CN101409667A - Data interactive method, equipment and system for radio base station - Google Patents
Data interactive method, equipment and system for radio base stationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101409667A CN101409667ACNA2007101758223ACN200710175822ACN101409667ACN 101409667 ACN101409667 ACN 101409667ACN A2007101758223 ACNA2007101758223 ACN A2007101758223ACN 200710175822 ACN200710175822 ACN 200710175822ACN 101409667 ACN101409667 ACN 101409667A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- wireless device
- node
- time slot
- control node
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
- H04B7/2643—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile using time-division multiple access [TDMA]
- H04B7/2656—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile using time-division multiple access [TDMA] for structure of frame, burst
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Time-Division Multiplex Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及通信技术领域,尤其涉及无线电基站中的数据交互方法、设备及系统。The invention relates to the field of communication technology, in particular to a data interaction method, device and system in a radio base station.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,随着无线通信系统基站设计技术的发展,无线电基站中的无线电设备控制(REC)节点与无线电设备(RE)节点趋向于物理分离,例如,RE节点可靠近天线,REC节点位于便于接入处。REC节点执行基带信号处理,而各RE节点在基带与无线电频率之间进行转换,并通过一个或多个天线发射或接收信息。REC节点通过独立的专用光链路和/或电链路与多个远程RE节点相连接。各链路从REC节点向RE节点下行传送数据,从RE节点向REC节点上行传送数据。In recent years, with the development of base station design technology in wireless communication systems, the radio equipment control (REC) node and the radio equipment (RE) node in the radio base station tend to be physically separated. For example, the RE node can be close to the antenna, and the REC node is located in the entrance. The REC nodes perform baseband signal processing, while each RE node converts between baseband and radio frequency and transmits or receives information through one or more antennas. The REC node is connected to multiple remote RE nodes through independent dedicated optical links and/or electrical links. Each link transmits data downlink from the REC node to the RE node, and transmits data uplink from the RE node to the REC node.
REC节点与RE节点之间交互的数据包括用户数据和控制数据。其中,用户数据是指从无线电基站传送到用户设备(或从用户设备传送到无线电基站)的用户操作数据。用户数据按复数形式传送,因此也称复数形式的用户数据为IQ数据,其中“I”对应于复信号的实部或同相分量,而“Q”对应于复信号的虚部或正交分量。经由一个物理Ir链路,可以发送若干个IQ数据流,各IQ数据流对应于一个载波的一个天线(称为天线载波(AxC))的数据。一个AxC与通过一个载波的一个天线接收或发送的用户数据量相关。The data exchanged between the REC node and the RE node includes user data and control data. Herein, user data refers to user operation data transmitted from the radio base station to the user equipment (or from the user equipment to the radio base station). User data is transmitted in complex form, so it is also called IQ data in complex form, where "I" corresponds to the real part or in-phase component of the complex signal, and "Q" corresponds to the imaginary part or quadrature component of the complex signal. Via one physical Ir link, several IQ data streams can be transmitted, each IQ data stream corresponding to the data of one antenna of one carrier (called Antenna Carrier (AxC)). One AxC is related to the amount of user data received or transmitted through one antenna of one carrier.
REC节点与RE节点之间交互的控制数据包括:操作维护数据(C&M数据)、同步数据、标识数据(如帧号)。其中,操作维护数据(C&M数据)用于对REC节点、RE节点、REC节点与RE节点之间的通信接口进行操作管理和维护,包括参数配置类消息、状态管理类消息、告警管理类消息、版本管理类等多种类型数据。同步数据是指REC节点与RE节点之间交互数据时的同步和定时信息,可以用于检测超组、帧的边界,以及相关编号。可以通过时分复用(TDM)方式将不同天线载波的IQ数据和同步数据复用到一个Ir链路上。标识数据用于唯一标识一个帧。The control data exchanged between the REC node and the RE node includes: operation and maintenance data (C&M data), synchronization data, and identification data (such as frame number). Among them, the operation and maintenance data (C&M data) is used to operate, manage and maintain the REC node, the RE node, and the communication interface between the REC node and the RE node, including parameter configuration messages, status management messages, alarm management messages, Various types of data such as version management classes. Synchronization data refers to synchronization and timing information when REC nodes and RE nodes exchange data, and can be used to detect supergroups, frame boundaries, and related numbers. The IQ data and synchronization data of different antenna carriers can be multiplexed onto one Ir link by means of time division multiplexing (TDM). Identification data is used to uniquely identify a frame.
为了实现REC节点与RE节点之间的数据交互,针对宽带码分多址(WCDMA)系统提出了通用公用无线接口(CPRI:Common Public RadioInterface)协议,该协议中,RE节点利用多个天线载波,通过射频接口接收或发送数据,REC节点与RE节点相分离且通过传输链路相连接。生成的控制数据和用户数据通过传输链路在REC节点和RE节点之间进行交互。其中,用户数据包括多个数据流,每个数据流对应单个天线上单个载波的数据。控制数据和用户数据通过时分复用方式合成一个时分复用(TDM)帧。In order to realize data interaction between REC nodes and RE nodes, a Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI: Common Public Radio Interface) protocol is proposed for Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) systems. In this protocol, RE nodes use multiple antenna carriers, To receive or send data through a radio frequency interface, the REC node is separated from the RE node and connected through a transmission link. The generated control data and user data are interacted between the REC node and the RE node through the transmission link. Wherein, the user data includes multiple data streams, and each data stream corresponds to data of a single carrier on a single antenna. Control data and user data are synthesized into a Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) frame by time division multiplexing.
CPRI协议中规定REC节点与RE节点间的接口线路速率为614.4Mbps、1.2288Gbps或2.4576Gbps。针对1.2288Gbps的线路速率,并采用如图1所示的帧结构,从图1中可以看出,一个TDM的基本帧由16个字组成,每个字占16bit位,一个基本帧中,第一个字(16bit)用于传输控制数据,其余的字用于传输用户数据。另外,如图2所示,一个基本帧包含16×16=256bit,由256个基本帧组合成一个TDM的超帧,由150个超帧组合成一个WCDMA无线帧。The CPRI protocol stipulates that the line rate of the interface between the REC node and the RE node is 614.4Mbps, 1.2288Gbps or 2.4576Gbps. Aiming at the line rate of 1.2288Gbps, and using the frame structure shown in Figure 1, it can be seen from Figure 1 that a TDM basic frame consists of 16 words, and each word occupies 16 bits. In a basic frame, the first One word (16bit) is used to transmit control data, and the remaining words are used to transmit user data. In addition, as shown in FIG. 2 , a basic frame includes 16*16=256 bits, 256 basic frames are combined into a TDM superframe, and 150 superframes are combined into a WCDMA radio frame.
发明人在实现本发明的过程中,发现存在如下技术需求:In the process of realizing the present invention, the inventor found that there are the following technical requirements:
REC节点与RE节点间的数据交互同样可以应用于TD-SCDMA系统。而对于TD-SCDMA系统,为了达到较好的系统性能,需要支持智能天线技术。在典型的智能天线应用场景中,需要考虑3个扇区/载波,每扇区/载波使用8单元的智能天线的情况,即需要支持24个IQ数据流,即24AxC。The data interaction between the REC node and the RE node can also be applied to the TD-SCDMA system. As for the TD-SCDMA system, in order to achieve better system performance, it is necessary to support smart antenna technology. In a typical smart antenna application scenario, 3 sectors/carriers need to be considered, and each sector/carrier uses an 8-unit smart antenna, that is, 24 IQ data streams need to be supported, that is, 24AxC.
TD-SCDMA系统中,为了达到较好的数据动态范围,用户数据中的每个数据流应采用16bit位采样,此时在利用CPRI协议的帧结构实现REC节点与RE节点间的数据交互时,由于控制数据在一个基本帧中占用了一个字长,实际上仅有15个字用于传输用户数据,使传输用户数据的数据流的个数不足24个,因此无法满足TD-SCDMA系统中典型的智能天线应用场景;在实现REC节点与RE节点在TD-SCDMA系统中交互数据时,无线电基站处理数据流的速率相对较低,系统性能相对较差。In the TD-SCDMA system, in order to achieve a better data dynamic range, each data stream in the user data should be sampled with 16 bits. At this time, when using the frame structure of the CPRI protocol to realize the data interaction between the REC node and the RE node, Since the control data occupies one word length in a basic frame, only 15 words are actually used to transmit user data, so that the number of data streams for transmitting user data is less than 24, so it cannot meet the typical requirements of the TD-SCDMA system. Smart antenna application scenarios; when REC nodes and RE nodes exchange data in a TD-SCDMA system, the rate at which the radio base station processes data streams is relatively low, and the system performance is relatively poor.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例提供一种在无线电设备控制节点与无线电设备节点之间交互数据的方法、设备及系统,用以提高无线电设备控制节点与无线电设备节点之间数据流的速率。Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, device and system for exchanging data between a radio equipment control node and a radio equipment node, so as to increase the rate of data flow between the radio equipment control node and the radio equipment node.
本发明实施例提供一种在无线电设备控制节点与无线电设备节点之间交互数据的方法,所述数据包括用户数据和控制数据,所述控制数据包括操作维护数据,An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for exchanging data between a radio equipment control node and a radio equipment node, where the data includes user data and control data, and the control data includes operation and maintenance data,
无线电设备控制节点在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送下行操作维护数据;无线电设备节点在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送上行操作维护数据。The radio equipment control node transmits downlink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment node in the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe; the radio equipment node transmits uplink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment control node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe data.
本发明实施例还提供一种无线电设备控制节点,与无线电设备节点之间交互数据,所述数据包括用户数据和控制数据,所述控制数据包括操作维护数据,包括:The embodiment of the present invention also provides a radio equipment control node, which exchanges data with the radio equipment node, the data includes user data and control data, and the control data includes operation and maintenance data, including:
第一发送模块,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送下行操作维护数据;The first sending module is used to transmit downlink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment node in the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe;
第一接收模块,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,接收无线电设备节点传送的上行操作维护数据。The first receiving module is used for receiving the uplink operation and maintenance data transmitted by the radio equipment node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe.
本发明实施例还提供一种无线电设备节点,与无线电设备控制节点之间交互数据,所述数据包括用户数据和控制数据,所述控制数据包括操作维护数据,包括:The embodiment of the present invention also provides a radio equipment node, which exchanges data with a radio equipment control node, the data includes user data and control data, and the control data includes operation and maintenance data, including:
第二发送模块,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送上行操作维护数据;The second sending module is used to transmit uplink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment control node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe;
第二接收模块,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,接收无线电设备控制节点传送的下行操作维护数据。The second receiving module is used for receiving the downlink operation and maintenance data transmitted by the radio equipment control node in the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe.
本发明实施例还提供一种无线电基站系统,包括无线电设备控制节点与无线电设备节点;所述无线电设备控制节点与无线电设备节点之间交互数据,所述数据包括用户数据和控制数据,所述控制数据包括操作维护数据,An embodiment of the present invention also provides a radio base station system, including a radio equipment control node and a radio equipment node; data is exchanged between the radio equipment control node and the radio equipment node, the data includes user data and control data, and the control The data includes operation and maintenance data,
无线电设备控制节点,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送下行操作维护数据;The radio equipment control node is used to transmit downlink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment node in the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe;
无线电设备节点,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送上行操作维护数据。The radio equipment node is used to transmit uplink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment control node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe.
本发明实施例中,无线电设备控制节点在TD-SCDMA帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送下行操作维护数据,使下行操作维护数据的传输不占用下行时隙,下行时隙中的控制数据不包含操作维护数据,在整个下行时隙中只占用很少一部分比特;无线电设备节点在TD-SCDMA帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送上行操作维护数据,使上行操作维护数据的传输不占用上行时隙,上行时隙中的控制数据不包含操作维护数据,在整个上行时隙中只占用很少一部分比特;从而大幅提高了用户数据的传输率,可以使用户数据中的每个数据流采用16比特位采样,达到较好的数据动态范围,并且可以保证在TD-SCDMA的智能天线应用场景中,8个天线承载3个载波,支持24个数据流的情况。In the embodiment of the present invention, the radio equipment control node transmits the downlink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment node in the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA frame, so that the transmission of the downlink operation and maintenance data does not occupy the downlink time slot, and the control in the downlink time slot The data does not contain operation and maintenance data, and only occupies a small part of bits in the entire downlink time slot; the radio equipment node transmits the uplink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment control node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA frame, so that the uplink operation and maintenance data The transmission does not occupy the uplink time slot, and the control data in the uplink time slot does not contain operation and maintenance data, and only occupies a small part of the bits in the entire uplink time slot; thus greatly improving the transmission rate of user data, which can make the user data in Each data stream adopts 16-bit sampling to achieve a better data dynamic range, and can ensure that in the TD-SCDMA smart antenna application scenario, 8 antennas carry 3 carriers and support 24 data streams.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为背景技术中基本帧的结构示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a basic frame in the background technology;
图2为背景技术中基本帧与WCDMA无线帧的组成关系示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the composition relationship between basic frames and WCDMA wireless frames in the background technology;
图3为本发明实施例中TD-SCDMA子帧的结构示意图;FIG. 3 is a schematic structural diagram of a TD-SCDMA subframe in an embodiment of the present invention;
图4为本发明实施例中组与TD-SCDMA帧的组成关系示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the composition relationship between a group and a TD-SCDMA frame in an embodiment of the present invention;
图5为本发明实施例中操作维护子信道中组的结构示意图;FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a group in an operation and maintenance sub-channel in an embodiment of the present invention;
图6为本发明实施例中组的结构示意图;Fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a group in an embodiment of the present invention;
图7为本发明实施例中每个超组的同步子信道的示意图;FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of synchronous subchannels of each supergroup in an embodiment of the present invention;
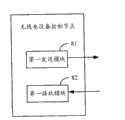
图8为本发明实施例中无线电设备控制节点的结构示意图;FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of a radio equipment control node in an embodiment of the present invention;
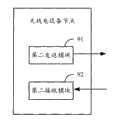
图9为本发明实施例中无线电设备节点的结构示意图;FIG. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of a radio device node in an embodiment of the present invention;
图10为本发明实施例中无线电设备基站系统的结构示意图。FIG. 10 is a schematic structural diagram of a radio equipment base station system in an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合说明书附图对本发明实施例进行详细说明。Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
TD-SCDMA系统中,一个TD-SCDMA帧由两个TD-SCDMA子帧组成,如图3所示,一个TD-SCDMA子帧包含有业务时隙(TS0~TS6)、上行导频时隙(UpPTS)、下行导频时隙(DwPTS)和保护间隔(GP);其中,下行业务时隙和下行导频时隙用于传送下行数据,称为下行时隙;上行业务时隙和上行导频时隙用于传送上行数据,称为上行时隙。In the TD-SCDMA system, a TD-SCDMA frame consists of two TD-SCDMA subframes, as shown in Figure 3, a TD-SCDMA subframe includes service time slots (TS0~TS6), uplink pilot time slots ( UpPTS), downlink pilot time slot (DwPTS) and guard interval (GP); among them, downlink business time slot and downlink pilot time slot are used to transmit downlink data, called downlink time slot; uplink business time slot and uplink pilot Time slots are used to transmit uplink data and are called uplink time slots.
基于上述TD-SCDMA子帧的结构特点,本发明实施例中,考虑将REC节点与RE节点之间交互的数据进行部分分离并传送。具体处理如下:Based on the structural features of the above TD-SCDMA subframe, in the embodiment of the present invention, it is considered to partially separate and transmit the data exchanged between the REC node and the RE node. The specific treatment is as follows:
将REC节点与RE节点之间交互的数据中,控制数据中的操作维护数据与其它控制数据分开传送。REC节点在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向RE节点传送下行操作维护数据;RE节点在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向REC节点传送上行操作维护数据。其中,REC节点与RE节点之间可以通过接口交互数据,如通过Ir接口或其它可用于REC节点与RE节点之间交互数据的接口。Among the data interacted between the REC node and the RE node, the operation and maintenance data in the control data is transmitted separately from other control data. The REC node transmits downlink operation and maintenance data to the RE node in the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe; the RE node transmits uplink operation and maintenance data to the REC node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe. Wherein, the REC node and the RE node can exchange data through an interface, such as an Ir interface or other interfaces that can be used for data exchange between the REC node and the RE node.
将操作维护数据从控制数据中分离出之后,REC节点利用TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙,向RE节点传送下行用户数据及除操作维护数据之外的其它控制数据,如同步数据和标识数据(帧号);RE节点利用TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙,向REC节点传送上行用户数据及除操作维护数据之外的其它控制数据,如同步数据和标识数据。After separating the operation and maintenance data from the control data, the REC node uses the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe to transmit the downlink user data and other control data except the operation and maintenance data to the RE node, such as synchronization data and identification data (frame number); the RE node uses the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe to transmit uplink user data and other control data except operation and maintenance data, such as synchronization data and identification data, to the REC node.
由于REC节点与RE节点之间交互的控制数据中,操作维护数据在整个控制数据中占很大比重,因此,利用上述将操作维护数据从控制数据中分离出并与其它控制数据在上下行时隙上分开传送的实施例方法,可以使REC节点与RE节点之间在交互数据时,TD-SCDMA子帧中控制数据的比重大幅下降,从而使更多的时隙用于传送用户数据,因此在用户数据中的每个数据流采用16bit位采样时,能够使传输用户数据的数据流的个数达到24个,满足TD-SCDMA系统中3个扇区/载波,每扇区/载波使用8单元的智能天线应用场景的需求。Since the operation and maintenance data accounts for a large proportion of the control data interacted between the REC node and the RE node, the operation and maintenance data is separated from the control data and shared with other control data when going up and down The embodiment method of separate transmission on the slot can make the proportion of control data in the TD-SCDMA subframe drop significantly when the REC node and the RE node exchange data, so that more time slots are used to transmit user data, so When each data stream in the user data adopts 16-bit sampling, the number of data streams transmitting user data can reach 24, satisfying 3 sectors/carriers in the TD-SCDMA system, and each sector/carrier uses 8 The requirements of the smart antenna application scenarios of the unit.
一个TD-SCDMA帧可以由多个TDM的超组组成,一个TDM的超组可以由多个TDM的组组成。如图4所示,组与TD-SCDMA帧的组成关系的一个具体实例为,由64个组(由变量X表示帧号)组合成一个TDM的超组(由变量Z表示帧号),由200个超组组合成一个TD-SCDMA帧。实施中,一个超组占用50微秒时长,一个TD-SCDMA帧占用10毫秒时长。A TD-SCDMA frame can be composed of multiple TDM supergroups, and a TDM supergroup can be composed of multiple TDM groups. As shown in Figure 4, a specific example of the composition relationship between the group and the TD-SCDMA frame is that 64 groups (representing the frame number by the variable X) are combined into a TDM supergroup (representing the frame number by the variable Z), which is represented by 200 supergroups are combined into one TD-SCDMA frame. In implementation, a supergroup takes 50 microseconds, and a TD-SCDMA frame takes 10 milliseconds.
一个具体实例为,在TD-SCDMA子帧中,利用Tsl和UpPTS传输下行C&M Data,利用Ts0和DwPTS传输上行C&M Data。A specific example is that in a TD-SCDMA subframe, Ts1 and UpPTS are used to transmit downlink C&M Data, and Ts0 and DwPTS are used to transmit uplink C&M Data.
对于下行来讲,一共有(864+160)×768比特/768比特=1024个Group可以作为Control plane。一个实施例中,将下行操作维护类数据分配给1024个子信道。每个子信道由包含768比特的Group组成,每个Group的组成如图5所示。For the downlink, there are a total of (864+160)×768 bits/768 bits=1024 Groups that can be used as Control planes. In one embodiment, downlink operation and maintenance data are allocated to 1024 sub-channels. Each sub-channel is composed of Groups containing 768 bits, and the composition of each Group is shown in FIG. 5 .
对于上行来讲,(864+96)×768比特/768比特=960个Group可以作为Control plane。一个实施例中,将上行操作维护类数据分配给960个子信道。每个子信道由包含768比特的Group组成,每个Group的组成如图5所示。For the uplink, (864+96)×768 bits/768 bits=960 Groups can be used as the Control plane. In one embodiment, uplink operation and maintenance data are allocated to 960 sub-channels. Each sub-channel is composed of Groups containing 768 bits, and the composition of each Group is shown in FIG. 5 .
图5中,四类操作维护数据(参数配置类消息、状态管理类消息、告警管理类消息、版本管理类消息)及reserved(保留)的数据所占的大小只是一个示意,具体所占的大小视实际网络中的需要而定。In Figure 5, the size of the four types of operation and maintenance data (parameter configuration messages, status management messages, alarm management messages, version management messages) and reserved (reserved) data is just an illustration, and the specific size It depends on the needs of the actual network.
另外,由于初始同步需要同步字连续,因此将初始同步数据放在C&M Data内。In addition, since initial synchronization requires continuous synchronization words, the initial synchronization data is placed in C&M Data.
如图6所示,一个TDM帧的组由24个字组成,每个字占32bit位,一个组包含24×32=768bit。与现有技术中CPRI协议的帧结构不同,本发明实施例在从控制数据中分离出操作维护数据后,在一个组中无需用一个字(16bit)长来传输除操作维护数据之外的控制数据,而可以将除操作维护数据之外的控制数据,如同步数据、标识数据(帧号)压缩为1bit,占用一个字中的最低位,而其余的比特位可用于传输用户数据,使用户数据在整个组中的比重大由提高。As shown in Figure 6, a TDM frame group consists of 24 words, each word occupies 32 bits, and a group contains 24*32=768 bits. Different from the frame structure of the CPRI protocol in the prior art, after the operation and maintenance data is separated from the control data in the embodiment of the present invention, there is no need to use a word (16bit) length to transmit control data other than the operation and maintenance data in a group. Data, but control data other than operation and maintenance data, such as synchronization data and identification data (frame number), can be compressed into 1 bit, occupying the lowest bit in a word, and the remaining bits can be used to transmit user data, so that users The proportion of data in the whole group is greatly improved.
图6所示的阴影部分为传输除操作维护数据之外的控制数据占用的比特位。由于该比特位位于整个组中最低位字节的最低位比特,因此,其对于整个组的用户数据传送影响非常小,近似可视为将整个组用于传送用户数据,从而使无线电基站处理数据流的速率明显加快。The shaded part shown in FIG. 6 is the bits occupied by the transmission of control data other than operation and maintenance data. Since this bit is located in the lowest bit of the lowest byte in the entire group, it has very little impact on the user data transmission of the entire group, and it can be roughly regarded as using the entire group to transmit user data, so that the radio base station processes the data The rate of flow is significantly accelerated.
图6中,每个Group由24个Words组成,索引为W=0...23。每个word中包含的字节数用T来表示,各个字对应于8位字节,每个字节中的比特用B=0......7表示。T的值取决于总数据率,该总数据率被称为Ir线路比特率。该示例中字的总长度为32bit,即T的取值为4,可获得的数据率为1228.8Mbps。利用索引B和索引T可以寻址一个字内的各位。其中B=0,T=0为最低位。将具有索引W=0的字的第一个比特用作控制字,即每个Group的第一个word的第一个bit即X.0.0作为Start of Super-Group、SGN和BFN(同步数据及标识数据),基本Group中的剩余比特用于传送用户数据。In Fig. 6, each Group consists of 24 Words, and the index is W=0...23. The number of bytes contained in each word is represented by T, each word corresponds to an 8-bit byte, and the bits in each byte are represented by B=0...7. The value of T depends on the total data rate, which is called the Ir line bit rate. In this example, the total word length is 32 bits, that is, the value of T is 4, and the available data rate is 1228.8 Mbps. Bits within a word can be addressed using index B and index T. Among them, B=0, T=0 is the lowest bit. The first bit of the word with index W=0 is used as the control word, that is, the first bit of the first word of each Group is X.0.0 as Start of Super-Group, SGN and BFN (synchronous data and identification data), and the remaining bits in the basic group are used to transmit user data.
图6的右侧以箭头方向来表示多个位的传输顺序。如果用“ABCDEFGH”来表示一个字节中从低位到高位的各个比特,在8B/10B编码后,从“A”开始将十个码组“ABCDEI FGHJ”作为串行数据流发送。即在8B/10B编码中,将一个编码位加入三个最高位中,将另一个编码位加入五个最低位中。The right side of FIG. 6 shows the transmission sequence of multiple bits in the direction of the arrows. If "ABCDEFGH" is used to represent each bit from low to high in a byte, after 8B/10B encoding, ten code groups "ABCDEI FGHJ" will be sent as a serial data stream starting from "A". That is, in 8B/10B encoding, one coded bit is added to the three highest bits, and another coded bit is added to the five lowest bits.
当然,图6所示的除操作维护数据之外的控制数据占用1bit的情况仅为本发明实施例中的一个具体实例,本发明实施例中,还可使除操作维护数据之外的控制数据占用组中其它字的最低位比特,例如,在组中依次选取不同字的最低位比特用于除操作维护数据之外的控制数据的传输。当然,一个组中除操作维护数据之外的控制数据所占用字的最低位比特的总数不能超过(15bit),这是由于当占用16bit后,一个组中传送用户数据的字只能有15个,此时也无法满足TD-SCDMA系统中3个扇区/载波,每扇区/载波使用8单元的智能天线应用场景的需求。Certainly, the situation that the control data other than the operation and maintenance data shown in FIG. 6 occupies 1 bit is only a specific example in the embodiment of the present invention. Occupying the least significant bits of other words in the group, for example, sequentially selecting the least significant bits of different words in the group for transmission of control data other than operation and maintenance data. Of course, the total number of the lowest bits of the words occupied by control data other than operation and maintenance data in a group cannot exceed (15 bits). This is because when 16 bits are occupied, there are only 15 words for transmitting user data in a group At this time, it is also unable to meet the requirements of 3 sectors/carriers in the TD-SCDMA system, and each sector/carrier uses 8 units of smart antenna application scenarios.
基于上述情况,可以根据用户需求及系统能力设置一阈值,一个组中除操作维护数据之外的控制数据所占用字的最低位比特的总数不得超过该阈值,以满足TD-SCDMA系统中3个扇区/载波,每扇区/载波使用8单元的智能天线应用场景的需求。当然,该阈值不得超过15。Based on the above situation, a threshold can be set according to user needs and system capabilities, and the total number of the lowest bits of words occupied by control data other than operation and maintenance data in a group must not exceed this threshold, so as to meet the requirements of the TD-SCDMA system. Sector/carrier, each sector/carrier uses 8-unit smart antenna application scenarios. Of course, the threshold must not exceed 15.
一个超组对应64个子信道,子信道的索引范围从0到63,一个子信道的控制字索引(Ns)具有四个可能值——0、1、2和3。由等式X=Ms+16×Ns给出超组内的控制字索引。A supergroup corresponds to 64 subchannels, and the index of subchannels ranges from 0 to 63. The control word index (Ns) of a subchannel has four possible values—0, 1, 2, and 3. The control word index within the supergroup is given by the equation X=Ms+16*Ns.
每个超组的同步子信道如图7所示。其中,同步数据对应于Ms=0和Ns=0处的第0个控制字到Ms=7和Ns=0的第7个控制字。如上所述,通过RE节点检测该控制字内包含的同步数据来实现REC节点与RE节点之间的同步和定时。SGN的低8位对应于Ms=0和Ns=1处的第16个控制字到Ms=7和Ns=1处的第23个控制字,SGN的高8位对应于Ms=0和Ns=2处的第32个控制字到Ms=7和Ns=2的第39个控制字。BFN的低8位对应于Ms=8和Ns=0处的第8个控制字到Ms=15和Ns=0的第15个控制字,BFN的高8位以及Ms=8和Ns=1处的第24个控制字到Ms=15和Ns=1的第31个控制字。其他控制字均作为reserved。The synchronization subchannels of each supergroup are shown in Fig. 7 . Wherein, the synchronization data corresponds to the 0th control word at Ms=0 and Ns=0 to the 7th control word at Ms=7 and Ns=0. As mentioned above, the synchronization and timing between the REC node and the RE node are realized by the RE node detecting the synchronization data contained in the control word. The lower 8 bits of SGN correspond to the 16th control word at Ms=0 and Ns=1 to the 23rd control word at Ms=7 and Ns=1, and the upper 8 bits of SGN correspond to Ms=0 and Ns= 32nd control word at 2 to 39th control word at Ms=7 and Ns=2. The lower 8 bits of BFN correspond to the 8th control word at Ms=8 and Ns=0 to the 15th control word at Ms=15 and Ns=0, the upper 8 bits of BFN and Ms=8 and Ns=1 The 24th control word of Ms=15 and the 31st control word of Ns=1. Other control words are reserved.
实施中,通过时分复用(TDM)方式将不同天线载波的用户数据、同步数据、标识数据复用到一个Ir链路上。由于同步数据、标识数据仅占用组中字的最低位比特,因此可以在不影响用户数据质量的前提下实现同步和定时。In implementation, user data, synchronization data, and identification data of different antenna carriers are multiplexed onto one Ir link by means of time division multiplexing (TDM). Since the synchronization data and identification data only occupy the lowest bit of the word in the group, synchronization and timing can be realized without affecting the quality of user data.
基于同一发明构思,本发明实施例还提供一种无线电设备控制节点,与无线电设备节点之间交互数据,交互的数据包括用户数据和控制数据,控制数据包括操作维护数据,其结构如图8所示,包括:第一发送模块81、第一接收模块82;其中,第一发送模块81,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送下行操作维护数据;第一接收模块82,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,接收无线电设备节点传送的上行操作维护数据。Based on the same inventive concept, an embodiment of the present invention also provides a radio equipment control node, which exchanges data with the radio equipment node. The interactive data includes user data and control data, and the control data includes operation and maintenance data. Its structure is shown in FIG. 8 shown, including: a
一个实施例中,控制数据还包括同步数据和标识数据;第一发送模块81还可以用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送下行用户数据、同步数据和标识数据;第一接收模块82还可以用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,接收无线电设备节点传送的上行用户数据、同步数据和标识数据。In one embodiment, the control data also includes synchronization data and identification data; the
一个实施例中,控制数据还包括同步数据和标识数据;第一发送模块81还可以用于在组中字的最低位比特向无线电设备节点传送下行同步数据和标识数据,所述最低位比特的总数不超过设定的阈值;第一接收模块82还可以用于在组中字的最低位比特接收无线电设备节点传送的上行同步数据和标识数据,所述最低位比特的总数不超过设定的阈值。In one embodiment, the control data also includes synchronization data and identification data; the
一个实施例中,第一发送模块81还可以用于在组中依次选取不同字的最低位比特向无线电设备节点传送下行同步数据和标识数据;第一接收模块82还可以用于在组中依次选取不同字的最低位比特接收无线电设备节点传送的上行同步数据和标识数据;或者,第一发送模块81还可以用于在组中最低位字的最低位比特向无线电设备节点传送下行同步数据和标识数据;第一接收模块82还可以用于在组中最低位字的最低位比特接收无线电设备节点传送的上行同步数据和标识数据。In one embodiment, the
基于同一发明构思,本发明实施例还提供一种无线电设备节点,与无线电设备控制节点之间交互数据,交互的数据包括用户数据和控制数据,控制数据包括操作维护数据,其结构如图9所示,包括:第二发送模块91、第二接收模块92;其中,第二发送模块91,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送上行操作维护数据;第二接收模块92,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,接收无线电设备控制节点传送的下行操作维护数据。Based on the same inventive concept, an embodiment of the present invention also provides a radio equipment node, which exchanges data with a radio equipment control node. The interactive data includes user data and control data, and the control data includes operation and maintenance data. Its structure is shown in FIG. 9 shown, including: a
一个实施例中,控制数据还包括同步数据和标识数据;第二发送模块91还可以用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送上行用户数据、同步数据和标识数据;第二接收模块92还可以用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,接收无线电设备控制节点传送的下行用户数据、同步数据和标识数据。In one embodiment, the control data also includes synchronization data and identification data; the
一个实施例中,控制数据还包括同步数据和标识数据;第二发送模块91还可以用于在组中字的最低位比特向无线电设备控制节点传送上行同步数据和标识数据,所述最低位比特的总数不超过设定的阈值;第二接收模块92还可以用于在组中字的最低位比特接收无线电设备控制节点传送的下行同步数据和标识数据,所述最低位比特的总数不超过设定的阈值。In one embodiment, the control data also includes synchronization data and identification data; the
一个实施例中,第二发送模块91还可以用于在组中依次选取不同字的最低位比特向无线电设备控制节点传送上行同步数据和标识数据;第二接收模块92还可以用于在组中依次选取不同字的最低位比特接收无线电设备控制节点传送的下行同步数据和标识数据;或者,第二发送模块91还可以用于在组中最低位字的最低位比特向无线电设备控制节点传送上行同步数据和标识数据;第二接收模块92还可以用于在组中最低位字的最低位比特接收无线电设备控制节点传送的下行同步数据和标识数据。In one embodiment, the
基于同一发明构思,本发明实施例还提供一种无线电基站系统,其结构如图10所示,包括无线电设备控制节点101与无线电设备节点102;无线电设备控制节点101与无线电设备节点102之间交互数据,交互的数据包括用户数据和控制数据,控制数据包括操作维护数据,无线电设备控制节点101,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备节点102传送下行操作维护数据;无线电设备节点102,用于在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点101传送上行操作维护数据。Based on the same inventive concept, an embodiment of the present invention also provides a radio base station system, the structure of which is shown in FIG. 10 , including a radio
本领域普通技术人员可以理解上述实施例方法中的全部或部分步骤是可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件完成,该程序可以存储于一计算机可读存储介质中,存储介质可以包括:ROM、RAM、磁盘或光盘等。Those skilled in the art can understand that all or part of the steps in the methods of the above embodiments can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program, and the program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium, and the storage medium can include: ROM, RAM, Disk or CD, etc.
本发明实施例中,无线电设备控制节点在TD-SCDMA帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送下行操作维护数据,使下行操作维护数据的传输不占用下行时隙,下行时隙中的控制数据不包含操作维护数据,在整个下行时隙中只占用很少一部分比特;无线电设备节点在TD-SCDMA帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送上行操作维护数据,使上行操作维护数据的传输不占用上行时隙,上行时隙中的控制数据不包含操作维护数据,在整个上行时隙中只占用很少一部分比特;从而大幅提高了用户数据的传输率,可以使用户数据中的每个数据流采用16比特位采样,达到较好的数据动态范围,并且可以保证在TD-SCDMA的智能天线应用场景中,8个天线承载3个载波,支持24个数据流的情况。In the embodiment of the present invention, the radio equipment control node transmits the downlink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment node in the uplink time slot of the TD-SCDMA frame, so that the transmission of the downlink operation and maintenance data does not occupy the downlink time slot, and the control in the downlink time slot The data does not contain operation and maintenance data, and only occupies a small part of bits in the entire downlink time slot; the radio equipment node transmits the uplink operation and maintenance data to the radio equipment control node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA frame, so that the uplink operation and maintenance data The transmission does not occupy the uplink time slot, and the control data in the uplink time slot does not contain operation and maintenance data, and only occupies a small part of the bits in the entire uplink time slot; thus greatly improving the transmission rate of user data, which can make the user data in Each data stream adopts 16-bit sampling to achieve a better data dynamic range, and can ensure that in the TD-SCDMA smart antenna application scenario, 8 antennas carry 3 carriers and support 24 data streams.
另一方面,本发明实施例中,无线电设备控制节点在TD-SCDMA子帧的下行时隙内,向无线电设备节点传送用户数据、同步数据和标识数据;无线电设备节点在TD-SCDMA子帧的上行时隙内,向无线电设备控制节点传送用户数据、同步数据和标识数据,从而在不影响用户数据质量,保证满足TD-SCDMA的智能天线应用场景需求的基础上实现同步和定时。On the other hand, in the embodiment of the present invention, the radio equipment control node transmits user data, synchronization data and identification data to the radio equipment node in the downlink time slot of the TD-SCDMA subframe; In the uplink time slot, transmit user data, synchronization data and identification data to the radio equipment control node, so as to achieve synchronization and timing without affecting the quality of user data and ensuring that the application scenario requirements of TD-SCDMA smart antennas are met.
显然,本领域的技术人员可以对本发明进行各种改动和变型而不脱离本发明的精神和范围。这样,倘若对本发明的这些修改和变型属于本发明权利要求及其等同技术的范围之内,则本发明也意图包含这些改动和变型在内。Obviously, those skilled in the art can make various changes and modifications to the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Thus, if these modifications and variations of the present invention fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention and equivalent technologies, the present invention also intends to include these modifications and variations.
Claims (16)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007101758223ACN101409667B (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2007-10-12 | Data interaction method, device and system in radio base station |
| KR1020107007454AKR101111156B1 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2008-10-10 | Data interation method, device and system in a base radio station |
| JP2010525184AJP5181148B2 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2008-10-10 | Interactive data transmission method, facility and system in radio base station |
| PCT/CN2008/001719WO2009049496A1 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2008-10-10 | Data interaction method, device and system in a base radio station |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007101758223ACN101409667B (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2007-10-12 | Data interaction method, device and system in radio base station |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101409667Atrue CN101409667A (en) | 2009-04-15 |
| CN101409667B CN101409667B (en) | 2011-08-24 |
Family
ID=40566991
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007101758223AActiveCN101409667B (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2007-10-12 | Data interaction method, device and system in radio base station |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5181148B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR101111156B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101409667B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2009049496A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011144085A3 (en)* | 2011-05-25 | 2012-04-26 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and node b |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010000741A (en)* | 2000-10-17 | 2001-01-05 | 최성곤 | A health drink composition for baby or infants and its process |
| CN107528667B (en)* | 2016-06-21 | 2020-09-11 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method and device for transmitting frame data between near-end equipment and far-end equipment |
| CN106899342B (en)* | 2016-12-27 | 2019-01-01 | 中国移动通信有限公司研究院 | A kind of encapsulation of data, transmission method and device |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE0302596D0 (en)* | 2003-09-30 | 2003-09-30 | Ericsson Telefon Ab L M | Improvements in or relating to base stations |
| US7529215B2 (en)* | 2003-11-17 | 2009-05-05 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Encapsulation of independent transmissions over internal interface of distributed radio base station |
| US7773578B2 (en)* | 2004-07-13 | 2010-08-10 | Utstarcom Telecom Co., Ltd. | Packet transmission method for wireless signals in a wireless base station system |
| CA2582065C (en) | 2004-10-12 | 2014-11-25 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Interface, apparatus, and method for communication between a radio equipment control node and one or more remote radio equipment nodes |
| WO2008120297A1 (en)* | 2007-03-28 | 2008-10-09 | Fujitsu Limited | Method for data communication between radio control equipment and radio equipment, radio control equipment and radio equipment |
- 2007
- 2007-10-12CNCN2007101758223Apatent/CN101409667B/enactiveActive
- 2008
- 2008-10-10JPJP2010525184Apatent/JP5181148B2/enactiveActive
- 2008-10-10KRKR1020107007454Apatent/KR101111156B1/enactiveActive
- 2008-10-10WOPCT/CN2008/001719patent/WO2009049496A1/enactiveApplication Filing
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011144085A3 (en)* | 2011-05-25 | 2012-04-26 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and node b |
| US8270321B1 (en) | 2011-05-25 | 2012-09-18 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Data transmission method and base station |
| US8693402B2 (en) | 2011-05-25 | 2014-04-08 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Data transmission method and base station |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101409667B (en) | 2011-08-24 |
| WO2009049496A1 (en) | 2009-04-23 |
| KR101111156B1 (en) | 2012-02-27 |
| JP2010539828A (en) | 2010-12-16 |
| KR20100072234A (en) | 2010-06-30 |
| JP5181148B2 (en) | 2013-04-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102300217B (en) | Cellular communication system and method for coexistence of dissimilar systems | |
| CN1905428B (en) | Transmission method of TDD mobile communication system with low delay character | |
| CN102946295B (en) | The method communicating and setting up is carried out based on the frame structure that can mate different carrier bandwidth | |
| CN101621326B (en) | Downlink multi-access transmission system and implementation device thereof | |
| CN101378286B (en) | Indication method and device for scheduling information | |
| CN101409667B (en) | Data interaction method, device and system in radio base station | |
| CN1518841A (en) | Synchronization of multi-mode base stations using a common system clock | |
| CA2521373A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for a spectrally compliant cellular communication system | |
| CN104135294B (en) | A kind of E Band wireless transmission signal generating apparatus | |
| CN102724749B (en) | Method, terminal and base station for uplink-downlink frame synchronization | |
| CN101232323A (en) | Mobile phone television broadcasting system based on TD-SCDMA network | |
| CN103516453B (en) | Multi-slot frame structure adopting time division multiple access mode and application thereof | |
| CN101325737A (en) | Method for adapting IQ data and CPRI interface of GSM/EDGE | |
| EP1681812B1 (en) | Method for transmitting broadcast channels in a cellular wireless communication system | |
| CN106358240A (en) | Virtual flexible CPRI (common public radio interface) data frame transmission method and device | |
| TWI256262B (en) | Wireless synchronous time divisional modem apparatus | |
| CN109586886B (en) | Data transmission system | |
| CN101426283B (en) | Data transmission method for time division duplexing system | |
| CN101686566A (en) | Methods for allocating downlink sub-frames, transmitting information and acquiring information of WiMAX evolution system | |
| CN101296390B (en) | Communication method and address automatic allocation and recognition method for inside node of base station | |
| CN101159485A (en) | TDD system signal transmission method and frame structure | |
| CN1905406B (en) | Synchronous method for wideband time division duplex cellular system | |
| CN101388716B (en) | Wireless sub-frame transmission method and system | |
| EP1989786B1 (en) | Generic parallel spreading | |
| CN101478327B (en) | Method and system for transmitting data on uplink code channel |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |