CN101046810B - System and method for automatically establishing relational model - Google Patents
System and method for automatically establishing relational modelDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101046810B CN101046810BCN2006100784230ACN200610078423ACN101046810BCN 101046810 BCN101046810 BCN 101046810BCN 2006100784230 ACN2006100784230 ACN 2006100784230ACN 200610078423 ACN200610078423 ACN 200610078423ACN 101046810 BCN101046810 BCN 101046810B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- class
- primary key
- model
- association
- mapped
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/28—Databases characterised by their database models, e.g. relational or object models
- G06F16/289—Object oriented databases
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/28—Databases characterised by their database models, e.g. relational or object models
- G06F16/284—Relational databases
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及数据库技术领域,特别是一种自动建立关系模型的系统及其方法。The invention relates to the technical field of databases, in particular to a system and method for automatically establishing a relational model.
背景技术Background technique
当前,在应用中通常将JAVA2企业版(J2EE)系统的体系结构分为三个基本层次:展示层、业务逻辑层和数据源层,其中展示层用于向最终用户提供界面,业务逻辑层用于进行各个领域中的业务逻辑处理,数据源层用于处理和关系数据库、消息系统的连接,并完成事务管理等功能。在上述三个基本层次中,数据源层是非常重要的层次,在实际应用中数据源的大多数应用场景是关系数据库。At present, the architecture of the JAVA2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) system is usually divided into three basic levels in the application: the presentation layer, the business logic layer and the data source layer. It is used to process business logic in various fields, and the data source layer is used to process connections with relational databases and message systems, and to complete functions such as transaction management. Among the above three basic levels, the data source layer is a very important level. In practical applications, most application scenarios of data sources are relational databases.
在J2EE的体系架构中,可以通过JAVA数据库连接技术(JDBC)直接对关系数据库进行访问,这也是大多数应用所采用的数据访问方式,但是在应用程序中使用JDBC访问数据库将会导致业务处理逻辑和数据访问代码混杂在一起,不利于后期的维护。而对象/关系映射技术是一种很好的替代方案,在关系数据库访问接口上使用对象/关系映射技术可以通过面向对象(OO)模型屏蔽后台数据库系统的差异,并且系统的数据模型易于理解,有利于提高编程的效率,还可以提高代码的可读性和可维护性。In the J2EE architecture, relational databases can be accessed directly through JAVA database connection technology (JDBC), which is also the data access method adopted by most applications, but using JDBC to access databases in applications will result in It is mixed with data access code, which is not conducive to later maintenance. The object/relational mapping technology is a good alternative. Using the object/relational mapping technology on the relational database access interface can shield the differences of the background database system through the object-oriented (OO) model, and the data model of the system is easy to understand. It is conducive to improving the efficiency of programming, and can also improve the readability and maintainability of the code.
目前比较成熟的对象/关系映射解决方案有三类,以下分别说明。There are currently three types of mature object/relational mapping solutions, which are described below.
第一类为基于对象模型的建模方案。基于对象模型的建模方案完全以对象模型为中心,主要是以统一模型化语言(UML)为代表的图形化建模工具。但是,该类方案没有针对数据访问层的应用场景做裁减,所以使用比较复杂;并且该类方案没有提供对象模型到关系模型的映射工具,关系模型的维护需要通过另外的工具实现,集成度较低;而且该方案没有针对对象/关系映射技术的集成,手工集成的工作量较大。The first category is the modeling scheme based on the object model. The modeling scheme based on the object model is completely centered on the object model, mainly a graphical modeling tool represented by the Unified Modeling Language (UML). However, this type of solution does not tailor the application scenarios of the data access layer, so it is more complicated to use; and this type of solution does not provide a mapping tool from the object model to the relational model, and the maintenance of the relational model needs to be realized through another tool, and the integration degree is relatively Low; and this solution does not have object/relational mapping technology integration, and the workload of manual integration is relatively large.
第二类为基于关系模型的建模方案。基于关系模型的解决方案完全以关系模型为中心,主要是以实体关系(ER)图为代表的图形化建模工具。但是这类方案没有提供对象模型到关系模型的映射工具,对象模型的维护需要通过另外的工具实现,集成度较低;而且没有针对对象/关系映射技术的集成,手工集成的工作量较大。The second category is the modeling scheme based on the relational model. The solution based on the relational model is completely centered on the relational model, mainly a graphical modeling tool represented by an entity-relationship (ER) diagram. However, this type of solution does not provide a mapping tool from object model to relational model, and the maintenance of the object model needs to be realized through another tool, and the integration degree is low; and there is no integration for object/relational mapping technology, and the workload of manual integration is relatively large.
第三类为基于配置文件的对象关系映射方案。这种方案以Hibernate技术为代表。使用这种映射方案,用户需要提供大量的配置文件,用户需要理解类之间的关联、继承、组合等关系,并把这些类和关系的映射规则手工编写成为对应的配置文件和映射文件。这种技术方案的缺点是其没有提供自动化的开发工具,完全依赖于用户的手工劳动;难于维护,配置文件、映射规则、数据库建表脚本都需要手工编写,任何一个地方修改都会牵涉其他地方的修改,修改过程中容易导致错误。The third category is the object-relational mapping scheme based on the configuration file. This solution is represented by Hibernate technology. Using this mapping scheme, the user needs to provide a large number of configuration files. The user needs to understand the association, inheritance, combination and other relationships between classes, and manually write the mapping rules of these classes and relationships into corresponding configuration files and mapping files. The disadvantage of this technical solution is that it does not provide automated development tools and completely relies on the manual labor of users; it is difficult to maintain, configuration files, mapping rules, and database table creation scripts need to be written manually, and any modification in one place will involve other places It is easy to make mistakes during the modification process.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本发明提出了一种建立关系模型的方法,用以提高系统集成度,降低手工集成工作量,从而提高开发效率。本发明的另一个目的是提供一种建立关系模型的系统。In view of this, the present invention proposes a method for establishing a relational model to improve system integration, reduce manual integration workload, and improve development efficiency. Another object of the present invention is to provide a system for building relational models.
为实现上述目的,本发明提供了一种自动建立关系模型的IDE系统,该系统包括:模型信息采集引擎,用于遍历对象模型、从对象模型采集得到模型关联信息,并将所述模型关联信息发送给自动转换引擎;第一自动转换引擎,用于根据预设的映射规则定义文件、所述模型关联信息和对象模型,生成映射文件;模型输出工具,用于根据所述映射文件生成关系模型。In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides an IDE system for automatically establishing a relational model. The system includes: a model information acquisition engine, which is used to traverse the object model, acquire model association information from the object model, and store the model association information Sent to the automatic conversion engine; the first automatic conversion engine is used to generate a mapping file according to the preset mapping rule definition file, the model association information and the object model; the model output tool is used to generate a relational model according to the mapping file .
本发明还提供了一种自动建立关系模型的方法,该方法包括以下步骤:设置对象模型到关系模型的映射规则,以及遍历对象模型、从对象模型中采集模型关联信息;根据所述映射规则和模型关联信息以及对象模型生成映射文件;根据映射文件生成关系模型。The present invention also provides a method for automatically establishing a relational model, which includes the following steps: setting the mapping rules from the object model to the relational model, traversing the object model, and collecting model association information from the object model; according to the mapping rules and A mapping file is generated from the model association information and the object model; a relational model is generated according to the mapping file.
所述映射文件包括Hibernate映射文件和Hibernate配置文件。The mapping file includes a Hibernate mapping file and a Hibernate configuration file.
所述模型关联信息包括单键实体类;所述映射规则包括:类映射到表;主键属性映射为表的主键;非主键属性映射为表的字段。或者所述模型关联信息包括复合主键实体类;所述映射规则包括:类映射到表;主键属性映射为表的主键,主键类所有的属性映射到表的复合主键字段;非主键属性映射为表的字段。The model association information includes a single-key entity class; the mapping rule includes: mapping a class to a table; mapping a primary key attribute to a primary key of a table; mapping a non-primary key attribute to a field of a table. Or the model association information includes a composite primary key entity class; the mapping rules include: class mapping to a table; primary key attributes are mapped to the primary key of the table, all attributes of the primary key class are mapped to the composite primary key field of the table; non-primary key attributes are mapped to the table field.
所述模型关联信息包括实体类型和值类型,且所述实体类与值类型为一对一关系;所述映射规则为:实体类映射到表;实体主键属性映射为表的主键;值类型的多个属性映射到实体类对应的表的多个字段;非主键属性映射为表的字段;或者所述映射规则为:实体类和值类型分别映射到两张独立的表;值类型对应的表中增加实体类的主键字段,作为值类型的主键和外键。The model association information includes an entity type and a value type, and the entity class and the value type have a one-to-one relationship; the mapping rules are: the entity class is mapped to the table; the entity primary key attribute is mapped to the primary key of the table; the value type Multiple attributes are mapped to multiple fields of the table corresponding to the entity class; non-primary key attributes are mapped to the fields of the table; or the mapping rules are: the entity class and the value type are respectively mapped to two independent tables; the table corresponding to the value type Add the primary key field of the entity class as the primary key and foreign key of the value type.
所述模型关联信息包括实体类型和值类型,且所述实体类与值类型为一对多关系;所述映射规则为:实体类和值类型分别映射到两张独立的表;值类型对应的表中增加实体类的主键字段,作为值类型的外键,且值类型有单独的主键字段。The model association information includes an entity type and a value type, and the entity class and the value type are in a one-to-many relationship; the mapping rule is: the entity class and the value type are respectively mapped to two independent tables; the value type corresponds to The primary key field of the entity class is added to the table as the foreign key of the value type, and the value type has a separate primary key field.
所述模型关联信息包括属性类型;所述属性类型为基本类型或基于扩展的基本类型时,所述映射规则包括:属性类型映射到数据库的字段;和/或所述属性类型为结构类型时,所述映射规则包括:结构类型与其所述的类映射到同一张表。The model association information includes an attribute type; when the attribute type is a basic type or an extension-based basic type, the mapping rule includes: mapping the attribute type to a database field; and/or when the attribute type is a structure type, The mapping rules include: the structure type and its class are mapped to the same table.
所述模型关联信息包括关联类与被关联类单向一对一关联关系和/或关联类和被关联类双向一对多关联关系。所述映射规则为:关联类映射到表;关联类和被关联类的属性映射到表的字段。或者所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;被关联类对应的表使用关联类的主键作为自己的主键和外键字段。或者所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;被关联类对应的表使用关联类的主键作为自己的外键字段,并使用单独的主键字段。The model association information includes a one-way one-to-one association relationship between an association class and an associated class and/or a two-way one-to-many association relationship between an association class and an associated class. The mapping rule is: the association class is mapped to the table; the attributes of the association class and the associated class are mapped to the fields of the table. Alternatively, the mapping rule is: the associated class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; the table corresponding to the associated class uses the primary key of the associated class as its primary key and foreign key fields. Alternatively, the mapping rule is: the associated class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; the table corresponding to the associated class uses the primary key of the associated class as its own foreign key field, and uses a separate primary key field.
所述模型关联信息包括关联类和被关联类单向一对多关联关系,和/或关联类和被关联类双向一对多关联关系,和/或关联类和被关联类双向多对一关联关系。所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;被关联类对应的表使用关联类的主键作为自己的外键字段。或者所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段。或者所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段,同时关联表有自己的主键字段。The model association information includes a one-way one-to-many association relationship between an association class and an associated class, and/or a two-way one-to-many association relationship between an association class and an associated class, and/or a two-way many-to-one association between an association class and an associated class relation. The mapping rule is: the associated class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; the table corresponding to the associated class uses the primary key of the associated class as its foreign key field. Or the mapping rule is: the association class and the associated class are respectively mapped to two tables; a new connection table is created, and the fields in the table include the primary key fields of the association class and the associated class. Or the mapping rule is: the association class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; create a new connection table, the fields in the table include the primary key fields of the associated class and the associated class, and the association table has its own primary key field .
所述模型关联信息包括关联类和被关联类单向多对一关联关系。所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;关联类使用被关联类的主键属性作为外键字段。或者所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段。或者所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段,连接表同时有自己的主键字段。The model association information includes a one-way many-to-one association relationship between an association class and an associated class. The mapping rule is as follows: the association class and the associated class are respectively mapped to two tables; the association class uses the primary key attribute of the associated class as a foreign key field. Or the mapping rule is: the association class and the associated class are respectively mapped to two tables; a new connection table is created, and the fields in the table include the primary key fields of the association class and the associated class. Or the mapping rule is: the associated class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; a new connection table is created, the fields in the table include the primary key fields of the associated class and the associated class, and the connection table has its own primary key field at the same time .
所述模型关联信息包括关联类和被关联类多对多关联关系和/或关联类和被关联类双向多对多关联关系。所述映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表,属性对象映射到一张连接表;创建一个新的连接表,该新连接表中的字段只包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段,并且新连接表的某个字段和前面的主键字段联合起来作为主键。The model association information includes a many-to-many association relationship between an association class and an associated class and/or a bidirectional many-to-many association relationship between an association class and an associated class. The mapping rules are as follows: the association class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively, and the attribute object is mapped to a connection table; a new connection table is created, and the fields in the new connection table only include the association class and the associated class The primary key field, and a field of the new connection table is combined with the previous primary key field as the primary key.
所述模型关联信息包括父类与子类的继承关系。所述映射规则为:每个层次的类的所有属性叠加到一张表中;父类使用类型字段表示自己所在的层次;所有的子类层次对应的表共用父类的主键作为外键唯一标识一条记录。或者所述映射规则为:每个子类生成一张单独的表;每个子类对应的表使用父类的主键作为外键唯一标识一条记录。或者所述映射规则为:每个具体类一张表,该表中包含了从最顶层的父类到该子类的所有字段的并集。The model association information includes the inheritance relationship between the parent class and the subclass. The mapping rules are as follows: all attributes of classes at each level are superimposed into one table; the parent class uses the type field to indicate its own level; tables corresponding to all subclass levels share the primary key of the parent class as a foreign key to uniquely identify a record . Or the mapping rule is: each subclass generates a separate table; the table corresponding to each subclass uses the primary key of the parent class as a foreign key to uniquely identify a record. Or the mapping rule is: one table for each concrete class, which contains the union of all fields from the topmost parent class to the subclass.
所述模型关联信息包括关联属性类和被关联属性类一对一组合关系。所述映射规则为:关联属性类映射到表;关联属性类主键属性映射为表的主键;被关联属性类的多个属性映射到关联类对应的表的多个字段;非主键属性映射为表的字段。或者所述映射规则为:关联属性类和被关联属性类分别映射到两张独立的表中;被关联属性类对应的表中增加关联属性类的主键字段,作为被关联属性类的主键和外键。The model association information includes a one-to-one combination relationship between an associated attribute class and an associated attribute class. The mapping rules are: the associated attribute class is mapped to the table; the associated attribute class primary key attribute is mapped to the primary key of the table; multiple attributes of the associated attribute class are mapped to multiple fields of the table corresponding to the associated class; non-primary key attributes are mapped to the table field. Or the mapping rule is: the associated attribute class and the associated attribute class are respectively mapped to two independent tables; the primary key field of the associated attribute class is added in the table corresponding to the associated attribute class, as the primary key and outer table of the associated attribute class key.
所述模型关联信息包括关联属性类和被关联属性类一对多组合关系。所述映射规则为:关联属性类和被关联属性类分别映射到两张独立的表中;被关联属性类对应的表中增加关联属性类的主键字段,作为被关联属性类的外键,且被关联属性类有单独的主键字段。The model association information includes a one-to-many combination relationship between associated attribute classes and associated attribute classes. The mapping rule is: the associated attribute class and the associated attribute class are respectively mapped to two independent tables; the primary key field of the associated attribute class is added in the table corresponding to the associated attribute class as the foreign key of the associated attribute class, and Associated attribute classes have a single primary key field.
从上述方案中可以看出,由于本发明从对象模型采集模型关联信息并设置映射规则,根据模型关联信息和映射规则以及对象模型自动生成关系模型以及自动生成映射文件,提高了对象模型到关系模型映射的自动化程度,提高了系统集成度,降低了手工集成工作量,简化了开发人员的工作,从而提高了开发效率,并且能降低由于开发人员手工定义导致的错误比率。另外,实施本发明时,只需要简单的映射规则设置,甚至不用设置而采用缺省的规则,就可以完成关系模型的自动生成、Hibernate映射文件的自动生成,大大提高的工作的效率。As can be seen from the above scheme, since the present invention collects model association information from the object model and sets mapping rules, automatically generates a relational model and automatically generates a mapping file according to the model association information and mapping rules and the object model, and improves the relationship between the object model and the relational model. The degree of automation of mapping improves system integration, reduces the workload of manual integration, simplifies the work of developers, improves development efficiency, and reduces the error rate caused by manual definitions by developers. In addition, when the present invention is implemented, only simple mapping rule settings are required, or even default rules are adopted without setting, and the automatic generation of relational models and Hibernate mapping files can be completed, greatly improving work efficiency.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明实施例的一种系统结构图。FIG. 1 is a system structure diagram of an embodiment of the present invention.
图2为本发明实施例的另一种系统结构图。Fig. 2 is another system structure diagram of the embodiment of the present invention.
图3为本发明实施例中所采用的对象模型的示意图。Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of an object model used in an embodiment of the present invention.
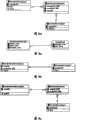
图4a和图4b分别为单键实体类以及对应的关系模型的示意图。FIG. 4a and FIG. 4b are schematic diagrams of a single-key entity class and a corresponding relationship model respectively.
图5a和图5b为复合主键实体类的示意图,图5c为对应的关系模型。Figure 5a and Figure 5b are schematic diagrams of composite primary key entity classes, and Figure 5c is a corresponding relationship model.
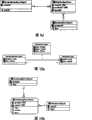
图6a为一对一的实体类和值类型的示意图,图6b和图6c为与图6a对应的关系模型;图6d为一对多的实体类和值类型的关系模型示意图。Figure 6a is a schematic diagram of one-to-one entity classes and value types, Figures 6b and 6c are relationship models corresponding to Figure 6a; Figure 6d is a schematic diagram of a one-to-many entity class and value type relationship model.
图7a为单向一对一关联关系的示意图,图7b为与图7a对应的基于主键的关系模型示意图。FIG. 7a is a schematic diagram of a one-way one-to-one association relationship, and FIG. 7b is a schematic diagram of a primary key-based relationship model corresponding to FIG. 7a.
图8a为单向一对多关联关系的示意图,图8b、图8c和图8d分别为与图8a对应的关系模型示意图。Fig. 8a is a schematic diagram of a one-way one-to-many association relationship, and Fig. 8b, Fig. 8c and Fig. 8d are respectively schematic diagrams of a relationship model corresponding to Fig. 8a.
图9a为单向多对一关联关系的示意图,图9b、图9c和图9d分别为与图9a对应的关系模型示意图。Fig. 9a is a schematic diagram of a one-way many-to-one association relationship, and Fig. 9b, Fig. 9c and Fig. 9d are respectively schematic diagrams of a relationship model corresponding to Fig. 9a.
图10a为单向多对多关联关系的示意图,图10b为与图10a对应的关系模型示意图。Fig. 10a is a schematic diagram of a one-way many-to-many association relationship, and Fig. 10b is a schematic diagram of a relationship model corresponding to Fig. 10a.
图11a为继承关系的示意图,图11b、图11c和图11d分别为与图11a对应的关系模型示意图。Fig. 11a is a schematic diagram of an inheritance relationship, and Fig. 11b, Fig. 11c and Fig. 11d are respectively schematic diagrams of a relationship model corresponding to Fig. 11a.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,以下举实施例对本发明进一步详细说明。In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the following examples are given to further describe the present invention in detail.
图1所示的是本发明实施例中的一种自动建立关系模型的集成开发环境(IDE)系统的示意图,该系统主要包括模型信息采集引擎和自动转换引擎。其中模型信息采集引擎从对象模型采集得到模型关联信息,然后将模型关联信息发送给自动转换引擎;自动转换引擎根据预先设置的映射规则定义文件、所述模型关联信息以及对象模型,生成映射文件和关系模型,用户可以利用得到的关系模型来访问数据库。其中模型信息采集引擎的采集过程可以为:遍历对象模型并获取模型关联信息。所述模型关联信息包括关联关系、继承关系、组合关系、类名称及其属性列表、属性名称及其类型等;所述映射规则定义文件包括类映射规则、属性映射规则、关联映射规则、继承映射规则、组合映射规则等。映射文件可以包括Hibernate映射文件和Hibernate配置文件。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an integrated development environment (IDE) system for automatically establishing a relational model in an embodiment of the present invention. The system mainly includes a model information acquisition engine and an automatic conversion engine. Wherein the model information collection engine acquires the model association information from the object model, and then sends the model association information to the automatic conversion engine; the automatic conversion engine generates the mapping file and the object model according to the preset mapping rule definition file, the model association information and the object model Relational model, users can use the obtained relational model to access the database. The collection process of the model information collection engine may be: traversing the object model and obtaining model association information. The model association information includes association relationship, inheritance relationship, combination relationship, class name and its attribute list, attribute name and its type, etc.; the mapping rule definition file includes class mapping rules, attribute mapping rules, association mapping rules, inheritance mapping rules, combined mapping rules, etc. Mapping files can include Hibernate mapping files and Hibernate configuration files.
图2所示的是本发明实施例的另一种系统结构,该系统包括模型信息采集引擎和自动转换引擎,自动转换引擎包括第一自动转换引擎以及模型输出工具,其中模型信息采集引擎从对象模型采集得到模型关联信息,然后将模型关联信息发送给自动转换引擎,自动转换引擎根据预先设置的映射规则定义文件以及模型关联信息和对象模型,生成关系模型和映射文件。在自动转换引擎中,第一自动转换引擎根据预先设置的映射规则定义文件、模型关联信息和对象模型生成映射文件,而模型输出工具根据映射文件生成关系模型,用户可以利用得到的关系模型来访问数据库。这里以模型输出工具是Hibernate模型输出工具为例,那么映射文件包括Hibernate映射文件和Hibernate配置文件。与图1所示的系统相比,图2所示的系统中Hibernate模型输出工具导出的关系模型只能是数据定义语言(DDL)语句的建表脚本。What Fig. 2 shows is another kind of system structure of the embodiment of the present invention, and this system comprises model information acquisition engine and automatic conversion engine, and automatic conversion engine comprises first automatic conversion engine and model output tool, and wherein model information acquisition engine is from object The model collects the model association information, and then sends the model association information to the automatic conversion engine, and the automatic conversion engine generates a relational model and a mapping file according to the preset mapping rule definition file, model association information and object model. In the automatic conversion engine, the first automatic conversion engine generates a mapping file according to the preset mapping rule definition file, model association information and object model, and the model output tool generates a relational model according to the mapping file, and the user can use the obtained relational model to access database. Here, the model output tool is Hibernate model output tool as an example, then the mapping file includes Hibernate mapping file and Hibernate configuration file. Compared with the system shown in Figure 1, the relational model exported by the Hibernate model output tool in the system shown in Figure 2 can only be a table-building script of a data definition language (DDL) statement.
本发明实施例采用上述自动建立关系模型的IDE系统,实现自动建立关系模型。本发明实施例的方法包括以下步骤:The embodiment of the present invention adopts the above-mentioned IDE system for automatically establishing a relational model to realize automatic establishment of a relational model. The method of the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
步骤S1,设置对象模型到关系模型的映射规则,形成映射规则定义文件,模型信息采集引擎从对象模型中采集得到模型关联信息,并将模型关联信息发送给自动转换引擎。其中,模型信息采集引擎从对象模型中采集模型关联信息的过程可以为:遍历对象模型,并获取模型关联信息。Step S1, setting the mapping rules from the object model to the relational model, forming a mapping rule definition file, the model information collection engine collects model association information from the object model, and sends the model association information to the automatic conversion engine. Wherein, the process of the model information collection engine collecting model association information from the object model may be: traversing the object model and obtaining model association information.
步骤S2,自动转换引擎根据所述映射规则和模型关联信息以及对象模型,自动生成关系模型。如果采用的是图1所示的系统,则自动转换引擎还可以进一步生成映射文件。如果采用的是图2所示的系统,则步骤S2可以分为以下两个步骤:第一自动转换引擎根据所述映射规则和模型关联信息以及对象模型生成映射文件;模型输出工具根据映射文件生成关系模型。所述映射文件包括Hibernate映射文件和Hibernate配置文件。In step S2, the automatic conversion engine automatically generates a relational model according to the mapping rule, model association information and object model. If the system shown in Figure 1 is used, the automatic conversion engine can further generate a mapping file. If the system shown in Figure 2 is used, then step S2 can be divided into the following two steps: the first automatic conversion engine generates a mapping file according to the mapping rules and model association information and the object model; the model output tool generates a mapping file according to the mapping file relational model. The mapping file includes a Hibernate mapping file and a Hibernate configuration file.
以下通过一个具体的对象模型来描述本发明的实施。The following describes the implementation of the present invention through a specific object model.
图3是本发明实施例中所采用的对象模型的UML图,图中所用图例为标准的UML图图例。该对象模型可以是预先通过IDE设计得到的域对象模型。在图3中,所示对象模型分为客户域、用户域、帐户域和产品域。Fig. 3 is a UML diagram of the object model adopted in the embodiment of the present invention, and the legend used in the figure is a standard UML diagram legend. The object model may be a domain object model designed in advance through the IDE. In Figure 3, the object model shown is divided into customer domain, user domain, account domain and product domain.
在客户域中,客户(Customer)拥有一个唯一的客户标识(customerId),客户拥有多个地址(Address),每个地址包括国家(country)和邮政编码(zipCode)两个字段;一个客户拥有0~n帐户(Account),即客户和帐户之间是一对多的关联关系。In the customer domain, the customer (Customer) has a unique customer ID (customerId), the customer has multiple addresses (Address), each address includes two fields of country (country) and zip code (zipCode); a customer has 0 ~n account (Account), that is, there is a one-to-many relationship between customers and accounts.
在用户域中,用户组(UserGroup)使用一个唯一的用户组标识(groupId);用户组和客户之间的关联关系是多对多的关联关系,该关联关系的属性使用客户用户组关系(CustomerUserGroupRela)标识;用户组和用户(User)是一对多的关联关系;用户使用唯一的用户标识(subsriberId),一个用户包含0~n个服务号码(ServiceNumber)、0~n个产品定购关系(ProductOrder)、以及0~n个支付关系(PaymentRelation);服务号码使用唯一的服务号码标识(serviceNumberId),服务号码分为电话号码(PhoneNumber)和综合业务数据网(ISDN)号码(IsdnMuber)两类,两类服务号码的共同属性放在服务号码中;每个产品定购关系使用唯一的定购关系标识(oerderId),每个产品定购关系包含0~n个参数(OrderParameters),并且唯一关联到一个产品(Product)。In the user domain, a user group (UserGroup) uses a unique user group identifier (groupId); the relationship between a user group and a customer is a many-to-many relationship, and the attributes of the relationship use the customer user group relationship (CustomerUserGroupRela ) identification; user groups and users (User) are one-to-many associations; users use unique user IDs (subsriberId), and a user includes 0~n service numbers (ServiceNumber), 0~n product order relationships (ProductOrder ), and 0 to n payment relations (PaymentRelation); the service number uses a unique service number identifier (serviceNumberId), and the service number is divided into two types: phone number (PhoneNumber) and integrated service data network (ISDN) number (IsdnMuber). The common attributes of service numbers are placed in the service number; each product order relationship uses a unique order relationship identifier (oerderId), each product order relationship contains 0~n parameters (OrderParameters), and is uniquely associated with a product (Product ).
在帐户域中,帐户使用唯一的帐户标识(accountId);每个支付关系唯一关联到一个帐户,并唯一关联到一个费用项(FeeItem);费用项使用唯一的费用项标识(feeItemId)。In the account domain, an account uses a unique account ID (accountId); each payment relationship is uniquely associated with an account and uniquely associated with a fee item (FeeItem); a fee item uses a unique fee item ID (feeItemId).
在产品域中,产品使用唯一的产品标识(productId)。In the product domain, a product uses a unique product ID (productId).
模型信息采集引擎从上述对象模型中采集得到如下模型关联信息:1)实体模型,包括实体类型和值类型(或者叫结构类型),实体类型例如用户、客户等,值类型例如地址、产品定购关系参数等;2)属性模型,根据属性的类型可以分为基本类型和扩展类型,扩展类型包括基于基本类型的扩展类型和结构类型;3)关联关系,分为单向关联和双向关联,其中单向关联包括一对一关联、一对多关联、多对一关联,双向关联包括一对一关联、一对多关联、多对一关联、多对多关联,另外关联中可以带有自己的属性;4)继承关系,只支持单根继承方式;5)组合关系,包括一对一的组合和一对多的组合。The model information collection engine collects the following model related information from the above object model: 1) Entity model, including entity type and value type (or structure type), entity type such as user, customer, etc., value type such as address, product order relationship parameters, etc.; 2) attribute model, which can be divided into basic types and extended types according to the type of attributes, and extended types include extended types and structural types based on basic types; Two-way associations include one-to-one associations, one-to-many associations, and many-to-one associations. Two-way associations include one-to-one associations, one-to-many associations, many-to-one associations, and many-to-many associations. In addition, associations can have their own attributes ; 4) Inheritance relationship, only supports single root inheritance; 5) Composition relationship, including one-to-one combination and one-to-many combination.
针对这些模型关联信息以及对象模型,描述相应的映射规则。For these model association information and object models, describe the corresponding mapping rules.
一、实体模型的映射规则。其中包括实体类型的映射规则和值类型的映射规则。1. The mapping rules of the entity model. These include mapping rules for entity types and mapping rules for value types.
1、实体类型的映射规则。实体类型映射包括单键实体类(SingleKeyEntity)的映射和复合主键(也成为多主键)实体类(MultiKeyEntity)的映射。单键实体类的映射规则为:类映射到同名或不同名的表;主键属性映射为表的主键;非主键属性映射为表的字段,并且字段的类型和约束可以在IDE中设置。例如,图4a所示的单键实体类根据该映射规则映射为图4b所示的关系模型。在图4a和图4b中,类以及表名称为单键实体(SingleKeyEntity),主键属性为长整型(Long)的标识(id),非主键属性包括字符串型(String)的名称(name)和描述(description)。1. Mapping rules for entity types. Entity type mapping includes the mapping of single key entity class (SingleKeyEntity) and the mapping of composite primary key (also known as multi-primary key) entity class (MultiKeyEntity). The mapping rules for a single-key entity class are: the class is mapped to a table with the same name or a different name; the primary key attribute is mapped to the primary key of the table; the non-primary key attribute is mapped to the field of the table, and the type and constraint of the field can be set in the IDE. For example, the single-key entity class shown in Figure 4a is mapped to the relational model shown in Figure 4b according to the mapping rule. In Figure 4a and Figure 4b, the name of the class and the table is a single key entity (SingleKeyEntity), the primary key attribute is the long integer (Long) identifier (id), and the non-primary key attribute includes the name (name) of the string type (String) and description.
复合主键实体类的映射规则为:类映射到表,类对应的表名称可以同名或者在IDE中设置;主键属性映射为表的主键,如果主键是主键类,则主键类所有的属性映射到表的复合主键字段;非主键属性映射为表的字段,并且字段的类型和约束可以在IDE中设置。在实际应用中,根据主键的处理方式,复合主键实体类包含如图5a和图5b所示的两种形式,在图5a中实体类主键是基于实体属性的复合主键;在图5b中实体类主键是基于单独的主键类的复合主键,在这种复合主键实体类的模型中需要指明哪个类是主键类型,哪个字段是主键。根据上述映射规则,图5a和图5b所示的两种复合主键类实体的都映射为如图5c所示的关系模型。The mapping rules of the composite primary key entity class are: the class is mapped to the table, and the table name corresponding to the class can be the same name or set in the IDE; the primary key attribute is mapped to the primary key of the table, if the primary key is the primary key class, all the attributes of the primary key class are mapped to the table Composite primary key fields; non-primary key attributes are mapped to table fields, and field types and constraints can be set in the IDE. In practical applications, according to the processing method of the primary key, the composite primary key entity class includes two forms as shown in Figure 5a and Figure 5b. In Figure 5a, the primary key of the entity class is a composite primary key based on entity attributes; in Figure 5b, the entity class The primary key is a composite primary key based on a separate primary key class. In the model of this composite primary key entity class, it is necessary to indicate which class is the primary key type and which field is the primary key. According to the above mapping rules, the two types of composite primary key entities shown in Figure 5a and Figure 5b are mapped to the relational model shown in Figure 5c.
2、值类型的映射规则。所谓的“值类型”是指结构类型等自定义类型,通常作为实体的一个属性存在,分为单成员属性和集合属性两种形式,因此值类型在和实体类型之间的关系是单向(从实体类型到值类型)一对一或者一对多关联。2. Mapping rules for value types. The so-called "value type" refers to a custom type such as a structure type, which usually exists as an attribute of an entity and is divided into two forms: single-member attribute and collection attribute, so the relationship between the value type and the entity type is one-way ( From entity types to value types) one-to-one or one-to-many associations.
其中,对于一对一值类型的映射,可使用映射到同一张表中的映射规则1:实体类映射到表,类对应的表名称可以同名或者在IDE中设置;实体主键属性映射为表的主键;值类型的多个属性映射到实体类对应的表的多个字段;非主键属性映射为表的字段,其中字段的类型和约束可以在IDE中设置。根据映射规则1,可以将如图6a所示的对象模型映射到如图6b所示的关系模型。还可以使用映射规则2:实体类和值类型分别映射到两张独立的表中;值类型对应的表中增加实体类的主键字段,作为值类型的主键和外键。可见,根据映射规则2,实体类和值类型分别映射到两张表中,使用主键和外键进行关联,根据映射规则2,可以将如图6a所示的对象模型映射为如图6c所示的关系模型。Among them, for the mapping of one-to-one value types, the
对于一对多值类型的映射,可以采用如下映射规则:实体类和值类型分别映射到两张独立的表中;值类型对应的表中增加实体类的主键字段,作为值类型的外键,值类型有单独的主键字段。采用该映射规则,得到的对象模型映射如图6d所示。在图6a至图6d中,类及表名称包括客户实体类型(CustomerEntityType)、地址值类型(AddressValueType),属性包括id、name、描述(desc)、country、address、zipcode等。For the mapping of one-to-many value types, the following mapping rules can be used: the entity class and the value type are mapped to two independent tables; the primary key field of the entity class is added to the table corresponding to the value type as the foreign key of the value type, Value types have separate primary key fields. Using this mapping rule, the resulting object model mapping is shown in Figure 6d. In Fig. 6a to Fig. 6d, the class and table names include customer entity type (CustomerEntityType), address value type (AddressValueType), and attributes include id, name, description (desc), country, address, zipcode, etc.
二、属性模型的映射规则。如前所述,根据属性的类型可以分为基本类型和扩展类型,扩展类型包括基于基本类型的扩展类型和结构类型。Second, the mapping rules of the attribute model. As mentioned above, according to the type of attribute, it can be divided into basic type and extended type. The extended type includes the extended type and structure type based on the basic type.
其中,基本类型包括原始类型和大数据类型,原始类型包括整型(integer)、长整型(long)、短整型(short)、浮点型(float)字符串(string)、日期date、时间(time)等,大数据类型包括二进制(binary)、文本(text)等。基本类型映射到数据库的字段,每个基本类型映射到字段的类型可以由使用给定的默认值,也可以由用户指定,例如字符串的长度。基于基本类型的扩展类型如IP地址(IPAddress)等,其映射规则与对应的基本类型一样。结构类型和其所属的类映射到同一张表。Among them, the basic types include primitive types and large data types, and primitive types include integers, longs, shorts, floats, strings, dates, Time (time), etc., large data types include binary (binary), text (text), etc. Basic types are mapped to database fields, and the type of each basic type mapped to a field can be given by using a default value or specified by the user, such as the length of a string. The extension type based on the basic type, such as IP address (IPAddress), etc., has the same mapping rules as the corresponding basic type. Structural types and the classes they belong to are mapped to the same table.
三、关联关系的映射规则。3. Mapping rules for association relationships.
1、单向关联的映射规则。单向关联可以分为单向一对一关联、单向一对多关联、单向多对一关联以及单向多对多关联,下面分别说明它们的映射规则。在下面的描述中,被关联类是指UML图中关联箭头所指向的类,关联类是指UML图中关联线另一侧所对应的类。1. Mapping rules for one-way associations. Unidirectional associations can be divided into unidirectional one-to-one associations, unidirectional one-to-many associations, unidirectional many-to-one associations, and unidirectional many-to-many associations. Their mapping rules are described below. In the following description, the associated class refers to the class pointed by the association arrow in the UML diagram, and the associated class refers to the class corresponding to the other side of the association line in the UML diagram.
1)单向一对一关联关系可以采用如下三种映射规则。第一种映射规则与前面所述的一对一值类型的映射规则相同,将关联类和被关联类合并为一张表,具体为:关联类映射到表,表名称可以同名或者在IDE中设置;关联类和被关联类的属性映射到表的字段,其中字段的类型和约束可以在IDE中设置。1) The unidirectional one-to-one association relationship can adopt the following three mapping rules. The first mapping rule is the same as the one-to-one value type mapping rule mentioned above. The associated class and the associated class are combined into one table, specifically: the associated class is mapped to the table, and the table name can be the same name or in the IDE Setting; the attributes of the associated class and the associated class are mapped to the fields of the table, and the types and constraints of the fields can be set in the IDE.
第二种映射规则是基于主键的关联映射实现,一张表的主键作为另外一张表的唯一外键,根据该规则可以将如图7a所示的关联关系映射为如图7b所示的关系模型。第二种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;被关联类对应的表使用关联类的主键作为自己的主键和外键字段,如图7b中的定购标识(orderId)字段。在图7a和图7b中,类及表名称包括定购关系实体类型(ProductOrderEntityType)、定购关系描述类型(ProductOrderDexcriptionType),属性包括orderId、用户标识(userId)、productId、description等。The second mapping rule is the implementation of association mapping based on the primary key. The primary key of one table is the only foreign key of another table. According to this rule, the association relationship shown in Figure 7a can be mapped to the relationship shown in Figure 7b Model. The second mapping rule is: the associated class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; the table corresponding to the associated class uses the primary key of the associated class as its primary key and foreign key field, as shown in the order ID (orderId) in Figure 7b field. In Figure 7a and Figure 7b, the class and table names include order relationship entity type (ProductOrderEntityType), order relationship description type (ProductOrderDexcriptionType), and attributes include orderId, user ID (userId), productId, description, etc.
第三种映射规则是基于外键的关联映射实现。第三种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;被关联类对应的表使用关联类的主键作为自己的外键字段,并使用单独的主键字段。基于关联表的映射实现,考虑到多表关联的性能问题,不推荐使用第三种映射规则。The third mapping rule is the implementation of association mapping based on foreign keys. The third mapping rule is: the associated class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; the table corresponding to the associated class uses the primary key of the associated class as its own foreign key field, and uses a separate primary key field. Based on the mapping implementation of the association table, considering the performance of multi-table association, the third mapping rule is not recommended.
2)单向一对多关联可以采用如下三种映射规则。第一种映射规则通过外键实现关联,将如图8a所示的对象关系映射到如图8b所示的关系模型,在帐户实体类型(AccountEntityType)4表中增加一个外键字段customerId。第一种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;被关联类对应的表使用关联类的主键作为自己的外键字段,如图8b中的customerId字段,被关联类有自己的主键属性。另外,图8a和图8b中,属性还包括标题(title)和平衡(balance)等。2) The one-way one-to-many association can adopt the following three mapping rules. The first mapping rule implements association through foreign keys, maps the object relationship shown in Figure 8a to the relationship model shown in Figure 8b, and adds a foreign key field customerId in the account entity type (AccountEntityType) 4 table. The first mapping rule is: the associated class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; the table corresponding to the associated class uses the primary key of the associated class as its foreign key field, as shown in the customerId field in Figure 8b, and the associated class has own primary key attribute. In addition, in FIG. 8a and FIG. 8b, the attributes also include title and balance.
第二种映射规则和第三种映射规则都使用连接表实现关联,分别将如图8a所示的对象关系映射为如图8c和图8d所示的。根据第二种和第三种映射规则,创建一张连接表客户帐户关联(CustomerAccountAssoc),该表中只存放两个外键customerId和accountId字段。在第二种映射规则中,关联表没有属于自己的主键,全部使用外键唯一标识,不需要指定主键的生成方式,该第二种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段只包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段。在第三种映射规则中,关联表有属于自己的主键关联标识(assocId),因此需要指定主键的生成方式,例如基于特定的算法或者基于数据库的组件生成策略,第三种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段只包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段,同时关联表有自己的主键字段。优选地,使用第三种映射规则。Both the second type of mapping rule and the third type of mapping rule use a connection table to realize association, and respectively map the object relationship shown in FIG. 8a to that shown in FIG. 8c and FIG. 8d. According to the second and third mapping rules, create a connection table customer account association (CustomerAccountAssoc), in which only two foreign key fields customerId and accountId are stored. In the second mapping rule, the association table does not have its own primary key, all of which are uniquely identified by foreign keys, and there is no need to specify the generation method of the primary key. The second mapping rule is: the association class and the associated class are respectively mapped to two Table; Create a new connection table, the fields in the table only contain the primary key fields of the associated class and the associated class. In the third mapping rule, the association table has its own primary key association identifier (assocId), so it is necessary to specify the generation method of the primary key, such as based on a specific algorithm or a database-based component generation strategy. The third mapping rule is: association The class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; create a new connection table, the fields in the table only contain the primary key fields of the associated class and the associated class, and the associated table has its own primary key field. Preferably, a third mapping rule is used.
3)单向多对一关联的可以使用如下三种映射规则。3) The following three mapping rules can be used for unidirectional many-to-one association.
第一种映射规则为基于外键的实现方式,将如图9a的对象关系映射为如图9b所示的关系模型。第一种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;关联类使用被关联类的主键属性作为外键字段。The first mapping rule is an implementation based on foreign keys, which maps the object relationship shown in Figure 9a to the relationship model shown in Figure 9b. The first mapping rule is: the association class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; the association class uses the primary key attribute of the associated class as the foreign key field.
第二种映射规则和第三种映射规则都是基于关联表的实现方式,如图9c和图9d所示,分别创建一张新的关联表定购产品关联(OrderProductAssoc),通过外键实现两张表的关联,图9c所示的根据第二种映射规则得到的关联表没有属于自己的主键,而图9d所示的根据第三种映射规则得到的关联表有属于自己的主键assocId,需要指定关联表的主键生成方式。第二种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段只包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段。第三种映射规则为:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段只包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段,连接表同时有自己的主键字段。另外,图9a至图9d中,类及表名称还包括产品定购实体类型(ProductOrderEntityType)5、产品类型(ProductType)5等。The second mapping rule and the third mapping rule are both based on the implementation of the association table, as shown in Figure 9c and Figure 9d, respectively create a new association table order product association (OrderProductAssoc), and realize two through foreign keys For the association of tables, the association table obtained according to the second mapping rule shown in Figure 9c does not have its own primary key, while the association table obtained according to the third mapping rule shown in Figure 9d has its own primary key assocId, which needs to be specified How to generate the primary key of the associated table. The second mapping rule is: the association class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; a new connection table is created, and the fields in the table only include the primary key fields of the association class and the associated class. The third mapping rule is: the association class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively; create a new connection table, the fields in the table only include the primary key fields of the association class and the associated class, and the connection table has its own primary key at the same time field. In addition, in Fig. 9a to Fig. 9d, the class and table names also include product order entity type (ProductOrderEntityType) 5, product type (ProductType) 5 and so on.
4)单向多对多关联使用如下映射规则:关联类和被关联类分别映射到两张表,属性对象映射到一张连接表;创建一个新的连接表,表中的字段只包含关联类和被关联类的主键字段,连接表的某个字段和前面的主键字段联合起来作为主键。根据该映射规则,将如图10a所示的对象关系映射为如图10b所示的关系模型。如图10a所示,单向多对多关联可以转换为两个一对多的关联,因此必须使用如图10b中所示的连接表实现单向多对多的关联,尤其是关联本身具有某些属性。和前面所述几种基于连接表的映射规则不同的是,这里有一个值对象用户组关联类型(UserGroupAssocType)4,因此转换到Hibernate映射文件需要指定该值对象的映射规则,例如基于特定的算法或者基于数据库的组件生成策略。另外,图10a和图10b中,类及表名称还包括关联类型(AssociationType)4、用户组实体类型(UserGroupEntityType)4、用户实体类型(UserEntityType)4,属性还包括状态(status)等。4) One-way many-to-many association uses the following mapping rules: the association class and the associated class are mapped to two tables respectively, and the attribute object is mapped to a connection table; create a new connection table, and the fields in the table only contain the association class With the primary key field of the associated class, a field of the connection table is combined with the previous primary key field as the primary key. According to the mapping rule, the object relationship shown in FIG. 10a is mapped to the relationship model shown in FIG. 10b. As shown in Figure 10a, a one-way many-to-many association can be transformed into two one-to-many associations, so a join table as shown in Figure 10b must be used to implement a one-way many-to-many association, especially if the association itself has certain some attributes. Different from the above-mentioned mapping rules based on the connection table, there is a value object user group association type (UserGroupAssocType) 4, so converting to the Hibernate mapping file needs to specify the mapping rules of the value object, such as based on a specific algorithm Or a database-based component generation strategy. In addition, in Figure 10a and Figure 10b, the class and table names also include association type (AssociationType) 4, user group entity type (UserGroupEntityType) 4, user entity type (UserEntityType) 4, attributes also include status (status), etc.
2、双向关联映射规则与单向关联映射规则的相同,这里不再赘述。具体为:2. The two-way association mapping rule is the same as the one-way association mapping rule, and will not be repeated here. Specifically:
1)双向一对一关联的映射规则与单向一对一关联的映射规则一样;1) The mapping rules for bidirectional one-to-one association are the same as those for unidirectional one-to-one association;
2)双向一对多关联的映射规则与单向一对多关联的映射规则一样,双向多对一关联的映射规则与一对多关联的映射规则一样;2) The mapping rules for bidirectional one-to-many associations are the same as those for unidirectional one-to-many associations, and the mapping rules for bidirectional many-to-one associations are the same as those for one-to-many associations;
3)双向多对多关联的映射规则与单向多对多关联的规则映射一样。3) The mapping rule of bidirectional many-to-many association is the same as that of unidirectional many-to-many association.
四、继承关系的映射规则。Fourth, the mapping rules of the inheritance relationship.
本发明实施例对于继承关系到关系模型的映射提供三种映射规则,第一种映射规则采用每个类分层结构一张表,第二种映射规则采用每个子类一张表,第三种映射规则采用每个具体类一张表。下面根据如图11a所示的对象关系,分别描述这三种映射规则。图11a至图11d中,类及表名称还包括服务(Service)、消息服务(MessagingService)、无线应用协议服务(WapService)、短消息服务(smsService)、多媒体消息服务(MmsService)、中间服务(MiddleService)、子服务(ChildService),属性还包括接入码(accessCode)、特征流(featureStr)、接入统一资源标识符(accessUrl)、主管统一资源标识符(chargingUrl)短消息网关标识(smsGatewayId)、邮箱(mailbox)等。The embodiment of the present invention provides three mapping rules for the mapping from inheritance relationship to relational model. The first mapping rule adopts a table for each class hierarchical structure, the second mapping rule adopts a table for each subclass, and the third The mapping rules take one table per concrete class. The following three mapping rules are described respectively according to the object relationship shown in FIG. 11a. In Figure 11a to Figure 11d, the class and table names also include Service (Service), Message Service (MessagingService), Wireless Application Protocol Service (WapService), Short Message Service (smsService), Multimedia Message Service (MmsService), Middle Service (MiddleService) ), child service (ChildService), attributes also include access code (accessCode), feature stream (featureStr), access uniform resource identifier (accessUrl), supervisor uniform resource identifier (chargingUrl), short message gateway identifier (smsGatewayId), Mailbox (mailbox), etc.
第一种映射规则为:每个层次的类的所有属性叠加到一张表中;父类使用类型(type)字段表示自己所在的层次;所有的子类层次对应的表共用父类的主键作为外键唯一标识一条记录。根据第一种映射规则,如图11a所示的对象模型只需要三张表实现,如图11b所示,同一继承层次的类的属性放在一张表中实现,这样不可避免的导致属性的冗余,子类层次对应的表与父类层次对应的表是一对一的关系。第一种映射规则中需要考虑的事情比较多,如同一层次类的字段名不能重名,子类类型的编码,并且很多不同类型的字段混合存放在一张表中,也不便于管理。The first mapping rule is: all attributes of classes at each level are superimposed into one table; the parent class uses the type (type) field to indicate its own level; all tables corresponding to the subclass level share the primary key of the parent class as a foreign key Uniquely identifies a record. According to the first mapping rule, the object model shown in Figure 11a only needs three tables to implement, and as shown in Figure 11b, the attributes of classes at the same inheritance level are implemented in one table, which inevitably leads to redundancy of attributes , the table corresponding to the subclass level has a one-to-one relationship with the table corresponding to the parent class level. There are many things to consider in the first mapping rule, such as the field names of the same level class cannot have the same name, the encoding of the subclass type, and many fields of different types are mixed and stored in one table, which is not easy to manage.
第二种映射规则为:每个子类生成一张单独的表;每个子类对应的表使用父类的主键作为外键唯一标识一条记录。使用第二种映射规则得到如图11c所示的关系模型。第二种映射规则的优点是:可以清楚的表达类之间的继承关系,对于包含三层以上的继承关系时比较合适,并且每个子类对应的表可以有自己的主键生成策略;缺点是:需要使用多表操作,性能有所下降。The second mapping rule is: each subclass generates a separate table; the table corresponding to each subclass uses the primary key of the parent class as a foreign key to uniquely identify a record. Use the second mapping rule to get the relationship model shown in Figure 11c. The advantage of the second mapping rule is that it can clearly express the inheritance relationship between classes, which is more suitable for inheritance relationships with more than three layers, and the table corresponding to each subclass can have its own primary key generation strategy; the disadvantages are: Multi-table operations need to be used, and the performance is degraded.
第三种映射规则为:每个具体类一张表,该表中包含了从最顶层的父类到该子类的所有字段的并集。如图11a所示的对象关系使用第三种映射规则得到的关系模型如图11d所示。第三种映射规则的局限在于:类的继承层次较多时,子类表中冗余字段较多;主键的生成需要考虑统一的生成策略,不允许子类有自己的主键生成策略;父类和子类不能有重名的字段。The third mapping rule is: one table for each concrete class, which contains the union of all fields from the topmost parent class to the subclass. The relationship model obtained by using the third mapping rule for the object relationship shown in Figure 11a is shown in Figure 11d. The limitations of the third mapping rule are: when there are many inheritance levels of classes, there are many redundant fields in the subclass table; the generation of the primary key needs to consider a unified generation strategy, and subclasses are not allowed to have their own primary key generation strategy; the parent class and Subclasses cannot have fields with the same name.
五、组合关系的映射规则。5. Mapping rules for composition relations.
对象之间的组合关系包括一对一组合关系和一对多组合关系,这两种关系的映射规则与值类型的映射规则相似。Composition relations among objects include one-to-one composition relations and one-to-many composition relations, and the mapping rules of these two relations are similar to those of value types.
其中,对于一对一组合关系的映射,可使用映射到同一张表中的第一种映射规则:关联属性类映射到表,类对应的表名称可以同名或者在IDE中设置;关联属性类主键属性映射为表的主键;被关联属性类的多个属性映射到关联属性类对应的表的多个字段;非主键属性映射为表的字段,其中字段的类型和约束可以在IDE中设置。对于一对一组合关系的映射还可以使用第二种映射规则:关联属性类和被关联属性类分别映射到两张独立的表中;被关联属性类对应的表中增加关联属性类的主键字段,作为被关联属性类的主键和外键。根据第二种映射规则,关联属性类和被关联属性类分别映射到两张表中,使用主键和外键进行关联。Among them, for the mapping of one-to-one combination relationship, the first mapping rule mapped to the same table can be used: the associated attribute class is mapped to the table, and the table name corresponding to the class can have the same name or be set in the IDE; the associated attribute class primary key attribute mapping is the primary key of the table; multiple attributes of the associated attribute class are mapped to multiple fields of the table corresponding to the associated attribute class; non-primary key attributes are mapped to the fields of the table, and the type and constraints of the fields can be set in the IDE. For the mapping of one-to-one combination relationship, the second mapping rule can also be used: the associated attribute class and the associated attribute class are mapped to two independent tables; the primary key field of the associated attribute class is added to the table corresponding to the associated attribute class , as the primary key and foreign key of the associated attribute class. According to the second mapping rule, the associated attribute class and the associated attribute class are mapped to two tables respectively, and the primary key and foreign key are used for association.
对于一对多值组合关系的映射,可以采用如下映射规则:关联属性类和被关联属性类分别映射到两张独立的表中;被关联属性类对应的表中增加关联属性类的主键字段,作为被关联属性类的外键,被关联属性类有单独的主键字段。For the mapping of a one-to-many value combination relationship, the following mapping rules can be used: the associated attribute class and the associated attribute class are mapped to two independent tables; the primary key field of the associated attribute class is added to the table corresponding to the associated attribute class, As the foreign key of the associated attribute class, the associated attribute class has a separate primary key field.
以上所述仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并不用以限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所作的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The above descriptions are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent replacements, improvements, etc. made within the spirit and principles of the present invention shall be included in the scope of the present invention. within the scope of protection.
Claims (14)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006100784230ACN101046810B (en) | 2006-05-26 | 2006-05-26 | System and method for automatically establishing relational model |
| PCT/CN2007/000218WO2007137468A1 (en) | 2006-05-26 | 2007-01-19 | Method and system for creating relational model automatically |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006100784230ACN101046810B (en) | 2006-05-26 | 2006-05-26 | System and method for automatically establishing relational model |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101046810A CN101046810A (en) | 2007-10-03 |
| CN101046810Btrue CN101046810B (en) | 2010-09-08 |
Family
ID=38771426
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006100784230AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101046810B (en) | 2006-05-26 | 2006-05-26 | System and method for automatically establishing relational model |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101046810B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2007137468A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105956054A (en)* | 2016-04-27 | 2016-09-21 | 国家电网公司 | Relational database-based power grid CIM model data storage method |
Families Citing this family (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102541867A (en)* | 2010-12-15 | 2012-07-04 | 金蝶软件(中国)有限公司 | Data dictionary generating method and system |
| CN103186620A (en)* | 2011-12-31 | 2013-07-03 | 上海可鲁系统软件有限公司 | CIM mapping method |
| CN103186628B (en)* | 2011-12-31 | 2016-09-28 | 上海可鲁系统软件有限公司 | A kind of mapping method between common information model and relevant database |
| CN102999575B (en)* | 2012-11-12 | 2015-10-14 | 北京华通伟业科技发展有限公司 | A kind of collocation method of Hibernate Map Profile and system |
| CN108630319A (en)* | 2017-03-21 | 2018-10-09 | 中国移动通信有限公司研究院 | A kind of prediction technique and device based on medical data modeling |
| CN108491364A (en)* | 2018-01-25 | 2018-09-04 | 苏州麦迪斯顿医疗科技股份有限公司 | Medical treatment and nursing paperwork management system |
| CN108509485B (en)* | 2018-02-07 | 2021-06-22 | 深圳壹账通智能科技有限公司 | Data preprocessing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN109542409B (en)* | 2018-11-28 | 2022-09-30 | 中国海洋石油集团有限公司 | Storage method and device based on object-oriented design idea |
| CN111382198B (en)* | 2018-12-28 | 2023-09-19 | 中国移动通信集团山西有限公司 | Data recovery method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN110955736B (en)* | 2019-11-06 | 2023-05-12 | 科大国创软件股份有限公司 | Management model modeling method of basic data |
| CN110826151B (en)* | 2019-11-15 | 2023-01-24 | 国家电网有限公司 | Electric automobile model design method |
| CN111008189B (en)* | 2019-11-26 | 2023-08-25 | 浙江电子口岸有限公司 | Dynamic data model construction method |
| CN110955805B (en)* | 2019-12-18 | 2023-08-25 | 重庆大数据研究院有限公司 | Data automation processing method based on mapping relation |
| CN111506640B (en)* | 2020-04-21 | 2023-06-30 | 北京中电普华信息技术有限公司 | Mapping method and device |
| CN111797277A (en)* | 2020-05-19 | 2020-10-20 | 武汉乐程软工科技有限公司 | Method and device for mapping object system and relation system, computer readable storage medium and terminal equipment |
| CN111797278A (en)* | 2020-05-19 | 2020-10-20 | 武汉乐程软工科技有限公司 | Method for mapping associated object and relation |
| CN112199254B (en)* | 2020-10-12 | 2022-05-17 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Data model scanning method, system, computer device and storage medium |
| CN113377871B (en)* | 2021-06-22 | 2024-03-22 | 特赞(上海)信息科技有限公司 | Data synchronization method, device and storage medium |
| CN114547085B (en)* | 2022-03-22 | 2023-05-05 | 中国铁塔股份有限公司 | Data processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN115185982A (en)* | 2022-09-14 | 2022-10-14 | 浩鲸云计算科技股份有限公司 | Data preparation method and system based on data set arrangement |
| US11973660B1 (en)* | 2022-12-09 | 2024-04-30 | Arista Networks, Inc. | Method and system for data model mapping for network management |
| CN118170851B (en)* | 2024-05-11 | 2024-08-13 | 浪潮云信息技术股份公司 | Heterogeneous database data field synchronization method and system |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5548749A (en)* | 1993-10-29 | 1996-08-20 | Wall Data Incorporated | Semantic orbject modeling system for creating relational database schemas |
| US5819086A (en)* | 1995-06-07 | 1998-10-06 | Wall Data Incorporated | Computer system for creating semantic object models from existing relational database schemas |
| CN1773453A (en)* | 2004-11-10 | 2006-05-17 | 东软集团有限公司 | System constituting method based on data definition |
- 2006
- 2006-05-26CNCN2006100784230Apatent/CN101046810B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2007
- 2007-01-19WOPCT/CN2007/000218patent/WO2007137468A1/enactiveApplication Filing
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 朱庆伟,吴宇红.一种对象/关系映射框架的分析和应用.电子科技 2004年第1期.2004,(2004年第1期),54-57.* |
| 洪欣.基于XDR模式的XML文档与关系数据库的映射技术研究.华侨大学,2004,20-21.* |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105956054A (en)* | 2016-04-27 | 2016-09-21 | 国家电网公司 | Relational database-based power grid CIM model data storage method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101046810A (en) | 2007-10-03 |
| WO2007137468A1 (en) | 2007-12-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101046810B (en) | System and method for automatically establishing relational model | |
| US5694598A (en) | Method for mapping data between a relational format and an object-oriented format | |
| CN107491510A (en) | One kind mixing heterogeneous data source unified query system and distributed enquiring method | |
| CN101256650A (en) | A business entity-based enterprise data extraction method and system | |
| US20080222192A1 (en) | Method and system for transferring information using metabase | |
| CN103729460A (en) | Graphical data model managing method and system based on metadata | |
| CN105808853B (en) | A kind of ontological construction management of Engineering Oriented application and ontology data automatic obtaining method | |
| CN109344601A (en) | A method and system for access control of role rights | |
| CN103186628B (en) | A kind of mapping method between common information model and relevant database | |
| US10650044B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for converting from a source database system to a destination database system | |
| CN101178798A (en) | Process monitoring method across business systems | |
| CN115617776A (en) | A data management system and method | |
| CN104573065A (en) | Report display engine based on metadata | |
| CN110008230A (en) | Object Query method and device, computer readable storage medium | |
| CN103049482A (en) | Method for achieving data fusion storage in distributed heterogeneous system | |
| CN102571400A (en) | Method, system and device for updating communication network resource model | |
| CN114338855A (en) | Method for realizing parsing and generating HL7, FHIR standard and custom XML message | |
| CN102063666A (en) | Platform system for water conservancy information integration and comprehensive data processing | |
| CN106657282B (en) | A method and device for integrating operating status information of converter station equipment | |
| CN115905628A (en) | Dynamic resource directory construction method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114115837B (en) | MIS self-adaptive generator based on object information and using method | |
| CN102571381B (en) | A kind of information storage means and information-storing device | |
| CN115269552A (en) | Multi-version metadata storage and consistency detection method for power grid data warehouse | |
| CN102214092A (en) | Software development aided tool bag | |
| CN105824279A (en) | Method for establishing flexible and effective CMDB (Configuration Management Database) of machine room monitoring system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20201210 Address after:Unit 2414-2416, main building, no.371, Wushan Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province Patentee after:GUANGDONG GAOHANG INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OPERATION Co.,Ltd. Address before:518129 Bantian HUAWEI headquarters office building, Longgang District, Guangdong, Shenzhen Patentee before:HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co.,Ltd. Effective date of registration:20201210 Address after:No.88 Liaohe West Road, Pizhou Economic Development Zone, Xuzhou City, Jiangsu Province Patentee after:SU Normal University Semiconductor Materials and Equipment Research Institute (Pizhou) Co.,Ltd. Address before:Unit 2414-2416, main building, no.371, Wushan Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province Patentee before:GUANGDONG GAOHANG INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OPERATION Co.,Ltd. | |
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20100908 Termination date:20200526 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |