CN100477568C - A data transmission method of a mobile packet network - Google Patents
A data transmission method of a mobile packet networkDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100477568C CN100477568CCNB031279910ACN03127991ACN100477568CCN 100477568 CCN100477568 CCN 100477568CCN B031279910 ACNB031279910 ACN B031279910ACN 03127991 ACN03127991 ACN 03127991ACN 100477568 CCN100477568 CCN 100477568C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- tunnel
- protocol
- network
- layer
- carried
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及网络中的数据传输技术,特别是指一种移动分组网络的数据传输方法。The invention relates to the data transmission technology in the network, in particular to a data transmission method of the mobile packet network.
背景技术Background technique
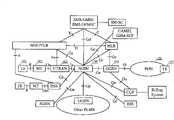
在宽带码分多址(WCDMA)分组网络中,终端设备(TE)使用分组域业务时,通常TE发送的网际协议(IP)数据包在WCDMA分组网络上承载。图1为WCDMA分组网络结构组成示意图,如图1所示,TE 101发送的IP数据包在WCDMA分组网络上承载,即经过移动终端(MT)102、通用陆地无线接入网(UTRAN)103、通用分组无线业务支持节点(SGSN)104、通用分组无线业务网关支持节点(GGSN)105的承载,然后通过Gi接口发送到公共数据网(PDN)106或互联网(Internet)上,最后IP数据包经过PDN 106发送至目的TE 107。IP数据包的反方向传送过程为上述过程的逆向过程。此处的TE 101和MT 102为可实现不同目的的设备,TE 101为用户提供操作界面的设备,MT 102为支持用户所作操作的设备。In a wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA) packet network, when a terminal equipment (TE) uses a packet domain service, usually an Internet Protocol (IP) data packet sent by the TE is carried on the WCDMA packet network. Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the WCDMA packet network structure, as shown in Figure 1, the IP data packet sent by TE 101 is carried on the WCDMA packet network, that is, through a mobile terminal (MT) 102, a universal terrestrial radio access network (UTRAN) 103, General Packet Radio Service Support Node (SGSN) 104, General Packet Radio Service Gateway Support Node (GGSN) 105 bearer, then send to public data network (PDN) 106 or the Internet (Internet) through the Gi interface, and finally the IP data packet passes through PDN 106 sends to destination TE 107. The reverse transmission process of the IP data packet is the reverse process of the above process. Here, TE 101 and MT 102 are devices that can achieve different purposes, TE 101 is a device that provides an operation interface for users, and
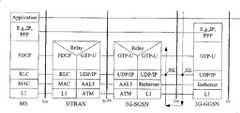
图2为数据包在WCDMA分组网络中的传输过程示意图,如图2所示,移动台(MS)为TE与MT的组合,数据包的传输如图中箭头所示。在Gi接口外遵循IP协议或端对端协议(PPP)。在MS和GGSN上具有用于用户应用承载的对等协议层,例如IP协议层或PPP协议层,该协议层的数据包被作为WCDMA分组网络核心网上传输的净荷。在无线接口(Uu)上,数据包承载在分组数据会聚协议(PDCP)、无线链路控制层(RLC)协议、媒体接入控制层(MAC)协议和物理层(L1)协议的协议栈上;在Iu-PS接口上,数据包承载在通用分组无线业务用户面隧道协议(GTP-U)、用户数据报协议(UDP)或IP协议、异步传输模式适配层(ALL5)协议和异步传输模式(ATM)协议的协议栈上;在Gn接口上,数据包承载在GTP-U协议、UDP协议或IP协议、链路层(L2)协议和L1协议的协议栈上;在Gn接口和Gi接口上,数据包将通过IP网常用的链路层协议,例如以太网(Ethernet)协议,在IP广域网上进行传输。Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the transmission process of data packets in the WCDMA packet network. As shown in Figure 2, the mobile station (MS) is a combination of TE and MT, and the transmission of data packets is shown by the arrow in the figure. Follow the IP protocol or peer-to-peer protocol (PPP) outside the Gi interface. There is a peer-to-peer protocol layer for user application bearer on the MS and GGSN, such as the IP protocol layer or the PPP protocol layer, and the data packets of this protocol layer are used as the payload transmitted on the core network of the WCDMA packet network. On the radio interface (Uu), data packets are carried on the protocol stack of packet data convergence protocol (PDCP), radio link control layer (RLC) protocol, medium access control layer (MAC) protocol and physical layer (L1) protocol ; On the Iu-PS interface, data packets are carried in the General Packet Radio Service User Plane Tunneling Protocol (GTP-U), User Datagram Protocol (UDP) or IP protocol, Asynchronous Transfer Mode Adaptation Layer (ALL5) protocol and Asynchronous Transport On the protocol stack of the ATM protocol; on the Gn interface, the data packet is carried on the protocol stack of the GTP-U protocol, UDP protocol or IP protocol, the link layer (L2) protocol and the L1 protocol; on the Gn interface and Gi On the interface, the data packet will be transmitted on the IP wide area network through the link layer protocol commonly used in the IP network, such as the Ethernet (Ethernet) protocol.
当前考虑到Internet上Ethernet的最大传输单元为1500字节(BYTES),制定了遵循几种通用协议的帧格式。图3为遵循几种通用协议的帧结构示意图,如图3所示,图3(A)为Ethernet II协议帧结构示意图,遵循EthernetII协议的帧一般包括:目的地址6BYTES、原地址6BYTES、协议类型6BYTES和数据46~1500BYTES;图3(B)为802.2协议帧结构示意图,遵循802.2协议的帧一般包括:目的地址6BYTES、原地址6BYTES、帧长度2BYTES、目的服务访问点(DSAP)1BYTES、源服务访问点(SSAP)1BYTES、控制域(control domain)1~2BYTES和数据46~1500BYTES;图3(C)为802.3协议帧结构示意图,遵循802.3协议的帧一般包括:目的地址6BYTES、原地址6BYTES、帧长度2BYTES和数据46~1500BYTES。Considering that the maximum transmission unit of Ethernet on the Internet is 1500 bytes (BYTES), frame formats following several common protocols have been formulated. Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of the frame structure following several general protocols. As shown in Figure 3, Figure 3 (A) is a schematic diagram of the frame structure of the Ethernet II protocol. The frame following the Ethernet II protocol generally includes: destination address 6BYTES, original address 6BYTES, protocol type 6BYTES and data 46~1500BYTES; Figure 3 (B) is a schematic diagram of the frame structure of the 802.2 protocol. A frame following the 802.2 protocol generally includes: destination address 6BYTES, original address 6BYTES, frame length 2BYTES, destination service access point (DSAP) 1BYTES, source service Access point (SSAP) 1BYTES, control domain (control domain) 1~2BYTES and data 46~1500BYTES; Figure 3(C) is a schematic diagram of the 802.3 protocol frame structure, and frames following the 802.3 protocol generally include: destination address 6BYTES, original address 6BYTES, Frame length 2BYTES and data 46~1500BYTES.
为使网络的传输效率达到最高,第三代移动通信协议将WCDMA分组网络的服务质量(QoS,Quality of Service)参数中的最大传输单元确定为1500BYTES,保证在Gi接口上和Internet互连时,不会发生IP数据包的分片和重组,以此使网络的传输效率达到最高。In order to maximize the transmission efficiency of the network, the third-generation mobile communication protocol determines the maximum transmission unit in the quality of service (QoS, Quality of Service) parameter of the WCDMA packet network as 1500BYTES, ensuring that when the Gi interface is interconnected with the Internet, Fragmentation and reassembly of IP data packets will not occur, so that the transmission efficiency of the network can be maximized.
基于PPP协议进行的端对端连接,出于相同原因的考虑,确定最大传输单元为1502BYTES。For the end-to-end connection based on the PPP protocol, for the same reason, the maximum transmission unit is determined to be 1502BYTES.
数据包经过各承载协议层时,需要在该承载协议层上进行封装和解包。每一承载协议层都有各自的最大传输单元(MTU)。如果数据包的长度超过了通过该承载协议层的最大传输单元,则需要对该数据包进行数据包分片,当数据包传输至下一接口时,还需要对其进行重组。这样,最大传输单元的合理设置可有效避免传输过程中数据包的频繁分片和重组,对于提高网络的传输效率十分重要。如果WCDMA分组网络的最大传输单元大于L2层的最大传输单元,就会导致数据包的频繁分片和重组,大大降低了WCDMA分组网络的性能。通常通信系统会对该网络承载的最大数据单元进行统一规定,尽量避免数据包传输过程中的频繁分片和重组。但是,当前最大传输单元的设置只考虑到了Gi接口的互连性,而忽略了WCDMA分组网络自身的传输特性。When a data packet passes through each bearer protocol layer, it needs to be encapsulated and unpacked on the bearer protocol layer. Each bearer protocol layer has its own maximum transmission unit (MTU). If the length of the data packet exceeds the maximum transmission unit passing through the bearer protocol layer, the data packet needs to be fragmented, and when the data packet is transmitted to the next interface, it needs to be reassembled. In this way, a reasonable setting of the maximum transmission unit can effectively avoid frequent fragmentation and reassembly of data packets during transmission, which is very important for improving the transmission efficiency of the network. If the maximum transmission unit of the WCDMA packet network is larger than the maximum transmission unit of the L2 layer, it will cause frequent fragmentation and reassembly of data packets, which greatly reduces the performance of the WCDMA packet network. Usually, the communication system will uniformly specify the maximum data unit carried by the network, and try to avoid frequent fragmentation and reassembly during data packet transmission. However, the current setting of the maximum transmission unit only considers the interconnectivity of the Gi interface, while ignoring the transmission characteristics of the WCDMA packet network itself.
在第三代合作伙伴计划(3GPP)协议中规定,数据包在WCDMA分组网络中通过通用分组无线业务隧道协议(GTP)隧道进行传输,GTP隧道承载于UDP/IP协议层之上。According to the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) agreement, data packets are transmitted in the WCDMA packet network through the General Packet Radio Service Tunneling Protocol (GTP) tunnel, and the GTP tunnel is carried on the UDP/IP protocol layer.
按照通常的组网方式,WCDMA分组网络中的SGSN节点和GGSN节点间承载于IP骨干网之上,而且一般通过以太网链路层进行传输。According to the usual networking mode, the SGSN nodes and GGSN nodes in the WCDMA packet network are carried on the IP backbone network, and are generally transmitted through the Ethernet link layer.
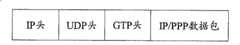
图4为Gn接口数据包封装示意图,如图4所示,IP/PPP数据包在Gn接口的GTP隧道中传输时,GTP隧道会将IP/PPP数据包封装上GTP协议头、UDP协议头和IP协议头。Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of Gn interface data packet encapsulation, as shown in Figure 4, when the IP/PPP data packet is transmitted in the GTP tunnel of the Gn interface, the GTP tunnel will encapsulate the IP/PPP data packet on the GTP protocol header, UDP protocol header and IP protocol header.
由图4可看出,如果IP/PPP数据包的长度接近最大传输单元1500BYTES时,通过在Gn接口GTP隧道中的传输,将IP/PPP数据包封装上GTP协议头、UDP协议头和IP协议头后,很可能会使封装后的数据包的长度超出以太网链路层上的最大传输单元1500BYTES。It can be seen from Figure 4 that if the length of the IP/PPP data packet is close to the maximum transmission unit 1500BYTES, the IP/PPP data packet will be encapsulated with the GTP protocol header, UDP protocol header and IP protocol through the transmission in the GTP tunnel of the Gn interface. After the header, it is likely that the length of the encapsulated data packet will exceed the maximum transmission unit 1500BYTES on the Ethernet link layer.
从目前Internet上的业务统计情况来看,为提高传输效率,一些大数据量业务中,例如,遵循文件传输协议(FTP)的文件传输、视频点播等,服务器通常将发送的数据包长度设置为以太网链路层的最大传输单元1500BYTES,这就导致SGSN和GGSN会接收大量的分片数据包。另外,作为WCDMA分组网络的网元,SGSN和GGSN是作为GTP隧道的端节点而存在的,根据GTP隧道的特性,如果数据包在发送端GTP隧道被分片,则在接收端GTP隧道需将数据包进行重组,因此,在接收数据包的SGSN或GGSN上需重组数据包,从而大幅度降低SGSN和GGSN的处理性能。Judging from the current business statistics on the Internet, in order to improve transmission efficiency, in some services with large data volumes, such as file transfers following the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), video on demand, etc., the server usually sets the length of the data packet sent to The maximum transmission unit of the Ethernet link layer is 1500BYTES, which causes SGSN and GGSN to receive a large number of fragmented data packets. In addition, as network elements of the WCDMA packet network, SGSN and GGSN exist as end nodes of GTP tunnels. According to the characteristics of GTP tunnels, if data packets are fragmented in the GTP tunnel at the sending end, the GTP tunnel at the receiving end needs to The data packet is reassembled. Therefore, the data packet needs to be reassembled on the SGSN or GGSN receiving the data packet, thereby greatly reducing the processing performance of the SGSN and GGSN.
此外,数据包的重组会大大增加GTP隧道中高速转发单元的设计难度。In addition, the reassembly of data packets will greatly increase the design difficulty of the high-speed forwarding unit in the GTP tunnel.
图5为数据包在WCDMA分组网络中传输过程的分片重组示意图,如图5所示,如果GGSN接收的数据包长度为1500BYTES,经过封装GTP协议头、UDP协议头和IP协议头,当封装后的数据包传送至承载以大网协议层时,即以太网链路层,封装后的数据包长度已超出1500BYTES,因此GGSN将封装后的数据包在501处进行分片,即承载网络层的UDP/IP层对数据包进行分片,然后再对数据包进行发送,根据GTP隧道的特性,SGSN接收到分片后的数据包后,对数据包在502处进行重组,即承载网络层的UDP/IP层对数据包进行重组,然后再发送至Iu-PS接口。反之,如果SGSN先接收长度为1500BYTES的数据包,同样会对该数据包进行分片,然后由GGSN对数据包进行重组。Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of fragmentation and reassembly of data packets in the WCDMA packet network transmission process. As shown in Figure 5, if the length of the data packet received by GGSN is 1500BYTES, after encapsulating the GTP protocol header, UDP protocol header and IP protocol header, when encapsulating When the final data packet is transmitted to the bearer network protocol layer, that is, the Ethernet link layer, the length of the encapsulated data packet has exceeded 1500BYTES, so the GGSN fragments the encapsulated data packet at 501, that is, the bearer network layer The UDP/IP layer fragments the data packet, and then sends the data packet. According to the characteristics of the GTP tunnel, after the SGSN receives the fragmented data packet, it reassembles the data packet at 502, that is, the bearer network layer The UDP/IP layer reassembles the data packet before sending it to the Iu-PS interface. Conversely, if the SGSN first receives a data packet with a length of 1500BYTES, it will also fragment the data packet, and then the GGSN will reassemble the data packet.
综上所述,目前WCDMA分组网络中最大传输单元的设置,只考虑到了封装前的最大传输单元,封装后的最大传输单元的长度实际上已经大于1500BYTES,这个最大传输单元的设置,与以太网链路层的最大传输单元1500BYTES是相互矛盾的,将使WCDMA分组网络核心网节点SGSN和GGSN对数据包进行大量的分片和重组工作,使其性能大大降低,复杂程度大大增加,这是WCDMA分组网络引进IP协议内容时,没有进行综合考虑而导致的。To sum up, the current maximum transmission unit setting in WCDMA packet network only considers the maximum transmission unit before encapsulation, and the length of the maximum transmission unit after encapsulation is actually greater than 1500BYTES. The setting of this maximum transmission unit is similar to that of Ethernet The maximum transmission unit 1500BYTES of the link layer is contradictory, which will cause the core network nodes SGSN and GGSN of the WCDMA packet network to perform a large number of fragmentation and reassembly work on the data packets, greatly reducing its performance and greatly increasing its complexity. When the content of the IP protocol is introduced into the packet network, there is no comprehensive consideration.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本发明的目的在于提供一种移动分组网络的数据传输方法,对最大传输单元进行优化,避免数据包在传输过程中的频繁分片和重组。In view of this, the object of the present invention is to provide a data transmission method for a mobile packet network, which optimizes the maximum transmission unit and avoids frequent fragmentation and reassembly of data packets during transmission.
为了达到上述目的,本发明提供了一种移动分组网络的数据传输方法,该方法包含以下步骤:In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a data transmission method of a mobile packet network, the method comprising the following steps:
A、通信协议层接收数据包后,判断该数据包长度是否大于网络承载的最大传输单元,如果大于,执行步骤B,否则,执行步骤C;A. After the communication protocol layer receives the data packet, it judges whether the length of the data packet is greater than the maximum transmission unit carried by the network. If it is greater, perform step B, otherwise, perform step C;
B、通信协议层对上述数据包进行分片,在隧道中对该数据包进行封装,然后在移动分组网络上进行传输,并在接收终端的通信协议层对分片后的数据包进行重组,最终传输至接收终端的应用层;B. The communication protocol layer fragments the above data packet, encapsulates the data packet in the tunnel, then transmits it on the mobile packet network, and reassembles the fragmented data packet at the communication protocol layer of the receiving terminal, Finally transmitted to the application layer of the receiving terminal;
C、在移动分组网络上传输数据包,直至传输至接收终端的应用层;C. Transmit data packets on the mobile packet network until they are transmitted to the application layer of the receiving terminal;
其中,所述网络承载的最大传输单元为,隧道承载的链路层的最大传输单元减去隧道承载的网络层协议封装长度,再减去隧道承载的传输层协议封装长度,最后减去隧道封装长度的结果。Wherein, the maximum transmission unit carried by the network is the maximum transmission unit of the link layer carried by the tunnel minus the encapsulation length of the network layer protocol carried by the tunnel, then subtracted the encapsulation length of the transport layer protocol carried by the tunnel, and finally subtracted the length of the tunnel encapsulation length result.
所述隧道为通用分组无线业务隧道时,宽带码分多址分组网络承载的最大传输单元为,通用分组无线业务隧道承载的链路层的最大传输单元减去通用分组无线业务隧道承载的网络层协议封装长度,再减去通用分组无线业务隧道的传输层协议封装长度,最后减去通用分组无线业务隧道封装长度的结果。When the tunnel is a general packet radio service tunnel, the maximum transmission unit carried by the broadband code division multiple access packet network is the maximum transmission unit of the link layer carried by the general packet radio service tunnel minus the network layer carried by the general packet radio service tunnel The protocol encapsulation length, the result of subtracting the transport layer protocol encapsulation length of the GPRS tunnel, and finally subtracting the encapsulation length of the GPRS tunnel.
所述通用分组无线业务隧道承载于用户数据包协议/网际协议层。The general packet radio service tunnel is carried on the user data packet protocol/internet protocol layer.
所述通用分组无线业务隧道遵循通用分组无线业务隧道协议1版本。The GPRS tunnel complies with
所述通用分组无线业务隧道遵循通用分组无线业务隧道协议0版本。The GPRS tunnel complies with version 0 of the GPRS Tunneling Protocol.
所述隧道承载的链路层的最大传输单元为:一个以上隧道承载的链路层最大传输单元中的最小值。The maximum transmission unit of the link layer carried by the tunnel is: a minimum value among the maximum transmission units of the link layer carried by more than one tunnel.
根据本发明提出的方法,使当前在网络承载层传输的数据包经过封装后,其长度不大于链路层的最大传输单元,可避免网络设备对数据包的频繁分片和重组,提升了网络设备的性能,从而提高了的网络传输效率。另外,依据本发明提出的优化最大传输单元的方法还可降低网络的复杂度,从而降低网络成本。According to the method proposed by the present invention, the length of the data packets currently transmitted at the network bearer layer is not greater than the maximum transmission unit of the link layer after encapsulation, which can avoid frequent fragmentation and reassembly of data packets by network equipment, and improve the network efficiency. The performance of the equipment, thus improving the network transmission efficiency. In addition, the method for optimizing the maximum transmission unit proposed by the present invention can also reduce the complexity of the network, thereby reducing the network cost.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为WCDMA分组网络结构组成示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of WCDMA packet network structure;
图2为数据包在WCDMA分组网络中的传输过程示意图;Fig. 2 is the schematic diagram of the transmission process of data packet in WCDMA packet network;
图3为遵循几种通用协议的帧结构示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of a frame structure following several general protocols;
图4为Gn接口数据包封装示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of Gn interface packet encapsulation;
图5为数据包在WCDMA分组网络中传输过程的分片重组示意图;Fig. 5 is the schematic diagram of fragmentation reorganization of data packet transmission process in WCDMA packet network;
图6为GTPv1协议头结构示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the GTPv1 protocol header;
图7为GTPv0协议头结构示意图;FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the GTPv0 protocol header;
图8为UDP协议头结构示意图;Fig. 8 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the UDP protocol header;
图9为IP协议头结构示意图;Fig. 9 is a structural schematic diagram of the IP protocol header;
图10为本发明中数据包在WCDMA分组网络中传输过程的分片重组示意图。FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram of the fragmentation reassembly process of data packets transmitted in the WCDMA packet network in the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面结合附图对本发明作进一步地详细描述。In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
本发明的关键是思想是:使Gn接口上传输隧道的最大传输单元与骨干网上的以太网链路层的最大传输单元相吻合。针对具有隧道封装特性的传输协议,在计算网络承载的最大传输单元时,应采用如下算法:网络承载的最大传输单元=隧道承载的链路层的最大传输单元-隧道承载的网络层协议封装长度-隧道承载的传输层协议封装长度-隧道封装长度。隧道承载的链路层可能会同时有多个,鉴于通用性的考虑,隧道承载的链路层的最大传输单元可取隧道承载的网络链路层常用协议的最大传输单元中的最小值。The key point of the present invention is that the idea is to make the maximum transmission unit of the transmission tunnel on the Gn interface coincide with the maximum transmission unit of the Ethernet link layer on the backbone network. For transmission protocols with tunnel encapsulation characteristics, the following algorithm should be used when calculating the maximum transmission unit carried by the network: maximum transmission unit carried by the network = maximum transmission unit of the link layer carried by the tunnel - encapsulation length of the network layer protocol carried by the tunnel -Encapsulation length of the transport layer protocol carried by the tunnel-Encapsulation length of the tunnel. There may be multiple link layers carried by the tunnel at the same time. In consideration of versatility, the maximum transmission unit of the link layer carried by the tunnel can be the minimum value among the maximum transmission units of the common protocols of the network link layer carried by the tunnel.
下面以WCDMA分组网络为例进行说明。The WCDMA packet network is taken as an example for description below.
在WCDMA分组网络中,上述算法可为:WCDMA分组网络承载的最大传输单元=GTP隧道承载的链路层的最大传输单元-GTP隧道承载的网络层协议封装长度-GTP隧道承载的传输层协议封装长度-GTP隧道封装长度=以太网链路层的最大传输单元-IP协议封装长度-UDP协议封装长度-GTP隧道封装长度。GTP隧道承载的链路层的最大传输单元选取以太网链路层的最大传输单元是出于通用性的考虑,虽然WCDMA分组网络的链路层承载形式可为多种,例如以太网等,但以太网链路层的最大传输单元是其中最小的,根据上述算法计算出的WCDMA分组网络承载的最大传输单元能够满足最小的最大传输单元,自然能够满足其他较大的链路层最大传输单元。In the WCDMA packet network, the above algorithm can be: the maximum transmission unit carried by the WCDMA packet network=the maximum transmission unit of the link layer carried by the GTP tunnel-the network layer protocol encapsulation length carried by the GTP tunnel-the transport layer protocol encapsulation carried by the GTP tunnel Length-GTP tunnel encapsulation length=Maximum transmission unit of the Ethernet link layer-IP protocol encapsulation length-UDP protocol encapsulation length-GTP tunnel encapsulation length. The maximum transmission unit of the link layer carried by the GTP tunnel is selected from the maximum transmission unit of the Ethernet link layer for the sake of versatility. Although the link layer of the WCDMA packet network can be carried in various forms, such as Ethernet, etc., but The maximum transmission unit of the Ethernet link layer is the smallest among them. The maximum transmission unit carried by the WCDMA packet network calculated according to the above algorithm can satisfy the smallest maximum transmission unit, and naturally can satisfy other larger link layer maximum transmission units.
下面介绍Gn接口各协议层的封装长度的计算。The following describes the calculation of the encapsulation length of each protocol layer of the Gn interface.
目前,GTP隧道遵循的GTP协议有两个版本:GTPv1协议和GTPv0协议。Currently, the GTP protocol followed by the GTP tunnel has two versions: GTPv1 and GTPv0.
图6为GTPv1协议头结构示意图,如图6所示,GTPv1协议头结构通常共包含12BYTES,第一字节中包含版本号(Version)、GTP协议类型(PT(*))、扩展头标识(E)、序列号标识(S)和N-PDU标识(PN)。Version对于GTPv1协议始终设置为1;PT(*)用于区分当前应用的是GTPv1协议还是GTPv0协议;E用于确定该GTPv1协议头结构中是否包含扩展头;S用于确定该GTPv1协议头结构中是否包含序列号;PN用于确定该GTPv1协议头结构中是否包含N-PDU,N-PDU用于SGSN间的路由更新,PDU为协议数据单元。第二字节为该GTPv1协议头的消息类型(Message Type)。第三至四字节为该GTPv1协议头的消息长度(Length)。第五至八字节为该GTPv1协议头的隧道标识(Tunnel Endpoint Identifier)。第九至十字节为该GTPv1协议头的序列号(Sequence Number)。第十一字节为该GTPv1协议头的N-PDU号(N-PDU Number)。第十二字节为该GTPv1协议头的扩展头类型(Next Extension Header Type)。Figure 6 is a schematic diagram of the GTPv1 protocol header structure. As shown in Figure 6, the GTPv1 protocol header structure usually contains 12BYTES in total, and the first byte contains the version number (Version), the GTP protocol type (PT(*)), and the extension header identifier ( E), sequence number identification (S) and N-PDU identification (PN). Version is always set to 1 for the GTPv1 protocol; PT(*) is used to distinguish whether the current application is the GTPv1 protocol or the GTPv0 protocol; E is used to determine whether the GTPv1 protocol header structure contains an extension header; S is used to determine the GTPv1 protocol header structure Whether it contains a sequence number; PN is used to determine whether the GTPv1 protocol header structure contains N-PDU, N-PDU is used for routing update between SGSNs, and PDU is a protocol data unit. The second byte is the message type (Message Type) of the GTPv1 protocol header. The third to fourth bytes are the message length (Length) of the GTPv1 protocol header. The fifth to eighth bytes are the tunnel identifier (Tunnel Endpoint Identifier) of the GTPv1 protocol header. The ninth to tenth bytes are the sequence number (Sequence Number) of the GTPv1 protocol header. The eleventh byte is the N-PDU number (N-PDU Number) of the GTPv1 protocol header. The twelfth byte is the extension header type (Next Extension Header Type) of the GTPv1 protocol header.
图7为GTPv0协议头结构示意图,如图7所示,GTPv0协议头结构通常共包含20BYTES,第一字节中包含版本号(Version)、GTP协议类型(PT(*))、空闲位(Spare)和SNDCP N-PDU标识(SNN)。Version对于GTPv0协议始终设置为0;PT(*)用于区分当前应用的是GTPv1协议还是GTPv0协议;SNN用于确定该GTPv0协议头结构中是否包含SNDCPN-PDU。第二字节为该GTPv0协议头的消息类型(Message Type)。第三至四字节为该GTPv0协议头的消息长度(Length)。第五至六字节为该GTPv0协议头的消息序列号(Sequence Number)。第七至八字节为该GTPv0协议头的GTP流标识(Flow Lable)。第九字节为该GTPv0协议头的SNDCPN-PDU号(SNDCP N-PDULLC Number)。第十至十二字节为该GTPv0协议头中的空闲位,例如数字1。第十三至二十字节为该GTPv0协议头的隧道标识(TID)。Figure 7 is a schematic diagram of the GTPv0 protocol header structure. As shown in Figure 7, the GTPv0 protocol header structure usually contains 20BYTES, and the first byte contains the version number (Version), GTP protocol type (PT(*)), and spare bits (Spare ) and SNDCP N-PDU identifier (SNN). Version is always set to 0 for the GTPv0 protocol; PT(*) is used to distinguish whether the current application is the GTPv1 protocol or the GTPv0 protocol; SNN is used to determine whether the GTPv0 protocol header structure contains SNDCPN-PDU. The second byte is the message type (Message Type) of the GTPv0 protocol header. The third to fourth bytes are the message length (Length) of the GTPv0 protocol header. The fifth to sixth bytes are the message sequence number (Sequence Number) of the GTPv0 protocol header. The seventh to eighth bytes are the GTP flow identifier (Flow Lable) of the GTPv0 protocol header. The ninth byte is the SNDCPN-PDU number (SNDCP N-PDULLC Number) of the GTPv0 protocol header. The tenth to twelve bytes are idle bits in the GTPv0 protocol header, such as the
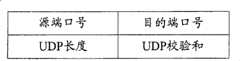
所有的GTP用户面数据包均是通过UDP/IP协议层承载的,UDP协议头的长度是固定的,为8BYTES。图8为UDP协议头结构示意图,如图8所示,UDP协议头包含2个字节的源端口号(Source Port Number)、2个字节的目的端口号(Destination Port Number)、2个字节的UDP长度(UDPLength)和2个字节的UDP校验和(UDP Checksum)。图9为IP协议头结构示意图,如图9所示,IP协议头的前一部分为20个字节的固定部分901,后一部分为不定长的选项部分902。固定部分901主要包括:版本、首部长度、服务类型、总长度、标识、源站IP地址、目的站IP地址等。选项部分902为长度可变的任选字段和填充部分,任选字段用来支持排错、测量以及安全等措施,内容很丰富,但是在Gn接口用户面的数据包中通常不带有选项部分902。All GTP user plane data packets are carried by the UDP/IP protocol layer, and the length of the UDP protocol header is fixed at 8BYTES. Figure 8 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the UDP protocol header. As shown in Figure 8, the UDP protocol header includes 2 bytes of source port number (Source Port Number), 2 bytes of destination port number (Destination Port Number), 2 characters Section UDP length (UDPLength) and 2 bytes of UDP checksum (UDP Checksum). FIG. 9 is a structural diagram of the IP protocol header. As shown in FIG. 9 , the first part of the IP protocol header is a
根据以上所述,GTP隧道遵循GTPv1协议时,各协议层的封装长度为GTPv1(12BYTES)+UDP(8BYTES)+IP(20BYTES)=40BYTES。GTP隧道遵循GTPv0协议时,各协议层的封装长度为GTPv0(20BYTES)+UDP(8BYTES)+IP(20BYTES)=48BYTES。依然是出于通用性的考虑,选取其中较大的48BYTES,根据以太网链路层的最大传输单元为1500BYTES,将GTP隧道看作用户面数据包的链路层协议,可计算Gn接口上GTP协议支持的最大传输单元为1500BYTES-48BYTES=1452BYTES。According to the above, when the GTP tunnel follows the GTPv1 protocol, the encapsulation length of each protocol layer is GTPv1(12BYTES)+UDP(8BYTES)+IP(20BYTES)=40BYTES. When the GTP tunnel follows the GTPv0 protocol, the encapsulation length of each protocol layer is GTPv0(20BYTES)+UDP(8BYTES)+IP(20BYTES)=48BYTES. Still for the sake of versatility, the larger 48BYTES is selected. According to the maximum transmission unit of the Ethernet link layer is 1500BYTES, the GTP tunnel is regarded as the link layer protocol of the user plane data packet, and the GTP on the Gn interface can be calculated. The maximum transmission unit supported by the protocol is 1500BYTES-48BYTES=1452BYTES.
根据以上所述设置WCDMA分组网络承载的最大传输单元,就可避免核心网节点SGSN和GGSN对数据包的频繁分片和重组,提高了SGSN和GGSN的处理性能。Setting the maximum transmission unit carried by the WCDMA packet network according to the above can avoid frequent fragmentation and reassembly of data packets by core network nodes SGSN and GGSN, and improve the processing performance of SGSN and GGSN.
图10为本发明中数据包在WCDMA分组网络中传输过程的分片重组示意图,如图10所示,GGSN接收数据包,如果该数据包长度不小于WCDMA分组网络承载的最大传输单元,例如1452BYTES,则GGSN在数据进入GTP隧道封装前,将数据包在1处进行分片,即位于GTP隧道之上的通信协议层对数据包进行分片,然后再封装上GTP协议头、UDP协议头和IP协议头。由于在封装GTP协议头、UDP协议头和IP协议头前,GGSN就对数据包进行分片操作,当封装后的数据包传送至以太网链路层时,该数据包的长度没有超出以太网链路层的最大传输单元,因此当数据包传送至SGSN时,SGSN不会对数据包进行重组操作,直至传送至Uu接口,MS在2处对数据包进行重组,即位于GTP隧道之上的通信协议层对数据包进行重组。反方向上,数据包在MS上进行分片操作后才进行传输。Figure 10 is a schematic diagram of the fragmentation reassembly of the data packet in the WCDMA packet network transmission process in the present invention, as shown in Figure 10, the GGSN receives the data packet, if the length of the data packet is not less than the maximum transmission unit carried by the WCDMA packet network, such as 1452BYTES , before the data enters the GTP tunnel for encapsulation, the GGSN fragments the data packet at 1, that is, the communication protocol layer above the GTP tunnel fragments the data packet, and then encapsulates the GTP protocol header, UDP protocol header and IP protocol header. Since the GGSN fragments the data packet before encapsulating the GTP protocol header, UDP protocol header, and IP protocol header, when the encapsulated data packet is transmitted to the Ethernet link layer, the length of the data packet does not exceed the Ethernet link layer. The maximum transmission unit of the link layer, so when the data packet is transmitted to the SGSN, the SGSN will not reassemble the data packet until it is transmitted to the Uu interface, and the MS reassembles the data packet at 2 places, that is, on the GTP tunnel The communication protocol layer reassembles the data packets. In the opposite direction, the data packet is transmitted after the fragmentation operation is performed on the MS.
通过本发明提出的方法,在WCDMA分组网络核心网节点SGSN和GGSN上不会对数据包进行频繁分片和重组,使SGSN和GGSN的处理特点与路由器相一致。Through the method proposed by the invention, the data packets will not be frequently fragmented and reassembled on the core network nodes SGSN and GGSN of the WCDMA packet network, so that the processing characteristics of the SGSN and GGSN are consistent with those of routers.
本发明适用于移动分组数据网络,例如WCDMA分组网络,移动IP网络(Mobile IP)等。The present invention is applicable to mobile packet data networks, such as WCDMA packet networks, mobile IP networks (Mobile IP) and the like.
总之,以上所述仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并非用于限定本发明的保护范围。In a word, the above descriptions are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (6)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB031279910ACN100477568C (en) | 2003-04-28 | 2003-04-28 | A data transmission method of a mobile packet network |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB031279910ACN100477568C (en) | 2003-04-28 | 2003-04-28 | A data transmission method of a mobile packet network |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1543104A CN1543104A (en) | 2004-11-03 |
| CN100477568Ctrue CN100477568C (en) | 2009-04-08 |
Family
ID=34322125
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB031279910AExpired - Fee RelatedCN100477568C (en) | 2003-04-28 | 2003-04-28 | A data transmission method of a mobile packet network |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100477568C (en) |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100433714C (en)* | 2005-07-29 | 2008-11-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for transmission processing IP fragment message |
| CN101335740B (en)* | 2007-06-26 | 2012-10-03 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and system for transmitting and receiving data |
| CN101184032B (en)* | 2007-10-31 | 2010-09-08 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Stacked system equipment communication method |
| CN101207571B (en)* | 2007-12-12 | 2011-04-20 | 华为技术有限公司 | Apparatus and method for forwarding packets |
| CN101552728B (en)* | 2009-05-12 | 2012-05-23 | 北京师范大学 | Path MTU discovery method and system facing to IPV6 |
| CN101932006A (en)* | 2009-06-19 | 2010-12-29 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method for sending, receiving and transmitting data packets and device therefor |
| CN102420713A (en)* | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-18 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Test data packet packaging method and equipment |
| EP2656556B1 (en)* | 2010-12-21 | 2018-02-21 | Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (publ) | An improvement on ip fragmentation in gtp tunnel |
| CN102916880B (en)* | 2011-08-01 | 2017-08-11 | 深圳市中兴微电子技术有限公司 | The method and device that packet sends and receives in a kind of packet switching network |
| CN102594505A (en)* | 2012-02-08 | 2012-07-18 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and device |
| CN106612245A (en)* | 2015-10-27 | 2017-05-03 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Message transmission method and system based on GTPU (GPRS Tunneling Protocol for the user plane) tunnel protocol |
| WO2017147824A1 (en)* | 2016-03-02 | 2017-09-08 | 臧利 | Data processing method and system for base station |
| CN109818904A (en)* | 2017-11-21 | 2019-05-28 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A kind of internet-of-things terminal data flow processing method and device |
| CN114629974A (en)* | 2022-05-10 | 2022-06-14 | 新华三技术有限公司 | Message transmission method, device and equipment |
- 2003
- 2003-04-28CNCNB031279910Apatent/CN100477568C/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1543104A (en) | 2004-11-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7286536B2 (en) | Method and system for early header compression | |
| CN100486225C (en) | Method for reducing data IP fragmentation quantity in PS network | |
| EP1329078B1 (en) | Defining header field compression for data packet connection | |
| JP4763682B2 (en) | Providing information on upper layer packet or frame boundary in GRE frame | |
| CA2440814C (en) | Method and apparatus for providing multiple quality of service levels in a wireless packet data services connection | |
| US7209491B2 (en) | Method and system for transmitting data in a packet based communication network | |
| CN101369977A (en) | Method, device and system for data transmission | |
| CN100477568C (en) | A data transmission method of a mobile packet network | |
| US20030179720A1 (en) | Congestion control in wireless telecommunication networks | |
| Kim | Protection against packet fragmentation attacks at 6LoWPAN adaptation layer | |
| US20130279464A1 (en) | Ip fragmentation in gtp tunnel | |
| CN101529827B (en) | Length indicator optimization | |
| CN101150497A (en) | Method, system and device for multi-packet transmission in mobile communication | |
| JP2006503501A (en) | Method and apparatus for use of microtunnels in a communication system | |
| WO2010020197A1 (en) | Data transmission method, communication equipment and communication system | |
| WO2009056061A1 (en) | Method, system and device for transmitting general packet radio service tunneling protocol datagram | |
| WO2009026845A1 (en) | Method for data transmitting and receiving, wireless access point apparatus, gateway and communication system | |
| CN102118792B (en) | Method and device for transmitting data packets | |
| CN101827031A (en) | Method and device for packet transmission in user datagram protocol UDP tunnel | |
| JP2015506151A (en) | Technology to improve header compression efficiency and mobile node security | |
| CN102547687B (en) | Method and device for processing data packet in wireless communication network | |
| CN108282391B (en) | VXLAN message fragmentation method and device | |
| KR100425745B1 (en) | Packet transmission method in communication system supporting header compression of packet | |
| Murugesan et al. | Improving the performance of IPv6 packet transmission over LAN | |
| Rawat et al. | Designing a header compression mechanism for efficient use of IP tunneling in wireless networks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20090408 Termination date:20200428 |