CN101287002A - A method for increasing the number of concurrent media streams in a streaming media server - Google Patents
A method for increasing the number of concurrent media streams in a streaming media serverDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101287002A CN101287002ACNA2008100477941ACN200810047794ACN101287002ACN 101287002 ACN101287002 ACN 101287002ACN A2008100477941 ACNA2008100477941 ACN A2008100477941ACN 200810047794 ACN200810047794 ACN 200810047794ACN 101287002 ACN101287002 ACN 101287002A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- media
- media server
- streaming
- streaming media
- server
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Information Transfer Between Computers (AREA)
- Two-Way Televisions, Distribution Of Moving Picture Or The Like (AREA)
- Computer And Data Communications (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于计算机存储系统媒体文件存取方法,具体涉及一种提高流媒体服务器并发媒体流数量的方法。The invention belongs to a method for accessing media files in a computer storage system, in particular to a method for increasing the number of concurrent media streams of a streaming media server.
背景技术Background technique
流媒体服务是存储系统的一个典型应用,存储系统所能支持的最大并发媒体流数量是存储系统提供流媒体服务时衡量其性能好坏的一个重要标准。分布式存储系统由多个流媒体服务器组成,单个流媒体服务器所能支持的并发媒体流数量直接决定了整个分布式存储系统所能支持的并发媒体流数量。因此,提高单个流媒体服务器所能支持的并发媒体流数量是提高整个分布式存储系统所能支持的并发媒体流数量的关键。Streaming media service is a typical application of the storage system. The maximum number of concurrent media streams that the storage system can support is an important criterion for measuring the performance of the storage system when providing streaming media services. The distributed storage system is composed of multiple streaming media servers. The number of concurrent media streams that a single streaming media server can support directly determines the number of concurrent media streams that the entire distributed storage system can support. Therefore, increasing the number of concurrent media streams that a single streaming media server can support is the key to increasing the number of concurrent media streams that the entire distributed storage system can support.
依据媒体文件被访问的顺序性,媒体文件一般被顺序地置于流媒体服务器上。一次媒体访问所需的数据一般被置于一个流媒体服务器上。提供流媒体服务的分布式存储系统由客户端、元数据服务器和流媒体服务器三部分组成,这三方的通讯过程可以描述为:客户端向元数据服务器发送媒体流建立申请,元数据服务器返回欲建立的媒体流所对应的流媒体服务器,客户端与流媒体服务器之间建立媒体流连接。客户端与流媒体服务器之间的媒体流具有动态性,具体表现在客户端可以随时申请与流媒体服务器建立媒体流连接,也可以随时终止与流媒体服务器已建立的媒体流连接。当客户端与流媒体服务器建立媒体流连接时,流媒体服务器分配一定的磁盘带宽给特定的媒体流,以保证媒体流的服务质量;反之,当客户端终止与流媒体服务器已建立的媒体流连接时,流媒体服务器立即收回已分配给该媒体流的磁盘带宽。基于此特点,流媒体服务器的磁盘带宽分配以媒体流为单位,而不是以某一个具体媒体文件或某一次具体的媒体数据请求为单位。According to the order in which the media files are accessed, the media files are generally sequentially placed on the streaming media server. The data required for a media access is typically placed on a streaming server. The distributed storage system that provides streaming media services is composed of three parts: client, metadata server and streaming media server. The communication process of these three parties can be described as: the client sends a media stream establishment request to the metadata server, and the metadata server returns A streaming media server corresponding to the established media stream, and a media streaming connection is established between the client and the streaming media server. The media flow between the client and the streaming media server is dynamic, specifically, the client can apply to establish a media streaming connection with the streaming media server at any time, and can also terminate the established media streaming connection with the streaming media server at any time. When the client establishes a media stream connection with the streaming media server, the streaming media server allocates a certain amount of disk bandwidth to the specific media stream to ensure the quality of service of the media stream; otherwise, when the client terminates the established media stream with the streaming media server Upon connection, the streaming server immediately reclaims the disk bandwidth allocated to the stream. Based on this feature, the disk bandwidth allocation of the streaming media server is based on media streams, not on a specific media file or a specific media data request.
客户端与流媒体服务器之间建立的各个媒体流均有其服务质量需求。普通的数据读写不允许有任何的数据损失,与其不同的是,流媒体服务允许在满足一定约束条件下的数据丢失。每个媒体流均有其特定的服务质量需求,此特定的服务质量需求对应着特定的数据丢失约束条件。依据媒体文件的编解码特征以及媒体流的服务质量需求,一般以(m,k)约束来表示每个媒体流特定服务质量需求下的数据丢失约束条件;如果将媒体文件分割为N个大小相同的数据单元,(m,k)约束的含义为:任意k个连续的数据单元中,至少有m个数据单元能够在特定的时间点之前由流媒体服务器传输到客户端;表达式(m,k)中,m≤k;m<k时,表示某媒体流允许部分数据未在特定的时间点之前由流媒体服务器传输到客户端;m=k时,表示某媒体流要求任何数据都必须在特定的时间点之前由流媒体服务器传输到客户端。(m,k)是针对特定媒体流的最坏数据丢失约束条件,也是针对具有特定编解码特征的具体的媒体文件的最坏数据丢失约束条件。Each media stream established between the client and the streaming media server has its quality of service requirements. Ordinary data reading and writing does not allow any data loss. Unlike streaming media services, data loss is allowed under certain constraints. Each media stream has its specific QoS requirements, which correspond to specific data loss constraints. According to the encoding and decoding characteristics of media files and the quality of service requirements of media streams, (m, k) constraints are generally used to represent the data loss constraints under the specific quality of service requirements of each media stream; if the media file is divided into N equal-sized The meaning of the (m, k) constraint is: among any k continuous data units, at least m data units can be transmitted from the streaming media server to the client before a specific time point; the expression (m, In k), m≤k; when m<k, it means that a certain media stream allows some data not to be transmitted from the streaming media server to the client before a specific point in time; when m=k, it means that a certain media stream requires that any data must be It is transmitted by the streaming media server to the client before a specific point in time. (m, k) is the worst data loss constraint condition for a specific media stream, and is also the worst data loss constraint condition for a specific media file with a specific codec feature.
现有的方法均利用缓存(Cache)替换算法的优化来提高流媒体服务器的并发媒体流数量。Renu Tewari等人分析了基于一个对象的两个视频流的时间间隔,通过时间间隔的大小判断是否将对象缓存以供其他流读取,从而避免过多的磁盘访问,但是该方案仅针对基于同一个对象的多个视频流的时间间隔进行优化,未针对同一个流媒体服务器的多个对象进行整体的优化,见Renu Tewari,Asit Dan,et al.“Bufferingand Caching in Large-Scale Video Servers”,Proceedings ofCOMPCON 1995。Weifeng Shi等人在Renu Tewari等人提出的方案的基础上明确指出了时间间隔的阈值,但是仍然没有将请求到达速率考虑在内,见Weifeng Shi et al,“Trading memory for disk bandwidthin Video on Demand”,Proceedings of 13th ACM Symposiumon Applied Computing,Feb.1998。Y W Park等人通过对请求到达速率进行分类来动态判断哪些对象需要提前置于缓存,哪些对象不能提前置于缓存,见Y W Park,W Seo,K D Chung,“Multi-phase interval caching for anews on demand server”,IEEE International Conference on MultimediaComputing and Systems,Florence,1999。但是这些方法均未利用媒体文件自身的特征来提高流媒体服务器并发媒体流数量。The existing methods all utilize the optimization of the cache (Cache) replacement algorithm to increase the number of concurrent media streams of the streaming media server. Renu Tewari et al. analyzed the time interval between two video streams based on an object, and judged whether to cache the object for other streams to read according to the size of the time interval, thereby avoiding excessive disk access. The time interval of multiple video streams of an object is optimized, and multiple objects of the same streaming server are not optimized as a whole, see Renu Tewari, Asit Dan, et al. "Buffering and Caching in Large-Scale Video Servers", Proceedings of COMPCON 1995. Weifeng Shi et al. clearly pointed out the threshold of the time interval based on the scheme proposed by Renu Tewari et al., but still did not take the request arrival rate into account, see Weifeng Shi et al, "Trading memory for disk bandwidth Video on Demand" , Proceedings of 13th ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Feb.1998. Y W Park and others dynamically judge which objects need to be placed in the cache in advance by classifying the request arrival rate, and which objects cannot be placed in the cache in advance, see Y W Park, W Seo, K D Chung, "Multi-phase interval caching for anews on demand server”, IEEE International Conference on Multimedia Computing and Systems, Florence, 1999. However, these methods do not use the characteristics of the media file itself to increase the number of concurrent media streams in the streaming media server.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明提出一种提高流媒体服务器并发媒体流数量的方法,目的在于充分利用媒体文件自身的特征,在满足一定的数据丢失约束条件的前提下,减小定位于其上的媒体流的带宽,从而在一定程度上提高流媒体服务器并发媒体流数量。The present invention proposes a method for increasing the number of concurrent media streams of a streaming media server, the purpose of which is to make full use of the characteristics of the media file itself, and reduce the bandwidth of the media streams located on it under the premise of satisfying certain data loss constraints. Thereby, the number of concurrent media streams of the streaming media server is increased to a certain extent.
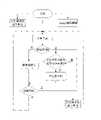
本发明的一种提高流媒体服务器并发媒体流数量的方法,在流媒体服务器上设置一个媒体流等待队列,包括:A kind of method of improving the concurrent media stream quantity of stream media server of the present invention, a media stream waiting queue is set on the stream media server, comprising:
(1)处理媒体流建立申请步骤;流媒体服务器每接收到客户端的媒体流建立申请,均将其置于媒体流等待队列队尾;(1) process the application step of setting up the media stream; every time the streaming media server receives the media stream setting up application of the client, it will be placed at the end of the media stream waiting queue;
(2)计算负载步骤;判断媒体流等待队列是否为空,是则等待,否则从媒体流等待队列队头取出一个媒体流建立申请,计算流媒体服务器的负载R:(2) Calculate the load step; judge whether the media stream waiting queue is empty, if so, wait, otherwise take out a media stream from the head of the media stream waiting queue to set up an application, and calculate the load R of the streaming media server:
其中,N为流媒体服务器与客户端之间建立的媒体流的个数,Bi为第i个媒体流Si所占磁盘带宽,B为流媒体服务器所能提供的峰值总带宽;Wherein, N is the number of media streams set up between the streaming media server and the client, Bi is the disk bandwidth occupied by the i-th media stream Si , and B is the peak total bandwidth that the streaming media server can provide;
(3)满载预判断步骤;判断R是否≥α,是则判定流媒体服务器满载,转步骤(5),否则判定流媒体服务器尚未满载,转步骤(4),α为系统管理员预先设定的满载阈值,0<α<1;(3) Full load pre-judgment step; judge whether R≥α, if it is determined that the streaming media server is fully loaded, turn to step (5), otherwise determine that the streaming media server is not yet fully loaded, turn to step (4), α is preset by the system administrator The full load threshold of , 0<α<1;
(4)媒体流建立步骤;流媒体服务器建立客户端到流媒体服务器之间的媒体流连接,转步骤(6);(4) media flow is set up step; The streaming media server sets up the media streaming connection between the client and the streaming media server, and turns to step (6);
(5)带宽重分配步骤;使部分媒体流定位到相应的编码之后的媒体文件,进行步骤(6);(5) Bandwidth reallocation step; Part media stream is positioned to the media file after corresponding coding, carries out step (6);
(6)满载判断步骤;重新计算流媒体服务器的负载R,判断是否R≥α,是则转步骤(5),否则转步骤(2);(6) Full load judging step; recalculate the load R of the streaming media server, judge whether R≥α, if yes then turn to step (5), otherwise turn to step (2);
(7)(m,k)编码删除步骤;流媒体服务器周期性的计算其负载R和所有对象的访问频率,当R<β时,依对象访问频率由低到高依次删除相应对象的(m,k)编码,β为系统管理员预先设定的轻载阈值,0<β<1;(7) (m, k) encoding deletion step; the streaming media server periodically calculates its load R and the access frequency of all objects, and when R<β, delete the corresponding object (m , k) coding, β is the light load threshold preset by the system administrator, 0<β<1;
所述步骤(1)、步骤(2)~(6)、步骤(7)三者独立进行。The steps (1), steps (2) to (6), and steps (7) are carried out independently.
所述的提高流媒体服务器并发媒体流数量的方法,其特征在于,所述带宽重分配步骤顺序包括下述过程:The method for improving the number of concurrent media streams in the streaming media server is characterized in that the sequence of steps for redistribution of bandwidth comprises the following processes:
(1)流媒体服务器判断是否所有对象均已存在相应的(m,k)编码,是则拒绝媒体流建立申请,否则进行过程(2);(1) The streaming media server judges whether all objects have corresponding (m, k) codes, if so, rejects the media stream establishment application, otherwise proceeds to process (2);
(2)对象热度排序过程;首先,计算流媒体服务器上各个尚未进行(m,k)编码的对象Oi的热度LOi,LOi=SOi,SOi为定位于对象Oi之上的媒体流个数;其次,将对象Oi依其热度按从大到小的顺序排序,并将对象编号依次置于数组L[NUM_OBJECT]中,NUM_OBJECT为流媒体服务器上对象的总个数,i=1,…,M;M为流媒体服务器上尚未进行(m,k)编码的对象个数;(2) Object popularity sorting process; first, calculate the popularity LOi of each object O i that has not yet been encoded (m, k) on the streaming media server, LOi =SOi ,SO iis positioned on the object Oi The number of media streams; secondly, sort the objects Oi in descending order according to their popularity, and place the object numbers in the array L[NUM_OBJECT] in turn, where NUM_OBJECT is the total number of objects on the streaming media server, i =1,...,M; M is the number of objects that have not yet been encoded by (m, k) on the streaming media server;
(3)从数组L[NUM_OBJECT]中依次取出前P个对象进行(m,k)编码,并将编码之后的对象置于流媒体服务器的空闲块,P为系统管理员事先设定的一个整数值;(3) Take out the first P objects in sequence from the array L[NUM_OBJECT] for (m, k) encoding, and put the encoded objects in the free block of the streaming media server, P is an integer set in advance by the system administrator value;
(4)将读取热点对象Oi的请求定位到(m,k)编码之后的对象MKOi上,转所述满载判断步骤。(4) Locate the request for reading the hotspot object Oi to the object MKOi after (m, k) encoding, and turn to the full-load judging step.
本发明充分利用了媒体文件自身的特征,在满足一定的数据丢失约束条件的前提下,减小了定位于其上的媒体流的带宽,从而在一定程度上提高了流媒体服务器并发媒体流数量。The present invention makes full use of the characteristics of the media file itself, and reduces the bandwidth of the media stream located on it under the premise of satisfying certain data loss constraints, thereby increasing the number of concurrent media streams of the streaming media server to a certain extent .
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明流程框图;Fig. 1 is a flow chart of the present invention;
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合实例对本发明做进一步说明。Below in conjunction with example the present invention will be further described.
设t时刻流媒体服务器支持100个媒体流(即取N=100),分别记为S1,S2,S3,......,S100。该100个媒体流所对应的带宽需求分别为B1,B2,B3,......,B100。假设B1=B2=B3=......=B100=1MB/s。流媒体服务器所能提供的峰值带宽为120MB/s(取B=120MB/s)。由于磁盘磁头定位延迟的存在,使得磁盘的实际带宽一般小于其峰值带宽。磁盘的实际带宽取决于请求所需数据在磁盘上的分布,如果请求所需数据在磁盘上连续分布,则磁盘实际带宽较高;反之,请求所需数据在磁盘上的随机离散分布将降低磁盘的实际带宽。假定流媒体服务器当前能够满足该100个媒体流的带宽需求。当第101个媒体流建立申请(设其所需带宽为2MB/s)到达时,首先将其置于流媒体服务器的媒体流等待队列队尾。此时流媒体服务器未处理任何的媒体流建立申请,进入计算负载步骤。流媒体服务器立即将该媒体流建立申请取出,并计算流媒体服务器的负载R,由
当第102个媒体流建立申请(假设其所需带宽为10MB/s)到达时,假设之前的101个媒体流均尚未终止。首先将其置于流媒体服务器的媒体流等待队列队尾。此时流媒体服务器未处理任何的媒体流建立申请,进入计算负载步骤。流媒体服务器立即将该媒体流建立申请取出,并计算流媒体服务器的负载R,由
在带宽重分配步骤,如果P取3,且H个对象的(m,k)约束条件均为(9,10)。则最多可节省0.9*3*1MB/s=2.7MB/s的磁盘带宽,然后进入满负载判断步骤。此时重新计算流媒体服务器的负载R,R=102-2.7+10/120=0.9108,易知R>α,此时再次进入带宽重分配步骤。首先流媒体服务器判断是否所有对象均已存在相应的(m,k)编码。判断的结果是并非所有对象均已存在相应的(m,k)编码,此时进入对象热度排序过程,计算流媒体服务器上所有尚未进行(m,k)编码的对象的热度,将对象依其热度按从大到小的顺序排序,并将对象编号依次置于数组L中。从数组L中顺次取P个对象进行(m,k)编码并将相应的媒体流定位到各个对象所对应的(m,k)编码对象上,最多可节省0.9*6*1MB/s=5.4MB/s的磁盘带宽,然后进入满负载判断步骤。此时重新计算流媒体服务器的负载R,R=102-5.4+10/120=0.8883,R<α,表明客户端到流媒体服务器之间的媒体流连接被接受。In the bandwidth reallocation step, if P is 3, and the constraints (m, k) of the H objects are all (9, 10). Then the disk bandwidth of 0.9*3*1MB/s=2.7MB/s can be saved at most, and then enter the full load judgment step. At this time, recalculate the load R of the streaming media server, R=102-2.7+10/120=0.9108, it is easy to know that R>α, and then enter the bandwidth reallocation step again. First, the streaming media server judges whether all objects have corresponding (m, k) codes. The result of the judgment is that not all objects have corresponding (m, k) codes. At this time, enter the object popularity sorting process, calculate the popularity of all objects that have not been coded (m, k) on the streaming media server, and sort the objects according to their The popularity is sorted in descending order, and the object numbers are placed in the array L in turn. Take P objects sequentially from the array L to perform (m, k) encoding and locate the corresponding media stream on the (m, k) encoding object corresponding to each object, which can save up to 0.9*6*1MB/s= 5.4MB/s disk bandwidth, and then enter the full load judgment step. At this time, the load R of the streaming media server is recalculated, R=102-5.4+10/120=0.8883, R<α, indicating that the media streaming connection between the client and the streaming media server is accepted.
Claims (2)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008100477941ACN101287002B (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2008-05-21 | Method for enhancing amount of concurrent media flow of flow media server |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008100477941ACN101287002B (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2008-05-21 | Method for enhancing amount of concurrent media flow of flow media server |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101287002Atrue CN101287002A (en) | 2008-10-15 |
| CN101287002B CN101287002B (en) | 2010-12-29 |
Family
ID=40058969
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008100477941AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101287002B (en) | 2008-05-21 | 2008-05-21 | Method for enhancing amount of concurrent media flow of flow media server |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101287002B (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102088486A (en)* | 2010-12-31 | 2011-06-08 | 汉王科技股份有限公司 | Handwriting recognition server and handling method thereof as well as handwriting recognition server cluster system |
| CN103313094A (en)* | 2012-03-14 | 2013-09-18 | 上海鱼游网络科技有限公司 | Multimedia playing method and system based on streaming media |
| CN107295080A (en)* | 2017-06-19 | 2017-10-24 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Date storage method and server applied to distributed server cluster |
| CN113296908A (en)* | 2021-04-30 | 2021-08-24 | 重庆紫光华山智安科技有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and medium for improving video image access speed |
| CN116366862A (en)* | 2023-04-07 | 2023-06-30 | 深圳市瑞驰信息技术有限公司 | Video file compression method and system based on Redis message |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100423504C (en)* | 2005-05-12 | 2008-10-01 | 复旦大学 | A method for real-time transmission of large concurrent streaming media |
| CN100469072C (en)* | 2005-09-29 | 2009-03-11 | 西安交通大学 | Multi-source streaming media transmission QoS control method |
| CN100579208C (en)* | 2007-03-30 | 2010-01-06 | Ut斯达康通讯有限公司 | Distributed streaming media distribution system and streaming media memory buffering and scheduling distribution method |
- 2008
- 2008-05-21CNCN2008100477941Apatent/CN101287002B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102088486A (en)* | 2010-12-31 | 2011-06-08 | 汉王科技股份有限公司 | Handwriting recognition server and handling method thereof as well as handwriting recognition server cluster system |
| CN103313094A (en)* | 2012-03-14 | 2013-09-18 | 上海鱼游网络科技有限公司 | Multimedia playing method and system based on streaming media |
| CN107295080A (en)* | 2017-06-19 | 2017-10-24 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Date storage method and server applied to distributed server cluster |
| CN113296908A (en)* | 2021-04-30 | 2021-08-24 | 重庆紫光华山智安科技有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and medium for improving video image access speed |
| CN116366862A (en)* | 2023-04-07 | 2023-06-30 | 深圳市瑞驰信息技术有限公司 | Video file compression method and system based on Redis message |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101287002B (en) | 2010-12-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109547566B (en) | Multithreading uploading optimization method based on memory allocation | |
| CN114564457B (en) | A storage space optimization method and system for database files | |
| CN101287002B (en) | Method for enhancing amount of concurrent media flow of flow media server | |
| US20120303905A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for implementing cache | |
| CN108710639A (en) | A kind of mass small documents access optimization method based on Ceph | |
| CA2335540A1 (en) | Server based smoothing of variable bit rate streams | |
| US10482084B2 (en) | Optimized merge-sorting of data retrieved from parallel storage units | |
| CN113553346A (en) | Large-scale real-time data stream integrated processing, forwarding and storing method and system | |
| CN107590191A (en) | A kind of HDFS mass small documents processing method and system | |
| CN105979274A (en) | Distributive cache storage method for dynamic self-adaptive video streaming media | |
| CN107832423A (en) | A kind of file read/write method for distributed file system | |
| CN102075581A (en) | Data transmission method and device oriented to distributed file system | |
| CN111857992A (en) | Thread resource allocation method and device in Radosgw module | |
| CN111444046A (en) | A data recovery method and distributed data recovery system | |
| CN113835613B (en) | A file reading method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| Anastasiadis et al. | Server-based smoothing of variable bit-rate streams | |
| CN113220212A (en) | Storage node scheduling method and device, storage node, equipment and readable medium | |
| US6742019B1 (en) | Sieved caching for increasing data rate capacity of a heterogeneous striping group | |
| Venkatasubramanian et al. | E ective load management for scalable video servers | |
| CN116723189A (en) | Cloud multi-device multi-data-volume concurrency optimization algorithm | |
| CN111598759B (en) | An urban resource integration system and an urban resource integration method | |
| Kim et al. | VBR video data scheduling using window-based prefetching | |
| Neufeld et al. | The design of a variable bit rate continuous media server | |
| Sarhan et al. | An integrated resource sharing policy for multimedia storage servers based on network-attached disks | |
| CN114546891A (en) | Cache capacity reduction method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20101229 Termination date:20200521 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |