CN101152111A - Pulmonary Artery Coarctation Stents for Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension - Google Patents
Pulmonary Artery Coarctation Stents for Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary HypertensionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101152111A CN101152111ACN 200710018613CN200710018613ACN101152111ACN 101152111 ACN101152111 ACN 101152111ACN 200710018613CN200710018613CN 200710018613CN 200710018613 ACN200710018613 ACN 200710018613ACN 101152111 ACN101152111 ACN 101152111A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- pulmonary artery
- stent
- pulmonary
- constriction
- artery constriction
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于医疗技术领域,特别涉及一种通过股静脉或外科开胸方式,对先天性心脏病合并肺动脉高压的患者于肺动脉内植入的覆膜的血管支架,即用于肺动脉高压外科治疗的缩窄支架。The invention belongs to the field of medical technology, and particularly relates to a covered vascular stent implanted in the pulmonary artery for patients with congenital heart disease combined with pulmonary hypertension through femoral vein or surgical thoracotomy, that is, it is used for surgical treatment of pulmonary hypertension Narrow the bracket.
背景技术Background technique
肺动脉高压是指各种原因所引起的肺动脉压力持久性增高,当肺动脉收缩压超过4.0千帕(30毫米汞柱),舒张压超过2.0千帕(15毫米汞柱)或平均压高于2.7千帕(20毫米汞柱)时称为肺动脉高压。根据病因肺动脉高压可分为原发性(不明原因、特发性)肺动脉高压和继发性肺动脉高压,其中由于先天性心脏病导致的继发性肺动脉高压最为常见,对人类健康造成的危害最大。先天性心脏病引起的继发性肺动脉高压,通常由于心脏内部或大血管水平存在左向右的分流(如房间隔缺损、室间隔缺损、动脉导管未闭等),导致肺循环血流量增加,初期为动力性肺动脉高压,继续发展会引起肺动脉压力持续增高,甚至超越主动脉压力,肺血管阻力升高,导致血液通过心内或心外异常通路产生双向或右向左分流,临床上出现发绀和右心衰竭,称为艾森曼格综合征。各种心内、心外畸形如房间隔缺损、室间隔缺损、动脉导管未闭等均有可能发展成艾森曼格综合征。艾森曼格综合征已经无法常规手术治疗,一般只能选择心肺联合移植,但手术费用高,手术远期存活率也比较低,未手术治疗的艾森曼格综合征患者主要死于因肺动脉高压引起的心力衰竭及继发性肺部感染。Pulmonary hypertension refers to a persistent increase in pulmonary artery pressure caused by various reasons. When the systolic pressure of the pulmonary artery exceeds 4.0 kPa (30 mm Hg), the diastolic pressure exceeds 2.0 kPa (15 mm Hg) or the mean pressure exceeds 2.7 kPa. Pa (20 mm Hg) is called pulmonary hypertension. According to the etiology, pulmonary hypertension can be divided into primary (unknown cause, idiopathic) pulmonary hypertension and secondary pulmonary hypertension, among which secondary pulmonary hypertension caused by congenital heart disease is the most common and the most harmful to human health . Secondary pulmonary hypertension caused by congenital heart disease is usually due to left-to-right shunts inside the heart or at the level of large blood vessels (such as atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, etc.), resulting in increased blood flow in the pulmonary circulation. It is dynamic pulmonary hypertension, and if it continues to develop, the pulmonary artery pressure will continue to increase, even surpassing the aortic pressure, and the pulmonary vascular resistance will increase, resulting in bidirectional or right-to-left shunt of blood through abnormal intracardiac or extracardiac pathways, clinically, cyanosis and Right heart failure, known as Eisenmenger syndrome. Various intracardiac and extracardiac malformations such as atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, etc. may develop into Eisenmenger syndrome. Eisenmenger syndrome can no longer be treated with routine surgery. Generally, combined heart-lung transplantation is the only choice, but the cost of surgery is high, and the long-term survival rate of surgery is relatively low. Patients with Eisenmenger syndrome who have not undergone surgery mainly die from pulmonary artery Heart failure and secondary lung infection caused by high pressure.
目前,在治疗先天性心脏病引起的肺动脉高压方面,应用一氧化氮、前列腺素等药物仅能够暂时缓解症状,不能阻止肺动脉高压的进一步发展。外科治疗方面,目前能够通过开胸手术的方式,将肺动脉通过束带的方式进行环缩(banding)手术。但该方法需要全身麻醉,开胸,手术创伤大,花费高,出现并发症的几率也明显增加,同时,对于需要进行再次手术的患者,该方法造成组织粘连,增加了再次手术的时间和死亡率。At present, in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension caused by congenital heart disease, the application of nitric oxide, prostaglandin and other drugs can only temporarily relieve symptoms, but cannot prevent the further development of pulmonary hypertension. In terms of surgical treatment, it is currently possible to perform a banding operation by banding the pulmonary artery through a thoracotomy. However, this method requires general anesthesia, thoracotomy, large surgical trauma, high cost, and significantly increased chance of complications. At the same time, for patients who need reoperation, this method causes tissue adhesion, which increases the time of reoperation and death Rate.
最近的研究试图通过介入微创的手段进行肺动脉高压的外科治疗,其代表性的实例公开在胡晓旻等人的实用新型专利03241986.4中。该装置为中空的漏斗状支架,利用记忆合金技术制作,入口处为圆筒部,出口处为漏斗部,外部覆膜,外表面有倒刺状倒钩防止支架移位。实际工作中,通过股静脉路径将定位于肺动脉内后释放,达到减少肺动脉血流,降低肺动脉压力的目的。该装置具有使用方便,可靠性高的特点。但同时由于设计为漏斗状,利用倒刺状倒钩防止支架移位的技术在实际应用中难以同时保证入口及出口同时与肺动脉紧密结合,因而会造成不同程度的渗漏及反流、涡流的现象,增加了血栓的形成几率;同时不利于精确放置到预期的部位;再次,该装置仅仅能够通过股静脉路径将支架植入肺动脉内,对于年幼患者及股静脉血管细小等患者的应用具有局限性;最后,装置采用镍钛记忆合金制作,虽然具有于37℃恢复记忆形态的特点,但合金的质地偏软,与覆膜支架的结合难以保证紧密,同时不利于完全展开于肺动脉内,发生支架移位的可能较大。Recent research attempts to perform surgical treatment of pulmonary hypertension by interventional minimally invasive means, and its representative example is disclosed in the utility model patent 03241986.4 of Hu Xiaomin et al. The device is a hollow funnel-shaped bracket made of memory alloy technology. The entrance is a cylinder, the exit is a funnel, and the outside is covered with a film. There are barbed barbs on the outer surface to prevent the bracket from shifting. In actual work, it will be positioned in the pulmonary artery through the femoral vein and then released, so as to reduce the blood flow of the pulmonary artery and reduce the pressure of the pulmonary artery. The device has the characteristics of convenient use and high reliability. But at the same time, due to the funnel-shaped design, it is difficult to ensure that the inlet and outlet are closely combined with the pulmonary artery at the same time in practical applications by using the barb-shaped barb to prevent the stent from shifting, which will cause leakage, reflux, and eddy currents to varying degrees. phenomenon, which increases the probability of thrombus formation; at the same time, it is not conducive to accurate placement to the expected site; thirdly, the device can only implant the stent into the pulmonary artery through the femoral vein route, which is especially useful for young patients and patients with small femoral veins. Limitations: Finally, the device is made of nickel-titanium memory alloy. Although it has the characteristics of restoring the memory shape at 37°C, the texture of the alloy is soft, and it is difficult to ensure a tight combination with the covered stent. At the same time, it is not conducive to complete deployment in the pulmonary artery. Stent migration is more likely to occur.
发明内容Contents of the invention
针对上述的缺陷,本发明的目的在于提供一种用于肺动脉高压外科治疗的肺动脉缩窄支架,以便实现肺动脉缩窄支架牢固贴覆于肺动脉内、能精确定位,可降低血栓的发生几率,适应不同年龄,使医生操作简单可靠。In view of the above-mentioned defects, the object of the present invention is to provide a pulmonary artery constriction stent for surgical treatment of pulmonary hypertension, so that the pulmonary artery constriction stent can be firmly attached to the pulmonary artery, can be accurately positioned, and can reduce the incidence of thrombus. Different ages make it easy and reliable for doctors to operate.
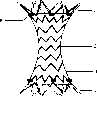
为了实现上述目的,本发明提供一种用于肺动脉高压外科治疗的肺动脉缩窄支架,其特征是:肺动脉缩窄支架体9呈两端直径大、中间直径小的中空腔体状;两端有可释放的呈波浪状入口1和呈波浪状的出口4,肺动脉缩窄支架体9表面有聚四氟乙烯膜3。In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a pulmonary artery constriction stent for surgical treatment of pulmonary hypertension, which is characterized in that: the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is in the shape of a hollow cavity with a large diameter at both ends and a small diameter in the middle;
所述的肺动脉缩窄支架体9是合金材料。The pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is an alloy material.
所述的肺动脉缩窄支架体9是记忆合金材料。The pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is a memory alloy material.
所述的肺动脉缩窄支架体9有黄金焊接标记8。The pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 has
所述的黄金焊接标记8在肺动脉缩窄支架体9两端。The
所述的肺动脉缩窄支架体9两端直径变动范围在4mm-30mm之间。The range of diameters at both ends of the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is between 4 mm and 30 mm.
所述的肺动脉缩窄支架体9中间与两端比例在0.1-0.9之间。The ratio between the middle and both ends of the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is between 0.1-0.9.
本发明由于肺动脉缩窄支架两端即入口及/或出口呈波浪状,可将肺动脉缩窄支架牢固固定于肺动脉内。支架中部的内径小,通过支架中部的小横截面积来控制支架内的血流量,以便降低血栓的发生几率。支架中部的内径有不同的内径规格可以选择,适应不同年龄的患者。输送时,覆膜的肺动脉缩窄支架可在体外收于鞘管内,锥体头部、输送鞘管和输送杆通过股静脉路径或小切口经胸壁方式进行安全植入,避免了外科开胸的创伤和相关并发症。在支架的两端均进行黄金焊接标记,能够在X线下清楚显影,便于精确定位。Because the two ends of the pulmonary artery constriction stent, that is, the inlet and/or the outlet, are wavy, the present invention can firmly fix the pulmonary artery constriction stent in the pulmonary artery. The inner diameter of the middle part of the stent is small, and the blood flow in the stent is controlled through the small cross-sectional area of the middle part of the stent, so as to reduce the occurrence probability of thrombus. The inner diameter of the middle part of the stent has different inner diameter specifications to choose from, which is suitable for patients of different ages. During delivery, the covered pulmonary artery stent can be placed in the sheath in vitro, and the cone head, delivery sheath and delivery rod can be safely implanted through the femoral vein or small incision through the chest wall, avoiding the risk of surgical thoracotomy. Trauma and related complications. Both ends of the stent are marked with gold welding, which can be clearly visualized under X-ray for precise positioning.
附图说明Description of drawings
下面结合实施例附图对本发明做进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings of the embodiments.
图1是本发明整体状态或肺动脉缩窄支架完全收回后的结构示意图;Fig. 1 is the overall state of the present invention or the structure diagram after the pulmonary artery constriction stent is fully retracted;
图2是肺动脉缩窄支架头部释放后的结构示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic structural view of the head of the pulmonary artery constriction stent after it is released;
图3是肺动脉缩窄支架完全释放后的结构示意图。Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the pulmonary artery constriction stent after it is completely released.
图中:1、入口;2、支架中部;3、聚四氟乙烯膜;4、出口;5、锥体头部;6、输送鞘管;7、输送杆;8、黄金焊接标记;9、肺动脉缩窄支架体。In the figure: 1. Inlet; 2. Middle part of stent; 3. Teflon membrane; 4. Outlet; 5. Cone head; 6. Delivery sheath; 7. Delivery rod; 8. Gold welding mark; 9. Pulmonary artery constriction stent body.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
图1所描述的是肺动脉缩窄支架体9完全收回后于鞘管内的体外结构示意图。FIG. 1 depicts a schematic view of the in vitro structure of the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 in the sheath tube after it is fully withdrawn.
肺动脉缩窄支架体9呈两端直径大、支架中部2直径小的中空腔体状,两端有可释放的呈波浪状入口1和呈波浪状的出口4,肺动脉缩窄支架体9两端直径释放变动范围在4mm-30mm之间。中间与两端比例变动在0.1-0.9之间。肺动脉缩窄支架体9表面有聚四氟乙烯膜3。The pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is in the shape of a hollow cavity with a large diameter at both ends and a small diameter in the middle part of the
肺动脉缩窄支架体9装入是通过输送体完成,输送体包括输送鞘管6、锥体头部5和输送杆7。装入时,肺动脉缩窄支架体9完全收回到输送鞘管6内,肺动脉缩窄支架体9一般可收缩入12-24F输送鞘管6。锥体头部5底端插入输送鞘管6内侧,输送杆7插入输送鞘管6另一侧内。肺动脉缩窄支架体9两端均有黄金焊接标记8,便于在X线下精确定位。肺动脉缩窄支架体9两端直径大于支架中部2的直径。入口1与锥体头部5相互连接,出口4与输送杆7连接。整体组装于输送鞘管6内。The loading of the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is accomplished through a delivery body, which includes a delivery sheath 6 , a cone head 5 and a delivery rod 7 . When loaded, the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 is completely retracted into the delivery sheath 6 , and the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 can generally be shrunk into the 12-24F delivery sheath tube 6 . The bottom end of the cone head 5 is inserted into the inner side of the delivery sheath 6 , and the delivery rod 7 is inserted into the other side of the delivery sheath 6 . There are gold welding marks 8 at both ends of the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9, which is convenient for accurate positioning under X-ray. The diameters of both ends of the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 are larger than the diameter of the
图2给出的是入口1释放,肺动脉缩窄支架体9自从黄金焊接标记8处开始向内覆聚四氟乙烯(ePTFE)膜3,聚四氟乙烯(ePTFE)膜3的应用能够防止血液从覆膜支架内发生渗漏。由于支架中部2内径小于两端的入口1和出口4的直径,可通过支架中部2的内径来控制和减少支架内血流。支架中部2的内径有不同的内径规格可以选择,适应不同年龄的患者。Figure 2 shows that the
图3所描述的是肺动脉缩窄支架体9头部释放后的结构示意图。肺动脉缩窄支架脱离输送体后释放,入口1和出口处4充分释放成扩径状。FIG. 3 depicts a structural schematic diagram of the pulmonary artery constriction stent body 9 after the head is released. The pulmonary artery constriction stent is released after detaching from the delivery body, and the
下面结合两种手术方案具体说明本发明的使用方法:The using method of the present invention is specifically described below in conjunction with two kinds of operation schemes:
①肺动脉缩窄支架股静脉径路的手术方案:①Pulmonary artery constriction stent-femoral vein approach operation plan:
于腹股沟下做一长约4cm的纵行切口,外科解剖暴露股静脉,穿刺股静脉,通过导丝建立股静脉-下腔静脉-右心室-肺动脉通路,将肺动脉缩窄支架及传输系统装入股静脉中,沿已建立的通路于X线引导下将支架及传输系统至于肺动脉内,释放支架,测量主肺动脉远近端的压力阶差,撤除鞘管及传输系统,缝合股静脉,结束手术。Make a longitudinal incision about 4 cm long under the groin, expose the femoral vein by surgical dissection, puncture the femoral vein, establish a femoral vein-inferior vena cava-right ventricle-pulmonary artery pathway through a guide wire, and install the pulmonary artery constriction stent and delivery system into the femoral vein. In the vein, place the stent and delivery system in the pulmonary artery along the established pathway under X-ray guidance, release the stent, measure the pressure gradient between the distal and proximal ends of the main pulmonary artery, remove the sheath and delivery system, suture the femoral vein, and end the operation.
②肺动脉缩窄支架胸壁径路的手术方案:②Surgical plan for pulmonary artery constriction stent chest wall approach:
于胸骨左缘第四肋间做-长约4cm的横切口,逐层分离组织,悬吊心包,暴露右室流出道并缝合荷包,穿刺右室流出道,通过导丝建立右心室-肺动脉通路,将肺动脉缩窄支架及传输系统沿已建立的通路于X线引导下将支架及传输系统至于肺动脉内,释放支架,测量主肺动脉远近端的压力阶差,撤除鞘管及传输系统,收紧已预置的荷包,放置引流,逐层关闭切口,结束手术。Make a transverse incision about 4 cm in the fourth intercostal space on the left edge of the sternum, separate the tissues layer by layer, suspend the pericardium, expose the right ventricular outflow tract and suture the purse bag, puncture the right ventricular outflow tract, and establish a right ventricle-pulmonary artery pathway through a guide wire , put the pulmonary artery constriction stent and delivery system along the established pathway under X-ray guidance, place the stent and delivery system into the pulmonary artery, release the stent, measure the pressure gradient between the distal and proximal ends of the main pulmonary artery, remove the sheath and delivery system, and tighten the Pre-placed purse, place drainage, close the incision layer by layer, and end the operation.
同背景技术提到的专利涉及的装置相比,本发明的特点是能够牢固贴覆于肺动脉内并可精确定位,通过支架内径来控制和减少肺动脉内血流,达到降低肺动脉压力的目的。Compared with the device mentioned in the patent mentioned in the background technology, the present invention is characterized in that it can be firmly attached to the pulmonary artery and can be precisely positioned, and the blood flow in the pulmonary artery can be controlled and reduced through the inner diameter of the stent to achieve the purpose of reducing the pulmonary artery pressure.
Claims (7)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200710018613CN101152111B (en) | 2007-09-07 | 2007-09-07 | Pulmonary Artery Coarctation Stents for Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200710018613CN101152111B (en) | 2007-09-07 | 2007-09-07 | Pulmonary Artery Coarctation Stents for Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101152111Atrue CN101152111A (en) | 2008-04-02 |
| CN101152111B CN101152111B (en) | 2010-07-14 |
Family
ID=39254137
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200710018613Expired - Fee RelatedCN101152111B (en) | 2007-09-07 | 2007-09-07 | Pulmonary Artery Coarctation Stents for Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101152111B (en) |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102462564A (en)* | 2011-10-25 | 2012-05-23 | 张石江 | Recyclable interventional stent for constricting blood vessels |
| CN102499802A (en)* | 2011-09-29 | 2012-06-20 | 微创医疗器械(上海)有限公司 | Filmed stent |
| CN101642395B (en)* | 2008-08-05 | 2013-03-20 | 王涛 | Ostomy bracket |
| CN103431931A (en)* | 2013-06-25 | 2013-12-11 | 杭州启明医疗器械有限公司 | Pulmonary artery support and pulmonary artery valve replacement device with same |
| CN103462726A (en)* | 2013-08-28 | 2013-12-25 | 苏州英络医疗器械有限公司 | Novel covered stent and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN105997298A (en)* | 2016-06-28 | 2016-10-12 | 黄连军 | Aortic stent |
| CN107174386A (en)* | 2017-04-27 | 2017-09-19 | 广州启骏生物科技有限公司 | A kind of device for treating pulmonary hypertension |
| CN107468391A (en)* | 2017-08-21 | 2017-12-15 | 北京赛铂医药科技有限公司 | A kind of cerebrovascular wire-pulling type falsework |
| CN108272487A (en)* | 2018-02-11 | 2018-07-13 | 南京普微森医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of braided support system |
| CN108601863A (en)* | 2015-12-11 | 2018-09-28 | 国家儿童医院研究所 | The system and method for patient-specific tissue engineering blood vessel graft for optimization |
| CN111938868A (en)* | 2020-08-20 | 2020-11-17 | 昆明市延安医院 | A device for treating severe pulmonary hypertension with patent ductus arteriosus and method of using the same |
| CN112137757A (en)* | 2019-09-08 | 2020-12-29 | 上海宏派医疗科技有限公司 | Novel coated blood vessel covered stent |
| CN112535561A (en)* | 2020-12-22 | 2021-03-23 | 上海腾复医疗科技有限公司 | Pulmonary artery stent |
| WO2022134193A1 (en)* | 2020-12-22 | 2022-06-30 | 上海腾复医疗科技有限公司 | Pulmonary artery stent |
| CN115737013A (en)* | 2023-01-04 | 2023-03-07 | 中国医学科学院阜外医院 | Edge atrial septal defect plugging device |
| US11925544B2 (en) | 2020-10-13 | 2024-03-12 | Shanghai Tendfo Medical Technologies Co. Ltd. | Pulmonary artery stent |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102462565B (en)* | 2011-10-25 | 2014-03-26 | 张石江 | Recyclable and adjustable interventional stent for constricting blood vessels |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6120534A (en)* | 1997-10-29 | 2000-09-19 | Ruiz; Carlos E. | Endoluminal prosthesis having adjustable constriction |
| US6953476B1 (en)* | 2000-03-27 | 2005-10-11 | Neovasc Medical Ltd. | Device and method for treating ischemic heart disease |
| IL158960A0 (en)* | 2003-11-19 | 2004-05-12 | Neovasc Medical Ltd | Vascular implant |
| CN2863016Y (en)* | 2005-09-09 | 2007-01-31 | 深圳市先健科技股份有限公司 | Blood vessel tectorial rack with protection function for branch vessel |
- 2007
- 2007-09-07CNCN 200710018613patent/CN101152111B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101642395B (en)* | 2008-08-05 | 2013-03-20 | 王涛 | Ostomy bracket |
| CN102499802A (en)* | 2011-09-29 | 2012-06-20 | 微创医疗器械(上海)有限公司 | Filmed stent |
| WO2013044823A1 (en)* | 2011-09-29 | 2013-04-04 | 上海微创医疗器械(集团)有限公司 | Membrane-covered stent |
| CN102462564A (en)* | 2011-10-25 | 2012-05-23 | 张石江 | Recyclable interventional stent for constricting blood vessels |
| CN103431931A (en)* | 2013-06-25 | 2013-12-11 | 杭州启明医疗器械有限公司 | Pulmonary artery support and pulmonary artery valve replacement device with same |
| CN103431931B (en)* | 2013-06-25 | 2015-10-28 | 杭州启明医疗器械有限公司 | Lung arterial support and there is the pulmonary artery valve replacement device of this lung arterial support |
| CN103462726A (en)* | 2013-08-28 | 2013-12-25 | 苏州英络医疗器械有限公司 | Novel covered stent and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN108601863A (en)* | 2015-12-11 | 2018-09-28 | 国家儿童医院研究所 | The system and method for patient-specific tissue engineering blood vessel graft for optimization |
| CN105997298A (en)* | 2016-06-28 | 2016-10-12 | 黄连军 | Aortic stent |
| CN107174386A (en)* | 2017-04-27 | 2017-09-19 | 广州启骏生物科技有限公司 | A kind of device for treating pulmonary hypertension |
| CN107468391B (en)* | 2017-08-21 | 2023-09-12 | 北京赛铂医药科技有限公司 | Cerebrovascular drawing-line type temporary support |
| CN107468391A (en)* | 2017-08-21 | 2017-12-15 | 北京赛铂医药科技有限公司 | A kind of cerebrovascular wire-pulling type falsework |
| CN108272487A (en)* | 2018-02-11 | 2018-07-13 | 南京普微森医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of braided support system |
| CN108272487B (en)* | 2018-02-11 | 2023-12-29 | 南京普微森医疗科技有限公司 | Braided support system |
| CN112137757A (en)* | 2019-09-08 | 2020-12-29 | 上海宏派医疗科技有限公司 | Novel coated blood vessel covered stent |
| CN111938868A (en)* | 2020-08-20 | 2020-11-17 | 昆明市延安医院 | A device for treating severe pulmonary hypertension with patent ductus arteriosus and method of using the same |
| US11925544B2 (en) | 2020-10-13 | 2024-03-12 | Shanghai Tendfo Medical Technologies Co. Ltd. | Pulmonary artery stent |
| US12329915B2 (en) | 2020-10-13 | 2025-06-17 | Shanghai Tendfo Medical Technologies Co., Ltd. | Pulmonary artery stent |
| CN112535561A (en)* | 2020-12-22 | 2021-03-23 | 上海腾复医疗科技有限公司 | Pulmonary artery stent |
| WO2022134193A1 (en)* | 2020-12-22 | 2022-06-30 | 上海腾复医疗科技有限公司 | Pulmonary artery stent |
| CN112535561B (en)* | 2020-12-22 | 2025-01-10 | 上海腾复医疗科技有限公司 | Pulmonary artery stent |
| CN115737013A (en)* | 2023-01-04 | 2023-03-07 | 中国医学科学院阜外医院 | Edge atrial septal defect plugging device |
| CN115737013B (en)* | 2023-01-04 | 2023-05-12 | 中国医学科学院阜外医院 | Edge atrial septal defect plugging device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101152111B (en) | 2010-07-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101152111A (en) | Pulmonary Artery Coarctation Stents for Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension | |
| US11027103B2 (en) | Conduit device and system for implanting a conduit device in a tissue wall | |
| US9510948B2 (en) | Systems, devices and methods for repair of heart valve lesions | |
| US20170112499A1 (en) | Cardiovascular valve and valve housing apparatuses and systems | |
| CN211381986U (en) | A transcatheter implantable heart valve clamp | |
| US10028741B2 (en) | Systems and methods for percutaneous access, stabilization and closure of organs | |
| CN104274224B (en) | Left atrial appendage occlusion device | |
| CN104706444B (en) | Left ventricle capacity-reduction device | |
| CN107205744A (en) | Set of adjustable invasively reducing blood flow stents and stents | |
| CN204521054U (en) | Left ventricle capacity-reduction device | |
| CN107595437B (en) | Valve clamping system | |
| US20100160939A1 (en) | Systems, apparatuses, and methods for cardiovascular cutting devices and valves | |
| CN108348666A (en) | Inflow Cannula and Flow Assist Systems | |
| US20060041244A1 (en) | Hemocirculatory catheter and method of use thereof | |
| Kluttig et al. | Invasive hemodynamic monitoring of aortic and pulmonary artery hemodynamics in a large animal model of ARDS | |
| CN110934674B (en) | Cuff device for isolating aneurysm cavity of aorta inner wall and using method | |
| CN115024857B (en) | An artificial blood vessel for aortic surgery | |
| RU2822548C1 (en) | Device for intraoperative positioning of aortic valve cusps in valve-preserving aortic root replacement | |
| CN220124889U (en) | Artificial blood vessel for full aortic arch replacement stent trunk | |
| Demirdaş et al. | Repair of coarctation of the aorta, bicuspid aortic valve, subaortic membrane and ascending aotic aneurysm in a single session | |
| WO2024158684A1 (en) | Device and method for monitoring left atrial pressure | |
| CN116211544A (en) | A valve blood flow regulating device | |
| CN115501463A (en) | A kind of superior vena cava shunt | |
| JP2020000828A (en) | Cannula for minimally invasive surgical tricuspid valve repair | |
| WHITING et al. | Double‐Outlet Right Ventricle for Relief of Pulmonic Stenosis in Dogs An Experimental Study |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20100714 Termination date:20160907 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |