CN101043301B - Data rearrangement and recombination method in wireless communication system and its base station - Google Patents
Data rearrangement and recombination method in wireless communication system and its base stationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101043301B CN101043301BCN2006100346359ACN200610034635ACN101043301BCN 101043301 BCN101043301 BCN 101043301BCN 2006100346359 ACN2006100346359 ACN 2006100346359ACN 200610034635 ACN200610034635 ACN 200610034635ACN 101043301 BCN101043301 BCN 101043301B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- arq
- pdu
- sequence number
- harq
- received
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及移动通信技术领域,更具体地说,涉及一种适合长期演进(LTE)网络的无线通信系统中的数据重排重组方法及其基站。The present invention relates to the technical field of mobile communication, and more specifically, relates to a method for rearranging and reorganizing data in a wireless communication system suitable for a long-term evolution (LTE) network and a base station thereof.
背景技术Background technique
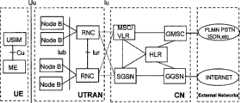
通用移动通信系统(Universal Mobile Telecommunication Systems,缩写UMTS)是采用WCDMA空中接口的第三代移动通信系统。通常也把UMTS系统称为WCDMA通信系统。从功能上,网络单元可以分为无线接入网络(Radio Access Network,缩写RAN)和核心网(Core Network,缩写CN)。其中无线接入网络用于处理所有与无线有关的功能,而核心网处理UMTS系统内所有话音呼叫、数据连接与外部网络的交换和路由。UMTS系统结构如图1所示,其网络单元包括用户设备(User Equipment,缩写为UE)即终端101、UMTS陆地无线接入网(UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network,缩写为UTRAN)102、3G核心网络的电路交换网(3G CS)103、3G核心网络的包交换网(3G PS)104、包括业务应用域的功能实体105、外部网络PSTN 106以及外部网络Internet网107。Universal Mobile Telecommunication Systems (UMTS for short) is a third-generation mobile communication system that uses the WCDMA air interface. The UMTS system is also usually referred to as the WCDMA communication system. Functionally, network units can be divided into radio access network (Radio Access Network, RAN for short) and core network (Core Network, CN for short). Among them, the wireless access network is used to handle all wireless-related functions, while the core network handles the switching and routing of all voice calls, data connections and external networks in the UMTS system. The structure of the UMTS system is shown in Figure 1, and its network units include user equipment (User Equipment, abbreviated as UE), namely
通用移动通信系统的网络构成的主要接口如图2所示,其中,Uu接口是WCDMA的无线接口,用于让UE通过Uu接口接入到UMTS系统的固定网络部分,而Iu接口是连接UTRAN和CN的接口。Iur接口是连接在各RNC(无线网络控制器的缩写)之间的接口,Iur接口是UMTS系统特有的接口,用于对RAN中移动台的移动管理。Iub接口是连接Node B与RNC的接口。The main interface of the network composition of the universal mobile communication system is shown in Figure 2, wherein, the Uu interface is the wireless interface of WCDMA, which is used to allow the UE to access the fixed network part of the UMTS system through the Uu interface, and the Iu interface is connected to UTRAN and CN interface. The Iur interface is an interface connected between RNCs (abbreviation for Radio Network Controller). The Iur interface is a specific interface of the UMTS system and is used for mobility management of the mobile station in the RAN. The Iub interface is an interface connecting Node B and RNC.
图2中的无线接口Uu的协议结构如图3所示,图3中各个缩略语列明如下:GC:通用控制;BMC:广播/多点传送控制协议;Nt:通知;RLC:无线链路控制;DC:专用控制;MAC:媒体接入控制;RRC:无线资源控制;PHY:物理层;PDCP:分组数据会聚协议。The protocol structure of the wireless interface Uu in Figure 2 is shown in Figure 3, and the abbreviations in Figure 3 are listed as follows: GC: General Control; BMC: Broadcast/Multicast Control Protocol; Nt: Notify; RLC: Radio Link Control; DC: Dedicated Control; MAC: Media Access Control; RRC: Radio Resource Control; PHY: Physical Layer; PDCP: Packet Data Convergence Protocol.
在无线接口协议中,自下而上分为三个协议层,物理层PHY(L1)、数据链路层(L2)以及网络层(L3),其中,数据链路层包括MAC、RLC、PDCP、BMC等四个子层。In the wireless interface protocol, it is divided into three protocol layers from bottom to top, physical layer PHY (L1), data link layer (L2) and network layer (L3), where the data link layer includes MAC, RLC, PDCP , BMC and other four sub-layers.
其中,MAC(媒质接入控制的缩写)子层的功能包括:逻辑信道和传输信道之间的映射;为每个传输信道选择适当的传送格式;UE数据流之间的优先级处理;UE之间采用动态预安排方法的优先级处理;DSCH(下行共享信道的缩写)和FACH(前向接入信道的缩写)上几个用户的数据流之间的优先级处理;公共传输信道上UE的标识;将高层PDU(协议数据单元的缩写)复接为通过传输信道传送给物理层的传送块,并将通过传输信道来自物理层的传送块复接为高层PDU(协议数据单元的缩写);业务量监视;动态传输信道类型切换;透明RLC加密;接入业务级别选择。Among them, the functions of the MAC (abbreviation for Medium Access Control) sublayer include: mapping between logical channels and transport channels; selection of an appropriate transport format for each transport channel; priority processing between UE data streams; Priority processing between dynamic pre-arrangement methods; priority processing between data streams of several users on DSCH (abbreviation for Downlink Shared Channel) and FACH (abbreviation for Forward Access Channel); Identification; multiplex high-level PDU (abbreviation for protocol data unit) into transport block transmitted to the physical layer through the transport channel, and multiplex transport block from the physical layer through the transport channel into high-level PDU (abbreviation for protocol data unit); Traffic monitoring; dynamic transmission channel type switching; transparent RLC encryption; access service level selection.
RLC(无线链路控制的缩写)子层功能包括:分割和重组、串联、填充、用户数据的传送、错误检测、按序发送高层PDU、副本检测、流控、非证实数据传送模式序号检查、协议错误检测和恢复、加密、挂起和恢复功能。RLC (abbreviation for radio link control) sublayer functions include: segmentation and reassembly, concatenation, filling, transmission of user data, error detection, sending high-level PDUs in sequence, copy detection, flow control, non-confirmed data transmission mode sequence number check, Protocol error detection and recovery, encryption, suspend and resume functions.
PDCP(分组数据会聚的缩写)子层功能包括:在发送与接收实体中分别执行IP数据流的头部压缩与解压缩;头部压缩方法对应与特定的网络层、传输层、或上层协议的组合;传输用户数据;将非接入层送来的PDCP-SDU(SDU:业务数据单元的缩写)转发到RLC层;将多个不同的RB(无线承载的缩写)复用到同一个RLC实体。PDCP (abbreviation for Packet Data Convergence) sublayer functions include: performing header compression and decompression of IP data streams in sending and receiving entities respectively; header compression methods correspond to specific network layer, transport layer, or upper layer protocols Combination; transmission of user data; forwarding PDCP-SDU (SDU: abbreviation of service data unit) sent by the non-access layer to the RLC layer; multiplexing multiple different RBs (abbreviation of radio bearer) to the same RLC entity .
BMC(广播/多播控制)子层功能包括:小区广播消息的存储、业务量监测和为CBS请求无线资源、BMC消息的调度、向UE发送BMC消息、向高层(NAS)传递小区广播消息。BMC (Broadcast/Multicast Control) sublayer functions include: storage of cell broadcast messages, traffic monitoring and requesting radio resources for CBS, scheduling of BMC messages, sending BMC messages to UE, and delivering cell broadcast messages to higher layers (NAS).
RLC子层的实体共支持三种类型业务,透明模式(TM)业务、无确认模式(UM)业务和确认模式业务(AM)。RLC子层实体模型如图4所示。透明模式TM 业务是由独立的发送和接收透明模式实体完成的。发送实体从高层接收SDU 划分成适当的RLC PDU,无须加任何开销,通过BCCH、PCCH、SHCCH、SCCH、DTCH等某一信道传送给MAC。接收实体从MAC子层接收到PDU,再将这些PDU重组成RLC SDU传送给上层。Entities in the RLC sublayer support three types of services in total, transparent mode (TM) services, unacknowledged mode (UM) services and acknowledged mode services (AM). The physical model of the RLC sublayer is shown in Figure 4. Transparent Mode™ services are performed by independent sending and receiving Transparent Mode entities. The sending entity receives SDUs from the upper layer and divides them into appropriate RLC PDUs without any overhead, and transmits them to MAC through a channel such as BCCH, PCCH, SHCCH, SCCH, DTCH, etc. The receiving entity receives PDUs from the MAC sublayer, and then reassembles these PDUs into RLC SDUs and sends them to the upper layer.
无确认模式UM业务是由独立的发送和接收无确认模式实体4完成的。发送实体从高层接收SDU分割成适当大小的RLC PDU或是将不同SDU进行连接组成一个RLC PDU,附上一个RLC头并放入发送缓存器通过某一个逻辑信道将其发送到MAC子层。接收实体通过某一逻辑信道从MAC子层接收PDU,去头并将其重组成SDU发送到高层。Unacknowledged mode UM services are completed by independent sending and receiving unacknowledged mode entities 4 . The sending entity receives the SDU from the upper layer and divides it into RLC PDUs of appropriate size or connects different SDUs to form an RLC PDU, attaches an RLC header and puts it into the sending buffer and sends it to the MAC sublayer through a certain logical channel. The receiving entity receives the PDU from the MAC sublayer through a logical channel, removes the header and reassembles it into an SDU and sends it to the upper layer.
确认模式AM业务是由一个联合的发送和接收确认模式实体完成的。发送和接收两种类型的PDU-控制PDU和业务PDU。发送侧实体从高层接收SDU分割或连接成RLC业务PDU,附加一个RLC头放入发送和重传缓存器通过一到两个逻辑信道将其发送到MAC子层。在确认模式下,所有发送的业务PDU都需要对等实体的确认来决定重传与否。控制PDU是由RLC实体自身生成的一些针对接收PDU的状态报告以及复位请求等。接收侧实体从MAC子层接收PDU,提取出捎带状态信息,放入接收缓存器,等待完整PDU重组SDU发送到上层,或是再通过其发送侧发送错误的接收确认要求对等实体重发PDU。Acknowledgment mode AM services are performed by a joint sending and receiving acknowledgment mode entity. Two types of PDUs are sent and received - Control PDUs and Service PDUs. The entity on the sending side receives the SDU from the upper layer and divides or connects it into an RLC service PDU, attaches an RLC header to the sending and retransmission buffer, and sends it to the MAC sublayer through one or two logical channels. In acknowledgment mode, all sent service PDUs need to be confirmed by the peer entity to decide whether to retransmit. Control PDUs are status reports and reset requests for received PDUs generated by the RLC entity itself. The receiving side entity receives the PDU from the MAC sublayer, extracts the piggyback status information, puts it into the receiving buffer, waits for the complete PDU to be reassembled and sends the SDU to the upper layer, or sends an erroneous reception confirmation through its sending side to request the peer entity to resend the PDU .
对于MAC子层,UE和UTRAN侧的结构有所不同,分别如图5、图6所示。根据WCDMA版本R6,接收端重排方案有如下几种机制:For the MAC sublayer, the UE and UTRAN structures are different, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6 respectively. According to WCDMA version R6, the rearrangement scheme at the receiving end has the following mechanisms:
1、AM业务重排重组机制:1. AM business rearrangement and reorganization mechanism:
在AM模式业务中,为支持重传,需要有一个窗口机制支持重排序功能。窗口为(VR(R),VR(MR)),其中VR(R)为下一个按序接收的PDU序号,VR(MR)=VR(R)+Configured_Rx_Window_Size,缓存等待最大值由高层配置。In the AM mode service, in order to support retransmission, a window mechanism is required to support the reordering function. The window is (VR(R), VR(MR)), where VR(R) is the sequence number of the next PDU received in sequence, VR(MR)=VR(R)+Configured_Rx_Window_Size, and the maximum value of buffer waiting is configured by the upper layer.
实际的窗口为(VR(R),VR(H)),其中VR(H)为接收到的PDU最大的序号,VR(H)<=VR(MR)。窗口的移动是通过更新由窗口下界实现的。收到与窗口内不相同序号的PDU被缓存在接收缓存内,收到序号在窗口外的PDU被删除。作为接收端只能被动等待VR(R),没有计时器等方法控制窗口移动。发送端可以通过计时器和/或最高重传次数限制PDU传输速率。对于每一个要发送的SDU都启动计时器,当计时器超时或PDU达到最高重传次数进行SDU discard(业务数据单元丢弃)并通知接收端进行窗口更新,最高重传次数达到没有SDUdiscard configured(业务数据单元丢失配置)的情况下触发RLC实体的reset(复位)。The actual window is (VR(R), VR(H)), where VR(H) is the largest sequence number of the received PDU, and VR(H)<=VR(MR). The movement of the window is achieved by updating the lower bound of the window. The received PDUs with sequence numbers different from those in the window are buffered in the receive buffer, and the received PDUs with sequence numbers outside the window are deleted. As the receiving end, it can only passively wait for VR(R), and there is no method such as timer to control the movement of the window. The sender can limit the PDU transmission rate by a timer and/or the maximum number of retransmissions. A timer is started for each SDU to be sent. When the timer expires or the PDU reaches the maximum number of retransmissions, SDU discard (service data unit discard) is performed and the receiving end is notified to update the window. When the maximum number of retransmissions reaches no SDUdiscard configured (business The reset (reset) of the RLC entity is triggered in the case of a data unit loss configuration).
重组机制可以根据设定的按序还是乱序,根据LI指示将完整SDU进行重组并送到高层。The reassembly mechanism can reassemble the complete SDU according to the LI instruction and send it to the upper layer according to the set sequence or disorder.
2.UM业务的SDU乱序重排重组2. SDU out-of-order rearrangement and reorganization of UM services
普通的UM业务由于没有重传,不需要重排,只要简单地按序重组,出现丢失的PDU时,将此PDU所涉及的SDU都删除。Because there is no retransmission, ordinary UM services do not need to be rearranged. They only need to be reorganized in sequence. When a lost PDU occurs, all the SDUs involved in this PDU will be deleted.
但自从R6进入MBMS(广播组播业务的缩写)业务后由于MCCH周期重传特性,引入MCCH接收端乱序重组机制。这个机制也是有一个窗口等待初始传输丢失重传的PDU,为了保证实时性,乱序重组SDU保证了接收端重组速率。However, since R6 entered the MBMS (abbreviation for broadcast multicast service) service, due to the periodic retransmission feature of the MCCH, an out-of-order reassembly mechanism at the receiving end of the MCCH was introduced. This mechanism also has a window to wait for PDUs that are lost and retransmitted during the initial transmission. In order to ensure real-time performance, out-of-order reassembly of SDUs ensures the reassembly rate of the receiving end.
使用的窗口为(VR(UOH)-OSD_Window_Size,VR(UOH)),其中VR(UOH)为收到了PDU最大的序号,缓存等待最大值由高层配置。对于收到序号在窗口内的PDU,缓存起来,将序号在窗口外的PDU进行VR(UOH)更新,窗口上界移动带动窗口的更新。计时器Timer_OSD用于控制VR(UOH)的更新,VR(UOH)每一次更新计时器重置,计时器超时,缓存内所有PDU被删除。The window used is (VR(UOH)-OSD_Window_Size, VR(UOH)), where VR(UOH) is the largest serial number of the received PDU, and the maximum value of buffer waiting is configured by the upper layer. For the PDUs whose serial numbers are received within the window, they are cached, and the PDUs whose serial numbers are outside the window are updated by VR (UOH), and the upper boundary of the window moves to drive the update of the window. The timer Timer_OSD is used to control the update of VR(UOH). The timer is reset every time VR(UOH) is updated. When the timer expires, all PDUs in the cache will be deleted.
对于缓存在窗口内的PDU进行重组,根据LI指示恢复出完整的SDU并送到高层而不管SDU顺序。Reassemble the PDUs buffered in the window, recover the complete SDU according to the LI instruction and send it to the upper layer regardless of the SDU sequence.
3.DAR重排3. DAR rearrangement
DAR是重复避免和重排序的英文缩写,由于WCDMA R6中MBMS的MTCH选择性合并机制,MTCH接收会出现副本和乱序到达的问题,因此,在MTCH接收端引入窗口机制进行重排序。DAR is the English abbreviation of Duplication Avoidance and Reordering. Due to the MTCH selective combination mechanism of MBMS in WCDMA R6, MTCH reception will have the problem of duplicate and out-of-order arrival. Therefore, a window mechanism is introduced at the MTCH receiving end for reordering.
窗口为(VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size,VR(UDH)],这里VR(UDH)表示收到了PDU最大的序号,缓存等待最大值由高层配置。实际窗口为(VR(UDR),VR(UDH)],其中VR(UDR)为下一个按序送到高层的PDU的序号,即小于这个SN的PDU都已经被按序送到高层。VR(UDR)>=VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size。收到实际窗口内的PDU进行缓存,收到序号大于窗口上界的PDU,进行窗口的更新,也是由窗口上界移动带动窗口更新。The window is (VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size, VR(UDH)], where VR(UDH) indicates that the maximum sequence number of the PDU has been received, and the maximum value of the cache wait is configured by the upper layer. The actual window is (VR(UDR), VR(UDH) ], where VR(UDR) is the sequence number of the next PDU sent to the upper layer in sequence, that is, the PDUs smaller than this SN have been sent to the higher layer in sequence. VR(UDR)>=VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size. Received The PDUs in the actual window are cached, and the window is updated when a PDU with a sequence number greater than the upper boundary of the window is received, and the window update is also driven by the movement of the upper boundary of the window.
当序号为VR(UDR)的PDU被接收后,检查窗口内现在最小的没有被正确接收的PDU的序号为多少,将VR(UDR)更新到此值,并将所有序号小于更新后VR(UDR)的PDU送到高层重组。如果当窗口前移导致VR(UDR)<VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size+1,更新VR(UDR)为更新窗口(VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size,VR(UDH)]内最小的没有收到的PDU,将VR(UDR)更新到此SN,并将所有序号小于更新后VR(UDR)的PDU送到高层重组。When the PDU with sequence number VR(UDR) is received, check the sequence number of the smallest PDU that has not been correctly received in the window, update VR(UDR) to this value, and make all sequence numbers smaller than the updated VR(UDR ) PDUs are sent to the upper layer for reassembly. If VR(UDR)<VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size+1 is caused by the forward movement of the window, update VR(UDR) to the smallest unreceived PDU in the update window (VR(UDH)-DAR_Window_Size, VR(UDH)], Update VR(UDR) to this SN, and send all PDUs with sequence numbers smaller than the updated VR(UDR) to the upper layer for reassembly.
计时器Timer_DAR和状态变量VR(UDT)控制接收窗长时间不移动。VR(UDT)初始设为窗口内最大序号,同时启动计时器Timer_DAR。当序号为VR(UDT)的PDU在计时器未超时被送到高层重组,计时器重启,VR(UDT)重置为窗口内最大序号。如果定时器超时,所有序号小于等于VR(UDT)和与VR(UDT)连续的PDU都被送入高层,VR(UDR)更新为现在缓存中最小没有收到的序号,同时重置VR(UDT)为窗口内PDU最大序号,重启定时器。The timer Timer_DAR and the state variable VR (UDT) control the receiving window to not move for a long time. VR(UDT) is initially set to the maximum serial number in the window, and the timer Timer_DAR is started at the same time. When the PDU with the sequence number VR(UDT) is sent to the upper layer for reassembly before the timer expires, the timer is restarted, and the VR(UDT) is reset to the maximum sequence number in the window. If the timer expires, all PDUs whose sequence numbers are less than or equal to VR(UDT) and continuous with VR(UDT) are sent to the upper layer, and VR(UDR) is updated to the smallest sequence number not received in the current cache, and VR(UDT) is reset at the same time. ) is the maximum sequence number of PDU in the window, restart the timer.
DAR重排和前两者不同在于,这个功能单元只重排不做重组,重组功能在高层做。The difference between DAR rearrangement and the previous two is that this functional unit is only rearranged without reorganization, and the reorganization function is performed at a high level.
4.HSPA重排4. HSPA rearrangement
HSPA是高速分组接入的缩写,HSDPA(高速下行分组接入的缩写)的重排机制和DAR机制相同。其目的是为了HARQ(混合自动重传请求的缩写)不同process重传的乱序,根据TSN序号进行重排保证收到的MAC-hs PDU按序进行恢复成MAC-d PDU送到MAC-d实体。HSPA is an abbreviation for High Speed Packet Access, and the reordering mechanism of HSDPA (an abbreviation for High Speed Downlink Packet Access) is the same as the DAR mechanism. Its purpose is to reorder the retransmissions of different processes according to the TSN sequence number to ensure that the received MAC-hs PDUs are restored in order into MAC-d PDUs and sent to MAC-d for HARQ (abbreviation for Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request). entity.
随着HSDPA、Enhanced Uplink等增强技术的引入,为保证3GPP无线接入技术在更长一些时间(如10年或更长)的竞争力,有人提出“Evolved UTRAand UTRAN”即LTE(Long Term Evolution,长期演进)即3GPP无线接入技术的长期演进需要被考虑。这种长期演进的重要部分包括降低的时延、更高的用户数据速率、改进的系统容量和覆盖和对运营商而言降低的成本。为达到上述目标,演进的无线接口和无线网络结构都应被考虑。为满足这种长期演进网络(下文缩写为LTE)各种性能的需求,网络结构、无线接口、协议栈功能都会发生相应改进。现有协议层结构造成很多重复的功能,比如RLC和MAC子层的重传、分割级联等等。为了减小延迟和简化协议,这些重复的功能必须考虑精简。另外,LTE系统提出的全IP要求,即网络传输全部是基于IP包业务,这一全新的需求也需要响应的机制去保证。With the introduction of enhanced technologies such as HSDPA and Enhanced Uplink, in order to ensure the competitiveness of 3GPP wireless access technology for a longer period of time (such as 10 years or longer), some people proposed "Evolved UTRA and UTRAN", that is, LTE (Long Term Evolution, Long-term evolution), ie, the long-term evolution of 3GPP radio access technologies, needs to be considered. Important parts of this long-term evolution include reduced latency, higher user data rates, improved system capacity and coverage, and reduced costs for operators. To achieve the above goals, both the evolved radio interface and radio network structure should be considered. In order to meet various performance requirements of this long-term evolution network (hereinafter abbreviated as LTE), the network structure, radio interface, and protocol stack functions will all be improved accordingly. The existing protocol layer structure results in many repetitive functions, such as retransmission, split concatenation, etc. of the RLC and MAC sublayers. In order to reduce latency and simplify the protocol, these repetitive functions must be considered streamlined. In addition, the all-IP requirement proposed by the LTE system, that is, all network transmissions are based on IP packet services, requires a corresponding mechanism to ensure this new requirement.
在众多网络改进方案中,RLC中很多功能被认为是重复冗余的。目前比较流行的观点认为RLC中的很多功能在MAC中都可以实现,因此,RLC将可以被合并到MAC实体中去。这里我们也认为RLC的重复功能将带来不必要的延迟和复杂度,简化合并到MAC中去是比较合理的方案。In many network improvement schemes, many functions in RLC are considered to be redundant. Currently, a popular view is that many functions in RLC can be realized in MAC, therefore, RLC can be merged into MAC entity. Here we also think that the repetition function of RLC will bring unnecessary delay and complexity, and it is a reasonable solution to simplify and merge it into MAC.
最近提出的LTE系统中MAC结构如图7和图8所示。对现有技术而言,上文已经讨论的WCDMA R6系统中共有以上4个三种重排机制,可以适合不同的重排需求。但结构复杂,功能冗余,降低了响应速度,无法应用于已有LTE网络,例如,将ARQ(自动重传请求的缩写)重传和HARQ(混合自动重传请求的缩写)分开处理,效率低下,增加了ARQ重传的延迟。The MAC structure in the recently proposed LTE system is shown in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8 . As far as the prior art is concerned, the WCDMA R6 system discussed above has the above four and three rearrangement mechanisms, which can be adapted to different rearrangement requirements. However, the complex structure and redundant functions reduce the response speed and cannot be applied to existing LTE networks. For example, separate processing of ARQ (abbreviation for Automatic Repeat Request) retransmission and HARQ (abbreviation for Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request) improves efficiency. Low, increasing the delay of ARQ retransmission.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明要解决的技术问题是,针对诸如演进网络的无线通信系统提出一种数据重排重组的方法,可以避免类似功能设置上的重复,简化简化基站协议结构,合并冗余功能,减少处理时延和缓存开销,从而达到有利于两层重传的交互,触发快速ARQ重传的目的。本发明的另一目的是提供一种具有上述优点达到无线通信系统的基站。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to propose a data rearrangement and reorganization method for a wireless communication system such as an evolved network, which can avoid duplication of similar function settings, simplify the base station protocol structure, combine redundant functions, and reduce processing time. Delay and cache overhead, so as to achieve the interaction that is beneficial to the retransmission of the two layers, and trigger the purpose of fast ARQ retransmission. Another object of the present invention is to provide a base station for a wireless communication system with the above advantages.
本发明上述技术问题这样解决,构造一种无线通信系统中的数据重排重组方法,包括:The above-mentioned technical problems of the present invention are solved in this way, and a method for rearranging and reorganizing data in a wireless communication system is constructed, including:
对混合自动重传HARQ进程接收的数据包进行校验;Check the data packets received by the hybrid automatic repeat HARQ process;
将校验正确的数据包送到解复用单元,解复用单元根据HARQ的协议数据单元PDU包头信息将HARQ PDU进行解复用后送到高层重传实现单元Outer ARQ进行重排;The correct data packet is sent to the demultiplexing unit, and the demultiplexing unit demultiplexes the HARQ PDU according to the HARQ protocol data unit PDU header information and then sends it to the high-level retransmission implementation unit Outer ARQ for rearrangement;
高层重传实现单元Outer ARQ根据预先制定好的重排机制,根据PDU序号进行PDU重排;The high-level retransmission implementation unit Outer ARQ performs PDU rearrangement according to the PDU sequence number according to the pre-established rearrangement mechanism;
依据重新排列的PDU根据预先制定好的重组策略对业务数据单元SDU进行重组并将重组后的SDU送到高层;Reorganize the service data unit SDU according to the rearranged PDU according to the pre-established reorganization strategy and send the reorganized SDU to the upper layer;
其中,所述预先制定的重排机制通过预先定义的滑动窗口控制HARQ缓存等待范围和ARQ缓存等待范围,对接收到的新协议数据进行处理,根据以上处理检测需要重组的协议数据包或/和协议数据单元丢失,进行数据包的重组或/和生成反馈。Wherein, the pre-established rearrangement mechanism controls the HARQ buffer waiting range and the ARQ buffer waiting range through a predefined sliding window, processes the received new protocol data, and detects protocol data packets that need to be reassembled according to the above processing or/and Protocol data unit loss, reassembly of data packets or/and generation of feedback.
在上述方法中,对于自动重传请求ARQ实体的重排重组可以用于经过HARQ重传功能,但不经过Outer ARQ重传功能的业务。In the above method, the reordering and reorganization of the automatic repeat request ARQ entity can be used for services that pass the HARQ retransmission function but do not pass the Outer ARQ retransmission function.
在上述方法中,所述预先制定好的重组策略包括,设置按序递交SDU和乱序递交SDU,如果配置为按序递交SDU,SDU必须按照PDU序号标识的先后顺序进行SDU的恢复和向高层递交;如果配置为乱序递交SDU,SDU可以按照任意顺序进行递交。In the above method, the pre-established recombination strategy includes setting SDUs delivered in sequence and SDUs delivered out of sequence. If the SDUs are delivered in sequence, the SDUs must be restored and sent to the upper layer in the order identified by the PDU sequence number. Delivery; if configured to deliver SDUs out of order, SDUs can be delivered in any order.
在上述方法中,所述的预先定义的滑动窗口控制的ARQ缓存等待范围是由HARQ缓存等待下界,ARQ按序接收PDU序号以及ARQ缓存等待最大值共同决定。In the above method, the ARQ buffer waiting range controlled by the predefined sliding window is jointly determined by the lower bound of the HARQ buffer waiting, the sequence number of the ARQ sequentially received PDUs and the maximum value of the ARQ buffer waiting.
在上述方法中,当ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU序号到HARQ允许缓存等待的最小值小于等于ARQ缓存等待最大值,ARQ缓存等待范围从ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU序号到HARQ允许缓存等待的最小值;当ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU序号到HARQ允许缓存等待的最小值大于ARQ缓存等待最大值,ARQ缓存等待范围从ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU序号到该下一个PDU序号加上ARQ缓存等待的最大值。In the above method, when the minimum value of the next PDU serial number received by ARQ in sequence to the minimum value of HARQ buffer waiting is less than or equal to the maximum value of ARQ buffer waiting, the ARQ buffer waiting range is from the next PDU serial number received by ARQ in sequence to the HARQ buffer waiting The minimum value; when the minimum value of the next PDU sequence number received by ARQ in sequence to the minimum value of HARQ buffer waiting is greater than the maximum value of ARQ buffer wait, the ARQ buffer wait range is from the next PDU sequence number received by ARQ in sequence to the next PDU sequence number plus The maximum value of the upper ARQ cache wait.
在上述方法中,所述的ARQ缓存等待最大值是由高层配置的。In the above method, the maximum value of waiting for the ARQ buffer is configured by a high layer.
在上述方法中,所述的缓存内收到的PDU最大的序号、HARQ缓存等待下界和ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU序号是由状态变量表示的。In the above method, the maximum sequence number of the PDU received in the cache, the lower bound of the HARQ cache waiting and the sequence number of the next PDU received by ARQ in sequence are represented by state variables.
在上述方法中,所述ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU是指ARQ缓存下一个按序希望接收的PDU,所有序号小于此PDU的协议数据单元都已经移出重排缓存。In the above method, the next PDU received by ARQ in sequence refers to the next PDU expected to be received in ARQ buffer in sequence, and all PDUs with sequence numbers smaller than this PDU have been moved out of the rearrangement buffer.
在上述方法中,所述对接收到的新协议数据进行处理方法在于如果这个新协议数据单元序号大于HARQ缓存等待范围,对此数据进行缓存并更新最高接收序号的状态变量,根据窗口机制进行其他状态变量更新,进行溢出检测;如果这个新协议数据单元序号位于HARQ缓存等待范围内且没有重复序号数据单元,缓存此PDU;如果这个新协议数据单元序号位于ARQ缓存等待范围内且没有重复序号数据单元,缓存此PDU,并根据接收反馈策略进行接收反馈;如果这个新协议数据单元序号等于ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU序号,进行重组SDU的检测。In the above method, the method for processing the received new protocol data is that if the new protocol data unit sequence number is greater than the HARQ cache waiting range, the data is cached and the state variable of the highest received sequence number is updated, and other operations are performed according to the window mechanism Update the state variable and perform overflow detection; if the new protocol data unit sequence number is within the waiting range of the HARQ buffer and there is no repeated sequence number data unit, cache the PDU; if the new protocol data unit sequence number is within the waiting range of the ARQ cache and there is no repeated sequence number data unit, caches the PDU, and performs receiving feedback according to the receiving feedback strategy; if the serial number of the new protocol data unit is equal to the serial number of the next PDU received by ARQ in sequence, detection of the reassembled SDU is performed.
在上述方法中,所述的溢出检测在于当最高接收的PDU序号被更新时,检测采用所述最高接收的PDU序号减去配置的HARQ缓存等待大小参数以及下一个按序接收的PDU序号后获得的值是否大于配置的最大ARQ缓存等待范围,如果是,则为溢出;检测到溢出后,接收端发送窗口溢出指示给发送端,挂起对等实体新数据传输,根据预先制定好的策略进行取消挂起的操作。In the above method, the overflow detection is that when the highest received PDU sequence number is updated, the detection is obtained after subtracting the configured HARQ buffer waiting size parameter and the next sequentially received PDU sequence number from the highest received PDU sequence number Whether the value of is greater than the configured maximum ARQ buffer waiting range, if yes, it is an overflow; after detecting the overflow, the receiving end sends a window overflow indication to the sending end, suspends the new data transmission of the peer entity, and proceeds according to the pre-established strategy Cancels a pending operation.
在上述方法中,所述的取消挂起的操作可以由发送端计时器控制或接收端检测ARQ窗口恢复到挂起前状态后发送指示。In the above method, the operation of canceling the suspension may be controlled by a timer at the sending end or the receiving end may send an indication after detecting that the ARQ window has returned to the state before the suspension.
在上述方法中,所述的检测需要重组的协议数据包的方法为1)如果配置为按序递交SDU,如果接收到序号等于ARQ按序接收的下一个PDU序号,检查从这个PDU开始的连续PDU直到出现不连续的协议数据单元,将这些连续PDU中含有的SDU重组出来并送到高层,并更新相应按序接收PDU的状态变量,2)如果配置为无序递交SDU,只要有协议数据单元中指示完整的SDU被接收到即将此SDU送到高层。In the above method, the method for detecting the protocol data packet that needs to be reassembled is 1) If it is configured to deliver SDUs in order, if the received sequence number is equal to the sequence number of the next PDU received by ARQ in sequence, check the consecutive PDUs starting from this PDU PDU until there are discontinuous protocol data units, reassemble the SDUs contained in these continuous PDUs and send them to the upper layer, and update the state variables of the corresponding received PDUs in sequence. 2) If it is configured to deliver SDUs out of order, as long as there are protocol data The unit indicates that a complete SDU is received and the SDU is sent to the upper layer.
在上述方法中,所述的检测协议数据单元丢失的方法为:在ARQ缓存等待范围内,序号为SN的协议数据单元没有收到,如果存在序号大于SN的协议数据单元已经被收到,则判断序号为SN的协议数据单元为丢失数据包。In the above method, the method for detecting the loss of the protocol data unit is: within the waiting range of the ARQ buffer, the protocol data unit with the sequence number SN is not received, if there is a protocol data unit with the sequence number greater than the SN that has been received, then It is judged that the protocol data unit whose sequence number is SN is a lost data packet.
在上述方法中,所述的预先定义的滑动窗口控制的HARQ缓存等待范围由接收协议数据单元情况和定时器控制;此HARQ缓存等待范围定义为上界为收到协议数据单元最大的序号,下界为超时定时器所对应的PDU中最大的序号。In the above method, the HARQ buffer waiting range controlled by the predefined sliding window is controlled by the situation of receiving the protocol data unit and the timer; this HARQ buffer waiting range is defined as the upper bound being the maximum sequence number of the received protocol data unit, and the lower bound It is the largest sequence number in the PDU corresponding to the timeout timer.
在上述方法中,所述的定时器设置方法为每一个从HARQ进程来的协议数据单元,启动对应的一个计时器;当计时器超时,对应协议数据单元序号大于HARQ缓存等待范围下界时,更新HARQ缓存等待范围下界为此协议数据单元序号;当协议数据单元的序号小于HARQ缓存等待范围下界时,停止对应计时器;当协议数据单元按序或乱序重组出全部的SDU时,停止对应的计时器。In the above method, the timer setting method is to start a corresponding timer for each protocol data unit from the HARQ process; when the timer is overtime, and the corresponding protocol data unit sequence number is greater than the lower bound of the HARQ cache waiting range, update The lower bound of the HARQ cache waiting range is the serial number of the protocol data unit; when the serial number of the protocol data unit is less than the lower bound of the HARQ buffer waiting range, stop the corresponding timer; when the protocol data unit reassembles all SDUs in sequence or out of order, stop the corresponding timer.
在上述方法中,所述的定时器大小由高层配置。In the above method, the size of the timer is configured by a high layer.
本发明另一目的通过构造一种基站实现的,该基站可用作无线通信系统中的一个单元,该无线通信系统在无线终端和包括其它无线终端的其它通信设备之间通过无线通信提供至少部分连接,其特征在于:该基站依附本发明上述数据重排重组方法的相应步骤作为接收端工作。Another object of the present invention is achieved by constructing a base station that can be used as a unit in a wireless communication system that provides at least part of wireless communication between a wireless terminal and other communication devices including other wireless terminals. The connection is characterized in that the base station works as a receiving end according to the corresponding steps of the above-mentioned data rearrangement and reorganization method of the present invention.
实施本发明提供的可用于LTE系统的无线通信系统中数据重排重组方法及其基站,和现有无线通信系统相比,由于将原先R6系统的RLC重排和HARQ重排都在ARQ实体中完成,并针对HARQ和ARQ重传在一个物理实体中的实现,提出功能合并简化以及具体实现机制,根据窗口和定时器控制进行HARQ接收缓存和ARQ接收缓存的区分,可以更快速触发ARQ重传减少由于重排带来的处理时延,也同时减少了两个重传合并重排的相互影响。按照本发明,重排重传功能都可在基站实现,重排可以一次完成,而无需分成两层单独进行重排,可避免ARQ重传时延的增加,降低了系统复杂性,提高了速度。Implement the data rearrangement and reorganization method and its base station in the wireless communication system that can be used in the LTE system provided by the present invention, compared with the existing wireless communication system, because the RLC rearrangement and HARQ rearrangement of the original R6 system are all in the ARQ entity Completed, and aiming at the realization of HARQ and ARQ retransmission in one physical entity, proposed function merging simplification and specific implementation mechanism, and distinguished HARQ receiving buffer and ARQ receiving buffer according to window and timer control, which can trigger ARQ retransmission more quickly The processing delay caused by reordering is reduced, and the interaction of two retransmissions combined with reordering is also reduced. According to the present invention, the rearrangement and retransmission functions can all be realized in the base station, and the rearrangement can be completed at one time without being divided into two layers for separate rearrangement, which can avoid the increase of ARQ retransmission delay, reduce the complexity of the system, and increase the speed .
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是通用移动通信系统中无线接入网络的系统结构示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a system structure of a wireless access network in a universal mobile communication system;
图2是通用移动通信系统中主要接口的结构示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of the main interface in the universal mobile communication system;
图3是通用移动通信系统中无线接口协议的结构示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic structural diagram of a radio interface protocol in a universal mobile communication system;
图4是无线链路控制RLC实体模型的结构示意图;FIG. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a radio link control RLC entity model;
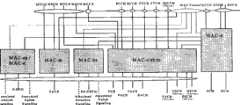
图5是用户设备侧的MAC结构示意图;FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of a MAC structure on the user equipment side;
图6是网络侧的MAC结构示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of a MAC structure on the network side;
图7是LTE网络中eNB中UL的MAC结构示意图;FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of the UL MAC structure in the eNB in the LTE network;
图8是LTE网络中用户设备DL的MAC结构示意图;FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of a MAC structure of a user equipment DL in an LTE network;
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明的无线通信系统中数据重排重组方法,可以应用于LTE网络,也可以应用于其它通用无线通信系统,这种数据的重排重组方法,其核心是接收端对收到解复用后的数据包根据其序号SN进行重排/重组,以及设置接收缓存条件,并根据该接收缓存条件对经过重排后的数据进行后续处理。在本发明的方法中,每个接收到的SDU或PDU均有序号SN,这里用于重排重组的SN是ARQ唯一的SN,即可以是重用高层的SDU SN,也可以是发送端ARQ加的ARQ SN。如果存在重传分割级联后的分段子序号,需要将每个SN对应的多块片端都收齐。ARQ单元就是根据其序号SN进行重排/重组;重排是对在接收与发送之间的乱序而进行的重新排序,重组是按PDU重组SDU。重组包括乱序递交的重组和按序递交的重组。HARQ根据HARQ PDU包头信息将需要重排的PDU送到各ARQ重排重组单元进行重排。The data rearrangement and reorganization method in the wireless communication system of the present invention can be applied to the LTE network, and can also be applied to other general wireless communication systems. The data packets are rearranged/reassembled according to their sequence number SN, and the receiving buffer condition is set, and the rearranged data is subsequently processed according to the receiving buffer condition. In the method of the present invention, each received SDU or PDU has a serial number SN, and the SN used for rearrangement and reorganization here is the unique SN of ARQ, that is, it can be the SDU SN of the reused upper layer, or it can be the ARQ plus SN of the sending end. The ARQ SN. If there is a segment sub-sequence number after retransmission segmentation and concatenation, it is necessary to collect all the multi-block segments corresponding to each SN. The ARQ unit performs rearrangement/reassembly according to its sequence number SN; rearrangement is to reorder the out-of-order between receiving and sending, and reorganization is to reorganize SDU according to PDU. Reorganization includes out-of-order delivery reorganization and in-order delivery reorganization. HARQ sends the PDUs that need to be rearranged to each ARQ rearrangement and reassembly unit for rearrangement according to the HARQ PDU header information.
在以LTE网络为例讨论本发明数据重排重组方法,主要针对AM和UM两种业务。对UM业务只用HARQ业务,重排机制只针对HARQ乱序。Taking the LTE network as an example to discuss the data rearrangement and reorganization method of the present invention, it is mainly aimed at AM and UM services. For UM business, only HARQ business is used, and the reordering mechanism is only for HARQ disorder.
对于AM业务,接收端各HARQ进程收到相应TB(传输块),如果校验正确,送到MUX单元进行解复用到各ARQ实体。ARQ重排功能单元根据PDU序号进行PDU重排并重组SDU送到高层,触发重传或删除相应重传缓存PDU。对于UM业务,接收端各HARQ进程收到相应的TB,如果校验正确,送到MUX单元进行解复用到各ARQ实体,对于UM,ARQ实体不做重传,只做分割级联。重排功能单元针对HARQ重传乱序进行排序,并重组SDU送到高层。对于某些HARQ禁止的实时业务,无需重排序。For the AM service, each HARQ process at the receiving end receives the corresponding TB (transport block), and if the verification is correct, it is sent to the MUX unit for demultiplexing to each ARQ entity. The ARQ rearrangement function unit performs PDU rearrangement according to the PDU sequence number and sends the reassembled SDU to the upper layer, triggers retransmission or deletes the corresponding retransmission cached PDU. For UM services, each HARQ process at the receiving end receives the corresponding TB. If the verification is correct, it is sent to the MUX unit for demultiplexing to each ARQ entity. For UM, the ARQ entity does not retransmit, but only splits and concatenates. The reordering functional unit sorts the out-of-order HARQ retransmissions, and sends reassembled SDUs to the upper layers. For some real-time services prohibited by HARQ, no reordering is required.
为实现重排,本发明的方法设置了HARQ接收缓存和ARQ接收缓存,分别用于缓存等待HARQ和ARQ重传的数据。由于采用一个缓存来缓存等待HARQ和ARQ重传带来的乱序,本发明提出了重排机制,包括窗口控制和定时器控制机制,用于区分HARQ重传乱序等待和ARQ重传乱序等待。下面讨论缓存及重排机制。In order to realize the rearrangement, the method of the present invention sets a HARQ receiving buffer and an ARQ receiving buffer, which are respectively used for buffering data waiting for HARQ and ARQ retransmission. Since a buffer is used to cache and wait for the disorder caused by HARQ and ARQ retransmission, the present invention proposes a reordering mechanism, including a window control and a timer control mechanism, to distinguish between HARQ retransmission disorder waiting and ARQ retransmission disorder wait. The caching and reordering mechanisms are discussed below.
1、HARQ缓存1. HARQ cache
一些参数和状态变量定义如下:Some parameters and state variables are defined as follows:
Highest_received_SN表示缓存内收到的PDU最高序号;Highest_received_SN indicates the highest serial number of the PDU received in the cache;
Next_expected_SN表示缓存内下一个按序送到高层或下一个功能单元的PDU序号;Next_expected_SN indicates the next PDU sequence number sent to the upper layer or the next functional unit in the cache in sequence;
HARQ_RcvWindow_Size表示高层配置的合适QoS的HARQ缓存等待最大值;HARQ_RcvWindow_Size indicates the maximum value of the HARQ cache waiting for the appropriate QoS configured by the upper layer;
将HARQ缓存窗口定义为(Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size,Highest_received_SN)。The HARQ buffer window is defined as (Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size, Highest_received_SN).
2、ARQ缓存窗口2. ARQ cache window
ARQ_RcvWindow_Size是高层配置的ARQ缓存等待最大值。ARQ_RcvWindow_Size is the maximum value of the ARQ cache waiting configured by the upper layer.
ARQ缓存窗口的定义包括:The definition of the ARQ buffer window includes:
如果Next_expected_SN<Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size,定义ARQ缓存窗口为:(Next_expected_SN,Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size);If Next_expected_SN<Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size, define the ARQ buffer window as: (Next_expected_SN, Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size);
如果Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN>ARQ_RcvWindow_Size,定义ARQ缓存窗口为(Next_expected_SN,Next_expected_SN+ARQ_RcvWindow_Size);If Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN>ARQ_RcvWindow_Size, define the ARQ buffer window as (Next_expected_SN, Next_expected_SN+ARQ_RcvWindow_Size);
3、ARQ缓存与HARQ缓存的关系3. The relationship between ARQ cache and HARQ cache
3-1)合并检测:如果Next_expected_SN<Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size,HARQ和ARQ缓存重合成一个。Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN<ARQ_RcvWindow_Size。3-1) Merge detection: if Next_expected_SN<Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size, the HARQ and ARQ buffers are merged into one. Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN<ARQ_RcvWindow_Size.
3-2)溢出检测:如果Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN>ARQ_RcvWindow_Size,发生窗口溢出,接收端发送窗口溢出指示给发送端,发送端相应ARQ实体新数据传输将会被挂起即只能进行重传不能进行新数据传输。3-2) Overflow detection: If Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN>ARQ_RcvWindow_Size, window overflow occurs, the receiving end sends a window overflow indication to the sending end, and the new data transmission of the corresponding ARQ entity at the sending end will be suspended, that is, only retransmission can be performed. Make a new data transfer.
3-3)脱节检测:如果Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN<ARQ_RcvWindow_Size这时会出现HARQ缓存窗口和ARQ缓存窗口脱节,原来两个窗口是重叠的,可以由接收端发送挂起结束指示给发送端,也可以由发送端根据重传缓存的状态进行配置。3-3) Disjoint detection: If Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size-Next_expected_SN<ARQ_RcvWindow_Size, the HARQ buffer window and the ARQ buffer window will be disconnected at this time. The original two windows overlap, and the receiving end can send a suspension end indication to the sending end, or It can be configured by the sender according to the state of the retransmission cache.
4、HARQ接收窗口参考边界4. HARQ receiving window reference boundary
本发明还可设定HARQ接收窗口参考边界作为重排机制。即定义:HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge为实际的HARQ缓存和ARQ缓存的边界,数值上对应于下一个HARQ按序收到的PDU序号。HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge<=Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size。当窗口上界即Highest_received_SN更新形成的窗口下界更新,如果SN为Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size的PDU在缓存中已经存在,将窗口实际下界HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge更新到现在窗口内最小的没有收到的PDU序号。ARQ窗口则变为(Next_expected_SN,HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge),其他ARQ相关操作同上述重排机制。The present invention can also set the HARQ receiving window reference boundary as a rearrangement mechanism. That is, the definition: HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge is the boundary between the actual HARQ buffer and the ARQ buffer, and the value corresponds to the sequence number of the next PDU received by HARQ in sequence. HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge<=Highest_received_SN−HARQ_Window_Size. When the upper bound of the window is the lower bound of the window formed by the update of Highest_received_SN, if the PDU whose SN is Highest_received_SN-HARQ_Window_Size already exists in the cache, the actual lower bound of the window HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge is updated to the smallest unreceived PDU sequence number in the current window. The ARQ window becomes (Next_expected_SN, HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge), and other ARQ related operations are the same as the above rearrangement mechanism.
定义定时器Timer_HARQ(T_SN),用于控制HARQ窗口移动,T_SN初始设为缓存内最大序号Highest_received_SN,同时启动各计时器Timer_HARQ。当序号为T_SN的PDU在计时器未超时即T_SN<=HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge收到时,计时器重启,T_SN重置为窗口内最大序号。如果定时器超时,T_SN>HARQ_RcvWindow_EdgeHARQ_RcvWindow_Edge被更新到(Highest_received_SN,T_SN)中没有收到的PDU最小序号,同时重置T_SN为窗口内PDU最大序号,重启定时器。The timer Timer_HARQ (T_SN) is defined to control the movement of the HARQ window. T_SN is initially set to the highest sequence number Highest_received_SN in the cache, and each timer Timer_HARQ is started at the same time. When the PDU with the sequence number T_SN is received before the timer expires, that is, T_SN<=HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge, the timer is restarted, and T_SN is reset to the maximum sequence number in the window. If the timer expires, T_SN>HARQ_RcvWindow_EdgeHARQ_RcvWindow_Edge is updated to the minimum sequence number of the unreceived PDU in (Highest_received_SN, T_SN), and at the same time, T_SN is reset to the maximum sequence number of the PDU in the window, and the timer is restarted.
5、采用定时器作为重排机制5. Use timer as rearrangement mechanism
每次从MUX单元收到一个ARQ PDU就启动定时器Timer_Rcv,状态变量HARQ_RcvWindow_EdgeT表示HARQ接收窗口边界,即为定时器已经超时的接收到PDU最大的序号。Highest_received_SN表示缓存内收到的PDU最高序号。Next_expected_SN表示缓存内下一个按序送到高层或下一个功能单元的PDU序号。Next_expected_SN可以小于HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge_T。Every time an ARQ PDU is received from the MUX unit, the timer Timer_Rcv is started, and the state variable HARQ_RcvWindow_EdgeT indicates the HARQ receiving window boundary, which is the maximum sequence number of the received PDU whose timer has timed out. Highest_received_SN indicates the highest sequence number of the PDU received in the cache. Next_expected_SN indicates the next PDU sequence number in the cache that is sent to the upper layer or the next functional unit in sequence. Next_expected_SN may be smaller than HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge_T.
ARQ_RcvWindow_Size是高层配置的ARQ缓存等待最大值(窗口大小)上限。ARQ接收缓存仍用窗口控制,接收窗口为(Next_expected_SN,HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge_T)一般缓存等待最大值小于等于ARQ_RcvWindow_Size,如果HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge_T-Next_expected_SN>ARQ_RcvWindow_Size,ARQ窗口定为(Next_expected_SN,Next_expected_SN+ARQ_RcvWindow_Size)接收端发送窗口溢出指示给发送端,发送端相应ARQ实体新数据传输将会被挂起即只能进行重传不能进行新数据传输。ARQ_RcvWindow_Size is the upper limit of the maximum value (window size) of the ARQ cache wait configured by the upper layer. The ARQ receive buffer is still controlled by the window. The receive window is (Next_expected_SN, HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge_T). Generally, the maximum value of buffer waiting is less than or equal to ARQ_RcvWindow_Size. If HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge_T-Next_expected_SN>ARQ_RcvWindow_Size, the ARQ window is set to (Next_expected_SN, Next_expected_SN+ARQ_Rizev) to send the window to the overflow of the receiving end. At the sending end, the new data transmission of the corresponding ARQ entity at the sending end will be suspended, that is, only retransmission can be performed but no new data transmission can be performed.
HARQ和ARQ缓存等待最大值(即窗口大小)根据业务可以由高层进行配置。The maximum value of HARQ and ARQ buffer waiting (that is, the window size) can be configured by the upper layer according to the service.
实施例一Embodiment one
当收到SN=x的PDU,进行以下处理(步骤号可以表示执行顺序,也可以不是执行顺序):When receiving the PDU of SN=x, carry out the following processing (the step number can represent the execution order, also can not be the execution order):
步骤1step 1
如果x在(Next_expected_SN,Highest_received_SN)之内成立,如果此SN对应数据已经在缓存中存在则删除此数据;如果x不在(Next_expected_SN,Highest_received_SN)之内,根据序号将PDU放入缓存;If x is established within (Next_expected_SN, Highest_received_SN), if the data corresponding to this SN already exists in the cache, delete this data; if x is not within (Next_expected_SN, Highest_received_SN), put the PDU into the cache according to the serial number;
步骤2:Step 2:
步骤3:Step 3:
实施例二Embodiment two
当收到SN=x的PDU,进行以下处理(步骤号可以表示执行顺序,也可以不是执行顺序):When receiving the PDU of SN=x, carry out the following processing (the step number can represent the execution order, also can not be the execution order):
步骤1:step 1:
如果x在(Next_expected_SN,Highest_received_SN)之内{if x is within (Next_expected_SN, Highest_received_SN) {
如果此SN对应数据已经在缓存中存在则删除此数据,否则,根据序号将PDU放入缓存};If the data corresponding to this SN already exists in the cache, delete this data, otherwise, put the PDU into the cache according to the sequence number};
步骤2:Step 2:
步骤3:Step 3:
如果SN等于HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge的PDU在缓存中,则{If the PDU with SN equal to HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge is in the cache, then {
检查是否有和这个PDU序号连续的PDU在缓存中,将HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge重新更新到最小的不连续的PDU序号;}Check whether there are PDUs with consecutive PDU serial numbers in the cache, and re-update HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge to the smallest discontinuous PDU serial number;}
步骤4:Step 4:
根据更新的HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge和状态报告触发原则触发相应状态报告;Trigger the corresponding status report according to the updated HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge and status report triggering principles;
步骤5:Step 5:
步骤6:Step 6:
在此同时,有以下定时器操作(步骤号可以表示执行顺序,也可以不是执行顺序):At the same time, there are the following timer operations (the step number may indicate the execution sequence, or it may not be the execution sequence):
步骤1:step 1:
如果缓存中有PDU,Timer_HARQ没有启动,则{If there are PDUs in the cache and Timer_HARQ is not started, then {
触发定时器Timer_HARQ;Trigger timer Timer_HARQ;
T_SN设置为缓存中最大的PDU序号。}T_SN is set to the largest PDU sequence number in the cache. }
步骤2:Step 2:
如果计时器超时之前,HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge>=T_SN,则停止计时器;If HARQ_RcvWindow_Edge>=T_SN before the timer expires, stop the timer;
步骤3:Step 3:
步骤4:Step 4:
实施例三Embodiment three
当收到SN=x的PDU,则进行以下步骤,步骤编号可以表示执行顺序,也可以不是执行顺序。When the PDU with SN=x is received, the following steps are performed, and the step number may indicate the execution sequence or not.
1、触发定时器Timer_cv;1. Trigger timer Timer_cv;
Claims (14)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006100346359ACN101043301B (en) | 2006-03-22 | 2006-03-22 | Data rearrangement and recombination method in wireless communication system and its base station |
| DE602007011221TDE602007011221D1 (en) | 2006-03-03 | 2007-02-06 | METHOD FOR RECOMBINING DATA IN A WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM AND DEVICE THEREFOR |
| EP07702289AEP1993241B1 (en) | 2006-03-03 | 2007-02-06 | A method for reassembling data in wireless communication system and an apparatus thereof |
| PCT/CN2007/000406WO2007098676A1 (en) | 2006-03-03 | 2007-02-06 | A method for reassembling data in wireless communication system and an apparatus thereof |
| AT07702289TATE492100T1 (en) | 2006-03-03 | 2007-02-06 | METHOD FOR REASSUMING DATA IN A WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM AND DEVICE THEREFOR |
| US12/203,799US20090046626A1 (en) | 2006-03-03 | 2008-09-03 | Method and device for reordering data in wireless communication system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006100346359ACN101043301B (en) | 2006-03-22 | 2006-03-22 | Data rearrangement and recombination method in wireless communication system and its base station |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101043301A CN101043301A (en) | 2007-09-26 |
| CN101043301Btrue CN101043301B (en) | 2011-08-10 |
Family
ID=38808542
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2006100346359AExpired - Fee RelatedCN101043301B (en) | 2006-03-03 | 2006-03-22 | Data rearrangement and recombination method in wireless communication system and its base station |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN101043301B (en) |
Families Citing this family (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7864815B2 (en)* | 2008-04-07 | 2011-01-04 | Mediatek Inc. | Methods and apparatus for performing protocol data unit header re-synchronization in a communication system |
| CN101998505B (en)* | 2009-08-12 | 2013-06-12 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Hsdpa data caching method and mobile terminal |
| CN101699898B (en)* | 2009-11-03 | 2012-11-28 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for transmitting grouped data in grouping service domain and system thereof |
| CN102255710B (en) | 2011-04-15 | 2014-01-29 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Method and device for storing encoding block |
| US20130088960A1 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2013-04-11 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | System and Method for Information Delivery with Multiple Point Transmission |
| US9838089B2 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2017-12-05 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | System and method for multiple point transmission in a communications system |
| CN103052033B (en)* | 2011-10-17 | 2015-01-28 | 鼎桥通信技术有限公司 | Data processing method of user equipment in private network |
| CN102883281B (en)* | 2012-01-30 | 2015-09-09 | 华为技术有限公司 | A kind of method, equipment and system sending message |
| EP2874461A4 (en)* | 2013-01-18 | 2015-10-07 | Huawei Tech Co Ltd | Data transmission method and device |
| CN104519524A (en)* | 2013-09-26 | 2015-04-15 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Data sorting method based on multi-stream transmission and receiving device |
| CN104798320B (en) | 2013-11-11 | 2018-11-09 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and device |
| CN104486793A (en)* | 2014-08-26 | 2015-04-01 | 上海华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and base station |
| US10397754B2 (en)* | 2015-08-06 | 2019-08-27 | Qualcomm Incorporation | Packet data convergence protocol reordering with enhanced component carriers |
| CN107094123A (en)* | 2016-02-18 | 2017-08-25 | 中国移动通信集团公司 | PDU transmission methods and device |
| CN107333298B (en)* | 2016-04-29 | 2020-03-24 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Data transmission method and related equipment |
| CN107359968B (en)* | 2016-05-10 | 2020-05-26 | 电信科学技术研究院 | Data transmission method and device for single-layer serial number |
| CN107707337A (en)* | 2016-08-09 | 2018-02-16 | 联发科技股份有限公司 | Rearrangement method and its device |
| WO2018166042A1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2018-09-20 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | Data unit transmission method and apparatus |
| CN107113658B (en)* | 2017-03-14 | 2020-06-19 | 北京小米移动软件有限公司 | Data unit transmission method and device |
| EP3766279B1 (en)* | 2018-07-10 | 2022-12-21 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and system for optimizing the feedback mechanism in data link layer |
| CN109327552B (en)* | 2018-12-05 | 2021-03-16 | 重庆邮电大学 | A smart street light data transmission management method based on NB-IoT |
| CN109936858B (en)* | 2019-02-20 | 2022-03-25 | 武汉虹信科技发展有限责任公司 | Method and system for processing wireless link control data |
| CN109884972A (en)* | 2019-02-26 | 2019-06-14 | 北京龙鼎源科技股份有限公司 | Processing method and processing device, storage medium and the electronic device of data |
| CN111132232B (en)* | 2020-01-02 | 2022-10-25 | 重庆邮电大学 | A method and device for intelligently receiving 5G NR RLC UMD PDU |
| CN112995960B (en)* | 2021-03-09 | 2023-10-31 | 保定市兆微软件科技有限公司 | Data transmission method for direct communication of chained networking terminal |
| CN113315608A (en)* | 2021-04-30 | 2021-08-27 | 上海微波技术研究所(中国电子科技集团公司第五十研究所) | Method, system, medium and communication system for dynamically determining retransmission PDU |
| WO2023197312A1 (en)* | 2022-04-15 | 2023-10-19 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Wireless communication method and apparatus |
| CN114679574B (en)* | 2022-05-27 | 2022-08-30 | 武汉中科通达高新技术股份有限公司 | Monitoring data distribution method and monitoring data distribution device |
| CN120021168A (en)* | 2023-11-17 | 2025-05-20 | 华为技术有限公司 | A communication method, device, readable storage medium and computer program product |
| CN117478615B (en)* | 2023-12-28 | 2024-02-27 | 贵州大学 | A method for reliable transmission in deterministic networks |
| CN118828760B (en)* | 2024-09-19 | 2024-11-29 | 成都爱瑞无线科技有限公司 | Cell switching method, device, electronic device, storage medium and program product |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1379557A (en)* | 2002-05-16 | 2002-11-13 | 武汉汉网高技术有限公司 | ARQ mechanism able to automatically request retransmissions for multiple rejections |
| CN1505416A (en)* | 2002-11-29 | 2004-06-16 | 华为技术有限公司 | System Information Receiving Reorganization Method in Third Generation Wireless Communication System |
| CN1523797A (en)* | 2003-02-17 | 2004-08-25 | ��������ͨ�ż����о�����˾ | Reordering Method of Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel HARQ in WCDMA System |
| CN1716835A (en)* | 2004-07-01 | 2006-01-04 | 日本电气株式会社 | Mobile wireless communication terminal equipment |
- 2006
- 2006-03-22CNCN2006100346359Apatent/CN101043301B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1379557A (en)* | 2002-05-16 | 2002-11-13 | 武汉汉网高技术有限公司 | ARQ mechanism able to automatically request retransmissions for multiple rejections |
| CN1505416A (en)* | 2002-11-29 | 2004-06-16 | 华为技术有限公司 | System Information Receiving Reorganization Method in Third Generation Wireless Communication System |
| CN1523797A (en)* | 2003-02-17 | 2004-08-25 | ��������ͨ�ż����о�����˾ | Reordering Method of Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel HARQ in WCDMA System |
| CN1716835A (en)* | 2004-07-01 | 2006-01-04 | 日本电气株式会社 | Mobile wireless communication terminal equipment |
Non-Patent Citations (7)
| Title |
|---|
| 3GPP.3GPP TR 25.813(v0.5.1):Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN) |
| 3GPP.3GPP TR 25.813(v0.5.1):Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN) Radio interface protocol aspects(Release 7).3GPP,2006,全文.* |
| 3GPP.3GPP TS 25.308 (v6.3.0):High Speed Downlink Packet Access(HSDPA) |
| 3GPP.3GPP TS 25.308 (v6.3.0):High Speed Downlink Packet Access(HSDPA) Overall description;Stage 2 (Release 6).3GPP,2004,第6节.* |
| Overall description |
| Radio interface protocol aspects(Release 7).3GPP,2006,全文. |
| Stage 2 (Release 6).3GPP,2004,第6节. |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101043301A (en) | 2007-09-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101043301B (en) | Data rearrangement and recombination method in wireless communication system and its base station | |
| EP1993241B1 (en) | A method for reassembling data in wireless communication system and an apparatus thereof | |
| US7636312B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for moving a receive window in a radio access network | |
| JP4318733B2 (en) | Control protocol data unit transmission / reception method including processing time information | |
| AU2004307900B2 (en) | Updating next-expected TSN and receiver window to avoid stall conditions | |
| CN102104535B (en) | Method, device and system for transmitting PDCP data | |
| RU2487485C2 (en) | Method of controlling transmission window and retransmission and transmitting device | |
| US20070291695A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for facilitating lossless handover in 3gpp long term evolution systems | |
| US20050039101A1 (en) | Method and system of retransmission | |
| EP2063579B1 (en) | Method for handling radio bearer messages during reset and reestablishment in a wireless system | |
| JP2003283596A (en) | System and method for avoiding cross situation using timer in high-speed downlink packet access system | |
| TW201212607A (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling a handover between UTRA R6 cells and R7 cells | |
| JP5069754B2 (en) | Control information transmission method in mobile communication system | |
| CN101141445B (en) | Transmission method and sending terminal equipment of transmission unit | |
| WO2007022694A1 (en) | An user plane protocol stack and a lossless movement method | |
| CN1875557B (en) | Update next expected TSN and receiver window to avoid stall condition | |
| CN101277174A (en) | Method and device for data retransmission based on quality of service and wireless communication system | |
| CN115865282A (en) | Data retransmission method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| HK1140893A (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling a handover between utra r6 cells and r7 cells | |
| HK1140893B (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling a handover between utra r6 cells and r7 cells |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20110810 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |