CN101523329A - Multi-mode haptic feedback system - Google Patents
Multi-mode haptic feedback systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101523329A CN101523329ACNA200780037012XACN200780037012ACN101523329ACN 101523329 ACN101523329 ACN 101523329ACN A200780037012X ACNA200780037012X ACN A200780037012XACN 200780037012 ACN200780037012 ACN 200780037012ACN 101523329 ACN101523329 ACN 101523329A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- vibration
- equipment
- frequency
- housing
- input interface
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- User Interface Of Digital Computer (AREA)
- Apparatuses For Generation Of Mechanical Vibrations (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
一种实施方式涉及触觉反馈系统。更具体地,一种实施方式涉及多模触觉反馈系统(multiple mode haptic feedback system)。One implementation involves a haptic feedback system. More specifically, one embodiment relates to a multiple mode haptic feedback system.
背景技术Background technique
电子设备制造商们努力为客户制造丰富的接口。传统的设备使用视觉和听觉提示为用户提供反馈。在一些接口设备(interface device)里,运动反馈(例如主动力和阻力反馈)和/或触觉反馈(例如振动、质地和热)也提供给用户,更一般地共同认知为“触觉反馈”。触觉反馈能提供提示以增强并简化用户接口。具体地,振动效果、或振动触觉的触觉效果在提供提示给电子设备的用户以警报用户特定事件的情况下是有用的,或提供真实的反馈以造成在模拟或虚拟环境里的更大的感官沉浸(sensory immersion)。Manufacturers of electronic devices strive to create rich interfaces for their customers. Traditional devices use visual and auditory cues to provide feedback to users. In some interface devices, motion feedback (such as active force and resistance feedback) and/or tactile feedback (such as vibration, texture, and heat) are also provided to the user, more generally commonly known as "haptic feedback." Haptic feedback can provide cues to enhance and simplify user interfaces. In particular, vibration effects, or vibrohaptic haptic effects, are useful in situations where cues are provided to a user of an electronic device to alert the user of a specific event, or to provide realistic feedback to create a greater sensory experience in a simulated or virtual environment. Immersion (sensory immersion).
触觉反馈也被日益合并到便携式电子设备,例如移动电话、个人数字助理(PDA)、便携式游戏设备以及许多其它的便携式电子设备。例如一些便携式游戏应用能够以与配置为提供触觉反馈的大型游戏系统共同使用的控制设备(比如,操纵杆等)相似的方式振动。此外,例如移动电话和PDA的设备能够通过振动的方式给用户提供各种警报。例如,移动电话能通过振动来警报用户来电了。类似地,PDA能警报用户所计划的日历项目,或向用户提供对“要做(to do)”的列表项目或日历约会的提醒。Haptic feedback is also increasingly being incorporated into portable electronic devices such as mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), portable gaming devices, and many others. For example, some portable gaming applications can vibrate in a manner similar to control devices (eg, joysticks, etc.) used with larger gaming systems configured to provide haptic feedback. In addition, devices such as mobile phones and PDAs can provide various alerts to the user through vibration. For example, a mobile phone can vibrate to alert the user of an incoming call. Similarly, a PDA can alert the user of planned calendar items, or provide the user with reminders of "to do" list items or calendar appointments.
对于便携式设备,成本是重要的驱动因素。因此,为了产生触觉效果,通常使用单个低成本的致动器,例如偏心转动惯量(“ERM”)电机或电磁电机。典型地,标准便携式电子设备,例如PDA和移动电话输出的振动是施加到便携式设备的壳体的简单振动,如通常或开或关以发出警报的二元振动器(binary vibrator)那样运行。也就是说,这些设备的振动能力通常被限制为全动力振动(full power vibration)(“完全开启”状态)或休息状态(“完全关闭”)。因此,一般来说,这种设备所能提供的振动的量级的变化很小。For portable devices, cost is an important driver. Therefore, to produce a haptic effect, a single low-cost actuator is typically used, such as an eccentric moment of inertia ("ERM") motor or an electromagnetic motor. Typically, the vibration output by standard portable electronic devices, such as PDAs and mobile phones, is a simple vibration applied to the housing of the portable device, operating as a binary vibrator that is normally on or off to sound an alarm. That said, the vibration capabilities of these devices are typically limited to full power vibration ("full on" state) or resting state ("full off"). Therefore, in general, the variation in the magnitude of the vibrations that such devices can provide is small.
逐渐地,便携式设备正在放弃使用物理按钮而采用只有触摸屏的接口。这种转变允许增强灵活性、减少零件数量并减少对容易发生故障的机械按钮的依赖,以及符合产品设计中出现的趋势。当使用触摸屏输入设备时,可用触觉来模拟有关按钮压下或其它用户接口动作的机械确认(mechanical confirmation)。为了有效并使用户高兴,用来模拟按钮的触觉应典型地主要被应用于触摸屏而不是壳体。然而,与便携式设备典型地一同提供的单个致动器通常不能产生触觉效果来产生壳体上的警报,并还产生其它触觉效果,以比如在触摸屏上模拟触摸屏按钮。因此需要一个或更多个附加致动器来产生所需要的多个触觉效果。不幸地是,这样增加了便携式设备的成本。Increasingly, portable devices are ditching the use of physical buttons in favor of touchscreen-only interfaces. This shift allows for increased flexibility, reduced part count and less reliance on failure-prone mechanical buttons, as well as conforming to emerging trends in product design. When using a touchscreen input device, haptics can be used to simulate mechanical confirmation of button presses or other user interface actions. To be effective and pleasing to the user, the haptics used to simulate buttons should typically be applied primarily to the touch screen rather than the housing. However, the single actuator typically provided with a portable device is often unable to generate haptic effects to generate an alert on the housing, and also to generate other haptic effects, such as simulating touch screen buttons on the touch screen. One or more additional actuators are therefore required to produce the desired number of haptic effects. Unfortunately, this increases the cost of the portable device.
基于前述的,需要一种使用单个致动器来产生多个触觉效果的系统和方法。Based on the foregoing, there is a need for a system and method for producing multiple haptic effects using a single actuator.
发明内容Contents of the invention
一种实施方式是触觉效果设备,其包括壳体和通过悬架(suspension)耦联到壳体的触摸屏。致动器耦联到触摸屏。悬架被调整(tune)为以便当致动器以第一频率产生第一振动时,第一振动实质上与壳体隔离并被应用在触摸屏上以模拟机械按钮。进一步,当致动器以第二频率产生第二振动时,第二振动实质上被传递到壳体以产生振动警报。One embodiment is a haptic effect device that includes a housing and a touch screen coupled to the housing by a suspension. The actuator is coupled to the touch screen. The suspension is tuned so that when the actuator produces a first vibration at a first frequency, the first vibration is substantially isolated from the housing and applied on the touch screen to simulate a mechanical button. Further, when the actuator generates a second vibration at a second frequency, the second vibration is substantially transmitted to the housing to generate a vibration alarm.
附图说明Description of drawings
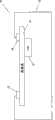
图1是依照一种实施方式的移动电话的剖视图。FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a mobile phone according to one embodiment.
图2是加速度量值与驱动信号频率的曲线图,示出在依照一种实施方式调整悬架后电话的频率响应。2 is a graph of acceleration magnitude versus drive signal frequency showing the frequency response of the phone after the suspension is adjusted in accordance with one embodiment.
图3是一种实施方式的对于点击振动频率的加速度量值与时间的曲线图。3 is a graph of acceleration magnitude versus time for click vibration frequency, according to one embodiment.
图4是与图3相同的实施方式的对于警报振动频率的加速度量值与时间的曲线图。FIG. 4 is a graph of acceleration magnitude versus time for alarm vibration frequency for the same embodiment as FIG. 3 .
具体实施方式Detailed ways
一种实施方式是包括用悬架耦联到设备壳体的触摸屏的设备。单个致动器产生触觉效果振动,该触觉效果振动实质上在一种模式中只被施加到触摸屏,而在另一种模式中被施加到壳体。One embodiment is a device that includes a touch screen coupled to a device housing with a suspension. A single actuator produces a haptic effect vibration that is essentially applied only to the touch screen in one mode and to the housing in the other mode.
在手持便携式触摸屏设备上典型地提供的一种类型的触觉效果是被施加到设备壳体的“警报”振动。警报振动当在100Hz-200Hz频率范围振动时是有效的。警报是一种振动的方法,用来通知用户现在、将来或过去的事件。这样的警报可以是发信号以告知来电的铃声,这里铃声已经被变换到相当于工作在手持设备上的振动。警报可以用来通知用户因为振铃(ringing)、忙和呼叫等待而未接的电话。警报的其它例子包括操作提示,来指导用户通过一个操作,例如对于每个菜单有不同感觉的发送(Send)/好(OK)和用于向下滚动屏幕的信息导航,并感觉已读信息和未读信息之间的不同。进一步,对于有GPS跟踪的移动电话,确定相距指定地理位置的距离的接近感测应用(proximity sensing application)能产生警报。One type of haptic effect typically provided on handheld portable touchscreen devices is an "alert" vibration applied to the device housing. Alarm vibration is effective when vibrating in the frequency range of 100Hz-200Hz. Alerts are a vibration method used to notify users of present, future, or past events. Such an alert could be a ringtone signaling an incoming call, where the ringtone has been transformed to the equivalent of vibration working on a handheld device. Alerts can be used to notify users of missed calls due to ringing, busy and call waiting. Other examples of alerts include action prompts to guide the user through an action, such as Send/OK for each menu with a different feel and message navigation for scrolling down the screen and feeling read and The difference between unread messages. Further, for mobile phones with GPS tracking, a proximity sensing application that determines the distance to a specified geographic location can generate an alert.
在手持便携式触摸屏设备上典型地提供的另一类型的触觉效果是被施加到触摸屏上以模拟按钮的压下的“点击”振动效果。传统的机械按钮的度量显示:令人高兴和满意的按钮感觉是以大约>200Hz范围的短而干脆的振动为特征的。为了最有效,触觉振动效果应主要被应用于触摸屏而不是壳体上。Another type of haptic effect typically provided on handheld portable touchscreen devices is a "click" vibration effect applied to the touchscreen to simulate the depression of a button. Measurements of conventional mechanical buttons show that a pleasing and satisfying button feel is characterized by short, crisp vibrations in the range >200 Hz. To be most effective, the haptic vibration effect should be applied primarily to the touch screen rather than the housing.
图1是依照一种实施方式的移动电话10的剖视图。电话10包括触摸屏14,触摸屏14显示能被用户通过触摸或对触摸屏14的其它接触来选择的电话键和其他功能键。电话10进一步包括包围电话10的内部部件并支撑触摸屏14的壳体或主体12。当用户使用电话10时,用户典型地通过壳体12来在一只手里拿着电话10,而用另一只手接触触摸屏14。其它实施方式不是移动电话且没有触摸屏,而是有其它类型的输入接口的触觉设备。除了触摸屏的其它输入接口可能是迷你操纵杆、滚轮、方向键、键盘、触摸敏感的表面等。与移动电话一样,对于这些设备,期望有连接到输入接口的点击感觉和在整个设备上产生的警报振动。1 is a cross-sectional view of a
触摸屏14被围绕触摸屏14的悬架18柔性地悬挂/漂浮或安装到壳体12。在一种实施方式中,悬架18由例如的泡沫材料制成的粘弹框密封垫(viscoelastic bezel sea1gasket)构成。在其它实施方式中,任何其它类型的材料能被用于悬架18,只要它能按如下所公开的方式进行“调整”。The
线性谐振致动器(“LRA”)或其它类型的致动器16(比如,形状记忆合金、电活化聚合物、压电的等)被刚性地耦联到触摸屏14。LRA包括附接到弹簧的磁性质量块(magnetic mass)。磁性质量块由电线圈供能并抵着弹簧在与触摸屏14垂直的方向上被前后驱动以产生振动。在一种实施方式中,致动器16具有大约150Hz-190Hz的谐振频率。谐振频率是加速度响应在其峰值时的频率范围。为了产生信号和动力给致动器16以造成期望的触觉效果,控制器/处理器、存储器设备和其它必要的部件(未显示)被耦联到致动器16。致动器16能以通过改变到致动器16的驱动信号的频率、振幅和定时的已知方式产生不同的触觉效果。振动可与触摸屏14垂直或在另外的方向(比如,在平面内)。在一种实施方式中,沿着屏幕表面的振动(X或Y振动)是有利的,因为它们产生等效的触觉信息,并由于屏幕在这些方向的固有硬度而也在整个触摸屏上更加均匀地分布。A linear resonant actuator (“LRA”) or other type of actuator 16 (eg, shape memory alloy, electroactive polymer, piezoelectric, etc.) is rigidly coupled to
在一种实施方式中,悬架18被调整为使设备10的壳体12与被施加到触摸屏14上的以点击频率(>200Hz)的振动隔离以模拟按钮压下,但是在约等于致动器16的谐振频率的警报频率(~150Hz)下把振动有效地传递到壳体12,以产生警报触觉效果。调整悬架18能通过例如,改变对材料的选择以得到期望的属性、改变总的截面面积、改变厚度等来实现。In one embodiment, the
图2是加速度量值与驱动信号频率的曲线图,示出在依照一种实施方式调整悬架18后电话10的频率响应。曲线20是在壳体12上测量的频率响应,并指示在警报频率(~150Hz)的谐振频率(f1)。曲线30是在触摸屏14上测量的频率响应,并指示在点击频率(>200Hz或~500Hz)的谐振频率(f2)。2 is a graph of acceleration magnitude versus drive signal frequency showing the frequency response of
在操作中,在按键压下确认(key-press confirmation)的情形下,触觉效果振动能可选地被产生为只传递到触摸屏14的点击振动,同时实质上通过悬架18而与壳体12隔离,这可通过在点击频率来产生该效果。类似地,触觉效果振动能可选地被产生为警报振动,振动传递到壳体12而实质上没有衰减,这可通过在警报频率来产生该效果。In operation, in the case of a key-press confirmation (key-press confirmation), the haptic effect vibration can optionally be generated as a click vibration that is only transmitted to the
图3是一种实施方式的对于点击频率(>200Hz)的加速度量值与时间的曲线图。在图3的实施方式中,使用每边一条的两条悬挂触摸屏14,而LRA带有~155Hz的谐振频率。迹线32使用曲线图左侧上的刻度指示触摸屏14上的加速度计读数。迹线34使用曲线图右侧上的刻度指示电话10的背面的壳体12上的加速度计读数。Figure 3 is a graph of acceleration magnitude versus time for click frequency (>200 Hz) of one embodiment. In the embodiment of Figure 3, two The
如显示的,与被支撑手(supporting hand)通过壳体的感受相比,振动主要被按压手指通过触摸屏感受(5:1的加速度比(accelerationratio))。此外,点击振动在驱动信号启动后~3ms迅速达到峰值,并在减速开始后~5ms衰退。这对于产生干脆的机械按钮感觉是理想的。As shown, the vibrations are felt primarily by pressing the finger through the touch screen (acceleration ratio of 5:1) compared to that felt by the supporting hand through the housing. In addition, the click vibration quickly peaked ~3 ms after the start of the drive signal and decayed ~5 ms after the onset of deceleration. This is ideal for producing a crisp mechanical button feel.
图4是图3的相同实施方式的对于警报振动频率(~150Hz)的加速度量值与时间的曲线图。迹线42使用曲线图左侧上的刻度指示触摸屏14上的加速度计读数。迹线44使用曲线图右侧上的刻度指示电话10的背面的壳体12上的加速度计读数。虽然触摸屏通过悬架18隔离,警报振动传递到壳体12并被支撑手感受而几乎没有衰减。这对于产生有效警报是理想的。Figure 4 is a graph of acceleration magnitude versus time for the alarm vibration frequency (-150 Hz) for the same embodiment of Figure 3 .
在这里具体示出和/或描述了几种实施方式。然而,将理解,本发明的更改和变化被以上教授的内容所覆盖,并在随附的权利要求的范围内,而不背离本发明的精神和意旨的范围。Several implementations are specifically shown and/or described herein. It will be understood, however, that modifications and variations of the present invention are covered by the above teaching and within the scope of the appended claims, without departing from the spirit and intended scope of the present invention.
例如,以上公开的一些实施方式实现为带有触摸屏的移动电话,其是能被用户抓住、夹住或以其它方式物理接触以及操作的物体。同样地,能在类似地由用户操作并需要两种触觉效果的模式的其它触觉启用的输入(haptics enabled input)和/或输出设备上使用本发明。这样的其它设备能包括其它触摸屏设备(比如,车辆上的全球定位系统(“GPS”)导航屏、自动柜员机(“ATM”)显示屏)、控制电子仪器的远程(比如,音频/视频、车库门、家庭安全等)和游戏控制器(比如,操纵杆、鼠标、游戏键盘专用控制器(gamepad specializedcontroller)等)。这种输入和/或输出设备的操作对于本领域技术人员是众所周知的。For example, some of the embodiments disclosed above are implemented as a mobile phone with a touch screen, which is an object that can be grasped, clamped, or otherwise physically contacted and manipulated by the user. Likewise, the invention can be used on other haptics enabled input and/or output devices that are similarly operated by the user and require two modes of haptic effects. Such other devices can include other touch screen devices (e.g., Global Positioning System (“GPS”) navigation screens on vehicles, automated teller machine (“ATM”) displays), remotes for controlling electronic instruments (e.g., audio/video, garage doors, home security, etc.) and game controllers (eg, joysticks, mice, gamepad specialized controllers, etc.). The operation of such input and/or output devices is well known to those skilled in the art.
Claims (31)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201410169213.7ACN103927017B (en) | 2006-10-05 | 2007-09-28 | Multiple mode haptic feedback system |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US82836806P | 2006-10-05 | 2006-10-05 | |
| US60/828,368 | 2006-10-05 | ||
| US11/735,096 | 2007-04-13 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201410169213.7ADivisionCN103927017B (en) | 2006-10-05 | 2007-09-28 | Multiple mode haptic feedback system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101523329Atrue CN101523329A (en) | 2009-09-02 |
Family
ID=41082463
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA200780037012XAPendingCN101523329A (en) | 2006-10-05 | 2007-09-28 | Multi-mode haptic feedback system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101523329A (en) |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102043465A (en)* | 2009-10-12 | 2011-05-04 | 三星电机株式会社 | Haptic feedback device and electronic device |
| CN102467280A (en)* | 2010-11-15 | 2012-05-23 | 台达电子工业股份有限公司 | Touch control device |
| CN103246390A (en)* | 2012-02-08 | 2013-08-14 | 阿尔卑斯电气株式会社 | Input device |
| CN103797441A (en)* | 2011-07-12 | 2014-05-14 | 森赛格有限公司 | Haptic device with touch gesture interface |
| CN104641326A (en)* | 2012-07-26 | 2015-05-20 | 苹果公司 | Elastic shear material that provides tactile response control |
| CN104731333A (en)* | 2015-03-25 | 2015-06-24 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Wearable electronic equipment |
| CN105353877A (en)* | 2009-03-12 | 2016-02-24 | 意美森公司 | Systems and methods for friction displays and additional haptic effects |
| US9772688B2 (en) | 2014-09-30 | 2017-09-26 | Apple Inc. | Haptic feedback assembly |
| US9798409B1 (en) | 2015-03-04 | 2017-10-24 | Apple Inc. | Multi-force input device |
| US9886116B2 (en) | 2012-07-26 | 2018-02-06 | Apple Inc. | Gesture and touch input detection through force sensing |
| US9910494B2 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2018-03-06 | Apple Inc. | Thresholds for determining feedback in computing devices |
| US10108265B2 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2018-10-23 | Apple Inc. | Calibration of haptic feedback systems for input devices |
| US10297119B1 (en) | 2014-09-02 | 2019-05-21 | Apple Inc. | Feedback device in an electronic device |
| US10564721B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2020-02-18 | Immersion Corporation | Systems and methods for using multiple actuators to realize textures |
| US10591368B2 (en) | 2014-01-13 | 2020-03-17 | Apple Inc. | Force sensor with strain relief |
| US10642361B2 (en) | 2012-06-12 | 2020-05-05 | Apple Inc. | Haptic electromagnetic actuator |
| CN111801240A (en)* | 2018-02-02 | 2020-10-20 | 贝洱海拉温控系统有限公司 | operating unit for automobiles |
| CN115250632A (en)* | 2021-02-26 | 2022-10-28 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Haptic feedback substrate, haptic feedback device and haptic feedback method |
- 2007
- 2007-09-28CNCNA200780037012XApatent/CN101523329A/enactivePending
Cited By (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10564721B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2020-02-18 | Immersion Corporation | Systems and methods for using multiple actuators to realize textures |
| US10466792B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2019-11-05 | Immersion Corporation | Systems and methods for friction displays and additional haptic effects |
| CN105353877A (en)* | 2009-03-12 | 2016-02-24 | 意美森公司 | Systems and methods for friction displays and additional haptic effects |
| CN105353877B (en)* | 2009-03-12 | 2019-02-05 | 意美森公司 | System and method for rub display and additional tactile effect |
| US10073526B2 (en) | 2009-03-12 | 2018-09-11 | Immersion Corporation | Systems and methods for friction displays and additional haptic effects |
| CN102043465A (en)* | 2009-10-12 | 2011-05-04 | 三星电机株式会社 | Haptic feedback device and electronic device |
| CN102467280A (en)* | 2010-11-15 | 2012-05-23 | 台达电子工业股份有限公司 | Touch control device |
| CN103797441A (en)* | 2011-07-12 | 2014-05-14 | 森赛格有限公司 | Haptic device with touch gesture interface |
| CN103797441B (en)* | 2011-07-12 | 2017-11-03 | 森赛格有限公司 | Haptic device with touch gestures interface |
| CN103246390A (en)* | 2012-02-08 | 2013-08-14 | 阿尔卑斯电气株式会社 | Input device |
| US9977499B2 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2018-05-22 | Apple Inc. | Thresholds for determining feedback in computing devices |
| US9910494B2 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2018-03-06 | Apple Inc. | Thresholds for determining feedback in computing devices |
| US9977500B2 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2018-05-22 | Apple Inc. | Thresholds for determining feedback in computing devices |
| US10108265B2 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2018-10-23 | Apple Inc. | Calibration of haptic feedback systems for input devices |
| US10642361B2 (en) | 2012-06-12 | 2020-05-05 | Apple Inc. | Haptic electromagnetic actuator |
| US9886116B2 (en) | 2012-07-26 | 2018-02-06 | Apple Inc. | Gesture and touch input detection through force sensing |
| CN104641326A (en)* | 2012-07-26 | 2015-05-20 | 苹果公司 | Elastic shear material that provides tactile response control |
| US10591368B2 (en) | 2014-01-13 | 2020-03-17 | Apple Inc. | Force sensor with strain relief |
| US10297119B1 (en) | 2014-09-02 | 2019-05-21 | Apple Inc. | Feedback device in an electronic device |
| US9772688B2 (en) | 2014-09-30 | 2017-09-26 | Apple Inc. | Haptic feedback assembly |
| US9939901B2 (en) | 2014-09-30 | 2018-04-10 | Apple Inc. | Haptic feedback assembly |
| US10162447B2 (en) | 2015-03-04 | 2018-12-25 | Apple Inc. | Detecting multiple simultaneous force inputs to an input device |
| US9798409B1 (en) | 2015-03-04 | 2017-10-24 | Apple Inc. | Multi-force input device |
| CN104731333A (en)* | 2015-03-25 | 2015-06-24 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Wearable electronic equipment |
| CN111801240A (en)* | 2018-02-02 | 2020-10-20 | 贝洱海拉温控系统有限公司 | operating unit for automobiles |
| CN111801240B (en)* | 2018-02-02 | 2023-09-19 | 贝洱海拉温控系统有限公司 | operating unit for automobiles |
| CN115250632A (en)* | 2021-02-26 | 2022-10-28 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Haptic feedback substrate, haptic feedback device and haptic feedback method |
| US12142134B2 (en) | 2021-02-26 | 2024-11-12 | Beijing Boe Technology Development Co., Ltd. | Haptic feedback substrate, haptic feedback apparatus and haptic feedback method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101523329A (en) | Multi-mode haptic feedback system | |
| US20170108931A1 (en) | Multiple mode haptic feedback system | |
| EP1748350B1 (en) | Touch device and method for providing tactile feedback | |
| US9733704B2 (en) | User interface impact actuator | |
| US7148789B2 (en) | Handheld device having multiple localized force feedback | |
| CN102111496B (en) | Method and apparatus for generating vibration in portable terminal | |
| US10275030B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing haptic feedback to non-input locations | |
| CN102713793B (en) | For increasing the system and method for the haptic bandwidth in electronic equipment | |
| KR101342812B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing tactile sensations | |
| KR101436655B1 (en) | Haptic effects with proximity detection | |
| CN104881175B (en) | Multi-touch device with dynamic haptic effects | |
| US8073501B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing haptic feedback to non-input locations | |
| KR20070032804A (en) | Handheld Device with Local Force Feedback | |
| JPWO2012114760A1 (en) | Electronic device with touch sensor | |
| WO2009045996A2 (en) | Keypad haptic communication | |
| WO2010056466A2 (en) | Haptic effect generation with an eccentric rotating mass actuator | |
| EP2538303A1 (en) | Optical navigation device with haptic feedback |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20090902 |