CN100367904C - endoscope device - Google Patents
endoscope deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN100367904C CN100367904CCNB2003101218458ACN200310121845ACN100367904CCN 100367904 CCN100367904 CCN 100367904CCN B2003101218458 ACNB2003101218458 ACN B2003101218458ACN 200310121845 ACN200310121845 ACN 200310121845ACN 100367904 CCN100367904 CCN 100367904C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- endoscope device
- head
- endoscope
- hollow catheter
- shape
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Endoscopes (AREA)
- Instruments For Viewing The Inside Of Hollow Bodies (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明是关于一种内视镜装置,特别是关于一种可以对人体体腔进行医学检查的工具。The invention relates to an endoscope device, in particular to a tool capable of performing medical inspection on a body cavity of a human body.
背景技术Background technique
一般内视镜是一条特制的管子,主要由摄影装置及光源构成,接上显示器后可将身体内部的构造显示在屏幕上。医生通过观察屏幕上的影像诊断受检者的疾病。身体内部的器官,只要有孔道与身体外相通,就可以利用内视镜进行检查,例如喉内视镜(检查声带、咽喉等)是经由鼻腔置入内视镜;上消化道内视镜(检查食道、胃及十二指肠)是经口腔置入;大肠镜则经由肛门进入等。若无孔道可以借助,也可由手术建立孔道来实现,例如腹腔镜检查时需要在腹部打洞;关节镜需要切开关节周围的皮肤等。Generally, the endoscope is a special tube, which is mainly composed of a camera and a light source. After being connected to a monitor, the internal structure of the body can be displayed on the screen. The doctor diagnoses the subject's disease by observing the images on the screen. Internal organs of the body, as long as there is a channel that communicates with the outside of the body, can be checked with an endoscope. For example, a laryngoscope (to check the vocal cords, throat, etc.) is inserted through the nasal cavity; an upper gastrointestinal endoscope (to check Esophagus, stomach and duodenum) are inserted through the mouth; colonoscopy is inserted through the anus, etc. If there is no hole to use, it can also be achieved by establishing a hole through surgery. For example, a hole needs to be made in the abdomen during laparoscopy; arthroscopy needs to cut the skin around the joint, etc.
内视镜检查是一种具有侵袭性的检查方式,在内视镜进入人体的过程中常会引起受检者的不适,严重者甚至会导致休克;同时体内的器官十分柔软、脆弱,稍微不慎就可能被内视镜管子碰伤。再者,由于现有的内视镜造价较高,故每次使用后都需要进行清洗、消毒,供下一位受检者使用,经常会有因消毒不彻底,造成患者交叉感染的病例发生。因此如何在使用内视镜时不引起痛苦、更易操作、无交叉感染,一直是业界亟待克服的瓶颈。Endoscopic examination is an invasive examination method. When the endoscope enters the human body, it often causes discomfort to the subject, and in severe cases, it may even lead to shock. At the same time, the organs in the body are very soft and fragile. It may be bruised by the endoscope tube. Furthermore, due to the high cost of the existing endoscopes, they need to be cleaned and disinfected after each use for the next examinee to use. There are often cases of cross-infection of patients due to incomplete disinfection. . Therefore, how to use the endoscope without causing pain, making it easier to operate, and avoiding cross-infection has always been a bottleneck that needs to be overcome in the industry.
近年来由于影像技术及光学纤维仪器的突破,使得内视镜不论是在体积上或是柔软度上都有显著的进步,甚至已发展出可操控弯曲角度的内视镜,如美国专利第6,432,043号。该专利发明了一种用于插入气管的内视镜,该内视镜除了插入部分、把手操作部分外,进一步包括操控弯曲的机制以及使插入部分弯曲的机制。该弯曲机制包括一长形弹性构件,此弹性构件的一端是位于插入部分的末端,另一端则固定在操控弯曲的机制中的L形把手的一端。弹性构件是在内视镜管内随着插入部分延伸,L形把手则是短边端在管内,长边端在管外。医疗人员借由握着管外部分的把手,以推-拉的方式操控内视镜插入部分的弯曲角度。不过以此方式控制的弯曲角度仍有其限制,它无法窥视被检查器官内部的全貌。In recent years, due to breakthroughs in imaging technology and optical fiber instruments, endoscopes have made significant progress in both volume and flexibility, and even endoscopes that can control the bending angle have been developed, such as US Patent No. 6,432,043 Number. This patent discloses an endoscope for inserting into the trachea, the endoscope further includes a mechanism for controlling bending and a mechanism for bending the insertion part in addition to the insertion part and the handle operation part. The bending mechanism includes an elongated elastic member, one end of which is located at the end of the insertion portion, and the other end is fixed to one end of an L-shaped handle in the bending mechanism. The elastic member extends along with the insertion part in the endoscope tube, and the L-shaped handle is in the tube at the short side end and outside the tube at the long side end. The medical staff controls the bending angle of the insertion part of the endoscope in a push-pull manner by holding the handle of the outer part of the tube. However, the bending angle controlled in this way still has its limitations, and it cannot peek into the whole picture of the interior of the organ being inspected.
此外,在肠胃道内视镜检查方面,当内视镜插入体内后,需对该内视镜施力,使内视镜的插入部分沿着消化管道前进,当内视镜前端遇到消化道的转弯处时,常会对消化道的内壁造成伤害,例如易造成穿孔。为了解决此类问题,发展出无线内视镜,例如美国专利第6,402,686、6,402,687以及6,428,469号。其中美国专利第6,428,469号发明了一种胶囊内视镜,它包括影像单位、连接至影像单位的控制单位以及连接至控制单位的电源。当用胶囊内视镜进行检查时,受检者必需先吞服该内视镜,并长时间随身穿戴厚重的感应器,以接收由进入体内并沿消化道前进的胶囊内视镜传回的影像,同时储存至硬盘中,待检查结束后,即可使用计算机观看所拍摄的影像,以进行诊断。由于该胶囊内视镜的电源是依赖内置的电池,所以当电池的电力耗尽后(约8小时)就无法继续拍摄消化道内的情形。又,该胶囊内视镜是沿人体的消化道持续前进,故无法来回重复观看同一部位,且也有可能发生胶囊卡在肠道内等问题。同时,长时间穿戴厚重的感应器也会造成受检者的负担与不适。此外,倘若受检者途中因故脱下感应器,则会中断影像的储存,导致影像无法连贯,进而影响检查结果与病情诊断。再者,这种胶囊内视镜的造价较高,再加上上述种种使用上的问题,使得该产品迄今仍难以遍及。In addition, in terms of endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract, when the endoscope is inserted into the body, it is necessary to apply force to the endoscope so that the insertion part of the endoscope advances along the digestive tract. When turning, it often causes damage to the inner wall of the digestive tract, such as perforation. In order to solve such problems, wireless endoscopes have been developed, such as US Pat. Nos. 6,402,686, 6,402,687 and 6,428,469. Among them, US Patent No. 6,428,469 has invented a capsule endoscope, which includes an imaging unit, a control unit connected to the imaging unit, and a power supply connected to the control unit. When checking with a capsule endoscope, the examinee must first swallow the endoscope and wear a heavy sensor for a long time to receive the information sent back by the capsule endoscope that enters the body and advances along the digestive tract. The images are stored in the hard disk at the same time. After the inspection is completed, the captured images can be viewed on the computer for diagnosis. Since the power supply of the capsule endoscope relies on the built-in battery, so when the power of the battery is exhausted (about 8 hours), the situation in the digestive tract cannot be continued. In addition, the capsule endoscope continues to advance along the digestive tract of the human body, so it is impossible to repeatedly view the same part back and forth, and problems such as the capsule getting stuck in the intestinal tract may also occur. At the same time, wearing a heavy sensor for a long time will also cause burden and discomfort to the examinee. In addition, if the subject takes off the sensor for some reason on the way, the storage of the image will be interrupted, causing the image to be incoherent, which will affect the test result and disease diagnosis. Furthermore, the high cost of this capsule endoscope, coupled with the above-mentioned various problems in use, makes this product still difficult to popularize so far.
发明内容Contents of the invention
为克服上述现有技术的缺点,本发明的主要目的在于提供一种医学上用的内视镜装置,该内视镜装置在伸入到人体的体腔进行检查时,其前部可进行180°旋转,开状记忆性中空导管可进行360°旋转,可对人体内的体腔进行完整的检查。In order to overcome the shortcomings of the above-mentioned prior art, the main purpose of the present invention is to provide a medical endoscope device, when the endoscope device is inserted into the body cavity of the human body for inspection, its front part can be 180 ° Rotating, the open-shaped memory hollow catheter can be rotated 360°, and can perform a complete inspection of the body cavity in the human body.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种医学上用的内视镜装置,该内视镜装置成本低廉,每次使用后即可抛弃,因此可避免交叉感染现象的发生。Another object of the present invention is to provide a medical endoscope device, which is low in cost and can be discarded after each use, thus avoiding the occurrence of cross-infection.
本发明的再一目的在于提供一种医学上用的内视镜装置,该内视镜装置具有操作简单,可成本低廉,可安装在手术工具,辅助手术的进行。Another object of the present invention is to provide a medical endoscope device, which has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, and can be installed on a surgical tool to assist the operation.
本发明的该内视镜装置包括:具有摄影及传输影像功能的头部;与该头部相连、且在邻接该相连处的部位经常保持弯曲状态的形状记忆性中空导管;以及套设于该形状记忆性中空导管外围,可借由在该形状记忆性中空导管上的移动,改变该形状记忆性中空导管弯曲角度的引导套管。The endoscope device of the present invention comprises: a head with functions of photographing and transmitting images; a shape-memory hollow catheter which is connected to the head and always keeps a curved state at the position adjacent to the connection; and is sleeved on the The periphery of the shape-memory hollow catheter can change the bending angle of the shape-memory hollow catheter by moving on the shape-memory hollow catheter.
本发明的内视镜装置可适用于耳、脑、脑下垂体、鼻窦、气管、口腔、食道、胃、小肠、大肠、直肠、胆、泌尿器官(尿道、膀胱、输尿管)、乳房、女性生殖器官(卵巢、输卵管、阴道、子宫)、罩丸、血管、骨髓、腹腔、胸腔以及关节的检查。The endoscopic device of the present invention can be applied to ear, brain, pituitary gland, sinuses, trachea, oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, gallbladder, urinary organs (urethra, bladder, ureter), breast, female reproductive organs Examination of organs (ovaries, fallopian tubes, vagina, uterus), pelvis, blood vessels, bone marrow, abdominal cavity, chest cavity, and joints.
本发明的内视镜装置具有拍摄无死角,本发明内视镜装置的拍摄范围可达180°,其形状记忆性中空导管可旋转360°;该装置操作简单、可使用普通计算机记录所拍摄的影像、成本低廉,每次使用后即可抛弃以及可安装在手术工具上,辅助手术的进行等。The endoscope device of the present invention has no dead angle for shooting, the shooting range of the endoscope device of the present invention can reach 180°, and its shape-memory hollow conduit can rotate 360°; the device is simple to operate and can use a common computer to record the photographed Imaging, low cost, can be discarded after each use and can be installed on surgical tools to assist in the operation, etc.
附图说明Description of drawings
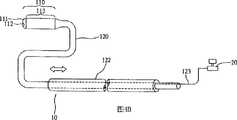
图1是本发明内视镜装置实施例1的外观图;Fig. 1 is the exterior view of embodiment 1 of endoscope device of the present invention;
图2是本发明内视镜装置中构成影像单元的要件;Fig. 2 is the key elements that form the image unit in the endoscope device of the present invention;
图3A至图3C是本发明内视镜装置中影像单元113的具体实施例;3A to 3C are specific embodiments of the
第4A至图4C是本发明内视镜装置的实施例2;4A to 4C are Embodiment 2 of the endoscope device of the present invention;
第5A至图5D是以胃为例,说明本发明内视镜装置的使用情形;5A to 5D take the stomach as an example to illustrate the use of the endoscopic device of the present invention;
图6是将本发明的内视镜装置设置或安装在手术工具上的实施例Fig. 6 is the embodiment that the endoscopic device of the present invention is set or installed on the surgical tool
具体实施方式Detailed ways
实施例1Example 1
图1是本发明内视镜装置10的实施例1,头部110位于内视镜装置10的前端,并与形状记忆性中空导管120相连接,且形状记忆性中空导管120在与头部110邻接处呈U形弯曲。形状记忆性中空导管120的材质并无特别限制,只要是能够弯曲成任意的形状、具有组织兼容性且可用于体内手术的材质皆可。考虑到卫生性及避免可能的感染,最好采用适用于抛弃式的材质(例如聚氯乙烯(Poly Vinyl Chloride,PVC)或热塑性聚胺聚甲酸酯(Thermoplastic polyurethane,TPU)等塑料材料)。Fig. 1 is the embodiment 1 of
头部110包括位于前端的透明窗口111,透明窗口111上有一引导线孔112(其可使引导线121穿过)以及影像单元113。自头部110连接出来的通用串行总线(Universal Serial Bus,USB)的连线123(其具有提供电源及影像传输功能),穿过形状记忆性中空导管120并且连接至计算机20。The
如图1所示,本发明内视镜装置10是使用引导线121控制头部110弯曲的角度。首先将引导线121插置在形状记忆性中空导管120的中空部分,当引导线121未穿过头部110时,本发明内视镜装置10与形状记忆性中空导管120邻接处是呈原始的弯曲状态;持续将引导线121向前推进,当其穿过头部110上的引导线孔112时,使得弯曲的形状记忆性中空导管120伸直,此时可借由操控引导线121向前或往后移动的程度以及旋转形状记忆性中空导管120,控制头部110旋转的角度,使医疗人员可完整地观察体腔内部。再者,若有需要,也可选择在头部110的前端开设引导线孔112,令引导线121可由该引导线孔112向外伸出。如有投放药物治疗的需求,也可经由该头部110上的引导线孔112对受检部位的患部直接投放药物,或者可经由引导线孔112对受检部位抽取或释放气体、抽取液体或排放液体、用机械手抓取组织以达到治疗或检查的目的。As shown in FIG. 1 , the
图2是说明本发明内视镜装置中,构成影像单元113的主要部件,它包括电源分配器1131、照明系统1132、摄影系统1133以及传输系统1134。电源分配器1131是提供电力给照明系统1132、摄影系统1133及传输系统1134。照明系统1132负责提供光源,使摄影系统1133可拍摄体腔中的影像。本发明中的光源并无特殊限制,可以是白光或红外线,也可混合使用。通常,光源为发光二极管(Light Emitting Diode,LED),并且将3至4个发光二极管设置在摄影系统1133的周围。传输系统1134则是将摄影系统1133拍摄到的影像,经由信号传送线123传至计算机20中,一方面医疗人员可通过计算机屏幕观看摄影系统1133拍摄的影像以观察受检者体腔内的情形,另一方面计算机也可实时录下所拍摄的影像,若医疗人员需要时可反复观所拍摄的人体内部影像,以做出最正确的诊断。FIG. 2 illustrates the main components constituting the
图3A至图3C是本发明内视镜装置中的影像单元113的具体实施例,其中包括通用串行总线连接处1131a、发光二极管1132a、镜头1133a、影像感应器(CMOS Sensor)与数字信号处理(Digital SignalProcess)1134a。此外也包括第一印刷电路板1135a、第二印刷电路板1135b、第三印刷电路板1135c及第四印刷电路板1135d以及软式排线1136。图3A是影像单元113的展开图,它显示出在第一印刷电路板1135a上装设有发光二极管1132a(位于第一印刷电路板1135a的另一侧);第二印刷电路板1135b上装设有镜头1133a、影像感应器与数字信号处理1134a;第三印刷电路板1135c上装设有数字信号处理部件;第四印刷电路板1135d上装设有通用串行总线连接处1131a(位于第四印刷电路板1135d的另一侧);以及用以连接四个印刷电路板的软式排线1136。图3B是影像单元113的另一侧的展开图,其中显示出位于第一印刷电路板1135a上的发光二极管1132a以及位于第四印刷电路板1135d上的通用串行总线连接处1131a。图3C是将图3A(或图3B)折叠后的立体图,也就是影像单元113的立体图,其中前端为发光二极管1132a,接着为镜头1133a、影像感应器与数字信号处理1134a以及通用串行总线连接处1131a。该影像单元113是借由自通用串行总线连接处1131a提供该影像单元113中的各个部件所需的电力,使照明系统1132、摄影系统1133以及传输系统1134正常发挥作用。3A to 3C are specific embodiments of the
实施例2Example 2
图4A至图4C是本发明内视镜装置的实施例2,其中是使用引导套管122控制头部110弯曲的角度。首先将引导套管122自形状记忆性中空导管120后端套入,再向前推至头部110与形状记忆性中空导管120相连接处,使弯曲的形状记忆性中空导管120伸直,此时可借由操控引导套管122向前或往后移动的程度,控制头部110旋转的角度。再者,图4A至图4C也是具有各种不同弯曲形状的本发明内视镜装置,图4A为U形弯曲的内视镜装置;图4B为S形弯曲的内视镜装置;以及图4C为O形弯曲的内视镜装置。4A to 4C are Embodiment 2 of the endoscope device of the present invention, in which a guiding
引导线121及引导套管122的材质并无特别限制,只要是具有组织兼容性,可用于体内手术的材质皆可。考虑到卫生性及为避免可能的感染,最好采用适于抛弃式的材质。相对于形状记忆性中空导管120,引导线121与引导套管122具有较大的坚韧性,可将原本为弯曲状的形状记忆性中空导管120伸直。此外,为使引导线121可滑顺地在形状记忆性中空导管120中前后移动,在引导线的外层涂覆一层自润性物质,例如特氟龙。The materials of the guide wire 121 and the
图5A至图5D所示,是以检查人体的胃部为例,说明本发明内视镜装置10的使用方法。在进行内视镜检查前先将引导套管122自形状记忆性中空导管120后端套入,向前推至头部110与形状记忆性中空导管120邻接处,使弯曲的形状记忆性中空导管120伸直。自人体口腔中、经由食道将本发明内视镜装置10插入胃中,如图5A。当医生要观察胃内的其它区域时,可在口腔外将引导套管向上拉,使部分形状记忆性中空导管120恢复到其原本的弯曲状态,也就是借由形状记忆性中空导管120恢复弯曲程度,调整本发明内视镜装置10中摄影系统1133可拍摄的角度,如图5B至图D,图中空心箭头所指的方向表示引导套管122移动的方向,空心箭头的大小表示引导套管122的移动程度。当医生要观察胃内右半部时,只需在口腔外稍微旋转形状记忆性中空导管120即可。因此,本发明的内视镜装置10可借由操纵引导套管122向前推或往后拉,控制形状记忆性中空导管120恢复弯曲的程度以及旋转形状记忆性中空导管120,使本发明的内视镜装置10可全方位地观察人体休腔内部。As shown in FIG. 5A to FIG. 5D , the method of using the
此外也可选择将本发明的内视镜装置10设置或安装在手术工具上,或将微型化的手术工具设置或安装在本发明的内视镜装置上。该手术工具可以是手术刀、剪刀、钳子、钻头或其它手术用的各种工具。In addition, the
如图6所示,这是将本发明的内视镜装置10设置或安装在手术刀30上,此时可选择将本发明内视镜装置10的形态记忆性控制部件省略不用。当进行手术时,医师可通过本发明的内视镜装置在计算机屏幕上清楚地看见手术中的微小区域,解决视差上的问题,提供无视差的影像,辅助医生精确地进行手术(例如切除肿瘤或需要仔细地去除不良组织),以避免因手术失误对病人造成伤害。同时,也可选择将手术过程通过本发明的内视镜装置10保存在计算机中,供日后参考教学或其它目的之用。As shown in FIG. 6 , the
综上所述,本发明的内视镜装置具有拍摄无死角(本发明内视镜装置的拍摄范围可达180°)、操作简单、可使用一般计算机记录所拍摄的影像、成本低廉,每次使用后即可抛弃以及可安装在手术工具可辅助手术进行等诸多优点。In summary, the endoscope device of the present invention has no dead angle for shooting (the shooting range of the endoscope device of the present invention can reach 180°), is simple to operate, can use a general computer to record the captured images, and is low in cost. It can be discarded after use and can be installed on surgical tools to assist surgery and many other advantages.
Claims (20)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2003101218458ACN100367904C (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2003-12-19 | endoscope device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2003101218458ACN100367904C (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2003-12-19 | endoscope device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1628603A CN1628603A (en) | 2005-06-22 |
| CN100367904Ctrue CN100367904C (en) | 2008-02-13 |
Family
ID=34844302
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2003101218458AExpired - Fee RelatedCN100367904C (en) | 2003-12-19 | 2003-12-19 | endoscope device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100367904C (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI626921B (en)* | 2017-02-15 | 2018-06-21 | 彩富電子股份有限公司 | Arthroscopic system with disposable arthroscope and a method for image transmitting in an arthroscopic system |
| US11109747B2 (en) | 2017-02-15 | 2021-09-07 | Dynacolor, Inc. | Arthroscopic system with disposable arthroscope having image rotation function and method thereof |
Families Citing this family (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8182422B2 (en) | 2005-12-13 | 2012-05-22 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope having detachable imaging device and method of using |
| US8872906B2 (en) | 2005-01-05 | 2014-10-28 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope assembly with a polarizing filter |
| US8797392B2 (en) | 2005-01-05 | 2014-08-05 | Avantis Medical Sytems, Inc. | Endoscope assembly with a polarizing filter |
| US8289381B2 (en) | 2005-01-05 | 2012-10-16 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with an imaging catheter assembly and method of configuring an endoscope |
| WO2007087421A2 (en) | 2006-01-23 | 2007-08-02 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope |
| WO2007092533A2 (en)* | 2006-02-06 | 2007-08-16 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope with an imaging catheter assembly and method of configuring an endoscope |
| US8287446B2 (en) | 2006-04-18 | 2012-10-16 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Vibratory device, endoscope having such a device, method for configuring an endoscope, and method of reducing looping of an endoscope |
| EP2023795A2 (en) | 2006-05-19 | 2009-02-18 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Device and method for reducing effects of video artifacts |
| US7927272B2 (en) | 2006-08-04 | 2011-04-19 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Surgical port with embedded imaging device |
| US8064666B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2011-11-22 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Method and device for examining or imaging an interior surface of a cavity |
| WO2009049322A2 (en)* | 2007-10-11 | 2009-04-16 | Avantis Medical Systems, Inc. | Endoscope assembly comprising retrograde viewing imaging device and instrument channel |
| CN101683256B (en)* | 2008-09-28 | 2013-04-24 | 德昌电机(深圳)有限公司 | Detection head and detection device provided with same |
| CN103841907B (en)* | 2011-02-15 | 2019-06-14 | 史密夫和内修有限公司 | Arthroscope device for excising |
| US20140275779A1 (en)* | 2013-03-12 | 2014-09-18 | Covidien Lp | Flexible Shaft with Multiple Flexible Portions |
| CN104970755A (en)* | 2015-06-18 | 2015-10-14 | 北京大学第三医院 | Auxiliary device for superfine endoscope biliary tract detection |
| CN105361842A (en)* | 2015-10-28 | 2016-03-02 | 李京 | 3D endoscope breast augmentation technique |
| CN105662328B (en)* | 2016-01-04 | 2017-11-14 | 重庆医科大学附属永川医院 | joint mirror assembly |
| CN107736869B (en)* | 2017-10-24 | 2023-10-20 | 齐鲁工业大学 | Double-head full-view colonoscope and application method thereof |
| CN109330658A (en)* | 2018-10-19 | 2019-02-15 | 中国人民解放军第二军医大学第二附属医院 | Liquid-cooled bone drill |
| CN118766395A (en)* | 2024-06-14 | 2024-10-15 | 中山市元盛电子科技有限公司 | An FPC circuit board structure of an endoscopic inspection device |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN85107091B (en)* | 1985-05-07 | 1988-05-25 | 旭光学工业株式会社 | Endoscope with solid image pick-up element |
| JPH02295530A (en)* | 1989-05-10 | 1990-12-06 | Sumitomo Bakelite Co Ltd | Endoscope catheter and method for using the same |
| JPH0865579A (en)* | 1994-08-23 | 1996-03-08 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Solid state image pickup device |
| CN1223845A (en)* | 1997-11-06 | 1999-07-28 | 株式会社东芝 | endoscope |
| JPH11225996A (en)* | 1998-02-19 | 1999-08-24 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Capsule type in vivo information detector |
| JP2001137182A (en)* | 1999-11-10 | 2001-05-22 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Capsule endoscope for medical use |
| JP2002095632A (en)* | 2000-09-22 | 2002-04-02 | Minolta Co Ltd | Endoscope system |
- 2003
- 2003-12-19CNCNB2003101218458Apatent/CN100367904C/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN85107091B (en)* | 1985-05-07 | 1988-05-25 | 旭光学工业株式会社 | Endoscope with solid image pick-up element |
| JPH02295530A (en)* | 1989-05-10 | 1990-12-06 | Sumitomo Bakelite Co Ltd | Endoscope catheter and method for using the same |
| JPH0865579A (en)* | 1994-08-23 | 1996-03-08 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Solid state image pickup device |
| CN1223845A (en)* | 1997-11-06 | 1999-07-28 | 株式会社东芝 | endoscope |
| JPH11225996A (en)* | 1998-02-19 | 1999-08-24 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Capsule type in vivo information detector |
| JP2001137182A (en)* | 1999-11-10 | 2001-05-22 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Capsule endoscope for medical use |
| JP2002095632A (en)* | 2000-09-22 | 2002-04-02 | Minolta Co Ltd | Endoscope system |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI626921B (en)* | 2017-02-15 | 2018-06-21 | 彩富電子股份有限公司 | Arthroscopic system with disposable arthroscope and a method for image transmitting in an arthroscopic system |
| US11109747B2 (en) | 2017-02-15 | 2021-09-07 | Dynacolor, Inc. | Arthroscopic system with disposable arthroscope having image rotation function and method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1628603A (en) | 2005-06-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TW589170B (en) | Endoscopic device | |
| CN100367904C (en) | endoscope device | |
| JP4472069B2 (en) | Medical capsule endoscope | |
| CN110151100B (en) | Endoscope apparatus and method of use | |
| JP4416990B2 (en) | System for operating a device in vivo | |
| KR101558719B1 (en) | Systems and methods for maintaining a narrow body lumen | |
| JP3490933B2 (en) | Swallowable endoscope device | |
| CN102448535B (en) | Optics guiding feeding tube, conduit are with and related methods | |
| JP5469867B2 (en) | Endoscope with imaging catheter assembly and method for constructing an endoscope | |
| KR100630624B1 (en) | Video rectal endoscope | |
| JP3490932B2 (en) | Swallowable endoscope device | |
| JP4578740B2 (en) | Capsule medical device | |
| US20210267438A1 (en) | Miniaturized intra-body controllable medical device employing machine learning and artificial intelligence | |
| US20080207996A1 (en) | Portable Imaging Apparatus | |
| JP3623894B2 (en) | In-vivo endoscope | |
| US7833176B2 (en) | Pressure-propelled system for body lumen | |
| CN108577904A (en) | A kind of flexible laparoscope system of roads Shuan Qian single hole | |
| CN120514313A (en) | Single use endoscope, cannula and obturator with integrated vision and illumination | |
| Abad et al. | Soft robotic systems for endoscopic interventions | |
| JP5318762B2 (en) | Endoscopic procedure fiberscope coupling device | |
| CN113384229B (en) | Electronic cystoscope | |
| JP2010502311A5 (en) | ||
| JP2010502311A6 (en) | Endoscopic procedure fiberscope coupling device | |
| CN113040688A (en) | Multi-point observation endoscope device and control method thereof | |
| JP4505445B2 (en) | Medical capsule endoscope |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20080213 Termination date:20141219 | |
| EXPY | Termination of patent right or utility model |