CN100385848C - Method and system for synchronizing node B frame numbers between base stations in wideband code division multiple access system - Google Patents
Method and system for synchronizing node B frame numbers between base stations in wideband code division multiple access systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100385848C CN100385848CCNB2004100945500ACN200410094550ACN100385848CCN 100385848 CCN100385848 CCN 100385848CCN B2004100945500 ACNB2004100945500 ACN B2004100945500ACN 200410094550 ACN200410094550 ACN 200410094550ACN 100385848 CCN100385848 CCN 100385848C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- node
- frame number
- base station
- count value
- signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Synchronisation In Digital Transmission Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及通信领域,特别涉及移动通信中的节点B帧号(Node BFrame Number,简称“BFN”)同步技术。The present invention relates to the communication field, in particular to a Node B Frame Number (Node B Frame Number, referred to as "BFN") synchronization technology in mobile communication.
背景技术Background technique
近20年来,移动通信技术的发展经历了两代,完成了从第一代的模拟蜂窝通信技术向第二代以全球移动通信系统(Global System for MobileCommunications,简称“GSM”)为代表的数字通信技术的过渡。现正在向第三代移动通信系统(Third Generation Mobile Communications System,简称“3G”)发展。其中,宽带码分多址(Wideband Code Division Multiple Access,简称“WCDMA”)技术作为国际电信联盟(International TelecommunicationUnion,简称“ITU”)规定的3G主要标准之一,是3G发展的一个主流技术。In the past 20 years, the development of mobile communication technology has gone through two generations, completing the transition from the first generation of analog cellular communication technology to the second generation of digital communication represented by the Global System for Mobile Communications (Global System for Mobile Communications, referred to as "GSM"). technology transition. Now it is developing towards the third generation mobile communication system (Third Generation Mobile Communications System, referred to as "3G"). Among them, Wideband Code Division Multiple Access ("WCDMA") technology, as one of the main 3G standards stipulated by the International Telecommunication Union ("ITU"), is a mainstream technology for 3G development.
在第三代伙伴计划(3rd Generation Partnership Project,简称“3GPP”)制定的WCDMA标准中规定,WCDMA系统中的Node B是异步的,但同步是可选的,因此对于异步的WCDMA系统来说,无需Node B间的同步,所以不需外部同步资源。熟悉本领域的技术人员可以理解,外部同步资源一般是全球定位系统(Global Position System,简称“GPS”)或者其他精确的时钟,如铯原子钟等。According to the WCDMA standard formulated by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project ("3GPP"), the Node B in the WCDMA system is asynchronous, but synchronization is optional. Therefore, for an asynchronous WCDMA system, No synchronization between Node Bs is required, so no external synchronization resources are required. Those skilled in the art can understand that the external synchronization resource is generally a Global Position System (Global Position System, “GPS”) or other precise clocks, such as cesium atomic clocks.
在移动通信系统中,一个影响服务质量的重要技术就是软切换。所谓的软切换,是指诸如手机、可移动计算机之类的用户设备(User Equipment,简称“UE”)需要与另一个基站(Base Station,简称“BS”或者Node B)通信时,先不中断与原Node B的连接,而是先与新Node B连接,UE测量收到的新Node B公共导频信道(Common Pilot Channel,简称“CPICH”)的信号强度并上报给无线网络控制器(Radio Network Controller,简称“RNC”),RNC根据上报的测量结果是否超过规定的阈值以及资源情况决定是否进行切换。In a mobile communication system, an important technology that affects the quality of service is soft handover. The so-called soft handover means that when a user equipment (User Equipment, referred to as "UE") such as a mobile phone or a mobile computer needs to communicate with another base station (Base Station, referred to as "BS" or Node B), it will not be interrupted first. Instead of connecting to the original Node B, connect to the new Node B first, and the UE measures the received signal strength of the Common Pilot Channel (CPICH) of the new Node B and reports it to the radio network controller (Radio Network Controller, referred to as "RNC"), the RNC decides whether to perform handover according to whether the reported measurement result exceeds a specified threshold and resource conditions.
而在异步WCDMA系统中,当UE在跨越不同Node B的小区进行软切换时,UE必须进行一系列的操作获得新Node B与原Node B之间的时间差别,从而得到一个共同的实际参考。However, in an asynchronous WCDMA system, when the UE performs soft handover across cells of different Node Bs, the UE must perform a series of operations to obtain the time difference between the new Node B and the original Node B, so as to obtain a common practical reference.
下面具体介绍现有WCDMA系统中,UE进行软切换时获得两个Node B间的时间差别过程。The following describes in detail the process of obtaining the time difference between two Node Bs when the UE performs soft handover in the existing WCDMA system.
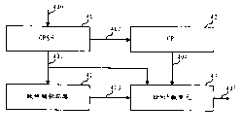
如图1所示,一个无线网络控制器10,两个Node B11,12构成一个无线网络子系统1,UE13进行从Node B11到Node B12的软切换。As shown in Figure 1, a
首先步骤100中,UE13检测收到的原Node B11的CPICH信号从其中得到Node B11的帧定时信息;First in
同样,在随后的步骤101中,与步骤100类似,UE13检测收到的新NodeB12的CPICH信号并得到Node B的帧定时信息,通过比较步骤100中得到的帧定时信息,从而获得了两个Node B的时间差别。UE13对两个Node B时间差别的处理如下:当Node B12和Node B13的时间差在10ms以内时,也就是说在一帧以内,可以从主扰码的相位中确定相对定时,因为扰码的帧长度也是10ms;而如果定时不确定性较大,UE13还需要对主CCPCH中广播信道译码和循环冗余校验(Cyclic Redundancy Check,简称“CRC”)校验。需要指出的是,这个过程复杂且耗时。Similarly, in
接下来在步骤102中,UE13将时间差别报告给Node B11;Next in
然后步骤103,Node B11将这个时间差别在发送到无线网络控制器10并由其进行处理;Then
接着在步骤104中,无线网络控制器将处理后的时间差别信息发送到Node B12;Then in
最后,步骤105中,Node B12根据收到的来自无线网络控制器10的时间差别信息调整下行链路的定时,并将调整后的下行链路信号发送到UE13。Finally, in
这样就实现了软切换的定时。从上面过程可以看出,WCDMA中UE进行软切换的定时操作过程比较复杂,这样会使移动设备耗电量的增加,更重要的是可能使软切换的功率控制产生延迟从而影响通信质量。In this way, the timing of the soft handover is realized. From the above process, it can be seen that the timing operation process of soft handover by UE in WCDMA is relatively complicated, which will increase the power consumption of mobile equipment, and more importantly, may cause delay in power control of soft handover, thereby affecting communication quality.
在3GPP制定的WCDMA标准中,定义了一些用于同步的计数参数有:Node B帧号(Node B Frame Number,简称“BFN”),无线网络控制器帧号(RNC Frame Number,简称“RFN”),系统帧号(System Frame Number,简称“SFN”)和连接帧号(Connection Frame Number,简称“CFN”)。In the WCDMA standard formulated by 3GPP, some counting parameters for synchronization are defined: Node B Frame Number (Node B Frame Number, referred to as "BFN"), Radio Network Controller Frame Number (RNC Frame Number, referred to as "RFN") ), system frame number (System Frame Number, referred to as "SFN") and connection frame number (Connection Frame Number, referred to as "CFN").
其中RFN,SFN分别作为RNC,Node B的一个小区的时间参考;CFN可以作为UE接入到网络的时间参考;BFN是Node B内部对长度为10ms的基本帧的计数,在一个Node B中是一致的,取值范围0-4096,对应的周期是40.96s,BFN也是SFN的基础,可以作为Node B发送和接受信号的时间参考,也可以用于确定不同Node B间的时间差别。在WCDMA系统运行中,SFN,RFN和CFN三者之间存在一定的同步关系。Among them, RFN and SFN are respectively used as the time reference of RNC and a cell of Node B; CFN can be used as the time reference of UE accessing the network; BFN is the count of basic frames with a length of 10ms inside Node B, and in a Node B it is Consistent, the value range is 0-4096, and the corresponding period is 40.96s. BFN is also the basis of SFN. It can be used as a time reference for Node B to send and receive signals, and can also be used to determine the time difference between different Node Bs. In the operation of the WCDMA system, there is a certain synchronization relationship among SFN, RFN and CFN.
如果使不同Node B间BFN同步,从而实现不同Node B的同步,就可以解决现有WCDMA中软切换定时复杂繁琐的缺点,提高整个网络的性能。If the BFN between different Node Bs is synchronized to realize the synchronization of different Node Bs, the shortcoming of complex and cumbersome soft handover timing in the existing WCDMA can be solved, and the performance of the entire network can be improved.
码分多址(Code Division Multiple Access,简称“CDMA”)网络是同步系统,各个Node B的时钟相位同步是通过GPS实现的。通常是在基站收发信机(Base Transceiver Station,简称“BTS”),和基站控制器(Base StationController,简称“BSC”)都装有GPS接收机,BTS和BSC从GPS接收机获得GPS绝对时间,熟悉本领域的技术人员知道,BTS和BSC构成基站子系统(Base Station Subsystem,简称“BSS”),所以通过GPS的时钟信号,CDMA网络内的各个BSS达到了同步。Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA for short) network is a synchronous system, and the clock phase synchronization of each Node B is realized through GPS. Usually, both the base transceiver station (Base Transceiver Station, referred to as "BTS") and the base station controller (Base Station Controller, referred to as "BSC") are equipped with GPS receivers, and BTS and BSC obtain GPS absolute time from the GPS receiver. Those skilled in the art know that BTS and BSC constitute a Base Station Subsystem ("BSS" for short), so through the clock signal of GPS, each BSS in the CDMA network is synchronized.
在实际应用中,上述方案存在以下问题:由于CDMA网络设计为同步系统,所以只需要对GPS信号稍做处理,就可以得到周期为2s的同步信号,而WCDMA设计为异步网络,所以CDMA的基站同步技术无法应用到WCDMA中。因此,目前在WCDMA系统中无法进行有效的BFN同步,从而影响了UE的切换成功率和系统容量,并且UE切换流程复杂,手机功耗较大。In practical application, the above scheme has the following problems: Since the CDMA network is designed as a synchronous system, it only needs to do a little processing on the GPS signal to obtain a synchronous signal with a period of 2s, while WCDMA is designed as an asynchronous network, so the base station of CDMA Synchronous technology cannot be applied to WCDMA. Therefore, effective BFN synchronization cannot be performed in the WCDMA system at present, thereby affecting the handover success rate of the UE and the system capacity, and the handover process of the UE is complicated, and the power consumption of the mobile phone is relatively large.
造成这种情况的主要原因在于,WCDMA与CDMA技术在同步标准上存在差异。The main reason for this situation is that WCDMA and CDMA technologies differ in synchronization standards.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本发明的主要目的在于提供一种宽带码分多址系统中基站间的节点B帧号同步方法及其系统,使得Node B在启动后较快地实现BFN同步,并在开始工作后保持BFN同步。In view of this, the main purpose of the present invention is to provide a Node B frame number synchronization method and system thereof between base stations in a wideband code division multiple access system, so that Node B can realize BFN synchronization more quickly after starting, and start working Then keep the BFN synchronized.
为实现上述目的,本发明提供了一种宽带码分多址系统中基站间的节点B帧号同步方法,包含以下步骤:To achieve the above object, the invention provides a Node B frame number synchronization method between base stations in a wideband code division multiple access system, comprising the following steps:
A全球定位系统卫星接收机从全球定位系统信号中获取全球定位系统绝对时间和秒脉冲信号,并发送给其对应的基站;A GPS satellite receiver obtains the GPS absolute time and second pulse signal from the GPS signal, and sends it to the corresponding base station;
B所述基站主时钟跟踪秒脉冲信号,实现频率跟踪后,启动相位跟踪,同时,所述基站根据全球定位系统绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的节点B帧号计数值,并在下一个秒脉冲信号到来时,将当前节点B帧号计数值调整为所述换算得到的节点B帧号计数值。The main clock of the base station in B tracks the second pulse signal, and after realizing the frequency tracking, the phase tracking is started, and at the same time, the base station converts the corresponding node B frame number count value in the next 1 second according to the absolute time of the global positioning system, and in the next When the second pulse signal arrives, adjust the current Node B frame number count value to the converted Node B frame number count value.
其中,所述节点B帧号计数值换算方法为:Wherein, the method for converting the count value of the Node B frame number is:
节点B帧号计数值=全球定位系统绝对时间×100 mod 4096,其中Node B frame number count value = GPS absolute time × 100 mod 4096, where
Mod代表取模运算。Mod stands for modulo operation.
所述步骤B还可以用以下步骤替换:Said step B can also be replaced with the following steps:
C所述基站每隔预定时间段,根据全球定位系统绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的节点B帧号计数值,并在下一个秒脉冲信号到来时,判断当前节点B帧号计数值与所述换算得到的节点B帧号计数值是否一致,如果不一致,则将当前节点B帧号计数值调整为所述换算得到的节点B帧号计数值。The base station in C converts the corresponding node B frame number count value for the next 1 second every predetermined time period according to the absolute time of the global positioning system, and judges the current node B frame number count value when the next second pulse signal arrives. Whether the converted Node B frame number count value is consistent, and if not, adjust the current Node B frame number count value to the converted Node B frame number count value.
所述相位跟踪用于保证基站主时钟的10ms信号与来自所述全球定位系统接收机的秒脉冲信号同步。The phase tracking is used to ensure that the 10ms signal of the master clock of the base station is synchronized with the pulse-per-second signal from the global positioning system receiver.
本方法的步骤A和步骤B在所述基站开工前执行。Step A and step B of the method are executed before the base station is started.
本发明还提供了一种宽带码分多址系统中基站间的节点B帧号同步系统,其中,所述系统包含至少2个基站,所述系统还包含至少2个全球定位系统接收机,其中,所述基站和所述全球定位系统接收机一一对应,The present invention also provides a Node B frame number synchronization system between base stations in a wideband code division multiple access system, wherein the system includes at least 2 base stations, and the system also includes at least 2 global positioning system receivers, wherein , there is a one-to-one correspondence between the base station and the global positioning system receiver,
所述全球定位系统卫星接收机用于从全球定位系统信号中获取全球定位系统绝对时间和秒脉冲信号,并发送给其对应的基站;The global positioning system satellite receiver is used to obtain the absolute time of the global positioning system and the second pulse signal from the global positioning system signal, and send it to its corresponding base station;
所述基站用于跟踪秒脉冲信号,实现频率跟踪后,启动相位跟踪,同时,所述基站根据全球定位系统绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的节点B帧号计数值,并在下一个秒脉冲信号到来时,将当前节点B帧号计数值调整为所述换算得到的节点B帧号计数值。The base station is used to track the second pulse signal. After the frequency tracking is realized, the phase tracking is started. At the same time, the base station converts the corresponding node B frame number count value in the next 1 second according to the absolute time of the global positioning system, and calculates the corresponding node B frame number count value in the next second. When the pulse signal arrives, the current node B frame number count value is adjusted to the converted node B frame number count value.
其中,所述节点B帧号计数值换算方法为:Wherein, the method for converting the count value of the Node B frame number is:
节点B帧号计数值=全球定位系统绝对时间×100 mod 4096,其中Mod代表取模运算。Node B frame number count value = GPS absolute time × 100 mod 4096, where Mod stands for modulo operation.
所述基站执行的相位跟踪用于保证基站主时钟的10ms信号与来自所述全球定位系统接收机的秒脉冲信号同步。Phase tracking performed by the base station is used to ensure that the 10 ms signal of the base station master clock is synchronized with the pulse-per-second signal from the GPS receiver.
本发明另提供了一种宽带码分多址系统中基站间的节点B帧号同步系统,其中,所述系统包含至少2个基站,所述系统还包含至少2个全球定位系统接收机,其中,所述基站和所述全球定位系统接收机一一对应,The present invention also provides a Node B frame number synchronization system between base stations in a wideband code division multiple access system, wherein the system includes at least 2 base stations, and the system also includes at least 2 global positioning system receivers, wherein , there is a one-to-one correspondence between the base station and the global positioning system receiver,
所述全球定位系统卫星接收机用于从全球定位系统信号中获取全球定位系统绝对时间和秒脉冲信号,并发送给其对应的基站;The global positioning system satellite receiver is used to obtain the absolute time of the global positioning system and the second pulse signal from the global positioning system signal, and send it to its corresponding base station;
所述基站用于每隔预定时间段,根据全球定位系统绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的节点B帧号计数值,并在下一个秒脉冲信号到来时,判断当前节点B帧号计数值与所述换算得到的节点B帧号计数值是否一致,如果不一致,则将当前节点B帧号计数值调整为所述换算得到的节点B帧号计数值。The base station is used to convert the corresponding node B frame number count value for the next 1 second according to the absolute time of the global positioning system at predetermined time intervals, and judge the current node B frame number count value when the next second pulse signal arrives Whether it is consistent with the converted Node B frame number count value, and if not, adjust the current Node B frame number count value to the converted Node B frame number count value.
通过比较可以发现,本发明的技术方案与现有技术的区别在于,由基站根据GPS卫星接收机从GPS信号中获取的GPS绝对时间,换算出相应的BFN计数值,作为当前BFN计数值;并且定期进行检查,发现实际值与要求的值不一致时,则将其替换为换算得到的BFN计数值。By comparison, it can be found that the difference between the technical solution of the present invention and the prior art is that the base station converts the corresponding BFN count value from the GPS absolute time obtained from the GPS signal according to the GPS satellite receiver, as the current BFN count value; and Check regularly, and if the actual value is found to be inconsistent with the required value, it will be replaced by the converted BFN count value.
这种技术方案上的区别,带来了较为明显的有益效果:有效地实现了WCDMA系统中不同Node B之间BFN的同步。并且具有简化UE的切换流程、提高UE的切换成功率、降低手机功耗的优点。The difference in this technical solution has brought obvious beneficial effects: effectively realizing the synchronization of BFN between different Node Bs in the WCDMA system. In addition, it has the advantages of simplifying the handover process of the UE, improving the handover success rate of the UE, and reducing the power consumption of the mobile phone.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是现有技术中WCDMA的软切换定时过程示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of the soft handover timing process of WCDMA in the prior art;
图2是根据本发明的一个实施例的WCDMA系统中BFN同步系统的结构示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a BFN synchronization system in a WCDMA system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明涉及的Node B软件锁相环路示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the Node B software phase-locked loop involved in the present invention;
图4是本发明中WCDMA系统不同Node B间的BFN同步原理的示意图;Fig. 4 is the schematic diagram of the BFN synchronous principle between different Node Bs of WCDMA system among the present invention;
图5是根据本发明的一个实施例的WCDMA系统不同Node B间BFN同步方法的流程示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic flow chart of a BFN synchronization method between different Node Bs of a WCDMA system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图6是根据本发明的另一个实施例的WCDMA系统不同Node B间BFN同步方法中,Node B开始工作后保持BFN同步的流程示意图。6 is a schematic flow diagram of maintaining BFN synchronization after the Node B starts working in a BFN synchronization method between different Node Bs in a WCDMA system according to another embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合附图对本发明作进一步地详细描述。In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
总的来说,本发明的原理在于,由基站根据来自GPS卫星接收机的GPS绝对时间,换算出相应的BFN计数值,作为当前BFN计数值。并且通过定期检查,针对实际值与要求的值不一致的情况,将其替换为换算得到的BFN计数值。由此实现了WCDMA系统中的Node B的BFN同步,提高了切换成功率和服务质量,也节省UE的功耗。In general, the principle of the present invention is that the base station converts the corresponding BFN count value according to the GPS absolute time from the GPS satellite receiver as the current BFN count value. And through regular inspection, if the actual value is inconsistent with the required value, replace it with the converted BFN count value. In this way, the BFN synchronization of Node B in the WCDMA system is realized, the handover success rate and service quality are improved, and the power consumption of the UE is also saved.
下面结合图2,说明根据本发明的一个实施例的WCDMA系统中Node B之间BFN同步系统的结构及其工作过程。Below in conjunction with FIG. 2, the structure and working process of the BFN synchronization system between Node Bs in the WCDMA system according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described.
如图2所示,WCDMA系统中基站间的BFN同步系统包含GPS卫星20,2个基站22、24,此外还包含2个GPS接收机21、23。其中,基站22、24与所述全球定位系统接收机一一对应。As shown in FIG. 2 , the BFN synchronization system between base stations in the WCDMA system includes a GPS satellite 20 , two base stations 22 , 24 , and also includes two GPS receivers 21 , 23 . Wherein, the base stations 22 and 24 are in one-to-one correspondence with the GPS receivers.
GPS卫星20用于向GPS接收机21和23发射GPS信号。GPS satellite 20 is used to transmit GPS signals to GPS receivers 21 and 23 .
GPS接收机21和23用于从GPS信号中获取GPS绝对时间和1PPS信号(秒脉冲信号),并发送给其对应的基站22和24。GPS receivers 21 and 23 are used to obtain GPS absolute time and 1PPS signal (pulse per second signal) from GPS signals, and send them to corresponding base stations 22 and 24 .
基站22和24用于跟踪1PPS信号,实现频率跟踪后,启动相位跟踪,同时,基站根据GPS绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的BFN,并在下个1PPS信号到来时,将当前BFN调整为所述换算得到的BFN,完成对BFN计数器的同步调整,从而使不同Node B的BFN达到一致。The base stations 22 and 24 are used to track the 1PPS signal. After the frequency tracking is realized, the phase tracking is started. At the same time, the base station converts the corresponding BFN for the next 1 second according to the GPS absolute time, and adjusts the current BFN to The BFN obtained by the conversion completes the synchronous adjustment of the BFN counter, so that the BFNs of different Node Bs are consistent.
需要指出,在本发明的另一个实施例中,基站22和24还用于每隔预定时间段,根据GPS绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的BFN,并在下个1PPS信号到来时,判断当前BFN与所述换算得到的BFN是否一致,如果不一致,则将当前BFN调整为换算得到的BFN。由此通过Node B定时检查BFN值,使得BFN同步得以保持。It should be pointed out that in another embodiment of the present invention, the base stations 22 and 24 are also used to calculate the corresponding BFN of the next 1 second according to the GPS absolute time every predetermined time period, and judge when the next 1PPS signal arrives Whether the current BFN is consistent with the converted BFN, and if not, adjust the current BFN to the converted BFN. Therefore, the Node B regularly checks the BFN value, so that the BFN synchronization can be maintained.
上面介绍了本发明提出的BFN同步系统的大体结构,下面进一步描述BFN同步系统的工作过程。The general structure of the BFN synchronization system proposed by the present invention has been introduced above, and the working process of the BFN synchronization system will be further described below.
首先,Node B22、24启动后,GPS卫星20不断向GPS接收机21,23发送GPS信号,GPS接收机21,23对接收到的GPS信号进行处理,从中得到GPS绝对时间和1PPS信号,后将其分别发送给相应Node B22、24。First, after Node B22, 24 starts, GPS satellite 20 constantly sends GPS signal to GPS receiver 21, 23, and GPS receiver 21, 23 processes the GPS signal received, obtains GPS absolute time and 1PPS signal therefrom, then sends They are sent to corresponding Node B22, 24 respectively.
接着,Node B22接收到GPS时间信号,其主时钟通过软件锁相环(PhaseLock Loop,简称“PLL”)跟踪1PPS信号,进行频率跟踪和相位跟踪。为了更具体地说明本发明的BFN同步系统工作原理,此处简单说明一下软件PLL。如图3所示,软件PLL3包含鉴相器30,滤波及状态估计算法31,数模转换器32(Digital Analog Converter,简称“DAC”)及恒温压控晶振33(Oven Control Voltage Control Crystal Oscillator,简称“OCVCXO”)。业务信号流300是外部参考时钟源,在本例中是1PPS信号,业务信号流301是实现锁相后与输入时钟同步的时钟信号,本例中输出的是10ms时钟信号。鉴相器30的逻辑部件实现Node B主时钟对1PPS信号的硬件鉴相计数,然后鉴相器30将鉴相计数值传给CPU,CPU通过滤波及状态估计算法31进行软件滤波和状态估计;然后CPU由相应算法产生DAC32的控制值,这个控制值使得DAC32产生控制电压来调整本地时钟源OCVCXO33的频率,再通过负反馈回路对OCVCXO33进行进一步调整,使OCVCXO33输出NodeB系统所需的高精度时钟信号。Then, Node B22 receives the GPS time signal, and its master clock tracks the 1PPS signal through a software phase-locked loop (PhaseLock Loop, referred to as "PLL") to perform frequency tracking and phase tracking. In order to describe the working principle of the BFN synchronization system of the present invention more specifically, here is a brief description of the software PLL. As shown in Figure 3, the software PLL3 includes a phase detector 30, a filtering and state estimation algorithm 31, a digital-to-analog converter 32 (Digital Analog Converter, referred to as "DAC") and a constant temperature voltage-controlled crystal oscillator 33 (Oven Control Voltage Control Crystal Oscillator, Abbreviated as "OCVCXO"). The service signal stream 300 is an external reference clock source, which is a 1PPS signal in this example, and the service signal stream 301 is a clock signal synchronized with the input clock after phase locking is implemented, and the output in this example is a 10ms clock signal. The logic part of the phase detector 30 realizes the hardware phase detection counting of the Node B master clock to the 1PPS signal, and then the phase detector 30 passes the phase detection count value to the CPU, and the CPU performs software filtering and state estimation by filtering and state estimation algorithm 31; Then the CPU generates the control value of DAC32 according to the corresponding algorithm. This control value makes DAC32 generate a control voltage to adjust the frequency of the local clock source OCVCXO33, and then further adjusts OCVCXO33 through a negative feedback loop to make OCVCXO33 output the high-precision clock required by the NodeB system. Signal.
在实现相位跟踪的同时,Node B22根据GPS绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒对应的BFN计数值,并在下一个1PPS信号到来时,将当前BFN计数值调整为所换算的BFN计数值,同样Node B24接收GPS接收机23的时间信号后,也进行相同的处理。由于Node B22、24接收到的GPS绝对时间是一致的,所以换算得到的BFN计数值必然相同。While realizing phase tracking, Node B22 converts the BFN count value corresponding to the next 1 second according to the GPS absolute time, and adjusts the current BFN count value to the converted BFN count value when the next 1PPS signal arrives. B24 also performs the same processing after receiving the time signal from the GPS receiver 23 . Since the GPS absolute time received by Node B22 and 24 is consistent, the converted BFN count values must be the same.
然后Node B22、24的各自BFN计数器以此BFN计数值为起点,对10ms帧信号在0-4095范围内周期计数,将产生的BFN计数值输出给各个业务板使用。因为Node B22、24的系统时钟信号与1PPS信号处在相位跟踪状态,也就是说用于计数的10ms帧信号与1PPS信号同步,所以由BFN计数器根据10ms帧信号产生的BFN计数值就同步于GPS的1PPS信号,这样就实现了Node B22、24间的BFN同步。Then the respective BFN counters of Node B22 and 24 start from this BFN count value, periodically count the 10ms frame signal in the range of 0-4095, and output the generated BFN count value to each service board for use. Because the system clock signal of Node B22 and 24 is in the phase tracking state with the 1PPS signal, that is to say, the 10ms frame signal used for counting is synchronized with the 1PPS signal, so the BFN count value generated by the BFN counter based on the 10ms frame signal is synchronized with the GPS 1PPS signal, thus realizing the BFN synchronization between Node B22 and 24.
在系统运行过程中,由于Node B系统时钟与GPS的1PPS信号是锁相的,所以基于系统时钟产生的BFN计数值是与GPS时间信号同步,这使得BFN的同步状态一般可以稳定保持。而为了防范意外的发生,需要Node B定时对BFN进行同步检查,这在上文的一个实施例中已经指出。下面结合图2进一步予以解释说明。During system operation, since the Node B system clock is phase-locked with the 1PPS signal of GPS, the BFN count value generated based on the system clock is synchronized with the GPS time signal, which makes the synchronization state of BFN generally stable. In order to prevent accidents, the Node B needs to periodically check the BFN synchronously, which has been pointed out in an embodiment above. Further explanation will be given below in conjunction with FIG. 2 .
Node B22、24每隔预定时间就根据GPS绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒对应的BFN计数值,并在下个1PPS信号到来时,判断当前BFN计数值与换算得到BFN计数值是否一致,如果一致,说明BFN与GPS时间信号保持同步,如果不一致,则将当前BFN计数值调整为所述换算得到的BFN计数值,这样就使Node B22、24间保持了BFN的同步。Node B22, 24 converts the BFN count value corresponding to the next 1 second according to the GPS absolute time every predetermined time, and judges whether the current BFN count value is consistent with the converted BFN count value when the next 1PPS signal arrives. , indicating that the BFN is synchronized with the GPS time signal. If not, the current BFN count value is adjusted to the converted BFN count value, so that the BFN synchronization between Node B22 and 24 is maintained.
熟悉本领域的技术人员知道,如果初始位置参数和时间设置比较准确,GPS接收机可以在分钟级的时间内很快跟踪到GPS卫星并输出时间信号。而对与本发明的WCDMA系统中不同Node B的BFN同步系统,要求在NodeB启动2分钟后,与Node B相连的GPS接收机要能够锁定足够的GPS卫星并处理输出时间信号,而GPS的锁相算法和硬件保证Node B在3分钟内实现BFN的同步调整,此后Node B才可以工作。也就是说GPS接收机要提供足够的支持使各个Node B在启动5分钟后可以达到BFN同步,从而进行正常工作。Those skilled in the art know that if the initial position parameters and time settings are relatively accurate, the GPS receiver can quickly track GPS satellites and output time signals within minutes. And to the BFN synchronous system of different Node B in WCDMA system of the present invention, require after NodeB starts 2 minutes, the GPS receiver that links to each other with Node B will be able to lock enough GPS satellites and process output time signal, and the lock of GPS The phase algorithm and hardware ensure that Node B realizes the synchronous adjustment of BFN within 3 minutes, after which Node B can work. That is to say, the GPS receiver should provide sufficient support so that each Node B can achieve BFN synchronization after 5 minutes of startup, so as to perform normal work.
对于上述BFN同步系统,还需要说明:GPS线路传输引起的信号延迟可以通过软件在安装时对GPS卡进行一次性的相应的时间补偿,但是这个延迟一般在ns量级,几乎不能影响BFN的同步,也可以不考虑。For the above-mentioned BFN synchronization system, it needs to be explained: the signal delay caused by GPS line transmission can be compensated for the corresponding time of the GPS card once by software during installation, but this delay is generally in the order of ns, which can hardly affect the synchronization of BFN , can also be ignored.
下面,参照图5和图6,进一步说明本发明提出的WCDMA系统中基站间的BFN同步方法。Next, with reference to FIG. 5 and FIG. 6 , the BFN synchronization method between base stations in the WCDMA system proposed by the present invention will be further described.
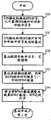
如图5所示,在本发明提出的BFN同步方法的一个实施例中包含2个大步骤。As shown in FIG. 5 , an embodiment of the BFN synchronization method proposed by the present invention includes two major steps.
在第一个大步骤中,GPS卫星接收机从GPS信号中获取GPS绝对时间和1PPS信号,并发送给其对应的基站。具体的说,本步骤分为以下几个子步骤:In the first big step, the GPS satellite receiver obtains the GPS absolute time and 1PPS signal from the GPS signal, and sends them to its corresponding base station. Specifically, this step is divided into the following sub-steps:
首先,在步骤500中,GPS接收机通过GPS卡40接收GPS信号400,通过处理得到GPS绝对时间402和1PPS信号401。First, in
接着,在步骤501中,GPS卡40将GPS绝对时间402和1PPS信号401发送给相应的Node B,具体来说,GPS绝对时间402通过推荐标准-232-C(Recommend Standard-232-C,简称“RS-232-C”)串口输出到相应Node B的处理器CPU42中,熟悉本领域的技术人员知道,RS-232-C是数据终端设备和数据通信设备间的串行二进制数据交换的接口。1PPS信号则是输出到相应Node B的软件PLL中。需要指出的是,GPS绝对时间是指此前上一个1PPS信号所对应的绝对时刻。Then, in
在第二个大步骤中,基站主时钟跟踪1PPS信号,实现频率跟踪后,启动相位跟踪,同时,基站根据GPS绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的BFN,并在下个1PPS信号到来时,将当前BFN调整为换算得到的BFN。需要指出的是,BFN计数值的计算采用以下公式:BFN计数值=GPS绝对时间长度×100 Mod 4096,GPS绝对时间长度一般是以GPS绝对零点,即1980年1月6号0时0分0秒,为起点的时间长度,单位为秒,Mod代表取模运算,在GPS绝对时间零点时,规定BFN计数值为0。由此公式可以求得任意时刻对应的BFN值,例如,假设当前GPS绝对时间为1980年1月6日0时59分59秒,其下1秒为1980年1月6日1时0分0秒,转化为GPS绝对时间长度为3600秒,由上面公式:3600×100 Mod 4096=3648,所以当前下一个1PPS信号对应的BFN计数值应为3648。In the second big step, the main clock of the base station tracks the 1PPS signal. After realizing the frequency tracking, the phase tracking is started. At the same time, the base station converts the corresponding BFN for the next 1 second according to the GPS absolute time, and when the next 1PPS signal arrives, Adjust the current BFN to the converted BFN. It should be pointed out that the BFN count value is calculated using the following formula: BFN count value = GPS absolute time length × 100 Mod 4096, and the GPS absolute time length is generally based on the GPS absolute zero point, that is, at 0:00:00 on January 6, 1980 Second is the length of time from the starting point, and the unit is second. Mod stands for modulo calculation. When the GPS absolute time is zero, the BFN count value is specified to be 0. From this formula, the BFN value corresponding to any time can be obtained. For example, assuming that the current absolute GPS time is 0:59:59 on January 6, 1980, the next second is 1:00:00 on January 6, 1980 Seconds, converted to GPS absolute time length is 3600 seconds, from the above formula: 3600×100 Mod 4096=3648, so the BFN count value corresponding to the next 1PPS signal should be 3648.
图4中示出本发明相关的BFN同步原理。图4中有GPS卡40、软件锁相环路41、CPU42以及BFN计数器43。熟悉本领域的技术人员知道,GPS卡40是GPS接收机的主要部件,用于对GPS信号进行处理,由它产生GPS绝对时间和1PPS信号;软件锁相环路41,CPU42和BFN计数器43分别在Node B的相应部件中,用于对GPS卡40的时间信号处理并实现BFN同步。FIG. 4 shows the BFN synchronization principle related to the present invention. There are
在上述基础上,下面对第二大步骤进行具体展开,该步骤包含以下子步骤:On the basis of the above, the second major step will be specifically expanded below, which includes the following sub-steps:
如图5所示,在步骤502中,Node B利用软件PLL41跟踪GPS的1PPS信号401,并对其锁频。As shown in Fig. 5, in
接着,执行步骤503,Node B的锁相环路41启动对1PPS信号401的相位跟踪;同时,Node B的CPU处理器42,根据步骤501中GPS卡传来的GPS绝对时间402,计算当前下一秒对应的BFN计数值,并将这个值送入到BFN逻辑计数器中预置。需要指出的是,CPU42计算BFN时同样按照如下公式进行计算:绝对时间长度×100 Mod 4096,得到的值即为对应于GPS绝对时间402下一秒的BFN计数值。Then, step 503 is executed, and the phase-locked
最后在步骤504中,在下一个1PPS信号脉冲来到时,将BFN值设定为步骤503中换算得到的BFN计数值,这就实现了不同Node BBFN的同步。Finally in
在本发明的另一个实施例中,为了使Node B在开始工作后,仍然能够保持BFN处于同步状态,因此,还包含一个大步骤:基站每隔预定时间段,根据GPS绝对时间,换算出接下来1秒相应的BFN,并在下个1PPS信号到来时,判断当前BFN与所述换算得到的BFN是否一致,如果不一致,则将当前BFN调整为所述换算得到的BFN。下面参照图6,对本步骤包含的几个子步骤做进一步说明。In another embodiment of the present invention, in order to enable Node B to keep the BFN in a synchronized state after starting to work, a large step is also included: the base station converts the received time according to the GPS absolute time every predetermined time period. Get the corresponding BFN for 1 second, and when the next 1PPS signal arrives, judge whether the current BFN is consistent with the converted BFN, if not, adjust the current BFN to the converted BFN. Referring to Fig. 6, several sub-steps included in this step will be further described.
首先,在步骤600中,Node B检查从上一次BFN同步调整算起到现在,是否到了预定的时间,如果到了就执行步骤601,如果没有就不操作。First, in
在步骤601中,Node B根据GPS绝对时间402计算下一秒所对应的BFN值,计算方法同步骤503,此处不再赘述。In
接着,进入步骤602,当下一个1PPS到来时,Node B判断当前BFN值与所换算的BFN是否一致,如果一致则判断结果为是,执行转向步骤600,如果不一致,则判断结果为否,执行步骤603。Then, enter
在步骤603中,将当前的BFN值调整为步骤601中得到的BFN值,然后转向执行步骤600。由此实现了在Node B开始工作后保持BFN同步的目的。In
虽然通过参照本发明的某些优选实施例,已经对本发明进行了图示和描述,但本领域的普通技术人员应该明白,可以在形式上和细节上对其作各种各样的改变,而不偏离所附权利要求书所限定的本发明的精神和范围。Although the present invention has been illustrated and described with reference to certain preferred embodiments thereof, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes in form and details may be made therein, and without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2004100945500ACN100385848C (en) | 2004-11-08 | 2004-11-08 | Method and system for synchronizing node B frame numbers between base stations in wideband code division multiple access system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2004100945500ACN100385848C (en) | 2004-11-08 | 2004-11-08 | Method and system for synchronizing node B frame numbers between base stations in wideband code division multiple access system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1773887A CN1773887A (en) | 2006-05-17 |
| CN100385848Ctrue CN100385848C (en) | 2008-04-30 |
Family
ID=36760677
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2004100945500AExpired - Fee RelatedCN100385848C (en) | 2004-11-08 | 2004-11-08 | Method and system for synchronizing node B frame numbers between base stations in wideband code division multiple access system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100385848C (en) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7986700B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2011-07-26 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Multiplexed data stream circuit architecture |
| US7809027B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2010-10-05 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Network clock synchronization floating window and window delineation |
| US8588209B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2013-11-19 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Multi-network compatible data architecture |
| US7675945B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2010-03-09 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Multi-component compatible data architecture |
| US8340101B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2012-12-25 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Multiplexed data stream payload format |
| US8494009B2 (en)* | 2006-09-25 | 2013-07-23 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Network clock synchronization timestamp |
| US8976796B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2015-03-10 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Bandwidth reuse in multiplexed data stream |
| US7813271B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2010-10-12 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Aggregated link traffic protection |
| US7961751B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2011-06-14 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Multiplexed data stream timeslot map |
| US8295310B2 (en) | 2006-09-25 | 2012-10-23 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Inter-packet gap network clock synchronization |
| CN101569147B (en) | 2007-01-26 | 2012-05-02 | 华为技术有限公司 | Multi-Component Compatible Data Architecture |
| CN101299822B (en)* | 2007-04-30 | 2012-07-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | System, method, equipment and apparatus for synchronous transmission |
| CN101388740B (en)* | 2007-09-10 | 2012-12-26 | 展讯通信(上海)有限公司 | Method and system for obtaining and transmitting GPS standard time in TD-SCDMA radio communication system |
| WO2010072180A1 (en)* | 2008-12-27 | 2010-07-01 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for frame synchronization |
| CN101888241B (en)* | 2010-05-27 | 2015-04-01 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method, device and equipment for detecting second pulse input signal inversion and automatically correcting error |
| CN102624512B (en)* | 2012-02-22 | 2015-10-21 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A kind of method and system realizing clock synchronous |
| US11683771B2 (en)* | 2020-11-30 | 2023-06-20 | Viettel Group | Method and apparatus for data frame synchronization of 5G base station |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1388714A (en)* | 2001-05-25 | 2003-01-01 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Radio communication system and frame synchronous method of base station |
| KR20040049588A (en)* | 2002-12-06 | 2004-06-12 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Soft handover method for mobile telecommunication system |
| KR20040060435A (en)* | 2002-12-30 | 2004-07-06 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | node synchronized device of the W-CDMA system and controlling method therefore |
- 2004
- 2004-11-08CNCNB2004100945500Apatent/CN100385848C/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1388714A (en)* | 2001-05-25 | 2003-01-01 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Radio communication system and frame synchronous method of base station |
| KR20040049588A (en)* | 2002-12-06 | 2004-06-12 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Soft handover method for mobile telecommunication system |
| KR20040060435A (en)* | 2002-12-30 | 2004-07-06 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | node synchronized device of the W-CDMA system and controlling method therefore |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| CFN在WCDMA系统同步中的作用及其控制算法实现. 许明艳等:.移动通信,第增刊期. 2003 |
| CFN在WCDMA系统同步中的作用及其控制算法实现. 许明艳等:.移动通信,第增刊期. 2003* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1773887A (en) | 2006-05-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN100385848C (en) | Method and system for synchronizing node B frame numbers between base stations in wideband code division multiple access system | |
| KR100984656B1 (en) | Air interface sync | |
| US8254355B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for utilizing a second receiver to establish time and frequency | |
| JP4240238B2 (en) | Circuit for synchronizing a CDMA mobile telephone | |
| CN111954295B (en) | Time and precision considered synchronization maintaining method and system for TDD-LTE (time division Duplex-Long term evolution) equipment | |
| WO2009097812A1 (en) | Wireless communication system, method for adjusting air-interfaces synchronously, base station and control device thereof | |
| WO2006082628A1 (en) | Inter-base station synchronization system, synchronization control device, and base station | |
| US20200404607A1 (en) | Synchronizing a cloud radio access network to a network time protocol reference clock | |
| WO2018210281A1 (en) | Clock adjustment and clock deviation calculation method, device and system | |
| TW201129151A (en) | Apparatus and method for providing handover trigger mechanisms using multiple metrics | |
| KR20090083899A (en) | Method and apparatus for automatic frequency correction of multi-mode devices | |
| WO2021174394A1 (en) | Synchronization method and apparatus | |
| US7457979B2 (en) | Synchronous follow-up apparatus and synchronous follow-up method | |
| US8406702B2 (en) | Clock signal generating arrangement for a communication device | |
| WO2020171802A1 (en) | Synchronization for 5gs time sensitive communications (tsc) using machine learning | |
| CN113225803A (en) | Wireless clock synchronization method and device for mining 5G base station | |
| CN103491623B (en) | Integrated circuit and communication method thereof | |
| CN101112110A (en) | Inter-base station synchronization system, synchronization control device and base station | |
| WO2020030062A1 (en) | Communication method and apparatus | |
| JP5394407B2 (en) | Soft handover timing update | |
| JP2002368729A (en) | Wireless communication terminal | |
| CN100525143C (en) | Inter base station synchronizing method in mobile communication system | |
| CN105657816A (en) | Method and device for keeping base stations synchronous | |
| WO2021159262A1 (en) | Threshold value adjustment method and apparatus for timing advance | |
| US20230328676A1 (en) | Wireless communication method, first device and second device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20080430 Termination date:20191108 |