CN100390186C - Organometallic iridium compound, method for preparing it, and method for preparing thin film - Google Patents
Organometallic iridium compound, method for preparing it, and method for preparing thin filmDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100390186C CN100390186CCNB2004800236201ACN200480023620ACN100390186CCN 100390186 CCN100390186 CCN 100390186CCN B2004800236201 ACNB2004800236201 ACN B2004800236201ACN 200480023620 ACN200480023620 ACN 200480023620ACN 100390186 CCN100390186 CCN 100390186C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- iridium
- compound
- general formula
- thin film
- preparing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Chemical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及能作为在衬底上制备铱基薄膜的母体的有机金属化合物,涉及制备此化合物的方法,以及涉及制备铱基薄膜的方法。The present invention relates to organometallic compounds that can be used as precursors for the preparation of iridium-based thin films on substrates, to methods for preparing such compounds, and to methods for preparing iridium-based thin films.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,在集成电路中,渴望研究利用铁电体的残余极化作用的铁电存贮器。具体地说,研究了钛酸锆酸铅(PZT:Pb(Ti,Zr)O3),钽酸铋锶(SBT:SrBi2Ta2O9)以及诸如此类物质。作为这些铁电体的电极材料,钌、铂、铱等贵金属薄膜,或这些贵金属的氧化物薄膜变得很需要。将来会特别考虑将铱或氧化铱作为电极材料的主要部分。作为生产铱和氧化铱薄膜的方法,采用了溅射法和化学蒸气淀积法(CVD法)。具体地说,基于下列理由,CVD法在将来将被认为是生产薄膜电极的方法的主流。CVD法易于生产均匀的膜而且具有优异的台阶覆盖性(step covarage),因此该方法对近来电路和电子部件的高密集生成会是适用的。In recent years, in integrated circuits, ferroelectric memories utilizing remnant polarization of ferroelectrics have been eagerly studied. Specifically, lead zirconate titanate (PZT:Pb(Ti,Zr)O3 ), strontium bismuth tantalate (SBT:SrBi2 Ta2 O9 ), and the like have been studied. As electrode materials for these ferroelectrics, thin films of noble metals such as ruthenium, platinum, and iridium, or oxide thin films of these noble metals have come to be required. In the future, iridium or iridium oxide will in particular be considered as the main part of the electrode material. As methods for producing thin films of iridium and iridium oxide, a sputtering method and a chemical vapor deposition method (CVD method) are used. Specifically, the CVD method will be considered as the mainstream method for producing thin film electrodes in the future for the following reasons. The CVD method is easy to produce a uniform film and has excellent step covarage, so this method may be suitable for the recent high-density production of circuits and electronic parts.
作为采用这种CVD法来形成薄膜的母体,人们认为,在金属化合物之中,具有低熔点及易于加工的有机金属化合物是适合的。迄今已研究将三(二新戊酰甲烷)合铱、三(乙酰丙酮根)合铱、(环戊二烯基)(1,5-环辛二烯)合铱等作为用于淀积铱或氧化铱薄膜的有机金属化合物。这些铱化合物在大气中具有高稳定性而且是无毒的,因此适于用作CVD母体。但是,这些铱化合物在常温下是固体,而且还存在母体气化和转移到衬底困难的问题。Among metal compounds, organometallic compounds having a low melting point and being easy to process are considered to be suitable as precursors for forming thin films by such a CVD method. So far, three (dipivaloylmethane) iridium, three (acetylacetonate) iridium, (cyclopentadienyl) (1,5-cyclooctadiene) iridium, etc. Or organometallic compound of iridium oxide thin film. These iridium compounds have high stability in the atmosphere and are non-toxic, and thus are suitable for use as CVD precursors. However, these iridium compounds are solid at normal temperature, and there are also problems in that the vaporization of the precursor and the transfer to the substrate are difficult.
近年来,渴望研究具有低熔点的铱络合物。作为制备具有低熔点铱络合物的方法,一种方法是将在环戊二烯基(1,5-环辛二烯)合铱的环戊二烯基环上的至少一个氢原子用烷基取代。In recent years, research on iridium complexes having a low melting point has been eagerly researched. As a method for preparing an iridium complex having a low melting point, one method is to replace at least one hydrogen atom on the cyclopentadienyl ring of cyclopentadienyl (1,5-cyclooctadiene) iridium with alkane base substitution.
例如,作为环戊二烯基衍生物,公开了(1,5-环辛二烯)(乙基-环戊二烯基)合铱(例如JP-A-11-292888)。因为该金属化合物在常温下是液体,而且其熔点与(环戊二烯基)(1,5-环辛二烯)合铱相比是低的,所以它被认为是具有用于CVD法的母体所必须特性的化合物。但是,此化合物具有极高的稳定性,而且此络合物的分解温度是高的。因此,在膜形成时必然要升高衬底的温度。其结果是遭遇这样一个问题:在膜形成时台阶覆盖性是低的。还遭遇这样一个问题:氧化铱薄膜的形成是困难的。在此同时,关于具有作为配位体的乙烯和环戊二烯基的铱络合物的报告,其中有合成(环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱的合成方法(例如见M.Dziallas,A.Hohn及H.Werner,J.Organomet.Chem,330(1987)207-219)。然而此化合物在室温下是固体,不适用作CVD母体。For example, (1,5-cyclooctadiene)(ethyl-cyclopentadienyl)iridium is disclosed as a cyclopentadienyl derivative (for example, JP-A-11-292888). Since this metal compound is liquid at normal temperature and its melting point is low compared with that of (cyclopentadienyl)(1,5-cyclooctadiene) iridium, it is considered to be useful in the CVD method. Compounds with the necessary properties of the parent. However, this compound has extremely high stability, and the decomposition temperature of this complex is high. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the temperature of the substrate at the time of film formation. As a result, a problem is encountered that the step coverage is low at the time of film formation. There is also encountered a problem that the formation of an iridium oxide thin film is difficult. At the same time, there are reports on iridium complexes having ethylene and cyclopentadienyl as ligands, among which there are synthetic methods for the synthesis of (cyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium (see, for example, M. Dziallas, A. Hohn and H. Werner, J. Organomet. Chem, 330 (1987) 207-219). However, this compound is solid at room temperature and is not suitable for use as a CVD precursor.
本发明的公开Disclosure of the invention
在考虑了上述技术问题后作出了本发明。也就是说,本发明涉及可作为制备铱基薄膜的母体的有机金属化合物,本发明的目的是提供具有低熔点、优异蒸发特性和在衬底上的低成膜温度的有机金属化合物,制备它的方法,以及采用此有机金属化合物来制备铱基薄膜的方法。The present invention has been made after considering the above-mentioned technical problems. That is to say, the present invention relates to an organometallic compound that can be used as a precursor for preparing an iridium-based thin film. The method, and the method of using this organometallic compound to prepare iridium-based thin film.
本发明的发明者作了广泛而深入的研究以解决上述问题。结果,通过将低级烷基引入到环戊二烯基环(以后称作“Cp环”)或(环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱的乙烯中,开发出了一种新颖的铱络合物,它具有在室温下是液体的熔点,良好的蒸发特性和分解特性。The inventors of the present invention have conducted extensive and intensive research to solve the above-mentioned problems. As a result, by introducing a lower alkyl group into a cyclopentadienyl ring (hereinafter referred to as "Cp ring") or ethylene of (cyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium, a novel iridium Complex, which has a melting point that is liquid at room temperature, good evaporation and decomposition properties.
本发明提供一种下列通式(1)所代表的有机金属铱化合物:The present invention provides a kind of organometallic iridium compound represented by the following general formula (1):
式中R1代表氢原子或低级烷基;而R2代表低级烷基。In the formula, R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a lower alkyl group; and R2 represents a lower alkyl group.
本发明还提供一种制备通式(1)所代表的有机金属铱化合物的方法,包括将下列通式(4)所代表的化合物:The present invention also provides a method for preparing an organometallic iridium compound represented by the general formula (1), comprising the compound represented by the following general formula (4):
式中R2代表低级烷基,而M代表碱金属,与下列通式(2)所代表的化合物或通式(3)所代表的化合物反应:In the formula, R represents a lower alkyl group, and M represents an alkali metal,which reacts with a compound represented by the following general formula (2) or a compound represented by the general formula (3):
式中R1与上面定义的相同,而X代表卤原子,In the formula, Ris the same as defined above, and X represents a halogen atom,
式中R1和X与上面定义的相同。In the formula, R1 and X are the same as defined above.
本发明还再提供制备铱基薄膜的方法,它包括使用通式(1)所代表的有机金属铱化合物作为母体。The present invention further provides a method for preparing an iridium-based thin film, which comprises using an organometallic iridium compound represented by the general formula (1) as a precursor.
附图的简要说明Brief description of the drawings
图1是表示实施例1中得到的铱化合物的GC/MS曲线图。FIG. 1 is a GC/MS graph showing the iridium compound obtained in Example 1. FIG.
图2是表示实施例1中得到的铱化合物的分解特性图。FIG. 2 is a graph showing the decomposition characteristics of the iridium compound obtained in Example 1. FIG.
图3是表示对比实施例1中得得的(1,5-环辛二烯)(乙基环戊二烯基)合铱的分解特性图。3 is a graph showing the decomposition characteristics of (1,5-cyclooctadiene)(ethylcyclopentadienyl)iridium compound obtained in Comparative Example 1. FIG.
图4是表示实施例2中得到的(甲基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱的GC/MS曲线图。FIG. 4 is a GC/MS graph showing the (methylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium obtained in Example 2. FIG.
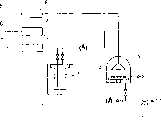
图5是用于实施例3中的CVD法的设备示意图。FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of equipment used in the CVD method in Example 3. FIG.
在附图中:In the attached picture:
1.母体的容器1. The parent container
2.油浴2. Oil bath
3.反应室3. Reaction chamber
4.衬底4. Substrate
5.氧化气体5. Oxidizing gas
6.计数管填充气6. Counting tube filling gas
7.载气7. Carrier gas
8.质量流量控制器8. Mass flow controller
9.质量流量控制器9. Mass flow controller
10.质量流量控制器10. Mass flow controller
11.真空泵11. Vacuum pump
12.废气12. Exhaust gas
实施本发明的最佳方式Best Mode for Carrying Out the Invention
本发明详述如下。The invention is described in detail below.
用于本说明书中的术语定义及其具体例子将描述如下。Definitions of terms used in this specification and specific examples thereof will be described as follows.
这里所用的术语“低级烷基”指含有1-6个碳原子的直链、支化或环状的烷基。因此,在R1和R2中采用的低级烷基的例子包括甲基、乙基、正丙基、异丙基、正丁基、异丁基、仲丁基、叔丁基、戊基、异戊基、新戊基、叔戊基、1-甲基丁基、2-甲基丁基、1,2-二甲基丙基、己基、异己基、1-甲基戊基、2-甲基戊基、3-甲基戊基、1,1-二甲基丁基、2,2-二甲基丁基、1,3-二甲基丁基、2,3-二甲基丁基、3,3-二甲基丁基、1-乙基丁基、2-乙基丁基、1,1,2-三甲基丙基、1,2,2-三甲基丙基、1-乙基-1-甲基丙基、1-乙基-2-甲基丙基、环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基、环丙基甲基、1-环丙基乙基、2-环丙基乙基及环丁基甲基。The term "lower alkyl" as used herein refers to straight chain, branched or cyclic alkyl groups having 1 to 6 carbon atoms. Thus, examples of lower alkyl employed in RandR include methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl, pentyl, Isopentyl, neopentyl, tert-pentyl, 1-methylbutyl, 2-methylbutyl, 1,2-dimethylpropyl, hexyl, isohexyl, 1-methylpentyl, 2- Methylpentyl, 3-methylpentyl, 1,1-dimethylbutyl, 2,2-dimethylbutyl, 1,3-dimethylbutyl, 2,3-dimethylbutyl Base, 3,3-dimethylbutyl, 1-ethylbutyl, 2-ethylbutyl, 1,1,2-trimethylpropyl, 1,2,2-trimethylpropyl, 1-ethyl-1-methylpropyl, 1-ethyl-2-methylpropyl, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cyclopropylmethyl, 1-cyclopropyl Ethyl, 2-cyclopropylethyl and cyclobutylmethyl.
在本发明中,R1代表氢原子或低级烷基。R1优选是甲基或氢原子,更优选是氢原子。另一方面,在本发明中,R2代表低级烷基。此低级烷基优选是甲基、乙基、丙基或丁基,更优选是甲基或乙基。在本发明中,X代表卤原子。卤原子的例子包括氟、氯、溴和碘。它们当中,氯和溴是优选的。在本发明中,M代表碱金属。碱金属的例子包括锂、钠和钾。它们当中,锂和钠是优选的。In the present invention, R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a lower alkyl group. R1 is preferably a methyl group or a hydrogen atom, more preferably a hydrogen atom. On the other hand, in the present invention, R2 represents lower alkyl. The lower alkyl group is preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl or butyl, more preferably methyl or ethyl. In the present invention, X represents a halogen atom. Examples of halogen atoms include fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine. Among them, chlorine and bromine are preferred. In the present invention, M represents an alkali metal. Examples of alkali metals include lithium, sodium and potassium. Among them, lithium and sodium are preferable.
本发明的通式(1)所代表的有机金属铱化合物可通过使通式(4)所代表的化合物与通式(2)所代表的化合物或通式(3)所代表的化合物反应而制得。在这种反应中反应条件不受特别限制。例如,这两种化合物每种可分别加至合适溶剂之中,并可以将各个溶液混合,并在低温下反应,后处理不受特别限制。通常采用的方法是:在反应结束后将混合溶液浓缩;用有机溶剂例如戊烷、己烷或乙醚从所得混合物中萃取所需要的化合物;选择合适的载体;将萃出液进行柱色谱分离,使用合适溶剂作为洗脱剂;把萃出液进行蒸馏,由此可获得所需要的有机金属铱化合物。The organometallic iridium compound represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention can be prepared by reacting a compound represented by the general formula (4) with a compound represented by the general formula (2) or a compound represented by the general formula (3). have to. The reaction conditions are not particularly limited in this reaction. For example, each of these two compounds may be separately added to a suitable solvent, and the respective solutions may be mixed and reacted at low temperature, and the post-treatment is not particularly limited. The method usually adopted is: after the reaction is finished, the mixed solution is concentrated; the desired compound is extracted from the resulting mixture with an organic solvent such as pentane, hexane or ether; a suitable carrier is selected; the extract is subjected to column chromatography, Using a suitable solvent as eluent; distilling the extract to obtain the desired organometallic iridium compound.
使用本发明通式(1)所代表的有机金属铱化合作为母体,可以制备铱基薄膜。这种制备方法的具体方式不受特别限制。例如,CVD法、原子层沉积法(ALD法)及旋涂法中的任一种均可采用。Using the organometallic iridium compound represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention as a matrix, an iridium-based thin film can be prepared. The specific mode of this preparation method is not particularly limited. For example, any of CVD, atomic layer deposition (ALD), and spin coating can be used.
在通过CVD法、ALD法等方法,使用本发明通式(1)所代表的有机金属铱化合物来制备铱基薄膜的情况时,把母体送至成膜室的方法不受特别限制。例如,可采用鼓泡法,也可采用液体注入法。When the organometallic iridium compound represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention is used to prepare an iridium-based thin film by CVD, ALD or the like, the method of sending the precursor to the film-forming chamber is not particularly limited. For example, a bubbling method may be used, and a liquid injection method may also be used.
在本发明中,在通过CVD法或ALD法来制备铱基薄膜的情况下,可以使用有机金属铱化合物本身,或者可以将它溶于有机溶剂中,然后以有机金属铱化合物溶液使用。In the present invention, in the case of producing an iridium-based thin film by CVD or ALD, the organometallic iridium compound itself may be used, or it may be dissolved in an organic solvent and then used as an organometallic iridium compound solution.
在以溶液使用有机溶剂的情况下,有机溶剂的例子包括醇类(例如甲醇、乙醇或异丙醇),酯类(例如乙酸乙酯、乙酸丁酯或乙酸异戊酯),乙二醇醚类(例如乙二醇单乙醚、乙二醇单甲醚或乙二醇单丁醚),醚类(例如乙醚、甘醇二甲醚、二甘醇二甲醚、三甘醇二甲醚或四氢呋喃),酮类(例如甲基丁基甲酮、甲基异丁基甲酮、乙基丁基甲酮、二丙基甲酮、二异丁基甲酮、甲基戊基甲酮或环己酮),以及烃类(例如己烷、环己烷、乙基环己烷、庚烷、辛烷、苯、甲苯或二甲苯)。但是本发明不受限于这些溶剂。In the case of using an organic solvent as a solution, examples of the organic solvent include alcohols (such as methanol, ethanol, or isopropanol), esters (such as ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, or isoamyl acetate), glycol ethers (such as ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether or ethylene glycol monobutyl ether), ethers (such as diethyl ether, glyme, diglyme, triglyme or Tetrahydrofuran), ketones (such as methyl butyl ketone, methyl isobutyl ketone, ethyl butyl ketone, dipropyl ketone, diisobutyl ketone, methyl amyl ketone or cyclohexanone), and hydrocarbons ( eg hexane, cyclohexane, ethylcyclohexane, heptane, octane, benzene, toluene or xylene). However, the present invention is not limited to these solvents.
实施例Example
参考下面实施例对本发明作更详细描述,但应该明白,本发明不应被认为受限于这些实施例。The present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the following examples, but it should be understood that the invention should not be construed as being limited to these examples.
实施例1Example 1
(乙基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱的合成及热分解特性Synthesis and Thermal Decomposition Properties of (Ethylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium
将49mg四(乙烯)合二μ-氯化二铱(I)加至10ml THF中,把反应烧瓶冷却至-78℃,然后加入17mg乙基环戊二烯基锂(lithium ethylcyclopentadienide)的THF溶液10ml。把所得混合物在-78℃搅拌30分钟,然后把温度逐步升至室温,并使得到的混合物再反应1小时,随后进行浓缩,得泥浆状混合物,用己烷萃取此泥浆状混合物,并使用氧化铝将此萃取溶液进行柱色谱(洗脱剂:己烷),得到14mg所需要的(乙基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱。Add 49mg tetra(ethylene)dimu-diiridium(I) chloride to 10ml THF, cool the reaction flask to -78°C, then add 17mg THF solution of ethylcyclopentadienyl lithium (lithium ethylcyclopentadienide) 10ml. The resulting mixture was stirred at -78°C for 30 minutes, then the temperature was gradually raised to room temperature, and the resulting mixture was allowed to react for another 1 hour, followed by concentration to obtain a slurry mixture, which was extracted with hexane, and used oxidation Aluminum The extracted solution was subjected to column chromatography (eluent: hexane) to obtain 14 mg of the desired (ethylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium.
淡黄色油状物质。Pale yellow oily substance.
1H-NMR(500MHz,苯-d6,δppm):1 H-NMR (500MHz, benzene-d6, δppm):
4.78-4.77(m,2H),4.66-4.65(m,2H),2.60-2.58(m,4H),1.90(q,J=2,5Hz,2H),0.94(t,J=2.5Hz,3H),0.94-0.91(m,4H)4.78-4.77(m, 2H), 4.66-4.65(m, 2H), 2.60-2.58(m, 4H), 1.90(q, J=2, 5Hz, 2H), 0.94(t, J=2.5Hz, 3H ), 0.94-0.91 (m, 4H)
IR(纯,cm-1):IR (pure, cm-1 ):
3040,2970,2920,2870,1480,1460,1435,1310,1165,1150,1035,1010,990,810,7903040, 2970, 2920, 2870, 1480, 1460, 1435, 1310, 1165, 1150, 1035, 1010, 990, 810, 790
MS(GC/MS,EI):MS (GC/MS, EI):
以193Ir来表示的(乙基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱的分子离子峰:m/z342(图1)Molecular ion peak of (ethylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium represented by193 Ir: m/z342 (Figure 1)
测得的该化合物的分解特性的结果示于图2。正如从图2看出的,本发明的有机金属铱化合物的分解开始温度在220℃附近,因此它能够在比后面描述的对比实施例1所获得化合物(通常的化合物)低的温度下分解。The results of the measured decomposition properties of this compound are shown in FIG. 2 . As seen from Fig. 2, the decomposition start temperature of the organometallic iridium compound of the present invention is around 220°C, so it can be decomposed at a lower temperature than the compound (common compound) obtained in Comparative Example 1 described later.
测量条件如下。The measurement conditions are as follows.
测量方法:功率补偿型差示扫描量热法(DSC)Measurement method: power compensation differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
测量条件:Measurement conditions:
参比物:氧化铝Reference substance: aluminum oxide
惰性气体:氮气,50ml/分钟Inert gas: nitrogen, 50ml/min
升温:10℃/分钟Heating: 10°C/min
对比实施例comparative example
(乙基环戊二烯基)(1,5-环辛二烯)合铱的热分解特性Thermal Decomposition Properties of (Ethylcyclopentadienyl)(1,5-cyclooctadiene)iridium
以与实施例1相同的方式测定(乙基环戊二烯基)(1,5-环辛二烯)合铱的分解特性,所得结果示于图3。如从图3看出的,这一通常产物的分解开始温度在370℃附近The decomposition characteristics of (ethylcyclopentadienyl)(1,5-cyclooctadiene)iridium were measured in the same manner as in Example 1, and the results obtained are shown in FIG. 3 . As can be seen from Figure 3, the decomposition onset temperature of this common product is around 370 °C
实施例2Example 2
(甲基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱的合成Synthesis of (methylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium
将0.97g四(乙烯)合二μ-氯化二铱(I)加至50ml THF中,又把反应烧瓶冷却至-78℃,然后加入178mg甲基环戊二烯基锂(lithiummethylcyclopentadienide)的THF溶液50ml。把所得溶液在-78℃搅拌1小时40分钟,然后把温度逐步升至室温,并使得到的混合物再反应1小时,随后进行浓缩,得泥浆状混合物,用己烷萃取此泥浆状混合物,并使用氧化铝将此萃取溶液进行柱色谱(洗脱剂:己烷),得到409mg所需要的(甲基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱。Add 0.97g of tetra(ethylene)dimu-diiridium(I) chloride to 50ml of THF, and cool the reaction flask to -78°C, then add 178mg of THF of lithiummethylcyclopentadienide Solution 50ml. The resulting solution was stirred at -78°C for 1 hour and 40 minutes, then the temperature was gradually raised to room temperature, and the resulting mixture was reacted for another 1 hour, followed by concentration to obtain a slurry mixture, which was extracted with hexane, and This extracted solution was subjected to column chromatography (eluent: hexane) using alumina to obtain 409 mg of the desired (methylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium.
乳白色固体milky white solid
1H-NMR(500MHz,苯-d6,δppm):1 H-NMR (500MHz, benzene-d6, δppm):
4.84(t,J=2.0Hz,2H),4.59(t,J=2.0Hz,2H),2.55-2.44(m,4H),1.51(s,3H),0.95-0.93(m,4H)4.84(t, J=2.0Hz, 2H), 4.59(t, J=2.0Hz, 2H), 2.55-2.44(m, 4H), 1.51(s, 3H), 0.95-0.93(m, 4H)
MS(GC/MS,EI):MS (GC/MS, EI):
以193Ir来表示的(甲基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱的分子离子峰:m/z328(图4)Molecular ion peak of (methylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium represented by193 Ir: m/z328 (Figure 4)
实施例3Example 3
用(乙基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱制备铱薄膜Preparation of Iridium Thin Films Using (Ethylcyclopentadienyl)bis(ethylene)iridium
使用图5所示的设备,并采用硅衬底作为衬底4,而此硅衬底在其表面已形成100nm厚的SiO2膜。往母体容器中加入约10g(乙基环戊二烯基)双(乙烯)合铱,并用油浴2将此容器加热,使之处于50℃恒温状态。使用真空泵11和压力控制阀,将反应室3调至10托,而将母体容器1调至100托。用氮气作为载气7,并用质量流量控制器10使其流量设置在100sccm。用氧气作为氧化气体5,并用氮气作为计数管填充气6。用质量流量控制器8将氧化气体的流量设置在10sccm,和用质量流量控制器9将计数管填充气的流量设置在90sccm。把衬底4设置在400℃,并进行薄膜生成60分钟,而在其同时维持被加热状态。形成的薄膜是金属铱薄膜,该膜厚度是300nm。The apparatus shown in FIG. 5 was used, and a silicon substrate on which a 100 nm-thickSiO2 film had been formed was used as the substrate 4. Add about 10 g of (ethylcyclopentadienyl) bis(ethylene)iridium to the parent container, and heat the container with an
虽然详细地并参考具体实施方案对本发明作了详细描述,但是对于本领域技术熟练人员来说,显而易见的是在不背离本发明的精神实质及范围的情况下,可进行各种改进和改变。While the invention has been described in detail and with reference to specific embodiments, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and changes can be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention.
本申请基于2003年8月19日申请的日本专利申请NO.2003-295329,2003年11月12日申请的NO.2003-383169,以及2004年1月13日申请的NO.2004-5503,它们的公开内容整体地被引用作为参考文献。This application is based on Japanese Patent Application No.2003-295329 filed on August 19, 2003, No.2003-383169 filed on November 12, 2003, and No.2004-5503 filed on January 13, 2004, which The disclosure of is incorporated by reference in its entirety.
工业适用性Industrial applicability
本发明的有机金属铱化合物,在使用CVD方法作为制备铱基薄膜的方法的情况下在气体鼓泡条件下是液体,因此它们能被定量地供应。此外,此有机金属铱化合物能在比通常物质低的温度下热分解。结果,可以在衬底上形成具有优异台阶覆盖性的铱基薄膜。本发明可能大量制备铱基薄膜。The organometallic iridium compounds of the present invention are liquid under gas bubbling conditions in the case of using the CVD method as a method for producing an iridium-based thin film, so they can be supplied quantitatively. In addition, this organometallic iridium compound can be thermally decomposed at a lower temperature than usual substances. As a result, an iridium-based thin film having excellent step coverage can be formed on a substrate. The invention may prepare iridium-based thin films in large quantities.
Claims (6)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003295329 | 2003-08-19 | ||
| JP295329/2003 | 2003-08-19 | ||
| JP383169/2003 | 2003-11-12 | ||
| JP005503/2004 | 2004-01-13 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1835961A CN1835961A (en) | 2006-09-20 |
| CN100390186Ctrue CN100390186C (en) | 2008-05-28 |
Family
ID=37003279
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2004800236201AExpired - Fee RelatedCN100390186C (en) | 2003-08-19 | 2004-08-11 | Organometallic iridium compound, method for preparing it, and method for preparing thin film |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100390186C (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5130172A (en)* | 1988-10-21 | 1992-07-14 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Low temperature organometallic deposition of metals |
| JPH11292888A (en)* | 1998-04-03 | 1999-10-26 | Kojundo Chem Lab Co Ltd | Ethylcyclopentadienyl (1, 5-cyclooctadiene) iridium and its production and production of iridium-containing thin film using the same |
| CN1357550A (en)* | 2000-10-11 | 2002-07-10 | 田中贵金属工业株式会社 | Organic metal compound for chemical vapor deposition and its prepn and chemical vapor deposition method of noble metal film and noble metal compound film |
- 2004
- 2004-08-11CNCNB2004800236201Apatent/CN100390186C/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5130172A (en)* | 1988-10-21 | 1992-07-14 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Low temperature organometallic deposition of metals |
| JPH11292888A (en)* | 1998-04-03 | 1999-10-26 | Kojundo Chem Lab Co Ltd | Ethylcyclopentadienyl (1, 5-cyclooctadiene) iridium and its production and production of iridium-containing thin film using the same |
| CN1357550A (en)* | 2000-10-11 | 2002-07-10 | 田中贵金属工业株式会社 | Organic metal compound for chemical vapor deposition and its prepn and chemical vapor deposition method of noble metal film and noble metal compound film |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1835961A (en) | 2006-09-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5136576B2 (en) | Organoruthenium compound and method for producing the same | |
| KR102474876B1 (en) | Tungsten precursor and Method of forming a tungsten-containing layer using the same | |
| US7547796B2 (en) | Organometallic compounds, processes for the preparation thereof and methods of use thereof | |
| JP4980679B2 (en) | Titanium complexes, methods for producing them, titanium-containing thin films, and methods for forming them | |
| JP5202905B2 (en) | Ruthenium compound, method for producing the same, ruthenium-containing thin film and method for producing the same | |
| JP5148186B2 (en) | Imido complex, method for producing the same, metal-containing thin film, and method for producing the same | |
| JP4517565B2 (en) | Ruthenium complex, method for producing the same, and method for producing the thin film | |
| US11760771B2 (en) | Ruthenium compound, raw material for forming thin film, and method for producing thin film | |
| US7619093B2 (en) | Organometallic compounds and mixtures thereof | |
| JP4696454B2 (en) | Novel organic iridium compound, method for producing the same, and method for producing the film | |
| US11999756B2 (en) | Method for producing organometallic compound and thin film fabricated using organometallic compound obtained thereby | |
| JP5732772B2 (en) | Ruthenium complex mixture, production method thereof, film-forming composition, ruthenium-containing film and production method thereof | |
| KR101126141B1 (en) | Organoiridium compound, process for producing the same, and process for producing film | |
| JP4553642B2 (en) | Organic iridium compound, process for producing the same, and process for producing film | |
| CN100390186C (en) | Organometallic iridium compound, method for preparing it, and method for preparing thin film | |
| KR20210058289A (en) | Tungsten Precursor, Method for Preparation of the Same, and Tungsten-Containing Thin Film, Method of Manufacturing the Same | |
| KR100984686B1 (en) | Novel organometallic iridium compound, preparation method thereof, and manufacturing method of thin film | |
| JP2024117104A (en) | Thin film forming material, thin film and method for producing thin film | |
| CN120774970A (en) | Precursor for depositing metal-containing film, and preparation method and application thereof | |
| TW202110866A (en) | Ruthenium compound, material for thin film formation, and process for thin film formation | |
| JP2006036780A (en) | Method for producing ruthenium complex |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20080528 Termination date:20170811 |