CN101367268A - Surface treatment method - Google Patents
Surface treatment methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101367268A CN101367268ACNA2008103046482ACN200810304648ACN101367268ACN 101367268 ACN101367268 ACN 101367268ACN A2008103046482 ACNA2008103046482 ACN A2008103046482ACN 200810304648 ACN200810304648 ACN 200810304648ACN 101367268 ACN101367268 ACN 101367268A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- temperature
- treatment method
- plastic
- surface treatment
- quenching
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Processing And Handling Of Plastics And Other Materials For Molding In General (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese本申请是申请号为200510037359.7专利申请的分案申请。200510037359.7号专利申请的申请日为2005年9月16日,名称为《表面处理方法》。This application is a divisional application of the patent application No. 200510037359.7. The filing date of patent application No. 200510037359.7 is September 16, 2005, and the title is "Surface Treatment Method".
技术领域technical field
本发明是关于一种表面处理方法,尤其是关于一种可改善表面性能的表面处理方法。The invention relates to a surface treatment method, in particular to a surface treatment method capable of improving surface properties.
背景技术Background technique
随着科技的发展,消费性电子产品的市场竞争也越来越激烈。为了吸引消费者购买电子产品,除了该产品的功能外,产品的外观已成为该产品成败的关键因素之一。With the development of technology, the market competition of consumer electronic products is becoming more and more fierce. In order to attract consumers to purchase electronic products, in addition to the functions of the product, the appearance of the product has become one of the key factors for the success or failure of the product.
常用的消费性电子产品外壳常采用塑料材料,该塑料未经处理时表面较粗糙,且黯淡无光,从而影响到产品外观。因消费性电子产品经常需要被触摸,故其耐磨性也很重要。此外,产品外壳还需承受一定的冲击力,从而不会因意外冲击或摔落而使产品外观被损坏。Commonly used consumer electronic product casings are often made of plastic materials. The surface of the plastic is rough and dull when untreated, which affects the appearance of the product. Abrasion resistance is also important because consumer electronics are often touched. In addition, the product casing also needs to withstand a certain impact, so that the appearance of the product will not be damaged due to accidental impact or drop.
为改善塑料外壳的表面性能,需要对其进行特殊处理。传统的制造工艺,常采用热处理的方式,如淬火、回火等。然而,传统的工艺因其淬火冷却至室温,其中产品外壳的晶粒较粗大,不仅影响产品表面的亮度及光滑度,而且韧性较低,不能满足消费者的要求。To improve the surface properties of plastic housings, special treatments are required. The traditional manufacturing process often adopts heat treatment methods, such as quenching and tempering. However, due to quenching and cooling to room temperature in the traditional process, the crystal grains of the product shell are relatively coarse, which not only affects the brightness and smoothness of the product surface, but also has low toughness, which cannot meet the requirements of consumers.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,有必要提供一种可改善产品外壳性能的表面处理方法。In view of this, it is necessary to provide a surface treatment method that can improve the performance of the product shell.
一种表面处理方法,其应用于塑料,该处理方法从塑料熔融温度降至塑料的玻璃转换温度,在该玻璃转换温度下对塑料进行保压处理,再从塑料的玻璃转换温度降至淬火温度,然后由淬火温度加热至回火温度,最后由回火温度冷却至室内温度,其中该淬火温度低于室内温度约5℃-20℃。A surface treatment method, which is applied to plastics, the treatment method is from the melting temperature of the plastic to the glass transition temperature of the plastic, and the plastic is subjected to pressure-holding treatment at the glass transition temperature, and then from the glass transition temperature of the plastic to the quenching temperature , and then heated from the quenching temperature to the tempering temperature, and finally cooled from the tempering temperature to the room temperature, wherein the quenching temperature is about 5°C-20°C lower than the room temperature.
相较现有技术,本发明表面处理方法通过快速淬火工艺及快速回火工艺,有效改善产品表面性能,有效提高了产品表面亮度、光滑度及断裂韧性。Compared with the prior art, the surface treatment method of the present invention effectively improves the surface performance of the product through the rapid quenching process and the rapid tempering process, and effectively improves the surface brightness, smoothness and fracture toughness of the product.
附图说明Description of drawings
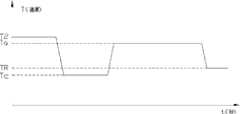
图1是本发明优选实施例塑料表面处理方法温度对时间的曲线图。Fig. 1 is the curve graph of temperature versus time of the plastic surface treatment method of the preferred embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明表面处理方法应用于改善消费性电子产品的塑料外壳的外观。The surface treatment method of the present invention is applied to improve the appearance of the plastic casing of consumer electronic products.
该表面处理方法通过快速淬火及快速回火工艺以改善塑料表面亮度及光滑度,且改善其韧性,以下结合具体图示来描述该表面处理方法。The surface treatment method improves the brightness and smoothness of the plastic surface through rapid quenching and rapid tempering processes, and improves its toughness. The surface treatment method is described below in conjunction with specific diagrams.
请参见图1,该淬火及回火温度曲线控制应用于塑料外壳射出成型前阶段。T2代表塑料玻璃转换温度,TR代表室内温度,Tq代表淬火温度,Ta代表回火温度。该塑料原料首先以塑料粒子方式载入射塑成型机的料筒内,经过加热至塑料融熔状态,熔融塑料温度通常为300℃左右,此时塑料具有充分的流动性,熔融塑料从料筒流入流道,再通过流道注入型腔内。在型腔完全充满熔融塑料后,再由该塑料融熔温度降至塑料玻璃转换温度,该玻璃转换温度设为T2,塑料材料的玻璃转换温度大约在100℃左右,之后在该温度下予以保压处理,通常时间为10秒;保压之后,将塑料从该玻璃转换温度T2迅速降到淬火温度Tq,该淬火温度Tq低于室内温度TR的范围约在5℃-20℃之间,从塑料玻璃转换温度T2降到淬火温度Tq要有较快的速度控制,其降温速率一般控制为5℃/秒-100℃/秒,优选采用20℃/秒-50℃/秒的范围。Please refer to Figure 1, the quenching and tempering temperature curve control is applied to the pre-injection molding stage of the plastic shell. T2 represents the plastic glass transition temperature, TR represents the room temperature, Tq represents the quenching temperature, and Ta represents the tempering temperature. The plastic raw material is first loaded into the barrel of the injection molding machine in the form of plastic particles, and is heated to the molten state of the plastic. The temperature of the molten plastic is usually about 300°C. At this time, the plastic has sufficient fluidity, and the molten plastic flows from the barrel Flow into the runner, and then inject into the cavity through the runner. After the cavity is completely filled with molten plastic, the melting temperature of the plastic is lowered to the plastic glass transition temperature. The glass transition temperature is set to T2. The glass transition temperature of the plastic material is about 100°C, and then it is kept at this temperature. Pressing treatment, usually for 10 seconds; after holding the pressure, quickly drop the plastic from the glass transition temperature T2 to the quenching temperature Tq , and the range of the quenching temperature Tq lower than the room temperatureTR is about 5°C-20°C In between, from the plastic glass transition temperature T2 to the quenching temperature Tq , there must be a faster speed control, and the cooling rate is generally controlled at 5°C/s-100°C/s, preferably 20°C/s-50°C/s seconds range.
再保持该淬火温度Tq大约10-20秒之后,将塑料从淬火温度Tq迅速增加到回火温度Ta,该回火温度Ta的范围在80-100℃,从淬火温度Tq升到回火温度Ta要有速度控制,通常其速率控制为5℃/秒-80℃/秒,优选回火升温的速率为10℃/秒-40℃/秒。在该回火温度Ta下保温20-60秒,之后,塑料将以10℃/秒-20℃/秒的速率降到室内温度TR,最后,打开型腔,顶出塑料外壳即可。After maintaining the quenching temperature Tq for about 10-20 seconds, the plastic is rapidly increased from the quenching temperature Tq to the tempering temperature Ta, and the tempering temperatureTa is in the range of 80-100 ° C. The fire temperature Ta should be speed controlled, usually the speed control is 5°C/s-80°C/s, preferably the tempering temperature rise rate is 10°C/s-40°C/s. Keep it warm at the tempering temperature Ta for 20-60 seconds, then the plastic will drop to the room temperature TR at a rate of 10°C/sec-20°C/sec, and finally, open the cavity and eject the plastic shell.
该塑料外壳采用快速淬火及快速回火,因淬火速度较快,且淬火温度低于室内温度TR,塑料晶粒没有时间扩散增长,从而可减少塑料内部晶粒尺寸,进而,可改善塑料外壳的表面亮度,光滑度及表面韧性。The plastic shell adopts rapid quenching and rapid tempering, because the quenching speed is fast, and the quenching temperature is lower than the room temperature TR , the plastic grains do not have time to diffuse and grow, thereby reducing the size of the plastic internal grains, and further improving the plastic shell Excellent surface brightness, smoothness and surface toughness.
为进一步防止熔融塑料于成型时被氧化,在快速淬火及快速回火时,可通过通风工艺填充氮气(N2)或其它惰性气体,如氩(Ar)、氦(He)之一或其组合等,以防止塑料表面被氧化或发黄。In order to further prevent the molten plastic from being oxidized during molding, during rapid quenching and rapid tempering, nitrogen (N2) or other inert gases, such as argon (Ar), helium (He) or a combination thereof, can be filled through a ventilation process. , to prevent the plastic surface from being oxidized or yellowed.
该塑料材料可以是合成材料,其可以为ABS塑料加玻璃纤维,该种塑料可应用于行动电话、笔记本计算机、桌上计算机,DVD,液晶显示器等。The plastic material can be a synthetic material, which can be ABS plastic plus glass fiber, and this kind of plastic can be used in mobile phones, notebook computers, desktop computers, DVDs, liquid crystal displays and the like.
采用上述工艺的快速淬火可极大改善塑料外壳的断裂韧性。通常材料的断裂韧性值越高,塑料表面性能越好。该断裂强度与晶粒尺寸平方根成反比,其可由如下公式来表示:Rapid quenching using the above process can greatly improve the fracture toughness of the plastic shell. Generally, the higher the fracture toughness value of the material, the better the surface properties of the plastic. The fracture strength is inversely proportional to the square root of the grain size, which can be expressed by the following formula:
K1c∝sy×(3.14159×c/d)0.5K1c ∝sy×(3.14159×c/d)0.5
其中K1c表示临界应力强度因子,sy表示屈服强度,c表示断裂长度,d表示晶粒尺寸,因此,晶粒尺寸越小,该临界应力强度因子的值越大,故其断裂韧性越高。在低于室温下淬火时,晶粒尺寸较小,故韧性得以增加。Among them, K1c represents the critical stress intensity factor, sy represents the yield strength, c represents the fracture length, and d represents the grain size. Therefore, the smaller the grain size, the greater the value of the critical stress intensity factor, so the higher the fracture toughness. When quenched below room temperature, the grain size is smaller, so the toughness is increased.
为进一步改善塑料外壳的外观亮度,可加入磷或纳米材料于合金中。该种发光材料可为硫化锌ZnS,硒化镉CdSe,硫化镉CdS,铕-锌氧化硅Eu-ZnSiOx,铕-三氧化镱Eu-YBO3及铕-钡镁氧化铝Eu-BaMgAlOx的一种或几种组合。In order to further improve the appearance brightness of the plastic shell, phosphorus or nanometer materials can be added to the alloy. The luminescent material can be one of zinc sulfide ZnS, cadmium selenide CdSe, cadmium sulfide CdS, europium-zinc oxide silicon Eu-ZnSiOx, europium-ytterbium trioxide Eu-YBO3 and europium-barium magnesium aluminum oxide Eu-BaMgAlOx or several combinations.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008103046482ACN101367268B (en) | 2005-09-16 | 2005-09-16 | Surface treatment method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008103046482ACN101367268B (en) | 2005-09-16 | 2005-09-16 | Surface treatment method |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2005100373597ADivisionCN1932045A (en) | 2005-09-16 | 2005-09-16 | Surface treatment method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101367268Atrue CN101367268A (en) | 2009-02-18 |
| CN101367268B CN101367268B (en) | 2011-03-30 |
Family
ID=40411328
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008103046482AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101367268B (en) | 2005-09-16 | 2005-09-16 | Surface treatment method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101367268B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105690812A (en)* | 2016-03-16 | 2016-06-22 | 中国科学院理化技术研究所 | Online cryogenic modification device of high polymer material injection molding equipment |
| CN106113338A (en)* | 2016-06-21 | 2016-11-16 | 爱普特聚合物江苏有限公司 | The surface-brightening processing method of non-injection grade thermoplastic plastic injecting part |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5489404A (en)* | 1994-08-08 | 1996-02-06 | General Electric Company | Process for annealing thermoplastics |
| US6932930B2 (en)* | 2003-03-10 | 2005-08-23 | Synecor, Llc | Intraluminal prostheses having polymeric material with selectively modified crystallinity and methods of making same |
- 2005
- 2005-09-16CNCN2008103046482Apatent/CN101367268B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105690812A (en)* | 2016-03-16 | 2016-06-22 | 中国科学院理化技术研究所 | Online cryogenic modification device of high polymer material injection molding equipment |
| CN105690812B (en)* | 2016-03-16 | 2019-06-21 | 中国科学院理化技术研究所 | Online cryogenic modification device of high polymer material injection molding equipment |
| CN106113338A (en)* | 2016-06-21 | 2016-11-16 | 爱普特聚合物江苏有限公司 | The surface-brightening processing method of non-injection grade thermoplastic plastic injecting part |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101367268B (en) | 2011-03-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Yang et al. | Microstructures and mechanical properties of titanium-reinforced magnesium matrix composites: Review and perspective | |
| US8800322B1 (en) | Composite magnetic recording medium | |
| JP2005515898A5 (en) | ||
| CN205217907U (en) | A cabinet -type electric furnace for isothermal forging | |
| CN101367268A (en) | Surface treatment method | |
| CN105648263A (en) | High-strength and easy-to-process copper matrix composite and preparation method thereof | |
| CN103667820B (en) | Aluminium alloy trough-type part and preparation technology thereof | |
| CN105436724A (en) | Methods of refinishing surface features in bulk metallic glass (bmg) articles by welding | |
| TW201348158A (en) | Three-dimensional glass and method for fabricating the same | |
| CN107530928B (en) | Injection molding method for thermosetting resin composition | |
| US20070062665A1 (en) | Method for molding products made from metal or plastic materials | |
| CN109440028A (en) | A kind of preparation method of grinding device for tread cleaner | |
| CN101401161A (en) | Optical discs using methyl methacrylate-acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer resin | |
| CN116179893A (en) | High-heat-conductivity composite material and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN105112741B (en) | Aluminum alloy material for electronic product shell and manufacturing method | |
| CN201281541Y (en) | High temperature bench vehicle type electrical resistance furnace | |
| CN107498017A (en) | A kind of alloy die cast technique | |
| KR102329620B1 (en) | Alumium alloy for die-casting | |
| CN104118088A (en) | Plastic product and molding method thereof | |
| KR101816324B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing aluminum-carbon nanotubes composite using casting and aluminum-carbon nanotubes composite manufactured by the same | |
| US20210087664A1 (en) | Heat-treatable aluminum alloy made from used beverage can scrap | |
| JP2004161540A (en) | Method and apparatus for manufacturing chemically strengthened glass | |
| CN103071794A (en) | Breathing type reduction method of metal powder and sintered product thereof | |
| CN104561630A (en) | Production method of aluminum alloy door and window profiles | |
| JPS62179913A (en) | How to mold plastic lenses |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20110330 Termination date:20150916 | |
| EXPY | Termination of patent right or utility model |