CN100538756C - A kind of reflection identification alarm system and alarm method - Google Patents
A kind of reflection identification alarm system and alarm methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100538756C CN100538756CCNB2007100090900ACN200710009090ACN100538756CCN 100538756 CCN100538756 CCN 100538756CCN B2007100090900 ACNB2007100090900 ACN B2007100090900ACN 200710009090 ACN200710009090 ACN 200710009090ACN 100538756 CCN100538756 CCN 100538756C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- image
- edge
- data
- abnormality
- alarm
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Closed-Circuit Television Systems (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明是关于采用图像分析技术,实现境界检测、物体检测、动体检测、度测量等功能的一种映像(图像)识别报警系统装置及报警方法。The invention relates to an image (image) recognition alarm system device and an alarm method for realizing boundary detection, object detection, moving body detection, degree measurement and other functions by using image analysis technology.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,关于办公楼、公共设施、个人住宅的侵入和盗窃等犯罪手段越来越巧妙,为了防止这些犯罪,对安防系统的需求也越来越高涨。安防系统的形式之一是通过监视由摄像头拍摄映像的系统。这样的系统是在建筑物内设置摄像头,把所拍摄的视频映像显示在监视屏上,由此确认侵入者的有无、再筛选出盗窃犯人等。In recent years, crimes such as intrusion and theft of office buildings, public facilities, and personal residences have become more sophisticated, and in order to prevent these crimes, the demand for security systems has also increased. One of the forms of security system is by monitoring the image captured by the camera system. Such a system installs a camera in a building and displays the captured video image on a monitor screen, thereby confirming the existence of intruders and screening out burglars, etc.
但是,这种通过监视由摄像头拍摄视频映像的安防系统,必须要求监视员实时盯着监视屏长时间地确认是否有可疑者侵入建筑物内,给监视工作带来很大的困难。此外,监视员一眨眼不注意就可能忽视犯罪的瞬间,因此这种安防系统的安防效果是有限的。However, this security system, which monitors the video image taken by the camera, must require the monitor to stare at the monitor screen for a long time in real time to confirm whether any suspicious person has invaded the building, which brings great difficulties to the monitoring work. In addition, the monitor may overlook the moment of crime if he blinks and does not pay attention, so the security effect of this security system is limited.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明鉴于上述的问题,目的在于提供一个不仅能实现减轻监视员监视工作量的图像监视安防系统及方法,该系统及方法也必须具备显著减少监视图像数据处理量的性能。In view of the above problems, the present invention aims to provide an image surveillance security system and method that can not only reduce the monitoring workload of monitors, but also must have the performance of significantly reducing the amount of surveillance image data processing.
为了达到上述的目的,本发明是具备对所定的摄像区域进行摄像的摄像装置,和对该所定的摄像区域的异常检测规约进行设定的规约设定装置,和对该摄像装置拍摄了的图像数据进行处理、发现上述的所定的摄像区域的异常的图像处理装置,和由该图像处理装置发现所定的摄像区域异常就发出警报信号的报警装置所组成的系统装置;In order to achieve the above objects, the present invention is provided with an imaging device for imaging a predetermined imaging area, a protocol setting device for setting an abnormality detection protocol for the predetermined imaging area, and an image captured by the imaging device A system device composed of an image processing device that processes data and finds an abnormality in the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area, and an alarm device that sends an alarm signal when the image processing device finds that the predetermined imaging area is abnormal;
摄像装置:是具备接受来自摄像区域的反射光、由能以电特性输出值反映受光量的感光器件,和把该感光器件所得到的模拟形式电特性输出转换为数字形式后生成数据图像数据的A/D变换,和把A/D变换所生成的图像数据进行压缩处理,和把所压缩了的数据以动画数据流的形式输出的系统装置。Imaging device: It is equipped with a photosensitive device that receives reflected light from the imaging area, reflects the amount of light received by an electrical characteristic output value, and converts the analog form electrical characteristic output obtained by the photosensitive device into a digital form to generate data image data A/D conversion, and a system device that compresses the image data generated by A/D conversion, and outputs the compressed data in the form of animation data stream.
规约设定装置:是具备在上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像上描画异常检测的领域,设定该异常检测的领域内及其近旁的异常检测的条件,输出该规约相关信号给上述的图像处理装置的规约设定信息的系统装置;Protocol setting device: It is equipped with the area of drawing abnormality detection on the image captured by the above-mentioned camera device, setting the conditions of abnormality detection in and around the abnormality detection area, and outputting the protocol-related signal to the above-mentioned image processing The system device of the protocol setting information of the device;
图像处理装置:是具备对上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像进行解析,抽出图像内物体的边缘,和对抽出的物体的边缘计算该边缘色彩变化,和计算该变化与上述规约设定信息终端系统装置所设定了的异常检测条件的相关,检测出上述的所定的摄像区域内、所设定了的异常检测规约下的异常的系统装置;Image processing device: it is equipped with analyzing the image captured by the above-mentioned camera device, extracting the edge of the object in the image, and calculating the color change of the edge for the edge of the extracted object, and calculating the change and the above-mentioned protocol setting information terminal system The correlation between the abnormality detection conditions set by the device, and the system device that detects the abnormality under the set abnormality detection protocol in the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area;
警报信号的报警装置:是具备接受来自图像处理装置所生成的报警信号与相应的图像数据,和分解该报警信号生成语音形式、文字形式、图信号形式、或者其他形式的电特性输出信号,和输出该相关的输出信号、和相应的图像数据给相关的处理装置的信息的系统装置。The alarm device for the alarm signal: it is capable of receiving the alarm signal and corresponding image data generated by the image processing device, and decomposing the alarm signal to generate an electrical characteristic output signal in the form of voice, text, graphic signal, or other forms, and System means for outputting the associated output signal, and corresponding image data information, to associated processing means.
上述规约设定终端系统装置是台式个人计算机或者笔记本型个人计算机或者手提电话或者其他移动通信终端的系统装置。The above protocol setting terminal system device is a desktop personal computer or a notebook personal computer or a mobile phone or other mobile communication terminal system device.
上述的图像处理装置具备对上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像,识别物体边缘存在比较大的色彩/明暗差异的特性,计算该图像邻近象素之间的差异,抽出物体的边缘图像。计算该物体边缘图像所在区域内的色彩变化,然后识别物体所在区域的变化的系统装置。The above-mentioned image processing device has the characteristics of recognizing relatively large color/brightness difference at the edge of the object in the image captured by the above-mentioned camera device, calculating the difference between adjacent pixels of the image, and extracting the edge image of the object. A system device that calculates the color change in the area where the edge image of the object is located, and then recognizes the change in the area where the object is located.
上述的图像处理装置是具备对上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像进行解析,抽出图像内物体的边缘,和对抽出的物体的边缘计算该边缘色彩变化,和计算该变化与上述规约设定信息终端系统装置所设定了的异常检测条件的相关,检测出上述的所定的摄像区域内、所设定了的异常检测规约下的异常的系统装置。The above-mentioned image processing device is equipped with analyzing the image captured by the above-mentioned camera device, extracting the edge of the object in the image, and calculating the color change of the edge for the edge of the extracted object, and calculating the change and the above-mentioned protocol setting information terminal. A system device that detects abnormalities within the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area and under the set abnormality detection protocol in relation to the abnormality detection conditions set by the system device.
上述的图像处理装置是具备在上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像上描画用于检测的境界线,该境界线上及其近旁,或者被该境界线包围着的领域内的物体边缘图像发生变化时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。The above-mentioned image processing device is equipped with drawing a boundary line for detection on the image captured by the above-mentioned imaging device, and when the boundary line and its vicinity, or the object edge image in the area surrounded by the boundary line changes, , a system device that detects an abnormality in the aforementioned predetermined imaging area.
在上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像上被上述用于检测的境界线包围着的领域内的动体移动时,导致该动体的边缘图像出现变化时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。When the moving body in the area surrounded by the boundary line used for detection moves on the image captured by the above-mentioned imaging device, when the edge image of the moving body changes, the abnormality of the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area is detected. system device.
在上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像上,识别被上述用于检测的境界线包围着的领域内的人物或者物体的边缘图像,随着时间的流失,该边缘图像消失时,导致该动体的边缘图像出现变化时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。On the image captured by the above-mentioned imaging device, the edge image of the person or object in the area surrounded by the boundary line used for detection is recognized. As time goes by, when the edge image disappears, resulting in the movement of the moving body A system device that detects an abnormality in the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area when the edge image changes.
在上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像上,被上述用于检测的境界线包围着的领域内,随着时间的流失识别了新的人物或者物体的边缘图像时,导致该动体的边缘图像出现变化时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。On the image captured by the above-mentioned camera device, in the area surrounded by the above-mentioned boundary line for detection, when the edge image of a new person or object is recognized as time goes by, the edge image of the moving body will appear. A system device that detects an abnormality in the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area when it changes.
在上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像上,指定某一动体、识别该动体的边缘图像,当检测出该动体以外的物体或者动体的边缘图像的变化时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。On the image captured by the above-mentioned imaging device, specify a certain moving body, recognize the edge image of the moving body, and detect the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area when an object other than the moving body or a change in the edge image of the moving body is detected abnormal system device.
在上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像上,指定某一动体、设定该动体的允许移动方向,当检测出该动体超出所设定的移动方向时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。On the image captured by the above-mentioned imaging device, specify a certain moving body and set the allowed moving direction of the moving body. When the moving body is detected to exceed the set moving direction, the abnormality of the above-mentioned specified imaging area is detected. system device.
监测由上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像的数据量,当检测出该数据量的一定量的变化时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。A system device that monitors the amount of data of an image captured by the above-mentioned imaging device, and detects an abnormality in the above-mentioned predetermined imaging area when a certain amount of change in the amount of data is detected.
监测由上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像的光度,该光度超过或者小于所定的閾值时,检测出上述所定的摄像区域的异常的系统装置。A system device that monitors the luminosity of an image captured by the aforementioned imaging device, and detects an abnormality in the aforementioned predetermined imaging area when the luminosity exceeds or falls below a predetermined threshold.
本发明一种映像识别报警方法,包括以下步骤:An image recognition and alarm method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
首先,摄像装置对所定的摄像区域进行摄像,把摄像生成的图像数据以动画数据流的形式送给规约设定装置和图像处理装置;Firstly, the imaging device takes an image of the predetermined imaging area, and sends the image data generated by the imaging to the protocol setting device and the image processing device in the form of an animation data stream;
规约设定装置接受以动画数据流的形式该图像数据,并可通过使用鼠标等画面操作装置设定对该图像的异常检测范围、异常动作条件、异常处理程序等规约;The protocol setting device accepts the image data in the form of an animation data stream, and can set protocols such as the abnormal detection range, abnormal action conditions, and abnormal handling procedures of the image by using a mouse or other screen operating device;
图像处理装置接受以动画数据流的形式该图像数据,并通过其边缘抽出部识别物体边缘存在比较大的色彩/明暗差异,计算该图像邻近象素之间的差异,解析出物体的边缘图像数据,提交图像数据量计测部;The image processing device accepts the image data in the form of an animation data stream, and through its edge extraction part, recognizes that there is a relatively large color/light and dark difference at the edge of the object, calculates the difference between adjacent pixels of the image, and analyzes the edge image data of the object , submit the image data volume measurement department;
图像数据量计测部按一定的时间间隔计测来自图像输入部32的数据流量的变化,计算出单位时间之间该数据流量的差分的绝对值;判断该绝对值是否超过所定的阀值;The image data amount measuring part measures the change of the data flow from the
当该差分的绝对值超过所定的阀值时,图像数据量计测部36判断该摄像领域内发生变化也就是可能出现异常;When the absolute value of the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, the image data
当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件相关时,异常检知部根据上述的所设定的异常检知条件判断其边缘图像变化的位置、变化的途径,生成报警输出信号,提交报警输出装置。When judging that the edge image change is related to the abnormality setting condition, the abnormality detection part judges the position and the way of the edge image change according to the above-mentioned set abnormality detection condition, generates an alarm output signal, and submits it to the alarm output device .
本发明是由对所定的摄像区域进行摄像的摄像装置,和对该所定的摄像区域的异常检测规约进行设定的规约设定装置,和对该摄像装置拍摄了的图像数据进行处理、发现上述的所定的摄像区域的异常的图像处理装置,和由该图像处理装置发现所定的摄像区域异常就发出警报信号的报警装置所组成的映像(图像)识别报警系统装置。其图像处理装置的特征在于,对上述的摄像装置拍摄了的图像,根据识别物体边缘存在比较大的色彩/明暗差异的特性,计算该图像邻近象素之间的差异,解析出物体的边缘图像,然后识别由该边缘所形成的图像数据的变化,检知出该摄像区域的异常。和传统的采用逐一比较像素的差异检知出被摄像区域的异常的方法相比较,可以大幅度的减少处理图像数据量。The present invention consists of an imaging device for imaging a predetermined imaging area, a protocol setting device for setting an abnormality detection protocol for the predetermined imaging area, and processing image data captured by the imaging device to discover the above-mentioned An image (image) recognition alarm system device composed of an image processing device for abnormalities in the predetermined imaging area, and an alarm device for sending out an alarm signal when the image processing device finds that the predetermined imaging area is abnormal. Its image processing device is characterized in that, for the image taken by the above-mentioned camera device, according to the characteristics of recognizing that there is a relatively large color/brightness difference at the edge of the object, the difference between the adjacent pixels of the image is calculated, and the edge image of the object is resolved , and then identify the change of the image data formed by the edge, and detect the abnormality of the imaging area. Compared with the traditional method of comparing the difference of pixels one by one to detect the abnormality of the photographed area, the amount of processed image data can be greatly reduced.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1、本发明的实施例1的监视系统构成的示意图。Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of a monitoring system according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
图2、本发明实施例1的摄像装置构成的示意图。FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the imaging device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
图3、本发明实施例1的规约设定装置构成的示意图。Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the configuration of the protocol setting device in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
图4、本发明实施例1的图像处理装置构成的示意图。FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of the structure of an image processing device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
图5、本发明实施例1的报警输出装置构成的示意图。Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the alarm output device in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
图6、本发明实施例1的监视系统关于摄像领域异常检测的工作流程图。Fig. 6 is a workflow diagram of the monitoring system in Embodiment 1 of the present invention regarding anomaly detection in the imaging field.
图7、本发明实施例1的生成边缘图像数据的说明图,(a)是用图像数据显示—摄像图像例的示意图、(b)是用从图像数据中抽出的边缘图像显示一边缘图像例的示意图。Fig. 7 is an explanatory diagram of generating edge image data according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, (a) is a schematic diagram of an example of displaying a captured image using image data, and (b) is an example of displaying an edge image using an edge image extracted from image data schematic diagram.
图8、本发明实施例1由摄像装置往图像处理装置传送图像数据时所摄像的图像出现变化时数据量也随之变化的推移曲线图例。FIG. 8 : An example of transition curves showing changes in the amount of data when the captured image changes when the image data is transmitted from the camera device to the image processing device in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
图9、本发明实施例1的异常检测范围为线状时,异常检测处理的说明图,(a)是异常检测范围设定为线状时正常情况下的边缘图像示意图、(b)是发生异常情况的边缘图像示意图。Fig. 9 is an explanatory diagram of the abnormality detection process when the abnormality detection range of Embodiment 1 of the present invention is linear, (a) is a schematic diagram of the edge image under normal conditions when the abnormality detection range is set to be linear, and (b) is the occurrence Schematic illustration of edge images for anomalous cases.
图10、本发明实施例1的异常检测范围为面状时,异常检测处理的说明图,(a)是异常检测范围设定为面状时正常情况下的边缘图像示意图、(b)是发生异常情况的边缘图像示意图。Fig. 10 is an explanatory diagram of abnormality detection processing when the abnormality detection range of Embodiment 1 of the present invention is planar, (a) is a schematic diagram of the edge image under normal conditions when the abnormality detection range is set as planar, and (b) is an edge image that occurs Schematic illustration of edge images for anomalous cases.
图11、本发明实施例1的异常检测范围内,原有的人物和物体移动时异常检测的处理的的说明图,(a)是上一时刻的边缘图像示意图、(b)是当前时刻的边缘图像示意图Fig. 11. An explanatory diagram of the original abnormality detection processing when people and objects move within the abnormality detection range of Embodiment 1 of the present invention, (a) is a schematic diagram of the edge image at the previous moment, and (b) is the current moment Schematic diagram of edge image
图12、本发明实施例1的异常检测范围内,原有的人物或物体不见了时异常检测的处理的的说明图,(a)是上一时刻的边缘图像示意图、(b)是当前时刻的边缘图像示意图。Fig. 12. An explanatory diagram of the abnormality detection process when the original person or object disappears within the abnormality detection range of Embodiment 1 of the present invention, (a) is a schematic diagram of the edge image at the previous moment, and (b) is the current moment Schematic diagram of the edge image.
图13、本发明实施例1的异常检测范围内,出现了原有没有的人物或物体时异常检测的处理的的说明图,(a)是上一时刻的边缘图像示意图、(b)是当前时刻的边缘图像示意图。Fig. 13. An explanatory diagram of abnormality detection processing when there are people or objects that did not appear in the abnormality detection range of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. (a) is a schematic diagram of the edge image at the previous moment, and (b) is the current Schematic diagram of edge images at moments.
图14、本发明实施例2的规约设定装置构成的示意图。Fig. 14 is a schematic diagram of the configuration of the protocol setting device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
图15、本发明实施例2的图像处理装置构成的示意图。Fig. 15 is a schematic diagram showing the structure of an image processing device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
图16、本发明实施例2的报警输出装置构成的示意图。Fig. 16 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the alarm output device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
图17、本发明实施例2的监视系统关于摄像领域异常检测的工作流程图。Fig. 17 is a workflow diagram of the surveillance system according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention regarding abnormality detection in the imaging field.
图18、本发明实施例2的图像数据的画面示意图,(a)是正常时的图像、(b)是异常时图像。Fig. 18 is a schematic diagram of image data screens according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, (a) is a normal image, and (b) is an abnormal image.
图19、本发明实施例3的规约设定装置构成的示意图。Fig. 19 is a schematic diagram of the configuration of a protocol setting device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
图20、本发明实施例3的图像处理装置构成的示意图。Fig. 20 is a schematic diagram of the structure of an image processing device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
图21、本发明实施例3的报警输出装置构成的示意图。Fig. 21 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the alarm output device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
图22、本发明实施例3的监视系统关于摄像领域异常检测的工作流程图。Fig. 22 is a working flow chart of the monitoring system according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention regarding anomaly detection in the imaging field.
图23、本发明实施例3的图像数据的画面示意图,(a)是正常时的图像、(b)是异常时图像。FIG. 23 : Schematic diagram of image data screens in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, (a) is a normal image, and (b) is an abnormal image.
图24、本发明实施例4的摄像装置构成的示意图。Fig. 24 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of the imaging device according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention.
图25、本发明实施例4的规约设定装置构成的示意图。Fig. 25 is a schematic diagram of the configuration of a protocol setting device according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention.
图26、本发明实施例4的图像处理装置构成的示意图。Fig. 26 is a schematic diagram of the structure of an image processing device according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention.
图27、本发明实施例4的报警输出装置构成的示意图。Fig. 27 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the alarm output device according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention.
图28、本发明实施例4的监视系统关于摄像领域异常检测的工作流程图。Fig. 28 is a working flow chart of the monitoring system according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention regarding abnormality detection in the imaging field.
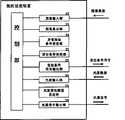
10摄像装置;11感光元素;12A/D变换部;13压缩部,14,26图像输出部;15光度计测部;16光量信号输出部;20图像处理装置;21,31控制部;22,32图像输入部;23图像输出部;24边缘抽出部;25指定范围信号输入部;26异常检知范围设定部;27图像数据量计测部;28异常检知部;29报警信号输出部;28动体识别部;30报警输出装置;33表示部;34异常检知范围指定部;35指定范围信号生成部;36指定范围信号生成部;37报警信号输入部;38警报输出部;39动体制定部;41动体范围信号输入部;42动体识别部;43移动方向指定信号输入部;44移动方向设定部;45光量信号输入部;51动体范围信号生成部;52动体范围信号输出部;53移动方向指定部;54移动方向指定信号生成部;55移动方向指定信号输出部;101,103边缘线;102可疑人物;104盆景;105人物10 camera device; 11 photosensitive element; 12 A/D conversion unit; 13 compression unit, 14, 26 image output unit; 15 photometric measurement unit; 16 light quantity signal output unit; 20 image processing device; 32 Image input unit; 23 Image output unit; 24 Edge extraction unit; 25 Specified range signal input unit; 26 Abnormality detection range setting unit; 27 Image data volume measurement unit; ; 28 moving body recognition part; 30 alarm output device; 33 display part; 34 abnormal detection range designation part; 35 designated range signal generation part; 36 designated range signal generation part; 41 Moving body range signal input part; 42 Moving body recognition part; 43 Moving direction designation signal input part; 44 Moving direction setting part; 45 Light quantity signal input part; 51 Moving body range signal generating part; 52 Moving body Body range signal output unit; 53 moving direction specifying unit; 54 moving direction specifying signal generating unit; 55 moving direction specifying signal output unit; 101, 103 edge line; 102 suspicious person; 104 bonsai;
具体实施方式Detailed ways
实施例1、本发明的第1实施例所构成的监视系统由图1所示,以下用图说明该系统的构成。Embodiment 1. The monitoring system constituted by the first embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 1 , and the configuration of the system will be described below with reference to the diagram.
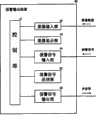
在本实施例所构成的监视系统是由对所定的摄像区域进行摄像的摄像装置10,和对由摄像装置10所摄像的图像(数字化视频图像)设定异常检测规约的规约设定装置20,和对摄像装置10所摄像的图像(数字化视频图像)进行处理、发现该所定摄像区域的异常的图像处理装置30,和对图像处理装置30检知出异常时,将该报警信号以图像形式显示在显示器上或者以声音的形式报警的报警装置40所构成。The monitoring system constituted in this embodiment is composed of an
下面,将这样的系统的各个构成部位10,20,30,40的构成以图面形式作详细说明。Next, the configuration of each
本发明的第1实施例所构成的摄像装置10由图2所示。An
例如,该摄像装置10具备数字视频摄像机性能。For example, this
如图2所示,摄像装置10接受来自摄像区域的反射光,由能以电特性输出值反映受光量的感光器件11,和由把该感光器件11所得到的模拟形式电特性输出转换为数字形式后生成图像数据的A/D变换部12,和由把A/D变换部12所生成的图像数据进行压缩处理的压缩部13,和由把压缩部13所压缩了的数据以视频数据流输出的图像输出部14所构成。As shown in Figure 2, the
上述的压缩部13的压缩方法是采用以帧差分压缩数据量的形式,例如MPEG2等。The above-mentioned compression method of the compression unit 13 adopts a method of compressing the amount of data by frame difference, for example, MPEG2 or the like.
在所摄像区域内的物体没有变动的情况下,或者物体持续一定的变动的情况下,被压缩的当前一帧图像与取得该图像的差分的前一帧图像的差是一定的。这时由摄像装置10送过来单位时间间隔的图像数据的数据量也是一定的。When the object in the captured area does not change, or when the object continues to move at a certain level, the difference between the compressed current frame image and the previous frame image obtained from the difference of the image is constant. At this time, the data amount of the image data per unit time interval sent from the
然而,在所摄像区域内任何物体一有变动,被压缩的当前一帧图像与取得该图像的差分的前一帧图像的差就会增大。导致由摄像装置10送过来单位时间间隔的图像数据的数据量也就增大。However, as soon as any object in the captured area changes, the difference between the compressed current frame image and the previous frame image obtained from the difference of the image will increase. As a result, the amount of image data sent by the
此外,该所摄像区域内变动的物体停止变动后,持续该不变动状态、被压缩的当前一帧图像与取得该图像的差分的前一帧图像的差就会减少并且维持一定。导致由摄像装置10送过来单位时间间隔的图像数据的数据量也是一定的。In addition, after the moving object in the captured area stops moving, the difference between the compressed current frame image and the previous frame image from which the difference of the image is obtained will decrease and remain constant. As a result, the data amount of the image data sent by the
本发明的第1实施例所构成的规约设定装置20由图3所示。The
如图3所示,该规约设定装置20是由对CPU等所构成规约设定装置20进行控制的控制部21、和接受上述的图像处理装置30所输出的图像数据的图像输入部22、和显示该图像数据以及边缘图像数据的图像显示部23、和由键盘和鼠标构成用于指定摄像区域内异常检知条件的异常检知条件设定部24、和确定异常检知条件设定部24所设定的异常检知条件数据与上述边缘图像数据的相关的设定条件处理部25、和把设定条件处理部25所生成的异常检知条件处理信号送往图像处理装置30的设定条件信号输出部36所构成。As shown in FIG. 3 , the
本发明的第1实施例所构成的图像处理装置30由图4所示。An
例如,该图像处理装置30是由可以连接到网络上的PC或者服务器等装置所构成。For example, the
如图4所示,该图像处理装置30是由对CPU等所构成图像处理装置30进行控制的控制部31、和通过网络接受上述的摄像装置10所输出的图像数据的图像输入部32、和把所输入的图像数据数输出到规约设定装置20和报警装置40的图像输出部33、和对所输入的图像数据的图像根据可识别物体边缘存在比较大的色彩/明暗差异的特性,计算该图像邻近象素之间的差异,解析出物体的边缘图像数据的边缘抽出部34、和接受来自规约设定装置20所指定的异常检知条件的异常检知条件信号输入部35、和以微分单位计测上述所输入的图像数据的数据量的变化,检知出摄像区域内的异常的图像数据量计测部36、和在图像数据量计测部36所检知的异常的基础上,计算上述解析出物体的边缘图像数据的变化部分和该变化部分与上述异常检知条件的相关,检知出详细的异常的异常检知部37、和把由异常检知部37所检知的异常相关报警信息送往报警装置40的报警信号输出部38所构成。As shown in FIG. 4, the
以下,把由摄像装置10摄像所生成的图像数据的图像称为摄像图像,把由图像处理装置30所计算出的边缘图像数据的图像称为边缘图像。Hereinafter, an image of the image data captured by the
图像数据量计测部36以所定的时间间隔的数据量、例如,以数据包为单位计测在图像输入部22所接受来自摄像装置10的图像数据。关于计测该数据量的构成与现有的方式一样,在此省略详细说明。The image data
异常检知部37对由边缘抽出部34所抽出的每帧或者每数帧边缘图像数据、比较这次所抽出的内容与上一次所抽出的内容,当检测出一定的变化时则判断摄像区域内发生了异常。The
本发明的第1实施例所构成的报警装置40由图5所示。The
例如,该报警装置40是由连接到所要监视的摄像区域内的用户网络上的PC或者手提电话等携带终端所构成。该报警装置40还具备信息的发送和接受功能、由显示器等显示图像功能、声音输出功能和振动等功能。For example, the
如图5所示,该报警装置40是由对CPU等所构成报警装置40进行控制的控制部41、和接受图像处理装置30所输出的图像数据的图像输入部42、和显示该图像数据以及边缘图像数据的图像显示部43、和接受图像处理装置30所输出的异常报警信息的报警信号输入部44、和处理该报警信号生成相应的报警形式信息的报警信号处理部45、和把报警信号处理部45所生成的报警信号以声音等形式输出的报警信号输出部46所构成。As shown in Figure 5, this
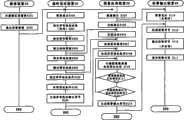
图6是关于用本发明的第1实施例的监视系统对摄像区域进行异常检知的动作流程图。以下,按该图说明监视系统的整个动作过程。Fig. 6 is a flow chart of the operation of abnormality detection in the imaging area by the monitoring system according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Hereinafter, the entire operation process of the monitoring system will be described with reference to this figure.
首先,摄像装置10对所定的摄像区域进行摄像(STEP-S101)。First, the
摄像装置10把摄像生成的图像数据以动画数据流的形式送给规约设定装置20和图像处理装置30(STEP-S102)。The
规约设定装置20的图像输入部22接受以动画数据流的形式该图像数据,在图像显示部23显示被摄图像(STEP-S103),作为规约设定基础图像提交异常检知条件设定部24。The
下一步,异常检知条件设定部24,在该基础图像上使用鼠标等画面操作装置,设定对该图像的异常检测范围、异常动作条件、异常处理程序等规约(STEP-S104),并将该规约数据提交给设定条件处理部25。Next, the abnormality detection
该异常检测范围可以指定为由线及其近旁所构成,也可以指定为由该线圈成的任意形状(比如:长方形)的区域所构成,也可以指定为该基础图像的全领域。The anomaly detection range can be specified to be composed of a line and its vicinity, or can be specified to be composed of an area of any shape (such as a rectangle) formed by the coil, or can be specified to be the entire area of the basic image.
下一步,设定条件处理部25处理上述基础图像与规约数据的相关,生成该异常检知处理规程(STEP-S105),提交设定条件信号输出部26。Next, the setting
下一步,设定条件信号输出部26受理该异常检知处理规程,生成设定条件输出信号,提交图像处理装置30(STEP-S106)。Next, the setting condition
图像处理装置30的图像输入部32接受以动画数据流的形式该图像数据,由图像输出部33将该图像数据提交报警输出装置40(STEP-S107)。The
下一步,边缘抽出部34识别物体边缘存在比较大的色彩/明暗差异,计算该图像邻近象素之间的差异,解析出物体的边缘图像数据(STEP-S108),提交图像数据量计测部36。In the next step, the
同时,异常检知条件信号输入部35接受规约设定装置20的设定条件信号输出部26的设定条件输出信号(STEP-S109),提交异常检知部37。At the same time, the abnormality detection condition
下一步,图像数据量计测部36按一定的时间间隔计测来自图像输入部32的数据流量的变化,计算出单位时间之间该数据流量的差分的绝对值(STEP-S110)。判断该绝对值是否超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111)。Next, the image data
该差分的绝对值不超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111/NO)时,图像数据量计测部36判断该摄像领域内没有变化也就是没有发生异常,则返回计测下一时间间隔的图像数据流量变化(STEP-S110,STEP-S111)。When the absolute value of the difference does not exceed the predetermined threshold (STEP-S111/NO), the image data
当该差分的绝对值超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111/Yes)时,图像数据量计测部36判断该摄像领域内发生变化也就是可能出现异常。When the absolute value of the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold (STEP-S111/Yes), the image data
当判断该异常发生时,异常检知部37根据上述的所设定的异常检知条件判断该变化内容,也就是其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件的相关,当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件无关(STEP-S112/NO)时,则返回计测下一时间间隔的图像数据流量变化(STEP-S110,STEP-S111)。When judging that the abnormality occurs, the
当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件相关(STEP-S112/YES)时,异常检知部37根据上述的所设定的异常检知条件判断其边缘图像变化的位置、变化的途径,生成报警输出信号(STEP-S113),提交报警输出装置40。When judging that the edge image change is related to the abnormal setting condition (STEP-S112/YES), the
报警输出装置40的图像输入部42接受图像处理装置30的图像输出部33的图像数据可由图像显示部42显示出被监视当前图像(STEP-S114)。The
当报警信号输入部44接受图像处理装置30的报警信号输出部38的报警信号时,报警信号处理部45生成不同形式的报警信号提交报警信号输出部45(STEP-S115)。When the alarm
报警信号输出部45以声音等形式输出报警信号,报知所监视的摄像区域内出现异常(STEP-S116)。同时可以在当前被摄像图里实时地显示出违规内容(STEP-S117)。The alarm
如上述说明,按本实施例,图像处理装置30计测被监视图像数据流量的变化,当该变化量的绝对值超过所定的阀值时,再通过对该被监视图像的边缘图像数据进行解析判断是否发生异常,在异常发生时才由报警输出装置40发出警报。与传统的采用逐一比较像素的差异检知出被摄像区域的异常的方法相比较,不仅大幅度的减少处理图像数据量,又能获得高精度的异常检知处理结果。As described above, according to this embodiment, the
例如,当所定的摄像区域内出现可疑者时,该摄像区域内的图像起了较大的变化,导致图像处理装置30所接受的图像数据的数据量明显的增加,当检测出该数据量的增加时,通过检测该边缘图像数据的边缘图像变化,即能高精度、详细地识别该可疑者窜入的事实。For example, when a suspicious person appears in the predetermined imaging area, the image in the imaging area changes greatly, resulting in a significant increase in the data volume of the image data received by the
边缘图像数据的生成方法:How to generate edge image data:
如前所述,按本实施例,图像处理装置30的边缘抽出部34是从通常的摄像数据的图像数据里将该画像内的物体以线的形式抽出其边缘(轮廓)图像数据。As mentioned above, according to the present embodiment, the
在这里,详细地说明该边缘(轮廓)图像数据的抽出过程。Here, the extraction process of the edge (contour) image data will be described in detail.
图像处理装置30的边缘抽出部34对来自摄像装置10的图像数据的图像按像素或者按所定的像素所组成的微小画面为单位计算该单位图像邻近像素之间的差异,抽出所定值以上差异单位图像,形成物体的边缘图像。并把所定值以下差异单位图像部分作为同一图像处理。这样就把原图像分离为边缘图像层和边缘图像以外层,此后图像处理装置30分别处理边缘图像数据和边缘图像以外的数据,有效地减轻数据处理的负荷。The
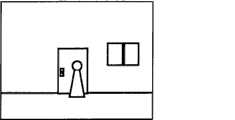
图7(a),(b)是本发明的实施例子关于边缘图像数据生成的说明,图7(a)是所拍摄的数据图像示意图,图7(b)是从该数据图像抽出边缘图像的示意图。Fig. 7 (a), (b) is the description about edge image data generation of embodiment example of the present invention, Fig. 7 (a) is the data image schematic diagram of taking, Fig. 7 (b) is to extract edge image from this data image schematic diagram.
如图7(a)所示在这个图像里映像出门、窗、墙等物体和人物。在这些物体和人物的轮廓及其近旁,存在比较大的色彩/明暗差异,通过计算该图像邻近象素之间的差异,抽出这些物体的边缘图像。Objects and people such as doors, windows, walls, etc. are reflected in this image as shown in Figure 7(a). There are relatively large color/light and shade differences in the outlines of these objects and people and their vicinity, and the edge images of these objects are extracted by calculating the difference between adjacent pixels of the image.
图7(a)所示图像通过解析抽出的边缘图像如图7(b)所示。如图7(b)所示边缘图像的数据只抽出存在比较大的色彩/明暗差异的部分的数据,忽略原图像的其他的部分的数据,因此与原图像相比较数据量显著减少。The edge image extracted from the image shown in Fig. 7(a) by analysis is shown in Fig. 7(b). As shown in FIG. 7( b ), only the data of the part with relatively large color/shading difference is extracted from the data of the edge image, and the data of other parts of the original image are ignored, so the amount of data is significantly reduced compared with the original image.
图像处理装置30的边缘抽出部34按来自摄像装置10的图像数据的数据量检知所定的摄像区域内出现异常。The
图8是由摄像装置10提交图像处理装置30的图像数据的数据量变化推移的示意图。FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram showing changes in data volume of image data submitted by the
如图8所示,在时间t1和t2之间,其数据量几乎是定量,数据量的变化几乎是零,也就是图像处理装置30判断所定的摄像区域内没有出现异常。As shown in FIG. 8 , between time t1 and t2 , the amount of data is almost constant, and the change of the amount of data is almost zero, that is, the
此后,t2以后,显示出超过閾值s1的数据量的变化。当图像处理装置30检测出该变化时,即识别可能在该所定的摄像区域内出现可疑者等导致图像数据量出现较大的变化,也就是检知出该所定的摄像区域内出现异常。Thereafter, after t2, a change in the amount of data exceeding the threshold s1 is shown. When the
由此,图像处理装置30监视着来自摄像装置10的图像数据的数据量的变化,当该变化超过閾值时,也就是检知出所定的摄像区域内出现异常,和传统的采用逐一比较像素的差异检知出被摄像区域的异常的方法相比较,能够大幅度的减少处理图像数据量。Thus, the
此外,通过调整检知异常的閾值等,可以防止误报例如由风吹导致植物晃动等的微小数据量的变化的异常。In addition, by adjusting the threshold for detecting anomalies, etc., it is possible to prevent false alarms of anomalies such as small changes in the amount of data such as plants shaking due to wind blowing.
此外,在这里出现超过閾值s1的数据量的增加时,也就是检知出该所定的摄像区域内出现异常。相反,在一般的情况下,所定的摄像区域内出现变动时,即发生异常,当该变动停止时数据量的变化则减少。此时图像处理装置30检知出超过閾值s2的数据量的减少。In addition, when there is an increase in the amount of data exceeding the threshold value s1, it is detected that an abnormality has occurred within the predetermined imaging area. On the contrary, in general, when there is a fluctuation in the predetermined imaging area, an abnormality occurs, and when the fluctuation stops, the change in the amount of data decreases. At this time, the
如前所述,当图像处理装置30根据图像数据的数据量检知出所定的摄像区域内出现异常时,在根据边缘图像的变化,详细地进行异常检知处理。As described above, when the
以下下面,以图面形式详细说明以线状构成异常检知范围、以面状构成异常检知范围的具体例子。Hereinafter, specific examples in which the abnormality detection range is configured in a line shape and the abnormality detection range is configured in a planar shape will be described in detail in the form of drawings.
1、异常检知范围以线状构成情况1. The range of abnormality detection is composed of lines
图9(a),(b)是本发明的第一实施例关于以线状构成异常检知范围的异常检知的说明,图9(a)是以线状构成异常检知范围时正常时的边缘图像的示意图,图9(b)以异常发生时的边缘图像的示意图。Fig. 9(a), (b) is the description of the abnormality detection in the first embodiment of the present invention, which constitutes the abnormality detection range in a line shape, and Fig. 9(a) is normal when the abnormality detection range is constituted in a line shape The schematic diagram of the edge image of Fig. 9(b) is a schematic diagram of the edge image when anomalies occur.
如图9(a)所示,用户通过异常检知条件设置部24在基础图像上描画线装境界线101,也就是该境界线及其近旁被设定为异常检知范围。As shown in FIG. 9( a ), the user draws the
如图9(b)所示,当可疑者102越界遮挡了境界线101时,该境界线101及其近旁的边缘图像就出现变化。As shown in FIG. 9( b ), when the
如前所述,图像装置30对边缘图像数据以帧或者以数帧为单位进行比较。在此图像装置30在图9(a)状态时该帧边缘图像数据和在图9(b)状态时该帧边缘图像数据进行比较,检测出该边缘图像的变化。As described above, the
此后,图像装置30检知出所定的摄像区域内出现异常,即输出警报信号给报警装置40,通知发生了异常。Thereafter, the
也就是,用户只需在图像显示部23所显示的摄像图像上描画用于异常检知的境界线101,就能简单地设定了异常检知范围。That is, the user can simply set the abnormality detection range by simply drawing the
2.异常检知范围以面状构成的情况:2. When the abnormality detection range is composed of planes:
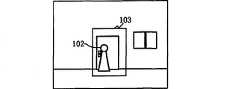
图10(a)、(b)是本发明的第一实施例关于以面状构成异常检知范围的异常检知的说明,图10(a)是以面状构成异常检知范围时正常时的边缘图像的示意图,图10(b)是异常发生时的边缘图像的示意图。Fig. 10(a), (b) is the description of the abnormality detection in the first embodiment of the present invention about the abnormality detection range formed in a planar shape, and Fig. 10(a) is normal when the abnormality detection range is constituted in a planar shape The schematic diagram of the edge image of Fig. 10(b) is a schematic diagram of the edge image when anomalies occur.
如图10(a)所示,用户通过异常检知条件设置部24在基础图像上描画长方形境界线103(即面状),也就是由该境界线所包围的面状被设定为异常检知范围。As shown in FIG. 10(a), the user draws a rectangular boundary line 103 (i.e., a plane) on the basic image through the abnormality detection
如图(b)所示,当可疑者102越界进入界线103所包围的面内时,该境界线所包围的面内的边缘图像就出现变化。As shown in figure (b), when the
在这里,图像装置30在图10(a)状态时该帧边缘图像数据和图10(b)状态时该帧边缘图像数据进行比较,检测出该边缘图像的变化。Here, the
此后,图像装置30检知出所定的摄像区域内出现异常,即输出警报信号给报警装置40,通知发生了异常。Thereafter, the
也就是,用户只需在图像显示部23所显示的摄像图像上描画用于异常检知的境界线103,就能简单地设定了异常检知范围。That is, the user can simply set the abnormality detection range by simply drawing the
此外,在上述所说明的例里,虽然只说明被境界线103所包围的异常检知范围内出现人物的情况,但在其他的应用场合也是可行的。In addition, in the example described above, although only the case of a person appearing in the abnormality detection range surrounded by the
以下,就其应用代表性的举3例说明。Hereinafter, three representative examples of its application will be described.
其一,原来存在该异常检知范围内的人物和物体出现变动的情况。例如:本来不应该变动的东西,比如贵金属被移动时该异常就被检知。First, there was a change in the characters and objects within the abnormality detection range. For example: things that should not change, such as precious metals, are detected when the anomaly is moved.
图11是原来存在该异常检知范围内的人物和物体出现变动,异常被检知的说明。图11(a)是前一时刻边缘图像的示意图,图11(b)是现在时刻边缘图像的示意图。Fig. 11 is an illustration of the change of people and objects that originally existed in the abnormality detection range, and the abnormality is detected. Fig. 11(a) is a schematic diagram of the edge image at the previous moment, and Fig. 11(b) is a schematic diagram of the edge image at the current moment.
如图11(a)所示,用户通过异常检知条件设置部24在基础图像上描画长方形境界线103(即面状),可疑者102位于异常检知范围内的左侧;如图11(b)所示可疑者102在可疑者102的左侧移动到右侧;本发明的图像装置30的异常检知部37检测出该边缘图像的变化,判断发生了异常。As shown in Figure 11 (a), the user draws a rectangular boundary line 103 (i.e., a plane) on the basic image through the abnormality detection
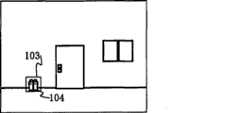
其二,原来存在该异常检知范围内的人物和物体不见了的情况。例如:该范围内放置的花瓶的边缘图像,其下一时刻所抽出的边缘图像时,该花瓶不见了,即判断发生该异常。Second, it turns out that people and objects within the abnormality detection range are missing. For example: when the edge image of the vase placed in this range is drawn at the next moment, the vase disappears, that is, it is judged that the abnormality occurs.
图12是原来存在该异常检知范围内的人物和物体不见了的情况,异常被检知的说明。图12(a)是前一时刻边缘图像的示意图,图12(b)是现在时刻边缘图像的示意图。FIG. 12 is an illustration of abnormality being detected when people and objects that originally existed within the abnormality detection range disappear. Fig. 12(a) is a schematic diagram of an edge image at a previous moment, and Fig. 12(b) is a schematic diagram of an edge image at a current moment.
如图12(a)所示,用户通过异常检知条件设置部24在基础图像上描画长方形境界线103,盆景104位于境界线103所定义的异常检知范围内;但在图11(b)的时刻,境界线103定义的异常检知范围内的盆景104消失了,本发明的图像装置30的异常检知部37检测出该边缘图像的变化,判断发生了异常。As shown in Figure 12 (a), the user draws a
其三,在该异常检知范围内出现了原来不存在的人物和物体的情况。例如:前一时刻,该范围内没有自行车的边缘图像,下一时刻所抽出的边缘图像是有自行车的边缘图像,即判断发生该异常。Third, there are people and objects that do not exist in the abnormality detection range. For example: at the previous moment, there was no edge image of a bicycle in the range, and the edge image extracted at the next moment is an edge image with a bicycle, that is, it is determined that the abnormality has occurred.
就这样,图像装置30能检知出异常检知范围的边缘图像的变化,也就是在任何情况下都能检知出所定的摄像区域内出现的异常。In this way, the
图13是在该异常检知范围内出现原来不存在的人物和物体不见了的情况,异常被检知的说明。图13(a)是前一时刻边缘图像的示意图,图13(b)是现在时刻边缘图像的示意图。FIG. 13 is an illustration of abnormality being detected when people and objects that do not exist in the abnormality detection range disappear. Fig. 13(a) is a schematic diagram of an edge image at a previous moment, and Fig. 13(b) is a schematic diagram of an edge image at a current moment.
如图13所示,用户通过异常检知条件设置部24在基础图像上描画长方形境界线103,境界线103所定义的异常检知范围内没有物体;但在图113(b)的时刻,境界线103所定义的异常检知范围内出现了盆景104,本发明图像装置30的异常检知部37检测出该边缘图像的变化,判断发生了异常。As shown in Figure 13, the user draws a
实施例2、前述的实施例1的监视系统是根据摄像领域或者被指定了的异常检知范围的边缘图像数据的变化,检知出该摄像领域内所发生的异常。Embodiment 2. The monitoring system of the aforementioned embodiment 1 detects abnormalities occurring in the imaging area or the edge image data of the specified abnormality detection range based on the change of the imaging area or the specified abnormality detection range.
在本实施例里,进一步考虑该摄像领域里或者被指定了的异常检知范围的移动着的人物和物体(以下,称为动体)的存在时,进行异常检知处理的情况。In this embodiment, it is further considered that abnormality detection processing is performed when there are moving persons and objects (hereinafter referred to as moving bodies) in the imaging area or in the specified abnormality detection range.
例如,在该摄像领域内一直活动者的狗。无论任何情况下,本实施例的监视系统都可以分别出移动着的狗和入侵的可疑者,只在可疑者入侵时才判断发生异常。For example, a dog that has been active in the camera field. In any case, the monitoring system of this embodiment can distinguish between moving dogs and intruding suspects, and only when the suspicious intrudes can it be judged that an abnormality occurs.
以下,除有特别说明外,本实施例的构成和动作等同实施例1进行说明。Hereinafter, unless otherwise specified, the configuration and operation of this embodiment are described in the same manner as in Embodiment 1. FIG.
图14是本发明的实施例2的规约设定装置20的构成示意图。FIG. 14 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of the
如图14所示,本实施例的规约设定装置20在第1实施例的规约设定装置20的基础上,加上动体指定部51和动体抽出部52和动体数据输出部53。As shown in FIG. 14 , the
在动体指定部51使用鼠标等画面操作装置指定被摄图像(即:基础图像)里的动体,提交动体抽出部52解析出该动体的图像数据(STEP-S202)、提交动体数据输出部53生成输出信号提交(STEP-S203)图像处理装置30。Use a screen operation device such as a mouse to designate a dynamic body in a subject image (that is, a basic image) in the dynamic body specifying part 51, and submit the dynamic
图15是本发明的第2实施例的图像处理装置30的构成示意图。FIG. 15 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of an
如图所示本实施例的图像处理装置30在第1实施例的规约设定装置20的基础上,加上接受来自规约设定装置20的动体数据输出部53的信号的动体数据输入部61和动体边缘抽出部62。As shown in the figure, the
动体数据输入部61接受来自规约设定装置20的动体数据输出部53的信号提交动体边缘抽出部62解析出该动体的边缘图像数据,识别跟踪该动体(STEP-S205)。The dynamic body
图16是本发明的第2实施例所构成的报警装置40的构成示意图。Fig. 16 is a schematic diagram showing the structure of an
如图所示本实施例的报警装置40的构成与第1实施例所构成的报警装置40相同,因此省略这部分的说明。As shown in the figure, the configuration of the
(第2实施例的动作)(Operation of the second embodiment)
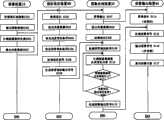
图17是本发明第2实施例的监视系统的动作流程图。Fig. 17 is a flow chart showing the operation of the monitoring system according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
以下,按该图说明监视系统的整个动作过程。Hereinafter, the entire operation process of the monitoring system will be described with reference to this figure.
此外,由摄像装置10所拍摄生成了的图像数据提交给规约设定装置20的显示部显示图像,对该图像设置异常检知规约条件;提交给图像处理装置30,抽出边缘图像和检知异常等处理;经图像处理装置30的图像输出部33提交报警装置40的显示部显示图像和报警内容等一连串的处理和第1实施例的处理(STEP-S101~S109)相同,因此省略这部分的说明。In addition, the image data captured and generated by the
用户在规约设定装置20的图像显示部确认被摄图像(即:基础图像),在动体指定部51指定动体及其活动范围(STEP-S201)。The user confirms the subject image (that is, the base image) on the image display unit of the
例如,在摄图像里该动体是狗的情况下,使用鼠标等画面操作装置将点击该狗或对画圈框住狗以指定该狗为所指定的动体。For example, in the case where the moving body in the photographed image is a dog, the dog is designated as the designated moving body by clicking on the dog or framing the dog using a screen operation device such as a mouse.
下一步,动体抽出部52解析出该动体的图像数据(STEP-S202)、提交动体数据输出部53生成输出信号提交(STEP-S203)图像处理30。Next, the dynamic
图像处理部30的动体数据输入部61接受来自规约设定装置20的动体数据输出部53的信号,由动体边缘抽出部62在所定的摄像区域的边缘图像全体里,认识该动体,并设定为动体的边缘图像(STEP-S205)。The dynamic body
然后,动体边缘抽出部62按时间系列跟踪认识该动体边缘图像的变化。此后,所设定了的动体的边缘图像有位置变化时,动体边缘抽出部62还将继续识别它为同一动体的边缘图像。对该动体的识别处理和原来一样,在此省略详细的说明。Then, the dynamic body
然后,图像数据量计测部36按一定的时间间隔计测来自图像输入部32的数据流量的变化,计算出单位时间之间该数据流量的差分的绝对值(STEP-S110)。判断该绝对值是否超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111)。Next, the image data
该差分的绝对值不超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111/NO)时,图像数据量计测部36判断该摄像领域内没有变化也就是没有发生异常,则返回计测下一时间间隔的图像数据流量变化(STEP-S110,STEP-S111)。When the absolute value of the difference does not exceed the predetermined threshold (STEP-S111/NO), the image data
当该差分的绝对值超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111/Yes)时,图像数据量计测部36判断该摄像领域内发生变化也就是可能出现异常。When the absolute value of the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold (STEP-S111/Yes), the image data
当判断该异常发生时,异常检知部37根据上述的所设定的异常检知条件判断该变化内容,也就是其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件的相关(STEP-S112)。When it is judged that the abnormality occurs, the
当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件无关(STEP-S112/NO)时,则返回计测下一时间间隔的图像数据流量变化(STEP-S110,STEP-S111)。When it is judged that the edge image change has nothing to do with the abnormal setting condition (STEP-S112/NO), then return to measure the image data flow change in the next time interval (STEP-S110, STEP-S111).
当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件相关(STEP-S112/YES)时,异常检知部37根据上述的所设定的异常检知条件判断其边缘图像变化的位置、变化的途径,生成报警输出信号(STEP-S113),提交报警输出装置40。When judging that the edge image change is related to the abnormal setting condition (STEP-S112/YES), the
此后,关于报警输出装置40的处理,和第1实施例的处理一样(STEP-S114)、(STEP-S115),在此省略详细的说明。Thereafter, the processing of the
如以上说明,根据本实施例,抽出包含在边缘图像数据中的动体数据,明确整体边缘图像的变化不包含该动体的边缘图像的变化,则可以容易地检测出该动体以外的可疑动体。As described above, according to the present embodiment, by extracting the moving object data included in the edge image data and making sure that the change of the overall edge image does not include the change of the edge image of the moving object, suspicious objects other than the moving object can be easily detected. moving body.
此外,由于抽出该动体后,该边缘图像数据量比原来的图像数据少,所以图像处理装置30所需处理的数据量也大幅度减少。In addition, since the data volume of the edge image is less than that of the original image data after the moving body is extracted, the data volume to be processed by the
(第2实施例的画面构成例)(Example of screen configuration in the second embodiment)
接下去,由图说明由本实施例报警输出装置40的图像显示部43边缘图像的表示例。Next, an example of displaying an edge image by the
图18(a)(b)是本发明的第2实施例的图像数据的画面表示例的示意图,图18(a)是正常时的图像,图18(b)是异常时的图像。Fig. 18(a)(b) is a schematic diagram showing an example of a screen display of image data in the second embodiment of the present invention, Fig. 18(a) is a normal image, and Fig. 18(b) is an abnormal image.
如图18(a)所示,使用鼠标等画面操作装置将点击人物105,将其指定为正常的动体的人物105,虽然该人物的边缘图像在变化,但看不出其他的边缘图像的变化。As shown in FIG. 18( a), use a screen operation device such as a mouse to click on a
然而,如图18(b)所示,异常时随着被指定为动体的人物105移动,其他的边缘图像盆景104也在移动时,该边缘图像发生变化。此时异常检知部37就判断异常发生。However, as shown in FIG. 18( b ), when the
实施例3、如前所述,在第2实施例的监视系统,从摄像领域里抽出预先指定的动体,从全边缘图像中分离该动体的边缘图像的变化,则可以只检测出可疑人物。Embodiment 3. As mentioned above, in the monitoring system of the second embodiment, the pre-designated moving body is extracted from the imaging field, and the change of the edge image of the moving body is separated from the full edge image, then only suspicious figure.
在本实施例,抽出包含在边缘图像数据中的动体数据,预先指定该动体的行动轨迹,当该动体的行动轨迹超出预先所指定了的轨迹时,则判断摄像领域里发生异常。In this embodiment, the moving object data included in the edge image data is extracted, the trajectory of the moving object is specified in advance, and when the trajectory of the moving object exceeds the specified trajectory, it is determined that an abnormality has occurred in the imaging area.
例如,本实施例的监视系统里,对于定义为单方向通行的路径上的动体出现逆方向移动时,则判断为出错。For example, in the monitoring system of this embodiment, when the moving body on the path defined as one-way traffic moves in the opposite direction, it is judged as an error.
以下,除特别注明外,本发明的构成和动作等同第2发明实施例一样进行说明(第3实施例的构成):Below, unless otherwise specified, the structure and actions of the present invention are described as the same as the second embodiment of the invention (the structure of the third embodiment):
图19是本发明的第3实施例的规约设定装置20的构成示意图。FIG. 19 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of the
如图所示,本实施例的规约设定装置20在第2实施例的规约设定装置20的基础上,加上对动体的移动轨迹进行规约的移动轨迹指定部54和移动轨迹数据输出部55。As shown in the figure, on the basis of the
在移动轨迹指定部54,使用鼠标等画面操作装置规约被摄图像(即:基础图像)里的动体的移动轨迹(例如:规定移动方向,行动路径等等),在移动轨迹数据输出部55生成动体移动轨迹数据提交图像处理装置30。In the moving
图20是本发明的第3实施例的图像处理装置30的构成示意图。FIG. 20 is a schematic configuration diagram of an
如图所示,本实施例的图像处理装置30在第2实施例的图像处理装置30的基础上,加上处理动体的移动轨迹数据输入部63。As shown in the figure, the
在本实施例,同第2发明实施例一样,动体认识部62识别动体边缘图像,由异常检知,进行说明。与第2实施例一样的图像处理装置30在第2实施例的图像处理装置30的基础上,加上处理动体的移动轨迹数据输入部63In the present embodiment, as in the second embodiment of the invention, the moving
图21是本发明的第2实施例的图像处理装置30的构成示意图。FIG. 21 is a schematic configuration diagram of an
如图所示本实施例的报警装置40的构成与第1实施例所构成的报警装置40相同,因此省略这部分的说明:(第3实施例的动作)As shown in the figure, the structure of the
图22是本发明第3实施例的监视系统的动作流程图。Fig. 22 is a flow chart showing the operation of the monitoring system according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
以下,按该图说明监视系统的整个动作过程。Hereinafter, the entire operation process of the monitoring system will be described with reference to this figure.
此外,由摄像装置10所拍摄生成了的图像数据提交给规约设定装置20的显示部显示图像,对该图像设置异常检知规约条件;提交给图像处理装置30,抽出边缘图像和检知异常等处理;经图像处理装置30的图像输出部33提交报警装置40的显示部显示图像和报警内容等一连串的处理和第1实施例的处理(STEP-S101~S109)相同,因此省略这部分的说明。In addition, the image data captured and generated by the
还有,关于动体边缘画面的设定处理和第2实施例的处理(STEP-S201~S204)相同,因此省略这部分的说明。In addition, the setting processing of the dynamic body edge screen is the same as the processing (STEP-S201 to S204) of the second embodiment, so the description of this part is omitted.
下一步,用户在规约设定装置20的图像显示部确认被摄图像(即:基础图像),在动体移动轨迹指定部54指定动体的移动方向(STEP-S205)。Next, the user confirms the captured image (ie, the base image) on the image display unit of the
然后,在移动轨迹数据输出部生成移动在轨迹指定部55指定了的动体的移动方向的信号,提交图像处理装置30(STEP-S206)。Then, a signal for moving the moving body specified by the
图像处理装置30的移动轨迹输入部63接受来自规约设定装置20的移动轨迹数据,由移动轨迹处理部64处理允许被识别的动体的行动轨迹(STEP-S207)。The movement
然后,图像数据量计测部检测图像数据量的变化(STEP-S207)。然后,图像计图像数据量计测部36按一定的时间间隔计测来自图像输入部32的数据流量的变化,计算出单位时间之间该数据流量的差分的绝对值(STEP-S110)。判断该绝对值是否超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111)。Then, the image data amount measuring unit detects a change in the image data amount (STEP-S207). Next, the image meter image data amount measuring
该差分的绝对值不超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111/NO)时,图像数据量计测部36判断该摄像领域内没有变化也就是没有发生异常,则返回计测下一时间间隔的图像数据流量变化(STEP-S110,STEP-S111)。When the absolute value of the difference does not exceed the predetermined threshold (STEP-S111/NO), the image data
当该差分的绝对值超过所定的阀值(STEP-S111/Yes)时,图像数据量计测部36判断该摄像领域内发生变化也就是可能出现异常。When the absolute value of the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold (STEP-S111/Yes), the image data
当判断该异常发生时,异常检知部37根据上述的所设定的异常检知条件判断该变化内容,也就是其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件的相关(STEP-S112)。When it is judged that the abnormality occurs, the
当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件无关(STEP-S112/NO)时,异常检知部37判断被图像数据量计测部36检测出的数据量的变化是由于动体的边缘图像的移动所导致,也就是检测出改动体边缘图像的移动的轨迹。When it is judged that the change in the edge image has nothing to do with the abnormality setting condition (STEP-S112/NO), the
采用这种轨迹检测方法还可以从动画的边缘图像的轮廓的数点求出重心点由此得出重心的移动轨迹。Using this trajectory detection method, the center of gravity can also be obtained from the points of the outline of the animated edge image, thereby obtaining the moving trajectory of the center of gravity.
下一步,异常检知部37参照所检测出的动体边缘图像的轨迹判断该轨迹是否超出移动轨迹指定部所设定了的移动条件(STEP-S112)。Next, the
当判断该轨迹不超出移动轨迹指定部所设定了的移动条件(STEP-S112/NO)时。异常检知部则判断当前的状态为正常状态,继续计测下一时间间隔的图像数据流量变化(STEP-S110,STEP-S111)。When it is judged that the trajectory does not exceed the movement condition set by the movement trajectory specifying unit (STEP-S112/NO). The abnormality detection part then judges that the current state is a normal state, and continues to measure the change of the image data flow in the next time interval (STEP-S110, STEP-S111).
当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件相关(STEP-S112/YES)时,也就是异常检知部37检测出该轨迹超出移动轨迹指定部所设定了的移动条件时,则生成报警输出信号(STEP-S113),提交报警输出装置40。When it is judged that its edge image change is related to the abnormal setting condition (STEP-S112/YES), that is, when the
此外,当判断其边缘图像变化与异常设定条件相关(STEP-S112/YES)时,异常检知部37还可以根据所设定的异常检知条件判断其边缘图像变化的位置、变化的途径,生成报警输出信号(STEP-S113),提交报警输出装置40。In addition, when it is judged that the change of the edge image is related to the abnormality setting condition (STEP-S112/YES), the
此后,关于报警输出装置40的处理,和第1实施例的处理一样(STEP-S114)、(STEP-S115),在此省略详细的说明。Thereafter, the processing of the
如上述说明,按照本实施例抽出边缘图像里所包含的动体边缘图像就可以在该动体的移动轨迹超出预先所设定行动轨迹范围时检测出异常。通常当发现异常的行动或可疑的行动时便能够把握。As described above, by extracting the edge image of the moving body included in the edge image according to this embodiment, an abnormality can be detected when the moving track of the moving body exceeds the range of the preset action track. Usually when unusual behavior or suspicious behavior is detected, it can be grasped.
此外,由于抽出动体边缘图像时所用的图像数据是比原始图像数据少很多的边缘图像数据,大幅度的减少了图像处理装置30所需要处理的数据量。In addition, since the image data used for extracting the edge image of the moving body is much less edge image data than the original image data, the amount of data to be processed by the
(第3实施例的画面构成例)(Screen configuration example of the third embodiment)
接下去,由图说明由本实施例的动体边缘图像的行动轨迹的检测,以及根据检测结果处理所发生的异常。Next, the detection of the action trajectory of the moving body edge image according to the present embodiment, and the processing of abnormalities that occur according to the detection results will be described with reference to the figure.
图23(a)(b)是本发明的第3实施例的图像数据的画面表示例的示意图,图23(a)是正常时的图像,图23(b)是异常时的图像。23( a ) and ( b ) are schematic diagrams showing an example of a screen display of image data according to the third embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 23( a ) is a normal image, and FIG. 23( b ) is an abnormal image.
如图23(a)所示,用户在规约设定装置20的图像显示部确认被摄图像(即:基础图像),在动体移动轨迹指定部54指定动体为人物105,其移动方向为圆圈106内的斜线部分表示允许动体的移动方向的方位。正常时人物105位于移动方向106的中心。As shown in FIG. 23(a), the user confirms the captured image (i.e., the basic image) on the image display unit of the
然而,如图23(b)所示,异常时人物105往移动方向106所示的斜线方向的相反方向移动时,图像处理装置30就检测出摄像领域内发生异常。However, as shown in FIG. 23( b ), when the
实施例4、如前所述,在第1~3实施例的监视系统,是根据图像上的边缘线的形状和位置的变化检测出摄像领域里所发生的异常。Embodiment 4. As mentioned above, in the monitoring systems of Embodiments 1 to 3, abnormalities occurring in the imaging field are detected based on changes in the shape and position of edge lines on the image.
然而,在本实施例的监视系统,是计测摄像领域里的光度的变化,当检测出该变化的值高于或小于预先所设定了的閥值时,则判断摄像领域里发生异常、报警。However, in the monitoring system of the present embodiment, the change of the luminosity in the imaging area is measured, and when it is detected that the value of the change is higher or lower than the preset threshold value, it is judged that an abnormality occurs in the imaging area, Call the police.
例如,当出现摄像装置10的光电器件(镜片等)被破坏、光线被阻塞、强烈闪光等相当的状态时,计测光度呈现显著的高低变化,则判断摄像领域里发生异常。以下,除特别注明外,本发明的构成和动作等同第2发明实施例一样进行说明:(第4实施例的构成)For example, when the photoelectric device (lens, etc.) of the
图24是本发明的第4实施例的摄像装置10的构成示意图。FIG. 24 is a schematic configuration diagram of an
如图24所示,本实施例的摄像装置10在第1实施例的摄像装置10的基础上,加上光度计测部15和光量信号输出部16。As shown in FIG. 24, the
光度计测部15在拍摄摄像领域的同时,计测该摄像领域的光度并生成该光度数据信号。光量信号输出部16与图像输出部14的图像数据同步将该光量数据按所定的时间间隔提交规约设定装置20和图像处理装置30。The photometric measurement unit 15 measures the luminosity of the imaging region and generates the photometric data signal while capturing the imaging region. The light quantity
图25是本发明的第4实施例的规约设定装置20的构成示意图。FIG. 25 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of the
如图25所示,本实施例的规约设定装置20在第1实施例的规约设定装置20的基础上,加上摄像领域的当前光度数据输入部54、光度变化閥值设定部55和光量信号输出部56。在光度变化閥值设定部55,使用游标或键入数字等方式对规约被摄图像(即:基础图像)的操作画面上设定允许光度变化范围的閥值,在光量信号输出部56生成光量信号提交图像处理装置30。As shown in FIG. 25 , the
图26是本发明的第4实施例的图像处理装置30的构成示意图。FIG. 26 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of an
如图所示,本实施例的图像处理装置30在第2实施例的图像处理装置30的基础上,加上光度输入部65、光量信号输入部66和光量变化处理部67。As shown in the figure, the
图27是本发明的第2实施例的图像处理装置30的构成示意图。如图所示本实施例的报警装置40的构成与第1实施例所构成的报警装置40相同,因此省略这部分的说明。FIG. 27 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of an
(第4实施例的动作)(Operation of the fourth embodiment)
图28是本发明第4实施例的监视系统的动作流程图。Fig. 28 is a flow chart showing the operation of the monitoring system according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention.
以下,按该图说明监视系统的整个动作过程。Hereinafter, the entire operation process of the monitoring system will be described with reference to this figure.
由摄像装置10所拍摄生成了的图像数据提交规约设定装置20的显示部显示图像,对该图像设置异常检知规约条件;提交图像处理装置30,抽出边缘图像和检知异常等处理;经图像处理装置30的图像输出部33提交报警装置40的显示部显示图像和报警内容等一连串的处理和第1实施例的处理(STEP-S101~S109)相同,因此省略这部分的说明。The image data captured and generated by the
在摄像装置10,由感光元件11开始拍摄被摄像领域时,与此同时光度计测部15按所定的时间间隔计测受光量(STEP-S301)。In the
然后,光度计测部15将所计测了的光度值转换生成为光量信号,由光量信号输出部16按所定的时间间隔提交规约设定装置20和图像处理装置30(STEP-S302)。此时所输出的光量信号被图像输出部14的图像数据所同步。Then, the photometric measurement unit 15 converts the measured photometric value into a light quantity signal, and the light quantity
在规约设定装置20的图像显示部确认被摄图像(即:基础图像),抽出光量数据(STEP-S303)提供光度变化閥值设定部55设定光度变化条件(STEP-S304),提交设定异常检知条件及其处理。Confirm the subject image (ie: basic image) in the image display part of the
图像处理装置30接受来自摄像装置10的图像数据和光度数据,抽出当前图像的光量数据(STEP-S305),同时接受来自规约设定装置20的异常检知数据,由异常检知部37比较当前图像的光量数据与异常检知数据的差距,判断当前图像的光量值是否在所设定的允许光度变化范围内(STEP-S306)。The
在当前图像的光量值不超出预先设定了的异常检知条件的范围时(STEP-S306/NO),异常检知部37判断摄像领域处于正常状态,继续监视下一时刻的光度值(STEP-S306)。When the light intensity value of the current image does not exceed the scope of the preset abnormal detection condition (STEP-S306/NO), the
然而,在当前图像的光量值超出预先设定了的异常检知条件的范围时(STEP-S306/YES),异常检知部37判断摄像领域发生异常,触发生成报警信号(STEP-S113),提交报警输出装置40。However, when the light value of the current image exceeds the range of the preset abnormality detection conditions (STEP-S306/YES), the
此后,关于报警输出装置40的处理,和第1实施例的处理一样(STEP-S114)、(STEP-S115),在此省略详细的说明。Thereafter, the processing of the
如上述说明,按照本实施例在所定的摄像领域内,当光度发生变化时能及时检测出该摄像领域的异常,因此在摄像领域里的照明被关掉、摄像装置10被认为造成不能摄像的情况下,则可以及时的发现和把握在该摄像领域里出现问题。As described above, according to this embodiment, in the predetermined imaging area, when the luminosity changes, the abnormality in the imaging area can be detected in time, so the illumination in the imaging area is turned off, and the
如上述说明,由于上述的实施例的监视系统的图像处理装置30首先计测图像数据的数据量的变化,只当该变化量超过所定的阈值时才判断摄像领域发生异常;然后触发报警装置发出警报。所以与原来采用诸一比较图像数据的像素变化检测图像的异常的系统相比,能大幅度地减少所需处理的数据量。As explained above, because the
此外,图像处理装置30按数据量检测出异常时,根据“边缘检测”及“色块模式匹配”的方法抽出图像数据里的边缘图像数据,检测边缘图像的变化,只当出现该变化量时,才判断摄像领域发生异常,与原来采用诸一比较图像数据的彩色像素变化检测图像的异常的系统相比,不仅能大幅度地减少所需处理的数据量,还能辨别发生异常的详细范围。In addition, when the
此外,上述的实施例的监视系统的图像处理装置30把报警信号提交报警装置40,该报警信号由报警装置40发出警报、也能强制显示发生异常的摄像领域、也能把该报警信息通过邮件的形式通知相关方面。In addition, the
上述第1~第4实施例的监视系统的功能可以根据需要进行适当的组合。The functions of the monitoring systems of the first to fourth embodiments described above can be appropriately combined as needed.
此外,上述的规约设定装置20或者图像处理装置30或者报警装置40主要是通过CPU和存储器驻留程序来实现。也可以通过任意的硬件和软件的组合构成类似的装置或者服务器来实现,具备这样高度的设计自由度必将被同行所理解。In addition, the aforementioned
此外,将上述的规约设定装置20或者图像处理装置30或者报警装置40构成软件模块群时,这些程序开已被记录在光记录媒体、磁记录媒体、光磁记录媒体、半导体记录媒体上,再从上述的记录媒体读出驻留到相应的装置,或者通过网络从外部设备下载到相应的装置。此外,上述的实施例只不过是任意的几个实施例,不是本发明的唯一实施例,再不脱离本发明的要点的范围内可以有各种各样的实施例。由上述的构成要素的任意组合,和本发明的构成要素与表现方法、装置、系统、计算机的程序、容纳计算机程序的媒体等等之间相互置换的内容均作为本发明的保护范围。In addition, when the above-mentioned
Claims (15)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2007100090900ACN100538756C (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2007-06-11 | A kind of reflection identification alarm system and alarm method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2007100090900ACN100538756C (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2007-06-11 | A kind of reflection identification alarm system and alarm method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN101192328A CN101192328A (en) | 2008-06-04 |
| CN100538756Ctrue CN100538756C (en) | 2009-09-09 |
Family
ID=39487295
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2007100090900AActiveCN100538756C (en) | 2007-06-11 | 2007-06-11 | A kind of reflection identification alarm system and alarm method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100538756C (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8594482B2 (en) | 2010-05-13 | 2013-11-26 | International Business Machines Corporation | Auditing video analytics through essence generation |
| WO2014017105A1 (en)* | 2012-07-26 | 2014-01-30 | 京セラ株式会社 | Image monitoring device, mobile body, program, and failure determination method |
| CN103151020A (en)* | 2013-02-18 | 2013-06-12 | 明基电通有限公司 | Display device |
| CN103268686A (en)* | 2013-05-14 | 2013-08-28 | 苏州福丰科技有限公司 | Anti-theft system based on face recognition |
| CN104270622A (en)* | 2014-10-29 | 2015-01-07 | 杭州凯达电力建设有限公司 | A switchgear detection method and system |
| CN104792795A (en)* | 2015-04-30 | 2015-07-22 | 无锡英斯特微电子有限公司 | Image testing method of optical mouse chip |
| CN106559635A (en)* | 2015-09-30 | 2017-04-05 | 杭州萤石网络有限公司 | A kind of player method and device of multimedia file |
| CN106559632B (en)* | 2015-09-30 | 2021-02-12 | 杭州萤石网络有限公司 | Multimedia file storage method and device |
| CN106781166A (en)* | 2016-12-08 | 2017-05-31 | 国网山东省电力公司烟台供电公司 | A kind of transmission line of electricity external force damage prevention early warning system |
| CN109544862A (en)* | 2018-12-21 | 2019-03-29 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Behavior recognition method and device based on smart home, storage medium and equipment |
| CN114170752A (en)* | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-11 | 潍坊欣龙生物材料有限公司 | Monitoring method for perimeter security |
| CN114821978B (en)* | 2022-06-27 | 2022-11-15 | 杭州觅睿科技股份有限公司 | Method, device and medium for eliminating false alarm |
- 2007
- 2007-06-11CNCNB2007100090900Apatent/CN100538756C/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101192328A (en) | 2008-06-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN100538756C (en) | A kind of reflection identification alarm system and alarm method | |
| US9286778B2 (en) | Method and system for security system tampering detection | |
| JP4629090B2 (en) | Camera tampering detection | |
| EP0967584B1 (en) | Automatic video monitoring system | |
| JP2010009134A (en) | Image processing system, image processing method, and program | |
| US20080136934A1 (en) | Flame Detecting Method And Device | |
| KR100837406B1 (en) | Portable terminal including video surveillance device, video surveillance method using same, and video surveillance system | |
| Parveen et al. | A motion detection system in python and opencv | |
| US20080137906A1 (en) | Smoke Detecting Method And Device | |
| CN101461239B (en) | Video verification system and method for central station alarm monitoring | |
| KR101046819B1 (en) | Intrusion monitoring method and intrusion monitoring system by software fence | |
| KR20230097854A (en) | Method and system for recognizing dangerous behavior of workers in power plant | |
| KR20130047131A (en) | Method and system for surveilling contents of surveillance using mobile terminal | |
| CN118570521A (en) | A method and device for identifying alarms based on intelligent analysis equipment and business models | |
| US9111237B2 (en) | Evaluating an effectiveness of a monitoring system | |
| TWI448992B (en) | Mothod for video monitoring | |
| KR20220000221A (en) | A camera apparatus for providing a intelligent security surveillance service based on edge computing | |
| CN102737225A (en) | Image monitoring system and person number calculating method | |
| Mariappan et al. | A design methodology of an embedded motion-detecting video surveillance system | |
| Zeng et al. | A novel campus fire monitoring system based on YOLOv5 | |
| TWM495585U (en) | Home security video surveillance system | |
| JP2012003595A (en) | Notification device | |
| Gopal et al. | Computer Vision and Tkinter Tool | |
| CN117132920A (en) | Video analysis method and device for transmission line terminal, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| Patil et al. | REVIEW ON IMAGE PROCESSING BASED FIRE DETETION USING RASPBERRY PI |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20230315 Address after:1213, Strait Building, No. 9, Hubin East Road, Siming District, Xiamen City, Fujian Province, 361000 Patentee after:Nuobishi Technology(Xiamen) Co.,Ltd. Address before:361000, room two, building 205, building A, innovation building, Xiamen Software Park, Fujian Patentee before:Nuobishi Technology(Xiamen) Co.,Ltd. Patentee before:Lu Shaoyan |