CN101496813A - Anti-tissue proliferation (vascular restenosis) compositions and methods of use - Google Patents
Anti-tissue proliferation (vascular restenosis) compositions and methods of useDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101496813A CN101496813ACN 200810014140CN200810014140ACN101496813ACN 101496813 ACN101496813 ACN 101496813ACN 200810014140CN200810014140CN 200810014140CN 200810014140 ACN200810014140 ACN 200810014140ACN 101496813 ACN101496813 ACN 101496813A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- stent
- paclitaxel
- drug
- rapamycin
- compositions
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription77
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription35
- 208000037803restenosisDiseases0.000titleabstractdescription57
- 230000002792vascularEffects0.000titleabstractdescription21
- 230000035755proliferationEffects0.000titledescription8
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription102
- 229930012538PaclitaxelNatural products0.000claimsabstractdescription76
- 229960001592paclitaxelDrugs0.000claimsabstractdescription76
- RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-NtaxolChemical compoundO([C@@H]1[C@@]2(C[C@@H](C(C)=C(C2(C)C)[C@H](C([C@]2(C)[C@@H](O)C[C@H]3OC[C@]3([C@H]21)OC(C)=O)=O)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)O)C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription76
- QFJCIRLUMZQUOT-HPLJOQBZSA-NsirolimusChemical compoundC1C[C@@H](O)[C@H](OC)C[C@@H]1C[C@@H](C)[C@H]1OC(=O)[C@@H]2CCCCN2C(=O)C(=O)[C@](O)(O2)[C@H](C)CC[C@H]2C[C@H](OC)/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C/[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](OC)[C@H](O)/C(C)=C/[C@@H](C)C(=O)C1QFJCIRLUMZQUOT-HPLJOQBZSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription69
- ZAHRKKWIAAJSAO-UHFFFAOYSA-NrapamycinNatural productsCOCC(O)C(=C/C(C)C(=O)CC(OC(=O)C1CCCCN1C(=O)C(=O)C2(O)OC(CC(OC)C(=CC=CC=CC(C)CC(C)C(=O)C)C)CCC2C)C(C)CC3CCC(O)C(C3)OC)CZAHRKKWIAAJSAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription68
- 229960002930sirolimusDrugs0.000claimsabstractdescription68
- HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-NHeparinChemical compoundOC1C(NC(=O)C)C(O)OC(COS(O)(=O)=O)C1OC1C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(O)C(OC2C(C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(OC3C(C(O)C(O)C(O3)C(O)=O)OS(O)(=O)=O)C(CO)O2)NS(O)(=O)=O)C(C(O)=O)O1HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 229960002897heparinDrugs0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 229920000669heparinPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000claimsdescription24
- 238000012377drug deliveryMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000003146anticoagulant agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription7
- 229960003444immunosuppressant agentDrugs0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000003018immunosuppressive agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000001861immunosuppressant effectEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 229940119336Microtubule stabilizerDrugs0.000claimsdescription4
- 229940127219anticoagulant drugDrugs0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000004615ingredientSubstances0.000claims1
- 230000035407negative regulation of cell proliferationEffects0.000claims1
- 239000007921spraySubstances0.000claims1
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000abstractdescription95
- 238000002513implantationMethods0.000abstractdescription24
- 206010020718hyperplasiaDiseases0.000abstractdescription11
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription9
- 238000007910systemic administrationMethods0.000abstractdescription6
- 230000005764inhibitory processEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000003511endothelial effectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000005507sprayingMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000description34
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description27
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description27
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description22
- 208000007536ThrombosisDiseases0.000description16
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description16
- 210000004204blood vesselAnatomy0.000description15
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description14
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000description12
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description11
- 241000700159RattusSpecies0.000description10
- 210000001715carotid arteryAnatomy0.000description9
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description8
- 230000004663cell proliferationEffects0.000description8
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description8
- 241000283973Oryctolagus cuniculusSpecies0.000description7
- 238000002399angioplastyMethods0.000description7
- 229920001577copolymerPolymers0.000description7
- 230000001575pathological effectEffects0.000description7
- 208000031481Pathologic ConstrictionDiseases0.000description6
- 238000007887coronary angioplastyMethods0.000description6
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description6
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description6
- 230000036262stenosisEffects0.000description6
- 208000037804stenosisDiseases0.000description6
- 102000029749MicrotubuleHuman genes0.000description5
- 108091022875MicrotubuleProteins0.000description5
- 230000010261cell growthEffects0.000description5
- 208000029078coronary artery diseaseDiseases0.000description5
- 210000004351coronary vesselAnatomy0.000description5
- 210000001105femoral arteryAnatomy0.000description5
- 210000004969inflammatory cellAnatomy0.000description5
- 210000004688microtubuleAnatomy0.000description5
- 239000008194pharmaceutical compositionSubstances0.000description5
- 229920000747poly(lactic acid)Polymers0.000description5
- 210000000329smooth muscle myocyteAnatomy0.000description5
- SOGAXMICEFXMKE-UHFFFAOYSA-NButylmethacrylateChemical compoundCCCCOC(=O)C(C)=CSOGAXMICEFXMKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 230000022131cell cycleEffects0.000description4
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description4
- 230000003902lesionEffects0.000description4
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description4
- 239000004626polylactic acidSubstances0.000description4
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description4
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description4
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description4
- 241001116500TaxusSpecies0.000description3
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description3
- 230000003111delayed effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000001419dependent effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000012010growthEffects0.000description3
- 238000001802infusionMethods0.000description3
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description3
- 230000010534mechanism of actionEffects0.000description3
- 229920001490poly(butyl methacrylate) polymerPolymers0.000description3
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description3
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description3
- 206010003210ArteriosclerosisDiseases0.000description2
- BSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-NAspirinChemical compoundCC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1C(O)=OBSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-NChloroformChemical compoundClC(Cl)ClHEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-NFormaldehydeChemical compoundO=CWSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000010190G1 phaseEffects0.000description2
- 229910000861Mg alloyInorganic materials0.000description2
- 206010028980NeoplasmDiseases0.000description2
- 230000018199S phaseEffects0.000description2
- 102000004243TubulinHuman genes0.000description2
- 108090000704TubulinProteins0.000description2
- 229960001138acetylsalicylic acidDrugs0.000description2
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description2
- 206010000891acute myocardial infarctionDiseases0.000description2
- 230000002776aggregationEffects0.000description2
- 238000004220aggregationMethods0.000description2
- 230000002769anti-restenotic effectEffects0.000description2
- 239000002246antineoplastic agentSubstances0.000description2
- 229940041181antineoplastic drugDrugs0.000description2
- 229940127217antithrombotic drugDrugs0.000description2
- 230000006907apoptotic processEffects0.000description2
- 208000011775arteriosclerosis diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 210000001367arteryAnatomy0.000description2
- 210000000013bile ductAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000012620biological materialSubstances0.000description2
- 230000007321biological mechanismEffects0.000description2
- 230000000740bleeding effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000017531blood circulationEffects0.000description2
- 229920006237degradable polymerPolymers0.000description2
- 206010012601diabetes mellitusDiseases0.000description2
- 239000003937drug carrierSubstances0.000description2
- 238000001035dryingMethods0.000description2
- 210000002889endothelial cellAnatomy0.000description2
- 210000003238esophagusAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000007943implantSubstances0.000description2
- 238000010253intravenous injectionMethods0.000description2
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description2
- 238000010827pathological analysisMethods0.000description2
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description2
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000description2
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000description2
- 230000002195synergetic effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000002560therapeutic procedureMethods0.000description2
- 230000007704transitionEffects0.000description2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- MQLACMBJVPINKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N10-[(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)methylidene]anthracen-9-oneChemical compoundC1=C(O)C(OC)=CC=C1C=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C21MQLACMBJVPINKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 206010002383Angina PectorisDiseases0.000description1
- 208000037260Atherosclerotic PlaqueDiseases0.000description1
- 206010006187Breast cancerDiseases0.000description1
- 208000026310Breast neoplasmDiseases0.000description1
- 102000016736CyclinHuman genes0.000description1
- 108050006400CyclinProteins0.000description1
- 102000004127CytokinesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000695CytokinesProteins0.000description1
- 208000010496Heart ArrestDiseases0.000description1
- 101000634900Homo sapiens Transcriptional-regulating factor 1Proteins0.000description1
- 206010061218InflammationDiseases0.000description1
- 206010027476MetastasesDiseases0.000description1
- 208000034827NeointimaDiseases0.000description1
- 208000008589ObesityDiseases0.000description1
- 206010033128Ovarian cancerDiseases0.000description1
- 206010061535Ovarian neoplasmDiseases0.000description1
- 208000012868OvergrowthDiseases0.000description1
- 102000035195PeptidasesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108091005804PeptidasesProteins0.000description1
- 108091000080PhosphotransferaseProteins0.000description1
- 208000035965Postoperative ComplicationsDiseases0.000description1
- 208000002158Proliferative VitreoretinopathyDiseases0.000description1
- 239000004365ProteaseSubstances0.000description1
- 102000001253Protein KinaseHuman genes0.000description1
- 201000004681PsoriasisDiseases0.000description1
- 241001506137RapaSpecies0.000description1
- 206010038934Retinopathy proliferativeDiseases0.000description1
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-NSerineNatural productsOCC(N)C(O)=OMTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description1
- 102000013530TOR Serine-Threonine KinasesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010065917TOR Serine-Threonine KinasesProteins0.000description1
- 241000202349Taxus brevifoliaSpecies0.000description1
- 241001149649Taxus wallichiana var. chinensisSpecies0.000description1
- 102100029446Transcriptional-regulating factor 1Human genes0.000description1
- 102000044209Tumor Suppressor GenesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108700025716Tumor Suppressor GenesProteins0.000description1
- 206010072810Vascular wall hypertrophyDiseases0.000description1
- 208000027418Wounds and injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 230000002159abnormal effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000description1
- 239000004480active ingredientSubstances0.000description1
- 239000013543active substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004712air sacAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000001028anti-proliverative effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003409anti-rejectionEffects0.000description1
- 230000002785anti-thrombosisEffects0.000description1
- 230000003143atherosclerotic effectEffects0.000description1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 238000005452bendingMethods0.000description1
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description1
- 239000012867bioactive agentSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 230000037396body weightEffects0.000description1
- 210000000481breastAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000000621bronchiAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000002327cardiovascular agentSubstances0.000description1
- 229940125692cardiovascular agentDrugs0.000description1
- 239000000969carrierSubstances0.000description1
- 230000032823cell divisionEffects0.000description1
- 230000001684chronic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007012clinical effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000001608connective tissue cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000001276controlling effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001672cytoproliferative effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description1
- 230000034994deathEffects0.000description1
- 230000008021depositionEffects0.000description1
- 239000002552dosage formSubstances0.000description1
- 231100000673dose–response relationshipToxicity0.000description1
- 229940000406drug candidateDrugs0.000description1
- 238000010828elutionMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 239000003777experimental drugSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000description1
- 208000024519eye neoplasmDiseases0.000description1
- 239000000835fiberSubstances0.000description1
- 238000009472formulationMethods0.000description1
- 210000003714granulocyteAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000003102growth factorSubstances0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 229940019334heparin group antithrombotic drugDrugs0.000description1
- 238000004128high performance liquid chromatographyMethods0.000description1
- 239000000017hydrogelSubstances0.000description1
- 239000001257hydrogenSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052739hydrogenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000000338in vitroMethods0.000description1
- 238000001727in vivoMethods0.000description1
- 230000001939inductive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000008595infiltrationEffects0.000description1
- 238000001764infiltrationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004054inflammatory processEffects0.000description1
- 230000028709inflammatory responseEffects0.000description1
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 238000003780insertionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037431insertionEffects0.000description1
- 230000016507interphaseEffects0.000description1
- 238000007918intramuscular administrationMethods0.000description1
- 238000010255intramuscular injectionMethods0.000description1
- 239000007927intramuscular injectionSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007912intraperitoneal administrationMethods0.000description1
- 238000011835investigationMethods0.000description1
- 230000001788irregularEffects0.000description1
- 231100001231less toxicToxicity0.000description1
- 238000011068loading methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000003120macrolide antibiotic agentSubstances0.000description1
- 210000002540macrophageAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description1
- 230000009401metastasisEffects0.000description1
- 230000025090microtubule depolymerizationEffects0.000description1
- 230000036456mitotic arrestEffects0.000description1
- 210000001616monocyteAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000002107myocardial effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000005445natural materialSubstances0.000description1
- 208000021971neovascular inflammatory vitreoretinopathyDiseases0.000description1
- 210000000440neutrophilAnatomy0.000description1
- HLXZNVUGXRDIFK-UHFFFAOYSA-Nnickel titaniumChemical compound[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni]HLXZNVUGXRDIFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910001000nickel titaniumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 231100000957no side effectToxicity0.000description1
- 231100000252nontoxicToxicity0.000description1
- 230000003000nontoxic effectEffects0.000description1
- 235000020824obesityNutrition0.000description1
- 201000008106ocular cancerDiseases0.000description1
- 210000000056organAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 206010033675panniculitisDiseases0.000description1
- 230000009589pathological growthEffects0.000description1
- 230000026731phosphorylationEffects0.000description1
- 238000006366phosphorylation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 102000020233phosphotransferaseHuman genes0.000description1
- 239000002504physiological saline solutionSubstances0.000description1
- -1polyethylene vinyl acetatePolymers0.000description1
- 239000002861polymer materialSubstances0.000description1
- 238000006116polymerization reactionMethods0.000description1
- 229920002689polyvinyl acetatePolymers0.000description1
- 239000011118polyvinyl acetateSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000750progressive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000002062proliferating effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000035752proliferative phaseEffects0.000description1
- 230000006785proliferative vitreoretinopathyEffects0.000description1
- 230000002035prolonged effectEffects0.000description1
- 108060006633protein kinaseProteins0.000description1
- 230000009822protein phosphorylationEffects0.000description1
- 238000001243protein synthesisMethods0.000description1
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description1
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 230000019491signal transductionEffects0.000description1
- 230000000391smoking effectEffects0.000description1
- 208000010110spontaneous platelet aggregationDiseases0.000description1
- 239000003381stabilizerSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001954sterilising effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000004659sterilization and disinfectionMethods0.000description1
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000description1
- 238000007920subcutaneous administrationMethods0.000description1
- 210000004304subcutaneous tissueAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000011477surgical interventionMethods0.000description1
- 230000001225therapeutic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000017423tissue regenerationEffects0.000description1
- 230000000699topical effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000003437tracheaAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000014616translationEffects0.000description1
- 238000002054transplantationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004614tumor growthEffects0.000description1
- 208000019553vascular diseaseDiseases0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于医药领域,尤其涉及治疗血管再狭窄或其他组织增生的组合物及其应用方法。The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and in particular relates to a composition for treating vascular restenosis or other tissue hyperplasia and an application method thereof.
背景技术Background technique
冠状动脉疾病coronary artery disease
冠状动脉粥样硬化疾病是一种由血管内膜组织增生导致的慢性的冠状动脉堵塞或变窄。从1900年起它已成为危害西方社会的头号疾病,近年代,尽管现代医学有着显著的进步,该病不仅在西方国家,在中国也成为患者死亡的最常见原因。在美国有接近1400万的美国人患有冠心病,其中约50万人死于急性的心肌梗塞;每年用在治疗该疾病的费用超过1120亿。目前广泛存在的冠心病危险因素如肥胖,糖尿病和吸烟均表明在今后相当长的一段时间内,该疾病将继续严重的危害到人类的健康。Coronary atherosclerotic disease is a chronic blockage or narrowing of coronary arteries caused by intimal tissue hyperplasia. Since 1900, it has become the number one disease that harms Western society. In recent years, despite the remarkable progress of modern medicine, this disease has become the most common cause of death not only in Western countries, but also in China. Nearly 14 million Americans suffer from coronary heart disease in the United States, and about 500,000 of them die from acute myocardial infarction; the annual cost of treating the disease exceeds 112 billion. The widespread risk factors of coronary heart disease such as obesity, diabetes and smoking all indicate that the disease will continue to seriously endanger human health for a long period of time in the future.
冠状动脉搭桥手术是治疗冠心病的常用方法,然而其较高死亡率和术后并发症,以及昂贵的手术费用限制了该方法的广泛应用。经皮冠状动脉腔内成形术(PTCA)和冠状动脉支架植入(Stenting)术这两种治疗方法,是近20年里才发展起来的治疗冠心病有效的方法,近几年内得到了长足的发展。Coronary artery bypass surgery is a common method for the treatment of coronary heart disease, but its high mortality rate and postoperative complications, as well as expensive surgery costs limit the wide application of this method. Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) and coronary artery stent implantation (Stenting) are two effective methods for the treatment of coronary heart disease that have only been developed in the past 20 years. develop.
冠状动脉腔内成形术是将带有可扩张球囊的导管插入到原发性冠状动脉粥状斑块或继发性的血管再狭窄内,从而提高阻塞血管的通畅性和增加心肌血流量。冠状动脉腔内成形术后的主要问题是术后冠脉突发性闭合。为了解决这一问题,临床心脏病医生于1986年引进了支架植入术,即在球囊扩张后的血管内植入金属支架,以保持血管的永久通畅。支架植入术的引入是介入心脏病学的一次革命。在冠状动脉支架植入术中,支架(细小金属支架)的作用是支撑血管壁和减少血管成形手术后再狭窄的风险。经皮冠状动脉内成形术及/或支架术的通常适应症为直径大于2.5mm的血管内(发生)阻塞而引起的心绞痛或急性心肌梗塞。Transluminal coronary angioplasty is the insertion of a catheter with an expandable balloon into primary coronary atherosclerotic plaque or secondary restenosis, thereby improving the patency of blocked vessels and increasing myocardial blood flow. The main problem after transluminal coronary angioplasty is the sudden closure of coronary artery after operation. In order to solve this problem, clinical cardiologists introduced stent implantation in 1986, that is, a metal stent is implanted in the blood vessel after balloon expansion to maintain the permanent patency of the blood vessel. The introduction of stent implantation was a revolution in interventional cardiology. In coronary artery stenting, stents (tiny metal stents) are used to support the vessel wall and reduce the risk of restenosis after angioplasty. The usual indications for percutaneous transcoronary angioplasty and/or stenting are angina pectoris or acute myocardial infarction caused by intravascular obstruction with a diameter greater than 2.5 mm.
根据美国心脏医学会的调查,在1997年约有130万的病人做了冠状动脉腔内成形术,其中一半患者需要放置支架。这种支架植入术和冠状动脉腔内成形术的结合已成为一种趋势,尤其随着药物释放支架的出现,这种趋势以每年20%的速率增长。每年花费在这方面的直接医疗费用超过20亿美元。According to a survey by the American Heart Association, about 1.3 million patients underwent endoluminal coronary angioplasty in 1997, and half of them required stent placement. This combination of stent implantation and coronary angioplasty has become a trend, especially with the emergence of drug-releasing stents, this trend is growing at a rate of 20% per year. Direct medical costs in this area exceed $2 billion per year.
血管再狭窄Vascular restenosis
血管再狭窄是指支架植入术或冠状动脉腔内成形术后的血管再狭窄,是由于血管内膜内由结缔组织和平滑肌细胞组成的一层血管内壁细胞的增生反应所引起的。在血管再狭窄的病人中,血管内膜的增生导致动脉阻塞和心脏供氧不足,并致使心率不齐或心搏停止。在药物涂层支架出现之前,血管成形手术后再狭窄一直是介入治疗中最大的问题。对于经皮冠状动脉内成形术,最初经球囊扩张6个月再狭窄复发率高达50%;支架植入术将这一数字降低到20-30%;而西罗莫司(CYPHERTM,CordisInc,Miami Lakes,Florida)和紫杉醇(TAXUSTM,Boston Scientific Inc,Natick,MA)药物释放支架能够显著降低再狭窄复发率至小于5%。然而,对于患有小血管或糖尿病以及弥漫性血管病变的病人,手术后再狭窄的风险仍然相当高。(金属裸支架是30%-60%,药物涂层支架是6%-18%)支架内再狭窄是一个多方面的,循序渐进的过程。尽管动脉血管组织的结构对于新植入的支架的反应机理仍在研究中,通常认为这个过程包括三个阶段:1)血栓形成阶段(支架置入0-3天后):这个阶段是动脉血管组织对新植入支架的最初反应,其特征为血小板和中性颗粒细胞的快速激活,黏附,凝聚和沉积以在受损害的位置形成血栓。抗血栓治疗贯穿着本阶段,其目的是预防支架植入后引起的血栓问题。2)恢复阶段:此阶段是在术后3-8天,其特征是渐进的炎性细胞浸润。本阶段包括粒细胞、单核细胞和巨噬细胞等炎性细胞被激活,并进而浸润到受损害的血管壁。随后,受损血管壁新生成的炎症细胞刺激引发了平滑肌细胞增生、转移。然而该些炎症细胞释放的细胞因子、化学因子及生长因子又进一步促进了损伤部位炎症反应,导致新内膜的增生。3)增生阶段:这个阶段持续1-3个月,其依赖于剩余血栓的厚度和生长速度。在这一阶段,炎症细胞转移至残余血栓,在附壁血栓上形成一个“帽状结构”。细胞渐进性增殖,吸收残余血栓,并最终被新生组织替代。新内膜生长过程与肿瘤组织的生长过程极为相似。该相似性导致了目前抗肿瘤药物紫杉醇和雷帕霉素药物支架的发明。Vascular restenosis refers to the restenosis of blood vessels after stent implantation or intraluminal coronary angioplasty, which is caused by the proliferation of cells in the inner wall of the blood vessel, which is a layer of connective tissue and smooth muscle cells in the intima. In patients with restenosis, overgrowth of the lining of the blood vessel leads to blockage of the artery and insufficient oxygen delivery to the heart, leading to irregular heartbeat or cardiac arrest. Before the emergence of drug-coated stents, restenosis after angioplasty has been the biggest problem in interventional therapy. For percutaneous transcoronary angioplasty, the initial 6-month restenosis recurrence rate was as high as 50% after balloon dilatation; stent implantation reduced this figure to 20-30%; Miami Lakes, Florida) and paclitaxel (TAXUSTM, Boston Scientific Inc, Natick, MA) drug-releasing stents were able to significantly reduce the restenosis recurrence rate to less than 5%. However, for patients with small vessels or diabetes and diffuse vascular disease, the risk of restenosis remains quite high. (30%-60% for bare metal stents and 6%-18% for drug-coated stents) In-stent restenosis is a multifaceted, gradual process. Although the mechanism of the structural response of the arterial vascular tissue to the newly implanted stent is still being studied, it is generally believed that this process includes three stages: 1) Thrombosis stage (0-3 days after stent implantation): this stage is that the arterial vascular tissue The initial response to a newly implanted stent is characterized by rapid activation, adhesion, aggregation, and deposition of platelets and neutrophils to form a thrombus at the damaged site. Antithrombotic therapy runs through this stage, and its purpose is to prevent thrombosis problems caused by stent implantation. 2) Recovery phase: This phase is 3-8 days after surgery, and is characterized by progressive inflammatory cell infiltration. This phase involves the activation of inflammatory cells such as granulocytes, monocytes, and macrophages, which in turn infiltrate the damaged vessel wall. Subsequently, the stimulation of newly generated inflammatory cells in the damaged vessel wall triggers the proliferation and metastasis of smooth muscle cells. However, the cytokines, chemical factors and growth factors released by these inflammatory cells further promote the inflammatory response at the injury site, leading to the hyperplasia of the neointimal membrane. 3) Proliferative phase: This phase lasts 1-3 months, depending on the thickness and growth rate of the remaining thrombus. At this stage, inflammatory cells migrate to the residual thrombus, forming a "cap" on the mural thrombus. The cells proliferate progressively, absorb the residual thrombus, and are eventually replaced by new tissue. The neointima growth process is very similar to the growth process of tumor tissue. This similarity led to the invention of the current antineoplastic drugs paclitaxel and rapamycin-drug stents.
药物释放支架包括三个基本的组成部分:金属支架、聚合物和生物活性剂。金属支架是药物释放支架的药物载体。聚合物则是用来储存药物。金属支架、聚合物、药物及血管壁的兼容性是药物释放支架是否成功的关键因素。Drug-releasing stents consist of three basic components: a metal stent, a polymer, and a bioactive agent. Metallic stents are drug carriers for drug-releasing stents. Polymers are used to store drugs. The compatibility of metal stents, polymers, drugs, and vessel walls is a key factor for the success of drug-releasing stents.
金属支架是向病变的动脉输送药物的装置,理想的药物输送装置应该有比较大的表面积,一定的支撑力和柔性。目前所有商业途径可获得的或正在研究中的药物洗脱支架都是用传统的支架作为载体。尽管今天使用的传统的冠状支架比十年前的支架有更强的柔韧度,弯曲性,更易到达分支血管,更小的金属覆盖等优点,但是它作为药物运输的工具还是有局限性的。A metal stent is a device for delivering drugs to diseased arteries. An ideal drug delivery device should have a relatively large surface area, a certain degree of support and flexibility. All drug-eluting stents currently commercially available or under investigation use conventional stents as carriers. Although the traditional coronary stents used today have advantages such as stronger flexibility, bending, easier access to branch vessels, and smaller metal coverage than the stents of ten years ago, they still have limitations as a tool for drug delivery.
聚合物是由很多小的重复单元组成的长链分子。他们形成药物储存槽并且有利于延长药物的输送。通常,用于药物释放支架的聚合体可以分为有机的、无机的、可降解的、不可降解的、合成的、天然的物质。涂层基体包括聚合物和抗再狭窄物质,是药物输送支架的重要组成部分。药物保存于涂层内,药物释放速率通过聚合物调节。药物涂层物质在杀菌后必须保持其物理化学性质不变,并且在支架扩张后能够伸展而不是脱落,分离。在支架置入后的4周内,药物缓慢释放以阻止平滑肌细胞的增生或移植。药物和支架表面的连接可以是共价键(e.g.,C-C bonds,sulfurbridges)或是非共价键(e.g.,ionic,hydrogen bonds)。Polymers are long chain molecules made up of many small repeating units. They form drug reservoirs and facilitate prolonged drug delivery. Generally, polymers used in drug-releasing stents can be classified into organic, inorganic, degradable, non-degradable, synthetic, and natural substances. The coating matrix includes polymers and anti-restenotic substances, which are important components of drug delivery stents. The drug is stored within the coating, and the rate of drug release is regulated by the polymer. The drug coating substance must keep its physical and chemical properties unchanged after sterilization, and be able to stretch rather than fall off and separate after the stent is expanded. During the 4 weeks after the stent is placed, the drug is slowly released to prevent the proliferation or engraftment of smooth muscle cells. The connection between the drug and the surface of the stent can be a covalent bond (e.g., C-C bonds, sulfurbridges) or a non-covalent bond (e.g., ionic, hydrogen bonds).
聚合物材料应为生物惰性物质,植入人体后不应引起组织的炎症反应。目前市场上还没有任何聚合物能满足类似要求。到目前为止,实验最成功的药物释放支架雷帕霉素和紫杉醇药物释放支架,均采用不可降解的生物材料为药物的聚合物:雷帕霉素药物支架是采用聚甲基丙烯酸丁酯和聚乙烯醋酸乙烯(polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate(PEVA)/poly n-butyl methacrylate(PBMA)共聚物包载西罗莫司,而紫杉醇药物支架系采用(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene)聚合物包载紫杉醇。The polymer material should be biologically inert and should not cause tissue inflammation after implantation in the human body. There are no polymers currently on the market that meet similar requirements. So far, the most successful experimental drug-releasing stents, rapamycin and paclitaxel drug-releasing stents, both use non-degradable biomaterials as drug polymers: the rapamycin drug-releasing stent is made of polybutylmethacrylate and poly Polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate (PEVA)/poly n-butyl methacrylate (PBMA) copolymer encapsulates sirolimus, while paclitaxel drug stent uses (styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene) polymer Packed with paclitaxel.
生物活性物质。寻找一有效抑制内膜增生的药物是药物洗脱支架成功的关键。理想的抗再狭窄的药物应对组织的再生具有高度的抑制作用,其非但对细胞没有毒害,而且应能允许支架植入后血管再次内皮化。biologically active substances. Finding a drug that effectively inhibits intimal hyperplasia is the key to the success of drug-eluting stents. An ideal anti-restenosis drug should be highly inhibitory to tissue regeneration, not only non-toxic to cells, but also allow re-endothelialization of vessels after stent implantation.
紫杉醇药物涂层支架paclitaxel drug-eluting stent
作用机理:紫杉醇,太平洋的红豆杉和短叶红豆杉的树皮中的提取物,是通常用于治疗乳腺癌和卵巢癌的抗肿瘤药物。紫杉醇的抗增生性能体现出浓度依赖性和与微管结合的可选择性,尤其对N末端的微管蛋白的beta组。这种结合通过减少聚合和阻止解聚时所需要的微管蛋白临界浓度来促进微管蛋白的聚合以形成稳定的微管。微管的结构通过捆绑和成倍增加数量来稳定。Mechanism of Action: Paclitaxel, an extract from the bark of Taxus chinensis and Taxus brevifolia, is an antineoplastic drug commonly used to treat breast and ovarian cancer. The antiproliferative properties of paclitaxel exhibited a concentration-dependent and selective binding to microtubules, especially the N-terminal beta group of tubulin. This binding promotes tubulin polymerization to form stable microtubules by reducing the critical concentration of tubulin required for polymerization and preventing depolymerization. The structure of microtubules is stabilized by bundling and multiplying in number.
紫杉醇在细胞内体现出明显的剂量依赖效果:低剂量通过诱导P53和P21肿瘤抑制基因使细胞分裂间期停留在G1阶段,从而引起细胞凋亡。高剂量被认为影响细胞周期的G2到M期:从G2期到M期的转变要求微管解聚,而紫杉醇可以稳定微管的结构,导致有丝分裂停止。另一方面,高剂量紫杉醇影响M到G1期过程,引起有丝分裂后停止甚至有可能是细胞凋亡。除此之外,某些蛋白酶和丝氨酸蛋白磷酸化都跟微观的结局有关,因而这些作用也会被紫杉醇所抑制。Paclitaxel exhibits obvious dose-dependent effects in cells: low dose induces P53 and P21 tumor suppressor genes to make interphase of cell division stay in G1 phase, thereby causing cell apoptosis. High doses are thought to affect the G2 to M phase of the cell cycle: the transition from G2 to M phase requires microtubule depolymerization, and paclitaxel can stabilize the structure of microtubules, leading to mitotic arrest. On the other hand, high-dose paclitaxel affects the M to G1 phase process, causing postmitotic arrest and possibly apoptosis. In addition, certain proteases and serine protein phosphorylation are associated with microscopic outcomes, and these effects are also inhibited by paclitaxel.
紫杉醇涂层支架的功效:紫杉醇涂层支架是在金属支架上涂上紫杉醇(1ug/mm2)和不可降解聚合物(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene)。短期内(<2年)紫杉醇涂层支架(TAXUS I,TAXUS II and TAXUS IV)和裸金属支架相比,具有明显的抑制血管再狭窄的作用。但其长期效果有待观察。Efficacy of paclitaxel-coated stents: paclitaxel-coated stents are coated with paclitaxel (1ug/mm2 ) and non-degradable polymers (styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene) on metal stents. In the short term (<2 years), paclitaxel-coated stents (TAXUS I, TAXUS II and TAXUS IV) have a significant inhibitory effect on restenosis compared with bare metal stents. But its long-term effect remains to be seen.
雷帕霉素药物涂层支架Rapamycin drug-coated stent
作用机理。雷帕霉素是一种新型大环内酯类免疫抑制剂,在1999年作为器官移植后的抗排斥药物获得美国FDA的核准。其应用于心血管药物支架的基础是通过其抑制组织增生的机制从而控制支架植入后的血管再狭窄。雷帕霉素的生物作用机制是:首先进入组织细胞,与组织细胞内的免疫亲和蛋白FK-12结合,形成RAPA-FK 12复合物,这种复合物能阻止信号传导,从而选择性的阻止蛋白质合成。在与免疫亲和蛋白FK-12结合后,雷帕霉素通过抑制哺乳动物的RAPA靶蛋白(mTOR)的活性和细胞周期依赖性激酶(cdk)及细胞周期蛋白(cyclin)复合物激酶的活性,以及眼癌(有遗传性的)的蛋白质的磷酸化,从而阻止细胞周期从G1期到S期的转化。mechanism of action. Rapamycin is a new type of macrolide immunosuppressant, which was approved by the US FDA in 1999 as an anti-rejection drug after organ transplantation. The basis of its application to cardiovascular drug stents is to control the restenosis of blood vessels after stent implantation through its mechanism of inhibiting tissue proliferation. The biological mechanism of rapamycin is: first enter the tissue cells, combine with the immunoaffinity protein FK-12 in the tissue cells to form a RAPA-FK 12 complex, this complex can prevent signal transduction, thereby selectively Block protein synthesis. After binding to the immunoaffinity protein FK-12, rapamycin inhibits the activity of mammalian RAPA target protein (mTOR) and the activity of cell cycle-dependent kinase (cdk) and cyclin complex kinase , and phosphorylation of proteins in eye cancer (hereditary), thereby preventing the transition of the cell cycle from G1 to S phase.
雷帕霉素药物释放支架的功效和注意事项:雷帕霉素药物涂层支架的组成包含一个金属支架,雷帕霉素(1.40μg/mm2)和50%的聚甲基丙烯酸丁酯和50%的聚乙烯醋酸纤维素的混合物组成的聚合物。药物层表面覆盖一层遮盖层,以控制药物的释放数度。支架植入后,药物在大约30天内通过聚合体慢慢的释放到血液中去。雷帕霉素涂层支架(CYPHERTM)是第一个被美国FDA批准上市的药物支架,目前在五十个国家得到广泛应用。与紫杉醇类似,其短期抑制再狭窄的效果明显,但长期效果有待进一步观察。Efficacy and precautions of rapamycin drug-releasing stent: The composition of rapamycin drug-eluting stent contains a metal stent, rapamycin (1.40μg/mm2 ) and 50% polybutylmethacrylate and Polymer composed of a mixture of 50% polyvinyl acetate. The surface of the drug layer is covered with a cover layer to control the release rate of the drug. After the stent is implanted, the drug is slowly released into the blood through the polymer within about 30 days. Rapamycin-coated stent (CYPHERTM ) is the first drug stent approved by the US FDA and is currently widely used in 50 countries. Similar to paclitaxel, its short-term inhibitory effect on restenosis is obvious, but the long-term effect needs further observation.
在临床上,介入心血管医生在选择药物释放支架时往往很难决定,因为目前仅有的雷帕霉素和紫杉醇药物支架,虽然作用机制不同,但临床效果不分伯仲。在很多的情况下,医生在同一病人血管内即植入雷帕霉素支架又植入紫杉醇支架.,此可被视为二者联合用药治疗再狭窄的前奏。最新的临床研究也表明,在同一病人的血管内植入不同药物的血管支架(雷帕霉素和紫杉醇)末见有任何副作用。Clinically, it is often difficult for interventional cardiologists to make a decision when choosing a drug-releasing stent, because the only rapamycin and paclitaxel drug stents currently have different mechanisms of action, but the clinical effects are equal. In many cases, doctors implant both rapamycin stents and paclitaxel stents in the same patient's blood vessels. This can be regarded as a prelude to the combination of the two drugs for the treatment of restenosis. The latest clinical research also shows that implanting different drug stents (rapamycin and paclitaxel) in the blood vessels of the same patient has no side effects.
早期的血栓聚集是导致再狭窄发生的一大诱因,临床上控制早期血栓形成的主要方法是在支架植入后静脉或口服给于大量的抗凝血药物如肝素,阿斯匹林等。但系统给于抗血栓药物的最大问题是用药后引发的出血。Early thrombus aggregation is a major cause of restenosis. Clinically, the main method to control early thrombus formation is to administer a large amount of anticoagulant drugs such as heparin and aspirin intravenously or orally after stent implantation. However, the biggest problem with systemic administration of antithrombotic drugs is bleeding after administration.
定义definition
“细胞增生状态”是指与动脉硬化,再狭窄,增生性玻璃体视网膜病变和银屑病相关的病态细胞生长。这个词并不意指和癌状态相关的细胞增生。"Cytoproliferative state" refers to pathological cell growth associated with arteriosclerosis, restenosis, proliferative vitreoretinopathy, and psoriasis. The term does not imply cell proliferation associated with a cancerous state.
“病态细胞增生”是指平滑肌细胞或原纤维细胞之非正常分裂。“病态细胞增生之抑制”则是指抑制此类细胞之病态生长。"Cell proliferation" refers to the abnormal division of smooth muscle cells or fibril cells. "Inhibition of proliferation of pathological cells" refers to inhibition of pathological growth of such cells.
“组合物”是指用于抑制再狭窄的所有药物混合物,比如包括紫杉醇和雷帕霉素的组合物。"Composition" refers to any mixture of drugs used to inhibit restenosis, such as a combination comprising paclitaxel and rapamycin.
“给药”在此包括给药途径,它包括能让组合物发挥作用(有效抑制细胞增生)的所有途径.包括通过系统给药(如:静脉注射)和局部的或是特殊部位给药,如皮下、非胃肠道、腹膜内等)、口服、透皮,或通过药物运输导管或是植入载药装置。"Administration" here includes administration routes, which include all routes that allow the composition to function (effectively inhibit cell proliferation), including systemic administration (such as: intravenous injection) and local or special site administration, Such as subcutaneous, parenteral, intraperitoneal, etc.), oral, transdermal, or through drug delivery catheters or implanted drug-loaded devices.
“有效剂量”是指能对病态细胞增生发挥充分抑制作用的药物剂量。有效剂量视具体情况而改变,比如细胞生长的类型,给药方式和部位,患者的体重,细胞生长的程度等。"Effective dose" refers to the dose of the drug that can fully inhibit the proliferation of pathological cells. The effective dose varies depending on specific conditions, such as the type of cell growth, the way and site of administration, the body weight of the patient, the degree of cell growth, and the like.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种能有效抑制血管再狭窄或动脉硬化形成的组合物,其中再狭窄是发生在血管,胆管,食道,和气管等管腔类组织。用于抑制细胞增生的组合物主要包括微管稳定剂和免疫抑制剂,还包括抗凝血剂。其中微管稳定剂是紫杉醇或其衍生物,免疫抑制剂是雷帕霉素或其衍生物,抗凝血剂是肝素或其衍生物。组合物的使用方法是全身系统给药的,其通过药物输送导管,导丝或支架输送到局部。一方面,应用方法为局部使用。给药方法,包括一方面采用导管局部给药,另一方面,通过支架缓慢释放。其中所述支架喷涂有组合物的有效成分。支架,是喷涂有组合物的支架—即药物涂层支架,进一步讲,药物涂层的方式包括多层逐级喷涂;或是药物预混后再喷涂于支架表面上。支架的种类包括但不局限于:一方面为可降解药物支架--将本发明组合物加入到可降解聚合物支架上。另一方面,金属支架,即在金属支架表面覆盖着该组合物。The object of the present invention is to provide a composition that can effectively inhibit the formation of vascular restenosis or arteriosclerosis, wherein the restenosis occurs in lumen tissues such as blood vessels, bile ducts, esophagus, and trachea. The composition for inhibiting cell proliferation mainly includes microtubule stabilizers and immunosuppressants, and also includes anticoagulants. Wherein the microtubule stabilizer is paclitaxel or its derivatives, the immunosuppressant is rapamycin or its derivatives, and the anticoagulant is heparin or its derivatives. The use method of the composition is systemic administration, which is delivered locally through a drug delivery catheter, guide wire or stent. In one aspect, the method of application is topical use. The administration method includes local administration through a catheter on the one hand, and slow release through a stent on the other hand. Wherein the stent is sprayed with active ingredients of the composition. The stent is a stent sprayed with a composition—that is, a drug-coated stent. Further, the method of drug coating includes multi-layer spraying; or the drug is premixed and then sprayed on the surface of the stent. The types of stents include but are not limited to: on the one hand, it is a degradable drug stent—the composition of the present invention is added to a degradable polymer stent. On the other hand, the metal stent is covered with the composition on the surface of the metal stent.
在另一方面,本发明包括抑制再狭窄有效剂量。In another aspect, the invention includes an amount effective to inhibit restenosis.
实验结果表明,局部给药物时,本发明中的药物配方组和比任何单一用药组更能有效的抑制支架植入后血管再狭窄的发生。另外一个发现是本发明的组合物比单一用药在同样剂量情况下对细胞的毒性更低。Experimental results show that when the drug is administered locally, the drug formula group in the present invention can more effectively inhibit the occurrence of vascular restenosis after stent implantation than any single drug group. Another finding is that the composition of the present invention is less toxic to cells than the single drug at the same dose.
本发明的组合物,用于血管,胆管,食道和支气管等人体管腔组织发生的组织增生或再狭窄。The composition of the invention is used for tissue hyperplasia or restenosis in human lumen tissues such as blood vessels, bile ducts, esophagus and bronchi.
本发明的生物机制及临床基础Biological mechanism and clinical basis of the present invention
血管再狭窄的发生机制与肿瘤生长的机制类似,都是以内膜增生为特征。联合用药在日常肿瘤的临床治疗中,是一种有效的、众所周知的方法。The mechanism of vascular restenosis is similar to that of tumor growth, both of which are characterized by intimal hyperplasia. Combination medicine is an effective and well-known method in daily clinical treatment of tumors.
在本发明的混合物中,雷帕霉素或紫杉醇都是脂溶性,具有相同的释放曲线,而二者又能独立的通过不同的途径有效的抑制内皮细胞的增生,因此,理论上,两种药物在药物涂层支架的联合应用时对防止再狭窄的发生应具有协同效应。同时由于二者的协同效应,其抑制再狭窄的所需的剂量也比单一用药时要低。雷帕霉素和紫杉醇主要作用于再狭窄发生的第二,三期。雷帕霉素和紫杉醇联合用药用于治疗血管再狭窄的作用机制:雷帕霉素是通过作用于细胞周期的S期而阻止内皮细胞的增生,而紫杉醇则是通过选择性的阻断细胞生长周期的M期而达到同样的抑制效果。本发明中,通过将二者联合,从不同的细胞生长周期多方位的阻断细胞的增生,从而提高治疗效果。In the mixture of the present invention, both rapamycin and paclitaxel are fat-soluble and have the same release profile, and the two can independently and effectively inhibit the proliferation of endothelial cells through different ways. Therefore, in theory, the two Drugs should have a synergistic effect on preventing restenosis when they are used in combination with drug-eluting stents. At the same time, due to the synergistic effect of the two, the dose required to inhibit restenosis is also lower than that of a single drug. Rapamycin and paclitaxel mainly act on the second and third stages of restenosis. The mechanism of action of the combination of rapamycin and paclitaxel for the treatment of vascular restenosis: rapamycin prevents endothelial cell proliferation by acting on the S phase of the cell cycle, while paclitaxel selectively blocks cell growth The same inhibitory effect can be achieved in the M phase of the cycle. In the present invention, by combining the two, cell proliferation is blocked in multiple directions from different cell growth cycles, thereby improving the therapeutic effect.
如前所述,早期的血小板的凝聚是诱发再狭窄的一主要因素。临床上控制早期血栓形成的主要方法是在支架植入后静脉或口服给于大量的抗凝血药物如肝素,阿斯匹林等。但系统给于抗血栓药物的最大问题是用药后引发的出血。在本混合物中的肝素,通过局部给药时可解决此一问题。如将混合物与聚合物一起覆膜在血管支架表面,因为肝素易溶于水,可以在支架植入后的数小时到数天内释放出来(再狭窄发生的第一期,从而可以极大地抑制早期血栓的形成。而雷帕霉素与紫杉醇均为脂溶性,在血管内释放较慢(28天内释放完月80%)As mentioned earlier, early platelet aggregation is a major factor in inducing restenosis. The main method of clinically controlling early thrombosis is to give a large amount of anticoagulant drugs such as heparin and aspirin intravenously or orally after stent implantation. However, the biggest problem with systemic administration of antithrombotic drugs is bleeding after administration. The heparin in this mixture solves this problem when administered topically. For example, the mixture and the polymer are coated on the surface of the vascular stent, because heparin is easily soluble in water and can be released within hours to days after the stent is implanted (the first stage of restenosis, which can greatly inhibit the early stage of restenosis). The formation of thrombus. Both rapamycin and paclitaxel are fat-soluble, and they are released slowly in blood vessels (80% of them are released within 28 days)
(再狭窄发生的第二,三期)。因而,本发明中的混合物药物释放支架一旦植入人体后可从不同的角度,不同的时期,多方位的阻断再狭窄的发生。(the second and third stages of restenosis). Therefore, once the mixture drug-releasing stent of the present invention is implanted into the human body, it can block the occurrence of restenosis in multiple directions from different angles and at different periods.
本发明中的实验数据首次证实雷帕霉素+紫杉醇混合物,雷帕霉素+紫杉醇+肝素混合物比任何单一用药时对支架植入后的血管内皮增生均具有更显著的抑制效果,这在后面附图中有充分的数据证明。Experimental data in the present invention firstly proves that the rapamycin+paclitaxel mixture, the rapamycin+paclitaxel+heparin mixture all has more significant inhibitory effect on the vascular endothelial hyperplasia after stent implantation than any single drug, this is in the back There is sufficient data proof in the accompanying drawings.
使用方法Instructions
本发明的(使用)方法,本发明中的药物组合物主要用于有可能或正患有增生性疾病的患者,经一定的给药途径给与有效的剂量。In the (use) method of the present invention, the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention is mainly used for patients who may or are suffering from proliferative diseases, and an effective dose is given through a certain route of administration.
在发明的组合物中所用到的首选药物是紫杉醇和雷帕霉素和肝素或它们的衍生物。本发明组合物中的所有药物都是市面上可得到的。The preferred drugs used in the inventive composition are paclitaxel and rapamycin and heparin or their derivatives. All drugs in the compositions of the present invention are commercially available.
在本发明中,上述描述组合物(雷帕霉素+紫杉醇或雷帕霉素+紫杉醇+肝素)被用来抑制血管再狭窄的形成。“抑制”在此包括降低,延迟或消除病态的细胞增生。“降低”意味着减少血管形成术后的平滑肌细胞增生所导致的血管内膜增厚。“延迟”意思是在血管成形术后,推迟的血管内膜增生发作的时间。“消除”意指完全降低或完全延迟内膜增生以致于血管中有足够的血流量并且不需要外科手术的介入。In the present invention, the composition described above (rapamycin+paclitaxel or rapamycin+paclitaxel+heparin) is used to inhibit the formation of vascular restenosis. "Inhibit" here includes reducing, delaying or eliminating pathological cell proliferation. "Reducing" means reducing intimal thickening of blood vessels caused by smooth muscle cell proliferation after angioplasty. "Delayed" means the delayed onset of intimal hyperplasia after angioplasty. "Abolished" means that intimal hyperplasia is completely reduced or completely delayed such that there is sufficient blood flow in the blood vessel and no surgical intervention is required.
本发明之组合物可通过任何有效的途径给于。这些途径包括但又不限于系统给药,如间断地或是持续的静脉注射,皮下组织,肌肉的,腹膜等的肌肉注射。The compositions of the present invention may be administered by any effective means. These routes include, but are not limited to, systemic administration, such as intermittent or continuous intravenous injection, subcutaneous tissue, intramuscular, peritoneal, etc. intramuscular injection.
其中一理想的给药方法是导管给药,导管通常有一个软竿,在竿的顶部有一个气囊。气囊上打有多个微孔,将气囊输送到病变区后,再加压而将药物注入到病变的组织内。也可将药物用于聚合物内,形成水凝胶,然后敷于气囊表面,再将球囊倒入到病变区内。One of the ideal methods of administering the drug is through a catheter, which usually has a soft stem with a balloon at the top of the stem. There are many micro-holes on the airbag, and after the airbag is delivered to the lesion area, it is repressurized to inject the medicine into the lesioned tissue. Drugs can also be used in the polymer to form a hydrogel, which is then applied to the surface of the air sac and then poured into the lesion.
另一理想的给药方式是使用灌输导管或药物输送导丝。将灌输导管末端插入病变地点,将导管和注射泵相连接,导管的末端通常有通路,通过该通路将药物注入到病变的组织。药物输送导丝,导丝是空的,并且为了药物的灌输,在它的末端有一个口子。Another ideal way to administer the drug is through the use of an infusion catheter or drug delivery guidewire. The end of the infusion catheter is inserted into the lesion, and the catheter is connected to a syringe pump. The end of the catheter usually has a channel through which the drug is injected into the diseased tissue. For drug delivery guidewires, the guidewire is hollow and has an opening at the end for drug infusion.
给药方式的另一选择是将药物覆盖于医疗器械内比如血管支架,然后植入病变区内。用于血管球囊成形术的血管内支架已是比较成熟的技术。Another option for the way of administration is to cover the drug in a medical device such as a vascular stent, and then implant it into the lesion. Intravascular stents for balloon angioplasty are a relatively mature technology.
用于给药的支架可以是金属支架。通常金属支架应具有良好的生物相容性。常用的支架材料包括镍钛合金和不锈钢。具体使用时,可将药物装载于支架表面的刻槽内或将药物溶于聚合物后再喷涂于支架表面。The stent used for drug delivery may be a metal stent. Usually metal stents should have good biocompatibility. Commonly used stent materials include Nitinol and stainless steel. In specific use, the drug can be loaded into the grooves on the surface of the stent or the drug can be dissolved in a polymer and then sprayed on the surface of the stent.
金属支架的另一种情况是,将金属支架作为平台,在金属支架表面覆盖一层纤维聚合物或是其他生物材料,将药物溶于聚合物内。在此金属支架充当聚合物输送药物的平台,为血管提供一机械支撑,聚合物则控制药物的释放。In another case of metal stents, the metal stent is used as a platform, and the surface of the metal stent is covered with a layer of fiber polymer or other biomaterials, and the drug is dissolved in the polymer. Here, the metal stent acts as a platform for the polymer to deliver drugs, providing a mechanical support for the blood vessel, and the polymer controls the release of the drug.
支架作为药物载体的另种情况是可降解支架,可降解支架即可以是生物可降解材料比如聚乳酸或金属可降解材料比如镁合金支架。在聚乳酸支架中,可以直接将药物加入到支架内,药物随支架的讲解而释放出来。在镁合金支架中,药物可以则需要喷涂于支架表面,然后再缓慢释放出来。Another case where a stent is used as a drug carrier is a degradable stent, which can be a biodegradable material such as polylactic acid or a metal degradable material such as a magnesium alloy stent. In the polylactic acid stent, the drug can be directly added to the stent, and the drug will be released as the stent is opened. In magnesium alloy stents, drugs may need to be sprayed on the surface of the stent and then released slowly.
为了证实该发明,我们将发明的药物配方组合物喷涂于金属支架表面,然后移植入大鼠颈动脉和兔子的股动脉内。以后将对这些研究状况进行讨论。In order to confirm the invention, we sprayed the inventive pharmaceutical formula composition on the surface of the metal stent, and then transplanted it into the carotid artery of rats and the femoral artery of rabbits. The status of these studies will be discussed later.
研究中所用的金属支架是不锈钢金属支架。The metal stents used in the study were stainless steel metal stents.
将装载药物配方组合物的支架如实例3所示插入大鼠颈动脉血管内。同时作为对照,将没有药物装载(裸支架),只装有紫杉醇,和只装有雷帕霉素三组支架也一并植入大鼠颈动脉内。The stent loaded with the pharmaceutical formulation composition was inserted into the rat carotid artery as shown in Example 3. At the same time as a control, three groups of stents without drug loading (bare stent), paclitaxel only, and rapamycin only were also implanted into the rat carotid artery.
在所有支架植入大鼠颈动脉一个月后,将大鼠处死,用福尔马林高压灌注颈动脉,仔细从组织中分离支架后再在显微镜下测量再狭窄的程度。计算再狭窄的公式:(正常的内膜面积-残留的内膜面积)/正常的内膜面积×100计算得到的。One month after all the stents were implanted in the carotid arteries of the rats, the rats were sacrificed, the carotid arteries were perfused with formalin under high pressure, the stents were carefully separated from the tissue, and the degree of restenosis was measured under a microscope. The formula for calculating restenosis: (normal intimal area-residual intimal area)/normal intimal area×100.
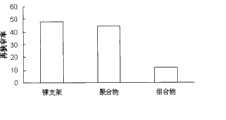
本发明之药物配方包裹的支架其狭窄率为5.8%。金属裸支架的狭窄率为16%。只载有紫杉醇狭窄率为12%,只载有雷帕霉素的支架其狭窄率为11.9%。附图5中是实验的总结。The stenosis rate of the stent wrapped by the pharmaceutical formula of the present invention is 5.8%. Bare metal stents had a stenosis rate of 16%. The stenosis rate of paclitaxel alone was 12%, and that of rapamycin only was 11.9%. A summary of the experiment is shown in Figure 5.
结果表明:雷帕霉素和紫杉醇联合用药比任何单一用药,在抑制血管再狭窄的发生方面有着更显著的疗效。The results show that the combination of rapamycin and paclitaxel has a more significant effect on inhibiting the occurrence of vascular restenosis than any single drug.
在另一研究中,支架表面覆盖有本发明的药物组合物。其中第一层包裹着紫杉醇,第二层包裹着雷帕霉素,最外层涂有肝素。In another study, the surface of the stent was covered with the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention. The first layer is wrapped with paclitaxel, the second layer is wrapped with rapamycin, and the outermost layer is coated with heparin.
试验时,将三个金属裸支架,三个聚合物覆膜支架,三个紫杉醇覆膜支架,三个雷帕霉素覆膜支架,三个肝素覆膜支架和三个混合药物包裹支架植入兔子的股动脉内。植入后一个月内,将兔子安乐死后,起出支架按上述的方法行病理切片观察分析。During the trial, three bare metal stents, three polymer covered stents, three paclitaxel covered stents, three rapamycin covered stents, three heparin covered stents and three mixed drug coated stents were implanted Inside the femoral artery of rabbits. Within one month after the implantation, the rabbits were euthanized, and the stents were taken out for observation and analysis of pathological sections according to the above method.
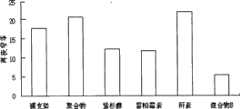
组合物B包裹的支架其狭窄率为5.3%。金属裸支架的狭窄率为18%。聚合物组为21%,只载有紫杉醇狭窄率为12%,只载有雷帕霉素的支架其狭窄率为11.9%。肝素包裹得支架为21%.附图6中是实验的总结。The stenosis rate of the stent coated with composition B was 5.3%. Bare metal stents had a stenosis rate of 18%. The stenosis rate was 21% in the polymer group, 12% in the paclitaxel-only stent, and 11.9% in the rapamycin-only stent. The heparin-coated scaffold was 21%. The summary of the experiment is shown in Figure 6.
结果表明,药物混合物B(雷帕霉素+紫杉醇+肝素)包裹支架比任何单一用药,在抑制血管再狭窄的发生方面有着更显著的疗效。试验中混合物中未见任何血管内血栓形成.The results showed that the drug mixture B (rapamycin+paclitaxel+heparin)-coated stent had a more significant curative effect on inhibiting the occurrence of vascular restenosis than any single drug. No intravascular thrombosis was observed in the mixture tested.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1阐明适用于各实施例的金属网状的金属架。FIG. 1 illustrates a metal mesh frame suitable for use in various embodiments.
图2阐明多层药物涂层的过程和方法,其中1为紫杉醇,2为雷帕霉素,3为聚合体。Figure 2 illustrates the process and method of multilayer drug coating, where 1 is paclitaxel, 2 is rapamycin, and 3 is polymer.
图3阐明预混和涂层药物的过程和方法。Figure 3 illustrates the process and method of premixing and coating the drug.
图4支架植入后一个月,本发明之药物涂层支架和单一药物涂层支架所引起的血管再狭窄的百分比。Fig. 4 Percentage of vascular restenosis caused by the drug-coated stent of the present invention and single drug-coated stent one month after stent implantation.
图5支架植入后一个月,本发明预混和药物之雷帕霉素、紫杉醇和其组合物涂层支架在兔子股动脉所引起的再狭窄的百分比。Fig. 5 is the percentage of restenosis caused by rapamycin, paclitaxel and the composition-coated stent of the present invention premixed with drugs in rabbit femoral artery one month after stent implantation.
图6:组合物与单一药物支架对抑制再狭窄的在体实验研究Figure 6: In vivo experimental study on the inhibition of restenosis by the composition and single-drug stent
图7:混合物中,不同比例的雷帕霉素与紫杉醇对血管再狭窄的抑制作用Figure 7: The inhibitory effect of different ratios of rapamycin and paclitaxel on restenosis in the mixture
实施例1Example 1
紫衫醇,雷帕霉素和肝素及其混合物混合物在PBMA/PEVA聚合物中的预混合涂层试验。Premix coating tests of paclitaxel, rapamycin and heparin and mixtures thereof in PBMA/PEVA polymer.
为了确定混合剂型能否涂抹在金属支架上,我们将四十个支架浸润在四种不同的药物共聚物剂型中:单一聚合体,单一雷帕霉素,单一紫衫醇,单一肝素组,雷帕霉素+紫衫醇组合物,雷帕霉素+紫杉醇+肝素组合物,每组有十个支架。高分子涂膜是由50%聚甲基丙烯酸丁酯和和50%聚乙烯醋酸乙烯。表格1是药物分组及每组药物的概括。To determine whether a mixed dosage form could be applied to metallic stents, we infiltrated forty stents with four different drug copolymer formulations: single polymer, single rapamycin, single paclitaxel, single heparin group, ray Pamycin+paclitaxel combination, rapamycin+paclitaxel+heparin combination, each group has ten stents. The polymer coating film is made of 50% polybutylmethacrylate and 50% polyethylene vinyl acetate. Table 1 is a summary of the drug groups and the drugs in each group.
实施例2Example 2
雷帕霉素,紫杉醇和肝素及其组合物A和B在PLA聚合物中的多层涂膜试验Rapamycin, paclitaxel and heparin and their compositions A and B in PLA polymer multilayer coating test
将PLA(聚乳酸)按6.7mg/ml的浓度溶于氯仿制得聚合物溶液。将溶液平均分为三部分,每一部分2ml。加5mg雷帕霉素到第一部分聚合物溶液中制得雷帕霉素-共聚体溶液(2.5mg/ml)。加5mg紫杉醇到第二部分聚合物溶液中制得紫杉醇-共聚物溶液(2.5mg/ml)。加5毫克肝素到第三部分中聚合物溶液中制得肝素-聚合物溶液.首先将裸金属支架浸入第一部分的雷帕霉素涂层溶液30秒中制得第一层涂层,自然干燥后,再将其浸入第二部分溶液(紫衫醇涂层溶液)30秒,室温下干燥后,最后再将支架浸入第三部分肝素涂层溶液30秒,完全晾干后,称量支架重量,然后根据药物溶液浓度计算药物/共聚物涂层的总重量。表格2是通过此方法每种包裹于支架的药物的总的数量的概要。PLA (polylactic acid) was dissolved in chloroform at a concentration of 6.7 mg/ml to prepare a polymer solution. The solution was equally divided into three portions of 2 ml each. A rapamycin-copolymer solution (2.5 mg/ml) was prepared by adding 5 mg of rapamycin to the first part of the polymer solution. A paclitaxel-copolymer solution (2.5 mg/ml) was prepared by adding 5 mg of paclitaxel to the second part of the polymer solution. Add 5 mg of heparin to the polymer solution in the third part to prepare the heparin-polymer solution. First, dip the bare metal stent into the rapamycin coating solution in the first part for 30 seconds to make the first layer of coating, and let it dry naturally After that, immerse it in the second part of the solution (taxol coating solution) for 30 seconds, dry it at room temperature, and finally immerse the stent in the third part of the heparin coating solution for 30 seconds. After it dries completely, weigh the stent , and then calculate the total weight of the drug/copolymer coating based on the drug solution concentration. Table 2 is a summary of the total amount of each drug entrapped in the stent by this method.
实施例3Example 3
雷帕霉素和紫杉醇药物释放测试。Rapamycin and paclitaxel drug release test.
为了确定雷帕霉素,紫杉醇的稳定性,我们在三个涂有混合物的支架上进一步实施了生物体外药物洗脱研究。实验中将每个支架放置在2.5ml生理盐水中,然后在37°c水浴器中以每分钟200转的速度不停的摇晃。每天更换生理盐水溶液以保持支架始终处于释放状态。在实验开始后的1,2,4周时,分别取出一个支架,将其置于1毫升的100%酒精中,然后用高压液相色谱仪测量酒精中雷帕霉素和紫杉醇的含量。实验结果,雷帕霉素和紫杉醇在三个时间段均可被探测到,表明二种药物在整个支架药物释放过程中是稳定的。To determine the stability of rapamycin, paclitaxel, we further performed in vitro drug elution studies on three stents coated with the mixture. In the experiment, each stent was placed in 2.5ml of physiological saline, and then kept shaking at a speed of 200 revolutions per minute in a 37°C water bath. The normal saline solution was changed daily to keep the stent released. At 1, 2, and 4 weeks after the start of the experiment, a stent was taken out, placed in 1 ml of 100% alcohol, and then the contents of rapamycin and paclitaxel in the alcohol were measured with a high-pressure liquid chromatography. The experimental results showed that both rapamycin and paclitaxel could be detected in three time periods, which indicated that the two drugs were stable throughout the drug release process of the stent.
实例施4Example 4
混合物药物支架植入大鼠颈动脉试验Implantation of mixed drug stent into rat carotid artery
为了确定雷帕霉素/紫杉醇混合涂层(混合物A)在抑制支架内再狭窄是否比单一雷帕霉素或紫杉醇涂层支架效果更好,我们进一步将实例1中描述的12个支架植入大鼠颈动脉。其中共聚物涂层支架(3个支架),雷帕霉素(3个支架),紫杉醇(3个支架),雷帕霉素/紫杉醇混合物(3个支架)。支架置入后4周,将所有实验的大鼠安乐致死。然后除去支架进行病理分析。In order to determine whether the rapamycin/paclitaxel hybrid coating (mixture A) is more effective in inhibiting in-stent restenosis than single rapamycin or paclitaxel coated stents, we further implanted the 12 stents described in Example 1 Rat carotid artery. Among them, copolymer-coated stents (3 stents), rapamycin (3 stents), paclitaxel (3 stents), and rapamycin/paclitaxel mixture (3 stents). Four weeks after stent implantation, all experimental rats were euthanized. The scaffolds were then removed for pathological analysis.
附图5描述了4组支架植入后血管内再狭窄率发生率的区别。和聚合物相比,雷帕霉素和紫杉醇涂层支架能够明显的减少支架内再狭窄率(分别是11.9%和12.1%vs.16.5%,P<0.05)。但是在紫杉醇单一涂层和雷帕霉素单一涂层组内,没有明显的区别(11.9%vs.12.1%,p>0.05),该结果与所有公开发表的有关雷帕霉素和紫杉醇单一涂层支架临床实验数据相同。最显著的发现是:雷帕霉素/紫杉醇混合涂层能够进一步降低血管内再狭窄率到5.8%,和单一雷帕霉素和单一紫杉醇涂层支架相比,再狭窄率降低了接近50%。Figure 5 describes the difference in the incidence of intravascular restenosis after stent implantation among the four groups. Compared with polymer, rapamycin and paclitaxel coated stents can significantly reduce the rate of in-stent restenosis (11.9% and 12.1% vs. 16.5%, respectively, P<0.05). However, within the paclitaxel single-coating and rapamycin single-coating groups, there was no significant difference (11.9% vs. The clinical experimental data of layer stents are the same. The most notable finding is that the rapamycin/paclitaxel hybrid coating can further reduce the intravascular restenosis rate to 5.8%, and the restenosis rate is reduced by nearly 50% compared with single rapamycin and single paclitaxel coated stents .
实例5:混合物药物B支架植入兔股动脉试验研究Example 5: Experimental study of mixture drug B stent implantation in rabbit femoral artery
将实例2中制得的聚乳酸-药物覆膜支架,其中裸支架(3个),共聚物涂层支架(3个支架),雷帕霉素(3个支架),紫杉醇(3个支架),肝素(3个),雷帕霉素/紫杉醇/肝素混合物(3个支架)。植入兔子股动脉,4周后,将所有实验的兔子安乐致死。然后取出支架进行病理分析。With the polylactic acid-drug covered stent made in example 2, wherein bare stent (3), copolymer coating stent (3 stent), rapamycin (3 stent), paclitaxel (3 stent) , heparin (3 stents), rapamycin/paclitaxel/heparin mixture (3 stents). The rabbit femoral artery was implanted, and all experimental rabbits were euthanized 4 weeks later. The stents were then removed for pathological analysis.
附图6描述了6组支架植入后血管内再狭窄率发生率的区别。和聚合物相比,雷帕霉素和紫杉醇涂层支架能够明显的减少支架内再狭窄率。但是在紫杉醇单一涂层和雷帕霉素单一涂层组内,没有明显的区别.肝素药物涂层支架与裸支架或聚合物支架没有显著的差异,表明肝素药物支架本身没有显著的抗再狭窄的作用,但可以防止血栓的形成.雷帕霉素/紫杉醇/肝素混合涂层能够进一步降低血管内再狭窄率到5.5%,和单一雷帕霉素和单一紫杉醇涂层支架相比,再狭窄率降低了接近50%。Figure 6 describes the differences in the incidence of intravascular restenosis after stent implantation among the six groups. Compared with polymers, rapamycin and paclitaxel-coated stents can significantly reduce the rate of in-stent restenosis. But within the paclitaxel single-coating and rapamycin single-coating groups, there was no significant difference. There was no significant difference between the heparin drug-coated stent and the bare stent or the polymer stent, indicating that the heparin drug-coated stent itself had no significant anti-restenotic effect However, it can prevent the formation of thrombus. Rapamycin/paclitaxel/heparin mixed coating can further reduce intravascular restenosis rate to 5.5%. Compared with single rapamycin and single paclitaxel coated stent, restenosis rate has been reduced by nearly 50%.
实施例6:混合物药物B中,不同比例的雷帕霉素与紫杉醇对血管再狭窄的影响。Example 6: Effects of different ratios of rapamycin and paclitaxel in mixture drug B on vascular restenosis.
为了确定不同药物在混合物中的最佳比例,我们进一步按上述方法制得不同比例成分的混合物,其中包括雷帕霉素:紫杉醇=50:50,60:40和70:30三组。在所有制得混合物中,肝素浓度不变。将制得的不同比例的混合物喷涂于支架表面,干燥后,如上所述植入大鼠颈动脉内,28天取出支架,进行病理切片分析。结果显示:三种不同比例的组合物对血管再狭窄均有抑制作用,但以在50:50的比例成分组效果最好。见图7。In order to determine the optimal ratio of different drugs in the mixture, we further prepared mixtures with different proportions according to the above method, including three groups of rapamycin:paclitaxel=50:50, 60:40 and 70:30. The heparin concentration was constant in all prepared mixtures. The prepared mixtures in different proportions were sprayed on the surface of the stent, and after drying, they were implanted into the carotid artery of rats as described above, and the stent was taken out after 28 days for pathological section analysis. The results showed that three compositions with different ratios all had inhibitory effects on vascular restenosis, but the composition with a ratio of 50:50 had the best effect. See Figure 7.
实施例7:混合物B中,不同比例的肝素对血管内血栓形成的影响。Example 7: In mixture B, the effect of different proportions of heparin on the formation of intravascular thrombus.
为了确定混合物中不同肝素浓度对血栓形成的影响,我们进一步按上述方法制得不同肝素比例的混合物,其中雷帕霉素:紫杉醇=50:50固定不变,肝素在总组合物中的比例分为10%,20%,和30%三组。将制得的不同比例的混合物喷涂于支架表面,干燥后,如上所述植入大鼠颈动脉内,28天取出支架,进行病理切片分析。结果显示:肝素浓度在组合物中占30%时,血管内几乎没有血栓的形成。In order to determine the influence of different heparin concentrations in the mixture on thrombus formation, we further prepared mixtures of different heparin ratios according to the above method, wherein rapamycin: paclitaxel = 50:50 was fixed, and the ratio of heparin in the total composition was Three groups of 10%, 20%, and 30%. The prepared mixtures in different proportions were sprayed on the surface of the stent, and after drying, they were implanted into the carotid artery of rats as described above, and the stent was taken out after 28 days for pathological section analysis. The results show that when the heparin concentration accounts for 30% in the composition, there is almost no thrombus formation in the blood vessel.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200810014140CN101496813B (en) | 2008-02-03 | 2008-02-03 | Application of composition in preparing medicine coating of anti-tissue proliferation (vascular restenosis) stent |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200810014140CN101496813B (en) | 2008-02-03 | 2008-02-03 | Application of composition in preparing medicine coating of anti-tissue proliferation (vascular restenosis) stent |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101496813Atrue CN101496813A (en) | 2009-08-05 |
| CN101496813B CN101496813B (en) | 2011-07-13 |
Family
ID=40944221
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200810014140ActiveCN101496813B (en) | 2008-02-03 | 2008-02-03 | Application of composition in preparing medicine coating of anti-tissue proliferation (vascular restenosis) stent |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101496813B (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105232182A (en)* | 2015-10-22 | 2016-01-13 | 上海交通大学 | Paclitaxel-loaded ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal stent and preparation method thereof |
| CN107496997A (en)* | 2017-07-25 | 2017-12-22 | 首都医科大学附属北京安贞医院 | Disposable combination drug coating coronary artery bougie |
| CN107998464A (en)* | 2017-11-29 | 2018-05-08 | 成都创客之家科技有限公司 | A kind of nasal septum stent |
| CN109498839A (en)* | 2018-11-13 | 2019-03-22 | 南开大学 | A kind of biology composite artificial blood vessel and application |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20070135893A1 (en)* | 2005-12-13 | 2007-06-14 | Robert Burgermeister | Polymeric stent having modified molecular structures in the flexible connectors and the radial arcs of the hoops |
- 2008
- 2008-02-03CNCN 200810014140patent/CN101496813B/enactiveActive
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105232182A (en)* | 2015-10-22 | 2016-01-13 | 上海交通大学 | Paclitaxel-loaded ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal stent and preparation method thereof |
| CN107496997A (en)* | 2017-07-25 | 2017-12-22 | 首都医科大学附属北京安贞医院 | Disposable combination drug coating coronary artery bougie |
| CN107998464A (en)* | 2017-11-29 | 2018-05-08 | 成都创客之家科技有限公司 | A kind of nasal septum stent |
| CN109498839A (en)* | 2018-11-13 | 2019-03-22 | 南开大学 | A kind of biology composite artificial blood vessel and application |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101496813B (en) | 2011-07-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7396538B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for delivery of mitomycin through an eluting biocompatible implantable medical device | |
| RU2360646C2 (en) | Endoluminal prosthesis containing medical agent | |
| US20050159809A1 (en) | Implantable medical devices for treating or preventing restenosis | |
| US20160220738A1 (en) | Progesterone-containing compositions and devices | |
| US20090030494A1 (en) | Method and devices for treatment of vulnerable (unstable) and/or stable atherosclerotic plaque by disrupting pathologic vasa vasorum of the atherosclerotic plaque | |
| JP5385785B2 (en) | Medical stent with a combination of melatonin and paclitaxel | |
| TWI455708B (en) | Delivery of highly lipophilic agents via medical devices | |
| JP5329435B2 (en) | Coronary stent with asymmetric drug release controlled coating | |
| HUP0402594A2 (en) | Drug delivery systems for the prevention and treatment of vascular diseases comprising rapamycin and derivatives thereof | |
| US20060193893A1 (en) | Medical devices | |
| CN105833358B (en) | A kind of intracranial drug-eluting stent system and preparation method thereof | |
| WO2010054121A2 (en) | Extracellular matrix modulating coatings for medical devices | |
| EP3515517B1 (en) | Polymer-free drug eluting vascular stents | |
| US20080085293A1 (en) | Drug eluting stent and therapeutic methods using c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor | |
| JP2008517662A (en) | Biocompatible and blood compatible polymer compositions | |
| CN101195048A (en) | Compound medicament washing bracket and method for preparing the same | |
| JP2004222953A (en) | Indwelling stent | |
| CN101496813A (en) | Anti-tissue proliferation (vascular restenosis) compositions and methods of use | |
| CN112263360A (en) | In vivo drug eluting stent and preparation method thereof | |
| US20090136558A1 (en) | Anti-Restenosis Coatings and Uses Thereof | |
| GB2448153A (en) | Coated Implantable Medical Devices | |
| JP2007531594A (en) | Bio-implantable device for eluting drug and drug preparation polymer system | |
| CN108338989A (en) | The compound anti-restenosis drugs and its controlled release system of coronary artery bracket for eluting medicament | |
| WO2006115279A1 (en) | Composition for preservation of vascular endothelium | |
| Costa | Drug-coated stents for restenosis |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| CB03 | Change of inventor or designer information | Inventor after:Wu Hao Inventor after:Wu Tiangen Inventor before:Wu Hao | |
| COR | Change of bibliographic data | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20160315 Address after:523808, room 5, building 1, Dongguan biotechnology cooperation center, 1 Taoyuan Road, Taiwan hi tech Industrial Development Zone, Songshan hi tech Industrial Development Zone, Guangdong, Dongguan, Patentee after:DONGGUAN TIANTIANXIANGSHANG MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD Address before:Two road 276826 in Shandong Province, Rizhao City island Patentee before:Wu Hao |