CN101336554A - Safety assigned handover signaling - Google Patents
Safety assigned handover signalingDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101336554A CN101336554ACNA2006800517083ACN200680051708ACN101336554ACN 101336554 ACN101336554 ACN 101336554ACN A2006800517083 ACNA2006800517083 ACN A2006800517083ACN 200680051708 ACN200680051708 ACN 200680051708ACN 101336554 ACN101336554 ACN 101336554A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- base station
- context
- target base
- handover
- mobile communication
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000011664signalingEffects0.000titleabstract2
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription28
- 238000012790confirmationMethods0.000claimsdescription36
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000claimsdescription34
- 238000010295mobile communicationMethods0.000claimsdescription26
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000claimsdescription15
- 230000015654memoryEffects0.000claimsdescription10
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000abstractdescription17
- 230000001413cellular effectEffects0.000description11
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description9
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description8
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description7
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description2
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 230000000153supplemental effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000010200validation analysisMethods0.000description2
- 238000012795verificationMethods0.000description2
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 239000012634fragmentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description1
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description1
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 230000008520organizationEffects0.000description1
- 238000009877renderingMethods0.000description1
- 238000005096rolling processMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/12—Detection or prevention of fraud
- H04W12/121—Wireless intrusion detection systems [WIDS]; Wireless intrusion prevention systems [WIPS]
- H04W12/122—Counter-measures against attacks; Protection against rogue devices
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/14—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for detecting or protecting against malicious traffic
- H04L63/1441—Countermeasures against malicious traffic
- H04L63/1458—Denial of Service
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0011—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection
- H04W36/0033—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection with transfer of context information
- H04W36/0038—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection with transfer of context information of security context information
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese相关申请的交叉引用Cross References to Related Applications
本申请要求2006年1月4日提交的申请号为60/755,793的美国临时申请的利益,其通过引用被结合在此。This application claims the benefit of US Provisional Application No. 60/755,793, filed January 4, 2006, which is incorporated herein by reference.
技术领域technical field
本发明通常涉及通信网络。具体来说,本发明提供在通信网络中的安全措施。The present invention generally relates to communication networks. Specifically, the present invention provides security measures in communication networks.
背景技术Background technique
通信网络已经在信息交换中占据重要地位。例如,用于移动媒体内容通信的网络提供了向大量客户传送媒体流的可升级方法。由于网络基础结构可用性的增加,可能实现增强的媒体服务的交换和通信。Communication networks already play an important role in information exchange. For example, networks for mobile media content communication provide a scalable method of delivering media streams to large numbers of customers. Due to the increased availability of the network infrastructure, enhanced exchange and communication of media services is possible.
在典型网络中,客户连接到网络服务。客户想要服务时,希望该服务对于客户来说是可获得的。然而,在很多情况下,由于违背了系统的安全,可能拒绝用户或者组织使用期望的服务。例如,可以发生中断服务提供或者甚至破坏系统中的编程或者所需文件的拒绝服务(DoS)攻击。该DoS攻击会导致时间和金钱两方面的较大花费。In a typical network, clients connect to web services. When a customer wants a service, that service is expected to be available to the customer. However, in many cases, a user or an organization may be denied use of a desired service due to violation of the security of the system. For example, Denial of Service (DoS) attacks can occur that interrupt service provision or even corrupt programming or required files in the system. This DoS attack can result in a large expense in both time and money.
在典型的DoS攻击中,用户被拒绝访问想要的资源。存在多种类型的DoS攻击,但是大部分具有一个共同的目标,即,对受害者剥夺其期望访问的服务和资源。该攻击可以导致生产力和资源的损失。因此,需要一种在通信系统上防止攻击的方法和系统,以保持通信系统的完整性和/或保证通信网络中正确的数据交换。In a typical DoS attack, a user is denied access to desired resources. There are many types of DoS attacks, but most of them have a common goal, that is, to deprive the victim of services and resources that he or she desires to access. This attack can result in loss of productivity and resources. Therefore, there is a need for a method and system for preventing attacks on a communication system in order to maintain the integrity of the communication system and/or ensure correct data exchange in the communication network.
发明内容Contents of the invention
为了提供对本发明的某些方面的基本理解,下面给出了概述。概述并不是本发明的详尽的概括。其目的既不在于标识本发明的关键点或者关键单元,也不在于界定本发明的范围。下述概要仅仅作为下述更详细说明的前序以简化的形式介绍本发明的某些概念。The following presents an overview in order to provide a basic understanding of certain aspects of the invention. This summary is not an extensive overview of the invention. It is intended to neither identify key points or elements of the invention nor to delineate the scope of the invention. The following summary merely presents some concepts of the invention in a simplified form as a prelude to the more detailed description that follows.
在本发明的一个例子中,提供了一种用于移动通信设备的安全切换过程的方法。在一个例子中,包括与移动通信设备相关联的Nonce的测量报告被送到源基站。源基站和目标基站可以通信上下文信息。In one example of the present invention, a method for a secure handover procedure of a mobile communication device is provided. In one example, a measurement report including a Nonce associated with the mobile communication device is sent to the source base station. The source base station and the target base station may communicate context information.
在另一例子中,移动通信设备可以与目标基站证实切换。在另一例子中,目标基站可以把被签名且部分加密的内容转发给核心网络,以用于切换消息的验证。In another example, the mobile communication device can confirm handover with the target base station. In another example, the target base station may forward the signed and partially encrypted content to the core network for verification of the handover message.
附图说明Description of drawings
通过结合相应的附图参考下述说明可以获得对本发明和其优点的更加完整的理解,其中相同的参考标记表示相同的部件,并且其中:A more complete understanding of the present invention and its advantages may be obtained by referring to the following description taken in conjunction with the corresponding drawings, wherein like reference numerals represent like parts, and in which:
图1示意了其中可以实现本发明的各个方面的无线通信系统的框图;Figure 1 illustrates a block diagram of a wireless communication system in which various aspects of the present invention may be implemented;
图2示意了依照本发明的方面的移动终端的框图;Figure 2 illustrates a block diagram of a mobile terminal in accordance with aspects of the invention;
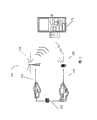
图3示意了依照本发明的方面的系统,其中可以经由相应的演进node-B(eNB)或基站来导出到目标设备的切换决定;Figure 3 illustrates a system in accordance with aspects of the present invention, wherein a handover decision to a target device can be derived via a corresponding evolved node-B (eNB) or base station;
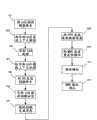
图4是依照本发明的方面的框图,其示出了主动无线电内部接入切换安全的例子;4 is a block diagram illustrating an example of active radio inter-access handover security in accordance with aspects of the present invention;
图5是依照本发明的方面的流程图,其示出了图4的主动无线电内部接入切换安全的例子;5 is a flow diagram illustrating an example of active radio internal access handover security of FIG. 4 in accordance with aspects of the present invention;
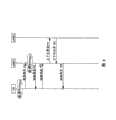
图6是依照本发明的方面示出具有新的往返行程的主动安全切换例子的示图;6 is a diagram illustrating an example of an active safety handover with a new round trip in accordance with aspects of the present invention;
图7是依照本发明的方面的流程图,其示出了图6的具有新的往返行程的主动安全切换的例子;7 is a flow diagram illustrating an example of the active safety handover of FIG. 6 with a new round trip in accordance with aspects of the invention;
图8是依照本发明的方面示出具有预先分配的SKC的主动切换例子的框图;以及8 is a block diagram illustrating an example of active handover with a pre-assigned SKC in accordance with aspects of the present invention; and
图9是依照本发明的方面的流程图,其示出了图8的具有预先分配的SKC的主动切换例子。9 is a flow diagram illustrating the active handover example of FIG. 8 with a pre-assigned SKC in accordance with aspects of the invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
在各种实施例的下述说明中,参考构成说明书一部分的相应的附图,并且在附图中显示了可以实现本发明的各种实施例。应当理解可以利用其它实施例,并且在不脱离本发明的精神和范围的情况下可以进行结构和功能的改进。In the following description of various embodiments, reference is made to the accompanying drawings which form a part hereof, and in which show various embodiments in which the invention may be practiced. It is to be understood that other embodiments may be utilized and structural and functional modifications may be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention.
可以在大量网络和通信协议中利用本发明。图1示意了可以采用本发明的系统和方法的无线通信系统110的例子,一个或多个网络使能的移动设备112,例如个人数字助理(PDA)、蜂窝电话、移动终端、个人视频记录器、便携电视、个人计算机、数码相机、数字可携式摄像机、便携音频设备、便携无线电或者其组合,通过广播网络114和/或蜂窝网络116与服务源122通信。尽管这里描述了移动设备,本发明决不限定于此。例如,可以在静止设备中提供本发明的方面。在静止设备的例子中,还可以提供用于联系服务提供实体的反向信道。移动终端/设备112可以包括数字广播接收机设备。服务源122可以连接到几个服务提供商,其中服务提供商可以把其实际的节目内容或者其服务和节目的信息或描述提供到服务源,服务源进一步把内容或信息提供到移动设备112。几个服务提供商可以包括,但不限定为,一个或多个电视和/或数字电视服务提供商、AM/FM无线服务提供商、SMS/MMS推送服务提供商、互联网内容或访问提供商。The present invention can be utilized in a large number of networks and communication protocols. 1 illustrates an example of a
广播网络114可以包括在DVB-H上的IP数据广播的无线电传输。广播网络114可以通过发射机118广播例如数字或模拟电视信号的服务以及与服务相关的补充内容。广播网络还可以包括无线的,电视或IP数据广播技术的广播网络。广播网络114还可以发送补充内容,其可以包括电视信号、音频和/或视频流、数据流、视频文件、音频文件、软件文件和/或视频游戏。在发送IP数据广播服务的情况中,服务源122可以通过广播网络114向用户设备112传送实际的节目内容,以及通过蜂窝网络116向用户设备112传送附加信息,例如用户权利和对该实际节目内容的访问信息。The
移动设备112还可以通过蜂窝网络116联系服务源122。蜂窝网络116可以包括无线网络和基站收发器发射机120。蜂窝网络可以包括第二/第三代/第四代(2G/3G/4G)蜂窝数据通信网络、全球移动通信网络系统网络(GSM)、OMA广播网络、FLO、MBMS,或者其它无线通信网络,例如WLAN或者WiMAX网络。
在本发明的一个方面中,移动设备112可以包括配置为在蜂窝网络116内发送和/或接收数字无线通信的无线接口。移动设备112通过蜂窝网络116或者广播网络114接收的信息可以包括用户选择、应用、服务、电子图像、音频片断、视频片断、和/或WTAI(无线电话应用接口)消息。作为蜂窝网络116的一部分,一个或多个基站(没有显示)可以支持当接收机设备位于蜂窝网络116的管理区域内时,与接收机设备112的数字通信。In one aspect of the invention,
如图2所示,移动设备112可以包括连接到用户接口130的处理器128、存储器134和/或其它存储器、以及显示器136。移动设备112还可以包括电池150、扬声器152以及天线154。用户接口130还可以包括键盘,触摸屏、语音接口、四方向键、操纵杆、数据手套、鼠标、滚动球、触摸屏,等等。此外,移动设备112可以包括分析模块180,用于接收服务向导(即,ESG片断)中的信息并分析该信息以确定用于编辑服务/交互提供或消息模板的单元、子单元和属性。而且,移动设备112可以包括模板编辑器190,用于基于ESG片断中的属性或者子单元来编辑消息模板。As shown in FIG. 2 ,
处理器128和移动设备112内的其它部件使用的计算机可执行指令和数据可以存储在计算机可读存储器134中。存储器可以实现为只读存储器模块或者随机接入存储器模块的任意组合,可选择的包括易失性和非易失性存储器,其中某些存储器模块可以是可拆卸的。软件140可以存储在存储器134和/或存储设备中,以向处理器128提供指令从而使得移动设备112能够执行各种功能。可替代的,移动设备112的某些或者全部计算机可执行指令可以具体化在硬件或者固件中(没有显示)。Computer-executable instructions and data used by
移动设备112可以被配置为通过特定DVB接收机141基于数字视频广播(DVB)标准——例如DVB-H或者DVB-MHP,来接收、解码并处理传输。此外,接收机设备112还可以被配置为通过FM/AM无线电接收机142、WLAN收发机143以及电信收发机144来接收、解码并处理传输。此外,移动设备可以被配置为基于数字音频广播(DAB)标准(没有显示)接收传输。在本发明的一个方面中,移动设备112可以接收无线电数据流(RDS)消息。The
在DVB标准的一个例子中,一个DVB 10Mbit/s传输可以具有200个50kbit/s的音频节目信道或者50个200kbit/s的视频(TV)节目信道。移动设备112可以被配置为基于数字视频广播-手持(DVB-H)标准或其它DVB标准,例如DVB-MHP、DVB-卫星(DVB-S)、DVB-陆地(DVB-T)或者DVB-电缆(DVB-C)接收、解码并处理传输。相似的,或者可以使用其它数字传输格式来传送补充服务的内容和可用性信息,例如ATSC(先进的电视系统协会)、NTSC(国家电视系统协议)、ISDB-T(综合服务数字广播-陆地)、DAB(数字音频广播)、DMB(数字多媒体广播)或者DIRECTV。此外,数字传输可以被时间分片,例如在DVB-H技术中。时间分片可以降低移动终端的平均功率消耗并且使得能够进行平滑和无缝的切换。时间分片包括与如果使用传统流机制发送数据所需的比特速率相比使用较高的即时比特率以突发的形式发送数据。在这种情况下,移动设备112可以具有一个或多个缓冲存储器,用来在呈现之前存储被解码的时间分片的传输。In one example of the DVB standard, a DVB 10Mbit/s transmission may have 200 audio program channels at 50kbit/s or 50 video (TV) program channels at 200kbit/s. The
图3示出了这样的系统,其中例如移动通信设备的用户设备(UE)可以经由相应的演进node-B(eNB)或基站来导出到目标设备的切换决定。如图3的例子所示,用户设备(UE)301可以与第一基站302交互以向第一基站302发送测量报告。测量报告可以包括,例如对应于UE 301的nonce(即,可以随着时间改变的参数,其可以限制或防止对数据的非授权访问)。UE 301可以进一步与第二基站303通信。例如,UE 301可以向第二基站303发送消息以证实切换。用于证实切换的消息可以包括各种参数。Figure 3 shows a system where a user equipment (UE), such as a mobile communication device, can derive a handover decision to a target device via a corresponding evolved node-B (eNB) or base station. As shown in the example of FIG. 3 , a user equipment (UE) 301 may interact with a first base station 302 to send a measurement report to the first base station 302 . The measurement report may include, for example, a nonce (i.e., a parameter that may change over time that may limit or prevent unauthorized access to data) corresponding to the UE 301. UE 301 may further communicate with second base station 303. For example, UE 301 may send a message to second base station 303 to confirm handover. The message used to confirm handover may include various parameters.
而且,第一基站302和第二基站303可以在切换过程中通信。例如,第一基站302可以向第二基站303发送消息以在关联消息中提供切换的上下文。上下文信息可以进一步被加密以防止第一基站302和第二基站303之间的偷听者。例如,上下文信息可以使用UE特定的保护密钥进行加密,该UE特定的保护密钥可以在第一基站302、第二基站303、以及UE 301的上下文信息中所列的任意基站之间共享。用于加密上下文信息的UE特定保护可以以加密的形式传输(在上下文信息中由第三节点304为第二eNB(例如第二基站303)加密。上下文信息还可以包括由网络中的第三节点304向第二基站加密的其它密钥材料。该其它密钥材料可以用于为UE和第二节点之间的会话创建加密和完整性保护密钥。Furthermore, the first base station 302 and the second base station 303 may communicate during the handover process. For example, the first base station 302 may send a message to the second base station 303 to provide the context of the handover in the associated message. The context information may further be encrypted to prevent eavesdroppers between the first base station 302 and the second base station 303 . For example, the context information may be encrypted using a UE-specific protection key that may be shared between the first base station 302, the second base station 303, and any base station listed in the context information of the UE 301. UE specific protection for encrypting context information may be transmitted in encrypted form (encrypted in context information by third node 304 for the second eNB (e.g. second base station 303). Context information may also include 304 Other keying material encrypted to the second base station. The other keying material may be used to create encryption and integrity protection keys for the session between the UE and the second node.
图4和图5示意了主动无线电内部接入切换安全的一个例子。在该例子中,UE 301可操作地连接到源基站(eNB1)302。UE 301向eNB1 302发送测量报告以发起到目标设备的切换。在该例子中,目标设备可操作地连接到目标基站(eNB2)303。测量报告可以是签名的测量报告,其可以包含对应于UE 301的nonce(NonceUE)。NonceUE可以进一步是之前没有用于创建加密密钥的新的NonceUE。Figures 4 and 5 illustrate an example of active radio inter-access handover security. In this example, a UE 301 is operatively connected to a source base station (eNB1 ) 302 . UE 301 sends a measurement report to eNB1 302 to initiate a handover to the target device. In this example, the target device is operatively connected to a target base station (eNB2) 303 . The measurement report may be a signed measurement report, which may contain a nonce corresponding to UE 301 (NonceUE ). The NonceUE may further be a new NonceUE that has not been used to create an encryption key before.
源基站302可以接收包括NonceUE的测量报告(401,步骤501)并且可以基于接收的测量报告和NonceUE导出到目标基站303的切换决定。因此,在该例子中,源基站302基于来自UE 301的测量报告发起UE 301的切换过程。源基站302可以产生消息(例如上下文推送消息)以发起UE 301的切换过程(402,步骤502)。上下文推送消息可以包括UE 301特定的会话密钥上下文(SKC)。上下文推送消息可以进一步包括源基站在测量报告中接收的NonceUE。此外,上下文推送消息可以包括源基站的标识符(例如IDeNB1)和/或目标基站的标识符(例如IDeNB2),以及与加密相关联的参数和信息,例如在源基站302产生的NonceNET、对应于UE的临时标识符或者UE_TID(UE临时标识符)参数和/或其它RAN上下文信息。该信息还可以被包含在上下文推送消息中并且可以对所发送的数据提供进一步的安全性。例如,可以加密UE_TID和RAN上下文信息,以防止偷听者窃听源基站302和目标基站303之间通信的消息。在一个例子中,可以使用对应于UE 301的会话密钥上下文保护密钥(SPK)(即,SPKUE)加密UE_TID和RAN上下文信息。SPKUE可以是在UE 301的SKC中所包含的基站之间共享的保护密钥,并且可以限定被授权进行数据访问的基站。例如,UE 301的SKC中的每一行可以包括为相应的基站加密的SPKUE。The source base station 302 may receive a measurement report including the NonceUE (401, step 501) and may derive a handover decision to the target base station 303 based on the received measurement report and the NonceUE . Therefore, in this example, the source base station 302 initiates the handover process of the UE 301 based on the measurement report from the UE 301 . The source base station 302 may generate a message (eg, a context push message) to initiate the handover procedure of the UE 301 (402, step 502). The context push message may include a UE 301 specific Session Key Context (SKC). The context push message may further include the NonceUE received by the source base station in the measurement report. In addition, the context push message may include an identifier of the source base station (eg IDeNB1 ) and/or an identifier of the target base station (eg IDeNB2 ), as well as parameters and information associated with encryption, such as the NonceNET generated at the source base station 302 , a temporary identifier corresponding to the UE or a UE_TID (UE Temporary Identifier) parameter and/or other RAN context information. This information can also be included in the context push message and can provide further security to the data sent. For example, UE_TID and RAN context information may be encrypted to prevent eavesdroppers from eavesdropping on messages communicated between the source base station 302 and the target base station 303 . In one example, UE_TID and RAN context information may be encrypted using a Session Key Context Protection Key (SPK) corresponding to UE 301 (ie, SPKUE ). SPKUE may be a protection key shared among base stations included in the SKC of UE 301, and may define base stations authorized for data access. For example, each row in the SKC of UE 301 may include SPKUE encrypted for the corresponding base station.
而且,在该例子中,目标基站303可以从源基站302接收上下文推送消息(402,步骤502)。基于所接收的上下文推送消息,目标基站303可以处理信息(步骤503)。例如,目标基站可以检验所接收的消息是否被正确的发送和接收,或者所接收的消息的目的地是否确实为该目标基站。可以用多种方式完成对消息的正确传送的验证。例如,上下文推送消息可以包括标识参数,例如IDeNB2,用于标识接收相应消息的目标基站。例如,把基站标识为目标基站可以防止数据分组被攻击者向多个基站重放。Also, in this example, the target base station 303 may receive a context push message from the source base station 302 (402, step 502). Based on the received context push message, the target base station 303 may process the information (step 503). For example, the target base station can check whether the received message is correctly sent and received, or whether the destination of the received message is indeed the target base station. Verification of correct delivery of the message can be accomplished in a number of ways. For example, the context push message may include an identification parameter, such as IDeNB2 , used to identify the target base station receiving the corresponding message. For example, identifying a base station as a target base station may prevent data packets from being replayed by an attacker to multiple base stations.
目标基站可以进一步验证核心网络(CN)中为目标基站创建的SKC的行,以验证来自源基站的上下文推送消息的完整性保护。而且,目标基站可以解密相应的SPKUE,并且可以为相应的UE 301创建相应的密码密钥(CK)和/或完整性密钥(IK)(即,CKUE_eNB2和IKUE_eNB2),并且可以解密从源基站接收的UE_TID(UE临时身份)、nonceUE、nonceNET、以及RAN上下文信息。The target base station can further verify the row of the SKC created for the target base station in the core network (CN) to verify the integrity protection of the context push message from the source base station. Moreover, the target base station can decrypt the corresponding SPKUE , and can create a corresponding cipher key (CK) and/or integrity key (IK) (ie, CKUE_eNB2 and IKUE_eNB2 ) for the corresponding UE 301, and can decrypt UE_TID (UE Temporary Identity), nonceUE , nonceNET , and RAN context information received from the source base station.
而且,为了加密数据通信的参数,目标基站可以创建对应于UE 301的密码密钥(CK)和/或完整性密钥(IK)(例如CKUE_eNB2和IKUE_eNB2)。例如,目标基站可以创建CKUE_eNB2并加密无线电链路标识符(例如RLIDeNB2)、上下文ID(CTXIDeNB2)和/或对应于目标基站的UE_TID。在另一例子中,目标基站可以基于目标基站的SKC行中的SKUE_eNB2、和/或NonceUE、和/或NonceNET、和/或UE_TID参数来创建CK和/或IK。因此可以在目标基站加密该内容并且对其进行签名。例如,可以使用从目标基站标识符(例如IDeNB2)和/或NonceUE和/或NonceNET中导出的完整性密钥(例如IKUE_eNB2)完成对加密内容的签名。Furthermore, the target base station may create a cipher key (CK) and/or an integrity key (IK) corresponding to UE 301 (eg, CKUE_eNB2 and IKUE_eNB2 ) in order to encrypt parameters of the data communication. For example, the target base station may create CKUE_eNB2 and encrypt the radio link identifier (eg, RLIDeNB2 ), the context ID (CTXIDeNB2 ), and/or the UE_TID corresponding to the target base station. In another example, the target base station may create CK and/or IK based on SKUE_eNB2 , and/or NonceUE , and/or NonceNET , and/or UE_TID parameters in the SKC row of the target base station. The content can thus be encrypted and signed at the target base station. For example, signing the encrypted content may be done using an integrity key (eg IKUE_eNB2 ) derived from the target base station identifier (eg IDeNB2 ) and/or NonceUE and/or NonceNET .
目标基站可以进一步向源基站发送消息(例如,上下文证实消息)(403,步骤504)。上下文证实消息可以包括,例如,签名的(例如SignUE_eNB2{<内容>})和加密的(例如EncryptUE_eNB2{<内容>})内容,其可以包括源和目标基站的标识符(例如,IDeNB1,IDeNB2)、NonceUE、NonceNet、以及无线电链路标识符(RLIDeNB2)和/或上下文ID(CTXIDeNB2)。上下文证实消息也可以被签名。例如,可以使用可以从SPKUE中导出的完整性密钥(例如IKUE_CTX)来签名上下文证实消息。The target base station may further send a message (for example, a context confirmation message) to the source base station (403, step 504). The context confirmation message may include, for example, signed (eg, SignUE_eNB2 {<content>}) and encrypted (eg, EncryptUE_eNB2 {<content>}) content, which may include identifiers of source and target base stations (eg, IDeNB1 , IDeNB2 ), NonceUE , NonceNet , and radio link identifier (RLIDeNB2 ) and/or context ID (CTXIDeNB2 ). Context confirmation messages can also be signed. For example, the context confirmation message can be signed using an integrity key (eg IKUE_CTX ) that can be derived from the SPKUE .
如图4和5的例子所示,源基站可以从目标基站接收上下文证实消息(步骤504),并且可以进一步在切换命令中转发该消息的内容(404,步骤505)。切换命令消息可以包括例如NonceNET,并且可以进一步使用对应于源基站的完整性密钥(例如,IKUE_eNB1)进行签名以及使用对应于目标基站的完整性密钥(IKUE_eNB2)进行完全地或者部分地签名。UE 301可以接收切换命令消息,并且可以验证来自源基站和目标基站的签名。因此,UE 301可以接收与包括NonceUE、NonceNET、AAA-Key、IDeNB2以及UE_TID的加密数据相对应的参数和数据。基于所接收的数据,UE 301可以导出对应于目标基站的完整性密钥(IK)和密码密钥(CK)(例如,IKUE_eNB2和CKUE_eNB2)。因此,UE 301可以基于IK和CK验证来自目标基站的签名,并且对所接收的RLIDeNB2和CTXIDeNB2进行解密。As shown in the examples of Figures 4 and 5, the source base station may receive the context confirmation message from the target base station (step 504), and may further forward the content of the message in the handover command (404, step 505). The handover command message may include, for example, a NonceNET , and may be further signed with an integrity key (eg, IKUE_eNB1 ) corresponding to the source base station and fully or partially signed with an integrity key (IKUE_eNB2 ) corresponding to the target base station. signature. UE 301 can receive the handover command message and can verify the signatures from the source and target base stations. Accordingly, UE 301 may receive parameters and data corresponding to encrypted data including NonceUE , NonceNET , AAA-Key, IDeNB2 and UE_TID. Based on the received data, UE 301 may derive an integrity key (IK) and a cipher key (CK) corresponding to the target base station (eg, IKUE_eNB2 and CKUE_eNB2 ). Therefore, UE 301 can verify the signature from the target base station based on IK and CK, and decrypt the received RLIDeNB2 and CTXIDeNB2 .
UE 301可以向目标基站发送消息以完成切换。例如,UE 301可以向目标基站发送切换证实消息(405,步骤506)。切换证实消息可以包括,例如,使用在UE 301和核心网络(CN)之间共享的密钥(例如,IKUE_CN和CKUE_CN)创建的被签名和加密的内容。而且,切换证实消息可以包含源和目标基站的标识参数(例如IDeNB1或者IDeNB2)、NonceUE、NonceNET、和/或UE_TID,还可以加密UE_TID从而可以防止基于UE_TID的位置追踪。可以进一步为源基站对该消息内容进行签名,从而使得源基站可以检验UE 301被成功地连接到目标基站。UE 301 may send a message to the target base station to complete the handover. For example, UE 301 may send a handover confirmation message to the target base station (405, step 506). The handover confirmation message may include, for example, signed and encrypted content created using keys shared between UE 301 and the core network (CN) (eg, IKUE_CN and CKUE_CN ). Moreover, the handover confirmation message may contain identification parameters (such as IDeNB1 or IDeNB2 ) of the source and target base stations, NonceUE , NonceNET , and/or UE_TID, and may also encrypt UE_TID so as to prevent location tracking based on UE_TID. The content of the message may be further signed for the source base station, so that the source base station can verify that the UE 301 is successfully connected to the target base station.
目标基站可以接收切换证实消息(步骤506),并且可以把该消息作为证实消息(例如切换完成消息)转发到源基站(406,步骤507)。源基站接收切换完成消息并且可以验证切换完成消息中的信息——例如NonceUE、基站的标识信息的NonceNET信息以及源自UE 301的信息——的准确性。The target base station may receive the handover confirmation message (step 506), and may forward the message as a confirmation message (eg, handover complete message) to the source base station (406, step 507). The source base station receives the handover complete message and can verify the accuracy of the information in the handover complete message, such as NonceUE , NonceNET information of the base station's identification information, and information originating from UE 301 .
此外,被签名和/或加密的信息可以被进一步转发到核心网络(包括移动性管理实体(MME)和/或用户平面实体(UPE))。例如,可以把消息用作核心网络中关于切换消息的验证。在该例子中,目标基站可以向UPE发送被签名且加密的消息(例如,改变映射消息)(407,步骤508),或者可以向MME发送被签名且加密的消息(例如,重定位指示消息)(408,步骤509)。改变映射消息和/或重定位指示消息可以包含对于核心网络签名并且部分加密的切换证实消息。这些消息可以进一步包括UE_TID。Furthermore, the signed and/or encrypted information may be further forwarded to the core network (including a Mobility Management Entity (MME) and/or a User Plane Entity (UPE)). For example, the message can be used as authentication in the core network for handover messages. In this example, the target base station may send a signed and encrypted message (for example, a change mapping message) to the UPE (407, step 508), or may send a signed and encrypted message to the MME (for example, a relocation indication message) (408, step 509). The change map message and/or the relocation indication message may contain a handover confirmation message signed and partially encrypted for the core network. These messages may further include UE_TID.
目标基站可以分别响应于改变映射消息和重定位指示消息,从UPE(409,步骤510)和/或从MME接收确认消息(410,步骤510)。此外,UPE可以通知MME(411,步骤511)。The target base station may receive an acknowledgment message (410, step 510) from the UPE (409, step 510) and/or from the MME in response to the change mapping message and the relocation indication message, respectively. In addition, the UPE may notify the MME (411, step 511).
在该例子中,消息中UE的签名可以防止被劫持的基站欺骗向核心网络(CN)以至MME或者UPE的位置更新。而且,签名的消息防止攻击者向核心网络(CN、MME、UPE)注入位置更新消息。在另一例子中,被劫持的基站可以并不重放位置更新消息并且并不对其他基站或者核心网络发起DoS攻击。In this example, the signature of the UE in the message can prevent the hijacked base station from spoofing the location update to the core network (CN) or MME or UPE. Furthermore, the signed messages prevent attackers from injecting location update messages into the core network (CN, MME, UPE). In another example, a hijacked base station may not replay location update messages and not launch a DoS attack on other base stations or the core network.
图6和7示意了具有新的往返行程的主动切换的另一例子。在该例子中,源基站可以从UE 301接收包括NonceUE的测量报告(601,步骤701)。源基站可以产生NonceNET,并向UE 301发送消息(例如,切换请求消息),以响应于从UE 301接收的测量报告和/或作为到目标基站的切换准备指示(602,步骤702)。切换请求可以包括从UE 301接收的NonceUE和NonceNET。而且,切换请求可以包含目标基站的标识符(例如,IDeNB2)。Figures 6 and 7 illustrate another example of active switching with a new round trip. In this example, the source base station may receive a measurement report including NonceUE from UE 301 (601, step 701). The source base station may generate NonceNET and send a message (eg, a handover request message) to UE 301 in response to a measurement report received from UE 301 and/or as a handover preparation indication to the target base station (602, step 702). The handover request may include NonceUE and NonceNET received from UE 301 . Also, the handover request may contain an identifier of the target base station (eg, IDeNB2 ).
UE 301可以从源基站接收切换请求(602),并且可以导出与UE 301和目标基站相关联的相应会话密钥(例如SKUE_eNB2)。会话密钥可以基于任何数量的加密关联参数,例如目标基站的标识符(IDeNB2)、NonceUE和/或NonceNET、UE_TID等。UE 301 may receive a handover request from a source base station (602), and may derive a corresponding session key (eg, SKUE_eNB2 ) associated with UE 301 and a target base station. The session key may be based on any number of cryptographically associated parameters, such as the target base station's identifier (IDeNB2 ), NonceUE and/or NonceNET , UE_TID, etc.
UE 301可以响应于来自源基站的切换请求消息,发送响应消息(例如,切换响应消息)(603,步骤703)。在该例子中,切换响应可以包括源基站的标识符信息(例如,IDeNB1)、目标基站的标识符信息(例如,IDeNB2)、NonceUE和/或NonceNET。此外,切换响应消息可以被签名和/或至少部分加密。UE 301 may send a response message (eg, a handover response message) in response to the handover request message from the source base station (603, step 703). In this example, the handover response may include identifier information of the source base station (eg, IDeNB1 ), identifier information of the target base station (eg, IDeNB2 ), NonceUE and/or NonceNET . Furthermore, the handover response message may be signed and/or at least partially encrypted.
源基站可以从UE 301接收切换响应消息(步骤703),并可以把该消息转发给目标基站(604,步骤704)。例如,源基站可以在上下文推送消息中把该消息转发给目标基站(步骤704)。上下文推送消息可以包含上述其它参数。The source base station may receive a handover response message from UE 301 (step 703), and may forward the message to the target base station (604, step 704). For example, the source base station may forward the message to the target base station in a context push message (step 704). The context push message may contain other parameters mentioned above.
目标基站可以从源基站接收上下文推送消息(604),并且可以处理该消息。例如,目标基站可以验证所接收的消息是否打算发送到该目标基站并且可以解密关于该目标基站的SKC条目。目标基站还可以导出与UE 301相关联的密码密钥(CK)和完整性密钥(IK)。例如,可以从SKPUE中导出CK和IK(例如,CKUE_CTX和IKUE_CTX)。而且,目标基站可以解密在上下文推送消息中接收的数据。例如,目标基站可以解密来自源基站的在上下文推送消息中接收的UE_TID、NonceUE、NonceNET以及RAN上下文。在另一例子中,目标基站还可以基于加密关联参数(例如,SKUE-eNB2、NonceUE、NonceNET、UE_TID)获得CK和IK(例如,CKUE-eNB2和IKUE_eNB2),可以检验UE签名,可以存储UE RAN上下文和SKC,并且可以保留与目标基站相关联的RLID和CTXID(例如,RLIDeNB2,CTXIDeNB2)。目标基站可以发送消息(例如,上下文证实消息)以向源基站证实该上下文(605,步骤705)。例如,目标基站可以发送上下文证实消息,该上下文证实消息可以被签名并且可以包括标识信息(例如,IDeNB1,IDeNB2)、NonceUE、NonceNET,以及加密信息,例如UE_TID、CTXIDeNB2、RLIDeNB2。The target base station can receive the context push message (604) from the source base station and can process the message. For example, the target base station can verify whether a received message is intended for the target base station and can decrypt the SKC entry for the target base station. The target base station may also derive a cipher key (CK) and an integrity key (IK) associated with UE 301 . For example, CK and IK (eg, CKUE_CTX and IKUE_CTX ) can be derived from the SKPUE . Also, the target base station can decrypt the data received in the context push message. For example, the target base station may decrypt the UE_TID, NonceUE , NonceNET and RAN context received in the context push message from the source base station. In another example, the target base station can also obtain CK and IK (for example, CKUE-eNB2 and IKUE_eNB2 ) based on encrypted association parameters (for example, SKUE-eNB2 , NonceUE , NonceNET , UE_TID ), and can verify the UE signature , the UE RAN context and SKC may be stored, and the RLID and CTXID (eg, RLIDeNB2 , CTXIDeNB2 ) associated with the target base station may be reserved. The target base station may send a message (eg, a context confirmation message) to confirm the context to the source base station (605, step 705). For example, the target base station may send a context confirmation message, which may be signed and may include identification information (eg, IDeNB1 , IDeNB2 ), NonceUE , NonceNET , and encrypted information, such as UE_TID, CTXIDeNB2 , RLIDeNB2 .
在该例子中,源基站可以进一步响应于上下文证实消息向UE 301发送消息。例如,源基站可以在切换命令中向UE转发上下文证实消息(606,步骤706)。UE可以接收切换命令并且可以验证源基站和目标基站的签名。UE 301还可以解密新的RLID和CTXID。In this example, the source base station may further send a message to UE 301 in response to the context confirmation message. For example, the source base station may forward the context confirmation message to the UE in the handover command (606, step 706). The UE may receive the handover command and may verify the signatures of the source and target base stations. UE 301 can also decrypt the new RLID and CTXID.
图8和9示意了具有预先分配的SKC和/或RAN上下文的主动切换的另一例子。在该例子中,源基站可以从UE 301接收包括NonceUE的测量报告(801,步骤901)。响应于从UE 301接收的测量报告,源基站可以产生NonceNET并向目标基站发送消息(例如,上下文预先推送消息)(802,步骤902)。可替代的,上下文预先推送消息可以独立于来自UE 301的测量报告。如果需要,源基站可以向一个或多个基站发送一个或多个消息(例如,上下文预先推进消息),用于准备基站以接收UE。上下文预先推送消息可以包括NonceNET以及从UE 301接收的NonceUE。而且切换请求消息可以包括源基站的标识符(例如,IDeNB1)、目标基站的标识符(例如,IDeNBx)、UE_TID、和或RAN上下文。如果上下文预先推送消息并不包含消息所发往的基站的标识符,则可以按原样向多个基站重新发送该消息。Figures 8 and 9 illustrate another example of active handover with pre-assigned SKC and/or RAN context. In this example, the source base station may receive a measurement report including NonceUE from UE 301 (801, step 901). In response to the measurement report received from UE 301, the source base station may generate a NonceNET and send a message (eg, a context pre-push message) to the target base station (802, step 902). Alternatively, the context pre-push message may be independent of the measurement report from UE 301 . If necessary, the source base station may send one or more messages (eg, context pre-push messages) to one or more base stations for preparing the base stations to receive the UE. The context pre-push message may include NonceNET and NonceUE received from UE 301 . And the handover request message may include an identifier of the source base station (eg, IDeNB1 ), an identifier of the target base station (eg, IDeNBx ), UE_TID, and or RAN context. If the context pre-push message does not contain the identifier of the base station to which the message was sent, the message may be resent as-is to multiple base stations.
在该例子中,目标基站接收上下文预先推送消息并且可以验证和解密关于目标基站的SKC条目,从SKPUE导出CK和IK(例如,CKUE_CTX和IDUE_CTX)并且验证上下文推送消息。此外,目标基站可以解密UE_TID、NonceUE、NonceNET以及RAN上下文,并且可以基于SKUE_eNBx、NonceUE、NonceNET、UE_TID导出与目标基站相关联的CK和IK(例如,CKUE_eNB2和IKUE_eNBx)。而且,目标基站可以存储UE RAN上下文和SKC,并且保留与目标基站相关联的RLID和CTXID(例如,RLIDeNBx和CTXIDeNBx)。目标基站还可以响应于上下文预先推送消息向源基站发送上下文预先证实消息。上下文预先证实消息可以被签名并且可以被部分加密,并且可以包括标识信息(例如,IDeNB1、IDeNBx、NonceUE、NonceNET、UE_TID、CTXIDeNBx、或RLIDeNBx。In this example, the target base station receives the context pre-push message and can verify and decrypt the SKC entry on the target base station, derive CK and IK (eg, CKUE_CTX and IDUE_CTX ) from the SKPUE and verify the context push message. In addition, the target base station can decrypt UE_TID, NonceUE , NonceNET , and RAN context, and can derive CK and IK (eg, CKUE_eNB2 and IKUE_eNBx ) associated with the target base station based on SKUE_eNBx , NonceUE , NonceNET , UE_TID. Also, the target base station may store the UE RAN context and SKC, and retain the RLID and CTXID associated with the target base station (eg, RLIDeNBx and CTXIDeNBx ). The target base station may also send a context pre-confirmation message to the source base station in response to the context pre-push message. The context pre-validation message may be signed and may be partially encrypted, and may include identification information (eg, IDeNB1 , IDeNBx , NonceUE , NonceNET , UE_TID, CTXIDeNBx , or RLIDeNBx .
源基站可以接收上下文预先证实并且可以存储所接收的消息。于是,源基站还可以从UE 301接收包含NonceUE的测量报告,并且可以响应于测量报告,定位与目标基站资源消息对应的消息。响应于接收测量报告,源基站可以向UE 301转发上下文预先证实消息作为切换命令。UE 301可以接收切换命令并且可以基于加密参数,例如,AAA-Key、IDeNBx、NonceUE、NonceNET和/或UE_TID,来导出SKUE-eNBx。The source base station may receive the context pre-validation and may store the received message. Then, the source base station can also receive a measurement report containing NonceUE from UE 301, and can locate a message corresponding to the resource message of the target base station in response to the measurement report. In response to receiving the measurement report, the source base station may forward the context pre-confirmation message to UE 301 as a handover command. UE 301 may receive the handover command and may derive SKUE-eNBx based on encryption parameters, eg, AAA-Key, IDeNBx , NonceUE , NonceNET and/or UE_TID.
本发明包括这里明确公开的任何新的特征或特征组合或者其任意概括。尽管已经根据包括执行本发明的优选模式的特定例子描述了本发明,本领域技术人员清楚上述系统和技术存在多种变化和改变。因此,本发明的精神和范围应当所附加的实施例阐明的那样被宽泛地解释。The invention includes any novel feature or combination of features explicitly disclosed herein or any generalization thereof. While the invention has been described in terms of specific examples including preferred modes of carrying out the invention, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that there are many variations and modifications to the above described systems and techniques. Therefore, the spirit and scope of the present invention should be interpreted broadly as illustrated in the appended examples.
Claims (30)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US75579306P | 2006-01-04 | 2006-01-04 | |
| US60/755,793 | 2006-01-04 | ||
| US11/616,337 | 2006-12-27 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101336554Atrue CN101336554A (en) | 2008-12-31 |
Family
ID=40198346
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2006800517083APendingCN101336554A (en) | 2006-01-04 | 2006-12-28 | Safety assigned handover signaling |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101336554A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102893645A (en)* | 2010-05-10 | 2013-01-23 | 诺基亚公司 | Key derivation during inter-network handover |
| CN109791590A (en)* | 2016-08-22 | 2019-05-21 | 诺基亚技术有限公司 | Security processes |
| CN112956236A (en)* | 2019-02-02 | 2021-06-11 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Method and device for processing safety information in switching process, network equipment and terminal |
- 2006
- 2006-12-28CNCNA2006800517083Apatent/CN101336554A/enactivePending
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102893645A (en)* | 2010-05-10 | 2013-01-23 | 诺基亚公司 | Key derivation during inter-network handover |
| US9264957B2 (en) | 2010-05-10 | 2016-02-16 | Nokia Technologies Oy | Key derivation during inter-network handover |
| CN102893645B (en)* | 2010-05-10 | 2016-04-13 | 诺基亚技术有限公司 | Key during switching between network is derived |
| CN109791590A (en)* | 2016-08-22 | 2019-05-21 | 诺基亚技术有限公司 | Security processes |
| CN112956236A (en)* | 2019-02-02 | 2021-06-11 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Method and device for processing safety information in switching process, network equipment and terminal |
| CN112956236B (en)* | 2019-02-02 | 2022-10-21 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Method and device, network device, and terminal for processing security information during handover |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7864731B2 (en) | Secure distributed handover signaling | |
| CN101110678B (en) | Method and apparatus for security data transmission in mobile communication system | |
| US8983065B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for security in a data processing system | |
| KR101299837B1 (en) | Trust establishment from forward link only to non-forward link only devices | |
| US8121296B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for security in a data processing system | |
| JP4898919B2 (en) | Method and system for continuously transmitting encrypted data of a broadcast service to a mobile terminal device | |
| AU2006202335B2 (en) | Inter-entity coupling method, apparatus and system for content protection | |
| CN103190131B (en) | End-to-end verification of multimedia content | |
| US9467285B2 (en) | Security of a multimedia stream | |
| US20100153709A1 (en) | Trust Establishment From Forward Link Only To Non-Forward Link Only Devices | |
| US8417933B2 (en) | Inter-entity coupling method, apparatus and system for service protection | |
| US20070189535A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for protecting contents supporting broadcast service between service provider and a plurality of mobile stations | |
| CN101336554A (en) | Safety assigned handover signaling | |
| CN101127596A (en) | A method and system for program stream secret key encryption in broadcast mobile TV service | |
| CN101552903A (en) | Television program distribution method and system | |
| EP2316211B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for parental control of wireless broadcast content | |
| CN101399960B (en) | Program stream key encryption method and system in broadcast type mobile television service | |
| EP2109314A1 (en) | Method for protection of keys exchanged between a smartcard and a terminal | |
| CN119342465A (en) | Access method, device and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN101754327A (en) | Multimedia broadcast/multicast business providing method, device and base station |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20081231 |