Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
This module provides layers and functions to supportsimulation of OFDM-based systems. The key component is theResourceGrid that defines how data and pilot symbolsare mapped onto a sequence of OFDM symbols with a given FFT size. The resourcegrid can also define guard and DC carriers which are nulled. In 4G/5G parlance,aResourceGrid would be a slot.Once aResourceGrid is defined, one can use theResourceGridMapper to map a tensor of complex-valueddata symbols onto the resource grid, prior to OFDM modulation using theOFDMModulator or further processing in thefrequency domain.
ThePilotPattern allows for a fine-grained configurationof how transmitters send pilots for each of their streams or antennas. As themanagement of pilots in multi-cell MIMO setups can quickly become complicated,the module provides theKroneckerPilotPattern classthat automatically generates orthogonal pilot transmissions for all transmittersand streams.
Additionally, the module contains blocks for channel estimation, precoding,equalization, and detection,such as theLSChannelEstimator, theRZFPrecoder, and theLMMSEEqualizer andLinearDetector.These are good starting points for the development of more advanced algorithmsand provide robust baselines for benchmarking.
This module also provides blocks for the computation of thePostEqualizationSINR of a possibly precoded channelPrecodedChannel. These features are useful forphysical layer abstraction, e.g., usingEffectiveSINR
Resource Grid
The following code snippet shows how to setup and visualize an instance ofResourceGrid:
rg=ResourceGrid(num_ofdm_symbols=14,fft_size=64,subcarrier_spacing=30e3,num_tx=1,num_streams_per_tx=1,num_guard_carriers=[5,6],dc_null=True,pilot_pattern="kronecker",pilot_ofdm_symbol_indices=[2,11])rg.show();

This code creates a resource grid consisting of 14 OFDM symbols with 64subcarriers. The first five and last six subcarriers as well as the DCsubcarriers are nulled. The second and eleventh OFDM symbol are reservedfor pilot transmissions.
Subcarriers are numbered from\(0\) to\(N-1\), where\(N\)is the FTT size. The index\(0\) corresponds to the lowest frequency,which is\(-\frac{N}{2}\Delta_f\) (for\(N\) even) or\(-\frac{N-1}{2}\Delta_f\) (for\(N\) odd), where\(\Delta_f\)is the subcarrier spacing which is irrelevant for the resource grid.The index\(N-1\) corresponds to the highest frequency,which is\((\frac{N}{2}-1)\Delta_f\) (for\(N\) even) or\(\frac{N-1}{2}\Delta_f\) (for\(N\) odd).
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.ResourceGrid(num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size,subcarrier_spacing,num_tx=1,num_streams_per_tx=1,cyclic_prefix_length=0,num_guard_carriers=(0,0),dc_null=False,pilot_pattern=None,pilot_ofdm_symbol_indices=None,precision=None)[source]
Defines aResourceGrid spanning multiple OFDM symbols and subcarriers
- Parameters:
num_ofdm_symbols (int) – Number of OFDM symbols
fft_size (int) – FFT size (, i.e., the number of subcarriers)
subcarrier_spacing (float) – Subcarrier spacing [Hz]
num_tx (int, (default 1)) – Number of transmitters
num_streams_per_tx (int, (default 1)) – Number of streams per transmitter
cyclic_prefix_length (int, (default 0)) – Length of the cyclic prefix
num_guard_carriers ((int,int), (default (0,0))) – List of two integers defining the number of guardcarriers at theleft and right side of the resource grid.
dc_null (bool, (defaultFalse)) – Indicates if the DC carrier is nulled or not
pilot_pattern (None (default) | “kronecker” | “empty” |
PilotPattern) – An instance ofPilotPattern, a stringshorthand for theKroneckerPilotPatternorEmptyPilotPattern, orNone.None is equivalent to“empty”.pilot_ofdm_symbol_indices (None (default) |list,int) – List of indices of OFDM symbols reserved for pilot transmissions.Only needed if
pilot_pattern="kronecker".precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- propertybandwidth
fft_size*subcarrier_spacing- Type:
float
- Type:
Occupied bandwidth [Hz]
- build_type_grid()[source]
Returns a tensor indicating the type of each resource element.
Resource elements can be one of
0 : Data symbol
1 : Pilot symbol
2 : Guard carrier symbol
3 : DC carrier symbol
- Output:
[num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size], tf.int32 – Tensor indicating for each transmitter and stream the type ofthe resource elements of the corresponding resource grid.The type can be one of [0,1,2,3] as explained above.
- propertycyclic_prefix_length
Length of the cyclic prefix
- Type:
int
- propertydc_ind
Index of the DC subcarrierIf
fft_sizeis odd, the index is (fft_size-1)/2.Iffft_sizeis even, the index isfft_size/2.- Type:
int
- propertydc_null
bool Indicates if the DC carriers is nulled or not
- propertyeffective_subcarrier_ind
Iindices of the effective subcarriers
- Type:
int
- propertyfft_size
FFT size
- Type:
int
- propertynum_data_symbols
Number of resource elements used for data transmissions
- Type:
int
- propertynum_effective_subcarriers
Number of subcarriers used for data and pilot transmissions
- Type:
int
- propertynum_guard_carriers
Number of left and right guard carriers
- Type:
int
- propertynum_ofdm_symbols
Number of OFDM symbols of the resource grid
- Type:
int
- propertynum_pilot_symbols
Number of resource elements used for pilot symbols
- Type:
int
- propertynum_resource_elements
Number of resource elements
- Type:
int
- propertynum_streams_per_tx
Number of streams per transmitter
- Type:
int
- propertynum_time_samples
number of time-domain samples occupied by the resource grid
- Type:
int
- propertynum_tx
Number of transmitters
- Type:
int
- propertynum_zero_symbols
Number of empty resource elements
- Type:
int
- propertyofdm_symbol_duration
Duration of an OFDM symbol with cyclic prefix [s]
- Type:
float
- propertypilot_pattern
Get/set used PilotPattern
- Type:
PilotPattern
- show(tx_ind=0,tx_stream_ind=0)[source]
Visualizes the resource grid for a specific transmitter and stream
- Input:
tx_ind (int) – Transmitter index
tx_stream_ind (int) – Stream index
- Output:
matplotlib.figure – A handle to a matplot figure object
- propertysubcarrier_spacing
Subcarrier spacing [Hz]
- Type:
float
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.ResourceGridMapper(resource_grid,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Maps a tensor of modulated data symbols to a ResourceGrid.
This layer takes as input a tensor of modulated data symbolsand maps them together with pilot symbols onto anOFDM
ResourceGrid. The output can beconverted to a time-domain signal with theModulatoror further processed in thefrequency domain.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_data_symbols],tf.complex – Modulated data symbols to be mapped onto the resource grid
- Output:
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex – Full OFDM resource grid in the frequency domain
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.ResourceGridDemapper(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Extracts data-carrying resource elements from a resource grid
This block takes as input an OFDM
ResourceGridandextracts the data-carrying resource elements. In other words, it implementsthe reverse operation ofResourceGridMapper.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
[batch_size, num_rx, num_streams_per_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size, data_dim],tf.complex – Full OFDM resource grid in the frequency domain.The last dimensiondata_dim is optional. Ifdata_dimis used, it refers to the dimensionality of the data that should bedemapped to individual streams. An example would be LLRs.
- Output:
[batch_size, num_rx, num_streams_per_rx, num_data_symbols, data_dim],tf.complex – The data that were mapped into the resource grid.The last dimensiondata_dim is only returned if it was used for theinput.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.RemoveNulledSubcarriers(resource_grid,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Removes nulled guard and/or DC subcarriers from a resource grid
- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex – Full resource grid
- Output:
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex – Resource grid without nulled subcarriers
Modulation & Demodulation
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.OFDMModulator(cyclic_prefix_length=0,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Computes the time-domain representation of an OFDM resource gridwith (optional) cyclic prefix
- Parameters:
cyclic_prefix_length (int (default 0) | [num_ofdm_symbols],int) – Integer or vector of integers indicating the length of thecyclic prefix that is prepended to each OFDM symbol. None of itselements can be larger than the FFT size.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
[…,num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size],tf.complex – Resource grid in the frequency domain
- Output:
[…,num_ofdm_symbols*(fft_size+cyclic_prefix_length)] or […,num_ofdm_symbols*fft_size+sum(cyclic_prefix_length)],tf.complex – Time-domain OFDM signal
- propertycyclic_prefix_length
Get/set the cyclic prefix length
- Type:
scalar or [num_ofdm_symbols], int
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.OFDMDemodulator(fft_size,l_min,cyclic_prefix_length=0,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Computes the frequency-domain representation of an OFDM waveformwith cyclic prefix removal
The demodulator assumes that the input sequence is generated by the
TimeChannel. For a single pair of antennas,the received signal sequence is given as:\[y_b = \sum_{\ell =L_\text{min}}^{L_\text{max}} \bar{h}_\ell x_{b-\ell} + w_b, \quad b \in[L_\text{min}, N_B+L_\text{max}-1]\]where\(\bar{h}_\ell\) are the discrete-time channel taps,\(x_{b}\) is the the transmitted signal,and\(w_\ell\) Gaussian noise.
Starting from the first symbol, the demodulator cuts the inputsequence into pieces of size
cyclic_prefix_length+fft_size,and throws away any trailing symbols. For each piece, the cyclicprefix is removed and thefft_size-point discrete Fouriertransform is computed. It is also possible that every OFDM symbolhas a cyclic prefix of different length.Since the input sequence starts at time\(L_\text{min}\),the FFT-window has a timing offset of\(L_\text{min}\) symbols,which leads to a subcarrier-dependent phase shift of\(e^{\frac{j2\pi k L_\text{min}}{N}}\), where\(k\)is the subcarrier index,\(N\) is the FFT size,and\(L_\text{min} \le 0\) is the largest negative time lag ofthe discrete-time channel impulse response. This phase shiftis removed in this layer, by explicitly multiplyingeach subcarrier by\(e^{\frac{-j2\pi k L_\text{min}}{N}}\).This is a very important step to enable channel estimation withsparse pilot patterns that needs to interpolate the channel frequencyresponse accross subcarriers. It also ensures that thechannel frequency responseseen by the time-domain channelis close to the
OFDMChannel.- Parameters:
fft_size (int) – FFT size (, i.e., the number of subcarriers).
l_min (int) – The largest negative time lag of the discrete-time channelimpulse response. It should be the same value as that used by thecir_to_time_channel function.
cyclic_prefix_length (int (default 0) | [num_ofdm_symbols],int) – Integer or vector of integers indicating the length of thecyclic prefix that is prepended to each OFDM symbol. None of itselements can be larger than the FFT size.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
[…,num_ofdm_symbols*(fft_size+cyclic_prefix_length)+n] or […,num_ofdm_symbols*fft_size+sum(cyclic_prefix_length)+n],tf.complex – Tensor containing the time-domain signal along the last dimension.n is a nonnegative integer.
- Output:
[…,num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size],tf.complex – Tensor containing the OFDM resource grid along the lasttwo dimension.
Pilot Pattern
APilotPattern defines how transmitters send pilotsequences for each of their antennas or streams over an OFDM resource grid.It consists of two components,amask andpilots. Themask indicates which resource elements arereserved for pilot transmissions by each transmitter and its respectivestreams. In some cases, the number of streams is equal to the number oftransmit antennas, but this does not need to be the case, e.g., for precodedtransmissions. Thepilots contains the pilot symbols that are transmittedat the positions indicated by themask. Separating a pilot pattern intomask andpilots enables the implementation of a wide range of pilotconfigurations, including trainable pilot sequences.
The following code snippet shows how to define a simple customPilotPattern for single transmitter, sending two streamsNote thatnum_effective_subcarriers is the number of subcarriers thatcan be used for data or pilot transmissions. Due to guardcarriers or a nulled DC carrier, this number can be smaller than thefft_size of theResourceGrid.
num_tx=1num_streams_per_tx=2num_ofdm_symbols=14num_effective_subcarriers=12# Create a pilot maskmask=np.zeros([num_tx,num_streams_per_tx,num_ofdm_symbols,num_effective_subcarriers])mask[0,:,[2,11],:]=1num_pilot_symbols=int(np.sum(mask[0,0]))# Define pilot sequencespilots=np.zeros([num_tx,num_streams_per_tx,num_pilot_symbols],np.complex64)pilots[0,0,0:num_pilot_symbols:2]=(1+1j)/np.sqrt(2)pilots[0,1,1:num_pilot_symbols:2]=(1+1j)/np.sqrt(2)# Create a PilotPattern instancepp=PilotPattern(mask,pilots)# Visualize non-zero elements of the pilot sequencepp.show(show_pilot_ind=True);
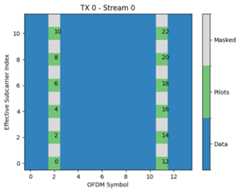
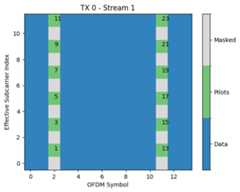
As shown in the figures above, the pilots are mapped onto the mask fromthe smallest effective subcarrier and OFDM symbol index to the highesteffective subcarrier and OFDM symbol index. Here, boths stream have 24pilot symbols, out of which only 12 are nonzero. It is important to keepthis order of mapping in mind when designing more complex pilot sequences.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.PilotPattern(mask,pilots,normalize=False,precision=None)[source]
Class defining a pilot pattern for an OFDM ResourceGrid
This class defines a pilot pattern object that is used to configurean OFDM
ResourceGrid.- Parameters:
mask ([num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],bool) – Tensor indicating resource elements that are reserved for pilot transmissions
pilots ([num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilots],tf.complex) – The pilot symbols to be mapped onto the
masknormalize (bool, (defaultFalse)) – Indicates if the
pilotsshould be normalized to an averageenergy of one across the last dimension.precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- propertymask
Mask of the pilot pattern
- Type:
[num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],bool
- propertynormalize
Get/set if the pilots are normalized or not
- Type:
bool
- propertynum_data_symbols
Number of data symbols per transmit stream
- Type:
int
- propertynum_effective_subcarriers
Number of effectvie subcarriers
- Type:
int
- propertynum_ofdm_symbols
Number of OFDM symbols
- Type:
int
- propertynum_pilot_symbols
Number of pilot symbols per transmit stream
- Type:
int
- propertynum_streams_per_tx
Number of streams per transmitter
- Type:
int
- propertynum_tx
Number of transmitters
- Type:
int
- propertypilots
Get/set thepossibly normalized tensor of pilot symbols. If pilots arenormalized, the normalization will be applied after new valuesfor pilots have been set. If this is not the desired behavior,turn normalization off.
- Type:
[num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilots],tf.complex
- show(tx_ind=None,stream_ind=None,show_pilot_ind=False)[source]
Visualizes the pilot patterns for some transmitters and streams.
- Input:
tx_ind (None (default) |int`| `list,int) – Indicates the indices of transmitters to be included.IfNone, all transmitters included.
stream_ind (None (default) |int`| `list,int) – Indicates the indices of streams to be included.IfNone, all streams included.
show_pilot_ind (bool, (defaultFalse)) – Indicates if the indices of the pilot symbols should be shown
- Output:
list (matplotlib.figure.Figure) – List of matplot figure objects showing each the pilot patternfrom a specific transmitter and stream
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.EmptyPilotPattern(num_tx,num_streams_per_tx,num_ofdm_symbols,num_effective_subcarriers,precision=None)[source]
Creates an empty pilot pattern
Generates a instance of
PilotPatternwithan emptymaskandpilots.- Parameters:
num_tx (int) – Number of transmitters
num_streams_per_tx (int) – Number of streams per transmitter
num_ofdm_symbols (int) – Number of OFDM symbols
num_effective_subcarriers (int) – Number of effective subcarriersthat are available for the transmission of data and pilots.Note that this number is generally smaller than the
fft_sizedue to nulled subcarriers.precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.KroneckerPilotPattern(resource_grid,pilot_ofdm_symbol_indices,normalize=True,seed=0,precision=None)[source]
Simple orthogonal pilot pattern with Kronecker structure
This function generates an instance of
PilotPatternthat allocates non-overlapping pilotsequences for all transmitters andstreams on specified OFDM symbols. As the same pilot sequences are reusedacross those OFDM symbols, the resulting pilot pattern has a frequency-timeKronecker structure. This structure enables a very efficient implementationof the LMMSE channel estimator. Each pilot sequence is constructed fromrandomly drawn QPSK constellation points.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – Resource grid to be usedpilot_ofdm_symbol_indices (list,int) – List of integers defining the OFDM symbol indices that are reservedfor pilots
normalize (bool, (defaultTrue)) – Indicates if the
pilotsshould be normalized to an averageenergy of one across the last dimension.seed (int, (default 0)) – Seed for the generation of the pilot sequence. Different seed valueslead to different sequences.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
Note
It is required that the
resource_grid’s propertynum_effective_subcarriersis aninteger multiple ofnum_tx*num_streams_per_tx. This condition isrequired to ensure that all transmitters and streams getnon-overlapping pilot sequences. For a large number of streams and/ortransmitters, the pilot pattern becomes very sparse in the frequencydomain.Examples
>>>rg=ResourceGrid(num_ofdm_symbols=14,...fft_size=64,...subcarrier_spacing=30e3,...num_tx=4,...num_streams_per_tx=2,...pilot_pattern="kronecker",...pilot_ofdm_symbol_indices=[2,11])>>>rg.pilot_pattern.show();

Channel Estimation
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.BaseChannelEstimator(resource_grid,interpolation_type='nn',interpolator=None,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Abstract block for implementing an OFDM channel estimator
Any block that implements an OFDM channel estimator must implement thisclass and its
estimate_at_pilot_locations()abstract method.This class extracts the pilots from the received resource grid
y, callstheestimate_at_pilot_locations()method to estimate the channel for the pilot-carrying resource elements,and then interpolates the channel to compute channel estimates for thedata-carrying resouce elements using the interpolation method specified byinterpolation_typeor theinterpolatorobject.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – Resource gridinterpolation_type ("nn" (default)|"lin" |"lin_time_avg") – The interpolation method to be used.It is ignored if
interpolatoris notNone.Available options areNearestNeighborInterpolator(“nn”)orLinearInterpolatorwithout (“lin”) or withaveraging across OFDM symbols (“lin_time_avg”).interpolator (None (default) |
BaseChannelInterpolator) – An instance of ,such asLMMSEInterpolator,orNone. In the latter case, the interpolator specfiedbyinterpolation_typeis used.Otherwise, theinterpolatoris used andinterpolation_typeis ignored.precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size],tf.complex) – Observed resource grid
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] or only the first n>=0 dims,tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel estimates accross the entire resource grid for alltransmitters and streams
err_var (Same shape as
h_hat,tf.float) – Channel estimation error variance accross the entire resource gridfor all transmitters and streams
- abstractestimate_at_pilot_locations(y_pilots,no)[source]
Estimates the channel for the pilot-carrying resource elements.
This is an abstract method that must be implemented by a concreteOFDM channel estimator that implement this class.
- Input:
y_pilots ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Observed signals for the pilot-carrying resource elements
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] or only the first n>=0 dims,tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for the pilot-carrying resource elements
err_var (Same shape as
h_hat,tf.float) – Channel estimation error variance for the pilot-carryingresource elements
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.BaseChannelInterpolator(*args,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Abstract class for implementing an OFDM channel interpolator
Any class that implements an OFDM channel interpolator must implement thiscallable class.
A channel interpolator is used by an OFDM channel estimator(
BaseChannelEstimator) to compute channel estimatesfor the data-carrying resource elements from the channel estimates for thepilot-carrying resource elements.- Input:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for the pilot-carrying resource elements
err_var ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimation error variances for the pilot-carrying resource elements
- Output:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel estimates accross the entire resource grid for alltransmitters and streams
err_var (Same shape as
h_hat,tf.float) – Channel estimation error variance accross the entire resource gridfor all transmitters and streams
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.LSChannelEstimator(resource_grid,interpolation_type='nn',interpolator=None,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Block implementing least-squares (LS) channel estimation for OFDM MIMO systems
After LS channel estimation at the pilot positions, the channel estimatesand error variances are interpolated accross the entire resource grid usinga specified interpolation function.
For simplicity, the underlying algorithm is described for a vectorized observation,where we have a nonzero pilot for all elements to be estimated.The actual implementation works on a full OFDM resource grid with sparsepilot patterns. The following model is assumed:
\[\mathbf{y} = \mathbf{h}\odot\mathbf{p} + \mathbf{n}\]where\(\mathbf{y}\in\mathbb{C}^{M}\) is the received signal vector,\(\mathbf{p}\in\mathbb{C}^M\) is the vector of pilot symbols,\(\mathbf{h}\in\mathbb{C}^{M}\) is the channel vector to be estimated,and\(\mathbf{n}\in\mathbb{C}^M\) is a zero-mean noise vector whoseelements have variance\(N_0\). The operator\(\odot\) denoteselement-wise multiplication.
The channel estimate\(\hat{\mathbf{h}}\) and error variances\(\sigma^2_i\),\(i=0,\dots,M-1\), are computed as
\[\begin{split}\hat{\mathbf{h}} &= \mathbf{y} \odot \frac{\mathbf{p}^\star}{\left|\mathbf{p}\right|^2} = \mathbf{h} + \tilde{\mathbf{h}}\\ \sigma^2_i &= \mathbb{E}\left[\tilde{h}_i \tilde{h}_i^\star \right] = \frac{N_0}{\left|p_i\right|^2}.\end{split}\]The channel estimates and error variances are then interpolated accrossthe entire resource grid.
- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – Resource gridinterpolation_type ("nn" (default)|"lin" |"lin_time_avg") – The interpolation method to be used.It is ignored if
interpolatoris notNone.Available options areNearestNeighborInterpolator(“nn”)orLinearInterpolatorwithout (“lin”) or withaveraging across OFDM symbols (“lin_time_avg”).interpolator (None (default) |
BaseChannelInterpolator) – An instance of ,such asLMMSEInterpolator,orNone. In the latter case, the interpolator specfiedbyinterpolation_typeis used.Otherwise, theinterpolatoris used andinterpolation_typeis ignored.precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size],tf.complex) – Observed resource grid
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] or only the first n>=0 dims,tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
h_ls ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols,fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel estimates accross the entire resource grid for alltransmitters and streams
err_var (Same shape as
h_ls,tf.float) – Channel estimation error variance accross the entire resource gridfor all transmitters and streams
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.LinearInterpolator(pilot_pattern,time_avg=False)[source]
Linear channel estimate interpolation on a resource grid
This class computes for each element of an OFDM resource grida channel estimate based on
num_pilotsprovided channel estimates anderror variances through linear interpolation.It is assumed that the measurements were taken at the nonzero positionsof aPilotPattern.The interpolation is done first across sub-carriers and thenacross OFDM symbols.
- Parameters:
pilot_pattern (
PilotPattern) – Used pilot patterntime_avg (bool, (defaultFalse)) – If enabled, measurements will be averaged across OFDM symbols(i.e., time). This is useful for channels that do not varysubstantially over the duration of an OFDM frame.
- Input:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for the pilot-carrying resource elements
err_var ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimation error variances for the pilot-carrying resource elements
- Output:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel estimates accross the entire resource grid for alltransmitters and streams
err_var (Same shape as
h_hat,tf.float) – Channel estimation error variances accross the entire resource gridfor all transmitters and streams
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.LMMSEInterpolator(pilot_pattern,cov_mat_time,cov_mat_freq,cov_mat_space=None,order='t-f')[source]
LMMSE interpolation on a resource grid with optional spatial smoothing
This class computes for each element of an OFDM resource grida channel estimate and error variancethrough linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) interpolation/smoothing.It is assumed that the measurements were taken at the nonzero positionsof a
PilotPattern.Depending on the value of
order, the interpolation is carried outaccross time (t), i.e., OFDM symbols, frequency (f), i.e., subcarriers,and optionally space (s), i.e., receive antennas, in any desired order.For simplicity, we describe the underlying algorithm assuming that interpolationacross the sub-carriers is performed first, followed by interpolation acrossOFDM symbols, and finally by spatial smoothing across receiveantennas.The algorithm is similar if interpolation and/or smoothing are performed ina different order.For clarity, antenna indices are omitted when describing frequency and timeinterpolation, as the same process is applied to all the antennas.
The input
h_hatis first reshaped to a resource grid\(\hat{\mathbf{H}} \in \mathbb{C}^{N \times M}\), by scattering the channelestimates at pilot locations according to thepilot_pattern.\(N\)denotes the number of OFDM symbols and\(M\) the number of sub-carriers.The first pass consists in interpolating across the sub-carriers:
\[\hat{\mathbf{h}}_n^{(1)} = \mathbf{A}_n \hat{\mathbf{h}}_n\]where\(1 \leq n \leq N\) is the OFDM symbol index and\(\hat{\mathbf{h}}_n\) isthe\(n^{\text{th}}\) (transposed) row of\(\hat{\mathbf{H}}\).\(\mathbf{A}_n\) is the\(M \times M\) matrix such that:
\[\mathbf{A}_n = \bar{\mathbf{A}}_n \mathbf{\Pi}_n^\intercal\]where
\[\bar{\mathbf{A}}_n = \underset{\mathbf{Z} \in \mathbb{C}^{M \times K_n}}{\text{argmin}} \left\lVert \mathbf{Z}\left( \mathbf{\Pi}_n^\intercal \mathbf{R^{(f)}} \mathbf{\Pi}_n + \mathbf{\Sigma}_n \right) - \mathbf{R^{(f)}} \mathbf{\Pi}_n \right\rVert_{\text{F}}^2\]and\(\mathbf{R^{(f)}}\) is the\(M \times M\) channel frequency covariance matrix,\(\mathbf{\Pi}_n\) the\(M \times K_n\) matrix that spreads\(K_n\)values to a vector of size\(M\) according to the
pilot_patternfor the\(n^{\text{th}}\) OFDM symbol,and\(\mathbf{\Sigma}_n \in \mathbb{R}^{K_n \times K_n}\) is the channel estimation error covariance built fromerr_varand assumed to be diagonal.Computation of\(\bar{\mathbf{A}}_n\) is done using an algorithm based on complete orthogonal decomposition.This is done to avoid matrix inversion for badly conditioned covariance matrices.The channel estimation error variances after the first interpolation pass are computed as
\[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(1)}_n = \text{diag} \left( \mathbf{R^{(f)}} - \mathbf{A}_n \mathbf{\Xi}_n \mathbf{R^{(f)}} \right)\]where\(\mathbf{\Xi}_n\) is the diagonal matrix of size\(M \times M\) that zeros thecolumns corresponding to sub-carriers not carrying any pilots.Note that interpolation is not performed for OFDM symbols which do not carry pilots.
Remark: The interpolation matrix differs across OFDM symbols as differentOFDM symbols may carry pilots on different sub-carriers and/or have differentestimation error variances.
Scaling of the estimates is then performed to ensure that theirvariances match the ones expected by the next interpolation step, and the error variances are updated accordingly:
\[\begin{split}\begin{align} \left[\hat{\mathbf{h}}_n^{(2)}\right]_m &= s_{n,m} \left[\hat{\mathbf{h}}_n^{(1)}\right]_m\\ \left[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(2)}_n\right]_{m,m} &= s_{n,m}\left( s_{n,m}-1 \right) \left[\hat{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(1)}_n\right]_{m,m} + \left( 1 - s_{n,m} \right) \left[\mathbf{R^{(f)}}\right]_{m,m} + s_{n,m} \left[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(1)}_n\right]_{m,m}\end{align}\end{split}\]where the scaling factor\(s_{n,m}\) is such that:
\[\mathbb{E} \left\{ \left\lvert s_{n,m} \left[\hat{\mathbf{h}}_n^{(1)}\right]_m \right\rvert^2 \right\} = \left[\mathbf{R^{(f)}}\right]_{m,m} + \mathbb{E} \left\{ \left\lvert s_{n,m} \left[\hat{\mathbf{h}}^{(1)}_n\right]_m - \left[\mathbf{h}_n\right]_m \right\rvert^2 \right\}\]which leads to:
\[\begin{split}\begin{align} s_{n,m} &= \frac{2 \left[\mathbf{R^{(f)}}\right]_{m,m}}{\left[\mathbf{R^{(f)}}\right]_{m,m} - \left[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(1)}_n\right]_{m,m} + \left[\hat{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(1)}_n\right]_{m,m}}\\ \hat{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(1)}_n &= \mathbf{A}_n \mathbf{R^{(f)}} \mathbf{A}_n^{\mathrm{H}}.\end{align}\end{split}\]The second pass consists in interpolating across the OFDM symbols:
\[\hat{\mathbf{h}}_m^{(3)} = \mathbf{B}_m \tilde{\mathbf{h}}^{(2)}_m\]where\(1 \leq m \leq M\) is the sub-carrier index and\(\tilde{\mathbf{h}}^{(2)}_m\) isthe\(m^{\text{th}}\) column of
\[\begin{split}\hat{\mathbf{H}}^{(2)} = \begin{bmatrix} {\hat{\mathbf{h}}_1^{(2)}}^\intercal\\ \vdots\\ {\hat{\mathbf{h}}_N^{(2)}}^\intercal \end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]and\(\mathbf{B}_m\) is the\(N \times N\) interpolation LMMSE matrix:
\[\mathbf{B}_m = \bar{\mathbf{B}}_m \tilde{\mathbf{\Pi}}_m^\intercal\]where
\[\bar{\mathbf{B}}_m = \underset{\mathbf{Z} \in \mathbb{C}^{N \times L_m}}{\text{argmin}} \left\lVert \mathbf{Z} \left( \tilde{\mathbf{\Pi}}_m^\intercal \mathbf{R^{(t)}}\tilde{\mathbf{\Pi}}_m + \tilde{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(2)}_m \right) - \mathbf{R^{(t)}}\tilde{\mathbf{\Pi}}_m \right\rVert_{\text{F}}^2\]where\(\mathbf{R^{(t)}}\) is the\(N \times N\) channel time covariance matrix,\(\tilde{\mathbf{\Pi}}_m\) the\(N \times L_m\) matrix that spreads\(L_m\)values to a vector of size\(N\) according to the
pilot_patternfor the\(m^{\text{th}}\) sub-carrier,and\(\tilde{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(2)}_m \in \mathbb{R}^{L_m \times L_m}\) is the diagonal matrix of channel estimation error variancesbuilt by gathering the error variances from (\(\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(2)}_1,\dots,\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(2)}_N\)) correspondingto resource elements carried by the\(m^{\text{th}}\) sub-carrier.Computation of\(\bar{\mathbf{B}}_m\) is done using an algorithm based on complete orthogonal decomposition.This is done to avoid matrix inversion for badly conditioned covariance matrices.The resulting channel estimate for the resource grid is
\[\hat{\mathbf{H}}^{(3)} = \left[ \hat{\mathbf{h}}_1^{(3)} \dots \hat{\mathbf{h}}_M^{(3)} \right]\]The resulting channel estimation error variances are the diagonal coefficients of the matrices
\[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(3)}_m = \mathbf{R^{(t)}} - \mathbf{B}_m \tilde{\mathbf{\Xi}}_m \mathbf{R^{(t)}}, 1 \leq m \leq M\]where\(\tilde{\mathbf{\Xi}}_m\) is the diagonal matrix of size\(N \times N\) that zeros thecolumns corresponding to OFDM symbols not carrying any pilots.
Remark: The interpolation matrix differs across sub-carriers as differentsub-carriers may have different estimation error variances computed by the firstpass.However, all sub-carriers carry at least one channel estimate as a result ofthe first pass, ensuring that a channel estimate is computed for all the resourceelements after the second pass.
Remark: LMMSE interpolation requires knowledge of the time and frequencycovariance matrices of the channel. The notebookOFDM MIMO Channel Estimation and Detection shows how to estimatesuch matrices for arbitrary channel models.Moreover, the functions
tdl_time_cov_mat()andtdl_freq_cov_mat()compute the expected time and frequencycovariance matrices, respectively, for theTDLchannel models.Scaling of the estimates is then performed to ensure that theirvariances match the ones expected by the next smoothing step, and theerror variances are updated accordingly:
\[\begin{split}\begin{align} \left[\hat{\mathbf{h}}_m^{(4)}\right]_n &= \gamma_{m,n} \left[\hat{\mathbf{h}}_m^{(3)}\right]_n\\ \left[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(4)}_m\right]_{n,n} &= \gamma_{m,n}\left( \gamma_{m,n}-1 \right) \left[\hat{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(3)}_m\right]_{n,n} + \left( 1 - \gamma_{m,n} \right) \left[\mathbf{R^{(t)}}\right]_{n,n} + \gamma_{m,n} \left[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(3)}_n\right]_{m,m}\end{align}\end{split}\]where:
\[\begin{split}\begin{align} \gamma_{m,n} &= \frac{2 \left[\mathbf{R^{(t)}}\right]_{n,n}}{\left[\mathbf{R^{(t)}}\right]_{n,n} - \left[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(3)}_m\right]_{n,n} + \left[\hat{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(3)}_n\right]_{m,m}}\\ \hat{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(3)}_m &= \mathbf{B}_m \mathbf{R^{(t)}} \mathbf{B}_m^{\mathrm{H}}\end{align}\end{split}\]Finally, a spatial smoothing step is applied to every resource element carryinga channel estimate.For clarity, we drop the resource element indexing\((n,m)\).We denote by\(L\) the number of receive antennas, and by\(\mathbf{R^{(s)}}\in\mathbb{C}^{L \times L}\) the spatial covariance matrix.
LMMSE spatial smoothing consists in the following computations:
\[\hat{\mathbf{h}}^{(5)} = \mathbf{C} \hat{\mathbf{h}}^{(4)}\]where
\[\mathbf{C} = \mathbf{R^{(s)}} \left( \mathbf{R^{(s)}} + \mathbf{\Sigma}^{(4)} \right)^{-1}.\]The estimation error variances are the digonal coefficients of
\[\mathbf{\Sigma}^{(5)} = \mathbf{R^{(s)}} - \mathbf{C}\mathbf{R^{(s)}}\]The smoothed channel estimate\(\hat{\mathbf{h}}^{(5)}\) and correspondingerror variances\(\text{diag}\left( \mathbf{\Sigma}^{(5)} \right)\) arereturned for every resource element\((m,n)\).
Remark: No scaling is performed after the last interpolation or smoothingstep.
Remark: All passes assume that the estimation error covariance matrix(\(\mathbf{\Sigma}\),\(\tilde{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(2)}\), or\(\tilde{\mathbf{\Sigma}}^{(4)}\)) is diagonal, whichmay not be accurate. When this assumption does not hold, this interpolator is onlyan approximation of LMMSE interpolation.
Remark: The order in which frequency interpolation, temporalinterpolation, and, optionally, spatial smoothing are applied, is controlled using the
orderparameter.Note
This block does not support graph mode with XLA.
- Parameters:
pilot_pattern (
PilotPattern) – Used pilot patterncov_mat_time ([num_ofdm_symbols, num_ofdm_symbols],tf.complex) – Time covariance matrix of the channel
cov_mat_freq ([fft_size, fft_size],t`f.complex) – Frequency covariance matrix of the channel
cov_time_space (None (default) | [num_rx_ant, num_rx_ant],tf.complex) – Spatial covariance matrix of the channel.Only required if spatial smoothing is requested (see
order).order (str,"t-f" (default)) – Order in which to perform interpolation and optional smoothing.For example,
"t-f-s"means that interpolation across the OFDM symbolsis performed first ("t": time), followed by interpolation across thesub-carriers ("f": frequency), and finally smoothing across thereceive antennas ("s": space).Similarly,"f-t"means interpolation across the sub-carriers followedby interpolation across the OFDM symbols and no spatial smoothing.The spatial covariance matrix (cov_time_space) is only required whenspatial smoothing is requested.Time and frequency interpolation are not optional to ensure that a channelestimate is computed for all resource elements.
- Input:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for the pilot-carrying resource elements
err_var ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimation error variances for the pilot-carrying resource elements
- Output:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel estimates accross the entire resource grid for alltransmitters and streams
err_var (Same shape as
h_hat,tf.float) – Channel estimation error variances accross the entire resource gridfor all transmitters and streams
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.NearestNeighborInterpolator(pilot_pattern)[source]
Nearest-neighbor channel estimate interpolation on a resource grid.
This class assigns to each element of an OFDM resource grid one of
num_pilotsprovided channel estimates and errorvariances according to the nearest neighbor method. It is assumedthat the measurements were taken at the nonzero positions of aPilotPattern.The figure below shows how four channel estimates are interpolatedaccross a resource grid. Grey fields indicate measurement positionswhile the colored regions show which resource elements are assignedto the same measurement value.

- Parameters:
pilot_pattern (
PilotPattern) – Used pilot pattern- Input:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for the pilot-carrying resource elements
err_var ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_pilot_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel estimation error variances for the pilot-carrying resource elements
- Output:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel estimates accross the entire resource grid for alltransmitters and streams
err_var (Same shape as
h_hat,tf.float) – Channel estimation error variances accross the entire resource gridfor all transmitters and streams
- sionna.phy.ofdm.tdl_time_cov_mat(model,speed,carrier_frequency,ofdm_symbol_duration,num_ofdm_symbols,los_angle_of_arrival=0.7853981633974483,precision=None)[source]
Computes the time covariance matrix of a
TDLchannel model.For non-line-of-sight (NLoS) model, the channel time covariance matrix\(\mathbf{R^{(t)}}\) of a TDL channel model is
\[\mathbf{R^{(t)}}_{u,v} = J_0 \left( \nu \Delta_t \left( u-v \right) \right)\]where\(J_0\) is the zero-order Bessel function of the first kind,\(\Delta_t\) the duration of an OFDM symbol, and\(\nu\) the Dopplerspread defined by
\[\nu = 2 \pi \frac{v}{c} f_c\]where\(v\) is the movement speed,\(c\) the speed of light, and\(f_c\) the carrier frequency.
For line-of-sight (LoS) channel models, the channel time covariance matrixis
\[\mathbf{R^{(t)}}_{u,v} = P_{\text{NLoS}} J_0 \left( \nu \Delta_t \left( u-v \right) \right) + P_{\text{LoS}}e^{j \nu \Delta_t \left( u-v \right) \cos{\alpha_{\text{LoS}}}}\]where\(\alpha_{\text{LoS}}\) is the angle-of-arrival for the LoS path,\(P_{\text{NLoS}}\) the total power of NLoS paths, and\(P_{\text{LoS}}\) the power of the LoS path. The power delay profileis assumed to have unit power, i.e.,\(P_{\text{NLoS}} + P_{\text{LoS}} = 1\).
- Input:
model (“A” | “B” | “C” | “D” | “E”) – TDL model for which to return the covariance matrix
speed (float) – Speed [m/s]
carrier_frequency (float) – Carrier frequency [Hz]
ofdm_symbol_duration (float) – Duration of an OFDM symbol [s]
num_ofdm_symbols (int) – Number of OFDM symbols
los_angle_of_arrival (float, (default pi/5)) – Angle-of-arrival for LoS path [radian]. Only used with LoS models.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Output:
cov_mat ([num_ofdm_symbols, num_ofdm_symbols],tf.complex) – Channel time covariance matrix
- sionna.phy.ofdm.tdl_freq_cov_mat(model,subcarrier_spacing,fft_size,delay_spread,precision=None)[source]
Computes the frequency covariance matrix of a
TDLchannel model.The channel frequency covariance matrix\(\mathbf{R}^{(f)}\) of a TDL channel model is
\[\mathbf{R}^{(f)}_{u,v} = \sum_{\ell=1}^L P_\ell e^{-j 2 \pi \tau_\ell \Delta_f (u-v)}, 1 \leq u,v \leq M\]where\(M\) is the FFT size,\(L\) is the number of paths for the selected TDL model,\(P_\ell\) and\(\tau_\ell\) are the average power and delay for the\(\ell^{\text{th}}\) path, respectively, and\(\Delta_f\) is the sub-carrier spacing.
- Input:
model (“A” | “B” | “C” | “D” | “E”) – TDL model for which to return the covariance matrix
subcarrier_spacing (float) – Sub-carrier spacing [Hz]
fft_size (int) – FFT size
delay_spread (float) – Delay spread [s]
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Output:
cov_mat ([fft_size, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel frequency covariance matrix
Precoding
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.RZFPrecoder(resource_grid,stream_management,return_effective_channel=False,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Regularized zero-forcing (RZF) precoding for multi-antenna transmissions
This block precodes a tensor containing OFDM resource grids usingthe
rzf_precoder(). For everytransmitter, the channels to all intended receivers are gatheredinto a channel matrix, based on the which the precoding matrixis computed and the input tensor is precoded. The block also outputsoptionally the effective channel after precoding for each stream.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be suedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedreturn_effective_channel (bool, (defaultFalse)) – Indicates if the effective channel after precoding should be returned
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
x ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Resource grids to be precoded.
h ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel knowledge based on which the precoding is computed
alpha (0. (default) | [batch_size, num_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size] (or broadcastable),float) – Regularization parameter for RZF precoding. If set to0, RZF is equivalentto ZF precoding.
- Output:
x_precoded ([batch_size, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Precoded resource grids
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Only returned if
return_effective_channel=True.The effectice channels for all streams after precoding. Can be used tosimulate perfect channel state information (CSI) at the receivers.Nulled subcarriers are automatically removed to be compliant with thebehavior of a channel estimator.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.PrecodedChannel(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Abstract base class to compute the effective channel after precoding
Its output can be used to compute the
PostEqualizationSINR.Let\(\mathbf{H}_{i,j}\in\mathbb{C}^{\text{num_rx_ant}\times\text{num_tx_ant}}\)be the channel matrix between transmitter\(j\)and receiver\(i\) and let\(\mathbf{G}_{j}\in\mathbb{C}^{\text{num_tx_ant}\times\text{num_streams_per_tx}}\)be the precoding matrix of transmitter\(j\).
The effective channel\(\widetilde{\mathbf{H}}_{i,j}\in\mathbb{C}^{\text{num_rx_ant}\times\text{num_streams_per_tx}}\)after precoding is given by
(60)\[\widetilde{\mathbf{H}}_{i,j} = \mathbf{H}_{i,j}\mathbf{G}_{j}\mathop{\text{diag}}(\sqrt{p_{j,1}},...,\sqrt{p_{j,\text{num_streams_per_tx}}})\]where\(p_{j,s}\) is the transmit power of stream\(s\) of transmitter\(j\).
- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
h ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Actual channel realizations
tx_power ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size] (or first n dims),tf.float32) – Power of each stream for each transmitter
h_hat (None (default) | [batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel knowledge based on which the precoding is computed. If set toNone,the actual channel realizations are used.
- Output:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – The effective channel after precoding. Nulled subcarriers areautomatically removed.
- apply_tx_power(g,tx_power)[source]
Apply transmit power to precoding vectors
- Input:
g ([batch_size, num_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size, num_tx_ant, num_streams_per_tx],tf.complex) – Precoding vectors
tx_power ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size] (or first n dims),tf.float32) – Power of each stream for each transmitter
- compute_effective_channel(h,g)[source]
Compute effective channel after precoding
- Input:
h ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Actual channel realizations
g ([batch_size, num_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size, num_tx_ant, num_streams_per_tx],tf.complex) – Precoding matrix
- Output:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – The effective channel after precoding. Nulled subcarriers areautomatically removed.
- get_desired_channels(h_hat)[source]
Get the desired channels for precoding
- Input:
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel knowledge based on which the precoding is computed
- Output:
h_pc_desired ([batch_size, num_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size, num_streams_per_tx, num_tx_ant],tf.complex) – Desired channels for precoding
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.CBFPrecodedChannel(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Compute the effective channel after conjugate beamforming (CBF) precoding
The precoding matrices are obtained from
cbf_precoding_matrix().- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
h ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Actual channel realizations
tx_power ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size] (or first n dims),tf.float32) – Power of each stream for each transmitter
h_hat (None (default) | [batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel knowledge based on which the precoding is computed. If set toNone,the actual channel realizations are used.
- Output:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – The effective channel after precoding. Nulled subcarriers areautomatically removed.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.EyePrecodedChannel(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Compute the effective channel after power allocation without precoding, i.e.,the identity matrix precoder is used
- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
h ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Actual channel realizations
tx_power ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size] (or broadcastable),tf.float32) – Power of each stream for each transmitter. Also a lower-rank tensor isaccepted if it is broadcastable to the requested shape.
- Output:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – The effective channel after power allocation. Nulled subcarriers areautomatically removed.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.RZFPrecodedChannel(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Compute the effective channel after RZF precoding
The precoding matrices are obtained from
rzf_precoding_matrix().- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
h ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Actual channel realizations
tx_power ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size] (or first n dims),tf.float32) – Power of each stream for each transmitter
h_hat (None (default) | [batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_tx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Channel knowledge based on which the precoding is computed. If set toNone,the actual channel realizations are used.
alpha (0. (default) | [batch_size, num_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size] (or first n dims),float) – Regularization parameter for RZF precoding. If set to0, RZF is equivalentto ZF precoding.
- Output:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – The effective channel after precoding. Nulled subcarriers areautomatically removed.
Equalization
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.OFDMEqualizer(equalizer,resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Block that wraps a MIMO equalizer for use with the OFDM waveform
The parameter
equalizeris a callable (e.g., a function) thatimplements a MIMO equalization algorithm for arbitrary batch dimensions.This class pre-processes the received resource grid
yand channelestimateh_hat, and computes for each receiver thenoise-plus-interference covariance matrix according to the OFDM and streamconfiguration provided by theresource_gridandstream_management, which also accounts for the channelestimation error varianceerr_var. These quantities serve as inputto the equalization algorithm that is implemented by the callableequalizer.This block computes soft-symbol estimates together with effective noisevariances for all streams which can, e.g., be used by aDemapperto obtain LLRs.Note
The callable
equalizermust take three inputs:y ([…,num_rx_ant], tf.complex) – 1+D tensor containing the received signals.
h ([…,num_rx_ant,num_streams_per_rx], tf.complex) – 2+D tensor containing the channel matrices.
s ([…,num_rx_ant,num_rx_ant], tf.complex) – 2+D tensor containing the noise-plus-interference covariance matrices.
It must generate two outputs:
x_hat ([…,num_streams_per_rx], tf.complex) – 1+D tensor representing the estimated symbol vectors.
no_eff (tf.float) – Tensor of the same shape as
x_hatcontaining the effective noise variance estimates.
- Parameters:
equalizer (Callable) – Callable object (e.g., a function) that implements a MIMO equalizationalgorithm for arbitrary batch dimensions
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
x_hat ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.complex) – Estimated symbols
no_eff ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.float) – Effective noise variance for each estimated symbol
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.LMMSEEqualizer(resource_grid,stream_management,whiten_interference=True,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
LMMSE equalization for OFDM MIMO transmissions
This block computes linear minimum mean squared error (LMMSE) equalizationfor OFDM MIMO transmissions. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Thedetection algorithm is thelmmse_equalizer(). The blockcomputes soft-symbol estimates together with effective noise variancesfor all streams which can, e.g., be used by aDemapperto obtain LLRs.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedwhiten_interference (bool, (defaultTrue)) – IfTrue, the interference is first whitened before equalization.In this case, an alternative expression for the receive filter is used whichcan be numerically more stable.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
x_hat ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.complex) – Estimated symbols
no_eff ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.float) – Effective noise variance for each estimated symbol
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.MFEqualizer(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
MF equalization for OFDM MIMO transmissions
This block computes matched filter (MF) equalizationfor OFDM MIMO transmissions. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Thedetection algorithm is themf_equalizer(). The blockcomputes soft-symbol estimates together with effective noise variancesfor all streams which can, e.g., be used by aDemapperto obtain LLRs.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
x_hat ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.complex) – Estimated symbols
no_eff ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.float) – Effective noise variance for each estimated symbol
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.ZFEqualizer(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
ZF equalization for OFDM MIMO transmissions
This block computes zero-forcing (ZF) equalizationfor OFDM MIMO transmissions. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Thedetection algorithm is thezf_equalizer(). The blockcomputes soft-symbol estimates together with effective noise variancesfor all streams which can, e.g., be used by aDemapperto obtain LLRs.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
x_hat ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.complex) – Estimated symbols
no_eff ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.float) – Effective noise variance for each estimated symbol
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.PostEqualizationSINR(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Abstract block that computes the SINR after equalization
This function computes the post-equalization SINR for every transmittedstream from the
PrecodedChannel.A stream goes from a specific transmitter to a specificreceiver and is characterized by a precoding vector and anequalization vector.Every transmitter is equipped withnum_tx_ant antennas and every receiveris equipped withnum_rx_ant antennas. All transmitters send the same numberof streams\(S\). A transmitter can allocate different power to different streams.
Let\(\mathbf{H}_{i,j}\in\mathbb{C}^{\text{num_rx_ant}\times\text{num_tx_ant}}\)be the complex channel matrix between receiver\(i\) and transmitter\(j\). We denote by\(\mathbf{g}_{j_,s}\in\mathbb{C}^{\text{num_tx_ant}}\) the precodingvectorfor stream\(s\) sent by transmitter\(j\).Then, the received signal at receiver\(i\) can be expressed as:
\[\mathbf{y}_i = \sum_{j,s} \mathbf{H}_{i,j} \mathbf{g}_{j,s} \sqrt{p_{j,s}} x_{j,s} + \mathbf{n}_{i}\]where\(x_{j,s}\) and\(p_{j,s}\) are the unit-power transmit symboland associated transmission power for stream\(s\), respectively, and\(\mathbf{n}_{i}\) is the additive noise, distributed as\(\mathcal{C}\mathcal{N}(0,\sigma^2 \mathbf{I})\).
By stacking the precoding vectors into a matrix\(\mathbf{G}_j=\left[\mathbf{g}_{j,1}, \ldots, \mathbf{g}_{j,S}\right]\),and using the definition of the precoded channel\(\widetilde{\mathbf{H}}_{i,j}\) in(60), the received signal can be rewritten as:
\[\mathbf{y}_i = \sum_j \widetilde{\mathbf{H}}_{i,j} \mathop{\text{diag}}(x_{j,1},...,x_{j,S}) + \mathbf{n}_{i}\]Next, let\(\mathbf{f}_{i,j,s} \in\mathbb{C}^{\text{num_rx_ant}}\)be the equalization vector for stream\(s\) of transmitter\(j\),applied by the intended receiver\(i\). Then, the useful signal power for stream\(s\) of transmitter\(j\) is:
\[u_{i,j,s} = p_{j,s} \left| \mathbf{f}_{i,j,s}^\mathsf{H} \mathbf{H}_{i,j} \mathbf{g}_{j, s} \right|^2.\]We assume that the transmitted symbols\(x_{j,s}\) are uncorrelated among eachother. Then, the interference power for this stream can be writtenas:
\[v_{i,j,s} = \sum_{(j',s') \ne (j,s)} p_{j',s'} \left| \mathbf{f}_{i,j,s}^\mathsf{H} \mathbf{H}_{i,j'} \mathbf{g}_{j', s'} \right|^2.\]The post-equalization noise power can be expressed as:
\[n_{i,j,s} = \sigma^2 \| \mathbf{f}_{i,j,s} \|^2.\]With these definitions, the SINR for this stream which is finally computed as:
\[\mathrm{SINR}_{i,j,s} = \frac{u_{i,j,s}}{v_{i,j,s} + n_{i,j,s}}.\]Note, that the intended receiver\(i\) for a particular stream\((j,s)\) is defined by the
StreamManagementobject.- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Effective channel after precoding as defined in(60)
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Noise variance
h_eff_hat (None (default) | [batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Estimated effective channel after precoding. If set toNone,the actual channel realizations are used.
- Output:
sinr ([batch_size, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx, num_streams_per_rx],tf.float) – SINR after equalization
- compute_desired_signal_power(h_eff_desired,f)[source]
Compute the desired signal power
- Input:
h_eff_desired ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Desired effective channels
f ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_streams_per_rx, num_rx_ant],tf.complex) – Receive combining vectors
- Output:
signal_power ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_streams_per_rx],tf.float) – Desired signal power
- compute_interference_covariance_matrix(no=None,h_eff_undesired=None)[source]
Compute the interference covariance matrix
- Input:
no (None (default) | [batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant],tf.float) – Noise variance
h_eff_undesired (None (default) | [batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_interfering_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Undesired effective channels. If set toNone, the actual channel realizations are used.
- Output:
s ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_rx_ant],tf.complex) – Interference covariance matrix
- compute_noise_power(no,f)[source]
Compute the noise power
- Input:
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant],tf.float) – Noise variance
f ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_streams_per_rx, num_rx_ant],tf.complex) – Receive combining vectors
- compute_sinr(h_eff_desired,h_eff_undesired,no,f)[source]
Compute the SINR
- Input:
h_eff_desired ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Desired effective channels
h_eff_undesired ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_interfering_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Undesired effective channels
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant],tf.float) – Noise variance
f ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Equalization matrix
- Output:
sinr ([batch_size, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx, num_streams_per_rx],tf.float) – Post-equalization SINR
- compute_total_power(h_eff_desired,h_eff_undesired,f)[source]
Compute the total power from all transmitters
- Input:
h_eff_desired ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Desired effective channels
h_eff_undesired ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_interfering_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Undesired effective channels
f ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers,)
num_streams_per_rx, num_rx_ant], `tf.complex` – Receive combining vectors
- Output:
total_power ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, 1],tf.float) – Total power
- get_per_rx_channels(h_eff)[source]
Extract desired and undesired channels for each receiver
- Input:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex,tf.complex) – Effective precoded channel. Can be estimated or true.
- Output:
h_eff_desired ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Desired effective channels
h_eff_undesired ([batch_size, num_rx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx_ant, num_interfering_streams_per_rx],tf.complex) – Undesired effective channels
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.LMMSEPostEqualizationSINR(resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Block that computes the SINR after LMMSE equalization
The equalization matrix is the one computed by
lmmse_matrix().- Parameters:
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
h_eff ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Effective channel after precoding as defined in(60)
no ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Noise variance
h_eff_hat (None (default) | [batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Estimated effective channel after precoding. If set toNone,the actual channel realizations are used.
interference_whitening (bool (default=True)) – If set toTrue, also the interference from undesired streams (e.g.,from other cells) is whitened
- Output:
sinr ([batch_size, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers, num_rx, num_streams_per_rx],tf.float) – SINR after equalization
Detection
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.OFDMDetector(detector,output,resource_grid,stream_management,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Block that wraps a MIMO detector for use with the OFDM waveform
The parameter
detectoris a callable (e.g., a function) thatimplements a MIMO detection algorithm for arbitrary batch dimensions.This class pre-processes the received resource grid
yand channelestimateh_hat, and computes for each receiver thenoise-plus-interference covariance matrix according to the OFDM and streamconfiguration provided by theresource_gridandstream_management, which also accounts for the channelestimation error varianceerr_var. These quantities serve as input to the detectionalgorithm that is implemented bydetector.Both detection of symbols or bits with either soft- or hard-decisions are supported.Note
The callable
detectormust take as input a tuple\((\mathbf{y}, \mathbf{h}, \mathbf{s})\) such that:y ([…,num_rx_ant], tf.complex) – 1+D tensor containing the received signals.
h ([…,num_rx_ant,num_streams_per_rx], tf.complex) – 2+D tensor containing the channel matrices.
s ([…,num_rx_ant,num_rx_ant], tf.complex) – 2+D tensor containing the noise-plus-interference covariance matrices.
It must generate one of following outputs depending on the value of
output:b_hat ([…, num_streams_per_rx, num_bits_per_symbol], tf.float) – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.x_hat ([…, num_streams_per_rx, num_points], tf.float) or ([…, num_streams_per_rx], tf.int) – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”. Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- Parameters:
detector (Callable) – Callable object (e.g., a function) that implements a MIMO detectionalgorithm for arbitrary batch dimensions. Either one of the existing detectors, e.g.,
LinearDetector,MaximumLikelihoodDetector, orKBestDetectorcan be used, or a custom detectorcallable provided that has the same input/output specification.output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedprecision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int32 – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.OFDMDetectorWithPrior(detector,output,resource_grid,stream_management,constellation_type=None,num_bits_per_symbol=None,constellation=None,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Block that wraps a MIMO detector that assumes prior knowledge of the bits orconstellation points is available, for use with the OFDM waveform
The parameter
detectoris a callable (e.g., a function) thatimplements a MIMO detection algorithm with prior for arbitrary batchdimensions.This class pre-processes the received resource grid
y, channelestimateh_hat, and the prior informationprior, and computes for each receiver thenoise-plus-interference covariance matrix according to the OFDM and streamconfiguration provided by theresource_gridandstream_management, which also accounts for the channelestimation error varianceerr_var. These quantities serve as input to the detectionalgorithm that is implemented bydetector.Both detection of symbols or bits with either soft- or hard-decisions are supported.Note
The callable
detectormust take as input a tuple\((\mathbf{y}, \mathbf{h}, \mathbf{prior}, \mathbf{s})\) such that:y ([…,num_rx_ant], tf.complex) – 1+D tensor containing the received signals.
h ([…,num_rx_ant,num_streams_per_rx], tf.complex) – 2+D tensor containing the channel matrices.
prior ([…,num_streams_per_rx,num_bits_per_symbol] or […,num_streams_per_rx,num_points], tf.float) – Prior for the transmitted signals. If
outputequals “bit”, then LLRs for the transmitted bits are expected. Ifoutputequals “symbol”, then logits for the transmitted constellation points are expected.s ([…,num_rx_ant,num_rx_ant], tf.complex) – 2+D tensor containing the noise-plus-interference covariance matrices.
It must generate one of the following outputs depending on the value of
output:b_hat ([…, num_streams_per_rx, num_bits_per_symbol], tf.float) – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.x_hat ([…, num_streams_per_rx, num_points], tf.float) or ([…, num_streams_per_rx], tf.int) – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”. Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- Parameters:
detector (Callable) – Callable object (e.g., a function) that implements a MIMO detectionalgorithm with prior for arbitrary batch dimensions. Either the existing detector
MaximumLikelihoodDetectorWithPriorcan be used, or a custom detectorcallable provided that has the same input/output specification.output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedconstellation_type (None (default) | “qam” | “pam” | “custom”) – For “custom”, an instance of
Constellationmust be provided.num_bits_per_symbol (int) – Number of bits per constellation symbol, e.g., 4 for QAM16.Only required for
constellation_typein [“qam”, “pam”].constellation (None (default) |
Constellation) – IfNone,constellation_typeandnum_bits_per_symbolmust be provided.precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
prior ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols x num_bits_per_symbol] or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float) – Prior of the transmitted signals.If
outputequals “bit”, LLRs of the transmitted bits are expected.Ifoutputequals “symbol”, logits of the transmitted constellation points are expected.err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.EPDetector(output,resource_grid,stream_management,num_bits_per_symbol=None,hard_out=False,l=10,beta=0.9,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
This block wraps the MIMO EP detector for use with the OFDM waveform
Both detection of symbols or bits with eithersoft- or hard-decisions are supported. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Theactual detector is an instance ofEPDetector.- Parameters:
output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usednum_bits_per_symbol (int) – Number of bits per constellation symbol, e.g., 4 for QAM16.Only required for
constellation_typein [“qam”, “pam”].hard_out (bool, (defaultFalse)) – IfTrue, the detector computes hard-decided bit values orconstellation point indices instead of soft-values.
l (int, (default 10)) – Number of iterations
beta (float, (default 0.9)) – Parameter\(\beta\in[0,1]\) for update smoothing
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int32 – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.KBestDetector(output,num_streams,k,resource_grid,stream_management,constellation_type=None,num_bits_per_symbol=None,constellation=None,hard_out=False,use_real_rep=False,list2llr=None,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
This block wraps the MIMO K-Best detector for use with the OFDM waveform
Both detection of symbols or bits with eithersoft- or hard-decisions are supported. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Theactual detector is an instance ofKBestDetector.- Parameters:
output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
num_streams (int`) – Number of transmitted streams
k (int) – Number of paths to keep. Cannot be larger than thenumber of constellation points to the power of the number ofstreams.
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedconstellation_type (None (default) | “qam” | “pam” | “custom”) – For “custom”, an instance of
Constellationmust be provided.num_bits_per_symbol (int) – Number of bits per constellation symbol, e.g., 4 for QAM16.Only required for
constellation_typein [“qam”, “pam”].constellation (None (default) |
Constellation) – IfNone,constellation_typeandnum_bits_per_symbolmust be provided.hard_out (bool, (defaultFalse)) – IfTrue, the detector computes hard-decided bit values orconstellation point indices instead of soft-values.
use_real_rep (bool, (defaultFalse)) – IfTrue, the detector use the real-valued equivalent representationof the channel. Note that this only works with a QAM constellation.
list2llr (None (default) |
List2LLR) – The function to be used to compute LLRs from a list of candidate solutions.IfNone, the default solutionList2LLRSimpleis used.precision (str,None (default) | ‘single’ | ‘double’) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int32 – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.LinearDetector(equalizer,output,demapping_method,resource_grid,stream_management,constellation_type=None,num_bits_per_symbol=None,constellation=None,hard_out=False,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
This block wraps a MIMO linear equalizer and a
Demapperfor use with the OFDM waveformBoth detection of symbols or bits with eithersoft- or hard-decisions are supported. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Theactual detector is an instance ofLinearDetector.- Parameters:
equalizer ("lmmse" |"zf" |"mf" |equalizer function) – Equalizer to be used. Either one of the existing equalizers, e.g.,
lmmse_equalizer(),zf_equalizer(), ormf_equalizer()can be used, or a custom equalizerfunction provided that has the same input/output specification.output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
demapping_method ("app" |"maxlog"]) – Demapping method used
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedconstellation_type (None (default) | “qam” | “pam” | “custom”) – For “custom”, an instance of
Constellationmust be provided.num_bits_per_symbol (int) – Number of bits per constellation symbol, e.g., 4 for QAM16.Only required for
constellation_typein [“qam”, “pam”].constellation (None (default) |
Constellation) – IfNone,constellation_typeandnum_bits_per_symbolmust be provided.hard_out (bool, (defaultFalse)) – IfTrue, the detector computes hard-decided bit values orconstellation point indices instead of soft-values.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int32 – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.MaximumLikelihoodDetector(output,demapping_method,resource_grid,stream_management,constellation_type=None,num_bits_per_symbol=None,constellation=None,hard_out=False,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Maximum-likelihood (ML) detection for OFDM MIMO transmissions
This block implements maximum-likelihood (ML) detectionfor OFDM MIMO transmissions. Both ML detection of symbols or bits with eithersoft- or hard-decisions are supported. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Theactual detector is an instance ofMaximumLikelihoodDetector.- Parameters:
output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
demapping_method ("app" |"maxlog"]) – Demapping method used
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedconstellation_type (None (default) | “qam” | “pam” | “custom”) – For “custom”, an instance of
Constellationmust be provided.num_bits_per_symbol (int) – Number of bits per constellation symbol, e.g., 4 for QAM16.Only required for
constellation_typein [“qam”, “pam”].constellation (None (default) |
Constellation) – IfNone,constellation_typeandnum_bits_per_symbolmust be provided.hard_out (bool, (defaultFalse)) – IfTrue, the detector computes hard-decided bit values orconstellation point indices instead of soft-values.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN noise
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int32 – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.MaximumLikelihoodDetectorWithPrior(output,demapping_method,resource_grid,stream_management,constellation_type=None,num_bits_per_symbol=None,constellation=None,hard_out=False,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
Maximum-likelihood (ML) detection for OFDM MIMO transmissions, assuming priorknowledge of the bits or constellation points is available
This block implements maximum-likelihood (ML) detectionfor OFDM MIMO transmissions assuming prior knowledge on the transmitted data is available.Both ML detection of symbols or bits with eithersoft- or hard-decisions are supported. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Theactual detector is an instance ofMaximumLikelihoodDetectorWithPrior.- Parameters:
output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
demapping_method ("app" |"maxlog"]) – Demapping method used
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usedconstellation_type (None (default) | “qam” | “pam” | “custom”) – For “custom”, an instance of
Constellationmust be provided.num_bits_per_symbol (int) – Number of bits per constellation symbol, e.g., 4 for QAM16.Only required for
constellation_typein [“qam”, “pam”].constellation (None (default) |
Constellation) – IfNone,constellation_typeandnum_bits_per_symbolmust be provided.hard_out (bool, (defaultFalse)) – IfTrue, the detector computes hard-decided bit values orconstellation point indices instead of soft-values.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
prior ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols x num_bits_per_symbol] or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float) – Prior of the transmitted signals.If
outputequals “bit”, LLRs of the transmitted bits are expected.Ifoutputequals “symbol”, logits of the transmitted constellation points are expected.err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN noise
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int32 – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.
- classsionna.phy.ofdm.MMSEPICDetector(output,demapping_method,resource_grid,stream_management,num_iter=1,constellation_type=None,num_bits_per_symbol=None,constellation=None,hard_out=False,precision=None,**kwargs)[source]
This block wraps the MIMO MMSE PIC detector for use with the OFDM waveform
Both detection of symbols or bits with eithersoft- or hard-decisions are supported. The OFDM and stream configuration are providedby a
ResourceGridandStreamManagementinstance, respectively. Theactual detector is an instance ofMMSEPICDetector.- Parameters:
output ("bit" |"symbol") – Type of output, either bits or symbols
demapping_method ("app" |"maxlog"]) – Demapping method used
resource_grid (
ResourceGrid) – ResourceGrid to be usedstream_management (
StreamManagement) – StreamManagement to be usednum_iter (int, (default 1)) – Number of MMSE PIC iterations
constellation_type (None (default) | “qam” | “pam” | “custom”) – For “custom”, an instance of
Constellationmust be provided.num_bits_per_symbol (int) – Number of bits per constellation symbol, e.g., 4 for QAM16.Only required for
constellation_typein [“qam”, “pam”].constellation (None (default) |
Constellation) – IfNone,constellation_typeandnum_bits_per_symbolmust be provided.hard_out (bool, (defaultFalse)) – IfTrue, the detector computes hard-decided bit values orconstellation point indices instead of soft-values.
precision (None (default) | “single” | “double”) – Precision used for internal calculations and outputs.If set toNone,
precisionis used.
- Input:
y ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_ofdm_symbols, fft_size],tf.complex) – Received OFDM resource grid after cyclic prefix removal and FFT
h_hat ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant, num_tx, num_streams_per_tx, num_ofdm_symbols, num_effective_subcarriers],tf.complex) – Channel estimates for all streams from all transmitters
prior ([batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols x num_bits_per_symbol] or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float) – Prior of the transmitted signals.If
outputequals “bit”, LLRs of the transmitted bits are expected.Ifoutputequals “symbol”, logits of the transmitted constellation points are expected.err_var ([Broadcastable to shape of
h_hat],tf.float) – Variance of the channel estimation errorno ([batch_size, num_rx, num_rx_ant] (or only the first n dims),tf.float) – Variance of the AWGN
- Output:
One of
[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols*num_bits_per_symbol],tf.float – LLRs or hard-decisions for every bit of every stream, if
outputequals“bit”.[batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols, num_points],tf.float or [batch_size, num_tx, num_streams, num_data_symbols],tf.int32 – Logits or hard-decisions for constellation symbols for every stream, if
outputequals“symbol”.Hard-decisions correspond to the symbol indices.