CN101335986B - Method, network equipment and user equipment for random access - Google Patents
Method, network equipment and user equipment for random accessDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101335986B CN101335986BCN2007101275196ACN200710127519ACN101335986BCN 101335986 BCN101335986 BCN 101335986BCN 2007101275196 ACN2007101275196 ACN 2007101275196ACN 200710127519 ACN200710127519 ACN 200710127519ACN 101335986 BCN101335986 BCN 101335986B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- channel
- random access
- sub
- channels
- uplink
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及通信领域,特别是涉及随机接入的方法、网络设备以及用户设备。The present invention relates to the communication field, in particular to a random access method, network equipment and user equipment.
背景技术Background technique
在UMTS、3GPP LTE和WiMAX等移动通信系统中,终端使用随机接入(Random Access)进程来初始接入无线接入网,并进行上行资源调度请求。In mobile communication systems such as UMTS, 3GPP LTE, and WiMAX, terminals use a random access (Random Access) process to initially access the wireless access network and request uplink resource scheduling.
在时分双工(Time Division Duplex,TDD)系统的随机接入进程中,需要利用随机接入信道(RACH)实现用户设备(User Equipment,UE)的上行同步,过程如下:UE首先在特定的基于竞争的RACH上发送前导序列(随机接入序列码,也称为序列码);基站(Base Station,BS)在成功检测到UE发送的随机接入序列码之后,估计该随机接入序列码到达的时间延时;将时序提前量反馈给终端;终端根据该时序提前量调整发送时间以完成UE的上行同步。In the random access process of a time division duplex (Time Division Duplex, TDD) system, it is necessary to use the random access channel (RACH) to realize the uplink synchronization of the user equipment (User Equipment, UE). The preamble sequence (random access sequence code, also called sequence code) is sent on the competing RACH; the base station (Base Station, BS) estimates that the random access sequence code arrives after successfully detecting the random access sequence code sent by the UE. The timing delay is delayed; the timing advance is fed back to the terminal; the terminal adjusts the sending time according to the timing advance to complete the uplink synchronization of the UE.
为实现好RACH随机接入序列码所承担的功能,对其有如下的要求:在低信噪比下保证检测概率;峰均功率比(Peak-to-Average Power Ratio,PAPR)低以提高上行功放效率;好的自相关性质保证同步精度;好的互相关性质保证不同用户之间的干扰小;足够多的个数来保证接入能力;较低的运算量来保证RACH响应快。In order to realize the function of the RACH random access sequence code, it has the following requirements: to ensure the detection probability under the low signal-to-noise ratio; the peak-to-average power ratio (Peak-to-Average Power Ratio, PAPR) is low to improve the uplink Power amplifier efficiency; good auto-correlation properties ensure synchronization accuracy; good cross-correlation properties ensure low interference between different users; sufficient numbers to ensure access capabilities; low computational load to ensure fast RACH response.
一种在3GPP LTE系统进行随机接入的现有技术中,UE在固定的带宽为1.25MHz持续时间为1ms的突发脉冲(RACH Burst)中随机选取接入码,构成码分复用(Code Division Multiplex,CDM)的RACH方式。为保证发送序列有较低的PAPR,LTE系统选用了Zadaoff-Chu序列。图1给出了LTE中RACH随机接入序列码的结构。In an existing technique of performing random access in a 3GPP LTE system, the UE randomly selects an access code from a RACH Burst with a fixed bandwidth of 1.25 MHz and a duration of 1 ms to form a Code Division Multiplexing (Code Division Multiplexing) Division Multiplex, CDM) RACH mode. In order to ensure that the transmission sequence has a lower PAPR, the LTE system selects the Zadaoff-Chu sequence. Figure 1 shows the structure of RACH random access sequence code in LTE.
图1所示的结构中,整个随机接入序列码的持续时间TPRE=0.8ms,循环前缀持续时间TCP=0.1ms,随机接入序列码(RACH随机接入序列码)所占带宽为BWRA=1.080MHz,对应864个间隔为1.25KHz的子载波。In the structure shown in Figure 1, the duration TPRE of the entire random access sequence code = 0.8ms, the cyclic prefix duration TCP = 0.1ms, and the bandwidth occupied by the random access sequence code (RACH random access sequence code) is BWRA =1.080MHz, corresponding to 864 subcarriers with an interval of 1.25KHz.
在进行本发明创造过程中,发明人发现上述现有随机接入的技术中至少存在以下问题:在多径衰落信道条件下网络侧检测随机接入序列码的难度大,影响上行同步的实现。During the creation process of the present invention, the inventor found that the above-mentioned existing random access technology has at least the following problems: it is difficult for the network side to detect the random access sequence code under the multipath fading channel condition, which affects the realization of uplink synchronization.
原因是:根据上述现有技术随机接入技术,在实现上行同步之前,由于UE没有上行同步,BS无法利用上行导频进行信道估计。因此,对于以上LTE的RACH结构,是采用随机信道的方式上传。由于采用随机信道上传随机接入序列码所占用的带宽(1.08MHz)远大于频率选择性信道(TU)的相干带宽(471KHz),造成上行信道衰落严重,因此会在网络侧对随机接入序列码的检测出现严重困难,很可能导致接收不到信号或接收到质量很差的信号,比如无法识别出随机接入序列码;另外,RACH是上行信道,因此发射功率受到UE的限制,又因为RACH是一个基于竞争的信道,在同一时隙内可能存在有多个不同的用户发出的不同步的随机接入序列码信号,因此用户间存在干扰,导致BS无法识别出随机接入序列码。实践中,针对随机接入序列码的检测,在10-2漏检概率的条件下,经过TU多径衰落信道后的漏检性能比加性高斯白噪声(Additive White Gaussian Noise,AWGN)信道条件下的漏检性能相差了10dB。若无法识别出随机接入序列码,则BS无法根据随机接入序列码计算出时间延时,也就无法实现上行同步。The reason is: according to the above random access technology in the prior art, before the uplink synchronization is realized, the BS cannot use the uplink pilot to perform channel estimation because the UE has no uplink synchronization. Therefore, for the RACH structure of the above LTE, it is uploaded in a random channel manner. Since the bandwidth (1.08MHz) occupied by uploading the random access sequence code on the random channel is much larger than the coherent bandwidth (471KHz) of the frequency selective channel (TU), the uplink channel is severely fading, so the random access sequence code will be modified on the network side. It is very difficult to detect the code, which may cause no signal or poor quality signal to be received, for example, the random access sequence code cannot be recognized; in addition, RACH is an uplink channel, so the transmit power is limited by the UE, and because RACH is a contention-based channel. There may be asynchronous random access sequence code signals sent by multiple different users in the same time slot. Therefore, there is interference between users, which makes the BS unable to identify the random access sequence code. In practice, for random access sequence code detection, under the condition of 10-2 missed detection probability, the missed detection performance after TU multipath fading channel is better than that of Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel condition The missed detection performance under the test is different by 10dB. If the random access sequence code cannot be identified, the BS cannot calculate the time delay according to the random access sequence code, and cannot realize uplink synchronization.
同时,发明人还发现:上述系统中由于采用了长达863点ZC序列,导致了计算复杂度的增加。At the same time, the inventor also found that: the above-mentioned system uses a ZC sequence as long as 863 points, resulting in an increase in computational complexity.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施方式要解决的技术问题是提供一种随机接入的方法、网络设备以及用户设备,可以提高随机接入码检测的成功率,提高随机接入的效率。The technical problem to be solved by the embodiments of the present invention is to provide a random access method, network equipment and user equipment, which can improve the success rate of random access code detection and improve the efficiency of random access.
提供一种随机接入的方法,包括:将随机接入信道分成若干子信道;按照上下行信道的互易性,根据所述下行信道的信息分析所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量;根据所述若干子信道的信道质量选择上行子信道;采用所述选择得到的上行子信道发送随机接入码。A random access method is provided, comprising: dividing a random access channel into several sub-channels; analyzing the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channels according to the information of the downlink channel according to the reciprocity of the uplink and downlink channels; Selecting uplink sub-channels according to the channel quality of the several sub-channels; using the selected uplink sub-channels to send random access codes.
提供一种随机接入的方法,包括:接收利用随机接入信道子信道发送的信息;判断所述接收到的信息中是否包括随机接入码;在所述接收到的信息中包括随机接入码时,根据所述随机接入码获得用户设备的双程时延RTD;下发所述RTD到所述用户设备。A random access method is provided, comprising: receiving information sent by using a random access channel sub-channel; judging whether the received information includes a random access code; including a random access code in the received information code, obtain the round-trip delay RTD of the user equipment according to the random access code; deliver the RTD to the user equipment.
提供一种用户设备,包括信道分割单元、信道质量分析单元、信道选择单元以及发送单元,所述信道分割单元用于将随机接入信道分成若干子信道;所述信道质量分析单元用于按照上下行信道的互易性,根据所述下行信道的信息分析所述信道分割单元分割得到的子信道的信道质量;所述信道选择单元用于根据所述信道质量分析单元得出的所述若干子信道的质量选择上行子信道;所述发送单元用于采用所述信道选择单元选择得到的上行子信道发送随机接入码。A user equipment is provided, including a channel segmentation unit, a channel quality analysis unit, a channel selection unit, and a sending unit, the channel segmentation unit is used for dividing a random access channel into several sub-channels; the channel quality analysis unit is used for The reciprocity of the uplink channel, analyzing the channel quality of the sub-channels obtained by the channel segmentation unit according to the information of the downlink channel; The quality of the channel selects an uplink sub-channel; the sending unit is configured to use the uplink sub-channel selected by the channel selection unit to send a random access code.
提供一种网络设备,包括接收单元、判断单元、时延获取单元以及下发单元,所述接收单元用于接收利用随机接入信道子信道发送的信息;所述判断单元用于判断所述接收单元接收到的信息中是否包括随机接入码;所述时延获取单元用于在所述判断单元判断出接收到的信息中包括随机接入码时,根据所述随机接入码获得用户设备的RTD;所述下发单元用于下发所述时延获取单元获得的RTD到所述用户设备。Provided is a network device, including a receiving unit, a judging unit, a delay obtaining unit, and a sending unit, the receiving unit is used to receive information sent by using a sub-channel of a random access channel; the judging unit is used to judge the received information Whether the information received by the unit includes a random access code; the delay obtaining unit is used to obtain the user equipment according to the random access code when the judging unit determines that the received information includes a random access code the RTD; the sending unit is configured to send the RTD obtained by the delay obtaining unit to the user equipment.
以上技术方案可以看出,由于本实施方式改变现有技术采用随机信道上传随机接入码的方式,而是首先将随机接入信道分成若干子信道,减少上行带宽大于相关带宽造成的信道衰落问题,其次根据下行信道的信息分析所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量,根据信道质量选择上行子信道来发送所述随机接入码,显然提高接收方随机接入码检测的成功率,进而提高随机接入的效率,避免现有技术由于信道衰落造成接收方难以检测到所述随机接入码的技术缺陷。It can be seen from the above technical solutions that this embodiment changes the prior art method of uploading random access codes through random channels, but first divides the random access channel into several sub-channels to reduce the channel fading problem caused by the uplink bandwidth being greater than the relevant bandwidth , and then analyze the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channel according to the information of the downlink channel, and select the uplink sub-channel to send the random access code according to the channel quality, which obviously improves the success rate of random access code detection at the receiver, and then The efficiency of random access is improved, and the technical defect in the prior art that it is difficult for the receiver to detect the random access code due to channel fading is avoided.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是现有技术随机接入码的结构图;FIG. 1 is a structural diagram of a random access code in the prior art;
图2是本发明随机接入方法第三实施方式的流程图;FIG. 2 is a flow chart of the third embodiment of the random access method of the present invention;
图3是图2中步骤A对上行信道进行分割的示意图;Fig. 3 is the schematic diagram that step A in Fig. 2 divides uplink channel;
图4是图2中步骤D发送的随机接入码的结构图;Fig. 4 is a structural diagram of the random access code sent in step D in Fig. 2;
图5是本发明随机接入方法实施方式中发送随机序列码阶段具体方法的流程图;Fig. 5 is a flow chart of a specific method in the stage of sending a random sequence code in the implementation manner of the random access method of the present invention;
图6是本发明随机接入方法实施方式中接收随机序列码阶段具体方法的流程图;FIG. 6 is a flowchart of a specific method at the stage of receiving a random sequence code in an implementation manner of the random access method of the present invention;
图7是图2中步骤F进行峰值检测具体方法的流程图;Fig. 7 is the flow chart of step F among Fig. 2 carrying out the specific method of peak detection;
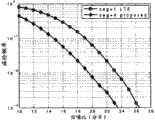
图8是采用本发明随机接入方法实施方式所得到的随机接入码检测成功率与现有技术的对比图;Fig. 8 is a comparison diagram of the detection success rate of the random access code obtained by adopting the implementation mode of the random access method of the present invention and the prior art;
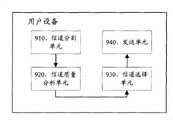
图9是本发明用户设备第一实施方式的原理框图;FIG. 9 is a functional block diagram of a first embodiment of a user equipment according to the present invention;
图10是本发明网络设备第一实施方式的原理框图。Fig. 10 is a functional block diagram of a first embodiment of a network device according to the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明实施方式主要针对现有无线通信系统中随机接入码随机接入序列码的检测性能受多径衰落影响严重的技术问题,以及接收算法计算复杂度高的技术问题,提出一种随机接入方法、网络设备以及用户设备,可以应用于比如TDD系统中。The embodiments of the present invention mainly aim at the technical problem that the detection performance of the random access sequence code of the random access code in the existing wireless communication system is seriously affected by multipath fading, and the technical problem of the high computational complexity of the receiving algorithm, and proposes a random access code The entry method, network equipment and user equipment can be applied to, for example, a TDD system.
本发明提供随机接入方法第一实施方式,包括以下步骤:The present invention provides a first implementation of a random access method, including the following steps:
步骤A:将随机接入信道分成若干子信道;Step A: dividing the random access channel into several sub-channels;
步骤B:按照上下行信道的互易性,根据所述下行信道的信息分析所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量;Step B: According to the reciprocity of the uplink and downlink channels, analyze the channel quality of the sub-channel of the random access channel according to the information of the downlink channel;
步骤C:根据所述若干子信道的信道质量选择上行子信道;Step C: selecting an uplink sub-channel according to the channel quality of the several sub-channels;
步骤D:采用所述选择得到的上行子信道发送随机接入码。Step D: using the selected uplink sub-channel to send a random access code.
以上实施方式中,改变现有技术采用随机信道上传随机接入码的方式,而是首先将随机接入信道分成若干子信道,进行频分(FDM),减少上行带宽大于相关带宽造成的信道衰落问题,其次根据下行信道的信息分析所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量,根据质量来选择上行子信道发送所述随机接入码,即有选择性地根据信道质量来选择上行子信道,显然提高接收方随机接入码检测的成功率,进而提高随机接入的效率,避免现有技术由于信道衰落而造成接收方难以检测到所述随机接入码的技术缺陷,。In the above embodiments, instead of using a random channel to upload random access codes in the prior art, the random access channel is first divided into several sub-channels, and frequency division (FDM) is performed to reduce the channel fading caused by the uplink bandwidth being greater than the relevant bandwidth. Problem, secondly, analyze the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channel according to the information of the downlink channel, select the uplink sub-channel to send the random access code according to the quality, that is, selectively select the uplink sub-channel according to the channel quality, Obviously, the success rate of random access code detection at the receiver is improved, thereby improving the efficiency of random access, and avoiding the technical defect that the receiver is difficult to detect the random access code due to channel fading in the prior art.
通过对随机接入码接收性能的分析可知,信号能量和无线信道情况是影响随机接入序列码检测性能两大关键因素,随着符号发射能量的增加(Ep/N0上升),随机接入序列码的漏检概率下降。随着信道状况的恶化(从AWGN变成TU信道),随机接入序列码的漏检概率上升。在本发明实施方式中,是通过对发送随机接入序列码的信道进行优选的方法,来提升随机接入序列码的检测性能。Through the analysis of the receiving performance of the random access code, it can be known that signal energy and wireless channel conditions are two key factors affecting the detection performance of the random access sequence code. With the increase of the symbol transmission energy (Ep/N0 rises), the random access The probability of missed detection of the sequence code is reduced. As the channel condition deteriorates (from AWGN to TU channel), the probability of missed detection of the random access sequence code increases. In the embodiment of the present invention, the detection performance of the random access sequence code is improved by optimizing the channel for sending the random access sequence code.
本发明实施方式应用于TDD系统中时,是假设在进行随机接入之前,用户设备已经通过下行的同步信道(SCH)获得了与基站的下行同步,因此通过SCH或者下行导频,用户设备可以获得下行信道的信息。由于TDD系统的上下行信道采用相同频率,上下行信道的衰落情况可以看作是相同、相似或对应的,因此上下行信道具有互易性。同时对于中低速移动的用户,在相当长的一段时间内,其信道条件不会发生剧烈的变化。因此本实施方式可以通过下行信道的信息来获得各个上行子信道的信息。当然,在本发明更多实施方式中,上下行信道可以采用大致相同的频率,也可以采用明显不同的频率;所述利用上下行信道的互易性方法中,也可以不限于利用下行信道的衰落情况来评估上行子信道的衰落情况,只要可以利用上下行信道之间的互易性来评估各个上行子信道的信道信息即可。When the embodiments of the present invention are applied to a TDD system, it is assumed that before performing random access, the user equipment has obtained downlink synchronization with the base station through the downlink synchronization channel (SCH), so through the SCH or downlink pilot, the user equipment can Get downlink channel information. Since the uplink and downlink channels of the TDD system use the same frequency, the fading conditions of the uplink and downlink channels can be regarded as the same, similar or corresponding, so the uplink and downlink channels have reciprocity. At the same time, for users moving at medium and low speeds, their channel conditions will not change drastically for a long period of time. Therefore, in this embodiment, the information of each uplink sub-channel can be obtained through the information of the downlink channel. Of course, in more embodiments of the present invention, the uplink and downlink channels may use approximately the same frequency, or may use significantly different frequencies; the reciprocity method using the uplink and downlink channels may not be limited The fading situation of the uplink sub-channel can be evaluated based on the fading situation, as long as the channel information of each uplink sub-channel can be evaluated by using the reciprocity between the uplink and downlink channels.
另外,在接收方,需要接收上传的所述随机接入码,于是本发明提供随机接入方法第二实施方式,包括以下步骤:In addition, on the receiving side, it is necessary to receive the uploaded random access code, so the present invention provides a second implementation of the random access method, including the following steps:
步骤E:接收利用随机接入信道子信道发送的信息;Step E: receiving the information sent by using the random access channel sub-channel;
步骤F:判断所述接收到的信息中是否包括随机接入码;Step F: judging whether the received information includes a random access code;
步骤G:在所述接收到的信息中包括随机接入码时,根据所述随机接入码获得用户设备的双程时延(Round-trip Time Delay,RTD);Step G: when the received information includes a random access code, obtain a round-trip time delay (Round-trip Time Delay, RTD) of the user equipment according to the random access code;
步骤H:下发所述RTD到所述用户设备,进行上行同步。Step H: sending the RTD to the user equipment for uplink synchronization.
上述实施方式是网络侧接收用户设备发送的随机接入码的方法,由于第一实施方式中分割的多个子信道发送信息,并非每个子信道都会发送随机接入码,因此在网络侧接收到利用随机接入信道子信道发送的信息后,需要判断从上行子信道上传的信息中是否包括随机接入码,如果包括,则利用此随机接入码获得用户设备的RTD,下发给用户设备以调整发送时间,实现上行同步。The above-mentioned embodiment is a method for the network side to receive the random access code sent by the user equipment. Since information is sent on multiple sub-channels divided in the first embodiment, not every sub-channel will send a random access code, so the network side receives the random access code using After randomly accessing the information sent by the sub-channel of the channel, it is necessary to judge whether the information uploaded from the uplink sub-channel includes a random access code. If so, use the random access code to obtain the RTD of the user equipment, and send it to the user equipment for Adjust the sending time to achieve uplink synchronization.
由于在随机接入序列码的发送端引入了上行信道的先验信息,同时采用频分FDM、码分(CDM)两种方式共同区分用户,也可以同时采用时分、码分两种方式共同区分用户,因此在本发明实施方式中这种RA方法称之为带信道感知的码频分随机接入(Channel Aware Code and Frequency DivisionMultiplex Random Access)。Since the prior information of the uplink channel is introduced at the sending end of the random access sequence code, two methods of frequency division FDM and code division (CDM) are used to distinguish users at the same time, and two methods of time division and code division can also be used to distinguish users user, so in the embodiment of the present invention, this RA method is called Channel Aware Code and Frequency Division Multiplex Random Access (CFRRA).
为使本发明的目的、技术方案、及优点更加清楚明白,以下参照附图并举实施方式,对本发明进一步详细说明。In order to make the purpose, technical solution, and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
参阅图2,本发明提供随机接入方法第三实施方式,包括以下步骤:Referring to FIG. 2, the present invention provides a third implementation of a random access method, including the following steps:
步骤A:将随机接入信道分成若干子信道;Step A: dividing the random access channel into several sub-channels;
首先,为减小频率选择性衰落对于随机接入序列码检测性能的影响,将整个RACH Burst的可用带宽按照一定的准则(例如相干带宽)分成若干个子信道。First, in order to reduce the impact of frequency selective fading on the detection performance of random access sequence codes, the available bandwidth of the entire RACH Burst is divided into several sub-channels according to certain criteria (such as coherent bandwidth).
考虑到TU信道的相干带宽为471KHz,可以将上行信道的1.08MHz总带宽平均分成4个带宽为270KHz的RACH子信道,分割后的子信道带宽小于带宽为471KHz的相干带宽。其中,每个分割后的子信道最少包含216个子载波,如图3示。Considering that the coherent bandwidth of the TU channel is 471KHz, the 1.08MHz total bandwidth of the uplink channel can be evenly divided into four RACH sub-channels with a bandwidth of 270KHz, and the divided sub-channel bandwidth is smaller than the coherent bandwidth with a bandwidth of 471KHz. Wherein, each divided subchannel includes at least 216 subcarriers, as shown in FIG. 3 .
这里,所述随机接入信道所占的频率对应于下行信道中的相应频带。Here, the frequency occupied by the random access channel corresponds to the corresponding frequency band in the downlink channel.
步骤B:按照上下行信道的互易性,根据所述下行信道的信息分析所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量;Step B: According to the reciprocity of the uplink and downlink channels, analyze the channel quality of the sub-channel of the random access channel according to the information of the downlink channel;
根据所述下行信道中的导频以及TDD信道的互易性获得所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量,可以采用以下方法:Obtain the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channel according to the pilot frequency in the downlink channel and the reciprocity of the TDD channel, the following methods can be used:
分析所述下行信道中各部分信道的衰落情况,分别得出与所述下行信道各部分信道的衰落负相关的所述对应随机接入信道子信道的信道质量。Analyzing the fading conditions of each part of the channel in the downlink channel, respectively obtaining the channel quality of the corresponding random access channel sub-channel that is negatively correlated with the fading of each part of the downlink channel.
也就是说,如果所述下行信道中某部分信道衰落比较多,则评估得出对应此部分下行信道的随机接入信道子信道其信道质量差的结论;如果所述下行信道的信道衰落比较少,则评估得出对应此部分下行信道的随机接入信道子信道其信道质量好的结论。所述随机接入信道子信道评估的结果作为选择发送所述随机接入码的上行信道的基础。That is to say, if a certain part of the channel in the downlink channel has a lot of channel fading, it is evaluated that the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channel corresponding to this part of the downlink channel is poor; if the channel fading of the downlink channel is less , then the evaluation concludes that the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channel corresponding to this part of the downlink channel is good. The evaluation result of the random access channel sub-channel is used as a basis for selecting an uplink channel for sending the random access code.
比如,下行信道包括频带1、2、3,则对应地随机接入信道可分割为1、2、3共3个子信道(当然也可以分为2、4、5个子信道等),其中随机接入信道的子信道1对应于下行信道的频带1,子信道2对应于频带2,子信道3对应于频带3。如果用户设备分析得出所述下行信道中的频带2衰落小,而频带1、3衰落较大,则可以评估得出随机接入信道的子信道2质量好,而随机接入信道的子信道1、3质量差,即评估得出的随机接入信道子信道质量与下行信道频带的衰落情况为负相关关系。For example, if the downlink channel includes
步骤C:根据所述若干子信道的信道质量选择上行子信道;Step C: selecting an uplink sub-channel according to the channel quality of the several sub-channels;
UE在发送随机接入序列码前根据上行信道的信息(例如上行子信道频域衰落幅度等),需要选取性能好的RACH子信道,然后在该子信道上传输随机序列码。基站可以根据检测到随机接入序列码所在的子信道和序列(包括循环移位)来区分不同的用户。Before sending the random access sequence code, the UE needs to select a RACH sub-channel with good performance according to the information of the uplink channel (such as the frequency-domain fading amplitude of the uplink sub-channel), and then transmit the random sequence code on the sub-channel. The base station can distinguish different users according to the subchannel and the sequence (including cyclic shift) where the random access sequence code is detected.
选择上行子信道的方法包括但不限于:Methods for selecting uplink sub-channels include but are not limited to:
在得出与所述下行信道的信道衰落负相关的所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量时,选择与信道衰落小的下行信道部分信道对应的随机接入信道子信道作为上行子信道。When obtaining the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channel negatively correlated with channel fading of the downlink channel, select the random access channel sub-channel corresponding to the downlink channel part channel with small channel fading as the uplink sub-channel.
上述方法还可以这样表述:在得出所述下行信道中信道幅度正相关的所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量时,选择所述下行信道的信道幅度高的所述随机接入信道子信道作为上行子信道。The above method can also be expressed as follows: when obtaining the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channels in the downlink channel whose channel amplitudes are positively correlated, select the random access channel sub-channels with high channel amplitudes of the downlink channel channel as an uplink sub-channel.
上述根据下行信道中信道幅度选择上行子信道的方法中,由于RACH子信道的带宽270KHz小于相干带宽的带宽471KHz,信道的频域冲击响应可以近似看作是平衰落。在这种情况下,影响网络侧对随机接入序列码识别的性能的主要因素是信道的幅度。在此可以使用如下统计量作为信道幅度特性的衡量。In the method for selecting the uplink sub-channel according to the channel amplitude in the downlink channel, since the bandwidth of the RACH sub-channel is 270 KHz less than the bandwidth of the coherent bandwidth 471 KHz, the frequency-domain impulse response of the channel can be approximately regarded as flat fading. In this case, the main factor affecting the performance of the network side in identifying the random access sequence code is the amplitude of the channel. Here, the following statistics can be used as a measure of the channel amplitude characteristics.
式中,H(k)为下行信道的频域冲击响应。ULi为第i个子信道的起始子载波序号,M为一个RACH子信道所包含的子载波个数。In the formula, H(k) is the frequency domain impulse response of the downlink channel. ULi is the starting subcarrier number of the i-th subchannel, and M is the number of subcarriers included in one RACH subchannel.
为提高随机接入序列码发送的能量效率,UE选择下行信道中最大的那个子信道作为发射子信道。即发送子信道的序号I满足如下关系。In order to improve the energy efficiency of random access sequence code transmission, the UE selects the The largest subchannel is used as the transmit subchannel. That is, the sequence number I of the sending subchannel satisfies the following relationship.
为保证随机接入序列码具有理想的循环自相关和恒定的循环互相关,同时保证发射信号有较低的PAPR,每个RACH子信道上可以使用长度为M=211的Zadaoff-Chu序列,定义如下式。总共有210个不同根的ZC序列。In order to ensure that the random access sequence code has ideal cyclic autocorrelation and constant cyclic cross-correlation, and at the same time ensure that the transmitted signal has a low PAPR, a Zadaoff-Chu sequence with a length of M=211 can be used on each RACH sub-channel, defined as follows. In total, there are 210 ZC sequences with different roots.
n=0,…,M-1n=0,...,M-1
v=1,…,Mv=1,...,M
步骤D:采用所述选择得到的上行子信道发送随机接入码。Step D: using the selected uplink sub-channel to send a random access code.
参阅图4,采用所述选择得到的上行子信道,并采用上下行转换点后的第一个上行时隙发送随机接入码。Referring to FIG. 4 , the selected uplink sub-channel is used, and the first uplink time slot after the uplink-downlink conversion point is used to send the random access code.
参阅图5,在一个具体实施方式中,发送随机接入码的方法可以包括:Referring to FIG. 5, in a specific implementation manner, a method for sending a random access code may include:
D1、将RACH序列进行串并转换;D1, performing serial-to-parallel conversion of the RACH sequence;
D2、将并行的RACH序列进行离散傅立叶变换(Discrete Fourier Transform,DFT)变换到频域上;D2, performing discrete Fourier transform (Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT) transformation on the parallel RACH sequence to the frequency domain;
D3、根据获得的下行信息,选择发送随机接入序列码所用的上行RACH子信道;D3. According to the obtained downlink information, select the uplink RACH subchannel used for sending the random access sequence code;
D4、使用快速逆傅立叶变换(Inverse Fast Fourier Transform,IFFT)将频域RACH序列调制到相应的RACH子信道的子载波上;D4, using Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform, IFFT) to modulate the frequency domain RACH sequence onto the subcarrier of the corresponding RACH subchannel;
D5、将完成OFDM调制之后的样本进行并串变换;D5, performing parallel-to-serial conversion on the samples after the OFDM modulation is completed;
D6、在OFDM符号前插入循环前缀。D6. Insert a cyclic prefix before the OFDM symbol.
为了保证上行信道估计的准确性,使RACH信道紧跟着下行信道的最后一个符号(其中包括上下行转换保护时隙)。In order to ensure the accuracy of the uplink channel estimation, the RACH channel is followed by the last symbol of the downlink channel (including the uplink and downlink conversion guard time slot).
以上描述可知,采用本发明随机接入方法在上行阶段的步骤,可以用质量好的信道可以发送包括随机接入序列码在内的各种上行信息,提高在随机接入阶段的信号上行质量。From the above description, it can be seen that by adopting the steps of the random access method in the uplink phase of the present invention, various uplink information including random access sequence codes can be sent through a channel with good quality, and the signal uplink quality in the random access phase can be improved.
以下继续描述本发明随机接入方法实施方式在网络侧接收阶段的步骤:The following continues to describe the steps of the random access method implementation of the present invention in the receiving phase of the network side:
步骤E:接收利用随机接入信道子信道发送的信息;Step E: receiving the information sent by using the random access channel sub-channel;
参阅图6,随机接入序列码的接收检测流程可以包括:Referring to Figure 6, the reception and detection process of the random access sequence code may include:
E1、在将通过天线接收的信号进行模/数(A/D)转换;E1, performing analog/digital (A/D) conversion on signals received through the antenna;
E2、移除随机接入序列码前的循环前缀,并进行串并转换;E2, remove the cyclic prefix before the random access sequence code, and perform serial-to-parallel conversion;
E3、使用快速傅立叶变换(Fast Fourier Transform,FFT)对接收到的时域信号进行OFDM解调;E3, using Fast Fourier Transform (Fast Fourier Transform, FFT) to perform OFDM demodulation on the received time domain signal;
步骤F:判断所述接收到的信息中是否包括随机接入码;Step F: judging whether the received information includes a random access code;
判断是否包括随机接入码的方法可以包括:The method for judging whether to include the random access code may include:
1)通过能量检测,判断哪些RACH子信道上有随机接入序列码的存在;或1) Through energy detection, determine which RACH sub-channels have random access sequence codes; or
2)通过峰值检测,判断哪些RACH子信道上有随机接入序列码的存在。2) Through peak detection, it is judged which RACH sub-channels have random access sequence codes.
这里简单介绍通过峰值检测来判断哪些RACH子信道上有随机接入序列码的存在的方法:Here is a brief introduction to the method of judging which RACH sub-channels have random access sequence codes through peak detection:
I、将本地序列的频域表达式与接收的所述信息进行频域点乘;1. Perform frequency-domain point multiplication of the frequency-domain expression of the local sequence and the received information;
II、进行逆离散傅立叶变换(Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform,IDFT)获得序列的循环时域互相关函数;II. Perform inverse discrete Fourier transform (Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform, IDFT) to obtain the cyclic time-domain cross-correlation function of the sequence;
III、通过循环峰值检测器检测所述时域互相关函数,得出是否包括随机接入码的检测结果。III. Detecting the time-domain cross-correlation function by using a cyclic peak detector to obtain a detection result of whether the random access code is included.
参阅图7,所述峰值检测及RTD估计模块的具体过程如下:Referring to Fig. 7, the specific process of described peak detection and RTD estimation module is as follows:
1)将循环自相关函数分成NCS(系统支持的随机接入序列码循环移位个数,且NCS≤TPRE/TCP)段;1) Divide the cyclic autocorrelation function into NCS (the number of cyclic shifts of random access sequence codes supported by the system, and NCS ≤ TPRE /TCP ) segments;
2)对于每一段进行如下流程:2) Carry out the following process for each segment:
2a.将每一段共E个样本输入循环移位寄存器;2a. Input a total of E samples into the cyclic shift register for each segment;
2b.使用第L号到第E-1号寄存器的值作为噪声估计样本;2b. Use the values of No. L to No. E-1 registers as noise estimation samples;
2c.判断第0号寄存器所对应的样本是否满足判决门限;2c. Judging whether the sample corresponding to the No. 0 register satisfies the judgment threshold;
2cI.如果大于门限,则判断为有随机接入序列码发出,并将循环移位次数通过换算获得首径时偏;2cI. If it is greater than the threshold, it is judged that there is a random access sequence code sent, and the number of cyclic shifts is converted to obtain the head path time offset;
2cII.如果循环移位次数超过D,则说明不存在随机接入序列码,结束流程;2cII. If the number of cyclic shifts exceeds D, it means that there is no random access sequence code, and the process ends;
2cIII.如果小于门限,则将移位寄存器中的值循环左移移位,将循环移位计数器增加1,回到2b处重新执行。2cIII. If it is less than the threshold, then rotate the value in the shift register to the left, increase the circular shift counter by 1, and return to 2b to execute again.
以上流程中的搜索次数D以及循环移位窗口长度E与RACH子信道中的子载波个数M、小区覆盖范围(CP长度TCP)以及系统支持的循环移位个数NCS有关,其满足如下的关系。The number of searches D and the length of the cyclic shift window E in the above process are related to the number of subcarriers M in the RACH subchannel, the coverage of the cell (CP length TCP ) and the number of cyclic shifts NCS supported by the system, which satisfy The relationship is as follows.
E=ceil(M/NCS)E=ceil(M/NCS )
D=ceil(TCPM/TPRE)D=ceil(TCP M/TPRE )
D≤ED≤E
多径扩展参数L满足以下条件:The multipath expansion parameter L satisfies the following conditions:
步骤G:在所述接收到的信息中包括随机接入码时,根据所述随机接入码获得用户设备的RTD;Step G: when the received information includes a random access code, obtain the RTD of the user equipment according to the random access code;
上述图7峰值检测及RTD估计模块的具体过程中的循环移位次数与RTD的对应关系如下式所示:The corresponding relationship between the number of cyclic shifts and the RTD in the specific process of the peak detection and RTD estimation module in Figure 7 above is shown in the following formula:
式中nCS是首次判断有随机接入序列码时循环移位计数器的读数。由此式可以得出下发给用户设备的RTD。In the formula, nCS is the reading of the cyclic shift counter when it is first judged that there is a random access sequence code. From this formula, the RTD delivered to the user equipment can be obtained.
步骤H:下发所述RTD到所述用户设备。Step H: sending the RTD to the user equipment.
下发RTD到所述用户设备后,用户设备即可以利用所述RTD发送时间,实现上行同步。After sending the RTD to the user equipment, the user equipment can use the RTD to send time to realize uplink synchronization.
以上本发明提供随机接入方法第四实施方式至少具有以下技术效果:The above fourth embodiment of the random access method provided by the present invention has at least the following technical effects:
1)随机接入序列码的检测性能有显著的提高1) The detection performance of the random access sequence code has been significantly improved
参阅图8,可以发现,在同时达到10-2的漏检概率条件下,采用本发明实施方式所获得的针对随机接入码的检测性能(菱形线)优于现有技术LTE系统针对随机接入码的检测性能(圆圈线)将近4dB。Referring to Fig. 8, it can be found that under the condition that the probability of missed detection reaches 10−2 at the same time, the detection performance (rhombic line) obtained by adopting the embodiment of the present invention for random access codes is better than that of the prior art LTE system for random access codes. The detection performance (circled line) of the encoded code is nearly 4dB.
产生性能增益的主要原因在于:对上行信道分割成若干子信道后,窄带的子信道落在相干带宽内,因此可以克服频率选择性衰落;同时采用了幅度优选又可以避免整个窄带信号落入深度衰落区域。The main reason for the performance gain is: after the uplink channel is divided into several sub-channels, the narrowband sub-channels fall within the coherent bandwidth, so frequency selective fading can be overcome; at the same time, the amplitude optimization can prevent the entire narrowband signal from falling into the depth fading area.
因此,可以高效率地检测随机接入序列码并进行后续上行同步等进程,通信效率得到提高。Therefore, it is possible to efficiently detect the random access sequence code and perform processes such as subsequent uplink synchronization, and the communication efficiency is improved.
当然,将下行信道分割成若干子信道,也可以使子信道的带宽等于或大于相干带宽,因为分割后的子信道带宽比未分割的总带宽小,显然这些实施方式所达到的技术效果也优于现有技术。Of course, dividing the downlink channel into several sub-channels can also make the bandwidth of the sub-channel equal to or greater than the coherent bandwidth, because the bandwidth of the divided sub-channel is smaller than the total bandwidth of the undivided, obviously the technical effect achieved by these implementations is also superior. in existing technology.
2)可以极大的降低算法的运算复杂度2) Can greatly reduce the computational complexity of the algorithm
由于采用了窄带的上行子信道,同时采用了FDM和CDM来区分用户,因此在不减少接入资源的前提下,缩短了用于接入的序列长度,从而降低了用户相关匹配计算量,可以将网络侧接收机的计算复杂度降低一个数量级以上。Due to the use of narrowband uplink sub-channels and the use of FDM and CDM to distinguish users, the sequence length for access is shortened without reducing access resources, thereby reducing the amount of user-related matching calculations. The computational complexity of the receiver at the network side is reduced by more than one order of magnitude.
在其他实施方式中,对于系统带宽为5MHz的LTE系统,可以支持4个1.25MHz的RACH信道。这时同样可以采用本发明中的方法,根据下行信道信息,利用TDD信道互易性选用上行信道衰落小的那个带宽为1.25MHz的RACH信道发射随机接入序列码。In other implementation manners, for an LTE system with a system bandwidth of 5 MHz, four 1.25 MHz RACH channels may be supported. At this time, the method in the present invention can also be adopted, and according to the downlink channel information, the RACH channel with a bandwidth of 1.25 MHz and a bandwidth of 1.25 MHz with small uplink channel fading is selected to transmit the random access sequence code by utilizing the reciprocity of the TDD channel.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述随机接入方法实施方式中的全部或部分步骤是可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件来完成,所述的程序可以存储于计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,可以包括前述本发明随机接入方法各个实施方式的内容。这里所称得的存储介质,如:ROM/RAM、磁碟、光盘等。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps in the implementation of the above random access method can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program, and the program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium, the program During execution, the contents of the foregoing random access method implementations of the present invention may be included. The storage medium referred to here, such as: ROM/RAM, magnetic disk, optical disk, etc.
本发明还提供用户设备第一实施方式,包括信道分割单元910、信道质量分析单元920、信道选择单元930以及发送单元940。The present invention also provides a first implementation manner of user equipment, including a channel division unit 910 , a channel quality analysis unit 920 , a channel selection unit 930 and a sending unit 940 .
所述信道分割单元910用于将随机接入信道分成若干子信道;所述信道质量分析单元920用于按照上下行信道的互易性,根据所述下行信道的信息分析所述信道分割单元910分割得到的子信道的信道质量;所述信道选择单元930用于在所述随机接入信道的若干子信道中,根据所述信道质量分析单元920得出的所述若干子信道的质量选择上行子信道;所述发送单元940用于采用所述信道选择单元930选择得到的上行子信道发送随机接入码。The channel segmentation unit 910 is used to divide the random access channel into several sub-channels; the channel quality analysis unit 920 is used to analyze the channel segmentation unit 910 according to the information of the downlink channel according to the reciprocity of the uplink and downlink channels The channel quality of the divided sub-channels; the channel selection unit 930 is configured to select an uplink channel according to the quality of the several sub-channels obtained by the channel quality analysis unit 920 among the several sub-channels of the random access channel Sub-channel: the sending unit 940 is configured to use the uplink sub-channel selected by the channel selection unit 930 to send a random access code.
以上本发明第一实施方式可以看出,由于本实施方式改变现有技术采用随机信道上传随机接入码的方式而是首先采用信道分割单元910将随机接入信道分成若干子信道,减少上行带宽大于相关带宽造成的信道衰落问题,其次采用信道质量分析单元920根据下行信道的信息分析所述随机接入信道子信道的信道质量,然后采用信道选择单元930根据子信道质量选择上行子信道发送所述随机接入码,有选择性地根据信道质量来选择上行子信道,显然提高接收方随机接入码检测的成功率,进而提高随机接入的效率,避免现有技术由于信道衰落而造成接收方难以检测到所述随机接入码的技术缺陷。As can be seen from the above first embodiment of the present invention, since this embodiment changes the prior art method of uploading a random access code through a random channel, the channel segmentation unit 910 is first used to divide the random access channel into several sub-channels to reduce the uplink bandwidth. The channel fading problem caused by being larger than the relevant bandwidth, secondly, the channel quality analysis unit 920 is used to analyze the channel quality of the random access channel sub-channel according to the information of the downlink channel, and then the channel selection unit 930 is used to select the uplink sub-channel according to the sub-channel quality. The random access code described above selectively selects the uplink sub-channel according to the channel quality, which obviously improves the success rate of random access code detection at the receiver, thereby improving the efficiency of random access, and avoiding the reception caused by channel fading in the prior art. It is difficult for the party to detect the technical defect of the random access code.
在其他实施方式中:In other implementations:
所述信道分割单元910具体用于将随机接入信道分成若干带宽小于相干带宽的子信道;The channel segmentation unit 910 is specifically configured to divide the random access channel into several sub-channels whose bandwidth is smaller than the coherent bandwidth;
所述信道质量分析单元920用于分析得出所述子信道的信道质量,包括分析所述下行信道中各部分信道的衰落情况,分别得出与所述下行信道各部分信道的衰落负相关的所述对应随机接入信道子信道的信道质量。所述信道选择单元930用于选择信道,包括选择与信道衰落小的下行信道中部分信道对应的随机接入信道子信道作为上行子信道。The channel quality analysis unit 920 is used to analyze and obtain the channel quality of the sub-channels, including analyzing the fading conditions of each part of the channel in the downlink channel, and obtain the negative correlation with the fading of each part of the downlink channel. The channel quality of the corresponding random access channel subchannel. The channel selection unit 930 is used to select a channel, including selecting random access channel sub-channels corresponding to some channels in the downlink channel with small channel fading as uplink sub-channels.
本发明还提供网络设备第一实施方式,包括接收单元1010、判断单元1020、时延获取单元1030以及下发单元1040。The present invention also provides a first implementation manner of a network device, including a receiving unit 1010 , a judging unit 1020 , a delay obtaining unit 1030 and a sending unit 1040 .
所述接收单元1010用于接收利用随机接入信道子信道发送的信息;The receiving unit 1010 is configured to receive information sent by using a random access channel sub-channel;
所述判断单元1020用于判断所述接收单元接收到的信息中是否包括随机接入码;The judging unit 1020 is configured to judge whether the information received by the receiving unit includes a random access code;
所述时延获取单元1030用于在所述判断单元判断出接收到的信息中包括随机接入码时,根据所述随机接入码获得用户设备的RTD;The delay obtaining unit 1030 is configured to obtain the RTD of the user equipment according to the random access code when the judging unit judges that the received information includes a random access code;
所述下发单元1040用于下发所述时延获取单元获得的RTD到所述用户设备。The sending unit 1040 is configured to send the RTD obtained by the delay obtaining unit to the user equipment.
上述网络设备对应上述本发明用户设备第一实施方式,与现有技术不同的是采用接收单元1010接收利用随机接入信道子信道发送的信息;采用判断单元1020判断所述接收单元接收到的信息中是否包括随机接入码,因此与上述本发明用户设备第一实施方式一起提高接收方随机接入码检测的成功率,提高随机接入的效率。The above-mentioned network device corresponds to the above-mentioned first embodiment of the user equipment of the present invention, and is different from the prior art in that the receiving unit 1010 is used to receive the information sent by using the sub-channel of the random access channel; the judging unit 1020 is used to judge the information received by the receiving unit Whether the random access code is included in the above-mentioned user equipment of the present invention, together with the first embodiment of the user equipment of the present invention, the success rate of random access code detection at the receiving side is improved, and the efficiency of random access is improved.
值得说明的是,前述本发明用户设备第一实施方式中的信道分割单元910、信道质量分析单元920、信道选择单元930以及发送单元940可以集成在一个处理模块中;同理,前述本发明网络设备第一实施方式中的各单元也可以集成在一个处理模块中;或者,前述各实施方式各单元中的任何两个或两个以上都可以集成在一个处理模块中。It is worth noting that the channel segmentation unit 910, the channel quality analysis unit 920, the channel selection unit 930, and the sending unit 940 in the aforementioned first embodiment of the user equipment of the present invention can be integrated into one processing module; similarly, the aforementioned network of the present invention The units in the first embodiment of the device may also be integrated into one processing module; or, any two or more of the units in the foregoing embodiments may be integrated into one processing module.
还值得说明的是,本发明用户设备、网络设备实施方式中的各单元既可以采用硬件的形式实现,可软件实现的部分也可以采用软件功能模块的形式实现。相应地,本发明用户设备、网络设备实施方式既可以作为独立的产品销售或使用,可软件实现的部分也可以存储在一个计算机可读取存储介质中进行销售或使用。It is also worth noting that each unit in the embodiment of the user equipment and the network equipment of the present invention can be implemented in the form of hardware, and the parts that can be implemented in software can also be implemented in the form of software function modules. Correspondingly, the embodiment of the user equipment and the network equipment of the present invention can be sold or used as an independent product, and the part that can be implemented by software can also be stored in a computer-readable storage medium for sale or use.
综上,本发明至少可以产生如下技术效果:In summary, the present invention can at least produce the following technical effects:
1、提高网络侧对随机序列码的检测成功率;1. Improve the detection success rate of random sequence codes on the network side;
2、降低算法的运算复杂度。2. Reduce the computational complexity of the algorithm.
以上对本发明所提供的一种随机接入的方法、网络设备以及用户设备通过具体实施例进行了详细介绍,以上实施例的说明只是用于帮助理解本发明的方法及其思想;同时,对于本领域的一般技术人员,依据本发明的思想,在具体实施方式及应用范围上均会有改变之处,综上所述,本说明书内容不应理解为对本发明的限制。The above describes a random access method, network equipment and user equipment provided by the present invention in detail through specific embodiments. The description of the above embodiments is only used to help understand the method and the idea of the present invention; at the same time, for the present invention Those of ordinary skill in the art will have changes in the specific implementation and scope of application according to the idea of the present invention. In summary, the contents of this specification should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
Claims (11)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007101275196ACN101335986B (en) | 2007-06-28 | 2007-06-28 | Method, network equipment and user equipment for random access |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007101275196ACN101335986B (en) | 2007-06-28 | 2007-06-28 | Method, network equipment and user equipment for random access |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101335986A CN101335986A (en) | 2008-12-31 |
| CN101335986Btrue CN101335986B (en) | 2011-11-02 |
Family
ID=40198226
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2007101275196AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101335986B (en) | 2007-06-28 | 2007-06-28 | Method, network equipment and user equipment for random access |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101335986B (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103298136B (en)* | 2012-02-29 | 2016-11-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | A kind of accidental access method, terminal, base station and system |
| CN103079227B (en)* | 2013-02-05 | 2015-04-29 | 武汉邮电科学研究院 | Random access detection method and system used in LTE (Long Term Evolution) system |
| CN104993858B (en)* | 2015-06-01 | 2018-07-20 | 武汉拓宝科技股份有限公司 | A kind of TDD communication means |
| CN108024359B (en) | 2016-11-04 | 2022-01-14 | 华为技术有限公司 | Uplink access method, base station and user equipment |
| KR101962145B1 (en)* | 2017-05-03 | 2019-07-17 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and user equipment for transmitting random access channel signal, and method and base station for receiving random access channel signal |
| CN110247743B (en)* | 2018-03-08 | 2021-11-19 | 中国移动通信有限公司研究院 | Random access method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN116112055A (en)* | 2022-01-11 | 2023-05-12 | 上海前瞻创新研究院有限公司 | Satellite-to-earth network communication link selection method, system, storage medium, and terminal |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1371584A (en)* | 1999-08-27 | 2002-09-25 | 西门子公司 | Method for allocating transmission resources of uplink of radio transmission |
| CN1533199A (en)* | 2003-03-18 | 2004-09-29 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method for detecting user's terminal random cut-in |
| CN1941689A (en)* | 2005-09-29 | 2007-04-04 | 上海原动力通信科技有限公司 | Method for dispatching sub-frequency band of time-division duplex OFDM system |
- 2007
- 2007-06-28CNCN2007101275196Apatent/CN101335986B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1371584A (en)* | 1999-08-27 | 2002-09-25 | 西门子公司 | Method for allocating transmission resources of uplink of radio transmission |
| CN1533199A (en)* | 2003-03-18 | 2004-09-29 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method for detecting user's terminal random cut-in |
| CN1941689A (en)* | 2005-09-29 | 2007-04-04 | 上海原动力通信科技有限公司 | Method for dispatching sub-frequency band of time-division duplex OFDM system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101335986A (en) | 2008-12-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7599327B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for accessing a wireless communication system | |
| KR100865251B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for pilot signal transmission | |
| US9565700B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus for random access in multi-carrier communication systems | |
| JP6031137B2 (en) | Configurable random access channel structure for distance extension in wireless communication systems | |
| EP1571770B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for assigning a ranging channel and transmitting and receiving a ranging signal in an OFDM system | |
| US8331298B2 (en) | Structure and construction method of uplink control channel in mobile wideband wireless access system | |
| CN101335986B (en) | Method, network equipment and user equipment for random access | |
| CN101326739A (en) | Synchronization method and system in communication system | |
| WO2006011953A2 (en) | Method and apparatus for accessing a wireless multi-carrier communication system | |
| US8630279B2 (en) | Method for generating downlink signal, and method for searching cell | |
| CN103108338B (en) | Detection method, device and base station for random access signal | |
| CN101567870B (en) | Detection method and device of home position, peak position and final position of channel response | |
| CN101094027B (en) | Transmitting and receiving method concealing signature sequence of sending structure of user's control information | |
| US20070281654A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for selecting antenna for ranging detection in orthogonal frequency division multiple access system | |
| EP1533968B1 (en) | Signal reception device and method of signal reception timing detection | |
| de Figueiredo et al. | Multi-stage based cross-correlation peak detection for LTE random access preambles | |
| CN102098259A (en) | Signal emission method in multi-subband orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system | |
| Zeng et al. | A novel OFDMA ranging method exploiting multiuser diversity | |
| US8311159B2 (en) | Methods and systems for time tracking in OFDM systems | |
| CN111107562B (en) | Detection method and detection device | |
| CN101931963B (en) | Multi-user ranging detection and collision processing method and device | |
| CN102316067B (en) | Synchronization method in communication system and system | |
| KR101040465B1 (en) | Channel Estimation Method in CAAC Code-based Mobile Communication Systems | |
| JP2010166186A (en) | Apparatus and method of measuring wireless quality | |
| CN102316575A (en) | Synchronized method and system thereof in communication system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20111102 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |