CN101270495A - Method for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on alloy surface - Google Patents
Method for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on alloy surfaceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101270495A CN101270495ACNA2008100275545ACN200810027554ACN101270495ACN 101270495 ACN101270495 ACN 101270495ACN A2008100275545 ACNA2008100275545 ACN A2008100275545ACN 200810027554 ACN200810027554 ACN 200810027554ACN 101270495 ACN101270495 ACN 101270495A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- micro
- arc oxidation
- electrolyte
- pulse
- ceramic coating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000007745plasma electrolytic oxidation reactionMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription88
- 238000005524ceramic coatingMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription48
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription37
- 239000000956alloySubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription31
- 229910045601alloyInorganic materials0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription30
- 238000005260corrosionMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription29
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription57
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium hydroxideChemical compound[OH-].[Na+]HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsabstractdescription33
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 239000000654additiveSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 239000004115Sodium SilicateSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-Nsodium silicateChemical group[Na+].[Na+].[O-][Si]([O-])=ONTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 229910052911sodium silicateInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 150000001412aminesChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 230000000996additive effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 239000008151electrolyte solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription18
- 239000000919ceramicSubstances0.000claimsdescription11
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene glycolChemical groupOCCOLYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-NTriethanolamineChemical compoundOCCN(CCO)CCOGSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- 229910021538boraxInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000004328sodium tetraborateSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 235000010339sodium tetraborateNutrition0.000claimsdescription9
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- ZGTMUACCHSMWAC-UHFFFAOYSA-LEDTA disodium salt (anhydrous)Chemical compound[Na+].[Na+].OC(=O)CN(CC([O-])=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC([O-])=OZGTMUACCHSMWAC-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription8
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlycerineChemical compoundOCC(O)COPEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 235000019832sodium triphosphateNutrition0.000claimsdescription5
- XMVONEAAOPAGAO-UHFFFAOYSA-Nsodium tungstateChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[O-][W]([O-])(=O)=OXMVONEAAOPAGAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription5
- VKYKSIONXSXAKP-UHFFFAOYSA-NhexamethylenetetramineChemical compoundC1N(C2)CN3CN1CN2C3VKYKSIONXSXAKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 235000010299hexamethylene tetramineNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004312hexamethylene tetramineSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000003647oxidationEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000007254oxidation reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- CMZUMMUJMWNLFH-UHFFFAOYSA-Nsodium metavanadateChemical compound[Na+].[O-][V](=O)=OCMZUMMUJMWNLFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000007704transitionEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910000838Al alloyInorganic materials0.000abstractdescription25
- 229910000861Mg alloyInorganic materials0.000abstractdescription13
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-NaluminiumChemical compound[Al]XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription7
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description16
- 230000007797corrosionEffects0.000description11
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description10
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description10
- 239000007921spraySubstances0.000description9
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description7
- 150000003839saltsChemical class0.000description7
- 230000007935neutral effectEffects0.000description6
- PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylenediamineChemical compoundNCCNPIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description5
- 239000011780sodium chlorideSubstances0.000description5
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description4
- 150000004645aluminatesChemical class0.000description3
- 238000005265energy consumptionMethods0.000description3
- 239000000523sampleSubstances0.000description3
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000description3
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000description3
- 2299100010946061 aluminium alloyInorganic materials0.000description2
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-NMagnesiumChemical compound[Mg]FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 229910001069Ti alloyInorganic materials0.000description2
- 229910052782aluminiumInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 239000011777magnesiumSubstances0.000description2
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description2
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description2
- QXNVGIXVLWOKEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-NDisodiumChemical class[Na][Na]QXNVGIXVLWOKEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- IMQLKJBTEOYOSI-GPIVLXJGSA-NInositol-hexakisphosphateChemical compoundOP(O)(=O)O[C@H]1[C@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=OIMQLKJBTEOYOSI-GPIVLXJGSA-N0.000description1
- BPQQTUXANYXVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-NOrthosilicateChemical compound[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-]BPQQTUXANYXVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitaniumChemical compound[Ti]RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- WTHXTWHYLIZJBH-UHFFFAOYSA-Nacetic acid;azaneChemical classN.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=OWTHXTWHYLIZJBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000description1
- 238000007743anodisingMethods0.000description1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 238000005266castingMethods0.000description1
- 230000015556catabolic processEffects0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000description1
- 238000005238degreasingMethods0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 238000003487electrochemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000012530fluidSubstances0.000description1
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000description1
- 238000011065in-situ storageMethods0.000description1
- 238000009413insulationMethods0.000description1
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 229910052749magnesiumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description1
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description1
- 238000010310metallurgical processMethods0.000description1
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000003348petrochemical agentSubstances0.000description1
- 235000002949phytic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 238000007639printingMethods0.000description1
- 230000001737promoting effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000002904solventSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001179sorption measurementMethods0.000description1
- 239000000725suspensionSubstances0.000description1
- 239000004753textileSubstances0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Other Surface Treatments For Metallic Materials (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种合金表面的防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层,具体涉及合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的方法,该方法单位面积能耗低,适于一次性在铝、镁合金构件表面大面积制备防腐、抗磨陶瓷涂层的表面。The invention relates to an anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating on the surface of an alloy, in particular to a method for preparing an anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of an alloy. The method has low energy consumption per unit area and is suitable for one-time coating on aluminum and magnesium alloy components The surface is prepared with anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating on a large area.
背景技术Background technique
微弧氧化制备铝、镁、钛合金表面陶瓷涂层技术系在较高电压作用下,绝缘层被击穿,在工件表面形成微等离子体环境。在这样的环境中,表面电化学反应、等离子辅助反应及物理冶金过程同时发生,最终在工件表面以原位生成致密、牢固的陶瓷涂层。该技术极大地扩展了铝、镁、钛合金材料的应用范围,在航空、航天、兵器、机械、汽车、石油化工、纺织、印刷、烟机、电子、轻工、医疗等行业受到越来越多的重视,在部分领域开始进入实际应用。Micro-arc oxidation preparation of aluminum, magnesium, titanium alloy surface ceramic coating technology is under the action of high voltage, the insulating layer is broken down, and a micro plasma environment is formed on the surface of the workpiece. In such an environment, surface electrochemical reactions, plasma-assisted reactions, and physical metallurgical processes occur simultaneously, and finally a dense and firm ceramic coating is formed in situ on the surface of the workpiece. This technology has greatly expanded the application scope of aluminum, magnesium and titanium alloy materials, and is increasingly popular in industries such as aviation, aerospace, weapons, machinery, automobiles, petrochemicals, textiles, printing, hoods, electronics, light industry, and medical treatment. More attention has been paid to it, and it has begun to enter practical applications in some fields.
目前,利用微弧氧化技术在促进膜的生长速度、提高膜的耐磨、抗蚀能力、表面致密度等多方面均取得很大进展。申请号为2006100009889.5的中国发明专利申请公开了铝酸盐体系铝合金表面微弧氧化方法,电压为305V-580V,电流密度为3A/dm2-5A/dm2。且铝酸盐电解质体系的一个特点是溶度积不高,易于形成悬浊态,电解质成分控制比较困难。申请号为01102262.0的中国发明专利采用硅酸钠电介质体系制备铝合金表面陶瓷膜。专利号为ZL200310122201.0的中国发明专利公开了混合富氧酸盐处理铝合金铸件的方法,实施电压较高,达到550-650V。At present, the use of micro-arc oxidation technology has made great progress in promoting the growth rate of the film, improving the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and surface density of the film. The Chinese invention patent application with application number 2006100009889.5 discloses a method for micro-arc oxidation on the surface of aluminate aluminum alloy with a voltage of 305V-580V and a current density of 3A/dm2-5A/dm2. And one of the characteristics of the aluminate electrolyte system is that the solubility product is not high, it is easy to form a suspension state, and it is difficult to control the electrolyte composition. The Chinese invention patent with application number 01102262.0 uses a sodium silicate dielectric system to prepare a ceramic film on the surface of an aluminum alloy. The Chinese invention patent with the patent number ZL200310122201.0 discloses a method for treating aluminum alloy castings with a mixed oxygen-rich salt, and the implementation voltage is relatively high, reaching 550-650V.
申请号为200410100411.4的专利中电解质以植酸盐为主要成分在镁合金表面制备陶瓷涂层。申请号为200510010500.4、200610042990.0、200610016709.6的系列专利采用硅酸盐体系或铝酸盐体系制备镁合金表面微弧氧化陶瓷涂层,既有直流电源模式,也有直流脉冲、交流脉冲电源模式。In the patent application number 200410100411.4, the electrolyte uses phytate as the main component to prepare a ceramic coating on the surface of the magnesium alloy. The series of patents with application numbers 200510010500.4, 200610042990.0, and 200610016709.6 use silicate system or aluminate system to prepare micro-arc oxidation ceramic coatings on the surface of magnesium alloys. There are not only DC power supply modes, but also DC pulse and AC pulse power supply modes.
上述专利技术中单位功率密度高是一个共性问题,甚至某些处理电解质的长期稳定性及成分可控性尚需改善:要求一次性处理1平方米面积的铝、镁合金表面,所需电源瞬时最大功率接近或远远超过100KVA。由于一次性处理大面积铝合金构件时需要大功率电源,给电网带来极大压力,同时生产能力也受到极大限制。如果把一个表面积大于2平方米的构件划分成为多个区域,采用上述专利技术对这些小区域逐一微弧氧化,从而达到大面积微弧氧化制备涂层涂层的方法,在小区域划分界限附近可能造成局部未覆盖或者涂层叠加,表面整体的一致均匀性将难以保证。因此研究开发环保、低能耗微弧氧化技术,达到一次性大面积处理铝、镁合金表面陶瓷涂层的目标显得十分重要。The high unit power density in the above-mentioned patented technologies is a common problem, and even the long-term stability and composition controllability of some processing electrolytes still need to be improved: it is required to treat the surface of aluminum and magnesium alloys with an area of 1 square meter at one time, and the required power supply instantaneous The maximum power is close to or far exceeds 100KVA. Due to the need for a high-power power supply when processing large-area aluminum alloy components at one time, it brings great pressure to the power grid, and the production capacity is also greatly limited. If a component with a surface area greater than 2 square meters is divided into multiple areas, the above-mentioned patented technology is used to micro-arc oxidize these small areas one by one, so as to achieve the method of preparing coatings by micro-arc oxidation on a large area, near the boundary of the small area division It may cause partial uncovering or superposition of coatings, and it will be difficult to guarantee the uniformity of the overall surface. Therefore, it is very important to research and develop environmental protection and low energy consumption micro-arc oxidation technology to achieve the goal of one-time large-area treatment of ceramic coatings on the surface of aluminum and magnesium alloys.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于克服现有技术存在的问题,提供一种单位功率密度低,成膜速度快、耐蚀性能好,表面硬度高的合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的方法,达到处理1平方米铝合金、镁合金表面的瞬时最大功率低于40千瓦,30分钟时间内获得30-50微米厚的陶瓷涂层。The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the problems existing in the prior art, and provide a method for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coatings by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of an alloy with low unit power density, fast film-forming speed, good corrosion resistance, and high surface hardness. The instantaneous maximum power to treat the surface of 1 square meter of aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy is lower than 40 kilowatts, and a ceramic coating with a thickness of 30-50 microns can be obtained within 30 minutes.
本发明的目的可通过如下技术方案来实现。The purpose of the present invention can be achieved through the following technical solutions.
一种合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的方法,包括如下步骤和工艺条件:A method for preparing an anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of an alloy, comprising the following steps and process conditions:
(1)配置电解液:电解液各组分浓度为硅酸钠20-100g/L、氢氧化钠5-10g/L和有机胺添加剂5-15ml/L;所述有机胺添加剂选自乙二胺、丙三醇、三乙醇胺、六次甲基四胺中的一种或多种;(1) Configure the electrolyte: the concentration of each component of the electrolyte is sodium silicate 20-100g/L, sodium hydroxide 5-10g/L and organic amine additive 5-15ml/L; the organic amine additive is selected from ethylene glycol One or more of amine, glycerol, triethanolamine, hexamethylenetetramine;
(2)设置非对称交、直流脉冲电源电参数:根据防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层膜厚,按1-1.5微米/分钟的膜层生长速度设置微弧氧化处理时间;并以电流方式控制输出电源,电流输出为非对称直流脉冲或交流非对称脉冲;采用非对称直流脉冲输出时,限制电压设置为500V,最大电流设置按照处理构件的总表面积计算设置,其中单位面积电流密度为50-100A/平方米;脉冲频率为100-700Hz,脉冲占空比为20-90%;采用非对称交流脉冲输出时,最小电压设置为-500V,最大正负脉冲电流的比值设置为10∶1-2∶1,正负脉冲数目比值设置为10∶1-2∶1;所述的非对称交、直流微弧氧化电源正负脉冲峰值可调,脉冲波型为方波,正相脉冲过度到负相脉冲的死区不超过60us;(2) Set the electrical parameters of asymmetric AC and DC pulse power supply: set the micro-arc oxidation treatment time according to the film growth rate of 1-1.5 microns/min according to the thickness of the anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating; and control the output power by current mode , the current output is asymmetrical DC pulse or AC asymmetrical pulse; when using asymmetrical DC pulse output, the limit voltage is set to 500V, and the maximum current setting is calculated and set according to the total surface area of the processing components, where the current density per unit area is 50-100A/ square meter; the pulse frequency is 100-700Hz, and the pulse duty cycle is 20-90%; when using asymmetric AC pulse output, the minimum voltage is set to -500V, and the ratio of the maximum positive and negative pulse current is set to 10:1-2: 1. The ratio of the number of positive and negative pulses is set to 10:1-2:1; the peak value of the positive and negative pulses of the asymmetric AC and DC micro-arc oxidation power supply is adjustable, the pulse waveform is square wave, and the positive phase pulse transitions to the negative phase The pulse dead zone does not exceed 60us;
(3)微弧氧化处理:将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,并置入电解液中,启动非对称交、直流微弧氧化电源,控制电解液温度不高于45℃,微弧氧化处理到步骤(2)的设置时间;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy component to the electrode rod, and put it into the electrolyte, start the asymmetrical AC and DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, control the temperature of the electrolyte not higher than 45°C, and micro-arc oxidation Arc oxidation treatment to the setting time of step (2); remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
所述步骤(1)的电解液还包括其它辅助添加剂组分,浓度为5-15g/L,其它辅助添加剂组分选自硼砂、钨酸钠、偏钒酸钠、三聚磷酸钠、乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐中的一种或多种。The electrolytic solution of described step (1) also includes other auxiliary additive components, and concentration is 5-15g/L, and other auxiliary additive components are selected from borax, sodium tungstate, sodium metavanadate, sodium tripolyphosphate, ethylene glycol One or more of the disodium salts of amine tetraacetic acid.
所述的控制电解液温度不高于45℃,通过如下方法控制温度:如果一次处理工件多,工件表面积大,电解质溶液温度升高超过45℃,启动压力泵,使电解液流经散热片,得到冷却,保证电解质溶液温度在45℃以下,电解质可以长期使用。The temperature of the control electrolyte is not higher than 45°C, and the temperature is controlled by the following method: if there are many workpieces to be processed at one time, the surface area of the workpiece is large, and the temperature of the electrolyte solution rises above 45°C, start the pressure pump to make the electrolyte flow through the heat sink, It is cooled to ensure that the temperature of the electrolyte solution is below 45°C, and the electrolyte can be used for a long time.
本发明和现有技术相比,具有如下优点和有益效果:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages and beneficial effects:
(1)本发明在铝、镁合金表面制备陶瓷涂层所需单位功率密度低,成膜速度快:采用100KVA电源,可以一次性处理至少2平方米铝合金表面积,陶瓷涂层生长速度达到1-1.5微米/分钟(在30分钟内获得30-45微米陶瓷涂层)。(1) The present invention prepares the required unit power density of ceramic coating on aluminum, magnesium alloy surface is low, and film-forming speed is fast: adopt 100KVA power supply, can process at least 2 square meters of aluminum alloy surface area at one time, ceramic coating growth speed reaches 1 - 1.5 microns/min (30-45 micron ceramic coating in 30 minutes).
(2)陶瓷涂层均匀致密,铝合金硬度达到1200-1300Hv(显微硬度),中性盐雾腐蚀试验超过1500小时,无明显腐蚀。镁合金表面纳米力学探针硬度1090,CASS盐雾试验96小时,无点蚀痕迹,9级以上。(2) The ceramic coating is uniform and dense, the hardness of the aluminum alloy reaches 1200-1300Hv (microhardness), and the neutral salt spray corrosion test exceeds 1500 hours without obvious corrosion. The nanomechanical probe hardness of the magnesium alloy surface is 1090, and the CASS salt spray test lasts for 96 hours. There is no pitting trace, and it is above
附图说明Description of drawings
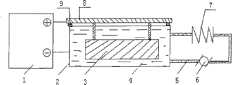
图1为本发明的合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的装置结构示意图。Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the device for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coatings by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of alloys of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了更好地理解本发明的技术特点,下面结合实施例对本发明作进一步的说明,需要说明的是,实施例并不是对本发明保护范围的限制。In order to better understand the technical characteristics of the present invention, the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the examples. It should be noted that the examples are not intended to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
如图1所示,合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的装置包括非对称交直流脉冲微弧氧化电源1、不锈钢电解质槽2、被处理构件3、电解质溶液4、导液管道5、压力泵6、散热片7、电极棒及工件挂具8和绝缘垫块9。非对称交直流脉冲微弧氧化电源1的正极与电极棒及工件挂具8连接,其负极与不锈钢电解质槽2连接,不锈钢电解质槽2内盛有电解质溶液4,被处理构件3通过电极棒及工件挂具8挂在电解质溶液4中,电解槽中的电解质溶液4通过导液管道5与压力泵6形成循环,并流经散热片7。电极棒置于电解槽上,采用绝缘垫块9将它们隔离。处理时,将铝合金被处理构件用5%氢氧化钠溶液或其它除油溶剂浸泡5分钟除去表面油污;然后用挂具在电极棒及工件挂具8上,将被处理构件3浸入电解质溶液4中;不锈钢电解槽连接微弧氧化电源1的一极(直流脉冲模式时,为阴极),电极棒及被处理构件连接微弧氧化电源的另一极(直流脉冲模式时,为阳极);电解质溶液超过45℃时启动压力泵6,使电解槽中的电解质通过管道5,流经散热片7获得冷却效果。根据构件大小、一次性处理面积制作相应容积的电解槽,确保待处理表面完全浸入电解液中。As shown in Figure 1, the device for preparing anti-corrosion and wear-resistant ceramic coatings by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of alloys includes an asymmetric AC-DC pulse micro-arc
本发明所用的非对称交直流微弧氧化电源的基本技术参数为正负脉冲峰值可调,占空比连续0-90%可调;正反电压0-500伏特连续可调;脉冲频率0-1000Hz连续可调;稳流状态工作时,平均电流波动小于1%;稳压状态工作时,电压波动小于1%;脉冲波型为方波,正相脉冲过度到负相脉冲的死区不超过60us;工作时间在0-1000分钟内任意设置;正负脉冲数目、脉冲形状可任意调节。该电源可采用IGBT电源。The basic technical parameters of the asymmetrical AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply used in the present invention are adjustable positive and negative pulse peak values, continuously adjustable duty cycle of 0-90%; positive and negative voltages of 0-500 volts continuously adjustable; pulse frequency of 0- 1000Hz continuously adjustable; when working in a steady current state, the average current fluctuation is less than 1%; when working in a steady voltage state, the voltage fluctuation is less than 1%; the pulse waveform is square wave, and the dead zone between the positive phase pulse and the negative phase pulse does not exceed 60us; the working time can be set arbitrarily within 0-1000 minutes; the number of positive and negative pulses and pulse shape can be adjusted arbitrarily. The power supply can use IGBT power supply.
实施例1:处理一批LY12铝合金构件,内外总表面积为0.3平方米Example 1: Treat a batch of LY12 aluminum alloy components with a total internal and external surface area of 0.3 square meters
一种铝合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的方法,包括如下步骤和工艺条件:A method for preparing an anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of an aluminum alloy, comprising the following steps and process conditions:
(1)配置电解液:配置电解质溶液100L,电解质成分为:硅酸钠50g/L、氢氧化钠5g/L、有机胺5ml/L(其中乙二胺占50%,三乙醇胺占50%)和其它辅助添加剂11g/L(其中,乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐2g/l、硼砂5g/l、钨酸钠3g/l和三聚磷酸钠1g/l)。(1) Prepare electrolyte: prepare 100L electrolyte solution, electrolyte composition: sodium silicate 50g/L, sodium hydroxide 5g/L, organic amine 5ml/L (among which ethylenediamine accounts for 50%, triethanolamine accounts for 50%) And other auxiliary additives 11g/L (among them, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt 2g/l, borax 5g/l, sodium tungstate 3g/l and sodium tripolyphosphate 1g/l).
(2)设置电源电参数:电源输出为非对称交流脉冲,最小电压设置为-500V,脉冲高度由电流大小控制:最大电流设置30A(100A/平方米);频率600Hz;正负脉冲数比4∶1;正负脉冲电流比3∶1;占空比55%;微弧氧化时间40分钟。(2) Set the electrical parameters of the power supply: the output of the power supply is an asymmetrical AC pulse, the minimum voltage is set to -500V, and the pulse height is controlled by the current size: the maximum current is set to 30A (100A/square meter); the frequency is 600Hz; the ratio of positive and negative pulses is 4 : 1; positive and negative pulse current ratio 3: 1; duty cycle 55%; micro-arc oxidation time 40 minutes.
(3)微弧氧化处理:用挂具将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,置入步骤(1)的电解液中,启动非对称交直流微弧氧化电源,微弧氧化处理到设置时间(微弧氧化时间30分钟),控制电解液温度不高于45℃;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后即可获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy component to the electrode rod with a hanger, put it into the electrolyte in step (1), start the asymmetric AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, and the micro-arc oxidation treatment reaches Set the time (micro-arc oxidation time 30 minutes), control the temperature of the electrolyte not higher than 45°C; remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
微弧氧化处理过程中:起弧电压160V,微弧氧化最终电压350V。获得均匀致密的棕灰色陶瓷涂层。经测试,表面陶瓷涂层厚度50微米,表面硬度为1300Hv,经1500小时3.5%NaCl中性盐雾试验,未见腐蚀痕迹。本实例中处LY12铝合金表面的最大瞬时电源输出功率为35KW/平方米(100AX350V),该值不足申请号2006100009889.5所需电源瞬时功率的一半(300AX305V)。与铝合金表面传统阳极氧化处理速度(0.2-0.5微米/分钟)、硬度(HV300-500)及耐蚀性比较,本发明所制备陶瓷涂层这些方面性能均有显著提高。During the micro-arc oxidation process: the arc starting voltage is 160V, and the final voltage of the micro-arc oxidation is 350V. A uniform and dense brown-gray ceramic coating is obtained. After testing, the thickness of the surface ceramic coating is 50 microns, and the surface hardness is 1300Hv. After 1500 hours of 3.5% NaCl neutral salt spray test, there is no trace of corrosion. In this example, the maximum instantaneous power output power on the surface of LY12 aluminum alloy is 35KW/square meter (100AX350V), which is less than half of the instantaneous power required by the application number 2006100009889.5 (300AX305V). Compared with the traditional anodizing treatment speed (0.2-0.5 micron/minute), hardness (HV300-500) and corrosion resistance of the aluminum alloy surface, the performance of the ceramic coating prepared by the invention is significantly improved in these aspects.
实施例2:处理一批LY12铝合金构件,内外总表面积为0.3平方米Example 2: processing a batch of LY12 aluminum alloy components with a total internal and external surface area of 0.3 square meters
一种铝合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的方法,包括如下步骤和工艺条件:A method for preparing an anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of an aluminum alloy, comprising the following steps and process conditions:
(1)配置电解液:配置电解质溶液100L,电解质成分为:硅酸钠50g/L、氢氧化钠5g/L、有机胺5ml/L(其中乙二胺占50%,三乙醇胺占50%)以及其它辅助添加剂11g/L(其中,乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐2g/l;硼砂5g/l;钨酸钠3g/l;三聚磷酸钠1g/l)。(1) Prepare electrolyte: prepare 100L electrolyte solution, electrolyte composition: sodium silicate 50g/L, sodium hydroxide 5g/L, organic amine 5ml/L (among which ethylenediamine accounts for 50%, triethanolamine accounts for 50%) And other auxiliary additives 11g/L (among them, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt 2g/l; borax 5g/l; sodium tungstate 3g/l; sodium tripolyphosphate 1g/l).
(2)设置电源电参数:电源输出为非对称交流脉冲,最小电压设置为-500V,脉冲高度由电流大小控制:最大电流设置15A(50A/平方米);频率300Hz;正负脉冲数比5∶1;正负脉冲电流比10∶1;占空比70%;微弧氧化时间30分钟。(2) Set the electrical parameters of the power supply: the output of the power supply is an asymmetrical AC pulse, the minimum voltage is set to -500V, and the pulse height is controlled by the current size: the maximum current is set to 15A (50A/square meter); the frequency is 300Hz; the ratio of positive and negative pulses is 5 : 1; positive and negative pulse current ratio 10: 1; duty cycle 70%; micro-arc oxidation time 30 minutes.
(3)微弧氧化处理:用挂具将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,置入电解液中,启动非对称交直流微弧氧化电源,微弧氧化处理到设置时间30分钟,控制电解液温度不高于45℃;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后即可获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy member to the electrode rod with a hanger, put it into the electrolyte, start the asymmetric AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, and the micro-arc oxidation treatment reaches the set time for 30 minutes. Control the temperature of the electrolyte not to be higher than 45°C; remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
微弧氧化处理过程中:起弧电压160V,微弧氧化最终电压330V。获得均匀致密的棕灰色陶瓷涂层。经测试,表面陶瓷涂层厚度28微米,表面硬度为1200Hv,经1500小时3.5%NaCl中性盐雾试验,未见腐蚀痕迹。During the micro-arc oxidation process: the arc starting voltage is 160V, and the final voltage of the micro-arc oxidation is 330V. A uniform and dense brown-gray ceramic coating is obtained. After testing, the thickness of the surface ceramic coating is 28 microns, and the surface hardness is 1200Hv. After 1500 hours of 3.5% NaCl neutral salt spray test, there is no trace of corrosion.
本实例中处LY12铝合金表面的最大瞬时电源输出功率为16.5KW/平方米(50AX330V),该值约为申请号2006100009889.5所需电源瞬时功率的五分之一(300AX305V)。In this example, the maximum instantaneous power output power on the surface of LY12 aluminum alloy is 16.5KW/square meter (50AX330V), which is about one-fifth of the instantaneous power required by the application number 2006100009889.5 (300AX305V).
实施例3:处理一批LY12铝合金构件,内外总表面积为0.3平方米Embodiment 3: processing a batch of LY12 aluminum alloy components, the total internal and external surface area is 0.3 square meters
一种铝合金表面微弧氧化制备防腐抗磨陶瓷涂层的方法,包括如下步骤和工艺条件:A method for preparing an anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on the surface of an aluminum alloy, comprising the following steps and process conditions:
(1)配置电解液:配置电解质溶液100L,电解质成分为:硅酸钠50g/L;氢氧化钠5g/L;有机胺5ml/L,其中乙二胺占50%,三乙醇胺占50%;其它辅助添加剂11g/L(其中,乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐2g/l;硼砂5g/l;钨酸钠3g/l;三聚磷酸钠1g/l)。(1) Configure electrolyte: configure 100L of electrolyte solution, and the electrolyte components are: sodium silicate 50g/L; sodium hydroxide 5g/L; organic amine 5ml/L, wherein ethylenediamine accounts for 50%, and triethanolamine accounts for 50%; Other auxiliary additives 11g/L (among them, disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid 2g/l; borax 5g/l; sodium tungstate 3g/l; sodium tripolyphosphate 1g/l).
(2)设置电源电参数:电源输出为非对称交流脉冲,最小电压设置为-500V,脉冲高度由电流大小控制:最大电流设置24A(80A/平方米);频率700Hz;正负脉冲数比2∶1;正负脉冲电流比3∶1;占空比20%;微弧氧化时间30分钟。(2) Set the electrical parameters of the power supply: the output of the power supply is an asymmetrical AC pulse, the minimum voltage is set to -500V, and the pulse height is controlled by the current size: the maximum current setting is 24A (80A/square meter); the frequency is 700Hz; the ratio of positive and negative pulses is 2 : 1; positive and negative pulse current ratio 3: 1; duty cycle 20%; micro-arc oxidation time 30 minutes.
(3)微弧氧化处理:用挂具将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,置入电解液中,启动非对称交直流微弧氧化电源,微弧氧化处理到设置时间30分钟,控制电解液温度不高于45℃;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后即可获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy member to the electrode rod with a hanger, put it into the electrolyte, start the asymmetric AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, and the micro-arc oxidation treatment reaches the set time for 30 minutes. Control the temperature of the electrolyte not to be higher than 45°C; remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
微弧氧化处理过程中:起弧电压160V,微弧氧化最终电压343V。获得均匀致密的棕灰色陶瓷涂层。经测试,表面陶瓷涂层厚度35微米,表面硬度为1230Hv,经1500小时3.5%NaCl中性盐雾试验,未见腐蚀痕迹。本实例中处LY12铝合金表面微弧氧化的最大瞬时电源输出功率为27.4KW/平方米(80AX343V)。During the micro-arc oxidation process: the arc starting voltage is 160V, and the final voltage of the micro-arc oxidation is 343V. A uniform and dense brown-gray ceramic coating is obtained. After testing, the thickness of the surface ceramic coating is 35 microns, and the surface hardness is 1230Hv. After 1500 hours of 3.5% NaCl neutral salt spray test, there is no trace of corrosion. In this example, the maximum instantaneous power output power of micro-arc oxidation on the surface of LY12 aluminum alloy is 27.4KW/square meter (80AX343V).
实施例4:处理一批6061铝合金构件,总面积0.4平方米Embodiment 4: processing a batch of 6061 aluminum alloy components with a total area of 0.4 square meters
(1)配置电解液:电解质溶液100L,电解质成分为:硅酸钠60g/L;氢氧化钠5g/L;乙二胺3ml/L;三乙醇胺3ml/L;乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐2g/l;硼砂10g/L。(1) Configure electrolyte: 100L electrolyte solution, electrolyte composition: sodium silicate 60g/L; sodium hydroxide 5g/L; ethylenediamine 3ml/L; triethanolamine 3ml/L; ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt 2g/l; borax 10g/L.
(2)设置电源电参数:电源输出为直流脉冲,限制电压设置为500V,脉冲高度由电流大小控制:最大电流设置40A(100A/平方米);频率500Hz;占空比90%;微弧氧化时间25分钟。(2) Set the electrical parameters of the power supply: the output of the power supply is DC pulse, the limit voltage is set to 500V, and the pulse height is controlled by the current size: the maximum current is set to 40A (100A/square meter); the frequency is 500Hz; the duty cycle is 90%; micro-arc oxidation Time 25 minutes.
(3)微弧氧化处理:用挂具将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,置入电解液中,启动非对称交直流微弧氧化电源,微弧氧化处理到设置时间25分钟,控制电解液温度不高于45℃;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后即可获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy component to the electrode rod with a hanger, put it into the electrolyte, start the asymmetric AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, and the micro-arc oxidation treatment reaches the set time of 25 minutes. Control the temperature of the electrolyte not to be higher than 45°C; remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
微弧氧化处理过程中:起弧电压130V,微弧氧化最终电压360V。获得均匀致密的乳白色陶瓷涂层。经测试,表面陶瓷涂层厚度40微米,表面硬度为1310Hv,经1500小时3.5%NaCl中性盐雾试验,未见腐蚀痕迹。本实例中最大瞬时电源输出功率为36KW/平方米(100AX360V)。During the micro-arc oxidation process: the arc starting voltage is 130V, and the final voltage of the micro-arc oxidation is 360V. A uniform and dense milky white ceramic coating is obtained. After testing, the thickness of the surface ceramic coating is 40 microns, and the surface hardness is 1310Hv. After 1500 hours of 3.5% NaCl neutral salt spray test, there is no trace of corrosion. In this example, the maximum instantaneous power output power is 36KW/square meter (100AX360V).
实施例5:处理一批6061铝合金构件,总面积0.4平方米Embodiment 5: processing a batch of 6061 aluminum alloy components with a total area of 0.4 square meters
(1)配置电解液:电解质溶液100L,电解质成分为:硅酸钠100g/L;氢氧化钠5g/L;三乙醇胺10ml/L;乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐2g/l;硼砂10g/L。(1) Configure electrolyte: 100L electrolyte solution, electrolyte composition: sodium silicate 100g/L; sodium hydroxide 5g/L; triethanolamine 10ml/L; edetate disodium salt 2g/l; borax 10g/L L.
(2)设置电源电参数:电源输出为直流脉冲,限制电压设置为500V,脉冲高度由电流大小控制:最大电流设置30A(75A/平方米);频率500Hz;占空比90%;微弧氧化时间25分钟。(2) Set the electrical parameters of the power supply: the output of the power supply is a DC pulse, the limit voltage is set to 500V, and the pulse height is controlled by the current size: the maximum current is set to 30A (75A/square meter); the frequency is 500Hz; the duty cycle is 90%; micro-arc oxidation Time 25 minutes.
(3)微弧氧化处理:用挂具将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,置入电解液中,启动非对称交直流微弧氧化电源,微弧氧化处理到设置时间25分钟,控制电解液温度不高于45℃;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后即可获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy component to the electrode rod with a hanger, put it into the electrolyte, start the asymmetric AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, and the micro-arc oxidation treatment reaches the set time of 25 minutes. Control the temperature of the electrolyte not to be higher than 45°C; remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
微弧氧化处理过程中:起弧电压120V,微弧氧化最终电压320V。获得均匀致密的乳白色陶瓷涂层。经测试,表面陶瓷涂层厚度33微米,表面硬度为1240Hv,经1500小时3.5%NaCl中性盐雾试验,未见腐蚀痕迹。本实例微弧氧化最大瞬时电源输出功率为24KW/平方米(75AX320V)。During the micro-arc oxidation process: the arc starting voltage is 120V, and the final voltage of the micro-arc oxidation is 320V. A uniform and dense milky white ceramic coating is obtained. After testing, the thickness of the surface ceramic coating is 33 microns, and the surface hardness is 1240Hv. After 1500 hours of 3.5% NaCl neutral salt spray test, there is no trace of corrosion. In this example, the maximum instantaneous power output power of micro-arc oxidation is 24KW/square meter (75AX320V).
实施例6:处理一批镁合金AZ91D构件,总面积0.35平方米Embodiment 6: processing a batch of magnesium alloy AZ91D components with a total area of 0.35 square meters
(1)配置电解液:电解质溶液100L,电解质成分为:硅酸钠40g/L;氢氧化钠15g/L;乙二胺3ml/L;三乙醇胺10ml/L;乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐2g/l;硼砂10g/L。(1) Configure electrolyte: 100L electrolyte solution, electrolyte composition: sodium silicate 40g/L; sodium hydroxide 15g/L; ethylenediamine 3ml/L; triethanolamine 10ml/L; ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt 2g/l; borax 10g/L.
(2)设置电源电参数:电源输出为非对称交流脉冲,最小电压设置为-500V,脉冲高度由电流大小控制:最大电流设置35A(100A/平方米);频率100Hz;正负脉冲数比3∶1;正负脉冲电流比3∶1;占空比55%;微弧氧化时间30分钟。(2) Set the electrical parameters of the power supply: the output of the power supply is an asymmetrical AC pulse, the minimum voltage is set to -500V, and the pulse height is controlled by the current size: the maximum current is set to 35A (100A/square meter); the frequency is 100Hz; the ratio of positive and negative pulses is 3 : 1; positive and negative pulse current ratio 3: 1; duty cycle 55%; micro-arc oxidation time 30 minutes.
(3)微弧氧化处理:用挂具将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,置入电解液中,启动非对称交直流微弧氧化电源,微弧氧化处理到设置时间30分钟,控制电解液温度不高于45℃;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后即可获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy member to the electrode rod with a hanger, put it into the electrolyte, start the asymmetric AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, and the micro-arc oxidation treatment reaches the set time for 30 minutes. Control the temperature of the electrolyte not to be higher than 45°C; remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
微弧氧化处理过程中:起弧电压150V,微弧氧化最终电压340V。获得均匀致密的乳白色陶瓷涂层。经测试,表面陶瓷涂层厚度30微米,表面硬度为纳米力学探针硬度1090,CASS盐雾试验96小时,无点蚀痕迹。本实例微弧氧化最大瞬时电源输出功率为34KW/平方米(100AX340V)。During the micro-arc oxidation process: the arc starting voltage is 150V, and the final voltage of the micro-arc oxidation is 340V. A uniform and dense milky white ceramic coating is obtained. After testing, the thickness of the ceramic coating on the surface is 30 microns, the surface hardness is 1090 by the nanomechanical probe, and the CASS salt spray test lasts for 96 hours, and there is no trace of pitting. In this example, the maximum instantaneous power output power of micro-arc oxidation is 34KW/square meter (100AX340V).
实施例7:处理一批镁合金AZ91D构件,总面积0.35平方米Example 7: Processing a batch of magnesium alloy AZ91D components with a total area of 0.35 square meters
(1)配置电解液:电解质溶液100L,电解质成分为:硅酸钠20g/L;氢氧化钠5g/L;三乙醇胺15ml/L;乙二胺四乙酸二钠盐2g/l;硼砂10g/L。(1) Configure electrolyte: 100L electrolyte solution, electrolyte composition: sodium silicate 20g/L; sodium hydroxide 5g/L; triethanolamine 15ml/L; edetate disodium salt 2g/l; borax 10g/L L.
(2)设置电源电参数:电源输出为非对称交流脉冲,最小电压设置为-500V,脉冲高度由电流大小控制:最大电流设置35A(100A/平方米);频率150Hz;正负脉冲数比3∶1;正负脉冲电流比3∶1;占空比55%;微弧氧化时间30分钟。(2) Set the electrical parameters of the power supply: the output of the power supply is an asymmetrical AC pulse, the minimum voltage is set to -500V, and the pulse height is controlled by the current size: the maximum current setting is 35A (100A/square meter); the frequency is 150Hz; the ratio of positive and negative pulses is 3 : 1; positive and negative pulse current ratio 3: 1; duty cycle 55%; micro-arc oxidation time 30 minutes.
(3)微弧氧化处理:用挂具将除油后的合金构件连接到电极棒上,置入电解液中,启动非对称交直流微弧氧化电源,微弧氧化处理到设置时间30分钟,控制电解液温度不高于45℃;取下被处理构件,流水洗净工件表面后,热风烘干后即可获得陶瓷涂层合金构件。(3) Micro-arc oxidation treatment: connect the degreased alloy member to the electrode rod with a hanger, put it into the electrolyte, start the asymmetric AC-DC micro-arc oxidation power supply, and the micro-arc oxidation treatment reaches the set time for 30 minutes. Control the temperature of the electrolyte not to be higher than 45°C; remove the treated component, wash the surface of the workpiece with running water, and dry it with hot air to obtain a ceramic-coated alloy component.
微弧氧化处理过程中:起弧电压155V,微弧氧化最终电压370V。获得均匀致密的乳白色陶瓷涂层。经测试,表面陶瓷涂层厚度31微米,表面硬度为纳米力学探针硬度1100,CASS盐雾试验96小时,无点蚀痕迹。本实例微弧氧化最大瞬时电源输出功率为37KW/平方米(100AX370V)。During the micro-arc oxidation process: the arc starting voltage is 155V, and the final voltage of the micro-arc oxidation is 370V. A uniform and dense milky white ceramic coating is obtained. After testing, the thickness of the ceramic coating on the surface is 31 microns, the surface hardness is 1100 of the nanomechanical probe hardness, and the CASS salt spray test lasts for 96 hours, and there is no trace of pitting. The maximum instantaneous power output power of micro-arc oxidation in this example is 37KW/square meter (100AX370V).
以上所有实例所需最大瞬时功率密度均小于40KW/平方米;成膜速度大于1微米/分钟。本发明开发低能耗微弧氧化技术。从微弧氧化过程微弧形成的机理来看,一是基于陶瓷电介质中电子雪崩效应,这种雪崩效应同电解质的成分密切相关;二是基于表面吸附气体放电。两种机理都同电解质成分及使用的相关电源参数密不可分。本发明在整个微弧氧化过程中,外加电源、电解质、金属表面形成的绝缘膜构成一个完整的电路系统。只有能够有效地把电解质、电源参数有效优化匹配,才可能降低起弧电压,在相同电流密度下获得较快的成膜速度。如采用本发明提及的电解液在镁合金表面想要制备均匀致密的陶瓷涂层,只有输出方式、频率等参数有机结合才能达到,否则极易在表面出现局部放电,出现明显点蚀,甚至难以形成完整的表面涂层。这是由于局部形成的陶瓷涂层与电源参数不匹配,从而导致局部短路,该区域局部电流密度非常高,因此出现较大面积的绝缘层击穿,此后电流将主要从该区域通过,不会再在整个表面形成均匀致密的移动微弧点。The maximum instantaneous power density required by all the above examples is less than 40KW/square meter; the film forming speed is greater than 1 micron/minute. The invention develops low energy consumption micro-arc oxidation technology. From the perspective of the mechanism of micro-arc formation in the micro-arc oxidation process, one is based on the electronic avalanche effect in the ceramic dielectric, which is closely related to the composition of the electrolyte; the other is based on surface adsorption gas discharge. Both mechanisms are inseparable from the composition of the electrolyte and the associated power parameters used. In the present invention, during the whole micro-arc oxidation process, an external power supply, electrolyte, and an insulating film formed on the metal surface form a complete circuit system. Only by effectively optimizing and matching the electrolyte and power supply parameters can it be possible to reduce the arcing voltage and obtain a faster film forming speed at the same current density. If the electrolytic solution mentioned in the present invention is used to prepare a uniform and dense ceramic coating on the surface of magnesium alloy, it can only be achieved by organically combining parameters such as output mode and frequency, otherwise partial discharge will easily occur on the surface, and obvious pitting corrosion will occur. It is difficult to form a complete surface coating. This is because the locally formed ceramic coating does not match the power supply parameters, resulting in a local short circuit. The local current density in this area is very high, so a large area of insulation layer breakdown occurs. After that, the current will mainly pass through this area and will not Then a uniform and dense moving micro-arc point is formed on the entire surface.
Claims (4)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008100275545ACN101270495B (en) | 2008-04-21 | 2008-04-21 | Method for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on alloy surface |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008100275545ACN101270495B (en) | 2008-04-21 | 2008-04-21 | Method for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on alloy surface |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101270495Atrue CN101270495A (en) | 2008-09-24 |
| CN101270495B CN101270495B (en) | 2010-10-27 |
Family
ID=40004708
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2008100275545AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101270495B (en) | 2008-04-21 | 2008-04-21 | Method for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on alloy surface |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101270495B (en) |
Cited By (33)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102304746A (en)* | 2011-09-26 | 2012-01-04 | 佳木斯大学 | Polypyrrole calcium phosphate/magnesium oxide bioceramic coating and preparation method thereof |
| CN102409380A (en)* | 2011-11-09 | 2012-04-11 | 南昌航空大学 | A Method for Improving the Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum Alloy Micro-arc Oxidation Film Layer |
| CN102428213A (en)* | 2009-04-22 | 2012-04-25 | 汉阳大学校产学协力团 | metal surface treatment |
| CN102877104A (en)* | 2012-10-09 | 2013-01-16 | 西南石油大学 | Low-voltage rapid micro-arc oxidation technique |
| CN103088390A (en)* | 2013-02-06 | 2013-05-08 | 惠州市裕元华阳精密部件有限公司 | Surface treatment method for magnesium alloy metal body |
| CN103233258A (en)* | 2013-04-28 | 2013-08-07 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for preparing dense enhancement type ceramic membrane based on micro-arc oxidizing and laser remelting |
| CN103339298A (en)* | 2011-02-08 | 2013-10-02 | 剑桥奈米科技有限公司 | Non-metallic coating and method of its production |
| CN103409782A (en)* | 2013-07-29 | 2013-11-27 | 西安交通大学 | Microarc oxidation-based surface super-hydrophobicity treatment technology for aluminium material |
| CN103695981A (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2014-04-02 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | Functional design method for aluminum alloy surface micro-arc oxidation film |
| CN103695980A (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2014-04-02 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | Preparation method of single-layer micro-arc oxidation ceramic film on surface of aluminum alloy |
| CN103789810A (en)* | 2014-01-15 | 2014-05-14 | 哈尔滨东安发动机(集团)有限公司 | Method for preparing micro-arc oxidation ceramic film layer on surface of magnesium alloy |
| CN104233427A (en)* | 2014-09-30 | 2014-12-24 | 西南交通大学 | Method for improving residual stress of aluminum alloy welding joint through micro-arc oxidation |
| CN104514027A (en)* | 2014-12-25 | 2015-04-15 | 广东省工业技术研究院(广州有色金属研究院) | Electrolyte solution for preparing aluminum and aluminum alloy ceramic membrane through micro-arc oxidation technology |
| CN104630863A (en)* | 2015-02-09 | 2015-05-20 | 山东核电设备制造有限公司 | Rapid anode oxidation method for asymmetric pole extra-large aluminum alloy plate |
| CN105506700A (en)* | 2015-12-10 | 2016-04-20 | 苏州市嘉明机械制造有限公司 | Wear-resisting insulation thrust runner collar preparation technology |
| CN106567116A (en)* | 2016-11-10 | 2017-04-19 | 长沙淮石新材料科技有限公司 | Heat-resisting moisture-preserving aluminum alloy and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN106591916A (en)* | 2016-11-30 | 2017-04-26 | 北京交通大学 | Surface treatment method for aluminum alloy part of contact net |
| CN106591919A (en)* | 2016-12-09 | 2017-04-26 | 深圳市新合富力科技有限公司 | Aluminum material surface nanometer treatment process |
| CN106702453A (en)* | 2017-01-19 | 2017-05-24 | 山西平阳重工机械有限责任公司 | Preparation method for brown micro arc oxidation film of surface of casting aluminum base composite material |
| CN106762631A (en)* | 2017-02-28 | 2017-05-31 | 珠海格力节能环保制冷技术研究中心有限公司 | A kind of scroll compressor thermomechanical components and its manufacture method and scroll compressor |
| CN106835233A (en)* | 2017-01-24 | 2017-06-13 | 西安天奥新材料科技有限公司 | Wear-resisting, etch-proof aluminium drill pipe preparation method and obtained aluminium drill pipe |
| CN106894071A (en)* | 2017-03-10 | 2017-06-27 | 国家开发投资公司 | A kind of aluminum alloy surface method for anticorrosion-treating |
| CN106894069A (en)* | 2017-01-24 | 2017-06-27 | 西安天奥新材料科技有限公司 | Wear-resisting, corrosion resistant the oil field preparation method and plunger of aluminium alloy plunger |
| CN107190298A (en)* | 2017-05-23 | 2017-09-22 | 桂林电子科技大学 | A kind of method that micro-arc oxidation of aluminum alloy surface black film layer |
| CN107355382A (en)* | 2017-08-29 | 2017-11-17 | 广东美芝制冷设备有限公司 | Compressor slide plate and rotary compressor |
| CN107435159A (en)* | 2016-05-02 | 2017-12-05 | 纳米及先进材料研发院有限公司 | Alloy Surface Color Treatment Using Micro-arc Oxidation Process |
| CN108004576A (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2018-05-08 | 南京工业大学 | Micro-arc oxidation process |
| CN109778278A (en)* | 2019-03-08 | 2019-05-21 | 北京致成生物医学科技有限公司 | Have the preparation method of the nail-stick system of wear-resistant bits coating and the nail-stick system of preparation |
| CN113088966A (en)* | 2021-03-31 | 2021-07-09 | 中国兵器科学研究院宁波分院 | Magnesium alloy composite coating and preparation method thereof |
| CN114507892A (en)* | 2022-01-14 | 2022-05-17 | 电子科技大学 | Tantalum alloy self-lubricating wear-resistant and wear-reducing composite coating and preparation method thereof |
| CN115478269A (en)* | 2022-10-11 | 2022-12-16 | 山西聚星辰新材料科技有限公司 | Preparation method of flexible aluminum-based ceramic insulating foil |
| CN116103722A (en)* | 2022-11-25 | 2023-05-12 | 新江科技(江苏)有限公司 | Preparation method of micro-arc oxidation film layer of large-surface-area rare earth magnesium alloy part |
| CN117503311A (en)* | 2023-11-09 | 2024-02-06 | 青岛九远医疗科技有限公司 | Magnesium alloy implant device, preparation method and application thereof |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102230205B (en)* | 2011-06-20 | 2013-11-27 | 华南理工大学 | Aluminum alloy micro-arc oxidation black ceramic film and preparation method thereof |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN2598252Y (en)* | 2002-06-10 | 2004-01-07 | 来永春 | Bipolar high power pulse power supply |
| CN100457981C (en)* | 2004-09-14 | 2009-02-04 | 青岛科技大学 | Method for plasma micro arc oxidizing of light metal surface |
| CN1928165A (en)* | 2006-06-13 | 2007-03-14 | 兰州理工大学 | Method for producing arc differential oxide ceramic layer on Mg metal surface |
- 2008
- 2008-04-21CNCN2008100275545Apatent/CN101270495B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (46)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102428213A (en)* | 2009-04-22 | 2012-04-25 | 汉阳大学校产学协力团 | metal surface treatment |
| CN103339298A (en)* | 2011-02-08 | 2013-10-02 | 剑桥奈米科技有限公司 | Non-metallic coating and method of its production |
| CN103339298B (en)* | 2011-02-08 | 2017-01-18 | 剑桥奈米科技有限公司 | Non-metallic coating and method of its production |
| CN102304746A (en)* | 2011-09-26 | 2012-01-04 | 佳木斯大学 | Polypyrrole calcium phosphate/magnesium oxide bioceramic coating and preparation method thereof |
| CN102409380B (en)* | 2011-11-09 | 2014-01-22 | 南昌航空大学 | Method for improving corrosion resistance of aluminum-alloy micro-arc oxidation film |
| CN102409380A (en)* | 2011-11-09 | 2012-04-11 | 南昌航空大学 | A Method for Improving the Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum Alloy Micro-arc Oxidation Film Layer |
| CN103695980B (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2016-04-13 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | A kind of preparation method of single-layer micro-arc oxidation ceramic film on surface of aluminum alloy |
| CN103695981A (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2014-04-02 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | Functional design method for aluminum alloy surface micro-arc oxidation film |
| CN103695980A (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2014-04-02 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | Preparation method of single-layer micro-arc oxidation ceramic film on surface of aluminum alloy |
| CN103695981B (en)* | 2012-09-27 | 2016-03-23 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | A kind of method of micro-arc oxidation of aluminum alloy surface film functionalized design |
| CN102877104A (en)* | 2012-10-09 | 2013-01-16 | 西南石油大学 | Low-voltage rapid micro-arc oxidation technique |
| CN103088390A (en)* | 2013-02-06 | 2013-05-08 | 惠州市裕元华阳精密部件有限公司 | Surface treatment method for magnesium alloy metal body |
| CN103088390B (en)* | 2013-02-06 | 2016-05-04 | 惠州市裕元华阳精密部件有限公司 | A kind of magnesium alloy metal body surface processing method |
| CN103233258B (en)* | 2013-04-28 | 2016-02-17 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A kind of preparation method of the compactness enhancement type ceramic film based on differential arc oxidation and laser remolten |
| CN103233258A (en)* | 2013-04-28 | 2013-08-07 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for preparing dense enhancement type ceramic membrane based on micro-arc oxidizing and laser remelting |
| CN103409782B (en)* | 2013-07-29 | 2016-06-29 | 西安交通大学 | Aluminum surface super-hydrophobic based on micro-arc oxidation processes technique |
| CN103409782A (en)* | 2013-07-29 | 2013-11-27 | 西安交通大学 | Microarc oxidation-based surface super-hydrophobicity treatment technology for aluminium material |
| CN103789810A (en)* | 2014-01-15 | 2014-05-14 | 哈尔滨东安发动机(集团)有限公司 | Method for preparing micro-arc oxidation ceramic film layer on surface of magnesium alloy |
| CN104233427A (en)* | 2014-09-30 | 2014-12-24 | 西南交通大学 | Method for improving residual stress of aluminum alloy welding joint through micro-arc oxidation |
| CN104514027A (en)* | 2014-12-25 | 2015-04-15 | 广东省工业技术研究院(广州有色金属研究院) | Electrolyte solution for preparing aluminum and aluminum alloy ceramic membrane through micro-arc oxidation technology |
| CN104630863A (en)* | 2015-02-09 | 2015-05-20 | 山东核电设备制造有限公司 | Rapid anode oxidation method for asymmetric pole extra-large aluminum alloy plate |
| CN105506700A (en)* | 2015-12-10 | 2016-04-20 | 苏州市嘉明机械制造有限公司 | Wear-resisting insulation thrust runner collar preparation technology |
| CN107435159A (en)* | 2016-05-02 | 2017-12-05 | 纳米及先进材料研发院有限公司 | Alloy Surface Color Treatment Using Micro-arc Oxidation Process |
| US10494730B2 (en) | 2016-05-02 | 2019-12-03 | Nano And Advanced Materials Institute Ltd | Surface color treatment of alloys with micro-arc oxidation process |
| CN106567116A (en)* | 2016-11-10 | 2017-04-19 | 长沙淮石新材料科技有限公司 | Heat-resisting moisture-preserving aluminum alloy and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN106567116B (en)* | 2016-11-10 | 2018-10-09 | 长沙淮石新材料科技有限公司 | A kind of heat-resisting moisturizing aluminium alloy and its preparation method and application |
| CN106591916A (en)* | 2016-11-30 | 2017-04-26 | 北京交通大学 | Surface treatment method for aluminum alloy part of contact net |
| CN106591919A (en)* | 2016-12-09 | 2017-04-26 | 深圳市新合富力科技有限公司 | Aluminum material surface nanometer treatment process |
| CN106702453A (en)* | 2017-01-19 | 2017-05-24 | 山西平阳重工机械有限责任公司 | Preparation method for brown micro arc oxidation film of surface of casting aluminum base composite material |
| CN106894069B (en)* | 2017-01-24 | 2019-01-15 | 西安天奥新材料科技有限公司 | The preparation method and plunger of wear-resisting, corrosion resistant oil field aluminium alloy plunger |
| CN106835233A (en)* | 2017-01-24 | 2017-06-13 | 西安天奥新材料科技有限公司 | Wear-resisting, etch-proof aluminium drill pipe preparation method and obtained aluminium drill pipe |
| CN106894069A (en)* | 2017-01-24 | 2017-06-27 | 西安天奥新材料科技有限公司 | Wear-resisting, corrosion resistant the oil field preparation method and plunger of aluminium alloy plunger |
| CN106835233B (en)* | 2017-01-24 | 2018-12-11 | 西安天奥新材料科技有限公司 | Wear-resisting, etch-proof aluminium drill pipe preparation method and aluminium drill pipe obtained |
| CN106762631A (en)* | 2017-02-28 | 2017-05-31 | 珠海格力节能环保制冷技术研究中心有限公司 | A kind of scroll compressor thermomechanical components and its manufacture method and scroll compressor |
| CN106894071A (en)* | 2017-03-10 | 2017-06-27 | 国家开发投资公司 | A kind of aluminum alloy surface method for anticorrosion-treating |
| CN106894071B (en)* | 2017-03-10 | 2019-07-26 | 国家开发投资公司 | A kind of anti-corrosion treatment method of aluminum alloy surface |
| CN107190298A (en)* | 2017-05-23 | 2017-09-22 | 桂林电子科技大学 | A kind of method that micro-arc oxidation of aluminum alloy surface black film layer |
| CN107355382A (en)* | 2017-08-29 | 2017-11-17 | 广东美芝制冷设备有限公司 | Compressor slide plate and rotary compressor |
| CN108004576A (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2018-05-08 | 南京工业大学 | Micro-arc oxidation process |
| CN109778278A (en)* | 2019-03-08 | 2019-05-21 | 北京致成生物医学科技有限公司 | Have the preparation method of the nail-stick system of wear-resistant bits coating and the nail-stick system of preparation |
| CN113088966A (en)* | 2021-03-31 | 2021-07-09 | 中国兵器科学研究院宁波分院 | Magnesium alloy composite coating and preparation method thereof |
| CN114507892A (en)* | 2022-01-14 | 2022-05-17 | 电子科技大学 | Tantalum alloy self-lubricating wear-resistant and wear-reducing composite coating and preparation method thereof |
| CN114507892B (en)* | 2022-01-14 | 2023-11-24 | 电子科技大学 | A self-lubricating, wear-resistant and wear-reducing composite coating of tantalum alloy and its preparation method |
| CN115478269A (en)* | 2022-10-11 | 2022-12-16 | 山西聚星辰新材料科技有限公司 | Preparation method of flexible aluminum-based ceramic insulating foil |
| CN116103722A (en)* | 2022-11-25 | 2023-05-12 | 新江科技(江苏)有限公司 | Preparation method of micro-arc oxidation film layer of large-surface-area rare earth magnesium alloy part |
| CN117503311A (en)* | 2023-11-09 | 2024-02-06 | 青岛九远医疗科技有限公司 | Magnesium alloy implant device, preparation method and application thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101270495B (en) | 2010-10-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101270495A (en) | Method for preparing anti-corrosion and anti-wear ceramic coating by micro-arc oxidation on alloy surface | |
| AU747068B2 (en) | Method for producing hard protection coatings on articles made of aluminium alloys | |
| CN103122475B (en) | A kind of aluminium alloy electric chemical brightening solution and a kind of aluminium alloy electric chemically polishing method | |
| JP5152574B2 (en) | Method for anodizing aluminum member | |
| CN100457981C (en) | Method for plasma micro arc oxidizing of light metal surface | |
| CN101245485A (en) | A kind of magnesium-lithium alloy surface treatment method | |
| CN101845662A (en) | Magnesium alloy surface treating method and magnesium alloy polished by same | |
| CN102286766A (en) | Aluminum alloy hard anode oxidation film and process method thereof | |
| CN112538651A (en) | Method for polishing titanium alloy by ultrasonic-assisted electrolytic plasma | |
| CN107245748A (en) | A kind of two-step anodization technique of aluminium alloy | |
| CN109609992A (en) | A kind of aluminum alloy mobile phone shell anode oxidative treatment method | |
| CN102409380B (en) | Method for improving corrosion resistance of aluminum-alloy micro-arc oxidation film | |
| CN106065488A (en) | A kind of method utilizing positive negative pulse stuffing anodizing to prepare anode aluminium foil | |
| CN109267136A (en) | The method of titanium bolt surface ceramic based on growth in situ | |
| CN1844484A (en) | Microarc Oxidation Treatment Method for High Strength Cast Rare Earth Magnesium Alloy | |
| CN103014812A (en) | Process for coloring titanium alloy through micro-arc oxidation | |
| CN100562609C (en) | Method for forming colored oxide film on aluminum and aluminum alloy surface in one step | |
| CN110777413B (en) | Method for laser remelting of surface of plasma cathode electrolytic deposition ceramic coating | |
| JP4417106B2 (en) | Magnesium anodizing system and method | |
| US20080087551A1 (en) | Method for anodizing aluminum alloy and power supply for anodizing aluminum alloy | |
| CN103397364A (en) | Aluminum-silicon alloy surface ceramic treatment method and apparatus | |
| CN105624757B (en) | A power frequency AC anodic oxidation method of anode aluminum foil for aluminum electrolytic capacitor | |
| CN105088308B (en) | High-copper silumin anodic oxidation environment-protective process | |
| CN101767269A (en) | Processing method for liquid-cooling anti-corrosion radiator | |
| CN108914184B (en) | A kind of preparation method of aluminum alloy micro-arc oxidation film with low energy consumption |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C17 | Cessation of patent right | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20101027 Termination date:20140421 |