CN100524211C - Update system and method for updating scanning subsystem in mobile communication frame - Google Patents
Update system and method for updating scanning subsystem in mobile communication frameDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100524211C CN100524211CCNB2004800169936ACN200480016993ACN100524211CCN 100524211 CCN100524211 CCN 100524211CCN B2004800169936 ACNB2004800169936 ACN B2004800169936ACN 200480016993 ACN200480016993 ACN 200480016993ACN 100524211 CCN100524211 CCN 100524211C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- renewal
- mobile communication
- scanning subsystem
- scanning
- handle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及移动通信设备的安全领域,具体地说,是关于扫描移动通信设备以侦测恶意软件。The present invention relates to the field of security of mobile communication devices, in particular, to scanning mobile communication devices to detect malicious software.
背景技术Background technique
在过去的十年中,移动蜂窝式电话的数目与使用增长迅速。最近一段时期,引入了无线设备,它能将移动电话与个人数字助理(PDA)的功能相结合。可以预计,在未来一段时间内,随着新型蜂窝式电信标准(例如:GPRS、UMTS及WAP)使得跨无线界面上的高速数据传输成为可能,这一领域将经历强劲的增长。The number and use of mobile cellular telephones has grown rapidly over the past decade. More recently, wireless devices have been introduced that combine the functionality of a mobile phone with a personal digital assistant (PDA). This area can be expected to experience strong growth in the coming period as new cellular telecommunication standards such as GPRS, UMTS and WAP enable high-speed data transmission across wireless interfaces.
可以预计,无线通信平台将有可能遭受到所谓的恶意软件(malware),如病毒、特洛伊木马、计算机蠕虫(下文中统称为‘病毒’),以及其它干扰性/有害内容的侵袭;其侵害方式与现今个人计算机以及工作站所受侵害方式大致相同。事实上已经有多种移动电话病毒被确认。It can be expected that the wireless communication platform may be attacked by so-called malicious software (malware), such as viruses, Trojan horses, computer worms (hereinafter collectively referred to as 'viruses'), and other disturbing/harmful content; Much the same way personal computers and workstations are compromised today. In fact, several mobile phone viruses have been identified.
为抵御病毒的袭击,必须在移动平台上布置安装防病毒软件,其方式与桌上型计算机环境的布置方式大致相同。多种不同的桌上型防病毒应用软件现已问世。这些应用软件的大部分依靠一种基本的扫描引擎,它会寻找可疑档案中是否存在预先确定的病毒签名。这些签名储存在一个数据库中,必须经常对其进行更新,以反映最新识别的病毒信息。To defend against virus attacks, antivirus software must be deployed on mobile platforms in much the same way as it is deployed in desktop computer environments. There are many different desktop antivirus applications out there. Most of these applications rely on a basic scan engine that looks for the presence of predetermined virus signatures in suspicious files. These signatures are stored in a database that must be updated frequently to reflect newly identified virus information.
一般来说,用户们可以每隔一段时间通过互连网、从接收的电子邮件、或从一张光盘和软盘下载替换用数据库。用户们也需要时常更新软件引擎,以便于在发现新类型的病毒时利用最新的病毒侦测技术。Typically, users can download replacement databases at regular intervals via the Internet, from incoming e-mail, or from a CD or floppy disk. Users also need to update the software engine from time to time, so as to take advantage of the latest virus detection technology when new types of viruses are found.
移动无线平台给软件开发商们(包括防病毒软件开发商)带来了一系列的问题。这些问题中主要是有限的内存和移动平台的处理能力,以及它们所拥有的有限的输入/输出能力(例如,无光盘驱动或软驱,无高带宽的固定线路网络或互联网连接)。不幸的是,这一缺点使得所有对移动通信设备进行的更新工作变得难以开展。Mobile wireless platforms present a host of problems for software developers, including antivirus software developers. Chief among these problems are the limited memory and processing power of mobile platforms, and the limited input/output capabilities they possess (eg, no CD-ROM or floppy drives, no high-bandwidth fixed-line network or Internet connections). Unfortunately, this shortcoming makes all updates to mobile communication devices difficult.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明提供了一种可有效更新移动通信设备中的扫描子系统的系统、方法和计算机程序产品。首先接收到的是用于更新一台移动通信设备的扫描子系统的第一部分更新程序。之后,除了接收到第一部分更新之外,还可以接收到更多的更新部分。然后该更新程序就被安装于该扫描子系统。The present invention provides a system, method and computer program product for efficiently updating a scanning subsystem in a mobile communication device. First received is the first part of the update program for updating the scanning subsystem of a mobile communication device. Afterwards, in addition to receiving the first part of the update, further parts of the update may be received. The update program is then installed on the scanning subsystem.
在一个实施例中,可确定更新程序是否具有完整性。相应地,根据该更新的完整性,该更新程序可有条件地安装于扫描子系统。In one embodiment, it may be determined whether the update has integrity. Accordingly, the update program may be conditionally installed on the scanning subsystem according to the integrity of the update.
作为一种选择,更新的完整性可以通过使用一个签名来决定。此签名可以通过更新的某一部分来接收(比如最后一部分)。之后,可以将该签名与另一个通过利用更新的每个部分而生成的签名进行比对。Alternatively, the integrity of the update can be determined by using a signature. This signature can be received by some part of the update (say the last part). This signature can then be compared against another signature generated by utilizing each part of the update.
为适应移动通信框架中固有的有限带宽问题,更新程序的一部分可以最小化。此外,可以针对更新程序的某些部分进行压缩。To accommodate the limited bandwidth issues inherent in mobile communication frameworks, part of the update procedure can be minimized. Additionally, some parts of the updater can be compressed.
在使用中,可以决定第一部分是否为空。由此,可以基于第一部分是否决定为空而针对更新程序的其它部分进行有条件的接收。同样,此特征对于解决移动通信框架中固有的有限带宽接收问题也有益处。In use, it can be determined whether the first part is empty or not. Thus, other parts of the update program can be conditionally accepted based on whether the first part is determined to be empty. Also, this feature is beneficial for solving the limited bandwidth reception problem inherent in the mobile communication framework.
作为一种选择,使用扫描子系统的扫描可以在接收到更新程序的时候暂停。此外,扫描可以在更新程序被安装于扫描子系统中之后继续进行。As an option, scanning using the scanning subsystem can be paused when an update is received. Additionally, scanning can continue after updates have been installed in the scanning subsystem.
在另外一个实例中,可将更新程序的每一部分的格式进行特殊设计,使其能适应移动通信框架固有的有限带宽的问题。例如,更新程序的每个部分可以包括一个头文件。该头文件可以指明一个与更新程序相关联部分的识别码、与更新程序相关联部分的一段长度等。In another example, each portion of the update program can be formatted specifically to accommodate the limited bandwidth inherent in mobile communication frameworks. For example, each section of the updater may include a header file. The header file may indicate an identification code of a part associated with the update program, a length of a part associated with the update program, and the like.
在另外一个实例中,可由移动通信设备发出更新请求。该更新可以由带有一请求数据结构的移动通信设备发出请求。该数据结构可以选择性地包括数个变量,例如一个统一资源定位器(URL)变量,一个移动通信识别码变量,一个应用程序接口版本变量,一个侦测逻辑变量,一个签名版本变量,和/或一个部分号码变量。In another example, the update request can be issued by the mobile communication device. The update can be requested by the mobile communication device with a request data structure. The data structure can optionally include several variables, such as a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) variable, a mobile communication identifier variable, an API version variable, a detection logic variable, a signature version variable, and/or or a partial number variable.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是移动通信框架一个实施例示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a mobile communication framework;
图2是移动通信框架另一个实施例示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of another embodiment of the mobile communication framework;
图3是与一个移动通信设备相关联的一个架构的实施例示意图;Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of an architecture associated with a mobile communication device;
图4是一个通过使用一台移动通信设备访问安全或内容分析功能的系统的实施例示意图;4 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a system for accessing security or content analysis functions through the use of a mobile communication device;
图5是根据图4所示系统的一个应用服务器的实施例,通过使用一台移动通信设备访问安全或内容分析功能框架的示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of accessing security or content analysis function framework by using a mobile communication device according to an embodiment of an application server of the system shown in Fig. 4;
图6是根据图4所示系统的一个重复加载函数库的实施例,通过使用一台移动通信设备访问安全或内容分析功能框架的示意图;Fig. 6 is a schematic diagram of accessing a security or content analysis function framework by using a mobile communication device according to an embodiment of a repeatedly loaded function library of the system shown in Fig. 4;
图7是在图4所示系统下执行的一个按需式扫描系统的示意图;Fig. 7 is a schematic diagram of an on-demand scanning system implemented under the system shown in Fig. 4;
图8是一个应用程序接口(API)的各种不同组件的一个阶梯状关系的实施例示意图,它可以用于在移动应用程序与一个扫描子系统之间提供接口;FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a ladder-like relationship of various components of an application program interface (API), which may be used to provide an interface between a mobile application and a scanning subsystem;
图9是一个示范型函数库接口启动的示意图;Fig. 9 is a schematic diagram of an exemplary function library interface starting;
图10是一个出错代码功能的一个示范性格式的实施例示意图;Fig. 10 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of an exemplary format of an error code function;
图11是一个扫描子系统API的调用次序的实施例示意图;Fig. 11 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of the calling sequence of the scanning subsystem API;
图12是一个示范性配置API的调用次序的实施例示意图;Fig. 12 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of the call sequence of an exemplary configuration API;
图13是各种不同的示范性扫描数据类型的示意图,这些数据类型可以由应用程序通过一个API传递到扫描子系统;Figure 13 is a schematic diagram of various exemplary scan data types that may be passed by an application to the scan subsystem through an API;
图14是一个包含恶意软件严重性标识和应用程序表现水准的位-域变量的示范性实施例示意图;14 is a schematic diagram of an exemplary embodiment of bit-field variables containing malware severity indications and application performance levels;
图15是一个图表示意图,该图阐述了运用扫描子系统进行扫描的时间作为通过图13中的变量所识别的数据类型的一个函数而变化的方式;Figure 15 is a schematic diagram of a graph illustrating how the time to scan using the scanning subsystem varies as a function of the data type identified by the variables in Figure 13;
图16是一个示范性流程的实施例示意图,该流程描述了该更新程序由一个用户界面启动的方式。FIG. 16 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of an exemplary flow describing the manner in which the update procedure is initiated by a user interface.
图17是对一台移动通信设备的一个扫描子系统进行有效更新的方法的实施例示意图。Fig. 17 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a method for efficiently updating a scanning subsystem of a mobile communication device.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
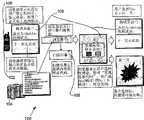
图1是一个移动通信框架100的实施例示意图。如图所示,该框架包括移动通信设备102以及能够通过无线网络进行通信的后端服务器104。在当前描述的环境下,移动通信设备102可包括(但并不局限于)蜂窝式电话、无线个人数字助理(PDA)、无线掌上电脑、无线手提式电脑或任何其它能够通过无线网络进行通信的移动设备。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a
在一个实施例中,移动通信设备102可配备一扫描子系统105。该扫描子系统105可包括任何能够储存于移动通信设备102或存放于所进行通信之中的扫描数据的子系统。当然,该扫描可以是访问式扫描、需求式扫描或者其他任何类型的扫描。此外,扫描可能牵涉到上述数据所代表的内容(即文本、图片等),以及对恶意软件进行的通用安全类型的扫描等等。In one embodiment, the mobile communication device 102 may be equipped with a
仍旧回到图1,移动通信设备102可以进一步配备有一个能够描绘多个图形用户界面108的显示器106,此显示器经过改装以用于管理包括以上所述扫描功能在内的各种功能。Still returning to FIG. 1, the mobile communication device 102 may be further equipped with a
使用时,移动通信设备102的显示器106用于在一个网络(如互联网等)上显示数据。请参见操作1。在当前的使用过程中,用户可以使用显示器106浏览各类网络上的数据,具体是通过后端服务器104选择链接或锚点以从网络上获取数据。请参见操作2。接着,在操作3中,扫描子系统105被调用以扫描所获取的数据。In use, the
在当前的实施例中,扫描子系统105显示出已经找到与操作4中所获取数据有关的恶意软件。此时,通过显示器106向一位用户提供了一个选项,即中断此次获取和/或使用/访问该数据而忽略所识别出的恶意软件,如操作5所示。基于操作5中的决定,用户会或不会成为一次‘攻击’的对象,如操作6所示。In the current embodiment, the
图2是基于另一个实施例的移动通信框架200的示意图。该移动通信框架200类似于图1所示的移动通信框架100,只是移动通信设备对所获取数据中恶意软件的识别作出反应的方式有所不同。Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of a
具体地,操作5中仅提供给用户一个选项。即,用户只能关闭任何与被发现包含恶意软件的数据有关的对话。Specifically, in
图3显示了基于一个实施例的与移动通信设备相关联的架构300。当前的架构300可以包含于图1和图2的移动通信设备。当然,架构300可在任何所需的场合执行。Figure 3 shows an
如图所示,当前的架构300可包括多个移动应用程序302。在当前描述的情况下,移动应用程序302可包括任何安装于移动通信设备中的应用程序或软件等,以利于开展不同的任务。还应该注意,该应用程序302也可以按用户的需要安装于固件、硬件等之中。As shown, the
在另一个实施例中,应用程序302可包括(但是并不限于)邮件应用程序,其任务包括管理电子邮件。此外,该应用程序可以包括浏览器应用程序,其任务包括浏览网络。另外,该应用程序还可以包括电话簿应用程序,其任务包括管理多个电话号码。作为一种选择,该应用程序可以包括消息应用程序,其任务包括消息通信。应该注意,该应用程序可为任何类行。例如,可以为Java应用程序或其他类似的程序。In another embodiment,
继续回到图3,通过第一个应用程序接口(API)306及第一个同扫描子系统304相关的函数库308,扫描子系统304与应用程序302进行通信。更多关于第一个应用程序接口306及第一个函数库308的可选择示范性信息将在下文讨论图4-12的时候作进一步阐述。Continuing back to FIG. 3 , the
作为一种选择,应用程序302可同扫描子系统304进行信息通信,以方便扫描子系统304的扫描工作。该信息可以同将要进行扫描的数据类型、及同此类扫描相关的时间安排有关。更多关于扫描子系统304同应用程序302以此种万式进行互动的示范性信息将在讨论图13-15的时候作进一步阐述。Alternatively,
如图3所示,第一个函数库308可包括更新管理器310、配置管理器312、以及一个签名数据库314。在使用中,该更新管理器310可管理签名数据库314更新扫描用的最新签名的过程。在一个实施例中,更新的过程可以进行简化以适应移动通信框架固有的有限带宽的问题。更多的关于该更新过程的示范性信息将在讨论图16-17时进行阐述。As shown in FIG. 3 , the
作为图3中架构300的一个组成部分又进一步提供了操作系统316,该操作系统安装于移动通信设备上并经过改装以方便执行应用程序302。在一个实施例中,扫描子系统304可以独立于平台,因此能够在任何操作系统/移动通信设备组合中加以执行。An
为适应这个特性,安排了第二个应用程序接口318以及第二个函数库320,其能够支持多种功能,例如系统/函数库初始化322、出错函数336、内存分配334、输入/输出(I/O)328、数据授权332、同步330、高级文本传送协议326、设备信息324、调试338、以及其他功能(即共享内存、系统时间,等)。在一个实施例中,第二个应用程序接口318可以是独立于平台的,类似于扫描子系统304。更多关于第二个应用程序接口318及第二个函数库320的可选择示范性细节将在讨论附件A时作进一步阐述。To adapt to this feature, a second
图4显示了基于一个实施例的系统400,其通过使用一台移动通信设备以访问安全或内容分析功能。在一个范例中,当前的系统400可在图3之架构300中的应用程序、扫描子系统以及操作系统环境下执行。但是应该注意到,当前的系统400可在任何所需的环境下加以执行。Figure 4 shows a
如图所示,这里包括了能通过无线网络进行通信的安装于一移动通信设备的操作系统402。另外还提供了安装于移动通信设备的应用程序404,其通过使用操作系统402加以执行并完成各种任务。As shown, there is included an
扫描子系统406通过一个应用程序接口及一个关联函数库(参见图3中的第一个应用程序接口306及第一个函数库308)保持与应用程序404进行通信。该扫描子系统406经过改装以访问安全或内容分析功能,以及应用程序404所进行的任务。在一个实施例中,安全或内容分析为安全分析。在另外一个实施例中,安全或内容分析为内容分析。另外,安全或内容分析可以包括按需式病毒扫描和/或存取式病毒扫描。The
在使用中,安全或内容分析功能可应用于与应用程序404所运行任务相关联的应用数据。在当前描述的环境下,应用数据可包括任何由应用程序404执行的任务所输入、处理、输出的数据或其他与之相关的数据。In use, security or content analysis functions may be applied to application data associated with tasks performed by the
通过应用程序接口使扫描子系统406与应用程序404紧密联合,可以降低管理费用与代码重复率。更多关于该应用程序接口与相关函数库的示范性信息将在讨论此后的图表时作进一步阐述。Tight coupling of the
图5基于图4中系统400的应用服务器,显示了通过使用移动通信设备访问安全或内容分析功能的框架500。应该注意到当前的框架500可以在任何所需的环境中加以执行。FIG. 5 shows a
如图所示,扫描子系统可包括扫描程序502,该扫描程序通过应用程序接口506以及一个关联的协议(例如uItron消息联络系统)与应用程序504进行通信。应用程序接口506会牵涉到一个与扫描程序502相关联的第一个组件508,以及与应用程序504相关联的第二个组件510,这会在下文中作进一步阐述。As shown, the scanning subsystem may include a
向应用程序接口506提供的多种不同的调用512可包括开放式的调用、数据调用、以及封闭式的调用。在使用中,扫描程序502可以扫描与应用程序504所运行的任务相关联的应用数据516。The number of
图6所示为一个通过使用移动通信设备用以访问安全或内容分析功能的框架600,该框架与图4中系统400的重复加载库实例相一致。应该注意,当前的框架600可以在任何所需的环境下加以执行。FIG. 6 shows a
如图所示,扫描子系统可包括一个重复加载函数库602。在使用中,扫描子系统重复加载函数库602可在运行时连接于应用程序604。由此,应用程序接口606可以被植入多个应用程序604中的每一个之中。As shown, the scanning subsystem may include a reload
类似于先前图5中的框架500,应用程序接口606可能涉及多种不同的调用612,包括开放式的调用、数据调用、以及封闭式的调用。在使用中,重复加载函数库602可以用于扫描与应用程序604所运行的任务相关的应用数据616。Similar to the
图7所示为一个在图4中系统400环境下执行的按需式扫描系统700。应该注意,当前系统700可以在任何所需的环境下加以执行。FIG. 7 shows an on-
按需式扫描对所储存应用数据702进行扫描,以侦测恶意内容或代码并在发现后将其除去。用户可以通过一个用户界面703来启动按需式扫描。此外,每个应用程序704可以调用扫描子系统706以运行针对储存于相应内存内对象进行的扫描。On-demand scanning scans stored
另一方面,按需式扫描在应用程序704处理或转换应用数据702之前提供了对恶意代码或内容的识别。在扫描子系统706侦测到恶意应用数据702之前,按需式扫描对于用户是透明的。On-demand scanning, on the other hand, provides identification of malicious code or content before the
图8基于一个实施例,显示了应用程序接口800的各种不同组件的层次体系,可用于在移动应用程序与一个扫描子系统之间提供接口。作为一种选择,当前的应用程序接口800可以在图4中系统400的环境下加以执行。但是应该注意到,当前的应用程序接口800可以在任何所需的环境下加以执行。Figure 8 shows a hierarchy of various components of an
如图8所示,应用程序接口的函数包括MdoScanOpen()802、MDoScanClose()804、MDoScanVersion()806、及MDoScanData()808。MoDoScanOpen()802和MDoScanClose()804是用于创建/打开并关闭一个扫描子系统对象实例。MDoScanVersion()806提供了扫描子系统及签名模式数据版本信息。MDoScanData()808运行内容/数据扫描及报告。同时包括在扫描应用程序接口中的有MDoScanUpdate()810,它能提供恶意软件签名数据库及侦测逻辑更新。当MDoScanUpdate()810由一次更新应用所调用时,函数库就会连接上一个远程后端服务器(参见例如图1)并下载最新的文件(例如mdo.sdb与mdo.pd)。As shown in FIG. 8 , the functions of the API include MdoScanOpen() 802 , MDoScanClose() 804 , MDoScanVersion() 806 , and MDoScanData() 808 . MoDoScanOpen() 802 and MDoScanClose() 804 are used to create/open and close a scanning subsystem object instance. MDoScanVersion() 806 provides scanning subsystem and signature mode data version information. MDoScanData() 808 runs content/data scanning and reporting. Also included in the scanning API is MDoScanUpdate() 810, which provides malware signature database and detection logic updates. When MDoScanUpdate() 810 is called by an update application, the function library will connect to a remote backend server (see eg Figure 1) and download the latest files (eg mdo.sdb and mdo.pd).
扫描子系统配置是通过运用MDoConfigOpen()812、MDoConfigClose()814、MDoConfigGet()816以及MDoConfigSet()818所达成的。一旦一个配置句柄通过调用当前的应用程序接口800而获得,进行调用的应用程序使用get与set配置API以查询并设定扫描子系统配置的各种变量。Scanning subsystem configuration is accomplished using MDoConfigOpen( ) 812 , MDoConfigClose( ) 814 , MDoConfigGet( ) 816 and MDoConfigSet( ) 818 . Once a configuration handle is obtained by calling the
同时包含于当前应用程序接口800的是一个称为MDoGetLastError()820的出错获取函数。该函数用于获取关于已发生的最后出错的信息。Also included in the
在作出任何API调用之前,最好是在启动时间,MDoSystemInit()825被调用以初始化函数库环境设置。该函数库保存了配置设置、恶意软件代码侦测逻辑(如mdo.pd)与签名数据库(如mdo.sdb)、及各种内部变量(如同步对象,等),并将其存放于固定的持续性储存地点。Before any API calls are made, preferably at startup time, MDoSystemInit() 825 is called to initialize the library environment settings. This function library saves configuration settings, malware code detection logic (such as mdo.pd) and signature database (such as mdo.sdb), and various internal variables (such as synchronization objects, etc.), and stores them in a fixed persistent storage location.
MDoLibraryOpen()830和MDoLibraryClose()840用于初始化函数库。一个应用程序可以在任何其它的API调用发生之前调用MDoLibraryOpen()830,而且应用程序可以在终止之前调用MDoLibraryClose()840。MDoLibraryOpen() 830 and MDoLibraryClose() 840 are used to initialize the function library. An application can call MDoLibraryOpen( ) 830 before any other API calls occur, and the application can call MDoLibraryClose( ) 840 before terminating.
应用程序接口800可以通过使用不同的应用程序接口组件从而能够支持各种不同的功能,例如系统环境初始化、版本状态信息获取、更新扫描子系统、扫描、配置扫描子系统,等。更多关于在应用程序接口800环境下上述功能的信息将在下文进行阐述。The
系统初始化system initialization
MDoSystemInit()825针对保存于特定永久储存域的数据进行验证与环境初始化工作。一个恶意代码/内容签名模式的数据库(即mdo.sdb)、侦测逻辑(即mdo.pd)、配置设置、以及同步对象可以储存于这些存储域中。MDoSystemInit()825可以在API函数中的任一函数被执行之前被调用一次(即在启动时)。MDoSystemInit() 825 performs verification and environment initialization for data stored in a specific permanent storage domain. A database of malware/content signature patterns (ie, mdo.sdb), detection logic (ie, mdo.pd), configuration settings, and synchronization objects can be stored in these storage domains. MDoSystemInit() 825 may be called once (ie at startup) before any of the API functions are executed.
表#1说明了关于MDoSystemInit()825的示范性信息。Table #1 illustrates exemplary information about MDoSystemInit() 825.
表#1Table 1
MDoSystemInitMDoSystemInit
描述describe
核实并初始化系统环境信息Verify and initialize system environment information
原型prototype
int MDoSystemInit(void);int MDoSystemInit(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
如成功则0,否则为零出错代码。0 if successful, otherwise Zero error codes.
函数库接口APIFunction library interface API
应用程序接口800包括多个函数库接口组件。API接口实例化可以通过使用MDoLibraryOpen()830来达成。使用该函数而获得的实例化函数库接口句柄可以用于其后的API调用。在该应用程序终结之前,MDoLibraryClose()840可以被调用以释放该句柄。图9说明了通过使用MDoLibraryOpen()830及MDoLibraryClose()840的一个示范性函数库接口初始化过程900。
表#2说明了关于MDoLibraryOpen()830的示范性信息。Table #2 illustrates exemplary information about MDoLibraryOpen() 830.
表#2Table 2
MDoLibraryOpenMDoLibraryOpen
描述describe
初始化并返回一个API函数库界面句柄Initialize and return an API function library interface handle
原型prototype
MDOLIB_HANDLE MDoLibraryOpen(void);MDOLIB_HANDLE MDoLibraryOpen(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
如成功,则返回函数库界面句柄,If successful, return the function library interface handle,
否则为INVALID_MDOLIB_HANDLE。Otherwise INVALID_MDOLIB_HANDLE.
也可参见see also
MDoLibraryClose()MDoLibraryClose()
表#3说明了关于MDoLibraryClose()840的示范性信息。
表#3table 3
MDoLibraryCloseMDoLibraryClose
描述describe
释放由MDoLibraryClose()函数返回的与一个API函数库句柄相关联的系Releases the relationship associated with an API library handle returned by the MDoLibraryClose() function.
统资源system resources
原型prototype
void MDoLibraryClose(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib);void MDoLibraryClose(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib);
参数parameter
hLibhLib
[in]由MDoLibraryOpen返回的函数库句柄[in] The function library handle returned by MDoLibraryOpen
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
MDoLibraryOpen()MDoLibraryOpen()
出错获取get error
一旦函数库已经成功地由MDoLibraryOpen()830初始化并实例化,MDoGetLastError()820向应用程序提供关于最近一次发生出错的信息。Once the library has been successfully initialized and instantiated by MDoLibraryOpen( ) 830, MDoGetLastError( ) 820 provides the application with information about the last time an error occurred.
表#4说明了关于MDoGetLastError()820的示范性信息。Table #4 illustrates exemplary information about MDoGetLastError() 820.
表#4Table 4
MDoGetLastErrorMDoGetLastError
描述describe
返回指定的函数库实例的最后一次出错值Returns the last error value of the specified library instance
原型prototype
MDoErrorCode MDoGetLastError(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib);MDoErrorCode MDoGetLastError(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib);
参数parameter
hLibhLib
[in]由MDoLibraryOpen返回的函数库句柄[in] The function library handle returned by MDoLibraryOpen
返回值return value
MDoErrorCode数据类型可以被定义为一个32位的无符号整数,它既包含组件又包含出错代码。通常,获取的出错信息可能被设定在平台抽象API层。有鉴于此,此处所给的MDoErrorCode格式类似于由抽象层API所定义的AlErrorCode格式(参见附件A)。图10基于一个实施例说明了一个MDoErrorCode的示范性格式1000。The MDoErrorCode data type can be defined as a 32-bit unsigned integer that contains both the component and the error code. Usually, the error information obtained may be set at the platform abstraction API layer. For this reason, the MDoErrorCode format given here is similar to the AlErrorCode format defined by the abstraction layer API (see Appendix A). FIG. 10 illustrates an
表#5说明了关于MDoGetLastError()820的示范性信息。
表#5table 5
MDoErrorCode被定义为:MDoErrorCode is defined as:
typedef unsigned long MDoErrorCode;typedef unsigned long MDoErrorCode;
也可参见see also
MDoLibraryOpen(),MDoScanOpenO,MDoScanData(),MDoLibraryOpen(), MDoScanOpenO, MDoScanData(),
MDoScanUpdate()MDoScanUpdate()
示范性计算机代码#1通过调用一次MDoGetLastError()820说明了一个样本函数库的调用次序。Exemplary Computer Code #1 illustrates a sample function library call sequence by calling MDoGetLastError() 820 once.
计算机代码#1Computer Code #1
出错代码error code
一个由MDoGetLastError820报告的出错代码包括两个部分:组件代码与出错代码。请参见附件A以获得更多信息。表#6列出了示范性出错代码及相应的组件代码。MDoGetLastError 820也返回设定于抽象函数库层的出错代码。应该注意,以下的列表仅仅出于说明的目的,不应该将其理解为在任何方式上具有限制性。An error code reported by MDoGetLastError820 consists of two parts: component code and error code. Please see Appendix A for more information. Table #6 lists exemplary error codes and corresponding component codes. MDoGetLastError 820 also returns the error code set at the abstract library level. It should be noted that the following list is for illustrative purposes only and should not be construed as limiting in any way.
表#6Table #6
扫描子系统APIScan Subsystem API
应用程序接口800包括多个扫描子系统组件。扫描子系统API组件提供了数据/内容扫描及签名更新服务。其中包括MDoScanOpen()802、MDoScanClose()804、MDoScanVersion()806、MDoScanUpdate()810、及MDoScanData()808。MDoScanOpen()802用于扫描子系统对象实例化。MDoScanVersion()806提供扫描子系统及签名数据库版本信息。MDoScanUpdate()810运行签名数据库更新。MDoScanData()808运行恶意代码/内容数据扫描。图11基于一个实施例说明了扫描子系统API调用次序1100。
MdoScanOpenMdoScanOpen
表#7说明了关于MDoScanOpen()802的示范性信息。
表#7
描述describe
返回一个扫描子系统实例句柄Returns a scan subsystem instance handle
原型prototype
MDOSCAN_HANDLE MDoScanOpen(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib)MDOSCAN_HANDLE MDoScanOpen(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib)
参数parameter
hLibhLib
[in]通过使用MDoLibraryOpen()函数而获得的函数库句柄[in] The function library handle obtained by using the MDoLibraryOpen() function
返回值return value
如成功,则返回扫描子系统实例句柄。If successful, returns the scanning subsystem instance handle.
如出错,则为INVALID_MDOSCAN_HANDLE。INVALID_MDOSCAN_HANDLE on error.
也可参见see also
MDoScanClose(),MDoScanData(),MDoScanUpdate(),MDoScanClose(), MDoScanData(), MDoScanUpdate(),
MDoLibraryOpen()MDoLibraryOpen()
MdoScanCloseMdoScanClose
表#8说明了关于MDoScanClose()804的示范性信息。
表#8
描述describe
释放扫描子系统实例及相关联的系统资源Releases the scanning subsystem instance and associated system resources
原型prototype
void MDoScanClose(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan);void MDoScanClose(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan);
参数parameter
hScanhScan
[in]通过使用MDoScanOpen()函数而获得的扫描子系统句柄[in] The scan subsystem handle obtained by using the MDoScanOpen() function
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
MDoScanOpen(),MDoScanDa ta(),MDoScanUpdate()MDoScanOpen(), MDoScanData(), MDoScanUpdate()
MdoScanVersionMdoScanVersion
表#9说明了关于MdoScanVersion()806的示范性信息。Table #9 illustrates exemplary information about MdoScanVersion() 806.
表#9Table #9
描述describe
从由MDoScanOpen()函数返回的一个扫描器句柄获得扫描子系统及签名版Obtain the scanning subsystem and signature from a scanner handle returned by the MDoScanOpen() function
本信息this information
原型prototype
int MDoScanVersion(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan,int MDoScanVersion(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan,
SVerlnfo* pVers ion);SVerlnfo* pVersion);
参数parameter
hScanhScan
[in]通过使用MDoScanOpen()函数而获得的扫描子系统句柄。[in] The scan subsystem handle obtained by using the MDoScanOpen() function.
pVersionpVersion
[out]指向一个包含版本信息结构的指针[out] Pointer to a structure containing version information
返回值return value
如成功则返回0,否则为-1。
也可参见see also
MDoScanOpen(),MDoScanClose(),MDoScanData(),MDoScanOpen(), MDoScanClose(), MDoScanData(),
MDoScanUpdate()MDoScanUpdate()
示范性计算机代码#2说明一个样本版本信息结构。Exemplary Computer Code #2 illustrates a sample version information structure.
计算机代码#2Computer Code #2
由MdoScanVersion()806所报告的移动通信设备识别字符串是通过由AlDevGetInfo所返回的使用设备识别字符串而设定的(参见附件A)。The mobile communication device identification string reported by MdoScanVersion() 806 is set by the usage device identification string returned by AlDevGetInfo (see Appendix A).
MdoScanDataMdoScanData
表#10说明了关于MDoScanData()808的示范性信息。Table #10 illustrates exemplary information about MDoScanData() 808.
表#10Table #10
描述describe
MDoScanData将从一个应用程序被调用以扫描一个特定的数据类型。调用应用程序指定了扫描的动作、扫描目标类型、一套用以访问数据的I/O函数、以及一个可选性回调函数。数据扫描的结果以一个调用函数提供的数据结构被返回。MDoScanData是重复加载的。MDoScanData will be called from an application to scan a specific data type. The calling application specifies the scan action, the scan target type, a set of I/O functions to access the data, and an optional callback function. The results of the data scan are returned in a data structure provided by the calling function. MDoScanData is loaded repeatedly.
原型prototype
int MDoScanData(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan,int MDoScanData(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan,
SScanParam* pParam,SScanParam* pParam,
SScanResult* pResult);SScanResult* pResult);
参数parameter
hScanhScan
[in]从一次调用MDoScanOpen()函数而获得的扫描子系统句柄[in] The scan subsystem handle obtained from a call to the MDoScanOpen() function
pParampParam
[in]指向一个包含数据扫描参数的结构的指针[in] Pointer to a structure containing data scan parameters
pResultpResult
[out]指向一个包含数据扫描结果的结构的指针[out] Pointer to a structure containing the result of the data scan
返回值return value
如成功则返回0,否则为-1而且出错代码被设定
也可参考Also refer to
MDoScanOpen(),MDoScanClose(),MDoScanVersion(),MDoScanOpen(), MDoScanClose(), MDoScanVersion(),
MDoScanUpdate()MDoScanUpdate()
MdoScanUDdateMdoScanUDdate
表#11说明了关于MDoScanUpdate()810的示范性信息。Table #11 illustrates exemplary information about MDoScanUpdate() 810.
表#11Table #11
描述describe
运行恶意代码/内容签名模式数据库(mdo.sdb)及侦测逻辑(mdo.pd)更新。Run malicious code/content signature pattern database (mdo.sdb) and detection logic (mdo.pd) updates.
原型prototype
int MDoScanUpdate(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan,int MDoScanUpdate(MDOSCAN_HANDLE hScan,
SUpdat eParam* pParam);SUpdat eParam* pParam);
参数parameter
hScanhScan
[in]通过使用MDoScanOpen()函数而获得的扫描句柄[in] The scan handle obtained by using the MDoScanOpen() function
pParampParam
[in]指向一个更新参数结构的指针,该结构包含一个用于更新取消/放弃及进程状态更新的回调函数指针[in] A pointer to an update parameter structure that contains a pointer to a callback function for update cancellation/abortion and process status update
示范性计算机代码#3说明了更新参数结构被定义的方式Exemplary
计算机代码#3
调用应用程序可以在调用函数的时候设定函数指针及将要传递给函数的数据。请注意表#12。The calling application can set the function pointer and the data to be passed to the function when calling the function. Note Table #12.
表#12Table #12
配臂APIArm API
应用程序接口800包括多个配置组件。包括一套用于获取并指定扫描子系统设定的函数。这些函数的一个目标是向应用程序及扫描子系统提供集中型的运行时间配置访问。其配置数据储存于非易失性永续型数据储存体(如闪存,等)。
图12基于一个实施例说明了一个示范性配置API调用次序1200。如图所示,MDoConfigOpen()830返回一个句柄,该句柄将被传递到配置获取及指定的函数。MDoConfigClose()814被用于释放并关闭由MDoConfigOpen()812返回的配置旬柄。MDoConfigSet()818用一个特定值设定了一个特定的配置变量,且MDoConfigGet()816为一个指定的变量返回一个配置值。在MDoConfigClose()814被调用前,由MDoConfSet()818所限定的配置变量设定并不一定被存放于永久储存体。FIG. 12 illustrates an exemplary configuration
当存取和/或指定一个变量值的时候,应用程序可以调用配置打开、获取或设定,并立刻在其后添加关闭函数。When accessing and/or specifying a variable value, the application can call the configuration open, get or set, and immediately follow it with the close function.
使用应用程序接口800配置组件而指定/获取的配置变量与值可以用以无效字符(’\0’)结尾的8位字符的字符串来代表。表#13列出了现有的各种配置变量。Configuration variables and values specified/retrieved using
表#13Table #13
MdoConfigOpenMdoConfigOpen
表#14说明了关于MDoConfigOpen()812的示范性信息。Table #14 illustrates exemplary information about MDoConfigOpen() 812.
表#14Table #14
描述describe
返回一个句柄到一个配置设定,然后将其传递给后面的调用MDoConfigGet()和MDoConfigSet().Returns a handle to a configuration setting, which is then passed to subsequent calls to MDoConfigGet() and MDoConfigSet().
原型prototype
MDOCONFIG_HANDLE MDoConfigOpen(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib);MDOCONFIG_HANDLE MDoConfigOpen(MDOLIB_HANDLE hLib);
参数parameter
hLibhLib
[in]通过使用MDoLibraryOpen()函数获得的函数库句柄[in] The function library handle obtained by using the MDoLibraryOpen() function
返回值return value
如成功则返回配置句柄。Returns a configuration handle on success.
如出错则返回INVALID_MDOCONPIG_HANDLE。Returns INVALID_MDOCONPIG_HANDLE if an error occurs.
也可参见see also
MDoConfigClose(),MDoConfigSet(),MDoConfigGet()MDoConfigClose(), MDoConfigSet(), MDoConfigGet()
MdoConfigCloseMdoConfigClose
表#15说明了关于MDoConfigClose()814的示范性信息。
表#15
描述describe
释放系统资源并关闭配置句柄Release system resources and close the configuration handle
原型prototype
void MDoConfigClose(MDOCONFIG_HANDLE hConfig);void MDoConfigClose(MDOCONFIG_HANDLE hConfig);
参数parameter
hConfighConfig
[in]由MDoConfigOpen()函数返回的配置句柄[in] The configuration handle returned by the MDoConfigOpen() function
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
MDoConfigOpen(),MDoConfigSet(),MDoConfigGet()MDoConfigOpen(), MDoConfigSet(), MDoConfigGet()
MdoConfigGetMdoConfigGet
表#16说明了关于MDoConfigGet()816的示范性信息。
表#16
描述describe
为指定的配置变量获得一个配置值Get a configuration value for the specified configuration variable
原型prototype
int MDoConfigGet(MDOCONFIG_HANDLE hConfigint MDoConfigGet(MDOCONFIG_HANDLE hConfig
char const* pszName,char const* pszName,
char* pBuffer,A char* pBuffer,
unsigned int uSize);unsigned int uSize);
参数parameter
hConfighConfig
[in]由MDoConfigOpen()函数返回的配置句柄[in] The configuration handle returned by the MDoConfigOpen() function
pszNamepszName
[in]以NULL-终止的配置变量名称[in] NULL-terminated configuration variable name
pBufferpBuffer
[out]配合所指定变量的以NULL-终止的配置设定/值[out] A NULL-terminated configuration setting/value that matches the specified variable
uSizeuSize
[in]以字节计算的pBuffer长度[in] The length of pBuffer in bytes
返回值return value
成功则返回0,否则为-1。
也可参见see also
MDoConfigOpen(),MDoConf igClose(),MDoConf igSet()MDoConfigOpen(), MDoConfigClose(), MDoConfigSet()
MdoConfigSetMdoConfigSet
表#17说明了关于MDoConfigSet()818的示范性信息。Table #17 illustrates exemplary information about MDoConfigSet() 818.
表#17Table #17
描述describe
为指定的配置变量设定一个值Sets a value for the specified configuration variable
原型prototype
int MDoConfigGet(MDOCONFIG_HANDLE hConfigint MDoConfigGet(MDOCONFIG_HANDLE hConfig
char const* pszName,char const* pszName,
char const* pszValue);char const* pszValue);
参数parameter
hConfighConfig
[in]由MDoConf igOpen()函数所返回的配置句柄[in] The configuration handle returned by the MDoConfigOpen() function
pszNamepszName
[in]以NULL-终结的配置变量名称[in] NULL-terminated configuration variable name
pszValuepszValue
[int]配合所指定变量的以NULL-终结的新的配置设定/值[int] The new NULL-terminated configuration setting/value for the specified variable
返回值return value
如成功则返回0,否则为-1
也可参见see also
MDoConfigOpen(),MDoConfigClose(),MDoConfigGet()MDoConfigOpen(), MDoConfigClose(), MDoConfigGet()
为便于扫描的应用程序/扫描子系统通信Application/scanning subsystem communication for easy scanning
如前所述,应用程序可与扫描子系统进行信息通信以方便扫描子系统进行扫描。这一通信可通过上面所描述的API得到便利。上述的信息可与被扫描的数据类型及与此类扫描相关联的时间安排有关。更多关于上述API达成此结果方式的描述将在下文作阐述。As mentioned earlier, the application program can communicate information with the scanning subsystem to facilitate scanning by the scanning subsystem. This communication can be facilitated through the API described above. The information described above may relate to the type of data being scanned and the timing associated with such scanning. More descriptions of how the above APIs achieve this result are given below.
扫描参数(SscanParam)Scanning parameters (SscanParam)
调用应用程序可以通过使用SScanParam结构向扫描子系统提供一个扫描参数。包含于扫描参数的信息向扫描子系统提供:The calling application can provide a scan parameter to the scan subsystem by using the SScanParam structure. The information contained in the scanning parameters provides to the scanning subsystem:
1)扫描子系统的动作类型(例如iAction),1) The action type of the scanning subsystem (such as iAction),
2)扫描数据类型(例如需要扫描的应用数据的类型-iDataType),2) scan data type (such as the type of application data that needs to be scanned - iDataType),
3)指向扫描目标的数据指针(例如pPrivate),3) a data pointer (eg pPrivate) pointing to the scan target,
4)获取数据大小(以字节为单位)的函数(例如pfGetSize),4) A function to get the size of the data in bytes (eg pfGetSize),
5)重置扫描数据大小的函数(例如pfSetSize),5) A function to reset the scan data size (such as pfSetSize),
6)扫描子系统用于获取一个扫描数据块的函数(例如pfRead),6) The scan subsystem is used to obtain a scan data block function (such as pfRead),
6)用于向扫描数据写入的函数(例如pfWrite),以及6) functions for writing to scan data (eg pfWrite), and
7)扫描子系统状态/进程报告的回调函数(例如pfCallBack)。7) Callback functions (eg pfCallBack) for scanning subsystem status/process reports.
示范性计算机代码#4说明了一个数据扫描参数的结构。Exemplary computer code #4 illustrates the structure of a data scan parameter.
计算机代码#4Computer Code #4
扫描动作(iAction)Scan action (iAction)
扫描动作指定了在被提供的应用数据上要运行的扫描的类型。表#18说明了各种不同的示范性扫描动作。A scan action specifies the type of scan to run on the provided application data. Table #18 illustrates various exemplary scan actions.
表#18Table #18
扫描数据类型(iDataType)Scan data type (iDataType)
调用应用程序可以通过使用这一变量向扫描子系统通知应用数据类型以及格式。The calling application can inform the scanning subsystem of the application data type and format by using this variable.
图13说明了各种不同的示范性应用数据类型1300,应用程序能够将其通过API向扫描子系统进行传送。Url-字符串的格式可以符合统一资源定位器(RFC1738)规格。Email-字符串的格式可以符合互联网电子邮件地址格式(RFC822)规格。缺省的域可以设置为任何所需的域。另外,电话号码字符串可以包括数字字符’0’至’9’,以及’#’与’*’字符。FIG. 13 illustrates various exemplary
扫描数据指针/句柄(pPrivate)Scan data pointer/handle (pPrivate)
另外会提供一个指向一个应用扫描对象的指针(或句柄)。扫描子系统并不一定使用该数据指针/句柄运行直接的内存I/O。数据指针/句柄被传递回调用函数以通过使用调用函数所指定的I/O函数进行读/写。Additionally a pointer (or handle) to an application scan object is provided. The scanning subsystem does not necessarily perform direct memory I/O using this data pointer/handle. The data pointer/handle is passed back to the calling function for reading/writing by using the I/O function specified by the calling function.
扫描数据大小(pfGetSize)Scan data size (pfGetSize)
当前的函数由扫描子系统用于从调用应用程序处获得扫描目标数据的大小(以字节为单位)。The current function is used by the scan subsystem to obtain the size of scan target data in bytes from the calling application.
扫描数据调整大小(pfSetSize)Scan data resize (pfSetSize)
该函数由扫描子系统用于请求调用应用程序调整被修复/清洗的应用数据至一个给定的大小(以字节为单位)。这一函数可以与扫描并修复/删除选项同时使用。This function is used by the scanning subsystem to request that the calling application resize the repaired/cleaned application data to a given size (in bytes). This function can be used together with the scan and repair/delete option.
扫描数据读取函数(pfRead)Scan data read function (pfRead)
该即时函数可由扫描子系统使用,用于从调用应用程序读取一个指定量的应用数据。This immediate function can be used by the scanning subsystem to read a specified amount of application data from the calling application.
扫描数据写入函数(pfWrite)Scan data write function (pfWrite)
这是一个可选的参数,可由扫描子系统使用,用于向扫描对象写入一个指定量的应用数据以作为修复过程的一部分。如扫描动作被设定为修复或删除,则这个函数指针可以进行设定。This is an optional parameter that can be used by the scanning subsystem to write a specified amount of application data to the scanned object as part of the repair process. This function pointer can be set if the scan action is set to repair or delete.
回调函数(pfCallBack)Callback function (pfCallBack)
如被指定,扫描子系统通过以下表格内所描述的信息调用该指定函数。如果返回的是一个负返回值,则回调函数放弃扫描过程。表#19阐述了一个示范性的回调代码列表。If specified, the scanning subsystem calls the specified function with the information described in the following table. If a negative return value is returned, the callback function aborts the scanning process. Table #19 illustrates an exemplary list of callback codes.
表#19Table #19
示范性的计算机代码#5说明了一个扫描子系统的回调结构。Exemplary
计算机代码#5
扫描结果(SScanResulf)Scan result (SScanResulf)
对象扫描的结果,即被侦测到的恶意软件信息,包含于由调用应用程序所提供的SScanResult结构被返回至调用应用程序。该SScanResult结构包含一个指向一个包含扫描结果信息结构的指针,以及一个指向一个被用于移除扫描结果资源函数的指针。用于存放扫描结果的内存由扫描子系统进行分配,并由调用pfDeleteResult指针所指向的函数所释放。The result of the object scan, ie the detected malware information contained in the SScanResult structure provided by the calling application is returned to the calling application. The SScanResult structure contains a pointer to a structure containing scan result information, and a pointer to a function used to remove the scan result resource. The memory used to store scan results is allocated by the scan subsystem and released by calling the function pointed to by the pfDeleteResult pointer.
示范性计算机代码#6说明了一个样本调用次序。Exemplary computer code #6 illustrates a sample call sequence.
计算机代码#6Computer Code #6
示范性计算机代码#7说明了一个被侦测到的恶意代码/内容信息结构。Exemplary
计算机代码#7
示范性计算机代码#8说明了一个扫描结果结构。Exemplary
计算机代码#8
严重性等级与行为级别(uBehavior)Severity and Behavior Levels (uBehavior)
图14基于一个示范性实施例,它表明了包括在SDetect结构内的含有恶意软件严重度标志及应用程序行为级别的位-域变量1400。Figure 14 illustrates bit-
表#20阐述了一个示范性恶意软件的严重性级别列表。Table #20 sets forth a list of severity levels for exemplary malware.
表#20Table #20
如被扫描过的应用数据包含对移动通信设备用户有害的恶意软件,则扫描子系统设定MDO_SC_USER标志。如果对移动通信设备本身有害,MDO_SC_TERMINAL标志被设定。如果其对用户和移动通信设备都有害,则MDO_SC_USER与MDO_SC_TERMINAL标志都被设定。If the scanned application data contains malicious software harmful to the user of the mobile communication device, the scanning subsystem sets the MDO_SC_USER flag. If harmful to the mobile communication device itself, the MDO_SC_TERMINAL flag is set. Both the MDO_SC_USER and MDO_SC_TERMINAL flags are set if it is harmful to both the user and the mobile communication device.
应用程序行为级别指定了对侦测到包含恶意软件的应用数据采取什么样的措施。表#21列出了行为级别的各种值及应用程序采取的相应行动。The application behavior level specifies what action to take on application data detected to contain malware. Table #21 lists the various values for the Behavior level and the corresponding actions taken by the application.
表#21Table #21
当在被扫描的数据中发现多个恶意代码,调用应用程序预期将以最高级别的行为级别来做出反应。例如,如果MDO_BC_LEVELO和MDO_BC_LEVEL3都被报告,应用程序可以采取MDO_BC_LEVEL3的行动。When multiple malicious codes are found in the scanned data, the calling application is expected to react with the highest level of behavior. For example, if both MDO_BC_LEVELO and MDO_BC_LEVEL3 are reported, the application can take an action of MDO_BC_LEVEL3.
图15说明了一个图表1500,阐明了扫描子系统的扫描时机安排作为通过图13的各变量被识别出数据类型的一个函数而变动的方式。FIG. 15 illustrates a
签名数据库更新Signature database update
如前所述,更新过程可被简化,以适应移动通信框架固有的有限带宽。更多关于可达成如此效果的各种不同方式将在下文作阐述。As mentioned earlier, the update process can be simplified to accommodate the limited bandwidth inherent in mobile communication frameworks. More on the various ways this can be achieved will be described below.
被更新的组件updated components
MDoScanUpdate函数随着更新服务提供了两个组件[例如恶意代码侦测逻辑(mdo.pd)与签名数据库(mdo.sdb)]。一个组件(例如mdo.pd)可包含侦测逻辑并在一个更新的版本出现时被完全更新。另一个组件(例如mdo.sdb)可以逐步更新直到n个先前的版本。对第二个组件的一次完全更新可在具有比n更早版本的移动通信设备上运行。例如,如果n被设定为5,而最新版本是20,那么会在一个比15更早版本的移动通信设备上进行一次完整的更新。The MDoScanUpdate function provides two components along with the update service [such as malicious code detection logic (mdo.pd) and signature database (mdo.sdb)]. A component (eg mdo.pd) may contain detection logic and be fully updated when a newer version becomes available. Another component (eg mdo.sdb) can be updated incrementally up to n previous versions. A full update to the second component can run on mobile communication devices with versions earlier than n. For example, if n is set to 5 and the latest version is 20, a complete update will be performed on a mobile communication device earlier than
通过用户界面激活Activate through the user interface
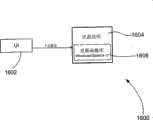
图16说明了一个基于一个实施例的示范性的流程1600,它描述了由一个用户界面启动的更新方式。如图所示,病毒码的更新可以由移动通信设备用户通过一个用户界面1602选择一个菜单输入来启动。一旦用户选择了该更新菜单,一个更新应用程序1604被激活,并通过适当的更新界面函数1606连接到一台后端服务器。Figure 16 illustrates an
通信协议letter of agreement
更新函数库可以通过HTTP协议与后端服务器进行通信。The update function library can communicate with the backend server through the HTTP protocol.
更新过程update process
图17基于一个实施例,它说明了用于有效地更新一台移动通信设备的一个扫描子系统的一个方法1700。在一个实施例中,当前的方法1700可以在图3的架构300中的应用程序、扫描子系统与操作系统、以及图1和2中的系统中执行。但是应该注意,当前的方法1700可以在任何所需的环境中加以执行。Figure 17 illustrates a
要初始化该过程,可以从至少一台移动通信设备向一台后端服务器发送一次更新请求。当然,在其他的实例中,更新可以不经过请求而发送。To initiate the process, an update request may be sent from at least one mobile communication device to a backend server. Of course, in other instances, updates may be sent without a request.
在一个实施例中,更新可以由移动通信设备通过使用一个请求数据结构而进行请求。此数据结构还可以选择性地包括统一资源定位器(URL)变量、移动通信识别变量、应用程序接口版本变量、侦测逻辑变量、签名版本变量、和/或部分号码变量等变量。In one embodiment, updates may be requested by the mobile communication device using a request data structure. The data structure may also optionally include variables such as Uniform Resource Locator (URL) variables, mobile identification variables, API version variables, detection logic variables, signature version variables, and/or partial number variables.
表#22说明了可以用于此目的的一个示范性的URL。Table #22 illustrates an exemplary URL that can be used for this purpose.
表#22Table #22
<BASE-URL>?dev=<DEV-ID>&mdo=<MDO-VER>&eng=<ENG-<BASE-URL>? dev=<DEV-ID>&mdo=<MDO-VER>&eng=<ENG-
VER>&sdb=<SDB-VER>&chk=<CHUNK>VER>&sdb=<SDB-VER>&chk=<CHUNK>
以下是一个描述上述URL变量的表格:Here is a table describing the above URL variables:
表#23说明了一个符合上述描述的URL的一个特定范例。Table #23 illustrates a specific example of a URL that fits the above description.
表#23Table #23
http://update.mcafeeacsa.com/504i?dev=X504i05&mdo=2&eng=3&sdb=56&chk=1http://update.mcafeeacsa.com/504i? dev=X504i05&mdo=2&eng=3&sdb=56&chk=1
以上表#23的URL指定了基本-URL″http://update.mcafeeacsa.com/504i″,″X504i05″为设备识别码,API版本2,恶意代码侦测逻辑版本3,以及签名数据库版本56。应该注意,当移动通信设备最初联络后端服务器的时候,其″数据块″或部分、号码可以设定为1。此外,基本-URL可以通过让MDoConfigGet API使用″UpdateURL″配置变量而获得。The URL in Table #23 above specifies the base-URL "http://update.mcafeeacsa.com/504i", "X504i05" as the device identifier, API version 2, malicious code
在收到请求之后,后端服务器通过将已储存的恶意代码侦测逻辑及签名数据库版本同在URL中编码存放的版本信息相比较,从而决定哪个更新包需要被下载。After receiving the request, the backend server determines which update package needs to be downloaded by comparing the stored malicious code detection logic and signature database version with the version information encoded in the URL.
如果不需要进行更新,后端会返回一个无内容的回应。在操作1701中,移动通信设备收到了作为第一部分的回应。如果决定第一部分包括上述的无内容回应(参见决定1702),方法1700被中止,这是因为没有更新需要下载。该特征对适应移动通信框架中固有的有限带宽是有益的。If no updates are required, the backend will return a response with no content. In
另一方面,如果一个更新包的第一个部分被返回,方法1700将在收到更新的第一部分之后(或者有可能的是与之同时)继续接收更新的其它部分。请注意操作1704-1708。应该注意第一部分可伴随着整包的大小及部分的计数信息。On the other hand, if the first part of an update package is returned, the
在下载剩余的更新部分时,可以对所下载URL的部分号码作限定。表#24说明了一个指定部分号码″3″的URL的特定范例。When downloading the remaining updated parts, the part number of the downloaded URL can be limited.
表#24
http://update.mcafeeacsa.com/504i?dev=X504i05&mdo=2&eng=3&sdb=56&chk=3http://update.mcafeeacsa.com/504i? dev=X504i05&mdo=2&eng=3&sdb=56&chk=3
在一个实施例中,可以决定更新的完整性。相应地,在是否被核实了更新的完整性的基础上,可以有条件地将更新安装于扫描子系统中。In one embodiment, the integrity of the update may be determined. Accordingly, the update may be conditionally installed in the scanning subsystem based on whether the integrity of the update has been verified.
作为一种选择,更新的完整性可以通过使用一个签名来确定。此签名可以同更新的一个部分一起接收(即一个最后部分)。之后,可以将该签名同使用更新的每个部分生成的另一签名进行比对。请注意操作1710。Alternatively, the integrity of the update can be determined by using a signature. This signature may be received together with a part of the update (ie a last part). This signature can then be compared against another signature generated using each part of the update. Note
在一个实施例中,签名可以通过一个RSA私钥生成并在移动通信设备上使用一个包含于更新内的相应公钥进行认证。签名核实及生成可通过使用一个特定的认证函数库作进一步运行。In one embodiment, the signature may be generated with an RSA private key and authenticated on the mobile communication device using a corresponding public key included in the update. Signature verification and generation can be further performed using a specific authentication function library.
假设完整性被核实,任何由扫描子系统运行的扫描会被停顿或中止。请注意操作1712。应该注意该停顿是可选择的。Assuming integrity is verified, any scans run by the scan subsystem are stalled or aborted. Note
接下来,可将更新安装于扫描子系统。请注意操作1714。在实例中任何扫描被停顿的地方,一旦更新被安装于扫描子系统,之后可以继续使用扫描子系统进行扫描。参见操作1716。Next, the update can be installed on the scanning subsystem. Note
为适应移动通信框架中固有的有限带宽,更新的某些部分的大小可以最小化。此外,可以对更新的部分进行压缩。To accommodate the limited bandwidth inherent in mobile communication frameworks, the size of certain parts of the update can be minimized. In addition, updated parts can be compressed.
在另一个实施例中,可将每个更新部分的格式设计为能够适应移动通信框架中固有的有限带宽。更多关于此类格式的信息将在下文作阐述。In another embodiment, each update portion may be formatted to accommodate the limited bandwidth inherent in mobile communication frameworks. More information on these formats is provided below.
表#25说明了一个下载更新各部分的示范性格式。Table #25 illustrates an exemplary format for downloading parts of an update.
表#25Table #25
在表#25中列出的上述部分的每一个部分在表#26中作如下定义。Each of the above sections listed in Table #25 is defined below in Table #26.
表#26Table #26
每个部分由一个文件头和数据组成。文件头可以指明更新的相关部分的一个识别码、更新的相关部分的一段长度等等。此外,文件头可以指定包含的数据名称与长度,并用一个额外的CR+LF对将其与实际数据相分隔。表#27列出了与文件头相关联的示范性数据/内容的名称。Each section consists of a file header and data. The file header may indicate an identification code of the updated relevant part, a length of the updated relevant part, and the like. In addition, the file header can specify the name and length of the included data, and use an additional CR+LF pair to separate it from the actual data. Table #27 lists the names of exemplary data/content associated with the file header.
表#27Table #27
表#28说明了一个示范性的更新包。Table #28 illustrates an exemplary update package.
表#28Table #28
抽象函数库APIAbstract library API
如前所述,提供了一个独立于平台的系统及相关的方法以用于一台移动通信设备。其包括一独立于平台的扫描子系统,可同用于扫描的移动通信设备的操作系统进行通信。另外还提供了一个独立于平台的应用程序接口,为操作系统及扫描子系统之间提供界面帮助。独立于平台的应用程序接口包括了一个抽象函数库,用于将独立于平台的扫描子系统接驳于移动通信设备及相关联的操作系统。As previously stated, a platform independent system and related method are provided for use with a mobile communication device. It includes a platform-independent scanning subsystem that communicates with the operating system of the mobile communication device for scanning. In addition, a platform-independent API is provided to facilitate the interface between the operating system and the scanning subsystem. The platform independent API includes a library of abstract functions for interfacing the platform independent scanning subsystem with the mobile communication device and associated operating system.
通过该设计,扫描子系统可以独立于平台,并由此能在任何类型的操作系统/移动通信设备的组合上加以执行。With this design, the scanning subsystem is platform independent and thus can be executed on any type of operating system/mobile communication device combination.
在一个实施例中,抽象函数库可以支持系统初始化、函数库初始化、出错函数、内存分配、输入/输出(I/O)、数据认证、同步、超文本传输协议、共享内存、系统时间、设备信息、以及调试。更多关于上述应用程序接口的一个可选择实例的示范性信息将在附件A中进行阐述。In one embodiment, the abstract library may support system initialization, library initialization, error functions, memory allocation, input/output (I/O), data authentication, synchronization, HTTP, shared memory, system time, device information, and debugging. More exemplary information on an alternative example of the API described above is set forth in Annex A.
虽然上文描述了不同的实施例,但容易理解,它们仅通过范例的形式被提出,而不具有限制性。因此,某个特定实例的应用广度与范围不应该由任何以上所描述的示范性实例所限制,而应只根据权利要求及与其有同等效果的陈述所确定。While various embodiments have been described above, it should be readily understood that they have been presented by way of example only, and not limitation. Therefore, the breadth and scope of application of a particular example should not be limited by any of the above-described exemplary examples, but should be determined only in accordance with the claims and statements of equivalents thereto.
附件AAnnex A
当前的应用程序接口(API)包括以下子系统:The current application programming interface (API) includes the following subsystems:
·系统初始化·system initialization
·函数库初始化·Function library initialization
·出错函数· Error function
·堆内存分配· Heap memory allocation
·永续性内存/储存体I/O· Persistent memory/storage I/O
·数据认证·Data Authentication
·同步对象(信标)· Synchronization object (beacon)
·HTTP API· HTTP API
·共享内存·Shared memory
·系统时间·system time
·设备信息·Device Information
·调试·debugging
本附件中还描述了一套定义于抽象函数库(AL)层的C-语言定义,供在API函数库中使用。This annex also describes a set of C-language definitions defined at the abstract function library (AL) level for use in the API function library.
系统初始化system initialization
依赖于平台/系统的启动初始化是由AlLibrarySysInit()函数运行的。该函数的设计使其能从先前描述过的MDoSystemlnit()函数被调用。Platform/system dependent startup initialization is performed by the AlLibrarySysInit() function. This function is designed so that it can be called from the previously described MDoSystemlnit() function.
AlLibrarySysInitAlLibrarySysInit
描述describe
运行依赖于系统的初始化Run system-dependent initialization
原型prototype
jnt AlLibrarySysInit(void);jnt AlLibrarySysInit(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
成功则返回0,否则为-1。
函数库初始化Library initialization
平台抽象API函数库通过使用Al InitLibrary()函数被初始化。在一个抽象API函数被调用之前,抽象函数库就被初始化一次。当AlCleanupLibrary()函数被调用时,由Al InitLibrary()获得并初始化的系统资源被释放。The platform abstract API function library is initialized by using the Al InitLibrary() function. Before an abstract API function is called, the abstract function library is initialized once. When the AlCleanupLibrary() function is called, the system resources acquired and initialized by Al InitLibrary() are released.
AlInitLibraryAlInitLibrary
描述describe
运行函数库初始化。该函数将由MDoLibraryOpen()函数调用。Run the library initialization. This function will be called by the MDoLibraryOpen() function.
原型prototype
int AlInitLibrary(void);int AlInitLibrary(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
成功则返回0,否则为-1。
AlCleanupLibraryAlCleanupLibrary
描述describe
释放由Al InitLibrary()函数获得的系统资源。该函数将由先前指定的MDoLibraryClose()函数调用。Release system resources obtained by Al InitLibrary() function. This function will be called by the previously specified MDoLibraryClose() function.
原型prototype
void AlCleanupLibrary(void);void AlCleanupLibrary(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
无none
出错函数error function
AL函数库包含了一套出错函数,该套函数用于设定并获取有关特定任务/线程的出错代码。抽象层实现者应负责设定适当的出错代码及组件代码。The AL library contains a set of error functions that are used to set and get error codes for specific tasks/threads. It is the responsibility of the implementer of the abstraction layer to set appropriate error codes and component codes.
AlGetLastErrorAlGetLastError
描述describe
返回调用任务/线程的最后出错代码值。函数通过使用AlSetLastError()函数设定返回的值。Returns the last error code value of the calling task/thread. The function sets the returned value by using the AlSetLastError() function.
AlErrorCode数据类型是使用一个32-位无符号值进行内部表达的数据类型。The AlErrorCode data type is a data type that uses a 32-bit unsigned value for internal representation.
原型prototype
AlErrorCode AlGetLastError(void);AlErrorCode AlGetLastError(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
调用线程/任务的最后出错值设定是通过使用AlSetLastError()函数完成的The last error value setting of the calling thread/task is done by using the AlSetLastError() function
AlSetLastErrorAlSetLastError
描述describe
为调用线程/任务设定最后出错代码Set the last error code for the calling thread/task
原型prototype
void AlSetLastError(AlErrorCode errorCode);void AlSetLastError(AlErrorCode errorCode);
参数parameter
errorCodeerrorCode
[in]32-位出错代码值[in] 32-bit error code value
返回值return value
无none
出错/状态代码Error/Status Code
上述的表格列出了一套AL组件及出错代码。一个使用AlSetLastError函数报告的出错是一个由组件代码与出错代码组合而形成的32-位的值。设定在AL层次的出错通过使用MDoGetLastError函数而获取,以方便在出错发生时采取适当的行动。The above table lists a set of AL components and error codes. An error reported using the AlSetLastError function is a 32-bit value formed by combining the component code and the error code. Errors set at the AL level are retrieved using the MDoGetLastError function, so that appropriate action can be taken when an error occurs.
堆内存分配heap memory allocation
抽象层提供了一个堆内存分配API,以方便一个调用应用程序(例如″调用函数″)来动态地分配所需的内存。被分配的内存被假设为可在全局范围内共享,即可以由多个应用/任务所存取。AlMemAlloc()与AlMemFree()API函数提供了堆内存的分配与取消分配。The abstraction layer provides a heap memory allocation API to facilitate a calling application (eg "call function") to dynamically allocate the required memory. The allocated memory is assumed to be globally shareable, ie accessible by multiple applications/tasks. The AlMemAlloc() and AlMemFree() API functions provide heap memory allocation and deallocation.
AlMemAllocAlMemAlloc
描述describe
分配一个指定量的动态内存并向该内存返回一个指针。被分配的内存块可直接由调用函数(即调用应用程序)所存取,而不需要一个特别的操作(即内存锁定)。Allocates a specified amount of dynamic memory and returns a pointer to that memory. The allocated memory block can be directly accessed by the calling function (ie, the calling application program) without requiring a special operation (ie, memory locking).
原型prototype
void*AlMemAlloc(unsigned int uSize);void *AlMemAlloc(unsigned int uSize);
参数parameter
uSizeuSize
[in]以字节计算的需分配内存的量[in] The amount of memory to be allocated in bytes
返回值return value
一个指向被分配内存的指针。如请求失败或请求大小为零则返回NULL。A pointer to the allocated memory. Returns NULL if the request fails or if the request size is zero.
也可参见see also
AlMemFree()AlMemFree()
AlMemFreeAlMemFree
描述describe
释放由AlMemAlloc()函数返回的动态内存块Frees the dynamic memory block returned by the AlMemAlloc() function
原型prototype
void AlMemFree(void* pData);void AlMemFree(void* pData);
参数parameter
pDatapData
[in]指向一个需释放内存块的指针[in] A pointer to a memory block to be freed
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
AlMemAlloc()AlMemAlloc()
永续性储存体I/Opersistent storage I/O
永续性储存体(例如:闪存)存取是通过使用一个文件I/O API进行的。参见下文:Persistent storage (eg, flash memory) access is performed using a file I/O API. See below:
文件句柄类型AL_FILE_HANDLE被定义为:The file handle type AL_FILE_HANDLE is defined as:
typedef struct AL_FILE_HANDLE_structtypedef struct AL_FILE_HANDLE_struct
{{
}*AL_FILE_HANDLE;}*AL_FILE_HANDLE;
而一个用来指定一个无效的永续性储存体句柄INVALID_AL_FILE_HANDLE的常量被定义为:And a constant to specify an invalid persistent storage handle INVALID_AL_FILE_HANDLE is defined as:
#define INVALID_AL_FILE_HANDLE((AL_FILE_HANDLE)0)#define INVALID_AL_FILE_HANDLE((AL_FILE_HANDLE)0)
文件状态缓冲区类型AlStatBuf被定义为The file status buffer type AlStatBuf is defined as
typedef struct AlStatBuf_structtypedef struct AlStatBuf_struct
{{
unsigned long ulsize;unsigned long ulsize;
unsigned long ulTime;unsigned long ulTime;
}AlStatBuf;}AlStatBuf;
AlFileOpenAlFileOpen
描述describe
打开指定的文件并返回其句柄。Opens the specified file and returns its handle.
原型prototype
AL_FILE_HANDLE AlFileOpen(const char* pszFilename,AL_FILE_HANDLE AlFileOpen(const char* pszFilename,
int iMode);int iMode);
参数parameter
pszFilenamepszFilename
[in]文件名/路径字符串[in] filename/path string
iModeiMode
[in]文件存取模式[in] file access mode
AL_OPEN_READ 打开文件供读取AL_OPEN_READ Open the file for reading
AL_OPEN_WRITE 打开文件供读取与写入AL_OPEN_WRITE Open the file for reading and writing
返回值return value
如成功则返回文件句柄,否则为INVALID_AL_FILE_HANDLE。Returns the file handle if successful, otherwise INVALID_AL_FILE_HANDLE.
也可参见see also
AlFileClose(),AlFileRead(),AlFileWrite()AlFileClose(), AlFileRead(), AlFileWrite()
AlFileCloseAlFileClose
描述describe
关闭并释放与特定文件句柄相关联的系统资源Close and free system resources associated with a specific file handle
原型prototype
void AlFileClose(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile);void AlFileClose(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile);
参数parameter
hFilehFile
[in]由AlFileOpen()返回的文件句柄[in] The file handle returned by AlFileOpen()
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
AlFileOpen(),AlFileRead(),AlFileWrite()AlFileOpen(), AlFileRead(), AlFileWrite()
AlFileSeekAlFileSeek
描述describe
重新定位读/写文件偏移量Relocate read/write file offset
原型prototype
long AlFileSeek(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,long AlFileSeek(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,
long lOffset,long long lOffset,
int iWhence);int iWhence);
参数parameter
hFilehFile
[in]一个打开文件句柄[in] An open file handle
lOffsetlOffset
[in]与iWhence指示符有关的文件偏移量[in] The file offset associated with the iWhence indicator
iWhenceiWhence
[in]初始位置。可能的值有:[in] Initial position. Possible values are:
AL_SEEK_SET 偏移量参数指定绝对文件偏移量。换言之,自文件开始处的偏移The AL_SEEK_SET offset parameter specifies an absolute file offset. In other words, the offset from the beginning of the file
量。 quantity.
MJ_SEEK_CUR 指定相对偏移量-偏移量参数从当前文件偏移量指定文件偏MJ_SEEK_CUR specifies the relative offset - the offset parameter specifies the file offset from the current file offset
移量。Amount of displacement.
AL_SEEK_END 从文件末尾指定文件偏移量。AL_SEEK_END specifies the file offset from the end of the file.
返回值return value
如成功则返回文件偏移量,否则为-ILReturns the file offset if successful, otherwise -IL
也可参见see also
AlFileOpen(),AlFileClose(),AlFileRead(),AlFileWrite()AlFileOpen(), AlFileClose(), AlFileRead(), AlFileWrite()
AlFileReadAlFileRead
描述describe
从一个文件读取一块数据read a block of data from a file
原型prototype
unsigned int AlFileRead(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,unsigned int AlFileRead(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,
vo id* pBuffer,vo id* pBuffer,
unsigned int uSize);unsigned int uSize);
参数parameter
hFilehFile
[in]一个打开文件句柄[in] An open file handle
pBufferpBuffer
[out]数据缓冲区[out] data buffer
uSizeuSize
[out]需读取数据的量[out] The amount of data to be read
返回值return value
如成功则返回读取的字节数,否则为-1Returns the number of bytes read if successful, otherwise -1
也可参见see also
AlFileOpen(),AlFileClose(),AlFileSeek(),AlFileWrite()AlFileOpen(), AlFileClose(), AlFileSeek(), AlFileWrite()
AlFileWriteAlFileWrite
描述describe
向一个文件写入一块数据write a block of data to a file
原型prototype
unsigned int AlFileWrite(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,unsigned int AlFileWrite(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,
void const* pBuffer,void const* pBuffer,
unsigned int uSize);unsigned int uSize);
参数parameter
hFilehFile
[in]一打开文件句柄[in] An open file handle
pBufferpBuffer
[int]存有需写入数据的缓冲区[int] The buffer that stores the data to be written
uSizeuSize
[out]需写入数据的量[out] Amount of data to be written
返回值return value
如成功则返回写入数据的量,否则为-1Returns the amount of written data if successful, otherwise -1
也可参见see also
AlFileOpen(),AlFileClose(),AlFileSeek(),AlFileRead()AlFileOpen(), AlFileClose(), AlFileSeek(), AlFileRead()
AlFileSetSizeAlFileSetSize
描述describe
调整打开文件大小。Adjust the open file size.
对于不支持本地文件调整大小的平台,抽象函数库在AlFileClose()函数被调用时通过限定储存在每个文件开始处的大小信息执行该功能。For platforms that do not support native file resizing, the abstraction library performs this function by limiting the size information stored at the beginning of each file when the AlFileClose() function is called.
原型prototype
unsigned int AlFileSetSize(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,unsigned int AlFileSetSize(AL_FILE_HANDLE hFile,
unsigned int uSize);unsigned int uSize);
参数parameter
hFilehFile
[in]引用一个带有写入模式的打开文件的句柄[in] A handle referring to an open file with write mode
uSizeuSize
[out]以字节计算的新文件的长度[out] The length of the new file in bytes
返回值return value
如成功则返回0,否则为-1
也可参见see also
AlFileStat()AlFileStat()
AlFileStatAlFileStat
描述describe
获取文件大小及创建时间戳。Get file size and creation timestamp.
对于不提供本地文件大小和/或时间戳信息获取方法的平台,抽象函数库通过在每个文件的开始处储存信息执行本函数。For platforms that do not provide native methods for obtaining file size and/or timestamp information, the abstract library implements this function by storing information at the beginning of each file.
原型prototype
int AlFileStat(char const*pszFilename,int AlFileStat(char const*pszFilename,
AlStatBuf*pStat);AlStatBuf*pStat);
参数parameter
pszFilenamepszFilename
[in]获取信息的文件名称[in] The name of the file to get the information
pStatpStat
[out]指向一个用于返回大小与时间戳信息结构的指针。该结构包含以下域:[out] Pointer to a structure used to return size and timestamp information. This structure contains the following fields:
typedef struct AlStatBuf structtypedef struct AlStatBuf struct
{{
unsigned long ulSize;/*以字节计算的大小*/unsigned long ulSize; /*size in bytes*/
unsigned long ulTime;/*创建时间*/unsigned long ulTime; /* creation time */
}AlStatBuf;}AlStatBuf;
返回值return value
如成功则返回0,否则为-1
数据认证data authentication
平台抽象API包括一套用于认证数据的函数。数据认证API用于认证所下载的恶意软件的签字数据库。The platform abstraction API includes a set of functions for authenticating data. The data authentication API is used to authenticate the signature database of downloaded malware.
一旦调用函数通过使用AlDaOpen函数获得了一个认证对象,会对AlDaVerify作出一次调用,以核实所提供的数据。Once the calling function obtains an authentication object using the AlDaOpen function, a call to AlDaVerify is made to verify the provided data.
AlDaGetSignerlnfo()用于获取一个签字者信息。AlDaClose()用于关闭并释放数据认证句柄及相关的系统资源。以下是一个示范性的数据认证APIAlDaGetSignerlnfo() is used to get a signer information. AlDaClose() is used to close and release the data authentication handle and related system resources. The following is an exemplary data authentication API
由AlDaOpen()函数返回的数据认证句柄被定义为The data authentication handle returned by the AlDaOpen() function is defined as
ALHANDLE(AL_DA_HANDLE);ALHANDLE(AL_DA_HANDLE);
#define INVALID_AL_DA_HANDLE((AL_DA_HANDLE)0)#define INVALID_AL_DA_HANDLE((AL_DA_HANDLE)0)
签名者信息结构被定义为The signer info structure is defined as
#define MAX_DA_SIGNER_NAME128#define MAX_DA_SIGNER_NAME128
typedef struct DaSignerlnfo_structtypedef struct DaSignerlnfo_struct
{{
char szSignerName[MAX_DA_SIGNER_NAME];char szSignerName[MAX_DA_SIGNER_NAME];
} DaSignerlnfo;} DaSignerInfo;
AlDaOpenAlDaOpen
描述describe
创建并返回一个数据认证句柄。Create and return a data authentication handle.
原型prototype
AL_DA_HANDLE AlDaOpen(const void* pSig,AL_DA_HANDLE AlDaOpen(const void* pSig,
unsigned int uSigSize);unsigned int uSigSize);
参数parameter
pSigpSig
[in]指向一个签名数据的指针[in] Pointer to a signature data
uSigSizeuSigSize
[in]以字节计算的签名大小[in] Signature size in bytes
返回值return value
如成功则返回数据认证句柄,否则为INVALID_AL_DA_HAWDLEReturns the data authentication handle if successful, otherwise INVALID_AL_DA_HAWDLE
也可参见see also
AlDaClose(),AlDaUpdate(),AlDaVerify(),AlDaClose(), AlDaUpdate(), AlDaVerify(),
AlDaGetSignerlnfo()AlDaGetSignerlnfo()
AlDaCloseAlDaClose
描述describe
释放用于一个数据认证句柄的系统资源。Releases system resources used for a data authentication handle.
原型prototype
void AlDaClose(AL_DA_HANDLE hDa);void AlDaClose(AL_DA_HANDLE hDa);
参数parameter
hDahDa
[in]由AlDaOpen返回的数据认证句柄。[in] Data authentication handle returned by AlDaOpen.
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
AlDaOpen(),AlDaUpdate(),AlDaVerify(),AlDaOpen(), AlDaUpdate(), AlDaVerify(),
AlDaGetSignerlnfo()AlDaGetSignerlnfo()
AlDaVerifyAlDaVerify
描述describe
运行数据认证run data authentication
原型prototype
intAlDaVerify(AL_DA_HANDLE hDa,intAlDaVerify(AL_DA_HANDLE hDa,
int(*pfRead)(void*,void*,int),int(*pfRead)(void*, void*, int),
int iTotalSize,int iTotalSize,
void *pPrivate);void *pPrivate);
参数parameter
hDahDa
[in]数据认证句柄[in] Data authentication handle
pfReadpfRead
[in]调用函数的回调函数,用以读取数据(参见)。如有一个出错它会返回-1,如再无数据可读则返回0,否则返回所读取数据的量,并返回到AlDaVerify函数。预计该函数将被多次调用。[in] The callback function to call the function to read the data (see). It returns -1 if there is an error, 0 if there is no more data to read, otherwise it returns the amount of data read and returns to the AlDaVerify function. The function is expected to be called multiple times.
iTotalSizeiTotalSize
[in]需核实的全部数据大小。[in] The total data size to be verified.
pPrivatepPrivate
[in]由pfRead回调函数传递的调用函数的私有数据。[in] The private data of the calling function passed by the pfRead callback function.
返回值return value
如应用数据得到认证则为0,否则为-1。0 if the application data is authenticated, -1 otherwise.
也可参见see also
AlDaOpen(),AlDaClose(),AlDaGetSignerlnfo()AlDaOpen(), AlDaClose(), AlDaGetSignerInfo()
以下为一个样本数据读取的回调函数。The following is a callback function for reading sample data.
AlDaGetSienerlnfoAlDaGetSienerlnfo
描述describe
获取数据认证签名者信息Get data authentication signer information
原型prototype
int AlDaGetSignerMo(ALJDAJHANDLE hDA,int AlDaGetSignerMo(ALJDAJHANDLE hDA,
DaSignerlnfo *pDSI);DaSignerlnfo *pDSI);
参数parameter
hDahDa
[in]数据认证句柄[in] Data authentication handle
pDSIpDSI
[out]指向一个含有签名者信息的结构的指针[out] Pointer to a structure containing signer information
返回值return value
如成功获得签名者信息则返回0,否则为-1
也可参见see also
AlDaOpen(),AlDaClose(),AlDaVerify()AlDaOpen(), AlDaClose(), AlDaVerify()
同步对象synchronization object
资源同步及控制是通过使用一个信标来达到的。抽象函数库内包括一套用以创建、打开、关闭并限定一个信标对象的函数。以下是一个示范性信标API。Resource synchronization and control is achieved by using a beacon. The library of abstract functions includes a set of functions to create, open, close and bound a beacon object. The following is an exemplary beacon API.
AlSemCreateAlSemCreate
描述describe
创建一个被命名的信标,设定内部计数为零,并返回其句柄。Creates the named beacon, sets the internal count to zero, and returns its handle.
原型prototype
AL_SEM_HANDLE·AlSemCreate(char const* pszName);AL_SEM_HANDLE·AlSemCreate(char const* pszName);
参数parameter
pszNamepszName
[in]信标名称字符串[in] beacon name string
返回值return value
如成功则返回信标句柄,否则为INVALro_AL_SEM_HANDLEReturns the beacon handle if successful, otherwise INVALro_AL_SEM_HANDLE
也可参见see also
AlSemOpen(),AlSemClose(),AlSeraGet(),AlSemRelease()AlSemOpen(), AlSemClose(), AlSeraGet(), AlSemRelease()
AlSemOpenAlSemOpen
描述describe
返回一个句柄至一个现存的信标。Returns a handle to an existing beacon.
原型prototype
AL_SEM_HANDLE AlSemOpeh(char const* pszName);AL_SEM_HANDLE AlSemOpeh(char const* pszName);
参数parameter
pszNamepszName
[in]信标名称[in] Beacon name
返回值return value
如成功则返回信标句柄,否则为INVALID_AL_SEM_HANDLEReturns the beacon handle if successful, otherwise INVALID_AL_SEM_HANDLE
也可参见see also
AlSemCreate(),AlSemClose(),AlSemGet(),AlSemRelease()AlSemCreate(), AlSemClose(), AlSemGet(), AlSemRelease()
AlSemCloseAlSemClose
描述describe
关闭并释放与特定信标句柄相关联的系统资源。信标使用/引用计数也减少,且如计数达到零,被引用的信标对象会被销毁。Closes and releases system resources associated with a specific beacon handle. The beacon usage/reference count is also decremented, and if the count reaches zero, the referenced beacon object is destroyed.
原型prototype
void AlSemClose(AL_SEM_HANDLE hSem);void AlSemClose(AL_SEM_HANDLE hSem);
参数parameter
hSemwxya
[in]使用AlSemCreate()or AlSemOpen()而获得的信标句柄[in] Beacon handle obtained by using AlSemCreate() or AlSemOpen()
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
AlSemCreate(),AlSemOpen(),AlSemGet(),AlSemRelease()AlSemCreate(), AlSemOpen(), AlSemGet(), AlSemRelease()
AlSemGetAlSemGet
描述describe
获得指定的信标。如进入时内部计数大于零,其数值会减少一位并立即被返回。如进入时内部计数为零,调用被阻止,直到其它任务/线程调用AlSemRelease()从而使之大于零。Get the specified beacon. If the internal count is greater than zero on entry, its value will be decremented by one and returned immediately. If the internal count is zero on entry, the call is blocked until another task/thread calls AlSemRelease() to make it greater than zero.
原型prototype
int AlSemGet(AL_SEM_HANDLE hSem);int AlSemGet(AL_SEM_HANDLE hSem);
参数parameter
hSemwxya
[in]信标句柄[in] Beacon handle
返回值return value
成功则返回0,否则为-1
也可参见see also
AlSemCreate(),AlSemOpen(),AlSemClose(),AlSemRelease()AlSemCreate(), AlSemOpen(), AlSemClose(), AlSemRelease()
AlSemReleaseAlSemRelease
描述describe
释放信标,内部计数增加1The beacon is released, and the internal count is incremented by 1
原型prototype
int AlSemRelease(AL_SEM_HANDLE hSem);int AlSemRelease(AL_SEM_HANDLE hSem);
参数parameter
hSemwxya
[in]信标句柄[in] Beacon handle
返回值return value
成功则返回0,否则为-1
也可参见see also
AlSemCreate(),AlSemOpen(),AlSeraClose(),AlSemGet()AlSemCreate(), AlSemOpen(), AlSeraClose(), AlSemGet()
HTTP APIHTTP APIs
抽象函数库内包括一套函数,该套函数能通过使用一个调用函数提供的回调结构提供HTTP网络I/O。以下是一个示范性的HTTP API。The abstract function library includes a set of functions that can provide HTTP network I/O by using a callback structure provided by a calling function. The following is an exemplary HTTP API.
由AlHttpOpen()函数返回的HTTP句柄被定义为:The HTTP handle returned by the AlHttpOpen() function is defined as:
typedef struct AL_HTTP HANDLE_structtypedef struct AL_HTTP HANDLE_struct
{{
}*AL_HTTP_HANDLE;}*AL_HTTP_HANDLE;
#define INVALID_AL_HTTP_HANDLE((ALJ3TTP_HANDLE)0)#define INVALID_AL_HTTP_HANDLE((ALJ3TTP_HANDLE)0)
HTTP回调结构AlHttpCallbacks被定义为:The HTTP callback structure AlHttpCallbacks is defined as:
typedef struct AlHttpCallbacks_structtypedef struct AlHttpCallbacks_struct
{{
unsigned int(*pWrite)(void* pPrivate,unsigned int(*pWrite)(void* pPrivate,
void const* pData,void const* pData,
unsigned int uSi ze);unsigned int uSi ze);
unsigned int(*pRead)(void* pPrivate.unsigned int(*pRead)(void* pPrivate.
void* pData,void* pData,
unsigned int uSize);unsigned int uSize);
unsigned int(*pGetSize)(void* pPrivate);unsigned int(*pGetSize)(void* pPrivate);
unsigned int(*pSetSize)(void* pPrivate,unsigned int(*pSetSize)(void* pPrivate,
unsigned int uSize);unsigned int uSize);
}AlHttpCallbacks;}AlHttpCallbacks;
在以上HTTP回调结构中所给出的回调函数提供了以下各种功能:The callback function given in the above HTTP callback structure provides the following functions:
pWrite 由系统HTTP函数库调用,以储存收到的HTTP请求数据。pWrite is called by the system HTTP function library to store the received HTTP request data.
pRead 用于获取申请数据,以便作为一个HTTP请求的一部分被发送。pRead is used to get application data to be sent as part of an HTTP request.
pGet Size 提供带申请者的内容数据大小的HTTP函数库,″Content-Length″。pGet Size provides an HTTP function library with the applicant's content data size, "Content-Length".
pSet Size 由HTTP函数库调用,以便在数据到位时向调用的应用程序通知收到的内容pSet Size is called by the HTTP library to notify the calling application of the received content when data is in place
数据的大小。The size of the data.
AlHttpOpenAlHttpOpen
描述describe
创建并向HTTP函数库返回一个句柄。Create and return a handle to the HTTP library.
原型prototype
AL_HTTP_HANDLE AlHttpOpen(void);AL_HTTP_HANDLE AlHttpOpen(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
如创建一个HTTP实例失败,则返回INVALID_AL_HTTP_HMTDLEIf creating an HTTP instance fails, return INVALID_AL_HTTP_HMTDLE
也可参见see also
AlHttpClose()AlHttpClose()
AlHttpCloseAlHttpClose
描述describe
关闭并释放与一个HTTP句柄相关联的系统资源。Close and free system resources associated with an HTTP handle.
原型prototype
void AlHttpClose(AL_HTTP_HANDLE hHTTP);void AlHttpClose(AL_HTTP_HANDLE hHTTP);
参数parameter
hHTTPhHTTP
[in]由AlHttpOpen()函数返回的HTTP函数库句柄。[in] The HTTP function library handle returned by the AlHttpOpen() function.
返回值return value
无none
也可参见see also
AlHttpClose()AlHttpClose()
AlHttpExecAlHttpExec
描述describe
在指定的URL上执行一个HTTP方法(″GET″或″POST″),并带有可选择的文件头信息。Executes an HTTP method ("GET" or "POST") on the specified URL, with optional file headers.
原型prototype
intAlHttpExec(AL_HTTP_HANDLE hHTTP,intAlHttpExec(AL_HTTP_HANDLE hHTTP,
char const* pszMethod,char const* pszMethod,
char const* pszURL,char const* pszURL,
AlHttpCal lbacks* pHttpCb,AlHttpCal lbacks* pHttpCb,
void*pPrivate);void*pPrivate);
参数parameter
hHTTPhHTTP
[in]由AlHttpOpen()函数返回的HTTP函数库句柄[in] HTTP function library handle returned by the AlHttpOpen() function
pszMethodpszMethod
[in]HTTP方法规格。HTTP″GET″或″POST″[in] HTTP method specification. HTTP "GET" or "POST"
pszURLpszURL
[in]作出HTTP请求所在地址的URL[in] The URL of the address where the HTTP request was made
pHttpCbpHttpCb
[in]指向一套调用函数指定的HTTP I/O函数的指针。HTTP函数库使用在AlHttpCallbacks结构中指定的函数,以进行数据I/O[in] Pointer to a set of HTTP I/O functions specified by the calling function. The HTTP function library uses the functions specified in the AlHttpCallbacks structure for data I/O
pPrivatepPrivate
[in/out]指向一个调用函数数据的指针,该调用函数数据需传回在AlHttpCallbacks结构中指定的回调函数[in/out] Pointer to a call function data, the call function data needs to be passed back to the callback function specified in the AlHttpCallbacks structure
返回值return value
成功则返回0,否则为-1
也可参见see also
AlHttpOpen(),AlHttpClose()AlHttpOpen(), AlHttpClose()
共享内存Shared memory
存放函数库的共享对象的系统内存地址是通过使用AlShmAddress()函数而得到的。该共享信息区域在设备启动时间被分配/准备,而且为函数库的不同实例所引用。The system memory address of the shared object storing the function library is obtained by using the AlShmAddress() function. This shared information area is allocated/prepared at device boot time and is referenced by different instances of the library.
AlShmAddressAlShmAddress
描述describe
返回共享内存地址。Returns the shared memory address.
原型prototype
void* AlShmAddress(void);void* AlShmAddress(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
如成功则返回共享内存的地址,否则为NULLReturns the address of the shared memory if successful, otherwise NULL
时间time
AlTmGetCurrent()向调用函数提供以秒为单位的当前系统时间。AlTmGetCurrent() provides the current system time in seconds to the calling function.
AlTmGetCurrentAlTmGetCurrent
描述describe
获得当前的系统时间。Get the current system time.
原型prototype
unsigned long AlTmGetCurrent(void);unsigned long AlTmGetCurrent(void);
参数parameter
无none
返回值return value
如成功,则返回自纪元(协调世界时00:00:00,1970年1月1日)以来的以秒为单位的时间。如出错,则返回((unsigned long)-1L)。On success, returns the time in seconds since the epoch (00:00:00 UTC, January 1, 1970). If an error occurs, return ((unsigned long)-1L).
设备信息Device Information
AlDevGetInfoAlDevGetInfo
描述describe
获取设备的特定信息。由此函数返回的设备识别字符串被API使用。Get device-specific information. The device identification string returned by this function is used by the API.
原型prototype
int AlDevGetInfo(AlDeviceInfo*pDeviceInfo);int AlDevGetInfo(AlDeviceInfo*pDeviceInfo);
参数parameter
pDeviceInfopDeviceInfo
[out]指向设备信息的指针[out] Pointer to device information
AlDeviceInfo结构被定义为The AlDeviceInfo structure is defined as
#define AL_MAX_DEVICE_ID32#define AL_MAX_DEVICE_ID32
typedef struct AlDevicelnfo structtypedef struct AlDevicelnfo struct
{{
charszDeviceID[AL_MAX_DEVICE_ID];charszDeviceID[AL_MAX_DEVICE_ID];
}AlDevicelnfo;}AlDeviceInfo;
识别字符串szDevicelD是一个独一无二的终端/设备识别码—它用来将一个特定的移动通信设备与所有其它的设备单独识别出来。此信息用于为移动通信设备构建一个恶意软件签名下载URL。它不能包含任何不允许在一个URL中出现的字符(即空格)。The identification string szDevicelD is a unique terminal/device identification code - it is used to uniquely identify a specific mobile communication device from all other devices. This information is used to construct a malware signature download URL for the mobile communication device. It cannot contain any characters that are not allowed in a URL (i.e. spaces).
返回值return value
成功则返回0,失败则为-1
调试debugging
AlDbgQutputAlDbgQuput
描述describe
向一个调试控制台输出调试字符串。该函数是一个用于发布版本的零函数。Output debug strings to a debug console. This function is a nil function for release builds.
原型prototype
int AlDbgOutput(char const* pszOutput);int AlDbgOutput(char const* pszOutput);
参数parameter
pszOutputpszOutput
[in]向调试控制台输出的字符串[in] String output to the debug console
返回值return value
成功则返回0,失败则为-1
Claims (24)
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US46388503P | 2003-04-17 | 2003-04-17 | |
| US60/463,885 | 2003-04-17 | ||
| US10/639,007 | 2003-08-11 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1981263A CN1981263A (en) | 2007-06-13 |
| CN100524211Ctrue CN100524211C (en) | 2009-08-05 |
Family
ID=38131597
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2004800169936AExpired - Fee RelatedCN100524211C (en) | 2003-04-17 | 2004-04-05 | Update system and method for updating scanning subsystem in mobile communication frame |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100524211C (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8353041B2 (en)* | 2008-05-16 | 2013-01-08 | Symantec Corporation | Secure application streaming |
| US9337668B2 (en)* | 2011-04-28 | 2016-05-10 | Zoll Circulation, Inc. | Viral distribution of battery management parameters |
| CN105204940A (en)* | 2014-05-28 | 2015-12-30 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Memory allocation method and device |
| CN110311889B (en)* | 2019-05-17 | 2021-09-03 | 中国电力科学研究院有限公司 | Method for verifying effectiveness of intelligent distribution transformer terminal APP |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1249112A (en)* | 1997-02-26 | 2000-03-29 | 艾利森电话股份有限公司 | Method and apparatus for remotely upgrading control software in a cellular telephone |
| CN1296227A (en)* | 1999-11-13 | 2001-05-23 | 埃维芮佐讷有限公司 | System and method for e-mail warning, scanning and processing computer virus |
| CN1304092A (en)* | 2000-01-11 | 2001-07-18 | 神达电脑股份有限公司 | Virus detection method with IDE hard disk device set in PIO transmission mode |
| US6286041B1 (en)* | 1994-02-14 | 2001-09-04 | Computer Associates Think, Inc. | System for software distribution in a digital computer network |
| US6457076B1 (en)* | 1996-06-07 | 2002-09-24 | Networks Associates Technology, Inc. | System and method for modifying software residing on a client computer that has access to a network |
- 2004
- 2004-04-05CNCNB2004800169936Apatent/CN100524211C/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6286041B1 (en)* | 1994-02-14 | 2001-09-04 | Computer Associates Think, Inc. | System for software distribution in a digital computer network |
| US6457076B1 (en)* | 1996-06-07 | 2002-09-24 | Networks Associates Technology, Inc. | System and method for modifying software residing on a client computer that has access to a network |
| CN1249112A (en)* | 1997-02-26 | 2000-03-29 | 艾利森电话股份有限公司 | Method and apparatus for remotely upgrading control software in a cellular telephone |
| CN1296227A (en)* | 1999-11-13 | 2001-05-23 | 埃维芮佐讷有限公司 | System and method for e-mail warning, scanning and processing computer virus |
| CN1304092A (en)* | 2000-01-11 | 2001-07-18 | 神达电脑股份有限公司 | Virus detection method with IDE hard disk device set in PIO transmission mode |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| . Norton AntiVirus Corporate Edition User's Guide.* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1981263A (en) | 2007-06-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101071597B1 (en) | Update system and method for updating a scanning subsystem in a mobile communication framework | |
| KR101046549B1 (en) | AP systems, methods and computer program products for accessing content / security analysis functionality in a mobile communication framework | |
| CA2517534C (en) | System, method and computer program product for content/context sensitive scanning utilizing a mobile communication device | |
| KR101046544B1 (en) | Platform-independent scanning subsystem API for Mobile Communications Framework | |
| CN100524211C (en) | Update system and method for updating scanning subsystem in mobile communication frame |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CP03 | Change of name, title or address | Address after:1209 Orange Street, Wilmington, New Fort, 19801, Delaware, USA Co-patentee after:NTT Mobile Communications Patentee after:Mike Non Ltd. Address before:California, USA Co-patentee before:NTT Mobile Communications Patentee before:Mcafee Inc. | |
| CP03 | Change of name, title or address | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20090805 | |
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |