中,CMI用于指示当前RLC/MAC块中各个CS帧的AMR模式。需要说明的是,RLC/MAC块中的各个CS帧可以使用不用的AMR模式,也可以使用相同的AMR模式。另外,FN用于指示当前RLC/MAC块中承载的有效CS帧的个数。需要说明的是,RLC/MAC块中承载的CS帧个数可以为一个或多个。可以理解的是,由CMI指示的AMR模式和FN指示的帧的个数就可以计算出RLC/MAC块中承载的数据的长度。Information indicating the length of valid data carried in the RLC/MAC block is added to the control field of the RLC/MAC block header, where the length of the valid data is the same as the length of the input data before encoding. Moreover, the length of the decoded output data is also the length of the valid data, that is, its length is the same as that of the valid data. Specifically, the information about the effective data length may include CMI and FN. Wherein, the CMI is used to indicate the AMR mode of each CS frame in the current RLC/MAC block. It should be noted that each CS frame in the RLC/MAC block may use different AMR modes, or may use the same AMR mode. In addition, FN is used to indicate the number of valid CS frames carried in the current RLC/MAC block. It should be noted that the number of CS frames carried in the RLC/MAC block may be one or more. It can be understood that the length of data carried in the RLC/MAC block can be calculated from the AMR mode indicated by the CMI and the number of frames indicated by the FN.
具体实现时,变长信道编码单元802可以包括两个子单元,分别是第一子单元和第二子单元(图中未示出)。During specific implementation, the variable-length
其中,第一子单元,用于根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度,选择变长信道编码速率;第二子单元,用于根据第一子单元选择的变长信道编码速率进行变长信道编码,例如,所述信道编码速率可以选择1/2或1/3卷积码。当然,也可以选择其他速率的卷积码。具体的,第二子单元可以选择变长打孔算法或填充冗余算法,通过打孔或填充冗余进行变长信道编码。Among them, the first subunit is used to select the variable-length channel coding rate according to the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after encoding; the second subunit is used to select the variable-length channel coding rate according to the first subunit Perform variable-length channel coding, for example, the channel coding rate may be 1/2 or 1/3 convolutional code. Of course, convolutional codes of other rates can also be selected. Specifically, the second subunit may select a variable-length puncturing algorithm or a padding redundancy algorithm, and perform variable-length channel coding by puncturing or padding redundancy.
当编码后的数据发送到接收端后,接收端可以根据RLC/MAC块的头中的控制域,获得解码后输出数据的长度。然后,根据解码前输入数据的长度和所述解码后输出数据的长度(即有效数据长度),推算出编码时使用的打孔或填充冗余的方法,进行正确的变长信道解码。After the encoded data is sent to the receiving end, the receiving end can obtain the length of the decoded output data according to the control field in the header of the RLC/MAC block. Then, according to the length of the input data before decoding and the length of the output data after decoding (that is, the effective data length), the method of puncturing or filling redundancy used in encoding is calculated to perform correct variable-length channel decoding.
本发明实施例提供的GSM分组域编码设备,由于控制域中增加了指示有效数据的长度的信息,发送端可以根据有效数据长度进行变长编码,接收端根据有效数据长度进行变长解码。采用本发明实施例提供的技术方案后,RLC/MAC块中承载的数据长度是可变的,这样,可以避免承载的帧中出现空闲比特或无效的填充字节,从而节省了有限的带宽资源,提高了链路性能。In the GSM packet field encoding device provided by the embodiment of the present invention, since information indicating the length of valid data is added in the control field, the sending end can perform variable-length encoding according to the effective data length, and the receiving end can perform variable-length decoding according to the effective data length. After adopting the technical solution provided by the embodiment of the present invention, the length of the data carried in the RLC/MAC block is variable, so that idle bits or invalid filling bytes can be avoided in the carried frame, thereby saving limited bandwidth resources , improving link performance.
设备实施例二:Equipment embodiment two:
参见图9,该图为基于本发明设备第二实施例示意图。Referring to Fig. 9, this figure is a schematic diagram of the second embodiment of the device based on the present invention.
本发明设备第二实施例与第一实施例的区别是增加了:校验单元901,该单元可以在变长信道编码单元802根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道编码之前,对重要比特进行循环冗余校验。The difference between the second embodiment of the device of the present invention and the first embodiment is that a check unit 901 is added, which can be variable-length in the variable-length
需要说明的是,校验位可以选择加在每个帧之后,也可以选择加在帧的其他位置。另外,上述重要比特具体可以是Ia类最重要比特。It should be noted that the parity bit can be selected to be added after each frame, or can be selected to be added to other positions of the frame. In addition, the above-mentioned important bits may specifically be the most important bits of type Ia.
进一步的,设备中还可以包括:尾比特增加单元,用于对每个帧增加TB。Further, the device may further include: a tail bit adding unit, configured to add TB to each frame.
另外,在编码的同时,可以在承载的CS帧最前端增加SB。SB用于指示当前RLC/MAC的头类型。In addition, while encoding, the SB can be added at the head of the carried CS frame. SB is used to indicate the header type of the current RLC/MAC.
本发明所述GSM分组域编码设备,有效利用了RLC/MAC块承载CS帧后的剩余空间,在信道编解码时进一步增加冗余,从而提升链路传输性能。而且,本发明实施例所述CS over GERAN利用变长信道编解码,对RLC/MAC块承载CS帧中最重要的比特进行CRC校验,提高了数据传输的精度。The GSM packet domain coding device of the present invention effectively utilizes the remaining space after the CS frame is carried by the RLC/MAC block, further increases redundancy during channel coding and decoding, thereby improving link transmission performance. Moreover, the CS over GERAN described in the embodiment of the present invention uses variable-length channel codec to perform CRC check on the most important bits in the CS frame carried by the RLC/MAC block, which improves the accuracy of data transmission.
本发明实施例提供一种GSM分组域编解码的系统。An embodiment of the present invention provides a GSM packet domain codec system.
系统实施例一:System embodiment one:
参见图10,该图为基于本发明系统第一实施例示意图。Referring to FIG. 10 , this figure is a schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the system based on the present invention.
本发明提供一种GSM分组域编解码的系统,包括发送端1001和接收端1002。The present invention provides a GSM packet domain encoding and decoding system, which includes a sending
需要说明的是,发送端1001可以是上述设备实施例中GSM分组域编码设备,此处不再赘述。It should be noted that the sending
接收端1002,用于接收到上述GSM分组域编码设备发送的数据后,根据所述解码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道解码。The receiving
具体的,接收端可以根据解码前输入数据的长度和有效数据的长度,推算出编码设备在编码时使用的打孔或填充冗余的方法,从而在接收端进行正确的变长信道解码。Specifically, the receiving end can calculate the method of puncturing or filling redundancy used by the encoding device during encoding according to the length of input data before decoding and the length of valid data, so as to perform correct variable-length channel decoding at the receiving end.
本发明实施例提供的GSM分组域编解码的系统,由于控制域中增加了指示有效数据的长度的信息,发送端可以根据有效数据长度进行变长编码,接收端根据有效数据长度进行变长解码。RLC/MAC块中承载的数据长度是可变的,避免承载的帧中出现空闲比特或无效的填充字节,从而节省了有限的带宽资源,提高了链路性能。In the GSM packet domain encoding and decoding system provided by the embodiment of the present invention, since information indicating the length of valid data is added in the control domain, the sending end can perform variable-length encoding according to the effective data length, and the receiving end can perform variable-length decoding according to the effective data length . The length of the data carried in the RLC/MAC block is variable, avoiding idle bits or invalid padding bytes in the carried frame, thereby saving limited bandwidth resources and improving link performance.
系统实施例二:System embodiment two:
参见图11,该图为基于本发明系统第二实施例示意图。Referring to FIG. 11 , this figure is a schematic diagram of the second embodiment of the system based on the present invention.
本实施例中的发送端1001包括判断单元1001a、校验单元1001b、尾比特增加单元1001c和变长信道编码单元1001d。The sending
所述判断单元1001a,用于判断无线链路控制/媒介接入控制RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中是否存在指示承载的有效数据长度的信息,所述有效数据长度为编码前输入数据的长度。The judging
所述校验单元1001b,用于对Ia类最重要比特进行循环冗余校验。校验位可以加在每个帧之后,也可以加在每个帧的其他位置。The
所述尾比特增加单元1001c,用于对每个帧增加尾比特。需要说明的是,编码的同时,在承载的CS帧最前端增加SB。SB用于指示当前RLC/MAC的头类型。The tail
变长信道编码单元1001d,用于当判断单元1001a的判断结果为RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中存在上述有效数据长度的信息时,根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道编码。The variable-length
接收端1002与系统实施例一相同,在此不再赘述。The receiving
本发明所述变长编解码的系统,有效利用了RLC/MAC块承载CS帧后的剩余空间,在信道编解码时进一步增加冗余,从而提升链路传输性能。而且,本发明实施例所述CS over GERAN利用变长信道编解码,对RLC/MAC块承载CS帧中最重要的比特进行CRC校验,提高了数据传输的精度。The variable-length encoding and decoding system of the present invention effectively utilizes the remaining space after the RLC/MAC block bears the CS frame, and further increases redundancy during channel encoding and decoding, thereby improving link transmission performance. Moreover, the CS over GERAN described in the embodiment of the present invention uses variable-length channel codec to perform CRC check on the most important bits in the CS frame carried by the RLC/MAC block, which improves the accuracy of data transmission.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述方法实施方式中的全部或部分步骤是可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件来完成,所述的程序可以存储于计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,可以包括前述的通信方法各个实施方式的内容。这里所称得的存储介质,如:ROM/RAM、磁碟、光盘等。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps in the implementation of the above method can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program, and the program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. When the program is executed , may include the contents of the foregoing communication method implementations. The storage medium referred to here, such as: ROM/RAM, magnetic disk, optical disk, etc.
综上所述,本发明实施例所提供的一种GSM分组域编解码的方法,在RLC/MAC块头的控制域中增加指示RLC/MAC块承载的有效数据的长度的信息。编码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度均与所述有效数据的长度相同。发送端根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道编码。接收端根据所述解码前输入数据的长度和解码后输出数据的长度进行变长信道解码。本发明提供的方法由于增加控制域指示有效数据的长度,发送端可以根据有效数据长度进行变长编码,接收端根据有效数据长度进行变长解码。RLC/MAC块中承载的数据长度是可变的,避免承载的帧中出现空闲比特或无效的填充字节,从而节省了有限的带宽资源,提高了链路传输的性能。To sum up, the embodiment of the present invention provides a GSM packet domain encoding and decoding method, which adds information indicating the length of valid data carried by the RLC/MAC block to the control field of the RLC/MAC block header. Both the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after decoding are the same as the length of the effective data. The sending end performs variable-length channel coding according to the length of the input data before encoding and the length of the output data after encoding. The receiving end performs variable-length channel decoding according to the length of the input data before decoding and the length of the output data after decoding. In the method provided by the invention, since the control field is added to indicate the length of effective data, the sending end can perform variable-length encoding according to the effective data length, and the receiving end can perform variable-length decoding according to the effective data length. The length of the data carried in the RLC/MAC block is variable, avoiding idle bits or invalid padding bytes in the carried frame, thereby saving limited bandwidth resources and improving the performance of link transmission.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述实施例方法中的全部或部分步骤是可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件来完成,所述的程序可以存储于一计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,包括如下步骤:判断无线链路控制/媒介接入控制RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中是否存在指示承载的有效数据长度的信息,所述有效数据长度为编码前输入数据的长度;当所述RLC/MAC块头中的控制域中存在所述有效数据长度的信息时,根据编码前输入数据的长度和编码后输出数据的长度,进行变长信道编码。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps in the method of the above-mentioned embodiments can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program, and the program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium, and the program can be executed during execution , including the following steps: judging whether there is information indicating the effective data length of the bearer in the control field in the radio link control/medium access control RLC/MAC block header, and the effective data length is the length of the input data before encoding; when When there is information about the effective data length in the control field of the RLC/MAC block header, variable-length channel coding is performed according to the length of input data before encoding and the length of output data after encoding.
Claims (8)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200810182901CN101753253B (en) | 2008-12-05 | 2008-12-05 | Method, equipment and system for encoding and decoding of GSM (global system for mobile communications) packet-switched domain |
| PCT/CN2009/075231WO2010063231A1 (en) | 2008-12-05 | 2009-12-01 | Global system for mobile communications (gsm) packet switched domain coding method, device and system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200810182901CN101753253B (en) | 2008-12-05 | 2008-12-05 | Method, equipment and system for encoding and decoding of GSM (global system for mobile communications) packet-switched domain |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101753253A CN101753253A (en) | 2010-06-23 |
| CN101753253Btrue CN101753253B (en) | 2013-01-23 |
Family
ID=42232898
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200810182901Expired - Fee RelatedCN101753253B (en) | 2008-12-05 | 2008-12-05 | Method, equipment and system for encoding and decoding of GSM (global system for mobile communications) packet-switched domain |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101753253B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2010063231A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102823193A (en)* | 2012-04-28 | 2012-12-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Signal processing method and device for digital subscriber line and digital subscriber line system |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101116277A (en)* | 2005-02-07 | 2008-01-30 | 三星电子株式会社 | Method and device for requesting/delivering a status report of a mobile communication system |
| CN101282164A (en)* | 2007-04-02 | 2008-10-08 | 华为技术有限公司 | A method and device for reducing wireless communication service delay |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1811727A3 (en)* | 2005-02-07 | 2008-03-26 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for transmitting a status report for retransmission control in a mobile communication system |
- 2008
- 2008-12-05CNCN 200810182901patent/CN101753253B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2009
- 2009-12-01WOPCT/CN2009/075231patent/WO2010063231A1/enactiveApplication Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101116277A (en)* | 2005-02-07 | 2008-01-30 | 三星电子株式会社 | Method and device for requesting/delivering a status report of a mobile communication system |
| CN101282164A (en)* | 2007-04-02 | 2008-10-08 | 华为技术有限公司 | A method and device for reducing wireless communication service delay |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2010063231A1 (en) | 2010-06-10 |
| CN101753253A (en) | 2010-06-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20220416945A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for code block division | |
| CN1223134C (en) | Methods and systems for decoding headers on radio channel | |
| KR101526990B1 (en) | Transmission block size determination method and signal transmission method using the same | |
| US8046668B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for code block segmentation in a mobile communication system | |
| US7486644B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving data with high reliability in a mobile communication system supporting packet data transmission | |
| CN108631789B (en) | Encoding and decoding method and device | |
| US8582603B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for configuring protocol header in wireless communication system | |
| WO2009096658A1 (en) | Method for determining transport block size and signal transmission method using the same | |
| CN106817192B (en) | Error estimation method, base station and terminal | |
| CN108289010A (en) | A data processing method and device | |
| EP3065329B1 (en) | Aggregated data frame structures | |
| JP4247774B2 (en) | Blind transport format detection method | |
| WO2006083132A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for providing broadcast parameter message in a mobile communication system | |
| CN103414543A (en) | Method and terminal for adjusting HARQ buffer memory amounts | |
| JP4989723B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for blind transport format detection using discontinuous transmission (DTX) detection | |
| CN110011753A (en) | A kind of method for processing business, transceiver and computer readable storage medium | |
| EP3526916B1 (en) | Data encoding and decoding | |
| CN101753253B (en) | Method, equipment and system for encoding and decoding of GSM (global system for mobile communications) packet-switched domain | |
| CN101252421A (en) | A encoding and decoding method and device for short response/negative response | |
| JP4037724B2 (en) | Method of blind transport format detection based on power transition | |
| CN110233697B (en) | Information data block processing method and sending end | |
| RU2304840C1 (en) | Method and device for high-reliability data transmission and reception in mobile communication system supporting burst data transfer | |
| CN103457693B (en) | communication method | |
| CN101123605B (en) | Method and device for message integrity protection | |
| KR101201600B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for the resolution to the delay caused by code for the protocol header in wireless communication system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20130123 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |