CN101005625B - Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method - Google Patents
Variable length coding method and variable length decoding methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN101005625B CN101005625BCN200610143687.XACN200610143687ACN101005625BCN 101005625 BCN101005625 BCN 101005625BCN 200610143687 ACN200610143687 ACN 200610143687ACN 101005625 BCN101005625 BCN 101005625B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- run
- value
- code
- level
- length
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Compression Or Coding Systems Of Tv Signals (AREA)
- Compression, Expansion, Code Conversion, And Decoders (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese本申请是申请号为02813282.3、申请日为2002年11月22日、发明名称为“可变长度编码方法以及可变长度解码方法”的专利申请的分案申请。This application is a divisional application of a patent application with the application number 02813282.3, the filing date being November 22, 2002, and the invention title being "Variable Length Coding Method and Variable Length Decoding Method".
技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种可变长度编码方法以及可变长度解码方法,特别涉及一种用于转换通过根据可变长度编码处理把图像数据的频率分量(量化系数)量化为被编码数据而获得的多个系数的方法,以及涉及用于根据一种可变长度解码处理来对该编码的数据进行解码以重构多个系数的方法。The present invention relates to a variable length coding method and a variable length decoding method, and more particularly to a method for converting multiple data obtained by quantizing frequency components (quantization coefficients) of image data into coded data according to variable length coding processing. coefficients, and methods for decoding the encoded data to reconstruct coefficients according to a variable length decoding process.
背景技术Background technique
在最近几年,我们迎来了多媒体时代,其中音频、视频和其他数据被集成地处理,并且例如报纸、杂志、电视、广播以及电话这样的传统信息媒体(即,用于把信息发送到个人的手段)已经被采用,作为多媒体的对象。通常“多媒体”的含义不但代表文字,而且还代表图像、语音以及特别是时间上相关的图像。为了处理传统的信息媒体作为多媒体的对象,把信息转换为数字格式是本质性的。In recent years we have ushered in the multimedia age in which audio, video, and other data are processed integrally, and traditional information media such as newspapers, magazines, television, radio, and telephones (i.e., used to send information to individuals means) have been adopted as multimedia objects. "Multimedia" generally means not only text, but also images, speech and especially time-related images. In order to deal with traditional information media as multimedia objects, it is essential to convert the information into digital format.
当由上述每个信息媒体所处理的数据量用数字数据量来估计时,在字符的情况中,用于每个字符的数据量是1-2个字节。但是,在语音的情况中,数据量为每秒64kbits(用于通信的质量),并且在运动图像的情况中,该数据量大于每秒100Mbits(用于当前电视广播的质量)。从而,对于上述信息媒体,以数字格式原样地处理这样大量的数据是不现实的。例如,可视电话已经通过具有64kbps~1.5Mbps的传输速率的ISDN(综合业务数字网)而投入使用,但是重要的是通过ISDN原样地传送具有大数据量的电视摄像机的输出图像。When the amount of data handled by each of the above information media is estimated by the amount of digital data, in the case of characters, the amount of data for each character is 1-2 bytes. However, in the case of voice, the amount of data is 64 kbits per second (quality for communication), and in the case of moving images, the amount of data is more than 100 Mbits per second (quality for current television broadcasting). Thus, for the above-mentioned information media, it is unrealistic to handle such a large amount of data as it is in digital format. For example, videophones have been put into use through ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) having a transmission rate of 64kbps˜1.5Mbps, but it is important to transmit the output image of a television camera having a large amount of data through ISDN as it is.
从而,需要数据压缩技术。例如,在可视电话的情况中,采用被ITU-T(国际电信联盟-电信部门)标准化为H.261和H.263的运动图像压缩技术。另外,根据基于MPEG-1的数据压缩技术,可以在一个普通的音乐CD(压缩光盘)中与音频数据一同记录图像数据。Thus, data compression techniques are required. For example, in the case of videophones, moving image compression techniques standardized as H.261 and H.263 by ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Sector) are employed. In addition, according to data compression technology based on MPEG-1, image data can be recorded together with audio data in an ordinary music CD (Compact Disc).
在此,MPEG(运动图像专家组)是与用于运动图像的图像信号的数字压缩相关的一种国际标准。在MPEG-1中,运动图像的图像信号被压缩为1.5Mbps,即,电视信号的数据被压缩为大约1/100。由于MPEG-1的传输速率主要限制为大约1.5Mbps,MPEG-2被标准化为满足更高图像质量的需求。在MPEG-2中,一个运动图像的图像信号被压缩为2-15Mbps。Here, MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group) is an international standard related to digital compression of image signals for moving pictures. In MPEG-1, an image signal of a moving image is compressed to 1.5 Mbps, that is, data of a television signal is compressed to approximately 1/100. Since the transmission rate of MPEG-1 was mainly limited to about 1.5 Mbps, MPEG-2 was standardized to meet the demand for higher image quality. In MPEG-2, an image signal of a moving image is compressed at 2-15 Mbps.
在现有的情况中,由对于MPEG-1和MPEG-2(ISO/IECJTC1/SC29/WG11)标准化的工作组实现具有更高压缩比的MPEG-4的标准化,MPEG-4不仅仅能够高效率地以较低位率进行编码,而且实现一种强的抗错误技术的引入,其即使在出现传输线错误时也可以减小主观的图像质量下降。另外,ITU-T开发H.26L标准作为下一代图像编码方法的标准,并且在此时最新的编码方法被称为“测试模型”(TML8)。In the existing situation, the standardization of MPEG-4 with a higher compression ratio is realized by the working group for the standardization of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 (ISO/IECJTC1/SC29/WG11), and MPEG-4 is not only capable of high efficiency Coding at a lower bit rate and enabling the introduction of a strong error resistance technique which reduces subjective image quality degradation even in the presence of transmission line errors. In addition, the ITU-T develops the H.26L standard as a standard of the next-generation image coding method, and the latest coding method at this time is called "Test Model" (TML8).
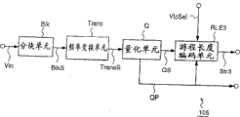
图30为示出传统的图像编码装置的方框图。Fig. 30 is a block diagram showing a conventional image encoding device.
该图像编码装置201a具有用于把一个所输入的图像信号Vin分块为分别包括预定数目的像素的单元区域(块)并且输出分块的图像信号BlkS的分块单元Blk,以及用于使得该输出BlkS受到频率变换以输出对应于各个块的频率分量TransS的频率变换单元Trans。在此,该块是在一个图像(图像空间)中的预定尺寸的区域,其是用于一个图像信号的编码处理的单元,并且其由预定数目的像素所构成。在此,该图像信号Vin对应于由多个图像所构成的一个运动图像。The
该图像编码装置201a进一步包括一个量化单元Q,用于量化来自该频率变换单元的输出(频率分量)TransS,并且输出对应于各个块的量化的分量(量化系数)QS;以及一个编码单元RLE0a,用于使得来自该量化单元的输出(量化分量)QS受到可变长度编码处理。The
接着,将描述其操作。Next, its operation will be described.
当一个图像信号Vin被输入到该图像编码装置201a时,分块单元Blk把输入的图像信号Vin分为对应于块单元的图像信号,以产生对应于每个块的图像信号(分块的图像信号)BlkS。该频率变换单元Trans根据DCT(离散余弦变换)把分块的图像信号BlkS分为频率分量TransS或者小波变换。该量化单元Q在一个预定的量化步骤中根据一个量化参数QP量化该频率分量TransS,以输出量化分量QS,以及输出量化参数QP。然后,该编码单元RLE0a使得该量化分量QS受到可变长度编码处理,并且输出一个编码流Str0a。When an image signal Vin is input to the
图31示出用于说明构成图像编码装置201a的编码单元RLE0a的方框图。FIG. 31 shows a block diagram for explaining the encoding unit RLE0a constituting the
该编码单元RLE0a具有一个曲折扫描仪Scan,用于把在一个二维阵列中的量化单元Q的输出(量化分量)QS变换为在一个一维阵列(即,预定次序)中的量化分量;以及一个可变长度编码器VLC,用于使得从曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef受到可变长度编码处理。The encoding unit RLE0a has a zigzag scanner Scan for transforming the output (quantized components) QS of the quantization unit Q in a two-dimensional array into quantized components in a one-dimensional array (i.e., in a predetermined order); and A variable length coder VLC is used to subject the quantized component Coef output from the zigzag scanner Scan to variable length code processing.
当从量化单元Q输出的量化分量QS被输出的编码单元RLE0a时,该曲折扫描仪Scan把在来自该量化单元Q的一个二维阵列中的量化分量QS变换为在一个一维阵列(预定次序)中的量化分量Coef,并且输出该量化分量。When the quantized components QS output from the quantization unit Q are output to the encoding unit RLE0a, the zigzag scanner Scan transforms the quantized components QS in a two-dimensional array from the quantization unit Q into a one-dimensional array (in a predetermined order) ) in the quantized component Coef, and output the quantized component.
图43为用于具体说明用于由曲折扫描仪Scan变换该量化分量QS的处理的示意图。FIG. 43 is a diagram for concretely explaining the process for transforming the quantized component QS by the meander scanner Scan.
如图43中所示,从量化单元Q输出的量化分量QS具有一个二维阵列,即,这样一个阵列,其中根据水平频率分量的大小和垂直频率分量的大小而在一个二维频率区域Fr上以矩阵的形式设置该量化分量QS。As shown in FIG. 43, the quantized components QS output from the quantization unit Q have a two-dimensional array, that is, an array in which the This quantized component QS is set in the form of a matrix.
该曲折扫描仪Scan执行一个处理用于按照如箭头Y1至Y7所示的曲折方式扫描在该二维阵列中的量化分量QS,以把该分量变换为在一个一维阵列中的量化分量Coef。也就是说,在该扫描处理中,对于在该二维阵列中的多个量化分量QS沿着扫描的过程设置预定次序。The zigzag scanner Scan performs a process for scanning the quantized components QS in the two-dimensional array in a zigzag manner as shown by arrows Y1 to Y7 to transform the components into quantized components Coef in a one-dimensional array. That is, in the scanning process, a predetermined order is set along the course of scanning for the plurality of quantized components QS in the two-dimensional array.
然后,该可变长度编码器VLC利用示出表示量化分量的大小与代码(代码字)之间的关系的代码表把代码分配到从曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef,以把该量化分量变换为对应于每个块的一个编码流Str0a。Then, the variable length coder VLC assigns codes to the quantized components Coef output from the zigzag scanner Scan using a code table showing the relationship between the size of quantized components and codes (codewords) to convert the quantized components into Converted to one coded stream Str0a corresponding to each block.
图32为用于说明对应于图30中所示的图像编码装置201a的图像解码装置202a的方框图。Fig. 32 is a block diagram for explaining an
该图像解码装置202a对从如图30中所示的常规图像编码装置201a输出的编码流Str0a进行解码。The
该图像解码装置202a具有用于解码从图像编码装置201a输出的编码流Str0a的解码单元RLD0a、以及用于使得来自解码单元RLD0a的输出(解码的量化分量)DQS受到反量化处理的反量化单元IQ。This
该图像解码装置202a进一步包括用于使得来自反量化单元IQ的输出(解码的频率分量)ITransS受到反频率变换处理的反频率变换单元ITrans、以及用于根据来自反频率变换单元ITrans的输出(解码的分块图像信号)DBlkS产生对应于每个图像的解码的图像信号Vout的解块单元DeBlk。This
下面,将描述其操作。Next, its operation will be described.
当该编码流Str0a被从图像编码装置201a到图像解码装置202a输入时,该解码单元RLD0a解码该编码流Str0a,并且输出解码的量化分量DQS。该解码单元RLD0a的操作与编码单元RLE0a的操作相反。When the encoded stream Str0a is input from the
该反量化单元IQ执行量化单元Q的操作的反操作,即,根据量化参数QP对解码的量化分量DQS进行反量化并且输出解码的频率分量ITransS的操作。该反频率变换单元ITrans执行频率变换单元Trans的操作的反操作,即,使得解码的频率分量ITransS受到反DCT或反小波变换,以重构对应于各个块的解码的图像信号DBlkS的操作。然后,该解块单元DeBlk结合各个块的解码的图像信号DBlkS,以输出一个对应于每个图像(帧)的解码的图像信号Vout。This inverse quantization unit IQ performs an inverse operation of the operation of the quantization unit Q, ie, an operation of inverse quantizing the decoded quantized component DQS according to the quantization parameter QP and outputting the decoded frequency component ITransS. The inverse frequency transform unit ITrans performs the inverse operation of the operation of the frequency transform unit Trans, ie, an operation of subjecting the decoded frequency component ITransS to inverse DCT or inverse wavelet transform to reconstruct the decoded image signal DBlkS corresponding to each block. Then, the deblocking unit DeBlk combines the decoded image signals DBlkS of the respective blocks to output a decoded image signal Vout corresponding to each image (frame).
图33为用于说明构成图像解码装置202a的解码单元RLD0a的方框图。FIG. 33 is a block diagram for explaining the decoding unit RLD0a constituting the
该解码单元RLD0a具有一个可变长度解码器VLD,用于使得编码流Str0a受到可变长度解码处理,以解码对应于包含在编码流Str0a中的每个代码的量化分量Coef;以及反曲折扫描仪IScan,用于从由可变长度解码器VLD输出的一维阵列的解码的量化分量DQS重构二维阵列的量化分量DQS。The decoding unit RLD0a has a variable length decoder VLD for subjecting the coded stream Str0a to variable length decoding processing to decode the quantized component Coef corresponding to each code contained in the coded stream Str0a; and a dezigzag scanner IScan for reconstructing the quantized components DQS of the two-dimensional array from the decoded quantized components DQS of the one-dimensional array output by the variable length decoder VLD.
在该解码单元RLD0a中,可变长度解码器VLD根据与可变长度编码器VLC相反的操作解码该编码流Str0a,并且输出对应于代码(代码字)的量化分量Coef。然后,该反曲折扫描仪IScan执行与曲折扫描仪Scan相反的操作,以从由可变长度解码器VLD输出的一维阵列的量化分量Coef重构二维阵列的解码的量化分量DQS,并且把该解码的量化分量DQS输出到该反量化单元IQ。In this decoding unit RLD0a, a variable length decoder VLD decodes the coded stream Str0a according to the reverse operation of the variable length coder VLC, and outputs quantized components Coef corresponding to codes (codewords). Then, the inverse scanner IScan performs the reverse operation of the zigzag scanner Scan to reconstruct the decoded quantized components DQS of the two-dimensional array from the quantized components Coef of the one-dimensional array output by the variable length decoder VLD, and convert The decoded quantized component DQS is output to the inverse quantization unit IQ.
日本专利申请No.6-311534中公开一种方法,其中一个图像信号被分为亮度信号和色差信号,以使得所获得的信号受到可变长度编码处理。Japanese Patent Application No. 6-311534 discloses a method in which an image signal is divided into a luminance signal and a color difference signal so that the obtained signal is subjected to variable length encoding processing.
对应于已经被设置预定次序的各个块的多个量化分量是包括高冗余度的数据,即,在一个非零的系数(非零系数)之后连续接着多个数值为零的系数(零系数)。为了编码这种量化分量,通常采用这样一种方法,其中对删除冗余信息的量化分量编码,例如,通过使用表示连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值而对量化分量编码的游程长度编码方法。A plurality of quantized components corresponding to respective blocks for which a predetermined order has been set is data including a high redundancy, that is, one non-zero coefficient (non-zero coefficient) is successively followed by a plurality of coefficients having a value of zero (zero coefficient ). In order to code such quantized components, a method is generally employed in which the redundant information-deleted quantized components are coded, for example, by using a run value representing the number of consecutive zero coefficients and a value representing the non-zero coefficients following the zero coefficient. A run-length coding method that encodes quantized components by level values of numerical values.
在下文中,将描述使用该游程长度编码方法的常规图像编码装置。Hereinafter, a conventional image encoding device using this run-length encoding method will be described.
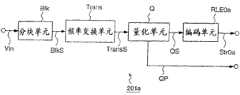
图34为示出执行游程长度编码的常规图像编码装置的方框图。Fig. 34 is a block diagram showing a conventional image encoding device that performs run-length encoding.
该图像编码装置201b包括取代图30中所示的图像编码装置201a的编码单元RLE0a的一个游程长度编码单元RLE0b,用于使得来自量化单元Q的输出(量化分量)QS受到游程长度编码,并且输出一个编码流Str0b。其他部分与图像编码装置201a的相同。This image encoding device 201b includes a run-length encoding unit RLE0b instead of the encoding unit RLE0a of the
该图像编码装置201b的操作不同于图像编码装置201a的操作之处仅仅在于编码单元RLE0b的操作。The operation of this image encoding device 201b differs from that of the
图35为示出在图像编码装置201b中的编码单元RLE0b的具体结构的方框图。Fig. 35 is a block diagram showing a specific structure of the encoding unit RLE0b in the image encoding device 201b.
该游程长度编码单元RLE0b类似于编码单元RLE0a,具有一个曲折扫描仪Scan,用于把来自量化单元Q的二维阵列的输出(量化分量)QS变换为一维(即,预定次序)的量化分量Coef。The run-length encoding unit RLE0b is similar to the encoding unit RLE0a, having a zigzag scanner Scan for transforming the output (quantized components) QS from the two-dimensional array of quantization units Q into one-dimensional (i.e., predetermined order) quantized components Coef.
然后,该游程长度编码单元RLE0b进一步包括:游程计算器RunCal,用于计算其数值为零的连续量化分量(零系数)Coef的数目,并且输出表示连续零系数的数目的游程数值Run;以及级别计算器LevCal,用于计算在该零系数之后数值非零的量化分量(非零系数)的数值,并且输出表示该非零系数的数值的级别数值Lev。Then, the run-length encoding unit RLE0b further includes: a run calculator RunCal for calculating the number of consecutive quantized components (zero coefficients) Coef whose value is zero, and outputs a run value Run representing the number of consecutive zero coefficients; and a level A calculator LevCal for calculating the value of a quantized component (non-zero coefficient) whose value is non-zero after the zero coefficient, and outputs a level value Lev representing the value of the non-zero coefficient.
该游程长度编码单元RLE0b进一步包括一个可变长度编码器LevVLC,用于使得从级别计算器LevCal输出的级别数值Lev受到可变长度编码处理,并且输出一个代码串(级别数值代码串)LStr;可变长度编码器RVLC,用于使得从游程计算器RunCal输出的游程数值Run受到可变长度编码处理,并且输出一个代码串(游程数值代码串)RStr;以及多路复用器MUX,用于对每个块复用级别数值代码串LStr和游程数值代码串RStr,并且输出一个复用的编码流Str0b。The run-length encoding unit RLE0b further includes a variable length encoder LevVLC for subjecting the level value Lev output from the level calculator LevCal to variable length encoding processing, and outputting a code string (level value code string) LStr; The variable length encoder RVLC is used to subject the run value Run output from the run length calculator RunCal to variable length encoding processing, and outputs a code string (run value code string) RStr; and the multiplexer MUX is used to Each block multiplexes the level numerical code string LStr and the run length numerical code string RStr, and outputs a multiplexed encoded stream Str0b.
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
该曲折扫描仪Scan把在从量化单元Q输出的二维阵列中的量化分量QS变换为一维阵列(预定次序)中的量化分量Coef,并且输出该量化分量Coef。由曲折扫描仪Scan对量化分量QS的变换处理按照与图像编码装置201a的编码单元RLE0a相同的方式执行。The meander scanner Scan transforms the quantized components QS in the two-dimensional array output from the quantization unit Q into the quantized components Coef in the one-dimensional array (predetermined order), and outputs the quantized components Coef. Transformation processing of the quantized component QS by the zigzag scanner Scan is performed in the same manner as the coding unit RLE0a of the
该游程计算器RunCal根据从曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef计算连续零系数的数目,并且输出表示所计算的数值的游程数值Run。该级别计算器LevCal根据从曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef计算在连续零系数之后的非零系数的数值,并且输出表示该数值的级别数值Lev。The run calculator RunCal calculates the number of consecutive zero coefficients from the quantized component Coef output from the meander scanner Scan, and outputs a run value Run representing the calculated value. The level calculator LevCal calculates the value of a non-zero coefficient following consecutive zero coefficients from the quantized component Coef output from the meander scanner Scan, and outputs a level value Lev representing the value.
在此,当在要被处理的目标块中检测最高的频率分量(最后的非零系数)时,该游程计算器RunCal产生一个特定数值EOB(块的结束),以表示后续的更高频率分量都具有零数值。Here, when the highest frequency component (last non-zero coefficient) is detected in the target block to be processed, the run length calculator RunCal generates a specific value EOB (End of Block) to represent the subsequent higher frequency components Both have a value of zero.
另外,该可变长度编码器RVLC使得从游程计算器RunCal输出的游程数值Run受到可变长度编码处理,用于根据一个代码表或算术运算把一个代码(代码字)分配到该游程数值,并且输出一个代码串RStr。该可变长度编码器LevVLC使得从级别计算器LevCal输出的级别数值Lev受到可变长度编码处理,用于根据代码表或算术运算把一个代码(代码字)分配到该级别数值,并且输出一个代码串LStr。In addition, the variable length coder RVLC subjects the run value Run output from the run length calculator RunCal to variable length coding processing for assigning a code (code word) to the run value according to a code table or arithmetic operation, and Output a code string RStr. The variable length coder LevVLC subjects the level value Lev output from the level calculator LevCal to variable length encoding processing for assigning a code (code word) to the level value according to a code table or arithmetic operation, and outputs a code String LStr.
该多路复用器MUX对于每个块复用该代码串LStr和代码串RStr,并且输出一个复用的编码流Str0b。The multiplexer MUX multiplexes the code string LStr and the code string RStr for each block, and outputs a multiplexed coded stream Str0b.
在此,对于每个块执行用于复用代码串LStr和代码串RStr的处理,例如按照对应于用于一个目标块的所有游程数值的代码串RStr之后接着对应于用于该目标块的所有级别数值的代码串LStr,或者对应于用于一个目标块的所有级别数值的代码串LStr之后接着对应于用于该目标块的所有游程数值的代码串RStr。Here, processing for multiplexing code string LStr and code string RStr is performed for each block, for example, such that code string RStr corresponding to all run values for one target block is followed by code string RStr corresponding to all run values for the target block. A code string LStr for a level value, or a code string LStr for all level values for a target block followed by a code string RStr for all run values for that target block.
如上文所述的,通过使用表示其数值为零(零系数)Coef的量化分量数目的游程数值Run和表示在该零系数之后其数值非零(非零系数)的量化分量的数值的级别数值Lev而按照预定次序编码多个量化系数的图像编码装置可以用较高的编码效率对多个量化系数进行编码,并且消除其冗余信息。As described above, by using the run value Run representing the number of quantized components whose value is zero (zero coefficient) Coef and the level value representing the value of quantized components following this zero coefficient whose value is non-zero (non-zero coefficient) Lev, an image encoding device that encodes a plurality of quantized coefficients in a predetermined order can encode a plurality of quantized coefficients with high encoding efficiency and eliminate redundant information thereof.
图36为用于说明对应于如图34中所示的图像编码装置201b的图像解码装置202b的方框图。Fig. 36 is a block diagram for explaining an
该图像解码装置202b对从如图34中所示恶图像编码装置201b输出的编码流Str0进行解码。The
该图像解码装置202b用一个游程长度解码单元RLD0b取代如图32中所示的图像解码装置202a的解码单元RLD0a,用于使得从图像编码装置201b输出的受到游程长度解码处理。其他部分与图像解码装置202a相同。The
该图像解码装置202b的操作不同于图像解码装置202a之处仅仅在于解码单元RLD0b的操作。The operation of this
图37为示出在图像解码装置202b中的游程长度解码单元RLD0b具体结构的方框图。Fig. 37 is a block diagram showing a specific structure of the run-length decoding unit RLD0b in the
该游程长度解码单元RLD0b具有一个多路分解器DMUX,用于对从图像编码装置201b输出的复用的编码流Strob进行多路分解,以获得对应于该级别数值的代码串LStr以及对应于游程数值的代码串LStr;可变长度解码器LVLD,用于使得该代码串LStr受到可变长度解码处理,以重构该级别数值Lev;可变长度编码器RVLC,用于使得代码串RStr受到可变长度解码处理,以重构该游程数值Run;以及反曲折扫描仪IScan,用于从由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run表示的一维阵列中的解码量化分量重构在二维阵列中的解码的量化分量DQS。The run-length decoding unit RLD0b has a demultiplexer DMUX for demultiplexing the multiplexed coded stream Strob output from the image coding device 201b to obtain a code string LStr corresponding to the level value and a code string corresponding to the run length Numerical code string LStr; variable length decoder LStr, used to make the code string LStr subject to variable length decoding processing, to reconstruct the level value Lev; variable length coder RVLC, used to make the code string RStr subject to possible a variable length decoding process to reconstruct the run value Run; and an inverse scanner IScan for reconstructing the decoded in a two dimensional array from the decoded quantized components in the one dimensional array represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run The quantization component DQS.
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
在图像解码装置202b中,该游程长度解码单元RLD0b执行对游程长度编码单元RLE0b的反操作。即,该游程长度解码单元RLD0b分解该复用的编码流Str0b,以获得对应于该级别数值的代码串LStr和对应于游程数值的代码串RStr。In the
然后,该可变长度解码器LVLD通过与可变长度编码器LevVLC相反的操作解码对应于该级别数值的代码串LStr,并且输出该级别数值Lev。该可变长度解码器RVLD通过与可变长度编码器RVLC相反的操作解码对应于该游程数值的代码串RStr,并且输出该游程数值Run。Then, the variable length decoder LVLD decodes the code string LStr corresponding to the level value by the reverse operation of the variable length coder LevVLC, and outputs the level value Lev. The variable length decoder RVLD decodes the code string RStr corresponding to the run value by the reverse operation of the variable length coder RVLC, and outputs the run value Run.
该反曲折扫描仪IScan通过与曲折扫描仪Scan相反的操作从由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的一维阵列中的量化分量重构在二维阵列中的解码的量化分量DQS,并且把该解码的量化分量输出到反量化单元IQ。但是,反曲折扫描仪IScan(参见图37)不同于如图33中所示的反曲折扫描仪IScan之处在于它被输入级别数值Lev和游程数值Run。因此,如图37中所示的反曲折扫描仪IScan具有把由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的系数转换为量化分量Coef的功能。The inverse scanner IScan reconstructs the decoded quantized components DQS in the two-dimensional array from the quantized components in the one-dimensional array represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run by the reverse operation of the meander scanner Scan, and puts The decoded quantized components are output to the inverse quantization unit IQ. However, the inverse scanner IScan (see FIG. 37 ) differs from the inverse scanner IScan shown in FIG. 33 in that it is input with a level value Lev and a run value Run. Therefore, the inverse scanner IScan as shown in FIG. 37 has a function of converting the coefficient represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run into quantized components Coef.
根据通过使用其数值为零(零系数)的量化分量Coef的数目以及表示在该零系数之后其数值非零的(非零系数)的量化分量Coef的数值的级别数值Lev按照预定次序执行对多个量化系数解码的解码处理的图像解码装置,能够满意地对通过根据以较高的编码效率除去冗余信息的游程长度编码方法编码而获得的被编码数据进行解码。The pairing is performed in a predetermined order according to the level value Lev representing the value of the quantized component Coef whose value is non-zero (non-zero coefficient) after the zero coefficient by using the number of quantized components Coef whose value is zero (zero coefficient). The image decoding apparatus for the decoding process of decoding quantized coefficients can satisfactorily decode encoded data obtained by encoding according to the run-length encoding method that removes redundant information with high encoding efficiency.
在下文中,将描述使用游程长度编码方法的常规图像编码装置的另一个例子。Hereinafter, another example of a conventional image encoding device using a run-length encoding method will be described.
图38为示出采用常规游程长度编码单元的图像编码装置的另一个例子的方框图。几乎所有与例如MPEG或H.261和H.263(ITU)这样的标准或者草案的H26L标准(TML8)相兼容的常规图像编码装置具有如图38中所示的结构。Fig. 38 is a block diagram showing another example of an image coding device employing a conventional run-length coding unit. Almost all conventional image encoding devices compatible with standards such as MPEG or H.261 and H.263 (ITU) or the draft H26L standard (TML8) have a structure as shown in FIG. 38 .
类似于如图34中所示的图像编码装置201b,该图像编码装置201c使用游程数值和级别数值执行量化系数恶编码,并且该图像编码装置201c不执行类似于图像编码装置201b的分别对于游程数值和级别数值的可变长度编码处理,而是对一对游程数值和级别数值(游程-级别对)执行可变长度编码处理。Similar to the image encoding device 201b shown in FIG. 34, the image encoding device 201c performs quantization coefficient coding using the run value and the level value, and the image encoding device 201c does not perform the respective run value similar to the image encoding device 201b Instead of variable-length encoding processing of sum and level values, variable-length encoding processing is performed on a pair of run values and level values (run-level pair).
更加具体来说,该图像编码装置201c类似于图像编码装置201b具有被输入一个图像信号Vin的分块单元Blk、用于使得来自该分块单元的输出BlkS受到频率变换恶频率变换单元、以及用于量化来自该变换单元的输出(频率分量)TransS的量化单元Q。该图像编码装置201c进一步包括一个游程长度编码单元RLE0c,用于使得来自该量化单元的输出(量化分量)QS受到一个游程长度编码处理,用于把包含一个游程数值和级别数值的一个游程-级别对变换为一个可变长度代码。More specifically, the image encoding device 201c has, similarly to the image encoding device 201b, a blocking unit Blk to which an image signal Vin is input, a frequency conversion unit for subjecting an output BlkS from the blocking unit to frequency conversion, and a frequency conversion unit with Quantization unit Q for quantizing the output (frequency components) TransS from this transform unit. The image encoding device 201c further includes a run-length encoding unit RLE0c for subjecting the output (quantization component) QS from the quantization unit to a run-length encoding process for converting a run-level value including a run-length value and a level value pair into a variable-length code.
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
该分块单元Blk把图像信号Vin分为对应于块单元的图像信号,以产生像素值分量(分块的图像信号)BlkS。该频率变换单元Trans根据DCT(离散余弦变换)或者小波变换把该像素值分量BlkS变换为频率分量TransS。该量化单元Q根据量化参数QP量化该频率分量TransS,以输出量化分量QS,以及输出该量化单元Q。该游程长度编码单元RLE0c使得该量化分量QS受到游程长度编码,并且输出一个编码流Str0c。The blocking unit Blk divides the image signal Vin into image signals corresponding to block units to generate pixel value components (blocked image signals) BlkS. The frequency transformation unit Trans transforms the pixel value component BlkS into a frequency component TransS according to DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) or wavelet transformation. The quantization unit Q quantizes the frequency component TransS according to a quantization parameter QP to output a quantized component QS, and outputs the quantization unit Q. The run-length encoding unit RLE0c subjects the quantized component QS to run-length encoding, and outputs an encoded stream Str0c.
在此,该块是在该图像(图像空间)中的预定尺寸的区域,它是在用于一个图像信号的编码处理中的一个单元,并且包括预定数目的像素。该游程长度编码是用于把包括表示数值为零(零系数)的连续量化分量的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的数值非零(非零系数)的量化分量的数值的级别数值的一对数值变换为一个可变长度代码的处理,换句话说,它是用于把一个可变长度代码(代码字)分配到一对游程数值和级别数值(游程-级别对)的处理。Here, the block is an area of a predetermined size in the image (image space), which is a unit in encoding processing for an image signal, and includes a predetermined number of pixels. The run-length encoding is for converting a run-length value including a run value representing the number of consecutive quantized components having a value of zero (zero coefficient) and a level value representing the value of a quantized component having a value of non-zero (non-zero coefficient) following the zero coefficient In other words, it is a process for assigning a variable-length code (code word) to a pair of run value and level value (run-level pair).
下面将具体描述游程长度编码单元RLE0c。The run-length encoding unit RLE0c will be specifically described below.
图39为示出一种常规的游程长度编码单元RLE0c的方框图。Fig. 39 is a block diagram showing a conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0c.
该游程长度编码单元RLE0c类似于如图35中所示的游程长度编码单元RLE0b具有一个曲折扫描仪Scan,用于把来自量化单元Q的二维阵列中的输出(量化分量)QS变换为在一维阵列(即,预定次序)中的量化分量Coef;游程计算器RunCal,用于计算其数值为零的数值(零系数)的量化分量Coef的连续数目,并且输出一个游程数值Run;以及级别计算器LevCal,用于计算在该零系数之后的非零的(非零系数)的量化分量Coef的数值,并且输出一个级别数值Lev。The run-length encoding unit RLE0c is similar to the run-length encoding unit RLE0b shown in FIG. Quantized components Coef in a dimensional array (i.e., in a predetermined order); a run calculator RunCal for calculating the consecutive number of quantized components Coef whose value is zero (zero coefficient), and outputting a run value Run; and a level calculation A device LevCal for calculating the value of the non-zero (non-zero coefficient) quantized component Coef following the zero coefficient, and outputs a level value Lev.
该游程长度编码单元RLE0c进一步包括一个游程级别编码器RunLevEnc,用于根据代码表或算术运算基于来自游程计算器RunCal和级别计算器LevCal的输出获得对应于一对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run的代码号Code;以及可变长度编码器VLC,用于把一个代码字分配到该代码号Code,以产生对应于该图像信号Vin的编码流Str0c。The run-length encoding unit RLE0c further includes a run-level encoder RunLevEnc for obtaining a code corresponding to a pair of a level value Lev and a run value Run based on outputs from the run calculator RunCal and the level calculator LevCal according to a code table or an arithmetic operation number Code; and a variable length coder VLC for assigning a code word to the code number Code to generate a coded stream Str0c corresponding to the image signal Vin.
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
在游程长度编码单元RLE0c中,类似于游程长度编码单元RLE0b,该曲折扫描仪Scan把从量化单元Q输出的二维阵列中的量化分量QS变换为一维阵列(预定次序)中的量化分量Coef,并且输出所获得的量化分量。In the run-length encoding unit RLE0c, similar to the run-length encoding unit RLE0b, the zigzag scanner Scan transforms the quantized components QS in the two-dimensional array output from the quantization unit Q into the quantized components Coef in the one-dimensional array (predetermined order) , and output the obtained quantized components.
图43为用于具体说明用于由曲折扫描仪Scan变换该量化分量QS的处理的示意图。FIG. 43 is a diagram for concretely explaining the process for transforming the quantized component QS by the meander scanner Scan.
从量化单元Q输出的量化分量QS具有如图43中所示的二维阵列,即,根据水平频率分量的大小和垂直频率分量的大小以矩阵形式在一个二维频率区域Fr上排列该量化分量QS的阵列。The quantized components QS output from the quantization unit Q have a two-dimensional array as shown in FIG. array of qs.
该曲折扫描仪Scan执行用于以曲折的方式在二维阵列中扫描该量化分量QS的处理,如图Y1至Y7中所示,以把该量化分量QS变换为一维阵列的量化分量Coef。也就是说,该扫描处理对于二维阵列的多个量化分量QS沿着该扫描路径设置一个预定次序。The zigzag scanner Scan performs processing for scanning the quantized component QS in a zigzag manner in a two-dimensional array, as shown in FIGS. Y1 to Y7, to transform the quantized component QS into a one-dimensional array of quantized components Coef. That is, the scanning process sets a predetermined order along the scanning path for the plurality of quantized components QS of the two-dimensional array.
该游程计算器RunCal根据从曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef计算连续的零系数的数目,并且输出表示所计算的数目的游程数值Run。该级别计算器LevCal根据从该曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef计算在连续零系数之后的一个非零系数的数值,并且输出表示所计算的数值的一个级别数值。在此,该游程计算器RunCal在要被处理的一个目标块中检测到最高频率分量(最后的非零系数)时输出一个指定数值EOB(块的结束),以表示在后续的更高频率分量都具有零数值。The run calculator RunCal calculates the number of consecutive zero coefficients from the quantized component Coef output from the meander scanner Scan, and outputs a run value Run representing the calculated number. The level calculator LevCal calculates the value of a non-zero coefficient following consecutive zero coefficients from the quantized component Coef output from the meander scanner Scan, and outputs a level value representing the calculated value. Here, the run calculator RunCal outputs a specified value EOB (end of block) when the highest frequency component (last non-zero coefficient) is detected in a target block to be processed, to indicate that the next higher frequency component Both have a value of zero.
另外,该游程级别编码器RunLevEnc根据一个代码表或者算术运算基于来自游程计算器RunCal和级别计算器LevCal的输出获得对应于一对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run的代码号Code。该可变长度编码器VLC编码由该转换器RunLevEnc所获得的代码号Code,即,把一个代码字(位串)分配到该代码号,以产生一个编码流Str0。In addition, the run level encoder RunLevEnc obtains a code number Code corresponding to a pair of level value Lev and run value Run based on a code table or arithmetic operation based on outputs from the run calculator RunCal and the level calculator LevCal. The variable length coder VLC encodes the code number Code obtained by the converter RunLevEnc, that is, assigns a code word (bit string) to the code number to generate a coded stream Str0.
图42示出由游程长度编码单元RLE0c所采用的一个代码表。图42中所示的代码表(第一代码表)T1示出与现在计划的草案H.26L标准相兼容的一个色差信号的直流分量的代码表。Fig. 42 shows a code table employed by the run-length encoding unit RLE0c. A code table (first code table) T1 shown in FIG. 42 shows a code table of a DC component of a color-difference signal compatible with the draft H.26L standard currently planned.
该代码表T包括:一个可规则生成部分,其包括对应于可以根据一种算术运算使用级别数值和游程数值(规则构造的VLC)计算的对应于级别数值和游程数值对的代码号;以及不规则部分,其包括不能够通过算术运算(表格查找VLC)而计算的对应于级别数值和游程数值对的代码号。另外,一个位串(未示出)被按照一一对应的关系分配给每个代码号Code,作为一个代码字。一个更短的代码字被分配给具有更小数值的一个代码号Code。The code table T includes: a rule-generating part, which includes code numbers corresponding to pairs of level values and run-length values that can be calculated using the level values and run-length values (rule-constructed VLC) according to an arithmetic operation; and A rule part that includes code numbers corresponding to pairs of level values and run values that cannot be calculated by arithmetic operations (table lookup VLC). In addition, a bit string (not shown) is assigned to each code number Code in a one-to-one relationship as a code word. A shorter code word is assigned to a code number Code with a smaller value.
下面将描述根据图像编码装置201c的常规解码装置。A conventional decoding device according to the image encoding device 201c will be described below.
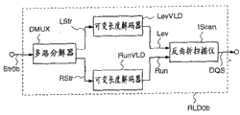
图40为示出采用常规的游程长度解码单元RLD0的一个图像解码装置202c的方框图。Fig. 40 is a block diagram showing an
该图像解码装置202c解码从如图39中所示的常规图像编码装置201c输出的编码流Str0c。This
该图像解码装置202c使用该游程数值和级别数值解码量化的系数,这与图36中所示的图像解码装置202b相同,并且该图像解码装置202c不相该图像解码装置202b那样分别执行该游程数值和级别数值的可变长度解码,而是执行包括该游程数值和级别数值(游程-级别对)的可变长度解码。The
更加具体来说,该图像解码装置202c具有一个游程长度解码单元RLD0c,其使用包括一个游程数值和级别数值的一个游程-级别对使得从图像编码装置201c输出的编码流Str0c受到游程长度解码处理。该图像解码装置202c与图像解码装置202b相同进一步具有一个反量化单元IQ,用于使得来自游程长度解码单元RLDc的输出(解码的量化分量)DQS受到反量化处理;反频率变换单元ITrans,用于使得来自反量化单元IQ的输出(解码的频率分量)ITransS受到反频率变换处理;以及解块单元DeBlk,用于根据来自反频率变换单元ITrans的输出(解码的图像信号)DBlkS产生对应于每个图像的解码的图像信号Vout。More specifically, the
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
在图像解码装置202c中,该游程长度解码单元RLD0c执行与游程长度编码单元RLE0c的操作的相反的操作。更加具体来说,该游程长度解码单元RLD0c使得编码流Str0c受到游程长度解码处理,以输出解码的量化分量DQS。该反量化单元IQ执行与量化单元Q相反的操作,即,参照量化参数QP对该解码的量化分量DQS进行反量化的操作,以输出解码的频率分量ITransS。该反频率变换单元ITrans执行与频率变换单元Trans相反的操作,即,使得解码的频率分量ITransS受到反DCT或者反小波变换,以重构对应于每个块的解码的像素值信号(解码的分块图像信号)DBlkS。该解块单元DeBlk结合用于各个块的图像像素值分量,并且输出对应于每个图像(帧)的解码的图像信号Vout。In the
下面将具体描述游程长度解码单元RLD0c。The run-length decoding unit RLDOc will be specifically described below.
图41为用于说明游程长度解码单元RLD0c的具体结构的方框图。Fig. 41 is a block diagram for explaining a specific structure of the run-length decoding unit RLDOc.
该游程长度解码单元RLD0c具有一个可变长度解码器VLD,用于使得该编码流Str0c受到可变长度解码处理,以获得对应于包含在编码流Str0c中的每个代码(代码字)的代码号Code;游程级别检测器RunLevDec,用于检测对应于该代码号Code的一对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run;以及反曲折扫描仪IScan,用于根据该对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run的从由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的一维阵列中的解码的量化分量重构在二维阵列中的解码的量化分量DQS。The run-length decoding unit RLDOc has a variable-length decoder VLD for subjecting the coded stream Str0c to variable-length decoding processing to obtain a code number corresponding to each code (codeword) contained in the coded stream Str0c Code; run level detector RunLevDec, used to detect a pair of level value Lev and run value Run corresponding to the code number Code; The decoded quantized components in the one-dimensional array represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run reconstruct the decoded quantized components DQS in the two-dimensional array.
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
在游程长度解码单元RLD0c中,该可变长度解码器VLD根据与可变长度编码器VLC相反的操作解码该编码流Str0c,并且输出对应于一个代码字(位串)的一个代码号Code。该游程级别检测器RunLevDec参照一个代码表或者执行算术运算,以根据与游程级别编码器RunLevEne相反的操作输出对应于代码号Code的一对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run。该反曲折扫描仪ISca根据与曲折扫描仪Scan相反的操作从由该对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的一维阵列中的量化分量在一个二维阵列中重构解码的量化分量DQS,并且把该解码的量化分量DQS输出到反量化单元IQ。In the run-length decoding unit RLD0c, the variable length decoder VLD decodes the coded stream Str0c according to the reverse operation of the variable length coder VLC, and outputs a code number Code corresponding to a code word (bit string). The run level detector RunLevDec refers to a code table or performs arithmetic operation to output a pair of level value Lev and run value Run corresponding to the code number Code according to the reverse operation of the run level encoder RunLevEne. The inverse scanner ISca reconstructs the decoded quantized components DQS in a two-dimensional array from the quantized components in the one-dimensional array represented by the pair of level values Lev and run values Run according to the reverse operation of the meander scanner Scan, And output the decoded quantization component DQS to the inverse quantization unit IQ.
日本专利申请No.6-237184公开一种游程长度编码方法,其中使用表示其数值为零的(零系数)的量化分量Coef的数目的游程数值Run和表示在该零系数之后其数值非零的(非零系数)的量化分量Coef的级别数值Lev按照预定次序编码多个系数。Japanese Patent Application No. 6-237184 discloses a run-length encoding method in which a run-length value Run representing the number of quantized components Coef whose value is zero (zero coefficient) and a value representing a non-zero value after the zero coefficient are used The level value Lev of the quantized component Coef (non-zero coefficient) encodes a plurality of coefficients in a predetermined order.
日本专利No.3144456(对应于日本专利申请No.8-79088)公开一种方法,其中当在用于预测地编码数字视频数据的方法中使用一个可变长度编码表对差分运动矢量值进行编码时根据该差分运动矢量值的数值改变可变长度编码表(VLC表)。Japanese Patent No. 3144456 (corresponding to Japanese Patent Application No. 8-79088) discloses a method in which differential motion vector values are encoded using a variable-length encoding table in a method for predictively encoding digital video data At this time, the variable length code table (VLC table) is changed according to the value of the differential motion vector value.
另外,已知这作为另一种方法的算术编码方法,通过该方法该像素值被可变长度编码,其中通过使用该像素值取预定数值的可能性根据一种算术运算执行可变长度编码。根据该算术编码,从该可能性导出一个代码,使得描述对应于各种情况的可能性的算术编码对应于该VLC表。在此,“所有关于MPEG-4”(由Miki Sukeichi所编著,由KogyoChosakai出版公司所出版,第一版,第一次印刷,第69-73页)描述一种方法,其通过根据用于从周围像素的像素值预测的一个编码目标像素的预测方法改变一个可能性表格而对对应于一个编码目标的像素的像素值进行算术编码。In addition, this is known as another method of an arithmetic coding method by which the pixel value is variable-length-coded in which variable-length coding is performed according to an arithmetic operation by using the possibility that the pixel value takes a predetermined value. According to the arithmetic code, a code is derived from the possibility so that the arithmetic code describing the possibility corresponding to each case corresponds to the VLC table. Herein, "All about MPEG-4" (edited by Miki Sukeichi, published by Kogyo Chosakai Publishing Co., first edition, first printing, pp. 69-73) describes a method by using the A prediction method of an encoding target pixel of pixel value prediction of surrounding pixels changes a possibility table to arithmetically encode the pixel value of a pixel corresponding to an encoding target.
上述常规的图像编码装置201a的编码单元RLE0a对通过对每个预定处理单元(块)量化图像数据的频率分量而获得的多个量化系数执行可变长度编码。该编码单元采用表示示出每个量化系数的大小的数值信息和代码(代码字)之间的对应关系的预定代码表。在由该编码单元执行可变长度编码处理中,包含在量化系数(要被处理的数据)中的冗余信息不能够被充分地除去,因此可以进一步提高压缩比。The encoding unit RLE0a of the above-described conventional
并且在该游程长度编码单元中,其使用表示其数值为零的(零系数)的量化分量Coef的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后其数值非零的(非零系数)的量化分量Coef的数值的级别数值执行多个量化系数的可变长度编码,类似于在常规图像编码装置201b或201c中的编码单元RLE0b或RLE0c,在该可变长度编码处理中包含在该量化系数中的冗余信息不被充分地除去。And in this run-length coding unit, it uses a run value representing the number of quantized components Coef whose value is zero (zero coefficient) and a quantized component representing the value of which is non-zero (non-zero coefficient) after the zero coefficient The rank value of the numerical value of Coef performs variable-length encoding of a plurality of quantized coefficients, similarly to the coding unit RLE0b or RLE0c in the conventional image encoding device 201b or 201c, in which the quantized coefficients included in the variable-length encoding process Redundant information is not sufficiently removed.
另外,常规的图像解码装置202a的解码单元RLD0a或常规的图像解码装置202b或202c的游程长度解码单元RLD0b或RLD0c对应于不能够在用于该量化系数的可变长度编码处理中充分地除去包含在该量化系数中的冗余信息的编码单元。In addition, the decoding unit RLD0a of the conventional
另外,对于在用于预测地编码数字视频数据的方法中当使用一个可变长度编码表对差分运动矢量值进行编码时根据该差分运动矢量值的数值改变可变长度编码表(VLC表)的方法,现在还没有在对类似于通过量化一个图像信号的频率分量而获得的量化系数这样具有随后接着的连续零系数的数目的特性的数据的可变长度编码处理中有效改变可变长度编码表的方法。Also, for changing the variable length coding table (VLC table) according to the numerical value of the differential motion vector value when a variable length coding table is used to code a differential motion vector value in the method for predictively coding digital video data method, there is no effective change of the variable length coding table in the variable length coding process for data having a characteristic of the number of successive zero coefficients like the quantized coefficients obtained by quantizing the frequency components of an image signal Methods.
本发明要解决上述问题,并且编码的目的是提供一种可变长度编码方法以及可变长度解码方法,其可以根据被量化的系数的特性和用于量化分量的编码处理的状态更加有效地消除包含在用于可变长度编码处理的目标数据(量化系数)中的冗余信息,从而进一步增加图像信号等等的压缩比。The present invention is to solve the above-mentioned problems, and an object of encoding is to provide a variable length encoding method and a variable length decoding method that can more effectively eliminate Redundant information contained in target data (quantization coefficients) for variable-length encoding processing, thereby further increasing the compression ratio of image signals and the like.
发明内容Contents of the invention
根据本发明,在此提供一种用于编码由多个系数所构成的系数数据的可变长度编码方法,其中包括:编码步骤,用于通过使用表示该系数的数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表,使得各个系数受到把系数数据变换为由多个代码所构成的被编码数据的编码处理,并且该编码步骤包括:代码表选择步骤,用于根据关于已经被编码的被编码系数和与该系数的编码处理相关的参数至少之一的信息选择该代码表;以及代码分配步骤,用于使用被选择的代码表把一个代码分配到一个还没有被编码的未编码的系数。因此,通过根据构成该系数数据的系数的特性或者对该系数的编码处理的状态选择代码表而有效地除去包含在作为要受到可变长度编码处理的对象的系数数据中的冗余信息,从而大大地增加用于图像信号等等的可变长度编码处理的编码效率。According to the present invention, there is provided a variable-length encoding method for encoding coefficient data constituted by a plurality of coefficients, which includes an encoding step of a plurality of code tables, so that each coefficient is subjected to an encoding process of transforming the coefficient data into encoded data constituted by a plurality of codes, and the encoding step includes: a code table selection step, for information of at least one of coefficients and parameters related to encoding processing of the coefficients to select the code table; and a code assignment step for assigning a code to an unencoded coefficient that has not been encoded using the selected code table. Therefore, redundant information contained in coefficient data that is an object to be subjected to variable-length coding processing is effectively removed by selecting a code table in accordance with the characteristics of the coefficients constituting the coefficient data or the state of coding processing for the coefficients, thereby The coding efficiency of variable-length coding processing for image signals and the like is greatly increased.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,通过根据对应于该图像数据的量化步骤量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且在该代码表选择步骤中,要用于该代码分配步骤中的代码表被根据该量化步骤的数值而选择。因此总是可以采用适用于该量化步骤的数值的代码表并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, the coefficients are obtained by quantizing the frequency components of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and in the code table selection step, to be used in the code assignment step The code table in is chosen according to the value of the quantization step. It is therefore always possible to use a code table which is suitable for the values of the quantization step and which maximizes the coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值被分别变换为一个代码,在该代码表选择步骤中,在用于根据该量化步骤的数值从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表的第一选择处理,以及用于根据该量化步骤的数值从表示该级别数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表的第二选择处理中的至少一个处理被执行,并且在该代码分配步骤中,根据被选择的代码表,一个代码被分配给对应于还没有被编码的一个未编码系数的游程数值和级别数值中的至少一个数值。因此,通过使用适合于该量化步骤的数值的代码表总是可以执行对游程数值和级别数值中的至少一个数值的代码分配,并且使得对应于所分配代码的总位数被最小化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, according to the encoding process for the coefficient, the run value indicating the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and the level indicating the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient Values are converted into a code respectively, and in the code table selection step, in the first selection for selecting a code table from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run values and codes based on the value in the quantization step processing, and at least one of a second selection process for selecting a code table from a plurality of code tables representing correspondences between the level values and codes according to the numerical value of the quantization step is performed, and at the code allocation In the step, a code is assigned to at least one of a run value and a level value corresponding to an uncoded coefficient which has not been coded according to the selected code table. Therefore, code allocation to at least one of the run value and the level value can always be performed by using a code table suitable for the value of the quantization step, with the total number of bits corresponding to the allocated code being minimized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,包括表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值以及表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值的游程-级别对被变换为一个代码,在该代码表选择步骤中,根据该量化步骤的数值,从表示该游程-级别对和该代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表中选择一个代码表,并且在该代码分配步骤中,根据所选择的代码表,一个代码被分配给对应于还没有被编码的未编码系数的一个游程-级别对。因此,通过使用一个适合于该量化步骤的数值的代码表总是可以执行对游程-级别对的代码分配,并且使得对应于所分配的代码的总位数最小化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, according to the encoding process of the coefficient, a run value indicating the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and a value indicating the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient are included. The run-level pair of level values is transformed into a code, and in the code table selection step, according to the value of the quantization step, selected from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run-level pair and the code a code table, and in the code assignment step, a code is assigned to a run-level pair corresponding to an uncoded coefficient that has not been coded according to the selected code table. Therefore, code allocation to run-level pairs can always be performed by using a code table suitable for the value of the quantization step, and the total number of bits corresponding to the allocated codes is minimized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,在该代码表选择步骤中,根据关于被编码系数的信息选择在该代码分配步骤中所用的代码表。因此,通过使用适合于未编码系数的数目的代码表总是可以执行用于量化系数的编码处理,并且使得该编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above variable length coding method, in the code table selection step, the code table used in the code assignment step is selected based on information on the coefficients to be coded. Therefore, encoding processing for quantized coefficients can always be performed by using a code table suitable for the number of unencoded coefficients, and the encoding efficiency is maximized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值以及表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值被分别变换为一个代码,在该代码表选择步骤中,在用于根据关于对应于该编码的游程数值的信息从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表的第一选择处理,以及用于根据关于对应于该被编码系数的级别数值的信息从表示该级别数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表的第二选择处理中的至少一个处理被执行,并且在该代码分配步骤中,根据所选择的代码表,一个代码被分配给对应于一个未编码系数的游程数值和级别数值中的至少一个数值。因此,通过使用适合于未编码系数的数目的代码表总是可以执行对游程数值和级别数值中的至少一个数值的代码分配,并且使得该编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, according to the encoding process for the coefficient, the run value indicating the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and the level indicating the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient Numerical values are respectively converted into a code, and in the code table selection step, a code is selected from a plurality of code tables indicating correspondence between the run numerical value and the code based on information on the run numerical value corresponding to the code. In the first selection process of a table, and in the second selection process for selecting a code table from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the class value and the code based on the information on the class value corresponding to the coded coefficient At least one process of is performed, and in the code assigning step, a code is assigned to at least one of a run value and a level value corresponding to an uncoded coefficient according to the selected code table. Therefore, code assignment to at least one of the run value and the level value can always be performed by using a code table suitable for the number of uncoded coefficients, and the coding efficiency is maximized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,在该代码表选择步骤中,根据已经被编码的被编码游程数值的数目从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表中选择一个代码表,并且在该代码分配步骤中,根据所选择的代码表,一个代码被分配给还没有被编码的一个未编码游程数值。因此,通过使用适合于还未处理的游程数值的数目的代码表总是可以执行对游程数值的代码分配,并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable-length encoding method, in the code table selection step, the number of coded run-length values that have been coded is selected from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run-length values and the codes. A code table is selected, and in the code assignment step, a code is assigned to an uncoded run value that has not been coded according to the selected code table. Therefore, code assignment to run values can always be performed by using a code table suitable for the number of run values that have not yet been processed, and the coding efficiency is maximized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,包括表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值的一个游程-级别对被变换为一个代码,在该代码表选择步骤中,根据关于对应于已经编码的被编码系数的游程-级别对的信息从表示该游程-级别对和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表,并且在该代码分配步骤中,根据被选择代码表,一个代码被分配给对应于还没有被编码的未编码系数的一个游程-级别对。因此,通过使用适合于还未处理的系数的数目的代码表,总是可以执行对该游程-级别对的分配,并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, according to the encoding process of the coefficient, a run value indicating the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and a value indicating the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient are included. A run-level pair of level values is converted into a code, and in the code table selection step, the distance between the run-level pair and the code is expressed from the information about the run-level pair corresponding to the coded coefficient that has already been encoded A code table is selected from a plurality of code tables corresponding to each other, and in the code assignment step, a code is assigned to a run-level pair corresponding to an uncoded coefficient that has not been coded according to the selected code table. Therefore, by using a code table suitable for the number of coefficients that have not been processed, the assignment of the run-level pair can always be performed, and the coding efficiency is maximized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,通过根据对应于该图像数据的量化步骤量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且在该编码步骤中,执行对该系数的编码处理,使得代码被分配给从高频分量到低频分量构成该系数数据的多个系数。因此,对应于被分配给该系数的代码的总位数可以被进一步减小。According to the present invention, in the above variable length encoding method, the coefficient is obtained by quantizing the frequency components of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and in the encoding step, an encoding process for the coefficient is performed such that Codes are assigned to a plurality of coefficients constituting the coefficient data from high-frequency components to low-frequency components. Therefore, the total number of bits corresponding to codes assigned to the coefficients can be further reduced.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,包括表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值的一个游程-级别对被转换为一个代码,用于由预定数目的系数所构成的每个块,并且在该代码表选择步骤中,根据在作为该编码处理的对象的目标块中已经受到编码处理的已处理系数的数目和在该目标块中还未被编码的未编码非零系数的数目之和,从表示该游程-级别对和该代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表中选择一个代码表,并且在该代码分配步骤,根据所选择的代码表,一个代码被分配到对应于在该目标块中的一个未编码系数的游程-级别对。因此,可以采用不包括不会出现的游程数值和级别数值的代码表,从而增加可变长度编码效率。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, according to the encoding process of the coefficient, a run value indicating the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and a value indicating the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient are included. A run-level pair of level values is converted into a code for each block constituted by a predetermined number of coefficients, and in the code table selection step, based on the The sum of the number of processed coefficients subjected to encoding processing and the number of unencoded non-zero coefficients not yet encoded in the target block, from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run-level pairs and the codes A code table is selected in , and in the code assignment step, a code is assigned to a run-level pair corresponding to an uncoded coefficient in the target block according to the selected code table. Therefore, it is possible to use a code table that does not include run values and level values that do not appear, thereby increasing variable-length coding efficiency.
根据本发明的,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,包括表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的级别数值的游程-级别对被转换为一个代码,该编码步骤包括一个代码表处理步骤,用于基于该第一代码表,根据构成该游程-级别对的游程数值和级别数值的组合,定期地改变在表示该游程-级别对和相应代码之间的对应关系的第一代码表中的该游程-级别对和该代码之间的对应关系,从而形成与第一代码表不同的具有在该游程-级别对和该代码之间的不同对应关系的第二代码表,并且在该代码表选择步骤中,根据关于已经处理的系数和与该系数的产生相关的参数至少之一的信息选择该第一和第二代码表之一。因此,当代码被分配到游程数值和级别数值对时,该第一和第二代码表之一被适应地选择作为要被使用的一个最佳代码表,从而可以有效地形成包含在要被处理的目标数据中的冗余信息。相应地,用于图像信号等等的压缩比可以被进一步提高,从而该可变长度编码方法是非常有用的。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, according to the encoding process of the coefficient, a run value indicating the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and indicating the level of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient are included The run-level pair of values is converted into a code, the encoding step comprising a code table processing step for periodically changing Correspondence between the run-level pair and the code in the first code table representing the correspondence between the run-level pair and the corresponding code, thereby forming a code table different from the first code table with the run-level A second code table of different correspondences between level pairs and the codes, and in the code table selection step, the first code table is selected based on information about at least one of the coefficients already processed and parameters related to the generation of the coefficients and one of the second code tables. Therefore, when the code is assigned to the pair of the run value and the level value, one of the first and second code tables is adaptively selected as an optimal code table to be used, thereby effectively forming the Redundant information in the target data of . Accordingly, the compression ratio for image signals and the like can be further improved, so that the variable length coding method is very useful.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,在第一和第二代码表中,较短的代码被相应地适用于具有构成该游程-级别对中的较小级别数值的各个游程-级别对,并且在第二代码表中,与第一代码表相比,与较短代码对应的游程-级别对的级别数值的平均值较小。因此,当用于构成要被处理的目标数据的系数的量化参数较大时,该可变长度编码方法是有用的。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, in the first and second code tables, shorter codes are correspondingly applied to each run-level with the smaller level value constituting the run-level pair Yes, and in the second code table, the average value of the level values for run-level pairs corresponding to shorter codes is smaller than in the first code table. Therefore, this variable length encoding method is useful when the quantization parameters for the coefficients constituting the target data to be processed are large.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,在该第一和第二代码表中,较短代码适应地对应于具有构成该游程-级别对的较小游程数值的各个游程-级别对,并且在第二代码表中,与第一代码表相比对应于较短代码的游程-级别对的游程数值的平均值较小。因此,当构成该目标数据的用于该系数的量化参数较小时,该可变长度编码方法是有用的。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable-length encoding method, in the first and second code tables, shorter codes are adaptively corresponding to each run-level pair having a smaller run value constituting the run-level pair, And in the second code table, the average value of the run values of the run-level pairs corresponding to shorter codes is smaller than that of the first code table. Therefore, the variable length coding method is useful when the quantization parameter for the coefficient constituting the target data is small.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,对于由预定数目的系数所构成的每个块执行游程-级别对到代码的变换,并且在该代码表处理步骤中,根据在作为编码处理的对象的目标块中已经受到编码处理的已处理系数的数目而形成第二代码表。因此,可以采用不包括不会出现的由游程数值和级别数值所构成的对的代码表作为第二代码表,从而进一步增加该可变长度编码效率。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding method, according to the encoding processing of the coefficients, conversion of run-level pairs to codes is performed for each block constituted by a predetermined number of coefficients, and in the code table processing step , the second code table is formed based on the number of processed coefficients that have been subjected to encoding processing in the target block that is the target of encoding processing. Therefore, a code table that does not include pairs of run values and level values that do not appear can be used as the second code table, thereby further increasing the variable-length coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,在该代码分配步骤中,从高频分量到低频分量,从对应于具有图像数据的最高频率分量的系数的游程-级别对执行对游程-级别对的代码分配。因此,通过使用不包括不会出现的游程数值和级别数值的对的代码表所获得的可变长度编码效率的增加量可以变得更大。According to the present invention, in the above variable length encoding method, in the code assignment step, from the high frequency component to the low frequency component, the run-level pair is performed from the run-level pair corresponding to the coefficient having the highest frequency component of the image data correct code assignment. Therefore, the increase in variable-length encoding efficiency obtained by using a code table that does not include pairs of run values and level values that do not occur can become even greater.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,通过在包含于第一代码表中的游程-级别对和代码之间的对应关系中仅仅改变可以定期操作的对应关系而形成该第二代码表。因此,可以减小形成该第二代码表所需的算术运算。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable-length encoding method, the second code table is formed by changing only the correspondence between the run-level pairs and the codes contained in the first code table, which can be periodically operated. . Therefore, arithmetic operations required to form the second code table can be reduced.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法,根据对应于该图像数据的量化步骤,通过量化图像数据的频率分量而获得构成该系数数据的系数,并且该代码表选择步骤是用于根据该量化步骤的数值在第一代码表和第二代码表之间切换的代码表切换步骤。因此,适用于该量化步骤的一个代码表可以被用作为要用于构成要被处理的目标数据的系数的可变长度编码处理中的代码表。According to the present invention, in the above variable length encoding method, the coefficients constituting the coefficient data are obtained by quantizing the frequency components of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and the code table selection step is for A code table switching step in which the value of the step is switched between the first code table and the second code table. Therefore, a code table suitable for the quantization step can be used as a code table to be used in variable-length coding processing of coefficients constituting target data to be processed.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法,该代码表选择步骤是用于根据一个切换指令信号在第一代码表和第二代码表之间切换的一个代码表切换步骤,并且在该编码步骤中,执行该切换指令信号的编码。因此,要用于对该系数的可变长度编码处理中的代码表可以根据该目标数据等等的特征而改变。According to the present invention, in the above variable length coding method, the code table selection step is a code table switching step for switching between the first code table and the second code table according to a switching command signal, and in the encoding step , the encoding of the switching instruction signal is performed. Therefore, the code table to be used in the variable-length coding process for the coefficient can be changed according to the characteristics of the target data and the like.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,根据对该系数的编码处理,对由预定数目的系数所构成的每个块执行游程-级别对到代码的变换,并且在该代码表处理步骤中,根据在作为编码处理的对象的一个目标块中已经受到编码处理的已处理系数的数目和在该目标块中还未编码的未编码非零系数的数目之和形成第二代码表。因此,不包括不会出现的游程数值和级别数值对的代码表可以被用作为第二代码表,从而进一步增加可变长度编码效率。According to the present invention, in the above variable length coding method, according to the coding processing of the coefficients, conversion of run-level pairs to codes is performed for each block constituted by a predetermined number of coefficients, and in the code table processing step , the second code table is formed from the sum of the number of processed coefficients that have been subjected to encoding processing in a target block that is an object of encoding processing and the number of unencoded non-zero coefficients that have not yet been encoded in the target block. Therefore, a code table that does not include pairs of run values and level values that do not occur can be used as the second code table, thereby further increasing variable-length coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在此提供一种用于编码由多个系数所构成的系数数据的可变长度编码装置,其中包括:编码单元,用于通过使用表示该系数的数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表,使得各个系数受到把系数数据变换为由多个代码所构成的被编码数据的编码处理,并且该编码单元包括:代码表选择单元,用于根据关于已经被编码的被编码系数和与该系数的编码处理相关的参数至少之一的信息选择该代码表;以及代码分配单元,用于使用被选择的代码表把一个代码分配到一个还没有被编码的未编码的系数。因此,通过根据构成该系数数据的系数的特性或者对该系数的编码处理的状态选择一个代码表而有效地删除包含在作为要受到可变长度编码处理的对象的系数数据中的冗余信息,从而大大地增加用于图像信号等等的可变长度编码处理的编码效率。According to the present invention, there is provided a variable-length coding apparatus for coding coefficient data composed of a plurality of coefficients, including: a coding unit for a plurality of code tables, so that each coefficient is subjected to an encoding process of transforming the coefficient data into encoded data constituted by a plurality of codes, and the encoding unit includes: a code table selection unit configured to information of at least one of coefficients and parameters related to encoding processing of the coefficients selects the code table; and a code assigning unit for assigning a code to an unencoded coefficient that has not been encoded using the selected code table. Therefore, redundant information contained in coefficient data which is an object to be subjected to variable-length encoding processing is effectively deleted by selecting a code table according to the characteristics of the coefficients constituting the coefficient data or the state of encoding processing of the coefficients, The coding efficiency of variable-length coding processing for image signals and the like is thereby greatly increased.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码方法中,通过根据对应于该图像数据的量化步骤量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且该代码表选择单元根据该量化步骤的数值选择要由该代码分配单元所用的代码表。因此,总是可以采用适用于该量化步骤的数值的代码表并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above variable length encoding method, the coefficient is obtained by quantizing the frequency components of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and the code table selection unit selects the The code table used by the code allocation unit. Therefore, it is always possible to adopt a code table suitable for the value of the quantization step and to maximize the coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码装置中,该代码表选择单元根据关于该被编码系数的信息,选择要由该代码分配单元所用的代码表。因此,总是可以通过采用适用于还未处理的系数的数目执行用于量化系数的编码处理,并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above variable length coding apparatus, the code table selection unit selects the code table to be used by the code allocation unit based on the information on the coded coefficient. Therefore, it is always possible to perform encoding processing for quantized coefficients by employing a number suitable for coefficients not yet processed, and to maximize encoding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码装置中,根据对该系数的编码处理,表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值被分别变换为一个代码,该代码表选择单元根据已经被分配代码的多个被编码游程数值,从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表中选择一个代码表,并且该代码分配单元根据被选择的代码表把一个代码分配给还未编码的一个未编码游程数值。因此,通过使用适用于还未处理的游程数值的数目的代码表,总是可以执行对游程数值的代码分配,并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable-length encoding apparatus, according to the encoding process of the coefficient, the run value indicating the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and the level indicating the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient the values are respectively converted into a code, the code table selection unit selects a code table from a plurality of code tables representing correspondence between the run value and the code based on a plurality of coded run values to which codes have been assigned, and The code assigning unit assigns a code to an uncoded run value that has not been coded based on the selected code table. Therefore, by using a code table suitable for the number of run values that have not yet been processed, code allocation to run values can always be performed and the coding efficiency is maximized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码装置中,根据对应于该图像数据的量化步骤,通过量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且该编码单元对编码单元该系数执行编码处理,使得代码被分配到从高频分量到低频分量构成该系数数据的多个系数。因此,对应于被分配到该系数的代码的总数可以被进一步减小。According to the present invention, in the above variable length coding apparatus, the coefficient is obtained by quantizing the frequency component of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and the coding unit performs coding processing on the coefficient of the coding unit so that the code Assigned to a plurality of coefficients constituting the coefficient data from high-frequency components to low-frequency components. Therefore, the total number of codes corresponding to the coefficients allocated to the coefficient can be further reduced.
根据本发明,在此提供一种存储介质,其中包括用于由计算机执行对由多个系数所构成的系数数据的编码的可变长度编码处理的程序,并且该程序包括:编码步骤,用于通过使用表示该系数的数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表,使得各个系数受到把系数数据变换为由多个代码所构成的被编码数据的编码处理,并且该编码步骤包括:代码表选择步骤,用于根据关于已经被编码的被编码系数和与该系数的编码处理相关的参数至少之一的信息选择该代码表;以及代码分配单元,用于使用被选择的代码表把一个代码分配到一个还没有被编码的未编码系数。因此,可以通过软件实现具有更高编码效率的可变长度编码处理,其通过根据构成该系数数据的系数的特性或者对该系数的编码处理的状态选择一个代码表而有效地删除包含在作为要受到可变长度编码处理的对象的系数数据中的冗余信息。According to the present invention, there is provided a storage medium including a program for executing, by a computer, a variable-length encoding process of encoding coefficient data composed of a plurality of coefficients, and the program includes: an encoding step for By using a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the numerical values of the coefficients and the codes, each coefficient is subjected to an encoding process of converting the coefficient data into encoded data composed of a plurality of codes, and the encoding step includes: a table selection step for selecting the code table based on information on at least one of the coded coefficients that have been coded and parameters related to the encoding process of the coefficients; and a code allocation unit for assigning a code table using the selected code table The code is assigned to an uncoded coefficient that has not yet been coded. Therefore, it is possible to realize variable-length coding processing with higher coding efficiency by software, which efficiently deletes a code table contained in a code table that is included as a desired code by selecting a code table according to the characteristics of the coefficients constituting the coefficient data or the state of the coding processing for the coefficients. Redundant information in coefficient data to be subjected to variable-length coding processing.
根据本发明,在此提供一种用于解码包括多个代码的被编码数据的可变长度解码方法,其中包括:解码步骤,用于使用表示该系数的数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表,使得各个代码受到对该被编码数据的解码处理,以重构由多个系数所构成的系数数据,并且该解码步骤包括:代码表选择步骤,用于根据关于已经被解码的被解码系数和与该系数的解码处理相关的参数至少之一的信息选择该代码表;以及数值检测步骤,用于通过使用所选择的代码表检测对应于还未解码的未解码代码的数值。因此,可以执行对应于具有更高的编码效率的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该编码处理通过改变代码表而有效地删除包含在系数数据中的冗余信息,以编码该系数数据。According to the present invention, there is provided a variable length decoding method for decoding coded data including a plurality of codes, which includes: a code table so that each code is subjected to decoding processing of the coded data to reconstruct coefficient data composed of a plurality of coefficients, and the decoding step includes: a code table selection step for according to information about the already decoded information of at least one of decoding coefficients and parameters related to decoding processing of the coefficients selects the code table; and a numerical value detection step of detecting a numerical value corresponding to an undecoded code that has not yet been decoded by using the selected code table. Therefore, it is possible to perform variable length decoding processing corresponding to variable length coding processing having higher coding efficiency, which efficiently deletes redundant information contained in coefficient data by changing the code table to code the coefficient data.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码处理中,通过根据对应于图像数据的量化步骤量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且在该代码表选择步骤中,根据该量化步骤的数值选择用于该数值检测步骤中的代码表。因此,可以执行对应于一种可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该编码处理通过总是采用适用于该量化步骤的代码表并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding process, the coefficient is obtained by quantizing the frequency component of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and in the code table selection step, the coefficient is selected according to the numerical value of the quantization step. The code table in the value detection step. Therefore, it is possible to perform variable-length decoding processing corresponding to a variable-length coding processing by always employing a code table suitable for the quantization step and maximizing coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码处理中,在用于该代码的解码处理中,一个代码被解码,以重构表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值以及表示在该零系数之后的一个非零系数的数值的级别数值,在该代码表选择步骤中,用于至少根据该量化步骤的数值从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表的第一选择处理,以及用于根据量化步骤的数值执行从表示该级别数值和该代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表的第二选择步骤的这两个步骤之一被执行,并且在该数值检测步骤中,根据所选择的代码表,对应于还未解码的未解码数据的游程数值和级别数值中的至少一个数值被检测。因此,通过总是使用适合于该量化步骤的数值并且使得对应于所分配代码的总位数最小化,可以执行对应于执行代码到至少一个游程数值和级别数值的分配的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable-length decoding process, in the decoding process for the code, a code is decoded to reconstruct a run-length value representing the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and a level value of the value of a non-zero coefficient following the coefficient, in the code table selection step, for selecting a code from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run value and the code at least based on the value of the quantization step One of the two steps of the first selection process of the table, and the second selection step of selecting a code table from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence relationship between the numerical value of the level and the code, based on the numerical value of the quantization step is performed, and in the value detecting step, according to the selected code table, at least one of a run value and a level value corresponding to undecoded data which has not yet been decoded is detected. Therefore, by always using values suitable for the quantization step and minimizing the total number of bits corresponding to the assigned codes, it is possible to perform variable length coding processing corresponding to assignment of execution codes to at least one run value and level value. Variable length decoding processing.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码处理中,根据用于代码的解码处理,一个代码被解码,以重构由表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的一个非零系数的数值的级别数值所构成的一个游程-级别对,在该代码表选择步骤,根据该量化步骤的数值,从表示该游程-级别对和该代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表,并且在该数值检测步骤中,根据被选择代码表,检测对应于一个还未解码的未解码代码的游程-级别对。因此,可以执行对应于一个可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该编码处理通过总是使用适合于该量化步骤的数值的代码表执行代码到游程-级别对的分配,并且使得对应于该被分配代码总位数最小化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding process, according to the decoding process for codes, a code is decoded to reconstruct the run value represented by the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and the value represented by the zero coefficient A run-level pair formed by the level value of the numerical value of a non-zero coefficient afterwards, in the code table selection step, according to the numerical value of the quantization step, from representing the corresponding relationship between the run-level pair and the code A code table is selected from a plurality of code tables, and in the value detecting step, a run-level pair corresponding to an undecoded code that has not yet been decoded is detected based on the selected code table. Therefore, it is possible to perform variable-length decoding processing corresponding to a variable-length encoding processing that performs assignment of codes to run-level pairs by always using a code table suitable for the value of the quantization step, and makes the corresponding The total number of assigned code bits is minimized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,在该代码表选择步骤中,根据关于被解码系数的信息选择在该数值检测步骤中使用的代码表。因此,可以执行对应于可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该编码处理通过总是使用适合于还未处理的系数数目的代码表而编码量化系数并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above variable length decoding method, in the code table selection step, the code table used in the value detection step is selected based on information on the coefficient to be decoded. Therefore, variable-length decoding processing corresponding to variable-length encoding processing that encodes quantized coefficients by always using a code table suitable for the number of coefficients that have not been processed and maximizes encoding efficiency can be performed.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,根据用于该代码的解码处理,该代码被解码以分别重构表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值,以及表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值,在该代码表选择步骤中,用于根据关于被解码的游程数值的信息从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表中选择一个代码表的第一选择处理,以及用于根据关于被解码的级别数值的信息从表示该级别数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表中选择一个代码表的第二选择处理中的至少一个处理被执行,并且在该数值检测步骤中,根据被选择的代码表检测对应于一个未解码代码的游程数值和级别数值中的至少一个数值。因此,可以执行对应于可变长度编码处理的一种可变长度解码处理,该可变长度编码处理总是通过使用适用于还未处理的系数的数目的代码表而执行代码到至少一个游程数值和级别数值的分配,并且使得该编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding method, according to the decoding process for the code, the code is decoded to respectively reconstruct the run value representing the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero, and the run value representing the A level value of the value of the non-zero coefficient following the coefficient, in the code table selection step, for selecting from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run value and the code based on the information about the decoded run value In the first selection process of a code table, and in the second selection process for selecting a code table from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the class value and the code based on the information on the decoded class value At least one process is performed, and in the value detecting step, at least one of a run value and a level value corresponding to an undecoded code is detected based on the selected code table. Therefore, it is possible to perform a variable-length decoding process corresponding to a variable-length encoding process that always performs encoding to at least one run value by using a code table suitable for the number of coefficients that have not yet been processed. and the allocation of level values, and maximize the coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,在该代码表选择步骤中,根据已经解码的已解码游程数值的数目,从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表,并且在该数值检测步骤中,根据被选择代码表检测对应于还未解码的未解码代码的一个游程数值。因此,可以执行对应于可变长度编码处理的一种可变长度解码处理,该可变长度编码处理总是通过使用适用于还未处理的系数的数目的代码表而执行代码到游程数值的分配,并且使得该编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable-length decoding method, in the code table selection step, a code table is selected from a plurality of code tables indicating the correspondence between the run values and the codes according to the number of decoded run-length values that have already been decoded. a code table, and in the value detection step, a run value corresponding to an undecoded code that has not yet been decoded is detected based on the selected code table. Therefore, it is possible to perform a variable-length decoding process corresponding to a variable-length encoding process that always performs assignment of codes to run values by using a code table suitable for the number of coefficients not yet processed , and maximize the coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,根据对代码的解码处理,一个代码被解码,以重构包括表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的多个非零系数的级别数值的游程-级别对,在该代码表选择步骤中,根据关于已经通过解码处理所获得的一个游程-级别对的信息从表示该游程-级别对和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表,并且在该数值检测步骤中,根据被选择代码表检测对应于还未解码的未解码代码的一个游程-级别对。因此,可以执行对应于可变长度编码处理的一种可变长度解码处理,该可变长度编码处理总是通过使用适用于还未处理的系数的数目的代码表而执行代码到游程-级别对的分配,并且使得该编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding method, according to the decoding process on the code, a code is decoded to reconstruct the run value including the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and the value representing A run-level pair of the level values of a plurality of non-zero coefficients, in the code table selection step, according to the information about a run-level pair that has been obtained through the decoding process from representing between the run-level pair and the code A code table is selected from a plurality of code tables corresponding to each other, and in the value detection step, a run-level pair corresponding to an undecoded code that has not yet been decoded is detected based on the selected code table. Therefore, it is possible to perform a variable-length decoding process corresponding to a variable-length encoding process that always executes code-to-run-level pairs by using a code table suitable for the number of coefficients that have not yet been processed. and maximize the coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,通过根据对应于图像数据的量化步骤量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且在解码步骤中,执行对代码的解码处理,从而从高频率分量到低频率分量获得对应于该代码的数值。因此,可以执行对应于可变长度编码处理的一种可变长度解码处理,该可变长度编码处理进一步减少对应于分配给该系数的代码的总位数。According to the present invention, in the variable length decoding method described above, the coefficients are obtained by quantizing the frequency components of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and in the decoding step, a decoding process for the code is performed, whereby the high frequency components to low frequency components get values corresponding to the code. Therefore, it is possible to perform a variable-length decoding process corresponding to a variable-length encoding process that further reduces the total number of bits corresponding to codes assigned to the coefficient.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,根据对代码的解码处理,对于由包括系数数据的预定系数的每个块,一个代码被解码以重构包括表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的一个游程-级别对,在该代码表选择步骤,根据在作为解码处理的一个对象的目标块中已经通过对该目标块的解码处理而获得的已处理系数的数目与还没有通过对该目标块的解码处理而获得的在该目标块中的未解码的非零系数数目之和,从表示该游程-级别对和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表中选择一个代码表,并且在该数值检测步骤中,根据所选择的代码表检测对应于在该目标块中的未解码系数的游程-级别对。因此,通过使用不包含不会出现的由游程数值和级别数值所构成的对的代码表,可以实现具有更高效率对应于可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding method, according to the decoding process of the codes, for each block consisting of predetermined coefficients including coefficient data, a code is decoded to reconstruct coefficients including consecutive zeros indicating that their values are zero and a run-level pair representing the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient, in the code table selection step, according to the target block that has passed through the target block as an object of the decoding process The sum of the number of processed coefficients obtained by the decoding process of the target block and the number of undecoded non-zero coefficients in the target block that have not been obtained by the decoding process of the target block, from the run-level pair sum code representing the A code table is selected from among a plurality of code tables corresponding to each other, and in the value detection step, run-level pairs corresponding to undecoded coefficients in the target block are detected based on the selected code table. Therefore, variable-length decoding processing corresponding to variable-length encoding processing with higher efficiency can be realized by using a code table that does not include pairs of run-length values and level values that do not occur.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,根据对该代码的解码处理,构成被编码数据的代码被解码,以重构包括表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值的一个游程-级别对,该解码步骤包括一个代码表处理步骤,用于根据构成该游程-级别对的游程数值和级别数值的组合,定期地改变在表示该游程-级别对和相应代码之间的对应关系的第一代码表中的游程-级别对和代码之间的对应关系,基于该第一代码表形成具有与第一代码表不同的在游程-级别对和代码之间的对应关系的第二代码表,并且在该代码表选择步骤中,根据关于已处理系数和与该系数的产生相关的参数的至少一个信息选择第一和第二代码表之一。因此,第一和第二代码表之一被适当地选择作为当代码被变换为游程数值和级别数值对时所使用的最佳代码表。相应地,满意地执行对应于有效地删除包含在目标数据中的冗余信息的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,从而该可变长度解码处理是非常有用的。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding method, according to the decoding process of the code, the code constituting the coded data is decoded to reconstruct the run-length value and representation including the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero A run-level pair of the level values of the values of the non-zero coefficients following the zero coefficient, the decoding step comprising a code table processing step for periodically Change the correspondence between the run-level pair and the code in the first code table representing the correspondence between the run-level pair and the corresponding code, based on which the first code table is formed A second code table for the correspondence between run-level pairs and codes, and in the code table selection step the first and One of the second code tables. Therefore, one of the first and second code tables is appropriately selected as the optimum code table used when the codes are converted into pairs of run value and level value. Accordingly, variable-length decoding processing corresponding to variable-length encoding processing that efficiently deletes redundant information contained in object data is satisfactorily performed, so that the variable-length decoding processing is very useful.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,在第一和第二代码表中,较短的代码被适应性地对应于具有构成该游程-级别对的更小级别数值的各个游程-级别对,并且在第二代码表中,对应于较短代码的游程-级别对的级别数值与第一代码表相比平均值较小。因此,在与构成要被处理的目标数据的系数相关的量化参数较大的情况下,该可变长度解码方法是有效地。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding method, in the first and second code tables, shorter codes are adaptively corresponded to the respective run-levels having smaller level values constituting the run-level pair Yes, and in the second code table, the level values for run-level pairs corresponding to shorter codes are smaller on average than in the first code table. Therefore, this variable length decoding method is effective in the case where quantization parameters related to coefficients constituting target data to be processed are large.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,在该第一和第二代码表中,较短代码被适应性地对应于具有构成该游程-级别对的较小游程数值的各个游程-级别对,并且在第二代码表中,第一代码表相比,对应于较短代码的游程-级别对的游程数值的平均值较小。因此,在与构成要被处理的目标数据的系数相关的该量化参数较小的情况下,该可变长度解码方法是有效的。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable-length decoding method, in the first and second code tables, shorter codes are adaptively corresponded to respective run-levels having smaller run-values constituting the run-level pair Yes, and in the second code table, the average value of the run values corresponding to the shorter code run-level pairs is smaller than in the first code table. Therefore, the variable length decoding method is effective in the case where the quantization parameter related to the coefficients constituting the target data to be processed is small.
根据本发明。在上述可变长度解码方法中,根据对该代码的解码处理,对由构成该系数数据的预定数目的系数所构成的每个块执行从一个代码重构一个游程-级别对,并且在该代码表处理步骤中,根据通过在作为解码处理的对象的一个目标块中的解码处理而获得的已处理系数的数目形成该第二代码表。因此,可以采用不包含不会出现的游程数值和级别数值对的代码表作为该第二代码表,从而可以实现对应于具有更高效率的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理。According to the present invention. In the variable length decoding method described above, according to the decoding process of the code, reconstruction of a run-level pair from a code is performed for each block constituted by a predetermined number of coefficients constituting the coefficient data, and in the code In the table processing step, the second code table is formed based on the number of processed coefficients obtained by decoding processing in a target block that is an object of the decoding processing. Therefore, a code table that does not include pairs of run value and level value that do not appear can be employed as the second code table, whereby variable length decoding processing corresponding to variable length encoding processing with higher efficiency can be realized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,在该数值检测步骤中,从高频分量到低频分量,由具有图像数据的最高频分量的一个游程-级别对执行对应于该代码的一个游程-级别对的检测。因此,可以采用不包含不会出现的游程数值和级别数值的一个代码表作为该第二代码表,从而可以实现对应于增加压缩比的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理。According to the present invention, in the above variable length decoding method, in the value detection step, from high frequency components to low frequency components, a run-level pair corresponding to the code is executed by a run-level pair having the highest frequency component of the image data. Detection of run-level pairs. Therefore, a code table that does not include run values and level values that do not appear can be used as the second code table, whereby variable length decoding processing corresponding to variable length encoding processing that increases the compression ratio can be realized.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,通过在包含于第一代码表中的游程-级别对之间的对应关系中仅仅改变可以定期操作的对应关系而形成第二代码表。因此可以减少用于第二代码表的形成所需的算术运算。According to the present invention, in the above variable length decoding method, the second code table is formed by changing only the correspondences that can be operated regularly among the correspondences between run-level pairs contained in the first code table. Arithmetic operations required for formation of the second code table can thus be reduced.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,根据对应于该图像数据的量化步骤,通过图像数据的量化频率分量而获得构成该系数数据的系数,并且在该代码表选择步骤中,根据该量化步骤的数值执行在第一代码表和第二代码表之间的切换。因此,可以采用适用于该量化步骤的一个代码表作为在用于构成要被处理的目标数据的系数的可变长度解码处理中使用的代码表。According to the present invention, in the above variable length decoding method, according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, the coefficients constituting the coefficient data are obtained by quantizing the frequency components of the image data, and in the code table selection step, according to the The value of the quantization step performs switching between the first code table and the second code table. Therefore, a code table suitable for the quantization step can be adopted as the code table used in the variable-length decoding process for the coefficients constituting the target data to be processed.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,该代码表选择步骤包括一个代码表切换步骤,用于根据一个切换指令信号在该第一代码表和第二代码表之间切换,并且在该解码步骤中,执行该切换指令信号的解码。因此,可以根据要被处理的目标数据的特性等等切换在该可变长度解码处理中使用的代码表。According to the present invention, in the above variable length decoding method, the code table selecting step includes a code table switching step for switching between the first code table and the second code table according to a switching instruction signal, and in the In the decoding step, the switching instruction signal is decoded. Therefore, the code table used in this variable-length decoding process can be switched according to the characteristics of the target data to be processed and the like.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码方法中,根据对该代码的解码处理,对包含由构成该系数数据的预定数目的系数的每个块执行从一个代码重构一个游程-级别对的操作,并且在该代码表处理步骤中,根据作为已经通过对目标块的解码处理而获得的在作为解码处理的对象的目标块中的已处理系数的数目与在还未通过对该块的解码处理而获得的目标块中的未解码的非零系数的数目之和形成第二代码表。因此,不包括不会出现的游程数值和级别数值对的一个代码表被用作为第二代码表,从而可以实现对应于具有更高效率的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding method, an operation of reconstructing a run-level pair from a code is performed for each block containing a predetermined number of coefficients constituting the coefficient data in accordance with the decoding process of the code , and in this code table processing step, according to the number of processed coefficients in the target block which is the object of the decoding process obtained as having passed through the decoding process on the target block and the number of coefficients which have not passed through the decoding process on the block And the obtained sum of the numbers of undecoded non-zero coefficients in the target block forms the second code table. Therefore, a code table that does not include pairs of run values and level values that do not occur is used as the second code table, so that variable length decoding processing corresponding to variable length encoding processing with higher efficiency can be realized.
根据本发明,在此提供一种用于对包括通过对由多个系数所构成的系数数据执行可变长度编码所获得多个代码的被编码数据解码的可变长度解码装置,其中包括:解码单元,用于使用表示该系数的数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表,使得各个代码受到对用于解码该被编码数据的解码处理,以重构由多个系数所构成的系数数据,并且该解码单元包括:代码表选择单元,用于根据关于已经被解码的被解码系数和与该系数的解码处理相关的参数至少之一的信息从多个代码表选择一个代码表;以及数值检测单元,用于通过使用所选择的代码表检测对应于还未解码的未解码代码的数值。因此,可以执行对应于具有更高的编码效率的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该编码处理通过改变代码表而有效地删除包含在系数数据中的冗余信息,以编码该系数数据。According to the present invention, there is provided a variable length decoding apparatus for decoding encoded data including a plurality of codes obtained by performing variable length encoding on coefficient data composed of a plurality of coefficients, including: a unit for using a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the numerical values of the coefficients and the codes so that the respective codes are subjected to decoding processing for decoding the encoded data to reconstruct a coefficient composed of a plurality of coefficients data, and the decoding unit includes: a code table selection unit for selecting a code table from a plurality of code tables based on information about at least one of a decoded coefficient that has been decoded and a parameter related to a decoding process of the coefficient; and A numerical value detecting unit for detecting a numerical value corresponding to an undecoded code which has not yet been decoded by using the selected code table. Therefore, it is possible to perform variable length decoding processing corresponding to variable length coding processing having higher coding efficiency, which efficiently deletes redundant information contained in coefficient data by changing the code table to code the coefficient data.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码装置中,通过根据对应于图像数据的量化步骤量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且在该代码表选择单元中,根据该量化步骤的数值选择用于该数值检测单元的代码表。因此,可以执行对应于一种可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该编码处理通过总是采用适用于该量化步骤的代码表并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding apparatus, the coefficient is obtained by quantizing the frequency component of the image data according to the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and in the code table selection unit, the coefficient is selected according to the numerical value of the quantization step. In the code table of the numerical detection unit. Therefore, it is possible to perform variable-length decoding processing corresponding to a variable-length coding processing by always employing a code table suitable for the quantization step and maximizing coding efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码装置中,该代码表选择单元根据关于一个被解码系数的信息选择由该数值检测单元所使用的代码表。因此,可以执行对应于一种可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该可变长度编码处理通过总是使用适合于未解码系数的数目的代码表而对被量化系数编码并且使得编码效率最大化。According to the present invention, in the above variable length decoding apparatus, the code table selection unit selects the code table used by the value detection unit based on information on a coefficient to be decoded. Therefore, it is possible to perform variable length decoding processing corresponding to a variable length coding processing that encodes quantized coefficients by always using a code table suitable for the number of undecoded coefficients and makes the coding efficiency maximize.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度解码装置中,根据对该代码的解码处理,该代码被解码,以分别重构表示其数值为零的连续零系数的数目的游程数值以及表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值,该代码表选择单元根据被解码的游程数值从表示该游程数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表选择一个代码表,并且该数值检测单元根据所选择的代码表检测对应于一个被解码代码的游程数值。因此,可以执行对应于可变长度编码处理的一种可变长度解码处理,该可变长度编码处理总是通过使用适用于未处理的游程数值的数目的代码表对游程数值编码并且可以实现编码效率的最大化。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length decoding apparatus, according to the decoding process of the code, the code is decoded to respectively reconstruct the run-length value representing the number of consecutive zero coefficients whose value is zero and the number of values represented in the zero coefficient After the level value of the value of the non-zero coefficient, the code table selection unit selects a code table from a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run value and the code according to the decoded run value, and the value detection unit according to The selected code table detects the run value corresponding to a decoded code. Therefore, it is possible to perform a variable-length decoding process corresponding to a variable-length encoding process that always encodes run-length values by using a code table suitable for the number of unprocessed run-length values and can realize encoding Maximize efficiency.
根据本发明,在上述可变长度编码装置中,通过根据对应于图像数据的量化步骤量化图像数据的频率分量而获得该系数,并且该解码单元对代码执行解码处理,以从高频分量到低频分量获得对应于该代码的数值。因此,可以执行对应于可变长度编码处理的一种可变长度解码处理,该可变长度编码处理可以进一步减小对应于分配给系数的代码的总位数。According to the present invention, in the above-mentioned variable length encoding device, the coefficient is obtained by quantizing the frequency components of the image data in accordance with the quantization step corresponding to the image data, and the decoding unit performs decoding processing on the code to convert from high frequency components to low frequency components. The component gets the value corresponding to that code. Therefore, a variable-length decoding process corresponding to a variable-length encoding process that can further reduce the total number of bits corresponding to codes allocated to coefficients can be performed.
根据本发明,在此提供一种记录介质,其中包括一个程序,用于通过计算机执行对包括由多个系数所构成的系数数据的可变长度编码而获得的多个代码的被编码数据解码的可变长度解码处理,并且该程序包括解码步骤,用于使用表示该系数的数值和代码之间的对应关系的多个代码表使得各个代码受到对该被编码数据解码的解码处理,以重构由多个系数所构成的系数数据,并且该解码步骤进一步包括:代码表选择步骤,用于根据关于已经被解码的被解码系数和与该系数的解码处理相关的参数至少之一的信息选择该代码表;以及数值检测步骤,用于通过使用所选择的代码表检测对应于还未解码的未解码代码的数值。因此,可以通过软件实现对应于具有更高的编码效率的可变长度编码处理的可变长度解码处理,该编码处理通过改变代码表而有效地删除包含在系数数据中的冗余信息,以编码该系数数据。According to the present invention, there is provided a recording medium including a program for decoding, by a computer, coded data including a plurality of codes obtained by variable-length coding of coefficient data composed of a plurality of coefficients. variable length decoding processing, and the program includes a decoding step for subjecting the respective codes to decoding processing for decoding the encoded data using a plurality of code tables representing correspondence between the numerical values of the coefficients and the codes to reconstruct coefficient data constituted by a plurality of coefficients, and the decoding step further includes: a code table selection step for selecting the code table based on information on at least one of decoded coefficients that have already been decoded and parameters related to decoding processing of the coefficients a code table; and a value detection step for detecting a value corresponding to an undecoded code that has not yet been decoded by using the selected code table. Therefore, variable-length decoding processing corresponding to variable-length coding processing with higher coding efficiency, which efficiently deletes redundant information contained in coefficient data by changing a code table to encode The coefficient data.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为用于说明根据本发明第一实施例的图像编码装置101的方框图。FIG. 1 is a block diagram for explaining an
图2为示出构成根据第一实施例的图像编码装置101的游程长度编码单元RLE1的方框图。FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing the run-length encoding unit RLE1 constituting the
图3(a)-3(d)为用于说明由游程长度编码单元RLE1所执行的曲折扫描的示意图,以及图3(e)和(f)为用于说明游程数值和级别数值的重新排序的示意图。3(a)-3(d) are schematic diagrams for explaining zigzag scanning performed by run-length encoding unit RLE1, and FIGS. schematic diagram.
图4为用于说明该游程长度编码单元RLE1的可变长度编码器LVLC中的处理的示意图:图4(a)为示出用于级别数值的可变长度编码处理的流程图,以及图4(b)为用于对该级别数值的可变长度编码处理中的一个代码表。FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram for explaining the processing in the variable length encoder LVLC of the run-length encoding unit RLE1: FIG. (b) is a code table used in the variable-length encoding process of the numerical value of the level.
图5为用于说明该游程长度编码单元RLE1的可变长度编码器RVLC中的处理的示意图:图5(a)为示出对一个游程数值的可变长度编码处理的流程图,以及图5(b)为在对该游程数值的可变长度编码处理中所用的一个代码表。Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram for explaining the processing in the variable-length coder RVLC of this run-length coding unit RLE1: Fig. 5 (a) is the flow chart showing the variable-length coding processing of a run-length value, and Fig. 5 (b) is a code table used in the variable length encoding process of the run value.
图6为分别示出在采用代码表L2(图6(a))以及在采用代码表L1(图6(b))的情况中对应于由可变长度编码器LevVLC分配给级别数值(量化参数相对较小)的代码的总位数的示意图。Fig. 6 respectively shows that in adopting code table L2 (Fig. 6 (a)) and adopting code table L1 (Fig. 6 (b)) in the situation of adopting code table L1 (Fig. Schematic representation of the total number of bits for a relatively small code.
图7为分别示出在采用代码表L2(图7(a))以及在采用代码表L1(图7(b))的情况中对应于由可变长度编码器LevVLC分配给级别数值(量化参数相对较大)的代码的总位数的示意图。Fig. 7 respectively shows that in adopting code table L2 (Fig. 7 (a)) and adopting code table L1 (Fig. 7 (b)) in the situation of adopting code table L1 (Fig. Schematic diagram of the total number of bits for a code that is relatively large).
图8为分别示出在采用一个特定代码表(图8(a))的情况、执行代码表的改变和游程数值的重新排序(图8(b))的情况以及仅仅改变代码表的情况(图8(c))的情况对应于由可变长度编码器RVLC分配给游程数值的代码的总位数的示意图。Fig. 8 is respectively shown in the case of adopting a specific code table (Fig. The case of FIG. 8(c)) corresponds to a schematic diagram of the total number of bits of the code assigned to the run-length value by the variable length coder RVLC.
图9为用于说明根据本发明第二实施例的图像解码装置102的方框图。FIG. 9 is a block diagram for explaining an image decoding device 102 according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
图10为示出构成根据第二实施例的图像解码装置102的游程长度解码单元RLD1的方框图。Fig. 10 is a block diagram showing the run-length decoding unit RLD1 constituting the image decoding device 102 according to the second embodiment.
图11为用于说明由可变长度解码器LVLD执行的可变长度解码处理的示意图:图11(a)为示出用于重构一个级别数值的可变长度解码处理的流程图,以及图11(b)为在该可变长度解码处理中使用的一个代码表。11 is a schematic diagram for explaining the variable length decoding process performed by the variable length decoder LVLD: FIG. 11(b) is a code table used in the variable length decoding process.
图12为用于说明由可变长度解码器RVLD执行可变长度解码处理的示意图:图12(a)示出用于重构一个游程数值的可变长度解码处理的流程图,以及图12(b)为在该可变长度解码处理中所用的一个代码表。FIG. 12 is a schematic diagram for explaining variable-length decoding processing performed by a variable-length decoder RVLD: FIG. 12( a) shows a flow chart of variable-length decoding processing for reconstructing a run-length value, and FIG. 12( b) is a code table used in the variable length decoding process.
图13为用于说明根据本发明第三实施例的图像编码装置103的方框图。FIG. 13 is a block diagram for explaining an
图14为示出构成根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103的游程长度编码单元RLE2的方框图。Fig. 14 is a block diagram showing the run-length encoding unit RLE2 constituting the
图15为示出根据第三实施例由游程长度编码单元RLE2所形成的一个代码表(第二代码表)的例子T2a(图15(a))和T2b(图15(b))的示意图。FIG. 15 is a diagram showing examples T2a (FIG. 15(a)) and T2b (FIG. 15(b)) of a code table (second code table) formed by the run-length encoding unit RLE2 according to the third embodiment.
图16为示出根据第三实施例由游程长度编码单元RLE2所形成的一个代码表(第二代码表)的其他例子T2c(图16(a))、T2d(图16(b))和T2e(图16(c))的示意图。FIG. 16 shows other examples T2c (FIG. 16(a)), T2d (FIG. 16(b)) and T2e of a code table (second code table) formed by the run-length encoding unit RLE2 according to the third embodiment. (Fig. 16(c)).
图17为示出根据第三实施例由游程长度编码单元RLE2所编码的量化分量的一个次序的例子的示意图。Fig. 17 is a diagram showing an example of an order of quantized components encoded by the run-length encoding unit RLE2 according to the third embodiment.
图18为用于说明根据本发明第四实施例的图像解码装置104的方框图。Fig. 18 is a block diagram for explaining an
图19为示出构成根据第四实施例的图像解码装置104的游程长度解码单元RLD2的方框图。Fig. 19 is a block diagram showing a run-length decoding unit RLD2 constituting the
图20为说明根据本发明第五实施例的图像编码装置105的方框图。FIG. 20 is a block diagram illustrating an
图21为说明构成根据第五实施例的图像编码装置105的游程长度编码单元RLE3的方框图。Fig. 21 is a block diagram illustrating the run-length encoding unit RLE3 constituting the
图22为用于说明根据本发明第六实施例的图像解码装置106的方框图。FIG. 22 is a block diagram for explaining an
图23为示出构成根据第六实施例的图像解码装置106的游程长度解码单元RLD3的方框图。Fig. 23 is a block diagram showing a run-length decoding unit RLD3 constituting the
图24为示出根据第五实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE3以及根据第六实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE3所使用的可变长度代码表的Ta(图24(a))、Tb(图24(b))和Tc(图24(c))的示意图。FIG. 24 is a diagram showing Ta ( FIG. 24( a )), Tb ( FIG. 24 (b)) and Tc (Fig. 24(c)).
图25为用于说明包含由一个计算机系统(图25(a)和25(b))以及计算机系统(图25(c))所实现的任何上述实施例的可变长度编码处理或可变长度解码处理的程序的一个数据存储介质的示意图。Fig. 25 is a diagram for explaining the variable length coding process or variable length coding process or variable length codes including any of the above-mentioned embodiments realized by a computer system (Fig. 25(a) and 25(b)) and computer system (Fig. 25(c)). A schematic diagram of a data storage medium for a program of decoding processing.
图26为用于说明根据任何实施例的图像编码方法和图像解码方法的一个应用的示意图,并且该图示出实现内容发布服务的内容提供系统。FIG. 26 is a schematic diagram for explaining one application of an image encoding method and an image decoding method according to any embodiment, and shows a content providing system realizing a content distribution service.
图27为用于说明采用根据任何实施例的图像编码方法和图像解码方法的便携式电话的示意图。FIG. 27 is a schematic diagram for explaining a cellular phone employing an image encoding method and an image decoding method according to any of the embodiments.
图28为示出如图27所示的便携式电话的方框图。FIG. 28 is a block diagram showing the portable telephone shown in FIG. 27. Referring to FIG.
图29为示出采用根据任何实施例的图像编码装置或图像解码装置的数字广播系统的示意图。FIG. 29 is a schematic diagram showing a digital broadcasting system employing an image encoding device or an image decoding device according to any embodiment.
图30为示出一种常规图像编码装置201a的方框图。Fig. 30 is a block diagram showing a conventional
图31为用于说明构成该常规图像编码装置201a的编码单元RLE0a的方框图。Fig. 31 is a block diagram for explaining the encoding unit RLE0a constituting the conventional
图32为用于说明根据该常规图像编码装置201a的常规图像解码装置202a的方框图。Fig. 32 is a block diagram for explaining a conventional
图33为用于说明构成该常规图像解码装置202a的解码单元RLD0a的方框图。Fig. 33 is a block diagram for explaining the decoding unit RLD0a constituting the conventional
图34为示出执行常规游程长度编码的图像编码装置201b的方框图。Fig. 34 is a block diagram showing an image encoding device 201b that performs conventional run-length encoding.
图35为用于说明构成该常规图像编码装置201b的游程长度编码单元RLE0b的方框图。Fig. 35 is a block diagram for explaining the run-length encoding unit RLE0b constituting the conventional image encoding device 201b.
图36为用于说明对应于该常规图像编码装置201b的图像解码装置202b的方框图。Fig. 36 is a block diagram for explaining an
图37为用于说明构成该常规图像编码装置201b的游程长度编码单元RLE0b的方框图。Fig. 37 is a block diagram for explaining the run-length encoding unit RLE0b constituting the conventional image encoding device 201b.
图38为用于说明执行常规游程长度编码的另一个图像编码装置201c的方框图。Fig. 38 is a block diagram for explaining another image encoding device 201c that performs conventional run-length encoding.
图39为说明构成该常规图像编码装置201c的游程长度编码单元RLE0c的方框图。Fig. 39 is a block diagram illustrating the run-length encoding unit RLE0c constituting the conventional image encoding apparatus 201c.
图40为用于说明对应于该常规图像编码装置201c的常规图像解码装置202c的方框图。Fig. 40 is a block diagram for explaining a conventional
图41为用于说明构成该常规图像解码装置202c的解码单元RLD0c的方框图。Fig. 41 is a block diagram for explaining the decoding unit RLD0c constituting the conventional
图42为示出由构成该常规图像编码装置201c的游程长度编码单元RLE0c所使用的一个代码表的例子的示意图。Fig. 42 is a diagram showing an example of a code table used by the run-length encoding unit RLE0c constituting the conventional image encoding device 201c.
图43为示出由该常规游程长度编码单元RLE0a、RLE0b或RLE0c所编码的量化分量的次序的例子的示意图。Fig. 43 is a diagram showing an example of the order of quantized components encoded by the normal run-length encoding unit RLE0a, RLE0b, or RLE0c.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
首先,将描述本发明的基本原理。First, the basic principle of the present invention will be described.
通常,当该量化步骤为粗略时,被量化的分量具有较小的绝对值。然后,该游程(连续零系数的长度)更长,并且相应地该级别数值(非零系数的数值)具有更小的绝对值。相反,当该量化步骤为精细时,被量化的分量具有更大的绝对值。因此,该游程更短并且相应地该级别数值具有更大的绝对值。Generally, when the quantization step is coarse, the quantized components have smaller absolute values. Then, the run (the length of consecutive zero coefficients) is longer, and correspondingly the level value (the number of non-zero coefficients) has a smaller absolute value. Conversely, when the quantization step is fine, the quantized components have larger absolute values. Therefore, the run is shorter and accordingly the level value has a larger absolute value.
另外,当已经在一个要被处理的目标块中完成许多被量化的分量的可变长度编码并且未编码的被量化分量的数目较小,则不会出现超过未编码的量化分量的数目的游程数值。因此,当除去这些游程数值和级别数值对时,增加编码效率。In addition, when variable-length coding of many quantized components has been completed in a target block to be processed and the number of uncoded quantized components is small, no run length exceeding the number of uncoded quantized components will occur value. Thus, coding efficiency is increased when these run-value and level-value pairs are removed.
从这一观点来看,本发明根据可变长度编码处理或用于被量化系数的可变长度解码处理的状态以及与被量化系数的产生相关的参数(量化参数),改变表示一个被量化系数的大小的数值信息和代码之间对应关系的一个代码表,从而有效地除去包含在该可变长度编码处理的目标数据(被量化系数)中的冗余信息。From this point of view, the present invention changes the representation of a quantized coefficient according to the state of the variable-length encoding process or the variable-length decoding process for the quantized coefficient and the parameter (quantization parameter) related to the generation of the quantized coefficient (quantization parameter). A code table of the corresponding relationship between the numerical information of the size and the code, thereby effectively removing redundant information contained in the target data (quantized coefficients) of the variable length coding process.
例如,根据被量化系数的处理状态,通过选择在常规可变长度编码或解码处理中使用的代码表(第一代码表)或者根据第一代码表形成并且对要被处理的数据优化的第二代码表而执行该代码表的改变。不必总是根据第一代码表形成第二代码表,但是适用于处理目标数据的任何代码表可以被选择作为一个代码表。For example, by selecting a code table (first code table) used in conventional variable-length encoding or decoding processing or a second code table formed from the first code table and optimized for the data to be processed according to the processing state of quantized coefficients, code table to perform changes to the code table. It is not always necessary to form the second code table based on the first code table, but any code table suitable for processing object data may be selected as a code table.
在下文中,将参照图1至25描述本发明的实施例。Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 25 .
[实施例1][Example 1]
图1为用于说明根据本发明第一实施例的图像编码装置的方框图。FIG. 1 is a block diagram for explaining an image coding apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
根据第一实施例的图像编码装置101具有用于根据量化参数QP和VLC选择信号VlcSel使得来自量化单元Q的输出QS受到可变长度编码处理并且输出一个编码流Str1的游程长度编码单元RLE1,取代如图3中所示的常规图像编码装置201b中的游程长度编码单元RLE0b,其使得来自量化单元Q的输出(量化分量)QS受到可变长度编码处理并且输出一个编码流Strob。The
在此,该量化参数QP是表示一个量化步骤的数值的参数,并且该量化步骤近似于与该量化参数QP成比例。更加具体来说,当量化参数QP较大时,被量化分量具有较小的绝对值,然后该被量化分量的零游程(数值为零的连续分量的长度)更长,并且一个级别数值具有较小的绝对值。Here, the quantization parameter QP is a parameter representing a value of one quantization step, and the quantization step is approximately proportional to the quantization parameter QP. More specifically, when the quantization parameter QP is large, the quantized component has a small absolute value, then the zero-run (the length of a continuous component whose value is zero) of the quantized component is longer, and a level value has a smaller small absolute value.
图2为用于说明该游程长度编码单元RLE1的具体结构的方框图。FIG. 2 is a block diagram for explaining the specific structure of the run-length encoding unit RLE1.
该游程长度编码单元RLE1类似于图35中所示的常规游程长度编码单元RLE0b,具有:曲折扫描仪Scan用于把从量化单元Q输出的二维阵列的(量化分量)QS变换为一维阵列的(即,预定次序)量化系数Coef;游程计算器RunCal,用于计算其数值为零(零系数)的量化分量Coef的连续数目并且输出表示连续零系数的数目的游程数值Run;以及级别计算器LevCal,用于计算在该零系数之后其数值非零的(非零系数)的量化分量Coef的数值,并且输出表示该非零系数的数值的级别数值Lev。This run-length encoding unit RLE1 is similar to the conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0b shown in FIG. 35, with a meander scanner Scan for transforming the (quantized components) QS of the two-dimensional array output from the quantization unit Q into a one-dimensional array (i.e., a predetermined order) of quantized coefficients Coef; a run calculator RunCal for calculating the consecutive number of quantized components Coef whose value is zero (zero coefficient) and outputting a run value Run representing the number of consecutive zero coefficients; and level calculation A device LevCal for calculating the value of the quantized component Coef whose value is non-zero (non-zero coefficient) after the zero coefficient, and outputs a level value Lev representing the value of the non-zero coefficient.
图3(a)示出对应于一个块的量化分量Q1至Q16的一个二维阵列,以及图3(b)由箭头A1至A15所示的在曲折扫描仪Scan中的量化分量Q1至Q16的扫描路径。在此,通过量化对应于一个图像信号的频率分量的直流分量而获得一个量化分量Q1,并且通过量化对应于该图像信号的频率分量的交流分量而获得量化分量Q2至Q16。图3(c)示出该量化分量Q1至Q16的一个一维阵列(编码次序),其通过在曲折扫描仪Scan中的曲折扫描而获得,并且图3(d)示出表示量化分量Q1至Q16的数值的具体数值的一维阵列。Fig. 3 (a) shows a two-dimensional array of quantized components Q1 to Q16 corresponding to one block, and Fig. 3 (b) shows the quantized components Q1 to Q16 in the zigzag scanner Scan by arrows A1 to A15 scan path. Here, a quantized component Q1 is obtained by quantizing a DC component corresponding to a frequency component of an image signal, and quantized components Q2 to Q16 are obtained by quantizing an AC component corresponding to a frequency component of the image signal. Fig. 3(c) shows a one-dimensional array (encoding order) of the quantized components Q1 to Q16 obtained by zigzag scanning in the zigzag scanner Scan, and Fig. 3(d) shows A one-dimensional array of concrete values for the value of Q16.
该游程长度编码单元RLE1进一步包括一个用于对从级别计算器LevCal输出的级别数值Lev重新排序的一个重新排序单元Lreodr;用于对从游程计算器RunCal输出的游程数值Run重新排序的重新排列单元Rreodr;以及用于根据来自游程计算器RunCal的输出计算在一个目标块中的未编码系数的数目Cnum并且输出所计算的数目的一个数目计算器NumClc。图3(e)示出从具有图3(c)和3(d)中所示的排列的量化分量的数值获得的游程数值和级别数值的次序。图3(f)示出在重新排列之后的游程数值和级别数值的次序。The run length encoding unit RLE1 further includes a reordering unit Lreodr for reordering the level value Lev output from the level calculator LevCal; a rearranging unit for reordering the run value Run output from the run length calculator RunCal Rreodr; and a number calculator NumClc for calculating the number Cnum of uncoded coefficients in a target block based on the output from the run length calculator RunCal and outputting the calculated number. Fig. 3(e) shows the sequence of run values and level values obtained from the values of the quantized components having the arrangement shown in Figs. 3(c) and 3(d). Fig. 3(f) shows the order of run values and level values after rearrangement.
该游程长度编码单元RLE1进一步包括:可变长度编码器LVLC,用于根据量化参数QP和选择信号VlcSel使得来自重新排列单元Lreodr的输出ROLev受到可变长度编码处理,并且输出一个代码串(级别数值代码串)LStr;可变长度编码器RVLC,用于根据未编码系数的数目Cnum使得来自重新排列单元Rreodr的输出RORun受到可变长度编码处理,并且输出一个代码串(游程数值代码串)RStr;以及多路复用器MUX,用于把用于每个块的代码串LStr和代码串RStr复用,并且输出一个复用的编码流Str1。The run-length encoding unit RLE1 further includes: a variable-length encoder LVLC for subjecting the output ROLev from the rearrangement unit Lreodr to variable-length encoding according to the quantization parameter QP and the selection signal VlcSel, and outputting a code string (level value a code string) LStr; a variable length coder RVLC for subjecting the output RORun from the rearrangement unit Rreodr to variable length coding according to the number Cnum of uncoded coefficients, and outputting a code string (run-length numerical code string) RStr; And a multiplexer MUX for multiplexing the code string LStr and the code string RStr for each block, and outputting a multiplexed coded stream Str1.
图4为用于说明由可变长度编码器LVLC所执行的可变长度编码处理的示意图。图4(a)为示出用于一个级别数值的可变长度编码处理的流程图,以及图4(b)为示出在用于该级别数值可变长度编码处理中使用的代码表的示意图。FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining variable length coding processing performed by a variable length coder LVLC. FIG. 4(a) is a flow chart showing variable-length encoding processing for a numerical value of one level, and FIG. 4(b) is a schematic diagram showing a code table used in the variable-length encoding processing for numerical values of this level .
图4(b)示出级别数值(Level)的排列Alev、在量化参数QP小于一个阈值的情况中的代码(代码字)的排列Cal、以及在量化参数QP等于或大于该阈值时的代码(代码字)的排列Ca2。4(b) shows an arrangement Alev of level values (Level), an arrangement Cal of codes (codewords) in the case where the quantization parameter QP is smaller than a threshold value, and a code (code word) when the quantization parameter QP is equal to or larger than the threshold value ( codeword) permutation Ca2.
在此,一个代码表L1由级别数值(Level)的排列Alev和在量化参数QP小于一个阈值时的代码(代码字)的排列Cal所构成。该代码表L1示出该级别数值(Level)和该量化参数QP小于该阈值的情况中的代码之间的对应关系。一个代码表L2由级别数值(Level)的排列Alev和在量化参数QP等于或大于该阈值时的代码(代码字)的排列Ca2所构成。该代码表L2示出级别数值(Level)和在量化参数QP等于或大于该阈值时的代码之间的对应关系。Here, one code table L1 is composed of an array Alev of level values (Level) and an array Cal of codes (codewords) when the quantization parameter QP is smaller than a threshold value. The code table L1 shows the correspondence between the level value (Level) and the code in the case where the quantization parameter QP is smaller than the threshold. A code table L2 is constituted by an arrangement Alev of level values (Level) and an arrangement Ca2 of codes (codewords) when the quantization parameter QP is equal to or greater than the threshold value. This code table L2 shows the correspondence between level values (Level) and codes when the quantization parameter QP is equal to or greater than the threshold value.
图5为用于说明由可变长度编码器RVLC所执行的可变长度编码处理的示意图。图5(a)为用于说明对一个游程数值的可变长度编码处理的流程图,以及图5(b)为示出在对该游程数值的可变长度编码处理中所用的代码表的示意图。FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining variable length coding processing performed by a variable length coder RVLC. FIG. 5(a) is a flowchart for explaining variable-length encoding processing of a run value, and FIG. 5(b) is a schematic diagram showing a code table used in the variable-length encoding process of the run value .
图5(b)示出游程数值(Run)的排列Arun、在未编码零系数的数目为1时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb1、在未编码零系数的数目为2时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb2、在未编码零系数的数目为3时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb3、在未编码零系数的数目为4时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb4、在未编码零系数的数目为5时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb5、在未编码零系数的数目为6时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb6、在未编码零系数的数目为7时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb7、以及在未编码零系数的数目为8时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb8。Fig. 5 (b) shows the arrangement Arun of the run length value (Run), the arrangement Cb1 of the code (code word) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 1, the code (code word) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 2 word), the permutation Cb2 of the code (code word) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 3, the permutation Cb4 of the code (code word) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 4, the permutation Cb4 of the code (code word) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 4, Arrangement Cb5 of codes (codewords) when the number of coefficients is 5, arrangement Cb6 of codes (codewords) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 6, codes (codewords) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 7 word), and an array Cb8 of codes (codewords) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is eight.
在此,代码表R1由游程数值(Run)的排列Arun和在未编码零系数的数目为1时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb1所构成,并且代码表R1示出游程数值(Run)和在未编码零系数的数目为1时的代码之间的对应关系。类似地,代码表R2、R3、R4、R5、R6和R7分别由游程数值(Run)的排列Arun和在未编码零系数的数目为2、3、4、5、6和7时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb、Cb3、Cb4、Cb5、Cb6和Cb7所构成,并且示出游程数值(Run)分别与在未编码零系数的数目为2、3、4、5、6和7时的代码之间的对应关系。另外,一个代码表R8由游程数值(Run)的排列Arun以及在未编码零系数的数目为8或更大时的代码(代码字)的排列Cb8所构成,并且示出该游程数值(Run)和在未编码零系数的数目为8或更大时的代码之间的对应关系。Here, the code table R1 is constituted by an arrangement Arun of run values (Run) and an arrangement Cb1 of codes (code words) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 1, and the code table R1 shows the run values (Run) and Correspondence between codes when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 1. Similarly, the code tables R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 and R7 consist of the arrangement Arun of the run length value (Run) and the codes ( codewords) permutations Cb, Cb3, Cb4, Cb5, Cb6, and Cb7, and show the run length value (Run) vs. Correspondence between codes. In addition, a code table R8 is composed of an arrangement Arun of run values (Run) and an arrangement Cb8 of codes (code words) when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 8 or more, and shows the run values (Run) and the correspondence between codes when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 8 or more.
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
在根据第一实施例的图像编码装置101中,该分块单元Blk、频率变换单元Trans和量化单元Q按照与常规图像编码装置201a(参见图30)或图像编码装置201b(参见图34)相同的方式而操作。In the
更加具体来说,当图像信号Vin被输入到图像编码装置101a时,该分块单元Blk把所输入的图像信号Vin分为块单元,以产生对应于各个块的图像信号(像素值分量)BlkS。该频率变换单元Trans把像素值分量BlkS根据DCT(离散余弦变换)或小波变换变换为频率分量TransS。该量化单元Q根据量化参数QP在一个预定量化步骤中量化该频率分量TransS,以输出量化分量QS,以及输出量化参数QP。该游程长度编码单元RLE1使得量化分量QS受到可变长度编码处理,并且步骤Sc一个编码流Str1。More specifically, when the image signal Vin is input to the image encoding device 101a, the blocking unit Blk divides the input image signal Vin into block units to generate image signals (pixel value components) BlkS corresponding to the respective blocks. . The frequency transform unit Trans transforms the pixel value component BlkS into a frequency component TransS according to DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) or wavelet transform. The quantization unit Q quantizes the frequency component TransS in a predetermined quantization step according to the quantization parameter QP to output the quantized component QS, and outputs the quantization parameter QP. The run-length encoding unit RLE1 subjects the quantized component QS to a variable-length encoding process, and steps Sc an encoded stream Str1.
在下文中,将具体描述游程长度编码单元RLE1的操作。Hereinafter, the operation of the run-length encoding unit RLE1 will be specifically described.
该曲折扫描仪Scan对从量化单元Q输出的量化分量QS(即,二维阵列中的多个量化分量Q1至Q16,如图3(a)中所示)的曲折扫描,以把该量化分量QS变换为量化分量Coef。在此,通过沿着由图3(b)中所示的箭头A1至A15的路线扫描如图3(a)中所示的二维阵列中的多个量化分量Q1至Q16而执行量化分量QS的曲折扫描,以把多个量化分量Q1至Q16的阵列变换为如图3(c)中所示的一维阵列(处理次序)。在此,图3(d)示出已经受到曲折扫描的多个量化分量Q1至Q16的具体数值的排列(20,-10,5,0,2,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,-1,0,0,1)。The zigzag scanner Scan zigzags the quantized component QS output from the quantizing unit Q (that is, a plurality of quantized components Q1 to Q16 in a two-dimensional array, as shown in FIG. QS is transformed into a quantized component Coef. Here, the quantization component QS is performed by scanning a plurality of quantization components Q1 to Q16 in a two-dimensional array as shown in FIG. zigzag scan to transform the array of multiple quantized components Q1 to Q16 into a one-dimensional array as shown in FIG. 3(c) (processing order). Here, FIG. 3( d) shows the arrangement of specific numerical values (20, -10, 5, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 ,0,-1,0,0,1).
该游程计算器RunCal根据从曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef计算连续零系数的数目,并且输出表示所计算的数目的游程数值Run。图3(e)示出根据该游程数值的输出次序连续从游程计算器RunCal输出的具体游程数值:(0,0,0,1,3,3,2)。另一方面,该级别计算器LevCal根据从曲折扫描仪Scan输出的量化分量Coef计算在该连续零系数之后的非零系数,并且输出表示所计算的数值的级别数值Lev。图3(e)示出根据该级别数值输出的次序从级别计算器LevCal连续输出的具体级别数值:(20,-10,5,2,1,-1,1)。The run calculator RunCal calculates the number of consecutive zero coefficients from the quantized component Coef output from the meander scanner Scan, and outputs a run value Run representing the calculated number. FIG. 3( e ) shows specific run values continuously output from the run calculator RunCal according to the output order of the run values: (0, 0, 0, 1, 3, 3, 2). On the other hand, the level calculator LevCal calculates non-zero coefficients following the consecutive zero coefficients from the quantized components Coef output from the meander scanner Scan, and outputs a level value Lev representing the calculated values. Fig. 3(e) shows the specific level values successively output from the level calculator LevCal according to the order of the level value output: (20, -10, 5, 2, 1, -1, 1).
重新排列单元Rreodr对已经从游程计算器RunCal连续输出的游程数值按照与游程数值输出的次序相反的相反次序重新排列。图3(f)示出已经被重新排列单元Rreodr重新排列的具体游程数值的改变后的次序:(2,3,3,1,0,0,0)。该数目计算器NumClc根据从游程计算器RunCal输出的游程数值Run计算未编码系数的数目,并且输出所计算的未编码系数的数目(在下文中,也称为未编码系数数目)Cnum。另一方面,该重新排序单元Lreodr对已经顺序地从级别计算器LevCal输出的级别数值按照与该级别数值被示出的次序相反的次序重新排序。图3(f)示出已经由该重新排序单元Lreodr重新排序的具体级别数值的改变次序:(1,-1,1,2,5,-10,20)。The rearrangement unit Rreodr rearranges the run values that have been successively output from the run calculator RunCal in the reverse order of the output of the run values. Fig. 3(f) shows the changed order of the specific run values that have been rearranged by the rearranging unit Rreodr: (2, 3, 3, 1, 0, 0, 0). The number calculator NumClc calculates the number of uncoded coefficients from the run value Run output from the run length calculator RunCal, and outputs the calculated number of uncoded coefficients (hereinafter, also referred to as the number of uncoded coefficients) Cnum. On the other hand, the reordering unit Lreodr reorders the level values that have been sequentially output from the level calculator LevCal in an order opposite to the order in which the level values are shown. Figure 3(f) shows the order of change of the concrete level values that have been reordered by the reordering unit Lreodr: (1, -1, 1, 2, 5, -10, 20).
该可变长度编码器RVLC使得作为来自重新排序单元Rreodr的输出的已经重新排序的游程数值RORun受到可变长度编码处理,用于根据从数目计算器NumClc输出的未编码零系数的数目Cum,通过使用表示该游程数值和代码(代码字)之间的对应关系的多个代码表,把代码(代码字)分配到游程数值RORun,并且输出一个游程数值代码串RStr。另一方面,该可变长度编码器LVLC根据从数目计算器NumClc输出的未编码零系数的数目Cum,通过使用表示该游程数值和代码(代码字)之间的对应关系的多个代码表,使得作为来自重新排序单元Lreodr的输出的被重新排序的游程数值ROLev受到可变长度编码处理,用于把代码(代码字)分配到游程数值RORun,并且输出一个游程数值代码串RStr。另一方面,该可变长度编码器LVLC根据来自量化单元Q的量化参数QP和来自可变长度编码的外部指示选择的选择信号VlcSel,通过使用表示级别数值和代码(代码字)之间的对应关系的多个代码表,使得作为来自重新排序单元Lreodr的输出的已经被重新排序的游程数值ROLev受到可变长度编码处理,用于把代码(代码字)分配到游程数值ROL,并且输出一个级别数值代码串LStr。This variable length coder RVLC subjects the already reordered run-length value RORun as an output from the reordering unit Rreodr to a variable length coding process for the number Cum of uncoded zero coefficients output from the number calculator NumClc by Using a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run value and codes (code words), codes (code words) are assigned to the run value RORun, and a run value code string RStr is output. On the other hand, the variable length coder LVLC uses a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run values and codes (code words) based on the number Cum of uncoded zero coefficients output from the number calculator NumClc, The reordered run value ROLev as output from the reordering unit Lreodr is subjected to variable length encoding processing for assigning codes (codewords) to the run value RORun, and a run value code string RStr is output. On the other hand, the variable length coder LVLC uses the correspondence between the value representing the level and the code (code word) in accordance with the quantization parameter QP from the quantization unit Q and the selection signal VlcSel from the variable length code externally indicating selection. A plurality of code tables of relations such that the already reordered run-length value ROLev as an output from the reordering unit Lreodr is subjected to variable-length encoding processing for assigning codes (codewords) to the run-length value ROL and outputting a level Numerical code string LStr.
然后,该多路复用器MUX一个块接着一个块地复用该级别数值代码串LStr和游程数值代码串RStr,并且输出一个复用的编码流Str1。Then, the multiplexer MUX multiplexes the level numerical code string LStr and the run length numerical code string RStr block by block, and outputs a multiplexed encoded stream Str1.
在此,一个块接着一个块地执行用于复用该级别数值代码串LStr和游程数值代码串RStr的处理,例如,按照这种方式,对应于所有目标块的游程数值的代码串RStr之后接着对应于该目标块的所有级别数值的代码串LStr,或者对应于该目标块的所有级别数值的代码串LStr之后接着对应于所有目标块的游程数值的代码串RStr。Here, processing for multiplexing the level value code string LStr and the run value code string RStr is performed block by block, for example, in this way, the code string RStr corresponding to the run value of all target blocks is followed by A code string LStr corresponding to all level values of the target block, or a code string LStr corresponding to all level values of the target block followed by a code string RStr corresponding to run-length values of all target blocks.
在下文中,将参照图4具体描述可变长度编码器LVLC的操作。Hereinafter, the operation of the variable length coder LVLC will be specifically described with reference to FIG. 4 .
该可变长度编码器LVLC从量化单元Q获得量化参数QP(步骤Sa1),并且确定所获得的量化参数QP的数值是否等于或大于保存在可变长度编码器LVLC中的量化参数QP的阈值(步骤Sa2)。The variable length coder LVLC obtains the quantization parameter QP from the quantization unit Q (step Sa1), and determines whether the value of the obtained quantization parameter QP is equal to or greater than the threshold value of the quantization parameter QP stored in the variable length coder LVLC ( Step Sa2).
当该确定结果表明所获得的量化参数QP的数值小于量化参数QP的阈值,则该可变长度编码器LVLC选择由级别数值的排列Alev和代码(代码字)的排列Ca1所构成的代码表L1(参见图4(b))(步骤Sa3),当所获得的量化参数QP的数值等于或大于量化参数QP的阈值时,选择由级别数值的排列Alev和代码(代码字)的排列Ca2所构成的代码表L2(参见图4(b)(步骤Sa4)。When the result of the determination indicates that the obtained quantization parameter QP value is smaller than the threshold value of the quantization parameter QP, the variable length coder LVLC selects the code table L1 composed of the arrangement Alev of level values and the arrangement Ca1 of codes (code words) (see Fig. 4 (b)) (step Sa3), when the numerical value of obtained quantization parameter QP is equal to or greater than the threshold value of quantization parameter QP, select the arrangement Ca2 that is formed by the arrangement Alev of level numerical value and code (code word) Code table L2 (see FIG. 4(b) (step Sa4).
然后,可变长度编码器LVLC确定在一个目标块中是否存在未编码的级别数值Lev(步骤Sa5)。当一个未编码的级别数值Lev被包含在该目标块中时,该可变长度编码器LVLC使用所选择的代码表执行用于对该级别数值编码的处理,即,用于把相应的代码分配给该级别数值的处理(步骤Sa6),然后执行步骤Sa5的处理。另一方面,当在步骤Sa5中的处理结果表明在该目标块中没有未编码的级别数值Lev时,则该可变长度编码器LVLC结束对级别数值Lev的可变长度编码处理。Then, the variable length coder LVLC determines whether there is an uncoded level value Lev in a target block (step Sa5). When an uncoded level value Lev is contained in the target block, the variable length coder LVLC performs processing for encoding the level value using the selected code table, i.e., for assigning the corresponding code The process of giving the level numerical value (step Sa6) then executes the process of step Sa5. On the other hand, when the result of the processing in step Sa5 indicates that there is no uncoded level value Lev in the target block, the variable length coder LVLC ends the variable length coding process on the level value Lev.
在此,当VLC选择信号VlcSel预先指定使用一个特定代码表的可变长度编码处理时,则该可变长度编码器LVLC通过使用特定代码表对该级别数值执行可变长度编码处理,而与量化参数QP的数值无关。Here, when the VLC selection signal VlcSel predesignates variable-length coding processing using a specific code table, the variable-length coder LVLC performs variable-length coding processing on the level value by using a specific code table, unlike quantization. The value of the parameter QP is irrelevant.
接着,将参照图5具体描述可变长度编码器RVLC的操作。Next, the operation of the variable length coder RVLC will be specifically described with reference to FIG. 5 .
该可变长度编码器RVLC根据来自数目计算器NumClc的输出(未编码系数的数目)Cnum确定在该目标块中是否存在任何未编码的非零系数(步骤Sb1)。当该确定结果表明存在一个未编码的非零系数时,该可变长度编码器RVLC根据来自数目计算器NumClc的输出Cnum计算在该目标块中的未编码的零系数的数目(步骤Sb2)。The variable length coder RVLC determines whether there are any uncoded non-zero coefficients in the target block from the output (number of uncoded coefficients) Cnum from the number calculator NumClc (step Sb1). When the determination result indicates that there is an uncoded non-zero coefficient, the variable length coder RVLC calculates the number of uncoded zero coefficients in the target block based on the output Cnum from the number calculator NumClc (step Sb2).
然后,该可变长度编码器RVLC根据未编码的零系数的所计算数目选择一个代码表(步骤Sb3)。更加具体来说,当未编码的零系数的数目为1时,该可变长度编码器RVLC选择由游程数值的排列Arun和代码(代码字)的排列Cb1(参见图5(b))。类似地,当未编码的零系数的数目为2时,该可变长度编码器RVLC选择代码表R2,当未编码的零系数的数目为3时选择代码表R3,以及当未编码的零系数的数目为4时选择代码表R4。另外,当未编码的零系数的数目为5时,该可变长度编码器RVLC选择代码表R5,当未编码的零系数的数目为6时选择代码表R6,以及当未编码的零系数的数目为7时选择代码表R7。另外,当未编码的零系数的数目为8或更大时,该可变长度编码器RVLC选择代码表R8。Then, the variable length coder RVLC selects a code table according to the calculated number of uncoded zero coefficients (step Sb3). More specifically, when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 1, the variable length coder RVLC selects the arrangement Arun of run-length values and the arrangement Cb1 of codes (codewords) (see FIG. 5(b)). Similarly, the variable length coder RVLC selects code table R2 when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 2, selects code table R3 when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 3, and selects code table R3 when the number of uncoded zero coefficients Select code table R4 when the number of is 4. In addition, the variable length coder RVLC selects code table R5 when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 5, selects code table R6 when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 6, and selects code table R6 when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 6, and when the number of uncoded zero coefficients When the number is 7, select code table R7. Also, when the number of uncoded zero coefficients is 8 or more, the variable length coder RVLC selects the code table R8.
接着,该可变长度编码器RVLC使用所选择的代码表执行对游程数值Run编码的处理,即,用于把相应代码分配到该游程数值的处理(步骤Sb4),然后执行步骤Sb1的确定处理。Next, the variable length coder RVLC performs a process of encoding the run value Run using the selected code table, that is, a process for assigning a corresponding code to the run value (step Sb4), and then performs the determination process of step Sb1 .
在此,当在步骤Sb1中的确定结果表明没有未编码的非零系数时,该可变长度编码器RVLC结束对游程数值的可变长度编码处理。Here, when the determined result in step Sb1 indicates that there are no uncoded non-zero coefficients, the variable length coder RVLC ends the variable length coding process for the run-length value.
接着,将描述一个具体例子,其中根据如上文所述的级别数值的可变长度编码中的量化参数选择一个代码表,从而增加编码效率。Next, a specific example will be described in which a code table is selected according to the quantization parameter in the variable-length coding of the level values as described above, thereby increasing the coding efficiency.
图6示出对应于当量化参数QP相对较小时,即,当来自级别计算器LevCal并且被重新排序和从重新排序单元Lreodr输出的级别数值为如图3(f)中所示的1,-1,1,2,5,-10,20时,对应于分配给级别数值的代码的总位数。Fig. 6 shows that corresponding to when the quantization parameter QP is relatively small, that is, when the level value from the level calculator LevCal and reordered and output from the reordering unit Lreodr is 1 as shown in Fig. 3(f), - 1, 1, 2, 5, -10, 20, corresponding to the total number of digits of the code assigned to the level value.
当该量化参数QP被确定为等于或大于一个阈值并且采用该代码表L2时,代码(代码字)被分配给如图6(a)中所示的各个级别数值,并且对应于被分配的代码的总位数为75位。When the quantization parameter QP is determined to be equal to or greater than a threshold and the code table L2 is used, codes (codewords) are assigned to respective level values as shown in Figure 6(a), and correspond to the assigned code The total number of bits is 75 bits.
另一方面,当量化参数QP被确定为小于该阈值并且采用该代码表L1时,代码(代码字)被分配到如图6(b)中所示的各个级别数值,并且对应于所分配的代码的总位数为47位。On the other hand, when the quantization parameter QP is determined to be smaller than the threshold value and the code table L1 is adopted, codes (codewords) are assigned to respective level values as shown in FIG. 6(b), and correspond to the assigned The total number of bits of the code is 47 bits.
当量化参数QP相对较小时,具有较大数值的被量化分量的出现频率较大。因此,与代码表L2相比,选择其中较短代码在平均值上相当于绝对值相对较大的级别数值的代码表L1是有效的,以增加编码效率。When the quantization parameter QP is relatively small, the frequency of occurrence of the quantized component having a larger value is larger. Therefore, it is effective to select the code table L1 in which the shorter codes are equivalent in average to a level value whose absolute value is relatively large compared with the code table L2 to increase the coding efficiency.
图7示出当量化参数QP相对较大时,即,当来自级别计算器LevCal的并且被重新排序和从该重新排序单元Lreodr输出的输出(级别数值)为与图3(f)中不同的1,-1,1,1,1,-2,3时,对应于被分配到级别数值的总位数。Fig. 7 shows that when the quantization parameter QP is relatively large, that is, when the output (level value) from the level calculator LevCal and reordered and output from the reordering unit Lreodr is different from that in Fig. 3(f) 1, -1, 1, 1, 1, -2, 3 correspond to the total number of digits assigned to the level value.
当确定量化参数QP等于或大于该阈值并且采用代码表L2时,代码(代码字)被分配到如图7(a)中所示的各个级别数值,并且对应于被分配代码的总位数为15位。When it is determined that the quantization parameter QP is equal to or greater than the threshold and the code table L2 is adopted, the codes (codewords) are assigned to the respective level values as shown in Figure 7(a), and the total number of bits corresponding to the assigned codes is 15 digits.
另一方面,当确定量化参数QP小于该阈值并且采用代码表L1时,代码(代码字)被分配到如图7(b)中所示的各个级别数值,并且对应于被分配代码的总位数为17位。On the other hand, when it is determined that the quantization parameter QP is smaller than the threshold and the code table L1 is adopted, the codes (codewords) are assigned to the respective level values as shown in Fig. 7(b), and correspond to the total bits of the assigned codes The number is 17 digits.
如上文所述,当量化参数QP的数值相对较大时,具有较大数值的量化系数的出现频率较低。因此,与代码表L1相比,选择其中较短代码集中地对应于绝对值相对较小的级别数值的代码表L2是有效的,以增加编码效率。As described above, when the numerical value of the quantization parameter QP is relatively large, the frequency of occurrence of quantization coefficients with large numerical values is low. Therefore, it is effective to select the code table L2 in which shorter codes collectively correspond to level values whose absolute values are relatively small compared with the code table L1 to increase coding efficiency.
图8示出当游程数值为如图3(e)中所示的0,0,0,1,3,3,2时对应于分配到从游程计算器RunCal输出的游程数值的代码的总位数。Fig. 8 shows the total bits corresponding to the code assigned to the run value output from the run calculator RunCal when the run value is 0, 0, 0, 1, 3, 3, 2 as shown in Fig. 3(e) number.
当不执行在游程长度编码单元RLE1中的游程数值的重新排序和代码表的改变而是总是采用如图5(b)中所示的代码表R8时,代码(代码字)被分配到如图8(a)中所示的各个游程数值,并且对应于被分配代码的总位数为21位。When the reordering of the run values in the run-length encoding unit RLE1 and the change of the code table are not performed but the code table R8 as shown in FIG. The respective run values are shown in FIG. 8(a), and the total number of bits corresponding to the assigned code is 21 bits.
当根据未编码零系数的数目执行在游程长度编码单元RLE1中的游程数值的重新排序和代码表的改变时,代码(代码字)被分配到如图8(b)所示的各个游程数值,并且对应于被分配代码的总位数为13位。在此,每次把一个代码分配到一个游程数值时,未编码系数的数目被减小通过把1加上紧接着在前被编码的一个游程数值所获得的数值。这是因为单个或连续零系数总是接着一个非零系数。另外,从重新排序单元Rreodr输出的对应于一个块的多个重新排序的游程数值获得的未编码零系数的数目为15。这是因为,要被处理的块总是具有至少一个非零系数。When the reordering of the run values and the change of the code table in the run-length encoding unit RLE1 are performed according to the number of uncoded zero coefficients, codes (code words) are assigned to the respective run values as shown in FIG. 8( b ), And the total number of bits corresponding to the assigned code is 13 bits. Here, each time a code is assigned to a run value, the number of uncoded coefficients is reduced by a value obtained by adding 1 to a run value coded immediately before. This is because a single or consecutive zero coefficient is always followed by a non-zero coefficient. In addition, the number of uncoded zero coefficients obtained from a plurality of reordered run values corresponding to one block output by the reordering unit Rreodr is 15. This is because a block to be processed always has at least one non-zero coefficient.
当不执行例如在游程长度编码单元RLE1中的游程数值的重新排序而是仅仅执行根据未编码的零系数的数目而改变代码表时,代码(代码字)被分配到如图8(c)中所示的各个游程数值,并且对应于被分配代码的总位数为20位。When the reordering of the run values, for example in the run-length encoding unit RLE1, is not performed but only changing the code table according to the number of uncoded zero coefficients is performed, the codes (codewords) are allocated as shown in Fig. 8(c) The individual run values are shown and correspond to a total of 20 bits for the assigned code.
如上文所述,根据第一实施例的图像编码装置101包括游程长度编码单元RLE1,其使用表示其数值为零的(零系数)的量化分量Coef的连续数目的游程数值Run和表示在该零系数之后的数值非零的(非零系数)的量化分量Coef的数值的级别数值Lev,编码通过量化一个图像信号的频率分量而获得的被量化系数。因此,通过除去冗余信息,可以用更高的编码效率对该被量化系数进行编码。As described above, the
另外,根据第一实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE1包括可变长度编码器LVLC,其根据量化参数QP的数值选择一个代码表,并且通过使用所选择的代码表执行级别数值的可变长度编码,从而减小对应于被分配到该级别数值的代码的总位数。该游程长度编码单元RLE1进一步包括重新排序单元Rreodr,其从高频分量到低频分量对从已经给定预定处理次序的被量化系数获得的多个游程数值重新排序;以及可变长度编码器RVLC,其根据在该目标块中的未编码的零系数的数目选择一个代码表,并且使用所选择的代码表执行重新排序的游程数值的可变长度编码。因此,有效地减小对应于分配到该游程数值的代码的总位数,从而增加编码效率。In addition, the run-length encoding unit RLE1 according to the first embodiment includes a variable length encoder LVLC that selects a code table according to the value of the quantization parameter QP, and performs variable length encoding of the level value by using the selected code table, Thereby reducing the total number of bits corresponding to the codes assigned to the numerical values of the level. This run-length encoding unit RLE1 further includes a reordering unit Rreodr that reorders a plurality of run values obtained from quantized coefficients to which a predetermined processing order has been given, from high frequency components to low frequency components; and a variable length coder RVLC, It selects a code table according to the number of uncoded zero coefficients in the target block, and performs variable length coding of the reordered run-length values using the selected code table. Therefore, the total number of bits of the code corresponding to the run value is effectively reduced, thereby increasing the coding efficiency.
在该第一实施例中,可变长度编码器RVLC根据在该目标块中的未编码的零系数的数目(即,从数目计算器NumClc输出的输出Cnum)选择一个代码表。但是,该可变长度编码器RVLC不但可以根据来自数目计算器NumClc的输出Cnum而且根据VLC选择信号VlcSel选择一个代码表。例如,当预先由VLC选择信号VlcSel指定使用一个特定代码表的可变长度编码处理时,该可变长度编码器RVLC通过使用特定代码表执行对该游程数值的可变长度编码处理,而与在该目标块中的未编码的零系数无关。In this first embodiment, the variable length coder RVLC selects a code table according to the number of uncoded zero coefficients in the target block (ie, the output Cnum from the number calculator NumClc). However, the variable length coder RVLC can select a code table not only based on the output Cnum from the number calculator NumClc but also based on the VLC selection signal VlcSel. For example, when variable length coding processing using a specific code table is designated in advance by the VLC selection signal VlcSel, the variable length coder RVLC executes variable length coding processing of the run value by using the specific code table, unlike in the Uncoded zero coefficients in this target block are irrelevant.
[实施例2][Example 2]
图9为用于说明根据本发明第二实施例的一个图像解码装置的方框图。Fig. 9 is a block diagram for explaining an image decoding apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
根据第二实施例的图像解码装置102例如解码从第一实施例的图像编码装置101输出的编码流Str1。The image decoding device 102 according to the second embodiment decodes, for example, the encoded stream Str1 output from the
该图像解码装置102具有根据量化参数QP和VLD选择信号VldSel使得所输入的编码流Str1受到可变长度解码处理以重构被量化系数的一个游程长度解码单元RLD1,其取代如图36中所示的使得所输入的编码流Str0b受到可变长度解码处理的游程长度解码单元RLD0b。除了游程长度解码单元RLD1之外,该结构与图36中所示的图像解码装置202b的结构相同。The image decoding device 102 has a run-length decoding unit RLD1 that subjects the input encoded stream Str1 to variable-length decoding processing to reconstruct quantized coefficients based on the quantization parameter QP and the VLD selection signal VldSel, instead of the A run-length decoding unit RLD0b that subjects the input encoded stream Str0b to variable-length decoding processing. The structure is the same as that of the
图10为用于说明游程长度解码单元RLD1的具体结构的方框图。Fig. 10 is a block diagram for explaining a specific structure of the run-length decoding unit RLD1.
该游程长度解码单元RLD1具有一个多路分解器DMUX,用于对从图像编码装置101输出的复用编码流Str1进行多路分解,以获得对应于级别数值的代码串LStr和对应于游程数值的代码串RStr,这与如图37中所示的常规游程长度解码单元RLD0b相同。The run-length decoding unit RLD1 has a demultiplexer DMUX for demultiplexing the multiplexed coded stream Str1 output from the
该游程长度解码单元RLD1具有一个可变长度解码器LVLD,用于根据量化参数QP和VLC选择信号VlcSel,使得通过把复用的编码流Str1多路分解而获得的级别数值代码串LStr受到可变长度解码处理,以重构游程数值ROLev;以及可变长度解码器RVLD,用于根据未解码系数的数目,使得通过对复用的编码流Str1多路分解而获得的游程数值代码串RStr受到可变长度解码处理,以重构游程数值RORun。The run-length decoding unit RLD1 has a variable length decoder LVLD for selecting the signal VlcSel according to the quantization parameter QP and VLC so that the level value code string LStr obtained by demultiplexing the multiplexed coded stream Str1 is subject to variable a length decoding process for reconstructing the run-length value ROLev; and a variable length decoder RVLD for subjecting the run-length value code string RStr obtained by demultiplexing the multiplexed coded stream Str1 to an acceptable value in accordance with the number of undecoded coefficients Variable-length decoding processing to reconstruct the run-length value RORun.
该游程长度解码单元RLD1进一步包括反重新排序单元LIreodr,其在编码结束时按照与重新排序单元Lreodr相反的次序重新排序由可变长度解码器LVLD输出的级别数值ROLev;反重新排序单元RIreodr,其在该编码结束时,按照与重新排序单元Rreodr相反的次序对由可变长度解码器RVLD输出的游程数值RORun重新排序;以及数目计算器NumClc,其根据来自反重新排序单元RIreodr的输出Run计算在一个目标块中的未解码系数的数目Cnum,并且输出所获得的数目。The run-length decoding unit RLD1 further includes an anti-reordering unit LIreodr, which reorders the level value ROLev output by the variable-length decoder LVLD in the reverse order of the reordering unit Lreodr at the end of encoding; an anti-reordering unit RIreodr, which At the end of this encoding, the run-length values RORun output by the variable length decoder RVLD are reordered in the reverse order of the reordering unit Rreodr; and the number calculator NumClc is calculated in The number Cnum of undecoded coefficients in one target block, and the obtained number is output.
该游程长度解码单元RLD1进一步包括反曲折扫描仪IScan,其从由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的一维阵列中的被解码量化分量重构二维阵列的解码的量化分量DQS。The run-length decoding unit RLD1 further comprises an inverse scanner IScan which reconstructs the decoded quantized components DQS of the two-dimensional array from the decoded quantized components in the one-dimensional array represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run.
图11为用于说明由可变长度解码器LVLD执行的可变长度解码处理。图11(a)为用于说明重构级别数值的可变长度解码处理的流程图,以及图11(b)为示出在该可变长度解码处理中所用的一个代码表的示意图。在此,在用于该级别数值的可变长度解码处理中采用的代码表L1和L2与用于在根据第一实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE1中的级别数值的编码处理中采用的代码表L1和L2相同。FIG. 11 is a diagram for explaining variable length decoding processing performed by a variable length decoder LVLD. Fig. 11(a) is a flowchart for explaining variable-length decoding processing of reconstructing level values, and Fig. 11(b) is a diagram showing a code table used in the variable-length decoding processing. Here, the code tables L1 and L2 used in the variable-length decoding process for the level value and the code table used in the encoding process for the level value in the run-length encoding unit RLE1 according to the first embodiment L1 and L2 are the same.
图12为用于说明由可变长度解码器RVLD执行的可变长度解码处理的示意图。图12(a)为用于说明用于重构游程数值的可变长度解码处理的流程图。图12(b)为示出在该可变长度解码处理中采用的代码表的示意图。在此,在对游程数值的可变长度解码处理中采用的代码表R1至R8分别与在根据第一实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE1中对游程数值的编码处理中采用的代码表R1和R8相同。FIG. 12 is a diagram for explaining variable length decoding processing performed by the variable length decoder RVLD. Fig. 12(a) is a flowchart for explaining variable-length decoding processing for reconstructing run-length values. FIG. 12(b) is a schematic diagram showing a code table used in this variable-length decoding process. Here, the code tables R1 to R8 employed in the variable-length decoding process of the run-length values are respectively the same as the code tables R1 and R8 employed in the encoding process of the run-length values in the run-length encoding unit RLE1 according to the first embodiment. same.
下面将描述其操作。Its operation will be described below.
当一个复用的量化单元Q例如被从根据第一实施例的图像编码装置101输入到图像解码装置102时,该游程长度解码单元RLD1使得该编码流Str1受到解码处理,并且输出解码的量化分量DQS。该游程长度解码单元RLD1的操作与游程长度编码单元RLE1的操作相反。When a multiplexed quantization unit Q is input to the image decoding device 102 from the
更加具体来说,在游程长度解码单元RLD1中,该多路分解器DMUX对所输入的富裕编码流Str1进行多路分解,以获得对应于级别数值的级别数值代码串LStr和对应于游程数值的游程数值代码串RStr,并且把该级别数值代码串和游程数值代码串分别输出到可变长度解码器LVLD和可变长度解码器RVLD。More specifically, in the run-length decoding unit RLD1, the demultiplexer DMUX demultiplexes the input rich coded stream Str1 to obtain the level value code string LStr corresponding to the level value and the level value code string LStr corresponding to the run value The run-length numerical code string RStr, and the level numerical code string and the run-length numerical code string are output to the variable length decoder LVLD and the variable length decoder RVLD, respectively.
该可变长度解码器LVLD通过使用表示该级别数值和代码(代码字)之间的对应关系的多个代码表,根据来自量化单元Q的量化参数QP和来自可变长度解码的外部指示选择的VLC选择信号VlcSel,对于从该多路分解器DMUX获得的级别数值代码串LStr获得对应于各个代码(代码字)的级别数值ROLev,并且把所获得的级别数值输出到反重新排序单元LIreodr。另一方面,该可变长度解码器RVLD通过使用表示该游程数值和代码(代码字)之间的对应关系的多个代码表,根据从数目计算器NumClc输出的未编码系数的数目Cnum,对从该多路分解器DMUX获得的游程数值代码串RStr获得对应于各个代码(代码字)的游程数值RORun,并且把所获得的游程数值输出到反重新排序单元RIreodr。This variable-length decoder LVLD selects the code according to the quantization parameter QP from the quantization unit Q and the external indication from the variable-length decoding by using a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the level value and the code (code word). The VLC selects the signal VlcSel, obtains the class value ROLev corresponding to each code (codeword) for the class value code string LStr obtained from the demultiplexer DMUX, and outputs the obtained class value to the anti-reordering unit LIreodr. On the other hand, the variable length decoder RVLD, by using a plurality of code tables representing the correspondence between the run values and codes (code words), based on the number Cnum of uncoded coefficients output from the number calculator NumClc, Run-length values RORun corresponding to respective codes (codewords) are obtained from the run-length value code string RStr obtained by the demultiplexer DMUX, and the obtained run-length values are output to the reverse reordering unit RIreodr.
该反重新排序单元LIreodr在编码结束时使得从该可变长度解码器LVLD输出的级别数值ROLev受到重新排序单元Lreodr的处理,以在编码结束时重构来自该级别计算器的输出Lev。另一方面,该反重新排序单元RIreodr在编码结束时使得从可变长度解码器RVLD输出的游程数值RORun受到与重新排序单元Rreodr的处理相反的排列处理,以在编码结束时重构来自该游程计算器的输出Run。另外,数目计算器NumClc根据来自反重新排序单元RIreodr的输出Run计算在一个目标块中的未解码系数的数目Cnum,并且把所获得的数目Cnum输出到可变长度解码器RVLD。The anti-reordering unit LIreodr subjects the level value ROLev output from the variable length decoder LVLD to the reordering unit Lreodr at the end of encoding to reconstruct the output Lev from the level calculator at the end of encoding. On the other hand, the anti-reordering unit RIreodr subjects the run-length value RORun output from the variable-length decoder RVLD to permutation processing opposite to that of the reordering unit Rreodr at the end of encoding to reconstruct the run-length value from the run-length value RORun at the end of encoding. Calculator output Run. Also, the number calculator NumClc calculates the number Cnum of undecoded coefficients in one target block from the output Run from the reverse reordering unit RIreodr, and outputs the obtained number Cnum to the variable length decoder RVLD.
然后,该反曲折扫描仪IScan执行与曲折扫描仪Scan相反的操作,以从由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的一维阵列的被量化分量重构二维阵列的解码的量化分量DQS,并且把所获得的量化分量DQS输出到反量化单元IQ。The inverse scanner IScan then performs the reverse operation of the meander scanner Scan to reconstruct the decoded quantized components DQS of the two-dimensional array from the quantized components of the one-dimensional array represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run, And output the obtained quantized component DQS to the inverse quantization unit IQ.
在下文中,将参照图11具体描述可变长度解码器LVLD的操作。Hereinafter, the operation of the variable length decoder LVLD will be specifically described with reference to FIG. 11 .
该可变长度解码器LVLD从图像编码装置101的量化单元Q获得量化参数QP(步骤Sc1),并且确定所获得的量化参数QP是否等于或大于保持在可变长度解码器LVLD中的量化参数QP的阈值(步骤Sc2)。The variable length decoder LVLD obtains the quantization parameter QP from the quantization unit Q of the image encoding device 101 (step Sc1), and determines whether the obtained quantization parameter QP is equal to or greater than the quantization parameter QP held in the variable length decoder LVLD threshold (step Sc2).
当该确定结果表明所获得的量化参数QP小于该量化参数QP的阈值,则该可变长度解码器LVLD选择由级别数值的排列Alev和代码(代码字)的排列Ca1所构成代码表L1(参见图11(b))(步骤Sc3),并且当获得的量化参数QP等于或大于量化参数QP的阈值时,选择由级别数值的排列Alev和排列Ca2所构成的代码表L2(参见图11(b))(步骤Sc4)。When the determination result shows that the obtained quantization parameter QP is smaller than the threshold value of the quantization parameter QP, the variable length decoder LVLD selects the code table L1 composed of the arrangement Alev of the level values and the arrangement Ca1 of the codes (codewords) (see Fig. 11 (b)) (step Sc3), and when the quantization parameter QP that obtains is equal to or greater than the threshold value of quantization parameter QP, select the code table L2 (referring to Fig. )) (step Sc4).
然后,该可变长度解码器LVLD确定在该目标块中是否有任何未解码的级别数值Lev(步骤Sc5)。当未解码的级别数值Lev被包含在该目标块中时,该可变长度解码器通过使用所选择的代码表执行用于重构级别数值Lev的解码处理,即,用于获得对应于代码的级别数值的处理(步骤Sc6),然后执行上述步骤Sc5的处理。另一方面,在步骤Sc5中的确定结果表明在该目标块中没有未解码的级别数值Lev,该可变长度解码器结束用于重构该级别数值Lev的可变长度解码处理。Then, the variable length decoder LVLD determines whether there is any undecoded level value Lev in the target block (step Sc5). When an undecoded level value Lev is contained in the target block, the variable length decoder performs a decoding process for reconstructing the level value Lev by using the selected code table, that is, for obtaining a value corresponding to the code The processing of the level value (step Sc6), and then the processing of the above-mentioned step Sc5 is performed. On the other hand, the determined result in step Sc5 indicates that there is no undecoded level value Lev in the target block, and the variable length decoder ends the variable length decoding process for reconstructing the level value Lev.
在此,当VLC选择信号VlcSel先前指定使用一个特定代码表的可变长度解码处理时,该可变长度解码器LVLD通过使用该特定代码表执行用于重构级别数值的可变长度解码处理,而与量化参数QP的数值无关。Here, when the VLC selection signal VlcSel previously designated variable-length decoding processing using a specific code table, the variable-length decoder LVLD performs variable-length decoding processing for reconstructing level values by using the specific code table, It has nothing to do with the numerical value of the quantization parameter QP.
接着,将参照图12具体描述可变长度解码器RVLD的操作。Next, the operation of the variable length decoder RVLD will be specifically described with reference to FIG. 12 .
该可变长度解码器RVLD根据来自数目计算器NumClc的输出(未解码系数的数目)Cnum确定在一个目标块中是否有任何未解码的非零系数(步骤Sd1)。当该确定结果表明存在未解码的非零系数,则该可变长度解码器根据该未解码系数的数目Cnum确定在该目标块中的未解码零系数的数目(步骤Sd2)。The variable length decoder RVLD determines whether there are any undecoded non-zero coefficients in a target block from the output (number of undecoded coefficients) Cnum from the number calculator NumClc (step Sd1). When the determination result indicates that there are undecoded non-zero coefficients, the variable length decoder determines the number of undecoded zero coefficients in the target block according to the number Cnum of undecoded coefficients (step Sd2).
该可变长度解码器RVLD根据未解码零系数的所获得数目选择一个代码表(步骤Sd3)。更加具体来说,当未解码零系数的数目为1时,该可变长度解码器选择由游程数值的排列Arun和代码(代码字)的排列Cb1所构成的代码表R1(参见图12(b))。类似地,当未解码零系数的数目为2时,该可变长度解码器选择代码表R2,当未解码零系数的数目为3时选择代码表R3,以及当未解码零系数的数目为4时选择代码表R4。另外,当未解码零系数的数目为5时,该可变长度解码器选择代码表R5,当未解码零系数的数目为6时选择代码表R6,以及当未解码零系数的数目为7时选择代码表R7。另外,当未解码零系数的数目为8或更大时,该可变长度解码器RVLD选择代码表R8。The variable length decoder RVLD selects a code table according to the obtained number of undecoded zero coefficients (step Sd3). More specifically, when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 1, the variable-length decoder selects the code table R1 (see FIG. )). Similarly, the variable length decoder selects code table R2 when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 2, selects code table R3 when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 3, and selects code table R3 when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 4 select code table R4. In addition, the variable length decoder selects code table R5 when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 5, selects code table R6 when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 6, and selects code table R6 when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 7 Select code table R7. Also, the variable length decoder RVLD selects the code table R8 when the number of undecoded zero coefficients is 8 or more.
接着,该可变长度解码器RVLD通过使用被选择的代码表执行用于重构游程数值Run的解码处理,即,用于获得对应于各个代码的游程数值的处理(步骤Sd4),并且然后执行上述步骤Sd1的确定处理。Next, the variable length decoder RVLD performs decoding processing for reconstructing the run value Run by using the selected code table, that is, processing for obtaining the run value corresponding to each code (step Sd4), and then executes The determination process of the above-mentioned step Sd1.
另外,当在步骤Sd1中的确定结果表明不存在未解码的非零系数时,该可变长度解码器RVLD结束用于重构游程数值的可变长度解码处理。Also, when the determined result in step Sd1 indicates that there is no undecoded non-zero coefficient, the variable length decoder RVLD ends the variable length decoding process for reconstructing the run value.
在根据第二实施例的图像解码装置102中,该反量化单元IQ、反频率变换单元ITrans和解块单元DeBlk按照与常规图像解码装置202a(参见图32)和图像解码装置202b(参见图36)相同的方式工作。In the image decoding device 102 according to the second embodiment, the inverse quantization unit IQ, the inverse frequency transform unit ITrans, and the deblocking unit DeBlk are in accordance with the conventional
具体来说,该反量化单元IQ执行量化单元Q的反操作,即,参照量化参数QP对解码的量化分量DQS执行反量化的操作,以输出解码的频率分量ITransS。该反频率变换单元ITrans执行频率变换单元Trans的反操作,即,根据反DCT或反小波变换变换对应于每个块的解码的频率分量ITransS的操作,以重构对应于各个块的解码的像素值信号DBlkS。然后,该解块单元DeBlk结合各个块的解码的像素值信号DBllkS,并且输出对应于每个图像(帧)的解码的图像信号Vout。Specifically, the inverse quantization unit IQ performs the inverse operation of the quantization unit Q, that is, performs an inverse quantization operation on the decoded quantized component DQS with reference to the quantization parameter QP to output the decoded frequency component ITransS. This inverse frequency transform unit ITrans performs the inverse operation of the frequency transform unit Trans, that is, the operation of transforming the decoded frequency components ITransS corresponding to each block according to inverse DCT or inverse wavelet transform, to reconstruct the decoded pixels corresponding to the respective blocks Value signal DBlkS. Then, the deblocking unit DeBlk combines the decoded pixel value signals DB1lkS of the respective blocks, and outputs a decoded image signal Vout corresponding to each image (frame).
如上文所述,根据第二实施例的图像解码装置102包括游程长度解码单元RLD1,其把构成被编码数据的游程数值代码串RStr和级别数值代码串LStr分别变换为表示连续零系数Coef的数目的游程数值Run和表示在该零系数之后的非零系数的数值的级别数值Lev,以根据该游程数值和级别数值重构被量化系数。因此,可以满意地执行对应于一种可变长度编码处理的解码处理,该编码处理可以除去冗余信息以更高编码效率编码的被量化系数。As described above, the image decoding device 102 according to the second embodiment includes the run-length decoding unit RLD1 that converts the run-length numerical code string RStr and the level numerical code string LStr constituting the encoded data into numbers representing consecutive zero coefficients Coef, respectively. The run value Run and the level value Lev representing the value of the non-zero coefficient following the zero coefficient are used to reconstruct the quantized coefficients according to the run value and the level value. Therefore, it is possible to perform satisfactorily a decoding process corresponding to a variable-length encoding process that can remove redundant information and encode quantized coefficients with higher encoding efficiency.
另外,根据第二实施例的游程长度解码单元RLD1包括可变长度解码器LVLD,其根据量化参数QP的数值选择一个代码表,并且通过使用被选择的代码表执行用于重构级别数值的可变长度解码。因此,可以满意地解码由对应于分配给级别数值的代码的减少的总位数所构成的级别数值代码串。In addition, the run-length decoding unit RLD1 according to the second embodiment includes a variable-length decoder LVLD that selects a code table according to the value of the quantization parameter QP, and performs possible reconfiguration of the level value by using the selected code table. Variable length decoding. Therefore, it is possible to satisfactorily decode the class value code string constituted by the reduced total number of bits corresponding to the codes assigned to the class value.
该游程长度解码单元RLD1进一步包括可变长度解码器RVLD,反量化单元IQ根据在一个目标块中的未解码零系数的数目选择一个代码表,并且通过使用被选择的代码表解码对应于重新排序的游程数值的代码串;以及反重新排序单元RIreodr,其按照与在游程长度解码单元RLD1中对游程数值的重新排序处理相反地次序,对由该解码处理所获得的游程数值重新排序。因此,对应于被分配到该游程数值的代码的总位数可以被有效地减小,并且可以满意地解码由该游程数值所构成的游程数值代码串。The run-length decoding unit RLD1 further includes a variable-length decoder RVLD, the inverse quantization unit IQ selects a code table according to the number of undecoded zero coefficients in a target block, and decodes the code corresponding to the reordering by using the selected code table and an anti-reordering unit RIreodr which reorders the run values obtained by the decoding process in reverse order to the reordering process of the run values in the run length decoding unit RLD1. Therefore, the total number of bits corresponding to the codes assigned to the run value can be effectively reduced, and the run value code string constituted by the run value can be satisfactorily decoded.
在该第二实施例中,该可变长度解码器RVLD根据在目标块中的未解码零系数的数目(即,来自数目计算器NumClc的输出Cnum)选择一个代码表,但是该可变长度解码器RVLD不但可以根据来自数目计算器NumClc的输出Cnum,而且还根据VLD选择信号VldSel选择该代码表。例如,当先前由VLD选择信号VldSel指定使用特定代码表的可变长度解码处理时,该可变长度解码器RVLD通过使用该特定代码表执行可变长度解码处理,以重构游程数值,而与在该目标块中的未解码零系数的数目无关。In the second embodiment, the variable length decoder RVLD selects a code table according to the number of undecoded zero coefficients in the target block (i.e., the output Cnum from the number calculator NumClc), but the variable length decoder The register RVLD can select the code list not only according to the output Cnum from the number calculator NumClc, but also according to the VLD selection signal VldSel. For example, when variable-length decoding processing using a specific code table was previously designated by the VLD selection signal VldSel, the variable-length decoder RVLD performs variable-length decoding processing by using the specific code table to reconstruct the run value, unlike The number of undecoded zero coefficients in the target block is irrelevant.
[实施例3][Example 3]
图13为用于说明根据本发明第三实施例的图像编码装置的方框图。Fig. 13 is a block diagram for explaining an image coding apparatus according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103具有根据量化参数QP或VLC选择信号VlcSel使得来自量化单元Q的输出QS受到可变长度编码处理并且输出一个编码流Str2的游程长度编码单元RLE2,其取代在图38中所示的图像编码装置201c中的游程长度编码单元RLE0c,其使得来自量化单元Q的输出(被量化分量)QS受到可变长度编码处理并且输出一个编码流Str0c。该第三实施例的图像编码装置103的其他部分与常规的图像编码装置201c相同。The
更加具体来说,类似于常规的游程长度编码单元RLE0c,该游程长度编码单元RLE2具有第一代码表T1(参见图42),其根据游程数值和级别数值的组合示出游程数值和级别数值对(在下文称为游程-级别对)和一个相应代码之间的对应关系。该游程长度编码单元RLE2根据该第一代码表定期改变游程-级别对和在该第一代码表中的代码之间的对应关系,以形成具有不同于第一代码表的对应关系的第二代码表,并且根据从量化单元Q输出的量化参数QP或者来自外部的VLC选择信号VlcSel选择第一和第二代码表之一,以及根据被选择的代码表把代码分配给与在要被处理的目标数据中的系数相关的游程-级别对。More specifically, similar to the conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0c, this run-length encoding unit RLE2 has a first code table T1 (see FIG. 42 ), which shows pairs of run-length values and level values according to combinations of run-length values and level values (hereinafter referred to as a run-level pair) and a corresponding code. The run-length encoding unit RLE2 periodically changes the correspondence between the run-level pairs and the codes in the first code table according to the first code table to form a second code having a correspondence different from the first code table table, and select one of the first and second code tables according to the quantization parameter QP output from the quantization unit Q or the VLC selection signal VlcSel from the outside, and assign codes to the target to be processed according to the selected code table The run-level pairs associated with the coefficients in the data.
在此,该量化参数QP是表示该量化步骤的数值的一个参数,并且该量化步骤近似于与量化参数QP成正比。更加具体来说,当量化参数QP较大时,该量化分量具有较小的绝对值,然后在该被量化分量中的零游程(其数值为零的连续分量的长度)更长,因此该级别数值具有更小的绝对值。因此,在这种情况中,把较小代码分配到包含较大游程数值和较小级别数值的游程-级别对的一个代码表被选择,从而增加编码效率。相反,当量化参数QP较小时,该被量化分量具有更大的绝对值。因此,把较小代码分配到包括较小游程数值和较大级别数值的一个代码表被选择,从而增加编码效率。Here, the quantization parameter QP is a parameter representing the value of the quantization step, and the quantization step is approximately proportional to the quantization parameter QP. More specifically, when the quantization parameter QP is large, the quantized component has a small absolute value, and then the run of zeros (the length of consecutive components whose value is zero) in the quantized component is longer, so the level Numeric values have smaller absolute values. Therefore, in this case, a code table that assigns smaller codes to run-level pairs containing larger run values and smaller level values is selected, thereby increasing coding efficiency. On the contrary, when the quantization parameter QP is smaller, the quantized component has a larger absolute value. Therefore, assigning smaller codes to a code table including smaller run values and larger class values is selected, thereby increasing coding efficiency.
另外,当输入来自图像编码装置103外部的VLC选择信号VlcSel时,该游程长度编码单元RLE2根据VLC选择信号VlcSel选择在该编码处理中所用的一个代码表。因此,当根据图像特性(图像的运动值、运动的复杂度、图案的细节等等)从外部选择一个适当的代码表时,或者当可以由仅仅包含一个代码表的一个图像解码装置所解码的数据流形成在图像编码装置103侧时,该图像编码装置103可以被VLC选择信号VlcSel所控制总是选择预定代码表。也就是说,还可以执行一种不改变一个代码表的可变长度编码处理,而是仅仅使用一个代码表。In addition, when the VLC selection signal VlcSel from outside the
图14为用于说明游程长度编码单元RLE2的具体结构的方框图。Fig. 14 is a block diagram for explaining the specific structure of the run-length encoding unit RLE2.
该游程长度编码单元RLE2类似于常规的游程长度编码单元RLE0c(参见图39)具有:曲折扫描仪Scan,用于把二维阵列的输出(量化分量)QS从量化单元Q转换为一维阵列(即,预定次序)的量化分量Coef;游程计算器RunCal,用于计算其数值为零的连续量化分量(零系数)的数目,并且输出一个游程数值Run;以及级别计算器LevCal,用于计算其数值非零(非零系数)的量化分量Coef的数值,并且输出一个级别数值Lev。This run-length encoding unit RLE2 is similar to the conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0c (see FIG. 39 ) having: a meander scanner Scan for converting the output (quantization component) QS of the two-dimensional array from the quantization unit Q into a one-dimensional array ( That is, a predetermined order) of quantized components Coef; a run calculator RunCal for calculating the number of consecutive quantized components (zero coefficients) whose value is zero, and outputting a run value Run; and a level calculator LevCal for calculating its The value of the quantized component Coef whose value is non-zero (non-zero coefficient), and outputs a level value Lev.
在该第三实施例中,该游程长度编码单元RLE2进一步具有一个游程转换器RunConv,用于根据量化参数QP或VLC选择信号VlcSel,执行把来自游程计算器RunCal的输出(游程数值)Run分为表示游程数值Run的高位数字的游程数值Run1和表示游程数值Run的低位数字的游程数值Run2的处理;以及级别转换器LevConv,用于根据量化参数QP或VLC选择信号VleSel,执行把来自级别计算器LevCal的输出(级别数值)Lev转换为表示级别数值Lev的高位数字的级别数值Lev1和表示级别数值Lev的低位数字的级别数值Lev2的处理。In the third embodiment, the run length encoding unit RLE2 further has a run length converter RunConv for performing dividing the output (run value) Run from the run length calculator RunCal according to the quantization parameter QP or the VLC selection signal VlcSel into Processing of the run value Run1 representing the upper digits of the run value Run and the run value Run2 representing the lower digits of the run value Run; and the level converter LevConv for selecting the signal VleSel according to the quantization parameter QP or VLC, and performing the conversion from the level calculator The process of converting the output (level value) Lev of LevCal into the level value Lev1 representing the upper digits of the level value Lev and the level value Lev2 representing the lower digits of the level value Lev.
该游程长度编码单元RLE2进一步包括一个游程级别编码器RunLevEnc,用于根据一个代码表或算术运算,获得对应于一对游程数值Run1和级别数值Lev1(在下文中称为游程-级别高位数字对)的代码号Code;以及重新排序单元ReOdr,用于根据量化参数QP或VLC选择信号VlcSel执行对游程-级别高位数字对重新排序的处理,使得对应于要被处理的一个目标块的游程-级别高位数字对根据游程-级别高位数字对和代码号Code对应于较小的代码号,并且输出对应于重新排序的游程-级别高位数字对的一个代码号ReOdrCode。The run-length encoding unit RLE2 further includes a run-level encoder RunLevEnc, which is used to obtain the corresponding pair of run-length value Run1 and level value Lev1 (hereinafter referred to as run-level high digit pair) according to a code table or arithmetic operation. a code number Code; and a reordering unit ReOdr for performing a process of reordering the run-level high-order digits according to the quantization parameter QP or the VLC selection signal VlcSel so that the run-level high-order digits corresponding to a target block to be processed The pair corresponds to the smaller code number according to the run-level high-order digit pair and the code number Code, and outputs a code number ReOdrCode corresponding to the reordered run-level high-order digit pair.
该游程长度编码单元RLE2进一步包括:位置计算器PosClc,用于从游程数值Run计算被编码的量化分量(被编码系数)的数目并且输出被编码系数的数目Pos;数目变换器CodeTrans,用于根据游程-级别高位数字对和代码号ReOdrCode之间的对应关系,从级别数值Lev2和游程数值Run2输出对应于由第二代码表所表示的一个游程-级别对的代码号ExtCode;以及可变长度编码器VLC,用于把一个位串(代码字)分配到代码号ExtCode,以产生一个编码流Str2。The run-length encoding unit RLE2 further includes: a position calculator PosClc for calculating the number of encoded quantized components (coded coefficients) from the run value Run and outputting the number Pos of coded coefficients; a number converter CodeTrans for Correspondence between the run length-level high digit pair and the code number ReOdrCode, the code number ExtCode corresponding to a run length-level pair represented by the second code table is output from the level value Lev2 and the run length value Run2; and variable length coding A device VLC for assigning a bit string (code word) to the code number ExtCode to generate a coded stream Str2.
在游程长度编码单元RLE2中的曲折扫描仪Scan、游程计算器RunCal、级别计算器LevCal和可变长度编码器VLC与如图39中所示的常规游程长度编码单元RLE0c相同。The meander scanner Scan, run length calculator RunCal, level calculator LevCal, and variable length coder VLC in the run-length encoding unit RLE2 are the same as the conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0c shown in FIG. 39 .
下面将描述其效果。The effect thereof will be described below.
该曲折扫描仪Scan把二维阵列的量化参数QP转换为一维阵列(即,设置一个次序)的量化分量Coef。该游程计算器RunCal计算连续零分量(其数值为零的量化分量)Coef的数目,并且输出表示获得的数目的游程数值Run。该级别计算器LevCal计算一个非零分量(在零分量之后的数值非零的量化分量)Coef,并且输出一个表示该非零分量的数值的级别数值Lev。The zigzag scanner Scan converts the quantization parameters QP of the two-dimensional array into the quantization components Coef of the one-dimensional array (ie, setting an order). The run calculator RunCal calculates the number of consecutive zero components (quantized components whose values are zero) Coef, and outputs a run value Run representing the obtained number. The level calculator LevCal calculates a non-zero component (quantization component whose value is non-zero after the zero component) Coef, and outputs a level value Lev representing the value of the non-zero component.
该游程计算器RunCal执行把游程数值Run分为表示游程数值Run的高位数字的游程数值Run1和表示游程数值Run的低位数字的游程数值Run2的转换处理。该级别计算器LevCal执行把级别数值Lev分为表示级别数值Lev的高位数字的级别数值Lev1和表示级别数值Lev的低位数字的级别数值Lev2的转换处理。The run calculator RunCal executes a conversion process of dividing the run value Run into a run value Run1 representing an upper digit of the run value Run and a run value Run2 representing a lower digit of the run value Run. The level calculator LevCal performs a conversion process of dividing the level value Lev into a level value Lev1 representing the upper digits of the level value Lev and a level value Lev2 representing the lower digits of the level value Lev.
该游程级别编码器RunLevEnc根据如图42中所示的代码表(第一代码表)或者根据算术运算,获得对应于一对级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run1(游程-级别高位数字对)的代码号Code。该重新排序单元ReOdr执行根据量化参数QP或VLC选择信号VlcSel对该游程-级别高位数字对重新排序的处理,并且输出对应于一个重新排序的游程-级别高位数字对的代码号ReOdrCode。根据对游程-级别高位数字对重新排序的处理,由游程级别编码器RunLevEnc所获得的游程-级别高位数字对和代码号Code之间的对应关系被转换为这样的对应关系,其中较小代码号对应于与在要被处理的较高频率分量相对应的游程-级别高位数字对。The run level encoder RunLevEnc obtains a code number corresponding to a pair of level value Lev1 and run value Run1 (run length-level high digit pair) according to the code table (first code table) as shown in Figure 42 or according to arithmetic operation Code. The reordering unit ReOdr performs reordering of the run-level upper digit pair according to the quantization parameter QP or the VLC selection signal VlcSel, and outputs a code number ReOdrCode corresponding to a reordered run-level upper digit pair. According to the process of reordering the run-level high-digit pairs, the correspondence between the run-level high-digit pairs obtained by the run-level encoder RunLevEnc and the code number Code is converted into such a correspondence, wherein the smaller code number Corresponds to the run-level high-order number pairs corresponding to the higher frequency components to be processed.
该位置计算器PosClc从游程数值Run计算被编码分量的数目,并且输出被编码系数的数目Pos。该数目变换器CodeTrans根据游程-级别高位数字对和代码号ReOdrCode之间的对应关系,输出对应于来自级别数值Lev2和游程数值Run2的一个游程-级别对。在此时,该数目变换器CodeTrans采用从位置计算器PosClc输出的被编码系数的数目Pos,以获得未编码分量的数目。The position calculator PosClc calculates the number of coded components from the run value Run, and outputs the number Pos of coded coefficients. The number converter CodeTrans outputs a run-level pair corresponding to the level value Lev2 and the run value Run2 according to the correspondence between the run-level high digit pair and the code number ReOdrCode. At this time, the number converter CodeTrans uses the number Pos of coded coefficients output from the position calculator PosClc to obtain the number of uncoded components.
在此,根据在该游程-级别对和代码号之间的对应关系不同于第一代码表的第二代码表,获得对应于从数目变换器CodeTrans输出的该游程-级别对的代码号ExtCode。该第二代码表如下形成:首先,通过重新排序单元ReOdr的重新排序处理形成具有不同于第一代码表的游程-级别对和代码号之间的对应关系的一个代码表,然后由重新排序单元ReOdr所形成的该代码表被数目变换器CodeTrans根据被编码系数的数目Pos而改变,使其不包含对应于超过未编码分量的数目的游程数值Run的在游程-级别对和代码号之间的对应关系。Here, the code number ExtCode corresponding to the run-level pair output from the number converter CodeTrans is obtained based on the second code table different from the first code table in the correspondence between the run-level pair and the code number. The second code table is formed as follows: first, a code table having a correspondence relationship between run-level pairs and code numbers different from that of the first code table is formed by the reordering process of the reordering unit ReOdr, and then by the reordering unit This code table formed by ReOdr is transformed by the number converter CodeTrans according to the number Pos of coded coefficients so that it does not contain the run-level pairs and code numbers corresponding to run values Run exceeding the number of uncoded components Correspondence.
该可变长度编码器VLC把一个位串(代码字)分配到代码号ExtCode,以产生一个编码流Str2。The variable length coder VLC assigns a bit string (code word) to the code number ExtCode to generate a coded stream Str2.
图15输出由游程长度编码单元RLE2根据第一代码表所形成的第二代码表的例子。在此,第一代码表与图42中所示的用于常规游程长度编码单元RLE0c中的代码表相同。在第一和第二代码表中,一个位串(代码字)被一一对应地分配给该代码号,不用说较短的代码字被分配给具有较小数值的代码号Code。FIG. 15 outputs an example of the second code table formed by the run-length encoding unit RLE2 from the first code table. Here, the first code table is the same as the code table used in the conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0c shown in FIG. 42 . In the first and second code tables, a bit string (code word) is assigned to the code number in one-to-one correspondence, and it goes without saying that a shorter code word is assigned to a code number Code having a smaller numerical value.
图15(a)示出第二代码表的一个例子,即,适用于量化参数QP较小的情况下的代码表T2a。Fig. 15(a) shows an example of the second code table, that is, a code table T2a suitable for the case where the quantization parameter QP is small.
该第二代码表T2a如下形成:This second code table T2a is formed as follows:
首先,对应于级别数值Lev的1/2的数值被指定为级别数值Lev1,并且(Lev1×2-Lev)的绝对值被指定为级别数值Lev2。First, a numerical value corresponding to 1/2 of the level value Lev is designated as the level value Lev1, and an absolute value of (Lev1×2−Lev) is designated as the level value Lev2.
在此,当级别数值Lev是一个奇数,通过把具有比该级别数值Lev大1的绝对值的一个偶数除以2所获得的数值被用作为级别数值Lev1。更加具体来说,当级别数值Lev为正数时,对应于(Lev+1)的1/2的数值被分配到级别数值Lev1,并且当级别数值Lev为负数时,对应于(Lev-1)的1/2的一个数值被分配到级别数值Lev1。Here, when the level value Lev is an odd number, a value obtained by dividing an even number having an absolute value greater than the level value Lev by 2 is used as the level value Lev1. More specifically, when the level value Lev is positive, a value corresponding to 1/2 of (Lev+1) is assigned to the level value Lev1, and when the level value Lev is negative, a value corresponding to (Lev-1) A value of 1/2 of is assigned to the level value Lev1.
然后,根据级别数值Lev和游程数值Run的组合从第一代码表(参见图42)获得对应于一对级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run的代码号Code。Then, the code number Code corresponding to a pair of the level value Lev1 and the run value Run is obtained from the first code table (see FIG. 42 ) based on the combination of the level value Lev and the run value Run.
另外,当Lev值为正数时根据下面的公式(1),以及当Lev值为负数时根据公式(2),转换对应于一对级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run的代码号Code。该第二代码表T2a示出该代码号和由上述转换所获得的游程-级别对之间的对应关系。In addition, the code number Code corresponding to a pair of level value Lev1 and run value Run is converted according to the following formula (1) when the value of Lev is positive and according to formula (2) when the value of Lev is negative. The second code table T2a shows the correspondence between the code numbers and the run-level pairs obtained by the above conversion.
2×(Code-Lev2)-l...(1)2×(Code-Lev2)-l...(1)
2×(Code-Lev2)...(2)2×(Code-Lev2)...(2)
例如,当把注意力放在图42中的代码表(第一代码表)中的一个游程-级别对(级别=-2,游程=1)上时,对应于该游程-级别对的代码号Code被从由图42中的第一代码表T1转换为由图15(a)中的第二代码表T2a所表示的“12”。For example, when paying attention to a run-level pair (level=-2, run=1) in the code table (first code table) in Fig. 42, the code number corresponding to the run-level pair Code is converted from the first code table T1 in FIG. 42 to "12" represented by the second code table T2a in FIG. 15(a).
也就是说,由于该游程-级别对(Lev,Run)这种情况中为(-2,1),则如下计算Lev1和Lev2。That is, since the run-level pair (Lev, Run) is (-2, 1) in this case, Lev1 and Lev2 are calculated as follows.
Lev1=LeV·(1/2)=-1Lev1 = LeV (1/2) = -1
Lev2=|Lev1·2-Lev1|=|-1·2-(-2)=0Lev2=|Lev1·2-Lev1|=|-1·2-(-2)=0
因此,(Lev1,Run)为(-1,1),并且根据第一代码表,该游程-级别对对应于代码号(Code=6)(参见图42)。Therefore, (Lev1, Run) is (-1, 1), and this run-level pair corresponds to a code number (Code=6) according to the first code table (see FIG. 42 ).
然后,通过采用公式(2)计算对应于该游程-级别对(Lev,Run)的代码号=(-2,1):Then, the code number = (-2, 1) corresponding to the run-level pair (Lev, Run) is calculated by using formula (2):
2×(Code-Lev2)=2×(6-0)=122×(Code-Lev2)=2×(6-0)=12
图15(a)中的代码表的特征在于较小的代码号(即,较短的代码字)被分配到这样的游程-级别对,该游程-级别对与图42中所示的代码表(第一代码表)相比由较小的游程数值和较大级别数值所构成,并且这适合于量化参数QP较小的情况。The code table in Figure 15(a) is characterized in that smaller code numbers (i.e., shorter codewords) are assigned to run-level pairs that are identical to the code table shown in Figure 42 (The first code table) is relatively composed of a smaller run value and a larger level value, and this is suitable for the case where the quantization parameter QP is small.
图15(b)示出第二代码表的另一个例子,即,适用于量化参数QP较大的情况中的第二代码表T2b。Fig. 15(b) shows another example of the second code table, that is, the second code table T2b suitable for the case where the quantization parameter QP is large.
该第二代码表T2b如下形成。This second code table T2b is formed as follows.
首先,对应于游程数值Run的1/2的数值被分配为游程数值Run1,并且(Run1×2-Run)的绝对值被分配为游程数值Run2。在此,当该游程数值为奇数时,对应于(Run+1)的1/2的数值被分配到游程数值Run1。First, a value corresponding to 1/2 of the run value Run is assigned as the run value Run1, and an absolute value of (Run1×2−Run) is assigned as the run value Run2. Here, when the run value is an odd number, a value corresponding to 1/2 of (Run+1) is assigned to the run value Run1.
然后,根据级别数值Lev和游程数值Run1的组合,从第一代码表(参见图42)获得,对应于一对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run1的代码号Code。Then, according to the combination of the level value Lev and the run value Run1, the code number Code corresponding to a pair of the level value Lev and the run value Run1 is obtained from the first code table (see FIG. 42 ).
另外,当Lev值为正数时根据下面的公式(3),以及当Lev值为负数时根据公式(4)转换对应于一对级别数值Lev和游程数值Run1的代码号Code。该第二代码表T2b示出该代码号和作为转换的结果而获得的游程-级别对之间的对应关系。In addition, the code number Code corresponding to a pair of level value Lev and run value Run1 is converted according to the following formula (3) when the value of Lev is positive, and according to formula (4) when the value of Lev is negative. The second code table T2b shows the correspondence between the code numbers and the run-level pairs obtained as a result of the conversion.
2×(Code+Run2)-1...(3)2×(Code+Run2)-1...(3)
2×(Code+Run2)-2...(4)2×(Code+Run2)-2...(4)
例如,当把注意力放在图42的代码表(第一代码表)中的一个游程-级别对(级别=-1,游程=2)时,对应于该游程-级别对的代码号Code被从由图42中的第一代码表T1所表示的“12”转换为由图15(b)中的第二代码表T2b所表示“10”。For example, when paying attention to a run-level pair (level=-1, run=2) in the code table (first code table) of FIG. 42, the code number Code corresponding to the run-level pair is Conversion from "12" represented by the first code table T1 in FIG. 42 to "10" represented by the second code table T2b in FIG. 15(b).
更加具体来说,由于在这种情况中的游程-级别对(Lev,Run)为(-1,2),因此如下计算Run1和Run2。More specifically, since the run-level pair (Lev, Run) in this case is (-1, 2), Run1 and Run2 are calculated as follows.
Run1=Run·(1/2)=1Run1=Run (1/2)=1
Run2=|Run1·2-Run|=|1·2-2|=0Run2=|Run1·2-Run|=|1·2-2|=0
因此,(Lev,Run1)为(-1,1),并且根据第一代码表,该游程-级别对对应于一个代码号(code=6)。Therefore, (Lev, Run1) is (-1, 1), and according to the first code table, the run-level pair corresponds to a code number (code=6).
然后,通过使用公式(4)计算对应于该游程-级别对(Lev,Run)=(-1,2)的一个代码号:Then, a code number corresponding to the run-level pair (Lev, Run)=(-1, 2) is calculated by using formula (4):
2×(Code+Run2)=2×(6-0)-2=102×(Code+Run2)=2×(6-0)-2=10
图15(b)中所示的第二代码表T2b的特征在于较少的代码号(即,较短代码)被分配到这样的游程-级别对,其与图42中所示的代码表(第一代码表)T1相比由较大游程数值和家小级别数值所构成,并且这适用于量化参数QP较大的情况。The second code table T2b shown in FIG. 15(b) is characterized in that fewer code numbers (i.e., shorter codes) are assigned to such run-level pairs, which is different from the code table ( The first code table) T1 is relatively composed of larger run length values and smaller level values, and this applies to the case where the quantization parameter QP is larger.
图16示出由游程长度编码单元RLE2根据第一代码表形成第二代码表的另一个例子。在此,该第一代码表与图42中所示的用于常规游程长度编码单元RLE0c中的代码表T1相同。FIG. 16 shows another example in which the second code table is formed by the run-length encoding unit RLE2 from the first code table. Here, the first code table is the same as the code table T1 used in the conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0c shown in FIG. 42 .
该数目变换器CodeTrans根据从位置计算器PosClc输出的被编码系数的数目Pos,计算在要被处理的目标块中的未编码分量的数目(还没有受到编码处理的系数的数目)。另外,从第一代码表形成的第二代码表不包括对应于包含超过未编码分量的数目的游程数值的游程-级别对的代码字。从而,能够以较高的压缩效率进行编码。The number converter CodeTrans calculates the number of uncoded components (the number of coefficients not yet subjected to encoding processing) in the target block to be processed based on the number Pos of encoded coefficients output from the position calculator PosClc. Additionally, the second code table formed from the first code table does not include codewords corresponding to run-level pairs containing run-level values exceeding the number of uncoded components. Thus, encoding can be performed with high compression efficiency.
图16(a)示出当未编码分量的数目为3或更大时所形成的第二代码表T2c。图16(b)示出当未编码分量的数目为2时形成的第二代码表T2d。图16(c)示出当未编码分量的数目1时所形成的第二代码表T2e。Fig. 16(a) shows the second code table T2c formed when the number of uncoded components is 3 or more. FIG. 16(b) shows the second code table T2d formed when the number of uncoded components is two. Fig. 16(c) shows the second code table T2e formed when the number of uncoded components is 1.
如上文所述,当在包括不会使用的游程数值的游程-级别对和代码之间的对应关系被从该代码表删除时,一个较短代码被分配到该游程-级别对。例如,根据如图16(c)中所示的第二代码表T2e,由一个游程数值[0]和一个级别数值[4]所构成的一个游程-级别对对应于一个代码号[7]。根据如图16(b)中所示的第二代码表T2b,由游程数值[0]和级别数值[4]所构成的游程-级别对对应于一个代码号[11],并且根据如图16(a)中所示的第二代码表T2c,由游程数值[0]和级别数值[4]所构成的游程-级别对对应于具有更大数值(未示出)的一个代码号。As described above, when the correspondence between a run-level pair including a run value that will not be used and a code is deleted from the code table, a shorter code is assigned to the run-level pair. For example, according to the second code table T2e as shown in FIG. 16(c), a run-level pair composed of a run value [0] and a level value [4] corresponds to a code number [7]. According to the second code table T2b shown in Figure 16 (b), the run-level pair formed by the run value [0] and the level value [4] corresponds to a code number [11], and according to Figure 16 In the second code table T2c shown in (a), a run-level pair constituted by a run value [0] and a level value [4] corresponds to a code number having a larger value (not shown).
图17示出根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103的游程长度编码单元RLE2的编码次序的一个例子。Fig. 17 shows an example of the encoding order of the run-length encoding unit RLE2 of the
通常,对应于低频分量的级别数值的绝对值较大,并且在该代码表中,具有较大数值的代码号Code对应于与低频分量相对应的游程-级别对。相反,对应于高频分量的级别数值的绝对值较小,并且在该代码表中,具有较小数值的代码表对应于与高频分量相对应的游程-级别对。Generally, the absolute value of the numerical value of the level corresponding to the low frequency component is large, and in this code table, the code number Code having the large numerical value corresponds to the run-level pair corresponding to the low frequency component. On the contrary, the absolute value of the level value corresponding to the high frequency component is small, and among the code tables, the code table with the small value corresponds to the run-level pair corresponding to the high frequency component.
如参照图16所述,通过从该代码表删除对应于包括超过未编码分量的数目的游程数值的游程-级别对的代码号(代码字)而获得的压缩效率的增量随着未编码分量的数目变小而增大,以及随着级别数值的绝对值的变大而增大,因为与没有删除代码号的情况相比,被分配的代码号的数值减小的比率变大。As described with reference to FIG. 16 , the increase in compression efficiency obtained by deleting from the code table corresponding to run-level pairs (codewords) that include run values exceeding the number of uncoded components increases with the increase in the number of uncoded components increases as the number becomes smaller, and increases as the absolute value of the level value becomes larger, because the rate at which the value of the assigned code number decreases becomes larger compared to the case where the code number is not deleted.
因此,当在由游程长度编码单元RLE2对被量化分量编码中具有级别数值的较大绝对值并且对应于低频分量的级别数值的被量化分量被较后地编码,类似于根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103,该压缩效率被进一步增加。Therefore, when the quantized component having a larger absolute value of the level value and corresponding to the level value of the low-frequency component is encoded later in the encoding of the quantized components by the run-length encoding unit RLE2, similar to that according to the third embodiment In the
更加具体来说,该重新排序单元ReOdr对被量化分量重新排序,以使其从对应于高频分量的一个被量化分量(最后的非零分量)的游程-级别对到对应于低频分量的被量化分量的游程-级别对顺序排列,如图17中的箭头X1至X7中所示,以把表示在一个目标块中的最后被编码分量的一个EOB添加在对应于具有最低频率分量的一个被量化分量的游程-级别对的代码字之后,从而增加压缩效率。More specifically, the reordering unit ReOdr reorders the quantized components so that they go from a run-level pair corresponding to a quantized component (the last non-zero component) corresponding to a high frequency component to a quantized component corresponding to a low frequency component. The run-level pairs of the quantized components are sequentially arranged as shown in arrows X1 to X7 in FIG. 17, so that an EOB representing the last coded component in a target block is added to a coded component corresponding to the one having the lowest frequency component. The codewords of the run-level pairs of quantized components are followed, thereby increasing compression efficiency.
另外,在第三实施例中,该量化参数QP和VLC选择信号VlcSel被提供到可变长度编码器LVLC、游程转换器RunConv、重新排序单元ReOdr以及数目变换器CodeTrans。因此,可以根据量化参数QP改变一个代码表,或者可以根据图像的内容(该图像的运动值、运动的复杂度或者图案的细节)从外部选择一个适当的代码表。Also, in the third embodiment, the quantization parameter QP and the VLC selection signal VlcSel are supplied to the variable length coder LVLC, the run length converter RunConv, the reordering unit ReOdr, and the number converter CodeTrans. Therefore, a code table can be changed according to the quantization parameter QP, or an appropriate code table can be externally selected according to the content of the picture (the motion value of the picture, the complexity of the motion, or the detail of the pattern).
例如,当用于该编码处理中的代码表被根据来自该图像编码装置外部的VLC选择信号VlcSel而改变时,该图像解码装置可以创建由仅仅具有一个代码表的解码单元来解码的一个数据流。For example, when the code table used in the encoding process is changed in accordance with the VLC selection signal VlcSel from outside the image encoding device, the image decoding device can create a stream decoded by a decoding unit having only one code table .
在该第三实施例中,对作为要被处理的目标数据的图像信号的被量化系数编码的该图像编码装置103包括游程长度编码单元RLE2,其使用一个代码表把可变长度代码分配到该被量化系数,并且该游程长度编码单元RLE2根据该第一代码表形成对要被处理的编码数据优化的第二代码表,并且根据量化参数QP或VLC选择信号VlcSel选择第一和第二代码表之一作为用于可变长度代码的分配的一个代码表。因此,可以有效地除去包含在目标数据中的冗余信息,从而进一步增加用于图像信号等等的压缩比。In the third embodiment, the
在该第三实施例中,游程长度编码单元RLE2包括用于增加压缩比的各种设备,即,游程转换器RunConv、级别转换器LevConv、重新排序单元ReOdr和数目变换器CodeTrans,如图14中所示。但是,该游程长度编码单元RLE2可以仅仅包含用于增加该压缩比的一些设备。在这种情况中,可以容易地安装该游程长度编码单元RLE2。In this third embodiment, the run-length encoding unit RLE2 includes various devices for increasing the compression ratio, namely, the run-length converter RunConv, the level converter LevConv, the reordering unit ReOdr, and the number converter CodeTrans, as shown in FIG. 14 shown. However, the run-length encoding unit RLE2 may only contain devices for increasing the compression ratio. In this case, the run-length encoding unit RLE2 can be easily installed.
另外,在第三实施例中,通过在构成第一代码表的部分中改变该游程-级别对和代码号之间的对应关系而获得第二代码表:可以通过算术运算(定期地构建VLC)而定期产生的部分,以及不能够定期产生的部分(表查找VLC)。但是,当该第一代码表具有可以由算术运算定期产生(定期地构建VLC)的部分以及不能够定期产生的部分(表查找VLC)时,该第二代码表可以通过仅仅改变作为可以定期地通过容易执行的运算而产生的第一代码表的部分而形成。在这种情况中,可以更加容易地执行游程长度编码单元RLE2的安装。In addition, in the third embodiment, the second code table is obtained by changing the correspondence between the run-level pair and the code number in the part constituting the first code table: it can be obtained by arithmetic operation (periodical construction of VLC) And the parts that are generated regularly, and the parts that cannot be generated regularly (table lookup VLC). However, when the first code table has a part that can be generated periodically by arithmetic operations (periodically built VLC) and a part that cannot be generated regularly (table lookup VLC), the second code table can be made periodically by only changing A portion of the first code table generated by an easily performed operation is formed. In this case, the installation of the run-length encoding unit RLE2 can be performed more easily.
根据该第三实施例,在通过使用游程-级别对执行被量化分量的可变长度编码的游程长度编码单元中,该被量化分量被从高频分量到低频分量连续地受到可变长度编码。但是,不用说,在使得对应于在该目标块中的被量化分量的游程数值和级别数值分别受到类似于第一实施例中的可变长度编码处理的游程长度编码单元中,对应于在该目标块中的被量化分量的游程数值和级别数值可以从高频分量到低频分量连续地受到可变长度编码处理。According to this third embodiment, in the run-length encoding unit that performs variable-length encoding of quantized components by using run-level pairs, the quantized components are continuously subjected to variable-length encoding from high-frequency components to low-frequency components. However, needless to say, in the run-length coding unit that subjects the run-length value and the level value corresponding to the quantized component in the target block to the variable-length coding process similar to that in the first embodiment, respectively, corresponding to the The run values and level values of the quantized components in the target block can be continuously subjected to variable length encoding processing from high frequency components to low frequency components.
[实施例4][Example 4]
图18为用于说明根据本发明第四实施例的图像解码装置的方框图。Fig. 18 is a block diagram for explaining an image decoding apparatus according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
根据第四实施例的图像解码装置104包括游程长度解码单元RLD2,其根据量化参数QP或可变长度解码选择信号(VLD选择信号)VldSel使得编码流Str2受到可变长度解码处理,并且输出解码的量化分量DQS,其取代如图40中所示的常规图像解码装置202c中的使得编码流Str0c受到可变长度解码处理并且输出解码的量化分量DQS的游程长度解码单元RLD0c。根据第四实施例的图像解码装置104的其他部分与常规图像解码装置202c中的部分相同。The
更加具体来说,该游程长度解码单元RLD2类似于常规游程长度解码单元RLD0c,具有第一代码表T1(参见图42),其根据该游程数值和级别数值的组合表示一对游程数值和级别数值(在下文中称为游程-级别对)和相应代码之间的对应关系。然后,该游程长度解码单元RLD2根据该第一代码表定期地改变在在游程-级别对和该第一代码表中的代码之间的对应关系,以形成具有不同于第一代码表的不同对应关系的第二代码表,并且根据从量化单元Q输出的量化参数QP或者来自外部的VLD选择信号VldSel选择第一和第二代码表之一,并且根据所选择的代码表,把构成该编码流Str2的代码表(位串)转换为与在要被处理的目标数据中的系数相关的游程数值和级别数值对。More specifically, this run-length decoding unit RLD2 is similar to the conventional run-length decoding unit RLDOc, and has a first code table T1 (see FIG. 42 ), which represents a pair of run-length values and level values according to combinations of the run-length values and level values (hereinafter referred to as the run-level pair) and the correspondence between the corresponding codes. Then, the run-length decoding unit RLD2 periodically changes the correspondence between the run-level pairs and the codes in the first code table according to the first code table to form different correspondences with different ones from the first code table. The second code table of the relationship, and select one of the first and second code tables according to the quantization parameter QP output from the quantization unit Q or the VLD selection signal VldSel from the outside, and according to the selected code table, compose the encoded stream The code table (bit string) of Str2 is converted into run value and level value pairs associated with coefficients in the target data to be processed.
如上文所述,该量化参数QP是表示量化步骤的数值的一个参数,并且该量化步骤近似于与量化参数QP成比例。更加具体来说,当量化参数QP较大时,该被量化分量具有较小的绝对值,然后被量化分量的零游程(其数值为零的连续分量的长度)变得更长,并且因此级别数值具有更小的绝对值。在这种情况中,相应地,选择这样一个代码表,其中较小代码被分配到由较大游程数值和较小级别数值的游程-级别对,从而进一步提高编码效率。相反,当量化参数QP较小时,该被量化分量具有绝对值,因此选择这样一个代码表,其中较小代码被分配到由较小游程数值和较大级别数值所构成的游程-级别对,从而增加编码效率。As described above, the quantization parameter QP is a parameter representing the value of the quantization step, and the quantization step is approximately proportional to the quantization parameter QP. More specifically, when the quantization parameter QP is large, the quantized component has a small absolute value, then the zero run of the quantized component (the length of a continuous component whose value is zero) becomes longer, and thus the level Numeric values have smaller absolute values. In this case, accordingly, a code table is selected in which smaller codes are assigned to run-level pairs consisting of larger run values and smaller level values, thereby further improving coding efficiency. Conversely, when the quantization parameter QP is small, the quantized component has an absolute value, so a code table is selected in which a smaller code is assigned to a run-level pair consisting of a smaller run value and a larger level value, thereby Increase coding efficiency.
图19未示出游程长度解码单元RLD2的具体结构的方框图。FIG. 19 does not show a block diagram of a specific structure of the run-length decoding unit RLD2.
该游程长度解码单元RLD2与常规游程长度解码单元RLD0c同样具有可变长度解码器VLD,并且该解码器VLD解码从根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103输出的编码流Str2,并且输出一个代码号ExtCode。This run-length decoding unit RLD2 has a variable length decoder VLD like the conventional run-length decoding unit RLD0c, and this decoder VLD decodes the encoded stream Str2 output from the
在该第四实施例中,该游程长度解码单元RLD2具有:一个数目反变换器ICodeTrans,用于执行数目反变换处理,以根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel,把代码号ExtCode分为对应于由级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run1、级别数值Lev2以及游程数值Run2所构成的游程-级别高位数字对;以及反重新排序单元IReOdr,用于把对应于要被处理的一个目标块的多个代码号PrmCode按照与游程-级别对的增加频率的次序重新排序,并且输出对应于该目标块和具有改变的次序的多个代码号Code。In the fourth embodiment, the run-length decoding unit RLD2 has: a number inverse converter ICodeTrans for performing number inverse transform processing to divide the code number ExtCode into corresponding A run-level high-digit pair formed by the level value Lev1 and the run value Run1, the level value Lev2, and the run value Run2; and an anti-reordering unit IReOdr for converting a plurality of code numbers corresponding to a target block to be processed PrmCode is reordered in order of increasing frequency of run-level pairs, and a plurality of code numbers Code corresponding to the target block and in changed order are output.
该游程长度解码单元RLD2进一步包括:游程级别检测器RunLevDec,用于根据代码表或算术运算检测对应于代码号Code的一个游程-级别对,并且输出由该游程-级别对所构成的级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run1;游程反转换器IRunConv,用于从表示游程数值Run的高位数字的游程数值Run1和表示游程数值Run的低位数字的游程数值Run2重构一个游程数值Run;以及级别反转换器ILevConv,用于从表示级别数值Lev的高位数字和级别数值Lev1和表示级别数值Lev的低位数字的级别数值Lev2重构一个级别数值Lev。The run-length decoding unit RLD2 further includes: a run-level detector RunLevDec, which is used to detect a run-level pair corresponding to the code number Code according to a code table or an arithmetic operation, and output the level value Lev1 formed by the run-level pair and the run value Run1; the run inverse converter IRunConv for reconstructing a run value Run from the run value Run1 representing the high digit of the run value Run and the run value Run2 representing the low digit of the run value Run; and the level inverse converter ILevConv , for reconstructing a level value Lev from the high digit representing the level value Lev, the level value Lev1, and the level value Lev2 representing the low digit of the level value Lev.
该游程长度解码单元RLD2与游程长度解码单元RLD0c相同进一步包括反曲折扫描仪IScan。该反曲折扫描仪IScan把由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的一维阵列的被量化分量变换为二维阵列的解码的量化分量DQS,并且输出。The run-length decoding unit RLD2 is identical to the run-length decoding unit RLDOc and further comprises an inverse scanner IScan. The inverse scanner IScan transforms the quantized components of the one-dimensional array represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run into the decoded quantized components DQS of the two-dimensional array, and outputs it.
在此,在游程长度解码单元RLD2中的可变长度解码器VLD、游程级别检测器RunLevDec和反曲折扫描仪IScan与在图41中所示的游程长度解码单元RLD0c相同。Here, the variable length decoder VLD, run level detector RunLevDec, and inverse scanner IScan in the run-length decoding unit RLD2 are the same as the run-length decoding unit RLD0c shown in FIG. 41 .
下面将描述其功能和效果。The function and effect thereof will be described below.
在游程长度解码单元RLD2中,该可变长度解码器VLD执行与可变长度编码器VLC相反的操作。也就是说,该可变长度解码器VLD解码编码流Str2,并且输出对应于构成该流的代码字(位串)的一个代码号ExtCode。该数目反变换器ICodeTrans根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel执行与数目变换器CodeTrans相反的操作,以把代码号ExtCode分为与由级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run1、级别数值Lev2和游程数值Run2所构成的游程-级别高位数字对的一个代码号PrmCode。In the run-length decoding unit RLD2, the variable length decoder VLD performs the reverse operation of the variable length coder VLC. That is, the variable length decoder VLD decodes the encoded stream Str2, and outputs a code number ExtCode corresponding to the code words (bit strings) constituting the stream. The number inverse converter ICodeTrans performs the opposite operation to the number converter CodeTrans according to the quantization parameter QP or the VLD selection signal VldSel, so as to divide the code number ExtCode into the corresponding numbers determined by the level value Lev1 and the run value Run1, the level value Lev2 and the run value Run2 A code number PrmCode of the formed run-level high digit pair.
该反重新排序单元IReOdr根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel执行与重新排序单元ReOdr相反的操作。从而,按照游程-级别对的增加频率的次序对与要被处理的目标块相对应的多个代码号PrmCode执行重新排序,并且输出具有改变的次序并且对应于该块的多个代码号Code。该游程级别检测器RunLevDec根据一个代码表或算术运算检测对应于代码号Code的游程-级别对,并且输出构成所检测的游程-级别对的级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run1。The anti-reordering unit IReOdr performs the reverse operation of the reordering unit ReOdr according to the quantization parameter QP or the VLD selection signal VldSel. Thus, reordering of the code numbers PrmCode corresponding to the target block to be processed is performed in order of increasing frequency of run-level pairs, and the code numbers Code having the changed order and corresponding to the block are output. The run level detector RunLevDec detects a run-level pair corresponding to a code number Code based on a code table or arithmetic operation, and outputs a level value Lev1 and a run value Run1 constituting the detected run-level pair.
该游程反转换器IRunConv根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel执行与游程转换器RunConv相反的操作,以从表示游程数值Run的高位数字的游程数值Run1和表示游程数值Run的多个位置的游程数值Run2重构该游程数值Run。另外,该级别反转换器ILevConv根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel执行与级别转换器LevConv相反的操作,以从表示级别数值Lev的高位数字的级别数值Lev1和表示级别数值Lev的低位数字的级别数值Lev2重构该级别数值Lev。The run length inverse converter IRunConv performs the reverse operation of the run length converter RunConv according to the quantization parameter QP or the VLD selection signal VldSel to convert from the run value Run1 representing the upper digit of the run value Run to the run values representing a plurality of positions of the run value Run Run2 reconstructs the run value Run. In addition, the level inverse converter ILevConv performs the reverse operation of the level converter LevConv according to the quantization parameter QP or the VLD selection signal VldSel to convert the level value Lev1 representing the upper digit of the level value Lev to the level of the lower digit representing the level value Lev. The value Lev2 reconstructs the value Lev of this level.
在此,在数目反变换器ICodeTrans、反重新排序单元IReOdr、游程反转换器IRunConv和级别反转换器ILevConv中,根据量化参数QP和VLD选择信号VldSel执行第一或第二代码表的选择,并且根据所选择的代码表执行该操作。Here, in the number inverse converter ICodeTrans, the inverse reordering unit IReOdr, the run-length inverse converter IRunConv and the level inverse converter ILevConv, the selection of the first or second code table is performed according to the quantization parameter QP and the VLD selection signal VldSel, and The operation is performed according to the selected code table.
反曲折扫描仪IScan执行与曲折扫描仪Scan相反的操作,以根据级别数值Lev和游程数值Run把由级别数值Lev和游程数值Run所表示的一维阵列的被量化分量变换为二维阵列的解码的量化分量DQS。The inverse scanner IScan performs the opposite operation to the zigzag scanner Scan to transform the quantized components of the one-dimensional array represented by the level value Lev and the run value Run into two-dimensional array decoding according to the level value Lev and the run value Run The quantization component DQS.
另外,当VLD选择信号VldSel被从外部输入时,该游程长度解码单元RLD2选择对应于由VLD选择信号VldSel所表示的图像内容(图像运动的数值、运动的复杂度、图案的细节)的适当代码表。In addition, when the VLD selection signal VldSel is input from the outside, the run-length decoding unit RLD2 selects an appropriate code corresponding to the image content (value of image motion, complexity of motion, detail of pattern) represented by the VLD selection signal VldSel. surface.
在该第四实施例中,量化参数QP和VLD选择信号VldSel被分别提供到数目反变换器ICodeTrans、反重新排序单元IReOdr、游程反转换器IRunConv、以及级别反转换器ILevConv。因此,一个代码表可以根据量化参数QP而改变,或者根据图像的特性,即,图像运动的数值、运动的复杂度、图案的细节等等,从该图像解码装置的外部选择一个适当的代码表。In this fourth embodiment, the quantization parameter QP and the VLD selection signal VldSel are respectively supplied to the number inverse converter ICodeTrans, the inverse reordering unit IReOdr, the run-length inverse converter IRunConv, and the level inverse converter ILevConv. Therefore, a code table can be changed according to the quantization parameter QP, or an appropriate code table can be selected from outside the picture decoding apparatus according to the characteristics of the picture, i.e., the value of the picture motion, the complexity of the motion, the detail of the pattern, etc. .
如上文所述,在该第四实施例中,对通过一个图像信号的被量化系数的可变长度编码而获得的被编码数据进行解码的图像解码装置104包括使用一个代码表用于把一个可变长度代码转换为被量化分量的游程长度解码单元RLD2。另外,该游程长度解码单元RLD2根据该第一代码表形成对要被处理的目标数据优化的第二代码表,并且根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel,选择第一和第二代码表之一作为在把可变长度代码转换为被量化系数中所采用的代码表。因此,能够满意地执行对应于可以有效地除去包含在要被处理的目标数据中的冗余信息的可变长度编码处理的解码处理。As described above, in the fourth embodiment, the image decoding means 104 for decoding encoded data obtained by variable-length encoding of quantized coefficients of an image signal includes a code table for encoding a The run-length decoding unit RLD2 converts variable-length codes into quantized components. In addition, the run-length decoding unit RLD2 forms a second code table optimized for the target data to be processed based on the first code table, and selects one of the first and second code tables based on the quantization parameter QP or the VLD selection signal VldSel As a code table used in converting variable-length codes into quantized coefficients. Therefore, decoding processing corresponding to variable-length coding processing that can efficiently remove redundant information contained in target data to be processed can be performed satisfactorily.
在该第四实施例中,如图19中所示,游程长度解码单元RLD2具有用于增加压缩比的各种设备,即,数目反变换器ICodeTrans、反重新排序单元IReOdr、游程反转换器IRunConv以及级别反转换器ILevConv,并且该游程长度解码单元RLD2可以仅仅具有这样用于增加压缩比的设备中的一些设备。在这种情况中,游程长度解码单元RLD2可以被更加容易地安装。In this fourth embodiment, as shown in FIG. 19, the run-length decoding unit RLD2 has various devices for increasing the compression ratio, namely, the number inverse transformer ICodeTrans, the inverse reordering unit IReOdr, the run-length inverse converter IRunConv and the level inverse converter ILevConv, and the run-length decoding unit RLD2 may have only some of such devices for increasing the compression ratio. In this case, the run-length decoding unit RLD2 can be installed more easily.
另外,在第四实施例中,通过在构成第一代码表的部分中改变该游程-级别对和代码号之间的对应关系而形成第二代码表:可以通过算术运算(定期地构建VLC)而定期产生的部分,以及不能够定期产生的部分(表查找VLC)。但是,当该第一代码表具有可以由算术运算定期产生(定期地构建VLC)的部分以及不能够定期产生的部分(表查找VLC)时,该第二代码表可以通过仅仅改变作为可以定期地通过容易执行的运算而产生的第一代码表的部分而形成。在这种情况中,可以更加容易地执行游程长度解码单元RLD2的安装。In addition, in the fourth embodiment, the second code table is formed by changing the correspondence between the run-level pair and the code number in the part constituting the first code table: it can be done by arithmetic operation (constructing VLC regularly) And the parts that are generated regularly, and the parts that cannot be generated regularly (table lookup VLC). However, when the first code table has a part that can be generated periodically by arithmetic operations (periodically built VLC) and a part that cannot be generated regularly (table lookup VLC), the second code table can be made periodically by only changing A portion of the first code table generated by an easily performed operation is formed. In this case, installation of the run-length decoding unit RLD2 can be performed more easily.
根据该第四实施例,在通过使用游程-级别对执行对应于被量化分量的编码数据的可变长度解码的游程长度解码单元中,从高频分量到低频分量连续地执行对应于被量化分量的编码数据的可变长度解码。但是,在使得对应于一个目标块中的被量化分量的游程数值和级别数值的被编码数据分别受到与第二实施例中相同的可变长度解码的可变长度解码单元中,对应于该目标块的被量化分量的游程数值和级别数值的被编码数据从高频分量到低频分量连续地受到可变长度解码。According to this fourth embodiment, in the run-length decoding unit that performs variable-length decoding of encoded data corresponding to quantized components by using run-level pairs, the Variable-length decoding of encoded data. However, in a variable-length decoding unit that subjects encoded data corresponding to run values and level values of quantized components in one target block to the same variable-length decoding as in the second embodiment, respectively, corresponding to the target Coded data of run values and level values of quantized components of a block are successively subjected to variable length decoding from high frequency components to low frequency components.
[实施例5][Example 5]
图20为用于说明根据本发明第五实施例的图像编码装置的方框图。Fig. 20 is a block diagram for explaining an image coding apparatus according to a fifth embodiment of the present invention.
该图像编码装置105包括取代在如图13中所示的根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103中的游程长度编码单元RLE2的游程长度编码单元RLE3,其编码一个游程-级别对以及非零分量的数目,类似于游程长度编码单元RLE2。根据第五实施例的图像编码装置105的其他部分与根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103中的部分相同。This
图21示出在图像编码装置105中的游程长度编码单元RLE3的具体结构。FIG. 21 shows a specific structure of the run-length encoding unit RLE3 in the
取代在如图14中所示的根据第三实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE2中的位置计算器PosClc,根据第五实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE3具有非零系数计算器NZcount,用于根据所输入的被量化分量计数非零分量的数目NZnum;以及位置计算器PosClc2,用于根据非零分量的计数数目NZnum和由游程计算器RunCal所计算的游程数值Run计算被编码系数的数目Pos2。Instead of the position calculator PosClc in the run-length encoding unit RLE2 according to the third embodiment as shown in FIG. 14, the run-length encoding unit RLE3 according to the fifth embodiment has a non-zero coefficient calculator NZcount for The input quantized component counts the number NZnum of non-zero components; and the position calculator PosClc2 is used to calculate the number Pos2 of encoded coefficients according to the count number NZnum of non-zero components and the run value Run calculated by the run calculator RunCal.
根据第五实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE3对来自数目变换器CodeTrans的输出(代码号)ExtCode进行编码,并且编码非零分量的数目NZnum,这与根据第三实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE2的可变长度编码器VLC不同。The run-length encoding unit RLE3 according to the fifth embodiment encodes the output (code number) ExtCode from the number converter CodeTrans, and encodes the number NZnum of non-zero components, which is different from that of the run-length encoding unit RLE2 according to the third embodiment Variable Length Coder VLC is different.
游程长度编码单元RLE3的其他部分与根据第三实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE2相同。The other parts of the run-length encoding unit RLE3 are the same as the run-length encoding unit RLE2 according to the third embodiment.
下面将描述其功能和效果。The function and effect thereof will be described below.
在根据第五实施例的图像编码装置105中的分块单元Blk、频率变换单元Trans以及量化单元Q的操作与根据第三实施例的图像编码装置103的操作相同。另外,除了根据第五实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE3中的非零系数计算器NZcount、位置计算器PosClc2、数目变换器CodeTrans以及可变长度编码器VLC2之外的其他部分的操作,即,曲折扫描仪Scan、游程计算器RunCal、级别计算器LevCal、游程转换器RunConv、级别转换器LevConv、游程级别编码器RunLevEnc以及重新排序单元ReOdr的操作与根据第三实施例的游程长度编码单元RLE2的操作相同。因此,在此将主要描述非零系数计算器NZcount、位置计算器PosClc2、数目变换器CodeTrans和可变长度编码器VLC2的操作。Operations of the blocking unit Blk, frequency transformation unit Trans, and quantization unit Q in the
当从量化单元Q输出的量化分量QS被输入到游程长度编码单元RLE3时,在游程长度编码单元RLE3中的非零系数计算器NZcount根据量化分量QS计数对应于各个块的多个被量化分量,并且把所获得的非零分量的数目NZnum输出到位置计算器PosClc2和可变长度编码器VLC2。When the quantized component QS output from the quantization unit Q is input to the run-length encoding unit RLE3, the non-zero coefficient calculator NZcount in the run-length encoding unit RLE3 counts a plurality of quantized components corresponding to respective blocks according to the quantized component QS, And the obtained number NZnum of non-zero components is output to the position calculator PosClc2 and the variable length coder VLC2.
该位置计算器PosClc2根据来自非零系数计算器NZcount的非零分量的数目NZnum和来自游程计算器RunCal的游程数值Run,计算在一个目标块中的被编码的零分量的数目和非零分量的数目之和,并且输出所获得的数值Pos2。The position calculator PosClc2 calculates the number of coded zero components and the number of nonzero components in a target block based on the number NZnum of nonzero components from the nonzero coefficient calculator NZcount and the run value Run from the run calculator RunCal. and output the obtained value Pos2.
该数目变换器CodeTrans根据游程-级别高位数字对和代码号ReOdrCode之间的对应关系,输出对应于来自级别数值Lev2和游程数值Run2的代码号ExtCode。在此时,该数目变换器CodeTrans采用从位置计算器PosClc2输出的所计算数值Pos2,以获得在该目标块中的未编码分量的数目。The number converter CodeTrans outputs the code number ExtCode corresponding to the level value Lev2 and the run value Run2 according to the correspondence between the runlength-level upper digit pair and the code number ReOdrCode. At this time, the number converter CodeTrans uses the calculated value Pos2 output from the position calculator PosClc2 to obtain the number of uncoded components in the target block.
在此,根据具有不同于第一代码表的在游程-级别对和代码号之间的对应关系的第二代码表获得从数目变换器CodeTrans输出的对应于一个游程-级别对的代码号ExtCode。该第二代码表如下形成:首先通过在重新排序单元ReOdr中的重新排序处理形成具有与第一代码表不同在游程-级别对和代码号之间的对应关系的一个代码表,然后通过根据所计算数值Pos2由数目变换器CodeTrans改变由重新排序单元ReOdr所形成的代码表,使得具有大于在该代码表中的最大游程数值Run的游程数值的游程-级别对对应于不被分配代码的代码号ExtCode。Here, the code number ExtCode corresponding to a run-level pair output from the number converter CodeTrans is obtained from a second code table having a different correspondence between run-level pairs and code numbers than the first code table. The second code table is formed by first forming a code table having a different correspondence between run-level pairs and code numbers from the first code table by reordering processing in the reordering unit ReOdr, and then by The calculation value Pos2 is changed by the number converter CodeTrans to the code table formed by the reordering unit ReOdr so that the run-level pairs having a run value greater than the maximum run value Run in this code table correspond to code numbers that are not assigned a code ExtCode.
该可变长度编码器VLC2对非零分量的数目NZnum编码,并且执行对代码号ExtCode的编码,以把一个位串(代码字)分配到代码号ExtCode,以产生一个编码流Str3。The variable length coder VLC2 codes the number NZnum of non-zero components, and performs coding of the code number ExtCode to assign a bit string (code word) to the code number ExtCode to generate a coded stream Str3.
在下文中,将具体描述可变长度编码器VLC2的操作。Hereinafter, the operation of the variable length coder VLC2 will be specifically described.
与根据第三实施例的可变长度编码器VLC不同,根据第五实施例的可变长度编码器VLC2不但编码对应于一个目标块的游程-级别对的代码号ExtCode,而且在编码该块的代码号ExtCode之前还编码在该目标块中的非零分量的数目NZnum。Unlike the variable length coder VLC according to the third embodiment, the variable length coder VLC2 according to the fifth embodiment not only codes the code number ExtCode corresponding to a run-level pair of a target block, but also codes The code number ExtCode is also coded the number NZnum of non-zero components in the target block.
如上文所述,当在编码一个块的代码号ExtCode之前编码非零分量的数目NZnum时,首先可以在解码时对该目标块的非零分量的数目NZnum进行解码,并且当已经重构对应于非零分量的数目NZnum的游程-级别对时,检查在该目标块中的最后游程-级别对的重构是否已经完成。从而,该可变长度编码器VLC2不需要由根据第三实施例的可变长度编码器VLC所需的在该目标块结束时编码的一个特定数值EOB(在最后的非零分量之后发送的一个数值)。As described above, when encoding the number NZnum of non-zero components before encoding the code number ExtCode of a block, the number NZnum of non-zero components of the target block can first be decoded at the time of decoding, and when the number of non-zero components NZnum corresponding to When the number of run-level pairs NZnum of non-zero components, check whether the reconstruction of the last run-level pair in the target block has been completed. Thus, the variable length coder VLC2 does not need a specific value EOB encoded at the end of the target block (a value sent after the last non-zero component) required by the variable length coder VLC according to the third embodiment value).
接着,将具体描述位置计算器PosClc2和数目变换器CodeTrans的操作。Next, the operations of the position calculator PosClc2 and the number converter CodeTrans will be specifically described.
假设一个目标块包括NBlock量化参数QP(包括零分量和非零分量),根据在该目标块中的非零分量的数目NZnum,最大游程长度(连续零系数的最大数目)为(NBlock-NZnum)。另外,当第一游程-级别对的编码已经完成时的最大游程数值(连续零系数的最大数目)MaxRun(1)由下述公式(5)使用该目标块的第一游程-级别对的游程数值FRun来表示。Assuming that a target block includes NBlock quantization parameters QP (including zero components and non-zero components), according to the number NZnum of non-zero components in the target block, the maximum run length (the maximum number of consecutive zero coefficients) is (NBlock-NZnum) . In addition, the maximum run value (maximum number of consecutive zero coefficients) MaxRun(1) when encoding of the first run-level pair has been completed uses the run length of the first run-level pair of the target block by the following formula (5) Value FRun to represent.
MaxRun(1)=NBlock-NZnum-FRun...(5)MaxRun(1)=NBlock-NZnum-FRun...(5)
通常,在一个块中的第i个游程-级别对的编码已经完成时的最大游程数值MaxRun(i)由下述公式(6)来表示。In general, the maximum run value MaxRun(i) when encoding of the i-th run-level pair in one block has been completed is represented by the following formula (6).
MaxRun(i)=NBlock-NZnum-{第一~第i游程数值之和}...(6)MaxRun(i)=NBlock-NZnum-{the sum of the values of the first to i-th runs}...(6)
因此,位置计算器PosClc2输出由下列公式(7)所表示的所计算数值Pos2,从而向数目变换器CodeTrans表明该最大游程数值MaxRun(i)是由公式(8)所表示的一个数值。Therefore, the position calculator PosClc2 outputs the calculated value Pos2 expressed by the following formula (7), thereby indicating to the number converter CodeTrans that the maximum run value MaxRun(i) is a value expressed by the formula (8).
Pos2=NZnum+{第一~第i游程数值之和}...(7)Pos2=NZnum+{the sum of the values of the first to i-th runs}...(7)
MaxRun(i)=NBlock-Pos2...(8)MaxRun(i)=NBlock-Pos2...(8)
该数目变换器CodeTrans形成第二代码表,其中不被分配代码的代码号ExtCode对应于具有大于最大游程数值MaxRun的游程数值。从而,消除由于把代码分配到不会出现的游程-级别对的编码处理中的冗余,从而增加压缩比。The number converter CodeTrans forms a second code table in which the code numbers ExtCode to which no code is assigned correspond to run values having a value greater than the maximum run value MaxRun. Thus, redundancy in the encoding process due to allocating codes to run-level pairs that do not occur is eliminated, thereby increasing the compression ratio.
当由通过算术运算所产生的第一部分(定期地构建VLC)和不能够由算术运算所产生的第二部分(表查找VLC)所构成的一个可变长度代码表被用作为对被量化分量执行可变长度编码处理的第一和第二代码表时,可以通过根据最大游程数值改变在第一代码表中的第一和第二部分而形成该第二代码表,或者通过仅仅改变可以根据最大游程数值容易执行的算术运算所产生的第一代码表中的第一部分而形成第二代码表。When a variable-length code table consisting of a first part (periodically constructed VLC) generated by arithmetic operations and a second part (table lookup VLC) that cannot be generated by arithmetic operations is used as the When the first and second code tables of the variable length coding process are processed, the second code table can be formed by changing the first and second parts in the first code table according to the maximum run value, or by only changing the code table according to the maximum The first portion of the first code table generated by the arithmetic operation performed on the run-length values easily forms the second code table.
另外,当根据在已经完成第i个游程-级别对的编码时的最大游程数值MaxRun(i)改变可变长度代码表时,不是把该代码表改变为没有把代码被分配到具有大于最大游程数值MaxRun(i)的游程数值Run的游程-级别对的代码表,可以把一个可变长度代码表直接改变为不把代码分配给具有大于最大游程数值MaxRun(i)的游程数值Run的游程-级别对的代码表。In addition, when the variable-length code table is changed according to the maximum run value MaxRun(i) when the encoding of the i-th run-level pair has been completed, the code table is not changed so that codes are not assigned to codes having a value greater than the maximum run length. A code table of run-level pairs for a run value of MaxRun(i) can directly change a variable-length code table to not assign codes to a run of run value Run having a value greater than the maximum run value MaxRun(i)- Code table for level pairs.
图24为示出可变长度代码表的例子。与代码表Tb(图24(b))相比,在一个代码表Ta中(图24(a)),较短代码被分配到较小的游程数值。与代码表Tc(图24(c))相比,在该代码表Tb(图24(b))中,较短的代码被分配到较小的游程数值。Fig. 24 is a diagram showing an example of a variable-length code table. In a code table Ta (FIG. 24(a)), shorter codes are assigned smaller run values compared to the code table Tb (FIG. 24(b)). In this code table Tb (FIG. 24(b)), shorter codes are assigned smaller run values than in the code table Tc (FIG. 24(c)).
另外,与代码表Tb(图24(b))相比,在该代码表Tc(图24(c))中,较短代码被分配到具有较小绝对值的级别数值。与代码表Ta(图24(a))相比,在该代码表Tb中,较短代码被分配到具有较小绝对值的级别数值。In addition, in this code table Tc (FIG. 24(c)), shorter codes are assigned to class values with smaller absolute values than in the code table Tb (FIG. 24(b)). In this code table Tb, shorter codes are assigned to class values with smaller absolute values than in the code table Ta (FIG. 24(a)).
因此,当最大游程数值MaxRun较小时,最好选择在图24(a)中的代码表,当最大游程数值MaxRun较大时,选择在图24(c)中的代码表Tc,以及当最大游程数值MaxRun为一个中间值时,选择在图24(b)中的代码表Tb。Therefore, when the maximum run value MaxRun is small, it is better to select the code table in Fig. 24(a), when the maximum run value MaxRun is large, select the code table Tc in Fig. 24(c), and when the maximum run value MaxRun When the value MaxRun is an intermediate value, the code table Tb in Fig. 24(b) is selected.
根据第五实施例,编码通过量化图像信号的频率分量而获得的被量化系数的图像编码装置105具有游程长度编码单元RLE3,其使用一个代码表把可变长度代码分配给该被量化分量。然后,该游程长度编码单元RLE3根据在要被编码的目标块中的被处理系数(被编码系数)的数目和在该目标块中的未编码非零系数的数目之和,换句话说是在该目标块中的非零系数的数目和在该目标块中的已处理游程数值的数目之和,选择删除不会出现的游程-级别对的一个代码表,从而增加可变长度编码效率。According to the fifth embodiment, an
根据该第五实施例,在通过使用游程-级别对执行对应于每个块的被量化分量的可变长度编码的游程长度编码单元中,在一个目标块中的非零分量的数目NZnum被编码。但是,可以在分别执行对应于每个块的被量化分量的游程数值和级别数值的可变长度编码的游程长度编码单元中,执行对一个目标块的非零分量的非零分量的数目NZnum的编码,这与第一实施例相同。这种情况中,在该目标块中的最大游程数值可以被设置在通过从该目标块中的所有分量的数目减去非零分量的数目NZnum而获得的数值。According to this fifth embodiment, in the run-length coding unit that performs variable-length coding of quantized components corresponding to each block by using run-level pairs, the number NZnum of non-zero components in one target block is coded . However, the calculation of the number of non-zero components NZnum of non-zero components of one target block may be performed in a run-length coding unit that performs variable-length coding of a run value and a level value of quantized components corresponding to each block, respectively. Encoding, which is the same as the first embodiment. In this case, the maximum run value in the target block may be set at a value obtained by subtracting the number NZnum of non-zero components from the number of all components in the target block.
[实施例6][Example 6]
图22为用于说明根据本发明第六实施例的图像解码装置的方框图。Fig. 22 is a block diagram for explaining an image decoding apparatus according to a sixth embodiment of the present invention.
取代根据如图18中所示的第四实施例的图像解码装置104中的游程长度解码单元RLD2,根据第六实施例的图像解码装置106具有游程长度解码单元RLD3,其与游程长度解码单元RLD2相同执行对被编码数据的解码处理,以重构在每个块中的游程-级别对的数目和非零分量的数目。根据第六实施例的图像解码装置106的其他部分与根据第四实施例的图像解码装置104的部分相同。Instead of the run-length decoding unit RLD2 in the
图23示出在图像解码装置106中的游程长度解码单元RLD3的具体结构。FIG. 23 shows a specific structure of the run-length decoding unit RLD3 in the
取代在根据如图19中所示的游程长度解码单元RLD2中的位置计算器PosClc,该第六实施例的游程长度解码单元RLD3包括一个位置计算器PosClc2,用于计算在要被解码的一个目标块中的解码的游程数值的数目和在该目标块中的非零分量的数目NZnum。Instead of the position calculator PosClc in the run-length decoding unit RLD2 according to FIG. 19, the run-length decoding unit RLD3 of the sixth embodiment includes a position calculator PosClc2 for calculating The number of decoded run values in the block and the number of non-zero components NZnum in the target block.
另外,根据第六实施例的游程长度解码单元RLD3的可变长度解码器VLD2不同于根据第四实施例的游程长度解码单元RLD2中的可变长度解码器VLD之处在于执行用于重构代码号ExtCode的解码处理和用于重构非零分量的数目NZnum的解码处理。In addition, the variable length decoder VLD2 of the run-length decoding unit RLD3 according to the sixth embodiment differs from the variable length decoder VLD in the run-length decoding unit RLD2 according to the fourth embodiment in that a code for reconstructing The decoding process for the number ExtCode and the decoding process for reconstructing the number NZnum of non-zero components.
下面将描述其功能和效果。The function and effect thereof will be described below.
在根据第六实施例的图像解码装置106中的反量化单元IQ、反频率变换单元ITrans和解块单元DeBlk的操作与第四实施例的图像解码装置104相同。另外,除了可变长度解码器VLD2、位置计算器PosClc2和数目反变换器ICodeTrans,根据第六实施例的游程长度解码单元RLD3的其他部分的操作,即,反重新排序单元IReOdr、游程级别检测器RunLevDec、级别反转换器ILevConv、游程反转换器IRunConv和反曲折扫描仪IScan的操作与根据第四实施例的游程长度解码单元RLD2相同。因此,在下文中主要描述可变长度解码器VLD2、位置计算器PosClc2和数目反变换器ICodeTrans的操作。The operations of the inverse quantization unit IQ, the inverse frequency transformation unit ITrans, and the deblocking unit DeBlk in the
该可变长度解码器VLD2解码编码流Str3,并且输出对应于由被编码流所构成的一个代码字(位串)的一个代码号ExtCode。该数目反变换器ICodeTrans根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel、以及被解码系数的数目和未解码的非零系数的数目之和Pos2,执行与数目变换器CodeTrans相反的操作,以把代码号ExtCode分为对应于包括级别数值Lev1和游程数值Run1的游程-级别高位数字对的代码号PrmCode、级别数值Lev2和游程数值Run2。The variable length decoder VLD2 decodes the coded stream Str3, and outputs a code number ExtCode corresponding to a code word (bit string) constituted by the coded stream. According to the quantization parameter QP or VLD selection signal VldSel and the sum Pos2 of the number of decoded coefficients and the number of undecoded non-zero coefficients, the number inverse converter ICodeTrans performs the reverse operation of the number converter CodeTrans to convert the code number ExtCode Divided into a code number PrmCode corresponding to a run-level high digit pair including a level value Lev1 and a run value Run1, a level value Lev2, and a run value Run2.
该反重新排序单元IReOdr、游程级别检测器RunLevDec、游程反转换器IRunConv、级别反转换器ILevConv以及反曲折扫描仪IScan执行与第四实施例相同的操作。The anti-reordering unit IReOdr, run-length level detector RunLevDec, run-length inverse converter IRunConv, level inverse converter ILevConv, and inverse zigzag scanner IScan perform the same operations as those of the fourth embodiment.
在此,数目反变换器ICodeTrans、反重新排序单元IReOdr、游程反转换器IRunConv以及级别反转换器ILevConv根据量化参数QP或VLD选择信号VldSel和系数和Pos2中的至少一个选择第一和第二代码表之一,并且根据所选择的代码表执行操作。Here, the number inverse converter ICodeTrans, the inverse reordering unit IReOdr, the run-length inverse converter IRunConv, and the level inverse converter ILevConv select the first and second codes according to at least one of the quantization parameter QP or the VLD selection signal VldSel and coefficients and Pos2 one of the tables and perform operations according to the selected code table.
在下文中,将具体描述可变长度解码器VLD2的操作。Hereinafter, the operation of the variable length decoder VLD2 will be specifically described.
根据第六实施例的可变长度解码器VLD2不同于根据第四实施例的可变长度解码器VLD之处在于它不但解码对应于一个游程-级别对的代码号ExtCode,而且还解码在该目标块中的非零分量的被编码数目NZnum。当在第NZnum个游程-级别对已经被解码的情况下通过解码获得非零分量的数目NZnum时,该第NZnum个游程-级别对被判断为最后的游程-级别对。从而,可变长度解码器VLD2不需要一个数值EOB,该数值是可变长度解码器VLD所需的,并且在该目标块结束时被编码。The variable length decoder VLD2 according to the sixth embodiment is different from the variable length decoder VLD according to the fourth embodiment in that it not only decodes the code number ExtCode corresponding to a run-level pair, but also Coded number NZnum of non-zero components in the block. When the number NZnum of non-zero components is obtained by decoding with the NZnum-th run-level pair already decoded, the NZnum-th run-level pair is judged to be the last run-level pair. Thus, the variable length decoder VLD2 does not need a value EOB, which is required by the variable length decoder VLD and is coded at the end of the target block.
例如,假设在该目标块中存在NBlock量化分量QS,包括零分量和非零分量,则根据在该目标块中的非零分量的数目NZnum,最大游程数值(连续零系数的最大数目)为(NBlock-NZnum)。另外,当用于重构第一游程-级别对的解码已经完成时的最大游程数值(连续零系数的最大数目)MaxRun(1)为如在第五实施例中所述的(NBlock-NZnum-FRun)。For example, assuming that there are NBlock quantized components QS in the target block, including zero components and non-zero components, then according to the number NZnum of non-zero components in the target block, the maximum run value (the maximum number of consecutive zero coefficients) is ( NBlock-NZnum). In addition, the maximum run value (maximum number of consecutive zero coefficients) MaxRun(1) when decoding for reconstructing the first run-level pair has been completed is (NBlock-NZnum- FRun).
通常,在已经执行用于重构在一个块中的第i个游程-级别对的解码时,最大游程数值MaxRun(i)如下获得:In general, when the decoding for reconstructing the ith run-level pair in a block has been performed, the maximum run value MaxRun(i) is obtained as follows:
MaxRun(i)=Nblock-Nznum-{第1~第i个游程数值之和}MaxRun(i)=Nblock-Nznum-{the sum of the 1st~ith run values}
因此,位置计算器PosClc2输出系数之和Pos2[=NZnum+{第1~第i游程数值之和}],从而向数目变换器CodeTrans表明在已经执行用于重构第i个游程-级别对的解码时已经执行的最大游程数值为(NBlock-Pos2)。Therefore, the position calculator PosClc2 outputs the sum of coefficients Pos2[=NZnum+{the sum of the 1st to i-th run values}], thereby indicating to the number converter CodeTrans that after decoding for reconstructing the i-th run-level pair has been performed The maximum number of runs that have been executed at this time is (NBlock-Pos2).
该数目反变换器ICodeTrans采用这样一个代码表,其中没有代码被分配到对应于由大于最大游程数值Run的游程数值所构成的游程-级别对的代码号,以获得对应于一个代码的代码号ExtCode,从而根据避免把代码分配到不会出现的游程-级别对的代码分配而解码分配到一个代码号的代码。The number inverse converter ICodeTrans uses a code table in which no code is assigned to a code number corresponding to a run-level pair formed by a run value greater than the maximum run value Run, to obtain a code number ExtCode corresponding to a code , thereby decoding a code assigned to a code number based on a code assignment that avoids assigning a code to a run-level pair that would not occur.
在此,当由可以通过算术运算而产生的第一部分(定期地构建VLC)和不能够定期产生的第二部分(表查找VLC)所构成的一个可变长度代码表被用作为在可变长度解码处理中的第一和第二代码表时,该第二代码表可以通过根据最大游程数值改变在第一代码表中的第一和第二部分而形成,并且第二代码表可以通过根据最大游程数值仅仅改变可以由容易执行的算术运算所产生的第一代码表的第一部分而形成。Here, when a variable-length code table composed of a first part that can be generated by an arithmetic operation (periodic construction VLC) and a second part that cannot be generated regularly (table lookup VLC) is used as a variable-length When decoding the first and second code tables in the process, the second code table may be formed by changing the first and second parts in the first code table according to the maximum run value, and the second code table may be formed by changing the first code table according to the maximum run value The run values are formed only by changing the first part of the first code table which can be generated by easily performed arithmetic operations.
另外,当在已经完成用于重构第i个游程-级别对的解码的情况下根据最大游程数值MaxRun改变可变长度代码表时,该可变长度代码表可以被直接改变为图24(a)中的代码表Ta、图24(b)中的代码表Tb或者图24(c)中的代码表Tc,取代把该代码表改变为不把代码分配到包含大于最大游程数值MaxRun的游程数值的游程-级别对的代码表的情况。In addition, when the variable-length code table is changed according to the maximum run value MaxRun when the decoding for reconstructing the ith run-level pair has been completed, the variable-length code table can be directly changed as shown in FIG. 24(a ), the code table Tb in FIG. 24(b), or the code table Tc in FIG. 24(c), instead of changing the code table to not assign codes to run values containing values greater than the maximum run value MaxRun The case of the code table for run-level pairs.
例如,当最大游程数值MaxRun较小时最好选择图24(a)中的代码表Ta,当最大游程数值MaxRun较大时最好选择图24(c)中的代码表Tc,以及当最大游程数值MaxRun为中间数值时最好选择图24(b)中的代码表Tb。For example, when the maximum run value MaxRun is small, it is better to select the code table Ta in Fig. 24(a), when the maximum run value MaxRun is large, it is better to select the code table Tc in Fig. 24(c), and when the maximum run value MaxRun When MaxRun is an intermediate value, it is better to choose the code table Tb in Fig. 24(b).
如上文所述,根据第六实施例,通过对被编码数据的解码处理重构量化图像信号的频率分量所获得的被量化系数的图像解码装置106被提供游程长度解码单元RLD3,用于通过采用一个代码表获得对应于一个可变长度的被量化系数。然后,该游程长度解码单元RLD3根据在一个目标块中的被处理的系数(被解码系数)数目和在该目标块中的未解码的非零系数的数目之和,选择不包含不会出现的游程-级别对的一个代码表。因此,可以满意地执行对应于能够根据有效地除去包含在要被处理的被量化系数中的冗余信息的可变长度编码处理的解码处理。As described above, according to the sixth embodiment, the
根据该第六实施例,在通过使用游程-级别对执行对每个块的被量化分量的可变长度解码的可变长度解码单元中,在一个目标块中的非零分量的数目NZnum被解码。但是,例如,在使得对应于每个块的被量化分量的游程数值和级别数值分别受到与第二实施例相同的可变长度解码处理的可变长度解码单元中,该目标块的非零分量的数目NZnum被解码。在这种情况中,在NZnum级别数值已经被解码时,可以判断第NZnum个级别数值是在该目标块中的最后级别数值。According to this sixth embodiment, in a variable length decoding unit that performs variable length decoding of quantized components of each block by using run-level pairs, the number NZnum of nonzero components in one target block is decoded . However, for example, in a variable-length decoding unit that subjects the run length value and the level value of the quantized component corresponding to each block to the same variable-length decoding process as in the second embodiment, respectively, the non-zero component of the target block The number NZnum to be decoded. In this case, when the NZnum class value has been decoded, it can be judged that the NZnum-th class value is the last class value in the target block.
在上述任何实施例中,该代码表被根据量化参数QP而改变,并且该代码表可以根据另一个参数而改变。例如,可以对每个块新推导和明确地切换另一个参数。In any of the above embodiments, the code table is changed according to the quantization parameter QP, and the code table may be changed according to another parameter. For example, another parameter can be newly derived and explicitly switched for each block.
在上述实施例中,作为用于使得例如被量化分量这样的系数受到可变长度编码(解码)处理的方法,示出一种方法,其中采用一个VLC表,并且根据至少关于已经受到编码(解码)处理的已处理系数,或者与该系数的产生相关的参数改变该VLC表。但是,根据本发明用于例如被量化分量这样的可变长度编码(解码)系数的方法不限于使用VLC表的方法。例如,用于对在第一、第三和第五实施例中所述的量化分量进行可变长度编码的方法可以是一种不采用VLC表的可变长度编码方法,并且根据关于已处理系数或者与该系数的产生相关的参数的信息中的至少一个信息改变对应于VLC表的一个代码表。另外,根据任何第二、第四和第六实施例对与被量化分量相应的被编码数据的可变长度解码方法可以是一种不采用VLC表的可变长度解码方法,并且根据关于被处理的系数或者与系数的产生相关的参数的信息中的至少一个信息,改变对应于VLC表的代码表。In the above-described embodiments, as a method for subjecting coefficients such as quantized components to variable-length coding (decoding) processing, a method is shown in which a VLC table is used, and based on at least about ) processed coefficients, or parameters related to the generation of the coefficients change the VLC table. However, the method for variable length encoded (decoded) coefficients such as quantized components according to the present invention is not limited to the method using a VLC table. For example, the method for variable-length coding the quantized components described in the first, third, and fifth embodiments may be a variable-length coding method that does not use a VLC table, and based on Or at least one of the information of the parameters related to the generation of the coefficient is changed to correspond to a code table of the VLC table. Also, the variable length decoding method for encoded data corresponding to quantized components according to any of the second, fourth and sixth embodiments may be a variable length decoding method that does not use a VLC table, and is based on At least one of the information of the coefficient or the parameter information related to the generation of the coefficient is changed, and the code table corresponding to the VLC table is changed.
根据上述实施例执行可变长度编码处理的图像编码装置或执行可变长度解码处理的图像解码装置由硬件实现,而这些装置可以由软件实现。在这种情况中,当执行根据任何上述实施例的可变长度编码或解码处理的程序被记录在例如软盘这样的数据存储介质中时,可以容易地在一个独立计算机系统中实现根据任何上述实施例的图像编码装置或图像解码装置。The image encoding device that performs variable-length encoding processing or the image decoding device that performs variable-length decoding processing according to the above-described embodiments is realized by hardware, and these devices may be realized by software. In this case, when a program for executing variable-length encoding or decoding processing according to any of the above-mentioned embodiments is recorded in a data storage medium such as a floppy disk, it is possible to easily implement the program according to any of the above-mentioned embodiments in an independent computer system. An example image coding device or image decoding device.
图25为用于说明执行根据第一、第三或第五实施例的可变长度编码处理,或者根据第二、第四或第六实施例的可变长度解码处理的计算机系统的示意图。25 is a schematic diagram for explaining a computer system that executes variable-length encoding processing according to the first, third, or fifth embodiment, or variable-length decoding processing according to the second, fourth, or sixth embodiment.
图25(a)示出作为包含用于该计算机系统中的程序的一种介质的软盘FD的正视图、截面视图、以及软盘体D。图25(b)示出软盘体D的物理格式的例子。FIG. 25(a) shows a front view, a sectional view, and a floppy disk body D of a floppy disk FD as a medium containing programs used in the computer system. FIG. 25(b) shows an example of the physical format of the floppy disk body D. As shown in FIG.
该软盘FD包括软盘体D和包含该软盘体D的壳体FC。在软盘体D的表面上,从该盘的外周到内周同心地形成多个记录道Tr。每个记录道在角度方向上被分为16扇区Se。因此,在包含上述程序、用于执行可变长度编码处理或可变长度解码处理的程序的数据的软盘FD被记录在软盘体D上的被分配存储区(扇区)中。The floppy disk FD includes a floppy disk body D and a case FC containing the floppy disk body D. As shown in FIG. On the surface of the floppy disk body D, a plurality of recording tracks Tr are concentrically formed from the outer periphery to the inner periphery of the disk. Each track is divided into 16 sectors Se in the angular direction. Therefore, data on the floppy disk FD containing the above-mentioned programs, programs for executing variable-length encoding processing or variable-length decoding processing is recorded in allocated memory areas (sectors) on the floppy disk body D.
图25(c)示出用于在软盘FD上记录或再现的结构。当程序记录在软盘FD上时,程序的数据被从计算机系统Cs通过软盘驱动器FDD写入到软盘FD中。当通过记录在软盘FD中的程序在计算机系统Cs中构造上述图像编码装置或图像解码装置时,通过软盘驱动器FDD从软盘FD中读取该程序,然后装载到计算机系统Cs。Fig. 25(c) shows a structure for recording or reproducing on a floppy disk FD. When the program is recorded on the floppy disk FD, the data of the program is written from the computer system Cs into the floppy disk FD through the floppy disk drive FDD. When the above image encoding device or image decoding device is constructed in the computer system Cs by a program recorded in the floppy disk FD, the program is read from the floppy disk FD through the floppy disk drive FDD and then loaded into the computer system Cs.
尽管在上述描述中,软盘被用作为包含用于执行可变长度编码处理或可变长度解码处理的存储介质,但是光盘也可以用作为该存储介质。并且在这种情况中,可以通过软件,按照类似于使用软盘的情况执行可变长度编码处理或可变长度解码处理。该存储介质不限于这些盘,并且任何介质可以被采用,只要它们可以包含该程序即可,例如,CD-ROM、存储卡或ROM。并且当采用这种数据存储介质时,可以由计算机系统按照与使用软盘的情况相同的方式执行可变长度编码处理或可变长度解码处理。Although in the above description, a floppy disk is used as a storage medium containing a variable-length encoding process or a variable-length decoding process, an optical disc may also be used as the storage medium. Also in this case, variable length encoding processing or variable length decoding processing can be performed by software similarly to the case of using a floppy disk. The storage medium is not limited to these discs, and any media may be employed as long as they can contain the program, for example, CD-ROM, memory card, or ROM. And when such a data storage medium is employed, variable length encoding processing or variable length decoding processing can be performed by a computer system in the same manner as the case of using a floppy disk.
根据任何上述实施例的图像编码方法或图像解码方法以及使用该方法的系统将在下文中描述。An image encoding method or an image decoding method according to any of the above embodiments and a system using the same will be described below.
图26为示出执行内容发布服务的一个内容提供系统1100的整体结构的方框图。FIG. 26 is a block diagram showing the overall structure of a
一个通信服务提供区域被分为所需尺寸的区域(小区),并且分别作为固定无线电台的基站1107至1110被建立在各个小区中,A communication service providing area is divided into areas (cells) of a required size, and
在该内容提供系统1100中,例如计算机1111、PDA(个人数字助理)1112、相机1113、便携式电话1114和具有摄像头的便携式电话1200例如被通过互联网服务提供商1102、电话网络1104和基站1107至1110连接到互联网1101。In this
但是,内容提供系统1100不限于包含所有图26中所示的多个设备的系统,而且可以是包含图26中所示的多个设备中的一些设备的系统。另外,各个设备可以直接连接到电话网络1104,而不通过作为固定无线电台的基站1107至1110。However, the
该相机1113是可以拍摄一个物体的运动图像的设备,例如数字摄像机。该便携式电话可以是根据任何PDC(个人数字通信)系统、CDMA(码分多址)系统、W-CDMA(宽带-码分多址)系统以及GSM(全球数字移动电话)系统或PHS(个人手持电话系统)的便携式电话机。The camera 1113 is a device that can take a moving image of an object, such as a digital video camera. The portable phone may be based on any PDC (Personal Digital Communications) system, CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) system, W-CDMA (Wideband-Code Division Multiple Access) system and GSM (Global Digital Mobile Phone) system or PHS (Personal Handheld telephone system) portable telephones.
一个流服务器1103通过基站1109和电话网络1104连接到相机1113。在该系统中,可以执行根据由使用相机1113的用户发送的被编码数据的实时发布。用于所拍摄图像的数据的编码处理可以由相机1113或发送数据的服务器所执行。通过相机1116拍摄一个物体的运动图像而获得的运动图像数据可以被通过计算机1111发送到流服务器1103。该相机1116是可以拍摄一个物体的静止图像或运动图像的设备,例如数字相机。在这种情况中,可以通过相机1116或计算机1111执行运动图像数据的编码。另外,通过包含在计算机1111或相机1116中的LSI1117执行该编码处理。A streaming server 1103 is connected to the camera 1113 through the
图像编码或解码软件可以存储在作为包含可以由计算机1111等等所读取的一个存储介质中(CD-ROM、软盘、硬盘等等)。该运动图像数据可以通过具有摄像头的便携式电话1200而发送。该运动图像数据是已经被包含在便携式电话1200中的LSI所编码的数据。The image encoding or decoding software can be stored as a storage medium (CD-ROM, floppy disk, hard disk, etc.) that can be read by the computer 1111 or the like. This video data can be transmitted through the
在该内容提供系统1100中,对应于由用户通过相机1113或相机1116所拍摄的图像的内容(例如,音乐会的实况录像)被按照与任何上述实施例相同的方式在该相机中编码,并且从该相机发送到流服务器1103。该内容数据受到从流服务器1103到请求客户机的流发布。In the
该客户机可以是任何可以解码该被编码数据的计算机1111、PDA1112、相机1113、便携式电话1114等等。The client can be any computer 1111,
在该内容提供系统1100中,该编码数据被在客户机侧接收和再现。当该数据被在客户机侧上实时地接收、解码和再现时,可以实现私人广播。In the
可以使用根据上述实施例的图像编码装置或图像解码装置执行在构成该系统的各个设备中的编码或解码。Encoding or decoding in each device constituting the system can be performed using the image encoding device or the image decoding device according to the above-described embodiments.
下面将描述作为图像编码或解码装置的一个例子的便携式电话。A portable telephone as an example of an image encoding or decoding device will be described below.
图27为示出采用根据任何上述实施例的图像编码方法和图像解码方法的便携式电话1200的示意图。FIG. 27 is a schematic diagram showing a
该便携式电话1200包括用于对基站1110发送/接收无线电波的天线1201、例如CCD相机这样可以拍摄物体的运动或静止图像的相机单元1203、以及例如液晶显示器这样用于显示由相机单元1203所拍摄的数据或者通过天线1201接收的视频图像的显示单元1202。This
该便携式电话1200进一步包括包含多个控制按键的主体1204、例如扩音器这样用于输出语音的语音输出单元1208、例如麦克风这样用于输入语音的语音输入单元1205、用于保存例如拍摄运动图像或静止图像的数据、或者所接收电子邮件的数据、运动图像数据或静止图像数据这样的编码数据或解码数据的存储介质1207、以及使得存储介质1207附着到便携式电话1200上的插槽单元1206。The
该存储介质1207具有作为例如EEPROM(电可擦除可编程只读存储器)类型的包含在塑料壳体中的电可编程可擦除非易失性存储器的快速存储器元件,例如SD卡。This
下面将参照入28更加具体地描述该便携式电话1200。The
该便携式电话1200具有执行用于包括显示单元1202和控制按键1204的主体的各个单元一般控制的主控制单元1241。This
该便携式电话1200进一步包括电源电路1240、操作输入控制单元1234、图像编码单元1242、相机接口单元1233、LCD(液晶显示器)控制单元1232、图像解码单元1239、多路复用/分解单元1238、记录/再现单元1237、调制/解调单元1236以及音频处理单元1235。该便携式电话1200的各个单元通过同步总线1250相互连接。This
当在用户的控制下启动呼叫结束/电源按键时,该电源电路1240把电能从一个电池组提供到各个单元,从而把具有摄像头的便携式电话1200激活为工作状态。The
在便携式电话1200中,各个单元在由CPU、ROM、RAM等等所构成的主控制单元1241的控制下操作。更加具体来说,在便携式电话1200中,由在语音通信模式中输入到语音输入单元1205的语音所获得音频信号被音频处理单元1235转换为数字音频数据。该数字音频数据受到调制/解调单元1236的扩频处理,进一步受到发送/接收电路1231的数模转换处理和频率转换处理,并且通过天线1201发送。In the
在该便携式电话1200中,在语音通信模式中通过天线1201接收的信号被放大,然后受到频率变换处理和模数转换处理。所接收的信号被在调制/解调单元1236中进一步受到反扩频处理,由音频处理单元1235转换为模拟音频信号,并且该模拟音频信号被通过语音输出单元1208输出。In this
当便携式电话1200在数据通信模式中发送电子邮件时,通过操作在主体上的控制按键1204而输入的电子邮件的文字数据被通过操作输入控制单元1234发送到主控制单元1241。该主控制单元1241控制各个单元,使得该文字数据在调制/解调单元1236中受到扩频处理,然后在发送/接收电路1231中受到数模转换处理和频率变换处理,然后通过天线1201发送到基站1110。When the
当便携式电话1200在数据通信模式中发送图像数据时,由相机单元1203所拍摄的图像数据被通过相机接口单元1233提供到图像编码单元1242。当便携式电话1200不发送图像数据时,由相机单元1203所拍摄的图像数据可以通过相机接口单元1233和LCD控制单元1232直接显示在显示单元1202上。When the
该图像编码单元1242包括根据上述任何实施例的图像编码装置。该图像编码单元1242通过根据任何上述实施例的图像编码方法对来自相机单元1203的图像数据进行压缩编码,以把其转换为编码的图像数据,并且把所获得的编码图像数据输出到多路复用/分解单元1238。与此同时,在由相机单元1203拍摄图像时,便携式电话1200把输入到语音输入单元1205的语音作为数字音频数据通过音频处理单元1235发送到多路复用/分解单元1238。The
该多路复用/分解单元1238通过预定方法对来自图像编码单元1242的编码图像数据和来自音频处理单元1235的音频数据进行多路复用。所获得的复用数据在调制/解调单元1236中受到扩频处理,然后进一步在发送/接收电路1231中的受到数模转换处理和频率变换处理,并且获得通过天线1201发送的数据。The multiplexing/decomposing
当便携式电话1200接收在数据通信模式中链接到一个主页等等的运动图像文件的数据时,通过天线1201从基站1110接收的信号被受到调制/解调单元1236的反扩频处理,并且所获得的复用数据被发送到多路复用/分解单元1238。When the
当通过天线1201接收的复用数据被解码时,该多路复用/分解单元1238对该多路复用数据进行多路分解,以把该数据分为对应于图像数据的编码位流和对应于音频数据的编码位流,并且该编码图像数据被提供到图像解码单元1239,以及该音频数据被通过同步总线1250提供到音频处理单元1235。When multiplexed data received through the
该图像解码单元1239包括根据任何上述实施例的图像解码装置。该图像解码单元1239通过对应于根据任何上述实施例的编码方法的解码方法对该图像数据的编码位流进行解码,以再现运动图像数据,并且把所再现的数据通过LCD控制单元1232提供到显示单元1202。从而,例如,包含在链接到该主页的运动图像文件中的运动图像数据被显示。与此同时,音频处理单元1235把该音频数据转换为模拟音频信号,然后把该模拟音频信号提供到语音输出单元1208。从而,例如,再现包含在链接到该主页的运动图像文件中的音频数据。This
在此,可以应用根据任何上述实施例的图像编码方法和图像解码方法的系统不限于上述内容提供系统。Here, the system to which the image encoding method and the image decoding method according to any of the above-described embodiments can be applied is not limited to the above-described content providing system.
最近,使用卫星或地面电波的数字广播被经常讨论,并且根据上述实施例的图像编码装置和图像解码装置也可以应用于如图29中所示的数字广播系统。Recently, digital broadcasting using satellite or terrestrial waves is frequently discussed, and the image encoding device and image decoding device according to the above-described embodiments can also be applied to a digital broadcasting system as shown in FIG. 29 .
更加具体来说,对应于视频信息的编码位流被从广播台1409通过无线通信发送到例如通信卫星或广播卫星这样的卫星1410。当该广播卫星1410接收对应于该视频信息的编码位流时,该卫星1410输广播的电波,并且这些电波由在包括卫星广播接收设施的住宅处的天线1406所接收。例如,电视(接收器)1401或机顶盒(STB)1407这样的装置解码该编码位流,并且再现该视频信息。More specifically, an encoded bit stream corresponding to video information is transmitted from a broadcasting station 1409 to a satellite 1410 such as a communication satellite or a broadcasting satellite through wireless communication. When the broadcast satellite 1410 receives the coded bit stream corresponding to the video information, the satellite 1410 transmits broadcast electric waves, and these electric waves are received by the antenna 1406 at a residence including a satellite broadcast receiving facility. For example, a device such as a television (receiver) 1401 or a set-top box (STB) 1407 decodes the coded bit stream, and reproduces the video information.
另外,根据任何上述实施例的图像解码装置也可以被安装在再现装置1403上,其可以读取和解码记录在例如CD或DVD(记录介质)这样的存储介质1402上的编码位流。In addition, the image decoding device according to any of the above-described embodiments may also be mounted on the reproducing device 1403, which can read and decode the encoded bit stream recorded on the storage medium 1402 such as CD or DVD (recording medium).
在这种情况中,一个被再现的视频信号被显示在监视器1404上。该图像解码装置可以安装在与用于有线电视1405的电缆或用于卫星/地面广播1406的天线相连接的机顶盒1407上,以再现要显示在电视的监视器1408上的该图像解码装置的输出。在这种情况中,该图像解码装置可以不包含在该机顶盒中,而是包含在该电视中。具有天线1411的一个车辆1412可以从卫星1410或基站1107接收一个信号,并且再现一个运动图像,以把其显示在安装在车辆1412上的车辆导航系统1413等等的显示设备上。In this case, a reproduced video signal is displayed on the monitor 1404. The image decoding device may be installed on a set-top box 1407 connected to a cable for cable television 1405 or an antenna for satellite/terrestrial broadcasting 1406 to reproduce the output of the image decoding device to be displayed on a monitor 1408 of a television . In this case, the image decoding device may not be contained in the set-top box, but contained in the television. A vehicle 1412 having an antenna 1411 can receive a signal from a satellite 1410 or a
另外,还可以由根据任何上述实施例的图像编码装置对一个图像信号编码,并且记录在记录介质中。In addition, one image signal may also be encoded by the image encoding device according to any of the above-described embodiments, and recorded in a recording medium.
一种记录设备的具体例子是例如把图像信号记录在DVD盘1421上的DVD录像机这样的录像机1420、以及在硬盘上记录图像信号的盘录像机。该图像信号可以记录在SD卡1422上。另外,当该录像机1420包含根据任何上述实施例的图像解码装置时,被记录在DVD盘1421或SD卡1422上的图像信号可以由录像机1420所再现,并且显示在监视器1408上。Specific examples of a recording device are a video recorder 1420 such as a DVD recorder that records image signals on a DVD disk 1421, and a disk recorder that records image signals on a hard disk. This image signal can be recorded on the SD card 1422 . In addition, when the video recorder 1420 includes the image decoding device according to any of the above-mentioned embodiments, the image signal recorded on the DVD disc 1421 or the SD card 1422 can be reproduced by the video recorder 1420 and displayed on the monitor 1408.
在此,车辆导航系统1413的结构除了相机单元1203、相机接口单元1233和图像编码单元1242之外例如可以包括如图28中所示的便携式电话机的组件,并且这同样可以应用于计算机1111或者电视(接收器)1401。Here, the structure of the car navigation system 1413 may include, for example, components of a cellular phone as shown in FIG. TV (Receiver) 1401.
另外,作为例如便携式电话1114这样的终端,可以安装三种终端之一:具有编码器和解码器的发送接收型终端、仅仅具有编码器的发送终端以及仅仅具有解码器的接收终端。In addition, as a terminal such as the cellular phone 1114, one of three types of terminals can be installed: a transmitting and receiving type terminal having an encoder and a decoder, a transmitting terminal having only an encoder, and a receiving terminal having only a decoder.
如上文所述,根据任何上述实施例的图像编码方法或图像解码方法可以应用于任何上述设备或系统,从而可以获得如上述实施例所述的效果。As mentioned above, the image encoding method or image decoding method according to any of the above embodiments can be applied to any of the above devices or systems, so that the effects described in the above embodiments can be obtained.
另外,不必说本发明的实施例和其应用不限于在该说明书中所述的内容。In addition, it is needless to say that the embodiments of the present invention and applications thereof are not limited to those described in this specification.
工业应用性Industrial Applicability
根据本发明的可变长度编码方法和可变长度解码方法通过选择适合于构成该系数数据的系数特性或者用于该系数的编码处理的状态的代码表,而有效地消除包含在作为可变长度编码处理的对象的系数数据中的冗余信息,从而大大地增加对图像信号等等的可变长度编码处理的编码效率。这些可变长度编码方法和可变长度解码方法被用于发送或存储运动图像数据的数据处理中。The variable length encoding method and the variable length decoding method according to the present invention effectively eliminate the code table included in the variable length encoding method by selecting a code table suitable for the coefficient characteristics constituting the coefficient data or the state of the encoding process for the coefficient. Redundant information in coefficient data which is an object of coding processing is thereby greatly increased coding efficiency of variable length coding processing on image signals and the like. These variable length encoding methods and variable length decoding methods are used in data processing for transmitting or storing moving image data.
Claims (2)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001358197 | 2001-11-22 | ||
| JP2001358197 | 2001-11-22 | ||
| JP2001-358197 | 2001-11-22 | ||
| JP200299227 | 2002-04-01 | ||
| JP2002099227 | 2002-04-01 | ||
| JP2002-99227 | 2002-04-01 |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB028132823ADivisionCN1301014C (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101005625A CN101005625A (en) | 2007-07-25 |
| CN101005625Btrue CN101005625B (en) | 2010-06-02 |
Family
ID=38045365
Family Applications (6)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200610143687.XAExpired - LifetimeCN101005625B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method |
| CN 200610143690Expired - LifetimeCN1946187B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length encoding method and variable length decoding method |
| CN200610107555.1AExpired - LifetimeCN101064843B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable Length Encoding Method |
| CN200610143686.5AExpired - LifetimeCN1946185B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method |
| CN200610143688.4AExpired - LifetimeCN100586190C (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length encoding method and variable length decoding method |
| CN 200610143689Expired - LifetimeCN1946186B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length encoding method and variable length decoding method |
Family Applications After (5)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200610143690Expired - LifetimeCN1946187B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length encoding method and variable length decoding method |
| CN200610107555.1AExpired - LifetimeCN101064843B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable Length Encoding Method |
| CN200610143686.5AExpired - LifetimeCN1946185B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method |
| CN200610143688.4AExpired - LifetimeCN100586190C (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length encoding method and variable length decoding method |
| CN 200610143689Expired - LifetimeCN1946186B (en) | 2001-11-22 | 2002-11-22 | Variable length encoding method and variable length decoding method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (6) | CN101005625B (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8179974B2 (en)* | 2008-05-02 | 2012-05-15 | Microsoft Corporation | Multi-level representation of reordered transform coefficients |
| JP2011024066A (en)* | 2009-07-17 | 2011-02-03 | Sony Corp | Image processing apparatus and method |
| US9338449B2 (en)* | 2011-03-08 | 2016-05-10 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Harmonized scan order for coding transform coefficients in video coding |
| CN103188486B (en)* | 2011-12-28 | 2016-04-20 | 联芯科技有限公司 | H.263 the variable-length coding method of Video coding and system |
| CN106877874A (en)* | 2017-01-17 | 2017-06-20 | 杭州清本科技有限公司 | A kind of compaction coding method |
| CN109474281B (en)* | 2018-09-30 | 2022-07-08 | 湖南瑞利德信息科技有限公司 | Data encoding and decoding method and device |
| MX2021006631A (en)* | 2018-12-26 | 2021-07-07 | Panasonic Ip Corp America | Three-dimensional data encoding method, three-dimensional data decoding method, three-dimensional data encoding device, and three-dimensional data decoding device. |
| CN117097906B (en)* | 2023-10-20 | 2023-12-26 | 河北天英软件科技有限公司 | Method and system for efficiently utilizing regional medical resources |
| CN117498873B (en)* | 2023-11-07 | 2024-03-29 | 东莞市杜氏诚发精密弹簧有限公司 | Intelligent processing system for vascular embolism spring assembly |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1117779A (en)* | 1993-12-16 | 1996-02-28 | 三星电子株式会社 | Adaptive Variable Length Coding and Decoding Method for Image Data |
| US5497153A (en)* | 1992-07-23 | 1996-03-05 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | System for variable-length-coding and variable-length-decoding digital data for compressing transmission data |
| US5539401A (en)* | 1994-08-31 | 1996-07-23 | Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha | Variable-length code table and variable-length coding device |
| US5555321A (en)* | 1993-11-19 | 1996-09-10 | Fujitsu Limited | Image data binary coding method and apparatus |
| US5812788A (en)* | 1995-07-21 | 1998-09-22 | Intel Corporation | Encoding/decoding video signals using quantization tables based on explicitly encoded base and scale matrices |
| US5825312A (en)* | 1996-11-25 | 1998-10-20 | Xerox Corporation | DX JPEG Huffman decoder |
| US5995148A (en)* | 1997-02-14 | 1999-11-30 | At&T Corp | Video coder having scalar dependent variable length coder |
| US6141446A (en)* | 1994-09-21 | 2000-10-31 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Compression and decompression system with reversible wavelets and lossy reconstruction |
| US6241778B1 (en)* | 1999-06-18 | 2001-06-05 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Methods and apparatus for implementing run-length limited and maximum transition run codes |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0536630B1 (en)* | 1991-09-30 | 1999-11-17 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Band-compressed signal processing apparatus and VTR |
| US5227878A (en)* | 1991-11-15 | 1993-07-13 | At&T Bell Laboratories | Adaptive coding and decoding of frames and fields of video |
| KR100209410B1 (en)* | 1995-03-28 | 1999-07-15 | 전주범 | Video signal coding device |
| US7099387B2 (en)* | 2002-03-22 | 2006-08-29 | Realnetorks, Inc. | Context-adaptive VLC video transform coefficients encoding/decoding methods and apparatuses |
- 2002
- 2002-11-22CNCN200610143687.XApatent/CN101005625B/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
- 2002-11-22CNCN 200610143690patent/CN1946187B/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
- 2002-11-22CNCN200610107555.1Apatent/CN101064843B/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
- 2002-11-22CNCN200610143686.5Apatent/CN1946185B/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
- 2002-11-22CNCN200610143688.4Apatent/CN100586190C/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
- 2002-11-22CNCN 200610143689patent/CN1946186B/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5497153A (en)* | 1992-07-23 | 1996-03-05 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | System for variable-length-coding and variable-length-decoding digital data for compressing transmission data |
| US5555321A (en)* | 1993-11-19 | 1996-09-10 | Fujitsu Limited | Image data binary coding method and apparatus |
| CN1117779A (en)* | 1993-12-16 | 1996-02-28 | 三星电子株式会社 | Adaptive Variable Length Coding and Decoding Method for Image Data |
| US5539401A (en)* | 1994-08-31 | 1996-07-23 | Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha | Variable-length code table and variable-length coding device |
| US6141446A (en)* | 1994-09-21 | 2000-10-31 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Compression and decompression system with reversible wavelets and lossy reconstruction |
| US5812788A (en)* | 1995-07-21 | 1998-09-22 | Intel Corporation | Encoding/decoding video signals using quantization tables based on explicitly encoded base and scale matrices |
| US5825312A (en)* | 1996-11-25 | 1998-10-20 | Xerox Corporation | DX JPEG Huffman decoder |
| US5995148A (en)* | 1997-02-14 | 1999-11-30 | At&T Corp | Video coder having scalar dependent variable length coder |
| US6241778B1 (en)* | 1999-06-18 | 2001-06-05 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Methods and apparatus for implementing run-length limited and maximum transition run codes |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| JP平10-271017A 1998.10.09 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1946185A (en) | 2007-04-11 |
| CN1946187B (en) | 2012-02-22 |
| CN1946185B (en) | 2014-07-23 |
| CN100586190C (en) | 2010-01-27 |
| CN101064843B (en) | 2010-08-18 |
| CN1946186B (en) | 2012-02-22 |
| CN101005626A (en) | 2007-07-25 |
| CN101064843A (en) | 2007-10-31 |
| CN1946186A (en) | 2007-04-11 |
| CN1946187A (en) | 2007-04-11 |
| CN101005625A (en) | 2007-07-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101001385B (en) | Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method | |
| CN101005625B (en) | Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method | |
| JP4100552B2 (en) | Decryption method | |
| JP4158985B2 (en) | Encoding method and encoding apparatus | |
| JP4158986B2 (en) | Decoding method and decoding apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right | Owner name:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC (AMERICA) INTELLECTUAL PROPERT Free format text:FORMER OWNER: MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC INDUSTRIAL CO, LTD. Effective date:20140714 | |
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20140714 Address after:California, USA Patentee after:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORPORATION OF AMERICA Address before:Osaka Japan Patentee before:Matsushita Electric Industrial Co.,Ltd. | |
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20151112 Address after:Tokyo, Japan Patentee after:Godo Kaisha IP Bridge 1 Address before:Seaman Avenue Torrance in the United States of California No. 20000 room 200 Patentee before:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORPORATION OF AMERICA | |
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | Granted publication date:20100602 | |
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |